A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke's International University, Tokyo, Japan. [email protected].
- 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
- PMID: 35470596
- PMCID: PMC9039193
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e121
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
Keywords: Hypotheses; Qualitative Research; Quantitative Research; Research Questions.
© 2022 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.

Publication types
- Qualitative Research
- Research Design*
Advertisement

- Previous Article
- Next Article
1. INTRODUCTION
2. background, 5. discussion, 6. conclusions, author contributions, competing interests, funding information, data availability, how common are explicit research questions in journal articles.
Handling Editor: Ludo Waltman
- Cite Icon Cite
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Permissions
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Search Site
Mike Thelwall , Amalia Mas-Bleda; How common are explicit research questions in journal articles?. Quantitative Science Studies 2020; 1 (2): 730–748. doi: https://doi.org/10.1162/qss_a_00041
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Although explicitly labeled research questions seem to be central to some fields, others do not need them. This may confuse authors, editors, readers, and reviewers of multidisciplinary research. This article assesses the extent to which research questions are explicitly mentioned in 17 out of 22 areas of scholarship from 2000 to 2018 by searching over a million full-text open access journal articles. Research questions were almost never explicitly mentioned (under 2%) by articles in engineering and physical, life, and medical sciences, and were the exception (always under 20%) for the broad fields in which they were least rare: computing, philosophy, theology, and social sciences. Nevertheless, research questions were increasingly mentioned explicitly in all fields investigated, despite a rate of 1.8% overall (1.1% after correcting for irrelevant matches). Other terminology for an article’s purpose may be more widely used instead, including aims, objectives, goals, hypotheses, and purposes, although no terminology occurs in a majority of articles in any broad field tested. Authors, editors, readers, and reviewers should therefore be aware that the use of explicitly labeled research questions or other explicit research purpose terminology is nonstandard in most or all broad fields, although it is becoming less rare.
Academic research is increasingly multidisciplinary, partly due to team research addressing practical problems. There are also now large multidisciplinary journals, such as PLOS ONE and Nature Scientific Reports , with editorial teams that manage papers written by people from diverse disciplinary backgrounds. There is therefore an increasing need for researchers to understand disciplinary norms in writing styles and paradigms. The authors of a research paper need to know how to frame its central contribution so that it is understood by multidisciplinary audiences. One strategy for this is to base an article around a set of explicitly named research questions that address gaps in prior research. Employing the standard phrase “research question” gives an unambiguous signpost for the purpose of an article and may therefore aid clarity. Other strategies include stating hypotheses, goals, or aims, or describing an objective without calling it an objective (e.g., “this paper investigates X”). Similarly, structured abstracts are believed to help readers understand a paper ( Hartley, 2004 ), perhaps partly by having an explicit aim, objective, or goal section. A paper that does not recognize or value the way in which the central contribution is conveyed may be rejected by a reviewer or editor if they are unfamiliar with the norms of the submitting field. It would therefore be helpful for authors, reviewers, and editors to know which research fields employ explicitly labeled research questions or alternative standard terminology.
Purpose statements and research questions or hypotheses are interrelated elements of the research process. Research questions are interrogative statements that reflect the problem to be addressed, usually shaped by the goal or objectives of the study ( Onwuegbuzie & Leech, 2006 ). For example, a healthcare article argued that “a good research paper addresses a specific research question. The research question—or study objective or main research hypothesis—is the central organizing principle of the paper” and “the key attributes are: (i) specificity; (ii) originality or novelty; and (iii) general relevance to a broad scientific community” ( Perneger & Hudelson, 2004 ).
The choice of terminology to describe an article’s purpose seems to be conceptually arbitrary, with the final decision based on community norms, journal guidelines, and author style. For example, a research paper investigating issue X could phrase its purpose in the following ways: “research question 1: is X true?,” “this paper aims to investigate X,” “the aim/objective/purpose/goal is to investigate X,” or “X?” (as in the current paper). Implicit purpose statements might include “this paper investigates X” or just “X,” where the context makes clear that this is the purpose. Alternatively, the reader might deduce the purpose of a paper after reading it, with all these options achieving the same result with different linguistic strategies. Some research purposes might not be easily expressible as a research question, however. For example, a humanities paper might primarily discuss an issue (e.g., “Aspects of the monastery and monastic life in Adomnán’s Life of Columba ”) but even these could perhaps be expressed as research questions, if necessary (e.g., “Which are the most noteworthy aspects of the monastery and monastic life in Adomnán’s Life of Columba ?”).
In which fields are explicitly named research questions commonly used?
Has the use of explicitly named research questions increased over time?
Are research purposes addressed using alternative language in different fields?
Do large journals guide authors to use explicitly named research questions or other terminology for purpose statements in different fields?
2.1. Advice for Authors
There are some influential guidelines for reporting academic research. In the social sciences, Swales’ (1990 , 2004) Create A Research Space (CARS) model structures research article introductions in three moves (establishing a territory, establishing a niche, and occupying a niche), which are subdivided into steps. Within the 1990 model, move 3 includes the steps “outlining purposes” and “announcing present research,” but research questions are not explicitly included, being similar the “question raising” step in move 2. In the updated 2004 model, move 3 includes an obligatory step named “announcing present research descriptively and/or purposively” (that joins the steps “outlining purposes” and “announcing present research” from the 1990 model), whereas “listing research questions or hypotheses” is a new optional step.
In medicine, the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) initiative is a checklist of items that should be included to improve reporting quality. One of these is a statement of objectives that “may be formulated as specific hypotheses or as questions that the study was designed to address” or may be less precise in early studies ( Vandenbroucke, von Elm, et al., 2014 ). This description therefore includes stating research questions as one of a range of ways of specifying objectives. An informal advice article in medicine instead starts by arguing that the paper’s aim should be clearly defined ( McIntyrei, Nisbet, et al., 2007 ).
Researchers may also be guided about the language to use in papers by any ethical or other procedures that they need to follow before conducting their work. For example, clinical trials often need to be registered and declared in a standard format, which may include explicit descriptions of objectives (e.g., see “E.2.1: Main objective of the trial” at: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2015-002555-10/GB ).
2.2. Empirical Evidence
Journal article research questions and other purpose statements, such as aims, objectives, goals, and hypotheses ( Shehzad, 2011 ), are usually included within Introduction sections or introductory phases, sometimes appearing as separate sections ( Kwan, 2017 ; Yang & Allison, 2004 ). Some studies have analyzed research article introductions in different disciplines and languages based on the Swales’ (1990 , 2004) CARS model. Although these studies analyze small sets of articles, they seem to agree that the research article introduction structure varies across disciplines (e.g., Joseph, Lim & Nor, 2014 ) and subdisciplines within a discipline, including for engineering ( Kanoksilapatham, 2012 ; Maswana, Kanamaru, & Tajino, 2015 ), applied linguistics ( Jalilifar, 2010 ; Ozturk, 2007 ) and environmental sciences ( Samraj, 2002 ). Introductions in English seem to follow this pattern more closely than introductions in other languages ( Ahamad & Yusof, 2012 ; Hirano, 2009 ; Loi & Evans, 2010 ; Rahimi & Farnia, 2017 ; Sheldon, 2011 ), reflecting cultural differences. Research questions and other purpose terminology, such as aims, objectives, goals, or hypotheses, might also reappear within the Results or Discussion sections ( Amunai & Wannaruk, 2013 ; Brett, 1994 ; Hopkins & Dudley-Evans, 1988 ; Kanoksilapatham, 2005 ).
Previous research has shown that research questions and hypotheses are more common among English-language papers than non-English papers ( Loi & Evans, 2010 ; Mur Dueñas, 2010 ; Omidi & Farnia, 2016 ; Rahimi & Farnia, 2017 ; Sheldon, 2011 ), especially those written by English native speakers ( Sheldon, 2011 ). However, a study analyzing 119 English research article introductions from Iranian and international journals in three subdisciplines within applied linguistics found that “announcing present research” was more used in international journals whereas research questions were proclaimed explicitly more often in local journals ( Jalilifar, 2010 ).
In some fields the verbs examine , determine , evaluate , assess , and investigate are associated with the research purpose ( Cortés, 2013 ; Jalali & Moini, 2014 ; Kanoksilapatham, 2005 ) and the verbs expect , anticipate , and estimate are associated with hypotheses ( Williams, 1999 ). Some computer scientists seem to prefer to write the details of the method(s) used rather than stating the purpose or describing the nature of their research and use assumptions or research questions rather than hypotheses ( Shehzad, 2011 ). Moreover, scholars might state the hypotheses in other ways, such as “it was hypothesized that” ( Jalali & Moini, 2014 ).
A study analyzing lexical bundles (usually phrases) in medical research article introductions showed that the most frequent four-word phrases are related to the research objective, such as “the aim of the,” “aim of the present,” and “study was to evaluate” ( Jalali & Moini, 2014 ). Another study examined lexical bundles in a million-word corpus of research article introductions from several disciplines, showing that the main bundle used to announce the research descriptively and/or purposefully included the terms aim , objective , and purpose (e.g., “the aim of this paper,” “the objective of this study,” “the purpose of this paper”), but no bundles related to research questions or hypotheses were identified ( Cortés, 2013 ).
These findings are in line with other previous studies investigating the structure of research articles, especially the introduction section, which report a much higher percentage of journal papers specifying the research purpose than the research questions or hypotheses across disciplines, regardless of the language in which they are published, with the exception of law articles (see Table 1 ). These studies also show that research questions and hypotheses are much more frequent among social sciences articles (see Table 1 ), which has also been found in other genres, such as PhD theses and Master’s theses (see Table 2 ).
Reference to a wide research purposes, without specifying if they are objectives or RQs/hypotheses.
Restating RQs in the result section.
Note: Studies that have based their analysis on the Swales’s (1990) CARS model ( Anthony, 1999 ; Posteguillo, 1999 ; Mahzari & Maftoon, 2007 ) report the percentage related to “outlining purposes” and “announcing present research.” For these studies, the column “Present the research purpose” reports the higher value. Moreover, for these studies, the value reported in the RQs/hypotheses column refers to the “Question raising” information.
A few studies have focused exclusively on research purposes, research questions, and hypotheses. Some have discussed the development of research questions in qualitative ( Agee, 2009 ) or mixed method ( Onwuegbuzie & Leech, 2006 ) studies, whereas others have examined the ways of constructing research questions or hypotheses within some fields, such as organization studies ( Sandberg & Alvesson, 2011 ) or applied linguistics doctoral dissertations ( Lim, 2014 ; Lim, Loi, & Hashim, 2014 ). Shehzad (2011) examined the strategies and styles employed by computer scientists outlining purposes and listing research questions. She found an increase in the use of research nature or purpose statements and suggested that the “listing research questions or hypotheses” step of Swales’s model was obligatory in computing. No study seems to have examined how often journal guidelines give authors explicit advice about research questions or other purpose statements, however.
The PMC (Pub Med Central) Open Access subset ( www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/tools/openftlist/ ) was downloaded in XML format in November 2018. This is a collection of documents from open access journals or open access articles within hybrid journals. The collection has a biomedical focus, but includes at least a few articles from all broad disciplinary areas. Although a biased subset is not ideal, this is apparently the largest open access collection. Only documents declared in their XML to be of type “research article” were retained for analysis. This excludes many short contributions, such as editorials, that would not need research goals.
The XML of the body section of each article was searched for the test strings “research question,” “RESEARCH QUESTION,” “Research Question,” or “Research question,” recording whether each article contained at least one. This would miss papers exclusively using abbreviations, such as RQ1.
Full body text searches are problematic because terms could be mentioned in other contexts, depending on the part of an article. For example, the phrase “research question” in a literature review section may refer to an article reviewed. For a science-wide analysis it is not possible to be prescriptive about the sections in which a term must occur, however, because there is little uniformity in section names or orders ( Thelwall, 2019 ). Making simplifying assumptions about the position in a text in which a term should appear, such as that a research question should be stated in the first part of an article, would also not be defensible. This is because the structure of articles varies widely between journals and fields. For example, methods can appear at the end rather than the middle, and some papers start with results, with little introduction. There are also international cultural differences in the order in which sections are presented in some fields ( Teufel, 1999 ). The current paper therefore uses full-text searches without any heuristics to restrict the results for transparency and to give an almost certain upper bound to the prevalence of terms, given the lack of a high-quality alternative.
Articles were separated into broad fields using the Science-Metrics public journal classification scheme ( Archambault, Beauchesne, & Caruso, 2011 ), which allocates each journal into exactly one category. This seems to be more precise than the Scopus or Web of Science schemes ( Klavans & Boyack, 2017 ). The Science-Metrics classification was extended by adding the largest 100 journals in the PMC collection that had not been included in the original Science-Metrics classification scheme. These were classified into a Science-Metrics category by first author based on their similarity to other journals in the Science-Metrics scheme.
Five of the broad fields had too little data to be useful (Economics & Business; Visual & Performing Arts; Communication & Text Studies; General Arts, Humanities & Social Sciences; Built Environment & Design) and were removed. Years before 2000 were not included because of their age and small amount of data. Individual field/year combinations were also removed when there were fewer than 30 articles, since they might give a misleading percentage. Each of the 17 remaining categories contained at least 630 articles ( Table 3 ), with exact numbers for each field and year available in the online supplementary material (columns AE to AW: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012 ). For all broad fields, most articles have been published in the last 5 years (2014–2018), with the exception of Historical Studies, Chemistry, and Enabling & Strategic Technology.
For the third research question, alternative terms for research goals were searched for in the full text of articles. These terms might all be used in different contexts, so a match is not necessarily related to the main goal of the paper (e.g., the term “question” could be part of a discussion of a questionnaire), but the rank order between disciplines may be informative and the results serve as an upper bound for valid uses. The terms searched for were “research questions,” “questions,” “hypotheses,” “aims,” “objectives,” “goals,” and “purposes” in both singular and plural forms. These have been identified above as performing similar functions in research. For this exploration, the term “question” is used in addition to “research question” to capture more general uses.
Any of the queried terms could be included in an article out of context. For example, “research question” could be mentioned in a literature review rather than to describe the purpose of the new article. To check the context in which each term was used, a random sample of 100 articles (using a random number generator) matching each term (200 for each concept, counting both singular and plural, totaling 1,400 checks) was manually examined to ascertain whether any use of the term in the article stated the purpose of the paper directly (e.g., “Our research questions were…”) or indirectly (e.g., “This answered our research questions”), unless mentioned peripherally as information to others (e.g., “The study research questions were explained to interviewees”). There did not seem to be stock phrases that could be used to eliminate a substantial proportion of the irrelevant matches (e.g., “objective function” or “microscope objective”). There also was not a set of standard phrases that collectively could unambiguously identify the vast majority of research questions (e.g., “Our research questions were” or “This article’s research question is”).
Journal guidelines given to authors were manually analyzed to check whether they give advice about research questions and other purpose statements. Three journals with the most articles in each of the 17 academic fields were selected for this (see online supplement doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012 ). This information is useful background context to help interpret the results.
4.1. RQ1 and RQ2: Articles Mentioning Research Questions
Altogether, 23,282 out of 1,314,412 articles explicitly mentioned the phrases “research question” or “research questions” (1.8%), although no field included them in more than a fifth of articles in recent years and there are substantial differences between broad fields ( Figure 1 ). When the terms are used in an article they usually (63%, from the 1,400 manual checks) refer to the article’s main research question(s). Other uses of these terms include referring to questions raised by the findings, and a discussion of other articles’ research questions in literature review sections or as part of the selection criteria of meta-analyses. Thus, overall, only 1.1% of PMC full-text research articles mention their research questions explicitly using the singular or plural form. There has been a general trend for the increasing use of these terms, however ( Figure 2 ).

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the phrases “research question” or “research questions” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 63% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s research question(s) ( n = 801,895 research articles).

As for Figure 1 but covering 2000–2018 ( n = 1,314,412 research articles). (All fields can be identified in the Excel versions of the graph within the online supplement 10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012).
If the terms “question” or “questions” are searched for instead, there are many more matches, although for a minority of articles in most fields ( Figures 3 and 4 ). When these terms are mentioned, they rarely (17%) refer to the hosting article’s research questions (excluding matches with the exact phrases “research question” or “research questions” to avoid overlaps with the previous figure). Common other contexts for these terms include questions in questionnaires and questions raised by the findings. Sometimes the term “question” occurred within an idiomatic phrase or issue rather than a query (e.g., “considerable temperature gradients occur within the materials in question” and “these effects may vary for different medications. Future studies are needed to address this important question”). In Philosophy & Theology, the matches could be for discussions of various questions within an article, rather than a research question that is an article’s focus. Similarly for Social Sciences and Public Health & Health Services, the question mentioned might be in questionnaires rather than being a research question. After correcting for the global irrelevant matches, which is a rough approximation, in all broad fields fewer than 14% of research articles use these terms to refer to research questions. Nevertheless, this implies that the terms “question” or “questions” are used much more often than the phrases “research question” or “research questions” (1.8%) to refer to an article’s research purposes.

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “question” or “questions” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 17% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s main research question(s) without using the exact phrases “research question” or “research questions,” not overlapping with Figure 1(a) ( n = 801,895 research articles).

As for Figure 3 , but covering 2000–2018 ( n = 1,314,412 research articles).
4.2. RQ3: Other Article Purpose Terms
The terms “hypothesis” and “hypotheses” are common in Psychology and Cognitive Science as well as in Biology ( Figure 5 ). They are used in a minority of articles in all other fields, but, by 2018 were used in at least 15% of all (or 4% after correcting for irrelevant matches). The terms can be used to discuss statistical results from other papers and in philosophy and mathematics they can be used to frame arguments, so not all matches relate to an article’s main purpose, and only 28% of the random sample checked used the terms to refer to the articles’ main hypothesis or hypotheses.

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “hypothesis” or “hypotheses” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 28% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s main hypothesis or hypotheses. A corresponding time series graph showing little change is in the online supplement ( n = 801,895 research articles).
The use of the terms “aim” and “aims” is increasing overall, possibly in all academic fields ( Figures 6 and 7 ). Fields frequently using the term include Philosophy & Theology, Information & Communication Technologies (ICTs) and Public Health & Health Services, whereas it is used in only about 20% of Chemistry and Biomedical Research papers. Articles using the terms mostly use them (especially the singular “aim”) to describe their main aim (70%), so these are the terms most commonly used to describe the purpose of a PMC full-text article. The terms are also sometimes used to refer to wider project aims or relevant aims outside of the project (e.g., “The EU’s biodiversity protection strategy aims to preserve…”).

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “aim” or “aims” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 70% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s main aim(s) ( n = 801,895 research articles).

As for Figure 6 , but covering 2000–2018 ( n = 1,314,412 research articles).
The terms “objective” and “objectives” are reasonably common in most academic fields ( Figure 8 ) and are used half of the time (52%) for the hosting article’s objectives. Other common uses include lenses and as an antonym of subjective (e.g., “high-frequency ultrasound allows an objective assessment…”). It is again popular within ICTs, Philosophy & Theology, and Public Health & Health Services, whereas it is used in only about 12% of Physics & Astronomy articles.

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “objective” or “objectives” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 52% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s objective(s). A corresponding time series graph showing little change is in the online supplement ( n = 801,895 research articles).
The terms “goal” and “goals” follow a similar pattern to “aim” and “objective” ( Figure 9 ), but refer to the hosting paper’s goals in only 28% of cases. Common other uses include methods goals (“the overall goal of this protocol is…”) and field-wide goals (e.g., “over the last decades, attempts to integrate ecological and evolutionary dynamics have been the goal of many studies”).

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “goal” or “goals” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 28% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s research question(s). A corresponding time series graph showing little change is in the online supplement ( n = 801,895 research articles).
Some articles may also use the terms “purpose” or “purposes” rather than the arguably more specific terms investigated above, and there are disciplinary differences in the extent to which they are used ( Figure 10 ). These terms may also be employed to explain or justify aspects of an article’s methods. When used, they referred to main purposes in fewer than a third of articles (29%), and were often instead used to discuss methods details (e.g., “it was decided a priori that physical examination measures would not be collected for the purpose of this audit”), background information (e.g., “species are harvested through fishing or hunting, mainly for alimentary purposes”) or ethics (e.g., “Animal care was carried out in compliance with Korean regulations regarding the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes.”).

The percentage of full-text research articles containing the terms “purpose” or “purposes” in the body of the text, 2014–2018, for articles in the PMC Open Access collection from 17 out of 22 Science-Metrics broad fields; 29% of occurrences of these terms described the hosting article’s purpose(s). A corresponding time series graph showing little change is in the online supplement ( n = 801,895 research articles).
4.3. RQ4: Journal Guidelines
“The motivation or purpose of your research should appear in the Introduction, where you state the questions you sought to answer” ( zookeys.pensoft.net/about )
“Define the purpose of the work and its significance, including specific hypotheses being tested” ( www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients/instructions )
“The introduction briefly justifies the research and specifies the hypotheses to be tested” ( www.ajas.info/authors/authors.php )
“A brief outline of the question the study attempts to address” ( onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/20457758/homepage/registeredreports.html )
“Acquaint the reader with the findings of others in the field and with the problem or question that the investigation addresses.” ( www.oncotarget.com )
“State the research objective of the study, or hypothesis tested” ( www.springer.com/biomed/human+physiology/journal/11517 )
In the first quote above, for example, “state the questions” could be addressed literally by listing (research) questions or less literally by stating the research objectives. Thus, journal guidelines seem to leave authors the flexibility to choose how to state their research purpose, even if suggesting that research questions or hypotheses are used. This also applies to the influential American Psychological Society guidelines, such as, “In empirical studies, [explaining your approach to solving the problem] usually involves stating your hypotheses or specific question” ( APA, 2009 , p. 28).
An important limitation of the methods is that the sample contains a small and biased subset of all open access research articles. For example, the open access publishers BMC, Hindawi, and MDPI have large journals in the data set. The small fields ( Table 3 ) can have unstable lines in the graphs because of a lack of data. Sharp changes between years for the same field are likely due to either small amounts of data or changes in the journals submitted to PubMed in those years, rather than changes in field norms. It is possible that the proportions discovered would be different for other collections. Another limitation is that although articles were searched with the text string “research question,” this may not always have signified research questions in the articles processed (e.g., if mentioned in a literature review or in a phrase such as “this research questions whether”). Although the corrections reported address this, they provide global correction figures rather than field-specific corrections. Conversely, a research question may just be described as a question (e.g., “the query of this research”) or phrased as a question without describing it as such (e.g., “To discover whether PGA implants are immunologically inert…”). Thus, the field-level results are only indicative.
RQ1: Only 23,282 (1.8%, 1.1% after correcting for irrelevant matches) out of 1,314,412 articles assessed in the current paper explicitly mentioned “research question(s),” with significant differences between fields. Although there has been a general trend for the increasing use of explicitly named research questions, they were employed in fewer than a quarter of articles in all fields. Research questions were mostly used by articles in Social Sciences, Philosophy & Theology, and ICTs, whereas they have been mentioned by under 2% of articles in engineering, physical, life, and medical sciences. Previous studies have shown that 73.3% of English articles in Physical Education ( Omidi & Farnia, 2016 ), 33% of Applied Linguistics articles ( Sheldon, 2011 ) and 32% of Computer Science articles ( Shehzad, 2011 ) included research questions or hypotheses. Studies focused on doctoral dissertations show that 97% of U.S. Applied Linguistics ( Lim, 2014 ), 90% of English Language Teaching ( Geçíklí, 2013 ), 70% of Education Management ( Cheung, 2012 ), and 50% of computing doctoral dissertations ( Soler-Monreal, Carbonell-Olivares, & Gil-Salom, 2011 ) listed research questions, a large difference.
The results also show that about 13% of Public Health and Health Services articles and 12% of Psychology and Cognitive Science articles use the term “research questions.” However, a study focused on Educational Psychology found that 35% of English-language papers listed research questions and 75% listed hypotheses ( Loi & Evans, 2010 ). Thus, the current results reveal a substantially lower overall prevalence than suggested by previous research.
RQ2: There has been a substantial increase in the use of the term “research questions” in some subjects, including ICTs, Social Sciences, and Public Health and Health Services ( Figure 2 ), as well as a general trend for increasing use of this term, but with most fields still rarely using it. This suggests that some disciplines are standardizing their terminology, either through author guidelines in journals (RQ4), formal training aided by frameworks such as Swales’ CARS model, or informal training or imitation. For example, the analysis of the “instructions for authors” given by 51 journals (online supplement doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012 ) showed that the three biology journals, the three psychology journals, and two biomedical journals included in the analysis referred to both research questions and hypotheses in their author guidelines.
RQ3: Terminology for the purpose of an article seems to be quite widely used, including aims, objectives, and goals ( Figures 5 – 9 ). This is in line with a study examining the lexical bundles identified in research article introductions from several disciplines, which reported the terms “aim,” “objective,” and “purpose” as the main terms used to announce the research descriptively and/or purposefully, although no phrase related to research questions or hypotheses was identified ( Cortés, 2013 ), and with another study reporting similar terminology in medical articles ( Jalali & Moini, 2014 ). Related to this (RQ4), the analysis of the “instructions for authors” given by 51 journals (online supplement 10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012) showed that “purpose” is the term mostly mentioned in the Abstract guidelines and “aims” is the term mainly used in the body of the text (Introduction or Background) guidelines. The term “objective” also appears in some article body guidelines, whereas the term “goal” is not mentioned in them. After correcting for irrelevant matches (e.g., articles using the term “hypothesis” but not for their main research hypotheses) using the percentages reported with the figures above, no terminology was found in a majority of articles in any field. Thus, at least from the perspective of PMC Open Access publications, there is no standardization of research terminology in any broad field.
There are substantial disciplinary differences in the terminology used. Whereas the term “research question” is relevant in Social Sciences, Philosophy & Theology, and ICTs, the term “hypothesis” is important in Psychology and Cognitive Science, used in over 60% of articles. This is in line with a study focused on Educational Psychology, which found that the 75% out of 20 English papers introduced the hypotheses, whereas 35% of them introduced the research questions ( Loi & Evans, 2010 ). The three psychology journals with the highest frequency in the data set used for this study referred to hypotheses in their author guidelines (see online supplement 10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012).
The terms “aim,” “objective,” and “goal” are mainly used in Philosophy, Theology, ICTs, and Health. The term “aim” is also quite often used in health, mathematics, and psychological articles, whereas the term “objective” is also used in engineering and mathematics articles. The term “goal” is also used in psychology and biomedical articles. Although most articles in all fields include a term that could be used to specify the purpose of an article (question or questions, hypothesis, aim, objective, goal), they are relatively scarce in Chemistry and Physics & Astronomy. The use of purpose-related terms has also increased over time in most academic fields. This agrees with a study about Computer Science research articles that found an increasing use of outlining purpose or stating the nature of the research ( Shehzad, 2011 ).
An example article from Chemistry illustrates how a research purpose can be implicit. The paper, “Fluid catalytic cracking in a rotating fluidized bed in a static geometry: a CFD analysis accounting for the distribution of the catalyst coke content” has a purpose that is clear from its title but that is not described explicitly in the text. Its abstract starts by describing what the paper offers, but not why, “Computational Fluid Dynamics is used to evaluate the use of a rotating fluidized bed in a static geometry for the catalytic cracking of gas oil.” The first sentence of the last paragraph of the introduction performs a similar role, “The current paper presents CFD simulations of FCC in a RFB-SG using a model that accounts for a possible nonuniform temperature and catalyst coke content distribution in the reactor.” Both sentences could easily be rephrased to start with, “The purpose of this paper is to,” but it is apparently a stylistic feature of chemical research not to do this. Presumably purposes are clear enough in typical chemistry research that they do not need to be flagged linguistically, but this is untrue for much social science and health research, for example, partly due to nonstandard goals (i.e., task uncertainty: Whitley, 2000 ).
5.1. Possible Origins of the Differences Found
Broad epistemological: Fields work with knowledge in different ways and naturally use different terminology as a result. Arts and humanities research may have the goal to critique or analyze, or may be practice-based research rather than having a more specific knowledge purpose. For this, research questions would be inappropriate. Thus, terminology variation may partly reflect the extent to which a broad field typically attempts to create knowledge.
Narrow epistemological: Narrow fields that address similar problems may feel that they do not need to use research problem terminology to describe their work because the purpose of a paper is usually transparent from the description of the methods or outcome. For example, it would be unnecessary to formulate, “This paper investigates whether treatment x reduces death rates from disease y” as a named research question or even explain that it is the goal of a paper. This may also be relevant for fields that write short papers. It may be most relevant for papers that use statistical methods and have high standards of evidence requirement (e.g., medicine) and clearly defined problems. In contrast, many social sciences research projects are not intrinsically clearly demarcated and need an explanation to define the problem (as for the current article). Thus, describing what the problem is can be an important and nontrivial part of the research. This relates to “task uncertainty,” which varies substantially between fields ( Whitley, 2000 ) and affects scholarly communication ( Fry, 2006 ).
Field or audience homogeneity: Fields with homogeneous levels and types of expertise may avoid terminology that field members would be able to deduce from the context. For example, a mixed audience paper might need to specify statistical hypotheses, whereas a narrow audience paper might only need to specify the result, because the audience would understand the implicit null and alternative hypotheses.
Field cultures for term choice: Academic publishing relies to some extent on imitation and reaching a consensus about the ways in which research is presented (e.g., Becher & Trowler, 2001 ). It might therefore become a field norm to use one term in preference to a range of synonyms, such as “aims” instead of “objectives.”
Field cultures for term meaning: Following from the above, a field culture may evolve an informal convention that two synonyms have different specific uses. For example, “aims” could be used for wider goals and “objectives” for the narrower goals of a paper.
Guidelines: Fields or their core journals may adopt guidelines that specify terminology, presumably because they believe that this standardization will improve overall communication clarity.
The results suggest that the explicit use of research questions, in the sense that they are named as such, is almost completely absent in some research fields, and they are at best a substantial minority (under 20%) in most others (ignoring the fields that did not meet the inclusion threshold). Although the word search approach does not give conclusive findings, the results suggest that alternative terminologies for describing the purpose of a paper are more widespread in some fields, but no single terminology is used to describe research purposes in a majority of articles in any of the broad fields examined.
The lack of standardization for purpose terminology in most or all fields may cause problems for reviewers and readers expecting to see explicit statements. It is not clear whether guidelines to standardize terminology for journals or fields would be practical or helpful, however, but this should be explored in the future. Presumably any guidelines should allow exceptions for articles that make nonstandard contributions, although there are already successful journals with prescriptive guidelines, and the advantage of standardization through structured abstracts seems to be accepted ( Hartley, 2004 ).
The disciplinary differences found may cause problems for referees, authors, editors, and readers of interdisciplinary research or research from outside of their natural field if they fail to find an article’s purpose expressed in the terminology that they expect. This issue could not reasonably be resolved by standardizing across science because of the differing nature of research. Instead, evidence in the current article of the existence of valid disciplinary differences in style may help reviewers and editors of large interdisciplinary journals to accept stylistic differences in research problem formulations.
Mike Thelwall: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing—original draft. Amalia Mas-Bleda: Investigation, Writing—original draft.
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
This research received no funding.
The data behind the results are available at FigShare ( https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.10274012 ).
Author notes
Email alerts, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 2641-3337
A product of The MIT Press
Mit press direct.
- About MIT Press Direct
Information
- Accessibility
- For Authors
- For Customers
- For Librarians
- Direct to Open
- Open Access
- Media Inquiries
- Rights and Permissions
- For Advertisers
- About the MIT Press
- The MIT Press Reader
- MIT Press Blog
- Seasonal Catalogs
- MIT Press Home
- Give to the MIT Press
- Direct Service Desk
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Statement
- Crossref Member
- COUNTER Member
- The MIT Press colophon is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
85k Accesses
28 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

Good Qualitative Research: Opening up the Debate
Beyond qualitative/quantitative structuralism: the positivist qualitative research and the paradigmatic disclaimer.

Unsettling Definitions of Qualitative Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
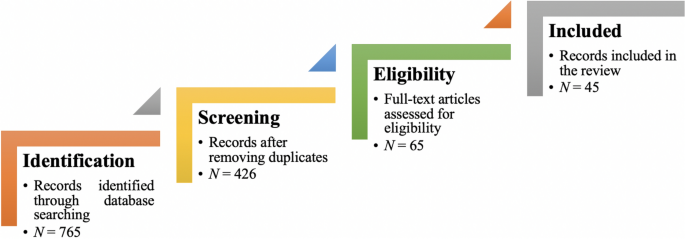
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Evaluating Information Sources
- Evaluate Your Sources
- Publication Types and Bias
Structure of Scientific Papers
Reading a scholarly article, additional reading tips, for more information.
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Impact Factors and Citation Counts
- Predatory Publishing
Research papers generally follow a specific format. Here are the different parts of the scholarly article.
Abstract (Summary)
The abstract, generally written by the author(s) of the article, provides a concise summary of the whole article. Usually it highlights the focus, study results and conclusion(s) of the article.
Introduction (Why)
In this section, the authors introduce their topic, explain the purpose of the study, and present why it is important, unique or how it adds to existing knowledge in their field. Look for the author's hypothesis or thesis here.
Introduction - Literature Review (Who else)
Many scholarly articles include a summary of previous research or discussions published on this topic, called a "Literature Review". This section outlines what others have found and what questions still remain.
Methodology / Materials and Methods (How)
Find the details of how the study was performed in this section. There should be enough specifics so that you could repeat the study if you wanted.
Results (What happened)
This section includes the findings from the study. Look for the data and statistical results in the form of tables, charts, and graphs. Some papers include an analysis here.
Discussion / Analysis (What it means)
This section should tell you what the authors felt was significant about their results. The authors analyze their data and describe what they believe it means.
Conclusion (What was learned)
Here the authors offer their final thoughts and conclusions and may include: how the study addressed their hypothesis, how it contributes to the field, the strengths and weaknesses of the study, and recommendations for future research. Some papers combine the discussion and conclusion.
A scholarly paper can be difficult to read. Instead of reading straight through, try focusing on the different sections and asking specific questions at each point.
What is your research question?
When you select an article to read for a project or class, focus on your topic. Look for information in the article that is relevant to your research question.
Read the abstract first as it covers basics of the article. Questions to consider:
- What is this article about? What is the working hypothesis or thesis?
- Is this related to my question or area of research?
Second: Read the introduction and discussion/conclusion. These sections offer the main argument and hypothesis of the article. Questions to consider for the introduction:
- What do we already know about this topic and what is left to discover?
- What have other people done in regards to this topic?
- How is this research unique?
- Will this tell me anything new related to my research question?
Questions for the discussion and conclusion:
- What does the study mean and why is it important?
- What are the weaknesses in their argument?
- Is the conclusion valid?
Next: Read about the Methods/Methodology. If what you've read addresses your research question, this should be your next section. Questions to consider:
- How did the author do the research? Is it a qualitative or quantitative project?
- What data are the study based on?
- Could I repeat their work? Is all the information present in order to repeat it?
Finally: Read the Results and Analysis. Now read the details of this research. What did the researchers learn? If graphs and statistics are confusing, focus on the explanations around them. Questions to consider:
- What did the author find and how did they find it?
- Are the results presented in a factual and unbiased way?
- Does their analysis agree with the data presented?
- Is all the data present?
- What conclusions do you formulate from this data? (And does it match with the Author's conclusions?)
Review the References (anytime): These give credit to other scientists and researchers and show you the basis the authors used to develop their research. The list of references, or works cited, should include all of the materials the authors used in the article. The references list can be a good way to identify additional sources of information on the topic. Questions to ask:
- What other articles should I read?
- What other authors are respected in this field?
- What other research should I explore?
When you read these scholarly articles, remember that you will be writing based on what you read.
While you are Reading:
- Keep in mind your research question
- Focus on the information in the article relevant to your question (feel free to skim over other parts)
- Question everything you read - not everything is 100% true or performed effectively
- Think critically about what you read and seek to build your own arguments
- Read out of order! This isn't a mystery novel or movie, you want to start with the spoiler
- Use any keywords printed by the journals as further clues about the article
- Look up words you don't know
How to Take Notes on the Article
Try different ways, but use the one that fits you best. Below are some suggestions:
- Print the article and highlight, circle and otherwise mark while you read (for a PDF, you can use the highlight text feature in Adobe Reader)
- Take notes on the sections, for example in the margins (Adobe Reader offers pop-up sticky notes )
- Highlight only very important quotes or terms - or highlight potential quotes in a different color
- Summarize the main or key points
Reflect on what you have read - draw your own conclusions . As you read jot down questions that come to mind. These may be answered later on in the article or you may have found something that the authors did not consider. Here are a few questions that might be helpful:
- Have I taken time to understand all the terminology?
- Am I spending too much time on the less important parts of this article?
- Do I have any reason to question the credibility of this research?
- What specific problem does the research address and why is it important?
- How do these results relate to my research interests or to other works which I have read?
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Article (Interactive tutorial) Andreas Orphanides, North Carolina State University Libraries, 2009
- How to Read an Article in a Scholarly Journal (Research Guide) Cayuga Community College Library, 2016
- How To Read a Scholarly Journal Article (YouTube Video) Tim Lockman, Kishwaukee College Library, 2012.
- How To Read a Scientific Paper (Interactive tutorial) Michael Fosmire, Purdue University Libraries, 2013. PDF
- How to Read a Scientific Paper (Online article) Science Buddies, 2012
- How to Read a Scientific Research Paper (Article) Durbin Jr., C. G. Respiratory Care, 2009
- The Illusion of Certainty and the Certainty of Illusion: A Caution when Reading Scientific Articles (Article) T. A. Lang, International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 2011,
- Infographic: How to Read Scientific Papers Natalia Rodriguez, Elsevier, 2015
- Library Research Methods: Read & Evaluate Culinary Institute of America Library, 2016
- << Previous: Publication Types and Bias
- Next: Impact Factors and Citation Counts >>
- Last Updated: Mar 8, 2024 1:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/evaluate
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
Chemical Biology and Nucleic Acid Chemistry
Computational biology, critical reviews and perspectives.
- Data Resources and Analyses
Gene Regulation, Chromatin and Epigenetics
Genome integrity, repair and replication.
- Methods Online
Molecular Biology
Nucleic acid enzymes, rna and rna-protein complexes, structural biology, synthetic biology and bioengineering.
- Advance Articles
- Breakthrough Articles
- Special Collections
- Scope and Criteria for Consideration
- Author Guidelines
- Data Deposition Policy
- Database Issue Guidelines
- Web Server Issue Guidelines
- Submission Site
- About Nucleic Acids Research
- Editors & Editorial Board
- Information of Referees
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Browse issues
Cover image.

Volume 52, Issue 9, 22 May 2024
Fourteen years of cellular deconvolution: methodology, applications, technical evaluation and outstanding challenges.

- View article
- Supplementary data
A novel transient receptor potential C3/C6 selective activator induces the cellular uptake of antisense oligonucleotides

Quantifying the activity profile of ASO and siRNA conjugates in glioblastoma xenograft tumors in vivo

Definition of the binding specificity of the T7 bacteriophage primase by analysis of a protein binding microarray using a thermodynamic model

m6ACali: machine learning-powered calibration for accurate m6A detection in MeRIP-Seq

High-density generation of spatial transcriptomics with STAGE

Genome-wide screening and functional validation of methylation barriers near promoters

RNA–RNA interactions between respiratory syncytial virus and miR-26 and miR-27 are associated with regulation of cell cycle and antiviral immunity

Processivity and specificity of histone acetylation by the male-specific lethal complex

The jet-like chromatin structure defines active secondary metabolism in fungi

Tracking pairwise genomic loci by the ParB–ParS and Noc-NBS systems in living cells

HBO1 determines SMAD action in pluripotency and mesendoderm specification

ATRX guards against aberrant differentiation in mesenchymal progenitor cells

WSB1/2 target chromatin-bound lysine-methylated RelA for proteasomal degradation and NF-κB termination

Catalytic residues of microRNA Argonautes play a modest role in microRNA star strand destabilization in C. elegans


Defining the contribution of microRNA-specific Argonautes with slicer capability in animals

Viral reprogramming of host transcription initiation

Correction of non-random mutational biases along a linear bacterial chromosome by the mismatch repair endonuclease NucS

DNA-PKcs suppresses illegitimate chromosome rearrangements

CSB and SMARCAL1 compete for RPA32 at stalled forks and differentially control the fate of stalled forks in BRCA2-deficient cells

LC3B drives transcription-associated homologous recombination via direct interaction with R-loops

SIRT2 promotes base excision repair by transcriptionally activating OGG1 in an ATM/ATR-dependent manner

S-phase checkpoint prevents leading strand degradation from strand-associated nicks at stalled replication forks

Defective transfer of parental histone decreases frequency of homologous recombination by increasing free histone pools in budding yeast

The discovery of novel noncoding RNAs in 50 bacterial genomes

Comprehensive profiling of L1 retrotransposons in mouse

Comprehensive genomic features indicative for Notch responsiveness

RecA-dependent or independent recombination of plasmid DNA generates a conflict with the host EcoKI immunity by launching restriction alleviation

Caspase-mediated processing of TRBP regulates apoptosis during viral infection

Activity reconstitution of Kre33 and Tan1 reveals a molecular ruler mechanism in eukaryotic tRNA acetylation

Live-cell imaging reveals the trade-off between target search flexibility and efficiency for Cas9 and Cas12a

SARS-CoV-2 nsp15 preferentially degrades AU-rich dsRNA via its dsRNA nickase activity

A combinatorial approach for achieving CNS-selective RNAi

Cryo-EM structure of SRP68/72 reveals an extended dimerization domain with RNA-binding activity

RNA-binding properties orchestrate TDP-43 homeostasis through condensate formation in vivo

A Fur family protein BosR is a novel RNA-binding protein that controls rpoS RNA stability in the Lyme disease pathogen

Dynamics of miRNA accumulation during C. elegans larval development

Nuclear RNA-related processes modulate the assembly of cytoplasmic RNA granules

UPF1 ATPase autoinhibition and activation modulate RNA binding kinetics and NMD efficiency

Biochemical and structural characterization of Fapy•dG replication by Human DNA polymerase β

CRISPR-Cas tools for simultaneous transcription & translation control in bacteria

Correction to ‘STIM1 translocation to the nucleus protects cells from DNA damage’
Retraction of ‘dissecting the splicing mechanism of the drosophila editing enzyme; dadar ’, netactivity enhances transcriptional signals by combining gene expression into robust gene set activity scores through interpretable autoencoders.

Examining chromatin heterogeneity through PacBio long-read sequencing of M.EcoGII methylated genomes: an m 6 A detection efficiency and calling bias correcting pipeline

SifiNet: a robust and accurate method to identify feature gene sets and annotate cells

Email alerts
- Editorial Board
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1362-4962
- Print ISSN 0305-1048
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

AI-assisted writing is quietly booming in academic journals. Here’s why that’s OK
Lecturer in Bioethics, Monash University & Honorary fellow, Melbourne Law School, Monash University
Disclosure statement
Julian Koplin does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Monash University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
If you search Google Scholar for the phrase “ as an AI language model ”, you’ll find plenty of AI research literature and also some rather suspicious results. For example, one paper on agricultural technology says:
As an AI language model, I don’t have direct access to current research articles or studies. However, I can provide you with an overview of some recent trends and advancements …
Obvious gaffes like this aren’t the only signs that researchers are increasingly turning to generative AI tools when writing up their research. A recent study examined the frequency of certain words in academic writing (such as “commendable”, “meticulously” and “intricate”), and found they became far more common after the launch of ChatGPT – so much so that 1% of all journal articles published in 2023 may have contained AI-generated text.
(Why do AI models overuse these words? There is speculation it’s because they are more common in English as spoken in Nigeria, where key elements of model training often occur.)
The aforementioned study also looks at preliminary data from 2024, which indicates that AI writing assistance is only becoming more common. Is this a crisis for modern scholarship, or a boon for academic productivity?
Who should take credit for AI writing?
Many people are worried by the use of AI in academic papers. Indeed, the practice has been described as “ contaminating ” scholarly literature.
Some argue that using AI output amounts to plagiarism. If your ideas are copy-pasted from ChatGPT, it is questionable whether you really deserve credit for them.
But there are important differences between “plagiarising” text authored by humans and text authored by AI. Those who plagiarise humans’ work receive credit for ideas that ought to have gone to the original author.
By contrast, it is debatable whether AI systems like ChatGPT can have ideas, let alone deserve credit for them. An AI tool is more like your phone’s autocomplete function than a human researcher.
The question of bias
Another worry is that AI outputs might be biased in ways that could seep into the scholarly record. Infamously, older language models tended to portray people who are female, black and/or gay in distinctly unflattering ways, compared with people who are male, white and/or straight.
This kind of bias is less pronounced in the current version of ChatGPT.
However, other studies have found a different kind of bias in ChatGPT and other large language models : a tendency to reflect a left-liberal political ideology.
Any such bias could subtly distort scholarly writing produced using these tools.
The hallucination problem
The most serious worry relates to a well-known limitation of generative AI systems: that they often make serious mistakes.
For example, when I asked ChatGPT-4 to generate an ASCII image of a mushroom, it provided me with the following output.
It then confidently told me I could use this image of a “mushroom” for my own purposes.
These kinds of overconfident mistakes have been referred to as “ AI hallucinations ” and “ AI bullshit ”. While it is easy to spot that the above ASCII image looks nothing like a mushroom (and quite a bit like a snail), it may be much harder to identify any mistakes ChatGPT makes when surveying scientific literature or describing the state of a philosophical debate.
Unlike (most) humans, AI systems are fundamentally unconcerned with the truth of what they say. If used carelessly, their hallucinations could corrupt the scholarly record.
Should AI-produced text be banned?
One response to the rise of text generators has been to ban them outright. For example, Science – one of the world’s most influential academic journals – disallows any use of AI-generated text .
I see two problems with this approach.
The first problem is a practical one: current tools for detecting AI-generated text are highly unreliable. This includes the detector created by ChatGPT’s own developers, which was taken offline after it was found to have only a 26% accuracy rate (and a 9% false positive rate ). Humans also make mistakes when assessing whether something was written by AI.
It is also possible to circumvent AI text detectors. Online communities are actively exploring how to prompt ChatGPT in ways that allow the user to evade detection. Human users can also superficially rewrite AI outputs, effectively scrubbing away the traces of AI (like its overuse of the words “commendable”, “meticulously” and “intricate”).
The second problem is that banning generative AI outright prevents us from realising these technologies’ benefits. Used well, generative AI can boost academic productivity by streamlining the writing process. In this way, it could help further human knowledge. Ideally, we should try to reap these benefits while avoiding the problems.
The problem is poor quality control, not AI
The most serious problem with AI is the risk of introducing unnoticed errors, leading to sloppy scholarship. Instead of banning AI, we should try to ensure that mistaken, implausible or biased claims cannot make it onto the academic record.
After all, humans can also produce writing with serious errors, and mechanisms such as peer review often fail to prevent its publication.
We need to get better at ensuring academic papers are free from serious mistakes, regardless of whether these mistakes are caused by careless use of AI or sloppy human scholarship. Not only is this more achievable than policing AI usage, it will improve the standards of academic research as a whole.
This would be (as ChatGPT might say) a commendable and meticulously intricate solution.
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Academic journals
- Academic publishing
- Hallucinations
- Scholarly publishing
- Academic writing
- Large language models
- Generative AI

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Research Fellow

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: increasing the llm accuracy for question answering: ontologies to the rescue.
Abstract: There is increasing evidence that question-answering (QA) systems with Large Language Models (LLMs), which employ a knowledge graph/semantic representation of an enterprise SQL database (i.e. Text-to-SPARQL), achieve higher accuracy compared to systems that answer questions directly on SQL databases (i.e. Text-to-SQL). Our previous benchmark research showed that by using a knowledge graph, the accuracy improved from 16% to 54%. The question remains: how can we further improve the accuracy and reduce the error rate? Building on the observations of our previous research where the inaccurate LLM-generated SPARQL queries followed incorrect paths, we present an approach that consists of 1) Ontology-based Query Check (OBQC): detects errors by leveraging the ontology of the knowledge graph to check if the LLM-generated SPARQL query matches the semantic of ontology and 2) LLM Repair: use the error explanations with an LLM to repair the SPARQL query. Using the chat with the data benchmark, our primary finding is that our approach increases the overall accuracy to 72% including an additional 8% of "I don't know" unknown results. Thus, the overall error rate is 20%. These results provide further evidence that investing knowledge graphs, namely the ontology, provides higher accuracy for LLM powered question answering systems.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

The Health for Life in Singapore (HELIOS) Study: delivering Precision Medicine research for Asian populations
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Theresia Mina
- ORCID record for Nilanjana Sadhu
- ORCID record for Dorrain Low
- ORCID record for Max Lam
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Asian people are under-represented in population-based, clinical, and genomic research. To address this gap, we have initiated the HELIOS longitudinal cohort study, comprising comprehensive behavioural, phenotypic, and genomic measurements from 10,004 Asian men and women of Chinese, Indian or Malay background. Phenotyping has been carried out using validated approaches, that are internationally interoperable. Health record linkage enriches both baseline phenotyping and evaluation of prospective outcomes. The integrated multi-omics data include whole-genome and RNA sequencing, quantification of DNA methylation, and metabolomic profiling. Our data reveal extensive lifestyle, physiological, genomic, and molecular diversity between the distinct Asian ethnic groups, and the biological interconnectivity between functional layers. This includes characterisation of divergent patterns of genome regulation between Asian individuals, that correlate with differences in educational attainment, dietary quality, and adiposity, and which overlap transcription factors and DNA methylation sites linked to the development of diabetes and other chronic diseases. Our unique HELIOS Asian Precision Medicine cohort study represents a state-of-the art platform to enable biomedical researchers to understand the aetiology and pathogenesis of diverse disease outcomes in Asia, and to generate insights that have the potential to improve health outcomes for Asian populations globally.
Competing Interest Statement
B.L.C.C. receives honorarium for obesity-related presentations and/or participates in the advisory board of Novo Nordisk, Abbott Nutrition and DKSH, and all honorariums were paid to Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore. J.N. receives research funding from Astra Zeneca. J.L. participates in the advisory board of Boehringer Ingelheim and is a council member of National Council Against Drug Abuse, Singapore. G.A.M, K.E.W, and P.A.S are employees of Metabolon. L.P.Y., and Y.Z.X. are employees of Ministry of Health, Singapore. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Funding Statement
This study is supported by Singapore Ministry of Health (MOH) National Medical Research Council (NMRC) under its OF-LCG funding scheme (MOH-000271-00), Singapore Translational Research (StaR) funding scheme (NMRC/StaR/0028/2017), the National Research Foundation, Singapore through the Singapore MOH NMRC and the Precision Health Research, Singapore (PRECISE) under the National Precision Medicine programme (NMRC/PRECISE/2020) and intramural funding from Nanyang Technological University, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine and the National Healthcare Group. RNA sequencing was partially funded by i) Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund Tier 1 Grant (RS09/20), ii) A*STAR-NHMRC Joint Grant Call (A20PRb0138), iii) Start-Up Grant (awarded to M.Loh [PI]) from Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and iv) Imperial - Nanyang Technological University Collaboration Fund (awarded to M.Loh [PI]). T.M. was funded by Deans Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine. This study made use of data generated by Ministry of Health (MOH) and Immigration and Checkpoints Authority (ICA). This study was supported by the Trusted Research and Real-World-Data Utilisation and Sharing Tech platform (TRUST Platform) developed by the Ministry of Health and Smart Nation and Digital Government Office, through the use of its research data analytics facilities. The views expressed are those of the author(s) are not necessarily those of the Government, MOH and ICA investigators or institutional partners. The computational work for this study was partially performed on resources of the National Supercomputing Centre, Singapore (https://www.nscc.sg).
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
Nanyang Technological University Institutional Review Board IRB-2016-11-030
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
In the previous version, the bibliography was incorrect (only 30 references). In this revised version, we have refreshed the bibligpraphy comprising 62 references.
Data Availability
The HELIOS phenotype and genotype data used in this manuscript are protected and are not publicly available due to data privacy regulations. Data access request can be submitted to the HELIOS Data Access Committee by emailing [email protected] for details. For accessing de-identified National Health and Administrative records linked through TRUST, please contact TRUST platform (https://trustplatform.sg) for details.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (324)
- Allergy and Immunology (632)
- Anesthesia (168)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2400)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (289)
- Dermatology (207)
- Emergency Medicine (381)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (850)
- Epidemiology (11799)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (705)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3769)
- Geriatric Medicine (350)
- Health Economics (637)
- Health Informatics (2409)
- Health Policy (940)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (905)
- Hematology (342)
- HIV/AIDS (787)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13347)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (769)
- Medical Education (369)
- Medical Ethics (105)
- Nephrology (401)
- Neurology (3524)
- Nursing (199)
- Nutrition (529)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (681)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (669)
- Oncology (1835)
- Ophthalmology (539)
- Orthopedics (221)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (234)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (447)
- Pediatrics (1038)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (424)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3190)
- Public and Global Health (6184)
- Radiology and Imaging (1291)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (751)
- Respiratory Medicine (832)
- Rheumatology (380)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (373)
- Sports Medicine (324)
- Surgery (406)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (147)
- Announcements
- In The News
Wednesday, May 22, 2024
Regional Research Institute helps launch new outreach journal
Heather Stephens is a co-founding editor of Reaching Regions, an academic journal that launched this month in partnership with WVU, Iowa State University and the North American Regional Science Council.
Publications are required to use non-technical language aimed at non-academic audiences and the open access journal aims to distribute articles quickly to help ensure the timely delivery of research important to policy-making.
“One of the goals of the journal is to make regional economics and other related research more accessible to the policymakers and the public,” Stephens said. “Most academics publish their research in journal articles, yet most of those journals are not compatible with research dissemination.”
To address the needs of the academic audience producing the research, Reaching Regions will be peer-reviewed. Submissions should address topics related to North America and formats may include descriptive analyses, non-technical summaries of published academic research, case studies with broader implications, research syntheses, data visualizations and other items of interest to readers.
John Winters, professor of economics at Iowa State’s Center for Agricultural and Rural Development, is the other co-founding editor. Kevin Kane of the Southern California Association of Governments, Amanda Weinstein of the Center on Rural Innovation, and Emily Wornell of the Center for Local and State Policy at Ball State University serve as co-editors.
Access Reaching Regions published by Iowa State University Digital Press.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Bras Pneumol
- v.42(6); Nov-Dec 2016
Developing research questions that make a difference
Desenvolvendo perguntas do estudo que fazem a diferença, cecilia maria patino.
1 Department of Preventive Medicine, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
2 Methods in Epidemiologic, Clinical and Operations Research (MECOR) Program, American Thoracic Society, New York, NY, USA, and Asociación Latinoamericana de Tórax, Montevideo, Uruguay.
Juliana Carvalho Ferreira
3 Divisão de Pneumologia, Instituto do Coração - InCor - Hospital das Clínicas, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brasil.
A clinical research question is defined as an uncertainty about a health problem that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. 1 For clinicians interested in conducting high-quality clinical research, it is essential to recognize the fact that the research process starts with developing a question about a specific health-related area of interest. This is important because once the research question is defined, it has an impact on every remaining component of the research process, including generating the hypothesis and defining the appropriate study design, as well as the study population, study variables, and statistical approach. However, conceiving a sound research question is not an easy task; it requires having a particular set of personal skills and utilizing structured approaches.
DEVELOPING AND WRITING A RESEARCH QUESTION
Developing a research question starts by identifying a clinical problem that is important to patients, being related to managing and ultimately improving their health. The process requires clinician scientists to be curious about and attentive to day-to-day practice outcomes, as well as to be avid readers of the scientific literature, to participate in scientific activities (e.g., journal clubs), and to have access to a scientific mentor or collaborators interested in clinical research.
The research question itself should meet certain criteria, as summarized by the acronym FINGER, which stands for Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Good (for your career), Ethical, and Relevant ( Chart 1 ). 1 We recommend going through the FINGER criteria systematically and discussing all issues with a mentor or colleague before writing the study protocol and conducting a study that will answer the proposed research question.

Once the research question has been defined, it should be written out in such a way that the answer can be expressed as either a number, typical of descriptive research questions (e.g., a prevalence related to disease burden, such as "What is the prevalence of asthma among favela residents in Brazil?"), or as a yes or no, typical of studies about associations between exposures and outcomes (e.g., "Is living in a favela in Brazil associated with increased mortality among adults with asthma?"). In addition, if the researcher has a hypothesis about the answer to the research question, 1 it is important that it be written out using a comprehensive approach, as summarized by the acronym PICOT, which stands for Population (the population to be included in the study), Intervention (treatment applied to participants in the treatment arm), Comparison (treatment applied to the control group), Outcome (the primary outcome variable), and Time (follow-up time to measure the outcome). 2
INVESTING THE TIME AND EFFORT TO COME UP WITH A HIGH-QUALITY, WELL-WRITTEN RESEARCH QUESTION IS WORTH IT!
As clinician scientists who train clinicians to become successful researchers, we cannot emphasize enough the importance of investing one's time wisely to develop a high-quality research question. Researchers who conceive and clearly state a research question about an important health-related problem are at an advantage because they are more likely to convince key individuals to provide them with the necessary resources and support to carry out the study, as well as to increase the reporting quality of the paper to be published. 3
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 14 May 2024
2023 summer warmth unparalleled over the past 2,000 years
- Jan Esper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3919-014X 1 , 2 ,
- Max Torbenson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2720-2238 1 &
- Ulf Büntgen 2 , 3 , 4
Nature ( 2024 ) Cite this article
7111 Accesses
3442 Altmetric
Metrics details
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
- Climate change
- Palaeoclimate
Including an exceptionally warm Northern Hemisphere (NH) summer 1 ,2 , 2023 has been reported as the hottest year on record 3-5 . Contextualizing recent anthropogenic warming against past natural variability is nontrivial, however, because the sparse 19 th century meteorological records tend to be too warm 6 . Here, we combine observed and reconstructed June-August (JJA) surface air temperatures to show that 2023 was the warmest NH extra-tropical summer over the past 2000 years exceeding the 95% confidence range of natural climate variability by more than half a degree Celsius. Comparison of the 2023 JJA warming against the coldest reconstructed summer in 536 CE reveals a maximum range of pre-Anthropocene-to-2023 temperatures of 3.93°C. Although 2023 is consistent with a greenhouse gases-induced warming trend 7 that is amplified by an unfolding El Niño event 8 , this extreme emphasizes the urgency to implement international agreements for carbon emission reduction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
The economic commitment of climate change
Urban development pattern’s influence on extreme rainfall occurrences
The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979
Author information, authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany
Jan Esper & Max Torbenson
Global Change Research Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic
Jan Esper & Ulf Büntgen
Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Ulf Büntgen
Department of Geography, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jan Esper .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Esper, J., Torbenson, M. & Büntgen, U. 2023 summer warmth unparalleled over the past 2,000 years. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07512-y
Download citation
Received : 16 January 2024
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07512-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

COMMENTS
Furthermore, selecting a good research question can be a time-consuming and challenging task: in one retrospective study, Mayo et al. reported that 3 out of 10 articles published would have needed a major rewording of the question. This paper explores some recommendations to consider before starting any research project, and outlines the main ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
This column is about research questions, the beginning of the researcher's process. For the reader, the question driving the researcher's inquiry is the first place to start when examining the quality of their work because if the question is flawed, the quality of the methods and soundness of the researchers' thinking does not matter.
The importance of formulating a sound and proper research question is summarized in three main motives: 1. Conducting an evidence-based study: Evidence-based studies, particularly, the systematic reviews in this case, rely on a research question developed to specifically address the problem with all required details. 2.
Creating discovery‐oriented questions can help a researcher use the process of developing and refining questions as a basis for a more rigorous and reflexive inquiry. With a qualitative study, a researcher is inquiring about such topics as how people are experiencing an event, a series of events, and/or a condition.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. ... A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Apr 25;37(16):e121. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37 ...
Purpose statements and research questions or hypotheses are interrelated elements of the research process. Research questions are interrogative statements that reflect the problem to be addressed, usually shaped by the goal or objectives of the study (Onwuegbuzie & Leech, 2006).For example, a healthcare article argued that "a good research paper addresses a specific research question.
- Is your research question clear? - Is your research question focused? (Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.) - Is your research question complex? (Questions shouldn't have a simple yes/no answer and should require research and analysis.) • Hypothesize. After you've come up with a question ...
This is especially true if research questions do not fit neatly within the confines of a single established methodology (Kahlke, 2014). It is therefore essential for researchers to have knowledge ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions. Advanced search. Find articles. with all of the words. with the exact phrase. with at least one of the words. without the ...
Research questions, lying at the basis of methodology, play a key role in the research design process. The post-positivist perspective recognizes that qualitative research methods can be impacted by the background and values of the researcher (Ryan, 2006). In this concept paper we will address common themes of research questions in the
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
When you read these scholarly articles, remember that you will be writing based on what you read. While you are Reading: Keep in mind your research question; Focus on the information in the article relevant to your question (feel free to skim over other parts) Question everything you read - not everything is 100% true or performed effectively
How their responses inform the academic research question constitutes the intellectual and reflexive work required of the researcher. In short, the activity of formulating interview questions is deceptively difficult. The challenge for the researcher is threefold. First, they must break down the research question into manageable parts and ...
You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution. ... Equally, there may be questions that haven't yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn't been considered ...
Very few job postings explicitly sought an interdisciplinary scholar, so I found myself applying for jobs with discipline-specific requirements that often seemed a stretch for me. When I did manage to get an interview, there were inevitable questions about whether I could teach certain core courses that the department needed instructors for.
Publishes the results of leading edge research into physical, chemical, biochemical and biological aspects of nucleic acids and proteins involved in nucleic acid metabolism and/or interactions. Fully open access.
Cancer Cytopathology is an international cytopathology journal publishing research related to topics concerning the etiology of cancer, its diagnosis and prevention. Skip to Article Content; Skip to Article Information ... Research and scholarly mentoring: A guide for pathology faculty and program directors. R. Lane Coffee Jr. PhD, MS,
An AI tool is your phone's autocomplete function than a human researcher. Another worry is that AI outputs might be biased in ways that could seep into the scholarly record. Infamously, older ...
There is increasing evidence that question-answering (QA) systems with Large Language Models (LLMs), which employ a knowledge graph/semantic representation of an enterprise SQL database (i.e. Text-to-SPARQL), achieve higher accuracy compared to systems that answer questions directly on SQL databases (i.e. Text-to-SQL). Our previous benchmark research showed that by using a knowledge graph, the ...
Asian people are under-represented in population-based, clinical, and genomic research. To address this gap, we have initiated the HELIOS longitudinal cohort study, comprising comprehensive behavioural, phenotypic, and genomic measurements from 10,004 Asian men and women of Chinese, Indian or Malay background. Phenotyping has been carried out using validated approaches, that are ...
Heather Stephens is a co-founding editor of Reaching Regions, an academic journal that launched this month in partnership with WVU, Iowa State University and the North American Regional Science Council. Publications are required to use non-technical language aimed at non-academic audiences and the open access journal aims to distribute articles ...
He is affiliated with the Leibniz Center for Science and Society (LCSS). His disciplinary interests comprise scientific habitus, scientific practices, relations between science and society, modes of resistance and methodological questions. He published various articles in the fields of Visual and Science Studies.
Developing a research question starts by identifying a clinical problem that is important to patients, being related to managing and ultimately improving their health. The process requires clinician scientists to be curious about and attentive to day-to-day practice outcomes, as well as to be avid readers of the scientific literature, to ...
Here, we combine observed and reconstructed June-August (JJA) surface air temperatures to show that 2023 was the warmest NH extra-tropical summer over the past 2000 years exceeding the 95% ...