Argumentative Essay Writing
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change


Make Your Case: A Guide to Writing an Argumentative Essay on Climate Change
Published on: Mar 2, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Argumentative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide
Learn How to Write an Argumentative Essay Outline
Best Argumentative Essay Examples for Your Help
Basic Types of Argument and How to Use Them?
Take Your Pick – 200+ Argumentative Essay Topics
Essential Tips and Examples for Writing an Engaging Argumentative Essay about Abortion
Crafting a Winning Argumentative Essay on Social Media
Craft a Winning Argumentative Essay about Mental Health
Strategies for Writing a Winning Argumentative Essay about Technology
Crafting an Unbeatable Argumentative Essay About Gun Control
Win the Debate - Writing An Effective Argumentative Essay About Sports
Ready, Set, Argue: Craft a Convincing Argumentative Essay About Wearing Mask
Crafting a Powerful Argumentative Essay about Global Warming: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share this article
With the issue of climate change making headlines, it’s no surprise that this has become one of the most debated topics in recent years.
But what does it really take to craft an effective argumentative essay about climate change?
Writing an argumentative essay requires a student to thoroughly research and articulate their own opinion on a specific topic.
To write such an essay, you will need to be well-informed regarding global warming. By doing so, your arguments may stand firm backed by both evidence and logic.
In this blog, we will discuss some tips for crafting a factually reliable argumentative essay about climate change!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Argumentative Essay about Climate Change?
The main focus will be on trying to prove that global warming is caused by human activities. Your goal should be to convince your readers that human activity is causing climate change.
To achieve this, you will need to use a variety of research methods to collect data on the topic. You need to make an argument as to why climate change needs to be taken more seriously.
Argumentative Essay Outline about Climate Change
An argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
The outline of your paper should include the following sections:
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Introduction
The first step is to introduce the topic and provide an overview of the main points you will cover in the essay.
This should include a brief description of what climate change is. Furthermore, it should include current research on how humans are contributing to global warming.
An example is:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis Statement For Climate Change Argumentative Essay
The thesis statement should be a clear and concise description of your opinion on the topic. It should be established early in the essay and reiterated throughout.
For example, an argumentative essay about climate change could have a thesis statement such as:
Climate Change Argumentative Essay Conclusion
The conclusion should restate your thesis statement and summarize the main points of the essay.
It should also provide a call to action, encouraging readers to take steps toward addressing climate change.
For example,
How To Write An Argumentative Essay On Climate Change
Writing an argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
Following are the steps to follow for writing an argumentative essay about climate change
Do Your Research
The first step is researching the topic and collecting evidence to back up your argument.
You should look at scientific research, articles, and data on climate change as well as current policy solutions.
Pick A Catchy Title
Once you have gathered your evidence, it is time to pick a title for your essay. It should be specific and concise.
Outline Your Essay
After selecting a title, create an outline of the main points you will include in the essay.
This should include an introduction, body paragraphs that provide evidence for your argument, and a conclusion.
Compose Your Essay
Finally, begin writing your essay. Start with an introduction that provides a brief overview of the main points you will cover and includes your thesis statement.
Then move on to the body paragraphs, providing evidence to back up your argument.
Finally, conclude the essay by restating your thesis statement and summarizing the main points.
Proofread and Revise
Once you have finished writing the essay, it is important to proofread and revise your work.
Check for any spelling or grammatical errors, and make sure the argument is clear and logical.
Finally, consider having someone else read over the essay for a fresh perspective.
By following these steps, you can create an effective argumentative essay on climate change. Good luck!
Examples Of Argumentative Essays About Climate Change
Climate Change is real and happening right now. It is one of the most urgent environmental issues that we face today.
Argumentative essays about this topic can help raise awareness that we need to protect our planet.
Below you will find some examples of argumentative essays on climate change written by CollegeEssay.orgâs expert essay writers.
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change And Global Warming
Persuasive Essay About Climate Change
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change In The Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Caused By Humans
Geography Argumentative Essay About Climate Change
Check our extensive blog on argumentative essay examples to ace your next essay!
Good Argumentative Essay Topics About Climate Change
Choosing a great topic is essential to help your readers understand and engage with the issue.
Here are some suggestions:
- Should governments fund projects that will reduce the effects of climate change?
- Is it too late to stop global warming and climate change?
- Are international treaties effective in reducing carbon dioxide emissions?
- What are the economic implications of climate change?
- Should renewable energy be mandated as a priority over traditional fossil fuels?
- How can individuals help reduce their carbon footprint and fight climate change?
- Are regulations on industry enough to reduce global warming and climate change?
- Could geoengineering be used to mitigate climate change?
- What are the social and political effects of global warming and climate change?
- Should companies be held accountable for their contribution to climate change?
Check our comprehensive blog on argumentative essay topics to get more topic ideas!
We hope these topics and resources help you write a great argumentative essay about climate change.
Now that you know how to write an argumentative essay about climate change, itâs time to put your skills to the test.
Overwhelmed with assignments and thinking, "I wish someone could write me an essay "?
Our specialized writing service is here to turn that wish into reality. With a focus on quality, originality, and timely delivery, our team of professionals is committed to crafting essays that align perfectly with your academic goals.
And for those seeking an extra edge, our essay writer , an advanced AI tool, is ready to elevate your writing to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction to climate change.
An introduction to a climate change essay can include a short description of why the topic is important and/or relevant.
It can also provide an overview of what will be discussed in the body of the essay.
The introduction should conclude with a clear, focused thesis statement that outlines the main argument in your essay.
What is a good thesis statement for climate change?
A good thesis statement for a climate change essay should state the main point or argument you will make in your essay.
You could argue that “The science behind climate change is irrefutable and must be addressed by governments, businesses, and individuals.”
Cathy A. (Medical school essay, Education)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Climate modelling
- Extreme weather
- Health and Security
- Temperature
- China energy
- Oil and gas
- Other technologies
- China Policy
- International policy
- Other national policy
- Rest of world policy
- UN climate talks
- Country profiles
- Guest posts
- Infographics
- Media analysis
- State of the climate
- Translations
- Daily Brief
- China Briefing
- Comments Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Global emissions
- Rest of world emissions
- UK emissions
- EU emissions
- Global South Climate Database
- Newsletters
- COP21 Paris
- COP22 Marrakech
- COP24 Katowice
- COP25 Madrid
- COP26 Glasgow
- COP27 Sharm el-Sheikh
- COP28 Dubai
- Privacy Policy
- Attribution
- Geoengineering
- Food and farming
- Nature policy
- Plants and forests
- Marine life
- Ocean acidification
- Ocean warming
- Sea level rise
- Human security
- Public health
- Public opinion
- Risk and adaptation
- Science communication
- Carbon budgets
- Climate sensitivity
- GHGs and aerosols
- Global temperature
- Negative emissions
- Rest of world temperature
- Tipping points
- UK temperature
- Thank you for subscribing
Social Channels
Search archive.

Receive a Daily or Weekly summary of the most important articles direct to your inbox, just enter your email below. By entering your email address you agree for your data to be handled in accordance with our Privacy Policy .

Analysis: Why scientists think 100% of global warming is due to humans

Zeke Hausfather
The extent of the human contribution to modern global warming is a hotly debated topic in political circles, particularly in the US.
During a recent congressional hearing, Rick Perry, the US energy secretary, remarked that “to stand up and say that 100% of global warming is because of human activity, I think on its face, is just indefensible”.
However, the science on the human contribution to modern warming is quite clear. Humans emissions and activities have caused around 100% of the warming observed since 1950, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) fifth assessment report .
Here Carbon Brief examines how each of the major factors affecting the Earth’s climate would influence temperatures in isolation – and how their combined effects almost perfectly predict long-term changes in the global temperature.
Carbon Brief’s analysis finds that:
- Since 1850, almost all the long-term warming can be explained by greenhouse gas emissions and other human activities.
- If greenhouse gas emissions alone were warming the planet, we would expect to see about a third more warming than has actually occurred. They are offset by cooling from human-produced atmospheric aerosols.
- Aerosols are projected to decline significantly by 2100 , bringing total warming from all factors closer to warming from greenhouse gases alone.
- Natural variability in the Earth’s climate is unlikely to play a major role in long-term warming.
How much warming is caused by humans?
In its 2013 fifth assessment report, the IPCC stated in its summary for policymakers that it is “extremely likely that more than half of the observed increase in global average surface temperature” from 1951 to 2010 was caused by human activity. By “extremely likely”, it meant that there was between a 95% and 100% probability that more than half of modern warming was due to humans.
This somewhat convoluted statement has been often misinterpreted as implying that the human responsibility for modern warming lies somewhere between 50% and 100%. In fact, as NASA’s Dr Gavin Schmidt has pointed out, the IPCC’s implied best guess was that humans were responsible for around 110% of observed warming (ranging from 72% to 146%), with natural factors in isolation leading to a slight cooling over the past 50 years.
Similarly, the recent US fourth national climate assessment found that between 93% to 123% of observed 1951-2010 warming was due to human activities.
These conclusions have led to some confusion as to how more than 100% of observed warming could be attributable to human activity. A human contribution of greater than 100% is possible because natural climate change associated with volcanoes and solar activity would most likely have resulted in a slight cooling over the past 50 years, offsetting some of the warming associated with human activities.
‘Forcings’ that change the climate
Scientists measure the various factors that affect the amount of energy that reaches and remains in the Earth’s climate. They are known as “radiative forcings”.
These forcings include greenhouse gases, which trap outgoing heat, aerosols – both from human activities and volcanic eruptions – that reflect incoming sunlight and influence cloud formation, changes in solar output, changes in the reflectivity of the Earth’s surface associated with land use, and many other factors.
To assess the role of each different forcing in observed temperature changes, Carbon Brief adapted a simple statistical climate model developed by Dr Karsten Haustein and his colleagues at the University of Oxford and University of Leeds . This model finds the relationship between both human and natural climate forcings and temperature that best matches observed temperatures, both globally and over land areas only.
The figure below shows the estimated role of each different climate forcing in changing global surface temperatures since records began in 1850 – including greenhouse gases (red line), aerosols (dark blue), land use (light blue), ozone (pink), solar (yellow) and volcanoes (orange).
The black dots show observed temperatures from the Berkeley Earth surface temperature project, while the grey line shows the estimated warming from the combination of all the different types of forcings.
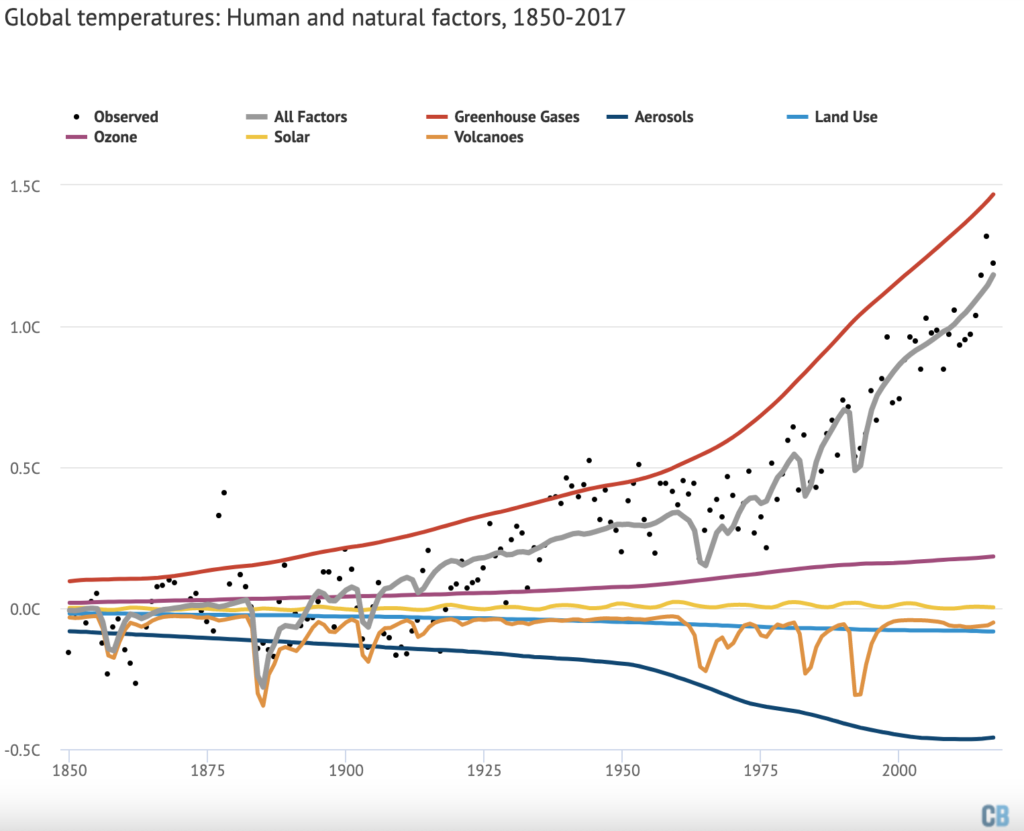
The combination of all radiative forcings generally matches longer-term changes in observed temperatures quite well. There is some year-to-year variability, primarily from El Niño events , that is not driven by changes in forcings. There are also periods from 1900-1920 and 1930-1950 where some larger disagreements are evident between projected and observed warming, both in this simple model and in more complex climate models .
The chart highlights that, of all the radiative forcings analysed, only increases in greenhouse gas emissions produce the magnitude of warming experienced over the past 150 years.
If greenhouse gas emissions alone were warming the planet, we would expect to see about a third more warming than has actually occurred.
So, what roles do all the other factors play?
- Q&A: How do climate models work?
- Interactive: The impacts of climate change at 1.5C, 2C and beyond
- Explainer: How scientists estimate ‘climate sensitivity’
- Mapped: How every part of the world has warmed – and could continue to warm
The extra warming from greenhouse gases is being offset by sulphur dioxide and other products of fossil fuel combustion that form atmospheric aerosols . Aerosols in the atmosphere both reflect incoming solar radiation back into space and increase the formation of high, reflective clouds, cooling the Earth.
Ozone is a short-lived greenhouse gas that traps outgoing heat and warms the Earth. Ozone is not emitted directly, but is formed when methane, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds break down in the atmosphere. Increases in ozone are directly attributable to human emissions of these gases.
In the upper atmosphere, reductions in ozone associated with chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other halocarbons depleting the ozone layer have had a modest cooling effect. The net effects of combined lower and upper atmospheric ozone changes have modestly warmed the Earth by a few tenths of a degree.
Changes in the way land is used alter the reflectivity of the Earth’s surface. For example, replacing a forest with a field will generally increase the amount of sunlight reflected back into space, particularly in snowy regions. The net climate effect of land-use changes since 1850 is a modest cooling.
Volcanoes have a short-term cooling effect on the climate due to their injection of sulphate aerosols high into the stratosphere, where they can remain aloft for a few years, reflecting incoming sunlight back into space. However, once the sulphates drift back down to the surface, the cooling effect of volcanoes goes away. The orange line shows the estimated impact of volcanoes on the climate, with large downward spikes in temperatures of up to 0.4C associated with major eruptions.

Finally, solar activity is measured by satellites over the past few decades and estimated based on sunspot counts in the more distant past. The amount of energy reaching the Earth from the sun fluctuates modestly on a cycle of around 11 years. There has been a slight increase in overall solar activity since the 1850s, but the amount of additional solar energy reaching the Earth is small compared to other radiative forcings examined.
Over the past 50 years, solar energy reaching the Earth has actually declined slightly , while temperatures have increased dramatically.
Human forcings match observed warming
The accuracy of this model depends on the accuracy of the radiative forcing estimates. Some types of radiative forcing like that from atmospheric CO2 concentrations can be directly measured and have relatively small uncertainties. Others, such as aerosols, are subject to much greater uncertainties due to the difficulty of accurately measuring their effects on cloud formation.
These are accounted for in the figure below, which shows combined natural forcings (blue line) and human forcings (red line) and the uncertainties that the statistical model associates with each. These shaded areas are based on 200 different estimates of radiative forcings, incorporating research attempting to estimate a range of values for each. Uncertainties in human factors increase after 1960, driven largely by increases in aerosol emissions after that point.
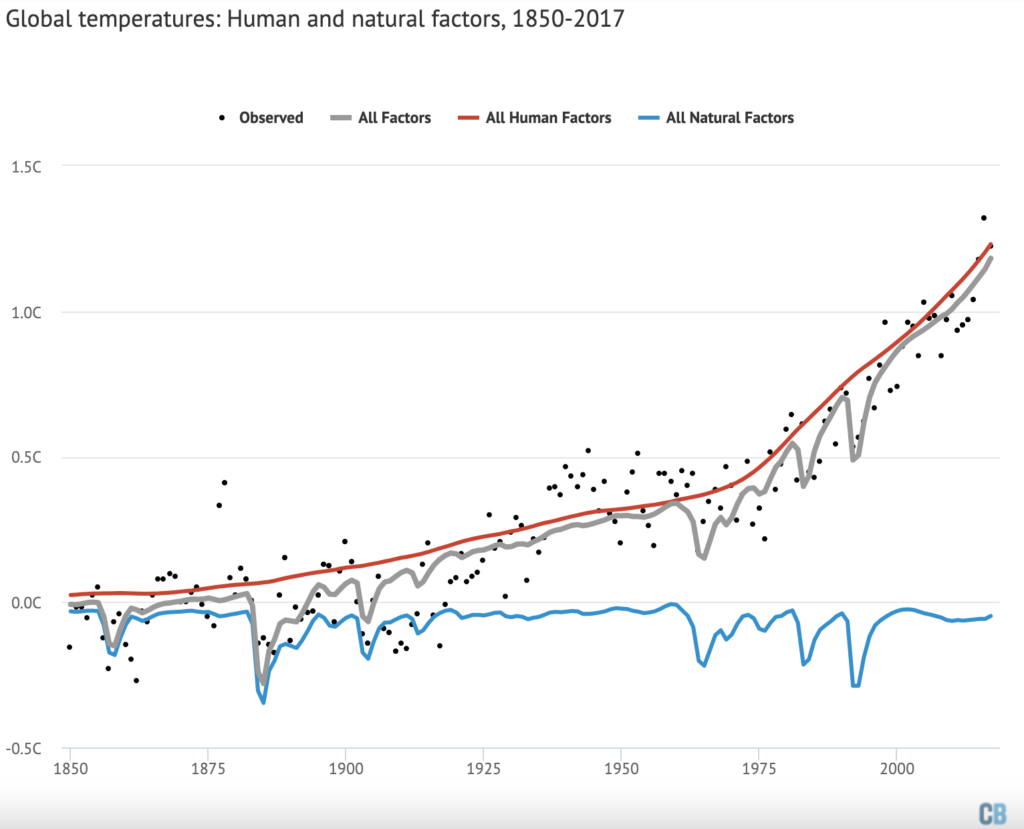
Overall, warming associated with all human forcings agrees quite well with observed warming, showing that about 104% of the total since the start of the “modern” period in 1950 comes from human activities (and 103% since 1850), which is similar to the value reported by the IPCC. Combined natural forcings show a modest cooling, primarily driven by volcanic eruptions.
The simple statistical model used for this analysis by Carbon Brief differs from much more complex climate models generally used by scientists to assess the human fingerprint on warming. Climate models do not simply “fit” forcings to observed temperatures. Climate models also include variations in temperature over space and time, and can account for different efficacies of radiative forcings in different regions of the Earth.
However, when analysing the impact of different forcings on global temperatures, complex climate models generally find results similar to simple statistical models. The figure below, from the IPCC’s Fifth Assessment Report, shows the influence of different factors on temperature for the period from 1950 to 2010. Observed temperatures are shown in black, while the sum of human forcings is shown in orange.
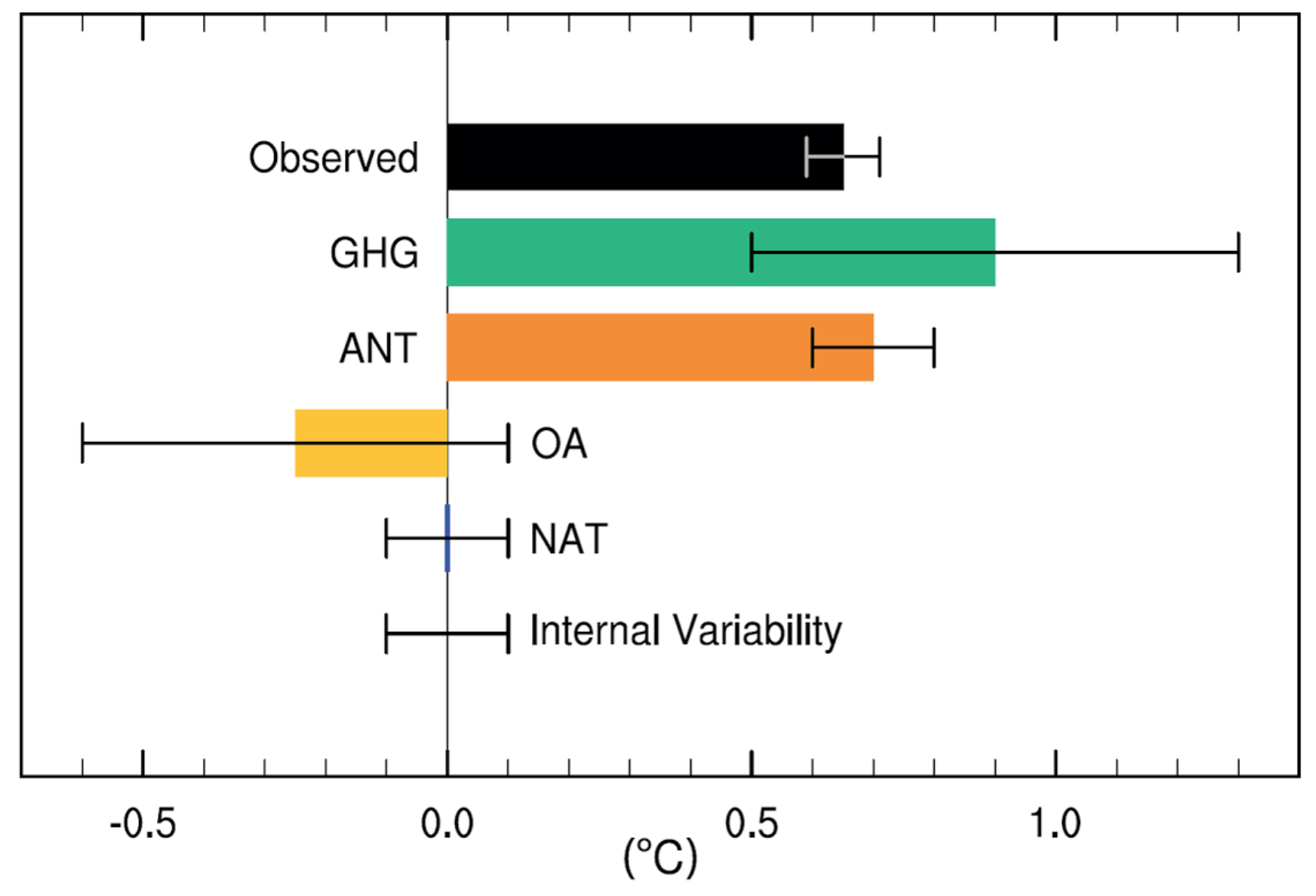
This suggests that human forcings alone would have resulted in approximately 110% of observed warming . The IPCC also included the estimated magnitude of internal variability over that period in the models, which they suggest is relatively small and comparable to that of natural forcings.
As Prof Gabi Hegerl at the University of Edinburgh tells Carbon Brief: “The IPCC report has an estimate that basically says the best guess is no contribution [from natural variability] with not that much uncertainty.”
Land areas are warming faster
Land temperatures have warmed considerably faster than average global temperatures over the past century, with temperatures reaching around 1.7C above pre-industrial levels in recent years. The land temperature record also goes back further in time than the global temperature record, though the period prior to 1850 is subject to much greater uncertainties .
Both human and natural radiative forcings can be matched to land temperatures using the statistical model. The magnitude of human and natural forcings will differ a bit between land and global temperatures. For example, volcanic eruptions appear to have a larger influence on land, as land temperatures are likely to respond faster to rapid changes in forcings.
The figure below shows the relative contribution of each different radiative forcing to land temperatures since 1750.
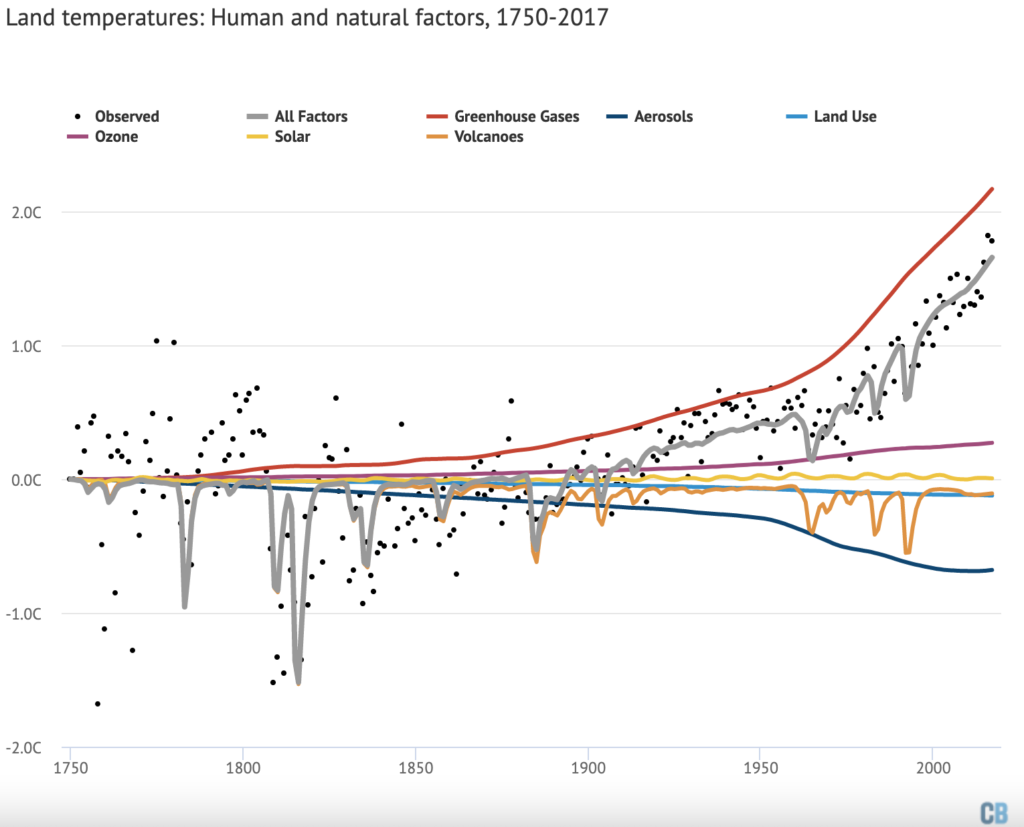
The combination of all forcings generally matches observed temperatures quite well, with short-term variability around the grey line primarily driven by El Niño and La Niña events. There is a wider variation in temperatures prior to 1850, reflecting the much larger uncertainties in the observational records that far back.
There is still a period around 1930 and 1940 where observations exceed what the model predicts, though the differences are less pronounced than in global temperatures and the 1900-1920 divergence is mostly absent in land records.
Volcanic eruptions in the late 1700s and early 1800s stand out sharply in the land record. The eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia in 1815 may have cooled land temperatures by a massive 1.5C, though records at the time were limited to parts of the Northern Hemisphere and it is, therefore, hard to draw a firm conclusion about global impacts. In general, volcanoes appear to cool land temperatures by nearly twice as much as global temperatures.
What may happen in the future?
Carbon Brief used the same model to project future temperature changes associated with each forcing factor. The figure below shows observations up to 2017, along with future post-2017 radiative forcings from RCP6.0 , a medium-to-high future warming scenario.
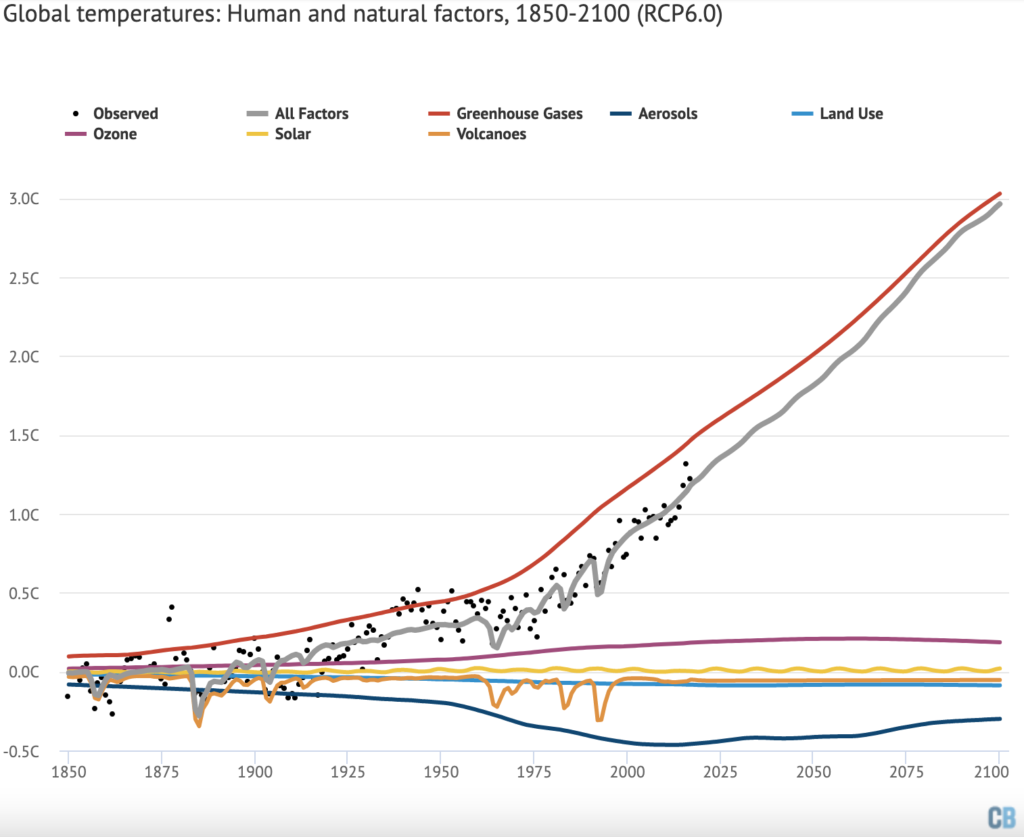
When provided with the radiative forcings for the RCP6.0 scenario, the simple statistical model shows warming of around 3C by 2100, nearly identical to the average warming that climate models find.
Future radiative forcing from CO2 is expected to continue to increase if emissions rise. Aerosols, on the other hand, are projected to peak at today’s levels and decline significantly by 2100 , driven in large part by concerns about air quality. This reduction in aerosols will enhance overall warming, bringing total warming from all radiative forcing closer to warming from greenhouse gases alone. The RCP scenarios assume no specific future volcanic eruptions, as the timing of these is unknowable, while solar output continues its 11-year cycle.
This approach can also be applied to land temperatures, as shown in the figure below. Here, land temperatures are shown between 1750 and 2100, with post-2017 forcings also from RCP6.0.
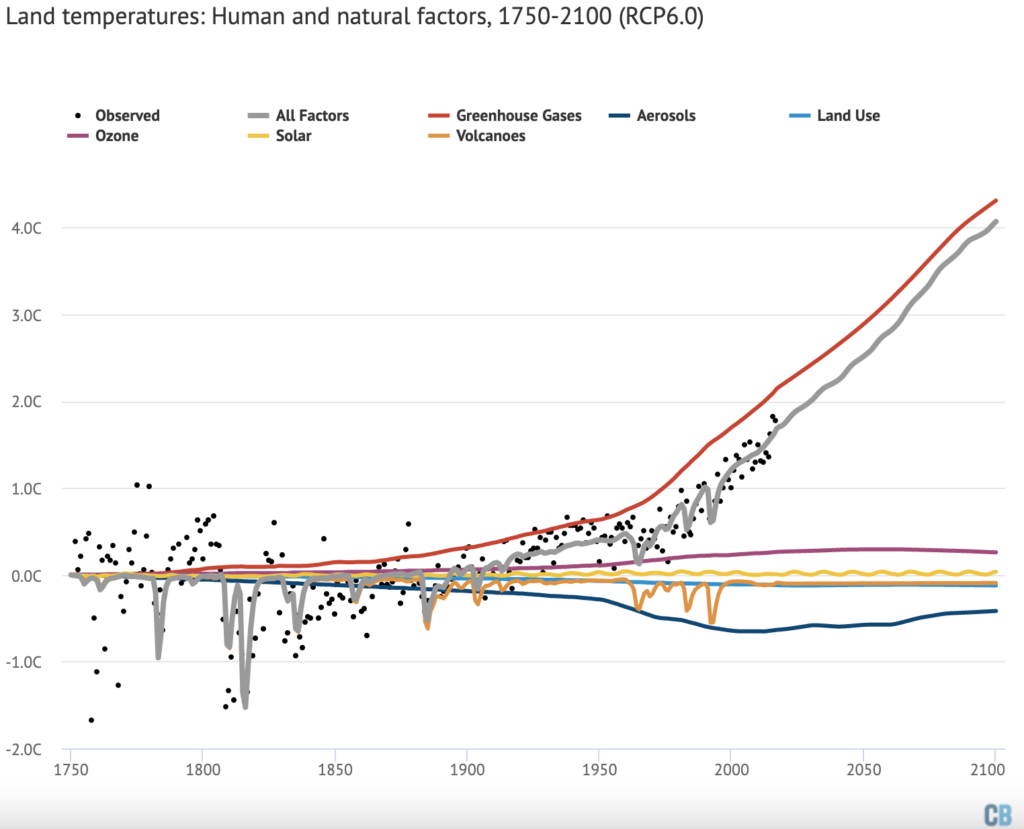
The land is expected to warm about 30% faster than the globe as a whole, as the rate of warming over the oceans is buffered by ocean heat uptake. This is seen in the model results, where land warms by around 4C by 2100 compared to 3C globally in the RCP6.0 scenario.
There is a wide range of future warming possible from different RCP scenarios and different values for the sensitivity of the climate system , but all show a similar pattern of declining future aerosol emissions and a larger role for greenhouse gas forcing in future temperatures.
The role of natural variability
While natural forcings from solar and volcanoes do not seem to play much of a role in long-term warming, there is also natural variability associated with ocean cycles and variations in ocean heat uptake.
As the vast majority of energy trapped by greenhouse gases is absorbed by the oceans rather than the atmosphere, changes in the rate of ocean heat uptake can potentially have large impacts on the surface temperature. Some researchers have argued that multidecadal cycles, such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) and Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), can play a role in warming at a decadal scale.
While human factors explain all the long-term warming, there are some specific periods that appear to have warmed or cooled faster than can be explained based on our best estimates of radiative forcing. For example, the modest mismatch between the radiative forcing-based estimate and observations during the mid-1900s might be evidence of a role for natural variability during that period.
A number of researchers have examined the potential for natural variability to impact long-term warming trends. They have found that it generally plays a limited role. For example, Dr Markus Huber and Dr Reto Knutti at the Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science (IAC) in Zurich found a maximum possible contribution of natural variability of around 26% (+/- 12%) over the past 100 years and 18% (+/- 9%) over the past 50 years.
Knutti tells Carbon Brief:
“We can never completely rule out that natural variability is larger than we currently think. But that is a weak argument: you can, of course, never rule out the unknown unknown. The question is whether there is strong, or even any evidence for it. And the answer is no, in my view.
Models get the short-term temperature variability approximately right. In many cases, they even have too much. And for the long term, we can’t be sure because the observations are limited. But the forced response pretty much explains the observations, so there is no evidence from the 20th century that we are missing something…
Even if models were found to underestimate internal variability by a factor of three, it is extremely unlikely [less than 5% chance] that internal variability could produce a trend as large as observed.”
Similarly, Dr Martin Stolpe and colleagues, also at IAC, recently analysed the role of multidecadal natural variability in both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. They found that “less than 10% of the observed global warming during the second half of the 20th century is caused by internal variability in these two ocean basins, reinforcing the attribution of most of the observed warming to anthropogenic forcings”.
Internal variability is likely to have a much larger role in regional temperatures. For example, in producing unusually warm periods in the Arctic and the US in the 1930s. However, its role in influencing long-term changes in global surface temperatures appears to be limited.
While there are natural factors that affect the Earth’s climate, the combined influence of volcanoes and changes in solar activity would have resulted in cooling rather than warming over the past 50 years.
The global warming witnessed over the past 150 years matches nearly perfectly what is expected from greenhouse gas emissions and other human activity, both in the simple model examined here and in more complex climate models. The best estimate of the human contribution to modern warming is around 100%.
Some uncertainty remains due to the role of natural variability, but researchers suggest that ocean fluctuations and similar factors are unlikely to be the cause of more than a small fraction of modern global warming.
Methodology
The simple statistical model used in this article is adapted from the Global Warming Index published by Haustein et al ( 2017 ). In turn, it is based on the Otto et al ( 2015 ) model.
The model estimates contributions to observed climate change and removes the impact of natural year-to-year fluctuations by a multiple linear regression of observed temperatures and estimated responses to total human-induced and total natural drivers of climate change. The forcing responses are provided by the standard simple climate model given in Chapter 8 of IPCC ( 2013 ), but the size of these responses is estimated by the fit to the observations. The forcings are based on IPCC (2013) values and were updated to 2017 using data from NOAA and ECLIPSE . 200 variations of these forcings were provided by Dr. Piers Forster of the University of Leeds , reflecting the uncertainty in forcing estimates. An Excel spreadsheet containing their model is also provided.
The model was adapted by calculating forcing responses for each of the different major climate forcings rather than simply total human and natural forcings, using the Berkeley Earth record for observations. The decay time of thermal response used in converting forcings to forcing responses was adjusted to be one year rather than four years for volcanic forcings to better reflect the fast response time present in observations. The effects of El Niño and La Niña (ENSO) events was removed from the observations using an approach adapted from Foster and Rahmstorf ( 2011 ) and the Kaplan El Niño 3.4 index when calculating the volcanic temperature response, as the overlap between volcanoes and ENSO otherwise complicates empirical estimates.
The temperature response for each individual forcing was calculated by scaling their forcing responses by the total human or natural coefficients from the regression model . The regression model was also run separately for land temperatures. Temperature responses for each forcing between 2018 and 2100 were estimated using forcing data from RCP6.0, normalised to match the magnitude of observed forcings at the end of 2017.
Uncertainties in total human and total natural temperature response was estimated using a Monte Carlo analysis of 200 different forcing series, as well as the uncertainties in the estimated regression coefficients. The Python code used to run the model is archived with GitHub and available for download .
Observational data from 2017 shown in the figures is based on the average of the first 10 months of the year and is likely to be quite similar to the ultimate annual value.
- Why scientists think 100% of global warming is due to humans
Expert analysis direct to your inbox.
Get a round-up of all the important articles and papers selected by Carbon Brief by email. Find out more about our newsletters here .
The climate is changing, but not just because of humans. Here's why that matters.

The climate is changing — the thing is, it isn’t just due to humans.
Natural forces beyond human control are also gradually affecting our climate. These geophysical forces are vital to understanding global warming. Man is indeed responsible for a large portion — possibly even a majority — of global warming. But also in play are complex gravitational interactions, including changes in the Earth’s orbit, axial tilt and torque.
This fact needs to be included in the public debate. Because these gravitational shifts, occurring over millennia, can influence climate patterns and ultimately lead to noticeable variations in seasons. Interestingly, research suggests climate change can alter the tilt of the Earth, but an unrelated change in tilt can also further change the climate. It is a balance-counterbalance relationship.
Changes in the Earth’s path around the Sun, or eccentricity, involve shifts in the orbit around the Sun from a roughly circular journey to more of an elliptical one . When the Earth gradually adopts a more elliptical orbit, there are more pronounced temperatures during the summer and winter months. This alteration is exacerbated when the Earth’s axial tilt is inclined to a sharper degree than usual. As this happens, it causes the North and South Poles to be positioned more directly toward the Sun.
Haven’t you noticed the recent rise in irregular weather patterns? This is not just a man-made problem. Gradual slight variations in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun can strongly influence temperature extremes. This is important because the conversation around climate change has become so politicized, we've totally lost sight of the science — and with it, any room for bipartisanship.

Tropical storms, for example, have been forming later in what we know as hurricane season. Based on my own analysis, over the past three decades, the majority of Category 3 or stronger storms to hit the United States appear from late August to early October. Earlier in the 20th century, storms usually occurred in June, July and early August.
It doesn’t stop there. Changes in seasons can also affect other types of storms, including severe winter snowstorms and tornadoes. Recall the Storm of the Century in 1993 on the heels of Hurricane Andrew the year prior. Or what about the recent string of snowstorms (with names like Snowpocalypse, Snowmageddon and Snowzilla) dovetailing with warm-weather superstorms. Climate extremes are evident, and not just with hurricanes.
The variations in the Earth’s orbit are known as the Milankovitch cycles — after the Serbian geophysicist Milutin Milanković, who hypothesized this phenomenon in the 1920s. He discovered that variations in the Earth’s path around the Sun, axial tilt and torque could together affect our climate.
Even a slight change or orientation in the precession of the Earth’s rotating body can cause a wobbling effect shifting torque in different areas since the planet is not a perfect sphere to some people’s surprise.
Now would seem a particularly apt time to act. The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season was an intense, record-setting period . With several landfall hurricanes — Harvey, Irma, Jose and Maria — barreling their way through the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico, devastating parts of the Leeward Islands and United States.
Still, even President Donald J. Trump has implied the whole of idea climate change may just be a hoax . Most Republicans seem to agree that it is not a serious problem.
Meanwhile, while some Democrats have tried to use the frequency and intensity of storms in the hopes of highlighting the climate change conversation, even this effort has seemed muted.
To make effective policy, it is important for politicians and activists alike to set aside their ideological differences.
There is now a real opportunity for new legislation, sound environmental legislation. But will we squander this unprecedented opportunity, punting the ball yet again? You can bet on it. Given the realities of everyday life, the extent of social beliefs, political attitudes and economic perspectives vary on a wide range of policy issues.
To make sound and effective policy, it is important for politicians and activists alike to set aside their ideological differences and return to the basics of science, in this case, the mechanics of science. After all, shouldn’t we be relying more heavily upon geoscientists and weather forecasters to provide evidence-based data and predictive modeling?
Risks to disasters are increasing. Population growth along coastlines worldwide, in addition to technological and infrastructural development, will inherently result in a concomitant increase in places prone to disasters. Modern society relies upon government for effective response to and recovery from such events.
Change is occurring and will continue to do so. As the population continues to explode and resources are consumed on a massive scale, trying to stop both is unrealistic. It is more than just being unrealistic, it is simply wasting critical time. I know, science isn’t sexy. The obsession on why storms are occurring in lieu of discussing the how is leading us down a dangerous path. A deadly path.
The heightened culture of disaster only feeds our attention on political banter and ideological semantics with no room for informed decision-making.
We get it, Mother Nature always wins. So, are we now faced with the sobering lesson that little can be done, and we should just throw in the towel? No, of course not. Though climate change is inevitable, we also need to have a healthy appreciation of the fact that climate shifts aren’t just limited to rapidly changing weather patterns.
Turning the corner into unexplored territory is always difficult. By having a broader sense of communal resiliency — social, political and economic standing — we can manage this unavoidable pendulum of climate extremes. With the recent sweeping of storms draining response efforts and budgetary resources, now is the time to set aside the theatrical shenanigans and engage in realpolitik.
Tonya T. Neaves is the director for the Centers on the Public Service at George Mason University’s Schar School of Policy and Government, where she also is a faculty member in its master of public administration program and coordinator for the Emergency Management and Homeland Security certificate.
Tonya T. Neaves is the director for the Centers on the Public Service at George Mason University’s Schar School of Policy and Government, where she also is a faculty member in its master of public administration program and coordinator for the Emergency Management and Homeland Security certificate.

Why climate change is still the greatest threat to human health
Polluted air and steadily rising temperatures are linked to health effects ranging from increased heart attacks and strokes to the spread of infectious diseases and psychological trauma.
People around the world are witnessing firsthand how climate change can wreak havoc on the planet. Steadily rising average temperatures fuel increasingly intense wildfires, hurricanes, and other disasters that are now impossible to ignore. And while the world has been plunged into a deadly pandemic, scientists are sounding the alarm once more that climate change is still the greatest threat to human health in recorded history .
As recently as August—when wildfires raged in the United States, Europe, and Siberia—World Health Organization Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in a statement that “the risks posed by climate change could dwarf those of any single disease.”
On September 5, more than 200 medical journals released an unprecedented joint editorial that urged world leaders to act. “The science is unequivocal,” they write. “A global increase of 1.5°C above the pre-industrial average and the continued loss of biodiversity risk catastrophic harm to health that will be impossible to reverse.”
Despite the acute dangers posed by COVID-19, the authors of the joint op-ed write that world governments “cannot wait for the pandemic to pass to rapidly reduce emissions.” Instead, they argue, everyone must treat climate change with the same urgency as they have COVID-19.
Here’s a look at the ways that climate change can affect your health—including some less obvious but still insidious effects—and why scientists say it’s not too late to avert catastrophe.
Air pollution
Climate change is caused by an increase of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in Earth’s atmosphere, mostly from fossil fuel emissions. But burning fossil fuels can also have direct consequences for human health. That’s because the polluted air contains small particles that can induce stroke and heart attacks by penetrating the lungs and heart and even traveling into the bloodstream. Those particles might harm the organs directly or provoke an inflammatory response from the immune system as it tries to fight them off. Estimates suggest that air pollution causes anywhere between 3.6 million and nine million premature deaths a year.
For Hungry Minds
“The numbers do vary,” says Andy Haines , professor of environmental change and public health at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and author of the recently published book Planetary Health . “But they all agree that it’s a big public health burden.”

People over the age of 65 are most susceptible to the harmful effects of air pollution, but many others are at risk too, says Kari Nadeau , director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University. People who smoke or vape are at increased risk, as are children with asthma.
Air pollution also has consequences for those with allergies. Carbon dioxide increases the acidity of the air, which then pulls more pollen out from plants. For some people, this might just mean that they face annoyingly long bouts of seasonal allergies. But for others, it could be life-threatening.
“For people who already have respiratory disease, boy is that a problem,” Nadeau says. When pollen gets into the respiratory pathway, the body creates mucus to get rid of it, which can then fill up and suffocate the lungs.
Even healthy people can have similar outcomes if pollen levels are especially intense. In 2016, in the Australian state of Victoria, a severe thunderstorm combined with high levels of pollen to induce what The Lancet has described as “the world’s largest and most catastrophic epidemic of thunderstorm asthma.” So many residents suffered asthma attacks that emergency rooms were overwhelmed—and at least 10 people died as a result.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to get worse, and wildfire smoke is especially toxic. As one recent study showed, fires can account for 25 percent of dangerous air pollution in the U.S. Nadeau explains that the smoke contains particles of everything that the fire has consumed along its path—from rubber tires to harmful chemicals. These particles are tiny and can penetrate even deeper into a person’s lungs and organs. ( Here’s how breathing wildfire smoke affects the body .)
Extreme heat
Heat waves are deadly, but researchers at first didn’t see direct links between climate change and the harmful impacts of heat waves and other extreme weather events. Haines says the evidence base has been growing. “We have now got a number of studies which has shown that we can with high confidence attribute health outcomes to climate change,” he says.

Most recently, Haines points to a study published earlier this year in Nature Climate Change that attributes more than a third of heat-related deaths to climate change. As National Geographic reported at the time , the study found that the human toll was even higher in some countries with less access to air conditioning or other factors that render people more vulnerable to heat. ( How climate change is making heat waves even deadlier .)
That’s because the human body was not designed to cope with temperatures above 98.6°F, Nadeau says. Heat can break down muscles. The body does have some ways to deal with the heat—such as sweating. “But when it’s hot outside all the time, you cannot cope with that, and your heart muscles and cells start to literally die and degrade,” she says.
If you’re exposed to extreme heat for too long and are unable to adequately release that heat, the stress can cause a cascade of problems throughout the body. The heart has to work harder to pump blood to the rest of the organs, while sweat leeches the body of necessary minerals such as sodium and potassium. The combination can result in heart attacks and strokes .
Dehydration from heat exposure can also cause serious damage to the kidneys, which rely on water to function properly. For people whose kidneys are already beginning to fail—particularly older adults—Nadeau says that extreme heat can be a death sentence. “This is happening more and more,” she says.
Studies have also drawn links between higher temperatures and preterm birth and other pregnancy complications. It’s unclear why, but Haines says that one hypothesis is that extreme heat reduces blood flow to the fetus.
Food insecurity
One of the less direct—but no less harmful—ways that climate change can affect health is by disrupting the world’s supply of food.
You May Also Like

2024 hurricane season forecasted to be record-breaking year

The U.S. plans to limit PFAS in drinking water. What does that really mean?

Here’s what extreme heat does to the body
Climate change both reduces the amount of food that’s available and makes it less nutritious. According to an Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) special report , crop yields have already begun to decline as a result of rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. Meanwhile, studies have shown that increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can leech plants of zinc, iron, and protein—nutrients that humans need to survive.

Malnutrition is linked to a variety of illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It can also increase the risk of stunting, or impaired growth , in children, which can harm cognitive function.
Climate change also imperils what we eat from the sea. Rising ocean temperatures have led many fish species to migrate toward Earth’s poles in search of cooler waters. Haines says that the resulting decline of fish stocks in subtropic regions “has big implications for nutrition,” because many of those coastal communities depend on fish for a substantial amount of the protein in their diets.
This effect is likely to be particularly harmful for Indigenous communities, says Tiff-Annie Kenny, a professor in the faculty of medicine at Laval University in Quebec who studies climate change and food security in the Canadian Arctic. It’s much more difficult for these communities to find alternative sources of protein, she says, either because it’s not there or because it’s too expensive. “So what are people going to eat instead?” she asks.
Infectious diseases
As the planet gets hotter, the geographic region where ticks and mosquitoes like to live is getting wider. These animals are well-known vectors of diseases such as the Zika virus, dengue fever, and malaria. As they cross the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Nadeau says, mosquitoes and ticks bring more opportunities for these diseases to infect greater swaths of the world.
“It used to be that they stayed in those little sectors near the Equator, but now unfortunately because of the warming of northern Europe and Canada, you can find Zika in places you wouldn’t have expected,” Nadeau says.
In addition, climate conditions such as temperature and humidity can impact the life cycle of mosquitoes. Haines says there’s particularly good evidence showing that, in some regions, climate change has altered these conditions in ways that increase the risk of mosquitos transmitting dengue .
There are also several ways in which climate change is increasing the risk of diseases that can be transmitted through water, such as cholera, typhoid fever, and parasites. Sometimes that’s fairly direct, such as when people interact with dirty floodwaters. But Haines says that drought can have indirect impacts when people, say, can’t wash their hands or are forced to drink from dodgier sources of freshwater.
Mental health
A common result of any climate-linked disaster is the toll on mental health. The distress caused by drastic environmental change is so significant that it has been given its own name— solastalgia .

Nadeau says that the effects on mental health have been apparent in her studies of emergency room visits arising from wildfires in the western U.S. People lose their homes, their jobs, and sometimes their loved ones, and that takes an immediate toll. “What’s the fastest acute issue that develops? It’s psychological,” she says. Extreme weather events such as wildfires and hurricanes cause so much stress and anxiety that they can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder and even suicide in the long run.
Another common factor is that climate change causes disproportionate harm to the world’s most vulnerable people. On September 2, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released an analysis showing that racial and ethnic minority communities are particularly at risk . According to the report, if temperatures rise by 2°C (3.6°F), Black people are 40 percent more likely to live in areas with the highest projected increases in related deaths. Another 34 percent are more likely to live in areas with a rise in childhood asthma.
Further, the effects of climate change don’t occur in isolation. At any given time, a community might face air pollution, food insecurity, disease, and extreme heat all at once. Kenny says that’s particularly devastating in communities where the prevalence of food insecurity and poverty are already high. This situation hasn’t been adequately studied, she says, because “it’s difficult to capture these shocks that climate can bring.”
Why there’s reason for hope
In recent years, scientists and environmental activists have begun to push for more research into the myriad health effects of climate change. “One of the striking things is there’s been a real dearth of funding for climate change and health,” Haines says. “For that reason, some of the evidence we have is still fragmentary.”
Still, hope is not lost. In the Paris Agreement, countries around the world have pledged to limit global warming to below 2°C (3.6°F)—and preferably to 1.5°C (2.7°F)—by cutting their emissions. “When you reduce those emissions, you benefit health as well as the planet,” Haines says.
Meanwhile, scientists and environmental activists have put forward solutions that can help people adapt to the health effects of climate change. These include early heat warnings and dedicated cooling centers, more resilient supply chains, and freeing healthcare facilities from dependence on the electric grid.
Nadeau argues that the COVID-19 pandemic also presents an opportunity for world leaders to think bigger and more strategically. For example, the pandemic has laid bare problems with efficiency and equity that have many countries restructuring their healthcare facilities. In the process, she says, they can look for new ways to reduce waste and emissions, such as getting more hospitals using renewable energy.
“This is in our hands to do,” Nadeau says. “If we don’t do anything, that would be cataclysmic.”
Related Topics
- AIR POLLUTION
- WATER QUALITY
- NATURAL DISASTERS
- PUBLIC HEALTH
- CLIMATE CHANGE

This summer's extreme weather is a sign of things to come

This African lake may literally explode—and millions are at risk

We got rid of BPA in some products—but are the substitutes any safer?
Fungi could be the key to major cancer research breakthroughs

How the additives in your vaccines rev up your immune system
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
The Center for Global Studies
Climate change argumentation.
Carmen Vanderhoof, Curriculum and Instruction, College of Education, Penn State
Carmen Vanderhoof is a doctoral candidate in Science Education at Penn State. Her research employs multimodal discourse analysis of elementary students engaged in a collaborative engineering design challenge in order to examine students’ decision-making practices. Prior to resuming graduate studies, she was a secondary science teacher and conducted molecular biology research.
- Subject(s): Earth Science
- Topic: Climate Change and Sustainability
- Grade/Level: 9-12 (can be adapted to grades 6-8)
- Objectives: Students will be able to write a scientific argument using evidence and reasoning to support claims. Students will also be able to reflect on the weaknesses in their own arguments in order to improve their argument and then respond to other arguments.
- Suggested Time Allotment: 4-5 hours (extra time for extension)
This lesson is derived from Dr. Peter Buckland’s sustainability presentation for the Center for Global Studies . Dr. Peter Buckland, a Penn State alumnus, is a postdoctoral fellow for the Sustainability Institute. He has drawn together many resources for teaching about climate change, sustainability, and other environmental issues.
While there are many resources for teaching about climate change and sustainability, it may be tough to figure out where to start. There are massive amounts of data available to the general public and students need help searching for good sources of evidence. Prior to launching into a search, it would be worthwhile figuring out what the students already know about climate change, where they learned it, and how they feel about efforts to reduce our carbon footprint. There are many options for eliciting prior knowledge, including taking online quizzes, whole-class discussion, or drawing concept maps. For this initial step, it is important that students feel comfortable to share, without engaging in disagreements. The main idea is to increase students’ understanding about global warming, rather than focus on the potential controversial nature of this topic.
A major goal of this unit is to engage students in co-constructing evidence-based explanations through individual writing, sharing, re-writing, group discussion, and whole group reflection. The argumentation format presented here contains claims supported by evidence and reasoning (Claims Evidence Reasoning – CER). Argumentation in this sense is different from how the word “argument” is used in everyday language. Argumentation is a collaborative process towards an end goal, rather than a competition to win (Duschl & Osborne, 2002). Scientific argumentation is the process of negotiating and communicating findings through a series of claims supported by evidence from various sources along with a rationale or reasoning linking the claim with the evidence. For students, making the link between claim and evidence can be the most difficult part of the process.
Where does the evidence come from?
Evidence and data are often used synonymously, but there is a difference. Evidence is “the representation of data in a form that undergirds an argument that works to answer the original question” (Hand et al., 2009, p. 129). This explains why even though scientists may use the same data to draw explanations from, the final product may take different forms depending on which parts of the data were used and how. For example, in a court case experts from opposing sides may use the same data to persuade the jury to reach different conclusions. Another way to explain this distinction to students is “the story built from the data that leads to a claim is the evidence” (Hand et al., 2009, p. 129). Evidence can come from many sources – results from controlled experiments, measurements, books, articles, websites, personal observations, etc. It is important to discuss with students the issue of the source’s reliability and accuracy. When using data freely available online, ask yourself: Who conducted the study? Who funded the research? Where was it published or presented?
What is a claim and how do I find it?
A scientific claim is a statement that answers a question or an inference based on information, rather than just personal opinion.
How can I connect the claim(s) with the evidence?
That’s where the justification or reasoning comes in. This portion of the argument explains why the evidence is relevant to the claim or how the evidence supports the claim.
Implementation
Learning context and connecting to state standards.
This interdisciplinary unit can be used in an earth science class or adapted to environmental science, chemistry, or physics. The key to adapting the lesson is guiding students to sources of data that fit the discipline they are studying.
For earth science , students can explain the difference between climate and weather, describe the factors associated with global climate change, and explore a variety of data sources to draw their evidence from. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for earth and space science (secondary): 3.3.12.A1, 3.3.12.A6, 3.3.10.A7.
For environmental science , students can analyze the costs and benefits of pollution control measures. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for Environment and Ecology (secondary): 4.5.12.C.
For chemistry and physics , students can explain the function of greenhouse gases, construct a model of the greenhouse effect, and model energy flow through the atmosphere. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for Physical Sciences (secondary): 3.2.10.B6.
New Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Connections
Human impacts and global climate change are directly addressed in the NGSS. Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCI): HS-ESS3-3, HS-ESS3-4, HS-ESS3-5, HS-ESS3-6.
Lesson 1: Introduction to climate change
- What are greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect? (sample answer: greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane contribute to overall heating of the atmosphere; these gases trap heat just like the glass in a greenhouse or in a car)
- What is the difference between weather and climate? (sample answer: weather is the daily temperature and precipitation measurements, while climate is a much longer pattern over multiple years)
Drawing of the greenhouse effect – as individuals or in pairs, have students look up the greenhouse effect and draw a diagram to represent it; share out with the class
- Optional: figure out students’ beliefs about global warming using the Yale Six Americas Survey (students answer a series of questions and at the end they are given one of the following categories: alarmed, concerned, cautious, disengaged, doubtful, dismissive).

Lesson 2: Searching for and evaluating evidence
- Compare different data sources and assess their credibility
- Temperature
- Precipitation
- Storm surge
- Ask the students to think about what types of claims they can make about climate change using the data they found (Sample claims: human activity is causing global warming or sea-level rise in the next fifty years will affect coastal cities like Amsterdam, Hong Kong, or New Orleans).
Lesson 3: Writing an argument using evidence
- Claim – an inference or a statement that answers a question
- Evidence – an outside source of information that supports the claim, often drawn from selected data
- Reasoning – the justification/support for the claim; what connects the evidence with the claim
- Extending arguments – have students exchange papers and notice the strengths of the other arguments they are reading (can do multiple cycles of reading); ask students to go back to their original argument and expand it with more evidence and/or more justification for why the evidence supports the claim
- Anticipate Rebuttals – ask students to think and write about any weaknesses in their own argument
Lesson 4: Argumentation discussion
- rebuttal – challenges a component of someone’s argument – for example, a challenge to the evidence used in the original argument
- counterargument – a whole new argument that challenges the original argument
- respect group members and their ideas
- wait for group members to finish their turns before speaking
- be mindful of your own contributions to the discussion (try not to take over the whole discussion so others can contribute too; conversely, if you didn’t already talk, find a way to bring in a new argument, expand on an existing argument, or challenge another argument)
- Debate/discussion – In table groups have students share their arguments and practice rebuttals and counterarguments
- Whole-group reflection – ask students to share key points from their discussion
Lesson 5: Argumentation in action case study
Mumbai, india case study.
Rishi is a thirteen year old boy who attends the Gayak Rafi Nagar Urdu Municipal school in Mumbai. There is a massive landfill called Deonar right across from his school. Every day 4,000 tons of waste are piled on top of the existing garbage spanning 132 hectares (roughly half a square mile). Rishi ventures out to the landfill after school to look for materials that he can later trade for a little bit of extra money to help his family. He feels lucky that he gets to go to school during the day; others are not so lucky. One of his friends, Aamir, had to stop going to school and work full time after his dad got injured. They often meet to chat while they dig through the garbage with sticks. Occasionally, they find books in okay shape, which aren’t worth anything in trade, but to them they are valuable.
One day Rishi was out to the market with his mom and saw the sky darken with a heavy smoke that blocked out the sun. They both hurried home and found out there was a state of emergency and the schools closed for two days. It took many days to put out the fire at Deonar. He heard his dad say that the fire was so bad that it could be seen from space. He wonders what it would be like to see Mumbai from up there. Some days he wishes the government would close down Deonar and clean it up. Other days he wonders what would happen to all the people that depend on it to live if the city shuts down Deonar.
Mumbai is one of the coastal cities that are considered vulnerable with increasing global temperature and sea level rise. The urban poor are most affected by climate change. Their shelter could be wiped out by a tropical storm and rebuilding would be very difficult.
Write a letter to a public official who may be able to influence policy in Mumbai.
What would you recommend they do? Should they close Deonar? What can they do to reduce air pollution in the city and prepare for possible storms? Remember to use evidence in your argument.
If students want to read the articles that inspired the case study direct them to: http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/climate-change/
http://www.bloomberg.com/slideshow/2012-07-06/top-20-cities-with-billions-at-risk-from-climate-change.html#slide16
http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-07-26/smelly-dumps-drive-away-affordable-homes-in-land-starved-mumbai
http://www.cnn.com/2016/02/05/asia/mumbai-giant-garbage-dump-fire/
Resources:
- Lines of Evidence video from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine http://nas-sites.org/americasclimatechoices/videos-multimedia/climate-change-lines-of-evidence-videos/
- Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network (CLEAN)
- Climate maps from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Sources of data from NASA
- Explore the original source of the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences (PNAS) study
Differentiated Instruction
- For visual learners – use diagrams, encourage students to map out their arguments prior to writing them
- For auditory learners – use the lines of evidence video
- For ESL students – provide them with a variety of greenhouse gases diagrams, allow for a more flexible argument format and focus on general meaning-making – ex. using arrows to connect their sources of evidence to claims
- For advanced learners – ask them to search through larger data sets and make comparisons between data from different sources; they can also research environmental policies and why they stalled out in congress
- For learners that need more support – print out excerpts from articles; pinpoint the main ideas to help with the research; help students connect their evidence with their claims; consider allowing students to work in pairs to accomplish the writing task
Argument write-up – check that students’ arguments contain claims supported by evidence and reasoning and that they thought about possible weaknesses in their own arguments.
Case study letter – check that students included evidence in their letter.
References:
Duschl, R. A., & Osborne, J. (2002). Supporting and promoting argumentation discourse in science education.
Hand, B. et al. (2009) Negotiating Science: The Critical Role of Argumentation in Student Inquiry. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
McNeill, K. L., & Krajcik, J. (2012). Claim, evidence and reasoning: Supporting grade 5 – 8 students in constructing scientific explanations. New York, NY: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
Sawyer, R. K. (Ed.). (2014). The Cambridge handbook of the learning sciences. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange/kids/basics/today/greenhouse-gases.html
http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/climate-change/

Russell Millner/Alamy
Defend Our Planet and Most Vulnerable Species
Your donation today will be triple-matched to power NRDC’s next great chapter in protecting our ecosystems and saving imperiled wildlife.
What Are the Causes of Climate Change?
We can’t fight climate change without understanding what drives it.
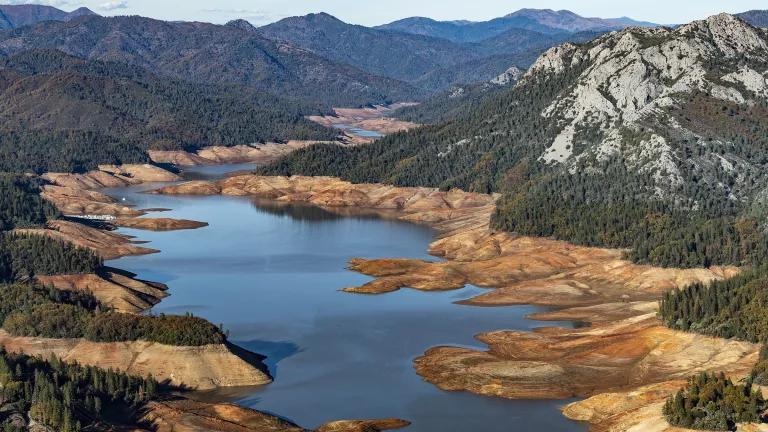

Low water levels at Shasta Lake, California, following a historic drought in October 2021
Andrew Innerarity/California Department of Water Resources

- Share this page block
At the root of climate change is the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect , the term scientists use to describe the way that certain atmospheric gases “trap” heat that would otherwise radiate upward, from the planet’s surface, into outer space. On the one hand, we have the greenhouse effect to thank for the presence of life on earth; without it, our planet would be cold and unlivable.
But beginning in the mid- to late-19th century, human activity began pushing the greenhouse effect to new levels. The result? A planet that’s warmer right now than at any other point in human history, and getting ever warmer. This global warming has, in turn, dramatically altered natural cycles and weather patterns, with impacts that include extreme heat, protracted drought, increased flooding, more intense storms, and rising sea levels. Taken together, these miserable and sometimes deadly effects are what have come to be known as climate change .
Detailing and discussing the human causes of climate change isn’t about shaming people, or trying to make them feel guilty for their choices. It’s about defining the problem so that we can arrive at effective solutions. And we must honestly address its origins—even though it can sometimes be difficult, or even uncomfortable, to do so. Human civilization has made extraordinary productivity leaps, some of which have led to our currently overheated planet. But by harnessing that same ability to innovate and attaching it to a renewed sense of shared responsibility, we can find ways to cool the planet down, fight climate change , and chart a course toward a more just, equitable, and sustainable future.
Here’s a rough breakdown of the factors that are driving climate change.
Natural causes of climate change
Human-driven causes of climate change, transportation, electricity generation, industry & manufacturing, agriculture, oil & gas development, deforestation, our lifestyle choices.
Some amount of climate change can be attributed to natural phenomena. Over the course of Earth’s existence, volcanic eruptions , fluctuations in solar radiation , tectonic shifts , and even small changes in our orbit have all had observable effects on planetary warming and cooling patterns.
But climate records are able to show that today’s global warming—particularly what has occured since the start of the industrial revolution—is happening much, much faster than ever before. According to NASA , “[t]hese natural causes are still in play today, but their influence is too small or they occur too slowly to explain the rapid warming seen in recent decades.” And the records refute the misinformation that natural causes are the main culprits behind climate change, as some in the fossil fuel industry and conservative think tanks would like us to believe.
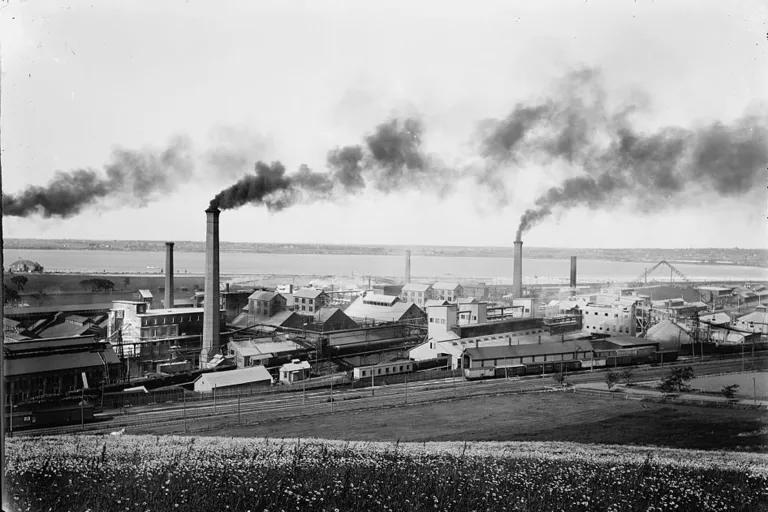

Chemical manufacturing plants emit fumes along Onondaga Lake in Solvay, New York, in the late-19th century. Over time, industrial development severely polluted the local area.
Library of Congress, Prints & Photographs Division, Detroit Publishing Company Collection
Scientists agree that human activity is the primary driver of what we’re seeing now worldwide. (This type of climate change is sometimes referred to as anthropogenic , which is just a way of saying “caused by human beings.”) The unchecked burning of fossil fuels over the past 150 years has drastically increased the presence of atmospheric greenhouse gases, most notably carbon dioxide . At the same time, logging and development have led to the widespread destruction of forests, wetlands, and other carbon sinks —natural resources that store carbon dioxide and prevent it from being released into the atmosphere.
Right now, atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane , and nitrous oxide are the highest they’ve been in the last 800,000 years . Some greenhouse gases, like hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HFCs) , do not even exist in nature. By continuously pumping these gases into the air, we helped raise the earth’s average temperature by about 1.9 degrees Fahrenheit during the 20th century—which has brought us to our current era of deadly, and increasingly routine, weather extremes. And it’s important to note that while climate change affects everyone in some way, it doesn’t do so equally: All over the world, people of color and those living in economically disadvantaged or politically marginalized communities bear a much larger burden , despite the fact that these communities play a much smaller role in warming the planet.
Our ways of generating power for electricity, heat, and transportation, our built environment and industries, our ways of interacting with the land, and our consumption habits together serve as the primary drivers of climate change. While the percentages of greenhouse gases stemming from each source may fluctuate, the sources themselves remain relatively consistent.
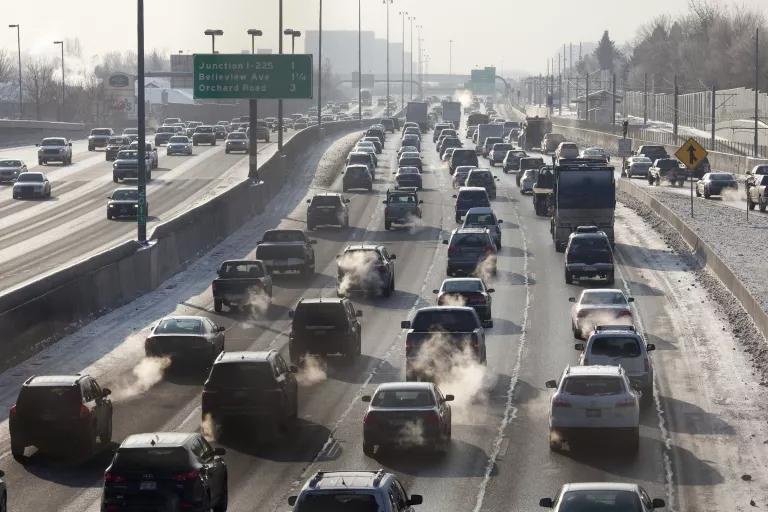

Traffic on Interstate 25 in Denver
David Parsons/iStock
The cars, trucks, ships, and planes that we use to transport ourselves and our goods are a major source of global greenhouse gas emissions. (In the United States, they actually constitute the single-largest source.) Burning petroleum-based fuel in combustion engines releases massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Passenger cars account for 41 percent of those emissions, with the typical passenger vehicle emitting about 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. And trucks are by far the worst polluters on the road. They run almost constantly and largely burn diesel fuel, which is why, despite accounting for just 4 percent of U.S. vehicles, trucks emit 23 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
We can get these numbers down, but we need large-scale investments to get more zero-emission vehicles on the road and increase access to reliable public transit .
As of 2021, nearly 60 percent of the electricity used in the United States comes from the burning of coal, natural gas , and other fossil fuels . Because of the electricity sector’s historical investment in these dirty energy sources, it accounts for roughly a quarter of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
That history is undergoing a major change, however: As renewable energy sources like wind and solar become cheaper and easier to develop, utilities are turning to them more frequently. The percentage of clean, renewable energy is growing every year—and with that growth comes a corresponding decrease in pollutants.
But while things are moving in the right direction, they’re not moving fast enough. If we’re to keep the earth’s average temperature from rising more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, which scientists say we must do in order to avoid the very worst impacts of climate change, we have to take every available opportunity to speed up the shift from fossil fuels to renewables in the electricity sector.
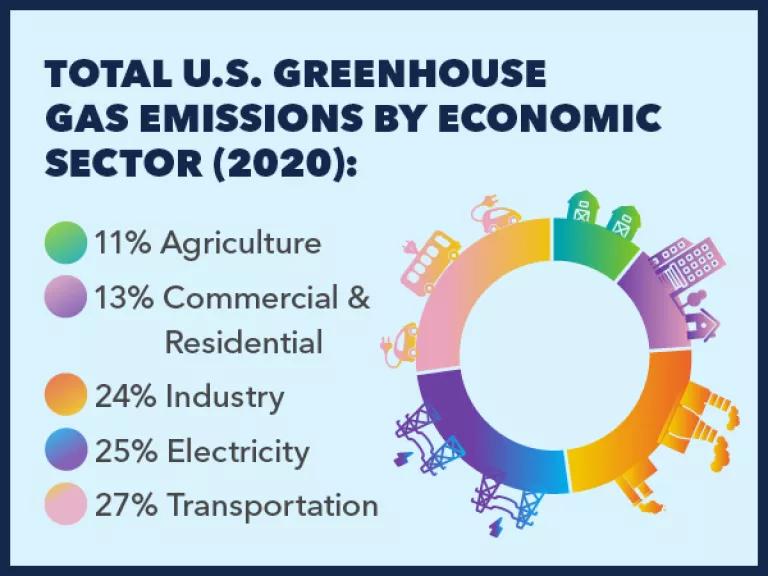
The factories and facilities that produce our goods are significant sources of greenhouse gases; in 2020, they were responsible for fully 24 percent of U.S. emissions. Most industrial emissions come from the production of a small set of carbon-intensive products, including basic chemicals, iron and steel, cement and concrete, aluminum, glass, and paper. To manufacture the building blocks of our infrastructure and the vast array of products demanded by consumers, producers must burn through massive amounts of energy. In addition, older facilities in need of efficiency upgrades frequently leak these gases, along with other harmful forms of air pollution .
One way to reduce the industrial sector’s carbon footprint is to increase efficiency through improved technology and stronger enforcement of pollution regulations. Another way is to rethink our attitudes toward consumption (particularly when it comes to plastics ), recycling , and reuse —so that we don’t need to be producing so many things in the first place. And, since major infrastructure projects rely heavily on industries like cement manufacturing (responsible for 7 percent of annual global greenhouse gas), policy mandates must leverage the government’s purchasing power to grow markets for cleaner alternatives, and ensure that state and federal agencies procure more sustainably produced materials for these projects. Hastening the switch from fossil fuels to renewables will also go a long way toward cleaning up this energy-intensive sector.
The advent of modern, industrialized agriculture has significantly altered the vital but delicate relationship between soil and the climate—so much so that agriculture accounted for 11 percent of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2020. This sector is especially notorious for giving off large amounts of nitrous oxide and methane, powerful gases that are highly effective at trapping heat. The widespread adoption of chemical fertilizers , combined with certain crop-management practices that prioritize high yields over soil health, means that agriculture accounts for nearly three-quarters of the nitrous oxide found in our atmosphere. Meanwhile, large-scale industrialized livestock production continues to be a significant source of atmospheric methane, which is emitted as a function of the digestive processes of cattle and other ruminants.
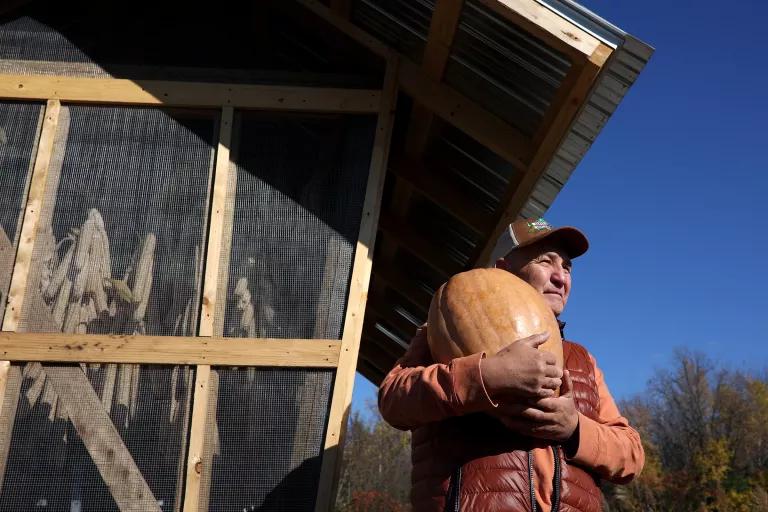

Stephen McComber holds a squash harvested from the community garden in Kahnawà:ke Mohawk Territory, a First Nations reserve of the Mohawks of Kahnawà:ke, in Quebec.
Stephanie Foden for NRDC
But farmers and ranchers—especially Indigenous farmers, who have been tending the land according to sustainable principles —are reminding us that there’s more than one way to feed the world. By adopting the philosophies and methods associated with regenerative agriculture , we can slash emissions from this sector while boosting our soil’s capacity for sequestering carbon from the atmosphere, and producing healthier foods.
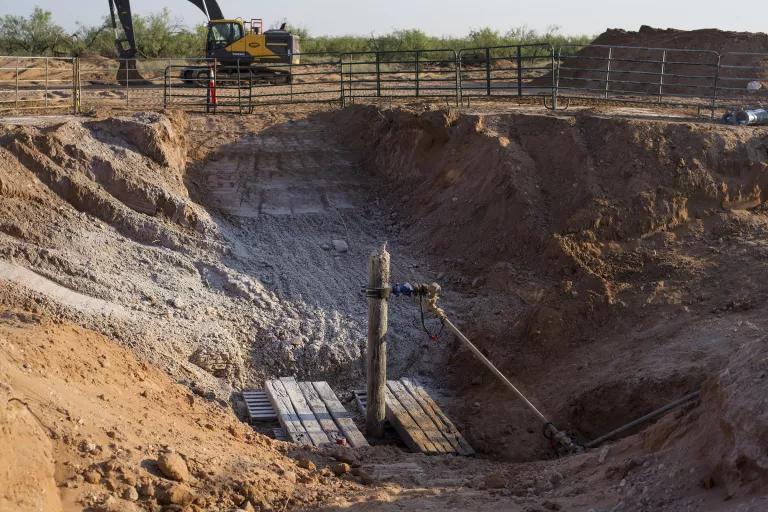

A decades-old, plugged and abandoned oil well at a cattle ranch in Crane County, Texas, in June 2021, when it was found to be leaking brine water
Matthew Busch/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Oil and gas lead to emissions at every stage of their production and consumption—not only when they’re burned as fuel, but just as soon as we drill a hole in the ground to begin extracting them. Fossil fuel development is a major source of methane, which invariably leaks from oil and gas operations : drilling, fracking , transporting, and refining. And while methane isn’t as prevalent a greenhouse gas as carbon dioxide, it’s many times more potent at trapping heat during the first 20 years of its release into the atmosphere. Even abandoned and inoperative wells—sometimes known as “orphaned” wells —leak methane. More than 3 million of these old, defunct wells are spread across the country and were responsible for emitting more than 280,000 metric tons of methane in 2018.
Unsurprisingly, given how much time we spend inside of them, our buildings—both residential and commercial—emit a lot of greenhouse gases. Heating, cooling, cooking, running appliances, and maintaining other building-wide systems accounted for 13 percent of U.S. emissions overall in 2020. And even worse, some 30 percent of the energy used in U.S. buildings goes to waste, on average.
Every day, great strides are being made in energy efficiency , allowing us to achieve the same (or even better) results with less energy expended. By requiring all new buildings to employ the highest efficiency standards—and by retrofitting existing buildings with the most up-to-date technologies—we’ll reduce emissions in this sector while simultaneously making it easier and cheaper for people in all communities to heat, cool, and power their homes: a top goal of the environmental justice movement.

An aerial view of clearcut sections of boreal forest near Dryden in Northwestern Ontario, Canada, in June 2019
River Jordan for NRDC
Another way we’re injecting more greenhouse gas into the atmosphere is through the clearcutting of the world’s forests and the degradation of its wetlands . Vegetation and soil store carbon by keeping it at ground level or underground. Through logging and other forms of development, we’re cutting down or digging up vegetative biomass and releasing all of its stored carbon into the air. In Canada’s boreal forest alone, clearcutting is responsible for releasing more than 25 million metric tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere each year—the emissions equivalent of 5.5 million vehicles.
Government policies that emphasize sustainable practices, combined with shifts in consumer behavior , are needed to offset this dynamic and restore the planet’s carbon sinks .

The Yellow Line Metro train crossing over the Potomac River from Washington, DC, to Virginia on June 24, 2022
Sarah Baker
The decisions we make every day as individuals—which products we purchase, how much electricity we consume, how we get around, what we eat (and what we don’t—food waste makes up 4 percent of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions)—add up to our single, unique carbon footprints . Put all of them together and you end up with humanity’s collective carbon footprint. The first step in reducing it is for us to acknowledge the uneven distribution of climate change’s causes and effects, and for those who bear the greatest responsibility for global greenhouse gas emissions to slash them without bringing further harm to those who are least responsible .
The big, climate-affecting decisions made by utilities, industries, and governments are shaped, in the end, by us : our needs, our demands, our priorities. Winning the fight against climate change will require us to rethink those needs, ramp up those demands , and reset those priorities. Short-term thinking of the sort that enriches corporations must give way to long-term planning that strengthens communities and secures the health and safety of all people. And our definition of climate advocacy must go beyond slogans and move, swiftly, into the realm of collective action—fueled by righteous anger, perhaps, but guided by faith in science and in our ability to change the world for the better.
If our activity has brought us to this dangerous point in human history, breaking old patterns can help us find a way out.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
We need climate action to be a top priority in Washington!
Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.

Urge President Biden and Congress to make equitable climate action a top priority in 2024
Related stories.

Greenhouse Effect 101
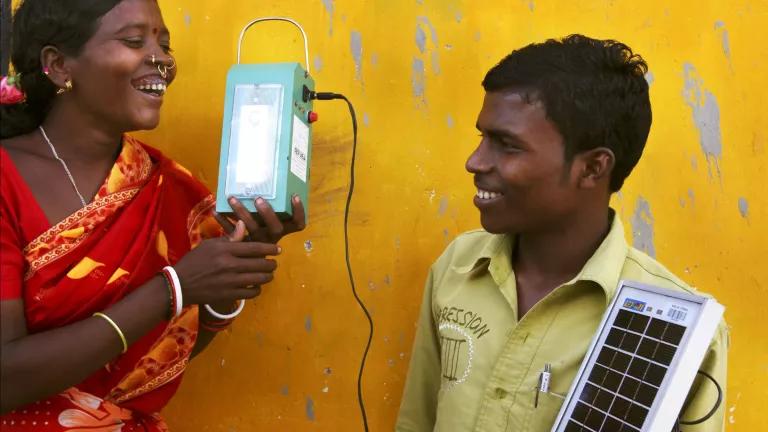

What Are the Solutions to Climate Change?
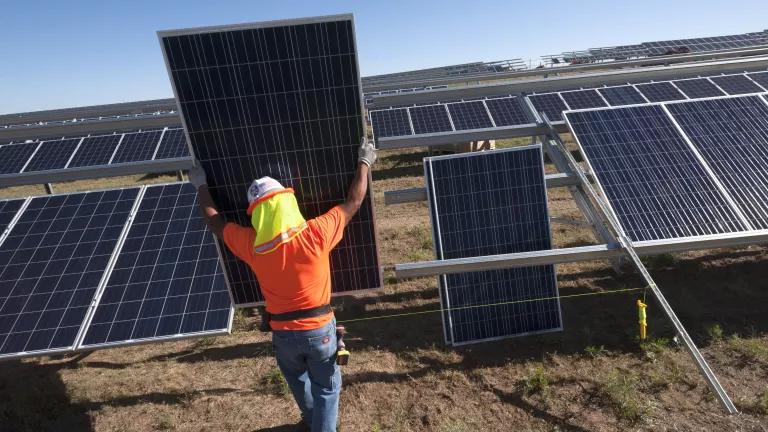

Failing to Meet Our Climate Goals Is Not an Option
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.

Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Isn't there a lot of disagreement among climate scientists about global warming?
No. By a large majority, climate scientists agree that average global temperature today is warmer than in pre-industrial times and that human activity is the most significant factor.

Today, there is no real disagreement among climate experts that humans are the primary cause of recent global warming. NOAA Climate.gov cartoon by Emily Greenhalgh.
Consensus of experts
The United States' foremost scientific agencies and organizations have recognized global warming as a human-caused problem that should be addressed. The U.S. Global Change Research Program has published a series of scientific reports documenting the causes and impacts of global climate change. NOAA , NASA , the National Science Foundation , the National Research Council , and the Environmental Protection Agency have all published reports and fact sheets stating that Earth is warming mainly due to the increase in human-produced heat-trapping gases.
On their climate home page , the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicines says, "Scientists have known for some time, from multiple lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth’s climate, primarily through greenhouse gas emissions," and that "Climate change is increasingly affecting people’s lives."

Soot from fires and air pollution contributes to global warming, and its impacts may be especially strong in the Arctic, where it darkens the snow and ice—as shown in this photo—and accelerates melting. Despite some uncertainty about just how much influence soot and other aerosol particles have played in climate change in the past century, there's little debate among climate scientists that the primary driver of recent global warming is carbon dioxide emissions. Photo from NOAA Ocean Today .
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) issued this position statement : "Scientific evidence indicates that the leading cause of climate change in the most recent half century is the anthropogenic increase in the concentration of atmospheric greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), chlorofluorocarbons, methane, tropospheric ozone, and nitrous oxide." (Adopted April 15, 2019)
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) issued this position statement : "Human activities are changing Earth's climate, causing increasingly disruptive societal and ecological impacts. Such impacts are creating hardships and suffering now, and they will continue to do so into the future—in ways expected as well as potentially unforeseen. To limit these impacts, the world's nations have agreed to hold the increase in global average temperature to well below 2°C (3.6°F) above pre-industrial levels. To achieve this goal, global society must promptly reduce its greenhouse gas emissions." (Reaffirmed in November 2019)
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) What We Know site states: "Based on the evidence, about 97 percent of climate scientists agree that human-caused climate change is happening."
Consensus of evidence
These scientific organizations have not issued statements in a void; they echo the findings of individual papers published in refereed scientific journals. The Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) maintains a database of over 8,500 peer-reviewed science journals, and multiple studies of this database show evidence of overwhelming agreement among climate scientists. In 2004, science historian Naomi Oreskes published the results of her examination of the ISI database in the journal Science . She reviewed 928 abstracts published between 1993 and 2003 related to human activities warming the Earth's surface, and stated, "Remarkably, none of the papers disagreed with the consensus position."
This finding hasn't changed with time. In 2016, a review paper summarized the results of several independent studies on peer-reviewed research related to climate. The authors found results consistent with a 97-percent consensus that human activity is causing climate change. A 2021 paper found a greater than 99-percent consensus.
Probably the most definitive assessments of global climate science come from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Founded by the United Nations in 1988, the IPCC releases periodic reports, and each major release includes three volumes: one on the science, one on impacts, and one on mitigation. Each volume is authored by a separate team of experts, who reviews, evaluates, and summarizes relevant research published since the prior report. Each IPCC report undergoes several iterations of expert and government review. The 2021 IPCC report, for instance, received and responded to more than 78,000 expert and government review comments.

Every five years, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change convenes hundreds of international scientists and government representatives to review and assess peer-reviewed research on climate science. In each cycle, the panel publishes three key reports: one on the basic science , one on impacts , and one on mitigation .
The IPCC does not involve just a few scientists, or even just dozens of scientists. An IPCC press release explains: "Thousands of people from all over the world contribute to the work of the IPCC. For the assessment reports, IPCC scientists volunteer their time to assess the thousands of scientific papers published each year to provide a comprehensive summary of what is known about the drivers of climate change, its impacts and future risks, and how adaptation and mitigation can reduce those risks."
Governments and climate experts across the globe nominate scientists for IPCC authorship, and the IPCC works to find a mix of authors, from developed and developing countries, among men and women, and among authors who are experienced with the IPCC and new to the process. Published in 2021, the Sixth Assessment Report was assembled by 751 experts from more than 60 countries (31 coordinating authors, 167 lead authors, 36 review editors, and 517 contributing authors). Collectively, the authors cited more than 14,000 scientific papers. In other words, the IPCC reports themselves are a comprehensive, consensus statement on the state climate science.
In the headline statements from the Sixth Assessment report's Summary for Policymakers, the IPCC concluded:
It is unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land. Widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere have occurred. The scale of recent changes across the climate system as a whole – and the present state of many aspects of the climate system – are unprecedented over many centuries to many thousands of years. Human-induced climate change is already affecting many weather and climate extremes in every region across the globe. Evidence of observed changes in extremes such as heatwaves, heavy precipitation, droughts, and tropical cyclones, and, in particular, their attribution to human influence, has strengthened since [our last report].
Cook, J., D. Nuccitelli, S.A. Green, M. Richardson, B. Winkler, R. Painting, R. Way, P. Jacobs, and A. Skuce (2013). Quantifying the consensus on anthropogenic global warming in the scientific literature. Environmental Research Letters , 8, 024024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024024 .
Cook, J., Oreskes, N., Doran, P.T., Anderegg, W.R.L., Verheggen, B., Mailbach, E.W., Carlton, J.S., Lewandowsky, S., Skuce, A.G., Green, S.A., Nuccitelli, D., Jacobs, P., Richardson, M., Winkler, B., Painting, R., Rice, K. (2016). Consensus on consensus: A synthesis of consensus estimates on human-caused global warming. Environmental Research Letters , 11, 048002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/048002 .
Doran, P., and M.K. Zimmerman (2009): Examining the Scientific Consensus on Climate Change. Eos , 90(3), 22–23.
IPCC. (2013). Factsheet: How does the IPCC select its authors? Accessed January 3, 2020.
IPCC. (2014). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva Switzerland. Accessed January 22, 2020.
IPCC. (2021). Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 3−32, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.001.
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report. (2021). https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
Lynas, M., Houlton, B.Z., Perry, S. (2021). Greater than 99% consensus on human caused climate change in the peer-reviewed scientific literature. Environmental Research Letters , 16, 114005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac2966 .
Oreskes, N. (2004). The Scientific Consensus on Climate Change. Science , 306, 1686. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1103618 .
Oreskes, N. (2018). The scientific consensus on climate change: How do we know we're not wrong? Climate Modelling , pp. 31–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65058-6_2 .
Sherwood, S. (2011, May 10). Trust us, we're climate scientists: The case for the IPCC . The Conversation .
We value your feedback
Help us improve our content
Related Content
News & features, talking with ipcc vice-chair ko barrett: on climate change and consensus building, what's it like to be an author for the ipcc report, 2016 arctic heat would have been virtually impossible without global warming, national climate assessment map shows uneven impact of future global warming on u.s. energy spending, maps & data, climate forcing, future climate, climate models, teaching climate, toolbox for teaching climate & energy, the smap/globe partnership: citizen scientists measure soil moisture, climate youth engagement, climate resilience toolkit, climate change 2007: the physical science basis, advancing the science of climate change, the effects of climate change on agriculture, land resources, water resources, and biodiversity in the united states.

There is unequivocal evidence that Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate. Human activity is the principal cause.

- While Earth’s climate has changed throughout its history , the current warming is happening at a rate not seen in the past 10,000 years.
- According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC ), "Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact." 1
- Scientific information taken from natural sources (such as ice cores, rocks, and tree rings) and from modern equipment (like satellites and instruments) all show the signs of a changing climate.
- From global temperature rise to melting ice sheets, the evidence of a warming planet abounds.
The rate of change since the mid-20th century is unprecedented over millennia.
Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 800,000 years, there have been eight cycles of ice ages and warmer periods, with the end of the last ice age about 11,700 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth’s orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives.
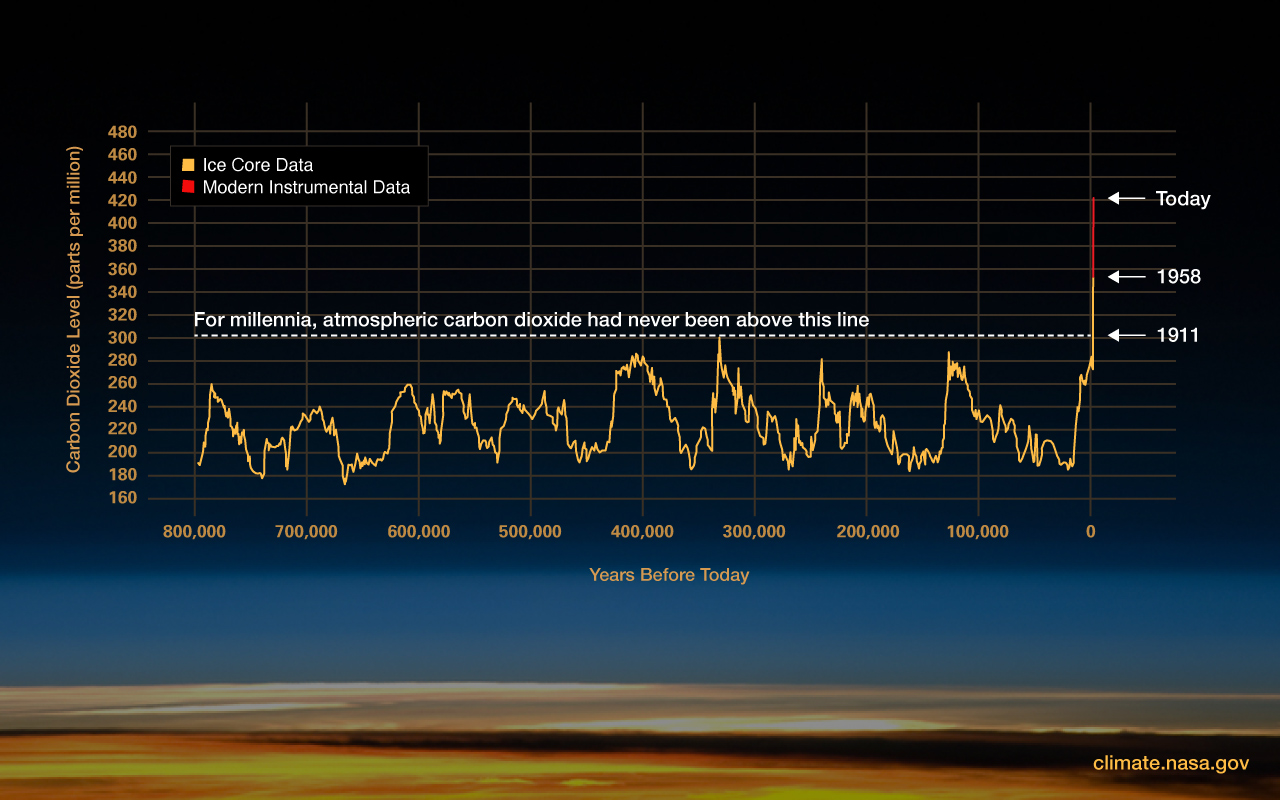
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun’s energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, and biosphere have occurred.
Earth-orbiting satellites and new technologies have helped scientists see the big picture, collecting many different types of information about our planet and its climate all over the world. These data, collected over many years, reveal the signs and patterns of a changing climate.
Scientists demonstrated the heat-trapping nature of carbon dioxide and other gases in the mid-19th century. 2 Many of the science instruments NASA uses to study our climate focus on how these gases affect the movement of infrared radiation through the atmosphere. From the measured impacts of increases in these gases, there is no question that increased greenhouse gas levels warm Earth in response.
Scientific evidence for warming of the climate system is unequivocal.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Ice cores drawn from Greenland, Antarctica, and tropical mountain glaciers show that Earth’s climate responds to changes in greenhouse gas levels. Ancient evidence can also be found in tree rings, ocean sediments, coral reefs, and layers of sedimentary rocks. This ancient, or paleoclimate, evidence reveals that current warming is occurring roughly 10 times faster than the average rate of warming after an ice age. Carbon dioxide from human activities is increasing about 250 times faster than it did from natural sources after the last Ice Age. 3
The Evidence for Rapid Climate Change Is Compelling:

Global Temperature Is Rising
The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities. 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest. The years 2016 and 2020 are tied for the warmest year on record. 5 Image credit: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.

The Ocean Is Getting Warmer
The ocean has absorbed much of this increased heat, with the top 100 meters (about 328 feet) of ocean showing warming of 0.67 degrees Fahrenheit (0.33 degrees Celsius) since 1969. 6 Earth stores 90% of the extra energy in the ocean. Image credit: Kelsey Roberts/USGS

The Ice Sheets Are Shrinking
The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets have decreased in mass. Data from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment show Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019, while Antarctica lost about 148 billion tons of ice per year. 7 Image: The Antarctic Peninsula, Credit: NASA

Glaciers Are Retreating
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world — including in the Alps, Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alaska, and Africa. 8 Image: Miles Glacier, Alaska Image credit: NASA

Snow Cover Is Decreasing
Satellite observations reveal that the amount of spring snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased over the past five decades and the snow is melting earlier. 9 Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
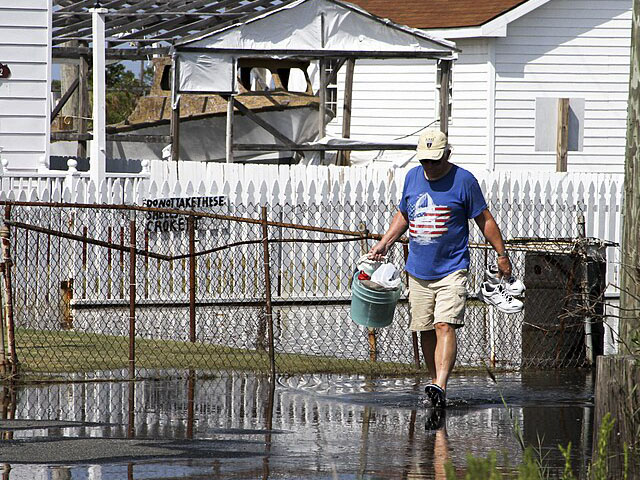

Sea Level Is Rising
Global sea level rose about 8 inches (20 centimeters) in the last century. The rate in the last two decades, however, is nearly double that of the last century and accelerating slightly every year. 10 Image credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Norfolk District

Arctic Sea Ice Is Declining
Both the extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice has declined rapidly over the last several decades. 11 Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
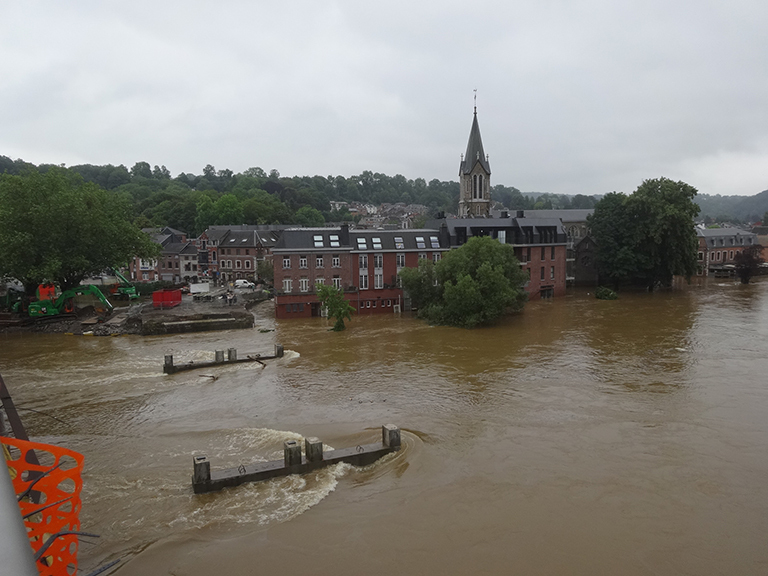

Extreme Events Are Increasing in Frequency
The number of record high temperature events in the United States has been increasing, while the number of record low temperature events has been decreasing, since 1950. The U.S. has also witnessed increasing numbers of intense rainfall events. 12 Image credit: Régine Fabri, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons

Ocean Acidification Is Increasing
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 30%. 13 , 14 This increase is due to humans emitting more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and hence more being absorbed into the ocean. The ocean has absorbed between 20% and 30% of total anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions in recent decades (7.2 to 10.8 billion metric tons per year). 1 5 , 16 Image credit: NOAA
1. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WGI, Technical Summary . B.D. Santer et.al., “A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere.” Nature 382 (04 July 1996): 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1038/382039a0. Gabriele C. Hegerl et al., “Detecting Greenhouse-Gas-Induced Climate Change with an Optimal Fingerprint Method.” Journal of Climate 9 (October 1996): 2281-2306. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2281:DGGICC>2.0.CO;2. V. Ramaswamy, et al., “Anthropogenic and Natural Influences in the Evolution of Lower Stratospheric Cooling.” Science 311 (24 February 2006): 1138-1141. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122587. B.D. Santer et al., “Contributions of Anthropogenic and Natural Forcing to Recent Tropopause Height Changes.” Science 301 (25 July 2003): 479-483. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084123. T. Westerhold et al., "An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years." Science 369 (11 Sept. 2020): 1383-1387. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094123
2. In 1824, Joseph Fourier calculated that an Earth-sized planet, at our distance from the Sun, ought to be much colder. He suggested something in the atmosphere must be acting like an insulating blanket. In 1856, Eunice Foote discovered that blanket, showing that carbon dioxide and water vapor in Earth's atmosphere trap escaping infrared (heat) radiation. In the 1860s, physicist John Tyndall recognized Earth's natural greenhouse effect and suggested that slight changes in the atmospheric composition could bring about climatic variations. In 1896, a seminal paper by Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius first predicted that changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels could substantially alter the surface temperature through the greenhouse effect. In 1938, Guy Callendar connected carbon dioxide increases in Earth’s atmosphere to global warming. In 1941, Milutin Milankovic linked ice ages to Earth’s orbital characteristics. Gilbert Plass formulated the Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climate Change in 1956.
3. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2 Vostok ice core data; NOAA Mauna Loa CO2 record O. Gaffney, W. Steffen, "The Anthropocene Equation." The Anthropocene Review 4, issue 1 (April 2017): 53-61. https://doi.org/abs/10.1177/2053019616688022.
4. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/monitoring https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/temperature/ http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp
5. https://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/news/20170118/
6. S. Levitus, J. Antonov, T. Boyer, O Baranova, H. Garcia, R. Locarnini, A. Mishonov, J. Reagan, D. Seidov, E. Yarosh, M. Zweng, " NCEI ocean heat content, temperature anomalies, salinity anomalies, thermosteric sea level anomalies, halosteric sea level anomalies, and total steric sea level anomalies from 1955 to present calculated from in situ oceanographic subsurface profile data (NCEI Accession 0164586), Version 4.4. (2017) NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/3M_HEAT_CONTENT/index3.html K. von Schuckmann, L. Cheng, L,. D. Palmer, J. Hansen, C. Tassone, V. Aich, S. Adusumilli, H. Beltrami, H., T. Boyer, F. Cuesta-Valero, D. Desbruyeres, C. Domingues, A. Garcia-Garcia, P. Gentine, J. Gilson, M. Gorfer, L. Haimberger, M. Ishii, M., G. Johnson, R. Killick, B. King, G. Kirchengast, N. Kolodziejczyk, J. Lyman, B. Marzeion, M. Mayer, M. Monier, D. Monselesan, S. Purkey, D. Roemmich, A. Schweiger, S. Seneviratne, A. Shepherd, D. Slater, A. Steiner, F. Straneo, M.L. Timmermans, S. Wijffels. "Heat stored in the Earth system: where does the energy go?" Earth System Science Data 12, Issue 3 (07 September 2020): 2013-2041. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-2013-2020.
7. I. Velicogna, Yara Mohajerani, A. Geruo, F. Landerer, J. Mouginot, B. Noel, E. Rignot, T. Sutterly, M. van den Broeke, M. Wessem, D. Wiese, "Continuity of Ice Sheet Mass Loss in Greenland and Antarctica From the GRACE and GRACE Follow-On Missions." Geophysical Research Letters 47, Issue 8 (28 April 2020): e2020GL087291. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087291.
8. National Snow and Ice Data Center World Glacier Monitoring Service
9. National Snow and Ice Data Center D.A. Robinson, D. K. Hall, and T. L. Mote, "MEaSUREs Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Cover Extent Daily 25km EASE-Grid 2.0, Version 1 (2017). Boulder, Colorado USA. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. doi: https://doi.org/10.5067/MEASURES/CRYOSPHERE/nsidc-0530.001 . http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/snow_extent.html Rutgers University Global Snow Lab. Data History
10. R.S. Nerem, B.D. Beckley, J. T. Fasullo, B.D. Hamlington, D. Masters, and G.T. Mitchum, "Climate-change–driven accelerated sea-level rise detected in the altimeter era." PNAS 15, no. 9 (12 Feb. 2018): 2022-2025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717312115.
11. https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/sea_ice.html Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS, Zhang and Rothrock, 2003) http://psc.apl.washington.edu/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/ http://psc.apl.uw.edu/research/projects/projections-of-an-ice-diminished-arctic-ocean/
12. USGCRP, 2017: Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume I [Wuebbles, D.J., D.W. Fahey, K.A. Hibbard, D.J. Dokken, B.C. Stewart, and T.K. Maycock (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, 470 pp, https://doi.org/10.7930/j0j964j6 .
13. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/What+is+Ocean+Acidification%3F
14. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/Ocean+Acidification
15. C.L. Sabine, et al., “The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2.” Science 305 (16 July 2004): 367-371. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097403.
16. Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate , Technical Summary, Chapter TS.5, Changing Ocean, Marine Ecosystems, and Dependent Communities, Section 5.2.2.3. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/technical-summary/
Header image shows clouds imitating mountains as the sun sets after midnight as seen from Denali's backcountry Unit 13 on June 14, 2019. Credit: NPS/Emily Mesner Image credit in list of evidence: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Critical analysis.
In extreme climate change, not enough has been done about recycling and lessening carbon emissions. Bill McKibben, who was responsible for The End of Nature book believes that humans should take steps toward creating a sustainable future by reducing their carbon footprint (Dujardin, 2022). The debate between Bill McKibben and Jim Jensen seeks to identify the role humans should play in addressing climate change. The responsibility to address climate change rests with every person on Earth to manage their carbon footprint by placing awareness on the environmental and climactic impact that individual actions will have on global climate change. What sets McKibben and Jensen apart is not their viewpoints per se, but rather the categorization of what each writer views as ‘responsibility’ when addressing the climate crisis (Howarth et al., 2022). This paper will further examine why McKibben’s arguments on the issue of responsibility and the role of ideology in understanding climate change seem far more logical than Jensen’s arguments on this particular topic.
In this debate, they argue that the current generation of Earth’s inhabitants should be more responsible than their parents and grandparents and that they must act now. McKibben’s argument is believable because he writes in a logical and persuasive way. He uses clear language that appeals to common sense but has some emotion thrown in for good measure. The author uses rhetorical devices such as ethos, pathos, and logos to make his point. His essay makes use of all three strategies: ethos (the author is credible), pathos (the author uses emotion effectively), and logos (the author presents an argument based on facts) (Dujardin, 2022). Jensen does not use much sentimentality or sensationalism in his argument. He focuses primarily on logic instead of emotion when making his points about how people should respond to climate change. It makes it seem like he has a good understanding of the science behind what he is saying, but this does not necessarily mean that people will believe him.
McKibben is trying to make the point that people are responsible for their actions and therefore have a responsibility to act. He states, “This is the moment when we must choose: whether we will be part of the problem or the solution” (Howarth et al., 2022). On the other hand, Jensen says people are not responsible for climate change because it is just an unfortunate occurrence; he says, “It’s not our fault” (Dujardin, 2022). McKibben uses pathos to make his audience sympathize with what they are going through and how they should respond. He writes: “We’re at a moment when this desperate problem demands an urgent response—and we know what action will get us there” (Dujardin, 2022). McKibben believes a huge problem needs immediate attention and feels obligated to lead by example. Jensen uses ethos in arguing against McKibben’s claim by saying that his argument relies too much on sentimentality. He uses emotional appeals instead of logical ones; he talks about how horrible it would be if there were no future generations because of climate change while ignoring the fact that other problems face humanity today, such as poverty or war (Dujardin, 2022).
In his essay, McKibben argues that the responsibility to address climate change falls on those most responsible for creating it. He states that if one wants to stop the destruction caused by climate change, one must acknowledge their role in its creation. The author argues that people should address climate change by taking personal responsibility for our actions and their impact on the environment. He claims that this approach will motivate people to do more than change what they consume and how they live their lives. McKibben uses much evidence to support his argument. He cites studies and reports from scientists who say that human activity is causing global warming and is a severe threat to humanity’s future. He also uses historical precedent: he points out that in the past century, carbon dioxide levels have risen 50% while temperatures have increased by 1°C (1°F) (Howarth et al., 2022).
The author relies heavily on evidence to make his point, but he sometimes neglects pathos, the emotional appeal of words, in favor of cold hard facts. For example, when addressing how much carbon dioxide we have released into our atmosphere this century, McKibben writes, “We have set ourselves on a course toward catastrophic warming” (Dujardin, 2022). This statement is accurate: we have emitted more carbon dioxide than ever before in human history. But there are many other ways to demonstrate this exact point that do not rely so heavily on numbers and facts.
McKibben uses the example of a small New England town dealing with droughts and flooding for years. He says they have done everything they can to protect themselves from these events but cannot stop them. McKibben claims that climate change is different from other natural disasters because humans have caused it, so people are responsible for fixing it. He claims that people need to invest in renewable energy sources and stop using fossil fuels immediately, or they could face serious consequences. While there are many facts about climate change, such as the fact that it has increased in severity since the Industrial Revolution began 100 years ago, which means humans are responsible (Howarth et al., 2022). There is also a lack of evidence that this will cause irreparable damage to our planet’s ecosystem. However, McKibben uses no pathos or ethos in his argument; he relies too much on cold hard facts without any use of emotion.
I believe both are credible people in the debate between McKibben and Jensen. McKibben is very well-spoken and logical in his arguments, while Jensen’s argument is persuasive because he uses statistics to back up his points. The first part of their discussion discusses responsibility and how it can influence climate change. McKibben believes one must be responsible for their actions, especially as a nation. He believes people should be taking action now to reduce fossil fuel use. The author further believes that individuals can impact the climate crisis through actions such as changing light bulbs or carpooling with friends. In addition, McKibben has a lot of credibilities because he has a long history as an environmental activist and climate change advocate (Howarth et al., 2022). He also has a strong voice with which he communicates his message, one that is thoroughly informed by his scientific education yet still has a sense of urgency about the situation. Even though McKibben may not have all the answers on how to solve climate change, he does have a unique and vital perspective on what needs to be done to address it.
Jensen counters these claims by explaining how much more work needs to be done before the change will occur on a large scale. He argues that if everyone acted individually instead of collectively, there would be no real impact on global warming. Jensen’s argument is believable because he uses ethos in two ways. First, he provides evidence from research studies showing how humans influence global warming (Howarth et al., 2022). Second, he provides evidence showing how countries can take action now using their resources but also save money down the road by investing in renewable energy infrastructure rather than later using fossil fuels.
In the case of the climate change argument, one would believe that environmental responsibility should take precedence over individual rights. First, and regarding the environment, humans are not inherently responsible for their environment; they are inherently responsible for each other. As spiritual ancestors have said, people do not inherit the Earth from their ancestors; they borrow it from their children. People are currently borrowing from their future, which is a violation of a sacred trust. It is not meant to be alarmist; instead, this is what the writer believes after researching the subject matter and applying logic and philosophical grounding.
It was an exciting and thought-provoking topic that forced the researcher to now look at the arguments from both sides of the spectrum. Before, the writer had a clear idea of personal stance on this debate. However, after researching both sides for a number of days and reading through numerous articles about the debate, the researcher found that he could no longer remain impartial. He now agree with McKibben more than he did with Jensen. Although Jensen has some good points about being cautious about geoengineering, he does not seem to understand how profound climate change is as a crisis. People often think it is not that big of a deal because it may happen in the future, but we already see the effects today. McKibben makes it very clear in his article why people must make drastic changes immediately before it is too late.
Dujardin, S. (2020). Planning with climate change? A poststructuralist approach to climate change adaptation . Annals of the American Association of Geographers , 110 (4), 1059-1074. Web.
Howarth, C., Lane, M., & Slevin, A. (2022). Addressing the climate crisis: local action in theory and practice . Palgrave Macmillan.
- Conflict Management in the Healthcare Workplace
- The Jensen Hughes Company's Team Management
- The Jensen Hughes Firm's Leadership Development and Training
- Climate Change: KWL Analysis and Reflection
- The Greenhouse Emissions Reduction
- Climate Change and Baseball: Bidirectional Relationship
- The Oil Industry's Impact on the Climate Crisis
- Climate Change Affecting Snow Management in Ski Resorts
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 28). Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility. https://ivypanda.com/essays/climate-change-crisis-the-role-of-responsibility/
"Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility." IvyPanda , 28 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/climate-change-crisis-the-role-of-responsibility/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility'. 28 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility." May 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/climate-change-crisis-the-role-of-responsibility/.
1. IvyPanda . "Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility." May 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/climate-change-crisis-the-role-of-responsibility/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility." May 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/climate-change-crisis-the-role-of-responsibility/.
Home / Everyday actions / 6 Claims Made by Climate Change Skeptics—and How to Respond
6 Claims Made by Climate Change Skeptics—and How to Respond
Filed Under: Everyday actions | Tagged: Climate Last updated November 1, 2022
It’s hard to believe, but apparently more than a few climate change deniers still roam our ever-heating planet. According to a recent study in the esteemed science journal PLOS , people systematically understate their disbelief in human-caused climate change when answering surveys, so skepticism is more prevalent than many of us realize.
Given the urgency of the climate crisis, it’s crucial that we all do our part to educate any doubters we might encounter. That’s why the Rainforest Alliance has compiled six arguments commonly made by climate change deniers, along with science-backed responses you can deploy to convince them of the truth: that climate change is real, accelerating, and that we need to take bold action ASAP.
1. Climate change denier claim: “This is the coldest winter we’ve had in years! So much for global warming.”

There’s a difference between climate and weather: Weather fluctuates day in, day out, whereas climate refers to long term trends—and the overall trend is clearly and indisputably a warming one. While the impacts of climate change have only just begun to hit the Global North, farmers in the tropics have been contending with impacts—from droughts to floods to a proliferation of crop-destroying pests—for years. That’s why the Rainforest Alliance works with farmers to take a climate-smart approach . That means first assessing a farm’s particular climate risks, taking the crop and local ecosystem into account, then finding the right combination of tools to manage the farms climate challenges. That’s what makes climate-smart agriculture “smart.”
2. “Climate change is natural and normal—it’s happened at other points in history.”
It’s true that there have been periods of global warming and cooling—also related to spikes and lulls in greenhouse gases—during the Earth’s long history. But those historic increases in CO 2 should be a warning to us: They led to serious environmental disruptions, including mass extinctions. Today, humans are emitting greenhouse gases at a far higher rate than any previous increase in history . (Before you collapse into a puddle of despair, however, find out about our work to promote natural climate solutions , like community forestry and regenerative agriculture.)
3. “There’s no consensus among scientists that climate change is real.”
Wrong. There is nearly 100 percent agreement among scientists. Moreover, the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) says that global warming is accelerating, and will reach 1.C above pre-Industrial levels around 2030 —a full decade earlier than previously forecast .
Sign up for useful tips to green your life and protect our planet.
4. “Plants and animals can adapt.”
Wrong again. Because human-caused climate change is happening so rapidly, species simply don’t have time to adapt . Frogs tell the story best: With their semi-permeable skin, unprotected eggs, and reliance on external temperatures to regulate their own, they are often among the first species to die off when ecosystems tip out of balance—and they’re dying off in droves. The Rainforest Alliance chose a frog as its mascot more than 30 years ago precisely because it’s a bio-indicator: A healthy frog population signals a healthy ecosystem, which is what we’ve been working to promote—along with thriving communities—since 1987.
5. “Climate change is good for us.”
It’s hard to even know where to begin to address this statement by climate change deniers, especially when you think about the human cost of a warming planet. The evidence points to a clear link between climate change and a surge in modern slavery : When crop failures, drought, floods, or fires wipe out livelihoods and homes, people migrate in the hopes of improving their lot—but can find themselves vulnerable to human trafficking and forced labor and other human rights abuses. And the overall economic cost is staggering: The global economy could lose $23 trillion to climate change by 2050 .
6. “OK, maybe climate change is real, but there’s nothing to be done—it’s too late.”
It’s true that we don’t have a moment to waste, but it’s not too late. If governments, business, and individuals begin taking drastic action now, we can keep warming within the 1.5C target set by the Paris Agreement. What can you do to make sure that happens? A lot. Here are actions you can take —both to make your daily life more sustainable and to push governments and companies to act—to secure a better future.
2023 Was One Of The Hottest Years On Record. Will 2024 Be Worse?
You might also like....

5 Ways to Build Collective Climate Impact through Individual Actions

Global Climate Strike: 5 Youth Activists Who Are Leading the Charge on Climate Action

5 of Your Favorite Foods Threatened by Climate Change

How to Talk to Kids About Climate Change (Without Freaking Them Out)
Coming soon, eudr deforestation risk assessment tool.
Does your company source cocoa and/or coffee? Sign up for our new tool to help meet your EUDR requirements.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Paul Krugman
The Stench of Climate Change Denial

By Paul Krugman
Opinion Columnist
This may sound a bit weird, but when I think about my adolescent years, I sometimes associate them with the faint smell of sewage.
You see, when I was in high school, my family lived on the South Shore of Long Island, where few homes had sewer connections. Most had septic tanks, and there always seemed to be an overflowing tank somewhere upwind.
Most of Nassau County eventually got sewered . But many American homes, especially in the Southeast, aren’t connected to sewer lines, and more and more septic tanks are overflowing, on a scale vastly greater than what I remember from my vaguely smelly hometown — which is both disgusting and a threat to public health.
The cause? Climate change. Along the Gulf and South Atlantic coasts, The Washington Post reported last week, “sea levels have risen at least six inches since 2010.” This may not sound like much, but it leads to rising groundwater and elevated risks of overflowing tanks.
The emerging sewage crisis is only one of many disasters we can expect as the planet continues to warm, and nowhere near the top of the list. But it seems to me to offer an especially graphic illustration of two points. First, the damage from climate change is likely to be more severe than even pessimists have tended to believe. Second, mitigation and adjustment — which are going to be necessary, because we’d still be headed for major effects of climate change even if we took immediate action to greatly reduce greenhouse gas emissions — will probably be far more difficult, as a political matter, than it should be.
On the first point: Estimating the costs of climate change and, relatedly, the costs polluters impose every time they emit another ton of carbon dioxide requires fusing results from two disciplines. On one side, we need physical scientists to figure out how much greenhouse gas emissions will warm the planet, how this will change weather patterns and so on. On the other, we need economists to estimate how these physical changes will affect productivity, health care costs and more.
Actually, there’s a third dimension: social and geopolitical risk. How, for example, will we deal with millions or tens of millions of climate refugees? But I don’t think anyone knows how to quantify those risks.
Anyway, the physical side of this endeavor looks very solid. There has, of course, been a decades-long campaign aiming to discredit climate research and, in some instances, defame individual climate scientists . But if you step back from the smears, you realize that climatology has been one of history’s great analytical triumphs. Climate scientists correctly predicted, decades in advance, an unprecedented rise in global temperatures. They even appear to have gotten the magnitude more or less right .
The economic side of the effort looks flakier. That’s not because economists haven’t tried. Indeed, in 2018, William Nordhaus received a Nobel largely for his work on “integrated assessment models” that try to put the climate science and the economic analysis together.
Yet with all due respect — Nordhaus happens to have been my first mentor in economics! — I’ve long been worried that these models understate the economic costs of climate change, because so many things you weren’t thinking of can go wrong. The prospect of part of America awash in sewage certainly wasn’t on my list.
There has been a trend in recent studies to mark up estimates of the damage from climate change. The uncertainty remains huge, but it’s a good guess that things will be even worse than you thought.
So what are we going to do about it? Even if we were to take drastic steps to reduce emissions right now, many of the consequences of past emissions, including much bigger increases in sea level than we’ve seen so far, are already, as it were, baked in. So we’re going to have to take a wide range of steps to mitigate the damage — including expanding sewer systems to limit the rising tide of, um, sludge.
But will we take those steps? Climate denial was originally all about fossil fuel interests, and to some extent it still is. But it has also become a front in the culture war , with politicians like Ron DeSantis of Florida — who happens to be the governor of one of the states at greatest immediate risk — apparently deciding that even mentioning climate change is woke.
Now imagine the collision between that kind of politics and the urgent need for substantial public spending, on everything from sea walls to sewer systems, to limit climate damage. Spending on that scale will almost surely require new tax revenue. How quickly do you think right-wing culture warriors will agree to that?
So I’m very worried about the climate future. We probably won’t do enough to limit emissions; President Biden has done far more than any of his predecessors, but it’s still not enough, and Donald Trump has promised oil executives that if he wins, he will reverse much of what Biden has done. Beyond that, we’re unlikely to do enough to limit the damage.
In short, it’s not hard to see some terrible outcomes in the not-too-distant future, even before full global catastrophe arrives. Bad stuff is coming, and we’re already starting to smell it.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Paul Krugman has been an Opinion columnist since 2000 and is also a distinguished professor at the City University of New York Graduate Center. He won the 2008 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his work on international trade and economic geography. @ PaulKrugman

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Introduction. The first step is to introduce the topic and provide an overview of the main points you will cover in the essay. This should include a brief description of what climate change is. Furthermore, it should include current research on how humans are contributing to global warming.
Today's climate change is driven by human activities. Scientists know that the warming climate is caused by human activities because: Human activities have increased the abundance of heat-trapping gases in the atmosphere. This increase is mostly due to burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
Humans emissions and activities have caused around 100% of the warming observed since 1950, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) fifth assessment report. Here Carbon Brief examines how each of the major factors affecting the Earth's climate would influence temperatures in isolation - and how their combined ...
By Tonya T. Neaves. The climate is changing — the thing is, it isn't just due to humans. Natural forces beyond human control are also gradually affecting our climate. These geophysical forces ...
Climate change is the long-term changes in global temperatures and other characteristics of the atmosphere such as wind patterns or the amount of precipitation. These shifts may affect one region, many regions, or the whole planet. The type of climate change that concerns our generation is global warming, as the planet warms quickly, mostly due ...
The scientific consensus. Within the scientific community, there is essentially no disagreement on the causes of climate change. Multiple studies have shown that at least 97 percent of scientists agree that global warming is happening and that human activity is the primary cause. Major scientific assessments also agree.
Air pollution is detrimental to human health. Malnutrition is linked to a variety of illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It can also increase the risk of stunting, or ...
Summary. Subject (s): Earth Science. Topic: Climate Change and Sustainability. Grade/Level: 9-12 (can be adapted to grades 6-8) Objectives: Students will be able to write a scientific argument using evidence and reasoning to support claims. Students will also be able to reflect on the weaknesses in their own arguments in order to improve their ...
Students were asked to submit essays on climate change, to raise their awareness about the environment. ... According to the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans cause a dramatic increase in global temperatures. Humans are the leading cause of global warming, and humans should be the ones who may stop it. This matter must ...
Building on two previous studies, a landmark 2013 peer-reviewed study evaluated 10,306 scientists to confirm that over 97 percent climate scientists agree, and over 97 percent of scientific articles find that global warming is real and largely caused by humans.. A 2016 peer-reviewed paper examined existing studies on consensus in climate research, and concluded that the 97 percent estimate is ...
A spark of change. "Most human beings have an almost infinite capacity for taking things for granted," says Aldous Huxley in one of his books. He perfectly summarises the biggest cause of the issues the world of today struggles with, the issues that are created by humans' tendency to ignore the consequences of their actions.
Despite decades of evidence, most Americans don't believe that humans are causing climate change. Last week during his tour of Asia, President Barack Obama struck a new global warming deal with ...
Argumentative Essay about Climate Change. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Climate change is regarded as an ethical issue on the basis that which moral framework must we follow in our decision-making patterns.
Climate denialists often point to these natural climate changes as a way to cast doubt on the idea that humans are causing climate to change today. However, that argument rests on a logical fallacy.
Natural causes of climate change. Some amount of climate change can be attributed to natural phenomena. Over the course of Earth's existence, volcanic eruptions, fluctuations in solar radiation ...
06/28/2021. Scientists have been exploring the cause of the planet's rising temperature since the 20th century. Climate change skeptics say that human-caused CO2 emissions don't have an effect. DW ...
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...
Full story. We know this warming is largely caused by human activities because the key role that carbon dioxide plays in maintaining Earth's natural greenhouse effect has been understood since the mid-1800s. Unless it is offset by some equally large cooling influence, more atmospheric carbon dioxide will lead to warmer surface temperatures.
Published October 29, 2020. Yes, by increasing the abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, human activities are amplifying Earth's natural greenhouse effect. Virtually all climate scientists agree that this increase in heat-trapping gases is the main reason for the 1.8°F (1.0°C) rise in global average temperature since the late ...
Published February 3, 2020. No. By a large majority, climate scientists agree that average global temperature today is warmer than in pre-industrial times and that human activity is the most significant factor. Today, there is no real disagreement among climate experts that humans are the primary cause of recent global warming.
While Earth's climate has changed throughout its history, the current warming is happening at a rate not seen in the past 10,000 years.; According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (), "Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact."
Introduction. In extreme climate change, not enough has been done about recycling and lessening carbon emissions. Bill McKibben, who was responsible for The End of Nature book believes that humans should take steps toward creating a sustainable future by reducing their carbon footprint (Dujardin, 2022). The debate between Bill McKibben and Jim Jensen seeks to identify the role humans should ...
4. "Plants and animals can adapt." Wrong again. Because human-caused climate change is happening so rapidly, species simply don't have time to adapt.Frogs tell the story best: With their semi-permeable skin, unprotected eggs, and reliance on external temperatures to regulate their own, they are often among the first species to die off when ecosystems tip out of balance—and they're ...
"The scientific understanding of climate change is now sufficiently clear to justify nations taking prompt action." Some argue that the recent global warming is due to natural fluctuations and not to human activities. This argument and its fallacies are discussed below. Argument 1: CO 2 is not coming from human activities CO 2
That's 19 more days than in a hypothetical world without human-caused warming. In some states, including Arizona and New Mexico in the Southwest and Washington and Oregon in the Northwest, the ...
The Stench of Climate Change Denial. This may sound a bit weird, but when I think about my adolescent years, I sometimes associate them with the faint smell of sewage. You see, when I was in high ...