- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes

You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A business budget estimates future revenue and expenses in detail, so that you can see whether you’re on track to meet financial expectations for the month, quarter or year. Think of your budget as a point of comparison — you run your actual numbers against it to determine if you’re over or under budget.
From there, you can make informed business decisions and pivot accordingly. For example, maybe you find that your expenses are over budget for the quarter, so you may hold off on a large equipment purchase.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for creating a business budget, along with why budgets are crucial to running a successful business.
» MORE: What is accounting? Definition and basics, explained

QuickBooks Online
How does a business budget work?
Budgeting uses past months’ numbers to help you make financially conservative projections for the future and wiser business decisions for the present. If you’ve had a few bad months and predict another slow one, you can prepare to minimize expenses where possible. If business has been booming and you’re bringing in new customers, maybe you invest in buying more inventory to satisfy increased demand.
Creating a business budget from scratch can feel tedious, but you might already have access to tools that can help simplify the process. Your small-business accounting software is a good place to start, since it houses your business’s financial data and may offer basic budgeting reports.
To create a budget in QuickBooks Online , for example, you break down your estimated income and expenses across each area of your business. Then, the software calculates figures like gross profit, net operating income and net income for you.
You can then compare actual versus projected figures side by side by running a Budget vs. Actuals report. Businesses that need more in-depth features, like cash flow forecasting or the ability to use different projection methods, might subscribe to business budgeting software in addition to accounting software.
If your small business doesn’t have access to these features or has simple financials, you can download free small-business budget templates to manually create and track your budget. Regardless of which option you choose, your business will likely benefit from hiring an accountant to help manage your budget, course-correct when the business gets off track, and make sure taxes are being paid correctly.
Why is a business budget important?
A business budget encourages you to look beyond next week and next month to next year, or even the next five years.
Creating a budget can help your business do the following:
Maximize efficiency.
Establish a financial plan that helps your business reach its goals.
Point out leftover funds that you can reinvest.
Predict slow months and keep you out of debt.
Estimate what it will take to become profitable.
Provide a window into the future so you can prepare accordingly.
Creating a business budget will make operating your business easier and more efficient. A business budget can also help ensure you’re spending money in the right places and at the right time to stay out of debt.
How to create a business budget in 6 steps
The longer you’ve been in business, the more data you’ll have to inform your forward-looking budget. If you run a startup, however, you’ll want to do extensive research into typical costs for businesses in your industry, so that you have working estimates for revenue and expenses.
From there, here’s how to put together your business budget:
1. Examine your revenue
One of the first steps in any budgeting exercise is to look at your existing business and find all of your revenue sources. Add all those income sources together to determine how much money comes into your business monthly. It’s important to do this for multiple months and preferably for at least the previous 12 months, provided you have that much data available.
Notice how your business’s monthly income changes over time and try to look for seasonal patterns. Your business might experience a slump after the holidays, for example, or during the summer months. Understanding these seasonal changes will help you prepare for the leaner months and give you time to build a financial cushion.
Then, you can use those historic numbers and trends to make revenue projections for future months. Make sure to calculate for revenue, not profit. Your revenue is the money generated by sales before expenses are deducted. Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted.
2. Subtract fixed costs
The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to reliably predict future ones. Fixed costs are those that stay the same no matter how much income your business is generating. They might occur daily, weekly, monthly or yearly, so make sure to get as much data as you can.
Examples of fixed costs within your business might include:
Debt repayment.
Employee salaries.
Depreciation of assets.
Property taxes.
Insurance .
Once you’ve identified your business’s fixed costs, you’ll subtract those from your income and move to the next step.
3. Subtract variable expenses
As you compile your fixed costs, you might notice other expenses that aren’t as consistent. Unlike fixed costs, variable expenses change alongside your business’s output or production. Look at how they’ve fluctuated over time in your business, and use that information to estimate future variable costs. These expenses get subtracted from your income, too.
Some examples of variable expenses are:
Hourly employee wages.
Owner’s salary (if it fluctuates with profit).
Raw materials.
Utility costs that change depending on business activity.
During lean months, you’ll probably want to lower your business’s variable expenses. During profitable months when there’s extra income, however, you may increase your spending on variable expenses for the long-term benefit of your business.
4. Set aside a contingency fund for unexpected costs
When you’re creating a business budget, make sure you put aside extra cash and plan for contingencies.
Although you might be tempted to spend surplus income on variable expenses, it’s smart to establish an emergency fund instead, if possible. That way, you’ll be ready when equipment breaks down and needs replacing, or if you have to quickly replace inventory that's damaged unexpectedly.
5. Determine your profit
Add up all of your projected revenue and expenses for each month. Then, subtract expenses from revenue. You may also see the resulting number referred to as net income . If you end up with a positive number, you can expect to make a profit. If not, that’s a loss — and that can be OK, too. Small businesses aren’t necessarily profitable every month, let alone every year. This is especially true when your business is just starting out. Compare your projected profits to past profits to confirm whether they’re realistic.
Looking for accounting software?
See our overall favorites, or choose a specific type of software to find the best options for you.
on NerdWallet's secure site
6. Finalize your business budget
Are the resulting profits enough to work with, or is your business overspending? This is your opportunity to set spending and earning goals for each month, quarter and year. These goals should be realistic and achievable. If they don’t line up with your projections, make sure to establish a strategy for making up the difference.
As time goes on, regularly compare your actual numbers to your budget to determine whether your business is meeting those goals, and course correct if necessary.
» MORE: Ways your small business can spend smarter
A business budget projects future revenue and expenses so you can create a smart, realistic spending plan. As the year progresses, comparing your actual numbers against your budget can help you hold your business accountable and make sure it reaches its financial goals.
A business budget includes projected revenue, fixed costs, variable costs and the resulting profits. You can also factor in contingency funds for unforeseen circumstances like equipment failure.
On a similar note...

Business growth
Business tips
7 free small business budget templates for future-proofing your finances

As a small business owner, you're likely balling with a lot more than your personal checking account. If you don't properly manage your business finances, there's more on the line than an overdraft fee—you now have an entire organization to account for.
Small business budgets are necessary to balance revenue, estimate how much you'll spend, and project financial forecasts, so you can stay out of the red and keep your business afloat.
But creating a small business budget template isn't a small task. Since I don't have a business to run, I did the heavy lifting for you—check out these free, downloadable templates for your small business budgeting.
Table of contents:
2. Overhead budget template
3. multiple-project budget template.
4. Startup budget template
5. Labor budget template
6. cash flow budget template, 7. administrative budget template, periodic budget reviews, how to design your small business budget plan, small business budget faq, 1. static budget template.
Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations
A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other budgets your business might use):
Cash flow projections: Estimations of how much money will flow into and out of your business. They also help you decide when, how, and what you should spend money on.
Total expected spending: All estimated expenses, including labor and administrative costs.
By integrating all of your budgets and projections, the static budget provides a full picture of your business's estimated expenses and financial strategy for the upcoming fiscal year.
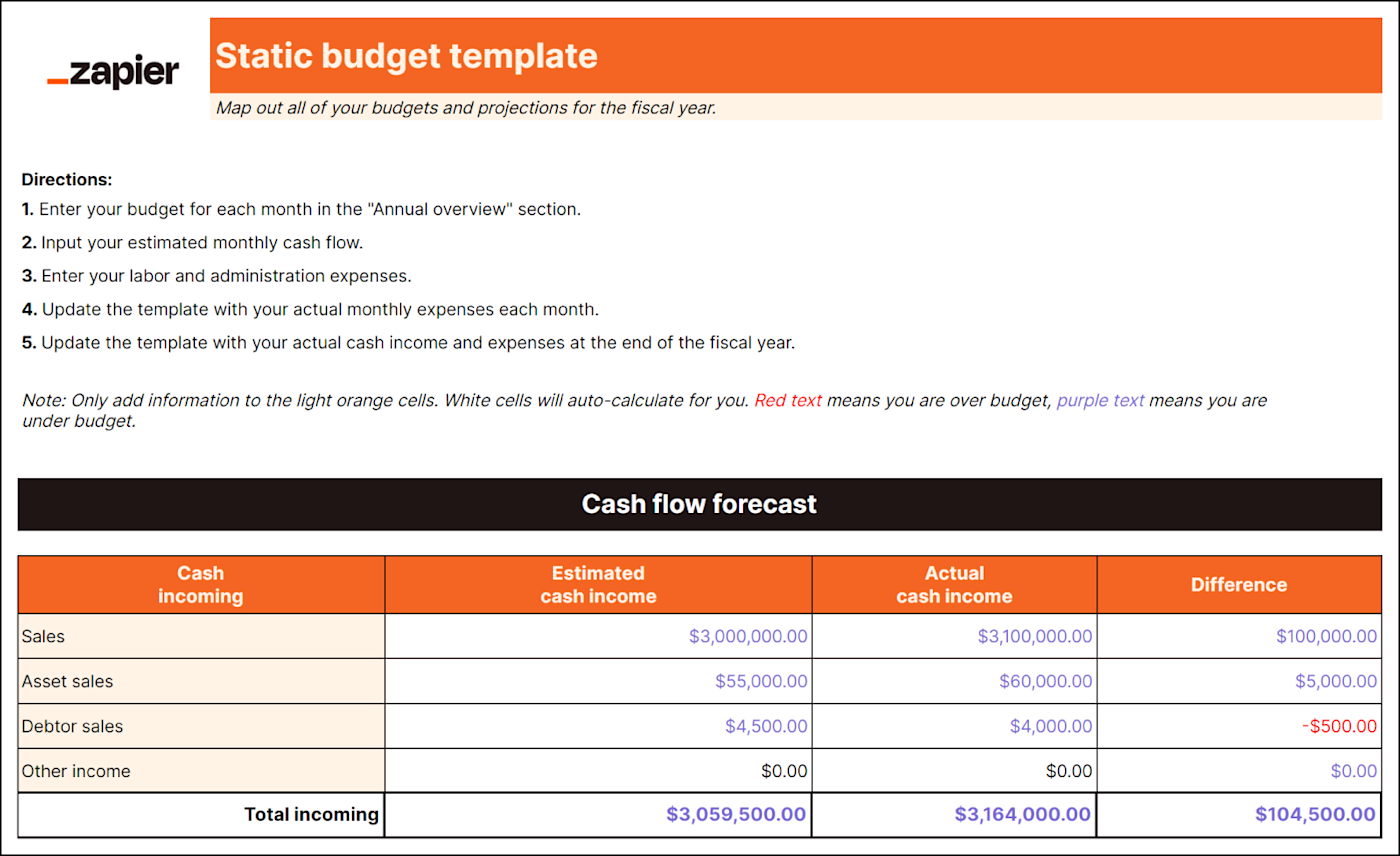
Best for: Service-based businesses
It's easy to forget about expenses that aren't directly tied to production, like delivery charges or utilities. But these costs exist (and can add up quickly), so you need an overhead budget. A detailed overhead budget template will include:
Administration expenses
It compares your budgeted amount to actual figures (warning: it may be a rude awakening) and can help improve accuracy for future financial planning.
Predicting overhead spending helps you plan how to use other funds more practically too—if you know how much you'll spend on overhead, you can make better business decisions. For example, you'd know whether you can afford to invest money into other initiatives like adding a delivery service or upgrading equipment.
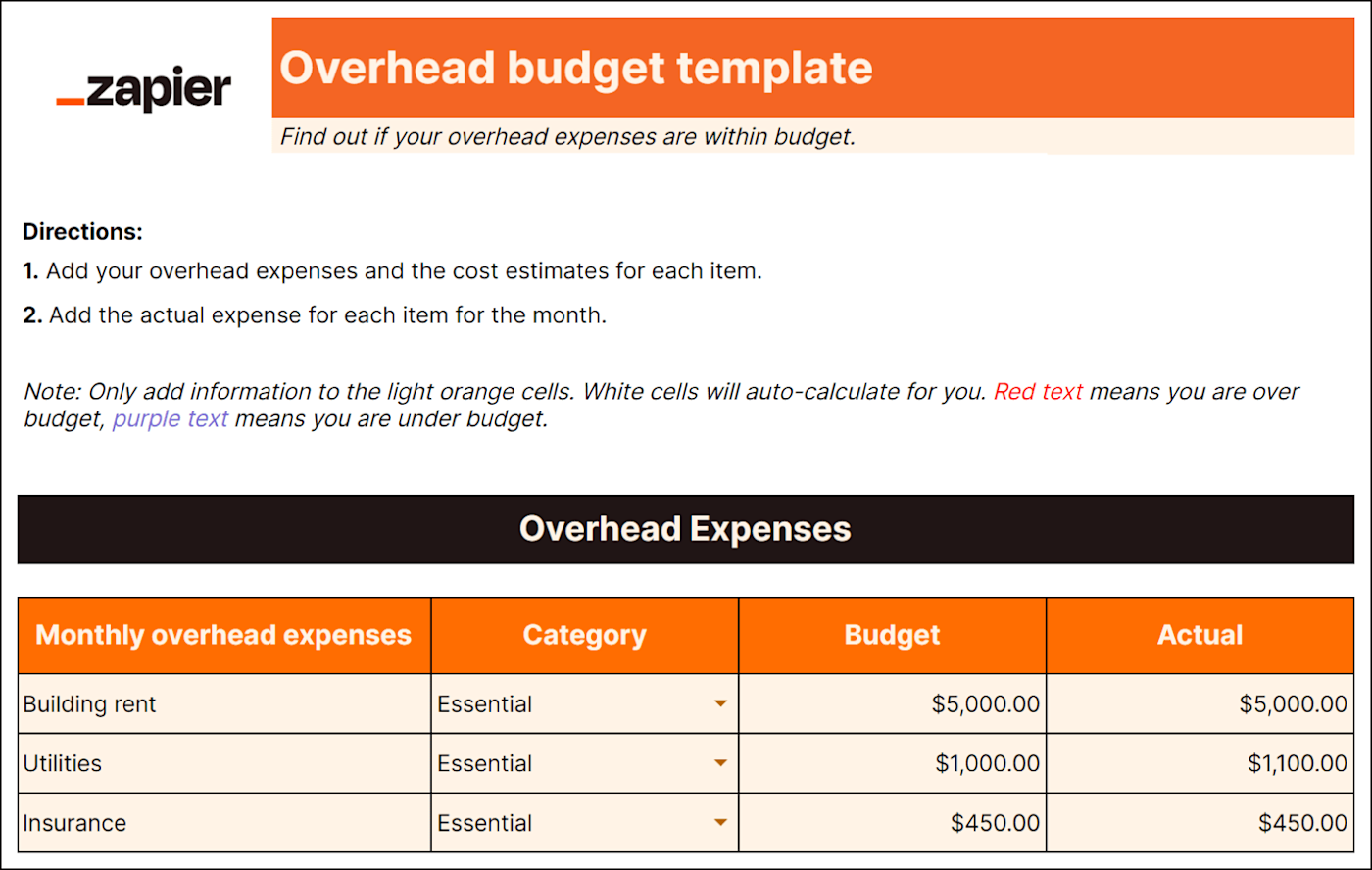
Best for: Project-based industries
If you're managing multiple projects like website development or event planning, each with its own budget and expenses, you need a multiple-project budget to help keep your head on straight. This type of budget will help you track the following items per project:
Product-by-product COGS (cost of goods sold)
Labor costs
Equipment and resource costs
Indirect project expenses like travel
A multiple-projects budget establishes estimates for everything you need to get projects across the finish line. It also lets you track costs to ensure you're not spending more than you accounted for in the budget.
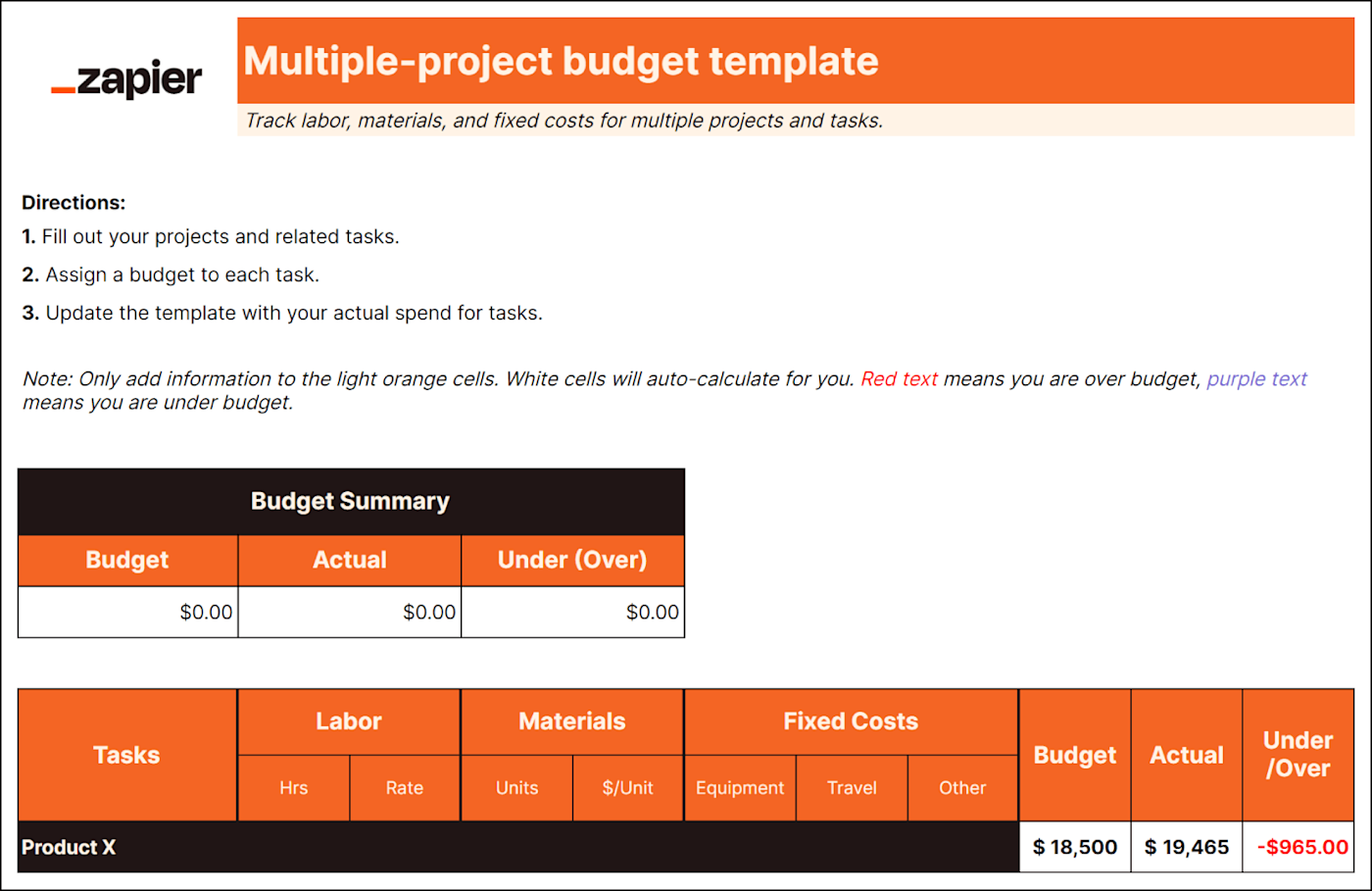
4. Startup budget template
Best for: New small businesses and startups
Startups need to ensure financial success from the get-go, so they can reinvest profit into the business and potentially attract more investors.
But unlike established small businesses, you don't have past financial data to base expenses on. That's why you need a startup budget to focus on expenses for your first year of business, including items like:
Funding from investors and loans
Licensing and permits
Logo and website design
Website domain
Business software
Security installation
Overhead expenses
Capital expenses
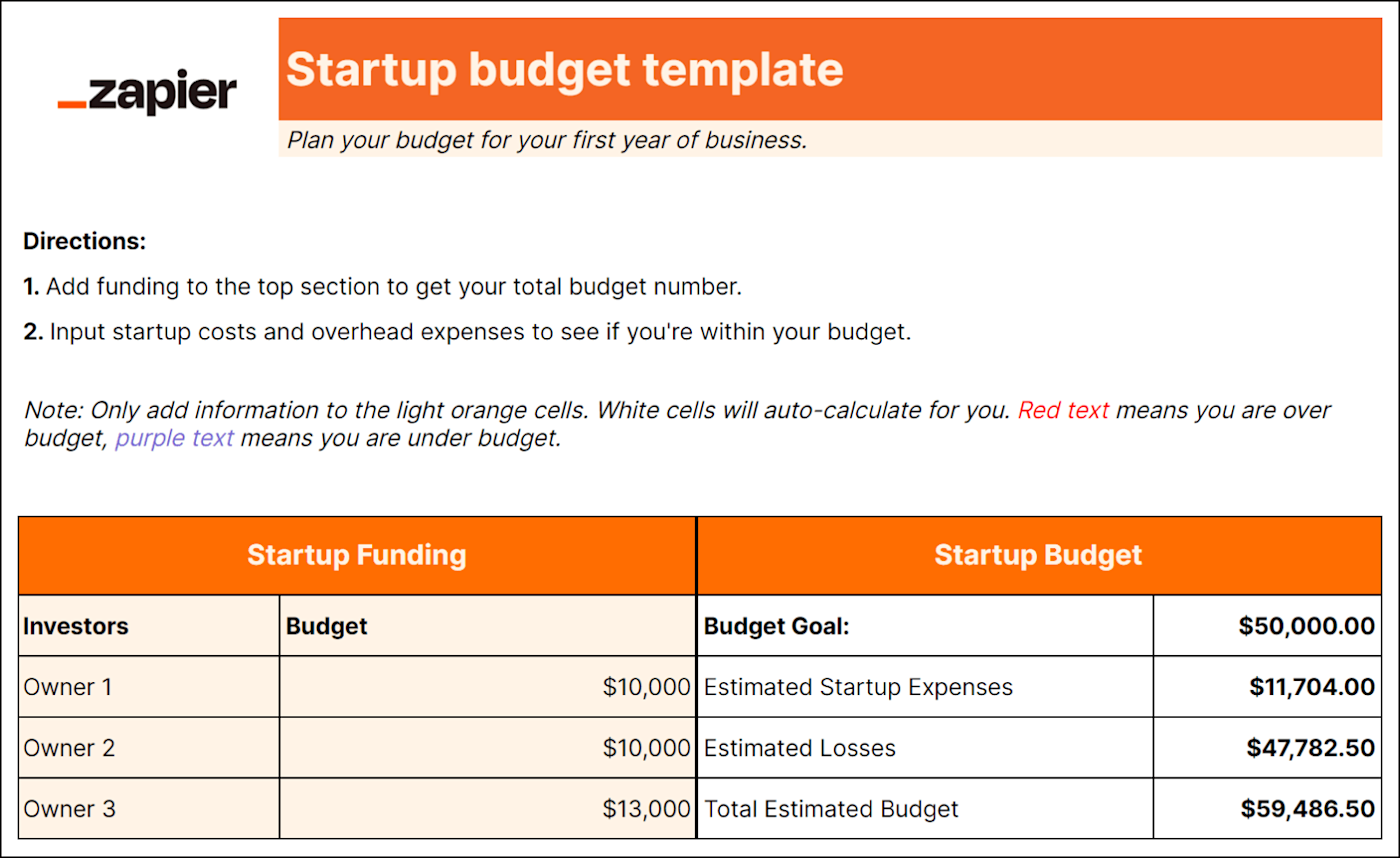
Best for: Larger businesses with lots of employees
Unless you're a one-person show, you'll need a labor budget. And even if you are a one-person show, it's good to know if you can afford to pay yourself. A labor budget breaks down all employee-related costs like:
Payroll taxes
Contract labor
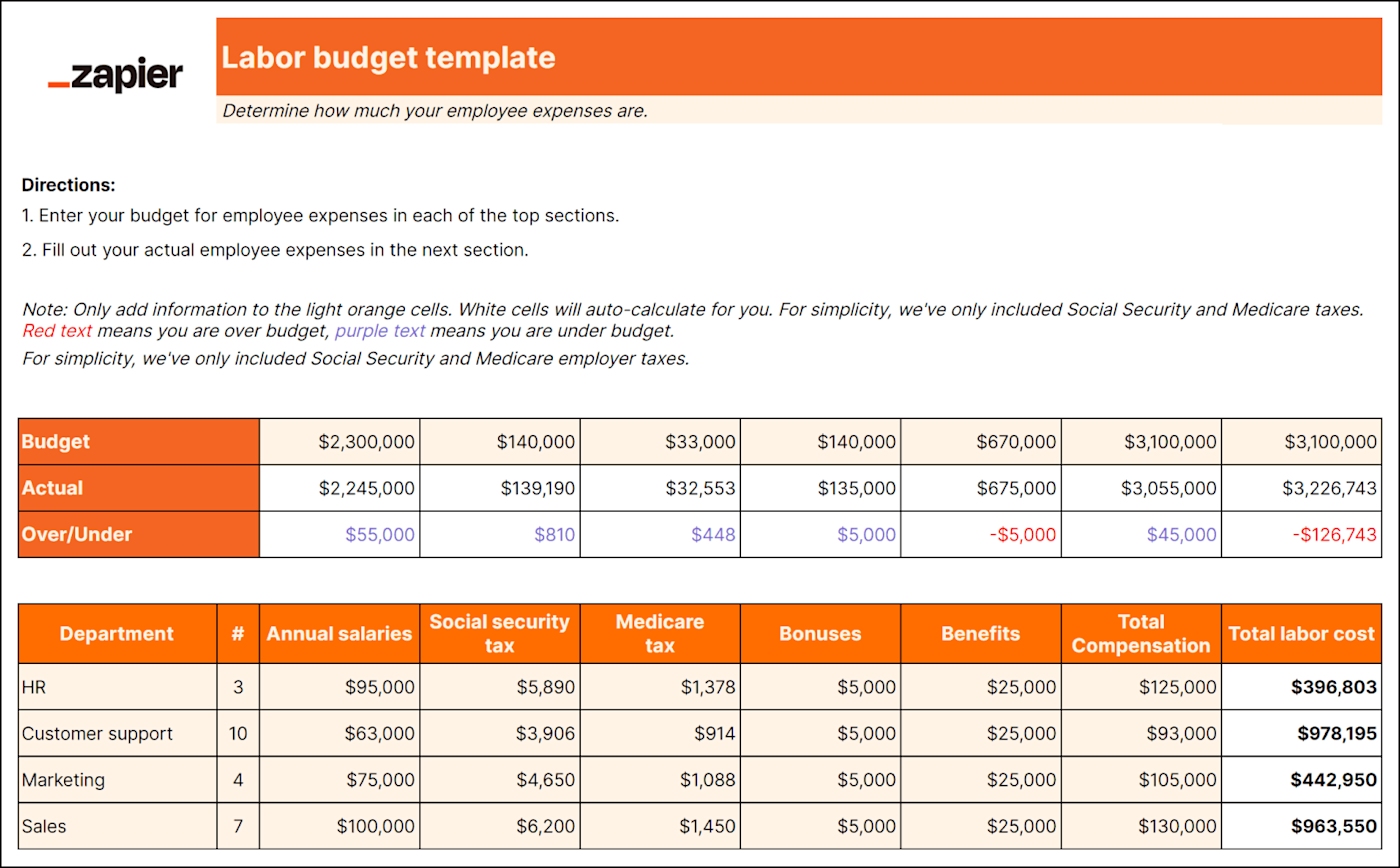
Break down employee costs into direct, indirect, fixed, and variable categories to clarify how your company allocates its resources. You can also consider different scenarios more easily when you understand the breakdown of labor costs.
For example, you can simulate the impact of adding or reducing staff in specific departments or assess the effects of different compensation structures on different teams.
An accurate forecast of labor costs ensures you can sustainably meet your staffing needs and can help you make informed hiring decisions. Down the road, it can also help you determine if you can afford to give your staff raises, bonuses, or additional benefits.
Best for: Businesses with fluctuating income and expenses; Seasonal businesses; Retail
As important as it is to be mindful of how much money you're spending, you should also track how much money you're making . A cash flow budget helps estimate how money is flowing in and out of your business. It includes:
Starting balance (set at the beginning of the month, quarter, or year)
Projected cash inflow from all revenue streams
Estimated cash expenditures
Ending balance (calculated at the end of the month, quarter, or year)
This type of budget lets you proactively manage your resources, anticipate potential cash shortages, and strategize for growth. For instance, if you know you're only going to break even this year, you may wait on expanding or making a large investment.
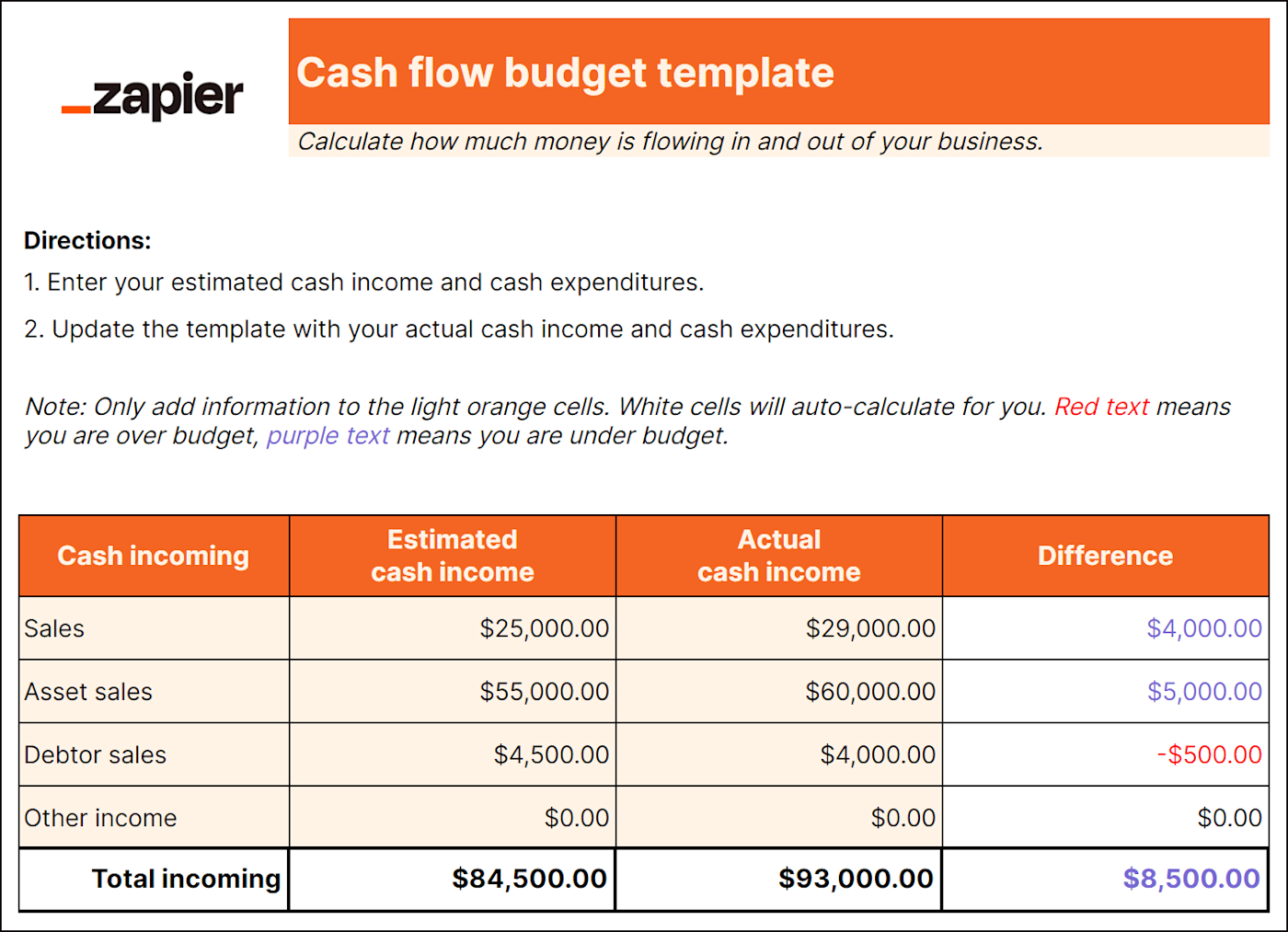
Best for: Businesses focused on streamlining operations
An administrative budget includes all those general expenses that the company as a whole needs to function. This type of budget accounts for:
Depreciation expenses
Training and development
Communication expenses
Accounting fees
While you could technically include administrative expenses in an overhead budget and call it a day, a separate administrative budget gives more of an eagle-eye view of how well your business is operating.
Without an eye on administrative costs, you may be spending unnecessarily or lose focus on areas where it'd be wiser to invest your money. In other words, you could be spending way too much on fancy pens when you should be saving up to upgrade your cash register.

A budget isn't a "set it and forget it" deal. Regular budget reviews can help you stay on track with your financial goals and respond proactively to changing market conditions.
You should compare your estimated budget to actual spending. Then you can see where you went over and where you can splurge more. Try to review your budget monthly, quarterly, and yearly.
Monthly: Compare actual performance against your budgeted figures for the month. Identify any deviations and look for insights into cash flow, sales trends, and expense management.
Quarterly: Dive deeper into performance over the last three months. Use trends to project revenue and expenses for the upcoming quarter and identify areas for improvement.
Yearly: Reflect on your long-term financial objectives for the fiscal year. Assess the effectiveness of your budgeting strategies, and set new budget targets for the upcoming year.
It's cliched but true: you gotta spend money to make money. But that's no excuse to start throwing cash at your business willy-nilly.
Budgeting forces you to prioritize your objectives, so you spend money on the things that matter most. Here's how to create a small business budget in four steps:
Identify your working capital for the budgeting period. Add up your current assets like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Then subtract current liabilities like accounts payable and short-term debt. The remaining amount is what you have left to cover your operational expenses during the budgeting period.
Separate business and personal expenses. If you haven't already, open a dedicated business bank account. This makes it easier to track, categorize, and analyze your finances.
Determine your fixed and variable costs. Make a list of costs that stay the same every month (fixed costs) and what changes (variable costs). These will change based on the purpose of the budget. For instance, a labor budget will only consider employee-related costs.
Calculate your total expenses. Add up all the costs for your business, including fixed costs, variable costs, labor, and any other applicable expenses. This total is how much your business needs to run. Any leftover money from your working capital can be allocated toward other business investments.
Budgeting methods
If you've budgeted before and hated it, you may just have been using an ineffective budgeting method for your preferences. Here are a few budgeting methods to try instead:
Traditional: This budget is set for a determined amount of time and uses last year's numbers as a benchmark. Once you set your budget, you don't change it unless you get approval for an adjustment.
Rolling: This dynamic approach spans a continuous time frame instead of a fixed time period. As each month or quarter passes, you add a new budget period and drop the oldest period. This lets businesses adjust projections based on real-time performance and market conditions.
Flexible: This budget changes along with your sales forecast. As real-time sales activity deviates from budgeted amounts, you recalculate the budget to reflect the new data.
Still don't know where to start with your small business budget? Check out the answers to these common questions before you open a new Google Sheet.
What should a business budget include?
A business budget should include all income sources and expenses. Income sources could include projected revenue from sales, loans, or potential investor funding. Expenses may include items like office space rent, employee salaries, insurance, and marketing. Add anything that helps paint a full picture of your finances.
How much does the average small business startup cost?
The average small business startup costs $40,000 in its first year of business. But this will absolutely vary depending on your type of business, unique expenses, and cash income. For instance, there are multiple types of businesses you can start with $10,000 or less.
What is the best free business budgeting software?
The best free budgeting business software will depend on what your business needs, but you can try apps like Mint or Wave. Or you can use a spreadsheet—scroll up for some free small business budget templates.
Automate your small business
Knowing when or where to invest money into your business is just one of the many tasks you have on your plate as a small business owner. Learn how automation for small businesses can help take some of those recurring tasks off your hands, so you can focus on growing your business.
Related reading:
The best free small business software
The best CRMs for small businesses
How to create effective document templates
21 free Google Sheets templates to boost productivity
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Cecilia Gillen
Cecilia is a content marketer with a degree in Media and Journalism from the University of South Dakota. After graduating, Cecilia moved to Omaha, Nebraska where she enjoys reading (almost as much as book buying), decor hunting at garage sales, and spending time with her two cats.
- Small business
- Finance & accounting
Related articles
How to enrich lead data for personalized outreach
How to enrich lead data for personalized...
What is a proof of concept? And how to write one (with template)
What is a proof of concept? And how to write...
How to choose the best automation software
AI in customer service: 11 ways to automate support
AI in customer service: 11 ways to automate...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Accounting | How To
How To Create a Small Business Budget [+Free Template]
Published June 20, 2023
Published Jun 20, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Tim Yoder, Ph.D., CPA
WRITTEN BY: Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
This article is part of a larger series on Bookkeeping .
- 1. Create a Budget Process
- 2. Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
- 3. Create the Sales Budget
- 4. Create the Inventory and Purchases Budget
- 5. Create the COGS Budget
- 6. Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
- 7. Create the Capital Budget
- 8. Create the Cash Budget
- 9. Assemble Proforma Financial Statements
Common Problems in Budgeting
Bottom line.
Creating a business budget is an important step in planning. A small business budget starts with creating the budgeting process, the operating budgets, such as sales, inventory and purchases, cost of goods sold (COGS), and sales and administrative, and ends with the financial budgets, such as cash, capital, and proforma financial statements.
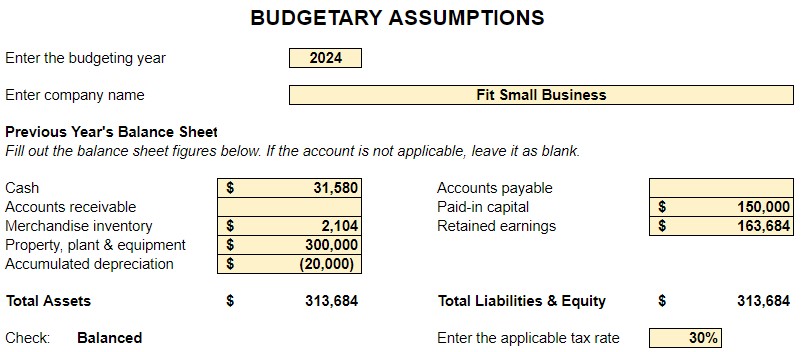
To help you get started, we’ve provided a very simplified version of a budget spreadsheet to illustrate how information from each area of your business is combined to form an annual budget. We’ll discuss how to use this spreadsheet throughout our article.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
FILE TO DOWNLOAD
Thank you for downloading!
Budgeting is an important subset of managerial accounting. Read our small business guide to managerial accounting and learn how managerial accounting concepts can be applied in a small business setup.
Step 1: Create a Budget Process
The budget process shows how the different departments of the business create a budget. Without a process, budgeting would be chaotic, and it would result in inefficiencies. In the budget process, you need to consider the following:
- Budget period: When are budgets created, reviewed, implemented, and evaluated against actual performance?
- Budgeting method: How are budgets created? Is it created from scratch (zero-based budgeting)? Is it based on actual results with adjustments (incremental budgeting)?
- Budget involvement: Who creates the budgets?
- Budget committee: Who oversees and approves the budgets?
- Budget manual: What are the guidelines for creating budgets?
Budget Period
The first thing to consider in the budget process is the budget period. How long should budgets be prepared? When will it be implemented? The budget period can be any time before the next business year begins. Hence, you can create next year’s budget three months prior to the end of the current year.
The crucial periods for budget planning are as follows:
- Budget preparation : The time at which managers and heads create a budget for their department.
- Budget review and approval : The time at which top management will review and approve all lower-level budgets.
- Budget implementation : The time at which all concerned parties will act upon planned activities stated in the budget. This phase runs until the effectiveness of the budget lasts.
- Budget accountability : The time at which top management will assess if the business is meeting its budgetary goals. This phase runs intermittently during the year, such as monthly, quarterly, or semiannually, especially during performance evaluation and review.
As a small business, you need not be particular about the phases. You can modify the phases depending on small business needs.
Budgeting Method
There are four different types of budgeting methods, but for small businesses, we picked only two, as they are the most appropriate for the setup:
- Zero-based budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that starts from scratch. It doesn’t use information from past budgets. Instead, departments and managers need to justify every dollar in the budget without referring to past performance or past budgeting practices.
- Incremental budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that uses actual figures from the past years and adjusts with a certain percentage. For example, if actual sales last year is $20,000, the incremental budgeted sales could be 10 percent more or $22,000.
Budget Involvement
Small businesses must consider what kind of involvement is needed during the budgeting process, given that budgets can be used to measure the performance of departments and managers. There are two kinds of budget involvement—for small businesses, authoritative budgeting is suitable if the small business owner is heavily involved in daily operations. Alternatively, participatory budgeting applies if the owner delegates decision-making to managers.
1. Authoritative budgeting
Also known as top-down budgeting, this budget involvement strategy only includes top management in the budgeting process, where operating personnel and lower-level employees have little to no say in the budget. It takes less time to create since there are fewer employees involved.
However, some operating personnel and lower-level employees may disagree with top management’s estimates in the budget. At the least, this strategy creates discord between top management and operating personnel due to conflicting views. But if prepared appropriately, authoritative budgeting reflects the business’ vision, mission, and goals better.
2. Participatory budgeting
This is also called bottom-up budgeting, and this budget involvement strategy includes operating personnel and lower-level employees in creating a budget. It is a budget co-created by everyone involved or affected by the budget being created.
It enhances the relationship between top management and operating personnel since everyone has a say in the budget. However, this strategy can take time since more employees are involved in the budgeting process. Also, some lower-level managers can use this opportunity to insert some budgetary slack so that they look good during performance.
Budget Committee
The budget committee is responsible for compiling all lower-level budgets and assembling them into one package called the master budget and reviewing and approving budgets from different departments. For small businesses, the composition of the budget committee can be the small business owners, chief executive officer (CEO), treasurer, budget coordinator, and chief accountant.
The role of the budget coordinator is to reach out to lower-level managers and communicate the wishes of the budget committee. If you’re a family-grown small business, family members, including the small business accountant or finance officer, can be committee members.
Budget Manual
The first order of business of the budget committee is to create a budget manual, which outlines the budgeting process. Lower-level managers and department heads will use the budget manual when creating lower-level budgets. The budget committee may also set specific budget formats and deadlines.
A budget manual standardizes the budgeting process—it ensures fairness and comparability among departments and managers. With this manual in place, you can prevent the instance of inserting unfamiliar line items in the budget or using different sources in forecasting budgeted figures.
The budget manual should include the following:
- Statements of budgetary purpose
- Budgetary activities, such as budget preparation, budget hearing and evaluation, budget approval, budget execution, and budget accountability
- Schedule of budgetary activities and deadlines
- Sample budgets
- Key assumptions used in budgeting
You can create a budget easily using QuickBooks Online. Its budgeting functions create budgets per account in the chart of accounts. Read our QuickBooks Online review for detailed information on our recommendation.
Step 2: Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
After performing the groundwork for budgeting, the next step is determining the key assumptions. These assumptions make it easy to prepare budgets since not all information is readily available until it happens. These assumptions are not arbitrary because they must be based on past experience and good business practices.
Examples of assumptions are:
- Sales forecast
- Selling price per unit
- Cost per unit
- Estimated discounts given to customers
- Estimated sales returns
- Desired ending inventory per month or quarter
- Number of raw materials used to produce one good unit
- Number of labor hours needed to produce one good unit
- Number of overhead hours (if any) needed to produce one good unit
- Inventory cost flow method used, such as first-in, first-out (FIFO), last-in, first-out (LIFO), or average cost
- Cash collection patterns
- Cash payments patterns
- Cash retention policies
Input your assumptions in the second tab of our downloadable spreadsheet. When done, all of the reports will automatically populate. It’s the quality of your assumptions that will determine if your budget is realistic. As you improve your budgeting process, you’ll come up with additional assumptions to include in the process.
Step 3: Create the Sales Budget
The sales budget is the first budget that should be prepared because almost all budgets will depend on the information in it. It is the responsibility of the sales department to forecast and create the sales budget of the company, and it is crucial that the department forecast sales reasonably using the appropriate forecasting method. Our article about sales forecasting discusses the method of sales forecasting and shows how CRM software can help.
Below is an example of the sales budget taken from our small business master budget template.
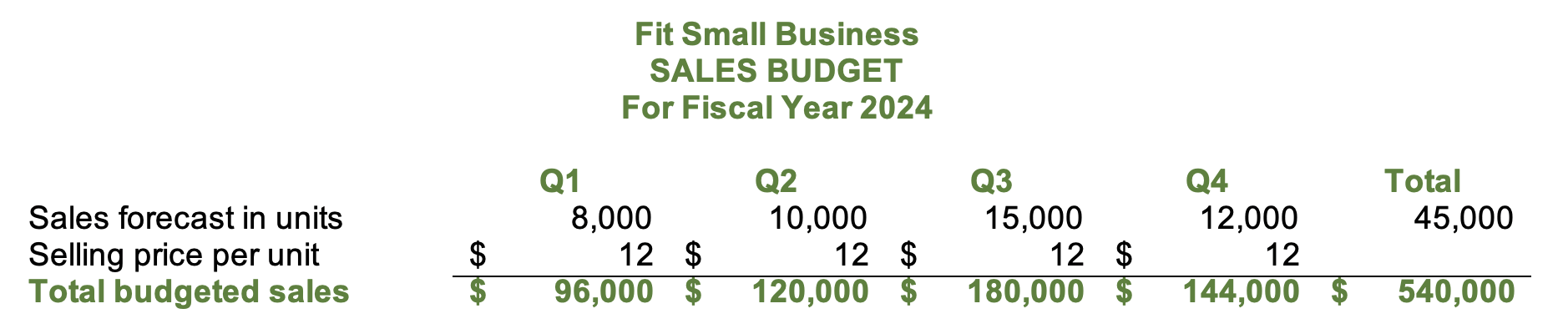
Sales budget
Step 4: Create the Inventory & Purchases Budget
There are two ways to call this budget: merchandising companies can call it inventory and purchases budget while manufacturing companies can call it production budget. However, the information shown in this budget remains the same. The inventory or production budget shows the number of units needed to meet the sales demand.
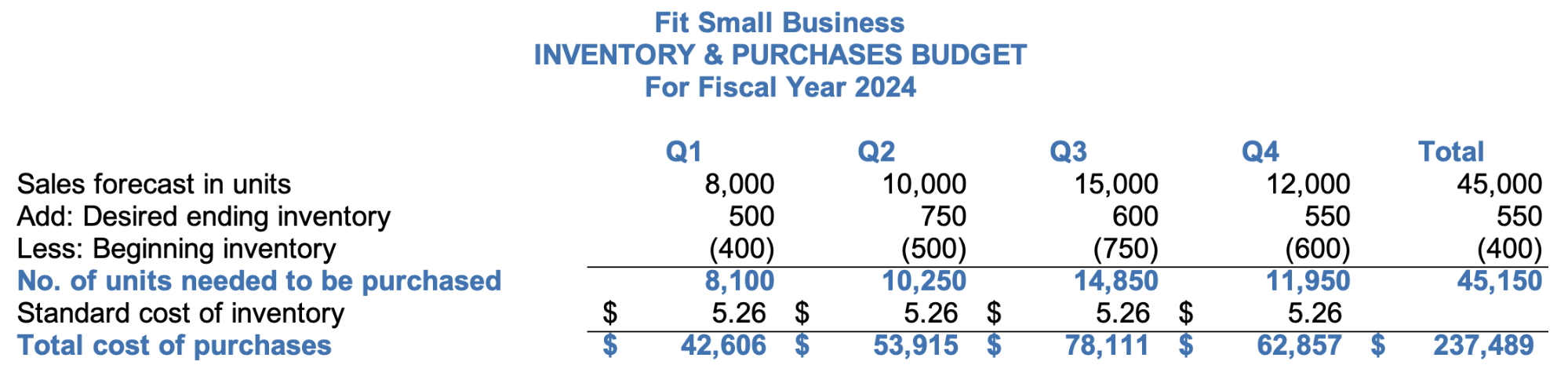
Inventory budget
The image above shows the sample inventory budget in our free template. One of our assumptions is that the business intends to keep 5% of next quarter’s sales forecast as current quarter’s ending inventory. In Q1, desired ending inventory is 500 units, which is 5% of 10,000 units of Q2’s sales forecast.
After determining the number of units needed, multiply them to the standard cost of inventory to get the total cost of inventory. The standard inventory cost is also the budgeted cost of inventory. Since some inventory prices fluctuate, setting standard costs makes it easy for us to budget.
When adding values in the total column, do not sum up the values in the beginning and desired ending inventory rows. Instead, the total beginning inventory in the total column should be the Q1 beginning inventory, while the total ending inventory should be the Q4 ending inventory.
Step 5: Create the COGS Budget
The next logical step after budgeting inventory and purchases is to determine the COGS. Through the COGS budget, we can estimate the level of COGS per quarter. This budget is necessary for preparing the proforma income statement.
Below is the COGS budget from our small business budget template:
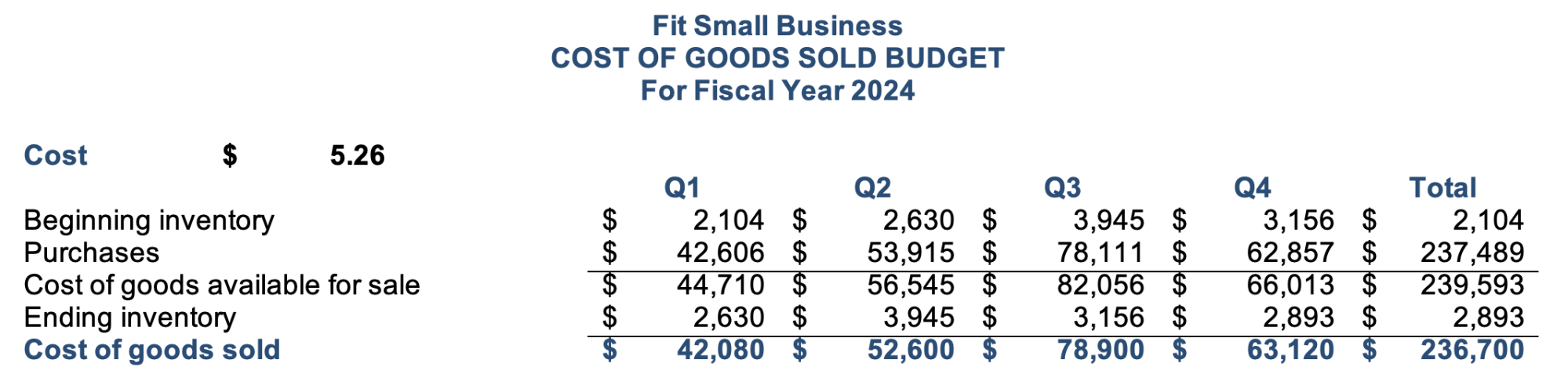
COGS budget
Step 6: Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
The sales and administrative (S&A) budget presents the budgeted costs for sales expenses, office expenses, and administrative expenses. This is necessary for budgeting the salaries of employees and other fixed expenses. The image below shows the sales and administrative budget from our template:
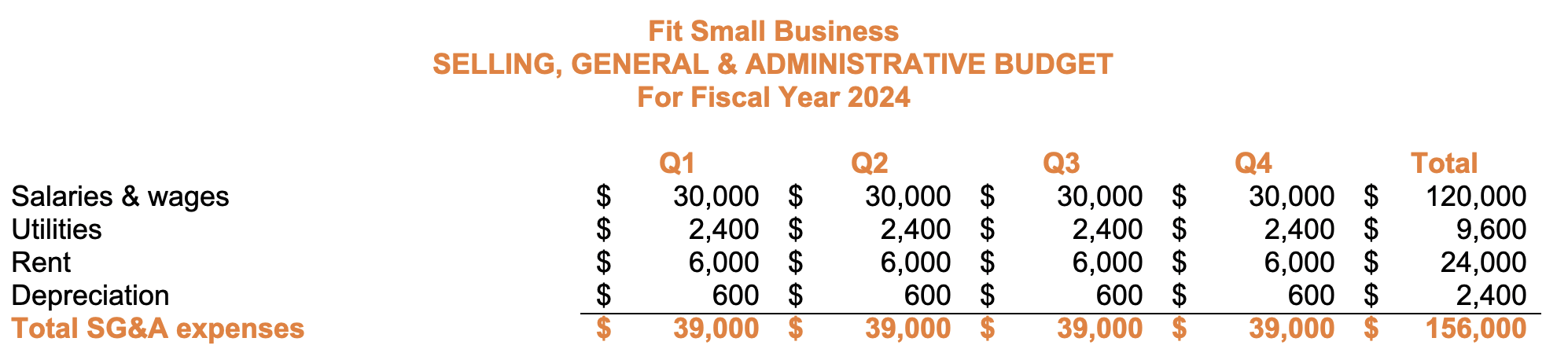
S&A budget
Most expenses in this budget are fixed costs. That’s why the amounts are the same for every quarter. Manufacturing companies may also call this budget a “fixed overhead budget.”
Step 7: Create the Capital Budget
A capital budget shows all the planned capital expenditures during the year. In our capital budget example below, there are no figures because the sample company didn’t plan any capital decisions for 2024. However, we’ve included common capital decisions for you to fill out when you use our template. For instance, a bank loan is a capital inflow while the purchase of equipment is a capital outflow.

Capital budget
The capital budget in our downloadable spreadsheet does not auto-populate from the assumptions tab. Instead, enter your budgeted loans and purchases directly in the report.
Step 8: Create the Cash Budget
The last budget that you need to prepare is the cash budget, which shows all the cash inflows and outflows from all budgets. Almost all budgets above affect cash flow. For example, the sales budget can show all cash inflows from cash sales and subsequent cash collections from credit sales.
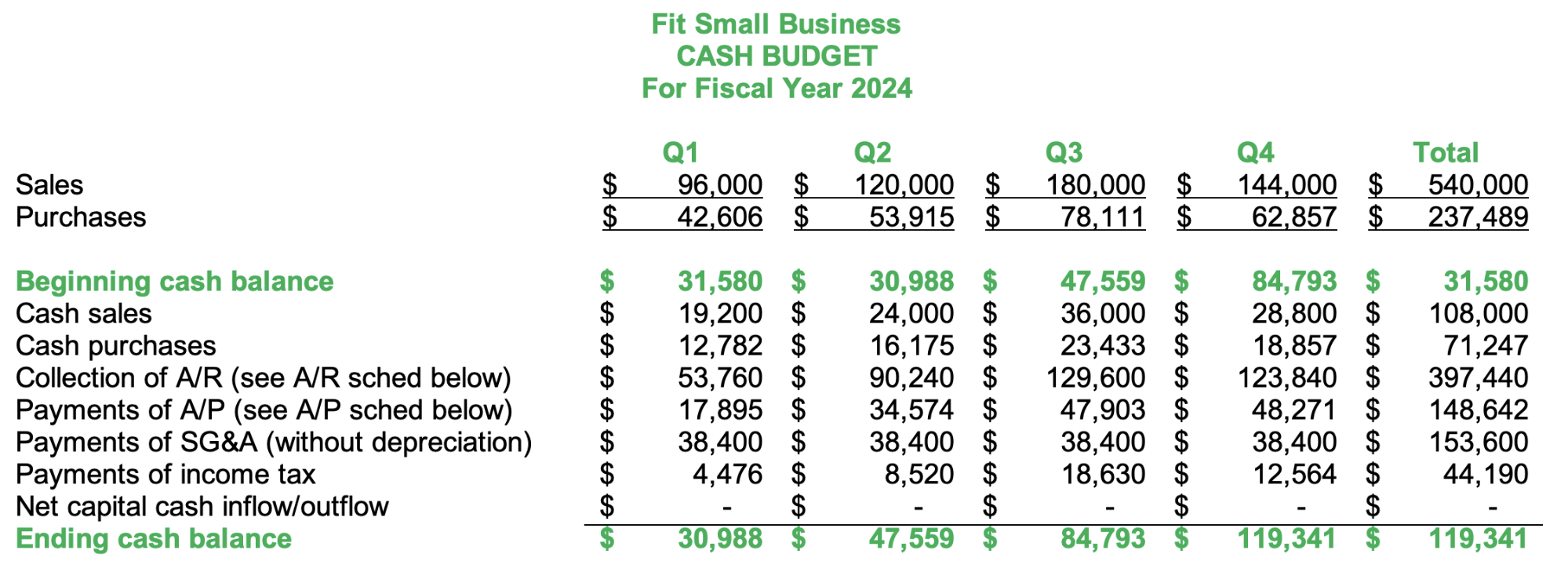
Cash budget
Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable Schedule
Collections from accounts receivables (A/R) and payments of accounts payable (A/P) are integral parts of the cash budget. Creating the A/R and A/P schedules helps in computing the ending balance of A/R and A/P and the amount of cash collections and payments per quarter. Below are the supporting A/R and A/P schedules for our cash budget above:
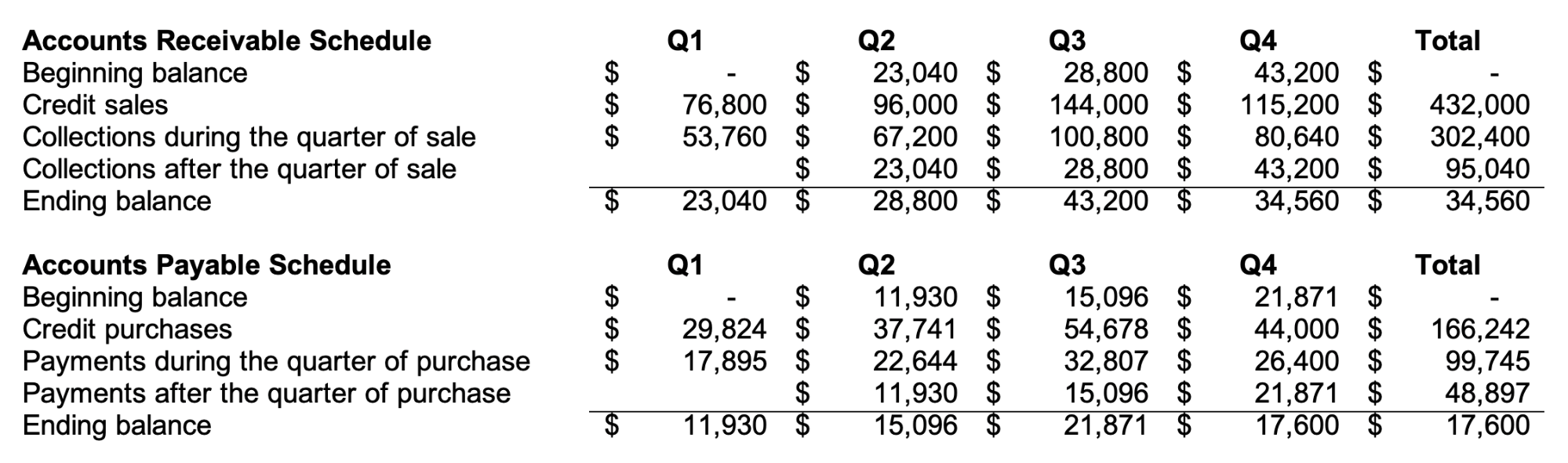
A/R and A/P schedules
Step 9: Assemble the Proforma Financial Statements Based on Budgeted Figures
The ultimate result of the budgeting process is the proforma financial statements, which are the budgeted or projected results of planned activities. If the budget goes as planned, the actual financial statements should be near the proforma financial statements. Below are the proforma income statement and balance sheet in our small business budget template.
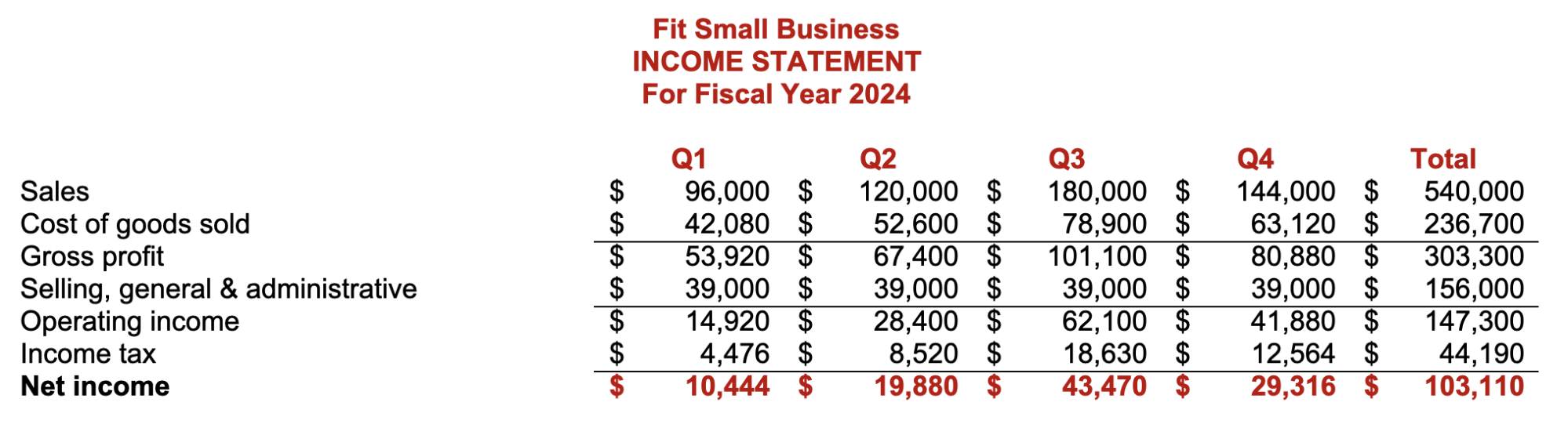
Proforma Income Statement
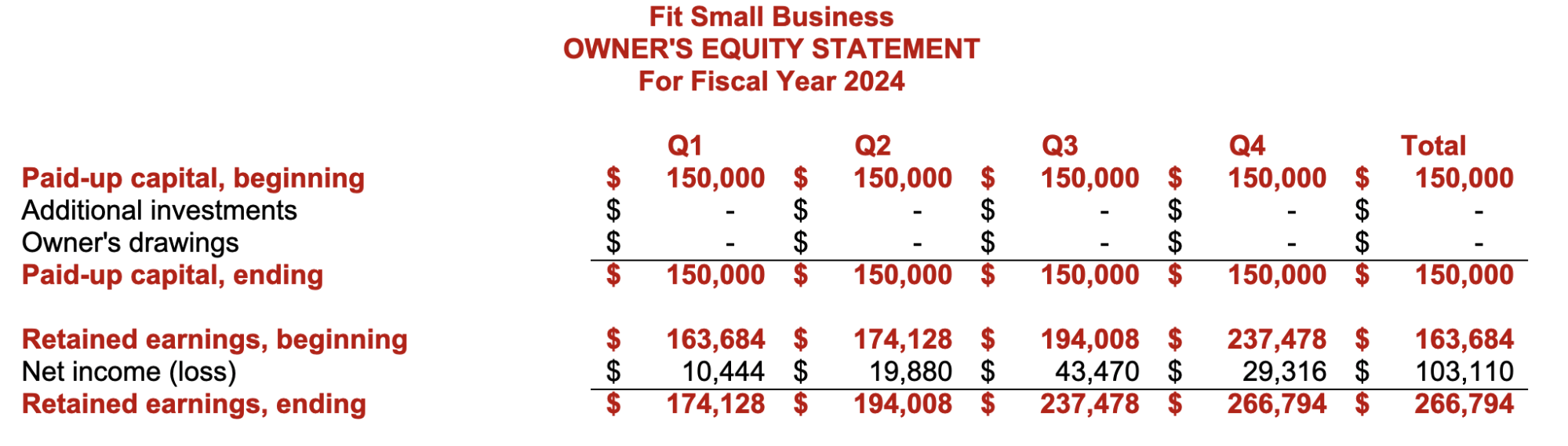
Proforma Owner’s Equity Statement
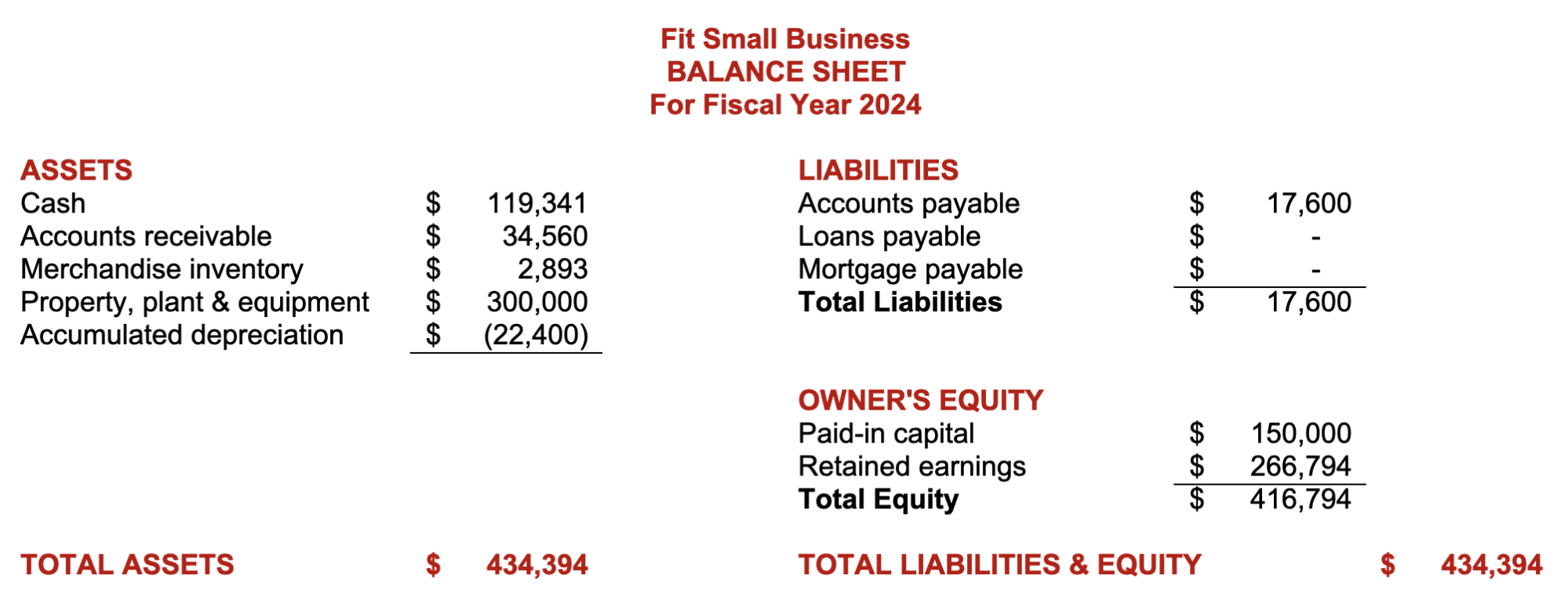
Proforma Balance Sheet
Budgeting helps businesses plan on future events and meet company goals. However, it is likely that you will experience difficulties and problems during the budgeting process. The four problems we’ll discuss are budgetary slack, goal incongruence, budget myopia, and standard setting.
Budgetary slack and goal incongruence occur when managers are not aligned with the business’s overall goals and objectives, while budget myopia happens when the business forgets to consider the impact of short-term decisions in the long run. Lastly, standard setting often poses a problem when standards are too high or ideal. Let’s discuss each of them in greater detail below.
Budgetary Slack
Sometimes, managers and heads can use budgets to preempt results to their favor. This unethical practice is called budgetary slack or budget padding. Budget slacks occur when managers underestimate revenue goals and overestimate expense goals and when the business follows the participatory budget involvement strategy.
When time for evaluation arrives, budget slacks will make the manager’s performance as exemplary. Managers tend to include budgetary slacks when top management is too strict and punitive whenever budgets aren’t met.
For example, the sales manager underestimates the sales forecast at $50,000 for the first quarter, knowing that they can achieve actual sales of $70,000. This example shows how budgetary slack can affect performance evaluation and create a false reflection of the company’s ability to generate revenue.
Goal Incongruence
Budgets are goals. When goals of management and employees don’t meet, the budget will not reflect the results that’s best for the business as a whole. Preventing goal incongruence enhances the quality of the budget. The goal of employees should be aligned with the business’s goals, and top management should provide opportunities for employees to pursue their career growth within the business.
Improper communication of business goals and ineffective leadership are the common causes of goal incongruence. As a small business owner or manager, you should show employees that you are committed to them with respect to their professional goals and that you expect them to align themselves with the business’s overall goals.
Budget Myopia
Budget myopia occurs when budgeting focuses only on short-term goals without considering how these goals will affect the company in the future. Managers become “myopic” in budgeting when they see budgets as measures for performance—they forget that the main objective of budgeting is to plan, organize, and manage the firm’s resources. As a result, budget realignments occur because there is a failure to plan future events.
Standard Setting
Another hurdle in budgeting is setting standards, which are tools for planning and controlling. If used inappropriately, they can cause problems in the budgeting process. It is important that you have to set your standards at a practical level.
Practical standards allow room for error or inefficiencies. It gives employees a chance to learn and improve their outputs without affecting performance. Unwise managers often impose ideal standards or standards that require optimum performance and perfection.
As a result, imposing ideal standards results in employee burnout, decreased productivity, and negative employee morale. Discouraged employees might also result in dysfunctional behavior that might be detrimental to the company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is budgeting important.
Budgets help in planning and managing business resources. Since plans and goals require an outflow of resources, budgets help the business determine the right amount of resources needed to achieve the goal.
Who should have an active participation in the budgeting process for small businesses?
The small business owner should have an active role in helping managers and supervisors craft their budgets. As the owner, you should guide your employees to align their goals with the business’ overall goals.
With our small business budget guide and template, you can create a small business master budget. We hope that the template will help you understand why budgeting is crucial to the planning, organizing, and controlling business operations.
About the Author

Find Eric Gerard On LinkedIn
Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
Eric is an accounting and bookkeeping expert for Fit Small Business. He has a CPA license in the Philippines and a BS in Accountancy graduate at Silliman University. Since joining FSB, Eric has used his expertise and authority in curating and writing content about small business accounting and bookkeeping, accounting software, financial accounting and reporting, managerial accounting, and financial management.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
How to Create a Small Business Budget in 5 Simple Steps
Want to protect the financial health of your small business? You need a business budget. Here's how to create one.

When you build a business, there are a lot of things to stay on top of, from marketing and finding new clients to building a website and establishing your digital presence. But there’s one element that you want to stay on top of from the very beginning—and that’s your business budget.
Having a detailed and accurate budget is a must if you want to build a thriving, sustainable business. But how, exactly, do you create one? What are the steps for business budget planning?
As a small business owner, let’s take a look at how to create a business budget in five simple, straightforward steps.
What’s a Business Budget—and Why Is It Important?
Before we jump into creating a business budget, let’s quickly cover what a business budget is—and why it’s so important for small businesses.
A business budget is an overview of your business funds. It outlines key information on both the current state of your finances (including income and expenses) and your long-term financial goals. Because your budget will play a key role in making sound financial decisions for your business, it should be one of the first tasks you tackle to improve business success.
And, as a financially savvy owners, you’ll also want to have a budget in place to help you:
- Make sound financial decisions. In many ways, your business budgets are like a financial road map. It helps you evaluate where your business finances currently stand—and what you need to do to hit your financial goals in the future for business growth.
- Identify where to cut spending or grow revenue. Your business budgets can help you identify areas to decrease your spending or increase your revenue, which will increase your profitability in the process, outline unexpected costs, and help your sustain your business goals.
- Land funding to grow your business. If you’re planning to apply for a business loan or raise funding from investors, you’ll need to provide a detailed budget that outlines your income and expenses.
Now that you understand why budget creation is so important to your business decisions, let’s jump into how to do it.
Business Budget Step 1: Tally Your Income Sources

First things first. When building a small business budget, you need to figure out how much money your business is bringing in each month and where that money is coming from – this will hep create an operating budget based on your business income.
Your sales figures (which you can access using the Profit & Loss report function in FreshBooks) are a great place to start. From there, you can add any other sources of income for your business throughout the month.
Your total number of income sources will depend on your business model.
For example, if you run a freelance writing business, you might have multiple sources of income from:
- Freelance writing projects
- A writing course you sell on your website
- Consulting with other writers who are starting small businesses
Or, if you run a brick-and-mortar retail business, you may only have one source of income from your store sales.
However many income sources you have, make sure to account for any and all income that’s flowing into your business—then tally all those sources to get a clear picture of your total monthly income to build your master business budget template.
Business Budget Step 2: Determine Fixed Costs
Once you’ve got a handle on your income, it’s time to get a handle of your costs—starting with fixed costs.
Your fixed costs are any expenses that stay the same from month to month. This can include expenses like rent, certain utilities (like internet or phone plans), website hosting, and payroll costs.
Review your expenses (either via your bank statements or through your FreshBooks reports) and see which costs have stayed the same from month to month. These are the expenses you’re going to categorize as fixed costs.
Once these costs are determined, add them together to get your total fixed and variable costs expense for the month.
TIP: If you’re just starting your business and don’t have financial data to review, make sure to use projected costs. For example, if you’ve signed a lease for office space, use the monthly rent you will pay moving forward.
Business Budget Step 3: Include Variable Expenses
Related articles.

Variable costs don’t come with a fixed price tag—and will vary each month based on your business performance and activity. These can include things like usage-based utilities (like electricity or gas), shipping costs, sales commissions, or travel costs.
Variable expenses will, by definition, change from month to month. When your profits are higher than expected, you can spend more on the variables that will help your business scale faster. But when your profits are lower than expected, consider cutting these variable costs until you can get your profits up.
At the end of each month, tally these expenses. Over time, you’ll get a sense of how these expenses fluctuate with your business performance or during certain months, which can help you make more accurate financial projections and budget accordingly.
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends
Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they’re fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don’t forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
If you know you have one-time spends on the horizon (for example, an upcoming business course or a new laptop), adding them to your budget can help you set aside the financial resources necessary to cover those expenses—and protect your business from unexpected costs in the form of a sudden or large financial burden.
On top of adding planned one-time spends to your budget, you should also add a buffer to cover any unplanned purchases or expenses, like fixing a damaged cell phone or hiring an IT consultant to deal with a security breach. That way, when an unexpected expense pops up (and they always do), you’re prepared!
Business Budget Step 5: Pull It All Together
You’ve gathered all of your income sources and all of your revenue and expenses. What’s next? Pulling it all together to get a comprehensive view of your financial standing for the month.
On your businesses master budget, you’ll want to tally your total income and your total expenses (i.e., adding your total fixed costs, variable expenses, cost of goods, and one-time spends)—then compare cash flow in (income) to cash flow out (expenses) to determine your overall profitability.
Having a hard time visualizing what a business budget looks like in action? Here’s an operating budget example to give you an idea of what your new business budget might look like each month:
A Client Hourly Earnings: $5,000 B Client Hourly Earnings: $4,500 C Client Hourly Earnings: $6,000 Product Sales: $1,500 Loans: $1,000 Savings: $1,000 Investment Income: $500
Total Income: $19,500
Fixed Costs
Rent: $1,000 Internet: $50 Payroll costs: $5,000 Website hosting: $50 Insurance: $50 Government and bank fees: $25 Cell phone: $50 Accounting services : $100 Legal services: $100
Total Fixed Costs: $6,425
Variable Expenses
Sales commissions: $2,000 Contractor wages: $500 Electricity bill: $125 Gas bill: $75 Water bill: $125 Printing services: $300 Raw materials: $200 Digital advertising costs: $750 Travel and events: $0 Transportation: $50
Total Variable Expenses: $4,125
One-Time Spends
Office furniture: $450 Office supplies for new location: $300 December business retreat: $1,000 New time tracking software: $500 Client gifts : $100
One-Time Spends: $2,350
Expenses: $12,900
Total Income ($19,500) – Total Expenses ($12,900) = Total Net Income ($6,600)
Above all, once you have a clear sense of your profitability for the month, you can use it to make the right financial decisions for your small business moving forward.

For example, if you realize you’re in the red and spending more than you earn, you might cut your spending and focus on finding new clients . Alternatively, if your income is significantly higher than your expenses, you might consider investing your profits back into your business (like investing in new software or equipment).
Use Your Business Budget to Stay on Track
Putting in the work to create a budget for your small business may seem like a hassle. But while it takes a bit of time and energy, it’s worth the extra effort. Thorough business budgeting gives you the financial insights you need to make the right decisions for your business to grow, scale, and prosper in the future.
This post was updated in October 2023

Written by Deanna deBara , Freelance Contributor
Posted on June 20, 2017
Freshly picked for you

Thanks for subscribing to the FreshBooks Blog Newsletter.
Expect the first one to arrive in your inbox in the next two weeks. Happy reading!
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Small Business
6 Steps to a Better Business Budget
A top-notch budget can help propel your business success
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/100378251brianbeersheadshot__brian_beers-5bfc26274cedfd0026c00ebd.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
You've just purchased or opened a small business and you know your trade. But when it comes to bookkeeping—and more specifically, budgeting —your skill set is lacking. The good news is that it is possible to come up with a budget (or at least a good estimation of what will be needed in terms of dollars and cents) fairly easily.
Estimating and matching expenses to revenue (real or anticipated) is important because it helps small business owners to determine whether they have enough money to fund operations, expand the business, and generate income for themselves. Without a budget or a plan, a business runs the risk of spending more money than it is taking in, or conversely, not spending enough money to grow the business and compete.
Key Takeaways
- A business budget helps owners determine if they have enough money to fund operations, expand, and generate income.
- Without a budget, a company runs the risk of spending money it doesn't have, not spending enough to compete, or failing to build a solid emergency fund.
- To create a budget, check industry standards to determine the average costs of doing business and create a spreadsheet estimating the amount of money you'll need to allocate toward your costs.
- Factor in some slack in your budget to cover unexpected costs and review areas where you could cut costs if times get tough.
- Review your budget every few months and shop around for new suppliers to save money on products or services for your business.
Getting Started With a Business Budget
Every small business owner tends to have a slightly different process, situation, or way of budgeting. However, there are some parameters found in nearly every budget that you can employ.
For example, many business owners must make rent or mortgage payments. They also have utility bills, payroll expenses, cost of goods sold (COGS) expenses (raw materials), interest, and tax payments. The point is every business owner should consider these items and any other costs specifically associated with the business when setting up shop or taking over an existing business.
With a business that is already up and running, you can make assumptions about future revenue based on recent trends in the business. If the business is a startup , you'll have to make assumptions based on your geographic area, hours of operation, and by researching other local businesses. Small business owners can often get a sense of what to expect by visiting other businesses that are for sale and asking questions about weekly revenue and traffic patterns.
After you've researched this information, you should then match the business's revenue with expenses. The goal is to figure out what an average weekly expense for overhead, utilities, labor, raw materials, etc. would look like. Based on this information, you may then be able to estimate or forecast whether you'll have enough extra money to expand the business or to tuck away some money into savings. On the flip side, owners may realize that in order to have three employees instead of two, the business will have to generate more in revenue each week.
These six simple tips will help you put together a top-notch small business budget:
1. Check Industry Standards
Not all businesses are alike, but there are similarities. Therefore, do some homework and peruse the internet for information about the industry , speak with local business owners, stop into the local library, and check the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website to get an idea of what percentage of the revenue coming in will likely be allocated toward cost groupings.
Small businesses can be extremely volatile as they are more susceptible to industry downturns than larger, more diversified competitors. So, you only need to look for an average here, not specifics.
2. Make a Spreadsheet
Prior to buying or opening a business, construct a spreadsheet to estimate what total dollar amount and percentage of your revenue will need to be allocated toward raw materials and other costs. It's a good idea to contact any suppliers you'd have to work with before you continue on. Do the same thing for rent, taxes, insurance(s), etc. It's also important you understand the different types of budgets you'll need to set up for your small business and how to implement them.
3. Factor in Some Slack
Remember that although you may estimate that the business will generate a certain rate of revenue growth going forward or that certain expenses will be fixed or can be controlled, these are estimates and not set in stone. Because of this, it's wise to factor in some slack and make sure that you have more than enough money socked away (or coming in) before expanding the business or taking on new employees.
4. Look to Cut Costs
If times are tight and money must be found somewhere in order to pay a crucial bill, advertise, or otherwise capitalize on an opportunity, consider cost-cutting . Specifically, take a look at items that can be controlled to a large degree. Another tip is to wait to make purchases until the start of a new billing cycle or to take full advantage of payment terms offered by suppliers and any creditors. Some thoughtful maneuvering here could provide the business owner with much-needed breathing and expansion room.
5. Review the Business Periodically
While many firms draft a budget yearly, small business owners should do so more often. In fact, many small business owners find themselves planning just a month or two ahead because business can be quite volatile, and unexpected expenses can throw off revenue assumptions. Establishing a budget planning calendar can be an effective tool for business owners to ensure they have enough capital to meet their business needs.
6. Shop Around for Services/Suppliers
Don't be afraid to shop around for new suppliers or to save money on other services being performed for your business. This can and should be done at various stages, including when purchasing or starting up a business, when setting annual or monthly budgets, and during periodic business reviews.
The Bottom Line
Budgeting is an easy, but essential process that business owners use to forecast (and then match) current and future revenue to expenses. The goal is to make sure that enough money is available to keep the business up and running, to grow the business, to compete, and to ensure a solid emergency fund.
University of California, Irvine, Accounting & Fiscal Services. " Understanding Fiscal Years and Fiscal Periods ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-485221701-581f4df15f9b581c0b6e2256.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Get expert advice delivered straight to your inbox.
How to Create a Basic Business Budget
8 Min Read | Mar 13, 2024

You’d never intentionally set your business up to fail, right? But if you don’t know your numbers and how to make a business budget, that’s exactly what you’re doing. Money problems and bad accounting are two reasons why many small businesses don’t make it past their first five years. 1
Talking about budgets can feel overwhelming. We get it. For a lot of business leaders, it’s a lot more comfortable dreaming up big ideas and getting stuff done than digging into numbers. But you can’t set yourself up for steady growth until you have a handle on the money flowing in and out of your company. You also can’t enjoy financial peace in your business.
Not a numbers person? That’s okay. Follow the simple steps below to learn how to create a budget for a business and manage your finances with confidence. We’ll even give you a link to an easy-to-use small-business budget template in the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances .
But before we get to that, let’s unpack what a budget is and why you need one.
Don't Let Your Numbers Intimidate You
With the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances, you can grow your profits without debt—even if numbers aren’t your thing. Plus, get a free business budget template as part of the guide!
What Is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a plan for how you’ll use the money your business generates every month, quarter and year. It’s like looking through a windshield to see the expenses, revenue and profit coming down the road. Your business budget helps you decide what to do with business profit, when and where to cut spending and grow revenue, and how to invest for growth when the time comes. Leadership expert John Maxwell sums it up: “A budget is telling your money where to go instead of wondering where it went.”
But here’s what a business budget is not: a profit and loss (P&L) report you read at the end of the month. Your P&L is like a rearview mirror—it lets you look backward at what’s already happened. Your P&L statement and budget are meant to work together so you can see your financial problems and opportunities and use those findings to forecast your future, set educated goals, and stay on track.
Why Do I Need to Budget for My Business?
Creating a budget should be your very first accounting task because your business won’t survive without it. Sound dramatic? Check this out: There are 33.2 million small businesses in the United States. Out of the small businesses that opened from 1994 to 2020, 67.7% survived at least two years. But less than half survived past five years. 2 The top reasons these businesses went under? They hit a wall with cash-flow problems, faced pricing and cost issues, and failed to plan strategically . 3
As a business owner, one of the worst feelings in the world is wondering whether you’ll be able to make payroll and keep your doors open. That’s why we can’t say it enough: Make a business budget to stay more in control and have more financial peace in running your business.
A budget won’t help you earn more money, but it will help you:
- Maximize the money you’ve got
- Manage your cash flow
- Spend less than your business earns
- Stay on top of tax payments and other bills
- Know if you’re hitting your numbers so you can move at the true speed of cash
How to Create a Budget for a Business
Your ultimate goal is to create a 12–18-month business budget—and you will get there! But start by building out your first month. Don’t even worry about using a fancy accounting program yet. Good ol’ pen and paper or a simple computer document is fine. Just start! Plus, setting up a monthly budget could become a keystone habit that helps kick-start other smart business habits.
Here’s how to create your first budget for business:
1. Write down your revenue streams.
Your revenue is the money you earn in exchange for your products or services. You’ll start your small- business budget by listing all the ways you make money. Look at last month’s P&L—or even just your checking account statement—to help you account for all your revenue streams. You’re not filling in numbers yet. Just list what brings in revenue.
For example, if you run an HVAC business, your revenue streams could be:
- Maintenance service calls
- Repair services and sales
- New unit installation
- Insulation installation
- Air duct cleaning
2. Write down the cost of goods sold (if you have them).
Cost of goods is also called inventory. These expenses are directly related to producing your product or service. In the HVAC example, your cost of goods would be the price you pay for each furnace and air conditioning unit you sell and install. It could also include the cost of thermostats, insulation and new ductwork.
3. List your expense categories.
It’s crazy how much money can slip through the cracks when we’re not careful about putting it in the budget. Think through all your business expenses—down to the last shoe cover your technicians wear to protect your customers’ flooring during house calls. Here’s a list of common business budget categories for expenses to get you started:
- Office supplies and equipment
- Technology services
- Training and education
Related articles : Product Launch: 10 Questions to Ask Before You Launch a New Product New Product Launch: Your 10-Step Checklist
4. Fill in your own numbers.
Now that you have a solid list of revenue and expense categories, plug in your real (or projected) numbers associated with them. It’s okay if you’re not sure how much you’ll sell just yet or exactly how much you’ll spend. Make an educated guess if you’re just starting out. If your business has been earning money for a while, use past P&L statements to guide what you expect to bring in. Your first budget is about combining thoughtful guesswork with history and then getting a more realistic picture month over month.
5. Calculate your expected profit (or loss).
Now, number nerds and number haters alike—buckle in. We’re about to do some basic accounting so you know whether you have a profit or loss. This is your chance to figure out exactly how much you’re spending and making in your business.
Take your gross revenue (the total amount of money you expect to make this month) and subtract your expenses and cost of goods sold to find your profit or loss. Here’s what that calculation looks like:
Revenue - Expenses - Cost of Goods Sold = Profit or Loss
Don’t freak out if your first budget shows a loss. That actually happens a lot with your first few monthly budgets. You’re learning and getting context on what’s coming in and going out so you can make adjustments. Keep doing your budget, and before you know it, you’ll be a rock star at telling your money where to go, planning for emergencies , investments and opportunities , and building momentum.
6. Review your budget often.
Whew! Once you get that first business budget under your belt, take a deep breath and celebrate. You’ve just done something huge for your business! (You’ll also be happy to know, budgeting gets easier from here since you can copy and paste your first one and tweak your income and expenses each month.)
But here’s the thing: Your budget can’t just sit in a drawer or on your computer. You’ve got to look at it consistently to make sure you’re actually following it.
Weekly Review
At least once a week, someone in your business (whether it’s you, a qualified team member or a bookkeeper) needs to track your transactions so you know what’s happening with your money all month. Then you can make adjustments before you have more month than money.
Every time you review your budget, ask yourself these three questions:
- Are we on target to hit our revenue goal this month?
- If not, what we can change to get there?
- Are there any expenses we can cut or minimize?
Monthly Review
You also need to review your business budget when you close your books every month to compare it to your actuals—your P&L. Otherwise, how can you know how you’re doing?
7. Work toward a 12–18-month budget.
Now that you’ve created your first month’s budget, move on to the next one. You’ve got this! The more budget-building reps you get in, the better you’ll be at looking forward and planning for growth. In no time, you’ll reach that ultimate goal of a 12–18-month budget. Just keep adjusting as you go based on all you’re learning about getting an accurate road map for your finances.
As you start owning your numbers, remember: It’s okay if you’re a little intimidated by the process of accounting and making a budget for business. But it’s not okay to avoid the financial details that will make or break you. So just keep applying the basics we covered and keep moving forward.
Follow the steps above to create your budget, and review it often to stay on track.
Want a tool to make budget building simpler? Check out the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances. It includes an easy-to-use small-business budget template in the extra resources section.
What are the benefits of budgeting?
A business budget will help you:
- Make informed, strategic decisions
- Invest in under-resourced areas
- Trim over-resourced areas
- Plan for the future
- Set goals and track your progress
Does using a small-business budget template save time?
Yes! Using a small-business budget template helps you plug in the numbers you need to operate with more confidence and fewer wrong turns. Check out the small-business-budget template inside our EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances .
How do I budget if I own a seasonal business?
Just like farmers put extra hay in the barn to cover leaner months, if you’re a seasonal business owner, you need to set aside resources in times of plenty to cover months your business turns down. Use your P&L statements to go back in time and look at financial performance year over year. Then, create your business budget based on what you learn and on any changes you see coming. You can also go to trade conferences to get an idea of your industry’s seasonal benchmarks.
Did you find this article helpful? Share it!

About the author
Ramsey Solutions has been committed to helping people regain control of their money, build wealth, grow their leadership skills, and enhance their lives through personal development since 1992. Millions of people have used our financial advice through 22 books (including 12 national bestsellers) published by Ramsey Press, as well as two syndicated radio shows and 10 podcasts, which have over 17 million weekly listeners. Learn More.
7 Tips for How to Run a Business Debt-Free
True or false: Running a business requires debt. The answer? False. The truth is, you can’t run a business if you’re broke—and debt increases your risk of going broke when a storm hits. Here’s how to run a business debt-free.
How to Create a Profit-Sharing Plan
It's easy to feel discouraged when trying to compete for top talent and keep your team happy. Learn how a profit-sharing plan can help you build and keep an awesome team even when the market shifts.
The Best Free Business Budget Templates
Published: October 12, 2023
Business budgets are a source of truth for your income and expenses. That includes all the money you spend — from A/B testing your marketing campaigns to your monthly office rent.

While organizing the numbers may sound difficult, using a business budget template makes the process simple. Plus, there are thousands of business budget templates for you to choose from.

We’ll share seven budget templates that can help organize your finances. But first, you’ll learn about different types of business budgets and how to create one.
What is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a spending plan that estimates the revenue and expenses of a business for a period of time, typically monthly, quarterly, or yearly.
The business budget follows a set template, which you can fill in with estimated revenues, plus any recurring or expected business expenses.
For example, say your business is planning a website redesign. You'd need to break down the costs by category: software, content and design, testing, and more.
Having a clear breakdown will help you estimate how much each category will cost and compare it with the actual costs.
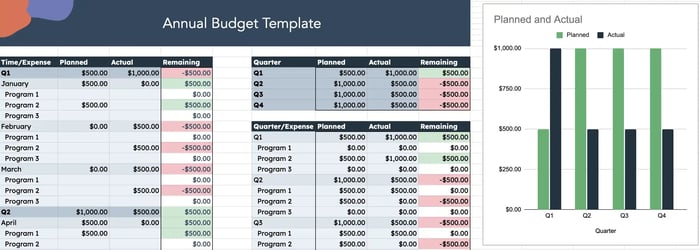
Image Source
Types of Budgets for a Business
Master budget, operating budget, cash budget, static budget, departmental budget, capital budget, labor budget, project budget.

Business budgets aren’t one size fits all. In fact, there are many different types of budgets that serve various purposes. Let’s dive into some commonly used budgets:
Think of a master budget as the superhero of budgets — it brings together all the individual budgets from different parts of your company into one big, consolidated plan. It covers everything from sales and production to marketing and finances.
It includes details like projected revenues, expenses, and profitability for each department or business unit. It also considers important financial aspects like cash flow, capital expenditures, and even creates a budgeted balance sheet to show the organization's financial position.
The master budget acts as a guide for decision-making, helps with strategic planning, and gives a clear picture of the overall financial health and performance of your company. It's like the master plan that ties everything together and helps the organization move in the right direction.
Your operating budget helps your company figure out how much money it expects to make and spend during a specific period, usually a year. It not only predicts the revenue your business will bring in, but also outlines expenses it will need to cover, like salaries, rent, bills, and other operational costs.
By comparing your actual expenses and revenue to the budgeted amounts, your company can see how it's performing and make adjustments if needed. It helps keep things in check, allowing your business to make wise financial decisions and stay on track with its goals.
.png)
Free Business Budget Templates
Manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
- Personal Budget Template
- Annual Budget Template
- Program Budget Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A cash budget estimates the cash inflows and outflows of your business over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It provides a detailed projection of cash sources and uses, including revenue, expenses, and financing activities.
The cash budget helps you effectively manage your cash flow, plan for cash shortages or surpluses, evaluate the need for external financing, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
By utilizing a cash budget, your business can ensure it has enough cash on hand to meet its financial obligations, navigate fluctuations, and seize growth opportunities.
A static budget is a financial plan that remains unchanged, regardless of actual sales or production volumes.
It’s typically created at the beginning of a budget period and doesn’t account for any fluctuations or changes in business conditions. It also assumes that all variables, such as sales, expenses, and production levels, will remain the same throughout the budget period.
While a static budget provides a baseline for comparison, it may not be realistic for businesses with fluctuating sales volumes or variable expenses.
A departmental budget focuses on the financial aspects of a specific department within your company, such as sales, marketing or human resources.
When creating a departmental budget, you may look at revenue sources like departmental sales, grants, and other sources of income. On the expense side, you consider costs such as salaries, supplies, equipment, and any other expenses unique to that department.
The goal of a departmental budget is to help the department manage its finances wisely. It acts as a guide for making decisions and allocating resources effectively. By comparing the actual numbers to the budgeted amounts, department heads can see if they're on track or if adjustments need to be made.
A capital budget is all about planning for big investments in the long term. It focuses on deciding where to spend money on things like upgrading equipment, maintaining facilities, developing new products, and hiring new employees.
The budget looks at the costs of buying new stuff, upgrading existing things, and even considers depreciation, which is when something loses value over time. It also considers the return on investment, like how much money these investments might bring in or how they could save costs in the future.
The budget also looks at different ways to finance these investments, whether it's through loans, leases, or other options. It's all about making smart decisions for the future, evaluating cash flow, and choosing investments that will help the company grow and succeed.
A labor budget helps you plan and manage the costs related to your employees. It involves figuring out how much your business will spend on wages, salaries, benefits, and other labor-related expenses.
To create a labor budget, you'll need to consider factors like how much work needs to be done, how many folks you'll need to get it done, and how much it'll all cost. This can help your business forecast and control labor-related expenses and ensure adequate staffing levels.
By having a labor budget in place, your business can monitor and analyze your labor costs to make informed decisions and optimize your resources effectively.
A project budget is the financial plan for a specific project.
Let's say you have an exciting new project you want to tackle. A project budget helps you figure out how much money you'll need and how it will be allocated. It covers everything from personnel to equipment and materials — basically, anything you'll need to make the project happen.
By creating a project budget, you can make sure the project is doable from a financial standpoint. It helps you keep track of how much you planned to spend versus how much you actually spend as you go along. That way, you have a clear idea of whether you're staying on track or if there are any financial challenges that need attention.
How to Create a Business Budget
While creating a business budget can be straightforward, the process may be more complex for larger companies with multiple revenue streams and expenses.
No matter the size of your business, here are the basic steps to creating a business budget.
1. Gather financial data.
Before you create a business budget, it’s important to gather insights from your past financial data. By looking at things like income statements, expense reports, and sales data, you can spot trends, learn from past experiences, and see where you can make improvements.
Going through your financial history helps you paint a true picture of your income and expenses. So, when you start creating your budget, you can set achievable targets and make sure your estimates match what's actually been happening in your business.
2. Find a template, or make a spreadsheet.
There are many free or paid budget templates online. You can start with an already existing budget template. We list a few helpful templates below.
You may also opt to make a spreadsheet with custom rows and columns based on your business.
3. Fill in revenues.
Once you have your template, start by listing all the sources of your business’ income. With a budget, you’re planning for the future, so you’ll also need to forecast revenue streams based on previous months or years. For a new small business budget, you’ll rely on your market research to estimate early revenue for your company.
When you estimate your revenue , you're essentially figuring out how much money you have to work with. This helps you decide where to allocate your resources and which expenses you can fund.
4. Subtract fixed costs for the time period.
Fixed costs are the recurring costs you have during each month, quarter, or year. Examples include insurance, rent for office space, website hosting, and internet.
The key thing to remember about fixed costs is that they stay relatively stable, regardless of changes in business activity. Even if your sales decrease or production slows down, these costs remain the same.
However, it's important to note that fixed costs can still change over the long term, such as when renegotiating lease agreements or adjusting employee salaries.
5. Consider variable costs.
Variable costs will change from time to time. Unlike fixed costs, variable costs increase or decrease as the level of production or sales changes.
Examples include raw materials needed to manufacture your products, packaging and shipping costs, utility bills, advertising costs, office supplies, and new software or technology.
You may always need to pay some variable costs, like utility bills. However, you can shift how much you spend toward other expenses, like advertising costs, when you have a lower-than-average estimated income.
6. Set aside time for business budget planning.
Unexpected expenses might come up, or you might want to save to expand your business. Either way, review your budget after including all expenses, fixed costs, and variable costs. Once completed, you can determine how much money you can save. It’s wise to create multiple savings accounts. One should be used for emergencies. The other holds money that can be spent on the business to drive growth.
Fill out the form to get the free templates.
How to manage a business budget.
There are a few key components to managing a healthy business budget.
Budget Preparation
The process all starts with properly preparing and planning the budget at the beginning of each month, quarter, or year. You can also create multiple budgets, some short-term and some long-term. During this stage, you will also set spending limits and create a system to regularly monitor the budget.
Budget Monitoring
In larger businesses, you might delegate budget tracking to multiple supervisors. But even if you’re a one-person show, keep a close eye on your budget. That means setting a time in your schedule each day or week to review the budget and track actual income and expenses. Be sure to compare the actual numbers to the estimates.
Budget Forecasting
With regular budget tracking, you always know how your business is doing. Check in regularly to determine how you are doing in terms of revenue and where you have losses. Find where you can minimize expenses and how you can move more money into savings.
Why is a Budget Important for a Business?
A budget is crucial for businesses. Without one, you could easily be drowning in expenses or unexpected costs.
The business budget helps with several operations. You can use a business budget to keep track of your finances, save money to help you grow the business or pay bonuses in the future, and prepare for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
You can also review your budget to determine when to take the next leap for your business. For example, you might be dreaming of a larger office building or the latest software, but you want to make sure you have a healthy net revenue before you make the purchase.
Best Free Business Budget Templates
1. marketing budget template.
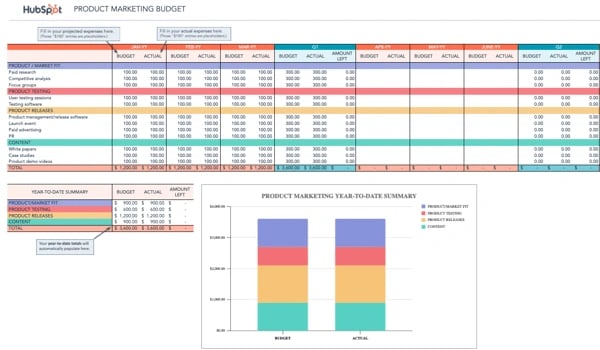
Knowing how to manage a marketing budget can be a challenge, but with helpful free templates like this marketing budget template bundle , you can track everything from advertising expenses to events and more.
This free bundle includes eight different templates, so you can create multiple budgets to help you determine how much money to put toward marketing, plus the return on your investment.
2. Small Business Budget Template
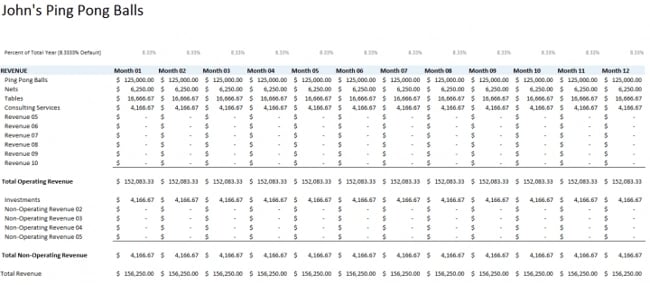
For small businesses, it can be hard to find the time to draw up a budget, but it’s crucial to help keep the business in good health.
Capterra offers a budget template specifically for small businesses. Plus, this template works with Excel. Start by inputting projections for the year. Then, the spreadsheet will project the month-to-month budget. You can input your actual revenue and expenses to compare, making profits and losses easy to spot.
3. Startup Budget Template
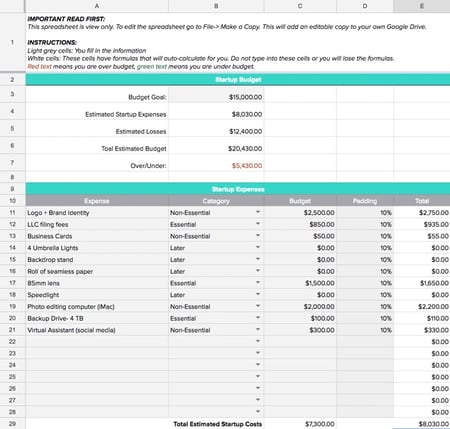
What if you don’t have any previous numbers to rely on to create profit and expense estimates? If you are a startup, this Gusto budget template will help you draw up a budget before your business is officially in the market. This will help you track all the expenses you need to get your business up and running, estimate your first revenues, and determine where to pinch pennies.
4. Free Business Budget Template
You might be familiar with Intuit. Many companies, big and small, rely on Intuit’s services like Quickbooks and TurboTax. Even if you don’t use the company’s paid financial services, you can take advantage of Intuit’s free budget template , which works in Google Sheets or Excel.
It features multiple spreadsheet tabs and simple instructions. You enter your revenue in one specific tab and expenses in another. You can also add additional tabs as needed. Then, like magic, the spreadsheet uses the data in the income and expense tabs to summarize the information. This template can even determine net savings and the ending balance.
5. Department Budget Sheet
A mid- to large-size company will have multiple departments, all with different budgetary needs. These budgets will all be consolidated into a massive, company-wide budget sheet. Having a specific template for each department can help teams keep track of spending and plan for growth.
This free template from Template.net works in either document or spreadsheet formats. This budget template can help different departments keep track of their income and spending.
6. Project Budget Template
Every new project comes with expenses. This free budget template from Monday will help your team estimate costs before undertaking a project. You can easily spot if you're going over budget midway through a project so you can adjust.
This template is especially useful for small companies that are reporting budgets to clients and for in-house teams getting buy-in for complex projects.
7. Company Budget Template
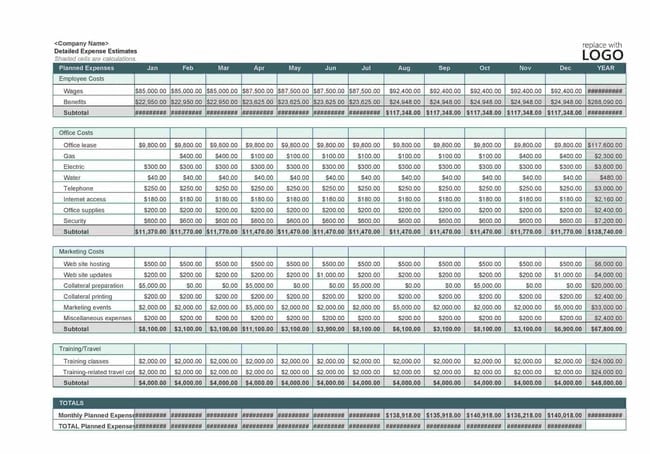
Want to keep track of every penny? Use this template from TemplateLab to draw up a detailed budget. The list of expenses includes fixed costs, employee costs, and variable costs. This business template can be especially useful for small businesses that want to keep track of expenses in one, comprehensive document.
Create a Business Budget to Help Your Company Grow
Making your first business budget can be daunting, especially if you have several revenue streams and expenses. Using a budget template can make getting started easy. And, once you get it set up, these templates are simple to replicate.
With little planning and regular monitoring, you can plan for the future of your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in September 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.


Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![small budget business plan Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20spend%20your%20marketing%20budget_featured.webp)
Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]
![small budget business plan How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20marketing%20leaders%20are%20navigating%20recession.webp)
How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]
![small budget business plan 3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-marketers-are-navigating-recession.jpg)
3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]
![small budget business plan Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20without%20budget.jpg)
Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]

24 Ways to Spend Your Marketing Budget Next Quarter

Startup Marketing Budget: How to Write an Incredible Budget for 2023
![small budget business plan How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-marketing-budget-templates_5.webp)
How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]

10 Best Free Project Management Budget Templates for Marketers

What Marketing Leaders Are Investing in This Year

The Best Free Business Budget Worksheets
6 templates to manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How to create a business budget
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email
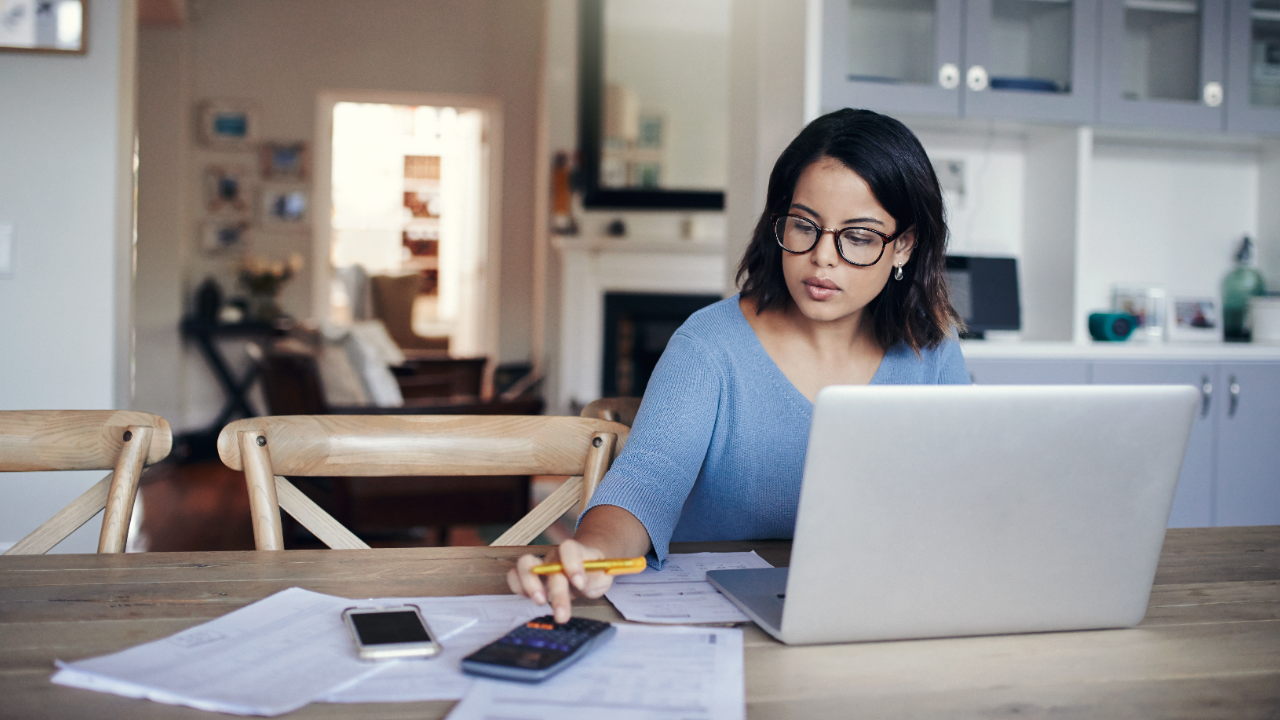

- • Small business loans
- • Bad credit loans

- • Funding inequality
- Connect with Emily Maracle on LinkedIn Linkedin
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our banking reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — the best banks, latest rates, different types of accounts, money-saving tips and more — so you can feel confident as you’re managing your money.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and, services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Our writers and editors used an in-house natural language generation platform to assist with portions of this article, allowing them to focus on adding information that is uniquely helpful. The article was reviewed, fact-checked and edited by our editorial staff prior to publication.
Key takeaways
- A business budget is a financial plan that helps estimate a company's revenue and expenses, making it an essential tool for small businesses
- The steps to creating a business budget include choosing budget and accounting software, listing expenses and forecasting revenue
- If a business finds itself in a budget deficit, strategies such as cutting costs, negotiating with suppliers and diversifying revenue streams can help
As a small business owner, keeping your finances organized through a business budget is crucial to running a successful company.
Business budgeting involves creating a financial plan that estimates future revenue and expenses to make informed financial decisions, which can ultimately move the needle on your business’s financial goals and help it grow in profitability.
What is a business budget?
A business budget is a financial plan that outlines the company’s current revenue and expenses. The budget also forecasts expected revenue that can be used for future business activities, such as purchasing equipment. It sets targets for your business’s revenue, expenses and profit and helps you determine if you’ll have more money coming in than you pay out.
A business budget is an essential tool that helps you make wise business decisions. Without it, it’s difficult to gauge your business’s financial health.
What is the difference between a cash flow statement and a business budget?
A cash flow statement (CFS) is a financial document that summarizes the movement of cash coming in and going out of a company. The CFS gauges how effectively a company manages its finances, including how it manages debt responsibilities and funds day-to-day operations.
It’s similar to a business budget in that you can see expenses and revenue. But while a budget gives a moment-in-time snapshot of your business’s financial performance compared to forecasts, the cash flow statement focuses on the actual inflows and outflows of money through your business.
Follow these steps to ensure a well-developed budget, from understanding your expenses to generating revenue and adjusting expenses to balance the budget.
1. Choose a budget and accounting software
First, you’ll want to store your expense and revenue information with accounting software to help you track your numbers and generate reports. Some software may also help you assign categories to the transactions, identify tax deductions and file taxes. Quickbooks is an example of accounting software.
Some business bank accounts also have accounting software built in, helping you stay organized by keeping your accounting and banking in one place.
2. List your business expenses
The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget:
- Fixed expenses: Fixed expenses cost a fixed amount monthly or within the assessed period. Those costs include rent, insurance, salaries and loan payments.
- Variable expenses: Variable expenses can change monthly or over time, making them trickier to budget. This might include materials, direct labor, utility bills or marketing expenses.
- Annual or one-time costs: Some costs only occur a few times per year, while others you’ll only pay for as needed, such as buying new equipment. You still want to budget for these expenses by allocating a portion of your weekly or monthly budget toward one-time expenses.
- Contingency funds: Unexpected business costs can throw a wrench in your budget if not planned for. Such costs could include emergency repairs, necessary equipment purchases, sudden tax increases or unforeseen legal fees. To plan for these costs, you can create a contingency or emergency fund that’s separate from your operational budget.
- Maintenance costs: To allocate funds for maintenance costs, begin by including regular inspections and maintenance in your budget. Then, make sure to leave room for changes and unexpected maintenance costs.
3. Forecast your revenue
To estimate your future revenue, start by deciding on a timeline for your forecast. A good place to start is the previous 12 months. Your accounting software may also include revenue forecasting as one of its features, which can automate this step for you.
The timeline and your recent past growth can help you understand how much revenue you’ll generate in the future. Consider external factors that could drive revenue growth, such as planned business activities like expansion, marketing campaigns or new product launches.
You’ll also want to think about anything that might slow your growth. Many businesses experience seasonal fluctuations, which can impact your budget if you don’t plan for it. To account for these changes, list the minimum expenses required to keep your business running. Use your financial statements to understand these costs, and consider averaging out irregular expenses over the year to avoid surprises.
Ideally, your business should build a cash reserve during profitable periods to cover expenses during slower seasons. If necessary, consider various financing options, such as a business credit card or line of credit, that you can draw from to manage cash flow during peak or off times.
4. Calculate your profits
The next step in creating a business budget is to calculate your business profits. You can look at your total profits by calculating revenue minus expenses. That way, you see how much money you have to work with, called your working capital .
You should also understand your profit margins for each of your products and services, which can help you set prices or decide whether to offer a new product or service.
How to calculate your profit margins
To find out your gross profit margin, you’ll first need to calculate the gross profit. To calculate your business’s gross profit, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your total revenue. COGS includes all the expenses related to producing your products and services.
Once you have the gross profit, use the gross profit margin formula: (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue x 100. This will give you a percentage that shows how much profit you gain from that particular product after accounting for the product’s costs.
5. Make a strategy for your working capital
Knowing what to do with extra revenue, which is your working capital, is crucial for managing your business finances and growth. Here’s how to get started with a financial strategy that propels your business goals forward:
- Set spending limits for different categories in your budget. When listing your expenses, you should have set a dollar amount for each category. You can estimate this by a monthly average or a general forecasted amount.
- Set realistic short- and long-term goals. These goals will motivate you to stick to your budget and guide your spending decisions.
- Compare your actual spending with your net income and priorities. Look at the areas you’re spending and consider whether you need to reallocate money to different categories. Consider separating expenses into business needs and extras.
- Adjust your budget and actual spending. Adjust your spending to ensure you do not overspend and can allocate money towards your goals. If you need to cut spending, consider the categories that are extras, such as types of marketing that you don’t know will generate a return on investment.
6. Review your budget and forecasts regularly
Finally, review your budget regularly. By frequently checking in on your budget, you can identify any discrepancies between your planned and actual expenses and adjust accordingly. This allows you to proactively handle any financial issues that may arise rather than reacting to them after they’ve become a problem.
Regular reviews also allow you to refine your budgeting process and improve its accuracy over time. Keep in mind that your budget is not set in stone but rather a tool to guide your financial decisions and help you achieve your business goals.
What to do if you have a deficit in your business budget
Finding a deficit in your small business budget can be alarming, but there are several strategies you can employ to handle this situation.
- Do a cash flow analysis. Begin by doing a cash flow analysis to review what your business is earning and spending money on. Identify potential problems and adjust the budget as needed to prevent overspending.
- Cut nonessential business costs. Cutting spending may involve eliminating nonessential costs and transferring funds from other categories to overspent categories. Your goal is a balanced or profitable budget.
- Negotiate with suppliers. Be transparent in your communications with suppliers and explain your quality standards and why you’re seeking cost reduction. Explore options for cost reduction that do not compromise quality, such as process improvements or ordering in larger quantities.
- Create a lean business model. By removing anything that doesn’t benefit your customer, your business can potentially save time and resources. Lean business models focus on continually improving processes and customer experience without adding additional resources, time or funds.
- Add revenue and diversify revenue streams. Raising revenue requires a realistic plan with measurable goals to increase sales and overall business income. You can also consider other products and services you could offer that would make your business profitable.
- Use financing to cover temporary gaps. Applying for a small business loan can help pay bills during an unplanned shortfall. Since this will add an expense to your budget, make sure you can handle the loan repayments and your regular expenses.
- Plan for a deficit. In some cases, a planned budget deficit might be a strategic decision, such as investing in new opportunities that promise long-term benefits.
Bottom line
Having a well-developed business budget is crucial for making informed decisions. You can effectively manage your small business’s finances by tracking and analyzing your business’s inflows and outflows, forecasting your expected revenue and adjusting your budget to stay balanced.
Even in the face of a budget deficit, there are various strategies you can use to keep your business profitable, including negotiating costs with your suppliers, assessing your business operations and offering new products and services.
With a solid business budget in place, you can confidently navigate financial challenges and drive long-term success for your small business.
Frequently asked questions
What are the benefits of a business budget, what are the components of a business budget, how do you calculate fixed and variable costs in a business budget.

Related Articles

How to get an equipment loan

How to finance a small business for the holidays

How to start a small business

How to build business credit: 7 steps
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

According to a study done by CBinsights, a few of the top reasons why small businesses fail include include pricing and cost issues, losing focus and running out of cash. These issues can be prevented by having a realistic budget in place.
Before you can focus on the budget, however, you need to identify what aspects of your business you’d like to improve. This will allow you to decide what can be done with your funds. Based on that list, you can set up short-term and long-term goals.
These goals will be directly affected by your incoming and outgoing cash. A short-term goal can be paying off a debt or purchasing new equipment. Long-term goals, like keeping aside marketing expenses, are crucial because they are connected to the overall growth of your business.
You should be practical about the goals you set. They should be purely based on your business’ capacity to spend and save. Once you have your goals in place, you can create an effective, foolproof budget by following these steps.
1. Analyze costs
Before you start drafting a budget, you must research the operating costs involved in your business. Knowing your costs inside and out gives you the baseline knowledge needed to craft an effective spending plan.
If you create a rough budget and later discover that you need more money for your business activities, this will jeopardize your goals. Your budget should be such that you can increase your revenue and profit enough as your business expands to handle your growing expenses. Your budget should factor in fixed, variable, one-time, and unexpected costs. Some examples of a fixed expense are rent, mortgages, salaries, internet, accounting services, and insurance. Examples of variable costs include cost of goods sold and commissions for labor.
There is not much harm in overestimating the costs involved since you will need enough cash to handle your future expenditures. If your business is new, then you must include start-up costs as well. Planning the budget this way will help you make informed decisions and tackle any unwanted financial surprises.
2. Negotiate costs with suppliers
This step will be useful for those businesses which have been functional for more than a year and are dependent on suppliers to sell products. Before you get started on your yearly budget, have a chat with your suppliers and try getting discounted rates for the materials, products, or services you need before you make your payments.
Negotiations allow you to create trustworthy relationships with your suppliers. This will be helpful when incoming cash is thin. For example, you might have a seasonal business. When you have enough cash saved, you can pay advance amounts to your suppliers as compensation for the times when you are unable to make payments. The main goal here is to find efficient ways to reduce cost of doing business.
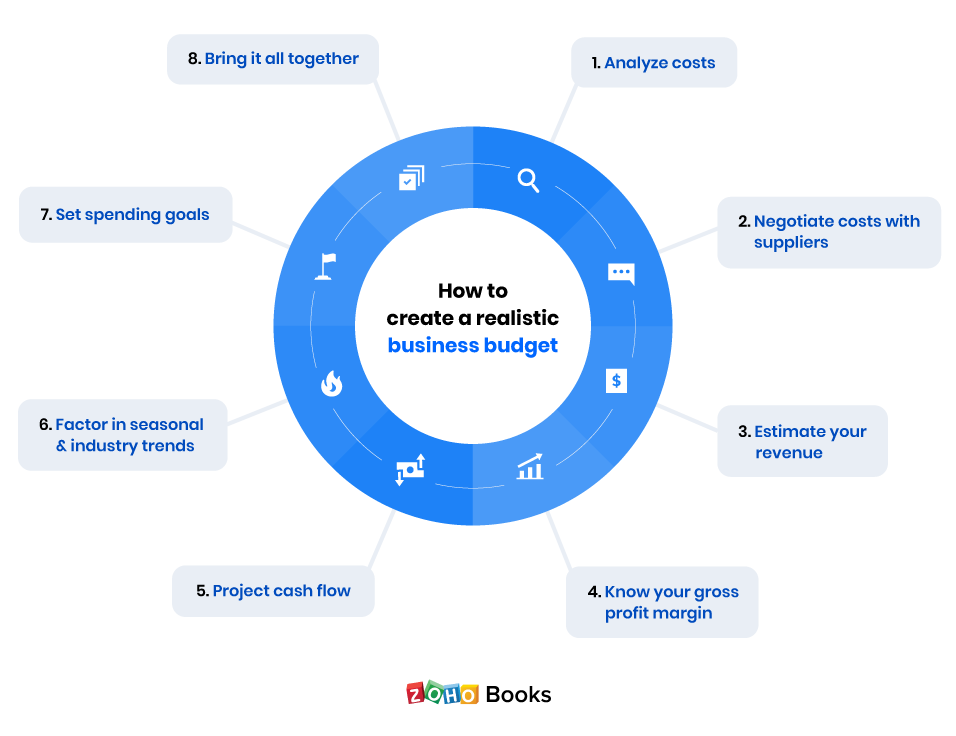
3. Estimate your revenue
Many businesses have failed in the past by overestimating revenue and borrowing more cash to meet operational needs. This defeats the very purpose of creating a budget. To keep things realistic, it’s a good idea to analyze previously recorded revenue. Businesses must track revenue periodically on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis.
Your previous year’s revenue figures can act as a reference point for the upcoming year. It’s important to rely solely on this empirical data. This will help you set realistic goals for your team, leading to the eventual growth of your business.
4. Know your gross profit margin
The gross profit margin is the cash you are left with after your business has dealt with all the expenses at the end of the year. It gives insight into the financial health of your business. Here’s an example of why you need to understand this parameter while creating a budget.
Suppose your business made a revenue $5,000,000 and yet there are debts to be paid. At the end of the year, your expenses are more than your revenue, which is not a good sign for a growing business. This tells you that you must identify the expenses that are not benefiting the business in any way and eliminate them. The best way to do this would be to list out the cost of goods sold for all materials and deduct them from the overall sales revenue. This information is needed to get a real picture on how your business is faring, allowing you to increase profit and reduce costs.
5. Project cash flow
There are two components to cash flow : customer payments and vendor payments. You need to balance these two components to keep the cash flowing in your organization.
To do your best to ensure timely customer payments, it’s important to have flexible payment terms and the ability to receive payments through common payment channels. Unfortunately you will need to deal with customers who might not comply to the stated terms. This might affect your cash flow forecast due to missing payments.
You can encourage payment by giving customers a grace period and creating strict business policies for paying late. Beyond this, you must have some money allocated in your budget for ‘bad debt,’ in case the customer never pays.
When you know your incoming cash flow, you can fix an amount for your employee salaries and travel expenses. You can also allocate some money to pay off your fixed vendor expenses. If you are still left with cash, you can then spend on business initiatives such as professional development or new equipment.
6. Factor in seasonal and industry trends
It’s unrealistic to expect that you will achieve every business goal and reach your estimates every month. In an annual cycle, there will be months where your business will be booming, and there may be a few months where sales are slow. Due to seasonal inconsistency and industry trends, you will have to spend cash effectively so that the business isn’t at risk of shutting down during slower periods.
To overcome this challenge while creating a budget, gather insights as to when your business performs better. The aim should be to generate enough revenue during peak months to sustain the business during off seasons.
For example, let’s assume that you are a business owner of a winter clothing company. Your products are on demand only during that season, so most of your revenue comes during that period. For the rest of the year, you can use the earnings to keep the business going and market to specific target groups, like hikers or travelers. This will help you gauge how successful your products are during off seasons, what revenue to expect, and how much to save during your peak periods.
7. Set spending goals
Making a budget is more than just adding your costs and subtracting them from your earnings. How wisely you spend your money determines how well your business will fare. Goals provide a system to check if your money is being spent on the right areas to avoid unwanted expenses.
For example, if you are spending money on stationary that is going unused for operational or marketing efforts, it may be time to cut those costs. This money can be better applied to your marketing campaigns, bringing in more leads and revenue. Gauge and invest in those expenses that would benefit your business in the long run.
8. Bring it all together
Once you have gathered all the information from the previous steps, it’s time to create your budget. After you have subtracted your fixed and variable expenses from your income, you will get an idea of the amount that you can work with. Be prepared to tackle the unexpected one-time expenses that come your way. You can then find ways to use the money effectively to achieve your short-term and long-term goals.
Role of accounting software in budgeting
Budgeting for a business is a large task, which is why you might need assistance. Creating a budget will involve analyzing costs, estimating revenue, and projecting cash flow. Having an accounting system in place will give you real-time information about your finances, helping you to create a feasible budget.
The key to creating a good budget is to evaluate the previous years’ data and draw realistic projections. An accounting system can give you access to all this information in one place, no matter when you need it.
The effectiveness of a budget also depends on how well any projected goals have been achieved by your business. To check this, an accounting system generates financial reports that record your actuals, and those can then be compared with the budget. Comparing your budget with your actuals is an important step to gauge the effectiveness of a budget.
Budgeting is an essential process, especially for small businesses, as it allows business owners to estimate and allocate money for different business activities. Preparing a budget also gives you a clear idea of the money that can be used to achieve business goals and ensure that there is enough in hand to handle a crisis. For small businesses, it might get a bit difficult to make estimations for the whole year as the initial stages of growing an organization are often volatile. In such cases, you can create smaller budget estimates for a duration of two or three months and keep reviewing it for better results. When an accounting system is introduced, the process becomes even more manageable. You can easily handle tasks like projecting cash flow or estimating costs, and you can set realistic goals for your business.
Related Posts
- Business Budget: What is it & Why is it important?
- How Is Cash Flow Calculated?
Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Great article, Easy to read, straight to the point, very informative.
Wonderful article! Just what I needed
a valuable information for person like me who doesn’t has finance background.
wonderful said,
I really like this article, it is very easy to read, gives an idea and try to make the budget process a much easier task
Simple and precise article
You might also like
Switch to smart accounting. try zoho books today.
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
How to Create a Business Budget, With Free Budget Template

Table of Contents
Creating a budget for your business may seem daunting. However, it’s a crucial first step in any successful business plan . While a business budget can take multiple forms, it will include how much money you have coming in and what you must spend to continue operating. It also shows how much money you must earn to continue making a profit and paying your expenses.
What is a business budget template?
A business budget template is a customizable worksheet business owners can use as a budget planning guide. Budget planning templates can be a huge help for business owners who don’t have time to create a business budget from scratch. They’re handy tools that give you a place to record all your numbers in an organized way, helping you set up an easy-to-read budget you can update quickly.
Budgets can be complicated, so consider downloading a template if this is your first time creating a business budget. Even if you choose to create your own, referring to templates or sample budgets may be helpful to keep yourself on the right track.
Free small business budget template
If you’re unsure where to begin, download Business.com’s free budget template . This template will help you track your expenses, estimate your monthly income and record what you earned and spent.
Our budget template has five tabs. To use it, take the following steps:
- Make a copy or download the template.
- On the first tab, Instructions , replace the Your business’s name text with your actual business name. Once you do that, your business name will automatically fill in on the other pages.
Here’s a breakdown of how to use the other four tabs.
Annual budget
The Annual Budget tab examines how much money your business brings in each year. Use this tab to input your company’s yearly revenue and expenses. Be as specific and detailed as possible because this information is used throughout the budget template.
Monthly budget
The Monthly Budget tab shows your monthly expenses. Since you already filled out the Annual Budget information, this data has been prorated and you have monthly estimates for each of your yearly totals.
By default, each month’s budget is weighted equally. However, you can change this by updating the percentages in line 5. Your percentages must add up to 100.
Monthly actuals
The Monthly Actuals tab is for financial tracking . You’ll use this tab to track your actual expenses and revenue as they come in each month, allowing you to see how much money your business is making.
The Overview tab shows how your actual numbers compare to your budget. It gives an overview of your annual and monthly budgets. This information helps you see where your business is doing well and identify areas for improvement. To see your finances for a particular month, select that month from the drop-down list in line 4.
Why do you need a business budget template?
A business budget template is vital to keep your expenses and financial goals updated. A good template makes it easy to see how much money you have available, what you need to pay for and how much money you have left after covering your necessary fixed and variable expenses .
Your business budget template will show you if you can grow your business, give yourself or your employees raises and purchase inventory and assets . If you don’t have sufficient money coming in, it will reveal which bills you don’t have the funds to pay or if you are nearing bankruptcy .
If you must apply for a business loan or grant, the application may ask for financial accounting documentation, such as a monthly or annual budget, to give the lender an idea of your business’s financial standing and how you manage your money. For these reasons, having an up-to-date budget from the beginning is in your best interest.
How do you create a startup business budget?
If your business is new or in the planning stages, creating a budget is tricky ― even with a template – because you don’t have actual numbers to plug in. Still, it’s something you need for your business plan and loan applications.
Here are five steps to help you create a startup budget to get your business off on the right foot.
1. Set your budget goal.
Your budget goal is the total amount you are willing to spend on your business. Setting this number helps you establish clear parameters for your budget from the beginning and keep your spending in check.
To set your goal, consider the amount of money you currently have or can realistically obtain. How much money makes sense for you to spend? Keep in mind that loans must be repaid, often with interest and you shouldn’t deplete your personal savings.
2. Categorize your expenses.
For this step, brainstorm all potential expenses on a budget worksheet. Begin with your startup costs , which are any one-time expenses related to starting your business.
Startup costs could include a building (if you’re buying, not renting), computers and photography equipment. Be specific and write down the exact costs of every item you must purchase and any associated costs. For example, to build a website, you must pay for a designer, host, domain name, plugins, stock photos and security software.
Next, categorize each item as “essential,” “nonessential,” or “later”:
- Essential items: Essential items, as the name suggests, are purchases crucial to starting your business, such as a business license.
- Nonessential items: Nonessential items will make your life easier but are not crucial to your business’s operation. For example, professionally designed logos or websites are likely nonessential elements. What you deem “nonessential” can be subjective but try to look at your business as a whole and use your best judgment.
- Later items: Later items can be put off for at least six months and are not required for your business’s immediate functions. Examples include a fresh coat of paint for your building or a state-of-the-art voice-over-internet-protocol phone system .
Add up your essential and nonessential items to get your estimated startup costs.
3. Estimate your losses.
Your losses are how long you will go without turning a profit while accumulating overhead expenses. Losses are a result of a new business needing time to build a customer base and your budget must reflect them.
Start by calculating your estimated monthly overhead costs, including subcontractors, payroll, software subscriptions, website fees, rent and advertising fees. This will create your operating budget.
Next, estimate how many months you will go without revenue. Forecasting income can be difficult when starting out, so determine your break-even number and use that figure to make an educated guess.
4. Build in a safety net.
Given the unpredictable nature of starting a business, it’s easy to exceed your estimated budget. Building some financial padding into your budget can help you cover unexpected costs.
Think of this money like a vehicle’s airbags ― they’re used only in an actual emergency. To create your safety net, add 10 percent to each expense in your startup budget and 15 percent to your monthly operating costs.
5. Refine your budget.
Now that you have some rough numbers to work with, it’s time to tighten them up to make your budget more actionable. Start by going through your nonessential startup items. Is there anything you can cut out or move to the “later” category? Can you reduce the cost of any items by buying something secondhand or trading labor?
Next, look at your overhead costs and determine if any are unnecessary and can be cut. If you can’t get your budget to balance, you can also reevaluate your essential costs. Go through them with a trusted advisor or colleague to determine if they are all truly essential to starting your business.
Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
- Skip to content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

The Thriving Small Business
Tips And Tools For Small Business Owners
10 Steps To Creating A Small Business Budget
October 14, 2020 By Patricia Lotich, MBA
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
If we have learned anything this year, it has been how to pivot our businesses. We have had to change how we clean, work, and manage our small business budget!
When getting a small business off the ground, it is crucial to determine how the bills are going to be paid.
Every small business needs a budget. Developing and managing a budget is how successful businesses allocate, track, and plan fiscal spending.
A formal budgeting process is the foundation for good business management, growth, and development.
Very similar to our personal finances, discipline, and planning should be the cornerstone of a business budgeting process.
So, where do we begin?
As with most things that come with managing an organization, budgeting needs to be driven by the vision (what we are trying to accomplish) and the strategic plan (the steps to get there).
Organizations that stay focused on their strategy and plan know exactly where they want to spend their resources .
This intentional plan helps keep them from spending money in areas that do not align with the vision (what we are trying to do) and mission (why we are doing it).
10 Steps To Creating And Managing A Small Business Budget
1. strategic plan.
Every organization, no matter the size, should know why it exists and what it hopes to accomplish.
This is articulated through a written Vision and Mission Statement .
A Strategic Plan is HOW the organization plans to achieve its mission.
The first step in the budgeting process is having a written strategic plan .
This ensures that organizational resources are used to support the strategy and development of the organization.
Simply put – budget toward the vision.
2. Business Goals
Annual business goals are the steps an organization takes to implement its strategic plan, and it is these goals that need to be funded by the budget.
Goals need to be developed, and there needs to be accountability for achieving goals.
This is typically the responsibility of the management team, board, or business owner.

The budget provides the financial resources to achieve goals.
For example, if your organization has outgrown its facility, and there is an objective to increase space, there must be dollars budgeted to expand or move business operations.
3. Revenue Projections
Revenue projections should be based on historical financial performance, as well as projected growth income.
The projected growth may be tied to organizational goals and planned initiatives that will initiate business growth.
For example, if there is a goal to increase sales by 10%, those sales projections should be part of the year’s revenue projections.
4. Fixed Cost Projections
Projecting fixed costs is simply a matter of looking at the monthly predictable costs that do not change.
Employee compensation costs, facility expenses, utility costs, mortgage or rent payments, insurance costs, etc.
Fixed costs do not change and are a minimal expense that needs to be funded in the budget.
For example, if there are open staff positions, the cost to fill those positions should be part of fixed cost projections.
5. Variable Cost Projections
Variable costs are costs that fluctuate from month to month, supply costs, overtime costs, etc.
These are expenses that can and should be budgeted and controlled.
For example, if higher Christmas sales drive overtime costs temporarily, those costs should be budgeted.
6. Annual Goal Expenses
Goal-related projects should also be given budgets.
Each initiative should have projected costs associated with the goals.
This is where the cost of implementing goals is incorporated into the annual budget.
Projections of costs should be identified, laid out, and incorporated into the departmental budget responsible for completing the goal.
For example, if the sales department aims to increase sales by 10%, costs associated with the increased sales (additional marketing materials, travel, entertainment) should be incorporated into that budget.
7. Target Profit Margin
Every organization, whether they are for-profit or not-for-profit, should have a targeted profit margin.
Profit margins allow for returns for the business owner or investors.
Not-for-profit organizations use their profit margins to reinvest in the facilities and development of the organization.
Profits are important for all organizations, and healthy profit margins are a strong indicator of an organization’s strength.
8. Board Approval
The governing board, president, owner, or head of the organization should approve the budget and keep current with budget performance.
Again, similar to your personal finances, the owner should be reviewing monthly financial statements for the following reasons.
- To monitor budget performance.
- To be familiar with all expenditures.
- To safeguard the organization against misappropriation of funds or employee fraud .
9. Budget Review
A budget review committee should meet monthly to monitor performance against goals.
This committee should review budget variances and assess issues associated with budget overages.
It is important to do this every month so there can be a correction to overspending or modify the budget if needed.
Waiting until the end of the year to make corrections could hurt the final budget outcome.
10. Dealing With Budget Variances
Budget variances should be reviewed with the responsible department manager, and questions should be raised as to what caused the variance.
Sometimes unforeseen situations arise that cannot be avoided, so it is also important (just like your personal budget) to have an emergency fund to help with those unplanned expenditures.
For example, if the HVAC system suddenly goes down and needs to be replaced, this would be a budget variance that needs to be funded.
Good budgeting processes can help develop and advance an organization, while sloppy budgeting and monitoring budgets can blindside an organization and affect its long-term financial health and viability.
Finally, without customers , there are no revenues to the budget. For this reason, strategic plans and budgets should be targeted at one thing and one thing only – the customer.
This is why it is imperative to identify who your customers are, find out what they want, and budget dollars to put systems and processes in place to meet their needs and exceed their expectations.
Isn’t that what we are all trying to do?
About Patricia Lotich, MBA
Patricia Lotich, MBA is a Certified Manager of Quality and Organizational Excellence through the American Society for Quality. She has a driving passion to help small businesses, nonprofits and churches fulfill their mission by managing their resources of - people, time and money.

Learning Library

Contact Us!
Join our weekly newsletter.
Join 4000+ subscribers! Get FREE articles to help you manage your organization better! And get a copy of our FREE E-Book - Implementing Strategy for Business Development and Growth. No charge. No spam. Only love. Don't worry you can unsubscribe anytime!.
Small Business Resources is now the Center for Business Empowerment.
Suggested Keywords
Center for Business Empowerment
How to create a budget for your business
January 16, 2024 | 7 minute read
If you want to increase the odds of having a successful small business, start by creating a budget. A budget is a powerful tool. It helps you understand how much money you have and what you’ve spent where — and provides clues about how much money you’ll need in the short and long term. It can also help shape key business decisions like whether to add staff and equipment or where to cut expenses to avoid cash flow issues .
A budget is critical, particularly at a time when companies are coping with rising costs. Seventy-nine percent of small business owners polled in Bank of America’s 2023 Small Business Owner Report said they are concerned about inflation and 68% said they are worried about commodity prices. Here’s how to create a budget and use it to make the best decisions today, tomorrow and in the future.
What is a business budget?
Simply put, a budget is a spending plan based on your business’ income and expenses. It shows your available capital, estimates spending and assists in predicting revenue. The information in your budget can help you plan your company’s next moves. A budget looks at activities for a specified time. Think of it as a tool to help you allocate resources toward the strategic priorities in your business plan.
What are the benefits of creating a business budget?
Budgeting enables you to allocate financial resources more effectively, track variances and make changes to your spending plan as needed. A budget provides a much-needed assist in maintaining daily operations, giving you the intel to deploy your cash more strategically so you don’t face a cash flow crunch. It can identify when you need to raise financing. Debt is a fact of life in many businesses. A budget can help you manage debts with controlled and planned financial activities.
A budget can also help you stay ready for the unexpected. Staying within your budget and creating a safety net for emergencies will give you a firmer financial foundation.
Types of business budgets
When it comes to business budgets, it’s not one and done. There are several types that may be helpful in your business.
Master budget
This type of budget uses inputs from financial statements, your cash forecast and your financial plan to create a single document you can use to keep your finger on the pulse of your business. Your management team can use it to plan the activities needed to reach business goals. Typically, small businesses use spreadsheets to create their master budgets or consider using budgeting software too, as it may help minimize mistakes.
Operating budget
This budget shows your projected revenue and expenses for a given period. Think of it as a profit and loss report , but for the future. The operating budget includes fixed and variable costs, as well as non-operating expenses. Capital expenditures are usually excluded from an operating budget. Each line item should be backed up with key details.
Fixed costs occur monthly.
Variable costs, like utilities , change depending on factors like usage.
Capital costs are one-time expenses, such as the purchase of a building.
The operating budget gives you a reality check on whether you’re spending according to plan. While this budget is often prepared at the start of each year, don’t set it and forget it. Update it throughout the year, be it monthly or quarterly, so you always know where your business stands.
Capital budget
Companies sometimes create a capital budget when they are looking to make a large purchase, such as a large piece of factory equipment or a new technology system that will require a substantial investment. This allows the finance team to determine the impact on cash flow and plan accordingly.
Cash budget or cash flow budget
This document will give you an estimate of how money comes in and goes out during a certain time horizon. You create a cash budget using the conclusions you draw from sales forecasts and production, and by estimating payables and receivables.
Labor budget
If you will hire employees , this type of budget is helpful in planning for the money you’ll need to meet payroll, not only for regular employees, but also for any temporary and seasonal staff.
Budgeting methods you can use
There’s more than one way to budget. Here are some common methods:
An incremental budget
This takes the current period’s budget or actual performance, uses it as a base and then adjusts it in incremental amounts to account for any increases in costs. Typically, when you put together an incremental budget, you use the rate of inflation as a guide for fine-tuning the amounts. One plus of budgeting this way is that it is relatively easy to do.
Zero-based budgeting
Here, you’re budgeting from scratch. You must scrutinize every expense or potential expense before deciding to add it to your budget. This helps you align your business goals with your expenses. Unlike other types of budgeting, it doesn’t focus on historical results. A zero-based budget is ideal when you’re looking to reduce expenses.
Activity-based budgeting
Actions speak louder than words. This type of budgeting looks at the inputs required to reach the targets or outputs set by the company. Say your business wants to achieve $5 million in revenue. First, you need to figure out the activities that need to happen to make that revenue a reality and then determine the costs of carrying out those activities.
Participative budgeting
There are more cooks in the kitchen with participative budgeting, which is often used by larger small businesses. Both middle management and lower levels of management share in the responsibility of putting together the budget. The budget begins with lower management then moves to middle managers before top management weighs in and signs off. An upside of this type of budgeting is that information is shared, and when management and staff are on the same page in terms of goals, they’re more likely to achieve those goals.
How to create a business budget
Creating a business budget takes several steps:
- Calculate your revenue . Include all your revenue streams, preferably over at least the last 12 months, to determine your monthly income. If your business is new, you can research what’s typical in your industry and use that as a guide to come up with estimates.
- Add up your fixed costs . Fixed costs are things like rent, payroll and debt repayment.
- Determine variable costs . In addition to utilities, these may include billable labor, materials, transaction fees and commissions.
Using a budget to make better decisions
If you make your budget a regular resource, you’ll be rewarded for your budgeting efforts. As you make spending decisions, consult your budget frequently and use it as a reality check. If you have budgeted for X amount and go beyond it, you’ll have some explaining to do, even if you’re only answering to yourself. Being disciplined can be challenging, but ultimately it will position your business for growth , both today and in the future.
Explore more

How to create a sales forecast

Understanding free cash flow
Important Disclosures and Information
QuickBooks is registered trademark of Intuit, Inc., used under license. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of Intuit, Inc. You are responsible for separately purchasing QuickBooks, QuickBooks Online, or QuickBooks Online Payroll, and Bank of America makes no warranties nor accepts any liability for such software.
Internet access may be required. Internet service provider fees may apply. Other bank fees may apply. See the Business Schedule of Fees available at bankofamerica.com/businessfeesataglance for details.
Bank of America and/or its affiliates or service providers may receive compensation from third parties for clients' use of their services.
Bank of America, Merrill, their affiliates and advisors do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. Consult your own legal and/or tax advisors before making any financial decisions. Any informational materials provided are for your discussion or review purposes only. The content on the Center for Business Empowerment (including, without limitations, third party and any Bank of America content) is provided “as is” and carries no express or implied warranties, or promise or guaranty of success. Bank of America does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, completeness, usefulness, non-infringement of intellectual property rights, or quality of any content, regardless of who originates that content, and disclaims the same to the extent allowable by law. All third party trademarks, service marks, trade names and logos referenced in this material are the property of their respective owners. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of any third party.
Not all materials on the Center for Business Empowerment will be available in Spanish.
Certain links may direct you away from Bank of America to unaffiliated sites. Bank of America has not been involved in the preparation of the content supplied at unaffiliated sites and does not guarantee or assume any responsibility for their content. When you visit these sites, you are agreeing to all of their terms of use, including their privacy and security policies.
Credit cards, credit lines and loans are subject to credit approval and creditworthiness. Some restrictions may apply.
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated (also referred to as “MLPF&S" or “Merrill") makes available certain investment products sponsored, managed, distributed or provided by companies that are affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“BofA Corp."). MLPF&S is a registered broker-dealer, registered investment adviser, Member SIPC , and a wholly owned subsidiary of BofA Corp.
Banking products are provided by Bank of America, N.A., and affiliated banks, Members FDIC, and wholly owned subsidiaries of BofA Corp.
“Bank of America” and “BofA Securities” are the marketing names used by the Global Banking and Global Markets division of Bank of America Corporation. Lending, derivatives, other commercial banking activities, and trading in certain financial instruments are performed globally by banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation, including Bank of America, N.A., Member FDIC. Trading in securities and financial instruments, and strategic advisory, and other investment banking activities, are performed globally by investment banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“Investment Banking Affiliates”), including, in the United States, BofA Securities, Inc., which is a registered broker-dealer and Member of SIPC , and, in other jurisdictions, by locally registered entities. BofA Securities, Inc. is a registered futures commission merchant with the CFTC and a member of the NFA.
Investment products:
Plan offerings and flexibility
Coverage and data speeds, customer support, should you sign up for us mobile, us mobile review: exceptional budget phone plans with unique flexibility.
When you buy through our links, Business Insider may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
If you're looking for the best cell phone plan on a budget, your search may end with US Mobile .
US Mobile offers single-line users, and even families and groups, a more affordable alternative to major carrier plans, much like popular budget-friendly mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) like Mint Mobile , Tello Mobile , or Visible Wireless . However, US Mobile offers some of the best value, flexibility, and plans we've seen and experienced among MNVOs so far. In several respects, US Mobile puts these popular choices on notice.
In fact, with full access to Verizon's or T-Mobile's 4G and 5G networks, identical coverage, identical or comparable speeds, generous amounts of high-speed data, and surprisingly good prices, major carriers don't have much to boast when compared to US Mobile, either.
US Mobile's plans are incredibly inexpensive considering how much data you get, as well as access to Verizon or T-Mobile's full networks, including high-band 5G. Starting at $29/month for 35GB of prioritized data, the Unlimited Starter plan offers the best value of US Mobile's plans and among comparable plans from MVNOs. US Mobile also offers multi-line discounts and plans with data pools, making it an easy recommendation for families, too.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Choice between Verizon or T-Mobile's full networks
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Multi-line discounts rare for budget-friendly carrier
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Speeds reduced to usable 1Mbps after all your data is used
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Good app and responsive customer service
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Shareable Data plans affordable for low data users or families on a budget
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Unlimited Flex plan only available with annual payment option
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. No options for data-connected smartwatches
US Mobile has three unlimited data plans, one plan with a customizable data pool that can be shared among several lines called "Shareable Data," and an inexpensive "Light Plan" for low data users.
US Mobile's unlimited plans are among the best in the industry in terms of value and features. They're offered in either monthly or annual options; as expected, the annual option is better value. Still, US Mobile's monthly plans put forward incredible value, with among the highest data per dollar plans you can find.
Only Visible Wireless' base plan and Tello Mobile's Unlimited plan, both $25/month, offer as much or more data as US Mobile's $29/month Unlimited Starter plan . However, Visible's and Tello's plans provide deprioritized data, which could become slower if their networks are congested by people using prioritized data. Meanwhile, US Mobile offers 35GB of prioritized data, at least on its Warp network option (more on this below).
When you've used up the allotted data in any of US Mobile's unlimited plans, data speeds are significantly reduced, which is common practice for budget-friendly and MVNO carriers. However, US Mobile's plans reduce speeds to 1Mbps, which gives you some semblance of usability, at least for basic data needs, compared to the typical 256Kbps reduced speeds on many other carriers.
The most distinctive thing about US Mobile is its "Warp" and "GSM" network options, which are US Mobile's nicknames for "Verizon" and "T-Mobile," respectively. No other carrier we've encountered gives you the choice between two major networks and lets you switch, making US Mobile particularly flexible.
The main difference between the two is coverage, where Warp is Verizon's network, and GSM is T-Mobile's network. The Warp network includes prioritized premium data, whereas the GSM network's data is deprioritized, but more on that below in the data speeds section. The other main difference is connectivity while abroad, which is currently only available on the GSM network option.
Which network is the best for you essentially depends on which network has the best coverage in the places you usually need it. If Verizon and T-Mobile both serve you well, the Verizon option (Warp) will consistently offer faster speeds within your data limit, as it isn't subject to deprioritization.
You can switch network options whenever you want up to twice a month via your account on a web browser. It's a fairly easy process that's essentially the same as setting up US Mobile on your phone for the first time — you use your camera to look at a QR code, tap the link that shows up, and the phone handles the rest. It takes about 15 minutes in total.
Finally, US Mobile offers multi-line discounts, which are more common in major carrier plans than on budget-friendly and MVNO carriers. More than other lower-cost carriers, US Mobile is an excellent option for families or groups.
Note that US Mobile doesn't support smartwatch connectivity. While it supports tablet data, it's only available in the Shareable Data plan, which is affordable even if it offers less value than the carrier's unlimited plans.
US Mobile's Warp provides Verizon's network coverage, while GSM offers T-Mobile's coverage. As such, the Warp (Verizon) network has better overall coverage that reaches deeper into rural areas, whereas the GSM (T-Mobile) network has excellent coverage in cities, towns, and highways, but it can start to decline the further you get from densely populated areas.
I mainly tried US Mobile with the Warp network, as I'm a Verizon customer myself and know exactly where to expect coverage and where the dark zones lurk. During my testing and general experience, I found US Mobile on Warp to offer identical coverage as full-fat Verizon, including Verizon's Ultra Wideband (UW) 5G network.
As far as data speeds go, US Mobile offers the full breadth of Verizon's and T-Mobile's 5G networks, including their fast high-band 5G networks.
On the US Mobile's Warp network, I reached the same data speeds I did on Verizon's 4G and 5G UW when I tested my own plan and phone against US Mobile on a separate phone (the Galaxy S24 Plus) at different locations. That's to say, US Mobile offers high-end, fast data. On the GSM network, I found that data speeds were also exceptionally fast.
US Mobile's Warp network has an advantage when it comes to data prioritization. Only the Warp network includes prioritized "premium" data, where a user's data isn't deprioritized and slowed down against prioritized Verizon customers during times and places where there's network congestion. That's not to say that you'd always get the top speeds available on the Warp network — network congestion can slow down a connection, even with premium prioritization, as shown by the last speed test result in the image above.
Meanwhile, US Mobile's GSM network offers T-Mobile's high-speed data, which is deprioritized against T-Mobile customers with prioritized premium data. If T-Mobile's network is congested at a certain location and time, data speeds on US Mobile's GSM network can be affected. That's typical for an MVNO. However, we haven't found that deprioritization poses much of a problem after testing T-Mobile and MVNO carriers that run on T-Mobile's network. Additionally, there's no indicator that suggests data is being deprioritized, and it can be hard to tell.
You can check Verizon's coverage map against T-Mobile's to see which option suits your area better.
I tried US Mobile's customer chat support via the app, and I was pleasantly surprised by the responsiveness and ability to exchange messages with a real person.
I didn't run into experience-breaking issues, so I couldn't test the effectiveness of US Mobile's support to fix a problem that affected connectivity. Still, there's a support phone number you can call to speak to someone, which can prove to be more efficient than a text-based chat service.
As far as the app goes, it's quite well laid out and easy to navigate to manage your plan and check up on data usage. However, the app currently lacks a way to switch between the Warp and GSM networks, as you have to make that change through a web browser.
For those covered by Verizon's or T-Mobile's networks in the US, we enthusiastically recommend US Mobile's offerings among the best cheap cell phone plans on the market.
While US Mobile's Unlimited plans aren't the absolute cheapest, they're not far, and they're quite simply the best. The small extra cost relative to other MVNO plans can easily be justified by the astounding option to switch between Verizon's and T-Mobile's networks — it's a singular and useful feature I've never seen before, whether on a budget or premium carrier, and it actually works.
US Mobile's multi-line discounts are also unique among MVNO and budget-friendly carriers, making it an ideal option for families.
The fact that US Mobile doesn't utterly deaden your data speeds after using up a month's data allotment, like most other carriers, is also a major benefit. Your speeds are reduced to a slow 1Mbps, but it's still usable for basic functions. To be sure, it's unlikely that most people would ever exceed 35GB in a single month, but it's nice to know you won't be totally disconnected if you do.
Which networks does US Mobile use?
US Mobile runs on Verizon's and T-Mobile's 4G and 5G networks and offers the unique ability to switch between the two networks.
The MVNO's Verizon-backed network is called Warp, while its T-Mobile-backed network is called GSM.
Is US Mobile deprioritized?
US Mobile features allotments of prioritized data through its Verizon-backed Warp network, while data on its GSM network is subject to deprioritization behind T-Mobile's premium customers.
You can purchase logo and accolade licensing to this story here . Disclosure: Written and researched by the Insider Reviews team. We highlight products and services you might find interesting. If you buy them, we may get a small share of the revenue from the sale from our partners. We may receive products free of charge from manufacturers to test. This does not drive our decision as to whether or not a product is featured or recommended. We operate independently from our advertising team. We welcome your feedback. Email us at [email protected] .

- Main content
Money latest: Holiday hack for cheaper internet abroad; the healthiest chocolate you can buy
Our cost of living specialist is back with a money-saving tip for using the internet abroad. Read all today's personal finance and consumer news - and listen to the latest Ian King Business Podcast below.
Friday 10 May 2024 09:54, UK
- Interest Rates
- UK exits recession, official figures show
- Interest rate held at 5.25% | Bank of England: June rate cut 'not ruled out but not fait accompli'
- Gordon Ramsay to open new restaurants on London skyscraper
Essential reads
- Ed Conway on economy: Britain out of recession with a bang
- How to avoid a holiday data roaming charge (while still using the internet)
- Mortgage rates up again this week - here are the best deals on the market
- How you can turn nightly chocolate into a superfood
- Cheapest 10 European cities for a holiday - and how costs compare
- Listen to the Daily above and tap here to follow wherever you get your podcasts
Sainsbury's is running a scheme that allows some shoppers to earn easy Nectar card points.
To earn extra points, shoppers just need to spend £1 across multiple transactions at Sainsbury's.
The supermarket says the scheme is available to "millions" of customers, though all it would say about the eligibility criteria is that it's "based on a range of factors".
Check if you're eligible
Log into your nectar card app and check to see if you have this message...
Make sure you opt in once you see the message.
From there, you simply need to spend £1 or more five times - earning extra points each time.
The number of bonus points on offer varies for each customer.
The offer runs until 4 June.
Britain is not just out of recession.
It is out of recession with a bang.
The economic growth reported this morning by the Office for National Statistics is not just faster than most economists expected, it's also the fastest growth we've seen since the tailend of the pandemic, when the UK was bouncing back from lockdown.
But, more than that, there are three other facts that the prime minister and chancellor will be gleeful about (and you can expect them to be talking about this number for a long time).
First, it's not just that the economy is now growing again after two quarters of contraction - that was the recession.
An economic growth rate of 0.6% is near enough to what economists used to call "trend growth", back before the crisis - in other words, it's the kind of number that signifies the economy growing at more or less "normal" rates.
And normality is precisely the thing the government wants us to believe we've returned to.
Second, that 0.6% means the UK is, alongside Canada, the fastest-growing economy in the G7 (we've yet to hear from Japan, but economists expect its economy to contract in the first quarter).
Third, it's not just gross domestic product that's up. So too is gross domestic product per head - the number you get when you divide our national income by every person in the country. After seven years without any growth, GDP per head rose by 0.4% in the first quarter.
And since GDP per head is a better yardstick for the "feelgood factor", perhaps this means people will finally start to feel better off.
But this is where the problems come in.
Because while this latest set of GDP figures is undoubtedly positive, the numbers that came before are undoubtedly grim.
GDP per head is still considerably lower, in real terms, than it was in 2022, before Liz Truss's disastrous mini-budget, or for that matter lower than in early 2019.
Raising another question: when people think about the state of the economy ahead of the election (and obviously these new figures are likely to increase the speculation about the date of the election), do they put more weight on the years of economic disappointment or the bounce back after them?
Do they focus on the fact that we're now growing at decent whack or on the fact that their income per head is, in real terms, no higher today than it was five years ago?
These are the questions we will all be mulling in the coming months - as the next election approaches. One thing is for sure: this won't be the last time you hear about these GDP numbers.
The chancellor is speaking to Sky News after the welcome news that the UK has exited a recession.
"It's encouraging that the UK economy is growing faster over the last quarter, not just than France, Germany or Italy, but actually faster than the United States," Jeremy Hunt says.
"But I think what's more encouraging is the longer-term data that we are now seeing about the economy."
He praises the government's handling of the economy.
"I think that for families who've been having a really tough time, this is an indication that difficult decisions that we've taken over recent years are beginning to pay off and we need to stick with them."
He nods to the Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey's comments yesterday that inflation is expected to fall to 2% in the coming months: "So we're seeing that inflation is falling faster and I think people recognise it's been a very, very challenging period."
He's then asked whether the UK can compete with the US's economy in the coming years.
Mr Hunt says he wants the UK to become "the new Silicon Valley" as a route into the tech sector.
"Tech is the sector that is growing the fastest and will continue to grow the fastest," he says.
Finally, he's asked when national insurance will be abolished - a recent Tory pledge.
"We haven't set a date... we'll only do it when it's affordable and when we can do so without impacting on public services."
Our economics editor Ed Conway is giving his first reaction to the ONS statistics that show the UK is no longer in recession.
"These are great numbers," he says.
"Certainly in the context of things, they are close to what we would normally historically call trend growth - a good rate of growth - and that's going back a long time.
"They're better than expected... this is definitely some good news."
The UK economy is no longer in recession, according to official figures.
Gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 0.6% between January and March, the Office for National Statistics said.
A recession, which is defined as two consecutive three-month periods where the economy contracts, was declared in February.
The previous set of figures showed that GDP, a major measure of economic growth, shrank 0.3% between October and December. It followed a contraction of 0.1% in the three months from July to September.
The slump was blamed on reduced consumer spending power as inflation and energy bills stayed high. Months of wet weather also contributed to keeping shoppers at home, commentators said.
Jeremy Hunt, the chancellor, was buoyant about the figures: "It has been a difficult few years, but today's growth figures are proof that the economy is returning to full health for the first time since the pandemic."
By Megan Harwood-Baynes , cost of living specialist
When my plane touched down on the runway of Manila airport, I was welcomed to the country with a text. Coming from Sky Mobile, the message informed me that using my phone abroad would incur hefty charges - including £2.16 for every megabyte (MB) of data I used.
One MB is equivalent to a short WhatsApp voice note message, and given my average monthly data allowance is 20GB (20,000MB), I would be quickly bankrupted if I continued to use my phone as normal. And while I love switching off from work while I am away, for me, the internet is as much a holiday essential as toothpaste and a hairbrush.
From the ability to check Google Maps when out and about, or do a quick search to check I am not being scammed, it is now something I always factor into my holiday budget.
Welcome to the world of eSims
An eSim is an industry-standard digital SIM card that allows you to activate a mobile plan on your phone without the need to install a physical SIM into your phone.
TLDR - it means you can activate a short, temporary internet plan while on holiday for a fraction of the price it would cost you through your network provider.
I used an app called Global Yo (other providers are available, but this is the one I used), which has 24-hour plans from as little as 99c (71p) for 1GB.
Once downloaded from the App Store, you can scroll through the list of countries to select your destination. Select the plan you want - while in the Philippines, I paid around £7 for a weekly plan that would give me 5GB of data. It is cheaper to do it day by day, but that also means you have to remember to top up each morning.
Once purchased, you are sent a QR code to scan - this will help you install the eSIM. The process varies by phone, but once installed, you go into the SIM manager settings on your phone. You can then toggle the settings so your calls and texts come via SIM 1 (your primary phone number), but mobile data uses the eSIM. This means you won't miss any vital text messages that come through to your phone number while on holiday.
The downsides
Not every network, or mobile phone, supports eSIMS, so check with your network provider before you shell out, and make sure your phone is unlocked. My sister, who lives in Hong Kong, wasn't able to install the eSIM on her phone but only realised this after paying £7.99 for a week's worth of data.
We also had some difficulty installing it on my mum's iPhone, but that could be because we are all Android users.
You also have to be connected to WiFi /the internet to install the eSIM in the first place, so make sure you do it while at your hotel in the morning. A few times while I was paying each day I would forget this, head out and be without internet for the day.
This wasn't exactly a hardship, but did mean I couldn't share with my Instagram followers what a great time I was having.
It can be hard to balance eating well without spending a lot.
In this series, we try to find the healthiest options in the supermarket for the best value - and have enlisted the help of Sunna Van Kampen , founder of Tonic Health, who went viral on social media for reviewing food in the search of healthier choices.
In this series we don't try to find the outright healthiest option, but help you get better nutritional value for as little money as possible.
Today we're looking at chocolate - and why, before sugar and dairy is added, it's a superfood, in Sunna's view.
A superfood is anything with a very high "nutritional density" - or lots of nutrients for few calories.
Superfoods need a high concentration of antioxidants - molecules which neutralise unstable molecules that can harm your cells.
You can get antioxidants by purchasing expensive "greens" powders, but Sunna says plenty of supermarket options can be classified as "superfood".
"Chocolate is not unhealthy, it is actually a superfood - it's the sugar we added to it that is the problem," he says.
"Chocolate in the supermarkets tends to come in at only £27.50/kg, which is almost half the price of your cheapest greens powder."
Sunna points out that cacao, from which chocolate is made, is in its own right a superfood and has more antioxidants than blueberries, acai berries and cranberries - well-known superfoods.
"Cacao actually has more than 40x the antioxidants of blueberries in its raw form," he says.
But, as he says, the added sugar is where the problems come in.
Sunna's guide to buying chocolate
Sunna recommends picking chocolate that contains a high proportion of cocoa solids - which brings down the sugar content.
Here's how the different kinds of chocolate stack up:
- Milk – 25% cocoa solids, 54g of sugar per 100g.
- Dark – 47% cocoa solids, 49g of sugar per 100g.
- 70% dark - 70% cocoa solids, 29g of sugar per 100g
- 85% dark - 85% cocoa solids, 15g of sugar per 100g
- 90% dark - 90% cocoa solids, 7g of sugar per 100g
"A typical milk chocolate only contains 25% cacao solids, and the first two ingredients are actually milk and sugar," Sunna says.
"For chocolate to be a superfood, it has to be dark chocolate - at a minimum of 70% dark ideally."
A couple of pieces after dinner each night means you'll be consuming 200g of superfood chocolate a week for £5.50.
"If you're a milk chocolate fan, don't fret," Sunna says. "It is possible to retrain your taste buds in just 10 days to get the superfood benefits of 70% and above."
That might sound easier said than done, but Sunna says the trick is to start with the lower percentages and work your way up to the higher ones.
"Get to a level you are comfortable with and then make sure you have a piece of chocolate every night for 10 days straight," he says.
"The more you train the taste buds, the less sugar you consume."
The switch from milk chocolate to 70% dark will save you 2.6kg of sugar a year, while working your way up to 90% will save you more than 4.8kg of sugar a year (assuming 200g consumption per week).
"Small chocolate changes - and a bit of work to train your tastebuds - can lead to huge sugar savings that are worth it not just for the reduction in sugar, but also the increase in antioxidants," Sunna concludes.
Read more from this series...
Every Friday we get an overview of the mortgage market with independent experts from Moneyfactscompare.co.uk . Today, finance expert Rachel Springall outlines what's been happening with mortgages this week, before honing in on the best rates for remortgaging…
Fixed-rate mortgage repricing has quietened down this week, but a couple of prominent lenders have made tweaks, such as Virgin Money increasing selected fixed by up to 0.2% and Barclays reducing by up to 0.39%.
This comes off the back of a busy week for repricing, as lenders reacted to rising swap rates.
The Bank of England's next rate decision will be in June, but it's uncertain whether a rate cut will happen, with some economists predicting no change until the last three months of the year.
Week on week, the overall average two and five-year fixed rates rose to 5.93% and 5.51%.
Looking at remortgaging, this week the lowest two-year fix for customers with 40% equity comes from The Co-operative Bank, priced at 4.76%, which comes with a £1,999 fee and offers borrowers £250 in cashback and provides a free valuation and free legal fees incentive package. This is available to those who borrow a minimum of £750,000.
Those looking to fix for longer will find the lowest five-year fixed remortgage deal comes from NatWest this week, available to those with 40% equity. Priced at 4.32%, this deal carries a £1,495 fee and offers a free valuation and free legal fees incentive package.
Best buy alternatives
As a remortgage customer, it's possible you are looking to save on the upfront cost of any deal. You might also want a deal to cover a valuation or legal fees. A best buy mortgage could be the most cost-effective choice in this instance.
This week the top packages on a two-year fixed remortgage deal at 60% or 75% loan-to-value come from First Direct, priced at 4.83% and 4.98% respectively, both of which come with a free valuation and free legal fees incentive package and charge a £490 product fee.
If you want to borrow more, then there is a best buy deal priced at 5.19% from Suffolk Building Society at 80% loan-to-value, which carries a free valuation and free legal fees incentive package and charges a £1,198 product fee.
A five-year fixed mortgage may be more appealing for you to guarantee your monthly repayments for longer.
Vernon Building Society has a deal priced at 4.49%, and charges a product fee of £999 but does not carry any incentives. If you are borrowing at 75% loan-to-value, then Cumberland Building Society has a best buy package priced at 4.58% for five years, which includes a free valuation and free legal fees incentive package and charges a £999 product fee.
Looking for some longer Money reads for your evening/commute/lunch break?
Here's four from the last few months you might like...
Should you offer kids cash rewards for good grades? The psychologist's view
As exam season gets under way, some parents are putting hundreds of pounds aside to reward their children if they achieve certain grades.
While some parents lambasted the idea as "absolute potatoes", others told Sky News they saw their children's focus increase after offering up to £250 for the top results.
We also spoke to teachers and a psychologist...
What can I do if flexible working request declined?
Every Monday we put your financial dilemmas or consumer disputes to industry experts. A few weeks ago Sky News reader AJ2024 asked...
"While on maternity leave my employer rejected my flexible work request and told me to pick from four new shift patterns or take redundancy if they didn't suit me. All new shifts were full working hours. No support as a new mother and ruined my last few precious weeks. What are my rights?"
We got an employment lawyer to answer...
'£2,000 landed in my account' - The people who say they're manifesting riches
Money blogger Jess Sharp spoke to people who swear they've made money from manifestation - before finding herself meditating under a tree to see if she could get in on the action...
The world of dark tourism - what is it, is it ethical, and where can you go?
Interest in a phenomenon known as "dark tourism" has been steadily rising in recent years - but what is it?
To find out, we spoke with tourism academic Dr Hayley Stainton and renowned dark tourist and author Dr Peter Hohenhaus, who runs a dark tourism website ...
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Tax Increases Won’t Hit Middle Class, Yellen Says
Republicans pressed the Treasury secretary on President Biden’s tax proposals and the fate of the Trump tax cuts that will expire in 2025.
- Share full article

By Alan Rappeport
Reporting from Washington
The battle lines of the next big tax fight were laid out on Tuesday as Treasury Secretary Janet L. Yellen sparred with Republicans over the Biden administration’s plans to raise taxes on businesses and wealthy Americans.
In recent weeks, Republicans have been amplifying their attacks on President Biden’s tax proposals, which have become central to the president’s re-election message. Many provisions in the $1.7 trillion tax cut that Republican lawmakers and former President Donald J. Trump enacted in 2017 are set to expire in 2025, including lower tax rates for individuals as well as many tax breaks for corporations.
Lawmakers are girding for a legislative battle over which ones — if any — will be extended next year. Renewing all of the tax measures for another decade would cost about $3 trillion, according to the Joint Committee on Taxation.
Republicans have begun warning that Mr. Biden plans to allow all of the tax cuts to expire, effectively raising taxes on businesses and families at a moment when inflation is pinching consumers.
“Instead of allowing families hit by these high prices to keep more of their hard-earned money, President Biden wants the highest tax increase on families and small businesses in American history,” Representative Jason Smith, Republican of Missouri and the chairman of the House Ways and Means Committee, told Ms. Yellen during a hearing on Tuesday.
The president fueled such criticism last week when he assailed the Trump tax cuts for benefiting the rich and increasing the federal debt and promising: “The tax cut is going to expire. If I’m re-elected, it’s going to stay expired.”
But on Tuesday, Ms. Yellen insisted that Mr. Biden would keep his promise to not raise taxes on Americans who earn less than $400,000 a year if he wins a second term.
“The president has been very clear that no family earning less than $400,000 will face a tax hike,” Ms. Yellen said.
“He has not proposed such a thing since he took office, and he’s not proposing to allow that to happen when parts of T.C.J.A. expire,” she added, referring to the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
The budget proposal that Mr. Biden released in March called for $3 trillion in tax increases that would go toward lowering the deficit and paying for other Biden administration priorities such as shoring up retirement programs.
Ms. Yellen said on Tuesday that some of the proposed tax increases could offset the costs of extending provisions of the 2017 tax law. She pointed to measures that would raise taxes on stock buybacks, increases in the corporate income tax and corporate alternative minimum taxes, and a new 25 percent “billionaire tax” on individuals with wealth, defined as the total value of their assets, of more than $100 million.
In a sign of the legislative challenge to come, Republicans on the Ways and Means Committee argued that middle-class Americans will still feel the impact of tax increases on businesses, pointing to research that claims workers and consumers bear much of the burden of a higher corporate tax rate. They also dismissed the international agreement on a “global minimum tax” that Ms. Yellen helped broker in 2021 as a giveaway to foreign governments, suggesting that Republicans remained unlikely to provide the votes needed to put the United States in compliance with the pact.
Asked by Representative Michelle Fischbach, Republican of Minnesota, how Mr. Biden would find a way to keep the tax cuts from expiring, Ms. Yellen said the president would work to let the cuts for the rich lapse while preserving the rest.
“There will be a negotiation over what to do when these tax cuts expire and the president, as he does in many other situations, will negotiate with Congress,” Ms. Yellen said.
The contours of the coming tax changes will depend heavily on the political makeup of the House and the Senate and who wins the presidency. Ms. Yellen acknowledged that Mr. Biden had not yet finalized all the details of his tax plan, but criticized the Trump tax cuts for failing to stimulate much business investment and for overwhelmingly benefiting the rich.
Mr. Trump said this year that if elected, he would enact “the biggest tax cuts” and a “brand-new Trump economic boom.”
Alan Rappeport is an economic policy reporter, based in Washington. He covers the Treasury Department and writes about taxes, trade and fiscal matters. More about Alan Rappeport
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Australian federal budget 2024: what we know so far and what to expect
Treasurer Jim Chalmers has promised more cost-of-living relief in his 14 May budget as well as spending for students and health
- Get our morning and afternoon news emails , free app or daily news podcast
On 14 May the treasurer, Jim Chalmers, will deliver his second full-year budget.
Chalmers has promised more cost-of-living relief in a budget that he says tackles inflation but sets Australia’s economy up for growth – neither scorched-earth nor a free-for-all of spending .
A second surplus is within reach, but that’s just speculation. Here’s what we know already about what is in the budget.
Tax cuts and cost of living
The biggest element of the cost-of-living relief in the budget is the changes to stage-three tax cuts, a $359bn 10-year tax cut package announced by Labor in January and legislated in February with opposition support.
The package means all Australian taxpayers (earning over the tax-free threshold of $18,200) get a tax cut, doubling the benefit for an average income earner compared with the Coalition’s original stage three proposal.
Labor says 84% of taxpayers are better off under its proposal, although those earning more than $146,486 would have received more under the Coalition’s model.
There will be other cost-of-living measures the government claims won’t add to inflation, which might point towards extending energy price relief .
Jim Chalmers has poured cold water on the Economic Inclusion Advisory Committee’s call for jobseeker to rise to 90% of the age pension, although he and the finance minister, Katy Gallagher, have seemed more open on increasing rent assistance. Chalmers has confirmed there will be “additional steps” on poverty reduction and “new initiatives for housing”.
Education, skills and Hecs
The government will wipe $3bn from student debts by indexing Hecs and Help debts to the lower of the consumer price index or the wage price index, backdated to June 2023.
The government will also pay student teachers, nurses, midwives and social workers $320 a week during their mandatory work placements , starting from July 2025. These two measures are aspects of the government’s response to the Universities Accord, but there will be more in the budget.
Sign up for Guardian Australia’s free morning and afternoon email newsletters for your daily news roundup
The government has announced $90.6m to boost the number of skilled workers in the construction and housing sector, creating 15,000 fee-free Tafe places and 5,000 places for pre-apprenticeships.
School funding will also rise as the federal government negotiates with the states to cover the 5% funding gap, most recently offering to lift its share of funding from 20% to 22.5%. This is estimated to cost $6bn over five years, although Chalmers has been coy about whether estimates will be reflected in the budget or only be added after education and health agreements are finalised.
There is no question childcare workers will be receiving a pay rise in this budget – the only questions are how much and how it will be distributed. With the industry in crisis due to staffing shortages, which have been exacerbated by staff leaving to work in aged care after that sector’s pay rise win , the government is expected to make wage increases for childcare workers a centre piece of the budget.
But it’s unclear whether the government will pull the trigger on scrapping the activity test, which sets a subsidy rate based on employment. It has indicated it wants to get rid of the measure as part of its plan to make childcare in Australia “universal”, though it’s not clear whether it will happen in this budget.
Health and aged care
Public hospitals are expected to get more funding, as the federal government works to finalise a new five-year agreement with the states to start in mid-2025. The commonwealth has reportedly offered to lift funding by an extra $4bn in 2025-26 and $13bn over the whole five years.
The government is also increasing funding for its medical research future fund over 13 years, with $1.1bn for existing projects plus $150m million to investigate rarely survived cancers, and $150m towards reducing inequalities in the health system. A further $500m will go to other research schemes.
The government is also yet to outline its response to March’s aged care taskforce report , which suggested new ways to pay for the system – including asking Australians with more wealth to pay more for the cost of their care.
The health minister, Mark Butler, also announced $49.1m would go toward offering longer consultations of 45 minutes or longer for endometriosis sufferers.
Among a total of $15.4bn in “unavoidable spending” to continue programs from the previous government is money set aside for palliative care, cancer supports, public health chronic conditions, and alcohol and other drug treatments.
Defence and foreign affairs
The budget will confirm that Australia’s defence spending will increase from 2.1% of Australia’s economic output next financial year to 2.4% by 2033-34, driven by a range of big-spending projects including the Aukus nuclear-powered submarines.
There will be some cuts to programs, however, with the government announcing last month that it would free up about $73bn over 10 years by cutting, delaying or changing the scope of some defence projects.
Even after these cuts are taken into account, the government says it has committed a net increase of $50.3bn for defence over the next 10 years. This includes a net increase of $5.7bn over the immediate four-year budget cycle.
This immediate funding includes $1bn over the next four years for long-range strike, targeting and autonomous systems.
In foreign affairs, the government has promised $492m for the Asian Development Fund’s 2025-28 pledging round, to “help respond to the needs of the region and deliver transformative development projects across the Indo-Pacific”.
Infrastructure
So far, western Sydney is the biggest winner in infrastructure after the minister, Catherine King, announced $1.9bn in funding for 14 road and transport projects. Those include road upgrades, planning projects and extra money for a business case to extend the train line into the city’s south-west.
Cyclists will also get a boost with $100m being set aside to build and upgrade bicycle and walking lines in cities and regional centres.
Canberra will also get a $50m injection to extend its light rail line from the northern suburbs past Parliament House and into the city’s south.
The nation’s capital are getting a good deal because $249.7m has also been announced for Australian Institute of Sport as the 2032 Brisbane Olympics inches closer.
The quarter of a billion-dollar sum will go towards refreshing the ageing site with new accommodation, an all-weather sports dome and a new training centre.
Beyond Canberra, road safety data from the states and territories will also be better harmonised with a $21m funding announcement to set up a national data hub.
Future Made in Australia
The government has announced funding for a range of projects under its Future Made in Australia policy, which aims to directly support Australian industry and innovation, particularly in green energy. These commitments include:
$1bn for the Solar Sunshot production of solar panels in the Hunter
$1bn to PsiQuantum to build the world’s first fault tolerant quantum computer in Brisbane
$840m for Arafura’s rare earth metals production in the Northern Territory
An export agreement to sell armoured vehicles made by the German defence manufacturer Rheinmetall
$566m over 10 years for GeoScience Australia to map what is under Australia’s soil and seabed
$400m in new loans to Alpha HPA for Australia’s first high-purity alumina processing facility in Queensland; and
$185m to Renascor Resources to fast-track the development of stage one of its Siviour Graphite Project in South Australia; and
$100m to speed up environmental approvals, including assistance for business.
Gender equality
The government has committed $925m for the leaving violence payment, a payment of $5,000 to help meet the costs of leaving a relationship. The existing trial will be extended and the new permanent program available from mid-2025.
The government has also said that parents will receive 12% superannuation – or about $106 a week – on their publicly funded paid parental leave from July 2025, full costings for which will be in the budget.
Indigenous affairs
The government has not foreshadowed any new major spending commitments in the Indigenous affairs space, but the budget will contain details and funding for several large programs in that portfolio that were recently unveiled.
The Closing The Gap commitments from February, including a $700m remote jobs program, and March’s announcement of a $4bn remote housing program for the Northern Territory, are expected to be the major components of the Indigenous affairs portfolio. Most of the new commitments in Indigenous affairs are typically contained in February’s Closing The Gap document rather than the May budget.
Attorney General’s Department
The government has pledged $161.3m to establish the national firearms register , and $11m for an app alerting Australians in real time if somebody tries to use their data to commit fraud.
The government will invest $166.4m to implement reforms to Australia’s anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regime.
- Australian budget 2024
- Australian politics
- Australian economy
- Jim Chalmers (Australian politician)
- Cost of living crisis
- Labor party
Comments (…)
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted. 2. Subtract fixed costs. The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to ...
How to design your small business budget plan. Small business budget FAQ. 1. Static budget template. Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations. A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other ...
Step 5: Create the COGS Budget. The next logical step after budgeting inventory and purchases is to determine the COGS. Through the COGS budget, we can estimate the level of COGS per quarter. This budget is necessary for preparing the proforma income statement. Below is the COGS budget from our small business budget template:
Ahmet Yüzbaşıoğlu, the Co-Founder of Peak Plans, explains the importance of budgeting for small businesses: "The success of your business is determined by the quality of your decisions.If you want to make informed decisions, you must have a budget. A budget can help you create a plan for the future, whether it's for your company as a whole or for smaller departments.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends. Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they're fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don't forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
2. Make a Spreadsheet. Prior to buying or opening a business, construct a spreadsheet to estimate what total dollar amount and percentage of your revenue will need to be allocated toward raw ...
How to create a small business budget in 6 steps. Now that you understand how important a budget is, here's how you can create one so you can ensure smooth business operation and facilitate efficient cash flow: 1. Separate your business finances from your personal finances. This is one of the cardinal rules to succeed in business.
1. Write down your revenue streams. Your revenue is the money you earn in exchange for your products or services. You'll start your small- business budget by listing all the ways you make money. Look at last month's P&L—or even just your checking account statement—to help you account for all your revenue streams.
A business budget is a spending plan that estimates the revenue and expenses of a business for a period of time, typically monthly, quarterly, or yearly. ... Small Business Budget Template. Image Source. For small businesses, it can be hard to find the time to draw up a budget, but it's crucial to help keep the business in good health. ...
2. List your business expenses. The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget: Fixed ...
Reading Time: 6 minutes According to a study done by CBinsights, a few of the top reasons why small businesses fail include include pricing and cost issues, losing focus and running out of cash. These issues can be prevented by having a realistic budget in place. Before you can focus on the budget, however, you need to identify what aspects of your business you'd like to improve.
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
Input the year-end balance sheet and income statement into your Excel template. Equity is the difference between assets and liabilities—the true value of your business. The $10,000 net income in the income statement increases equity in the year-end balance sheet. 2. Forecast future sales and costs.
This template will help you track your expenses, estimate your monthly income and record what you earned and spent. Our budget template has five tabs. To use it, take the following steps: Make a copy or download the template. On the first tab, Instructions, replace the Your business's name text with your actual business name.
1. Xero. Xero lets you easily create a budget using their Budget Manager feature. You can choose your start date for any budget, and prepare a budget of 3, 6, 12, or 24 months. Xero also allows ...
A Strategic Plan is HOW the organization plans to achieve its mission. The first step in the budgeting process is having a written strategic plan . This ensures that organizational resources are used to support the strategy and development of the organization. Simply put - budget toward the vision. 2.
A small business budget allows you to plan for expenses and analyze anticipated income against actual income. When creating a small business budget, consider the following factors: Specify Fixed and Variable Costs: Determine all fixed and variable costs involved in running your small business, such as office space, equipment, employee wages ...
Your marketing budget is always a specific percentage of your revenues. Suppose you're running a small business targeting B2B (Business to Business) customers, your marketing budget can be between 2 to 5% of the revenue. A B2C (Business to Consumer) business can have a higher budget between 5 to 10%.
What is a business budget? Simply put, a budget is a spending plan based on your business' income and expenses. It shows your available capital, estimates spending and assists in predicting revenue. The information in your budget can help you plan your company's next moves. A budget looks at activities for a specified time.
A small business marketing plan takes the limited resources of a small business and considers how that entity can effectively reach its target audience with its marketing. ... The goal of a marketing plan is to create basic parameters, such as a schedule and marketing budget, that help you optimize your promotional resources. Developing the ...
the American Rescue Plan Investing in America Small Business Opportunity Program, a $75 million ... families, including many of the country's small business owners. The proposed budget would restore
Starting at $29/month for 35GB of prioritized data, the Unlimited Starter plan offers the best value of US Mobile's plans and among comparable plans from MVNOs. US Mobile also offers multi-line ...
Read all today's personal finance and consumer news - and listen to the latest Ian King Business Podcast below. Thursday 9 May 2024 23:09, UK. Interest Rates;
But on Tuesday, Ms. Yellen insisted that Mr. Biden would keep his promise to not raise taxes on Americans who earn less than $400,000 a year if he wins a second term. "The president has been ...
However, the premium plans offered by Wix grant you the most features. Wix offers similar pricing on its most basic plan, but you'll likely need at least the Core plan to get the most out of the software. The Light plan is the most basic, only providing 2GB of storage, a handful of marketing tools, and a free domain for $17 per month. Most ...
The budget will confirm that Australia's defence spending will increase from 2.1% of Australia's economic output next financial year to 2.4% by 2033-34, driven by a range of big-spending ...