
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, mla works cited page: format, template & examples, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their....
Research Question 101 📖
Everything you need to know to write a high-quality research question
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2023
If you’ve landed on this page, you’re probably asking yourself, “ What is a research question? ”. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll explain what a research question is , how it’s differen t from a research aim, and how to craft a high-quality research question that sets you up for success.
Research Question 101
What is a research question.
- Research questions vs research aims
- The 4 types of research questions
- How to write a research question
- Frequently asked questions
- Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer .
In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery . Without a clear target, you won’t know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light throughout your project and informs every choice you make along the way.
Let’s look at some examples:
What impact does social media usage have on the mental health of teenagers in New York?
How does the introduction of a minimum wage affect employment levels in small businesses in outer London?
How does the portrayal of women in 19th-century American literature reflect the societal attitudes of the time?
What are the long-term effects of intermittent fasting on heart health in adults?
As you can see in these examples, research questions are clear, specific questions that can be feasibly answered within a study. These are important attributes and we’ll discuss each of them in more detail a little later . If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, you can find our RQ mega-list here .

Research Questions vs Research Aims
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “ How is a research question different from a research aim? ”. Within any given study, the research aim and research question (or questions) are tightly intertwined , but they are separate things . Let’s unpack that a little.
A research aim is typically broader in nature and outlines what you hope to achieve with your research. It doesn’t ask a specific question but rather gives a summary of what you intend to explore.
The research question, on the other hand, is much more focused . It’s the specific query you’re setting out to answer. It narrows down the research aim into a detailed, researchable question that will guide your study’s methods and analysis.
Let’s look at an example:
Research Aim: To explore the effects of climate change on marine life in Southern Africa.
Research Question: How does ocean acidification caused by climate change affect the reproduction rates of coral reefs?
As you can see, the research aim gives you a general focus , while the research question details exactly what you want to find out.
Need a helping hand?
Types of research questions
Now that we’ve defined what a research question is, let’s look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions – descriptive , comparative , relational , and explanatory .
Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a phenomena or situation . An example of a descriptive research question could be something like “What types of exercise do high-performing UK executives engage in?”. This would likely be a bit too basic to form an interesting study, but as you can see, the research question is just focused on the what – in other words, it just describes the situation.
Comparative research questions , on the other hand, look to understand the way in which two or more things differ , or how they’re similar. An example of a comparative research question might be something like “How do exercise preferences vary between middle-aged men across three American cities?”. As you can see, this question seeks to compare the differences (or similarities) in behaviour between different groups.
Next up, we’ve got exploratory research questions , which ask why or how is something happening. While the other types of questions we looked at focused on the what, exploratory research questions are interested in the why and how . As an example, an exploratory research question might ask something like “Why have bee populations declined in Germany over the last 5 years?”. As you can, this question is aimed squarely at the why, rather than the what.
Last but not least, we have relational research questions . As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables . Here, an example could be something like “What is the relationship between X and Y” or “Does A have an impact on B”. As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables are connected , and perhaps, whether one thing causes another.
Of course, depending on how fine-grained you want to get, you can argue that there are many more types of research questions , but these four categories give you a broad idea of the different flavours that exist out there. It’s also worth pointing out that a research question doesn’t need to fit perfectly into one category – in many cases, a research question might overlap into more than just one category and that’s okay.
The key takeaway here is that research questions can take many different forms , and it’s useful to understand the nature of your research question so that you can align your research methodology accordingly.

How To Write A Research Question
As we alluded earlier, a well-crafted research question needs to possess very specific attributes, including focus , clarity and feasibility . But that’s not all – a rock-solid research question also needs to be rooted and aligned . Let’s look at each of these.
A strong research question typically has a single focus. So, don’t try to cram multiple questions into one research question; rather split them up into separate questions (or even subquestions), each with their own specific focus. As a rule of thumb, narrow beats broad when it comes to research questions.
Clear and specific
A good research question is clear and specific, not vague and broad. State clearly exactly what you want to find out so that any reader can quickly understand what you’re looking to achieve with your study. Along the same vein, try to avoid using bulky language and jargon – aim for clarity.
Unfortunately, even a super tantalising and thought-provoking research question has little value if you cannot feasibly answer it. So, think about the methodological implications of your research question while you’re crafting it. Most importantly, make sure that you know exactly what data you’ll need (primary or secondary) and how you’ll analyse that data.
A good research question (and a research topic, more broadly) should be rooted in a clear research gap and research problem . Without a well-defined research gap, you risk wasting your effort pursuing a question that’s already been adequately answered (and agreed upon) by the research community. A well-argued research gap lays at the heart of a valuable study, so make sure you have your gap clearly articulated and that your research question directly links to it.
As we mentioned earlier, your research aim and research question are (or at least, should be) tightly linked. So, make sure that your research question (or set of questions) aligns with your research aim . If not, you’ll need to revise one of the two to achieve this.
FAQ: Research Questions
Research question faqs, how many research questions should i have, what should i avoid when writing a research question, can a research question be a statement.
Typically, a research question is phrased as a question, not a statement. A question clearly indicates what you’re setting out to discover.
Can a research question be too broad or too narrow?
Yes. A question that’s too broad makes your research unfocused, while a question that’s too narrow limits the scope of your study.
Here’s an example of a research question that’s too broad:
“Why is mental health important?”
Conversely, here’s an example of a research question that’s likely too narrow:
“What is the impact of sleep deprivation on the exam scores of 19-year-old males in London studying maths at The Open University?”
Can I change my research question during the research process?
How do i know if my research question is good.
A good research question is focused, specific, practical, rooted in a research gap, and aligned with the research aim. If your question meets these criteria, it’s likely a strong question.
Is a research question similar to a hypothesis?
Not quite. A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts an outcome, while a research question is a query that you’re trying to answer through your study. Naturally, there can be linkages between a study’s research questions and hypothesis, but they serve different functions.
How are research questions and research objectives related?
The research question is a focused and specific query that your study aims to answer. It’s the central issue you’re investigating. The research objective, on the other hand, outlines the steps you’ll take to answer your research question. Research objectives are often more action-oriented and can be broken down into smaller tasks that guide your research process. In a sense, they’re something of a roadmap that helps you answer your research question.
Need some inspiration?
If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, check out our research question mega list here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1-on-1 help developing a high-quality research question, consider our private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Write Compelling Research Questions

Are you ready to take your research to the next level? Crafting a powerful research question is the key to unlocking the full potential of your academic journey. It's like having a trusty compass that guides you through the vast wilderness of knowledge, ensuring you stay on track and reach your destination.
In this article, we'll walk you through the essential steps to develop a research question that packs a punch. From identifying your research topic to refining and evaluating your question, we've got you covered. Along the way, we'll explore what makes a good research question and share some helpful research questions examples to inspire you. So, whether you're a student, writer, or just curious about how to form a research question, join us as we embark on this exciting adventure of developing research questions that will elevate your research to new heights!
Identify Your Research Topic
Alright, let's dive into the exciting world of identifying your research topic! Picture yourself as an adventurer, ready to explore uncharted territories of knowledge. But before you embark on this thrilling journey, you need to choose a destination that sparks your curiosity and aligns with your goals.
Brainstorming Your Interests
- Start by brainstorming a list of subjects that pique your interest. Consider areas that haven't been thoroughly explored or present challenges within your field.
- Ask yourself questions like: What fascinates me? What problems do I want to solve? What knowledge gaps exist in my area of study?
- Engage in discussions with peers, professors, or experts to gain fresh perspectives and refine your ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Once you have a general topic in mind, it's time to do some background reading to narrow down your focus:
As you explore these resources, consider the following:
- Look for keywords and concepts that social scientists use to discuss your topic
- Identify specific cases or examples that can make your ideas more concrete
- Determine what aspects of the topic you want to focus on and find an angle to contribute through your project
Evaluating Your Topic
Before finalizing your research topic, ensure it meets the following criteria:
- Aligns with the assignment requirements and guidelines
- Has a substantial body of accessible and manageable related research
- Is interesting, relevant, and worthy of the time invested
- Allows for finding sufficient information in books or scholarly journals
- Fits your future professional path and enhances your skills
Remember, your research topic is not set in stone. It may evolve as you delve deeper into the research process. Embrace the opportunity to discover new insights and modify your topic accordingly.
Now that you've identified a captivating research topic, you're ready to embark on the next stage of your research adventure: conducting preliminary research to further refine your focus and develop a powerful research question.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Now that you've identified your research topic, it's time to dive deeper and conduct some preliminary research. This crucial step will help you narrow down your focus, identify key concepts, and lay the groundwork for developing a powerful research question.
- Use search engines like Google Scholar or your library's online catalog to find relevant articles, books, and other resources related to your topic.
- Explore Wikipedia to gain a broad understanding of your topic and discover potential subtopics or related areas of interest.
- As you read through your initial search results, take note of frequently used terms, phrases, and concepts related to your topic.
- Create a list of these key terms to help guide your further research and refine your focus.
- Assess the quantity and quality of the resources you've found so far.
- Determine if there is sufficient information available to support your research or if you need to adjust your topic's scope.
- Diversify your research by exploring various types of sources, such as:
- As you review the literature, look for areas where there is a lack of information or where scholars disagree.
- These gaps and debates can help you identify potential research questions and contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
- Based on your preliminary research, consider narrowing down your topic to a more specific focus.
- A well-defined and focused topic will make it easier to develop a clear and concise research question.
Remember, conducting preliminary research is an iterative process. As you learn more about your topic, you may need to adjust your focus, search for additional sources, or explore new angles. Embrace this process of discovery and let your curiosity guide you towards a compelling research question.
Define Your Research Problem
Alright, now that you've conducted some preliminary research and have a better understanding of your topic, it's time to define your research problem. This is where the real fun begins!
- Start by asking "how" and "why" questions about your general topic.
- For example, instead of asking, "Does social media affect mental health?" try, "How does social media impact the mental health of teenagers?"
- These types of questions encourage deeper exploration and analysis.
- Narrow down your research problem to a particular aspect of the broader topic.
- Consider focusing on a specific place, time, or group of people.
- Specify the aspects you will address and those you will not.
- Your research problem should be complex enough to require research and analysis, not just a simple yes/no answer.
- It should also be significant to you and potentially to others, addressing the "so what" factor.
Crafting the Research Question
Alright, now that you've defined your research problem, it's time to craft a powerful research question that will guide your study. A well-formulated research question should be clear, focused, and complex, avoiding simple yes/no answers and requiring research and analysis.
Characteristics of a Strong Research Question
A good research question exhibits the following characteristics:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Answerable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to the field of study and/or society
The PICO(T) Framework
When structuring your research question, consider using the PICO(T) framework:
Avoiding Common Mistakes
To ensure your research question is strong, avoid these common mistakes:
- Ambiguity: Use clear and specific language to avoid confusion
- Assumption: Avoid making assumptions or using loaded language
- Scope: Keep the scope of your question manageable and relevant
Formulating Your Question
When crafting your research question, consider the following formulations:
- Describing and exploring: "What are the characteristics of...?"
- Explaining and testing: "What is the relationship between...?"
- Evaluating and acting: "How effective is...?"
Remember, developing a research question is an iterative process that involves continuously updating your knowledge on the topic and refining your ideas. As you progress through your research, you may need to adjust your question to better align with your findings and insights.
Examples of Research Questions
- Descriptive: "What are the main challenges faced by small businesses during a pandemic?"
- Comparative: "How does the effectiveness of online learning compare to traditional classroom learning?"
- Correlational: "Is there a relationship between social media use and anxiety levels in teenagers?"
- Exploratory: "What factors contribute to the success of remote work arrangements?"
- Explanatory: "How does regular exercise impact cognitive function in older adults?"
- Evaluation: "To what extent do diversity and inclusion initiatives improve employee satisfaction and retention?"
By crafting a strong research question that is clear, focused, and complex, you'll set the foundation for a successful research project that contributes to your field of study and provides valuable insights.
Refine and Evaluate Your Question
Congratulations on crafting a powerful research question! Now, it's time to refine and evaluate your question to ensure it's the best it can be. Let's dive in and make your research question shine!
Determining Relationships and Selecting Variables
- Identify how variables are related to one another and how these relationships may contribute to your research problem.
- Summarize how you plan to consider and use these variables and how they might influence the study results.
Asking Critical Open-Ended Questions
Narrow down your research question by asking the following:
- Who is involved in your research?
- What specific aspects are you investigating?
- When and where will your research take place?
- How will you conduct your study?
- Why is this research important?
Apply these criteria to make your question more generative, relevant, original, and less obvious.
Seeking Feedback and Revising
Remember, receiving feedback and revising is a valuable step in creating impactful and precise research.
Evaluating Interestingness and Feasibility
Consider the following factors when evaluating your research question:
- Is the answer in doubt?
- Does it fill a gap in the research literature?
- Does it have important practical implications?
- Do you have enough time and money?
- Do you possess the necessary technical knowledge and skills?
- Do you have access to special equipment and research participants?
Striving for Simplicity and Precision
- Make your research question as specific and concise as possible.
- Seek input from experts, mentors, and colleagues to refine your question further.
- Consider how your research question influences factors such as methodology, sample size, data collection, and analysis.
By refining and evaluating your research question, you'll set the stage for a successful research project that contributes valuable insights to your field of study. Remember, a well-crafted research question is central to a well-written paper, sparking interest and leading to new or rethought perspectives.
Developing a powerful research question is the cornerstone of any successful research project. By identifying your research topic, conducting preliminary research, defining your research problem, and crafting a focused question, you'll set the foundation for a meaningful and impactful study. Remember to refine and evaluate your question, seeking feedback from mentors and peers to ensure its relevance and feasibility.
As you embark on your research journey, let your curiosity be your guide. Embrace the process of discovery, and don't be afraid to refine your question as you uncover new insights. By crafting a research question that is clear, focused, and complex, you'll contribute valuable knowledge to your field and make a lasting impact on the world of research. So go forth, intrepid researcher, and let your powerful research question be the beacon that illuminates your path to success!
What are the essential steps to formulate a research question?
To formulate a research question, follow these steps:
- Choose a general subject area or consider the one that has been assigned to you.
- Narrow down the topic to a more specific aspect of the general subject.
- Brainstorm various questions that could be asked about this narrower topic.
- Select the question that you find most intriguing or compelling.
How can I create a strong research question?
To develop a strong research question, you should:
- Conduct initial research on your topic to understand the current discourse.
- Identify a problem or a knowledge gap within your field.
- Ensure your question aims to contribute to ongoing debates within your field or society.
What is the five-step process for writing a research question?
When crafting a research question, you should:
- Select a broad topic of interest.
- Engage in preliminary research to gain background information.
- Keep in mind the audience for whom the research is intended.
- Develop a list of possible questions related to the topic.
- Review and refine the list of questions.
- Formulate the final research question.
What are the five key elements of an effective research question?
An effective research question typically includes the following five components:
- Population: the group you are studying.
- Intervention: the variable or treatment you are considering.
- Comparator: the standard or control you are comparing the intervention to.
- Outcome: the expected result or effect of the intervention.
- Time frame: the period during which the study is conducted.These components can be remembered through the acronyms PICOT and FINER, which stand for Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome, Time frame, and Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, respectively.
Sign up for more like this.

Developing a Research Question
by acburton | Mar 22, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
Selecting your research question and creating a clear goal and structure for your writing can be challenging – whether you are doing it for the first time or if you’ve done it many times before. It can be especially difficult when your research question starts to look and feel a little different somewhere between your first and final draft. Don’t panic! It’s normal for your research question to change a little (or even quite a bit) as you move through and engage with the writing process. Anticipating this can remind you to stay on track while you work and that it’ll be okay even if the literature takes you in a different direction.
What Makes an Effective Research Question?
The most effective research question will usually be a critical thinking question and should use “how” or “why” to ensure it can move beyond a yes/no or one-word type of answer. Consider how your research question can aim to reveal something new, fill in a gap, even if small, and contribute to the field in a meaningful way; How might the proposed project move knowledge forward about a particular place or process? This should be specific and achievable!
The CEWC’s Grad Writing Consultant Tariq says, “I definitely concentrated on those aspects of what I saw in the field where I believed there was an opportunity to move the discipline forward.”
General Tips
Do your research.
Utilize the librarians at your university and take the time to research your topic first. Try looking at very general sources to get an idea of what could be interesting to you before you move to more academic articles that support your rough idea of the topic. It is important that research is grounded in what you see or experience regarding the topic you have chosen and what is already known in the literature. Spend time researching articles, books, etc. that supports your thesis. Once you have a number of sources that you know support what you want to write about, formulate a research question that serves as the interrogative form of your thesis statement.
Grad Writing Consultant Deni advises, “Delineate your intervention in the literature (i.e., be strategic about the literature you discuss and clear about your contributions to it).”
Start Broadly…. then Narrow Your Topic Down to Something Manageable
When brainstorming your research question, let your mind veer toward connections or associations that you might have already considered or that seem to make sense and consider if new research terms, language or concepts come to mind that may be interesting or exciting for you as a researcher. Sometimes testing out a research question while doing some preliminary researching is also useful to see if the language you are using or the direction you are heading toward is fruitful when trying to search strategically in academic databases. Be prepared to focus on a specific area of a broad topic.
Writing Consultant Jessie recommends outlining: “I think some rough outlining with a research question in mind can be helpful for me. I’ll have a research question and maybe a working thesis that I feel may be my claim to the research question based on some preliminary materials, brainstorming, etc.” — Jessie, CEWC Writing Consultant
Try an Exercise
In the earliest phase of brainstorming, try an exercise suggested by CEWC Writing Specialist, Percival! While it is normally used in classroom or workshop settings, this exercise can easily be modified for someone working alone. The flow of the activity, if done within a group setting, is 1) someone starts with an idea, 2) three other people share their idea, and 3) the starting person picks two of these new ideas they like best and combines their original idea with those. The activity then begins again with the idea that was not chosen. The solo version of this exercise substitutes a ‘word bank,’ created using words, topics, or ideas similar to your broad, overarching theme. Pick two words or phrases from your word bank, combine it with your original idea or topic, and ‘start again’ with two different words. This serves as a replacement for different people’s suggestions. Ideas for your ‘word bank’ can range from vague prompts about mapping or webbing (e.g., where your topic falls within the discipline and others like it), to more specific concepts that come from tracing the history of an idea (its past, present, future) or mapping the idea’s related ideas, influences, etc. Care for a physics analogy? There is a particle (your topic) that you can describe, a wave that the particle traces, and a field that the particle is mapped on.
Get Feedback and Affirm Your Confidence!
Creating a few different versions of your research question (they may be the same topic/issue/theme or differ slightly) can be useful during this process. Sharing these with trusted friends, colleagues, mentors, (or tutors!) and having conversations about your questions and ideas with other people can help you decide which version you may feel most confident or interested in. Ask colleagues and mentors to share their research questions with you to get a lot of examples. Once you have done the work of developing an effective research question, do not forget to affirm your confidence! Based on your working thesis, think about how you might organize your chapters or paragraphs and what resources you have for supporting this structure and organization. This can help boost your confidence that the research question you have created is effective and fruitful.
Be Open to Change
Remember, your research question may change from your first to final draft. For questions along the way, make an appointment with the Writing Center. We are here to help you develop an effective and engaging research question and build the foundation for a solid research paper!
Example 1: In my field developing a research question involves navigating the relationship between 1) what one sees/experiences at their field site and 2) what is already known in the literature. During my preliminary research, I found that the financial value of land was often a matter of precisely these cultural factors. So, my research question ended up being: How do the social and material qualities of land entangle with processes of financialization in the city of Lahore. Regarding point #1, this question was absolutely informed by what I saw in the field. But regarding point #2, the question was also heavily shaped by the literature. – Tariq
Example 2: A research question should not be a yes/no question like “Is pollution bad?”; but an open-ended question where the answer has to be supported with reasons and explanation. The question also has to be narrowed down to a specific topic—using the same example as before—”Is pollution bad?” can be revised to “How does pollution affect people?” I would encourage students to be more specific then; e.g., what area of pollution do you want to talk about: water, air, plastic, climate change… what type of people or demographic can we focus on? …how does this affect marginalized communities, minorities, or specific areas in California? After researching and deciding on a focus, your question might sound something like: How does government policy affect water pollution and how does it affect the marginalized communities in the state of California? -Janella
Our Newest Resources!
- Best Practices for Emailing Instructors and Professors
- Incorporating Headings & Subheadings
- Revision vs. Proofreading
- Engaging With Sources Effectively
- The Dos and Don’ts of Using Tables and Figures in Your Writing
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
- How it works

How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Writing Studio
Formulating your research question (rq).
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Formulating Your Research Question Return to Writing Studio Handouts
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Research Topic Versus Research Question Examples
1. broad topic versus narrow question, 1a. broad topic.
“What forces affect race relations in America?”
1b. NARROWER QUESTION
“How do corporate hiring practices affect race relations in Nashville?”
The question “What is the percentage of racial minorities holding management positions in corporate offices in Nashville?” is much too specific and would yield, at best, a statistic that could become part of a larger argument.
2. Neutral Topic Versus Argumentative Question
2a. neutral topic.
“How does KFC market its low-fat food offerings?”
2b. Argumentative question
“Does KFC put more money into marketing its high-fat food offerings than its lower-fat ones?”
The latter question is somewhat better, since it may lead you to take a stance or formulate an argument about consumer awareness or benefit.
3. Objective Topic Versus Subjective Question
Objective subjects are factual and do not have sides to be argued. Subjective subjects are those about which you can take a side.
3a. Objective topic
“How much time do youth between the ages of 10 and 15 spend playing video games?”
3b. Subjective Question
“What are the effects of video-gaming on the attention spans of youth between the ages of 10 and 15?”
The first question is likely to lead to some data, though not necessarily to an argument or issue. The second question is somewhat better, since it might lead you to formulate an argument for or against time spent playing video games.
4. Open-Ended Topic Versus Direct Question
4a. open-ended topic.
“Does the author of this text use allusion?”
4b. Direct question (gives direction to research)
“Does the ironic use of allusion in this text reveal anything about the author’s unwillingness to divulge his political commitments?”
The second question gives focus by putting the use of allusion into the specific context of a question about the author’s political commitments and perhaps also about the circumstances under which the text was produced.
Research Question (RQ) Checklist
- Is my RQ something that I am curious about and that others might care about? Does it present an issue on which I can take a stand?
- Does my RQ put a new spin on an old issue, or does it try to solve a problem?
- Is my RQ too broad, too narrow, or OK?
- within the time frame of the assignment?
- given the resources available at my location?
- Is my RQ measurable? What type of information do I need? Can I find actual data to support or contradict a position?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer my RQ (journals, books, internet resources, government documents, interviews with people)?
Final Thoughts
The answer to a good research question will often be the THESIS of your research paper! And the results of your research may not always be what you expected them to be. Not only is this ok, it can be an indication that you are doing careful work!
Adapted from an online tutorial at Empire State College: http://www.esc.edu/htmlpages/writerold/menus.htm#develop (broken link)
Last revised: November 2022 | Adapted for web delivery: November 2022
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.
Not sure how to log in to access library resources? Click here to learn how!
Library Home
- Library Website
- Research Basics
Developing a Research Question
- Introduction
- The Research Process
- Scholarly & Peer-Reviewed
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative
- Evaluating Sources
What is a research question?
A research question is an essential tool to help guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It poses a specific question that you are seeking to answer in your paper. Research questions can be broad or narrow, and can change throughout the research process.
A good research question should be:
- Focused on a single issue
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly in your paper
- Feasible to answer within the length of your paper
- Researchable using the resources available to you
- Relevant to your field of study and/or to society at large
The length of your paper and the research you're able to locate will help to shape your research question. A longer paper, like a thesis or dissertation, may require multiple research questions.
The answer to your research question develops into your thesis statement .

Writing Your Research Question
Chose a Topic
You should choose a research topic that is interesting to you. This will make the research and writing process much more bearable.
A good way to begin brainstorming research questions is to list all the questions you would like to see answered, or topics you would like to learn more about. You may have been provided a list of potential topics by your professor, if none are interesting to you ask if you can develop your own.
It is better to start broad and narrow down your focus as you go.
Do Preliminary Research

Reference materials like encyclopedias can also be good for this purpose.
Narrow Your Topic
Now that you have a basic idea of what research exists on your topic, you can begin to narrow your focus.
Make sure that your question is specific enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the length of your paper.
Developing a Research Question Video Tutorial
Using Keywords Video Tutorial
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: The Research Process >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2023 3:47 PM
- URL: https://library.ndnu.edu/researchbasics
Academic Success Center
Emergency Information

© 2023 Notre Dame de Namur University. All rights reserved.
Notre Dame de Namur University 1500 Ralston Avenue Belmont, CA 94002 Map
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
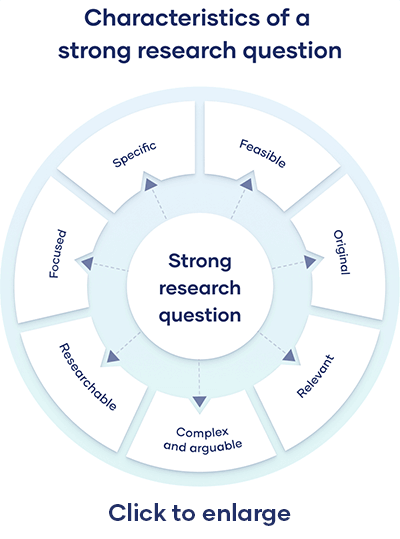
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Write a Research Question
Last Updated: April 20, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 75,817 times.
A research question helps you narrow your research and write a clear, arguable thesis. Your research question needs to be concise, arguable, and focused on your particular topic. Before writing your research question, narrow down your topic and brainstorm possible questions. Then, select the best question and craft it into a good research question. As another option, choose the type of research question that fits your purpose and format your question to fit that style.
Research Questions

Narrowing Your Topic

- When you decide on a research question for your work, it's best to run it by your instructor.

- For instance, great topics for a high school paper might include family dynamics during the civil war, body image among teens, or type 2 diabetes.
- If you're doing a college-level project, a good topic might be the environment's influence on human development, cultural influences on a poet's work, or the ethics of technological advancements.
- In some cases, your topic may be provided to you, such as when you're writing a paper for a class. You can still use the same process for narrowing your topic and selecting a research question.

- The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources.

- What, why, and how questions make the best research questions.
- Write down the first questions that come to mind without worrying if they'll make a good research question. You can always revise your question later to make it better.
- For example, let's say you chose body image among teens as your topic. You might write questions like, “How does social media impact body image?” “How does the amount of time spent on Instagram relate to a teen's sense of self-worth?” “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” and “What factors make teens more likely to have a poor body image?”
- Similarly, you might write a college paper about the ethics of technological advancements. Questions you might ask include, "How is social media altering the culture of society?" "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" and "How might current advancements affect society over the next 25 years?"
Tip: If you find yourself drawn to a particular question, don't keep brainstorming potential questions. Instead, start evaluating the question that interests you to figure out if it might be right for your research project.
Crafting an Effective Research Question

- As an example, the question "What jobs will humans lose to robots over the next 50 years?" may be too difficult to answer. Instead, you might ask, "How has the field of robotics changed the manufacturing industry?"
Tip: When choosing your question, consider your skill level and purpose. If you're doing this project for a class, how will it be graded? What are your instructor's expectations? Additionally, make sure your question fits the scope of the assignment.

- Is this question clear enough to guide my research?
- Is this question specific?
- Does this question allow for research and analysis?
- Can I answer this question based on current research? If so, could I easily find the answer by looking at basic reference works (which means the question is too easy to answer), or will it require more in-depth analysis using multiple sources?
- Has this question already been answered?
- Can I answer the question in an objective manner, based on evidence?
- Can I answer this question in the time I have allotted for this project?

- “What factors cause teens to have poor body image?” is better stated “What environmental and social factors contribute to poor body image in teens?”
- “How does T.S. Elliot use symbolism?” becomes “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”
- “What happened to family dynamics during the civil war?” can be narrowed to “How did the fracturing of families during the civil war affect society?”
- "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" might be narrowed to "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?"

- For instance, questions like, "What season of the year do parrots typically breed?" or "What era did William Wordsworth write?" are not great research questions because they are too easy to answer.
- The research question “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” is arguable because you could make a case for either peers or family members having a greater influence on teenagers. Similarly, “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'” is arguable because different critics may have varying interpretations of the poem.
- As another example, "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?" is debatable because you can focus on different effects. It's possible to interpret these effects differently, depending on your stance on the issue.
Tip: Research your question and see what comes up. If you feel like the search results effectively cover what you want to say, then you might want to pick a different question.
Choosing a Type of Research Question

- "What environmental factors cause birds to move nests?"
- "What changes to the habitat can encourage parrots to mate?"
- "What political conditions contributed to the start of the War of 1812?"
- "What symbols does T.S. Elliot use in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”

- "If two different plants are both provided the same amount of sunlight and fertilizer, will they grow at the same rate?"
- "If two identical solutions are exposed to different quantities of an element, will they show equal or different reactions?"
- "If two test subjects are asked to perform a task alone and then together, how will collaboration affect their outcome?"

- "Will the introduction of a new plant to a biodome affect the ecosystem?"
- "Does changing team assignments cause workers to lose morale?"
- "Do metered ramps on highways change driver behavior?"
Community Q&A
- Make sure your research question is narrow enough to write a specific paper. If it's too broad, your paper will be too general and vague to make a clear point. A narrow research question will help you write a focused paper. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- A clear, specific research question will help you create a good thesis for your paper. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you're doing your research as part of a class assignment, talk to your instructor if you're having trouble writing your research question. Tell them what you're considering and ask them for guidance. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraries.indiana.edu/sites/default/files/Develop_a_Research_Question.pdf
- ↑ https://www.pewresearch.org/our-methods/u-s-surveys/writing-survey-questions/
- ↑ https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/develop/tutorials/question
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/how-to-write-a-research-question
About this article

To write a research question, start by writing a list of open-ended questions that relate to the topic you're researching. For example, if your topic was social media, your questions might look something like "How does social media impact body image?" or "What impact does social media have on our culture?" Next, choose the question that interests you the most, and try to make it as specific as possible. Also, make sure it can't be easily answered since you want a topic that you can thoroughly examine. For more advice, like how to choose a topic to research, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Apr 7, 2022
Did this article help you?

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Where to Put the Research Question in a Paper
Silke Haidekker has a PhD in Pharmacology from the University of Hannover. She is a Clinical Research Associate in multiple pharmaceutical companies in Germany and the USA. She now works as a full-time medical translator and writer in a small town in Georgia.
Of Rats and Panic Attacks: A Doctoral Student’s Tale
You would probably agree that the time spent writing your PhD dissertation or thesis is not only a time of taking pride or even joy in what you do, but also a time riddled with panic attacks of different varieties and lengths. When I worked on my PhD thesis in pharmacology in Germany many years back, I had my first panic attack as I first learned how to kill rats for my experiments with a very ugly tool called a guillotine! After that part of the procedure, I was to remove and mash their livers, spike them with Ciclosporin A (an immunosuppressive agent), and then present the metabolites by high-pressure liquid chromatography.
Many rats later, I had another serious panic attack. It occurred at the moment my doctoral adviser told me to write my first research paper on the Ciclosporin A metabolites I had detected in hundreds of slimy mashes of rat liver. Sadly, this second panic attack led to a third one that was caused by living in the pre-internet era, when it was not as easy to access information about how to write research papers .
How I got over writing my first research paper is now ancient history. But it was only years later, living in the USA and finally being immersed in the language of most scientific research papers, that my interest in the art of writing “good” research papers was sparked during conferences held by the American Medical Writers Association , as well as by getting involved in different writing programs and academic self-study courses.
How to State the Research Question in the Introduction Section
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections . This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the Introduction, explains at least three major elements:
a) What is known or believed about the research topic?
B) what is still unknown (or problematic), c) what is the question or hypothesis of your investigation.
Some medical writers refer to this organizational structure of the Introduction as a “funnel shape” because it starts broadly, with the bigger picture, and then follows one scientifically logical step after the other until finally narrowing down the story to the focal point of your research at the end of the funnel.
Let’s now look in greater detail at a research question example and how you can logically embed it into the Introduction to make it a powerful focal point and ignite the reader’s interest about the importance of your research:
a) The Known
You should start by giving your reader a brief overview of knowledge or previous studies already performed in the context of your research topic.
The topic of one of my research papers was “investigating the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD).” So in the Introduction, I first presented the basic knowledge that diabetes is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and thus made the reader better understand our interest in this specific study population. I then presented previous studies already showing that diabetes indeed seems to represent an independent risk factor for death in the general population. However, very few studies had been performed in the ESRD population and those only yielded controversial results.
Example : “It seems well established that there is a link between diabetic nephropathy and hypertensive nephropathy and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in Western countries. In 2014, 73% of patients in US hospitals had comorbid ESRD and type 2 diabetes (1, 2, 3)…”
b) The Unknown
In our example, this “controversy” flags the “unknown” or “problematic” and therefore provides strong reasons for why further research is justified. The unknown should be clearly stated or implied by using phrases such as “were controversial” (as in our example), “…has not been determined,” or “…is unclear.” By clearly stating what is “unknown,” you indicate that your research is new. This creates a smooth transition into your research question.
Example : “However, previous studies have failed to isolate diabetes as an independent factor, and thus much remains unknown about specific risk factors associated with both diabetes and ESRD .”
c) The Research Question (Hypothesis)
Your research question is the question that inevitably evolves from the deficits or problems revealed in the “Unknown” and clearly states the goal of your research. It is important to describe your research question in just one or two short sentences, but very precisely and including all variables studied, if applicable. A transition should be used to mark the transition from the unknown to the research question using one word such as “therefore” or “accordingly,” or short phrases like “for this reason” or “considering this lack of crucial information.”
In our example, we stated the research question as follows:
Example : “Therefore, the primary goal of our study was to perform a Kaplan-Meier survival study and to investigate, by means of the Cox proportional hazard model, the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in diabetic patients with ESRD.”
Note that the research question may include the experimental approach of the study used to answer the research question.
Another powerful way to introduce the research question is to state the research question as a hypothesis so that the reader can more easily anticipate the answer. In our case, the question could be put as follows:
Example : “To test the hypothesis that diabetes is an independent predictor of death in people with ESRD, we performed a Kaplan-Survival study and investigated the value of diabetes by means of the Cox proportional hazard model.”
Note that this sentence leads with an introductory clause that indicates the hypothesis itself, transitioning well into a synopsis of the approach in the second half of the sentence.
The generic framework of the Introduction can be modified to include, for example, two research questions instead of just one. In such a case, both questions must follow inevitably from the previous statements, meaning that the background information leading to the second question cannot be omitted. Otherwise, the Introduction will get confusing, with the reader not knowing where that question comes from.
Begin with your research purpose in mind
To conclude, here is my simple but most important advice for you as a researcher preparing to write a scientific paper (or just the Introduction of a research paper) for the first time: Think your research question through precisely before trying to write it down; have in mind the reasons for exactly why you wanted to do this specific research, what exactly you wanted to find out, and how (by which methods) you did your investigation. If you have the answers to these questions in mind (or even better, create a comprehensive outline ) before starting the paper, the actual writing process will be a piece of cake and you will finish it “like a rat up a drainpipe”! And hopefully with no panic attacks.
Wordvice Resources
Before submitting your master’s thesis or PhD dissertation to academic journals for publication, be sure to receive proofreading services (including research paper editing , manuscript editing , thesis editing , and dissertation editing ) to ensure that your research writing is error-free. Impress your journal editor and get into the academic journal of your choice.
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Personal Finance
How to start an online business in 8 steps.

Our evaluations and opinions are not influenced by our advertising relationships, but we may earn a commission from our partners’ links. This content is created independently from TIME’s editorial staff. Learn more about it.
The internet has reshaped where, when, and how people shop for goods and services. The popularity of digital shopping has opened a world of opportunities for online business owners. With a computer and a stable internet connection, you can work from anywhere, set your own schedule, and sell to customers worldwide while avoiding the hassle and costs of owning a brick-and-mortar business.
Whether you're just starting to brainstorm about the best online business ideas or already have a concept in mind, here are some tips for getting your business up and running.
8 Ways to start your online business
1. establish a business niche.
If you haven't done so already, you'll need to decide what you want to offer and who your target customers will be. Here are a few factors to consider:
Your interests
Mark Twain once said, "Find a job you enjoy doing, and you will never have to work a day in your life." While only some would agree with this work/life approach, it's a good starting point for choosing a business niche. Think about your passions, skills, and expertise, then focus on ideas where they intersect.
Target audience
Consider your target audience and whether they have a problem no one else is solving or a product no one else is providing. If so, do they have the discretionary income to afford your product or service and are they willing to pay for it? Will there be adequate demand?
Profit potential
Consider if your niche has profit potential in an online environment. For example, an overly large or heavy product may be too expensive to ship at a reasonable cost. Is the idea scalable so you can accommodate more customers and transactions in the future?
2. Choose a business model
A business model is how your company will provide products or services to customers and make money. Some options to consider include:
- Affiliate marketing. Promote other businesses and receive a commission for each sale you make.
- Coaching and consulting. Share your expertise and offer guidance.
- E-commerce. Launch a website and sell products online using one of the best payment gateways .
- Franchising. Pay a franchise fee and operate under an established brand.
- Freelancing. Offer a service such as writing, programming, web design, or social media marketing.
- Information products. Create and sell eBooks or online courses.
- Subscriptions. Package software or subscription boxes and charge a recurring fee.
3. Write a business plan
A good business plan outlines the steps to start and manage your business. The important thing is to think through the key elements of your venture while focusing on your goals. According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), a traditional business plan format includes some combination of the following:
Executive summary
Explain what your company is and why it will be successful. This section should include your mission statement, product or service, basic company information, and financial details if you need financing.
Company description
Provide detailed information about your company: the problem it solves, your target audience, and your competitive advantages.
Market analysis
Explain your industry outlook, what other businesses are doing, and how you can do it better.
Organization and management
Outline who will run your company and how it will be structured. Will it be a general or limited partnership, a C or S corporation, limited liability company (LLC), or are you a sole proprietor?
Service or product line
Describe the product or service you offer, explaining how it benefits your target customers.
Marketing and sales
Explain how you will attract and retain customers and the steps for making a sale.
Funding request
Explain the level of funding you'll need over the next five years and how you'll use it. Include financial projections detailing your forecasted income, cash flow, and budgets. Research how to get a business loan , and familiarize yourself with the SBA website to learn more about its loan programs.
4. Develop your brand
Once you know what you'll sell and how you'll run the business, developing your brand is next. You'll have to choose a business name and create a logo. This process can be relatively simple if you already have ideas in mind—or challenging if you're starting from scratch. You might want to hire a graphic designer to implement your vision.
5. Create a website
Once you have developed your brand, it’s time to build a website. You’ll need to lock in a domain name and choose a hosting service. There are website builders, such as Squarespace , available to help you get started—or you can hire someone to do the work for you.
6. Cover legal bases
The next step is to make your business official. While the requirements vary by business, here are the essential action items:
Register your business
Registering with your state gives you legal grounds to use your brand's name. You can utilize a service like LegalZoom to register as a sole proprietor, LLC, corporation (C corp or S corp), nonprofit, or DBA (doing business as). Consult a tax specialist for help choosing the best business structure for your situation.
Apply for an EIN
You'll need an Employer Identification Number (EIN)—a federal tax ID—to pay federal taxes, apply for business licenses and permits, open a business bank account , and hire employees. You can apply for an EIN for free on the IRS website . The IRS says to beware of websites that charge for this free service.
Licenses and permits
Depending on your business activities and location, you may need licenses and permits from your state, county, or city. Check with your state's website (e.g., ca.gov, nc.gov) to determine your necessary licenses and permits.
Most businesses must file an annual income tax return, and the form you use depends on how your business is structured. Online services like Found, a banking and tax app designed for small business owners, have tools to make keeping track of taxes easier. It's also helpful to establish a relationship with a trusted tax specialist.
7. Market your business
Once your online business is ready for the world, it's time to market it. While marketing strategies vary depending on your business model and target audience, here are a few options to consider:
- Include your brand in online directories.
- Create social media profiles and share high-quality content often.
- Launch compelling email marketing campaigns.
- Use SEO best practices to optimize your site for search engines.
- Collaborate with influencers to promote your brand.
- Leverage your network—including professional contacts, friends, and family.
8. Reward customer loyalty
Keeping existing customers happy is often easier than generating new leads, so it can be worth the extra effort to reward them for their loyalty. Consider offering discounts to repeat customers or perks to patrons who refer friends and family. You might also provide spending-based rewards or incentives for sharing positive reviews on social media.
Of course, one of the best ways to reward loyalty is to connect with your customers personally, making sure they always feel welcome and appreciated. That way, they'll be more likely to become repeat customers, recommend you to friends and family, and help you grow a thriving online business.
Why should you consider starting an online business?
Consumers increasingly prefer shopping online, providing virtually unlimited opportunities for digital entrepreneurs to reach a global audience. Further, many of the traditionally time-consuming aspects of starting a business have been simplified—and made more affordable—by websites such as LegalZoom .
One outcome of the pandemic was the emergence of new and enhanced tools that make remote work not only possible, but more efficient. As a result, it's easier than ever to work anywhere in the world with a laptop and a reliable internet connection.
How to save when starting an online business
Businesses have a slew of start-up costs that can be difficult to manage before you're up and running. Here are a few ways to make balancing the budget a little easier.
Rewards credit cards
A business credit card is an excellent way to keep your business and personal expenses separate for accounting purposes, but that's not the only perk. With the best small business credit cards , you can also earn rewards on your spending, enjoy perks like free travel insurance, and score a hefty welcome bonus.
Tax prep software
A good way to save money in the early days of your business is to use upgradable tax prep and other business-related software. Start with the free version, then upgrade to the premium package once your business takes off.
Payment processing
You'll need a payment service provider to accept online payments. Not surprisingly, some payment solutions are more expensive than others. For example, Square charges 2.9% + $0.30 for online transactions, while Venmo costs 1.9% + $0.10 between Venmo accounts. Of course, fees shouldn't be the only consideration when choosing a payment service provider. Still, they're worth paying attention to; even small differences can add up over time.
TIME Stamp: Research and strategy are key to success
Starting an online business involves many of the same steps as opening a brick-and-mortar business. You’ll need to determine your niche, conduct market research, craft a well-thought-out business plan, and develop a brand and website. Implementing a successful marketing plan is also key to building and retaining a solid customer base.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is the best type of online business to start.
The best online business for you depends on your professional background, skills, interests, and goals. Think about what you're good at and enjoy doing, then brainstorm ideas for monetizing it.
Which kind of online business is most profitable?
There are a wide variety of online businesses ranging from e-commerce to private tutoring. How profitable one is over the other depends on a number of factors. The start-up and ongoing costs of some are nominal compared to others. For example, an online tutoring business would typically have much lower costs than selling collectibles online. Demand, competition, and how well an online business is managed also impact profitability.
Can I start an online business with $100?
You can start an online business on a shoestring budget. With $100, you’ll be able to buy a domain name, build a basic website (using a free template), and publish the site through a web hosting provider long enough to get you started. Of course, some ventures have higher start-up costs, so you may well need considerably more than $100, depending on your business.
The information presented here is created independently from the TIME editorial staff. To learn more, see our About page.
Is it ethical to have children as climate change heats up our world?
- Published: May. 28, 2024, 12:59 p.m.

Sasser uses her research to show how climate emotions land hardest on marginalized groups, people of color and low-income groups. Jade Sasser
- Victoria St. Martin | Inside Climate News
Sign up for The Meltdown, a weekly newsletter highlighting the latest apocalyptic dramas, debunking climate myths, and sharing sustainability hacks, all while arming you with information to hold polluters and the government accountable. Enter your email to subscribe.
This article originally appeared on Inside Climate News , a nonprofit, independent news organization that covers climate, energy and the environment. It is republished with permission. Sign up for their newsletter here .
Jade S. Sasser has been studying reproductive choices in the context of climate change for a quarter century. Her 2018 book, “ Infertile Ground ,” explored how population growth in the Global South has been misguidedly framed as a crisis—a perspective that Sasser argues had its roots in long-standing racial stereotypes about sexuality and promiscuity.
But during the COVID-19 pandemic, Sasser, an environmental scientist who teaches at the University of California, Riverside , started asking different questions, this time about reproductive choices in the Global North. In an era in which the planet is getting hotter by the day, she wondered, is it morally, ethically or practically sound to bring children into the world? And do such factors as climate anxiety , race and socio-economic status shape who decides to have kids and who doesn’t?
The result is her latest book, “ Climate Anxiety and the Kid Question ,” which was published last month by the University of California Press and centers on a range of issues that are part of a broader conversation among those who try to practice climate-conscious decision-making.
From the outset, Sasser cautions that her work does not attempt to draw any conclusions about what the future might hold or how concerns about global warming might affect population growth going forward.
“This book is not predictive,” Sasser said in a recent interview with Inside Climate News. “It’s too soon to be able to say, ‘OK, these are going to be the trends. These people are not going to have children, or are going to have fewer children or this many, that many.’ We’re at the beginning of witnessing what could be a significant trend.”
Sasser said that one of the most compelling findings of her research was how survey results showed that women of color were the demographic cohort that reported that they were most likely to have at least one child fewer than what they actually want because of climate change. “No other group in that survey responded that way,” Sasser said.
Those survey results, Sasser said, underscore the prevalence of climate anxiety among communities of color. A Yale study published last year found that Hispanic Americans were five times as likely to experience feelings of climate change anxiety when compared to their white counterparts; Black Americans were twice as likely to have those feelings.
“There is a really large assumption that we don’t experience climate anxiety,” said Sasser, who is African American. “And we do. How could we not? We experience most of the climate impacts first and worst. And the few surveys that have been done around people of color and climate emotions showed that Black and Latinx people feel more worry and more concerned about climate change than other groups.”
Sasser, who also produced a seven-episode podcast as part of the project, said that she hopes her work can help fill what she sees as a void in the public’s awareness of climate anxiety in communities of color.
“Every single thing I was reading just didn’t include us in the discussion at all,” Sasser said. “I found myself in conversations with people who were not people of color and they were saying, ‘Well, I think people of color are just more resilient and don’t feel climate anxiety. And this doesn’t factor into their reproductive lives.’
That’s just simply not true. But how would we know that without the research to tell us? But now I’ve started down that road, and I really, really hope that other researchers will take up the mantle and continue studying these questions in the context of race in the future.”
Sasser recently sat down with Inside Climate News to talk about the book and how she uses her research to show how climate emotions land hardest on marginalized groups, people of color and low-income groups.
This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
How did you come to write “Climate and the Kid Question”?
This is a book that I was not expecting to write. It was my pandemic pivot project. I was working on something very different, focused on household energy in the Global South. And then COVID happened and I could no longer travel. And so I had to turn to the things that I had been compiling as part of a project that I saw as being on the back burner.
And what I had been compiling was articles about young women climate activists who were talking about not having children in response to climate change. And when I had first encountered these articles, I misunderstood them. I thought that these women were motivated by erroneous ideas about overpopulation, or that they weren’t having children because they thought there were too many people on the earth, things like that.
But when I delved more deeply into what I was reading, I began to become aware of the whole world of eco-emotions and climate emotions. And that’s when I was introduced to the terms eco-anxiety and climate anxiety. And then I began to understand where these young people were coming from on a much, much deeper level. And so this book is my response to three years of research delving into climate emotions, distressing emotions, in particular, how those emotions are impacting how young people feel morally and ethically about having children, about raising children, about the future. And also what race and inequality have to do with it all.
You’ve been studying issues of population growth for a while now, right? That was the focus of your first book, “On Infertile Ground.”
I’ve been having those conversations for, I guess, 25 years now. And in those conversations, I’ve always been curious about what motivates young women to want or not want children, to have or not have them at any particular moment in time. And in the first book those questions centered around “how do these really large scale ideas and policies that are informed by ideas about overpopulation, overconsumption of resources, who should or should not have children?”
I, at that time, was curious about how that was informing activism, and how everyday experience in places like Madagascar was shaped by that.
This book is very different. What is different is that I focus on the United States. I also look at movements in Canada and in England, but I’m not looking at the Global South at all, intentionally. And the reason why is because people in the Global North—specifically the U.S. and Canada and Britain—have really different perspectives on personal reproductive behavior and environmental issues. And what is different is here you have a lot of young people who are very climate aware and climate literate.
They’re reading the science. They’re taking environmental studies classes. They’re asking questions about what this means for their personal lives, and they’re making decisions about their personal lives based on what they anticipate is coming in the future. And to see the racial inequality and socio-economic inequality as it shapes those questions—it’s very context specific.
And I wanted to get into that context specific stuff here in the United States, because I think it’s really easy for some people to skim over that. I’ve read articles and op-eds in the past saying things like, well, “people in the United States are worried about having children in the context of climate change.”
And it makes sense because people in the U.S. over-consume resources. So people in the U.S. are not all the same. We’re not all having the same experiences. We don’t occupy the same social location. We are not impacted by climate change in the same ways.
And so I wanted to really shine a light on how social inequality right here makes the experience of climate change and climate injustice very, very difficult for people of color. And how those climate inequalities and climate impacts land on the mental health and emotional health of people of color. And how people of color feel differently about bringing children into the world as a result.
Are you a mother? Do you have children? The decision of having a child is such a personal one.
I’m not a mother. I think actually that it’s a personal decision that has been made political for so long. And I think that the way that most people talk and write about this issue is that they are actively saying do or don’t. Unfortunately, most environmentalists throughout the history of environmentalism have fallen on the side of saying don’t have children. And I think that has been a very dangerous thing to say in particular, because those that they’ve been telling not to have children have tended to be low-income people and people of color.
I think that the other thing is one of the arguments I make in the book that you’ll see is that I personally don’t actually think that this is private. And what I mean by that is the conditions of climate change, which are the conditions that young people today are living in as they make their reproductive decisions. Those aren’t private. Those aren’t personal. Those are public. Those are big public actions that these big actors, corporations and governments and militaries are taking. And we are all living in this big collective shared experience of climate change. And if that’s the social circumstance in which you have to think about whether to have kids or not, it’s really not a private decision.
You have to respond to the big social conditions you’re living in. And when people take it on as a private issue or a personal matter, that tends to lead to more feelings of guilt or stigma or like they’re doing something wrong or like there’s something wrong with them for perhaps not wanting to have kids. And so I actually advocate for having this conversation more in public. And really placing responsibility on those who deserve it. And that is the big corporate actors, the fossil fuel companies, the military and governments, government actors, elected officials, who are not creating and supporting climate-forward legislation.
In terms of research, the study of climate emotions is still fairly new, right?
So, climate emotions have really only been studied in the last 20 years. And as they’re being studied, they are ramping up in real time. So climate emotions are any kind of emotional changes or emotional impact that results from how people experience—either learning about, or living through, or anticipating—the impacts of climate change. So those who don’t necessarily ever experience evacuation from a wildfire or hurricane or flood might still be deeply distressed by climate impacts.
If they’re reading the science, they’re looking at the reports or, you know, they’re watching TV, or engrossed in social media and hearing about other people who are experiencing those things. And what climate emotions researchers have been uncovering is that this emotional distress lands hardest on younger people, especially Generation Z.
What those researchers have studied less of, and what I do in this book, is understand how other groups, particularly socially marginalized groups, people of color and low-income groups are also people on whom those climate emotions land hardest. And when I say climate emotions, distressing emotions, include things like anxiety, depression, grief, sadness, fear and other emotions like that.
How does race play a factor in how we all process those emotions?
What I found in a survey that I conducted, doing this research is that for people of color, the most distressing emotions were reported by people of color, who in a statistically significant way, most identified feeling traumatized by the impact of climate change. They also reported feeling fear more so than white respondents.
And they also reported feeling overwhelmed. And that came out a lot in interviews, too. What I was not anticipating—but this is also significant—is that when it came to parenting in the midst of climate change, people of color in my study were most likely to report positive or action-oriented emotions, including feeling motivated, feeling determined, feeling a sense of happiness or optimism. Because that was a quantitative survey, I wasn’t able to ask questions about why those positive emotions were there.
But I can only imagine that it’s because people of color really have long histories of facing existential threat. Black and Indigenous people, in particular, have had to develop tools to become resilient, to become resilient within community, within family and within social movements. And so I can only imagine that those responses of motivation, joy, determination and happiness come from that sense of “we will survive, we will endure and whatever future is ahead we will be—and we will find a way to thrive.”
So, does your work really underscore the importance of African Americans and communities of color—in the face of these threats—drawing strength from family?
Not just family. We can trace a long history in the United States of Black people, literally, facing threats to our existence, from literally the earliest days of being in this country through slavery. And so one of the things that has always been a really important institution to protect us from the harms of the outside world is family, and not just family, but multigenerational family. And for us, that often includes chosen family.
We all have “play cousins,” “play aunties,” “play uncles”—people who are not biological kin. But the lack of biological relationship does not matter at all. They are members of the family. Building and sustaining those multi-generational ties has always been important to strengthen us, not just against big existential threats, but to strengthen us in a society in which we often don’t have the necessary resources and social supports that we need.
We often have the absence of a social safety net to provide for us in the ways that we need to be provided for. Other institutions provide those supports, as well. The church, for example. Say what you want about the Black church—there are challenges, there have always been challenges, but the Black church has been a really important institution in the lives of African Americans, not just for religious reasons, but for social reasons. It was a very important institution throughout the civil rights movement.
And it provides a space of safety, solace and community as a buffer against a lot of the challenges of the outside world. How does all of this come back to climate anxiety and the kid question? Well, when you don’t have research that includes African Americans, for example, then you tend to assume that we don’t experience climate anxiety or that, if we do, it doesn’t have any impact on kid questions for us. And that’s not true.
We can’t make that assumption, [but] people do make that assumption in the absence of research. And this research is the first and only of its kind that asks these questions and puts race at the center. And why did I want to do that? I wanted to establish an evidence base so that we are not left out of the discussion when it comes to climate, mental health and the kinds of resources that will be provided to communities to respond to the negative mental health impacts of climate change. And I also don’t want us to be left out of the discussion of how climate mental health impacts do, or potentially, will impact reproductive changes. I just want us to be in the discussion, and we can’t be if we’re left out of the research.
What was the most surprising finding in your research? And what does all of this mean for the future?
The thing that surprised me most, this came out in interviews, is that among some young people—especially those who have taken environmental studies classes in college or were environmental studies majors—there is more and more peer pressure to not have kids, and I was not expecting that. I was expecting to hear things along the lines of, “I really want kids, but I feel like I can’t have them. The world is a scary place, you know, climate change is getting worse.”
And I did hear that a lot. But I expected that to be the overwhelming sentiment and what I heard, a number of times and was always surprised, was that, some people I interviewed said, “Well, when I talk to my friends and I say that I want children or that I want a large family, their response is ‘Eww, why would you want that? That’s awful.’” I was not expecting anti-child peer pressure among Gen Z. I did not anticipate that. Those are people who are planning to have one less child. Planning and behavior are not the same thing.
So, you know, no one can predict what they will actually do. What does this mean for the future? I think that’s exactly the right question to ask, and none of us can predict. But what we need for the future is for our young people to feel excited and hopeful about the future that’s ahead of them, and to feel empowered to make the decisions that would make them happy in their lives, whether that is having children, adopting children, step-parenting or not being in children’s lives at all.
So, for me and for people I interviewed, it’s not fundamentally about babies or about children. That is a way, a high stakes way of getting us to what it fundamentally is about, which is how can we aggressively fight climate change right now and combat lackadaisical attitudes or profit-driven attitudes that really just favor business as usual, because ultimately the problem that needs to be solved is not climate anxiety, it’s climate change. Climate anxiety is a normal, natural response to climate change. Let’s fight and solve climate change, and then you won’t have the thing to be anxious about.
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting

COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
A good research question should: Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose. Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper. Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1. Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer. In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery. Without a clear target, you won't know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light ...
Reflect on the potential impact of your research when refining your question. 4. Ensure you have access to necessary resources, such as data, participants, or equipment. Remember, receiving feedback and revising is a valuable step in creating impactful and precise research.
How to Write Research Questions. Guide for Writing Research Questions: Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions. Use clear language: Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is ...
Selecting your research question and creating a clear goal and structure for your writing can be challenging - whether you are doing it for the first time or if you've done it many times before. It can be especially difficult when your research question starts to look and feel a little different somewhere between your first and final draft.
Steps to Develop your Research Question. Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature. Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues. Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address. Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche.
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will ...
In essence, the research question that guides the sciences and social sciences should do the following three things:2. 1) Post a problem. 2) Shape the problem into a testable hypothesis. 3) Report the results of the tested hypothesis. There are two types of data that can help shape research questions in the sciences and social sciences ...
A research question is an essential tool to help guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It poses a specific question that you are seeking to answer in your paper. Research questions can be broad or narrow, and can change throughout the research process. A good research question should be: The length of your paper and the research you're ...
Adapted from: George Mason University Writing Center. (2008). How to write a research question. ... You may not know right away what your research question is. Gather information on the broader topic to explore new possibilities and to help narrow your topic. • Choose an interesting topic. If you're interested in your topic, chances are ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources. 4. Write a list of open-ended questions about your topic. Do a brainstorming session to generate questions you may have based on your research.
In a sense, writing a research question is like setting a goal and posting it prominently on your wall. Steps to develop a research question. Since research questions are such a crucial part of a research paper, you'll want to devote a reasonable amount of time and effort to writing them well. The following six steps can guide you through the ...
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections. This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the ...
Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd. For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don't miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review.
Unit 4 IP Download the Research Prospectus template in the Doctoral Resource Center (you can use the link uploaded in the Learning Materials Unit 4 section), and address the following in your assignment submission: • Read the guidelines for the Problem Statement section of the prospectus. • Locate at least 3 peer-reviewed scholarly articles from the library academic databases that have ...
Offer a service such as writing, programming, web design, or social media marketing. ... You'll need to determine your niche, conduct market research, craft a well-thought-out business plan, and ...
Jade Sasser's research explores one of the biggest questions facing the climate-conscious. Her new book focuses on the racial dimensions of eco-anxiety and reproduction decisions.
Whether you are writing a fictional recounting of the life of Vlad the Impaler (as I have) or the true-crime career of a shoplifter in Burnaby, B.C. (as I haven't), the raw ingredients and building blocks of your writing—facts—will need to be discovered and dealt with. The self-imposed pressure to get the facts "right" is enormous. Most writers imagine a panel of experts ready to ...
Researchers are learning that handwriting engages the brain in ways typing can't match, raising questions about the costs of ditching this age-old practice, especially for kids.
Before you start writing your cover letter, consider these helpful tips: Research the company Knowing the company's mission, its services and its culture will help you tailor your cover letter in a way that shows you're a perfect fit. Proofread and edit your cover letter Ensure your letter is free from typos, spelling mistakes and grammatical ...