

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay On Covid-19: 100, 200 and 300 Words

- Updated on
- Apr 30, 2024

COVID-19, also known as the Coronavirus, is a global pandemic that has affected people all around the world. It first emerged in a lab in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and quickly spread to countries around the world. This virus was reportedly caused by SARS-CoV-2. Since then, it has spread rapidly to many countries, causing widespread illness and impacting our lives in numerous ways. This blog talks about the details of this virus and also drafts an essay on COVID-19 in 100, 200 and 300 words for students and professionals.
Table of Contents
- 1 Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
- 2 Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
- 3 Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
- 4 Short Essay on Covid-19
Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a global pandemic. It started in late 2019 and has affected people all around the world. The virus spreads very quickly through someone’s sneeze and respiratory issues.
COVID-19 has had a significant impact on our lives, with lockdowns, travel restrictions, and changes in daily routines. To prevent the spread of COVID-19, we should wear masks, practice social distancing, and wash our hands frequently.
People should follow social distancing and other safety guidelines and also learn the tricks to be safe stay healthy and work the whole challenging time.
Also Read: National Safe Motherhood Day 2023
Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
COVID-19 also known as coronavirus, became a global health crisis in early 2020 and impacted mankind around the world. This virus is said to have originated in Wuhan, China in late 2019. It belongs to the coronavirus family and causes flu-like symptoms. It impacted the healthcare systems, economies and the daily lives of people all over the world.
The most crucial aspect of COVID-19 is its highly spreadable nature. It is a communicable disease that spreads through various means such as coughs from infected persons, sneezes and communication. Due to its easy transmission leading to its outbreaks, there were many measures taken by the government from all over the world such as Lockdowns, Social Distancing, and wearing masks.
There are many changes throughout the economic systems, and also in daily routines. Other measures such as schools opting for Online schooling, Remote work options available and restrictions on travel throughout the country and internationally. Subsequently, to cure and top its outbreak, the government started its vaccine campaigns, and other preventive measures.
In conclusion, COVID-19 tested the patience and resilience of the mankind. This pandemic has taught people the importance of patience, effort and humbleness.
Also Read : Essay on My Best Friend
Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a serious and contagious disease that has affected people worldwide. It was first discovered in late 2019 in Cina and then got spread in the whole world. It had a major impact on people’s life, their school, work and daily lives.
COVID-19 is primarily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets produced and through sneezes, and coughs of an infected person. It can spread to thousands of people because of its highly contagious nature. To cure the widespread of this virus, there are thousands of steps taken by the people and the government.
Wearing masks is one of the essential precautions to prevent the virus from spreading. Social distancing is another vital practice, which involves maintaining a safe distance from others to minimize close contact.
Very frequent handwashing is also very important to stop the spread of this virus. Proper hand hygiene can help remove any potential virus particles from our hands, reducing the risk of infection.
In conclusion, the Coronavirus has changed people’s perspective on living. It has also changed people’s way of interacting and how to live. To deal with this virus, it is very important to follow the important guidelines such as masks, social distancing and techniques to wash your hands. Getting vaccinated is also very important to go back to normal life and cure this virus completely.
Also Read: Essay on Abortion in English in 650 Words
Short Essay on Covid-19
Please find below a sample of a short essay on Covid-19 for school students:
Also Read: Essay on Women’s Day in 200 and 500 words
to write an essay on COVID-19, understand your word limit and make sure to cover all the stages and symptoms of this disease. You need to highlight all the challenges and impacts of COVID-19. Do not forget to conclude your essay with positive precautionary measures.
Writing an essay on COVID-19 in 200 words requires you to cover all the challenges, impacts and precautions of this disease. You don’t need to describe all of these factors in brief, but make sure to add as many options as your word limit allows.
The full form for COVID-19 is Corona Virus Disease of 2019.
Related Reads
Hence, we hope that this blog has assisted you in comprehending with an essay on COVID-19. For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Simran Popli
An avid writer and a creative person. With an experience of 1.5 years content writing, Simran has worked with different areas. From medical to working in a marketing agency with different clients to Ed-tech company, the journey has been diverse. Creative, vivacious and patient are the words that describe her personality.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
10 destination west coast college towns.
Cole Claybourn May 16, 2024

Scholarships for Lesser-Known Sports
Sarah Wood May 15, 2024

Should Students Submit Test Scores?
Sarah Wood May 13, 2024

Poll: Antisemitism a Problem on Campus
Lauren Camera May 13, 2024

Federal vs. Private Parent Student Loans
Erika Giovanetti May 9, 2024

14 Colleges With Great Food Options
Sarah Wood May 8, 2024

Colleges With Religious Affiliations
Anayat Durrani May 8, 2024

Protests Threaten Campus Graduations
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 6, 2024

Protesting on Campus: What to Know
Sarah Wood May 6, 2024

Lawmakers Ramp Up Response to Unrest
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 3, 2024

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Covid 19 Essay in English
Essay on Covid -19: In a very short amount of time, coronavirus has spread globally. It has had an enormous impact on people's lives, economy, and societies all around the world, affecting every country. Governments have had to take severe measures to try and contain the pandemic. The virus has altered our way of life in many ways, including its effects on our health and our economy. Here are a few sample essays on ‘CoronaVirus’.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19
200 words essay on covid 19, 500 words essay on covid 19.

COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very short period of time. It has affected lives, economies and societies across the world, leaving no country untouched. The virus has caused governments to take drastic measures to try and contain it. From health implications to economic and social ramifications, COVID-19 impacted every part of our lives. It has been more than 2 years since the pandemic hit and the world is still recovering from its effects.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the world has been impacted in a number of ways. For one, the global economy has taken a hit as businesses have been forced to close their doors. This has led to widespread job losses and an increase in poverty levels around the world. Additionally, countries have had to impose strict travel restrictions in an attempt to contain the virus, which has resulted in a decrease in tourism and international trade. Furthermore, the pandemic has put immense pressure on healthcare systems globally, as hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients suffering from the virus. Lastly, the outbreak has led to a general feeling of anxiety and uncertainty, as people are fearful of contracting the disease.
My Experience of COVID-19
I still remember how abruptly colleges and schools shut down in March 2020. I was a college student at that time and I was under the impression that everything would go back to normal in a few weeks. I could not have been more wrong. The situation only got worse every week and the government had to impose a lockdown. There were so many restrictions in place. For example, we had to wear face masks whenever we left the house, and we could only go out for essential errands. Restaurants and shops were only allowed to operate at take-out capacity, and many businesses were shut down.
In the current scenario, coronavirus is dominating all aspects of our lives. The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc upon people’s lives, altering the way we live and work in a very short amount of time. It has revolutionised how we think about health care, education, and even social interaction. This virus has had long-term implications on our society, including its impact on mental health, economic stability, and global politics. But we as individuals can help to mitigate these effects by taking personal responsibility to protect themselves and those around them from infection.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Education
The outbreak of coronavirus has had a significant impact on education systems around the world. In China, where the virus originated, all schools and universities were closed for several weeks in an effort to contain the spread of the disease. Many other countries have followed suit, either closing schools altogether or suspending classes for a period of time.
This has resulted in a major disruption to the education of millions of students. Some have been able to continue their studies online, but many have not had access to the internet or have not been able to afford the costs associated with it. This has led to a widening of the digital divide between those who can afford to continue their education online and those who cannot.
The closure of schools has also had a negative impact on the mental health of many students. With no face-to-face contact with friends and teachers, some students have felt isolated and anxious. This has been compounded by the worry and uncertainty surrounding the virus itself.
The situation with coronavirus has improved and schools have been reopened but students are still catching up with the gap of 2 years that the pandemic created. In the meantime, governments and educational institutions are working together to find ways to support students and ensure that they are able to continue their education despite these difficult circumstances.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Economy
The outbreak of the coronavirus has had a significant impact on the global economy. The virus, which originated in China, has spread to over two hundred countries, resulting in widespread panic and a decrease in global trade. As a result of the outbreak, many businesses have been forced to close their doors, leading to a rise in unemployment. In addition, the stock market has taken a severe hit.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Health
The effects that coronavirus has on one's health are still being studied and researched as the virus continues to spread throughout the world. However, some of the potential effects on health that have been observed thus far include respiratory problems, fever, and coughing. In severe cases, pneumonia, kidney failure, and death can occur. It is important for people who think they may have been exposed to the virus to seek medical attention immediately so that they can be treated properly and avoid any serious complications. There is no specific cure or treatment for coronavirus at this time, but there are ways to help ease symptoms and prevent the virus from spreading.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
Students’ Essays on Infectious Disease Prevention, COVID-19 Published Nationwide
As part of the BIO 173: Global Change and Infectious Disease course, Professor Fred Cohan assigns students to write an essay persuading others to prevent future and mitigate present infectious diseases. If students submit their essay to a news outlet—and it’s published—Cohan awards them with extra credit.
As a result of this assignment, more than 25 students have had their work published in newspapers across the United States. Many of these essays cite and applaud the University’s Keep Wes Safe campaign and its COVID-19 testing protocols.
Cohan, professor of biology and Huffington Foundation Professor in the College of the Environment (COE), began teaching the Global Change and Infectious Disease course in 2009, when the COE was established. “I wanted very much to contribute a course to what I saw as a real game-changer in Wesleyan’s interest in the environment. The course is about all the ways that human demands on the environment have brought us infectious diseases, over past millennia and in the present, and why our environmental disturbances will continue to bring us infections into the future.”
Over the years, Cohan learned that he can sustainably teach about 170 students every year without running out of interested students. This fall, he had 207. Although he didn’t change the overall structure of his course to accommodate COVID-19 topics, he did add material on the current pandemic to various sections of the course.
“I wouldn’t say that the population of the class increased tremendously as a result of COVID-19, but I think the enthusiasm of the students for the material has increased substantially,” he said.
To accommodate online learning, Cohan shaved off 15 minutes from his normal 80-minute lectures to allow for discussion sections, led by Cohan and teaching assistants. “While the lectures mostly dealt with biology, the discussions focused on how changes in behavior and policy can solve the infectious disease problems brought by human disturbance of the environment,” he said.
Based on student responses to an introspective exam question, Cohan learned that many students enjoyed a new hope that we could each contribute to fighting infectious disease. “They discovered that the solution to infectious disease is not entirely a waiting game for the right technologies to come along,” he said. “Many enjoyed learning about fighting infectious disease from a moral and social perspective. And especially, the students enjoyed learning about the ‘socialism of the microbe,’ how preventing and curing others’ infections will prevent others’ infections from becoming our own. The students enjoyed seeing how this idea can drive both domestic and international health policies.”
A sampling of the published student essays are below:
Alexander Giummo ’22 and Mike Dunderdale’s ’23 op-ed titled “ A National Testing Proposal: Let’s Fight Back Against COVID-19 ” was published in the Journal Inquirer in Manchester, Conn.
They wrote: “With an expansive and increased testing plan for U.S. citizens, those who are COVID-positive could limit the number of contacts they have, and this would also help to enable more effective contact tracing. Testing could also allow for the return of some ‘normal’ events, such as small social gatherings, sports, and in-person class and work schedules.
“We propose a national testing strategy in line with the one that has kept Wesleyan students safe this year. The plan would require a strong push by the federal government to fund the initiative, but it is vital to successful containment of the virus.
“Twice a week, all people living in the U.S. should report to a local testing site staffed with professionals where the anterior nasal swab Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test, used by Wesleyan and supported by the Broad Institute, would be implemented.”
Kalyani Mohan ’22 and Kalli Jackson ’22 penned an essay titled “ Where Public Health Meets Politics: COVID-19 in the United States ,” which was published in Wesleyan’s Arcadia Political Review .
They wrote: “While the U.S. would certainly benefit from a strengthened pandemic response team and structural changes to public health systems, that alone isn’t enough, as American society is immensely stratified, socially and culturally. The politicization of the COVID-19 pandemic shows that individualism, libertarianism and capitalism are deeply ingrained in American culture, to the extent that Americans often blind to the fact community welfare can be equivalent to personal welfare. Pandemics are multifaceted, and preventing them requires not just a cultural shift but an emotional one amongst the American people, one guided by empathy—towards other people, different communities and the planet. Politics should be a tool, not a weapon against its people.”
Sydnee Goyer ’21 and Marcel Thompson’s ’22 essay “ This Flu Season Will Be Decisive in the Fight Against COVID-19 ” also was published in Arcadia Political Review .
“With winter approaching all around the Northern Hemisphere, people are preparing for what has already been named a “twindemic,” meaning the joint threat of the coronavirus and the seasonal flu,” they wrote. “While it is known that seasonal vaccinations reduce the risk of getting the flu by up to 60% and also reduce the severity of the illness after the contamination, additional research has been conducted in order to know whether or not flu shots could reduce the risk of people getting COVID-19. In addition to the flu shot, it is essential that people remain vigilant in maintaining proper social distancing, washing your hands thoroughly, and continuing to wear masks in public spaces.”
An op-ed titled “ The Pandemic Has Shown Us How Workplace Culture Needs to Change ,” written by Adam Hickey ’22 and George Fuss ’21, was published in Park City, Utah’s The Park Record .
They wrote: “One review of academic surveys (most of which were conducted in the United States) conducted in 2019 found that between 35% and 97% of respondents in those surveys reported having attended work while they were ill, often because of workplace culture or policy which generated pressure to do so. Choosing to ignore sickness and return to the workplace while one is ill puts colleagues at risk, regardless of the perceived severity of your own illness; COVID-19 is an overbearing reminder that a disease that may cause mild, even cold-like symptoms for some can still carry fatal consequences for others.
“A mandatory paid sick leave policy for every worker, ideally across the globe, would allow essential workers to return to work when necessary while still providing enough wiggle room for economically impoverished employees to take time off without going broke if they believe they’ve contracted an illness so as not to infect the rest of their workplace and the public at large.”

Women’s cross country team members and classmates Jane Hollander ’23 and Sara Greene ’23 wrote a sports-themed essay titled “ This Season, High School Winter Sports Aren’t Worth the Risk ,” which was published in Tap into Scotch Plains/Fanwood , based in Scotch Plains, N.J. Their essay focused on the risks high school sports pose on student-athletes, their families, and the greater community.
“We don’t propose cutting off sports entirely— rather, we need to be realistic about the levels at which athletes should be participating. There are ways to make practices safer,” they wrote. “At [Wesleyan], we began the season in ‘cohorts,’ so the amount of people exposed to one another would be smaller. For non-contact sports, social distancing can be easily implemented, and for others, teams can focus on drills, strength and conditioning workouts, and skill-building exercises. Racing sports such as swim and track can compete virtually, comparing times with other schools, and team sports can focus their competition on intra-team scrimmages. These changes can allow for the continuation of a sense of normalcy and team camaraderie without the exposure to students from different geographic areas in confined, indoor spaces.”
Brook Guiffre ’23 and Maddie Clarke’s ’22 op-ed titled “ On the Pandemic ” was published in Hometown Weekly, based in Medfield, Mass.
“The first case of COVID-19 in the United States was recorded on January 20th, 2020. For the next month and a half, the U.S. continued operating normally, while many other countries began their lockdown,” they wrote. “One month later, on February 29th, 2020, the federal government approved a national testing program, but it was too little too late. The U.S. was already in pandemic mode, and completely unprepared. Frontline workers lacked access to N-95 masks, infected patients struggled to get tested, and national leaders informed the public that COVID-19 was nothing more than the common flu. Ultimately, this unpreparedness led to thousands of avoidable deaths and long-term changes to daily life. With the risk of novel infectious diseases emerging in the future being high, it is imperative that the U.S. learn from its failure and better prepare for future pandemics now. By strengthening our public health response and re-establishing government organizations specialized in disease control, we have the ability to prevent more years spent masked and six feet apart.”
In addition, their other essay, “ On Mass Extinction ,” was also published by Hometown Weekly .
“The sixth mass extinction—which scientists have coined as the Holocene Extinction—is upon us. According to the United Nations, around one million plant and animal species are currently in danger of extinction, and many more within the next decade. While other extinctions have occurred in Earth’s history, none have occurred at such a rapid rate,” they wrote. “For the sake of both biodiversity and infectious diseases, it is in our best interest to stop pushing this Holocene Extinction further.”
An essay titled “ Learning from Our Mistakes: How to Protect Ourselves and Our Communities from Diseases ,” written by Nicole Veru ’21 and Zoe Darmon ’21, was published in My Hometown Bronxville, based in Bronxville, N.Y.
“We can protect ourselves and others from future infectious diseases by ensuring that we are vaccinated,” they wrote. “Vaccines have high levels of success if enough people get them. Due to vaccines, society is no longer ravaged by childhood diseases such as mumps, rubella, measles, and smallpox. We have been able to eradicate diseases through vaccines; smallpox, one of the world’s most consequential diseases, was eradicated from the world in the 1970s.
“In 2000, the U.S. was nearly free of measles, yet, due to hesitations by anti-vaxxers, there continues to be cases. From 2000–2015 there were over 18 measles outbreaks in the U.S. This is because unless a disease is completely eradicated, there will be a new generation susceptible.
“Although vaccines are not 100% effective at preventing infection, if we continue to get vaccinated, we protect ourselves and those around us. If enough people are vaccinated, societies can develop herd immunity. The amount of people vaccinated to obtain herd immunity depends on the disease, but if this fraction is obtained, the spread of disease is contained. Through herd immunity, we protect those who may not be able to get vaccinated, such as people who are immunocompromised and the tiny portion of people for whom the vaccine is not effective.”
Dhruvi Rana ’22 and Bryce Gillis ’22 co-authored an op-ed titled “ We Must Educate Those Who Remain Skeptical of the Dangers of COVID-19 ,” which was published in Rhode Island Central .
“As Rhode Island enters the winter season, temperatures are beginning to drop and many studies have demonstrated that colder weather and lower humidity are correlated with higher transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19,” they wrote. “By simply talking or breathing, we release respiratory droplets and aerosols (tiny fluid particles which could carry the coronavirus pathogen), which can remain in the air for minutes to hours.
“In order to establish herd immunity in the US, we must educate those who remain skeptical of the dangers of COVID-19. Whether community-driven or state-funded, educational campaigns are needed to ensure that everyone fully comprehends how severe COVID-19 is and the significance of airborne transmission. While we await a vaccine, it is necessary now more than ever that we social distance, avoid crowds, and wear masks, given that colder temperatures will likely yield increased transmission of the virus.”
Danielle Rinaldi ’21 and Verónica Matos Socorro ’21 published their op-ed titled “ Community Forum: How Mask-Wearing Demands a Cultural Reset ” in the Ewing Observer , based in Lawrence, N.J.
“In their own attempt to change personal behavior during the pandemic, Wesleyan University has mandated mask-wearing in almost every facet of campus life,” they wrote. “As members of our community, we must recognize that mask-wearing is something we are all responsible and accountable for, not only because it is a form of protection for us, but just as important for others as well. However, it seems as though both Covid fatigue and complacency are dominating the mindsets of Americans, leading to even more unwillingness to mask up. Ultimately, it is inevitable that this pandemic will not be the last in our lifespan due to global warming creating irreversible losses in biodiversity. As a result, it is imperative that we adopt the norm of mask-wearing now and undergo a culture shift of the abandonment of an individualistic mindset, and instead, create a society that prioritizes taking care of others for the benefit of all.”

Shayna Dollinger ’22 and Hayley Lipson ’21 wrote an essay titled “ My Pandemic Year in College Has Brought Pride and Purpose. ” Dollinger submitted the piece, rewritten in first person, to Jewish News of Northern California . Read more about Dollinger’s publication in this News @ Wesleyan article .
“I lay in the dead grass, a 6-by-6-foot square all to myself. I cheer for my best friend, who is on the stage constructed at the bottom of Foss hill, dancing with her Bollywood dance group. Masks cover their ordinarily smiling faces as their bodies move in sync. Looking around at friends and classmates, each in their own 6-by-6 world, I feel an overwhelming sense of normalcy.
“One of the ways in which Wesleyan has prevented outbreaks on campus is by holding safe, socially distanced events that students want to attend. By giving us places to be and things to do on the weekends, we are discouraged from breaking rules and causing outbreaks at ‘super-spreader’ events.”
An op-ed written by Luna Mac-Williams ’22 and Daëlle Coriolan ’24 titled “ Collectivist Practices to Combat COVID-19 ” was published in the Wesleyan Argus .
“We are embroiled in a global pandemic that disproportionately affects poor communities of color, and in the midst of a higher cultural consciousness of systemic inequities,” they wrote. “A cultural shift to center collectivist thought and action not only would prove helpful in disease prevention, but also belongs in conversation with the Black Lives Matter movement. Collectivist models of thinking effectively target the needs of vulnerable populations including the sick, the disenfranchised, the systematically marginalized. Collectivist systems provide care, decentering the capitalist, individualist system, and focusing on how communities can work to be self-sufficient and uplift our own neighbors.”
An essay written by Maria Noto ’21 , titled “ U.S. Individualism Has Deadly Consequences ,” is published in the Oneonta Daily Star , based in Oneonta, N.Y.
She wrote, “When analyzing the cultures of certain East Asian countries, several differences stand out. For instance, when people are sick and during the cold and flu season, many East Asian cultures, including South Korea, use mask-wearing. What is considered a threat to freedom by some Americans is a preventive action and community obligation in this example. This, along with many other cultural differences, is insightful in understanding their ability to contain the virus.
“These differences are deeply seeded in the values of a culture. However, there is hope for the U.S. and other individualistic cultures in recognizing and adopting these community-centered approaches. Our mindset needs to be revolutionized with the help of federal and local assistance: mandating masks, passing another stimulus package, contact tracing, etc… However, these measures will be unsuccessful unless everyone participates for the good of a community.”
A published op-ed by Madison Szabo ’23 , Caitlyn Ferrante ’23 ran in the Two Rivers Times . The piece is titled “ Anxiety and Aspiration: Analyzing the Politicization of the Pandemic .”
John Lee ’21 and Taylor Goodman-Leong ’21 have published their op-ed titled “ Reassessing the media’s approach to COVID-19 ” in Weekly Monday Cafe 24 (Page 2).
An essay by Eleanor Raab ’21 and Elizabeth Nefferdorf ’22 titled “ Preventing the Next Epidemic ” was published in The Almanac .
- Keep Wes Safe
- student publications
- Teaching during the pandemic
Related Articles
Gallery: Students Enjoy Spring Fling 2024 Festivities
Patricelli center awards funding to three new student ventures, wesleyan in the news: may 2024, previous matesan's new book explores political violence, islamist mobilization in egypt and indonesia, next students launch fun, interactive virtual program for school-aged kids.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
How to Write About the Impact of the Coronavirus in a College Essay
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many -- a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
[ Read: How to Write a College Essay. ]
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
[ Read: What Colleges Look for: 6 Ways to Stand Out. ]
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them -- and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
[ Read: The Common App: Everything You Need to Know. ]
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic -- and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
Recommended Stories
Dolphins owner stephen ross reportedly declined $10 billion for team, stadium and f1 race.
The value of the Dolphins and Formula One racing is enormous.
PGA Championship: Will Zalatoris says group of players considered asking for postponement after death, Scottie Scheffler arrest
It was a surreal day at the PGA Championship.
Housing experts revise mortgage rate forecasts for remainder of 2024
Experts are revising their forecasts about mortgage rates and home prices for the rest of the year.
Oleksandr Usyk defeats Tyson Fury by split decision to become first undisputed heavyweight champion in 24 years
Boxing hadn't had an undisputed heavyweight king since 2000.
Preakness Stakes 2024 winner, payouts, results: Seize the Grey wins at Pimlico, Mystik Dan finishes 2nd, ending Triple Crown bid
Live updates from the 149th Preakness Stakes at Pimlico Race Course in Baltimore
UFC Vegas 92: Piera Rodríguez DQ'd for multiple illegal headbutts vs. Ariane Carnelossi
Rodríguez was warned by the ref to watch her head. She responded by headbutting her opponent even harder.
The Mavericks' major gambles pay off as Luka Dončić, Kyrie Irving lead charge to West finals
Shrewd moves and timely deals have the aggressive Mavericks moving on in the postseason — and perhaps to an even better tomorrow.
Report: Fanatics files lawsuit against Cardinals rookie WR Marvin Harrison Jr. for breach of contract
Marvin Harrison Jr., Fanatics said, “rejected or ignored every request” from the company while refusing to fulfill obligations of their contract that was signed last May.
Auburn RB Brian Battie critically wounded in Sarasota shooting
Battie's older brother Tommie was killed and three others were shot early Saturday morning .
2024 NBA Mock Draft 7.0: Who will the Hawks take at No. 1? Our projections for every pick with lottery order now set
With the lottery order set, here's a look at Yahoo Sports' projections for both rounds of the 2024 NBA Draft.
The top RBs for 2024 fantasy football, according to our experts
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first running back rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
NBA Draft Combine reactions: Edey oh my, Bronny James is ready & whose stock is rising? | On the Clock with Krysten Peek
Yahoo Sports NBA draft expert Krysten Peek is back for another season of On the Clock with Krysten Peek. Krysten just spent the week in Chicago at the NBA Draft Combine and kicks off draft season joined by CBS Sports' Kyle Boone.
Apple will reportedly offer higher trade-in credit for old iPhones for the next two weeks
According to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman, Apple will be offering a little more than usual for some trade-ins starting next week in the US and Canada. That's as long as you're getting one of the iPhone 15 models.

Caitlin Clark, Fever facing plenty of growing pains early after another blowout loss in home debut
The atmosphere was electric for Clark's home debut and there were brief flashes from the Fever, but it's clear they've got plenty to work on before they can compete with the WNBA's elite teams.
The Spin: Making a call on 5 slumping fantasy baseball stars
All five of these hitters were drafted highly in fantasy baseball leagues. So far, they have not lived up to their ADPs — and that's an understatement. Scott Pianowski analyzes.
Your favorite WNBA rookies didn’t make the cut. So what’s their path back to the league?
For rookies who were waived, the climb to their pro dreams is steeper, but the path ahead is well-worn with trail markers of established success.
Tyson Fury vs. Oleksandr Usyk full results: Usyk stays undefeated, becomes undisputed with split decision win
Fury and Usyk finally fought for all of the heavyweight titles Saturday with the Ukrainian fighter coming out on top.
Attorneys say Scottie Scheffler likely won't face felony conviction: 'Probably about a zero percent chance'
Scottie Scheffler will likely avoid the most serious charges filed against him stemming from Friday morning's altercation with police.
Amid uncertainty around Social Security, here's what financial advisers are telling clients
One of the biggest retirement fears is a reduction in Social Security benefits. Here's what advisers say to do to prepare.
What scouts think of Bronny James' NBA prospects
The biggest question looming over the NBA draft combine this week: How will Bronny James do?

Codeswitch / Life Kit
Listen live.

Fresh Air Weekend
Fresh Air opens the window on contemporary arts and issues with guests from worlds as diverse as literature and economics. Fresh Air Weekend collects the best segments from the week's programs and crafts them together for great weekend listening.
Coronavirus: The world has come together to flatten the curve. Can we stay united to tackle other crises?
Watching the world come together gives me hope for the future, writes mira patel, a high school junior..
Mira Patel and her sister Veda. (Courtesy of Dee Patel)
Related Content

This 24-year-old entrepreneur is helping Black-owned restaurants survive coronavirus
Black and Mobile is an online delivery service that caters to Black-owned restaurants. The coronavirus shutdown has increased demand for its service.
4 years ago

Home desks won’t replace Philly’s high-rise office towers anytime soon, analysts say
Philadelphia’s office market might fare better post-coronavirus than those of other U.S. cities, CBRE analysts said in a new report.
Before the pandemic, I had often heard adults say that young people would lose the ability to connect in-person with others due to our growing dependence on technology and social media. However, this stay-at-home experience has proven to me that our elders’ worry is unnecessary. Because isolation isn’t in human nature, and no advancement in technology could replace our need to meet in person, especially when it comes to learning.
As the weather gets warmer and we approach summertime, it’s going to be more and more tempting for us teenagers to go out and do what we have always done: hang out and have fun. Even though the decision-makers are adults, everyone has a role to play and we teens can help the world move forward by continuing to self-isolate. It’s incredibly important that in the coming weeks, we respect the government’s effort to contain the spread of the coronavirus.
In the meantime, we can find creative ways to stay connected and continue to do what we love. Personally, I see many 6-feet-apart bike rides and Zoom calls in my future.
If there is anything that this pandemic has made me realize, it’s how connected we all are. At first, the infamous coronavirus seemed to be a problem in China, which is worlds away. But slowly, it steadily made its way through various countries in Europe, and inevitably reached us in America. What was once framed as a foreign virus has now hit home.
Watching the global community come together, gives me hope, as a teenager, that in the future we can use this cooperation to combat climate change and other catastrophes.
As COVID-19 continues to creep its way into each of our communities and impact the way we live and communicate, I find solace in the fact that we face what comes next together, as humanity.
When the day comes that my generation is responsible for dealing with another crisis, I hope we can use this experience to remind us that moving forward requires a joint effort.
Mira Patel is a junior at Strath Haven High School and is an education intern at the Foreign Policy Research Institute in Philadelphia. Follow her on Instagram here.
Becoming a storyteller at WHYY, your local public media station, is easier than you might think. Text STORYTELLER to 267-494-9949 to learn more.
WHYY is your source for fact-based, in-depth journalism and information. As a nonprofit organization, we rely on financial support from readers like you. Please give today.
Part of the series

Coronavirus Pandemic
You may also like.

Threats and violence suspend high school football games Friday night
Fight breaks out at a game between Pennsauken and Camden High Schools, threats suspend games in Chester and Northampton Counties.
3 years ago

Philly students get vaxxed at the zoo before heading back to school
The event is the first of its kind for the school district, but arrives after months of partnering with CHOP to organize other vaccination clinics around the city.

Montco high school senior reflects on missing experiences because of coronavirus
Grace Honeyman, a senior at Harriton High School, talks with her father about how she’s dealing with missing milestones due to coronavirus.
Want a digest of WHYY’s programs, events & stories? Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Together we can reach 100% of WHYY’s fiscal year goal
A Year After Coronavirus: An Inclusive ‘New Normal’

Six months into a new decade, 2020 has already been earmarked as ‘the worst’ year in the 21st century. The novel coronavirus has given rise to a global pandemic that has destabilized most institutional settings. While we live in times when humankind possesses the most advanced science and technology, a virus invisible to the naked eye has massively disrupted economies, healthcare, and education systems worldwide. This should serve as a reminder that as we keep making progress in science and research, humanity will continue to face challenges in the future, and it is upon us to prioritize those issues that are most relevant in the 21st century.
Even amidst the pandemic, Space X, an American aerospace manufacturer, managed to become the first private company to send humans to space. While this is a tremendous achievement and prepares humanity for a sustainable future, I feel there is a need to introspect the challenges that we are already facing. On the one hand, we seem to be preparing beyond the 21st century. On the other hand, heightened nationalism, increasing violence against marginalized communities and multidimensional inequalities across all sectors continue to act as barriers to growth for most individuals across the globe. COVID-19 has reinforced these multifaceted economic, social and cultural inequalities wherein those in situations of vulnerability have found it increasingly difficult to get quality medical attention, access to quality education, and have witnessed increased domestic violence while being confined to their homes.
Given the coronavirus’s current situation, some households have also had time to introspect on gender roles and stereotypes. For instance, women are expected to carry out unpaid care work like cooking, cleaning, and looking after the family. There is no valid reason to believe that women ought to carry out these activities, and men have no role in contributing to household chores. With men having shared household chores during the lockdown period, it gives hope that they will realize the burden that women have been bearing for past decades and will continue sharing responsibilities. However, it would be naïve to believe that gender discrimination could be tackled so easily, and men would give up on their decades' old habits within a couple of months. Thus, during and after the pandemic, there is an urgent need to sensitize households on the importance of gender equality and social cohesion.
Moving forward, developing quality healthcare systems that are affordable and accessible to all should be the primary objective for all governments. This can be done by increasing expenditure towards health and education and simultaneously reducing expenditure on defence equipment where the latter mainly gives rise to an idea that countries need to be prepared for violence. There is substantial evidence that increased investment in health and education is beneficial in the long-term and can potentially build the basic foundation of a country.
If it can be established that usage of nuclear weapons, violence and war are not solutions to any problem, governments (like, for example, Costa Rica) could move towards disarmament of weapons and do their part in building a more peaceful planet that is sustainable for the future. This would further promote global citizenship wherein nationality, race, gender, caste, and other categories, are just mere variables and they do not become identities of individuals that restrict their thought process. The aim should be to build responsible citizens who play an active role in their society and work collectively in helping develop a planet that is well-governed, inclusive, and environmentally sustainable.
‘A year after Coronavirus’ is still an unknown, so I think that our immediate focus should be to tackle the complex problems that have emerged from the pandemic so that we make the year after coronavirus one which highlights recovery and acts as a pathway to fresh beginnings. While there is little to gain from such a fatal cause, it is vital that we also use it to make the ‘new normal’ in favour of the environment and ensure that no one is left behind.
Related items
- Country page: India
- UNESCO Office in New Delhi
- SDG: SDG 3 - Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
This article is related to the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals .

Other recent articles

Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Covid19
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
11 min read

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to write a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic?
Writing a compelling and informative essay about this global crisis can be challenging. It requires researching the latest information, understanding the facts, and presenting your argument persuasively.
But don’t worry! with some guidance from experts, you’ll be able to write an effective and persuasive essay about Covid-19.
In this blog post, we’ll outline the basics of writing a persuasive essay . We’ll provide clear examples, helpful tips, and essential information for crafting your own persuasive piece on Covid-19.
Read on to get started on your essay.
- 1. Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 2. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
- 3. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
- 4. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
- 5. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
- 6. Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
- 7. Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 8. Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Here are the steps to help you write a persuasive essay on this topic, along with an example essay:
Step 1: Choose a Specific Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on a specific aspect of COVID-19. It should be debatable and clear. For example:
Step 2: Research and Gather Information
Collect reliable and up-to-date information from reputable sources to support your thesis statement. This may include statistics, expert opinions, and scientific studies. For instance:
- COVID-19 vaccination effectiveness data
- Information on vaccine mandates in different countries
- Expert statements from health organizations like the WHO or CDC
Step 3: Outline Your Essay
Create a clear and organized outline to structure your essay. A persuasive essay typically follows this structure:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Body Paragraphs (with supporting evidence)
- Counterarguments (addressing opposing views)
Step 4: Write the Introduction
In the introduction, grab your reader's attention and present your thesis statement. For example:
Step 5: Provide Background Information
Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance:
Step 6: Develop Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should present a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis statement. Use clear topic sentences, evidence, and analysis. Here's an example:
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and refute them with strong counterarguments. This demonstrates that you've considered different perspectives. For example:
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in the conclusion. End with a strong call to action or thought-provoking statement. For instance:
Step 9: Revise and Proofread
Edit your essay for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. Ensure that your argument flows logically.
Step 10: Cite Your Sources
Include proper citations and a bibliography page to give credit to your sources.
Remember to adjust your approach and arguments based on your target audience and the specific angle you want to take in your persuasive essay about COVID-19.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
When writing a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic, it’s important to consider how you want to present your argument. To help you get started, here are some example essays for you to read:
Check out some more PDF examples below:
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
If you're in search of a compelling persuasive essay on business, don't miss out on our “ persuasive essay about business ” blog!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others.
A persuasive essay about the Covid-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects.
Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
Covid19 Vaccine Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay on Covid Vaccines
Interested in thought-provoking discussions on abortion? Read our persuasive essay about abortion blog to eplore arguments!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Covid19 has drastically changed the way people interact in schools, markets, and workplaces. In short, it has affected all aspects of life. However, people have started to learn to live with Covid19.
Writing a persuasive essay about it shouldn't be stressful. Read the sample essay below to get idea for your own essay about Covid19 integration.
Persuasive Essay About Working From Home During Covid19
Searching for the topic of Online Education? Our persuasive essay about online education is a must-read.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
Covid-19 has been an ever-evolving issue, with new developments and discoveries being made on a daily basis.
Writing an argumentative essay about such an issue is both interesting and challenging. It allows you to evaluate different aspects of the pandemic, as well as consider potential solutions.
Here are some examples of argumentative essays on Covid19.
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 Sample
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion
Looking for a persuasive take on the topic of smoking? You'll find it all related arguments in out Persuasive Essay About Smoking blog!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Do you need to prepare a speech about Covid19 and need examples? We have them for you!
Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate for specific changes in policies or simply raise awareness about the virus.
Check out some examples of persuasive speeches on Covid-19:
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Persuasive Speech About Vaccine For Covid-19
You can also read persuasive essay examples on other topics to master your persuasive techniques!
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively.
Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic:
Choose a Specific Angle
Start by narrowing down your focus. COVID-19 is a broad topic, so selecting a specific aspect or issue related to it will make your essay more persuasive and manageable. For example, you could focus on vaccination, public health measures, the economic impact, or misinformation.
Provide Credible Sources
Support your arguments with credible sources such as scientific studies, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Reliable sources enhance the credibility of your essay.
Use Persuasive Language
Employ persuasive techniques, such as ethos (establishing credibility), pathos (appealing to emotions), and logos (using logic and evidence). Use vivid examples and anecdotes to make your points relatable.
Organize Your Essay
Structure your essay involves creating a persuasive essay outline and establishing a logical flow from one point to the next. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and transitions between paragraphs should be smooth and logical.
Emphasize Benefits
Highlight the benefits of your proposed actions or viewpoints. Explain how your suggestions can improve public health, safety, or well-being. Make it clear why your audience should support your position.
Use Visuals -H3
Incorporate graphs, charts, and statistics when applicable. Visual aids can reinforce your arguments and make complex data more accessible to your readers.
Call to Action
End your essay with a strong call to action. Encourage your readers to take a specific step or consider your viewpoint. Make it clear what you want them to do or think after reading your essay.
Revise and Edit
Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Make sure your arguments are well-structured and that your writing flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback
Have someone else read your essay to get feedback. They may offer valuable insights and help you identify areas where your persuasive techniques can be improved.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Here are some persuasive essay topics on COVID-19:
- The Importance of Vaccination Mandates for COVID-19 Control
- Balancing Public Health and Personal Freedom During a Pandemic
- The Economic Impact of Lockdowns vs. Public Health Benefits
- The Role of Misinformation in Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy
- Remote Learning vs. In-Person Education: What's Best for Students?
- The Ethics of Vaccine Distribution: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations
- The Mental Health Crisis Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
- Global Cooperation vs. Vaccine Nationalism in Fighting the Pandemic
- The Future of Telemedicine: Expanding Healthcare Access Post-COVID-19
In search of more inspiring topics for your next persuasive essay? Our persuasive essay topics blog has plenty of ideas!
To sum it up,
You have read good sample essays and got some helpful tips. You now have the tools you needed to write a persuasive essay about Covid-19. So don't let the doubts stop you, start writing!
If you need professional writing help, don't worry! We've got that for you as well.
MyPerfectWords.com is a professional persuasive essay writing service that can help you craft an excellent persuasive essay on Covid-19. Our experienced essay writer will create a well-structured, insightful paper in no time!
So don't hesitate and place your ' write my essay online ' request today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about covid-19.
Yes, there are ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19. It's essential to ensure the information is accurate, not contribute to misinformation, and be sensitive to the pandemic's impact on individuals and communities. Additionally, respecting diverse viewpoints and emphasizing public health benefits can promote ethical communication.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The impact of COVID-19 on society is far-reaching. It has led to job and economic losses, an increase in stress and mental health disorders, and changes in education systems. It has also had a negative effect on social interactions, as people have been asked to limit their contact with others.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Coronavirus: All you need to know in under 500 words
Virus reported to have originated in China’s Wuhan has killed more than 957,000 people and infected over 30 million.

The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the new coronavirus outbreak , which originated in Wuhan, China, a pandemic.
As of September 20, the global death toll surpassed 957,000 amid more than 30.8 million cases. Over 21 million people have recovered from the disease worldwide, according to the data collected by the Johns Hopkins University in the United States.
Keep reading
Coronavirus: all you need to know about symptoms and risks, timeline: how the new coronavirus spread, coronavirus: which countries have confirmed cases.
Here is what you need to know:
What is a coronavirus?
The coronavirus family causes illnesses ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), according to the WHO.
They circulate in animals and some can be transmitted between animals and humans. Several coronaviruses are circulating in animals that have not yet infected humans.
The new coronavirus, the seventh known to affect humans, has been named COVID-19.
What are the symptoms?
Common signs of infection include fever, coughing and breathing difficulties. In severe cases, it can cause pneumonia, multiple organ failure and death.
The incubation period of COVID-19 is thought to be between one and 14 days. It is contagious before symptoms appear, which is why so many people get infected.
Infected patients can be also asymptomatic, meaning they do not display any symptoms despite having the virus in their systems.
Where did it come from?
China alerted the WHO to cases of unusual pneumonia in Wuhan on December 31.
COVID-19 is thought to have originated in a seafood market where wildlife was sold illegally.
On February 7, Chinese researchers said the virus could have spread from an infected animal to humans through illegally trafficked pangolins, prized in Asia for food and medicine.
Scientists have pointed to either bats or snakes as possible sources.

Should I worry? How can I protect myself?
The WHO declared the virus a pandemic on March 11 and said it was “deeply concerned by the alarming levels of spread and severity” of the outbreak.
The WHO recommends basic hygiene such as regularly washing hands with soap and water, and covering your mouth with your elbow when sneezing or coughing.
Maintain “ physical distancing ” – keeping at least 1 metre (three feet) between yourself and others – particularly if they are coughing and sneezing, and avoid touching your face, eyes and mouth with unwashed hands.
Avoid unnecessary, unprotected contact with animals and be sure to thoroughly wash hands after contact.
MINI REVIEW article
Covid-19: emergence, spread, possible treatments, and global burden.

- 1 Department of Pharmacology, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, India
- 2 Department of Health Sciences, School of Education and Health, Cape Breton University, Sydney, NS, Canada
The Coronavirus (CoV) is a large family of viruses known to cause illnesses ranging from the common cold to acute respiratory tract infection. The severity of the infection may be visible as pneumonia, acute respiratory syndrome, and even death. Until the outbreak of SARS, this group of viruses was greatly overlooked. However, since the SARS and MERS outbreaks, these viruses have been studied in greater detail, propelling the vaccine research. On December 31, 2019, mysterious cases of pneumonia were detected in the city of Wuhan in China's Hubei Province. On January 7, 2020, the causative agent was identified as a new coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and the disease was later named as COVID-19 by the WHO. The virus spread extensively in the Wuhan region of China and has gained entry to over 210 countries and territories. Though experts suspected that the virus is transmitted from animals to humans, there are mixed reports on the origin of the virus. There are no treatment options available for the virus as such, limited to the use of anti-HIV drugs and/or other antivirals such as Remdesivir and Galidesivir. For the containment of the virus, it is recommended to quarantine the infected and to follow good hygiene practices. The virus has had a significant socio-economic impact globally. Economically, China is likely to experience a greater setback than other countries from the pandemic due to added trade war pressure, which have been discussed in this paper.
Introduction
Coronaviridae is a family of viruses with a positive-sense RNA that possess an outer viral coat. When looked at with the help of an electron microscope, there appears to be a unique corona around it. This family of viruses mainly cause respiratory diseases in humans, in the forms of common cold or pneumonia as well as respiratory infections. These viruses can infect animals as well ( 1 , 2 ). Up until the year 2003, coronavirus (CoV) had attracted limited interest from researchers. However, after the SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV, the coronavirus was looked at with renewed interest ( 3 , 4 ). This also happened to be the first epidemic of the 21st century originating in the Guangdong province of China. Almost 10 years later, there was a MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) outbreak in 2012, which was caused by the MERS-CoV ( 5 , 6 ). Both SARS and MERS have a zoonotic origin and originated from bats. A unique feature of these viruses is the ability to mutate rapidly and adapt to a new host. The zoonotic origin of these viruses allows them to jump from host to host. Coronaviruses are known to use the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor or the dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) protein to gain entry into cells for replication ( 7 – 10 ).
In December 2019, almost seven years after the MERS 2012 outbreak, a novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) surfaced in Wuhan in the Hubei region of China. The outbreak rapidly grew and spread to neighboring countries. However, rapid communication of information and the increasing scale of events led to quick quarantine and screening of travelers, thus containing the spread of the infection. The major part of the infection was restricted to China, and a second cluster was found on a cruise ship called the Diamond Princess docked in Japan ( 11 , 12 ).
The new virus was identified to be a novel Coronavirus and was thus initially named 2019-nCoV; later, it was renamed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) ( 13 ), and the disease it causes is now referred to as Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) by the WHO. The virus was suspected to have begun its spread in the Huanan seafood wholesale market in the Wuhan region. It is possible that an animal that was carrying the virus was brought into or sold in the market, causing the spread of the virus in the crowded marketplace. One of the first claims made was in an article published in the Journal of Medical Virology ( 14 ), which identified snakes as the possible host. A second possibility was that pangolins could be the wild host of SARS-CoV-2 ( 15 ), though the most likely possibility is that the virus originated from bats ( 13 , 16 – 19 ). Increasing evidence and experts are now collectively concluding the virus had a natural origin in bats, as with previous such respiratory viruses ( 2 , 20 – 24 ).
Similarly, SARS and MERS were also suspected to originate from bats. In the case of MERS, the dromedary camel is an intermediate host ( 5 , 10 ). Bats have been known to harbor coronaviruses for quite some time now. Just as in the case of avian flu, SARS, MERS, and possibly even HIV, with increasing selection and ecological pressure due to human activities, the virus made the jump from animal to man. Humans have been encroaching increasingly into forests, and this is true over much of China, as in Africa. Combined with additional ecological pressure due to climate change, such zoonotic spillovers are now more common than ever. It is likely that the next disease X will also have such an origin ( 25 ). We have learned the importance of identification of the source organism due to the Ebola virus pandemic. Viruses are unstable organisms genetically, constantly mutating by genetic shift or drift. It is not possible to predict when a cross-species jump may occur and when a seemingly harmless variant form of the virus may turn into a deadly strain. Such an incident occurred in Reston, USA, with the Reston virus ( 26 ), an alarming reminder of this possibility. The identification of the original host helps us to contain future spreads as well as to learn about the mechanism of transmission of viruses. Until the virus is isolated from a wild animal host, in this case, mostly bats, the zoonotic origin will remain hypothetical, though likely. It should further be noted that the virus has acquired several mutations, as noted by a group in China, indicating that there are more than two strains of the virus, which may have had an impact on its pathogenicity. However, this claim remains unproven, and many experts have argued otherwise; data proving this are not yet available ( 27 ). A similar finding was reported from Italy and India independently, where they found two strains ( 28 , 29 ). These findings need to be further cross-verified by similar analyses globally. If true, this finding could effectively explain why some nations are more affected than others.
Transmission
When the spread of COVID-19 began ( Figure 1 ), the virus appeared to be contained within China and the cruise ship “Diamond Princess,” which formed the major clusters of the virus. However, as of April 2020, over 210 countries and territories are affected by the virus, with Europe, the USA, and Iran forming the new cluster of the virus. The USA ( Figure 2 ) has the highest number of confirmed COVID-19 cases, whereas India and China, despite being among the most population-dense countries in the world, have managed to constrain the infection rate by the implementation of a complete lockdown with arrangements in place to manage the confirmed cases. Similarly, the UK has also managed to maintain a low curve of the graph by implementing similar measures, though it was not strictly enforced. Reports have indicated that the presence of different strains or strands of the virus may have had an effect on the management of the infection rate of the virus ( 27 – 29 ). The disease is spread by droplet transmission. As of April 2020, the total number of infected individuals stands at around 3 million, with ~200,000 deaths and more than 1 million recoveries globally ( 30 , 34 ). The virus thus has a fatality rate of around 2% and an R 0 of 3 based on current data. However, a more recent report from the CDC, Atlanta, USA, claims that the R 0 could be as high as 5.7 ( 35 ). It has also been observed from data available from China and India that individuals likely to be infected by the virus from both these countries belong to the age groups of 20–50 years ( 36 , 37 ). In both of these countries, the working class mostly belongs to this age group, making exposure more likely. Germany and Singapore are great examples of countries with a high number of cases but low fatalities as compared to their immediate neighbors. Singapore is one of the few countries that had developed a detailed plan of action after the previous SARS outbreak to deal with a similar situation in the future, and this worked in their favor during this outbreak. Both countries took swift action after the outbreak began, with Singapore banning Chinese travelers and implementing screening and quarantine measures at a time when the WHO recommended none. They ordered the elderly and the vulnerable to strictly stay at home, and they ensured that lifesaving equipment and large-scale testing facilities were available immediately ( 38 , 39 ). Germany took similar measures by ramping up testing capacity quite early and by ensuring that all individuals had equal opportunity to get tested. This meant that young, old, and at-risk people all got tested, thus ensuring positive results early during disease progression and that most cases were mild like in Singapore, thus maintaining a lower death percentage ( 40 ). It allowed infected individuals to be identified and quarantined before they even had symptoms. Testing was carried out at multiple labs, reducing the load and providing massive scale, something which countries such as the USA did quite late and India restricted to select government and private labs. The German government also banned large gatherings and advocated social distancing to further reduce the spread, though unlike India and the USA, this was done quite late. South Korea is another example of how a nation has managed to contain the spread and transmission of the infection. South Korea and the USA both reported their first COVID-19 cases on the same day; however, the US administration downplayed the risks of the disease, unlike South Korean officials, who constantly informed their citizens about the developments of the disease using the media and a centralized messaging system. They also employed the Trace, Test, and Treat protocol to identify and isolate patients fast, whereas the USA restricted this to patients with severe infection and only later broadened this criterion, like many European countries as well as India. Unlike the USA, South Korea also has universal healthcare, ensuring free diagnostic testing.
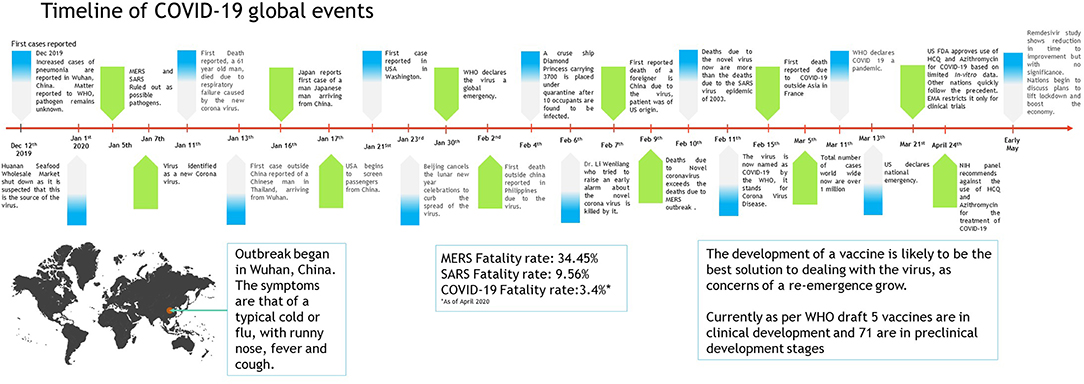
Figure 1 . Timeline of COVID-19 progression ( 30 – 32 ).
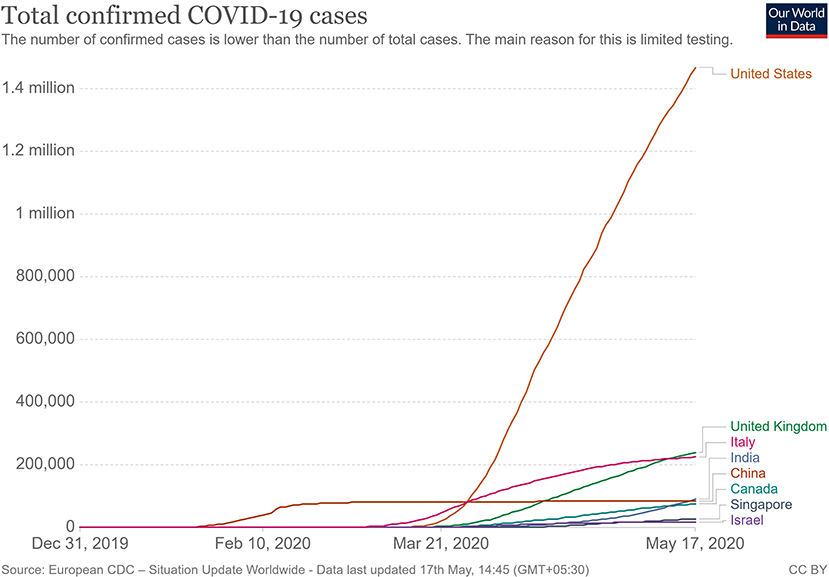
Figure 2 . Total confirmed COVID 19 cases as of May 2020 ( 33 ).
The main mode of transmission of 2019-nCoV is human to human. As of now, animal-to-human transfer has not yet been confirmed. Asymptomatic carriers of the virus are at major risk of being superinfectors with this disease, as all those infected may not develop the disease ( 41 ). This is a concern that has been raised by nations globally, with the Indian government raising concerns on how to identify and contain asymptomatic carriers, who could account for 80% of those infected ( 42 ). Since current resources are directed towards understanding the hospitalized individuals showing symptoms, there is still a vast amount of information about asymptomatic individuals that has yet to be studied. For example, some questions that need to be answered include: Do asymptomatic individuals develop the disease at any point in time at all? Do they eventually develop antibodies? How long do they shed the virus for? Can any tissue of these individuals store the virus in a dormant state? Asymptomatic transmission is a gray area that encompasses major unknowns in COVID-19.
The main route of human-to-human transmission is by droplets, which are generated during coughing, talking, or sneezing and are then inhaled by a healthy individual. They can also be indirectly transmitted to a person when they land on surfaces that are touched by a healthy individual who may then touch their nose, mouth, or eyes, allowing the virus entry into the body. Fomites are also a common issue in such diseases ( 43 ).
Aerosol-based transmission of the virus has not yet been confirmed ( 43 ). Stool-based transmission via the fecal-oral route may also be possible since the SARS-CoV-2 has been found in patient feces ( 44 , 45 ). Some patients with COVID-19 tend to develop diarrhea, which can become a major route of transmission if proper sanitation and personal hygiene needs are not met. There is no evidence currently available to suggest intrauterine vertical transmission of the disease in pregnant women ( 46 ).
More investigation is necessary of whether climate has played any role in the containment of the infection in countries such as India, Singapore, China, and Israel, as these are significantly warmer countries as compared with the UK, the USA, and Canada ( Figure 2 ). Ideally, a warm climate should prevent the virus from surviving for longer periods of time on surfaces, reducing transmissibility.
Pathophysiology
On gaining entry via any of the mucus membranes, the single-stranded RNA-based virus enters the host cell using type 2 transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2) and ACE2 receptor protein, leading to fusion and endocytosis with the host cell ( 47 – 49 ). The uncoated RNA is then translated, and viral proteins are synthesized. With the help of RNA-dependant RNA polymerase, new RNA is produced for the new virions. The cell then undergoes lysis, releasing a load of new virions into the patients' body. The resultant infection causes a massive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that causes a cytokine storm.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of the disease resembles beta coronavirus infections. The virus has an incubation time of 2–14 days, which is the reason why most patients suspected to have the illness or contact with an individual having the illness remain in quarantine for the said amount of time. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 causes severe pneumonia, intermittent fever, and cough ( 50 , 51 ). Symptoms of rhinorrhoea, pharyngitis, and sneezing have been less commonly seen. Patients often develop acute respiratory distress syndrome within 2 days of hospital admission, requiring ventilatory support. It has been observed that during this phase, the mortality tends to be high. Chest CT will show indicators of pneumonia and ground-glass opacity, a feature that has helped to improve the preliminary diagnosis ( 51 ). The primary method of diagnosis for SARS-CoV-2 is with the help of PCR. For the PCR testing, the US CDC recommends testing for the N gene, whereas the Chinese CDC recommends the use of ORF lab and N gene of the viral genome for testing. Some also rely on the radiological findings for preliminary screening ( 52 ). Additionally, immunodiagnostic tests based on the presence of antibodies can also play a role in testing. While the WHO recommends the use of these tests for research use, many countries have pre-emptively deployed the use of these tests in the hope of ramping up the rate and speed of testing ( 52 – 54 ). Later, they noticed variations among the results, causing them to stop the use of such kits; there was also debate among the experts about the sensitivity and specificity of the tests. For immunological tests, it is beneficial to test for antibodies against the virus produced by the body rather than to test for the presence of the viral proteins, since the antibodies can be present in larger titers for a longer span of time. However, the cross-reactivity of these tests with other coronavirus antibodies is something that needs verification. Biochemical parameters such as D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and variations in neutrophil and lymphocyte counts are some other parameters that can be used to make a preliminary diagnosis; however, these parameters vary in a number of diseases and thus cannot be relied upon conclusively ( 51 ). Patients with pre-existing diseases such as asthma or similar lung disorder are at higher risk, requiring life support, as are those with other diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, or obesity. Those above the age of 60 have displayed the highest mortality rate in China, a finding that is mirrored in other nations as well ( Figure 3 ) ( 55 ). If we cross-verify these findings with the population share that is above the age of 70, we find that Italy, the United Kingdom, Canada, and the USA have one of the highest elderly populations as compared to countries such as India and China ( Figure 4 ), and this also reflects the case fatality rates accordingly ( Figure 5 ) ( 33 ). This is a clear indicator that aside from comorbidities, age is also an independent risk factor for death in those infected by COVID-19. Also, in the US, it was seen that the rates of African American deaths were higher. This is probably due to the fact that the prevalence of hypertension and obesity in this community is higher than in Caucasians ( 56 , 57 ). In late April 2020, there are also claims in the US media that young patients in the US with COVID-19 may be at increased risk of stroke; however, this is yet to be proven. We know that coagulopathy is a feature of COVID-19, and thus stroke is likely in this condition ( 58 , 59 ). The main cause of death in COVID-19 patients was acute respiratory distress due to the inflammation in the linings of the lungs caused by the cytokine storm, which is seen in all non-survival cases and in respiratory failure. The resultant inflammation in the lungs, served as an entry point of further infection, associated with coagulopathy end-organ failure, septic shock, and secondary infections leading to death ( 60 – 63 ).
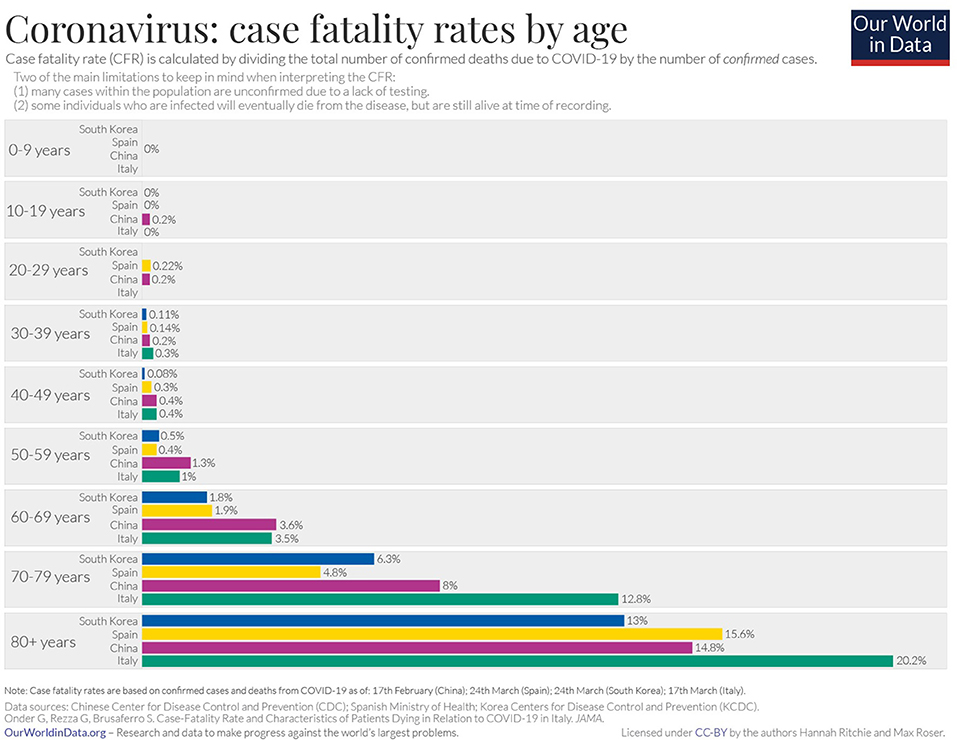
Figure 3 . Case fatality rate by age in selected countries as of April 2020 ( 33 ).
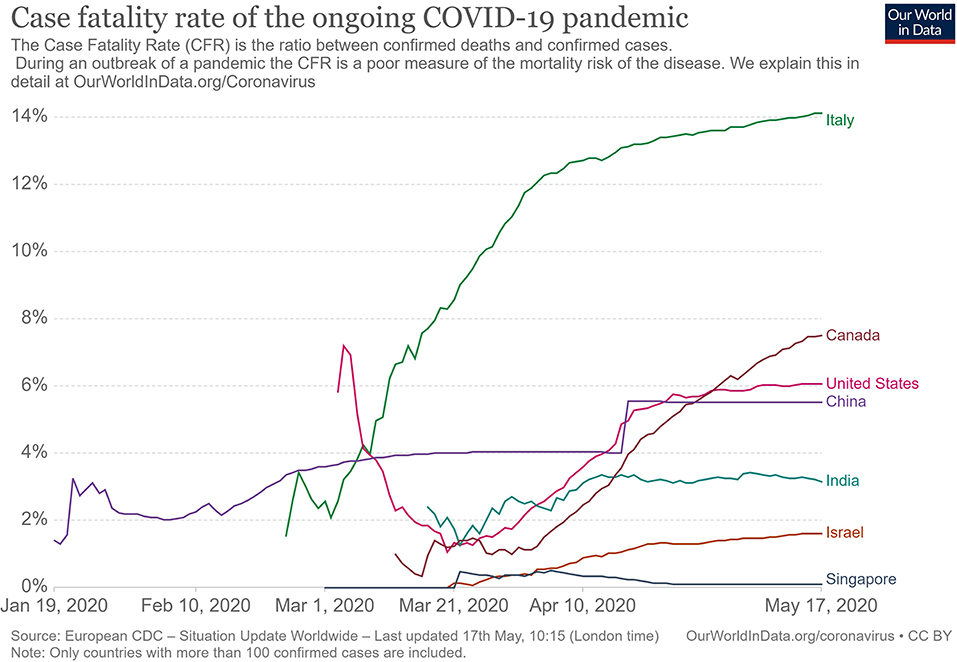
Figure 4 . Case fatality rate in selected countries ( 33 ).
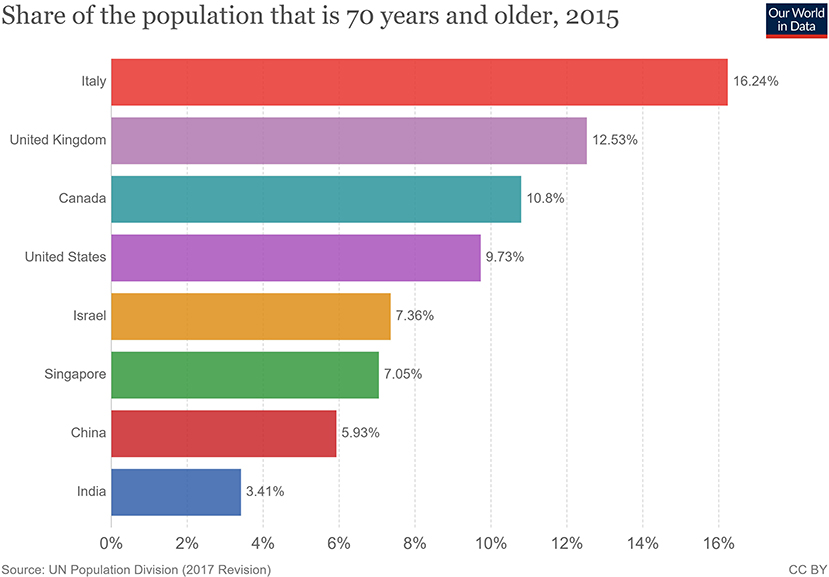
Figure 5 . Population share above 70 years of age ( 33 ).
For COVID-19, there is no specific treatment available. The WHO announced the organization of a trial dubbed the “Solidarity” clinical trial for COVID-19 treatments ( 64 ). This is an international collaborative study that investigates the use of a few prime candidate drugs for use against COVID-19, which are discussed below. The study is designed to reduce the time taken for an RCT by over 80%. There are over 1087 studies ( Supplementary Data 1 ) for COVID-19 registered at clinicaltrials.gov , of which 657 are interventional studies ( Supplementary Data 2 ) ( 65 ). The primary focus of the interventional studies for COVID-19 has been on antimalarial drugs and antiviral agents ( Table 1 ), while over 200 studies deal with the use of different forms of oxygen therapy. Most trials focus on improvement of clinical status, reduction of viral load, time to improvement, and reduction of mortality rates. These studies cover both severe and mild cases.
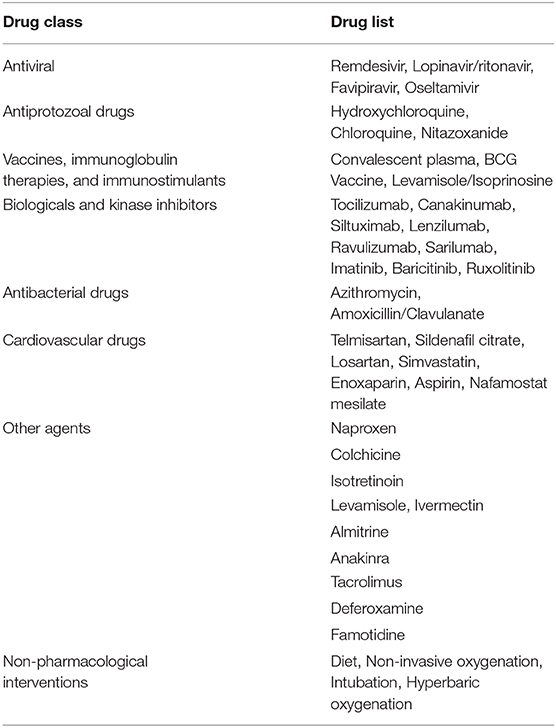
Table 1 . List of therapeutic drugs under study for COVID-19 as per clinical trials registered under clinicaltrials.gov .
Use of Antimalarial Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2
The use of chloroquine for the treatment of corona virus-based infection has shown some benefit in the prevention of viral replication in the cases of SARS and MERS. However, it was not validated on a large scale in the form of a randomized control trial ( 50 , 66 – 68 ). The drugs of choice among antimalarials are Chloroquine (CQ) and Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). The use of CQ for COVID-19 was brought to light by the Chinese, especially by the publication of a letter to the editor of Bioscience Trends by Gao et al. ( 69 ). The letter claimed that several studies found CQ to be effective against COVID-19; however, the letter did not provide many details. Immediately, over a short span of time, interest in these two agents grew globally. Early in vitro data have revealed that chloroquine can inhibit the viral replication ( 70 , 71 ).
HCQ and CQ work by raising the pH of the lysosome, the cellular organelle that is responsible for phagocytic degradation. Its function is to combine with cell contents that have been phagocytosed and break them down eventually, in some immune cells, as a downstream process to display some of the broken proteins as antigens, thus further enhancing the immune recruitment against an antigen/pathogen. The drug was to be administered alone or with azithromycin. The use of azithromycin may be advocated by the fact that it has been seen previously to have some immunomodulatory role in airway-related disease. It appears to reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in respiratory illnesses ( 72 ). However, HCQ and azithromycin are known to have a major drug interaction when co-administered, which increases the risk of QT interval prolongation ( 73 ). Quinine-based drugs are known to have adverse effects such as QT prolongation, retinal damage, hypoglycemia, and hemolysis of blood in patients with G-6-PD deficiency ( 66 ). Several preprints, including, a metanalysis now indicate that HCQ may have no benefit for severe or critically ill patients who have COVID-19 where the outcome is need for ventilation or death ( 74 , 75 ). As of April 21, 2020, after having pre-emptively recommended their use for SARS-CoV-2 infection, the US now advocates against the use of these two drugs based on the new data that has become available.
Use of Antiviral Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2
The antiviral agents are mainly those used in the case of HIV/AIDS, these being Lopinavir and Ritonavir. Other agents such as nucleoside analogs like Favipiravir, Ribavirin, Remdesivir, and Galidesivir have been tested for possible activity in the prevention of viral RNA synthesis ( 76 ). Among these drugs, Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and Remdesivir are listed in the Solidarity trial by the WHO.
Remdesivir is a nucleotide analog for adenosine that gets incorporated into the viral RNA, hindering its replication and causing chain termination. This agent was originally developed for Ebola Virus Disease ( 77 ). A study was conducted with rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2 ( 78 ). In that study, after 12 h of infection, the monkeys were treated with either Remdesivir or vehicle. The drug showed good distribution in the lungs, and the animals treated with the drug showed a better clinical score than the vehicle group. The radiological findings of the study also indicated that the animals treated with Remdesivir have less lung damage. There was a reduction in viral replication but not in virus shedding. Furthermore, there were no mutations found in the RNA polymerase sequences. A randomized clinical control study that became available in late April 2020 ( 79 ), having 158 on the Remdesivir arm and 79 on the placebo arm, found that Remdesivir reduced the time to recovery in the Remdesivir-treated arm to 11 days, while the placebo-arm recovery time was 15 days. Though this was not found to be statistically significant, the agent provided a basis for further studies. The 28-days mortality was found to be similar for both groups. This has now provided us with a basis on which to develop future molecules. The study has been supported by the National Institute of Health, USA. The authors of the study advocated for more clinical trials with Remdesivir with a larger population. Such larger studies are already in progress, and their results are awaited. Remdesivir is currently one of the drugs that hold most promise against COVID-19.
An early trial in China with Lopinavir and Ritonavir showed no benefit compared with standard clinical care ( 80 ). More studies with this drug are currently underway, including one in India ( 81 , 82 ).
Use of Convalescent Patient Plasma
Another possible option would be the use of serum from convalescent individuals, as this is known to contain antibodies that can neutralize the virus and aid in its elimination. This has been tried previously for other coronavirus infections ( 83 ). Early emerging case reports in this aspect look promising compared to other therapies that have been tried ( 84 – 87 ). A report from China indicates that five patients treated with plasma recovered and were eventually weaned off ventilators ( 84 ). They exhibited reductions in fever and viral load and improved oxygenation. The virus was not detected in the patients after 12 days of plasma transfusion. The US FDA has provided detailed recommendations for investigational COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma use ( 88 ). One of the benefits of this approach is that it can also be used for post-exposure prophylaxis. This approach is now beginning to be increasingly adopted in other countries, with over 95 trials registered on clinicaltrials.gov alone, of which at least 75 are interventional ( 89 ). The use of convalescent patient plasma, though mostly for research purposes, appears to be the best and, so far, the only successful option for treatment available.
From a future perspective, the use of monoclonal antibodies for the inhibition of the attachment of the virus to the ACE-2 receptor may be the best bet. Aside from this, ACE-2-like molecules could also be utilized to attach and inactivate the viral proteins, since inhibition of the ACE-2 receptor would not be advisable due to its negative repercussions physiologically. In the absence of drug regimens and a vaccine, the treatment is symptomatic and involves the use of non-invasive ventilation or intubation where necessary for respiratory failure patients. Patients that may go into septic shock should be managed as per existing guidelines with hemodynamic support as well as antibiotics where necessary.
The WHO has recommended that simple personal hygiene practices can be sufficient for the prevention of spread and containment of the disease ( 90 ). Practices such as frequent washing of soiled hands or the use of sanitizer for unsoiled hands help reduce transmission. Covering of mouth while sneezing and coughing, and disinfection of surfaces that are frequently touched, such as tabletops, doorknobs, and switches with 70% isopropyl alcohol or other disinfectants are broadly recommended. It is recommended that all individuals afflicted by the disease, as well as those caring for the infected, wear a mask to avoid transmission. Healthcare works are advised to wear a complete set of personal protective equipment as per WHO-provided guidelines. Fumigation of dormitories, quarantine rooms, and washing of clothes and other fomites with detergent and warm water can help get rid of the virus. Parcels and goods are not known to transmit the virus, as per information provided by the WHO, since the virus is not able to survive sufficiently in an open, exposed environment. Quarantine of infected individuals and those who have come into contact with an infected individual is necessary to further prevent transmission of the virus ( 91 ). Quarantine is an age-old archaic practice that continues to hold relevance even today for disease containment. With the quarantine being implemented on such a large scale in some countries, taking the form of a national lockdown, the question arises of its impact on the mental health of all individuals. This topic needs to be addressed, especially in countries such as India and China, where it is still a matter of partial taboo to talk about it openly within the society.
In India, the Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga, and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy (AYUSH), which deals with the alternative forms of medicine, issued a press release that the homeopathic, drug Arsenicum album 30, can be taken on an empty stomach for 3 days to provide protection against the infection ( 92 ). It also provided a list of herbal drugs in the same press release as per Ayurvedic and Unani systems of medicine that can boost the immune system to deal with the virus. However, there is currently no evidence to support the use of these systems of medicine against COVID-19, and they need to be tested.
The prevention of the disease with the use of a vaccine would provide a more viable solution. There are no vaccines available for any of the coronaviruses, which includes SARS and MERS. The development of a vaccine, however, is in progress at a rapid pace, though it could take about a year or two. As of April 2020, no vaccine has completed the development and testing process. A popular approach has been with the use of mRNA-based vaccine ( 93 – 96 ). mRNA vaccines have the advantage over conventional vaccines in terms of production, since they can be manufactured easily and do not have to be cultured, as a virus would need to be. Alternative conventional approaches to making a vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 would include the use of live attenuated virus as well as using the isolated spike proteins of the virus. Both of these approaches are in progress for vaccine development ( 97 ). Governments across the world have poured in resources and made changes in their legislation to ensure rapid development, testing, and deployment of a vaccine.
Barriers to Treatment
Lack of transparency and poor media relations.
The lack of government transparency and poor reporting by the media have hampered the measures that could have been taken by healthcare systems globally to deal with the COVID-19 threat. The CDC, as well as the US administration, downplayed the threat and thus failed to stock up on essential supplies, ventilators, and test kits. An early warning system, if implemented, would have caused borders to be shut and early lockdowns. The WHO also delayed its response in sounding the alarm regarding the severity of the outbreak to allow nations globally to prepare for a pandemic. Singapore is a prime example where, despite the WHO not raising concerns and banning travel to and from China, a country banned travelers and took early measures, thus managing the outbreak quite well. South Korea is another example of how things may have played out had those measures by agencies been taken with transparency. Increased transparency would have allowed the healthcare sector to better prepare and reduced the load of patients they had to deal with, helping flatten the curve. The increased patient load and confusion among citizens arising from not following these practices has proved to be a barrier to providing effective treatments to patients with the disease elsewhere in the world.
Lack of Preparedness and Protocols
Despite the previous SARS outbreak teaching us important lessons and providing us with data on a potential outbreak, many nations did not take the important measures needed for a future outbreak. There was no allocation of sufficient funds for such an event. Many countries experienced severe lack of PPE, and the lockdown precautions hampered the logistics of supply and manufacturing of such essential equipment. Singapore and South Korea had protocols in place and were able to implement them at a moment's notice. The spurt of cases that Korea experienced was managed well, providing evidence to this effect. The lack of preparedness and lack of protocol in other nations has resulted in confusion as to how the treatment may be administered safely to the large volume of patients while dealing with diagnostics. Both of these factors have limited the accessibility to healthcare services due to sheer volume.
Socio-Economic Impact
During the SARS epidemic, China faced an economic setback, and experts were unsure if any recovery would be made. However, the global and domestic situation was then in China's favor, as it had a lower debt, allowing it to make a speedy recovery. This is not the case now. Global experts have a pessimistic outlook on the outcome of this outbreak ( 98 ). The fear of COVID-19 disease, lack of proper understanding of the dangers of the virus, and the misinformation spread on the social media ( 99 ) have caused a breakdown of the economic flow globally ( 100 ). An example of this is Indonesia, where a great amount of fear was expressed in responses to a survey when the nation was still free of COVID-19 ( 101 ). The pandemic has resulted in over 2.6 billion people being put under lockdown. This lockdown and the cancellation of the lunar year celebration has affected business at the local level. Hundreds of flights have been canceled, and tourism globally has been affected. Japan and Indonesia are estimated to lose over 2.44 billion dollars due to this ( 102 , 103 ). Workers are not able to work in factories, transportation in all forms is restricted, and goods are not produced or moved. The transport of finished products and raw materials out of China is low. The Economist has published US stock market details indicating that companies in the US that have Chinese roots fell, on average, 5 points on the stock market as compared to the S&P 500 index ( 104 ). Companies such as Starbucks have had to close over 4,000 outlets due to the outbreak as a precaution. Tech and pharma companies are at higher risk since they rely on China for the supply of raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients. Paracetamol, for one, has reported a price increase of over 40% in India ( 104 – 106 ). Mass hysteria in the market has caused selling of shares of these companies, causing a tumble in the Indian stock market. Though long-term investors will not be significantly affected, short-term traders will find themselves in soup. Politically, however, this has further bolstered support for world leaders in countries such as India, Germany, and the UK, who are achieving good approval ratings, with citizens being satisfied with the government's approach. In contrast, the ratings of US President Donald Trump have dropped due to the manner in which the COVID-19 pandemic was handled. These minor impacts may be of temporary significance, and the worst and direct impact will be on China itself ( 107 – 109 ), as the looming trade war with the USA had a negative impact on the Chinese and Asian markets. The longer production of goods continues to remain suspended, the more adversely it will affect the Chinese economy and the global markets dependent on it ( 110 ). If this disease is not contained, more and more lockdowns by multiple nations will severely affect the economy and lead to many social complications.
The appearance of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus has added and will continue to add to our understanding of viruses. The pandemic has once again tested the world's preparedness for dealing with such outbreaks. It has provided an outlook on how a massive-scale biological event can cause a socio-economic disturbance through misinformation and social media. In the coming months and years, we can expect to gain further insights into SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19.
Author Contributions
KN: conceptualization. RK, AA, JM, and KN: investigation. RK and AA: writing—original draft preparation. KN, PN, and JM: writing—review and editing. KN: supervision.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions made by Dr. Piya Paul Mudgal, Assistant Professor, Manipal Institute of Virology, Manipal Academy of Higher Education towards inputs provided by her during the drafting of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00216/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Data 1, 2. List of all studies registered for COVID-19 on clinicaltrials.gov .
1. McIntosh K, Dees JH, Becker WB, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1967) 57:933–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.933
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Esper F, Weibel C, Ferguson D, Landry ML, Kahn JS. Evidence of a novel human coronavirus that is associated with respiratory tract disease in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. (2005) 191:492–8. doi: 10.1086/428138
3. Stöhr K. A multicentre collaboration to investigate the cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. (2003) 361:1730–3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13376-4
4. Peiris JSM, Lai ST, Poon LLM, Guan Y, Yam LYC, Lim W, et al. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. (2003) 361:1319–25. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13077-2
5. Zumla A, Hui DS, Perlman S. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet. (2015) 386:995–1007. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60454-8
6. Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus ADME, Fouchier RAM. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:1814–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211721
7. Perlman S, Netland J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2009) 7:439–50. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2147
8. Li W, Moore MJ, Vasllieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. (2003) 426:450–4. doi: 10.1038/nature02145
9. Ge X-Y, Li J-L, Yang X-L, Chmura AA, Zhu G, Epstein JH, et al. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature. (2013) 503:535–8. doi: 10.1038/nature12711
10. Wang M, Hu Z. Bats as animal reservoirs for the SARS coronavirus: Hypothesis proved after 10 years of virus hunting. Virol Sin. (2013) 28:315–7. doi: 10.1007/s12250-013-3402-x
11. Diamond Princess Cruise Ship in Japan Confirms 99 New Coronavirus Cases | World news | The Guardian. Available online at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/feb/17/coronavirus-japan-braces-for-hundreds-more-cases-as-another-china-city-locked-down (accessed February 17, 2020).
Google Scholar
12. Diamond Princess Coronavirus & Quarantine Updates - Notices & Advisories - Princess Cruises. Available online at: https://www.princess.com/news/notices_and_advisories/notices/diamond-princess-update.html (accessed February 17, 2020).
13. Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, Groot RJ, de Drosten C, Gulyaeva AA, et al. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. (2020) 5:536–44. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
14. Ji W, Wang W, Zhao X, Zai J, Li X. Homologous recombination within the spike glycoprotein of the newly identified coronavirus may boost cross-species transmission from snake to human. J Med Virol . (2020) 7:jmv.25682. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25682
15. Cyranoski D. Did pangolins spread the China coronavirus to people? Nature . (2020) doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00364-2
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. (2020) 395:565–74. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
17. Wassenaar TM, Zou Y. 2019_nCoV: Rapid classification of betacoronaviruses and identification of traditional Chinese medicine as potential origin of zoonotic coronaviruses. Lett Appl Microbiol. (2020) 70:324–48. doi: 10.1111/lam.13285
18. Velavan TP, Meyer CG. The Covid-19 epidemic. Trop Med Int Heal . (2020) 25:278–80. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13383
19. Guarner J. Three Emerging Coronaviruses in Two Decades. Am J Clin Pathol . (2020) 153:420–21. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa029
20. Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, Ren W, Smith C, Epstein JH, et al. Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science. (2005) 310:676–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1118391
21. Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. (2020) 579:270–3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
22. Menachery VD, Yount BL, Debbink K, Agnihothram S, Gralinski LE, Plante JA, et al. A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence. Nat Med. (2015) 21:1508–13. doi: 10.1038/nm.3985
23. COVID-19 Coronavirus Epidemic has a Natural Origin—ScienceDaily. Available online at: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/03/200317175442.htm (accessed April 22, 2020).
24. Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med . (2020) 26:450–2. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9
25. Prioritizing Diseases for Research and Development in Emergency Contexts. Available online at: https://www.who.int/activities/prioritizing-diseases-for-research-and-development-in-emergency-contexts (accessed April 22, 2020).
26. Albariño CG, Guerrero LW, Jenks HM, Chakrabarti AK, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, et al. Insights into Reston virus spillovers and adaption from virus whole genome sequences. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0178224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178224
27. Yao H, Lu X, Chen Q, Xu K, Chen Y, Cheng L, et al. Patient-derived mutations impact pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv. (2020). doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3578153
28. Stefanelli P, Faggioni G, Lo Presti A, Fiore S, Marchi A, Benedetti E, et al. Whole genome and phylogenetic analysis of two SARS-CoV-2 strains isolated in Italy in January and February 2020: additional clues on multiple introductions and further circulation in Europe. Eurosurveillance. (2020) 25:2000305. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.13.2000305
29. Yadav P, Potdar V, Choudhary M, Nyayanit D, Agrawal M, Jadhav S, et al. Full-genome sequences of the first two SARS-CoV-2 viruses from India. Indian J Med Res. (2020) 151:200–9. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_663_20
30. WHO | Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 26. Beijing (2020). Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/list_gzbd.shtml (accessed February 16, 2020).
31. WHO | Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). World Health Organization (2020).
32. WHO | Summary of Probable SARS Cases With Onset of Illness From 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. World Health Organization (2015).
33. Worldometer. Coronavirus cases. Worldometer. (2020) 1−22.
34. Update on the Outbreak of New Coronavirus Pneumonia as of 24 hours on 15 February. Beijing (2020). Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/list_gzbd.shtml (accessed February 16, 2020).
35. Sanche S, Lin YT, Xu C, Romero-Severson E, Hengartner N, Ke R. High contagiousness and rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. (2020) 26. doi: 10.3201/eid2607.200282
36. 83% of India's Coronavirus Patients Are Below the Age of 50: Health ministry data - India News. Available online at: https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/83-of-india-s-coronavirus-patients-are-below-the-age-of-50-health-ministry-data-1663314-2020-04-04 (accessed April 23, 2020).
37. 42% of Coronavirus Patients in 21-40 age bracket: Govt. Available online at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/42-of-coronavirus-patients-in-21-40-age-bracket-govt/articleshow/74987254.cms (accessed April 23, 2020).
38. Why COVID-19 Case Counts Are so Low in Singapore Hong Kong and Taiwan | Advisory Board Daily Briefing. Available online at: https://www.advisory.com/daily-briefing/2020/03/19/asian-countries (accessed April 29, 2020).
39. Coronavirus: Why so Few Deaths Among Singapore's 14000 Covid-19 Infections? | South China Morning Post. Available online at: https://www.scmp.com/weekasia/health-environment/article/3081772/coronavirus-why-so-few-deaths-among-singapores-14000 (accessed April 29, 2020).
40. Stafford N. Covid-19: Why Germany's case fatality rate seems so low. BMJ. (2020) 7:369. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1395
41. Rothe C, Schunk M, Sothmann P, Bretzel G, Froeschl G, Wallrauch C, et al. Transmission of 2019-NCOV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. N Engl J Med . (2020) 382:970–1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2001468
42. Coronavirus pandemic | 80% of COVID-19 Cases Either Asymptomatic or Show Mild Symptoms. Health ministry - Moneycontrol.com. Available online at: https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/india/coronavirus-pandemic-80-of-covid-19-cases-either-asymptomatic-or-show-mild-symptoms-health-ministry-5170631.html (accessed April 24, 2020).
43. WHO | Q&A on Coronaviruses. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses (accessed February 16, 2020).
44. Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, et al. First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States. N Engl J Med . (2020) 382:929–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001191
45. Yeo C, Kaushal S, Yeo D. Enteric involvement of coronaviruses: is faecal–oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2 possible? Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:335–37. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30048-0
46. Chen H, Guo J, Wang C, Luo F, Yu X, Zhang W, et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records. Lancet. (2020) 395:809–15. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30360-3
47. Fehr AR, Perlman S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In: Coronaviruses: Methods and Protocols (New York: Springer), 1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1
48. Chen Y, Liu Q, Guo D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J Med Virol. (2020) 92:418–23. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25681
49. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Mü MA, Drosten C, Pö S. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. (2020) 181:271–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
50. Cheng VCC, Chan JFW, To KKW, Yuen KY. Clinical management and infection control of SARS: Lessons learned. Antiviral Res. (2013) 100:407–19. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.08.016
51. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. (2020) 395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
52. Udugama B, Kadhiresan P, Kozlowski HN, Malekjahani A, Osborne M, Li VYC, et al. Diagnosing COVID-19: the disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano . (2020) 14:3822–35. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02624
53. Testing, | CDC,. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/testing/index.html (accessed April 29, 2020).
54. Advice on the Use of Point-of-Care Immunodiagnostic Tests for COVID-19. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/advice-on-the-use-of-point-of-care-immunodiagnostic-tests-for-covid-19 (accessed April 29, 2020).
55. Zhang Yanping. The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) — China, 2020. (2020) Available online at: http://weekly.chinacdc.cn/en/article/id/e53946e2-c6c4-41e9-9a9bfea8db1a8f51 (accessed February 18, 2020).
56. Petersen R, Pan L, Blanck HM. Racial and ethnic disparities in adult obesity in the United States: CDC's tracking to inform state and local action. Prev Chronic Dis. (2019) 16:180579. doi: 10.5888/pcd16.180579
57. Wang L, Southerland J, Wang K, Bailey BA, Alamian A, Stevens MA, et al. Ethnic differences in risk factors for obesity among adults in California, the United States. (2017) 2017:2427483. doi: 10.1155/2017/2427483
58. Covid-19 Causes Sudden Strokes in Young Adults Doctors Say - CNN. Available online at: https://edition.cnn.com/2020/04/22/health/strokes-coronavirus-young-adults/index.html (accessed April 24, 2020).
59. Wang J, Hajizadeh N, Moore EE, McIntyre RC, Moore PK, Veress LA, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) treatment for COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): a case series. J Thromb Haemost . (2020) 1–4. doi: 10.1111/jth.14828
60. Lancet T, Medicine R. Comment Understanding pathways to death in patients with. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 2019:2019–21. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30165-X
61. Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA . (2020) 323:1775–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683
62. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. (2020) 395:1054–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
63. Doctors Warn COVID-19 Might Cause Strokes in Young Adults. Available online at: https://nypost.com/2020/04/23/doctors-warn-covid-19-might-cause-strokes-in-young-adults/ (accessed April 24, 2020).
64. “Solidarity” Clinical Trial for COVID-19 Treatments. Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/global-research-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/solidarity-clinical-trial-for-covid-19-treatments (accessed April 23, 2020).
65. Search, of: COVID-19 - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov . Available online at: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=COVID-19&term=&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed May 1, 2020).
66. De Wilde AH, Jochmans D, Posthuma CC, Zevenhoven-Dobbe JC, Van Nieuwkoop S, Bestebroer TM, et al. Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2014) 58:4875–84. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03011-14
67. Tai DYH. Pharmacologic treatment of SARS: current knowledge and recommendations. Ann Acad Med Singapore. (2007) 36:438–43.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
68. Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Leist SR, Schäfer A, Won J, Brown AJ, et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:222. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6
69. Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends. (2020) 14:72–73. doi: 10.5582/bst.2020.01047
70. Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. (2020) 30:269–71. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
71. Vincent MJ, Bergeron E, Benjannet S, Erickson BR, Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, et al. Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread. Virol J. (2005) 2:1–0. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-69
72. Cramer CL, Patterson A, Alchakaki A, Soubani AO. Immunomodulatory indications of azithromycin in respiratory disease: a concise review for the clinician. Postgrad Med. (2017) 129:493–9. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2017.1285677
73. Plaquenil™ Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets USP Description. Available online at: http://www.cdc.gov/malaria (accessed April 21, 2020).
74. Magagnoli J, Narendran S, Pereira F, Cummings T, Hardin JW, Sutton SS, et al. Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19. medRxiv. (2020) doi: 10.1101/2020.04.16.20065920
75. Shamshirian A, Hessami A, Heydari K, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Ghasemian R, et al. Hydroxychloroquine Versus COVID-19: A Rapid Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. medRxiv. (2020) doi: 10.1101/2020.04.14.20065276
76. Li G, De Clercq E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov . (2020) 19:149–50. doi: 10.1038/d41573-020-00016-0
77. Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, Ray AS, Mackman RL, Soloveva V, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature. (2016) 531:381–5. doi: 10.1038/nature17180
78. Williamson BN, Feldmann F, Schwarz B, Meade-White K, Porter DP, Schulz J, et al. Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv. (2020) doi: 10.1101/2020.04.15.043166
79. Wang Y, Zhang D, Du G, Du R, Zhao J, Jin Y, et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet. (2020) 395:1569–78. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
80. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe covid-19. N Engl J Med . (2020) 382:1787–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
81. Search, of: Lopinavir, Ritonavir, | COVID - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov . Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=Lopinavir%2CRitonavir&cond=COVID&draw=4&rank=22#rowId21 (accessed April 23, 2020).
82. Bhatnagar T, Murhekar M, Soneja M, Gupta N, Giri S, Wig N, et al. Lopinavir/ritonavir combination therapy amongst symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 patients in India: protocol for restricted public health emergency use. Indian J Med Res. (2020) 151:184–9. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_502_20
83. Yeh K-M, Chiueh T-S, Siu LK, Lin J-C, Chan PKS, Peng M-Y, et al. Experience of using convalescent plasma for severe acute respiratory syndrome among healthcare workers in a Taiwan hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2005) 56:919–22. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki346
84. Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, et al. Treatment of 5 critically Ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA . (2020) 323:1582–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783
85. Cao W, Liu X, Bai T, Fan H, Hong K, Song H, et al. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin as a therapeutic option for deteriorating patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Open Forum Infect Dis . (2020) 7:1–6. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102
86. Bloch EM, Shoham S, Casadevall A, Sachais BS, Shaz B, Winters JL, et al. Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. J Clin Invest . (2020) 138745:1–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI138745
87. Ye M, Fu D, Ren Y, Wang F, Wang D, Zhang F, et al. Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol. (2 020) doi: 10.1002/jmv.25882
88. Recommendations for Investigational COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma | FDA. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/investigational-new-drug-ind-or-device-exemption-ide-process-cber/recommendations-investigational-covid-19-convalescent-plasma (accessed April 23, 2020).
89. Search, of: plasma | Interventional Studies | COVID - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov . Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=plasma&cond=COVID&Search=Apply&age_v=&gndr=&type=Intr&rslt= (accessed April 23, 2020).
90. Infection Prevention and Control. Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/infection-prevention-and-control (accessed February 17, 2020).
91. Wilder-Smith A, Freedman DO. Isolation, quarantine, social distancing and community containment: pivotal role for old-style public health measures in the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak. J Travel Med . (2020) 27:taaa020. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa020
92. Press Information Bureau AYUSH Advisory for Corona virus. Press Inf Bereau. Available online at: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1600895 (accessed February 17, 2020).
93. CanSino, Biologics : China Announces First Human Trials of Covid-19 Vaccine | MarketScreener,. Available online at: https://www.marketscreener.com/CANSINO-BIOLOGICS-INC-59318312/news/CanSino-Biologics-China-announces-first-human-trials-of-Covid-19-vaccine-30183232/ (accessed April 7, 2020).
94. Safety, and Immunogenicity Study of 2019-nCoV Vaccine (mRNA-1273) for Prophylaxis SARS CoV-2 Infection - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov . Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04283461 (accessed April 7, 2020).
95. NIH, Clinical Trial of Investigational Vaccine for COVID-19 Begins | National Institutes of Health (NIH),. Available at: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-clinical-trial-investigational-vaccine-covid-19-begins (accessed April 7, 2020).
96. Novel, Coronavirus vaccine manufacturing contract signed — The Jenner Institute,. Available online at: https://www.jenner.ac.uk/about/news/novel-coronavirus-vaccine-manufacturing-contract-signed (accessed April 7, 2020).
97. Xie L, Sun C, Luo C, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Yang J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV Spike-RBD structure and receptor binding comparison and potential implications on neutralizing antibody and vaccine development. bioRxiv [Preprint]. (2020). doi: 10.1101/2020.02.16.951723
98. The Global Economic Impact of the Coronavirus Outbreak – Harvard Gazette. Available online at: https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2020/02/the-global-economic-impact-of-the-coronavirus-outbreak/ (accessed February 17, 2020).
99. Shimizu K. 2019-nCoV, fake news, and racism. Lancet . (2020) 395:685–6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30357-3
100. ROHDE RODNEY. 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Update: Uncoating the Virus. Am Soc Microbiol. (2020). Available online at: https://asm.org/Articles/2020/January/2019-Novel-Coronavirus-2019-nCoV-Update-Uncoating
101. Virus-free Indonesia more threatened by COVID-19 than Singapore Malaysia: Survey - World - The Jakarta Post. Available online at: https://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2020/02/18/virus-free-indonesia-more-threatened-by-covid-19-than-singapore-malaysia-survey.html (accessed February 18, 2020).
102. Japan, May Lose $1,.29 Billion in Tourism Revenue Due to COVID-19 Outbreak | The Japan Times. Available online at: https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2020/02/16/business/economy-business/japan-lose-billion-tourism-revenue-covid19-outbreak/#.XkvxX0fitPY (accessed February 18, 2020).
103. Coronavirus's Effect on Tourism Will Carry Into 2021 Experts Say - Bloomberg. Available online at: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-02-13/coronavirus-s-effect-on-tourism-will-carry-into-2021-experts-say (accessed February 18, 2020).
104. The, week in charts - The cost of covid-19 | Graphic detail | The Economist,. Available online at: https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2020/02/14/the-cost-of-covid-19 (accessed February 17, 2020).
105. coronavirus: Covid-19 Impact: Pharma Companies Feel the Pain as Prices of Key Inputs Shoot Up - The Economic Times. Available online at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/healthcare/biotech/pharmaceuticals/covid-19-impact-pharma-companies-feel-the-pain-as-prices-of-key-inputs-shoot-up/articleshow/74144044.cms?from=mdr (accessed February 17, 2020).
106. Coronavirus Outbreak: Paracetamol Prices Jump 40% In India As Coronavirus Shuts Down China. Available online at: https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/coronavirus-outbreak-paracetamol-prices-jump-40-in-india-as-coronavirus-shuts-down-china-2181480 (accessed February 18, 2020).
107. The coronavirus could cripple China's economy for longer than Wall Street wants to believe | Business Insider India. Available online at: https://www.businessinsider.in/international/news/the-coronavirus-could-cripple-chinas-economy-for-longer-than-wall-street-wants-to-believe/articleshow/74162183.cms (accessed February 17, 2020).
108. Viral Slowdown - How China's Coronavirus Epidemic Could Hurt the World Economy | Leaders | The Economist. Available online at: https://www.economist.com/leaders/2020/02/13/how-chinas-coronavirus-epidemic-could-hurt-the-world-economy (accessed February 17, 2020).
109. China's Economic Battle With COVID-19 | The ASEAN Post. Available online at: https://theaseanpost.com/article/chinas-economic-battle-covid-19 (accessed February 17, 2020).
110. The Coronavirus Could Cost China's Economy $60 Billion this Quarter. - CNN. Available online at: https://edition.cnn.com/2020/01/31/economy/china-economy-coronavirus/index.html (accessed February 18, 2020).
Keywords: 2019-nCoV, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, coronavirus, pandemic, SARS
Citation: Keni R, Alexander A, Nayak PG, Mudgal J and Nandakumar K (2020) COVID-19: Emergence, Spread, Possible Treatments, and Global Burden. Front. Public Health 8:216. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00216
Received: 21 February 2020; Accepted: 11 May 2020; Published: 28 May 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Keni, Alexander, Nayak, Mudgal and Nandakumar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Krishnadas Nandakumar, mailnandakumar77@gmail.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Essay on Coronavirus Prevention
500+ words essay on coronavirus prevention.
The best way of coronavirus prevention is not getting it in the first place. After extensive research, there are now COVID-19 vaccines available to the public. Everyone must consider getting it to lead healthy lives. Further, we will look at some ways in this essay in how one can lower their chances of getting the virus or stopping it from spreading.

The Spread of Coronavirus
The COVID-19 virus spreads mainly via droplets that are sent out by people while talking, sneezing, or coughing. However, they do not generally stay in the air for long. Similarly, they cannot go farther than 6 feet.
However, this virus can also travel via tiny aerosol particles that have the capacity to linger for around three hours. Likewise, they may also travel farther away. Therefore, it is essential to wear a face covering.
The face mask can prevent you from getting the virus as it helps you to avoid breathing it in. Further, one can also catch this virus if they touch something that an infected person has touched and then they touch their eyes, mouth, or nose.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How to Prevent Coronavirus
The first and foremost thing for coronavirus prevention is that everyone must do is get the vaccine as soon as it is their turn. It helps you avoid the virus or prevent you from falling seriously ill. Apart from this, we must not forget to take other steps as well to reduce the risk of getting the virus.
It includes avoiding close contact with people who are sick or are showing symptoms. Make sure you are at least 6 feet away from them. Similarly, you also remain at the same distance as others if you have contracted the virus.
What’s important to know is that you may have COVID-19 and spread it to others even if you are not showing any symptoms or aren’t aware that you have COVID-19. Moreover, we must avoid crowds and indoor places that are not well-ventilated.
Most importantly, keep washing your hands frequently with soap and water. If these are not present, carry an alcohol-based sanitiser with you. It must have a minimum amount of 60% alcohol.
In addition, wearing a face mask is of utmost importance in public spaces. Such places come with a higher risk of transmission of the virus. Thus, use surgical masks if they are available.
It is important to cover your mouth and nose when you are coughing or sneezing. If you don’t have a tissue, cover it with your elbow. Do not touch your eyes, nose and mouth. Likewise, do not share dishes, towels, glasses and other household items with a sick person.
Do not forget to clean and disinfect surfaces that people touch frequently like electronics, switchboards, counters, doorknobs, and more. Also, stay at home if you feel sick and do not take public transport as well.
To sum it up, coronavirus prevention can be done easily. We must work together to create a safe environment for everyone to live healthily. Make sure to do your bit so that everyone can stay safe and fit and things may return to normal like before.
FAQ of Essay on Coronavirus Prevention
Question 1: How long does it take for coronavirus symptoms to appear?
Answer 1: It may take around five to six days on average when someone gets infected with the virus. But, some people also take around 14 days.
Question 2: What are some coronavirus prevention tips?
Answer 2: One must get the vaccine as soon as possible. Further, always wear a mask properly and sanitize or wash your hands. Clean or disinfect areas that people touch frequently like door handles, electronics, and more. Always cover your mouth when sneezing or coughing and maintain physical distancing.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- Home Planet
- 2024 election
- Supreme Court
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/66606035/1207638131.jpg.0.jpg)
The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
Will you support Vox today?
We believe that everyone deserves to understand the world that they live in. That kind of knowledge helps create better citizens, neighbors, friends, parents, and stewards of this planet. Producing deeply researched, explanatory journalism takes resources. You can support this mission by making a financial gift to Vox today. Will you join us?
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Next Up In Culture
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

The known unknowns about Ozempic, explained

Is it ever okay to film strangers in public?

“I lost trust”: Why the OpenAI team in charge of safeguarding humanity imploded

ChatGPT can talk, but OpenAI employees sure can’t

Why are Americans spending so much?

Blood, flames, and horror movies: The evocative imagery of King Charles’s portrait
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Editor in Chief's Introduction to Essays on the Impact of COVID-19 on Work and Workers
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared that COVID-19 was a global pandemic, indicating significant global spread of an infectious disease ( World Health Organization, 2020 ). At that point, there were 118,000 confirmed cases of the coronavirus in 110 countries. China had been the first country with a widespread outbreak in January, and South Korea, Iran and Italy following in February with their own outbreaks. Soon, the virus was in all continents and over 177 countries, and as of this writing, the United States has the highest number of confirmed cases and, sadly, the most deaths. The virus was extremely contagious and led to death in the most vulnerable, particularly those older than 60 and those with underlying conditions. The most critical cases led to an overwhelming number being admitted into the intensive care units of hospitals, leading to a concern that the virus would overwhelm local health care systems. Today, in early May 2020, there have been nearly 250,000 deaths worldwide, with over 3,500,000 confirmed cases ( Hopkins, 2020 ). The human toll is staggering, and experts are predicting a second wave in summer or fall.
As the deaths rose from the virus that had no known treatment or vaccine countries shut their borders, banned travel to other countries and began to issue orders for their citizens to stay at home, with no gatherings of more than 10 individuals. Schools and universities closed their physical locations and moved education online. Sporting events were canceled, airlines cut flights, tourism evaporated, restaurants, movie theaters and bars closed, theater productions canceled, manufacturing facilities, services, and retail stores closed. In some businesses and industries, employees have been able to work remotely from home, but in others, workers have been laid off, furloughed, or had their hours cut. The International Labor Organization (ILO) estimates that there was a 4.5% reduction in hours in the first quarter of 2020, and 10.5% reduction is expected in the second quarter ( ILO, 2020a ). The latter is equivalent to 305 million jobs ( ILO, 2020a ).
Globally, over 430 million enterprises are at risk of disruption, with about half of those in the wholesale and retail trades ( ILO, 2020a ). Much focus in the press has been on the impact in Europe and North America, but the effect on developing countries is even more critical. An example of the latter is the Bangladeshi ready-made-garment sector ( Leitheiser et al., 2020 ), a global industry that depends on a supply chain of raw material from a few countries and produces those garments for retail stores throughout North America and Europe. But, in January 2020, raw material from China was delayed by the shutdown in China, creating delays and work stoppages in Bangladesh. By the time Bangladeshi factories had the material to make garments, in March, retailers in Europe and North American began to cancel orders or put them on hold, canceling or delaying payment. Factories shut down and workers were laid off without pay. Nearly a million people lost their jobs. Overall, since February 2020, the factories in Bangladesh have lost nearly 3 billion dollars in revenue. And, the retail stores that would have sold the garments have also closed. This demonstrates the ripple effect of the disruption of one industry that affects multiple countries and sets of workers, because consider that, in turn, there will be less raw material needed from China, and fewer workers needed there. One need only multiply this example by hundreds to consider the global impact of COVID-19 across the world of work.
The ILO (2020b) notes that it is difficult to collect employment statistics from different countries, so a total global unemployment rate is unavailable at this time. However, they predict significant increase in unemployment, and the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits in the United States may be an indicator of the magnitude of those unemployed. In the United States, over 30 million filed for unemployment between March 11 and April 30 ( Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 ), effectively this is an unemployment rate of 18%. By contrast, in February 2020, the US unemployment rate was 3.5% ( Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 ).
Clearly, COVID-19 has had an enormous disruption on work and workers, most critically for those who have lost their employment. But, even for those continuing to work, there have been disruptions in where people work, with whom they work, what they do, and how much they earn. And, as of this writing, it is also a time of great uncertainty, as countries are slowly trying to ease restrictions to allow people to go back to work--- in a “new normal”, without the ability to predict if they can prevent further infectious “spikes”. The anxieties about not knowing what is coming, when it will end, or what work will entail led us to develop this set of essays about future research on COVID-19 and its impact on work and workers.
These essays began with an idea by Associate Editor Jos Akkermans, who noted to me that the global pandemic was creating a set of career shocks for workers. He suggested writing an essay for the Journal . The Journal of Vocational Behavior has not traditionally published essays, but these are such unusual times, and COVID-19 is so relevant to our collective research on work that I thought it was a good idea. I issued an invitation to the Associate Editors to submit a brief (3000 word) essay on the implications of COVID-19 on work and/or workers with an emphasis on research in the area. At the same time, a group of international scholars was coming together to consider the effects of COVID-19 on unemployment in several countries, and I invited that group to contribute an essay, as well ( Blustein et al., 2020 ).
The following are a set of nine thoughtful set of papers on how the COVID-19 could (and perhaps will) affect vocational behavior; they all provide suggestions for future research. Akkermans, Richardson, and Kraimer (2020) explore how the pandemic may be a career shock for many, but also how that may not necessarily be a negative experience. Blustein et al. (2020) focus on global unemployment, also acknowledging the privileged status they have as professors studying these phenomena. Cho examines the effect of the pandemic on micro-boundaries (across domains) as well as across national (macro) boundaries ( Cho, 2020 ). Guan, Deng, and Zhou (2020) drawing from cultural psychology, discuss how cultural orientations shape an individual's response to COVID-19, but also how a national cultural perspective influences collective actions. Kantamneni (2020) emphasized the effects on marginalized populations in the United States, as well as the very real effects of racism for Asians and Asian-Americans in the US. Kramer and Kramer (2020) discuss the impact of the pandemic in the perceptions of various occupations, whether perceptions of “good” and “bad” jobs will change and whether working remotely will permanently change where people will want to work. Restubog, Ocampo, and Wang (2020) also focused on individual's responses to the global crisis, concentrating on emotional regulation as a challenge, with suggestions for better managing the stress surrounding the anxiety of uncertainty. Rudolph and Zacher (2020) cautioned against using a generational lens in research, advocating for a lifespan developmental approach. Spurk and Straub (2020) also review issues related to unemployment, but focus on the impact of COVID-19 specifically on “gig” or flexible work arrangements.
I am grateful for the contributions of these groups of scholars, and proud of their ability to write these. They were able to write constructive essays in a short time frame when they were, themselves, dealing with disruptions at work. Some were home-schooling children, some were worried about an absent partner or a vulnerable loved one, some were struggling with the challenges that Restubog et al. (2020) outlined. I hope the thoughts, suggestions, and recommendations in these essays will help to stimulate productive thought on the effect of COVID-19 on work and workers. And, while, I hope this research spurs to better understand the effects of such shocks on work, I really hope we do not have to cope with such a shock again.
- Akkermans J., Richardson J., Kraimer M. The Covid-19 crisis as a career shock: Implications for careers and vocational behavior. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blustein D.L., Duffy R., Ferreira J.A., Cohen-Scali V., Cinamon R.G., Allan B.A. Unemployment in the time of COVID-19: A research agenda. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (2020). Labor Force Statistics from the Current Population Survey. Retrieved May 6, 2020 from https://data.bls.gov/cgi-bin/surveymost .
- Cho E. Examining boundaries to understand the impact of COVID-19 on vocational behaviors. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan Y., Deng H., Zhou X. Understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on career development: Insights from cultural psychology. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johns Hopkins (2020) Coronavirus Outbreak Mapped: Retrieved May 5, 2020 from https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html .
- International Labor Organization ILO monitor: COVID-19 and the world of work. Third edition updated estimates and analysis. 2020. https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/@dgreports/@dcomm/documents/briefingnote/wcms_743146.pdf Retrieved May 5, 2020 from:
- International Labor Organization (2020b) COVID-19 impact on the collection of labour market statistics. Retrieved May 6, 2020 from: https://ilostat.ilo.org .
- Kantamneni, N. (2020). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on marginalized populations in the United States: A research agenda. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 119 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Kramer A., Kramer K.Z. The potential impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on occupational status, work from home, and occupational mobility. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leitheiser, E., Hossain, S.N., Shuvro, S., Tasnim, G., Moon, J., Knudsen, J.S., & Rahman, S. (2020). Early impacts of coronavirus on Bangladesh apparel supply chains. https://www.cbs.dk/files/cbs.dk/risc_report_-_impacts_of_coronavirus_on_bangladesh_rmg_1.pdf .
- Restubog S.L.D., Ocampo A.C., Wang L. Taking control amidst the Chaos: Emotion regulation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rudolph C.W., Zacher H. COVID-19 and careers: On the futility of generational explanations. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spurk D., Straub C. Flexible employment relationships and careers in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization (2020). World Health Organization Coronavirus Update. Retrieved May 5, 2020 from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 .

COMMENTS
Essay On Covid-19: 100, 200 and 300 Words. COVID-19, also known as the Coronavirus, is a global pandemic that has affected people all around the world. It first emerged in a lab in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and quickly spread to countries around the world. This virus was reportedly caused by SARS-CoV-2. Since then, it has spread rapidly to ...
This essay is an opportunity to share your pandemic experience and the lessons learned. The college admissions process has experienced significant changes as a result of COVID-19, creating new challenges for high school students. Since the onset of the pandemic, admissions officers have strongly emphasized a more holistic review process.
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App ...
How to Write About Coronavirus Using the Special COVID-19 (250-Word) Section on the Common App. Option 1: The Straightforward Way. Option 2: The Slightly More Creative Way. How to Write About Coronavirus Using the (650-Word) Additional Information Section.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic. The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges. Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams. Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on individuals, societies, and economies worldwide. Its multifaceted nature presents a wealth of topics suitable for academic exploration. This essay provides guidance on developing engaging and insightful essay topics related to COVID-19, offering a comprehensive range of perspectives to choose from.
If students submit their essay to a news outlet—and it's published—Cohan awards them with extra credit. As a result of this assignment, more than 25 students have had their work published in newspapers across the United States. Many of these essays cite and applaud the University's Keep Wes Safe campaign and its COVID-19 testing protocols.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
Becoming a storyteller at WHYY, your local public media station, is easier than you might think. Text STORYTELLER to 267-494-9949 to learn more. WHYY is your source for fact-based, in-depth journalism and information. As a nonprofit organization, we rely on financial support from readers like you. Please give today.
Paragraph Writing on Covid-19 in 100 Words. Coronavirus is an infectious disease and is commonly called Covid-19. It affects the human respiratory system causing difficulty in breathing. It is a contagious disease and has been spreading across the world like wildfire. The virus was first identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China.
As a young member of the screening committee for the pan India essay contest on 'A Year After Coronavirus', it has been heartening to realize that regardless of their age, the youth have collectively shared an aspiration to move towards an inclusive future post the global pandemic. Abhinav Kumar. Screening Committee Member.
COVID-19 Coronavirus Abstract First appearing in China in late 2019, the novel Coronavirus COVID-19 has become the most significant global pandemic event in a century. As of October 28, 2020 the total number of cases worldwide was 44 million with 1.17 million deaths. The United States has had an extremely politicized response to the virus, and despite having less than five percent of the world ...
FAQ on Essay on Coronavirus and Coronavirus Symptoms. Question 1: What was the origin of Coronavirus? Answer 1: The city of Wuhan in China was the one that first reported the case of COVID-19 in December 2019. Further, the WHO (World Health Organization) declared the outbreak of this disease as a pandemic in March 2020.
Step 5: Provide Background Information. Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance: Background Information: COVID-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and quickly spread worldwide, leading to millions of infections and deaths.
The WHO declared the virus a pandemic on March 11 and said it was "deeply concerned by the alarming levels of spread and severity" of the outbreak. The WHO recommends basic hygiene such as ...
COVID-19: Emergence, Spread, Possible Treatments, and Global Burden. The Coronavirus (CoV) is a large family of viruses known to cause illnesses ranging from the common cold to acute respiratory tract infection. The severity of the infection may be visible as pneumonia, acute respiratory syndrome, and even death.
500+ Words Essay on Coronavirus Tips. Coronavirus continues to be a serious health risk for the public. As it is a virus, it is essential to understand that viruses will change continually and new versions will keep emerging. Consequently, we must be ready with everything to tackle it accordingly.
Answer 2: One must get the vaccine as soon as possible. Further, always wear a mask properly and sanitize or wash your hands. Clean or disinfect areas that people touch frequently like door handles, electronics, and more. Always cover your mouth when sneezing or coughing and maintain physical distancing.
Check spelling and grammar before sending. Optional: Before you write your draft, ask the person for a coffee or lunch meeting to catch up (over Zoom). Exercise 2 - Keep a Gratitude Journal. In ...
The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good ...
The Journal of Vocational Behavior has not traditionally published essays, but these are such unusual times, and COVID-19 is so relevant to our collective research on work that I thought it was a good idea. I issued an invitation to the Associate Editors to submit a brief (3000 word) essay on the implications of COVID-19 on work and/or workers ...
Essay on Covid 19 in English 500 Words. Coronavirus essay in English - Corona Virus which is commonly known as COVID-19 is an infectious disease that causes illness in the respiratory system in ...