- Patient Care & Health Information
- Diseases & Conditions
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
COVID-19, also called coronavirus disease 2019, is an illness caused by a virus. The virus is called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, or more commonly, SARS-CoV-2. It started spreading at the end of 2019 and became a pandemic disease in 2020.
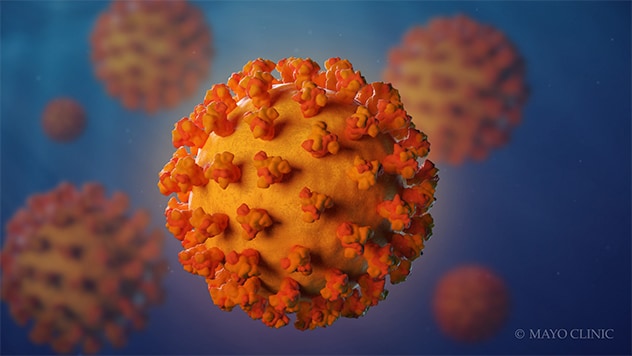
- Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses. These viruses cause illnesses such as the common cold, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
The virus that causes COVID-19 spreads most commonly through the air in tiny droplets of fluid between people in close contact. Many people with COVID-19 have no symptoms or mild illness. But for older adults and people with certain medical conditions, COVID-19 can lead to the need for care in the hospital or death.
Staying up to date on your COVID-19 vaccine helps prevent serious illness, the need for hospital care due to COVID-19 and death from COVID-19 . Other ways that may help prevent the spread of this coronavirus includes good indoor air flow, physical distancing, wearing a mask in the right setting and good hygiene.
Medicine can limit the seriousness of the viral infection. Most people recover without long-term effects, but some people have symptoms that continue for months.

Products & Services
- A Book: Endemic - A Post-Pandemic Playbook
- A Book: Future Care
- Begin Exploring Women's Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
Typical COVID-19 symptoms often show up 2 to 14 days after contact with the virus.
Symptoms can include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Loss of taste or smell.
- Extreme tiredness, called fatigue.
- Digestive symptoms such as upset stomach, vomiting or loose stools, called diarrhea.
- Pain, such as headaches and body or muscle aches.
- Fever or chills.
- Cold-like symptoms such as congestion, runny nose or sore throat.
People may only have a few symptoms or none. People who have no symptoms but test positive for COVID-19 are called asymptomatic. For example, many children who test positive don't have symptoms of COVID-19 illness. People who go on to have symptoms are considered presymptomatic. Both groups can still spread COVID-19 to others.
Some people may have symptoms that get worse about 7 to 14 days after symptoms start.
Most people with COVID-19 have mild to moderate symptoms. But COVID-19 can cause serious medical complications and lead to death. Older adults or people who already have medical conditions are at greater risk of serious illness.
COVID-19 may be a mild, moderate, severe or critical illness.
- In broad terms, mild COVID-19 doesn't affect the ability of the lungs to get oxygen to the body.
- In moderate COVID-19 illness, the lungs also work properly but there are signs that the infection is deep in the lungs.
- Severe COVID-19 means that the lungs don't work correctly, and the person needs oxygen and other medical help in the hospital.
- Critical COVID-19 illness means the lung and breathing system, called the respiratory system, has failed and there is damage throughout the body.
Rarely, people who catch the coronavirus can develop a group of symptoms linked to inflamed organs or tissues. The illness is called multisystem inflammatory syndrome. When children have this illness, it is called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, shortened to MIS -C. In adults, the name is MIS -A.
When to see a doctor
Contact a healthcare professional if you test positive for COVID-19 . If you have symptoms and need to test for COVID-19 , or you've been exposed to someone with COVID-19 , a healthcare professional can help.
People who are at high risk of serious illness may get medicine to block the spread of the COVID-19 virus in the body. Or your healthcare team may plan regular checks to monitor your health.
Get emergency help right away for any of these symptoms:
- Can't catch your breath or have problems breathing.
- Skin, lips or nail beds that are pale, gray or blue.
- New confusion.
- Trouble staying awake or waking up.
- Chest pain or pressure that is constant.
This list doesn't include every emergency symptom. If you or a person you're taking care of has symptoms that worry you, get help. Let the healthcare team know about a positive test for COVID-19 or symptoms of the illness.
More Information
- COVID-19 vs. flu: Similarities and differences
- COVID-19, cold, allergies and the flu
- Unusual symptoms of coronavirus
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
COVID-19 is caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, also called SARS-CoV-2.
The coronavirus spreads mainly from person to person, even from someone who is infected but has no symptoms. When people with COVID-19 cough, sneeze, breathe, sing or talk, their breath may be infected with the COVID-19 virus.
The coronavirus carried by a person's breath can land directly on the face of a nearby person, after a sneeze or cough, for example. The droplets or particles the infected person breathes out could possibly be breathed in by other people if they are close together or in areas with low air flow. And a person may touch a surface that has respiratory droplets and then touch their face with hands that have the coronavirus on them.
It's possible to get COVID-19 more than once.
- Over time, the body's defense against the COVID-19 virus can fade.
- A person may be exposed to so much of the virus that it breaks through their immune defense.
- As a virus infects a group of people, the virus copies itself. During this process, the genetic code can randomly change in each copy. The changes are called mutations. If the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 changes in ways that make previous infections or vaccination less effective at preventing infection, people can get sick again.
The virus that causes COVID-19 can infect some pets. Cats, dogs, hamsters and ferrets have caught this coronavirus and had symptoms. It's rare for a person to get COVID-19 from a pet.
Risk factors
The main risk factors for COVID-19 are:
- If someone you live with has COVID-19 .
- If you spend time in places with poor air flow and a higher number of people when the virus is spreading.
- If you spend more than 30 minutes in close contact with someone who has COVID-19 .
Many factors affect your risk of catching the virus that causes COVID-19 . How long you are in contact, if the space has good air flow and your activities all affect the risk. Also, if you or others wear masks, if someone has COVID-19 symptoms and how close you are affects your risk. Close contact includes sitting and talking next to one another, for example, or sharing a car or bedroom.
It seems to be rare for people to catch the virus that causes COVID-19 from an infected surface. While the virus is shed in waste, called stool, COVID-19 infection from places such as a public bathroom is not common.
Serious COVID-19 illness risk factors
Some people are at a higher risk of serious COVID-19 illness than others. This includes people age 65 and older as well as babies younger than 6 months. Those age groups have the highest risk of needing hospital care for COVID-19 .
Not every risk factor for serious COVID-19 illness is known. People of all ages who have no other medical issues have needed hospital care for COVID-19 .
Known risk factors for serious illness include people who have not gotten a COVID-19 vaccine. Serious illness also is a higher risk for people who have:
- Sickle cell disease or thalassemia.
- Serious heart diseases and possibly high blood pressure.
- Chronic kidney, liver or lung diseases.
People with dementia or Alzheimer's also are at higher risk, as are people with brain and nervous system conditions such as stroke. Smoking increases the risk of serious COVID-19 illness. And people with a body mass index in the overweight category or obese category may have a higher risk as well.
Other medical conditions that may raise the risk of serious illness from COVID-19 include:
- Cancer or a history of cancer.
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- Weakened immune system from solid organ transplants or bone marrow transplants, some medicines, or HIV .
This list is not complete. Factors linked to a health issue may raise the risk of serious COVID-19 illness too. Examples are a medical condition where people live in a group home, or lack of access to medical care. Also, people with more than one health issue, or people of older age who also have health issues have a higher chance of severe illness.
Related information
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? - Related information COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
Complications
Complications of COVID-19 include long-term loss of taste and smell, skin rashes, and sores. The illness can cause trouble breathing or pneumonia. Medical issues a person already manages may get worse.
Complications of severe COVID-19 illness can include:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome, when the body's organs do not get enough oxygen.
- Shock caused by the infection or heart problems.
- Overreaction of the immune system, called the inflammatory response.
- Blood clots.
- Kidney injury.
Post-COVID-19 syndrome
After a COVID-19 infection, some people report that symptoms continue for months, or they develop new symptoms. This syndrome has often been called long COVID, or post- COVID-19 . You might hear it called long haul COVID-19 , post-COVID conditions or PASC. That's short for post-acute sequelae of SARS -CoV-2.
Other infections, such as the flu and polio, can lead to long-term illness. But the virus that causes COVID-19 has only been studied since it began to spread in 2019. So, research into the specific effects of long-term COVID-19 symptoms continues.
Researchers do think that post- COVID-19 syndrome can happen after an illness of any severity.
Getting a COVID-19 vaccine may help prevent post- COVID-19 syndrome.
- Long-term effects of COVID-19
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a COVID-19 vaccine for everyone age 6 months and older. The COVID-19 vaccine can lower the risk of death or serious illness caused by COVID-19.
The COVID-19 vaccines available in the United States are:
2023-2024 Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 6 months and older.
Among people with a typical immune system:
- Children age 6 months up to age 4 years are up to date after three doses of a Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
- People age 5 and older are up to date after one Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
- For people who have not had a 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccination, the CDC recommends getting an additional shot of that updated vaccine.
2023-2024 Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 6 months and older.
- Children ages 6 months up to age 4 are up to date if they've had two doses of a Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
- People age 5 and older are up to date with one Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
2023-2024 Novavax COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 12 years and older.
- People age 12 years and older are up to date if they've had two doses of a Novavax COVID-19 vaccine.
In general, people age 5 and older with typical immune systems can get any vaccine approved or authorized for their age. They usually don't need to get the same vaccine each time.
Some people should get all their vaccine doses from the same vaccine maker, including:
- Children ages 6 months to 4 years.
- People age 5 years and older with weakened immune systems.
- People age 12 and older who have had one shot of the Novavax vaccine should get the second Novavax shot in the two-dose series.
Talk to your healthcare professional if you have any questions about the vaccines for you or your child. Your healthcare team can help you if:
- The vaccine you or your child got earlier isn't available.
- You don't know which vaccine you or your child received.
- You or your child started a vaccine series but couldn't finish it due to side effects.
People with weakened immune systems
Your healthcare team may suggest added doses of COVID-19 vaccine if you have a moderately or seriously weakened immune system. The FDA has also authorized the monoclonal antibody pemivibart (Pemgarda) to prevent COVID-19 in some people with weakened immune systems.
Control the spread of infection
In addition to vaccination, there are other ways to stop the spread of the virus that causes COVID-19 .
If you are at a higher risk of serious illness, talk to your healthcare professional about how best to protect yourself. Know what to do if you get sick so you can quickly start treatment.
If you feel ill or have COVID-19 , stay home and away from others, including pets, if possible. Avoid sharing household items such as dishes or towels if you're sick.
In general, make it a habit to:
- Test for COVID-19 . If you have symptoms of COVID-19 test for the infection. Or test five days after you came in contact with the virus.
- Help from afar. Avoid close contact with anyone who is sick or has symptoms, if possible.
- Wash your hands. Wash your hands well and often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. Or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes. Cough or sneeze into a tissue or your elbow. Then wash your hands.
- Clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces. For example, clean doorknobs, light switches, electronics and counters regularly.
Try to spread out in crowded public areas, especially in places with poor airflow. This is important if you have a higher risk of serious illness.
The CDC recommends that people wear a mask in indoor public spaces if you're in an area with a high number of people with COVID-19 in the hospital. They suggest wearing the most protective mask possible that you'll wear regularly, that fits well and is comfortable.
- COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts - Related information COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts
- Comparing the differences between COVID-19 vaccines - Related information Comparing the differences between COVID-19 vaccines
- Different types of COVID-19 vaccines: How they work - Related information Different types of COVID-19 vaccines: How they work
- Debunking COVID-19 myths - Related information Debunking COVID-19 myths
Travel and COVID-19
Travel brings people together from areas where illnesses may be at higher levels. Masks can help slow the spread of respiratory diseases in general, including COVID-19 . Masks help the most in places with low air flow and where you are in close contact with other people. Also, masks can help if the places you travel to or through have a high level of illness.
Masking is especially important if you or a companion have a high risk of serious illness from COVID-19 .
- COVID-19 travel advice
- COVID-19 vaccines
- COVID-19 vaccines for kids: What you need to know
- Debunking coronavirus myths
- Different COVID-19 vaccines
- Fight coronavirus (COVID-19) transmission at home
- Herd immunity and coronavirus
- How well do face masks protect against COVID-19?
- Safe outdoor activities during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Safety tips for attending school during COVID-19
- COVID-19 and vitamin D
- COVID-19: How can I protect myself?
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How dirty are common surfaces?
- Mayo Clinic Minute: You're washing your hands all wrong
- Goldman L, et al., eds. COVID-19: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, community prevention, and prognosis. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Elsevier; 2024. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed Dec. 17, 2023.
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed Dec. 18, 2023.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Testing, symptoms. Mayo Clinic; Nov. 2, 2023.
- Symptoms of COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html. Accessed Dec. 20, 2023.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Outpatient management. Mayo Clinic; Oct. 10, 2023.
- Morris SB, et al. Case series of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection — United Kingdom and United States, March-August 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2020;69:1450. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6940e1external icon.
- COVID-19 testing: What you need to know. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/testing.html. Accessed Dec. 20, 2023.
- SARS-CoV-2 in animals. American Veterinary Medical Association. https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/one-health/covid-19/sars-cov-2-animals-including-pets. Accessed Jan. 17, 2024.
- Understanding exposure risk. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/risks-exposure.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- People with certain medical conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Factors that affect your risk of getting very sick from COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/risks-getting-very-sick.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Regan JJ, et al. Use of Updated COVID-19 Vaccines 2023-2024 Formula for Persons Aged ≥6 Months: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, September 2023. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2023; 72:1140–1146. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7242e1.
- Long COVID or post-COVID conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Stay up to date with your vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html#CoV-19-vaccination. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Use and care of masks. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/about-face-coverings.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- How to protect yourself and others. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- People who are immunocompromised. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-who-are-immunocompromised.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Masking during travel. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/masks. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Testing. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- COVID-19 test basics. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/covid-19-test-basics. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- At-home COVID-19 antigen tests — Take steps to reduce your risk of false negative results: FDA safety communication. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/home-covid-19-antigen-tests-take-steps-reduce-your-risk-false-negative-results-fda-safety. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- Interim clinical considerations for COVID-19 treatment in outpatients. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/outpatient-treatment-overview.html. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- Know your treatment options for COVID-19. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID:19 Drug regimens and other treatment options. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- Preventing spread of respiratory viruses when you're sick. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/prevention/precautions-when-sick.html. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Quarantine and isolation. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- COVID-19 resource and information guide. National Alliance on Mental Illness. https://www.nami.org/Support-Education/NAMI-HelpLine/COVID-19-Information-and-Resources/COVID-19-Resource-and-Information-Guide. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- COVID-19 overview and infection prevention and control priorities in non-U.S. healthcare settings. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/non-us-settings/overview/index.html. Accessed Jan. 16, 2024.
- Kim AY, et al. COVID-19: Management in hospitalized adults. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Jan. 17, 2024.
- O'Horo JC, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 with the Mayo Clinic Model of Care and Research. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2021; doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.006.
- At-home OTC COVID-19 diagnostic tests. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/home-otc-covid-19-diagnostic-tests. Accessed Jan. 22, 2024.
- Emergency use authorizations for drugs and non-vaccine biological products. U.S. Food and Drug Association. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/emergency-use-authorizations-drugs-and-non-vaccine-biological-products. Accessed March 25, 2024.
- Coronavirus infection by race
- COVID-19 and pets
- COVID-19 and your mental health
- COVID-19 drugs: Are there any that work?
- COVID-19 in babies and children
- COVID-19 variant
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
- How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
- Is hydroxychloroquine a treatment for COVID-19?
- Pregnancy and COVID-19
- Sex and COVID-19
- Treating COVID-19 at home
Associated Procedures
- Convalescent plasma therapy
- COVID-19 antibody testing
- COVID-19 tests
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
News from Mayo Clinic
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Who should get the latest COVID-19 vaccine? Nov. 21, 2023, 01:30 p.m. CDT
- Can you get COVID-19 and the flu at the same time? A Mayo Clinic expert weighs in Oct. 16, 2023, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- At-home COVID-19 tests: A Mayo Clinic expert answers questions on expiration dates and the new variants Sept. 18, 2023, 04:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert answers questions about the new COVID-19 vaccine Sept. 13, 2023, 04:15 p.m. CDT
- Study identifies risk factors for long-haul COVID disease in adults Sept. 13, 2023, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo researchers find vaccine may reduce severity of long-haul COVID symptoms Aug. 23, 2023, 04:34 p.m. CDT
- Corticosteroids lower the likelihood of in-hospital mortality from COVID-19 Aug. 04, 2023, 03:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 vaccine administration simplified April 21, 2023, 07:00 p.m. CDT
- Science Saturday: COVID-19 -- the pandemic that's forever changed laboratory testing April 15, 2023, 11:00 a.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert talks about the new omicron variant April 13, 2023, 02:13 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic to ease universal face mask requirement April 04, 2023, 03:05 p.m. CDT
- 'Deaths of Despair' contribute to 17% rise in Minnesota's death rate during COVID-19 pandemic March 13, 2023, 12:00 p.m. CDT
- Rising cases of COVID-19 variant, XBB.1.5 Jan. 09, 2023, 05:15 p.m. CDT
- Bivalent COVID-19 booster approved for children 6 months and older Dec. 09, 2022, 09:33 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How to self-care at home when you have COVID-19 Dec. 06, 2022, 05:00 p.m. CDT
- Halloween safety tips from a Mayo Clinic infectious diseases expert Oct. 27, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19, RSV and flu--season of respiratory infections Oct. 26, 2022, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccines for kids 5-11 approved, Mayo Clinic awaits supply Oct. 13, 2022, 04:54 p.m. CDT
- Questions answered about the COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccines Oct. 12, 2022, 03:30 p.m. CDT
- Will the COVID-19 booster be like an annual flu shot? Sept. 12, 2022, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Who needs back-to-school COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters? Sept. 04, 2022, 11:00 a.m. CDT
- Q&A podcast: Updated COVID-19 boosters target omicron variants Sept. 02, 2022, 12:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Back-to-school COVID-19 vaccinations for kids Aug. 15, 2022, 03:15 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic research shows bebtelovimab to be a reliable option for treating COVID-19 in era of BA.2, other subvariants Aug. 15, 2022, 02:09 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: New variants of COVID-19 Aug. 04, 2022, 12:30 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 variant BA.5 is dominant strain; BA.2.75 is being monitored July 28, 2022, 02:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic researchers pinpoint genetic variations that might sway course of COVID-19 July 25, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: BA.5 omicron variant fueling latest COVID-19 surge July 15, 2022, 12:00 p.m. CDT
- What you need to know about the BA.5 omicron variant July 14, 2022, 06:41 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: The importance of COVID-19 vaccines for children under 5 July 06, 2022, 01:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 vaccination for kids age 5 and younger starting the week of July 4 at most Mayo sites July 01, 2022, 04:00 p.m. CDT
- Patients treated with monoclonal antibodies during COVID-19 delta surge had low rates of severe disease, Mayo Clinic study finds June 27, 2022, 03:00 p.m. CDT
- Long COVID and the digestive system: Mayo Clinic expert describes common symptoms June 21, 2022, 02:43 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: COVID-19 update June 17, 2022, 01:08 p.m. CDT
- Study finds few COVID-19 patients get rebound symptoms after Paxlovid treatment June 14, 2022, 10:06 a.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: What to expect with COVID-19 vaccinations for youngest kids June 08, 2022, 04:35 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: Community leaders are key to reaching people underrepresented in research May 26, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 booster vaccinations extended to kids 5-11 May 20, 2022, 06:10 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert shares tips for navigating a return to work with long COVID May 19, 2022, 02:08 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: COVID-19 update May 17, 2022, 01:14 p.m. CDT
- Symptoms & causes
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Doctors & departments
- COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts
- How well do face masks protect against coronavirus?
- Post-COVID Recovery
News on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Learn the latest medical news about COVID-19 on Mayo Clinic News Network.
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
About COVID-19
What is covid-19.
COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) is a disease caused by a virus named SARS-CoV-2. It can be very contagious and spreads quickly. Over one million people have died from COVID-19 in the United States.
COVID-19 most often causes respiratory symptoms that can feel much like a cold, the flu, or pneumonia. COVID-19 may attack more than your lungs and respiratory system. Other parts of your body may also be affected by the disease. Most people with COVID-19 have mild symptoms, but some people become severely ill.
Some people including those with minor or no symptoms will develop Post-COVID Conditions – also called “Long COVID.”
How does COVID-19 spread?
COVID-19 spreads when an infected person breathes out droplets and very small particles that contain the virus. Other people can breathe in these droplets and particles, or these droplets and particles can land on their eyes, nose, or mouth. In some circumstances, these droplets may contaminate surfaces they touch.
Anyone infected with COVID-19 can spread it, even if they do NOT have symptoms.
The risk of animals spreading the virus that causes COVID-19 to people is low. The virus can spread from people to animals during close contact. People with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 should avoid contact with animals.
What are antibodies and how do they help protect me?
Antibodies are proteins your immune system makes to help fight infection and protect you from getting sick in the future. A positive antibody test result can help identify someone who has had COVID-19 in the past or has been vaccinated against COVID-19. Studies show that people who have antibodies from an infection with the virus that causes COVID-19 can improve their level of protection by getting vaccinated.
Who is at risk of severe illness from COVID-19?
Some people are more likely than others to get very sick if they get COVID-19. This includes people who are older , are immunocompromised (have a weakened immune system), have certain disabilities , or have underlying health conditions . Understanding your COVID-19 risk and the risks that might affect others can help you make decisions to protect yourself and others .
What are ways to prevent COVID-19?
There are many actions you can take to help protect you, your household, and your community from COVID-19. CDC’s Respiratory Virus Guidance provides actions you can take to help protect yourself and others from health risks caused by respiratory viruses, including COVID-19. These actions include steps you can take to lower the risk of COVID-19 transmission (catching and spreading COVID-19) and lower the risk of severe illness if you get sick.
CDC recommends that you
- Stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines
- Practice good hygiene (practices that improve cleanliness)
- Take steps for cleaner air
- Stay home when sick
- Seek health care promptly for testing and treatment when you are sick if you have risk factors for severe illness . Treatment may help lower your risk of severe illness.
Masks , physical distancing , and tests can provide additional layers of protection.
What are variants of COVID-19?
Viruses are constantly changing, including the virus that causes COVID-19. These changes occur over time and can lead to new strains of the virus or variants of COVID-19 . Slowing the spread of the virus, by protecting yourself and others , can help slow new variants from developing. CDC is working with state and local public health officials to monitor the spread of all variants, including Omicron.
- COVID-19 Testing
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Preventing Respiratory Viruses
- Reinfection
- Difference Between Flu and COVID-19
- COVID Data Tracker
Search for and find historical COVID-19 pages and files. Please note the content on these pages and files is no longer being updated and may be out of date.
- Visit archive.cdc.gov for a historical snapshot of the COVID-19 website, capturing the end of the Federal Public Health Emergency on June 28, 2023.
- Visit the dynamic COVID-19 collection to search the COVID-19 website as far back as July 30, 2021.
To receive email updates about COVID-19, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Create mode – the default mode when you create a requisition and PunchOut to Bio-Rad. You can create and edit multiple shopping carts
- Edit mode – allows you to edit or modify an existing requisition (prior to submitting). You will be able to modify only the cart that you have PunchedOut to, and will not have access to any other carts
- Inspect mode – when you PunchOut to Bio-Rad from a previously created requisition but without initiating an Edit session, you will be in this mode. You cannot modify any Cart contents
- Order Status
- Quick Order
- Bioprocessing
- Clinical Research
- Drug Discovery & Development
- Translational Research
- Wastewater Surveillance
- Diabetes / Hemoglobinopathies
- Hospital / Clinical Core Lab
- Infectious Disease
- Newborn Screening
- Transfusion Medicine
- Quality Control
- Food & Beverage Testing
- Classroom Education
- Bioprocess Analytics
- Bioprocess Chromatography
- Cell Line Development / Characterization
- Cell Research
- Gene Expression Analysis
- Mutation Detection
- Pathogen Detection
- Protein Expression / Characterization / Quantitation
- Viral / Vector Characterization
- Bacteriology
- Blood Typing, Screening & Antibody Identification
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Infectious Disease Testing
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Data Management Systems
- Proficiency Testing & EQAS
- Verification & Validation
- Food & Beverage Safety Testing
- Cannabis Testing
- Veterinary Diagnostics
- Water Quality Testing
- Biotechnology Textbook & Program
- DNA, PCR & Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
- Genetic Engineering, Microbiology & Model Organisms
- Proteins, Enzymes & ELISA
- COVID-19 Assay & Research
- Cell Isolation & Analysis
- Chromatography
- Digital PCR
- Electrophoresis & Blotting
- Flow Cytometers
- Immunoassays
- PCR & qPCR
- Sample Preparation & Quantitation
- Transfection
- Autoimmune Testing
- Blood Typing & Antibody Detection
- Diabetes Testing
- Hemoglobinopathy Testing
- Microbiology Testing
- Quality Controls
- Software & Data Analysis
- Molecular Testing
- B2B Commerce Solutions
- Custom PCR Plastics & Reagents
- Expert Care Service
- New Labs & New Grants
- Remote Diagnostic Services
- Supply Center Program
- Instrument Service Support Plans
- Trade-Up Program
- Certificate of Analysis
- Literature Library
- Electronic IFUs
- Product Safety Data Sheets
- Quality Management Systems Certificates
- Quality Control Inserts
- Life Science
- Clinical Testing Solutions
- Bioprocess Chromatography Resources
- Classroom Resources
- Product News
- Corporate News
COVID-19 Teaching Resources

Your students may have a lot of questions about COVID-19, from how it spreads to how it is detected and how it can be treated. This presents a rich opportunity to teach key concepts in biology through the lens of an ongoing real-world context. Bio-Rad offers a flexible array of hands-on kits, free resources, and lessons to help you teach the biology and detection of the SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The Biology of SARS-CoV-2 and Detection Methods

What Is the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus?
Help your students understand the biology of SARS-CoV-2 by reviewing its origin, structure, and ways to prevent the spread of infection. This PowerPoint presentation walks you and your students through key biology concepts of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
Download PPT (PPT 16.3 MB)

How Do We Detect COVID-19?
Every day brings new developments in the race for effective and accurate COVID-19 testing, but most strategies are based on a few key fundamental technologies. This PowerPoint presentation explains some fundamental techniques and emerging strategies in COVID-19 detection.
Download PPT (PPT 23.3 MB)
Hands-On Laboratory Activities for Your Students
Teach your students the science behind SARS-CoV-2 detection using these hands-on laboratory activities. Use these three Bio-Rad Explorer Classroom Kits to teach relevant life science concepts in the context of COVID-19.
ELISA Antibody Detection
Several existing and emerging SARS-CoV-2 detection methods rely on the specificity of antibodies. In this activity, use real antibodies to determine whether simulated patients are or were infected with SARS-CoV-2.
This activity uses the reagents and antibodies from the ELISA Immuno Explorer Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 23.3 MB)

PCR Detection
Investigate the real life spread of SARS-CoV-2 that occurred in a restaurant. In this activity, students use agarose gel electrophoresis to analyze pre-amplified DNA samples from simulated patients and propose ways the virus may have spread.
This activity uses the Virus Detection and Transmission Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 13.4 MB)
Real-Time PCR Detection
Real-time PCR is currently the gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis. In this activity, use real-time PCR to detect SARS-CoV-2 in simulated patient samples. Students analyze amplification and melt curves to determine which patients are positive and then quantify viral RNA.
This activity uses the reagents and DNA samples from the Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Real-Time PCR Starter Kit .
Download the instructions and presentation (PPT 27.4 MB)

Additional Resources
ELISA Paper Model Activity
Your students can use this paper model activity to get a solid grasp of the components of an ELISA and how they work together in antibody/antigen detection.
Download PDF (PDF 2.6 MB) Download PPT (PPT 65.9 MB)
Animation: ELISA Antibody Test Animation: ELISA Antigen Test
Visualize two types of ELISA in these step-by-step animations.
Animation: Polymerase Chain Reaction
The steps of PCR are best visualized through animation.
These pages list our product offerings in these areas. Some products have limited regional availability. If you have a specific question about products available in your area, please contact your local sales office or representative .
- Bio-rad LinkedIn Bio-rad Antibodies LinkedIn
- Bio-rad YouTube Bio-rad Antibodies YouTube
- Bio-rad Twitter Bio-rad Antibodies Twitter
- Bio-rad Facebook Bio-rad Antibodies Facebook
- Bio-rad Instagram
- Bio-rad Pinterest
About Bio-Rad
Bioradiations, sustainability, investor relations.
What is 'FLiRT' COVID? Scientists predict spike of new coronavirus variants
by JACKSON WALKER | The National Desk

WASHINGTON (TND) — Scientists are forecasting a rise in coronavirus cases throughout May as a new set of variants emerges, according to disease researcher Eric Topol.
The variants, known as “FLiRT,” are distinguished by mutations in the disease’s spike proteins. These proteins help viruses attach to surfaces and are one of the factors behind the infectious nature of COVID-19.
FliRT variants have mutations in areas designated “F for L” and “R for T,” Topol wrote via Substack. While these variants could lead to a rise in cases of COVID-19, Topol, who is a professor of molecular medicine at Scripps Research, explained the public has little to fear.
My impression is that it won’t [create a new wave] since they are mutations we’ve been exposed to before,” Topol wrote. “My projection is that we could see a wavelet but not a significant new wave of infections as a result of the FLiRT variants in the next couple of months. I think it will take a much bigger challenge of our immune response than what we see with the FLiRTs.”
Continuing, Topol noted high-risk individuals should remain aware of , but not worried about, the new variants.
“Covid’s not going away, but I don’t think there is a significant short-term threat of the emerging FLiRT variants,” he wrote. “High-risk people should continue to take precautions, keeping up with boosters, and all forms of protection. Even if FLiRT doesn’t kick in, there’s plenty more ways that SARS-CoV2 can reinvent itself and find new ways or better ways to evade our immune response.”
The CDC did not respond to a request for comment from The National Desk Friday.
READ MORE | Fmr. Biden Admin officials testify on pressuring Big Tech to censor pandemic posts
How the government responded to the initial outbreak of COVID-19 remains a hot-button issue on Capitol Hill. Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky., suggested in April Dr. Anthony Fauci conspired with an organization researching coronaviruses to hide its loss of government funding.
"To a lot of us looking at it, it looks like a cover-up," Sen. Paul reportedly said.
Follow Jackson Walker on X at @_jlwalker_ for the latest trending national news. Have a news tip? Send it to [email protected].
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
COVID-19 vaccine rollout update – 10 May 2024
This presentation, delivered on 10 May 2024, contains an update to Australia's COVID-19 vaccine rollout.

Scroll down to access downloads and media.
Download [Publication] COVID-19 vaccine rollout update – 10 May 2024 (PDF) as PDF - 524.56 KB - 11 pages
We aim to provide documents in an accessible format. If you're having problems using a document with your accessibility tools, please contact us for help .
- Immunisation
- COVID-19 vaccines
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Is there anything wrong with this page?
Help us improve health.gov.au
If you would like a response please use the enquiries form instead.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

teacher appreciation
11 templates

memorial day
12 templates

13 templates

rain forest
23 templates

amusement park
5 templates
Coronavirus Breakthrough
Coronavirus breakthrough presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Coronavirus is affecting the way society works right now, so information is key. Any findings about COVID-19 is more than welcome, so how about you create a presentation on the latest breakthroughs about this disease by customizing our free template?
Medical presentations always need to get the attention of the audience, especially when useful information is being provided. With the use of a palette based on green and many illustrations of fluorescent viruses on the, otherwise, abstract backgrounds, you can get a striking appearance which is actually balanced. Infographics and layouts are cool and varied, and it’s because the combination with a condensed typeface for titles that everything works well together.
Features of this template
- A green slide deck with abstract backgrounds and illustrations of viruses
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 26 different slides to impress your audience
- Available in different colors
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics, maps and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Sfl - invitation to presentation of q1 2024 results.
SFL Corporation Ltd. ("SFL" or the “Company”) (NYSE: SFL) plans to release its preliminary financial results for the first quarter of 2024 on Tuesday, May 14, 2024.
SFL plans to host a conference call and webcast for all stakeholders and interested parties on Tuesday, May 14, 2024, at 10:00 AM (EST) / 4:00 PM (CET). Relevant material will on the same day be available from the Investor Relations section of the Company’s website at www.sflcorp.com.
In order to listen to the conference call and presentation, you may do one of the following: A: Join Conference Call Webcast In Listen Only Mode: Visit the Investor Relations section of the Company’s website at www.sflcorp.com and click on the link to "Webcast", or access directly via the webcast link below. The webcast with slideshow will be played live from this platform:
SFL Corporation Ltd. Q1 2024 Webcast B: Join Conference Call And P articipat e in Live Q&A through Zoom : Join through the Zoom link below to ask a question:
SFL Q1 2024 Q&A
Meeting ID: 931 2830 1828 Passcode: 268304
A replay of the conference call will be available via the webcast on SFL’s website.
SFL Corporation Ltd. Hamilton, Bermuda
Investor and Analyst Contacts: Aksel Olesen, Chief Financial Officer, SFL Management AS +47 23 11 40 36 André Reppen, Chief Treasurer & Senior Vice President, SFL Management AS +47 23 11 40 55 Sander Borgli, Vice President - IR, SFL Management AS +47 23 11 40 73 Media Contact: Ole B. Hjertaker, Chief Executive Officer, SFL Management AS +47 23 11 40 11
SFL has a unique track record in the maritime industry and has paid dividends every quarter since its initial listing on the New York Stock Exchange in 2004. The Company’s fleet of vessels is comprised of tanker vessels, bulkers, container vessels, car carriers and offshore drilling rigs. SFL’s long term distribution capacity is supported by a portfolio of long term charters and significant growth in the asset base over time. More information can be found on the Company's website: www.sflcorp.com
Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward Looking Statements
This press release may contain forward looking statements. These statements are based upon various assumptions, many of which are based, in turn, upon further assumptions, including SFL management’s examination of historical operating trends, data contained in the Company’s records and other data available from third parties. Although SFL believes that these assumptions were reasonable when made, because assumptions are inherently subject to significant uncertainties and contingencies which are difficult or impossible to predict and are beyond its control, SFL cannot give assurance that it will achieve or accomplish these expectations, beliefs or intentions.
Important factors that, in the Company’s view, could cause actual results to differ materially from those discussed in the forward looking statements include the strength of world economies, fluctuations in currencies and interest rates, general market conditions in the seaborne transportation industry, which is cyclical and volatile, including fluctuations in charter hire rates and vessel values, changes in demand in the markets in which the Company operates, including shifts in consumer demand from oil towards other energy sources or changes to trade patterns for refined oil products, changes in market demand in countries which import commodities and finished goods and changes in the amount and location of the production of those commodities and finished goods, technological innovation in the sectors in which we operate and quality and efficiency requirements from customers, increased inspection procedures and more restrictive import and export controls, changes in the Company’s operating expenses, including bunker prices, dry-docking and insurance costs, performance of the Company’s charterers and other counterparties with whom the Company deals, the impact of any restructuring of the counterparties with whom the Company deals, and timely delivery of vessels under construction within the contracted price, governmental laws and regulations, including environmental regulations, that add to our costs or the costs of our customers, potential liability from pending or future litigation, potential disruption of shipping routes due to accidents, political instability, terrorist attacks, piracy or international hostilities, the length and severity of the ongoing coronavirus outbreak and governmental responses thereto and the impact on the demand for commercial seaborne transportation and the condition of the financial markets, and other important factors described from time to time in the reports filed by the Company with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. SFL disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.

CHPC - Research Computing and Data Support for the University
University information technology, main navigation, spring 2024 chpc presentation schedule.
All CHPC presentations are conducted exclusively via Zoom. There are no in-person presentations at this time.
Presentations are typically one hour, from 1-2pm, while hands on-presentations, marked with * in the schedule below, run two hours from 1-3pm.
The ACCESS (formerly XSEDE) HPC workshops will take place throughout the semester.
There is no charge for any of the CHPC presentations. Also, there is no registration.
Please note that for the Fall Presentation Series is held on a Monday-Wednesday-Friday schedule while the Spring and Summer Series are held on a Tuesday-Thursday schedule.
The zoom information for all of the CHPC presentations is:
- Media Resources
- 2030 Agenda
World Migration Report 2024 Reveals Latest Global Trends and Challenges in Human Mobility

- International remittances surged by 650 per cent, from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion between 2000 and 2022.
- Migrant remittances surpass foreign direct investment in boosting the GDP of developing nations.
- 281 million international migrants globally; number of those displaced hit a record high by the end of 2022 at 117 million.
Dhaka/Geneva, 7 May – The International Organization for Migration (IOM) today launched the World Migration Report 2024 , which reveals significant shifts in global migration patterns, including a record number of displaced people and a major increase in international remittances.
IOM Director General Amy Pope formally released the report in Bangladesh, which stands at the forefront of migration challenges, including emigration, immigration and displacement.
“The World Migration Report 2024 helps demystify the complexity of human mobility through evidence-based data and analysis,” IOM Director General Amy Pope said at the launch. “In a world grappling with uncertainty, understanding migration dynamics is essential for informed decision-making and effective policy responses, and the World Migration Report advances this understanding by shedding light on longstanding trends and emerging challenges.”
The report highlights that international migration remains a driver of human development and economic growth, highlighted by a more than 650 per cent increase in international remittances from 2000 to 2022, rising from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion. The growth continued despite predictions from many analysts that remittances would decrease substantially because of COVID-19.
Of that 831 billion in remittances, 647 billion were sent by migrants to low– and middle-income countries. These remittances can constitute a significant portion of those countries' GDPs, and globally, these remittances now surpass foreign direct investment in those countries.
Highlighting key findings, the report reveals that while international migration continues to drive human development, challenges persist. With an estimated 281 million international migrants worldwide, the number of displaced individuals due to conflict, violence, disaster, and other reasons has surged to the highest levels in modern-day records, reaching 117 million, underscoring the urgency of addressing displacement crises.
Migration, an intrinsic part of human history, is often overshadowed by sensationalized narratives. However, the reality is far more nuanced than what captures headlines. Most migration is regular, safe, and regionally focused, directly linked to opportunities and livelihoods. Yet, misinformation and politicization have clouded public discourse, necessitating a clear and accurate portrayal of migration dynamics.
By choosing Dhaka as the report's launch site, IOM not only highlights the country's efforts in supporting vulnerable migrants and fostering pathways for regular migration but also recognizes Bangladesh's important role in shaping global migration discourse and policy.
As a Global Compact for Safe, Orderly, and Regular Migration Champion country, Bangladesh has demonstrated a strong commitment to addressing migration issues and implementing policies that safeguard migrants' rights. This proactive engagement aligns with IOM's strategic objectives, making Bangladesh an ideal location to launch the 2024 World Migration Report.
IOM’s World Migration Report, with its innovative digital tools and comprehensive analysis, aims to help dispel myths, provide critical insights, and inspire meaningful action in addressing the challenges and opportunities of human mobility.
"We hope the report inspires collaborative efforts to harness the potential of migration as a driver for human development and global prosperity," DG Pope said.
“As one of the GCM champion countries, Bangladesh will not only continue to act upon the pledges it has made for its domestic context but would also take up emerging issues and challenges pertaining to migration and development for informed deliberations at the international level,” said Dr. Hasan Mahmud, Honourable Foreign Minister, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh.
Notes to editors:
This launch is part of IOM Director General’s first three-day visit to Bangladesh.
For more information, please contact:
Marie McAuliffe, World Migration Report Editor at [email protected]
For media requests: Florence Kim at [email protected]
RELATED NEWS
Iom's world migration report shows global displacement rising despite covid-19 mobility limits, iom’s world migration report 2020 wins international design awards , world migration report launches dynamic new data visualization platform, world migration report 2020 launched.
Migration updates
Subscribe to IOM newsletter to receive the latest news and stories about migration.
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately
Due to the downward trend in respiratory viruses in Maryland, masking is no longer required but remains strongly recommended in Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. Read more .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines
News & Publications
Johns hopkins all children's hosts the 2024 central florida triangle metabolism meeting.

Researchers from four Central Florida medical institutions — Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital, the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, the AdventHealth Translational Research Institute for Diabetes and Metabolism and the University of Florida — co-sponsored the second annual Central Florida Triangle Metabolism Meeting, held March 14-15 on the Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital campus in St. Petersburg, Florida.
The conference title highlights the collaborative partnership among these four major central Florida Research organizations, focused on metabolism and physiology and emphasizes that the regulatory principles of fundamental metabolism are deeply rooted in all physiologic processes. The symposium provided an opportunity for cross-disciplinary biomedical researchers to present their recent research and to continue to explore unifying theory of metabolism.
Close to 100 attendees pre-registered for the event and an additional 25-50 people logged onto the video conference link to participate in the two-day event. “We could not have handled this event without the skilled assistance of Lorenzo Thomas, who expertly handled all the logistics as our academic coordinator,” says Timothy Osborne, Ph.D. , conference co-organizer, associate dean for basic research, director of the Institute for Fundamental Biomedical Research at the Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital, and professor of medicine in the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “This collaboration among institutions has proven a tremendous success.
“This second annual Central Florida Triangle Metabolism Meeting was sub-themed around metabolic control through the central nervous system and cancer. This year, the conference featured two keynote lectures, each emphasizing this year’s focus on the brain, which also integrated our conference with two special lectureship programs at Johns Hopkins All Children’s.
“On the first day of the meeting, Joel Elmquist, D.V.M., Ph.D., from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, delivered the Vice Dean’s Lecture which is a semi-annual event hosted by Dr. George Jallo. On the second day of the meeting, Tamas Horvath, D.V.M., Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Comparative Medicine at Yale University, delivered the Pediatric Grand Rounds Lecture, which is a weekly event hosted by the Continuing Medical Education program.”
Keynote Address
Joel Elmquist, D.V.M., Ph.D. , director of the Center for Hypothalamic Research and vice chair of research in the department of internal medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, offered a keynote address titled “SF-1 Targets in the Hypothalamus: A Molecular Link Between Energy Balance and Exercise.” His lecture described laboratory experiments using animal models and focusing on steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) transcription factor and its role in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH), a complex brain structure important for neuroendocrine functions, including glucose regulation and also social and sexual behaviors.
The researchers aimed at developing a better understanding of the functions of SF-1 in the VMH by looking at what happens when those genes are “knocked out” in one group of laboratory animals as compared to control groups that maintained those genes.
Their ongoing investigations into SF-1 and VMH, as well as other genes, are ultimately aimed at shedding light on metabolism in humans to be potentially informative with regard to human metabolism and metabolic diseases.
Other Selected Presentations
After the keynote address, the conference continued with 20 speakers from over a dozen research institutions and universities across the United States (see box), each presenting their research on metabolism and physiology, covering a wide range of topics, including cancer; glaucoma; metabolic diseases; sensory systems; pulmonary research; fatty liver disease and diabetes; neural metabolism in aging and neurodegeneration; and obesity.
Selected presentation highlights:
Padhu Pattabiraman, Ph.D. (Indiana University) spoke on a potential advancement in the treatment of glaucoma. In his presentation, titled "Novel Mechanistic Insights into the Role of Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins in the Regulation of Intraocular Pressure,” Pattabiraman discussed a novel way to reduce high intraocular pressure (IOP) in the eyes, a cause of glaucoma.
According to Pattabiraman, glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness and the goal for slowing the progression of glaucoma rests in finding new ways to lower IOP by keeping open the internal pathway by which the IOP can be “drained.” Current treatments depend on eye drops or surgery to lower IOP.
He discussed the experimental use of a small molecule called “fatostatin” to target this pathway and reducing IOP by blocking activation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs), thereby changing the cellular biomechanics in the eye by affecting the lipids that modulate “cell stiffening.” Cell stiffening causes pathway blockage and fatostatin helps in restructuring the mechanical forces that cause cell stiffening and, in doing so, potentially lowers IOP.
Mioara Larion, Ph.D. , (NIH), who leads the Cancer Metabolism Research Program at the Neuro-Oncology Branch (NOB) at NIH, studies the metabolic needs of cancer cells and how tumors process nutrients for their growth. A goal is to develop targeted metabolic approaches that can delay tumor growth. In her presentation, titled “Brain Tumor Metabolism: An Underexplored Therapeutic Vulnerability,” Larion spoke on tumor metabolism and how a “lipid imbalance” can trigger defects in organelles, subcellular structures that perform a variety of functions in the cell. One aspect of her research is related to how targeting that imbalance may induce “apoptosis,” or programmed cell death, a process that can kill cancer cells.
She is interested in the metabolic needs of cancer cells and how they process nutrients, in order to develop targeted approaches that delay tumor growth. She and her colleagues are particularly interested in identifying metabolic vulnerabilities in glioblastomas, a fast-growing type of central nervous system tumor that forms from tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
Xiangbo Ruan, Ph.D. , (Johns Hopkins All Children’s Institute for Fundamental Biomedical Research) spoke on the “Mechanism of impaired amino acid catabolism (the break-down of complex molecules) in fatty liver diseases and type 2 diabetes.” For Ruan, impaired amino acid metabolism in the liver is a hallmark of both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Despite the critical role of impaired AA catabolism linking NAFLD with T2D, a molecular mechanism explaining this dysregulation is unknown. However, Ruan and his colleagues have found a mechanism of action for a human-specific long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). Gene expression is regulated by lncRNAs at multiple levels and plays a role in suppressing amino acid catabolism. This finding may explain impaired amino acid catabolism, present in both NAFLD and T2D.
Aya G. Elmarsafawi, Ph.D., (The H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute) offered a presentation titled “The polyamine-hypusine axis regulates CD8+ T-cell fate and functions” which was the topic of her Ph.D. studies in the laboratory of John Cleveland, Ph.D., who is the Director of the Moffitt Cancer Institute. Elmarsafawi discussed the role played by CD8+ immune cells in “adoptive cell therapy” (ACT), a recent advancement in cancer immunotherapy that sources the patient’s own CD8+ immune cells which are subsequently “reprogrammed” and expanded in the laboratory, then injected back into the patient to boost immunity.
According to Elmarsafawi, strategies that would enhance the function of CD8+ cells are “an urgent clinical need.” He explained how the “polyamine-hypusine axis,” shown to regulate T-cell function, is a metabolic “checkpoint” that can be exploited to augment to generation of CD8+ cells to improve the efficacy of T-cell based immunotherapies.
Tamas Horvath (Yale University)
Tamas Horvath, D.V.M., Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Comparative Medicine and also the director of the Yale “Program on Integrative Cell Signaling and Neurobiology of Metabolism,” offered the second keynote lecture titled “Hunger drives life.” Horvath explained recent research carried out in his lab that investigated specific neurons that potentially play a role in anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder characterized by an abnormally low body weight that, among other specifics, often may result in addictive exercise to help cause and maintain low body weight. AN is a condition that is more likely to be fatal in women than in men.
The Yale researchers found that food-restricted mice all died within 72 hours of their compulsive running, but when elevated fats were added to their diet, deaths were prevented and the researchers have hypothesized that a specific neuron that is activated by food restriction, called the “hypothalamic agouti-related peptide” (AgRP), plays a role in determining when anorexia becomes fatal, as the exercise-addicted animals lacking a high fat diet were unable to properly mobilize fuel during food restricted exercise. The finding suggests that those in medical care for anorexia nervosa, and at-risk of dying, may benefit from a high fat diet.
“We were very happy with our attendance this year,” says co-conference organizer Gina De Nicola, Ph.D., from Moffitt Cancer Center’s Department of Metabolism and Physiology and leader of Moffitt’s Metabolism Program. “We had twice as many posters as last year, and the poster session was popular as many great discussions took place around them. Also, the presentations included interesting new themes and new technologies for studying metabolism and physiology.”
Universities and Research Organization Affiliations of Invited Speakers
Johns Hopkins All Children’s
The Johns Hopkins University
The H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute
AdventHealth Translational Research Institute
University of Florida
University of Kansas
University of Illinois, Chicago
University of Massachusetts
The Ohio State University
University of Colorado
National Institutes of Health
Indiana University
Yale University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
COVID-19 is an infectious disease of the human respiratory system caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The disease is almost always mild and causes fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. ... This presentation summarizes important basic information on the current pandemic. It was written for high school and college non-science-major ...
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention.
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. The coronavirus outbreak has become one of the most notorious events of the decade, if not the current century. Every bit of information helps a lot, so let us help you create useful and informative presentations about this virus with our latest template. We've got a serious matter at hand ...
COVID-19 is a disease caused by a virus. The most common symptoms are fever, chills, and sore throat, but there are a range of others. Most people make a full recovery without needing hospital treatment. People with severe symptoms should seek medical care as soon as possible. Over 760 million cases and 6.9 million deaths have been recorded ...
COVID-19 is the disease caused by a coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2. WHO first learned of this new virus on 31 December 2019, following a report of a cluster of cases of so-called viral pneumonia in Wuhan, People's Republic of China.
The clinical presentation of COVID-19 ranges from asymptomatic to critical illness. An infected person can transmit SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, before the onset of symptoms. Symptoms can change over the course of illness and can progress in severity. Uncommon presentations of COVID-19 can occur, might vary by the age of the ...
Coronavirus Presentation templates Raise awareness about one of the hottest topics of the 21st century by downloading and editing our free PPT templates and Google Slides themes about Coronavirus. Filter by. ... The COVID-19 vaccine has improved the pandemic situation. We are gradually returning to our pre-COVID-19 lifestyle.
COVID-19 Data. Monitoring the impact of COVID-19 and the effectiveness of prevention and control strategies remains a public health priority. CDC continues to provide sustainable, high-impact, and timely information to inform decision-making. COVID Data Tracker.
A novel coronavirus (CoV) named '2019-nCoV' or '2019 novel coronavirus' or 'COVID-19' by the World Health Organization (WHO) is in charge of the current outbreak of pneumonia that began at the beginning of December 2019 near in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China [1-4]. COVID-19 is a pathogenic virus. From the phylogenetic analysis ...
If a patient tests negative by Rapid Antigen Test (RAT) FDA recommends. If symptomatic, test at least twice 48 hours apart. A third test might be needed if the patient is concerned they have COVID-19. If asymptomatic, but believe they have been exposed, test with RAT at least 3 times, each 48 hours apart to be considered truly negative.
Areas covered. Direct person-to-person respiratory transmission has rapidly amplified the spread of coronavirus. In the absence of any clinically proven treatment options, the current clinical management of COVID-19 includes symptom management, infection prevention and control measures, optimized supportive care, and intensive care support in severe or critical illness.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious viral illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). COVID-19 has had a catastrophic effect on the world, resulting in more than 6 million deaths worldwide. After the first cases of this predominantly respiratory viral illness were reported in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, in late December 2019, SARS ...
Critical COVID-19 illness means the lung and breathing system, called the respiratory system, has failed and there is damage throughout the body. Rarely, people who catch the coronavirus can develop a group of symptoms linked to inflamed organs or tissues. The illness is called multisystem inflammatory syndrome.
COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) is a disease caused by a virus named SARS-CoV-2. It can be very contagious and spreads quickly. Over one million people have died from COVID-19 in the United States. COVID-19 most often causes respiratory symptoms that can feel much like a cold, the flu, or pneumonia. COVID-19 may attack more than your lungs ...
Use this free Covid-19 PowerPoint template to showcase the virus's effect on the health system capacity. The template includes several different slide variations. 15. Coronavirus PowerPoint Template. Use this coronavirus PowerPoint template for free to create informative presentations about coronavirus measures, treatments, and protection.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention. Older people and those with underlying medical ...
This PowerPoint presentation walks you and your students through key biology concepts of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Download PPT (PPT 16.3 MB) How Do We Detect COVID-19? Every day brings new developments in the race for effective and accurate COVID-19 testing, but most strategies are based on a few key fundamental technologies.
Our latest medical template is ready for you to customize and use to talk about the infamous coronavirus. Let's raise awareness about this disease and talk about how to prevent it! We've wanted to create a slide deck that is able to catch everyone's attention easily. At first glance, you'll notice a color palette focused on purple ...
Clinical presentation. Similar to other coronaviruses, SARS‐CoV‐2 is predominantly spread by respiratory droplets, although spread by contact with contaminated fomites also occurs, as does transmission by aerosols in certain circumstances.1 Based on the experience in China, the typical incubation period of COVID‐19 infection has been estimated to be a median of 5.1 days (95% CI, 4.5-5. ...
Therefore, it is a challenge for health-care professionals to discriminate between dengue and COVID-19 on early clinical presentation, and in addition, health-care workers in dengue-endemic areas across the country should be aware of coinfection of DENV and SARS-CoV-2. Hence, the objectives of the study were to describe the common symptoms, the ...
WASHINGTON (TND) — Scientists are forecasting a rise in coronavirus cases throughout May as a new set of variants emerges, according to disease researcher Eric Topol. The variants, known as "FLiRT," are distinguished by mutations in the disease's spike proteins. These proteins help viruses attach to surfaces and are one of the factors behind the infectious nature of COVID-19.
This presentation, delivered on 10 May 2024, contains an update to Australia's COVID-19 vaccine rollout. COVID-19 vaccine rollout update - 10 May 2024 | Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
To investigate morphologic and clinical presentations of mpox in diverse populations, researchers conducted a review of the records of 54 individuals (mean age, 42.4 years) diagnosed with mpox at ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Coronavirus is affecting the way society works right now, so information is key. Any findings about COVID-19 is more than welcome, so how about you create a presentation on the latest breakthroughs about this disease by customizing our free template? Medical presentations always need to get the ...
SFL Corporation Ltd. ("SFL" or the "Company") (NYSE: SFL) plans to release its preliminary financial results for the first quarter of 2024 on Tuesday, May 14, 2024. SFL plans to host a ...
Keep physical distance of at least 1 metre from others, even if they don't appear to be sick. Avoid crowds and close contact. Wear a properly fitted mask when physical distancing is not possible and in poorly ventilated settings. Clean your hands frequently with alcohol-based hand rub or soap and water.
University of Utah COVID-19 Updates. The University of Utah. CHPC - Research Computing and Data Support for the University University Information Technology. About Us ... Presentations are typically one hour, from 1-2pm, while hands on-presentations, marked with * in the schedule below, run two hours from 1-3pm. The ACCESS (formerly XSEDE) HPC ...
International remittances surged by 650 per cent, from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion between 2000 and 2022. Migrant remittances surpass foreign direct investment in boosting the GDP of developing nations. 281 million international migrants globally; number of those displaced hit a record high by the end of 2022 at 117 million.
COVID-19 vaccine accelerated development. As of 2nd March 2021, there are 76 COVID-19 candidate vaccines in clinical development of which 12 are in Phase III and 4 in Phase IV trials. There are another 182 candidate vaccines in preclinical development. More than 90% of all top candidate vaccines will be delivered through.
Covid-19. Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately. ... In her presentation, titled "Brain Tumor Metabolism: An Underexplored Therapeutic Vulnerability," Larion spoke on tumor metabolism and how a "lipid imbalance" can trigger defects in organelles, subcellular structures that perform a variety of ...