- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff


News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
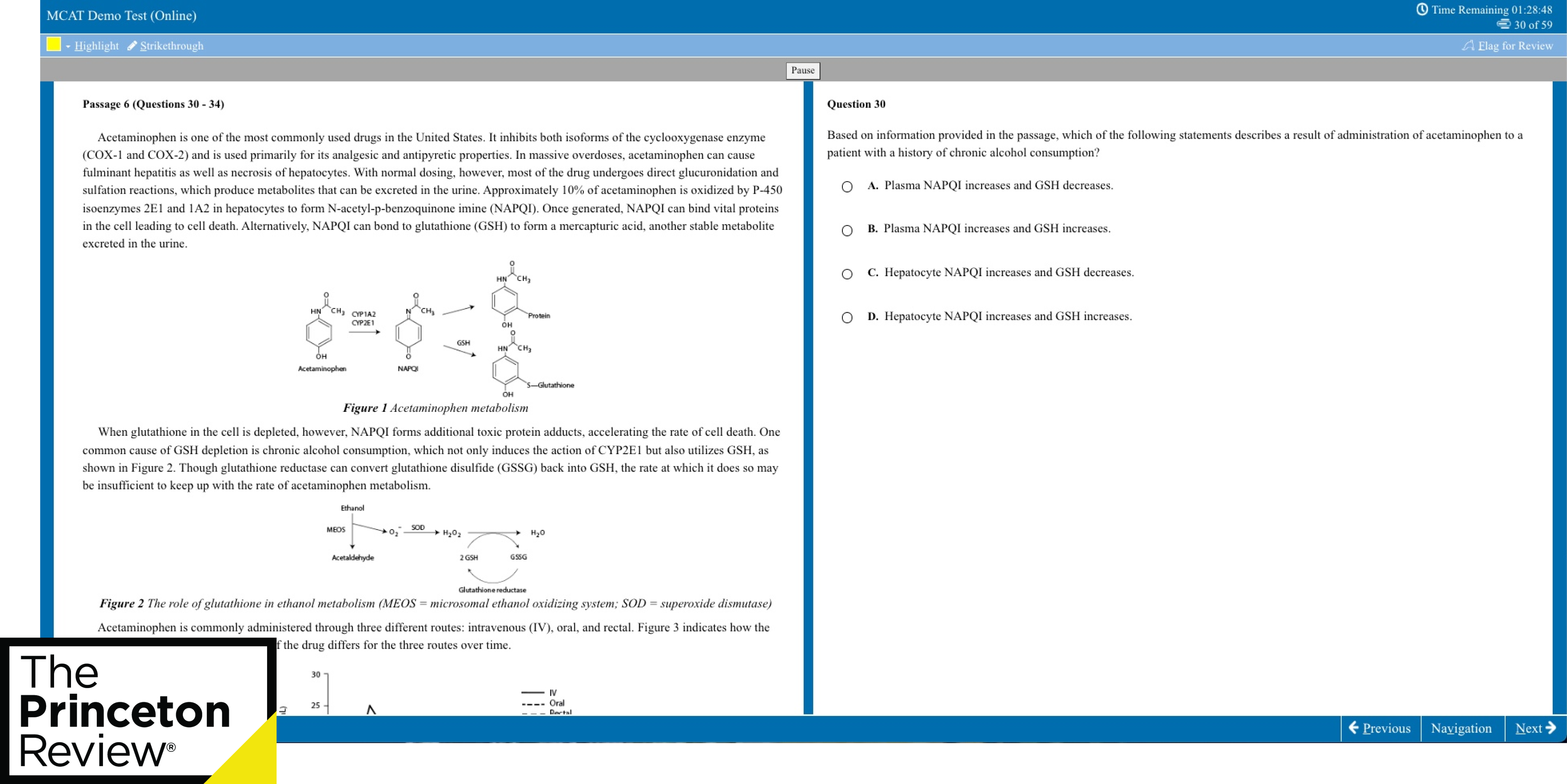
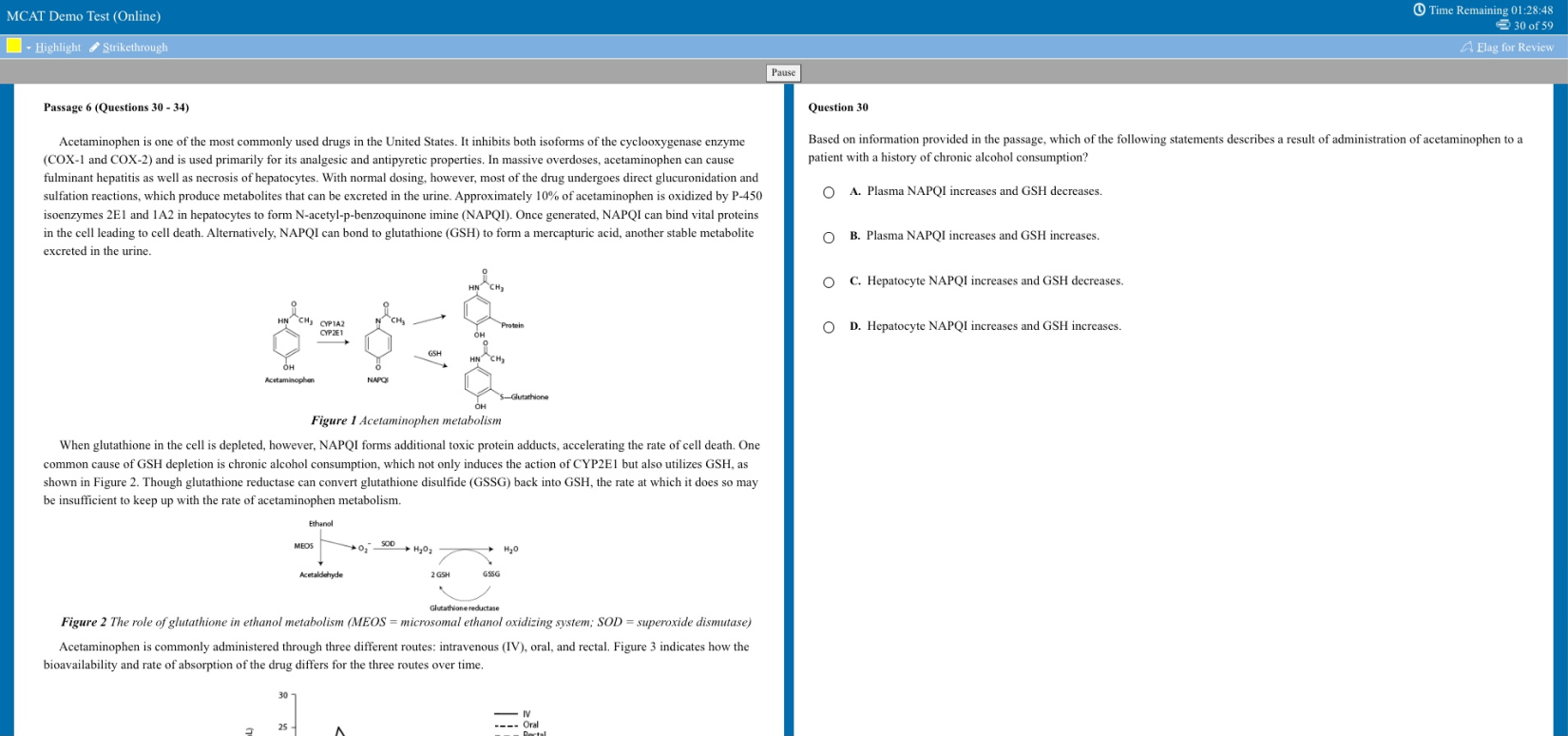
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
The Truth About Homework Stress: What Parents & Students Need to Know
- Fact Checked
Written by:
published on:
- December 21, 2023
Updated on:
- January 9, 2024
Looking for a therapist?
Homework is generally given out to ensure that students take time to review and remember the days lessons. It can help improve on a student’s general performance and enhance traits like self-discipline and independent problem solving.
Parents are able to see what their children are doing in school, while also helping teachers determine how well the lesson material is being learned. Homework is quite beneficial when used the right way and can improve student performance.
This well intentioned practice can turn sour if it’s not handled the right way. Studies show that if a student is inundated with too much homework, not only do they get lower scores, but they are more likely to get stressed.
The age at which homework stress is affecting students is getting lower, some even as low as kindergarten. Makes you wonder what could a five year old possibly need to review as homework?
One of the speculated reasons for this stress is that the complexity of what a student is expected to learn is increasing, while the breaks for working out excess energy are reduced. Students are getting significantly more homework than recommended by the education leaders, some even nearly three times more.
To make matters worse, teachers may give homework that is both time consuming and will keep students busy while being totally non-productive.
Remedial work like telling students to copy notes word for word from their text books will do nothing to improve their grades or help them progress. It just adds unnecessary stress.
Explore emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in affordable online therapy. With 30,000+ licensed therapists and plans starting from only $65 per week, BetterHelp makes self-care accessible to all. Complete the questionnaire to match with the right therapist.
Effects of homework stress at home
Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.
Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students.
Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and time spent doing homework, a child can get headaches, sleep deprivation or even ulcers.
And homework stress doesn’t just impact grade schoolers. College students are also affected, and the stress is affecting their academic performance.
Even the parent’s confidence in their abilities to help their children with homework suffers due increasing stress levels in the household.
Fights and conflict over homework are more likely in families where parents do not have at least a college degree. When the child needs assistance, they have to turn to their older siblings who might already be bombarded with their own homework.
Parents who have a college degree feel more confident in approaching the school and discussing the appropriate amount of school work.
“It seems that homework being assigned discriminates against parents who don’t have college degree, parents who have English as their second language and against parents who are poor.” Said Stephanie Donaldson Pressman, the contributing editor of the study and clinical director of the New England Center for Pediatric Psychology.
With all the stress associated with homework, it’s not surprising that some parents have opted not to let their children do homework. Parents that have instituted a no-homework policy have stated that it has taken a lot of the stress out of their evenings.
The recommended amount homework
The standard endorsed by the National Education Association is called the “10 minute rule”; 10 minutes per grade level per night. This recommendation was made after a number of studies were done on the effects of too much homework on families.
The 10 minute rule basically means 10 minutes of homework in the first grade, 20 minute for the second grade all the way up to 120 minutes for senior year in high school. Note that no homework is endorsed in classes under the first grade.
Parents reported first graders were spending around half an hour on homework each night, and kindergarteners spent 25 minutes a night on assignments according to a study carried out by Brown University.
Making a five year old sit still for half an hour is very difficult as they are at the age where they just want to move around and play.
A child who is exposed to 4-5 hours of homework after school is less likely to find the time to go out and play with their friends, which leads to accumulation of stress energy in the body.
Their social life also suffers because between the time spent at school and doing homework, a child will hardly have the time to pursue hobbies. They may also develop a negative attitude towards learning.
The research highlighted that 56% of students consider homework a primary source of stress.
And if you’re curious how the U.S stacks up against other countries in regards to how much time children spend on homework, it’s pretty high on the list .
Signs to look out for on a student that has homework stress
Since not every student is affected by homework stress in the same way, it’s important to be aware of some of the signs your child might be mentally drained from too much homework.
Here are some common signs of homework stress:
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent stomachaches and headaches
- Decreased appetite or changed eating habits
- New or recurring fears
- Not able to relax
- Regressing to behavior they had when younger
- Bursts of anger crying or whining
- Becoming withdrawn while others may become clingy
- Drastic changes in academic performance
- Having trouble concentrating or completing homework
- Constantly complains about their ability to do homework
If you’re a parent and notice any of these signs in your child, step in to find out what’s going on and if homework is the source of their stress.
If you’re a student, pay attention if you start experiencing any of these symptoms as a result of your homework load. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or parents for help if the stress of homework becomes too much for you.
What parents do wrong when it comes to homework stress
Most parents push their children to do more and be more, without considering the damage being done by this kind of pressure.
Some think that homework brought home is always something the children can deal with on their own. If the child cannot handle their homework then these parents get angry and make the child feel stupid.
This may lead to more arguing and increased dislike of homework in the household. Ultimately the child develops an even worse attitude towards homework.
Another common mistake parents make is never questioning the amount of homework their children get, or how much time they spend on it. It’s easy to just assume whatever the teacher assigned is adequate, but as we mentioned earlier, that’s not always the case.
Be proactive and involved with your child’s homework. If you notice they’re spending hours every night on homework, ask them about it. Just because they don’t complain doesn’t mean there isn’t a problem.
How can parents help?
- While every parent wants their child to become successful and achieve the very best, it’s important to pull back on the mounting pressure and remember that they’re still just kids. They need time out to release their stress and connect with other children.
- Many children may be afraid to admit that they’re overwhelmed by homework because they might be misconstrued as failures. The best thing a parent can do is make home a safe place for children to express themselves freely. You can do this by lending a listening ear and not judging your kids.
- Parents can also take the initiative to let the school know that they’re unhappy with the amount of homework being given. Even if you don’t feel comfortable complaining, you can approach the school through the parent-teacher association available and request your representative to plead your case.
- It may not be all the subjects that are causing your child to get stressed. Parents should find out if there is a specific subject of homework that is causing stress. You could also consult with other parents to see what they can do to fix the situation. It may be the amount or the content that causes stress, so the first step is identifying the problem.
- Work with your child to create a schedule for getting homework done on time. You can set a specific period of time for homework, and schedule time for other activities too. Strike a balance between work and play.
- Understanding that your child is stressed about homework doesn’t mean you have to allow them not to try. Let them sit down and work on it as much as they’re able to, and recruit help from the older siblings or a neighbor if possible.
- Check out these resources to help your child with their homework .
The main idea here is to not abolish homework completely, but to review the amount and quality of homework being given out. Stress, depression and lower grades are the last things parents want for their children.
The schools and parents need to work together to find a solution to this obvious problem.
Take the stress test!
Join the Find-a-therapist community and get access to our free stress assessment!
Additional Resources
Online therapy.
Discover a path to emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in convenient and affordable online therapy. With a vast network of 30,000+ licensed therapists, they’re committed to helping you find the one to support your needs. Take advantage of their Free Online Assessment, and connect with a therapist who truly understands you. Begin your journey today.
Relationship Counceling
Whether you’re facing communication challenges, trust issues, or simply seeking to strengthen your connection, ReGain’ s experienced therapists are here to guide you and your partner toward a healthier, happier connection from the comfort of your own space. Get started.
Therapist Directory
Discover the perfect therapist who aligns with your goals and preferences, allowing you to take charge of your mental health. Whether you’re searching for a specialist based on your unique needs, experience level, insurance coverage, budget, or location, our user-friendly platform has you covered. Search here.
About the author
You might also be interested in
Behavioral Health vs. Mental Health: Distinct Features
4 Reasons People Keep Letting You Down (And What to do About it)
10 Best Meditation Books to Add to Your Reading List
Disclaimers
Online Therapy, Your Way
Follow us on social media
We may receive a commission if you click on and become a paying customer of a therapy service that we mention.
The information contained in Find A Therapist is general in nature and is not medical advice. Please seek immediate in-person help if you are in a crisis situation.
Therapy Categories
More information
If you are in a life threatening situation – don’t use this site. Call +1 (800) 273-8255 or check these resources to get immediate help.
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- Local Gardener Lifts Spirits by Grooming on the Hospital’s Animal Topiaries
- Pediatric ICU Nurse Honored With 3 Employee Awards
- Celebrating Hematology and Oncology Doctors From Diverse Backgrounds
- Stanford Heart Team Keeps Extremely Ill Baby Alive With Finesse and Teamwork
- Helping Your Child Cope With Anxiety and Depression

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford School of Medicine
- Stanford Health Care
- Stanford University
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
School Stress Takes A Toll On Health, Teens And Parents Say
Patti Neighmond

Colleen Frainey, 16, of Tualatin, Ore., cut back on advanced placement classes in her junior year because the stress was making her physically ill. Toni Greaves for NPR hide caption
Colleen Frainey, 16, of Tualatin, Ore., cut back on advanced placement classes in her junior year because the stress was making her physically ill.
When high school junior Nora Huynh got her report card, she was devastated to see that she didn't get a perfect 4.0.
Nora "had a total meltdown, cried for hours," her mother, Jennie Huynh of Alameda, Calif., says. "I couldn't believe her reaction."
Nora is doing college-level work, her mother says, but many of her friends are taking enough advanced classes to boost their grade-point averages above 4.0. "It breaks my heart to see her upset when she's doing so awesome and going above and beyond."
And the pressure is taking a physical toll, too. At age 16, Nora is tired, is increasingly irritated with her siblings and often suffers headaches, her mother says.
Teens Talk Stress
When NPR asked on Facebook if stress is an issue for teenagers, they spoke loud and clear:
- "Academic stress has been a part of my life ever since I can remember," wrote Bretta McCall, 16, of Seattle. "This year I spend about 12 hours a day on schoolwork. I'm home right now because I was feeling so sick from stress I couldn't be at school. So as you can tell, it's a big part of my life!"
- "At the time of writing this, my weekend assignments include two papers, a PowerPoint to go with a 10-minute presentation, studying for a test and two quizzes, and an entire chapter (approximately 40 pages) of notes in a college textbook," wrote Connor West of New Jersey.
- "It's a problem that's basically brushed off by most people," wrote Kelly Farrell in Delaware. "There's this mentality of, 'You're doing well, so why are you complaining?' " She says she started experiencing symptoms of stress in middle school, and was diagnosed with panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder in high school.
- "Parents are the worst about all of this," writes Colin Hughes of Illinois. "All I hear is, 'Work harder, you're a smart kid, I know you have it in you, and if you want to go to college you need to work harder.' It's a pain."
Parents are right to be worried about stress and their children's health, says Mary Alvord , a clinical psychologist in Maryland and public education coordinator for the American Psychological Association.
"A little stress is a good thing," Alvord says. "It can motivate students to be organized. But too much stress can backfire."
Almost 40 percent of parents say their high-schooler is experiencing a lot of stress from school, according to a new NPR poll conducted with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the Harvard School of Public Health. In most cases, that stress is from academics, not social issues or bullying, the poll found. (See the full results here .)
Homework was a leading cause of stress, with 24 percent of parents saying it's an issue.
Teenagers say they're suffering, too. A survey by the American Psychological Association found that nearly half of all teens — 45 percent — said they were stressed by school pressures.
Chronic stress can cause a sense of panic and paralysis, Alvord says. The child feels stuck, which only adds to the feeling of stress.
Parents can help put the child's distress in perspective, particularly when they get into what Alvord calls catastrophic "what if" thinking: "What if I get a bad grade, then what if that means I fail the course, then I'll never get into college."
Then move beyond talking and do something about it.

Colleen pets her horse, Bishop. They had been missing out on rides together because of homework. Toni Greaves for NPR hide caption
Colleen pets her horse, Bishop. They had been missing out on rides together because of homework.
That's what 16-year-old Colleen Frainey of Tualatin, Ore., did. As a sophomore last year, she was taking all advanced courses. The pressure was making her sick. "I didn't feel good, and when I didn't feel good I felt like I couldn't do my work, which would stress me out more," she says.
Mom Abigail Frainey says, "It was more than we could handle as a family."
With encouragement from her parents, Colleen dropped one of her advanced courses. The family's decision generated disbelief from other parents. "Why would I let her take the easy way out?" Abigail Frainey heard.
But she says dialing down on academics was absolutely the right decision for her child. Colleen no longer suffers headaches or stomachaches. She's still in honors courses, but the workload this year is manageable.
Even better, Colleen now has time to do things she never would have considered last year, like going out to dinner with the family on a weeknight, or going to the barn to ride her horse, Bishop.
Psychologist Alvord says a balanced life should be the goal for all families. If a child is having trouble getting things done, parents can help plan the week, deciding what's important and what's optional. "Just basic time management — that will help reduce the stress."
- Children's Health
Opinion | Social-Emotional Learning
If we’re serious about student well-being, we must change the systems students learn in, here are five steps high schools can take to support students' mental health., by tim klein and belle liang oct 14, 2022.

Shutterstock / SvetaZi
Educators and parents started this school year with bated breath. Last year’s stress led to record levels of teacher burnout and mental health challenges for students.
Even before the pandemic, a mental health crisis among high schoolers loomed. According to a survey administered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2019, 37 percent of high school students said they experienced persistent sadness or hopelessness and 19 percent reported suicidality. In response, more than half of all U.S. states mandated that schools have a mental health curriculum or include mental health in their standards .
As mental health professionals and co-authors of a book about the pressure and stress facing high school students, we’ve spent our entire careers supporting students’ mental health. Traditionally, mental health interventions are individualized and they focus on helping students manage and change their behaviors to cope with challenges they’re facing. But while working with schools and colleges across the globe as we conducted research for our book , we realized that most interventions don’t address systemic issues causing mental health problems in the first place.
It’s time we acknowledge that our education systems are directly contributing to the youth mental health crisis. And if we are serious about student well-being, we must change the systems they learn in.
Here are five bold steps that high schools can take to boost mental health.
Limit Homework or Make it Optional
Imagine applying for a job, and the hiring manager informs you that in addition to a full workday in the office, you’ll be assigned three more hours of work every night. Does this sound like a healthy work-life balance? Most adults would consider this expectation ridiculous and unsustainable. Yet, this is the workload most schools place on high school students.
Research shows that excessive homework leads to increased stress, physical health problems and a lack of balance in students' lives. And studies have shown that more than two hours of daily homework can be counterproductive , yet many teachers assign more.
Homework proponents argue that homework improves academic performance. Indeed, a meta-analysis of research on this issue found a correlation between homework and achievement. But correlation isn’t causation. Does homework cause achievement or do high achievers do more homework? While it’s likely that homework completion signals student engagement, which in turn leads to academic achievement, there’s little evidence to suggest that homework itself improves engagement in learning.
Another common argument is that homework helps students develop skills related to problem-solving, time-management and self-direction. But these skills can be explicitly taught during the school day rather than after school.
Limiting homework or moving to an optional homework policy not only supports student well-being, but it can also create a more equitable learning environment. According to the American Psychological Association, students from more affluent families are more likely to have access to resources such as devices, internet, dedicated work space and the support necessary to complete their work successfully—and homework can highlight those inequities .
Whether a school limits homework or makes it optional, it’s critical to remember that more important than the amount of homework assigned, is designing the type of activities that engage students in learning. When students are intrinsically motivated to do their homework, they are more engaged in the work, which in turn is associated with academic achievement.
Cap the Number of APs Students Can Take
Advanced Placement courses give students a taste of college-level work and, in theory, allow them to earn college credits early. Getting good grades on AP exams is associated with higher GPAs in high school and success in college, but the research tends to be correlational rather than causational.
In 2008, a little over 180,000 students took three or more AP exams. By 2018, that number had ballooned to almost 350,000 students .
However, this expansion has come at the expense of student well-being.
Over the years, we’ve heard many students express that they feel pressure to take as many AP classes as possible, which overloads them with work. That’s troubling because studies show that students who take AP classes and exams are twice as likely to report adverse physical and emotional health .
AP courses and exams also raise complex issues of equity. In 2019, two out of three Harvard freshmen reported taking AP Calculus in high school, according to Jeff Selingo, author of “ Who Gets In and Why: A Year Inside College Admissions ,” yet only half of all high schools in the country offer the course. And opportunity gaps exist for advanced coursework such as AP courses and dual enrollment, with inequitable distribution of funding and support impacting which students are enrolling and experiencing success. According to the Center for American Progress, “National data from the Civil Rights Data Collection show that students who are Black, Indigenous, and other non-Black people of color (BIPOC) are not enrolled in AP courses at rates comparable to their white and Asian peers and experience less success when they are—and the analysis for this report finds this to be true even when they attend schools with similar levels of AP course availability.”
Limiting the number of AP courses students take can protect mental health and create a more equitable experience for students.
Eliminate Class Rankings
In a study we conducted about mental health problems among high school girls, we found that a primary driver of stress was their perception of school as a hypercompetitive, zero-sum game where pervasive peer pressure to perform reigns supreme.
Class rankings fuel these cutthroat environments. They send a toxic message to young people: success requires doing better than your peers.
Ranking systems help highly selective colleges decide which students to admit or reject for admission. The purpose of high school is to develop students to their own full potential, rather than causing them to fixate on measuring up to others. Research shows that ranking systems undercut students’ learning and damage social relationships by turning peers into opponents.
Eliminating class rankings sends a powerful message to students that they are more than a number.
Become an Admission Test Objector
COVID-19 ushered in the era of test-optional admissions. De-centering standardized tests in the college application process is unequivocally a good thing. Standardized tests don’t predict student success in college , they only widen the achievement gap between privileged and underprivileged students and damage students' mental health .
Going “test optional” is an excellent first step, but it's not enough.
Even as more colleges have made tests optional, affluent students submit test scores at a higher rate than their lower-income peers and are admitted at higher rates , suggesting that testing still gives them an edge.
High schools must adhere to standardized test mandates, but they don’t have to endorse them. They can become test objectors by publicly proclaiming that these tests hold no inherent value. They can stop teaching to the test and educate parents on why they are doing so. Counseling departments can inform colleges that their school is a test objector so admission teams won’t penalize students.
Of course, students and families will still find ways to wield these tests as a competitive advantage. Over time, the more schools and educators unite to denounce these tests, the less power they will hold over students and families.
Big change starts with small steps.
Stand For What You Value
Critics may argue that such policies might hurt student outcomes. How will colleges evaluate school rigor if we limit AP courses and homework? How will students demonstrate their merits without class rankings and standardized test scores?
The truth is, the best school systems in the world succeed without homework, standardized test scores or an obsession with rigorous courses. And many U.S. schools have found creative and empowering ways to showcase student merit beyond rankings and test scores.
If we aren’t willing to change policies and practices that have been shown to harm students’ well-being, we have to ask ourselves: Do we really value mental health?
Thankfully, it doesn’t have to be an either/or scenario: We can design school systems that help students thrive academically and psychologically.
Belle Liang and Tim Klein are mental health professionals and co-authors of “How To Navigate Life: The New Science of Finding Your Way in School, Career and Life.”
More from EdSurge

Teacher Well-Being Depends on Workload, School Climate and Feeling Supported
By nadia tamez-robledo.

Education Workforce
At least a dozen states are considering free child care for early educators, by emily tate sullivan.

What Would It Take to Attract Gen Z to Teaching?

EdSurge Podcast
‘college for what' high school students want answers before heading to campus, by jeffrey r. young.
Journalism that ignites your curiosity about education.
EdSurge is an editorially independent project of and
- Product Index
- Write for us
- Advertising
FOLLOW EDSURGE
© 2024 All Rights Reserved
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., homework wars: high school workloads, student stress, and how parents can help.

Studies of typical homework loads vary : In one, a Stanford researcher found that more than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive. The research , conducted among students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities, found that too much homework resulted in stress, physical health problems and a general lack of balance.
Additionally, the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education , found that with the exception of nine-year-olds, the amount of homework schools assign has remained relatively unchanged since 1984, meaning even those in charge of the curricula don't see a need for adding more to that workload.
But student experiences don’t always match these results. On our own Student Life in America survey, over 50% of students reported feeling stressed, 25% reported that homework was their biggest source of stress, and on average teens are spending one-third of their study time feeling stressed, anxious, or stuck.
The disparity can be explained in one of the conclusions regarding the Brown Report:
Of the three age groups, 17-year-olds have the most bifurcated distribution of the homework burden. They have the largest percentage of kids with no homework (especially when the homework shirkers are added in) and the largest percentage with more than two hours.
So what does that mean for parents who still endure the homework wars at home?
Read More: Teaching Your Kids How To Deal with School Stress
It means that sometimes kids who are on a rigorous college-prep track, probably are receiving more homework, but the statistics are melding it with the kids who are receiving no homework. And on our survey, 64% of students reported that their parents couldn’t help them with their work. This is where the real homework wars lie—not just the amount, but the ability to successfully complete assignments and feel success.
Parents want to figure out how to help their children manage their homework stress and learn the material.
Our Top 4 Tips for Ending Homework Wars
1. have a routine..
Every parenting advice article you will ever read emphasizes the importance of a routine. There’s a reason for that: it works. A routine helps put order into an often disorderly world. It removes the thinking and arguing and “when should I start?” because that decision has already been made. While routines must be flexible to accommodate soccer practice on Tuesday and volunteer work on Thursday, knowing in general when and where you, or your child, will do homework literally removes half the battle.
2. Have a battle plan.
Overwhelmed students look at a mountain of homework and think “insurmountable.” But parents can look at it with an outsider’s perspective and help them plan. Put in an extra hour Monday when you don’t have soccer. Prepare for the AP Chem test on Friday a little at a time each evening so Thursday doesn’t loom as a scary study night (consistency and repetition will also help lock the information in your brain). Start reading the book for your English report so that it’s underway. Go ahead and write a few sentences, so you don’t have a blank page staring at you. Knowing what the week will look like helps you keep calm and carry on.

3. Don’t be afraid to call in reserves.
You can’t outsource the “battle” but you can outsource the help ! We find that kids just do better having someone other than their parents help them —and sometimes even parents with the best of intentions aren’t equipped to wrestle with complicated physics problem. At The Princeton Review, we specialize in making homework time less stressful. Our tutors are available 24/7 to work one-to-one in an online classroom with a chat feature, interactive whiteboard, and the file sharing tool, where students can share their most challenging assignments.
4. Celebrate victories—and know when to surrender.
Students and parents can review completed assignments together at the end of the night -- acknowledging even small wins helps build a sense of accomplishment. If you’ve been through a particularly tough battle, you’ll also want to reach reach a cease-fire before hitting your bunk. A war ends when one person disengages. At some point, after parents have provided a listening ear, planning, and support, they have to let natural consequences take their course. And taking a step back--and removing any pressure a parent may be inadvertently creating--can be just what’s needed.
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- How It Works
- Sleep Meditation
- VA Workers and Veterans

- How It Works 01
- Sleep Meditation 02
- Mental Fitness 03
- Neurofeedback 04
- Healium for Business 05
- VA Workers and Veterans 06
- Sports Meditation 07
- VR Experiences 08
- Social Purpose 11
Does Homework Cause Stress? Exploring the Impact on Students’ Mental Health
How much homework is too much?

Jump to: The Link Between Homework and Stress | Homework’s Impact on Mental Health | Benefits of Homework | How Much Homework Should Teacher’s Assign? | Advice for Students | How Healium Helps
Homework has become a matter of concern for educators, parents, and researchers due to its potential effects on students’ stress levels. It’s no secret students often find themselves grappling with high levels of stress and anxiety throughout their academic careers, so understanding the extent to which homework affects those stress levels is important.
By delving into the latest research and understanding the underlying factors at play, we hope to curate insights for educators, parents, and students who are wondering is homework causing stress in their lives?
The Link Between Homework and Stress: What the Research Says
Over the years, numerous studies investigated the relationship between homework and stress levels in students.
One study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that students who reported spending more than two hours per night on homework experienced higher stress levels and physical health issues . Those same students reported over three hours of homework a night on average.
This study, conducted by Stanford lecturer Denise Pope, has been heavily cited throughout the years, with WebMD eproducing the below video on the topic– part of their special report series on teens and stress :
Additional studies published by Sleep Health Journal found that long hours on homework on may be a risk factor for depression while also suggesting that reducing workload outside of class may benefit sleep and mental fitness .
Lastly, a study presented by Frontiers in Psychology highlighted significant health implications for high school students facing chronic stress, including emotional exhaustion and alcohol and drug use.
Homework’s Potential Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects.
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming.
• Sleep Disturbances : Homework-related stress can disrupt students’ sleep patterns, leading to sleep anxiety or sleep deprivation, both of which can negatively impact cognitive function and emotional regulation.
• Reduced Motivation: Excessive homework demands could drain students’ motivation, causing them to feel fatigued and disengaged from their studies. Reduced motivation may lead to a lack of interest in learning, hindering overall academic performance.
2. Potential Physical Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Impaired Immune Function: Prolonged stress could weaken the immune system, making students more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
• Disrupted Hormonal Balance : The body’s stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which, when chronically elevated due to stress, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.
• Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Stress has been known to affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, and other digestive problems.
• Cardiovascular Impact: The increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure associated with stress can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of heart-related issues in the long run.
• Brain impact: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones may impact the brain’s functioning , affecting memory, concentration, and cognitive abilities.
The Benefits of Homework
It’s important to note that homework also offers many benefits that contribute to students’ academic growth and development, such as:
• Development of Time Management Skills: Completing homework within specified deadlines encourages students to manage their time efficiently. This valuable skill extends beyond academics and becomes essential in various aspects of life.
• Preparation for Future Challenges : Homework helps prepare students for future academic challenges and responsibilities. It fosters a sense of discipline and responsibility, qualities that are crucial for success in higher education and professional life.
• Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Homework often presents students with challenging problems to solve. Tackling these problems independently nurtures critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
While homework can foster discipline, time management, and self-directed learning, the middle ground may be to strike a balance that promotes both academic growth and mental well-being .
How Much Homework Should Teachers Assign?
As a general guideline, educators suggest assigning a workload that allows students to grasp concepts effectively without overwhelming them . Quality over quantity is key, ensuring that homework assignments are purposeful, relevant, and targeted towards specific objectives.
Advice for Students: How to balance Homework and Well-being
Finding a balance between academic responsibilities and well-being is crucial for students. Here are some practical tips and techniques to help manage homework-related stress and foster a healthier approach to learning:
• Effective Time Management : Encourage students to create a structured study schedule that allocates sufficient time for homework, breaks, and other activities. Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can prevent last-minute rushes and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
• Break Tasks into Smaller Chunks : Large assignments can be daunting and may contribute to stress. Students should break such tasks into smaller, manageable parts. This approach not only makes the workload seem less intimidating but also provides a sense of accomplishment as each section is completed.
• Find a Distraction-Free Zone : Establish a designated study area that is free from distractions like smartphones, television, or social media. This setting will improve focus and productivity, reducing time needed to complete homework.
• Be Active : Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and enhance mood. Encourage students to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, whether it’s going for a walk, playing a sport, or doing yoga.
• Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques : Encourage students to engage in mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to alleviate stress and improve concentration. Taking short breaks to relax and clear the mind can enhance overall well-being and cognitive performance.
• Seek Support : Teachers, parents, and school counselors play an essential role in supporting students. Create an open and supportive environment where students feel comfortable expressing their concerns and seeking help when needed.
How Healium is Helping in Schools
Stress is caused by so many factors and not just the amount of work students are taking home. Our company created a virtual reality stress management solution… a mental fitness tool called “Healium” that’s teaching students how to learn to self-regulate their stress and downshift in a drugless way. Schools implementing Healium have seen improvements from supporting dysregulated students and ADHD challenges to empowering students with body awareness and learning to self-regulate stress . Here’s one of their stories.
By providing students with the tools they need to self-manage stress and anxiety, we represent a forward-looking approach to education that prioritizes the holistic development of every student.
To learn more about how Healium works, watch the video below.
About the Author

Sarah Hill , a former interactive TV news journalist at NBC, ABC, and CBS affiliates in Missouri, gained recognition for pioneering interactive news broadcasting using Google Hangouts. She is now the CEO of Healium, the world’s first biometrically powered immersive media channel, helping those with stress, anxiety, insomnia, and other struggles through biofeedback storytelling. With patents, clinical validation, and over seven million views, she has reshaped the landscape of immersive media.
The New York Times
Motherlode | when homework stresses parents as well as students, when homework stresses parents as well as students.

Educators and parents have long been concerned about students stressed by homework loads , but a small research study asked questions recently about homework and anxiety of a different group: parents. The results were unsurprising. While we may have already learned long division and let the Magna Carta fade into memory, parents report that their children’s homework causes family stress and tension — particularly when additional factors surrounding the homework come into play.
The researchers, from Brown University, found that stress and tension for families (as reported by the parents) increased most when parents perceived themselves as unable to help with the homework, when the child disliked doing the homework and when the homework caused arguments, either between the child and adults or among the adults in the household.
The number of parents involved in the research (1,173 parents, both English and Spanish-speaking, who visited one of 27 pediatric practices in the greater Providence area of Rhode Island) makes it more of a guide for further study than a basis for conclusions, but the idea that homework can cause significant family stress is hard to seriously debate. Families across income and education levels may struggle with homework for different reasons and in different ways, but “it’s an equal opportunity problem,” says Stephanie Donaldson-Pressman , a contributing editor to the research study and co-author of “ The Learning Habit .”
“Parents may find it hard to evaluate the homework,” she says. “They think, if this is coming home, my child should be able to do it. If the child can’t, and especially if they feel like they can’t help, they may get angry with the child, and the child feels stupid.” That’s a scenario that is likely to lead to more arguments, and an increased dislike of the work on the part of the child.
The researchers also found that parents of students in kindergarten and first grade reported that the children spent significantly more time on homework than recommended. Many schools and organizations, including the National Education Association and the Great Schools blog , will suggest following the “10-minute rule” for how long children should spend on school work outside of school hours: 10 minutes per grade starting in first grade, and most likely more in high school. Instead, parents described their first graders and kindergartners working, on average, for 25 to 30 minutes a night. That is consistent with other research , which has shown an increase in the amount of time spent on homework in lower grades from 1981 to 2003.
“This study highlights the real discrepancy between intent and what’s actually happening,” Ms. Donaldson-Pressman said, speaking of both the time spent and the family tensions parents describe. “When people talk about the homework, they’re too often talking about the work itself. They should be talking about the load — how long it takes. You can have three problems on one page that look easy, but aren’t.”
The homework a child is struggling with may not be developmentally appropriate for every child in a grade, she suggests, noting that academic expectations for young children have increased in recent years . Less-educated or Spanish-speaking parents may find it harder to evaluate or challenge the homework itself, or to say they think it is simply too much. “When the load is too much, it has a tremendous impact on family stress and the general tenor of the evening. It ruins your family time and kids view homework as a punishment,” she said.
At our house, homework has just begun; we are in the opposite of the honeymoon period, when both skills and tolerance are rusty and complaints and stress are high. If the two hours my fifth-grade math student spent on homework last night turn out the be the norm once he is used to the work and the teacher has had a chance to hear from the students, we’ll speak up.
We should, Ms. Donaldson-Pressman says. “Middle-class parents can solve the problem for their own kids,” she says. “They can make sure their child is going to all the right tutors, or get help, but most people can’t.” Instead of accepting that at home we become teachers and homework monitors (or even taking classes in how to help your child with his math ), parents should let the school know that they’re unhappy with the situation, both to encourage others to speak up and to speak on behalf of parents who don’t feel comfortable complaining.
“Home should be a safe place for students,” she says. “A child goes to school all day and they’re under stress. If they come home and it’s more of the same, that’s not good for anyone.”
Read more about homework on Motherlode: Homework and Consequences ; The Mechanics of Homework ; That’s Your Child’s Homework Project, Not Yours and Homework’s Emotional Toll on Students and Families.
What's Next
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Is Homework a Waste of Students' Time? Study Finds It's the Biggest Cause of Teen Stress
As the debate over the need for homework continues, a new study found that it's the biggest cause of teen stress, leading to sleepless nights and poor academic performance
Julie Mazziotta is the Sports Editor at PEOPLE, covering everything from the NFL to tennis to Simone Biles and Tom Brady. She was previously an Associate Editor for the Health vertical for six years, and prior to joining PEOPLE worked at Health Magazine. When not covering professional athletes, Julie spends her time as a (very) amateur athlete, training for marathons, long bike trips and hikes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/J.Mazziotta2334-e3daa71fe1a745929e739c08e585253f.jpg)
It’s the bane of every teen’s existence. After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to get started on mountains of homework. And educators are mixed on its effectiveness . Some say the practice reinforces what students learned during the day, while others argue that it put unnecessary stress on kids and parents , who are often stuck nagging or helping.
According to a new study, conducted by the Better Sleep Council , that homework stress is the biggest source of frustration for teens, with 74 percent of those surveyed ranking it the highest, above self-esteem (51 percent) parental expectations (45 percent) and bullying (15 percent).
Homework is taking up a large chunk of their time , too — around 15-plus hours a week, with about one-third of teens reporting that it’s closer to 20-plus hours.
The stress and excessive homework adds up to lost sleep, the BSC says. According to the survey, 57 percent of teenagers said that they don’t get enough sleep, with 67 reporting that they get just five to seven hours a night — a far cry from the recommended eight to ten hours. The BSC says that their research shows that when teens feel more stressed, their sleep suffers. They go to sleep later, wake up earlier and have more trouble falling and staying asleep than less-stressed teens.
“We’re finding that teenagers are experiencing this cycle where they sacrifice their sleep to spend extra time on homework, which gives them more stress — but they don’t get better grades,” said Mary Helen Rogers, the vice president of marketing and communications for the BSC.
RELATED VIDEO: To Help Or Not To Help: Moms Talk About Whether Or Not They Help Their Children With Homework
Another interesting finding from this study: students who go to bed earlier and wake up earlier do better academically than those who stay up late, even if those night owls are spending that time doing homework.
To end this cycle of sleep deprivation and stress, the BSC recommends that students try setting a consistent time to go to sleep each night, regardless of leftover homework. And their other sleep tips are good for anyone, regardless of age — keep the temperature between 65 and 67 degrees, turn off the electronic devices before bed, make sure the mattress is comfy and reduce noise with earplugs or sound machines.
Related Articles
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Stress and The Dangers of Homework
The anxiety of not completing an assignment that you have been stuck on for the past hour can be overwhelming, right? What if I told you millions of people feel the same way you do and there can be consequences of it, I’m not talking grade wise, I’m talking mentally. Homework as we have experienced causes a great amount of stress which can lead you to a poor mental state, sleep deprivation, and many more bad things. Which can be prevented by decreasing the amount of homework significantly and/or being taught how to combat such stress. [A couple of such ways is by managing time, controlling emotions, and monitoring your motivation.] (https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1054844.pdf)
[Controlling Emotion] (https://www.rewireme.com/brain-insight/how-to-control-your-emotions/)
[Time Management] (https://www.liquidplanner.com/blog/7-essential-time-management-strategies/)
[Motivation] (https://ucsccaps.wordpress.com/2019/05/03/staying-motivated/)
A school can start to teach these things so life can be easier for the students, but not just for them though but their family and their teachers too. A study made in 2017 about [the effects of homework on middle class families] (https://digitalcommons.csp.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1069&=&context=cup_commons_grad_edd&=&sei-redir=1&referer=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252Furl%253Fq%253Dhttps%253A%252F%252Fdigitalcommons.csp.edu%252Fcgi%252Fviewcontent.cgi%253Farticle%25253D1069%252526context%25253Dcup_commons_grad_edd%2526sa%253DD%2526source%253Deditors%2526ust%253D1616434140114000%2526usg%253DAOvVaw0FRSYatcLU9NO7fYRvpdUB#search=%22https%3A%2F%2Fdigitalcommons.csp.edu%2Fcgi%2Fviewcontent.cgi%3Farticle%3D1069%26context%3Dcup_commons_grad_edd%22) shows that homework is the leading cause of stress in the household because it’s hard to have a “healthy balance of homework and family life”. This stress and less family time can lead to troubles in a family, and might even lead to divorce if it is disruptive enough.
The Parent Teacher Association (PTA), suggests there to be ten minutes of homework per grade level which is seemed to not be followed, [some kindergarteners are getting up to] (https://www.healthline.com/health-news/children-more-homework-means-more-stress-031114) 25 minutes of homework per day when they even aren’t supposed to get homework at all according to the National Education Association (NEA), and some second and third graders are even getting 28-29 minutes of homework per day taken in a survey in rhode island. It just doesn’t affect younger grades [but college students as] (https://mellowed.com/homework-stress/) well.
[Chart] (https://mellowed.com/homework-stress/)
The stress can be overwhelming sometimes but the United States is not the only country with a homework problem, Italy, UK, France, and many more suffer the consequences. A survey taken in the UK, in March of 2020 shows that 66% of students in the age range of 8-17 said that “they felt most stressed about homework and/or exams” compared to everything else. Which is pretty alarming considering that this was a survey with almost 2,000 kids, and 66% of 2,000 is 1,320. Just imagine how many people are struggling with it as well on a global level.
Now you might be wondering how can we stop this monstrosity of stress, well looking at countries like [Finland, Japan, and South Korea] (https://www.geekycamel.com/countries-give-less-homework-theyre-successful/#:~:text=Finland,they%20are%20seven%20years%20old.) which are countries that give very little homework per week, ranging from 2.9 hours to 3.9. They mostly rely on trust in the teachers and students, more testing, and new ways to learn that is more beneficial for the students later in life. And it seems to have paid off, Finland, South Korea, and Japan seem to be at the [top in the world for Math and Science at the age of 15.] (https://www.bbc.com/news/education-37716005) So why don’t we start making the change to no homework? Well, that’s the next step, students should start to spread awareness and make petitions to the school board calling for change.
[Bibliography] (https://docs.google.com/document/d/1JCUpxbJm75pB3KNpx6rgm3gX1t_oSuAePhx-5FVyNws/edit#)
No comments have been posted yet.
Log in to post a comment.
You can also log in with your email address.
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Procrastination, depression and anxiety symptoms in university students: a three-wave longitudinal study on the mediating role of perceived stress
- Anna Jochmann 1 ,
- Burkhard Gusy 1 ,
- Tino Lesener 1 &
- Christine Wolter 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 276 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to negative consequences. However, evidence for negative consequences of procrastination is still limited and it is also unclear by which mechanisms they are mediated. Therefore, the aim of our study was to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. We selected the procrastination-health model as our theoretical foundation and tried to evaluate the model’s assumption that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress in a temporal perspective. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and hypothesized that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, and that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress.
To examine these relationships properly, we collected longitudinal data from 392 university students at three occasions over a one-year period and analyzed the data using autoregressive time-lagged panel models.
Procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, perceived stress was not a mediator of this effect. Procrastination did not lead to perceived stress over time, nor did perceived stress lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time.
Conclusions
We could not confirm that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress, as assumed in the procrastination-health model. Nonetheless, our study demonstrated that procrastination can have a detrimental effect on mental health. Further health outcomes and possible mediators should be explored in future studies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
“Due tomorrow? Do tomorrow.”, might be said by someone who has a tendency to postpone tasks until the last minute. But can we enjoy today knowing about the unfinished task and tomorrow’s deadline? Or do we feel guilty for postponing a task yet again? Do we get stressed out because we have little time left to complete it? Almost everyone has procrastinated at some point when it came to completing unpleasant tasks, such as mowing the lawn, doing the taxes, or preparing for exams. Some tend to procrastinate more frequently and in all areas of life, while others are less inclined to do so. Procrastination is common across a wide range of nationalities, as well as socioeconomic and educational backgrounds [ 1 ]. Over the last fifteen years, there has been a massive increase in research on procrastination [ 2 ]. Oftentimes, research focuses on better understanding the phenomenon of procrastination and finding out why someone procrastinates in order to be able to intervene. Similarly, the internet is filled with self-help guides that promise a way to overcome procrastination. But why do people seek help for their procrastination? Until now, not much research has been conducted on the negative consequences procrastination could have on health and well-being. Therefore, in the following article we examine the effect of procrastination on mental health over time and stress as a possible facilitator of this relationship on the basis of the procrastination-health model by Sirois et al. [ 3 ].
Procrastination and its negative consequences
Procrastination can be defined as the tendency to voluntarily and irrationally delay intended activities despite expecting negative consequences as a result of the delay [ 4 , 5 ]. It has been observed in a variety of groups across the lifespan, such as students, teachers, and workers [ 1 ]. For example, some students tend to regularly delay preparing for exams and writing essays until the last minute, even if this results in time pressure or lower grades. Procrastination must be distinguished from strategic delay [ 4 , 6 ]. Delaying a task is considered strategic when other tasks are more important or when more resources are needed before the task can be completed. While strategic delay is viewed as functional and adaptive, procrastination is classified as dysfunctional. Procrastination is predominantly viewed as the result of a self-regulatory failure [ 7 ]. It can be understood as a trait, that is, as a cross-situational and time-stable behavioral disposition [ 8 ]. Thus, it is assumed that procrastinators chronically delay tasks that they experience as unpleasant or difficult [ 9 ]. Approximately 20 to 30% of adults have been found to procrastinate chronically [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Prevalence estimates for students are similar [ 13 ]. It is believed that students do not procrastinate more often than other groups. However, it is easy to examine procrastination in students because working on study tasks requires a high degree of self-organization and time management [ 14 ].
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to negative consequences [ 4 ]. Negative consequences are even part of the definition of procrastination. Research indicates that procrastination is linked to lower academic performance [ 15 ], health impairment (e.g., stress [ 16 ], physical symptoms [ 17 ], depression and anxiety symptoms [ 18 ]), and poor health-related behavior (e.g., heavier alcohol consumption [ 19 ]). However, most studies targeting consequences of procrastination are cross-sectional [ 4 ]. For that reason, it often remains unclear whether an examined outcome is a consequence or an antecedent of procrastination, or whether a reciprocal relationship between procrastination and the examined outcome can be assumed. Additionally, regarding negative consequences of procrastination on health, it is still largely unknown by which mechanisms they are mediated. Uncovering such mediators would be helpful in developing interventions that can prevent negative health consequences of procrastination.
The procrastination-health model
The first and only model that exclusively focuses on the effect of procrastination on health and the mediators of this effect is the procrastination-health model [ 3 , 9 , 17 ]. Sirois [ 9 ] postulates three pathways: An immediate effect of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease and two mediated pathways (see Fig. 1 ).
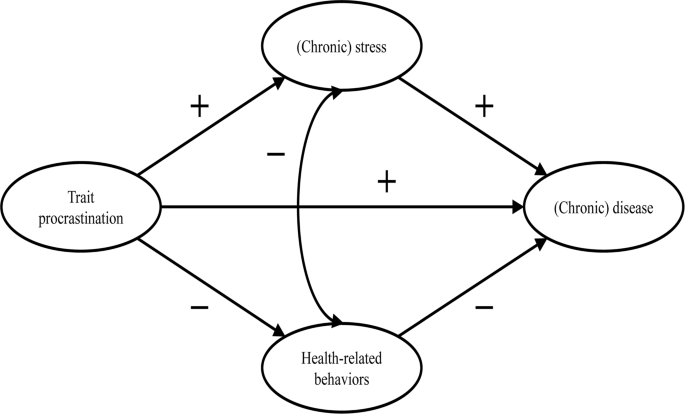
Adopted from the procrastination-health model by Sirois [ 9 ]
The immediate effect is not further explained. Research suggests that procrastination creates negative feelings, such as shame, guilt, regret, and anger [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. The described feelings could have a detrimental effect on mental health [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
The first mediated pathway leads from trait procrastination to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. Sirois [ 9 ] assumes that procrastination creates stress because procrastinators are constantly aware of the fact that they still have many tasks to complete. Stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) system, increases autonomic nervous system arousal, and weakens the immune system, which in turn contributes to the development of diseases. Sirois [ 9 ] distinguishes between short-term and long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by stress. She believes that, in the short term, single incidents of procrastination cause acute stress, which leads to acute health problems, such as infections or headaches. In the long term, chronic procrastination, as you would expect with trait procrastination, causes chronic stress, which leads to chronic diseases over time. There is some evidence in support of the stress-related pathway, particularly regarding short-term effects [ 3 , 17 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. However, as we mentioned above, most of these studies are cross-sectional. Therefore, the causal direction of these effects remains unclear. To our knowledge, long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress have not yet been investigated.
The second mediated pathway leads from trait procrastination to (chronic) disease via poor health-related behavior. According to Sirois [ 9 ], procrastinators form lower intentions to carry out health-promoting behavior or to refrain from health-damaging behavior because they have a low self-efficacy of being able to care for their own health. In addition, they lack the far-sighted view that the effects of health-related behavior only become apparent in the long term. For the same reason, Sirois [ 9 ] believes that there are no short-term, but only long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by poor health-related behavior. For example, an unhealthy diet leads to diabetes over time. The findings of studies examining the behavioral pathway are inconclusive [ 3 , 17 , 26 , 28 ]. Furthermore, since most of these studies are cross-sectional, they are not suitable for uncovering long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by poor health-related behavior.
In summary, previous research on the two mediated pathways of the procrastination-health model mainly found support for the role of (chronic) stress in the relationship between trait procrastination and (chronic) disease. However, only short-term effects have been investigated so far. Moreover, longitudinal studies are needed to be able to assess the causal direction of the relationship between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease. Consequently, our study is the first to examine long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, using a longitudinal design. (Chronic) disease could be measured by a variety of different indicators (e.g., physical symptoms, diabetes, or coronary heart disease). We choose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease because they signal mental health complaints before they manifest as (chronic) diseases. Additionally, depression and anxiety symptoms are two of the most common mental health complaints among students [ 29 , 30 ] and procrastination has been shown to be a significant predictor of depression and anxiety symptoms [ 18 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Until now, the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model with depression and anxiety symptoms as the health outcome has only been analyzed in one cross-sectional study that confirmed the predictions of the model [ 35 ].
The aim of our study is to evaluate some of the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, particularly the relationships between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease over time, surveyed in the following analysis using depression and anxiety symptoms.
In line with the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, we postulate (see Fig. 2 ):
Procrastination leads to perceived stress over time.
Perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time.
Procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress.
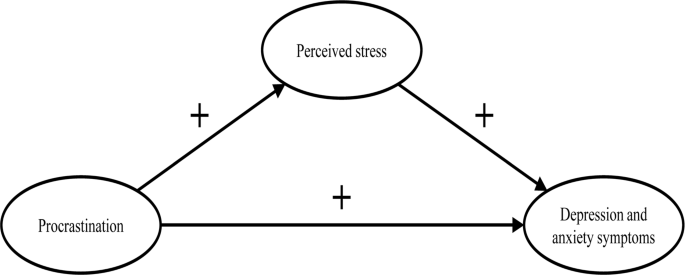
The section of the procrastination-health model we examined
Materials and methods
Our study was part of a health monitoring at a large German university Footnote 1 . Ethical approval for our study was granted by the Ethics Committee of the university’s Department of Education and Psychology. We collected the initial data in 2019. Two occasions followed, each at an interval of six months. In January 2019, we sent out 33,267 invitations to student e-mail addresses. Before beginning the survey, students provided their written informed consent to participate in our study. 3,420 students took part at the first occasion (T1; 10% response rate). Of these, 862 participated at the second (T2) and 392 at the third occasion (T3). In order to test whether dropout was selective, we compared sociodemographic and study specific characteristics (age, gender, academic semester, number of assessments/exams) as well as behavior and health-related variables (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) between the participants of the first wave ( n = 3,420) and those who participated three times ( n = 392). Results from independent-samples t-tests and chi-square analysis showed no significant differences regarding sociodemographic and study specific characteristics (see Additional file 1: Table S1 and S2 ). Regarding behavior and health-related variables, independent-samples t-tests revealed a significant difference in procrastination between the two groups ( t (3,409) = 2.08, p < .05). The mean score of procrastination was lower in the group that participated in all three waves.
The mean age of the longitudinal respondents was 24.1 years ( SD = 5.5 years), the youngest participants were 17 years old, the oldest one was 59 years old. The majority of participants was female (74.0%), 7 participants identified neither as male nor as female (1.8%). The respondents were on average enrolled in the third year of studying ( M = 3.9; SD = 2.3). On average, the students worked about 31.2 h ( SD = 14.1) per week for their studies, and an additional 8.5 h ( SD = 8.5) for their (part-time) jobs. The average income was €851 ( SD = 406), and 4.9% of the students had at least one child. The students were mostly enrolled in philosophy and humanities (16.5%), education and psychology (15.8%), biology, chemistry, and pharmacy (12.5%), political and social sciences (10.6%), veterinary medicine (8.9%), and mathematics and computer science (7.7%).
We only used established and well evaluated instruments for our analyses.
- Procrastination
We adopted the short form of the Procrastination Questionnaire for Students (PFS-4) [ 36 ] to measure procrastination. The PFS-4 assesses procrastination at university as a largely stable behavioral disposition across situations, that is, as a trait. The questionnaire consists of four items (e.g., I put off starting tasks until the last moment.). Each item was rated on a 5-point scale ((almost) never = 1 to (almost) always = 5) for the last two weeks. All items were averaged, with higher scores indicating a greater tendency to procrastinate. The PFS-4 has been proven to be reliable and valid, showing very high correlations with other established trait procrastination scales, for example, with the German short form of the General Procrastination Scale [ 37 , 38 ]. We also proved the scale to be one-dimensional in a factor analysis, with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.90.
Perceived stress
The Heidelberger Stress Index (HEI-STRESS) [ 39 ] is a three-item measure of current perceived stress due to studying as well as in life in general. For the first item, respondents enter a number between 0 (not stressed at all) and 100 (completely stressed) to indicate how stressed their studies have made them feel over the last four weeks. For the second and third item, respondents rate on a 5-point scale how often they feel “stressed and tense” and as how stressful they would describe their life at the moment. We transformed the second and third item to match the range of the first item before we averaged all items into a single score with higher values indicating greater perceived stress. We proved the scale to be one-dimensional and Cronbach’s alpha for our study was 0.86.
Depression and anxiety symptoms
We used the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) [ 40 ], a short form of the Patient Health Questionnaire [ 41 ] with four items, to measure depression and anxiety symptoms. The PHQ-4 contains two items from the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2) [ 42 ] and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale-2 (GAD-2) [ 43 ], respectively. It is a well-established screening scale designed to assess the core criteria of major depressive disorder (PHQ-2) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD-2) according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). However, it was shown that the GAD-2 is also appropriate for screening other anxiety disorders. According to Kroenke et al. [ 40 ], the PHQ-4 can be used to assess a person’s symptom burden and impairment. We asked the participants to rate how often they have been bothered over the last two weeks by problems, such as “Little interest or pleasure in doing things”. Response options were 0 = not at all, 1 = several days, 2 = more than half the days, and 3 = nearly every day. Calculated as the sum of the four items, the total scores range from 0 to 12 with higher scores indicating more frequent depression and anxiety symptoms. The total scores can be categorized as none-to-minimal (0–2), mild (3–5), moderate (6–8), and severe (9–12) depression and anxiety symptoms. The PHQ-4 was shown to be reliable and valid [ 40 , 44 , 45 ]. We also proved the scale to be one-dimensional in a factor analysis, with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.86.
Data analysis
To test our hypotheses, we performed structural equation modelling (SEM) using R (Version 4.1.1) with the package lavaan. All items were standardized ( M = 0, SD = 1). Due to the non-normality of some study variables and a sufficiently large sample size of N near to 400 [ 46 ], we used robust maximum likelihood estimation (MLR) for all model estimations. As recommended by Hu and Bentler [ 47 ], we assessed the models’ goodness of fit by chi-square test statistic, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), standardized root mean square residual (SRMR), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), and comparative fit index (CFI). A non-significant chi-square indicates good model fit. Since chi-square is sensitive to sample size, we also evaluated fit indices less sensitive to the number of observations. RMSEA and SRMR values of 0.05 or lower as well as TLI and CFI values of 0.97 or higher indicate good model fit. RMSEA values of 0.08 or lower, SRMR values of 0.10 or lower, as well as TLI and CFI values of 0.95 or higher indicate acceptable model fit [ 48 , 49 ]. First, we conducted confirmatory factor analysis for the first occasion, defining three factors that correspond to the measures of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms. Next, we tested for measurements invariance over time and specified the measurement model, before testing our hypotheses.
Measurement invariance over time
To test for measurement invariance over time, we defined one latent variable for each of the three occasions, corresponding to the measures of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms, respectively. As recommended by Geiser and colleagues [ 50 ], the links between indicators and factors (i.e., factor loadings and intercepts) should be equal over measurement occasions; therefore, we added indicator specific factors. A first and least stringent step of testing measurement invariance is configural invariance (M CI ). It was examined whether the included constructs (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) have the same pattern of free and fixed loadings over time. This means that the assignment of the indicators to the three latent factors over time is supported by the underlying data. If configural invariance was supported, restrictions for the next step of testing measurement invariance (metric or weak invariance; M MI ) were added. This means that each item contributes to the latent construct to a similar degree over time. Metric invariance was tested by constraining the factor loadings of the constructs over time. The next step of testing measurement invariance (scalar or strong invariance; M SI ) consisted of checking whether mean differences in the latent construct capture all mean differences in the shared variance of the items. Scalar invariance was tested by constraining the item intercepts over time. The constraints applied in the metric invariance model were retained [ 51 ]. For the last step of testing measurement invariance (residual or strict invariance; M RI ), the residual variables were also set equal over time. If residual invariance is supported, differences in the observed variables can exclusively be attributed to differences in the variances of the latent variables.
We used the Satorra-Bentler chi-square difference test to evaluate the superiority of a more stringent model [ 52 ]. We assumed the model with the largest number of invariance restrictions – which still has an acceptable fit and no substantial deterioration of the chi-square value – to be the final model [ 53 ]. Following previous recommendations, we considered a decrease in CFI of 0.01 and an increase in RMSEA of 0.015 as unacceptable to establish measurement invariance [ 54 ]. If a more stringent model had a significant worse chi-square value, but the model fit was still acceptable and the deterioration in model fit fell within the change criteria recommended for CFI and RMSEA values, we still considered the more stringent model to be superior.
Hypotheses testing
As recommended by Dormann et al. [ 55 ], we applied autoregressive time-lagged panel models to test our hypotheses. In the first step, we specified a model (M 0 ) that only included the stabilities of the three variables (procrastination, perceived stress, depression and anxiety symptoms) over time. In the next step (M 1 ), we added the time-lagged effects from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T2) and from procrastination (T2) to perceived stress (T3) as well as from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T2) and from perceived stress (T2) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3). Additionally, we included a direct path from procrastination (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3). If this path becomes significant, we can assume a partial mediation [ 55 ]. Otherwise, we can assume a full mediation. We compared these nested models using the Satorra-Bentler chi-square difference test and the Akaike information criterion (AIC). The chi-square difference value should either be non-significant, indicating that the proposed model including our hypotheses (M 1 ) does not have a significant worse model fit than the model including only stabilities (M 0 ), or, if significant, it should be in the direction that M 1 fits the data better than M 0 . Regarding the AIC, M 1 should have a lower value than M 0 .
Table 1 displays the means, standard deviations, internal consistencies (Cronbach’s alpha), and stabilities (correlations) of all study variables. The alpha values of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms are classified as good (> 0.80) [ 56 ]. The correlation matrix of the manifest variables used for the analyses can be found in the Additional file 1: Table S3 .
We observed the highest test-retest reliabilities for procrastination ( r ≥ .74). The test-retest reliabilities for depression and anxiety symptoms ( r ≥ .64) and for perceived stress ( r ≥ .54) were a bit lower (see Table 1 ). The pattern of correlations shows a medium to large but positive relationship between procrastination and depression and anxiety symptoms [ 57 , 58 ]. The association between procrastination and perceived stress was small, the one between perceived stress and depression and anxiety symptoms very large (see Table 1 ).
Confirmatory factor analysis showed an acceptable to good fit (x 2 (41) = 118.618, p < .001; SRMR = 0.042; RMSEA = 0.071; TLI = 0.95; CFI = 0.97). When testing for measurement invariance over time for each construct, the residual invariance models with indicator specific factors provided good fit to the data (M RI ; see Table 2 ), suggesting that differences in the observed variables can exclusively be attributed to differences of the latent variables. We then specified and tested the measurement model of the latent constructs prior to model testing based on the items of procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms. The measurement model fitted the data well (M M ; see Table 3 ). All items loaded solidly on their respective factors (0.791 ≤ β ≤ 0.987; p < .001).
To test our hypotheses, we analyzed the two models described in the methods section.
The fit of the stability model (M 0 ) was acceptable (see Table 3 ). Procrastination was stable over time, with stabilities above 0.82. The stabilities of perceived stress as well as depression and anxiety symptoms were somewhat lower, ranging from 0.559 (T1 -> T2) to 0.696 (T2 -> T3) for perceived stress and from 0.713 (T2 -> T3) to 0.770 (T1 -> T2) for depression and anxiety symptoms, respectively.
The autoregressive mediation model (M 1 ) fitted the data significantly better than M 0 . The direct path from procrastination (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3) was significant (β = 0.16; p < .001), however, none of the mediated paths (from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T2) and from perceived stress (T2) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3)) proved to be substantial. Also, the time-lagged paths from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T2) and from procrastination (T2) to perceived stress (T3) were not substantial either (see Fig. 3 ).
To examine whether the hypothesized effects would occur over a one-year period rather than a six-months period, we specified an additional model with paths from procrastination (T1) to perceived stress (T3) and from perceived stress (T1) to depression and anxiety symptoms (T3), also including the stabilities of the three constructs as in the stability model M 0 . The model showed an acceptable fit (χ 2 (486) = 831.281, p < .001; RMSEA = 0.048; SRMR = 0.091; TLI = 0.95; CFI = 0.95), but neither of the two paths were significant.
Therefore, our hypotheses, that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time (H1) and that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time (H2) must be rejected. We could only partially confirm our third hypothesis, that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety over time, mediated by perceived stress (H3), since procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, this effect was not mediated by perceived stress.
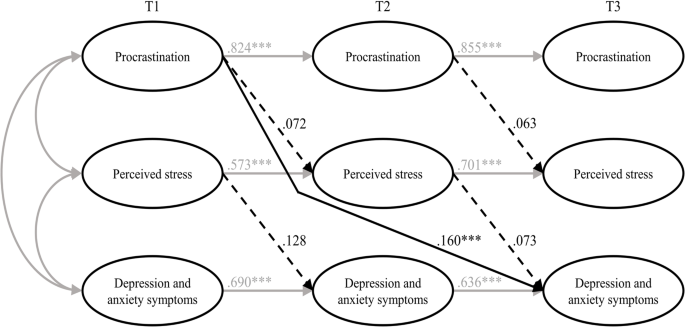
Results of the estimated model including all hypotheses (M 1 ). Note Non-significant paths are dotted. T1 = time 1; T2 = time 2; T3 = time 3. *** p < .001
To sum up, we tried to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. Hence, we selected the procrastination-health model by Sirois [ 9 ] as a theoretical foundation and tried to evaluate some of its key assumptions in a temporal perspective. The author assumes that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and postulated, in line with the key assumptions of the procrastination-health model, that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time (H1), that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time (H2), and that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, mediated by perceived stress (H3). To examine these relationships properly, we collected longitudinal data from students at three occasions over a one-year period and analyzed the data using autoregressive time-lagged panel models. Our first and second hypotheses had to be rejected: Procrastination did not lead to perceived stress over time, and perceived stress did not lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. However, procrastination did lead to depression and anxiety symptoms over time – which is in line with our third hypothesis – but perceived stress was not a mediator of this effect. Therefore, we could only partially confirm our third hypothesis.
Our results contradict previous studies on the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model, which consistently found support for the role of (chronic) stress in the relationship between trait procrastination and (chronic) disease. Since most of these studies were cross-sectional, though, the causal direction of these effects remained uncertain. There are two longitudinal studies that confirm the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model [ 27 , 28 ], but both studies examined short-term effects (≤ 3 months), whereas we focused on more long-term effects. Therefore, the divergent findings may indicate that there are short-term, but no long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress.
Our results especially raise the question whether trait procrastination leads to (chronic) stress in the long term. Looking at previous longitudinal studies on the effect of procrastination on stress, the following stands out: At shorter study periods of two weeks [ 27 ] and four weeks [ 28 ], the effect of procrastination on stress appears to be present. At longer study periods of seven weeks [ 59 ], three months [ 28 ], six months, and twelve months, as in our study, the effect of procrastination on stress does not appear to be present. There is one longitudinal study in which procrastination was a significant predictor of stress symptoms nine months later [ 34 ]. The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, though, because the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic fell within the study period, which could have contributed to increased stress symptoms [ 60 ]. Unfortunately, Johansson et al. [ 34 ] did not report whether average stress symptoms increased during their study. In one of the two studies conducted by Fincham and May [ 59 ], the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak also fell within their seven-week study period. However, they reported that in their study, average stress symptoms did not increase from baseline to follow-up. Taken together, the findings suggest that procrastination can cause acute stress in the short term, for example during times when many tasks need to be completed, such as at the end of a semester, but that procrastination does not lead to chronic stress over time. It seems possible that students are able to recover during the semester from the stress their procrastination caused at the end of the previous semester. Because of their procrastination, they may also have more time to engage in relaxing activities, which could further mitigate the effect of procrastination on stress. Our conclusions are supported by an early and well-known longitudinal study by Tice and Baumeister [ 61 ], which compared procrastinating and non-procrastinating students with regard to their health. They found that procrastinators experienced less stress than their non-procrastinating peers at the beginning of the semester, but more at the end of the semester. Additionally, our conclusions are in line with an interview study in which university students were asked about the consequences of their procrastination [ 62 ]. The students reported that, due to their procrastination, they experience high levels of stress during periods with heavy workloads (e.g., before deadlines or exams). However, the stress does not last, instead, it is relieved immediately after these periods.
Even though research indicates, in line with the assumptions of the procrastination-health model, that stress is a risk factor for physical and mental disorders [ 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 ], perceived stress did not have a significant effect on depression and anxiety symptoms in our study. The relationship between stress and mental health is complex, as people respond to stress in many different ways. While some develop stress-related mental disorders, others experience mild psychological symptoms or no symptoms at all [ 67 ]. This can be explained with the help of vulnerability-stress models. According to vulnerability-stress models, mental illnesses emerge from an interaction of vulnerabilities (e.g., genetic factors, difficult family backgrounds, or weak coping abilities) and stress (e.g., minor or major life events or daily hassles) [ 68 , 69 ]. The stress perceived by the students in our sample may not be sufficient enough on its own, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. However, since we did not assess individual vulnerability and stress factors in our study, these considerations are mere speculation.
In our study, procrastination led to depression and anxiety symptoms over time, which is consistent with the procrastination-health model as well as previous cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence [ 18 , 21 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. However, it is still unclear by which mechanisms this effect is mediated, as perceived stress did not prove to be a substantial mediator in our study. One possible mechanism would be that procrastination impairs affective well-being [ 70 ] and creates negative feelings, such as shame, guilt, regret, and anger [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 62 , 71 ], which in turn could lead to depression and anxiety symptoms [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Other potential mediators of the relationship between procrastination and depression and anxiety symptoms emerge from the behavioral pathway of the procrastination-health model, suggesting that poor health-related behaviors mediate the effect of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease. Although evidence for this is still scarce, the results of one cross-sectional study, for example, indicate that poor sleep quality might mediate the effect of procrastination on depression and anxiety symptoms [ 35 ].
In summary, we found that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time and that perceived stress is not a mediator of this effect. We could not show that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, nor that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. For the most part, the relationships between procrastination, perceived stress, and depression and anxiety symptoms did not match the relationships between trait procrastination, (chronic) stress, and (chronic) disease as assumed in the procrastination-health model. Explanations for this could be that procrastination might only lead to perceived stress in the short term, for example, during preparations for end-of-semester exams, and that perceived stress may not be sufficient enough on its own, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. In conclusion, we could not confirm long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, as assumed for the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model.
Limitations and suggestions for future research
In our study, we tried to draw causal conclusions about the harmful consequences of procrastination on students’ stress and mental health. However, since procrastination is a trait that cannot be manipulated experimentally, we have conducted an observational rather than an experimental study, which makes causal inferences more difficult. Nonetheless, a major strength of our study is that we used a longitudinal design with three waves. This made it possible to draw conclusions about the causal direction of the effects, as in hardly any other study targeting consequences of procrastination on health before [ 4 , 28 , 55 ]. Therefore, we strongly recommend using a similar longitudinal design in future studies on the procrastination-health model or on consequences of procrastination on health in general.
We chose a time lag of six months between each of the three measurement occasions to examine long-term effects of procrastination on depression and anxiety symptoms mediated by perceived stress. However, more than six months may be necessary for the hypothesized effects to occur [ 72 ]. The fact that the temporal stabilities of the examined constructs were moderate or high (0.559 ≤ β ≤ 0.854) [ 73 , 74 ] also suggests that the time lags may have been too short. The larger the time lag, the lower the temporal stabilities, as shown for depression and anxiety symptoms, for example [ 75 ]. High temporal stabilities make it more difficult to detect an effect that actually exists [ 76 ]. Nonetheless, Dormann and Griffin [ 77 ] recommend using shorter time lags of less than one year, even with high stabilities, because of other influential factors, such as unmeasured third variables. Therefore, our time lags of six months seem appropriate.
It should be discussed, though, whether it is possible to detect long-term effects of the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model within a total study period of one year. Sirois [ 9 ] distinguishes between short-term and long-term effects of procrastination on health mediated by stress, but does not address how long it might take for long-term effects to occur or when effects can be considered long-term instead of short-term. The fact that an effect of procrastination on stress is evident at shorter study periods of four weeks or less but in most cases not at longer study periods of seven weeks or more, as we mentioned earlier, could indicate that short-term effects occur within the time frame of one to three months, considering the entire stress-related pathway. Hence, it seems appropriate to assume that we have examined rather long-term effects, given our study period of six and twelve months. Nevertheless, it would be beneficial to use varying study periods in future studies, in order to be able to determine when effects can be considered long-term.
Concerning long-term effects of the stress-related pathway, Sirois [ 9 ] assumes that chronic procrastination causes chronic stress, which leads to chronic diseases over time. The term “chronic stress” refers to prolonged stress episodes associated with permanent tension. The instrument we used captures perceived stress over the last four weeks. Even though the perceived stress of the students in our sample was relatively stable (0.559 ≤ β ≤ 0.696), we do not know how much fluctuation occurred between each of the three occasions. However, there is some evidence suggesting that perceived stress is strongly associated with chronic stress [ 78 ]. Thus, it seems acceptable that we used perceived stress as an indicator for chronic stress in our study. For future studies, we still suggest the use of an instrument that can more accurately reflect chronic stress, for example, the Trier Inventory for Chronic Stress (TICS) [ 79 ].
It is also possible that the occasions were inconveniently chosen, as they all took place in a critical academic period near the end of the semester, just before the examination period began. We chose a similar period in the semester for each occasion for the sake of comparability. However, it is possible that, during this preparation periods, stress levels peaked and procrastinators procrastinated less because they had to catch up after delaying their work. This could have introduced bias to the data. Therefore, in future studies, investigation periods should be chosen that are closer to the beginning or in the middle of a semester.
Furthermore, Sirois [ 9 ] did not really explain her understanding of “chronic disease”. However, it seems clear that physical illnesses, such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, are meant. Depression and anxiety symptoms, which we chose as indicators for chronic disease, represent mental health complaints that do not have to be at the level of a major depressive disorder or an anxiety disorder, in terms of their quantity, intensity, or duration [ 40 ]. But they can be viewed as precursors to a major depressive disorder or an anxiety disorder. Therefore, given our study period of one year, it seems appropriate to use depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for chronic disease. At longer study periods, we would expect these mental health complaints to manifest as mental disorders. Moreover, the procrastination-health model was originally designed to be applied to physical diseases [ 3 ]. Perhaps, the model assumptions are more applicable to physical diseases than to mental disorders. By applying parts of the model to mental health complaints, we have taken an important step towards finding out whether the model is applicable to mental disorders as well. Future studies should examine additional long-term health outcomes, both physical and psychological. This would help to determine whether trait procrastination has varying effects on different diseases over time. Furthermore, we suggest including individual vulnerability and stress factors in future studies in order to be able to analyze the effect of (chronic) stress on (chronic) diseases in a more differentiated way.
Regarding our sample, 3,420 students took part at the first occasion, but only 392 participated three times, which results in a dropout rate of 88.5%. At the second and third occasion, invitation e-mails were only sent to participants who had indicated at the previous occasion that they would be willing to participate in a repeat survey and provided their e-mail address. This is probably one of the main reasons for our high dropout rate. Other reasons could be that the students did not receive any incentives for participating in our study and that some may have graduated between the occasions. Selective dropout analysis revealed that the mean score of procrastination was lower in the group that participated in all three waves ( n = 392) compared to the group that participated in the first wave ( n = 3,420). One reason for this could be that those who have a higher tendency to procrastinate were more likely to procrastinate on filling out our survey at the second and third occasion. The findings of our dropout analysis should be kept in mind when interpreting our results, as lower levels of procrastination may have eliminated an effect on perceived stress or on depression and anxiety symptoms. Additionally, across all age groups in population-representative samples, the student age group reports having the best subjective health [ 80 ]. Therefore, it is possible that they are more resilient to stress and experience less impairment of well-being than other age groups. Hence, we recommend that future studies focus on other age groups as well.
It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to lower academic performance, health impairment, and poor health-related behavior. However, evidence for negative consequences of procrastination is still limited and it is also unclear by which mechanisms they are mediated. In consequence, the aim of our study was to examine the effect of procrastination on mental health over time and stress as a possible facilitator of this relationship. We selected the procrastination-health model as a theoretical foundation and used the stress-related pathway of the model, assuming that trait procrastination leads to (chronic) disease via (chronic) stress. We chose depression and anxiety symptoms as indicators for (chronic) disease and collected longitudinal data from students at three occasions over a one-year period. This allowed us to draw conclusions about the causal direction of the effects, as in hardly any other study examining consequences of procrastination on (mental) health before. Our results indicate that procrastination leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time and that perceived stress is not a mediator of this effect. We could not show that procrastination leads to perceived stress over time, nor that perceived stress leads to depression and anxiety symptoms over time. Explanations for this could be that procrastination might only lead to perceived stress in the short term, for example, during preparations for end-of-semester exams, and that perceived stress may not be sufficient on its own, that is, without the presence of other risk factors, to cause depression and anxiety symptoms. Overall, we could not confirm long-term effects of trait procrastination on (chronic) disease mediated by (chronic) stress, as assumed for the stress-related pathway of the procrastination-health model. Our study emphasizes the importance of identifying the consequences procrastination can have on health and well-being and determining by which mechanisms they are mediated. Only then will it be possible to develop interventions that can prevent negative health consequences of procrastination. Further health outcomes and possible mediators should be explored in future studies, using a similar longitudinal design.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
University Health Report at Freie Universität Berlin.
Abbreviations
Comparative fit index
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale-2
Heidelberger Stress Index
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical
Robust maximum likelihood estimation
Short form of the Procrastination Questionnaire for Students
Patient Health Questionnaire-2
Patient Health Questionnaire-4
Root mean square error of approximation
Structural equation modeling
Standardized root mean square residual
Tucker-Lewis index
Lu D, He Y, Tan Y, Gender S, Status. Cultural differences, Education, family size and procrastination: a sociodemographic Meta-analysis. Front Psychol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.719425 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yan B, Zhang X. What research has been conducted on Procrastination? Evidence from a systematical bibliometric analysis. Front Psychol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809044 .
Sirois FM, Melia-Gordon ML, Pychyl TA. I’ll look after my health, later: an investigation of procrastination and health. Pers Individ Dif. 2003;35:1167–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(02)00326-4 .
Article Google Scholar
Grunschel C. Akademische Prokrastination: Eine qualitative und quantitative Untersuchung von Gründen und Konsequenzen [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]: Universität Bielefeld; 2013.
Steel P. The Nature of Procrastination: a Meta-Analytic and Theoretical Review of Quintessential Self-Regulatory failure. Psychol Bull. 2007;133:65–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.65 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Corkin DM, Yu SL, Lindt SF. Comparing active delay and procrastination from a self-regulated learning perspective. Learn Individ Differ. 2011;21:602–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.07.005 .
Balkis M, Duru E. Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2016;31:439–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-015-0266-5 .
Schulz N. Procrastination und Planung – Eine Untersuchung zum Einfluss von Aufschiebeverhalten und Depressivität auf unterschiedliche Planungskompetenzen [Doctoral dissertation]: Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster; 2007.
Sirois FM. Procrastination, stress, and Chronic Health conditions: a temporal perspective. In: Sirois FM, Pychyl TA, editors. Procrastination, Health, and well-being. London: Academic; 2016. pp. 67–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802862-9.00004-9 .
Harriott J, Ferrari JR. Prevalence of procrastination among samples of adults. Psychol Rep. 1996;78:611–6. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1996.78.2.611 .
Ferrari JR, O’Callaghan J, Newbegin I. Prevalence of Procrastination in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia: Arousal and Avoidance delays among adults. N Am J Psychol. 2005;7:1–6.
Google Scholar
Ferrari JR, Díaz-Morales JF, O’Callaghan J, Díaz K, Argumedo D. Frequent behavioral Delay tendencies by adults. J Cross Cult Psychol. 2007;38:458–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022107302314 .
Day V, Mensink D, O’Sullivan M. Patterns of academic procrastination. JCRL. 2000;30:120–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10790195.2000.10850090 .
Höcker A, Engberding M, Rist F, Prokrastination. Ein Manual Zur Behandlung Des Pathologischen Aufschiebens. 2nd ed. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2017.
Kim KR, Seo EH. The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: a meta-analysis. Pers Individ Dif. 2015;82:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038 .
Khalid A, Zhang Q, Wang W, Ghaffari AS, Pan F. The relationship between procrastination, perceived stress, saliva alpha-amylase level and parenting styles in Chinese first year medical students. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2019;12:489–98. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S207430 .
Sirois FM. I’ll look after my health, later: a replication and extension of the procrastination–health model with community-dwelling adults. Pers Individ Dif. 2007;43:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.003 .
Reinecke L, Meier A, Aufenanger S, Beutel ME, Dreier M, Quiring O, et al. Permanently online and permanently procrastinating? The mediating role of internet use for the effects of trait procrastination on psychological health and well-being. New Media Soc. 2018;20:862–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444816675437 .
Westgate EC, Wormington SV, Oleson KC, Lindgren KP. Productive procrastination: academic procrastination style predicts academic and alcohol outcomes. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2017;47:124–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12417 .
Feyzi Behnagh R, Ferrari JR. Exploring 40 years on affective correlates to procrastination: a literature review of situational and dispositional types. Curr Psychol. 2022;41:1097–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02653-z .
Rahimi S, Hall NC, Sticca F. Understanding academic procrastination: a longitudinal analysis of procrastination and emotions in undergraduate and graduate students. Motiv Emot. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-023-10010-9 .
Patrzek J, Grunschel C, Fries S. Academic procrastination: the perspective of University counsellors. Int J Adv Counselling. 2012;34:185–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-012-9150-z .
Watson D, Clark LA, Carey G. Positive and negative affectivity and their relation to anxiety and depressive disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 1988;97:346–53. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-843x.97.3.346 .
Cândea D-M, Szentagotai-Tătar A. Shame-proneness, guilt-proneness and anxiety symptoms: a meta-analysis. J Anxiety Disord. 2018;58:78–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.07.005 .
Young CM, Neighbors C, DiBello AM, Traylor ZK, Tomkins M. Shame and guilt-proneness as mediators of associations between General Causality orientations and depressive symptoms. J Soc Clin Psychol. 2016;35:357–70. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2016.35.5.357 .
Stead R, Shanahan MJ, Neufeld RW. I’ll go to therapy, eventually: Procrastination, stress and mental health. Pers Individ Dif. 2010;49:175–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.03.028 .
Dow NM. Procrastination, stress, and sleep in tertiary students [Master’s thesis]: University of Canterbury; 2018.
Sirois FM, Stride CB, Pychyl TA. Procrastination and health: a longitudinal test of the roles of stress and health behaviours. Br J Health Psychol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12658 .
Hofmann F-H, Sperth M, Holm-Hadulla RM. Psychische Belastungen Und Probleme Studierender. Psychotherapeut. 2017;62:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00278-017-0224-6 .
Liu CH, Stevens C, Wong SHM, Yasui M, Chen JA. The prevalence and predictors of mental health diagnoses and suicide among U.S. college students: implications for addressing disparities in service use. Depress Anxiety. 2019;36:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22830 .
Aftab S, Klibert J, Holtzman N, Qadeer K, Aftab S. Schemas mediate the Link between Procrastination and Depression: results from the United States and Pakistan. J Rat-Emo Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2017;35:329–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-017-0263-5 .
Flett AL, Haghbin M, Pychyl TA. Procrastination and depression from a cognitive perspective: an exploration of the associations among Procrastinatory Automatic thoughts, rumination, and Mindfulness. J Rat-Emo Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2016;34:169–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-016-0235-1 .
Saddler CD, Sacks LA. Multidimensional perfectionism and academic procrastination: relationships with Depression in University students. Psychol Rep. 1993;73:863–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/00332941930733pt123 .
Johansson F, Rozental A, Edlund K, Côté P, Sundberg T, Onell C, et al. Associations between procrastination and subsequent Health outcomes among University students in Sweden. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.49346 .
Gusy B, Jochmann A, Lesener T, Wolter C, Blaszcyk W. „Get it done – schadet Aufschieben Der Gesundheit? Präv Gesundheitsf. 2023;18:228–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11553-022-00950-4 .
Glöckner-Rist A, Engberding M, Höcker A, Rist F. Prokrastinationsfragebogen für Studierende (PFS): Zusammenstellung sozialwissenschaftlicher items und Skalen. ZIS - GESIS Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences; 2014.
Klingsieck KB, Fries S. Allgemeine Prokrastination: Entwicklung Und Validierung Einer Deutschsprachigen Kurzskala Der General Procrastination Scale (Lay, 1986). Diagnostica. 2012;58:182–93. https://doi.org/10.1026/0012-1924/a000060 .
Lay CH. At last, my research article on procrastination. J Res Pers. 1986;20:474–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3 .
Schmidt LI, Obergfell J. Zwangsjacke Bachelor?! Stressempfinden Und Gesundheit Studierender: Der Einfluss Von Anforderungen Und Entscheidungsfreiräumen Bei Bachelor- Und Diplomstudierenden Nach Karaseks Demand-Control-Modell. Saarbrücken: VDM Verlag Dr. Müller; 2011.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Löwe B. An Ultra-brief Screening Scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(09)70864-3 .
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ Primary Care Study. JAMA. 1999;282:1737–44. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.282.18.1737 .
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The Patient Health Questionnaire-2: validity of a two-item Depression Screener. Med Care. 2003;41:1284–92.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Monahan PO, Löwe B. Anxiety disorders in Primary Care: prevalence, impairment, Comorbidity, and detection. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:317–25. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-146-5-200703060-00004 .
Khubchandani J, Brey R, Kotecki J, Kleinfelder J, Anderson J. The Psychometric properties of PHQ-4 depression and anxiety screening scale among College Students. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016;30:457–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2016.01.014 .
Löwe B, Wahl I, Rose M, Spitzer C, Glaesmer H, Wingenfeld K, et al. A 4-item measure of depression and anxiety: validation and standardization of the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) in the general population. J Affect Disorders. 2010;122:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2009.06.019 .
Boomsma A, Hoogland JJ. The robustness of LISREL modeling revisited. In: Cudeck R, Du Toit S, Sörbom D, editors. Structural equation modeling: Present and Future: a festschrift in honor of Karl Jöreskog. Lincolnwood: Scientific Software International; 2001. pp. 139–68.
Hu L, Bentler PM. Fit indices in Covariance structure modeling: sensitivity to Underparameterized Model Misspecification. Psychol Methods. 1998;3:424–53. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.3.4.424 .
Schermelleh-Engel K, Moosbrugger H, Müller H. Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: test of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. MPR. 2003;8:23–74.
Hu L, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in Covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria Versus New Alternatives. Struct Equ Model. 1999;6:1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118 .
Geiser C, Eid M, Nussbeck FW, Courvoisier DS, Cole DA. Analyzing true change in Longitudinal Multitrait-Multimethod studies: application of a Multimethod Change Model to Depression and anxiety in children. Dev Psychol. 2010;46:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017888 .
Putnick DL, Bornstein MH. Measurement invariance conventions and reporting: the state of the art and future directions for psychological research. Dev Rev. 2016;41:71–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2016.06.004 .
Satorra A, Bentler PM. A scaled difference chi-square test statistic for moment structure analysis. Psychometrika. 2001;66:507–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296192 .
Geiser C. Datenanalyse Mit Mplus: Eine Anwendungsorientierte Einführung. Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Chen F, Curran PJ, Bollen KA, Kirby J, Paxton P. An empirical evaluation of the use of fixed cutoff points in RMSEA Test Statistic in Structural equation models. Sociol Methods Res. 2008;36:462–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124108314720 .
Dormann C, Zapf D, Perels F. Quer- und Längsschnittstudien in der Arbeitspsychologie [Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies in occupational psychology.]. In: Kleinbeck U, Schmidt K-H,Enzyklopädie der Psychologie [Encyclopedia of psychology]:, Themenbereich D, Serie III, Band 1, Arbeitspsychologie [Subject Area, Series D. III, Volume 1, Industrial Psychology]. Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag; 2010. pp. 923–1001.
Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1994.
Gignac GE, Szodorai ET. Effect size guidelines for individual differences researchers. Pers Indiv Differ. 2016;102:74–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.06.069 .
Funder DC, Ozer DJ. Evaluating effect size in Psychological Research: sense and nonsense. Adv Methods Practices Psychol Sci. 2019;2:156–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/2515245919847202 .
Fincham FD, May RW. My stress led me to procrastinate: temporal relations between perceived stress and academic procrastination. Coll Stud J. 2021;55:413–21.
Daniali H, Martinussen M, Flaten MA. A Global Meta-Analysis of Depression, anxiety, and stress before and during COVID-19. Health Psychol. 2023;42:124–38. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0001259 .
Tice DM, Baumeister RF. Longitudinal study of procrastination, performance, stress, and Health: the costs and benefits of Dawdling. Psychol Sci. 1997;8:454–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00460.x .
Schraw G, Wadkins T, Olafson L. Doing the things we do: a grounded theory of academic procrastination. J Educ Psychol. 2007;99:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.1.12 .
Slavich GM. Life Stress and Health: a review of conceptual issues and recent findings. Teach Psychol. 2016;43:346–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0098628316662768 .
Phillips AC, Carroll D, Der G. Negative life events and symptoms of depression and anxiety: stress causation and/or stress generation. Anxiety Stress Coping. 2015;28:357–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/10615806.2015.1005078 .
Hammen C. Stress and depression. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:293–319. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.143938 .
Blazer D, Hughes D, George LK. Stressful life events and the onset of a generalized anxiety syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 1987;144:1178–83. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.144.9.1178 .
Southwick SM, Charney DS. The Science of Resilience: implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Depression. Science. 2012;338:79–82. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222942 .
Ingram RE, Luxton DD. Vulnerability-stress models. In: Hankin BL, Abela JR, editors. Development of psychopathology: a vulnerability-stress perspective. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2005. pp. 32–46.
Chapter Google Scholar
Maercker A. Modelle Der Klinischen Psychologie. In: Petermann F, Maercker A, Lutz W, Stangier U, editors. Klinische psychologie – Grundlagen. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2018. pp. 13–31.
Krause K, Freund AM. Delay or procrastination – a comparison of self-report and behavioral measures of procrastination and their impact on affective well-being. Pers Individ Dif. 2014;63:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.01.050 .
Grunschel C, Patrzek J, Fries S. Exploring reasons and consequences of academic procrastination: an interview study. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2013;28:841–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-012-0143-4 .
Dwyer JH. Statistical models for the social and behavioral sciences. New York: Oxford University Press; 1983.
Cohen JA, Power Primer. Psychol Bull. 1992;112:155–9. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.112.1.155 .
Ferguson CJ. An effect size primer: a Guide for clinicians and Researchers. Prof Psychol Res Pr. 2009;40:532–8. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015808 .
Hinz A, Berth H, Kittel J, Singer S. Die zeitliche Stabilität (Test-Retest-Reliabilität) Von Angst Und Depressivität Bei Patienten Und in Der Allgemeinbevölkerung. Z Med Psychol. 2011;20:24–31. https://doi.org/10.3233/ZMP-2010-2012 .
Adachi P, Willoughby T. Interpreting effect sizes when controlling for stability effects in longitudinal autoregressive models: implications for psychological science. Eur J Dev Psychol. 2015;12:116–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2014.963549 .
Dormann C, Griffin M. Optimal time lags in Panel studies. Psychol Methods. 2015;20:489–505. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000041 .
Weckesser LJ, Dietz F, Schmidt K, Grass J, Kirschbaum C, Miller R. The psychometric properties and temporal dynamics of subjective stress, retrospectively assessed by different informants and questionnaires, and hair cortisol concentrations. Sci Rep. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37526-2 .
Schulz P, Schlotz W, Becker P. TICS: Trierer Inventar Zum chronischen stress. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2004.
Heidemann C, Scheidt-Nave C, Beyer A-K, Baumert J, Thamm R, Maier B, et al. Health situation of adults in Germany - results for selected indicators from GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. J Health Monit. 2021;6:3–25. https://doi.org/10.25646/8459 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Open Access Funding provided by Freie Universität Berlin.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Prevention and Psychosocial Health Research, Department of Education and Psychology, Freie Universität Berlin, Habelschwerdter Allee 45, 14195, Berlin, Germany
Anna Jochmann, Burkhard Gusy, Tino Lesener & Christine Wolter
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: A.J., B.G., T.L.; methodology: B.G., A.J.; validation: B.G.; formal analysis: A.J., B.G.; investigation: C.W., T.L., B.G.; data curation: C.W., T.L., B.G.; writing–original draft preparation: A.J., B.G.; writing–review and editing: A.J., T.L., B.G., C.W.; visualization: A.J., B.G.; supervision: B.G., T.L.; project administration: C.W., T.L., B.G.; All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Anna Jochmann or Burkhard Gusy .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Department of Education and Psychology, Freie Universität Berlin. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Selective dropout analysis and correlation matrix of the manifest variables
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jochmann, A., Gusy, B., Lesener, T. et al. Procrastination, depression and anxiety symptoms in university students: a three-wave longitudinal study on the mediating role of perceived stress. BMC Psychol 12 , 276 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01761-2
Download citation
Received : 25 May 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01761-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Student health
- Longitudinal study
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Supporting College Students During a Mental Health Crisis
It’s time we change the mental health landscape for today’s youth..
Posted May 22, 2024 | Reviewed by Davia Sills
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- A growing concern for college students and their families is the mental health support available on campus.
- College students are at increased risk of mental health problems, including stress, depression, and suicide.
- Awareness and knowledge of mental health services at higher education institutions is crucial.
When families and students explore their college and university options, they consider factors such as a school’s academics, co-curricular activities, student-body makeup, social life , and job placement for alumni.
Today, however, amid the growing mental health crisis in the U.S., an additional consideration has entered the fray—an institution’s track record and resources when it comes to supporting the mental health and well-being of its students. As part of Mental Health Awareness Month, we, as a society, need to recognize this escalating trend and commit to doing more to address the stigma that surrounds mental health, especially as it impacts our young people, and ensure that students have increased access to mental health support.
The need for increased support and awareness is urgent. The current generation of college students includes young adults who are coming of age in the wake of a pandemic, which entailed a worldwide shutdown and its ensuing isolation. Add to that landscape the prevalence of social media and the social expectations that come with it, and it is no surprise that students are facing an unprecedented array of mental health challenges.
According to a 2023 study by Gallup and the Lumina Foundation , 41 percent of students were considering dropping out of college or university, citing emotional stress and personal mental health as the top two reasons. A separate study in the spring of 2022 from the American College Health Association’s National College Health Assessment found that 75 percent of students reported moderate or serious psychological distress. Further, about 1,100 college students commit suicide each year, according to the National Institutes of Health . A student’s suicide has a significant impact on their family as well as their peers, faculty, staff, and administrators.
As U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy said during a Senate hearing in June 2023, due to the “stubborn and pervasive stigmatization of mental health” that prevents young people “from seeking help and receiving the long-term recovery supports they need,” America needs to invest in “local-level programs, policies and physical elements of a community that facilitate bringing people together.”
While local-level programming is certainly needed to combat the stigma and connect young adults with increased resources, even more important is the establishment of a national framework that puts mental health at the forefront of student needs. This initiative should increase awareness and knowledge of mental health services at higher education institutions throughout the United States and continually encourage the expansion of this support. It is essential that prospective students and their families are equipped with comprehensive knowledge and data points about the availability of the services and forms of mental health support that they may need on campus. Yet, to date, this crucial information has been glaringly absent for families when they are researching their options.
In an effort to address this problem, one recently launched initiative saw the Ruderman Family Foundation team up with The Princeton Review to create a comprehensive database on the availability of mental health resources on college and university campuses nationwide. As a society, we need to ensure that mental health needs are a priority across the board for today’s youth; only then will that filter down to a greater commitment from our colleges on the local level.
Institutions are also making strides in creating a more supportive culture and environment, even before students begin their first class. Bennington College faculty and staff, for example, assist first-year students with managing their ideas and expectations of college life. The array of initiatives emphasizes purposeful work in the world, activities promoting well-being, access to mental health counseling, an emphasis on restorative justice, and building closer connections to faculty and peers. It also attempts to empower students through arts, events, and programs to become more resilient , better attuned to their own needs, and more aware of available resources.
It is imperative that we guide students through the process of making informed decisions about their mental health in an environment void of any stigmatization or prejudice , while providing leadership , faculty, and staff with evidence-based approaches and recommendations for promoting a campus culture of caring when it comes to mental health.
More is being done than ever before to ensure that mental health support is a priority for our institutions of higher education, yet much more needs to be done to reach students before, during, and after a crisis. No one should feel ashamed or belittled or isolated because they are dealing with anxiety , depression , stress, loneliness , or any other mental health challenge. We must not stigmatize anyone who reaches out for help.

This Mental Health Awareness Month, our message is this—it’s time we change the landscape of how mental health is addressed and prioritized for today’s youth and revolutionize the way schools address the issue of mental health on their campuses.

Sharon Shapiro is Trustee and Community Liaison at the Ruderman Family Foundation. Laura Walker is the eleventh president of Bennington College.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Broken drink machine, smoking cannabis: Groups of Brockton students can stress restaurants
BROCKTON —– Charleys Cheesesteaks sits across Belmont Street from Brockton High Schoo l. The restaurant’s Manager Barry Hoffman said a group of 20 or so BHS students will come in nearly every day from the time school lets out at 1:50 until 3 p.m.
He said one kid will buy something while the others hang out at the tables or clump in front of the store’s doorway. A month or two ago, Hoffman said, the students took the fire extinguisher off the wall and sprayed it inside the restaurant.
“It’s just kids being kids and they don’t respect other people,” he said. “We have to put stipulations on the kids.”
Hoffman started setting rules for the BHS students who come by his restaurant. If they don’t order food, he’ll usually make them leave.
“We wouldn’t let kids in without a parent because it’s out of control,” Hoffman said. “I’ve called the cops a couple times.”
Inside BHS, a small group of students has been causing chaos throughout the building, and Interim Principal José Duarte said that some students leave the school’s campus during the day and head to the local businesses.
What about the Belmont Street McDonald's?
Hoffman’s shop isn’t the only business surrounding the school where managers say students cause trouble. Deunilson Medina, general manager of the Belmont Street McDonald’s, said students will smoke marijuana in his store’s parking lot or bathrooms.
“That’s the major concern,” he said.
Medina said roughly 60 kids will come to the McDonald's every weekday, and he estimated that 40% don’t buy anything.
“Sometimes we have to call the police officers,” Medina said.
'This isn't a good reflection' Mayor creates tie for School Committee vice chair position
Brockton High students at local businesses
At the Burger King just down the street from Brockton High, Manager Keny da Silva said a group of students broke a drink machine about a year ago. It still hasn’t been fixed.
The Burger King has been open at that location since before 2000, and da Silva said the problem has existed for a long time.
“It was bad before, really bad,” she said. “Now, it’s okay.”
BPS teachers depict chaos in school 'Never seen Brockton High in such disarray'
Do students leave Brockton High during school hours?
In November, one week after Duarte took over at BHS, he said the school would crack down on students leaving the building and going to nearby businesses during school hours.
Medina and Hoffman confirmed they see students at their stores during school hours, but the damage mostly comes right after school.
"We will enforce consequences for those who leave the school grounds without permission and remind seniors about the appropriate protocols for signing out prior to exercising their senior privileges," Duarte said.
What is the school department doing about it?
BPS officials declined to comment when asked by The Enterprise if the school has implemented any preventive action plans.
But, Hoffman said he’s been to the school to discuss the problem, and Medina said McDonald's and the school “do have a great relationship.”
“Since [Duarte's] come on board, it seems the high school is getting better,” Medina said. “They’re definitely doing something better.”
Are things improving? Brockton High principal paints stark picture of just how chaotic school has become
Helping or hurting business?
Medina said being located across from the school means a few students will place mobile orders and bring in more business, but the disruptions caused by students does drive other customers away. He said there are positives and negatives.
A new Starbucks is under construction adjacent to Medina's McDonald's. The drive-thru coffee shop was approved by the city in April 2023.
Hoffman said the problems are greatest at the start of the school year and it becomes a daily routine throughout the year until things slow down by the summer season.
“We have to go through the process every step every time," he said.

COMMENTS
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with: * Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up." Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well.
Effects of homework stress at home. Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.. Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students. Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and ...
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
Health Hazards of Homework. Pediatrics. A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework "experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.".
shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a ... "More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our ...
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress, defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems. • Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework, even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study.
Keywords: homework, stress, mental health The outcomes of adolescent mental health is a threat to students' health and wellbeing, more so than it ever has been in the modern era. As of 2019, the CDC reported a nearly 40. percent increase in feelings of sadness or hopelessness over the last ten years, and similar.
"It can motivate students to be organized. But too much stress can backfire." ... Homework was a leading cause of stress, with 24 percent of parents saying it's an issue.
Research shows that excessive homework leads to increased stress, physical health problems and a lack of balance in students' lives. And studies have shown that more than two hours of daily homework can be counterproductive, yet many teachers assign more.. Homework proponents argue that homework improves academic performance. Indeed, a meta-analysis of research on this issue found a ...
Studies of typical homework loads vary: In one, a Stanford researcher found that more than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive.The research, conducted among students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities, found that too much homework resulted in stress, physical health problems and a general lack of balance.
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
It's no secret that homework causes stress for many students. Whether it's a big test around the corner or an upcoming deadline for an assignment, sometimes it can be impossible to avoid homework stress. From Grades one through twelve, homework is a big part of children's education. But when homework causes frustration and leads to ...
That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right. Students, read the entire article, then tell us ...
Stress is the body's emotional, physical, or behavioral response to environmental change. Stress can be a short-term reaction in response to an upcoming event, such as homework deadlines, an upcoming exam, or speaking in front of the class. Stress can also result from traumatic or ongoing experiences, such as coping with parents' divorce ...
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress: • Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming. • Sleep Disturbances: Homework-related stress ...
Educators and parents have long been concerned about students stressed by homework loads, but a small research study asked questions recently about homework and anxiety of a different group: parents. The results were unsurprising. While we may have already learned long division and let the Magna Carta fade into memory, parents report that their children's homework causes family stress and ...
According to a new study, conducted by the Better Sleep Council, that homework stress is the biggest source of frustration for teens, with 74 percent of those surveyed ranking it the highest ...
Homework as we have experienced causes a great amount of stress which can lead you to a poor mental state, sleep deprivation, and many more bad things. Which can be prevented by decreasing the amount of homework significantly and/or being taught how to combat such stress. [A couple of such ways is by managing time, controlling emotions, and ...
Background It is generally assumed that procrastination leads to negative consequences. However, evidence for negative consequences of procrastination is still limited and it is also unclear by which mechanisms they are mediated. Therefore, the aim of our study was to examine the harmful consequences of procrastination on students' stress and mental health. We selected the procrastination ...
According to a 2023 study by Gallup and the Lumina Foundation, 41 percent of students were considering dropping out of college or university, citing emotional stress and personal mental health as ...
Medina said being located across from the school means a few students will place mobile orders and bring in more business, but the disruptions caused by students does drive other customers away ...