
Excel Charts: A Complete Overview
Charts in Excel are used to represent data graphically. There are many types of charts in Excel that you can use based on the data.
In this Excel tutorial, you will learn everything about charts in Excel. You can learn to create a chart, format, move, copy or filter it.
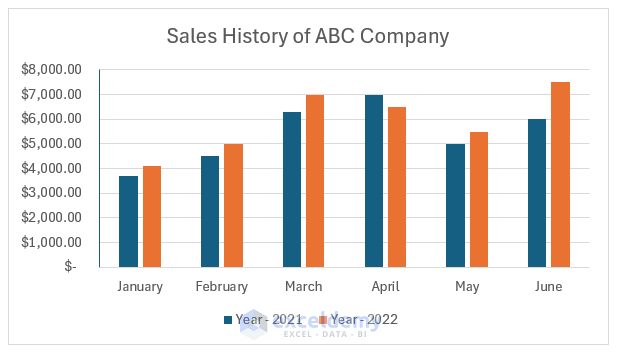
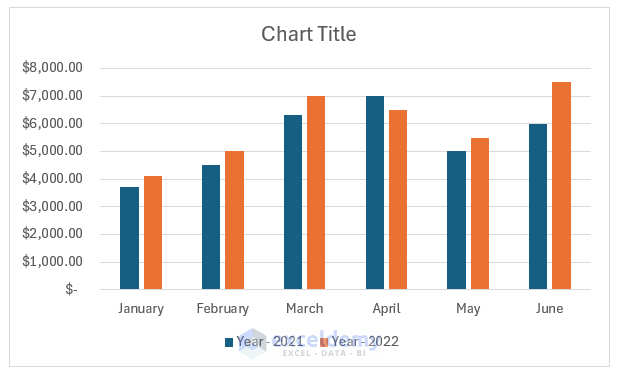
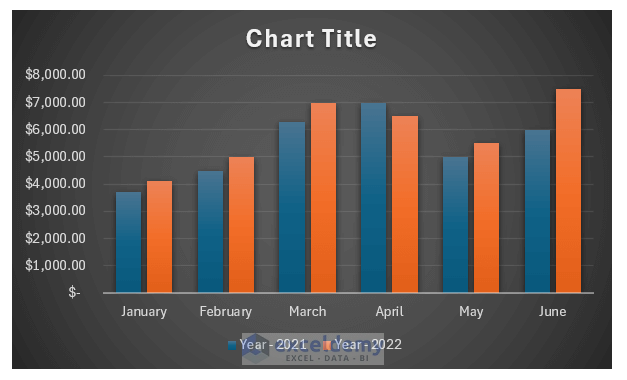
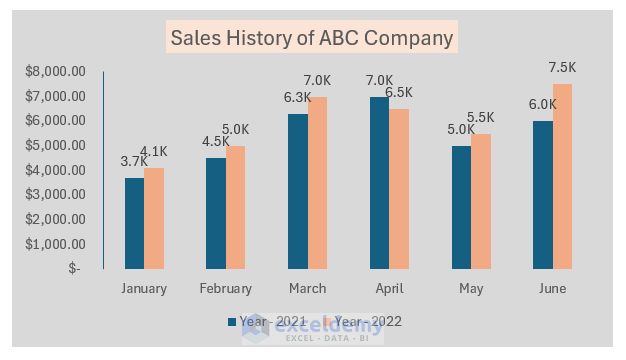
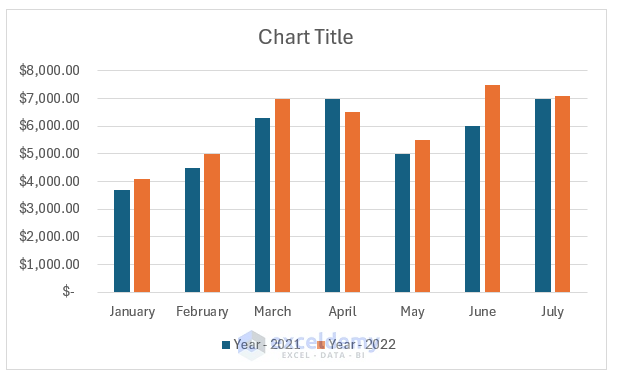
The image below shows a 2-D column chart in Excel. It represents the year-wise sales of the first six months of ABC company.
What Is a Chart in Excel?
A chart is a graphical and visual representation of data. In Excel, there are different kinds of charts. You can insert the data in a worksheet and Excel can provide you with beautiful and meaningful charts.
A chart can help viewers to understand the data, trends of the data, and future values easily. Column chart, pie chart, line chart, and bar chart are the most commonly used charts.
Types of Charts in Excel
1. column chart.
The chart that contains the categories on the horizontal axis and values on the vertical axis is called a column chart. It is also called a vertical bar chart. It helps to get an easy comparison between different categories and values.
2. Line Chart
The chart where category data is evenly distributed on the horizontal or X-axis and values are evenly distributed on the vertical axis or Y-axis is called a line chart . A line chart is basically used to show the trend over time.
3. Pie Chart
A pie chart displays one series of data through slices of a pie to understand the proportion or percentage of each item compared to the sum of all items. It is useful when you have only one data series and none of them are zero or less than zero.
4. Bar Chart
A chart where categories are plotted along a vertical axis and values are plotted along the horizontal axis is called a Bar chart . The Bar chart allows users to understand the comparison between individual items. It is available in 2-D and 3-D format in Excel.
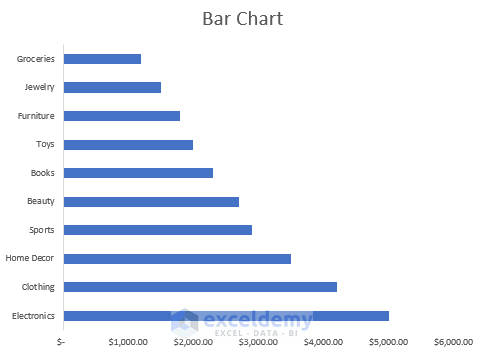
5. Area Chart
An area chart is basically a combination of a bar chart and a line chart. It illustrates the trends over time and total values across a trend. It allows us to compare the connection between parts of a whole. The 3-D format is also available for an area chart in Excel.
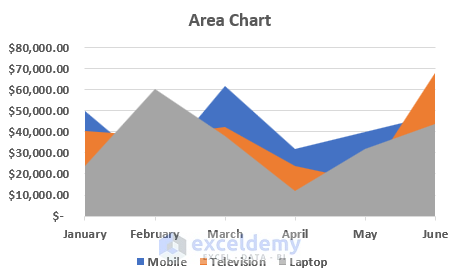
6. Scatter Chart
A scatter chart displays the data point for two variables in a two-dimensional plane. One variable is plotted along a horizontal axis and another is along a vertical axis. The data points are represented by dots in a scattered manner. You need to add more data to your scatter chart to get a better comparison.
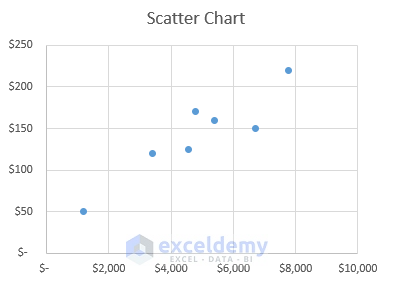
7. Map Chart
A map chart represents the values and categories across geographical regions. But there must be regions/countries/states or postal codes in your data.
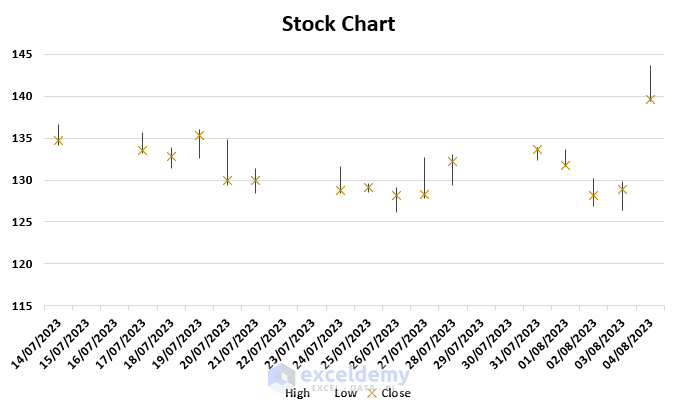
8. Stock Chart
A stock chart displays the data of stock price like opening price, closing price, high price, low price, and volume. It helps to understand the fluctuations in stock prices.
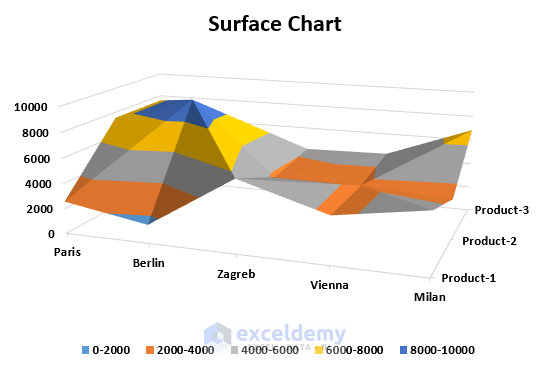
9. Surface Chart
A surface chart is a three-dimensional chart that represents the relations among three sets of data. It uses a topographic map, colors, and patterns to highlight areas for the same range of values.
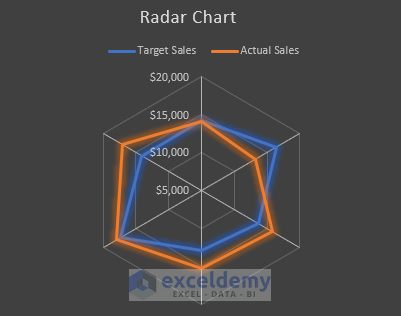
10. Radar Chart
A radar chart is used to compare multiple series of data. It uses several axes to highlight data originating from a central point. And connects data points for each variable using lines and areas.
11. Treemap Chart
A treemap chart gives a hierarchical view of your data to compare different levels of category. It uses different colors for categories and is helpful for lots of data that is difficult to highlight in other charts.
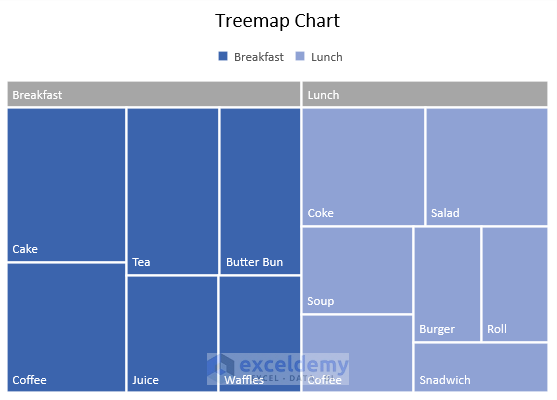
Note: Available on the newer versions since Office 2016.
12. Sunburst Chart
The sunburst chart is also used for displaying hierarchical data. A ring or circle represents each level of the hierarchy and the innermost circle is considered as the top level of the hierarchy. For one level a sunburst chart will look like a doughnut chart.
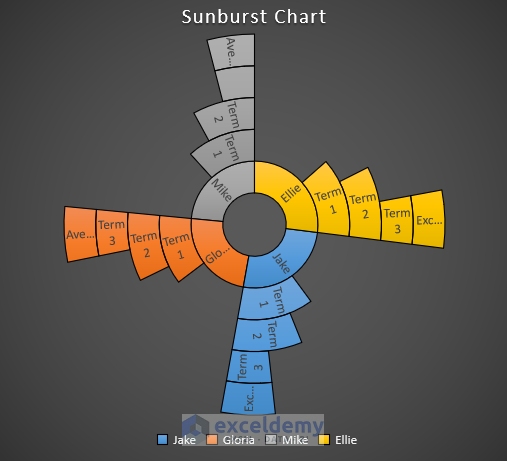
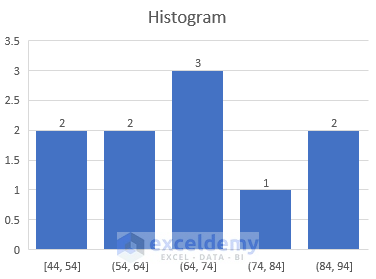
13. Histogram Chart
A chart where data is plotted to show frequencies within a distribution is called a histogram chart . Each column of a histogram chart is called a bin.
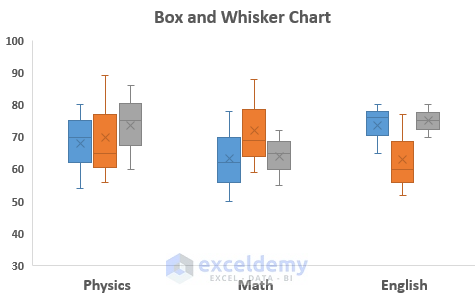
14. Box & Whisker Chart
A box and whisker chart is used to display the distribution of data into quartiles and highlight the mean. The vertical lines through boxes are called “whiskers”. The variability of quartiles is represented by the size of the lower or upper portion of the lines.
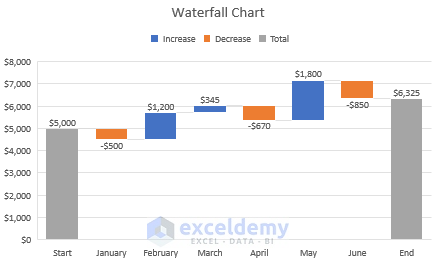
15. Waterfall Chart
A waterfall chart displays the running total of financial data. It helps to understand the effect of any addition or subtraction of data in the total. To differentiate between positive and negative data, color codes are used.
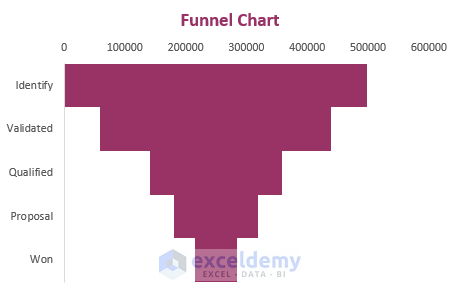
16. Funnel Chart
A chart that displays the values of multiple levels in a process is called a funnel chart . As the values are represented in descending order that’s why the shape of this chart looks like a funnel.
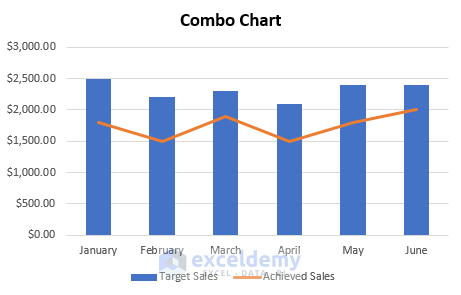
17. Combo Chart
When a chart combines different charts for a wide range of data for better understanding then it is called a combo chart . It includes a secondary axis.
Note: Available on the newer versions since Office 2013.
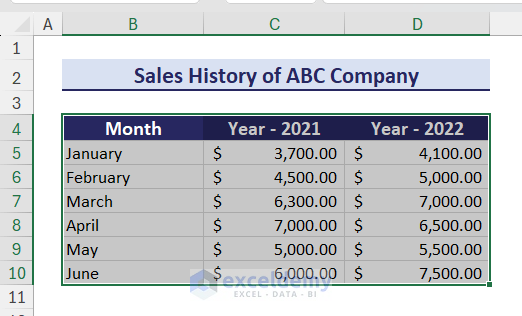
How to Create a Chart in Excel
We can create a chart in Excel by following some easy steps. Suppose, we have a dataset in the range B4:D10 that contains the yearly sales history of a company.
Let’s follow the steps below to create a chart in Excel:
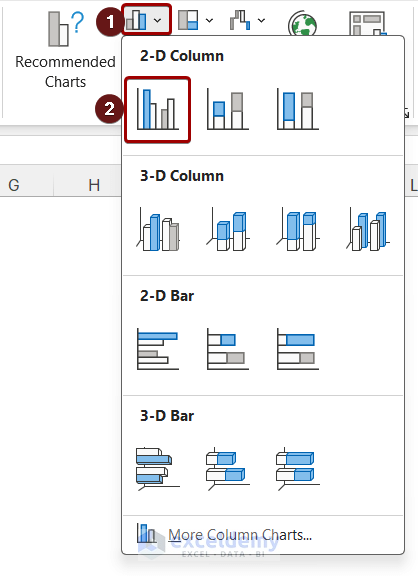
- Now, click on the Insert Column icon. A drop-down will appear.
As a result, a Clustered Column will appear on the worksheet.
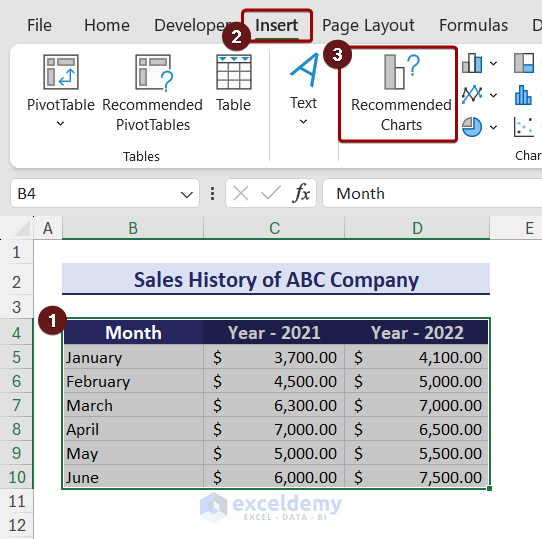
Create a chart using Recommended Charts option:
The ‘Recommended Charts’ option gives different types of charts based on your data. To create a chart using the Recommended Charts, you can follow the steps below:
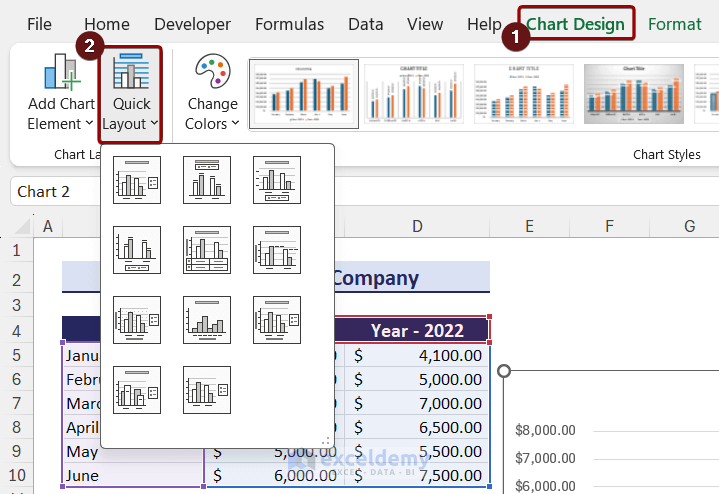
How to Change Chart Layout and Style in Excel
Changing the chart layout will change the arrangement of different chart elements. To change the layout, follow the steps below:
- Select the chart to get the Chart Design tab on the ribbon.
- After that, click on the Quick Layout option. A drop-down menu will appear.
After selecting the desired layout, the chart will automatically change.
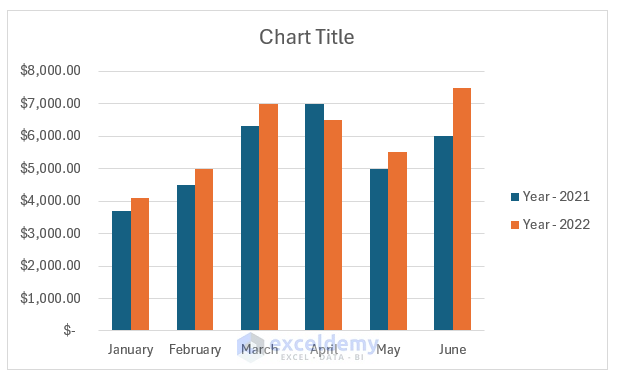
To change the chart style in Excel , you need to follow the steps below:
- Select a style from the Chart Styles group.
How to Add, Change or Remove Chart Elements in Excel
There are different kinds of elements in a chart in Excel. A chart in Excel contains Axes, Axis Titles, Chart Title, Data Table, Data Labels, Error Bars, Gridlines, Legend, Lines, Trendline, and Up/Down Bars. You can easily add, change, or remove these elements in Excel.
To add a chart element, you can follow the steps below:
- Click on the chart to get the Chart Design tab.
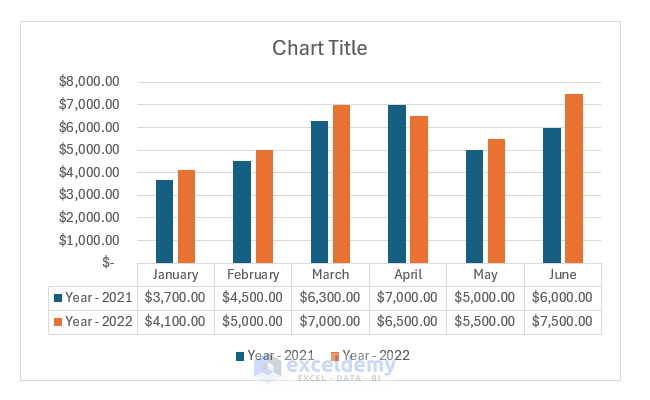
After that, you can see the chart with a data table.
When you select a chart, a plus icon appears on the top-right side. If you click on the plus icon, you will see the chart elements. You can select or deselect the elements to add or remove them.
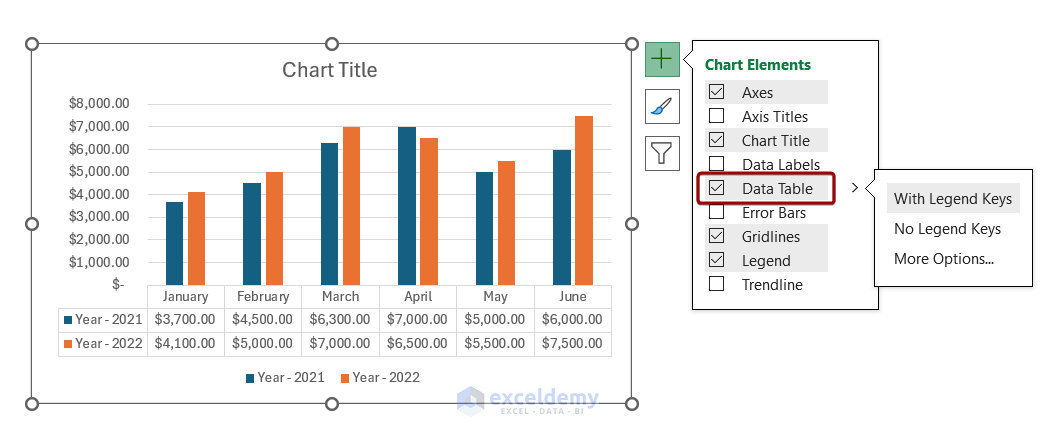
If you double-click on the Data Table, you will get a Format Data Table pane on the right side of the worksheet. You can select different options from there and format the data table.
To remove a chart element, select the element and press the Delete key from your keyboard.
How to Switch Row and Column Data in Excel Chart
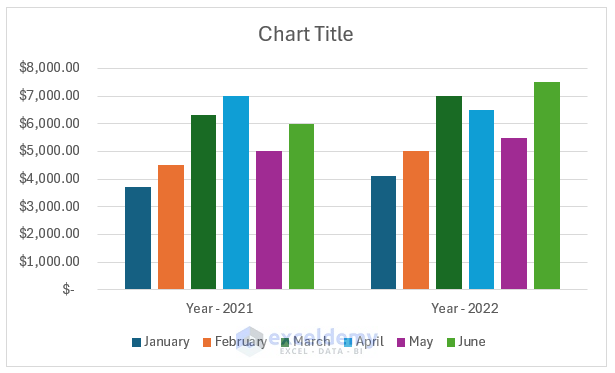
Sometimes, you may need to change the way a chart groups the data. In that case, you can use the Switch Row/Column option. For example, our chart shows year-wise sales data. To see month-wise data in a year, you can switch row/column.
To switch row/column, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart and go to the Chart Design tab.
After selecting the Switch Row/Column option, the chart will look like the image below.
How to Change Chart Type in Excel
After creating a chart, you may need to change the chart type based on the requirement. To change the chart type follow the steps below:
How to Format Charts in Excel
After creating a chart, you need to format it to make it visually attractive. You can format different chart elements to give it a better look. Here are some basic chart formatting in Excel :
1. Format Chart Axis
A chart generally has two axes: X and Y. You can format the axes by following the steps below:
As a result, you will see the changes on the Y-axis. You can follow the same steps to format the X-axis.
You can also change the position of the labels and number system of the axis from the Format Axis pane.
2. Format Chart Title
Chart title is an important element as it gives an overview of the chart. To add or edit a chart title, you can follow the steps below:
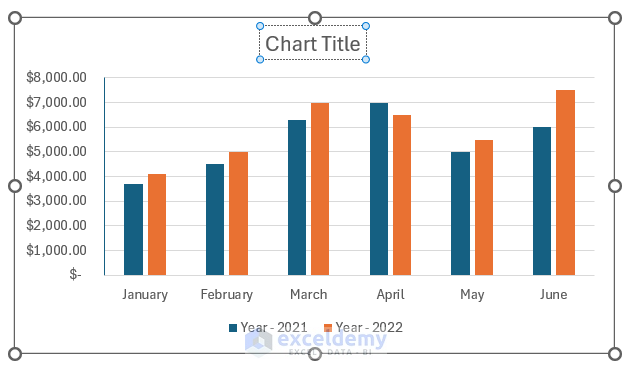
To format the chart title, you can double-click on it. It will open the Format Chart Title pane. Here, we have added a solid fill color to the chart title box. You can also explore different types of Title and Text options from here.
3. Format Legend
To format the legends, double-click on the legend. It will open the Format Legend pane. You can select different options from there.
For example, if you select the Legend Position as Right , you will see legends like the image below.
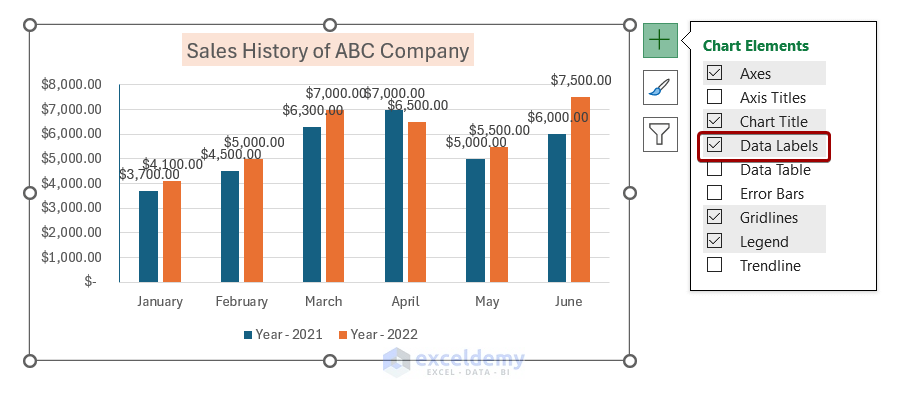
4. Format Data Label
Before formatting the data label, you need to add them to the chart. To add data labels, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart > click on the plus icon.
After adding data labels, you can format them using the following steps:
- Double-click on the data labels to open the Format Data Labels pane. You can select different options for different purposes. Here, we will change the number formatting of the data labels.
- To change the number formatting, go to the Number section.
5. Format Data Series
We can format the data series to make the charts look more attractive. To do so, you can follow the steps below:
- Double-click on the data series to open the Format Data Series pane.
6. Format Chart Area
You can format the chart area and change its color to make the chart report-friendly. To format the chart area, follow the steps below:
- Double-click on the chart area to open the Format Chart Area pane.
As a result, you will see the color of the chart area has been changed.
How to Move a Chart in Excel
In Excel, there are times when you need to move the chart to a different sheet. You can do that using the Move Chart option easily. Follow the steps below to move a chart in Excel:
- Select the chart to get the Chart Design option.
As a result, the chart will be moved into a new sheet.
You can also move the chart as an object on a different sheet. You need to select the second option from the Move Chart box and choose the desired worksheet.
How to Copy a Chart in Excel
While creating dashboards or reports, you need to copy a chart . You can copy a chart and paste it on any location. Follow the steps below to copy a chart:
How to Resize a Chart in Excel
Resizing a chart is often necessary when you are working with a lot of data. You can resize the chart using the double-headed arrow. To resize a chart, follow the steps below:
- Select the chart and place the cursor on the small circle of the chart. The cursor will change into a double-headed arrow.
You can also resize the chart using the Format tab. Click on the chart and the Format tab will appear. You can resize the chart from the Size group.
How to Filter Chart in Excel
Filtering a chart can help you visualize a specific amount of data in Excel. To filter a chart, you can follow the steps below:
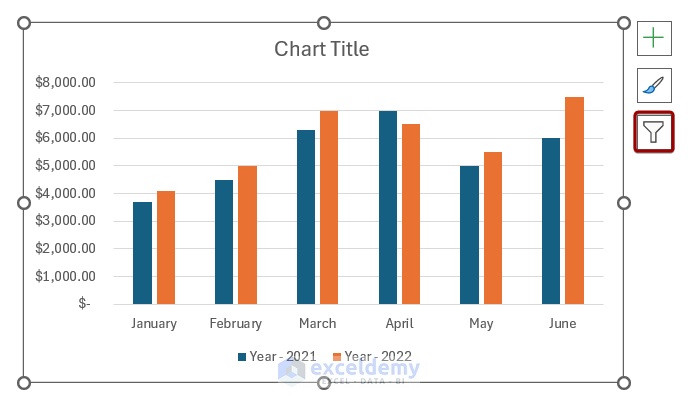
- You can check/uncheck Series and Categories from the filter options. Here, we unchecked April and May from the Categories section.
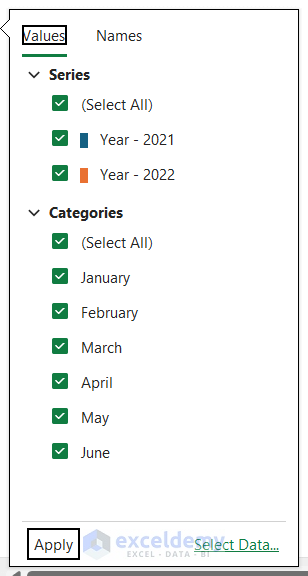
After applying the filter, the chart will show the selected data.
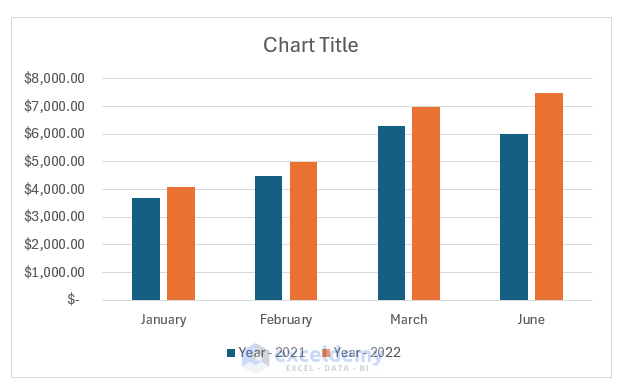
How to Keep Charts Up to Date in Excel
Sometimes, after creating a chart, we need to add new data to the chart. In that case, the chart doesn’t update the data automatically. For example, if we add the data for July to the chart, the chart doesn’t update the data.
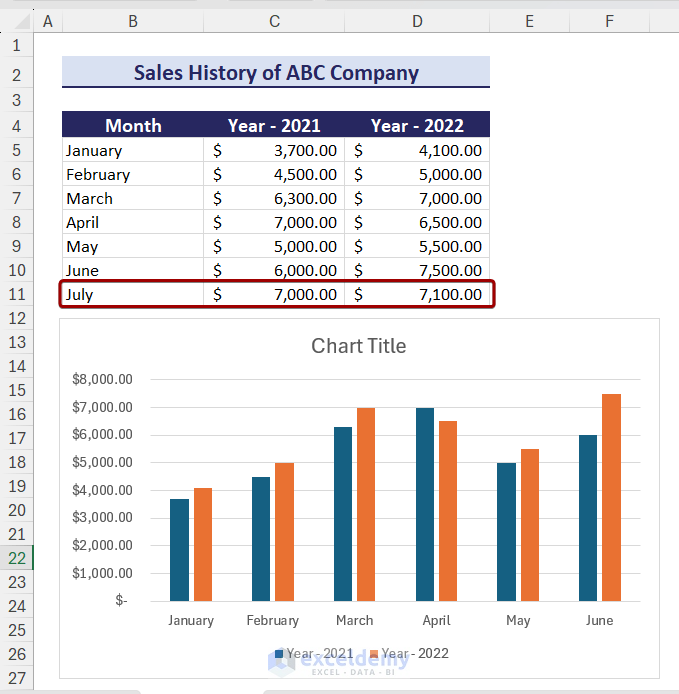
To keep charts up to date, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart area and the chart data will be selected automatically.
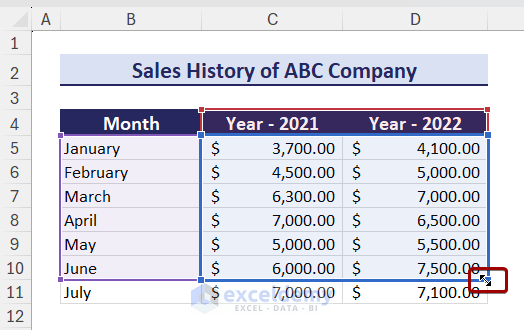
As a result, the chart will also show the new data.
Tips: Before creating a chart, you can convert the chart data range into a table and then, create a chart using the data. In this way, the new data will automatically be updated on the chart.
How to Select the Best Chart in Excel
There are many types of charts in Excel. To select the best type of chart, you need to understand what type of data you are working with. You need to keep the following things in mind while selecting the chart:
- Understand the data
- What you need to show through your chart
- Identify the chart type
- Determine patterns and trends
- Different charts for different data
Download Practice Workbook
In this article, we have described everything related to charts in Excel. You can create, format, and customize using different steps in Excel. You can also learn to move, copy, and resize charts from this article. In Excel, there are many types of charts and each one has different uses. This article will help you to learn everything. If you have any queries or suggestions, let us know in the comment section.
Excel Charts: Knowledge Hub
- Create Embedded Chart in Excel
- Refresh Chart in Excel
- Use Chart Elements in Excel
- Add a Trendline in Excel
- Customize Excel Charts
- Excel Axis Scale
- Data for Excel Chart
- Add Data Series in Excel Chart
- Add a Data Table with Legend Keys
- Create Dot Plot in Excel
- Create Thermometer Chart in Excel
- Bubble Chart in Excel
- Excel Doughnut Chart
- Excel Pareto Chart
- Burndown Chart in Excel
- Excel Distribution Chart
- Make a Comparison Chart in Excel
- Progress Chart in Excel
- Excel Control Chart
- How to Plot an Equation in Excel
- Excel Chart Not Working
- Excel Advanced Charting
- Find Intersection of Two Curves in Excel
- Show Intersection Point in Excel Graph
- Create a Weight Loss Graph in Excel
- Make a Budget Constraint Graph on Excel
- Create Mekko/Marimekko Chart in Excel
- Create Activity Relationship Chart in Excel
- Secondary Axis in Excel
- Markers in Excel
- Dynamic Excel Charts
- Matrix Chart in Excel
- Meter Chart in Excel
- Excel Standard Curve
- Gantt Chart in Excel
<< Go Back To Learn Excel
What is ExcelDemy?
Tags: Learn Excel

Mursalin Ibne Salehin holds a BSc in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology. Over the past 2 years, he has actively contributed to the ExcelDemy project, where he authored over 150 articles. He has also led a team with content development works. Currently, he is working as a Reviewer in the ExcelDemy Project. He likes using and learning about Microsoft Office, especially Excel. He is interested in data analysis with Excel, machine learning,... Read Full Bio
Leave a reply Cancel reply
ExcelDemy is a place where you can learn Excel, and get solutions to your Excel & Excel VBA-related problems, Data Analysis with Excel, etc. We provide tips, how to guide, provide online training, and also provide Excel solutions to your business problems.
Contact | Privacy Policy | TOS
- User Reviews
- List of Services
- Service Pricing

- Create Basic Excel Pivot Tables
- Excel Formulas and Functions
- Excel Charts and SmartArt Graphics
- Advanced Excel Training
- Data Analysis Excel for Beginners

Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions PDF

Excel Charting Basics: How to Make a Chart and Graph
By Joe Weller | January 22, 2018 (updated May 3, 2022)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Organizations of all sizes and across all industries use Excel to store data. While spreadsheets are crucial for data management, they are often cumbersome and don’t provide team members with an easy-to-read view into data trends and relationships. Excel can help to transform your spreadsheet data into charts and graphs to create an intuitive overview of your data and make smart business decisions.
In this article, we’ll give you a step-by-step guide to creating a chart or graph in Excel 2016. Additionally, we’ll provide a comparison of the available chart and graph presets and when to use them, and explain related Excel functionality that you can use to build on to these simple data visualizations.
What Are Graphs and Charts in Excel?
Charts and graphs in Microsoft Excel provide a method to visualize numeric data. While both graphs and charts display sets of data points in relation to one another, charts tend to be more complex, varied, and dynamic.
People often use charts and graphs in presentations to give management, client, or team members a quick snapshot into progress or results. You can create a chart or graph to represent nearly any kind of quantitative data — doing so will save you the time and frustration of poring through spreadsheets to find relationships and trends.
It’s easy to create charts and graphs in Excel, especially since you can also store your data directly in an Excel Workbook, rather than importing data from another program. Excel also has a variety of preset chart and graph types so you can select one that best represents the data relationship(s) you want to highlight.
Tired of static spreadsheets? We were, too.
Although Microsoft Excel is familiar, you were never meant to manage work with it. See how Excel and Smartsheet compare across five factors: work management, collaboration, visibility, accessibility, and integrations.
Watch the full comparison
When to Use Each Chart and Graph Type in Excel
Excel offers a large library of charts and graphs types to display your data. While multiple chart types might work for a given data set, you should select the chart that best fits the story that the data is telling.
In Excel 2016, there are five main categories of charts or graphs:
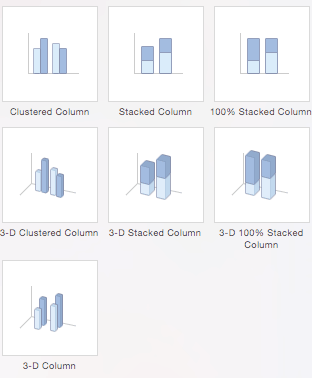
- Column Charts: Some of the most commonly used charts, column charts, are best used to compare information or if you have multiple categories of one variable (for example, multiple products or genres). Excel offers seven different column chart types: clustered, stacked, 100% stacked, 3-D clustered, 3-D stacked, 3-D 100% stacked, and 3-D, pictured below. Pick the visualization that will best tell your data’s story.
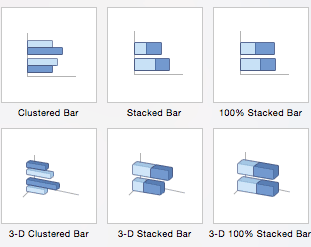
- Bar Charts: The main difference between bar charts and column charts are that the bars are horizontal instead of vertical. You can often use bar charts interchangeably with column charts, although some prefer column charts when working with negative values because it is easier to visualize negatives vertically, on a y-axis.
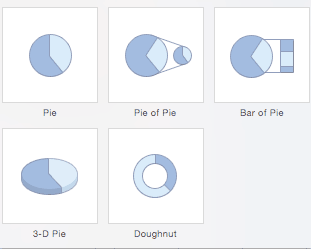
- Pie Charts: Use pie charts to compare percentages of a whole (“whole” is the total of the values in your data). Each value is represented as a piece of the pie so you can identify the proportions. There are five pie chart types: pie, pie of pie (this breaks out one piece of the pie into another pie to show its sub-category proportions), bar of pie, 3-D pie, and doughnut.
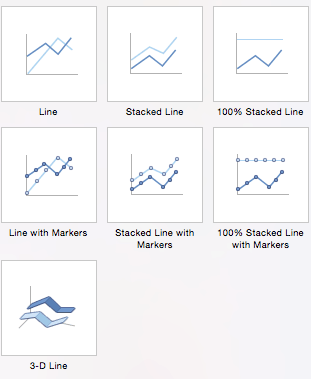
- Line Charts: A line chart is most useful for showing trends over time, rather than static data points. The lines connect each data point so that you can see how the value(s) increased or decreased over a period of time. The seven line chart options are line, stacked line, 100% stacked line, line with markers, stacked line with markers, 100% stacked line with markers, and 3-D line.
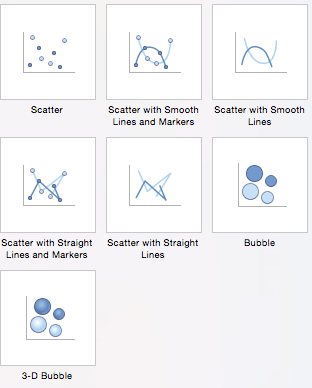
- Scatter Charts: Similar to line graphs, because they are useful for showing change in variables over time, scatter charts are used specifically to show how one variable affects another. (This is called correlation.) Note that bubble charts, a popular chart type, is categorized under scatter. There are seven scatter chart options: scatter, scatter with smooth lines and markers, scatter with smooth lines, scatter with straight lines and markers, scatter with straight lines, bubble, and 3-D bubble.
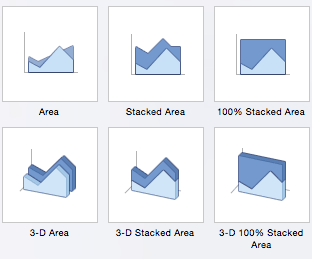
There are also four minor categories. These charts are more use case-specific:
- Area: Like line charts, area charts show changes in values over time. However, because the area beneath each line is solid, area charts are useful to call attention to the differences in change among multiple variables. There are six area charts: area, stacked area, 100% stacked area, 3-D area, 3-D stacked area, and 3-D 100% stacked area.
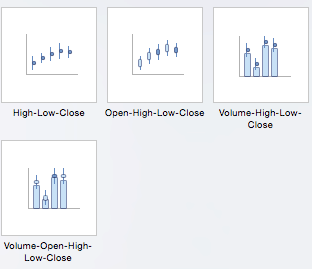
- Stock: Traditionally used to display the high, low, and closing price of stock, this type of chart is used in financial analysis and by investors. However, you can use them for any scenario if you want to display the range of a value (or the range of its predicted value) and its exact value. Choose from high-low-close, open-high-low-close, volume-high-low-close, and volume-open-high-low-close stock chart options.
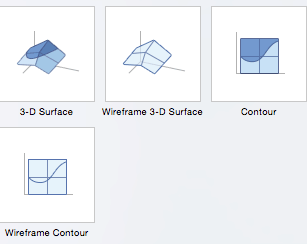
- Surface: Use a surface chart to represent data across a 3-D landscape. This additional plane makes them ideal for large data sets, those with more than two variables, or those with categories within a single variable. However, surface charts can be difficult to read, so make sure your audience is familiar with them. You can choose from 3-D surface, wireframe 3-D surface, contour, and wireframe contour.
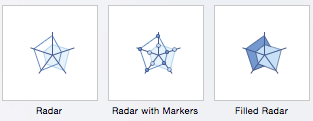
- Radar: When you want to display data from multiple variables in relation to each other use a radar chart. All variables begin from the central point. The key with radar charts is that you are comparing all individual variables in relation to each other — they are often used for comparing strengths and weaknesses of different products or employees. There are three radar chart types: radar, radar with markers, and filled radar.
Another popular chart is a waterfall chart, which is essentially a series of column graphs that show positive and negative changes over time. There is no Excel preset for a waterfall chart, but you can download a template to help make the process easier. For a full walkthrough, read How to Create a Waterfall Chart in Excel .
Download Waterfall Chart Template in Excel
Top 5 Excel Chart and Graph Best Practices
Although Excel provides several layout and formatting presets to enhance the readability of your charts, you can maximize their effectiveness with other methods. Below are the top five best practices to make your charts and graphs as useful as possible:
Make It Clean: Cluttered graphs — those with excessive colors or texts — can be difficult to read and aren’t eye catching. Remove any unnecessary information so your audience can focus on the point you’re trying to get across.
Choose Appropriate Themes: Consider your audience, the topic, and the main point of your chart when selecting a theme. While it can be fun to experiment with different styles, choose the theme that best fits your purpose.
Use Text Wisely: While charts and graphs are primarily visual tools, you will likely include some text (such as titles or axis labels). Be concise but use descriptive language, and be intentional about the orientation of any text (for example, it’s irritating to turn your head to read text written sideways on the x-axis).
Place Elements Intelligently: Pay attention to where you place titles, legends, symbols, and any other graphical elements. They should enhance your chart, not detract from it.
Sort Data Prior to Creating the Chart: People often forget to sort data or remove duplicates before creating the chart, which makes the visual unintuitive and can result in errors.
How to Chart Data in Excel
To generate a chart or graph in Excel, you must first provide the program with the data you want to display. Follow the steps below to learn how to chart data in Excel 2016.
Step 1: Enter Data into a Worksheet
- Open Excel and select New Workbook .
- Enter the data you want to use to create a graph or chart. In this example, we’re comparing the profit of five different products from 2013 to 2017. Be sure to include labels for your columns and rows. Doing so enables you to translate the data into a chart or graph with clear axis labels. You can download this sample data below.
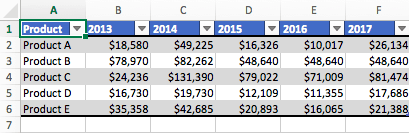
Download Column Chart Practice Data
Step 2: Select Range to Create Chart or Graph from Workbook Data
- Highlight the cells that contain the data you want to use in your graph by clicking and dragging your mouse across the cells.
- Your cell range will now be highlighted in gray and you can select a chart type.
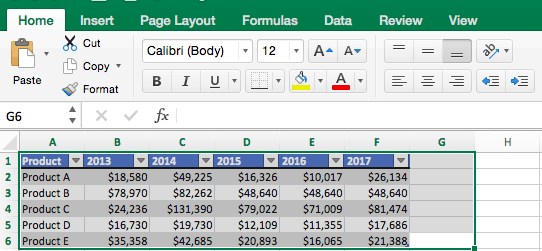
In the following section, we’ll walk you through the specifics of creating a clustered column chart in Excel 2016.
How to Make a Chart in Excel
After you input your data and select the cell range, you’re ready to choose the chart type. In this example, we’ll create a clustered column chart from the data we used in the previous section.
Step 1: Select Chart Type
Once your data is highlighted in the Workbook, click the Insert tab on the top banner. About halfway across the toolbar is a section with several chart options. Excel provides Recommended Charts based on popularity, but you can click any of the dropdown menus to select a different template.
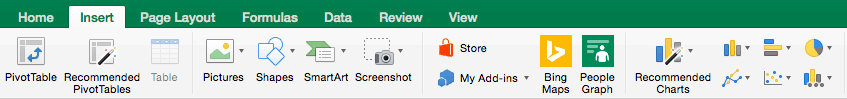
Step 2: Create Your Chart
- From the Insert tab, click the column chart icon and select Clustered Column .
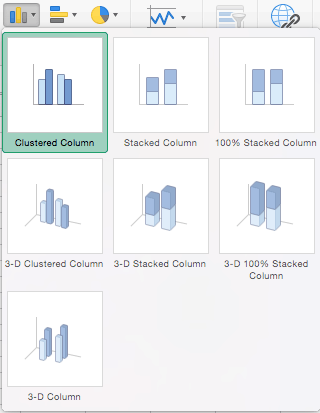
- Excel will automatically create a clustered chart column from your selected data. The chart will appear in the center of your workbook.
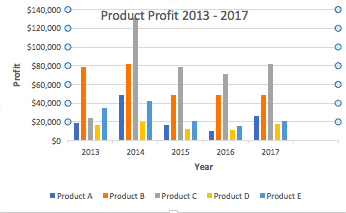
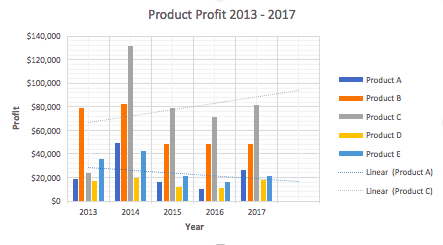
- To name your chart , double click the Chart Title text in the chart and type a title. We’ll call this chart “Product Profit 2013 - 2017.”
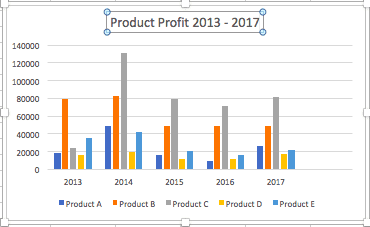
We’ll use this chart for the rest of the walkthrough. You can download this same chart to follow along.
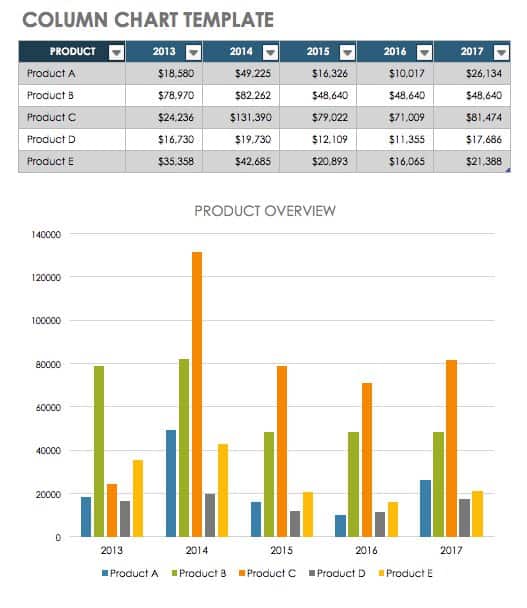
Download Sample Column Chart Template
There are two tabs on the toolbar that you will use to make adjustments to your chart: Chart Design and Format . Excel automatically applies design, layout, and format presets to charts and graphs, but you can add customization by exploring the tabs. Next, we’ll walk you through all the available adjustments in Chart Design .
Step 3: Add Chart Elements
Adding chart elements to your chart or graph will enhance it by clarifying data or providing additional context. You can select a chart element by clicking on the Add Chart Element dropdown menu in the top left-hand corner (beneath the Home tab).
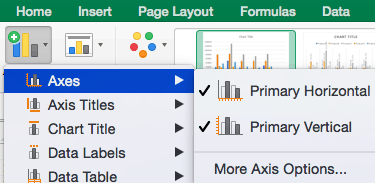
To Display or Hide Axes:
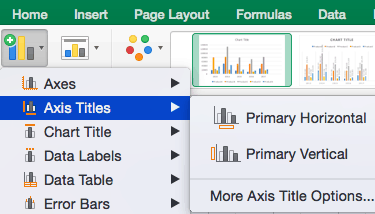
To Add Axis Titles:
To Remove or Move Chart Title:
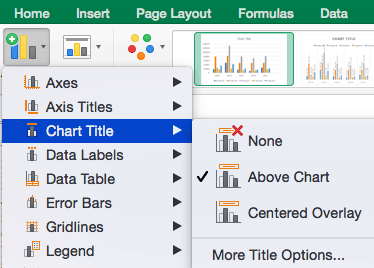
- Click None to remove chart title.
- Click Above Chart to place the title above the chart. If you create a chart title, Excel will automatically place it above the chart.
- Click Centered Overlay to place the title within the gridlines of the chart. Be careful with this option: you don’t want the title to cover any of your data or clutter your graph (as in the example below).
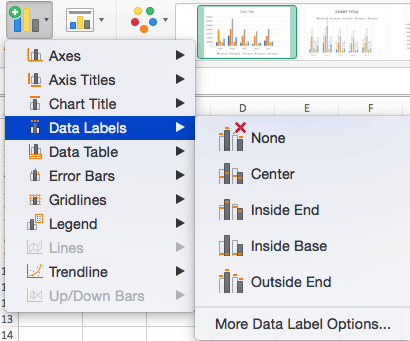
To Add Data Labels:
To Add a Data Table:
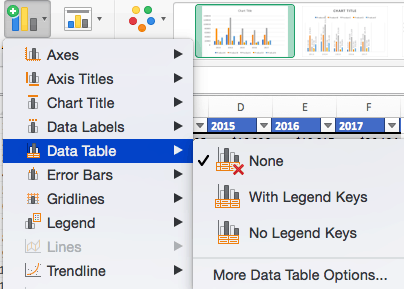
- None is the default setting, where the data table is not duplicated within the chart.
Note: If you choose to include a data table, you’ll probably want to make your chart larger to accommodate the table. Simply click the corner of your chart and use drag-and-drop to resize your chart.
To Add Error Bars:
To Add Gridlines:
To Add a Legend:
To Add Lines: Lines are not available for clustered column charts. However, in other chart types where you only compare two variables, you can add lines (e.g. target, average, reference, etc.) to your chart by checking the appropriate option.
To Add a Trendline:
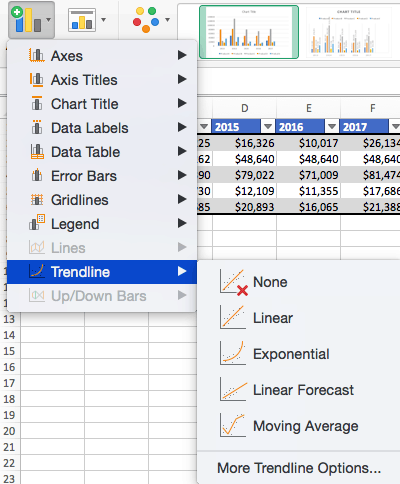
Note: You can create separate trendlines for as many variables in your chart as you like. For example, here is our chart with trendlines for Product A and Product C.
To Add Up/Down Bars: Up/Down Bars are not available for a column chart, but you can use them in a line chart to show increases and decreases among data points.
Step 4: Adjust Quick Layout

Step 5: Change Colors
The next dropdown menu in the toolbar is Change Colors . Click the icon and choose the color palette that fits your needs (these needs could be aesthetic, or to match your brand’s colors and style).
Step 6: Change Style
For cluster column charts, there are 14 chart styles available. Excel will default to Style 1, but you can select any of the other styles to change the chart appearance. Use the arrow on the right of the image bar to view other options.

Step 7: Switch Row/Column
In this example, switching the row and column swaps the product and year (profit remains on the y-axis). The chart is now clustered by product (not year), and the color-coded legend refers to the year (not product). To avoid confusion here, click on the legend and change the titles from Series to Years .
Step 8: Select Data
Step 9: Change Chart Type
You can also save your chart as a template by clicking Save as Template …
Step 10: Move Chart
Step 11: Change Formatting

Step 12: Delete a Chart
To delete a chart, simply click on it and click the Delete key on your keyboard.
How to Make a Graph in Excel
Because graphs and charts serve similar functions, Excel groups all graphs under the “chart” category. To create a graph in Excel, follow the steps below.
Select Range to Create a Graph from Workbook Data
Now you have a graph. To customize your graph, you can follow the same steps explained in the previous section. All functionality for creating a chart remains the same when creating a graph.
How to Create a Table in Excel
If you don’t need to visualize your data, you can create a table in Excel instead. There are two ways to format a data set as a table: manually, or with the Format as a Table button.
- Manually: In this example, we manually added data and formatted as a table by including column and row names (products and years).
- Use Excel’s Format as Table Preset: You can also input raw data (numbers without any column and row names).

Related Excel Functionality
Excel is one of the most widely-used tools across all industries and types of organizations. Charts and graphs are great tools to visualize your work, but there are many ways to elevate your data in Excel.
We’ve created a list of additional features that allow you to do more with your data:
- Pivot Tables: A pivot table allows you to extract certain columns or rows from a data set and reorganize or summarize that subset in a report. This is useful tool if you only want to view a particular segment of a large data set, or if you want to view data from a new perspective.
- Conditional Formatting : A powerful feature that allows you to apply specific formatting to certain cells in your spreadsheet. You can use conditional formatting to highlight key pieces of information, track changes, see deadlines, and perform many other data organization functions.
- Dashboards: A powerful, visual reporting feature that pulls data from one or several datasets to display key performance indicators (KPIs), project or task status, and several other metrics. This gives the audience (team members, executives, clients, etc.) a snapshot view into project progress without surfacing private information.
- Collaborative Charts: To avoid version control issues and allow multiple team members to edit a chart simultaneously, you’ll want to use a collaborative chart tool. The desktop versions of Excel do not support this, but you can use Excel for Office 365, Microsoft’s cloud-based web application, or several other online chart tools.
- Data Series: A data series is any row or column stored in your workbook that you’ve plotted into a chart or graph. Once you’ve created your chart, you can add additional data series to it: Simply highlight the additional data you want to add and the chart will automatically update.
Make Better Decisions, Faster with Charts in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How-To Geek
How to make a graph in microsoft excel.
Create a helpful chart to display your data and then customize it from top to bottom.
Quick Links
How to create a graph or chart in excel, how to customize a graph or chart in excel.
Graphs and charts are useful visuals for displaying data. They allow you or your audience to see things like a summary, patterns, or trends at glance. Here's how to make a chart, commonly referred to as a graph, in Microsoft Excel.
Excel offers many types of graphs from funnel charts to bar graphs to waterfall charts . You can review recommended charts for your data selection or choose a specific type. And once you create the graph, you can customize it with all sorts of options.
Start by selecting the data you want to use for your chart. Go to the Insert tab and the Charts section of the ribbon. You can then use a suggested chart or select one yourself.
Choose a Recommended Chart
You can see which types of charts Excel suggests by clicking "Recommended Charts."
On the Recommended Charts tab in the window, you can review the suggestions on the left and see a preview on the right. If you'd like to use a chart you see, select it and click "OK."
Choose Your Own Chart
If you would prefer to select a graph on your own, click the All Charts tab at the top of the window. You'll see the types listed on the left. Select one to view the styles for that type of chart on the right. To use one, select it and click "OK."
Another way to choose the type of chart you want to use is by selecting it in the Charts section of the ribbon.
There is a drop-down arrow next to each chart type for you to pick the style. For example, if you choose a column or bar chart , you can select 2-D or 3-D column or 2-D or 3-D bar.
Whichever way you go about choosing the chart you want to use, it will pop right onto your sheet after you select it.
From there, you can customize everything from the colors and style to the elements that appear on the chart.
Related: How to Make a Bar Chart in Microsoft Excel
Just like there are various ways to select the type of chart you want to use in Excel, there are different methods for customizing it. You can use the Chart Design tab, the Format Chart sidebar, and on Windows, you can use the handy buttons on the right of the chart.
Use the Chart Design Tab
To display the Chart Design tab, select the chart. You'll then see many tools in the ribbon for adding chart elements, changing the layout, colors, or style, choosing different data, and switching rows and columns.
If you believe a different type of graph would work better for your data, simply click "Change Chart Type" and you'll see the same options as when you created the chart. So you can easily switch from a column chart to a combo chart , for instance.
Use the Format Chart Sidebar
For customizing the font, size, positioning , border, series, and axes, the sidebar is your go-to spot. Either double-click the chart or right-click it and pick "Format Chart Area" from the shortcut menu. To work with the different areas of your chart, go to the top of the sidebar.
Related: How to Lock the Position of a Chart in Excel
Click "Chart Options" and you'll see three tabs for Fill & Line, Effects, and Size & Properties. These apply to the base of your chart.
Click the drop-down arrow next to Chart Options to select a specific part of the chart. You can choose things like Horizontal or Vertical Axis, Plot Area, or a Series of data.
Click "Text Options" for any of the above Chart Options areas and the sidebar tabs change to Text Fill & Outline, Text Effects, and Textbox.
For whichever area you work with, each tab has its options directly below. Simply expand to customize that particular item.
As an example, if you choose to create a Pareto chart , you can customize the Pareto line with the type, color, transparency, width, and more.
Use the Chart Options on Windows
If you use Excel on Windows, you'll get a bonus of three helpful buttons to the right when you select your chart. From top to bottom, you have Chart Elements, Chart Styles, and Chart Filters.
Chart Elements : Add, remove, or position elements of the chart such as the axis titles, data labels , gridlines, trendline, and legend.
Chart Styles : Select a theme for your chart with different effects and backgrounds. Or choose a color scheme from colorful and monochromatic color palettes.
Chart Filters : For viewing particular parts of the data in your chart, you can use filters. Check the boxes under Series or Categories and click "Apply" at the bottom to update your chart and only include your selections.
Chart Filters are only available for certain types of charts.
Hopefully this guide will get you off to a great start with your chart. And if you use Sheets in addition to Excel, learn how to make a graph in Google Sheets too.

- Chart Guide
- Data Makeover
0 comments
Visualizing Data in Excel: A Comprehensive Guide
By STC
July 15, 2023
Explore the diverse data visualization possibilities in Excel that aid in analyzing and interpreting your data effectively.
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on visualizing data in Excel. In this article, we will delve into the world of data visualization and provide you with valuable insights on how to create compelling visual representations of your data using Excel. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced Excel user, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to effectively communicate your data through visually appealing charts and graphs.
Why Data Visualization Matters

Data visualization is a powerful tool that enables us to make sense of complex datasets. It allows us to identify patterns, trends, and outliers that might not be immediately apparent in raw data. Visualizing data in Excel not only enhances our understanding of the information at hand but also enables us to communicate our findings to others in a clear and concise manner.
Getting Started with Excel Charts
- Selecting the Right Chart Type Choosing the appropriate chart type is crucial for effectively representing your data. Excel offers a wide range of chart options, including bar charts, line charts, pie charts, scatter plots, and more. Consider the nature of your data and the message you want to convey when selecting the most suitable chart type.
- Formatting and Customization Excel provides extensive formatting and customization options to refine the appearance of your charts. From adjusting axis labels to modifying colors and styles, these features allow you to create visually appealing charts that align with your brand or presentation requirements.
- Adding Data Labels and Annotations To enhance the clarity of your visualizations, Excel enables you to add data labels and annotations. These labels provide additional context and make it easier for your audience to interpret the information being presented. You can include axis labels, data point labels, and explanatory text to further enrich your charts.
Advanced-Data Visualization Techniques
- Creating PivotCharts PivotCharts are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to visualize data from pivot tables. By summarizing and aggregating data, pivot tables provide a comprehensive overview that can be transformed into dynamic and interactive charts. Utilizing PivotCharts enables you to explore and analyze complex datasets with ease.
- Utilizing Advanced Charting Features Excel offers advanced charting features that can take your visualizations to the next level. From trendlines and error bars to 3D charts and sparklines, these tools allow you to add depth and sophistication to your data representations. Experimenting with these features can help you create visually striking charts that captivate your audience.
Best Practices for Effective Data Visualization
To ensure your data visualizations have maximum impact, keep the following best practices in mind:
- Simplify and Declutter Avoid cluttering your charts with excessive information or unnecessary embellishments. Focus on the key message you want to convey and remove any elements that distract from that message. Remember, simplicity is key when it comes to effective data visualization.
- Use Color Strategically Colors can evoke emotions and draw attention to specific areas of your charts. Use color strategically to highlight important data points or to group related information. However, be mindful of accessibility considerations and ensure that your color choices are accessible to individuals with color vision deficiencies.
- Tell a Story with Your Data Data visualization is not just about presenting numbers; it’s about telling a story. Structure your visualizations in a way that guides your audience through a narrative. Start with an introduction, present the main findings, and conclude with a clear takeaway or call to action.
In conclusion, mastering the art of visualizing data in Excel can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and communicate complex information. By selecting the right chart types, utilizing advanced techniques, and following best practices, you can create visually compelling representations that effectively convey your data’s story. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge and inspiration to create outstanding data visualizations in Excel. Start exploring the power of data visualization today and unlock new insights from your data.
Check StoryTelling with Charts – The Full Story

About the author
We are passionate about the power of visual storytelling and believe that charts can convey complex information in a captivating and easily understandable way. Whether you're a data enthusiast, a business professional, or simply curious about the world around you, this page is your gateway to the world of data visualization.
Never miss a good story!
Subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with the latest trends!
Table of Contents
What is a graph in excel , what are the types of graphs available in excel, data cleaning, how to make a graph in excel, choose the right course, a step-by-step guide on how to make a graph in excel.

Microsoft Excel is a very useful data management tool used widely by almost every organization today to analyze and interpret data. A Graph in Excel is a design tool that helps us visualize data. Excel has a variety of graphs and charts that can be used to represent data in different ways. This article will help you understand the different types of graphs available in Excel, and learn how to make a graph in Excel.
In simple terms, a graph is a visual element that represents data in a worksheet . You will be able to analyze the data more efficiently by looking at a graph in Excel rather than numbers in a dataset. Excel covers a wide range of graphs that you can use to represent your data. Creating a graph in Excel is easy. The graph below depicts the sum of active COVID cases that are grouped by WHO region.
Looking at a graph helps us analyze various metrics just by taking a glance at it.
The next section will help you understand the different types of graphs available.
Become a Data Scientist with Hands-on Training!
Excel has most of the common graphs that are used for statistics. The types of graphs in Excel include:
1. Bar/Column Graphs
A bar graph shows information about two or more groups. Bar graphs are mainly used to make comparisons across a range.

2. Pie Graphs
A pie chart is nothing but a circular graph representing data in the form of a pie/circle. It is divided into different sections, each one representing a proportion of the whole.
3. Line Graphs
A line graph is formed by connecting a series of values/data points using straight lines. A line graph can be used when you want to check whether the values are increasing or decreasing over some time.
4. Scatter Plot
A scatter plot, also called a coordinate graph, uses dots to represent the data values for two different variables, one on each axis. This graph is used to find a pattern/ relationship between two sets of data.
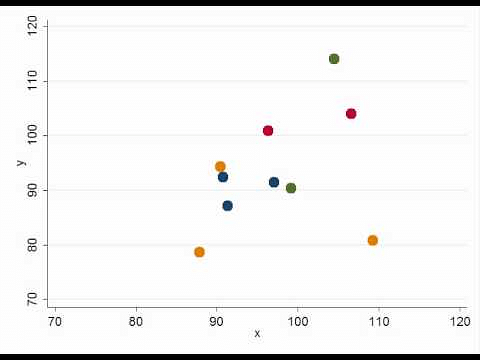
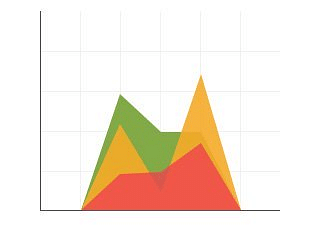
5. Area Chart
An area chart depicts the change of two or more data points over time. They are similar to the line charts, except the area charts are filled with color below the line. This chart is useful to visualize the area of various series relative to each other.
Before you make a graph in Excel, it is important to first cleanse your data. The next section will cover a few Data Cleaning techniques.
Let’s move forward and understand how to make a graph in Excel.
Data cleaning is the most crucial step to eliminate incomplete and inconsistent data.
Remove Duplicate Values
You need to make sure your data is organized and free from duplicates. Duplicate values strongly affect the data that you are working on while creating graphs. Hence, it is essential to eliminate duplicate data by clicking on the Remove Duplicates option available on the Data Tab.
Use Find and Replace Tool to Clean Data
When it comes to Data Cleansing, find and replace is a great tool. Using this, you can find all the zeros and remove them. You can also replace all the formula references.
Remove Extra Spaces
You can get rid of unwanted spaces between words or numbers which aren’t visible using the TRIM function. The syntax is:
=TRIM(text)
This function takes input as text and eliminates extra spaces. This results in no leading and trailing spaces, and only one space between the words.
- You must select the data for which a chart is to be created.
- In the INSERT menu, select Recommended Charts.
- Choose any chart from the list of charts Excel recommends for your data on the Recommended Charts tab, and click it to preview how it will look with your data.
- Please click on All Charts if you are unable to locate a chart you like.
- Click on the chart that you prefer and then click OK.
- You can add chart elements such as axis titles or data labels, customize the appearance of the chart, or change the data displayed in the chart by clicking on Chart Elements, Chart Styles, and Chart Filters in the upper-right corner of the chart.
- Click on the chart TOOLS tab on the ribbon to add additional design and formatting capabilities and then click the options you desire under the DESIGN and FORMAT tabs.
Creating a graph in Excel is easy. This step-by-step tutorial will show you how to make a graph in Excel. The demo helps you create:
- Scatter Plot
NOTE: The dataset that we will be using comprises the latest data on Coronavirus cases, country-wise. It has records of:
- WHO Region of every country.
- Confirmed cases
- Active cases
- Recovered cases
You can download the above dataset using this link . Take a look at a summary of the dataset below.
Let’s move on to understand how to create a bar graph in an easy and simple way.
1. Bar Graph
A bar graph helps you display data using rectangular bars, where the length of each bar is a numeric value depending on the category it belongs to.
Follow the steps listed below to know how to create a bar graph in Excel.
- Import the data: There are numerous other ways to import data into your Excel workbook, depending on your file format. To do this, locate the Data tab → Get & Transform Data section → Get Data option and click on it. On clicking, a list of various options will appear, to import data from different sources. You can copy and paste this data into your workbook as well.
- When you choose to work on a specific set of data within the dataset in discussion, you can use the Filter option. This option filters the data based on the requirements you’ve selected. Inorder to do this, select the whole dataset, locate the Data tab and click on the Filter option.
- Once you click on the Filter option, a downward-pointing arrow appears on the column headers of the particular dataset. You will need to click on the arrow to reveal options to select the required data.
- In this case, let's filter the data according to a particular WHO Region.
- You can do so by selecting the Filter option that appears on the column header - WHO Region.
- You will be able to locate a drop-down box with various filters. These can be added to the data.
- The filters can be applied on multiple parameters and sorted in ascending or descending order.
- Here, select the South-East Asia region, and by clicking OK, you will be able to view data from the South-East Asian regions alone.
- Once data that is required is ready, a bar graph can now be created. As shown you locate the INSERT TAB → Charts section → Bar Graph option and select the type of bar graph that best suits your requirement.
- After selecting the appropriate bar chart, you can see a blank window that is open on the Excel sheet. On right-clicking on this blank window, you should find an option to Select Data. Clicking on it will open the Select Data Source window on your screen.
- Now, select the Legend entries (or Vertical axis). In the current example, we would select the Y-axis values as confirmed cases, recovered cases, deaths, and active cases.
- On the other hand, as for the horizontal axis, select all the countries that we have filtered in the current example from the WHO region, i.e., South-East Asia.
- After specifying the appropriate values, click on OK. Excel will now display a graph on your worksheet. You can go ahead and format your graph based on your requirement.
- Double click on the chart window to locate various customization options in the toolbar, available to you.
- You may also arrive here by selecting the option beside the chart.
- This will open a drop-down box consisting of various Chart Elements.
For this example, do select the Legend checkbox for displaying the confirmed cases, recovered cases, active cases, and deaths on the graph. Further, the Chart Title box can be selected to add a title.
This was all about creating a bar graph in Excel. Let’s move ahead and learn how to create a pie chart.
2. Pie Chart
A pie chart is a circular graph that represents data by dividing the circle into sectors, where each sector illustrates a proportion to the whole.
Follow the steps mention below to learn to create a pie chart in Excel.
- From your dashboard sheet, select the range of data for which you want to create a pie chart. We will create a pie chart based on the number of confirmed cases, deaths, recovered, and active cases in India in this example.
- Select the data range. Then, click on the Insert Tab. You will find the PIE chart option available in the charts group.
- Select an appropriate pie chart from a range of pie charts available. Clicking on it will open the PIE chart in a window. Right-click on the chart window and click on Select Data. The Select Data Source window will be opened where you can choose what data you want to be displayed on your pie chart.
- Here, the chart data range can be added by simply hovering your mouse to select the data required.
- You can now select the legend entries (or vertical axis). In this current example, you will need to select India to display the cases pertaining to a specific country.
- For labels on the horizontal axis labels, you may select confirmed cases, deaths, recovered, and active cases, and depict them on the chart.
- After specifying the entries, click on OK. This will display the pie chart on your window.
- You can click on the icons next to the chart to add your finishing touches to it. Clicking on the chart elements will show you options where you can choose to display or hide data labels, chart tiles, and legend. You can choose from various styles by clicking on the chart styles. This lets you style your chart based on your requirement. You can also add multiple colors in your graph to make it look more presentable.
- You can also format the data by clicking on the Format data labels. This will show you different label options from which you can check and uncheck the different options available under it.
In the next section, you will learn how to create a Scatter Plot in Excel.
3. Scatter Plot
A Scatter Plot consists of a horizontal axis, a vertical axis, and a series of dots where each dot represents data values.
To demonstrate this, we use a Day-wise COVID dataset that has the columns:
- Confirmed Cases
- Recovered Cases
- Active Cases
Follow the steps below to understand how to create a Scatter Plot in Excel.
- Select the required data. In this example, we depict the relation between date and confirmed cases using a Scatter Plot. So, we select only the columns containing the date and confirmed Cases.
- Go to Insert Tab → Charts Section → Scatter Plot Option.
- Click on the appropriate Scatter Plot option. This will plot the values. You can format the chart, select a chart title, and add axis labels too. As you can notice, we have created a scatter plot on Date vs. Confirmed Cases. From the figure, we can easily conclude how the confirmed cases of COVID rise drastically every day.
In the final section, let’s look at how to make a histogram.
4. Histogram
A Histogram is a frequency distribution graph that uses rectangles/bars to group data into ranges and indicates the frequency of occurrence for each range.
To understand how histograms work, let’s look at an example.
The following Employee Salary dataset contains the columns:
- Employee ID
- Employee Name
We will demonstrate how to create a histogram that depicts the number of employees under each salary group.
Follow the steps mentioned below to create a simple histogram.
- Select the data from the sheet on which you want to make a histogram.
- Click on the Insert Tab, you will find the Insert Statistic Chart option in the Charts group.
- A drop down will appear from where you can select the desired histogram chart.
- The histogram chart gets displayed. To customize your histogram, click on the icons that appear next to it.
- Clicking on the chart elements will show you options where you can choose to display or hide axis titles, data labels, chart tiles, and Legend, etc.
- Clicking on the chart styles lets you style your chart to your requirement. You can add multiple colors in your graph to make it look more presentable.
- To format your histogram plot, double click on the graph. You will see the Format Axis window open on the right side.
- Click on Axis options → Horizontal Axis.
- You will find a list of different options to modify your histogram chart.
- By Category: You can select this option if you have repeated lists of categories and if you want to know the sum or count based on those categories.
- Automatic: This is the default option. It automatically decides what bins to create in the histogram. As you can notice, 5 bins are created in our chart.
- Bin Width: This option defines the range width.
In this example, we have specified the bin width as 40000.
- Number of Bins: In this option, you can enter the number of required bins. The chart will be created with the specified number of bins.
- Overflow Bin: This can be used when you want all the values over a certain value to be grouped together in the histogram.
We have specified 300000 as our overflow value. Any value higher than 300000 will be grouped under the last range.
- Underflow Bin: This can be used when you want all the values below a certain value to be grouped together in the histogram.
We have specified 80000 as our overflow value. Any value lower than 80000 will be grouped under the last range.
- Right-click on the chart and click on Add Data Labels to include the values on top of each range.
- After formatting the histogram accordingly, we arrived at the following graph.
This histogram successfully depicts the total number of employees grouped by salary range.
This is all you need to know about creating a graph in Excel.
Simplilearn's Data Science courses provide a comprehensive understanding of key data science concepts, tools, and techniques. With industry-recognized certification, hands-on projects, and expert-led training, our courses help learners gain the skills needed to succeed in the data-driven world. Upgrade your career with Simplilearn today!
Program Name Post Graduate Program In Data Science Professional Certificate Course In Data Science DS Master's Geo Non US Program IN All Geos University Caltech IIT Kanpur Simplilearn Course Duration 11 Months 11 Months 11 Months Coding Experience Required No Yes Basic Skills You Will Learn 8+ skills including Supervised & Unsupervised Learning Deep Learning Data Visualization, and more 8+ skills including NLP, Data Visualization, Model Building, and more 10+ skills including data structure, data manipulation, NumPy, Scikit-Learn, Tableau and more Additional Benefits Upto 14 CEU Credits Caltech CTME Circle Membership Live masterclasses from IIT Kanpur faculty and certificate from E&ICT Academy, IIT Kanpur Applied Learning via Capstone and 25+ Data Science Projects Cost $$$$ $$$ $$ Explore Program Explore Program Explore Program
Graphs make it easier to analyze trends and patterns in data. We hope this article has helped you provide a basic introduction to the types of graphs available and how to make a graph in Excel.
Improve your Excel skills by enrolling in the Post Graduate Program In Data Science offered by Simplilearn.
If you have any questions, please mention them in the comments section, and our experts will get back to you as soon as possible!
Data Science & Business Analytics Courses Duration and Fees
Data Science & Business Analytics programs typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Recommended Reads
Data Science Career Guide: A Comprehensive Playbook To Becoming A Data Scientist
Data Science Graduate Programs to Launch Your Career in 2024
The Best Introduction to Data Science
Free eBook: Top Programming Languages For A Data Scientist
Introducing the Post Graduate Program in Cyber Security
What Is Data Science: Lifecycle, Applications, Prerequisites and Tools
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Caltech post graduate program in data science.
- Earn a program completion certificate from Caltech CTME
- Curriculum delivered in live online sessions by industry experts
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- [email protected]
- +91-8750676667 , +91-9871076667

Data Visualization with Excel: Creating Compelling Charts and Graphs

Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis, but it can be challenging to make sense of large data sets. That’s where data visualization comes in. By creating charts and graphs, you can quickly and easily identify trends and patterns in your data. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of data visualization with Excel, and show you how to create compelling charts and graphs that will make your data come alive.
Why Use Data Visualization?
Data visualization is a process of creating graphical representations of data. It is an essential tool for anyone who works with data, from data analysts and scientists to business owners and marketers. By visualizing your data, you can quickly identify outliers, compare data sets, and draw conclusions from your data. This makes it an incredibly powerful tool for Excel training in Gurgaon , where the ability to work with data effectively is crucial for success.
Data visualization is an essential tool for anyone who works with data, from data analysts and scientists to business owners and marketers. It allows you to communicate complex data sets in a way that is easy to understand, and it can help you to make better decisions based on your data.
Understanding Chart Types
Before you start creating charts and graphs in Excel, it’s important to understand the different types of charts that are available. Each chart type is designed to represent specific types of data and to highlight different aspects of your data.
- Column Charts
Column charts are one of the most common chart types used in Excel. They are used to represent data that is arranged in columns or rows. Column charts are useful for comparing data sets and for showing changes over time. They are also useful for showing data that is related to categories, such as sales by region.
- Line Charts
Line charts are used to show trends in data over time. They are useful for identifying patterns and for predicting future trends. Line charts are often used in financial analysis to show changes in stock prices or sales figures.
Pie charts are used to show the relationship between different parts of a whole. They are useful for showing percentages and proportions, and for comparing the sizes of different categories. Pie charts are often used in marketing to show market share or customer demographics.
Bar charts are similar to column charts, but they are used to represent data that is arranged horizontally. They are useful for comparing data sets and for showing changes over time. Bar charts are often used in scientific research to show experimental results.
Creating Charts and Graphs in Excel
Now that you understand the different types of charts and graphs that are available, let’s take a look at how to create them in Excel.
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
The first step in creating a chart or graph in Excel is to prepare your data. Your data should be arranged in columns or rows, with a clear header row that identifies each column. You should also remove any unnecessary data, such as blank rows or columns.
Step 2: Select Your Data
Once your data is prepared, select the data that you want to include in your chart or graph. You can do this by clicking and dragging over the cells that you want to include.
Step 3: Choose Your Chart Type
With your data selected, click on the Insert tab in Excel, and then click on the chart type that you want to create. Excel will then create a chart or graph based on the data that you selected.
Step 4: Customize Your Chart
Once you have created your chart or graph, you can customize it to meet your needs. You can change the chart type, adjust the axis labels, and change the colors and fonts used in the chart.
Step 5: Save and Share Your Chart
Once you have customized your chart or graph, save it to your computer or share it with others. You can save your chart as an image, word or any form which ever you like.
Choosing the Right Chart Type
Choosing the right chart type is a critical step in data visualization and analysis. If you’re taking advanced Excel classes in Gurgaon , you’re likely learning about the different chart types available in Excel and how to use them effectively.
- Column Charts: These are useful for comparing values across categories or showing trends over time.
- Line Charts: These are ideal for showing trends over time, particularly when there are multiple data series to compare.
- Pie Charts: These are useful for showing the proportion of each category in a data set.
- Bar Charts: These are similar to column charts, but are best suited for showing comparisons between individual items rather than categories.
- Area Charts: These are similar to line charts, but are useful for showing the total value of a data series over time, rather than individual data points.
When choosing your chart type, it’s important to consider the type of data you’re working with and the message you want to convey. Be sure to choose a chart type that accurately represents your data and makes it easy for your audience to understand.
Formatting Your Charts
Once you’ve chosen the right chart type for your data, it’s important to format your chart in a way that’s clear and easy to understand. Here are some best practices for formatting your charts:
- Use a clear and concise title that accurately reflects the content of your chart.
- Choose colors that are easy to distinguish and don’t clash with one another.
- Use clear and legible fonts that are easy to read, even at small sizes.
- Remove any unnecessary clutter, such as gridlines or chart borders.
- Use a consistent format across all charts in your report or presentation.
By following these best practices, you can create charts that are visually appealing and easy to understand, making it easier to communicate your findings and insights.

Using Data Labels and Annotations
In addition to choosing the right chart type and formatting your chart for clarity and impact, it’s important to use data labels and annotations to highlight key insights and trends in your data. Data labels are text labels that appear next to data points on your chart, providing additional context and information. Annotations are text boxes that can be placed anywhere on your chart to provide additional information or call out specific trends or data points.
Here are some tips for using data labels and annotations effectively:
- Use data labels sparingly, focusing on the most important data points or trends.
- Make sure your data labels are positioned in a way that’s easy to read and doesn’t overlap with other labels or data points.
- Use annotations to highlight key insights or trends in your data, such as significant changes over time or outliers.
- Keep your annotations concise and to the point, using clear and simple language.
By using data labels and annotations effectively, you can draw your audience’s attention to the most important insights and trends in your data, making it easier to communicate your findings and recommendations.
Visualize your data like a pro with Excel
Excel is a powerful tool for data visualization and analysis, making it an essential skill for professionals in many industries. With Excel classes in Gurgaon , you can learn how to create impactful charts and graphs that effectively communicate your data. Excel provides a vast array of chart and graph options, from column charts to pie charts, making it easy to find the right visualization for your data set. By customizing your charts with colors, fonts, and layouts, you can create professional-looking visuals that are sure to impress. Additionally, Excel’s built-in features, such as pivot tables and sparklines, can further enhance your data analysis and visualization capabilities. With Excel classes in Gurgaon, you can become an expert in data visualization and make a real impact in your professional life.
- Advanced Excel (5)
- MIS Training (3)
- Power BI (6)
- VBA Macros (2)
Recent Posts

The Do’s and Don’ts of Power BI in…

The Power-Packed Advantages of Microsoft Power BI

10 Common Microsoft Excel Mistakes That Can Mess…

The Vital Role of MIS Reports in Education
- Schedule a Free Demo
- Make an Enquiry
Quick Enquiry
If you have interested any of above course which we provide, So send us a mail we will reply you soon !!
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Spreadsheets
- Microsoft Excel
How to Create a Graph in Excel
Last Updated: April 26, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd . Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,860,738 times. Learn more...
If you're looking for a great way to visualize data in Microsoft Excel, you can create a graph or chart. Whether you're using Windows or macOS, creating a graph from your Excel data is quick and easy, and you can even customize the graph to look exactly how you want. This wikiHow tutorial will walk you through making a graph in Excel.
Creating an Excel Graph
- Open a Blank workbook in Excel.
- Click Insert chart .
- Select the type of graph you want to make (e.g., pie, bar, or line graph).
- Plug in the graph’s headers, labels, and all of your data.
- Click and drag your mouse to select all your data, then click Insert .
- Select the type and format for the graph you want to create.
- Add a title to your graph and save your document.

- Bar - Displays one or more sets of data using vertical bars. Best for listing differences in data over time or comparing two similar sets of data.
- Line - Displays one or more sets of data using horizontal lines. Best for showing growth or decline in data over time.
- Pie - Displays one set of data as fractions of a whole. Best for showing a visual distribution of data.

- For example, to create a set of data called "Number of Lights" and another set called "Power Bill", you would type Number of Lights into cell B1 and Power Bill into C1
- Always leave cell A1 blank.

- For example, if you're comparing your budget with your friend's budget in a bar graph, you might label each column by week or month.
- You should add a label for each row of data.

- You can press the Tab ↹ key once you're done typing in one cell to enter the data and jump one cell to the right if you're filling in multiple cells in a row.

- A bar graph resembles a series of vertical bars.
- A line graph resembles two or more squiggly lines.
- A pie graph resembles a sectioned-off circle.

- You can also hover over a format to see a preview of what it will look like when using your data.

- On a Mac, you'll instead click the Design tab, click Add Chart Element , select Chart Title , click a location, and type in the graph's title. [2] X Research source

- Windows - Click File , click Save As , double-click This PC , click a save location on the left side of the window, type the document's name into the "File name" text box, and click Save .
- Mac - Click File , click Save As... , enter the document's name in the "Save As" field, select a save location by clicking the "Where" box and clicking a folder, and click Save .
Community Q&A
- You can change the graph's visual appearance on the Design tab. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you don't want to select a specific type of graph, you can click Recommended Charts and then select a graph from Excel's recommendation window. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Some graph formats won't include all of your data, or will display it in a confusing manner. It's important to choose a graph format that works with your data. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 4
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L5LBon70v_o
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxilXspS2UA
About This Article
1. Enter the graph’s headers. 2. Add the graph’s labels. 3. Enter the graph’s data. 4. Select all data including headers and labels. 5. Click Insert . 6. Select a graph type. 7. Select a graph format. 8. Add a title to the graph. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

Excel Tutorial: How To Make Graphical Presentation In Excel
Introduction.
When it comes to analyzing and presenting data, graphical presentations in Excel can be a game-changer. These visual representations of data not only make it easier to understand complex information but also help in making informed decisions. In this tutorial, we will take you through the process of creating graphical presentations in Excel and explore the benefits of incorporating visuals into your data analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Graphical presentations in Excel are crucial for understanding complex data and making informed decisions.
- Understanding the basics of creating graphical presentations is essential, including the different types of graphs and charts available in Excel.
- Selecting the appropriate data and organizing it effectively is key to creating effective graphical presentations.
- Utilizing Excel's advanced features and customization options can elevate the visual appeal and insights provided by graphical presentations.
- Adding finishing touches such as visual elements and annotations can enhance the overall look and clarity of graphical presentations.
Understanding the basics of creating graphical presentations in Excel
Graphical presentations are an essential tool for visualizing data and conveying information in a clear and concise manner. In Microsoft Excel, creating graphical presentations is a straightforward process that can greatly enhance the impact of your data. In this tutorial, we will explore the basics of creating graphical presentations in Excel.
Excel offers a wide range of graph and chart types, each suited for different data sets and presentation purposes. Some of the most commonly used graph and chart types in Excel include:
- Column and Bar Charts: These charts are used to compare values across different categories.
- Line Charts: Line charts are useful for showing trends and changes over time.
- Pie Charts: Pie charts are ideal for displaying the proportion of different categories in a data set.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables.
When creating a graphical presentation in Excel, it's important to include key components that help convey the information effectively.
The title of the graph or chart should clearly indicate the subject of the presentation.
Axis Labels
Axis labels are essential for providing context to the data being presented. The x-axis and y-axis should be clearly labeled to indicate what each represents.
The data being used for the graphical presentation should be clearly defined and organized to ensure accuracy and relevance.
By understanding the different types of graphs and charts available in Excel and the key components of a graphical presentation, you can effectively create visual representations of your data that are both impactful and easy to understand.
Selecting the appropriate data for your graphical presentation
When creating graphical presentations in Excel, it is essential to carefully choose the data that best suits the intended visualization. Here are some key points to consider:
- Look for trends or patterns: Data that shows clear trends or patterns are ideal for graphical representation. This can include sales figures over time, survey responses, or market trends.
- Comparing data: Data that needs to be compared across different categories or variables, such as product sales by region or customer demographics, can be effectively presented graphically.
- Highlighting relationships: If you want to showcase the relationship between different sets of data, such as correlation between variables or cause-and-effect relationships, graphical representation can be very effective.
- Clean and structured data: Ensure that your data is clean and well-structured before importing it into Excel. This includes removing any unnecessary columns or rows, and organizing the data in a logical manner.
- Use proper labels and headers: Clearly label your data and use headers to identify different categories or variables. This will make it easier to interpret and visualize the data in Excel.
- Convert text to numerical values: If your data includes text that needs to be represented graphically, such as categories or labels, consider converting them to numerical values or using a numerical equivalent for easier graphing in Excel.
- Remove outliers or irrelevant data: If there are outliers or irrelevant data points that could skew the visualization, consider removing them or addressing them separately to ensure the accuracy of the graphical presentation.
Step-by-step guide to creating graphical presentations in Excel
Excel is a versatile tool not only for data analysis and calculations but also for creating visually appealing graphical presentations. In this tutorial, we will walk you through the process of creating simple bar or pie charts using Excel's chart tools and then show you how to utilize Excel's graph customization features to enhance the visual appeal of your presentation.
A. Creating a simple bar or pie chart using Excel's chart tools
Excel's chart tools make it easy to create visually stunning bar or pie charts to represent your data. Follow these simple steps:
- Select your data: Start by selecting the data that you want to include in your chart. This will typically be a range of cells containing your data.
- Insert a chart: Once you have selected your data, go to the "Insert" tab and select the type of chart you want to create, such as a bar chart or a pie chart.
- Customize your chart: Excel will automatically generate a basic chart based on your selected data. You can then customize the chart by adding titles, labels, and modifying the colors and styles to suit your presentation.
- Finalize your chart: Once you are happy with the appearance of your chart, you can further customize it by adding data labels, adjusting the axis scales, or adding a trendline.
B. Utilizing Excel's graph customization features to enhance the visual appeal of your presentation
Excel offers a range of graph customization features that allow you to enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Here's how to make the most of these features:
- Modify chart elements: Excel allows you to modify various elements of your chart, such as the axis titles, data labels, and gridlines. You can also add or remove chart elements to make your chart more visually appealing.
- Change chart styles: Excel provides a range of pre-set chart styles that you can apply to your chart to change its appearance. You can also manually adjust the colors, fonts, and effects to create a custom look for your chart.
- Add visual effects: Excel allows you to add visual effects to your chart, such as shadows and glows, to make it stand out. You can also adjust the transparency of chart elements to create a more subtle and polished look.
- Format data series: Excel enables you to format individual data series within your chart, allowing you to highlight specific data points or make certain elements stand out.
Adding the finishing touches to your graphical presentation
Once you have created your graphical presentation in Excel, it's time to add the finishing touches to make it visually appealing and easy to understand for your audience.
Visual elements play a crucial role in making your graphical presentation stand out. Here are a few tips on how to use colors and fonts effectively:
- Use a cohesive color scheme: Select a color palette that complements your data and helps in conveying your message effectively. Avoid using too many colors that can make the presentation look cluttered.
- Choose readable fonts: Use clear and legible fonts for your titles, labels, and annotations. Make sure the font size is appropriate for the audience to read comfortably.
- Emphasize important data points: Use different colors or fonts to highlight important data points or trends in your presentation.
Titles, legends, and annotations help provide context and clarity to your graphical presentation. Here's how to effectively incorporate these elements:
- Include a descriptive title: A clear and concise title helps the audience understand the purpose of the graphical presentation. It should convey the main message or insight from the data.
- Utilize legends for clarity: If your graphical presentation includes multiple data series or categories, use a legend to provide clarity on what each element represents.
- Add annotations for additional information: Annotations can help provide additional context or explanations for specific data points. They can be used to highlight outliers, trends, or any other important details in the visualization.
Utilizing trendlines, sparklines, and other advanced chart elements to provide deeper insights
When creating graphical presentations in Excel, it's important to go beyond basic charts and graphs to provide deeper insights. Utilizing advanced features such as trendlines and sparklines can help you achieve this.
- Adding trendlines to your charts can help you identify and visualize patterns and trends in your data. This can be especially useful for predicting future values based on historical data.
- Customizing trendlines allows you to further refine your graphical presentation, adjusting the type of trendline (e.g., linear, exponential, polynomial) to best fit your data.
- Interpreting trendlines is essential for understanding the implications of the data. You can use the equation of the trendline to make predictions or analyze the relationship between variables.
- Integrating sparklines into your data tables or dashboards can provide a quick and concise visualization of trends and variations, without taking up too much space.
- Customizing sparklines allows you to adjust the appearance and layout to best suit your graphical presentation, ensuring clarity and effectiveness.
- Interpreting sparklines involves understanding the patterns and variations they display, providing quick insights into the data at a glance.
Exploring additional tools and features to further customize and polish your graphical presentation
Excel offers a range of additional tools and features to help you further customize and polish your graphical presentation, elevating it to a professional level.
Data Labels and Callouts
- Adding data labels to your charts can provide additional context and clarity, allowing viewers to easily interpret the data points.
- Using callouts to highlight specific data points or trends can draw attention to key insights, making your graphical presentation more impactful.
Interactive Elements
- Utilizing interactive elements such as drop-down menus, buttons, or sliders can make your graphical presentation more engaging and dynamic, allowing viewers to interact with the data.
- Creating interactive dashboards with linked charts and tables can provide a comprehensive view of the data, allowing for seamless exploration and analysis.
Formatting and Design
- Applying consistent formatting across all elements of your graphical presentation can create a cohesive and professional look, enhancing visual appeal and readability.
- Using design elements such as color schemes, fonts, and shapes can help convey a specific message or theme, adding depth and personality to your graphical presentation.
In conclusion, this tutorial covered the essential steps for creating graphical presentations in Excel . We discussed the process of selecting the data, choosing the appropriate chart type, customizing the design, and adding final touches to enhance the visual appeal. Now that you have the knowledge and tools at your disposal, I encourage you to start creating your own graphical presentations in Excel. Practice makes perfect, and with a little creativity, you can transform your data into compelling visuals that effectively communicate your message.

Immediate Download
MAC & PC Compatible
Free Email Support
Related aticles

The Benefits of Excel Dashboards for Data Analysts

Unlock the Power of Real-Time Data Visualization with Excel Dashboards

Unlocking the Potential of Excel's Data Dashboard

Unleashing the Benefits of a Dashboard with Maximum Impact in Excel

Exploring Data Easily and Securely: Essential Features for Excel Dashboards

Unlock the Benefits of Real-Time Dashboard Updates in Excel

Unleashing the Power of Excel Dashboards

Understanding the Benefits and Challenges of Excel Dashboard Design and Development

Leverage Your Data with Excel Dashboards

Crafting the Perfect Dashboard for Excel

An Introduction to Excel Dashboards

How to Create an Effective Excel Dashboard
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

- Certifications

Data Visualization with Excel Charts: A Comprehensive Guide
- December 27, 2022
What are Excel Charts?
An Excel chart is a graphical representation of data. It helps provides an opportunity to tell a compelling story to the audience through data visualization.
Data visualization helps to understand the data patterns and connections. It is important to focus on the information that matters and tell a story derived from the data.
According to Cambridge dictionary [1] , a chart is a drawing that shows information in a simple way, often using lines and curves to show amounts.
Quite often we spend a lot of time on data analysis . Being able to choose the right type of chart to give a correct representation of data is equally important as doing the right analysis. If the chart type is not correct, it becomes difficult to say a convincing story.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of charts and type of data they are suitable for.
A bar chart is the most commonly used chart type. As the name suggest, it is composed of a series of bars illustrating a variables development. It is easy to read and understand. A Bar chart is frequently used to compare data across time frames (like revenue/ profit increase from one time to another).
These charts are great to use when we want them to track the development of one or two variables. For example, if we want to compare the revenues vs previous year.
Limitation of Bar chart is that we cannot use it to compare more than 1 or 2 variables. If we have multiple variables on the Bar chart, it is difficult to understand the trend of the variables.
Do you know 10 most used Financial Functions in Excel
Stacked Column Chart
A stacked column chart is most commonly used to compare data over time. In this chart, the data series is stacked on top of each other in vertical columns. Such charts are also easy to create and understand.
An example for usage of this chart is for comparing revenue contribution by segments.
The limitation of this chart is that it may appear complex and difficult to read if there are more than 4 or 5 segments or if the data series is too long.
To get over such limitation, we can also show data with 100% stacked column chart (as shown below).
Know more about 80 PowerPoint Shortcut Keys
A line chart is a chart showing a line or multiple lines showing development of single or multiple variables over time. It allows us to track development of several variables over time in a single chart. Such charts are easy to read and understand.
Such charts are most used while comparing share price movements for multiple companies, indices etc. over both short term and long term. See Example of a line chart showing share price movement of top three Private Banks in India.
Line charts are also used by analysts to understand the correlation between two or more different variables. Like movement in Oil Prices with Oil Rig deployment or comparing base metal prices with consumption/demand etc.
Such charts are useful to analyze data for a time series. It cannot be used if we do not have data for a time series/period.
Combination Chart
Combination charts is created by combining different type of charts. Like a Combo Bar chart and a line chart . Such charts are useful when we want to analyze data trend over a time.
For example, comparing the revenue growth with margins. Such charts are useful when we want to compare data across multiple variables.
A Pie chart is a circular chart showing slices (breakup) of data by proportions. The entire pie chart represents 100% of data while the slices represent proportions of data. Sum of all slices should be equal to the Total Pie (100%).
For example, if we want to see revenue contribution by different segments of a company, we can use a Pie chart. A larger Pie size for a segment means, the larger share of revenue contribution by that segment.
The limitation of using a Pie chart is that it can only be used for one single variable . We cannot use the pie chart when we have more than one variable or if we want to see change in variable from one period to the other.
Learn 100+ Useful Excel Short Cuts
Scatter Plot
These charts are often used in field of statistics and data science. It consists of data points depicted across two variables (x-y axis).
A scatter plot chart is used when we want to see the pattern/ correlation between two variables. For example, if we want to see a correlation between Customer satisfaction index and Total revenues, we can show the correlation through a scatter plot chart.
Relationships between variables could differ by situations. For Example, it could have positive or negative correlation or have linear or non-linear correlation.
A scatter plot chart cannot be used when we don’t have 2 or more variables or when want to see the time pattern.
Waterfall Charts
A waterfall chart is a great way to show variance analysis from one point to the other. These charts help easily visualize the drivers which are responsible for the change. For Example. how the profit or revenue of a company grew from one period to the other.
We can’t use the waterfall chart for data that does not explain the drivers for change from one period to another. Therefore, if we do not have the intermediary steps or variables leading to change in performance from one period to another, we cannot use the waterfall chart.
Learn to use charts in business presentation and make it effective.
Tree Map Charts
A Tree map chart is not often used but is an effective chart for data visualization. It is a hierarchical chart. It is useful for visualization of data which has multiple level of segmentation. It gives a pictorial representation of how data is spread across various segments/ sub-segments. In a Tree Map, each segment is represented by a large rectangle and segments of data are represented by smaller rectangles. Tree map charts are great highlighting the contribution of each items to the whole.
A Tree Map chart cannot be used if the data set is not hierarchical meaning when data cannot be divided into segments and sub segments. It also cannot be used if we want to see the time pattern for multiple variables in a data set.
Bubble Chart
A Bubble chart is an extension of a scatter plot chart, where in addition to a scatter plot (2 dimensions represented by the x axis and y axis), the size of the bubble represents the 3 rd variable.
It is often used effectively to show the performance comparison across different segments of a company or across different peers.
In the above chart, shows the performance comparison across different companies in an industry. The x-axis shows the revenue growth, the y-axis shows the margin and the size of the bubbles represent the revenues for different Companies.
A bubble chart also cannot be used when we don’t have 2 or more variables or when want to see the time pattern.
Histogram Chart
A Histogram chart is similar to a Bar Chart and is used when we want to show the frequency distribution of data. For this chart, we can group data into different bins, and we can easily summarize where the data concentration is.
This chart is very effective when we want to show the distribution of data within a range. For example, Data showing average Weight of population between in a society.
A Histogram Chart cannot be used, If the data set has multiple categories of variables.
While data analysis is important, the correct presentation of data is equally important. Therefore, It is necessary to choose the right type of chart for data visualization, so that we are able to say a compelling story to the audience.
To improve your data analysis and visualization skills, please visit our online course Data Analyst Skills Training in Excel . This program will help you Go from beginner to an Expert in Data Analytics and Visualization skills in Excel? Join this program to create reports quickly through hands-on projects.
Keep Learning.
[1] https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/chart
Share This Post:
6 thoughts on “data visualization with excel charts: a comprehensive guide”.
[…] charts are a type of data visualization tool that display changes in a value over time. They are particularly useful for showing the impact […]
[…] To learn more about how to use these different types of charts, check out our comprehensive guide on making charts with Excel. […]
Say, you got a nice post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
I am so grateful for your article post.Really thank you! Really Great.
Your writing is both informative and engaging. This post was a fantastic read!
What’s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon thisI have discovered It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads.I’m hoping to contribute & help other customers like its helped me.Good job.
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get A 5X Raise In Salary
Reset Password
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

- Excel Data Analysis Tutorial
- Excel Data Analysis - Home
- Data Analysis - Overview
- Data Analysis - Process
- Excel Data Analysis - Overview
- Working with Range Names
- Cleaning Data with Text Functions
- Cleaning Data Contains Date Values
- Working with Time Values
- Conditional Formatting
- Subtotals with Ranges
- Quick Analysis
- Lookup Functions
- PivotTables
- Data Visualization
- Data Validation
- Financial Analysis
- Working with Multiple Sheets
- Formula Auditing
- Advanced Data Analysis
- Advanced Data Analysis - Overview
- Data Consolidation
- What-If Analysis
- What-If Analysis with Data Tables
- What-If Analysis Scenario Manager
- What-If Analysis with Goal Seek
- Optimization with Excel Solver
- Importing Data into Excel
- Exploring Data with PivotTables
- Exploring Data with Powerpivot
- Exploring Data with Power View
- Exploring Data Power View Charts
- Exploring Data Power View Maps
- Exploring Data PowerView Multiples
- Exploring Data Power View Tiles
- Exploring Data with Hierarchies
- Aesthetic Power View Reports
- Key Performance Indicators
- Excel Data Analysis Resources
- Excel Data Analysis - Quick Guide
- Excel Data Analysis - Resources
- Excel Data Analysis - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Excel Data Analysis - Data Visualization
You can display your data analysis reports in a number of ways in Excel. However, if your data analysis results can be visualized as charts that highlight the notable points in the data, your audience can quickly grasp what you want to project in the data. It also leaves a good impact on your presentation style.
In this chapter, you will get to know how to use Excel charts and Excel formatting features on charts that enable you to present your data analysis results with emphasis.
Visualizing Data with Charts
In Excel, charts are used to make a graphical representation of any set of data. A chart is a visual representation of the data, in which the data is represented by symbols such as bars in a Bar Chart or lines in a Line Chart. Excel provides you with many chart types and you can choose one that suits your data or you can use the Excel Recommended Charts option to view charts customized to your data and select one of those.
Refer to the Tutorial Excel Charts for more information on chart types.
In this chapter, you will understand the different techniques that you can use with the Excel charts to highlight your data analysis results more effectively.
Creating Combination Charts
Suppose you have the target and actual profits for the fiscal year 2015-2016 that you obtained from different regions.

We will create a Clustered Column Chart for these results.

As you observe, it is difficult to visualize the comparison quickly between the targets and actual in this chart. It does not give a true impact on your results.
A better way of distinguishing two types of data to compare the values is by using Combination Charts. In Excel 2013 and versions above, you can use Combo charts for the same purpose.
Use Vertical Columns for the target values and a Line with Markers for the actual values.
- Click the DESIGN tab under the CHART TOOLS tab on the Ribbon.
- Click Change Chart Type in the Type group. The Change Chart Type dialog box appears.

Click Combo.
Change the Chart Type for the series Actual to Line with Markers. The preview appears under Custom Combination.

Your Customized Combination Chart will be displayed.

As you observe in the chart, the Target values are in Columns and the Actual values are marked along the line. The data visualization has become better as it also shows you the trend of your results.
However, this type of representation does not work well when the data ranges of your two data values vary significantly.
Creating a Combo Chart with Secondary Axis
Suppose you have the data on the number of units of your product that was shipped and the actual profits for the fiscal year 2015-2016 that you obtained from different regions.

If you use the same combination chart as before, you will get the following −

In the chart, the data of No. of Units is not visible as the data ranges are varying significantly.
In such cases, you can create a combination chart with secondary axis, so that the primary axis displays one range and the secondary axis displays the other.
- Click the INSERT tab.
- Click Combo in Charts group.
- Click Create Custom Combo Chart from the drop-down list.

The Insert Chart dialog box appears with Combo highlighted.
For Chart Type, choose −
- Line with Markers for the Series No. of Units
- Clustered Column for the Series Actual Profits
- Check the Box Secondary Axis to the right of the Series No. of Units and click OK.
A preview of your chart appears under Custom Combination.

Your Combo chart appears with Secondary Axis.

You can observe the values for Actual Profits on the primary axis and the values for No. of Units on the secondary axis.
A significant observation in the above chart is for Quarter 3 where No. of Units sold is more, but the Actual Profits made are less. This could probably be assigned to the promotion costs that were incurred to increase sales. The situation is improved in Quarter 4, with a slight decrease in sales and a significant rise in the Actual Profits made.
Discriminating Series and Category Axis
Suppose you want to project the Actual Profits made in Years 2013-2016.

Create a clustered column for this data.

As you observe, the data visualization is not effective as the years are not displayed. You can overcome this by changing year to category.
Remove the header year in the data range.

Now, year is considered as a category and not a series. Your chart looks as follows −

Chart Elements and Chart Styles
Chart Elements give more descriptions to your charts, thus helping visualizing your data more meaningfully.
- Click the Chart
Three buttons appear next to the upper-right corner of the chart −

For a detailed explanation of these, refer to Excel Charts tutorial.
- Click Chart Elements.
- Click Data Labels.

- Click Chart Styles
- Select a Style and Color that suits your data.

You can use Trendline to graphically display trends in data. You can extend a Trendline in a chart beyond the actual data to predict future values.

Data Labels
Excel 2013 and later versions provide you with various options to display Data Labels. You can choose one Data Label, format it as you like, and then use Clone Current Label to copy the formatting to the rest of the Data Labels in the chart.
The Data Labels in a chart can have effects, varying shapes and sizes.
It is also possible to display the content of a cell as part of the Data Label with Insert Data Label Field.

Quick Layout
You can use Quick Layout to change the overall layout of the chart quickly by choosing one of the predefined layout options.
- Click the chart.
- Click the DESIGN tab under CHART TOOLS.
- Click Quick Layout.
Different possible layouts will be displayed. As you move on the layout options, the chart layout changes to that particular option.

Select the layout you like. The chart will be displayed with the chosen layout.
Using Pictures in Column Charts
You can create more emphasis on your data presentation by using a picture in place of columns.
Click on a Column on the Column Chart.
In the Format Data Series, click on Fill.
Select Picture.
Under Insert picture from, provide the filename or optionally clipboard if you had copied an image earlier.

The picture you have chosen will appear in place of columns in the chart.

You might have to present customer survey results of a product from different regions. Band Chart is suitable for this purpose. A Band Chart is a Line Chart with an added shaded area to display the upper and lower boundaries of groups of data.
Suppose your customer survey results from the east and west regions, month wise are −

Here, in the data < 50% is Low, 50% - 80% is Medium and > 80% is High.
With Band Chart, you can display your survey results as follows −

Create a Line Chart from your data.

Change the chart type to −
- East and West Series to Line with Markers.
- Low, Medium and High Series to Stacked Column.

Your chart looks as follows.

- Click on one of the columns.
- Change gap width to 0% in Format Data Series.

You will get Bands instead of columns.

To make the chart more presentable −
- Add Chart Title.
- Adjust Vertical Axis range.
- Change the colors of the bands to Green-Yellow-Red.
- Add Labels to bands.
The final result is the Band Chart with the defined boundaries and the survey results represented across the bands. One can quickly and clearly make out from the chart that while the survey results for the region West are satisfactory, those for the region East have a decline in the last quarter and need attention.

Thermometer Chart
When you have to represent a target value and an actual value, you can easily create a Thermometer Chart in Excel that emphatically shows these values.
With Thermometer chart, you can display your data as follows −

Arrange your data as shown below −

- Select the data.
- Create a Clustered Column chart.

As you observe, the right side Column is Target.
- Click on a Column in the chart.
- Click on Switch Row/Column on the Ribbon.

- Right click on the Target Column.
- Click on Format Data Series.
- Click on Secondary Axis.

As you observe the Primary Axis and Secondary Axis have different ranges.
- Right click the Primary Axis.
- In the Format Axis options, under Bounds, type 0 for Minimum and 1 for Maximum.
- Repeat the same for Secondary Axis.

Both Primary Axis and Secondary Axis will be set to 0% - 100%. The Target Column hides the Actual Column.
- Right click the visible column (Target)
- No fill for FILL
- Solid line for BORDER
- Blue for Color

- Axis → Primary Horizontal
- Axis → Secondary Vertical
- Chart Title
- In the chart, right click on Primary Vertical Axis
- In Format Axis options, click on TICK MARKS
- For Major type, select Inside

- Right click on the Chart Area.
- No line for BORDER

Resize the chart area, to get the shape of a thermometer.

You got your thermometer chart, with the actual value as against target value being shown. You can make this thermometer chart more impressive with some formatting.
- Insert a rectangle shape superimposing the blue rectangular part in the chart.
- Gradient fill for FILL
- Linear for Type
- 180 0 for Angle
- Set the Gradient stops at 0%, 50% and 100%.
- For the Gradient stops at 0% and 100%, choose the color black.
- For the Gradient stop at 50%, choose the color white.

- Insert an oval shape at the bottom.
- Format shape with same options.
The result is the Thermometer Chart that we started with.

Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is a chart in which a series of horizontal lines shows the amount of work done in certain periods of time in relation to the amount of work planned for those periods.
In Excel, you can create a Gantt chart by customizing a Stacked Bar chart type so that it depicts tasks, task duration, and hierarchy. An Excel Gantt chart typically uses days as the unit of time along the horizontal axis.
Consider the following data where the column −
- Task represents the Tasks in the project
- Start represents number of days from the Start Date of the project
- Duration represents the duration of the Task
Note that Start of any Task is Start of previous Task + Duration. This is the case when the Tasks are in hierarchy.

- Create Stacked Bar Chart.

- Right-click on Start Series.
- In Format Data Series options, select No fill.

- Right-click on Categories Axis.
- In Format Axis options, select Categories in reverse order.

- Adjust the range
- Major Tick Marks at 5 day intervals
- Minor Tick Marks at 1 day intervals
- Format Data Series to make it look impressive
- Give a Chart Title

Waterfall Chart
Waterfall Chart is one of the most popular visualization tools used in small and large businesses. Waterfall charts are ideal for showing how you have arrived at a net value such as net income, by breaking down the cumulative effect of positive and negative contributions.
Excel 2016 provides Waterfall Chart type. If you are using earlier versions of Excel, you can still create a Waterfall Chart using Stacked Column Chart.
The columns are color coded so that you can quickly tell positive from negative numbers. The initial and the final value columns start on the horizontal axis, while the intermediate values are floating columns. Because of this look, Waterfall Charts are also called Bridge Charts.
Consider the following data.

Prepare the data for Waterfall Chart
Ensure the column Net Cash Flow is to the left of the Months Column (This is because you will not include this column while creating the chart)
Add 2 columns – Increase and Decrease for positive and negative cash flows respectively
Add a column Start - the first column in the chart with the start value in the Net Cash Flow
Add a column End - the last column in the chart with the end value in the Net Cash Flow
Add a column Float – that supports the intermediate columns
Compute the values for these columns as follows

In the Float column, insert a row in the beginning and at the end. Place n arbitrary value 50000. This just to have some space to the left and right of the chart
The data will be as follows.

- Select the cells C2:H18 (Exclude Net Cash Flow column)
- Create Stacked Column Chart

- Right click on the Float Series.
- Click Format Data Series.

- Right click on Negative Series.
- Select Fill Color as Red.

- Right click on Positive Series.
- Select Fill Color as Green.

- Right click on Start Series.
- Select Fill Color as Grey.
- Right click on End Series.
- Delete the Legend.

- Right click on any Series
- In Format Data Series options, select Gap Width as 10% under Series Options

Give the Chart Title. The Waterfall Chart will be displayed.

Sparklines are tiny charts placed in single cells, each representing a row of data in your selection. They provide a quick way to see trends.
You can add Sparklines with Quick Analysis tool.
- Select the data for which you want to add Sparklines.
- Keep an empty column to the right side of the data for the Sparklines.

Click SPARKLINES . The chart options displayed are based on the data and may vary.

Click Line . A Line Chart for each row is displayed in the column to the right of the data.

PivotCharts
Pivot Charts are used to graphically summarize data and explore complicated data.
A PivotChart shows Data Series, Categories, and Chart Axes the same way a standard chart does. Additionally, it also gives you interactive filtering controls right on the chart so that you can quickly analyze a subset of your data.
PivotCharts are useful when you have data in a huge PivotTable, or many complex worksheet data that includes text and numbers. A PivotChart can help you make sense of this data.
You can create a PivotChart from
- A PivotTable.
- A Data Table as a standalone without PivotTable.
PivotChart from PivotTable
To create a PivotChart follow the steps given below −
- Click the PivotTable.
- Click ANALYZE under PIVOTTABLE TOOLS on the Ribbon.
- Click on PivotChart. The Insert Chart dialog box appears.

Select Clustered Column from the option Column.

Click OK. The PivotChart is displayed.

The PivotChart has three filters – Region, Salesperson and Month.
Click the Region Filter Control option. The Search Box appears with the list of all Regions. Check boxes appear next to Regions.
Select East and South options.

The filtered data appears on both the PivotChart and the PivotTable.

PivotChart without a PivotTable
You can create a standalone PivotChart without creating a PivotTable.
- Click the Data Table.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click PivotChart in Charts group. The Create PivotChart window appears.
- Select the Table/Range.
- Select the Location where you want the PivotChart to be placed.
You can choose a cell in the existing worksheet itself, or in a new worksheet. Click OK.

An empty PivotChart and an empty PivotTable appear along with the PivotChart Field List to build the PivotChart.

Choose the Fields to be added to the PivotChart
Arrange the Fields by dragging them into FILTERS, LEGEND (SERIES), AXIS (CATEGORIES) and VALUES
Use the Filter Controls on the PivotChart to select the Data to be placed on the PivotChart
Excel will automatically create a coupled PivotTable.

To Continue Learning Please Login

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2: Graphical Representations of Data
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 22222

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
In this chapter, you will study numerical and graphical ways to describe and display your data. This area of statistics is called "Descriptive Statistics." You will learn how to calculate, and even more importantly, how to interpret these measurements and graphs.
- 2.1: Introduction In this chapter, you will study numerical and graphical ways to describe and display your data. This area of statistics is called "Descriptive Statistics." You will learn how to calculate, and even more importantly, how to interpret these measurements and graphs. In this chapter, we will briefly look at stem-and-leaf plots, line graphs, and bar graphs, as well as frequency polygons, and time series graphs. Our emphasis will be on histograms and box plots.
- 2.2: Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs A stem-and-leaf plot is a way to plot data and look at the distribution, where all data values within a class are visible. The advantage in a stem-and-leaf plot is that all values are listed, unlike a histogram, which gives classes of data values. A line graph is often used to represent a set of data values in which a quantity varies with time. These graphs are useful for finding trends. A bar graph is a chart that uses either horizontal or vertical bars to show comparisons among categories.
- 2.3: Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs A histogram is a graphic version of a frequency distribution. The graph consists of bars of equal width drawn adjacent to each other. The horizontal scale represents classes of quantitative data values and the vertical scale represents frequencies. The heights of the bars correspond to frequency values. Histograms are typically used for large, continuous, quantitative data sets. A frequency polygon can also be used when graphing large data sets with data points that repeat.
- 2.4: Using Excel to Create Graphs Using technology to create graphs will make the graphs faster to create, more precise, and give the ability to use larger amounts of data. This section focuses on using Excel to create graphs.
- 2.5: Graphs that Deceive It's common to see graphs displayed in a misleading manner in social media and other instances. This could be done purposefully to make a point, or it could be accidental. Either way, it's important to recognize these instances to ensure you are not misled.
- 2.E: Graphical Representations of Data (Exercises) These are homework exercises to accompany the Textmap created for "Introductory Statistics" by OpenStax.
Contributors and Attributions
Barbara Illowsky and Susan Dean (De Anza College) with many other contributing authors. Content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] .
Artificial Intelligence
Supercharging graph neural networks with large language models: the ultimate guide.
Table Of Contents

Graphs are data structures that represent complex relationships across a wide range of domains, including social networks, knowledge bases, biological systems, and many more. In these graphs, entities are represented as nodes, and their relationships are depicted as edges.
The ability to effectively represent and reason about these intricate relational structures is crucial for enabling advancements in fields like network science, cheminformatics, and recommender systems.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful deep learning framework for graph machine learning tasks. By incorporating the graph topology into the neural network architecture through neighborhood aggregation or graph convolutions, GNNs can learn low-dimensional vector representations that encode both the node features and their structural roles. This allows GNNs to achieve state-of-the-art performance on tasks such as node classification, link prediction, and graph classification across diverse application areas.
While GNNs have driven substantial progress, some key challenges remain. Obtaining high-quality labeled data for training supervised GNN models can be expensive and time-consuming. Additionally, GNNs can struggle with heterogeneous graph structures and situations where the graph distribution at test time differs significantly from the training data (out-of-distribution generalization).
In parallel, Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, and LLaMA have taken the world by storm with their incredible natural language understanding and generation capabilities. Trained on massive text corpora with billions of parameters, LLMs exhibit remarkable few-shot learning abilities, generalization across tasks, and commonsense reasoning skills that were once thought to be extremely challenging for AI systems.
The tremendous success of LLMs has catalyzed explorations into leveraging their power for graph machine learning tasks. On one hand, the knowledge and reasoning capabilities of LLMs present opportunities to enhance traditional GNN models. Conversely, the structured representations and factual knowledge inherent in graphs could be instrumental in addressing some key limitations of LLMs, such as hallucinations and lack of interpretability.
In this article, we will delve into the latest research at the intersection of graph machine learning and large language models. We will explore how LLMs can be used to enhance various aspects of graph ML, review approaches to incorporate graph knowledge into LLMs, and discuss emerging applications and future directions for this exciting field.
Graph Neural Networks and Self-Supervised Learning
To provide the necessary context, we will first briefly review the core concepts and methods in graph neural networks and self-supervised graph representation learning.
Graph Neural Network Architectures

Graph Neural Network Architecture – source
The key distinction between traditional deep neural networks and GNNs lies in their ability to operate directly on graph-structured data. GNNs follow a neighborhood aggregation scheme, where each node aggregates feature vectors from its neighbors to compute its own representation.
Numerous GNN architectures have been proposed with different instantiations of the message and update functions, such as Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs), GraphSAGE , Graph Attention Networks (GATs), and Graph Isomorphism Networks (GINs) among others.
More recently, graph transformers have gained popularity by adapting the self-attention mechanism from natural language transformers to operate on graph-structured data. Some examples include GraphormerTransformer , and GraphFormers . These models are able to capture long-range dependencies across the graph better than purely neighborhood-based GNNs.
Self-Supervised Learning on Graphs
While GNNs are powerful representational models, their performance is often bottlenecked by the lack of large labeled datasets required for supervised training. Self-supervised learning has emerged as a promising paradigm to pre-train GNNs on unlabeled graph data by leveraging pretext tasks that only require the intrinsic graph structure and node features.

Self-Supervised Graph
Some common pretext tasks used for self-supervised GNN pre-training include:
- Node Property Prediction : Randomly masking or corrupting a portion of the node attributes/features and tasking the GNN to reconstruct them.
- Edge/Link Prediction : Learning to predict whether an edge exists between a pair of nodes, often based on random edge masking.
- Contrastive Learning : Maximizing similarities between graph views of the same graph sample while pushing apart views from different graphs.
- Mutual Information Maximization : Maximizing the mutual information between local node representations and a target representation like the global graph embedding.
Pretext tasks like these allow the GNN to extract meaningful structural and semantic patterns from the unlabeled graph data during pre-training. The pre-trained GNN can then be fine-tuned on relatively small labeled subsets to excel at various downstream tasks like node classification, link prediction, and graph classification.
By leveraging self-supervision, GNNs pre-trained on large unlabeled datasets exhibit better generalization, robustness to distribution shifts, and efficiency compared to training from scratch. However, some key limitations of traditional GNN-based self-supervised methods remain, which we will explore leveraging LLMs to address next.
Enhancing Graph ML with Large Language Models
Integration of Graphs and LLM – source
The remarkable capabilities of LLMs in understanding natural language, reasoning, and few-shot learning present opportunities to enhance multiple aspects of graph machine learning pipelines. We explore some key research directions in this space:
A key challenge in applying GNNs is obtaining high-quality feature representations for nodes and edges, especially when they contain rich textual attributes like descriptions, titles, or abstracts. Traditionally, simple bag-of-words or pre-trained word embedding models have been used, which often fail to capture the nuanced semantics.
Recent works have demonstrated the power of leveraging large language models as text encoders to construct better node/edge feature representations before passing them to the GNN. For example, Chen et al. utilize LLMs like GPT-3 to encode textual node attributes, showing significant performance gains over traditional word embeddings on node classification tasks.
Beyond better text encoders, LLMs can be used to generate augmented information from the original text attributes in a semi-supervised manner. TAPE generates potential labels/explanations for nodes using an LLM and uses these as additional augmented features. KEA extracts terms from text attributes using an LLM and obtains detailed descriptions for these terms to augment features.
By improving the quality and expressiveness of input features, LLMs can impart their superior natural language understanding capabilities to GNNs, boosting performance on downstream tasks.
Alleviating Reliance on Labeled Data
A key advantage of LLMs is their ability to perform reasonably well on new tasks with little to no labeled data, thanks to their pre-training on vast text corpora. This few-shot learning capability can be leveraged to alleviate the reliance of GNNs on large labeled datasets.
One approach is to use LLMs to directly make predictions on graph tasks by describing the graph structure and node information in natural language prompts. Methods like InstructGLM and GPT4Graph fine-tune LLMs like LLaMA and GPT-4 using carefully designed prompts that incorporate graph topology details like node connections, neighborhoods etc. The tuned LLMs can then generate predictions for tasks like node classification and link prediction in a zero-shot manner during inference.
While using LLMs as black-box predictors has shown promise, their performance degrades for more complex graph tasks where explicit modeling of the structure is beneficial. Some approaches thus use LLMs in conjunction with GNNs – the GNN encodes the graph structure while the LLM provides enhanced semantic understanding of nodes from their text descriptions.

Graph Understanding with LLM Framework – Source
GraphLLM explores two strategies: 1) LLMs-as-Enhancers where LLMs encode text node attributes before passing to the GNN, and 2) LLMs-as-Predictors where the LLM takes the GNN's intermediate representations as input to make final predictions.
GLEM goes further by proposing a variational EM algorithm that alternates between updating the LLM and GNN components for mutual enhancement.
By reducing reliance on labeled data through few-shot capabilities and semi-supervised augmentation, LLM-enhanced graph learning methods can unlock new applications and improve data efficiency.
Enhancing LLMs with Graphs
While LLMs have been tremendously successful, they still suffer from key limitations like hallucinations (generating non-factual statements), lack of interpretability in their reasoning process, and inability to maintain consistent factual knowledge.
Graphs, especially knowledge graphs which represent structured factual information from reliable sources, present promising avenues to address these shortcomings. We explore some emerging approaches in this direction:
Knowledge Graph Enhanced LLM Pre-training
Similar to how LLMs are pre-trained on large text corpora, recent works have explored pre-training them on knowledge graphs to imbue better factual awareness and reasoning capabilities.
Some approaches modify the input data by simply concatenating or aligning factual KG triples with natural language text during pre-training. E-BERT aligns KG entity vectors with BERT's wordpiece embeddings, while K-BERT constructs trees containing the original sentence and relevant KG triples.
The Role of LLMs in Graph Machine Learning:
Researchers have explored several ways to integrate LLMs into the graph learning pipeline, each with its unique advantages and applications. Here are some of the prominent roles LLMs can play:
- LLM as an Enhancer : In this approach, LLMs are used to enrich the textual attributes associated with the nodes in a TAG. The LLM's ability to generate explanations, knowledge entities, or pseudo-labels can augment the semantic information available to the GNN, leading to improved node representations and downstream task performance.
For example, the TAPE (Text Augmented Pre-trained Encoders) model leverages ChatGPT to generate explanations and pseudo-labels for citation network papers, which are then used to fine-tune a language model. The resulting embeddings are fed into a GNN for node classification and link prediction tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results.
- LLM as a Predictor : Rather than enhancing the input features, some approaches directly employ LLMs as the predictor component for graph-related tasks. This involves converting the graph structure into a textual representation that can be processed by the LLM, which then generates the desired output, such as node labels or graph-level predictions.
One notable example is the GPT4Graph model, which represents graphs using the Graph Modelling Language (GML) and leverages the powerful GPT-4 LLM for zero-shot graph reasoning tasks.
- GNN-LLM Alignment : Another line of research focuses on aligning the embedding spaces of GNNs and LLMs, allowing for a seamless integration of structural and semantic information. These approaches treat the GNN and LLM as separate modalities and employ techniques like contrastive learning or distillation to align their representations.
The MoleculeSTM model, for instance, uses a contrastive objective to align the embeddings of a GNN and an LLM, enabling the LLM to incorporate structural information from the GNN while the GNN benefits from the LLM's semantic knowledge.
Challenges and Solutions
While the integration of LLMs and graph learning holds immense promise, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Efficiency and Scalability : LLMs are notoriously resource-intensive, often requiring billions of parameters and immense computational power for training and inference. This can be a significant bottleneck for deploying LLM-enhanced graph learning models in real-world applications, especially on resource-constrained devices.
One promising solution is knowledge distillation , where the knowledge from a large LLM (teacher model) is transferred to a smaller, more efficient GNN (student model).
- Data Leakage and Evaluation : LLMs are pre-trained on vast amounts of publicly available data, which may include test sets from common benchmark datasets, leading to potential data leakage and overestimated performance. Researchers have started collecting new datasets or sampling test data from time periods after the LLM's training cut-off to mitigate this issue.
Additionally, establishing fair and comprehensive evaluation benchmarks for LLM-enhanced graph learning models is crucial to measure their true capabilities and enable meaningful comparisons.
- Transferability and Explainability : While LLMs excel at zero-shot and few-shot learning, their ability to transfer knowledge across diverse graph domains and structures remains an open challenge. Improving the transferability of these models is a critical research direction.
Furthermore, enhancing the explainability of LLM-based graph learning models is essential for building trust and enabling their adoption in high-stakes applications. Leveraging the inherent reasoning capabilities of LLMs through techniques like chain-of-thought prompting can contribute to improved explainability.
- Multimodal Integration : Graphs often contain more than just textual information, with nodes and edges potentially associated with various modalities, such as images, audio, or numeric data. Extending the integration of LLMs to these multimodal graph settings presents an exciting opportunity for future research.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
The integration of LLMs and graph machine learning has already shown promising results in various real-world applications:
- Molecular Property Prediction : In the field of computational chemistry and drug discovery, LLMs have been employed to enhance the prediction of molecular properties by incorporating structural information from molecular graphs. The LLM4Mol model , for instance, leverages ChatGPT to generate explanations for SMILES (Simplified Molecular-Input Line-Entry System) representations of molecules, which are then used to improve the accuracy of property prediction tasks.
- Knowledge Graph Completion and Reasoning : Knowledge graphs are a special type of graph structure that represents real-world entities and their relationships. LLMs have been explored for tasks like knowledge graph completion and reasoning, where the graph structure and textual information (e.g., entity descriptions) need to be considered jointly.
- Recommender Systems : In the domain of recommender systems, graph structures are often used to represent user-item interactions, with nodes representing users and items, and edges denoting interactions or similarities. LLMs can be leveraged to enhance these graphs by generating user/item side information or reinforcing interaction edges.
The synergy between Large Language Models and Graph Machine Learning presents an exciting frontier in artificial intelligence research. By combining the structural inductive bias of GNNs with the powerful semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs, we can unlock new possibilities in graph learning tasks, particularly for text-attributed graphs.
While significant progress has been made, challenges remain in areas such as efficiency, scalability, transferability, and explainability. Techniques like knowledge distillation, fair evaluation benchmarks, and multimodal integration are paving the way for practical deployment of LLM-enhanced graph learning models in real-world applications.

What is AlphaFold 3? The AI Model Poised to Transform Biology
SIMA: Scaling Up AI Agents Across Virtual Worlds for Diverse Applications

I have spent the past five years immersing myself in the fascinating world of Machine Learning and Deep Learning. My passion and expertise have led me to contribute to over 50 diverse software engineering projects, with a particular focus on AI/ML. My ongoing curiosity has also drawn me toward Natural Language Processing, a field I am eager to explore further.
You may like

Optimizing Memory for Large Language Model Inference and Fine-Tuning

Decoder-Based Large Language Models: A Complete Guide

Snowflake Arctic: The Cutting-Edge LLM for Enterprise AI

Everything You Need to Know About Llama 3 | Most Powerful Open-Source Model Yet | Concepts to Usage

The Rise of AI Software Engineers: SWE-Agent, Devin AI and the Future of Coding

Beyond Search Engines: The Rise of LLM-Powered Web Browsing Agents

Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
A Survey of Large Language Models for Graphs
HKUDS/Awesome-LLM4Graph-Papers
Folders and files, repository files navigation, awesome-llm4graph-papers.
A collection of papers and resources about Large Language Models ( LLM ) for Graph Learning ( Graph ).
Graphs are an essential data structure utilized to represent relationships in real-world scenarios. Prior research has established that Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) deliver impressive outcomes in graph-centric tasks, such as link prediction and node classification. Despite these advancements, challenges like data sparsity and limited generalization capabilities continue to persist. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained attention in natural language processing. They excel in language comprehension and summarization. Integrating LLMs with graph learning techniques has attracted interest as a way to enhance performance in graph learning tasks.

🤗 We're actively working on this project, and your interest is greatly appreciated! To keep up with the latest developments, please consider hit the STAR and WATCH for updates.
🔥 We gave a tutorial on LLM4Graph at TheWebConf (WWW) 2024!
Our survey paper: A Survey of Large Language Models for Graphs is now ready.
This repository serves as a collection of recent advancements in employing large language models (LLMs) for modeling graph-structured data. We categorize and summarize the approaches based on four primary paradigms and nine secondary-level categories. The four primary categories include: 1) GNNs as Prefix, 2) LLMs as Prefix, 3) LLMs-Graphs Intergration, and 4) LLMs-Only
- GNNs as Prefix

- LLMs as Prefix

- LLMs-Graphs Intergration

We hope this repository proves valuable to your research or practice in the field of self-supervised learning for recommendation systems. If you find it helpful, please consider citing our work:
- Table of Contents
Related Resources
Node-level tokenization, graph-level, embs. from llms for gnns, labels from llms for gnns, alignment between gnns and llms, fusion training of gnns and llms, llms agent for graphs, tuning-free, tuning-required, contributing, acknowledgements.
- Large language models on graphs: A comprehensive survey [ paper ]
- A Survey of Graph Meets Large Language Model: Progress and Future Directions [ paper ]
🌐 GNNs as Prefix
- (SIGIR'2024) GraphGPT: Graph instruction tuning for large language models [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) HiGPT: Heterogeneous Graph Language Model [ paper ]
- (WWW'2024) GraphTranslator: Aligning Graph Model to Large Language Model for Open-ended Tasks [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) UniGraph: Learning a Cross-Domain Graph Foundation Model From Natural Language [ paper ]
- (NeurIPS'2024) GIMLET:Aunifiedgraph-textmodelforinstruction-based molecule zero-shot learning [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) GraphLLM: Boosting graph reasoning ability of large language model [ paper ]
- (Computers in Biology and Medicine) GIT-Mol: A multi-modal large language model for molecular science with graph, image, and text [ paper ]
- (EMNLP'2023) MolCA: Molecular graph-language modeling with cross- modal projector and uni-modal adapter [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) InstructMol: Multi-modal integration for building a versatile and reliable molecular assistant in drug discovery [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) G-Retriever: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Textual Graph Understanding and Question Answering [ paper ]
- (AAAI'2024) Graph neural prompting with large language models [ paper ]
🌐 LLMs as Prefix
- (arxiv'2023) Prompt-based node feature extractor for few-shot learning on text-attributed graphs [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) SimTeG: A frustratingly simple approach improves textual graph learning [ paper ]
- (KDD'2023) Graph-aware language model pre-training on a large graph corpus can help multiple graph applications [ paper ]
- (ICLR'2024) One for all: Towards training one graph model for all classification tasks [ paper ]
- (ICLR'2024) Harnessing explanations: Llm-to-lm interpreter for enhanced text-attributed graph representation learning [ paper ]
- (WSDM'2024) LLMRec: Large language models with graph augmentation for recommendation [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) OpenGraph: Towards Open Graph Foundation Models [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Label-free node classification on graphs with large language models (LLMs) [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) GraphEdit: Large Language Models for Graph Structure Learning [ paper ]
- (WWW'2024) Representation learning with large language models for recommendation [ paper ]
🌐 LLMs-Graphs Intergration
- (arxiv'2022) A molecular multimodal foundation model associating molecule graphs with natural language [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) ConGraT: Self-supervised contrastive pretraining for joint graph and text embeddings [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Prompt tuning on graph-augmented low-resource text classification [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) GRENADE: Graph-Centric Language Model for Self-Supervised Representation Learning on Text-Attributed Graphs [ paper ]
- (Nature Machine Intelligence'2023) Multi-modal molecule structure–text model for text-based retrieval and editing [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Pretraining language models with text-attributed heterogeneous graphs [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2022) Learning on large-scale text-attributed graphs via variational inference [ paper ]
- GreaseLM: Graph reasoning enhanced language models for question answering [ paper ]
- Disentangled representation learning with large language models for text-attributed graphs [ paper ]
- Efficient Tuning and Inference for Large Language Models on Textual Graphs [ paper ]
- (WWW'2024) Can GNN be Good Adapter for LLMs? [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2022) Graph Agent: Explicit Reasoning Agent for Graphs [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Call Me When Necessary: LLMs can Efficiently and Faithfully Reason over Structured Environments [ paper ]
- (ICLR'2024) Reasoning on graphs: Faithful and interpretable large language model reasoning [ paper ]
🌐 LLMs-Only
- (NeurIPS'2024) Can language models solve graph problems in natural language? [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) GPT4Graph: Can large language models understand graph structured data? an empirical evaluation and benchmarking [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) BeyondText:ADeepDiveinto Large Language Models’ Ability on Understanding Graph Data [ paper ]
- (KDD'2024) Exploring the potential of large language models (llms) in learning on graphs [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Graphtext: Graph reasoning in text space [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Talk like a graph: Encoding graphs for large language models [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) LLM4DyG:Can Large Language Models Solve Problems on Dynamic Graphs? [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Which Modality should I use–Text, Motif, or Image?: Understanding Graphs with Large Language Models [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) When Graph Data Meets Multimodal: A New Paradigm for Graph Understanding and Reasoning [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2023) Natural language is all a graph needs [ paper ]
- (NeurIPS'2024) Walklm:A uniform language model fine-tuning framework for attributed graph embedding [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) LLaGA: Large Language and Graph Assistant [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) InstructGraph: Boosting Large Language Models via Graph-centric Instruction Tuning and Preference Alignment [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) ZeroG: Investigating Cross-dataset Zero-shot Transferability in Graphs [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) GraphWiz: An Instruction-Following Language Model for Graph Problems [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) GraphInstruct: Empowering Large Language Models with Graph Understanding and Reasoning Capability [ paper ]
- (arxiv'2024) MuseGraph: Graph-oriented Instruction Tuning of Large Language Models for Generic Graph Mining [ paper ]
If you have come across relevant resources, feel free to submit a pull request.
To add a paper to the survey, please consider providing more detailed information in the PR 😊
The design of our README.md is inspired by Awesome-LLM-KG and Awesome-LLMs-in-Graph-tasks , thanks to their works!
Contributors 2
- DSA with JS - Self Paced
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
- JavaScript Program for Binary Representation of Next Number
- JavaScript Program to Reverse Digits of a Number
- Floating point number precision in JavaScript
- JavaScript Program to Convert a Number to Binary
- Print all Positive Numbers in JavaScript Array
- Binary Representations in Digital Logic
- JavaScript Number Static Properties
- JavaScript Program to Divide Large Number Represented as String
- Javascript Program to Generate all rotations of a number
- Print all Odd Numbers in a Range in JavaScript Array
- Javascript Program to Rotate digits of a given number by K
- JavaScript Program for Division of Two Numbers
- Find the Repeating & Missing Numbers in JavaScript Array ?
- Print all Positive Numbers in a Range in JavaScript Array
- What is the use of reverse() method in JavaScript Arrays ?
- JavaScript Program to Handle Number Overflow
- JavaScript Program to Find Maximum Number of Pieces in N Cuts
- Binary representation of previous number
- Binary representation of next number
Binary Representation of Previous Number in JavaScript
Given a binary input of a positive number, our task is to find the binary representation of a number that is one less than a given binary number n in JavaScript .
- The function “previousBinary1” converts the input binary string to a decimal number using “parseInt(binary, 2)”.
- It subtracts 1 from the decimal value to find the previous number.
- The function converts the resulting decimal number back to a binary string using “toString(2)”.
- The resulting binary string, which represents the previous number, is returned by the function.
- The function call console.log(previousBinary1(‘100010’)) prints the previous binary number, resulting in ‘100001’.
Example: The example below shows how to Find the binary representation of previous number using Brute Force Approach.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(log M)
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- JavaScript-DSA
- Web Technologies
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Notification: View the latest site access restrictions, updates, and resources related to the coronavirus (COVID-19) »
NREL Battery Supply Chain Database Maps Out the State of North America's Manufacturing Base

As the United States continues to transition to clean energy, strengthening the domestic supply chain by increasing the availability of critical materials is paramount to enabling greater domestic manufacturing.
This focus on securing the clean energy supply chain—in particular domestically—is a key part of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory's (NREL's) research supporting the energy transition. NREL researchers across clean energy technology areas investigate ways to optimize supply chains through data collection, assessments, benchmarking, and cost/sensitivity analyses.
NREL's support was critical to the recent U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) report, " America's Strategy to Secure the Supply Chain for a Robust Clean Energy Transition ," which outlines key areas for strengthening supply chain resiliency, including increasing the availability of critical materials and expanding domestic manufacturing capabilities. In addition, NREL is partnering directly with industry on lithium-ion batteries—one of the critical research areas identified in the report—to advance collaboration between U.S. private sector industries across the supply chain.
As part of ongoing efforts to map the battery landscape, NAATBatt International and NREL established the Lithium-Ion Battery Supply Chain Database to identify every company in North America involved in building lithium-ion batteries, from mining to manufacturing to recycling and everything in between. NREL and NAATBatt have recently released a new version of this first-of-its-kind database—first launched in 2021—with additional entries and an online interface that makes it even easier to map and filter the hundreds of entries detailing companies and their facilities and various segments in the supply chain.
"In response to industry requests, we have made this release of the database more intuitive, with easy- to-find information about companies involved in any aspect of the supply chain," said NREL's Vicky Putsche. "We've even added an online version of the North American map to show a visual representation of where these companies are located."
"We added filters to find companies working in different parts of the supply chain, allowing industry to identify competitors and collaborators and to help policymakers understand the current state of the U.S. industry," said NREL's Maggie Mann, supply chain analytics group manager.
Scoping the Early Supply Chain Landscape
The lithium-ion battery manufacturing cycle interlinks facilities participating in specific phases of battery development like mining or processing raw materials. The U.S. Federal Consortium of Advanced Batteries' National Blueprint for Lithium Batteries developed a blueprint to establish and expand the domestic supply chain for lithium-ion batteries, shifting away from relying on global dependence for such batteries. Both the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the Inflation Reduction Act passed by the U.S. Congress in 2021 and 2022, respectively, are investing billions of dollars in support of the battery and electric vehicles industries to develop a strong manufacturing supply chain in the United States.
The NREL-developed-and-managed Lithium-Ion Battery Supply Chain Database showcases key areas for coordination between supply chain companies, such as linking end-of-life facilities with midstream manufacturing capabilities.
"This database is an important step in better understanding the lithium-ion battery market and its North American players," said NREL's Ahmad Pesaran, the laboratory's chief energy storage engineer. "The new online interface makes it even easier for companies in the supply chain and individual companies to find and connect with other players in this space, ultimately strengthening our supply chain security."
As of March 2024, the database now offers a directory of nearly 700 companies and 850 facilities in North America across lithium-ion battery supply chain segments, including mining, material processing, cell and pack manufacturing, research and development, services, end-of-life management, and product distributors.
It also includes important information on each facility, including company, location, workforce, and type of products and services. Critically, the database summarizes key information such as installed battery manufacturing capacity and material production capability, plans for future capacity, types of chemistries and processes, and expansion plans by segment (e.g., upstream and downstream). An Excel version of the database is also available with detailed source information.
Additionally, the updated database includes other new and improved features:
- An easy-to-use interactive map to explore facilities, companies, and segments within the database directory, offering users the ability to search and filter products and companies by keyword, location, and supply chain segments and sub-segments
- Numerous new companies and facilities
- Changes to existing facilities, such as updates in volume production or workforce
- A new segment for professional services such as legal, investment, consulting, and insurance services that are expert in the battery space.
In the span of under three years, the number of companies/facilities in the North American lithium-ion battery supply chain has doubled—increasing from more than 400 to over 800 from September 2021 until March of 2024, Pesaran added. This increase has been the most notable for raw material manufacturing facilities, jumping from only about 25 to more than 80.
"We're proud that we've been able to strengthen the database's offerings to provide a more comprehensive picture of the supply chain landscape in lithium-ion battery material processing, manufacturing, and recycling," Pesaran said. "We have received a lot of compliments on the value and usefulness of the database."
Help Us Update the Database
As the lithium-ion battery supply chain landscape grows, the online database will keep pace with that growth.
Click on "Access Database" on the website to access the new online interface and/or download the Excel version of the database.
The database is regularly updated. To add your company or update your information, fill out the database questionnaire . All companies in the database are encouraged to review these updates and email NREL with any corrections.
Learn more about NREL's supply chain manufacturing , energy storage and sustainable transportation research. And sign up for NREL's quarterly transportation and mobility research newsletter, Sustainable Mobility Matters , to stay current on the latest news.

COMMENTS
What Is a Chart in Excel? A chart is a graphical and visual representation of data. In Excel, there are different kinds of charts. You can insert the data in a worksheet and Excel can provide you with beautiful and meaningful charts. A chart can help viewers to understand the data, trends of the data, and future values easily.
To create a column chart in Excel: Select the data range A1:D13. Click the "Insert" tab in the Excel ribbon. Click on the columns icon dropdown, and under the "2-D Column" category, choose "Clustered Column". You can now see a column chart that displays the number of units sold for each product category by the month.
Learn how to create charts and graphs in Excel 2016 to visualize numeric data and make smart business decisions. Compare different chart and graph types, presets, and best practices.
Choose Your Own Chart. If you would prefer to select a graph on your own, click the All Charts tab at the top of the window. You'll see the types listed on the left. Select one to view the styles for that type of chart on the right. To use one, select it and click "OK."
Navigate to the Insert tab: Once your data is selected, go to the Insert tab in the Excel ribbon. Choose a chart type: From the Charts group, select the type of chart you want to create. For a basic chart, you can choose from options like a column, line, or pie chart. B. Instructions on inserting and customizing a basic chart.
Creating PivotCharts. PivotCharts are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to visualize data from pivot tables. By summarizing and aggregating data, pivot tables provide a comprehensive overview that can be transformed into dynamic and interactive charts. Utilizing PivotCharts enables you to explore and analyze complex datasets with ease.
Learn how to create, edit, and improve graphs and charts in Excel with this step-by-step guide and tips. CFI is a leading provider of financial modeling and data visualization courses and templates.
Follow the steps mention below to learn to create a pie chart in Excel. From your dashboard sheet, select the range of data for which you want to create a pie chart. We will create a pie chart based on the number of confirmed cases, deaths, recovered, and active cases in India in this example. Select the data range.
Data visualization is a process of creating graphical representations of data. It is an essential tool for anyone who works with data, from data analysts and scientists to business owners and marketers. ... The first step in creating a chart or graph in Excel is to prepare your data. Your data should be arranged in columns or rows, with a clear ...
Step 1 − Select the data. Step 2 − Click Recommended Charts. A window displaying the charts that suit your data will be displayed. Excel Charts - Introduction - In Microsoft Excel, charts are used to make a graphical representation of any set of data. A chart is a visual representation of data, in which the data is represented by symbols ...
Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis, but it can be challenging to make sense of large data sets. ... Data visualization is a process of creating graphical representations of data. It is an ...
Open a Blank workbook in Excel. Click Insert chart. Select the type of graph you want to make (e.g., pie, bar, or line graph). Plug in the graph's headers, labels, and all of your data. Click and drag your mouse to select all your data, then click Insert. Select the type and format for the graph you want to create.
Selecting the appropriate data for your graphical presentation. When creating graphical presentations in Excel, it is essential to carefully choose the data that best suits the intended visualization. Here are some key points to consider: A. Identifying the specific data sets that best lend themselves to graphical representation
What are Excel Charts? An Excel chart is a graphical representation of data. It helps provides an opportunity to tell a compelling story to the audience through data visualization. Data visualization helps to understand the data patterns and connections. It is important to focus on the information that matters and tell a story derived from the ...
Data Visualization is the representation of data in a graphical format. It makes the data easier to understand. Data Visualization can be done using tools like Tableau, Google charts, DataWrapper, and many more. Excel is a spreadsheet that is used for data organization and data visualization as well.
Enter the data into Excel, each number in its own cell. Create a grouped frequency distribution. We need to use a grouped frequency distribution (where there are ranges of numbers instead of individual numbers) because there are too many individual numbers. The idea is to summarize the data, not show the exact same data in graphical form.
Page 4 Excel: Charts, Rel. 1.1, 1/14/2021 A chart is a graphic representation of worksheet data. Using a chart to represent worksheet data often leads to a better understanding of the data rather than simply presenting the numbers on a spreadsheet. Illustrated below is a spreadsheet showing the Sales for Widget
( Advanced MS Excel 2010 - https://www.edureka.co/advanced-ms-excel-self-paced )Watch Sample Class recording: http://www.edureka.co/advanced-ms-excel-self-pa...
In Excel, charts are used to make a graphical representation of any set of data. A chart is a visual representation of the data, in which the data is represented by symbols such as bars in a Bar Chart or lines in a Line Chart. Excel provides you with many chart types and you can choose one that suits your data or you can use the Excel ...
A frequency polygon can also be used when graphing large data sets with data points that repeat. 2.4: Using Excel to Create Graphs Using technology to create graphs will make the graphs faster to create, more precise, and give the ability to use larger amounts of data. This section focuses on using Excel to create graphs. 2.5: Graphs that Deceive
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Graphical Representation of Data: In today's world of the internet and connectivity, there is a lot of data available, and some or other method is needed for looking at large data, the patterns, and trends in it. There is an entire branch in mathematics dedicated to dealing with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting numerical data in visual form in such a way that it becomes ...
SPSS shines when it comes to the graphical representation of statistical data. It automatically generates a variety of charts and graphs that are ready for professional reports.
1 Nasa's Eyes on Asteroids. Image Source. If you are interested in exploring data visualization topics in space exploration, check out this striking data visualization created by NASA. NASA's Eyes on Asteroids is one of the best data visualizations due to its exceptional design and functionality.
Graph Understanding with LLM Framework - Source. GraphLLM explores two strategies: 1) LLMs-as-Enhancers where LLMs encode text node attributes before passing to the GNN, and 2) LLMs-as-Predictors where the LLM takes the GNN's intermediate representations as input to make final predictions.
Awesome-LLM4Graph-Papers. A collection of papers and resources about Large Language Models ( LLM) for Graph Learning ( Graph ). Graphs are an essential data structure utilized to represent relationships in real-world scenarios. Prior research has established that Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) deliver impressive outcomes in graph-centric tasks ...
It subtracts 1 from the decimal value to find the previous number. The function converts the resulting decimal number back to a binary string using "toString (2)". The resulting binary string, which represents the previous number, is returned by the function. The function call console.log (previousBinary1 ('100010')) prints the previous ...
Graphic by Joelynn Schroeder, NREL ... "We've even added an online version of the North American map to show a visual representation of where these companies are located." ... (e.g., upstream and downstream). An Excel version of the database is also available with detailed source information. Additionally, the updated database includes other ...