Popular Posts
- Contact Amy ==>

HOW TO – Format papers in standard academic format (using Microsoft Word)
This guide explains how to format your documents in Microsoft Word so that they follow the standard rules for formatting academic papers as described in most MLA and APA style books for undergraduate writing. These rules apply to most of the papers you will submit in your college classes, but in some cases your professors will want you to follow specific guidelines that may differ from those below. Always clarify with your professor which set of guidelines he or she wants you to follow before you submit a paper.
Using standard formatting for academic papers shows that you understand the customs of the university community and therefore helps to boost your own credibility. Using unusual or highly distinctive formatting, on the other hand, suggests that your previous schooling did not adequately prepare you for university work. Consider the impact of unusual formatting: not only does it call attention to your paper in a way that might not be positive, professors might also see it as a sign that you’re trying to artificially inflate page length.
Note: These instructions apply to all versions of Word for Mac and for the 2003 version of Word for Windows. I haven’t yet updated them to include instructions for the 2007 version of Word for Windows, but the tools should nevertheless be easy to find if you look around on the toolbar at the top.
- 2 DOCUMENT MARGINS
- 3 INDENTATION
- 5 ALIGNMENT
- 6.1 Heading
- 6.3 Sample First Page
- 7 PAGE NUMBERS
- 8.1 Document Spacing
- 8.2 Paragraph Spacing
- 9 CREATE NEW PAGE
- 10 BLOCKED QUOTATIONS
- 11 RESOURCES
DOCUMENT MARGINS
Rule : Papers submitted for review or grading should have 1” margins all around. This should be the default for Word, but if your default setting is to have left and right margins of 1.25”, change your default. Page length requirements are based on 1” margins.
Instructions : Go to the Format menu, drag down to Document, change the margins, and the click on the Default button and accept the change to the Normal template. Make sure you leave the gutter set to 0” or you’ll mess up your document formatting.
INDENTATION
Rule : The first line of each paragraph should be automatically indented.
Instructions : This should be the default for Word, but if not, you might want to change your Normal style, as described above. To change the indentation format for a document, choose Select All from the Edit menu. Then go to the Format menu, drag down to Paragraph, look under the “Special” drop-down menu in the Indentation section, and select “First Line.” This setting automatically indents the first line of a new paragraph so that you don’t have to do it manually.
Rule : College papers should be in a standard academic font: either Times New Roman or Cambria, in 12pt size. (If you submit a paper in another font, I will change it on the file I download.)
Instructions : Times New Roman or Cambria 12pt should be the default for Word, but if yours is different then change your default. Go to the Format menu, drag down to Style, make sure “Normal” is selected from the list of styles, and click “modify.” Choose the correct font and size from the Formatting menu. Click “OK” to make the change to your default settings.
Rule : The text of your paper should be left aligned, NOT justified, as justified text is hard to read if it hasn’t been professionally typeset. The default in Word is left alignment, so don’t change it.
FIRST PAGE FORMAT
Rule : In the upper left corner of the first page of your document, type your name, the date, the course number and section (or topic), and the version of the paper (such as Paper 1 Second Draft), each on a separate line. Be sure to change the date and paper version when you submit revisions and final versions. See the sample below.
DO NOT use the “headers” feature from the header/footer menu to create this full heading as that will make it appear on every page, which is not customary in academic writing. Also do NOT use a title page unless the assignment specifically asks for one.
Rule : Skip a line after the heading and center an original title that conveys the topic of your paper. Do not use underlining or italics in the heading (unless you’re referring to the title of a book or periodical). Do not use bold text or ALL CAPS.
Sample First Page
Page numbers.
Rule : All papers should have automatically inserted page numbers that show in the upper right corner on all pages except the first. Do not insert these page numbers by hand. Instead, use Word’s Header/Footer tool.
For documents following MLA format, put your last name and page number in the upper right corner. For documents following APA format, put a short version of your title (instead of your last name) and the page number in the upper right corner.
Instructions : Go to the View menu and choose “Header and Footer.” You’ll see a header box appear at the top and a footer box at the bottom. Click in the header box, type your last name (or title), make it align to the right, and then select Page Numbers from the Insert menu.
When you’re finished, click on the “Close” tab under the Header view. Each page of your document should now display a page number at the upper right that updates automatically when you make changes to the document. It will appear as grayed out text unless you active the Header and Footer tool to make changes.
To change the setting so that page numbers do not display on the first page, go to the Format men, drag down to Document, and click on the Layout button. Then check the box next to “Different First Page.” Click OK. If necessary, remove the header that appears on the first page and insert a header on the second page, which will automatically appear on all subsequent pages as well.
Document Spacing
Rule : The entire paper should be double-spaced, including the heading and bibliography.
Instructions : Choose “Select All” from the Edit menu, go to the Format menu and drag down to Paragraph, and choose “double” from the “line spacing” menu in the Spacing section. Or you can use these keyboard shortcuts. On a Mac, use Cmd-A to select all and Cmd-2 to double-space. On a PC, use Ctrl-A to select all and Ctrl-2 to double space.
Paragraph Spacing
Rule : Papers should have no extra spacing after paragraphs. This should be the default for Word, but if your default setting is to have 10pt spacing after paragraphs, change your default.
Instructions : Go to the Format menu, drag down to Style, make sure “Normal” is selected from the list of styles, and click “modify.” In the lower left corner, select the dropdown menu that starts with “Format” and drag down to Paragraph. In the paragraph settings menu that pops up, change the settings for Spacing After to 0pt.
CREATE NEW PAGE
Instead of using a lot of returns before starting your bibliography, create a new page for it following these instructions.
Go to the Insert menu, drag down to Break, and then drag over to Page Break.
BLOCKED QUOTATIONS
Rule : If a quotation will exceed four lines within a paragraph, you should separate it out by blocking and indenting it. As with any quotation, a blocked quotation should be clearly introduced by the sentence that leads up to it and it should also be properly cited, but the rules for blocked quotations are somewhat different. The blocking take the place of quotation marks, and unlike in a regular in-paragraph quotation, the parenthetical citation goes outside of the final period instead of inside of it (given that the blocked quote might contain several sentences.)
Instructions : Type the quotation in its own paragraph, without quotation marks, and remove the indent from the first line. Type the source in parentheses after the last period of the last sentence. With your cursor, select the quotation, from the first word to the end of the parenthetical citation, and click the Increase Indent button from the Paragraph Formatting menu.
- MLA Formatting Guidelines for College Papers
- APA Formatting Guidelines for College Papers
- Search for:
WHAT IS THIS SITE? See the About tab in the top menu.
UNDER PERPETUAL REVISION : All materials on this site are subject to ongoing revision and improvement!
© 2017 - Amy Goodloe - All Rights Reserved
HELP & HOW-TO
- HOW TO: Capture & Edit Video (18)
- HOW TO: Find & Edit Images (13)
- HOW TO: Make Screen Recordings (7)
- HOW TO: Record & Edit Audio (16)
- HOW TO: Use Google Drive (19)
- HOW TO: Use iMovie (13)
- HOW TO: Use Social Media Tools for Class (3)
- HOW TO: Use the Class Blog (Wordpress) (35)
- HOW TO: Use Your WordPress.com Blog (12)
- INSPIRATIONS & FYI'S (21)
- NIFTY APPS & TOOLS (7)
- PLANNING & DRAFTING New Media Projects (23)
- RESOURCES: About New Media Writing (7)
- RESOURCES: Animations & Comics (9)
- RESOURCES: Apps for Creating New Media Projects (22)
- RESOURCES: Digital Storytelling (17)
- RESOURCES: Presentations & Information Design (6)
- RESOURCES: Storytelling Prompts (14)
- RESOURCES: Writing for the Web (4)
- TECH TIPS (28)
STUDENT SAMPLES
- SAMPLES – Academic Analyses (9)
- SAMPLES – Audio Narratives & Essays (16)
- SAMPLES – CDS-Style Digital Storytelling (30)
- SAMPLES – Educational Presentations & Web Sites (9)
- SAMPLES – Educational Visuals (14)
- SAMPLES – Graphic Storytelling (16)
- SAMPLES – Mini-Documentary (15)
- SAMPLES – Multimedia Commentary (8)
- SAMPLES – Pop Culture Artifact Analyses (13)
- SAMPLES – Turning Points & Epiphanies (7)
- SAMPLES – WRTG 3020: Rhetoric of G&S (96)
- SAMPLES – WRTG 3090: New Media Storytelling (33)
- HOW TO – Format papers in standard academic format (using Microsoft Word) 118,204 views
- HOW TO – Put your file into a shared folder on Google Drive 85,097 views
- HOW TO – Make Preview the Default PDF Reader on a Mac 52,498 views
- HOW TO – Create a Hyperlink (Turn a Word into a Link) 42,916 views
- HOW TO – Export an mp3 out of GarageBand 29,446 views
- HOW TO – Add a shortcut to a shared folder to My Drive (for easy access) 22,365 views
- Creative non-fiction writing exercises 19,160 views
- TROUBLESHOOTING – Audio problems when recording with QuickTime X 12,247 views
- TIPS – Camera Angles and Shooting Tips for Digital Storytelling 9,993 views
- HOW TO – Save a Google Docs document 9,927 views

Customize or create new styles
You can use styles to quickly apply a set of formatting choices consistently throughout your document. If you want formatting choices that are not available from the built-in styles and themes available in Word, you can modify an existing style and customize it to suit your needs. You can change the formatting (such as font size, color, and text indentation) in styles applied to titles, headings, paragraphs, lists, and so on. You can also select formatted text in your document to create a new style in the Styles gallery .
The styles covered in this article are located in the Styles gallery, a visual menu located on the Home tab. To apply a style, simply select the text you want to format, and then click the style you want in the Styles gallery. To learn more, see Apply a style to text in Word .
Modify an existing style
You can modify an existing style in the Styles gallery in two ways:
Modify a style by updating it to match formatting in your document
Modify a style manually in the modify style dialog box.
If you have text in your document that already has a style applied, you can change the formatting of that text and apply it to the style in the Styles gallery.
Select text in your document that has the style applied, such as Heading 1.
When you select text that has a style applied, that style is highlighted in the Styles gallery.
Format the selected text with the new attributes that you want.
For example, you might want to change the point size for the Heading 1 style from 16 points to 14 points.
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, right-click the style that you want to change, and then click Update [Style Name] to Match Selection .
Note: All text with the style that you changed will automatically change to match the new style that you defined.
You can modify a style directly in the Styles gallery, without using the text in your document.
On the Home tab, right-click any style in the Styles gallery and click Modify .
In the Formatting section, make any formatting changes you want, such as font style, size, or color, alignment, line spacing, or indentation.
Choose whether the style change applies to the current document or to all future documents.
Create a new style based on document formatting
You can select formatted text in your document to create a new style that you add to the Styles gallery.
Right-click the text on which you want to base a new style.
In the mini toolbar that appears, click Styles , and then click Create a Style .
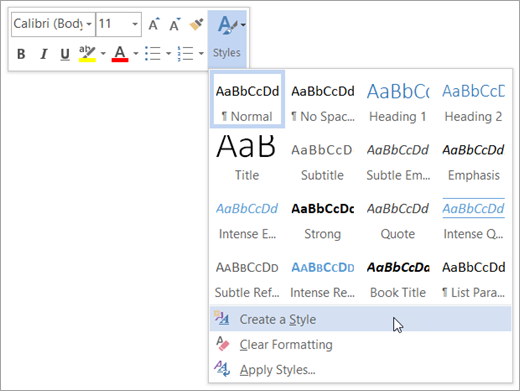
In the Create New Style from Formatting dialog box, give your style a name and click OK .
Your new style will now appear in the Styles gallery.
Note: If you want your new style to appear in all new Word documents, right-click it in the Styles gallery, click Modify , and then select New documents based on this template at the bottom of the dialog box.
Apply a style to text in Word

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
APA (7th Edition) Referencing Guide
- Information for EndNote Users
- Authors - Numbers, Rules and Formatting
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Books & eBooks
- Book chapters
- Journal Articles
- Conference Papers
- Newspaper Articles
- Web Pages & Documents
- Specialised Health Databases
- Using Visual Works in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Using Visual Works in Theses and Publications
- Using Tables in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Custom Textbooks & Books of Readings
- ABS AND AIHW
- Videos (YouTube), Podcasts & Webinars
- Blog Posts and Social Media
- First Nations Works
- Dictionary and Encyclopedia Entries
- Personal Communication
- Theses and Dissertations
- Film / TV / DVD
- Miscellaneous (Generic Reference)
- AI software
APA 7th examples and templates
Apa formatting tips, thesis formatting, tables and figures, acknowledgements and disclaimers.
- What If...?
- Other Guides

You can view the samples here:
- APA Style Sample Papers From the official APA Style and Grammar Guidelines
Quick formatting notes taken from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association 7th edition
Use the same font throughout the text of your paper, including the title and any headings. APA lists the following options (p. 44):
- Sans serif fonts such as 11-point Calibri, 11 point-Arial, 10-point Lucida,
- Serif fonts such as 12-point Times new Roman, 11-point Georgia or 10-point Computer Modern.
(A serif font is one that has caps and tails - or "wiggly bits" - on it, like Times New Roman . The font used throughout this guide is a sans serif [without serif] font). You may want to check with your lecturer to see if they have a preference.
In addition APA suggests these fonts for the following circumstances:
- Within figures, use a sans serif font between 8 and 14 points.
- When presenting computer code, use a monospace font such as 10-point Lucida Console or 10-point Courier New.
- Footnotes: a 10-point font with single line spacing.
Line Spacing:
"Double-space the entire paper, including the title page, abstract, text, headings, block quotations, reference list, table and figure notes, and appendices, with the following exceptions:" (p. 45)
- Table and figures: Words within tables and figures may be single-, one-and-a-half- or double-spaced depending on what you decide creates the best presentation.
- Footnotes: Footnotes appearing at the bottom of the page to which they refer may be single-spaced and formatted with the default settings on your word processing program i.e. Word.
- Equations: You may triple- or quadruple-space before and after equations.
"Use 1 in. (2.54 cm) margins on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right) of the page." If your subject outline or lecturer has requested specific margins (for example, 3cm on the left side), use those.
"Align the text to the left and leave the right margin uneven ('ragged'). Do not use full justification, which adjusts the spacing between words to make all lines the same length (flush with the margins). Do not manually divide words at the end of a line" (p. 45).
Do not break hyphenated words. Do not manually break long DOIs or URLs.
Indentations:
"Indent the first line of every paragraph... for consistency, use the tab key... the default settings in most word-processing programs are acceptable. The remaining lines of the paragraph should be left-aligned." (p. 45)
Exceptions to the paragraph indentation requirements are as follows:
- Title pages to be centred.
- The first line of abstracts are left aligned (not indented).
- Block quotes are indented 1.27 cm (0.5 in). The first paragraph of a block quote is not indented further. Only the first line of the second and subsequent paragraphs (if there are any) are indented a further 1.27 cm (0.5 in). (see What if...Long quote in this LibGuide)
- Level 1 headings, including appendix titles, are centred. Level 2 and Level 3 headings are left aligned..
- Table and figure captions, notes etc. are flush left.
Page numbers:
Page numbers should be flush right in the header of each page. Use the automatic page numbering function in Word to insert page numbers in the top right-hand corner. The title page is page number 1.
Reference List:
- Start the reference list on a new page after the text but before any appendices.
- Label the reference list References (bold, centred, capitalised).
- Double-space all references.
- Use a hanging indent on all references (first line is flush left, the second and any subsequent lines are indented 1.27 cm (0.5 in). To apply a hanging indent in Word, highlight all of your references and press Ctrl + T on a PC, or Command (⌘) + T on a Mac.
Level 1 Heading - Centered, Bold, Title Case
Text begins as a new paragraph i.e. first line indented...
Level 2 Heading - Flush Left, Bold, Title Case
Level 3 Heading - Flush Left, Bold, Italic, Title Case
Level 4 Heading Indented, Bold, Title Case Heading, Ending With a Full Stop. Text begins on the same line...
Level 5 Heading, Bold, Italic, Title Case Heading, Ending with a Full Stop. Text begins on the same line...
Please note : Any formatting requirements specified in the subject outline or any other document or web page supplied to the students by the lecturers should be followed instead of these guidelines.
What is an appendix?
Appendices contain matter that belongs with your paper, rather than in it.
For example, an appendix might contain
- the survey questions or scales you used for your research,
- detailed description of data that was referred to in your paper,
- long lists that are too unweildy to be given in the paper,
- correspondence recieved from the company you are analysing,
- copies of documents being discussed (if required),
You may be asked to include certain details or documents in appendices, or you may chose to use an appendix to illustrate details that would be inappropriate or distracting in the body of your text, but are still worth presenting to the readers of your paper.
Each topic should have its own appendix. For example, if you have a survey that you gave to participants and an assessment tool which was used to analyse the results of that survey, they should be in different appendices. However, if you are including a number of responses to that survey, do not put each response in a separate appendix, but group them together in one appendix as they belong together.
How do you format an appendix?
Appendices go at the very end of your paper , after your reference list. (If you are using footnotes, tables or figures, then the end of your paper will follow this pattern: reference list, footnotes, tables, figures, appendices).
Each appendix starts on a separate page. If you have only one appendix, it is simply labelled "Appendix". If you have more than one, they are given letters: "Appendix A", "Appendix B", "Appendix C", etc.
The label for your appendix (which is just "Appendix" or "Appendix A" - do not put anything else with it), like your refrerence list, is placed at the top of the page, centered and in bold , beginning with a capital letter.
You then give a title for your appendix, centered and in bold , on the next line.
Use title case for the appendix label and title.
The first paragraph of your appendix is not indented (it is flush with the left margin), but all other paragraphs follow the normal pattern of indenting the first line. Use double line spacing, just like you would for the body of your paper.
How do I refer to my appendices in my paper?
In your paper, when you mention information that will be included or expanded upon in your appendices, you refer to the appendix by its label and capitalise the letters that are capitalised in the label:
Questions in the survey were designed to illicit reflective responses (see Appendix A).
As the consent form in Appendix B illustrates...
How do I use references in my appendices?
Appendices are considered to be part of your paper for the purpose of referencing. Any in-text citations used in your appendix should be formatted exactly the same way you would format it in the body of your paper, and the references cited in your appendices will go in your reference list (they do not go in a special section of your reference list, but are treated like normal references).
If you have included reproduced matter in your appendices, treat them like an image or a table that has been copied or adapted. Place the information for the source in the notes under the reproduced matter (a full copyright acknowledgement for theses or works being published, or the shorter version used at JCU for assignments), and put the reference in the reference list.
- Thesis Formatting Guide Our Library Guide offers some advice on formatting a thesis for JCU higher degrees.
- Setting up a table in APA 7th
- Setting up a figure in APA 7th
If you are required to include an acknowledgement or disclaimer (for example, a statement of whether any part of your assignment was generated by AI, or if any part of your assignment was re-used, with permission, from a previous assignment), this should go in an author note .
The author note is placed on the bottom half of the title page, so if you are using an author note, you will need to use a title page. Place the section title Author Note in centre and in bold. Align the paragraph text as per a normal paragraph, beginning with an indent. See the second image on this page for an example of where to place the author note: Title Page Setup .
The APA Publication Manual lists several paragraphs that could be included in an author note, and specifies the order in which they should appear. For a student assignment, you will probably only require a paragraph or sentence on disclosures and acknowledgements.
An example author note for a student paper could be:
Author Note
This paper was prepared using Bing Copilot to assist with research and ChatGPT to assist with formatting the reference list. No generative AI software was used to create any part of the submitted text.
No generative AI software was used to create any part of this assignment.
- If the use of generative AI was permitted for drafting or developing parts of your assignment, you will need to include a description in the methodology section of your paper specifying what software was used, what it was used for and to what extent.
- If your subject outline has a specific disclaimer to use, use that wording in your author's note.
- If the use of generative AI software is permitted, you will still need to review the material produced by the software for suitability and accuracy, as the author of the paper is ultimately responsible for all of the content.
- << Previous: AI software
- Next: What If...? >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 5:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/apa

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
How to Format a Word Document to Look Professional
Last Updated: March 14, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Megaera Lorenz, PhD . Megaera Lorenz is an Egyptologist and Writer with over 20 years of experience in public education. In 2017, she graduated with her PhD in Egyptology from The University of Chicago, where she served for several years as a content advisor and program facilitator for the Oriental Institute Museum’s Public Education office. She has also developed and taught Egyptology courses at The University of Chicago and Loyola University Chicago. There are 18 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 29,631 times. Learn more...
Whether you’re writing a research paper for class, composing an article for a newsletter, or trying to create the perfect cover letter, you’ll want your Word doc to look as polished and professional as possible. Fortunately, Word gives you all the tools you need to make your documents stand out and look great. In this article, we’ll talk you through the basics—like how to adjust your font or pick the right paragraph style—as well as some more advanced tips and tricks, like turning on hidden formatting marks.
Formatting Basics

- To choose a font, go to the Home tab at the top of your document. Select the font you like best from the drop-down font menu at the right side of the menu ribbon.
- There are hundreds of fonts to choose from, but try to stick to fonts with a simple, classic look to keep your document looking professional and easy to read. Avoid anything overly elaborate or artsy.

- While Comic Sans is a popular and easy-to-read sans-serif font, it’s gained a bit of a bad rap for looking childish and unprofessional. Avoid using comic sans if you want your doc to have a polished and mature look.

- Type the text you’d like to use for a heading. For instance, you might write something like “Section 1” or “Introduction.”
- Select the heading text.
- Open the Home tab and go to the Styles section of the ribbon menu, at the top right side of the document.
- Select the heading style you want from the list of styles. For instance, if you’re creating a top-level heading, select Heading 1 . For subheadings, choose Heading 2 or Heading 3 .

- It works well to combine serif fonts in the headings with sans-serif fonts in the body of your document. For instance, you might use Didot for your headings and Gill Sans for the body text.
- If you don’t want to change the font of each heading manually, go to the Home tab and open the Styles Pane . Select the drop-down menu for the heading style you want, choose Modify Style… and select the font you want.

- You can also change the text alignment by going to the Format menu at the top of your screen and picking Paragraph from the drop-down list. Set the alignment to Left in the general settings menu.
- While left alignment looks best in most cases, there are exceptions. For instance, you will typically center the title and author lines at the top of a paper. You might also choose to center your headings.
- In most cases, it’s best to avoid using the “justify” alignment, which makes the text even on both the right and left sides. This formatting style works best in documents written in narrow columns, like brochures, magazine articles, and newsletters. [6] X Research source

- Word’s default combination of 12-point font size and 1 in (2.5 cm) margin size is required by a lot of professional citation and formatting styles, like APA and MLA. [8] X Research source If you’re completing a writing assignment for class or a publication, check the guidelines about margins and font size.
- While you can make your margins smaller, your document will be less readable and pleasant to look at if the text crowds the edges of the page.

- You can also use the Layout tab in Word to automatically indent each paragraph. Set the Indent setting in the middle of the ribbon menu to the desired size. For example, set the Left indent to .5 inches (1.3 cm). Every time you hit ⏎ Return to start a new paragraph, it will be automatically indented.
- You can also make these adjustments by opening up Paragraph… in the Format dropdown menu. Set the exact indent size you want in the Indentation section of the settings window.
- If you’d rather use Tab ↹ to indent each paragraph, you can also adjust the tab stop setting to change the size of the indent. Go to the Home tab and click the Increase Indent or Decrease Indent buttons in the central paragraph section of the ribbon menu. [10] X Trustworthy Source Microsoft Support Technical support and product information from Microsoft. Go to source

- You can also simply hit ⏎ Return twice after each paragraph to create an extra line space.
- To apply your preferred paragraph spacing automatically to the whole document, change the paragraph spacing settings in the Layout tab.
- Alternatively, go to the Design tab at the top of your document and select the Paragraph Spacing dropdown menu. Select the preset spacing you want to automatically apply the style to your entire document.

- If you’ve already started writing your document, you’ll need to select the text you want to format first. Otherwise, simply set your line spacing before you start writing.
- If your document doesn’t have any particular spacing requirements, you can still adjust the spacing to make it easier to look at. Open the Line Spacing menu in the Home tab to enter a custom amount of space between each line (such as 1.08 spaces). [16] X Research source
Advanced Techniques

- If you find a problem—such as a paragraph marker where there’s not supposed to be one—you can simply delete it to resolve any troublesome formatting issues. For instance, blank paragraphs can sometimes cause unwanted extra pages to appear in your document with no content.
- You can even fine-tune which formatting marks are visible, if you like. In Word for Windows, go to the File menu, then open Options and select Display . Go to the Always show these formatting marks on the screen section to select which marks you want to see.
- If you’re using a Mac, go to the Word menu, then open Preferences and select View . Select the marks you want to see under Show Non-Printing Characters .

- Open the Format menu and select Font . Select the Advanced tab and check the box next to Kerning for fonts .
- In the Points and above box, adjust the point size you want the kerning to apply to. It should automatically fill in the current point size for the font you’re using.

- Click the Autoformat as You Type tab.
- Go to the Replace as you type section.
- Check the box next to Straight quotes with smart quotes .
- While you’re at it, you can also adjust other autoformatting options, such as replacing double dashes (--) with a single long em-dash (–).

- Go to the Home tab and open the Styles Pane .
- Select the style you want, then open the drop-down menu for the style and select Modify…
- Make any adjustments you want to the style in the Modify Style window. For instance, you can change the font size and color, or make adjustments to paragraph or line spacing.
- You can also right-click the style you want in the ribbon menu (or use Ctrl -click if you’re on a Mac) and select Modify Style .
- If you want a different set of preset styles to work with, go to the Design tab at the top of your document and choose one of the themes from the ribbon menu. This will change the overall look of your document.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about making effective presentations, check out our in-depth interview with Vikas Agrawal .
- ↑ https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/business-communication/choosing-fonts-for-business-documents/1/
- ↑ https://accessibility.psu.edu/legibility/fontface/
- ↑ https://iteach.msu.edu/my-campus-ties/groups/accessible-course-design-learning-community/stories/170
- ↑ https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-typography-determines-readability-serif-vs-sans-serif-and-how-to-combine-fonts-629a51ad8cce/
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/align-text-left-or-right-center-text-or-justify-text-on-a-page-70da744d-0f4d-472e-916d-1c42d94dc33f
- ↑ https://ontariotraining.net/to-justify-or-not-to-justify-text/
- ↑ https://www.ferrum.edu/downloads/careers/cover-letters.pdf
- ↑ https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/microsoft-word/margins
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/paragraph-format
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/set-tab-stops-and-paragraph-indents-in-microsoft-word-34361115-2b5a-9fcc-2d34-9d7c9e007b71
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/job_search_writing/job_search_letters/cover_letters_1_quick_tips/quick_formatting_tips.html
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/change-spacing-between-paragraphs-ee4c7016-7cb8-405e-90a1-6601e657f3ce
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_general_format.html
- ↑ https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/word2013/line-and-paragraph-spacing/1/
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/show-or-hide-tab-marks-in-word-84a53213-5d02-404a-b022-09cae1a3958b
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/change-the-spaces-between-text-e9b96011-1c42-45c0-ad8f-e8a6e4a33462
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/smart-quotes-in-word-702fc92e-b723-4e3d-b2cc-71dedaf2f343
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/customize-or-create-new-styles-d38d6e47-f6fc-48eb-a607-1eb120dec563
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help:
Tech troubles got you down? We've got the tips you need
We use cookies to ensure we give you the best experience of our website. By browsing this site you accept we use cookies to improve and personalise our services and marketing. Read our privacy statement for more about what we do with your data, as well as your rights and choices.
- Studying by distance learning
- Get prepared for study
- How much time will you need?
- International and studying from overseas
- About our qualifications
- How to decide what to study
- Full-time or part-time study?
- How we'll support your studies
- Online tools and resources
- Te tautoko i te angitū o ngā ākonga Māori - Supporting Māori learner success
- Pasifika learner support
- Disability and Access Services
- Access to local campus services
- Fees free study
- Paying your fees
- Student loans
- Scholarships, awards and financial assistance
- Learner stories
- Choose courses
- How to apply to enrol
- Enrolment dates
- Recognising previous study and experience
- English language entry requirements
- Providing proof of your identity
- Terms and conditions of enrolment
- Fees and funding
- Changes to your enrolment
- Changes to benefit Open Polytechnic learners
- Student Advisory Group
- Disclaimer and copyright statement
- Notice of meetings
- Jobs at Open Polytechnic
- Who are our learners?
- Our Māori learners
- Our Pasifika learners
- Media Contact
- Publications
- First Impressions Survey
- Academic research
- Hei whaiwhakaaro i mua i tō ako - Some things to think about before you study
- Te whakatau he aha hei ako māu - Deciding what to study
- Whakawhiwhinga ākonga Māori - Scholarships and awards for ākonga Māori
- Message from Pule Ma’ata - Pasifika
- Meet our kaimahi Pasifika
- Pasifika success
- Scholarships for Pasifika
- Getting started with online learning
- Course and study support
- Supporting Māori learner success
- Dyslexia and the Dyslexia-Friendly Quality Mark
- Meet some of our learners
- Get help with academic writing and research skills
- Mental health support
- Using iQualify
- MyOP learner portal and app download
- Accessing your learner email and free Microsoft software
- Our library
- Assistive technology tools
- Helperbird free assistive technology tool
- How to re-enrol
- Withdrawals and course transfers
- Learner forms
- Get your student ID card
- Get started
- Make a plan
- Set study goals
- Reading skills
- Active learning
- Taking notes
- Mind mapping
- Researching
- Evaluating information
- Critical thinking for reading and research
- Step-by-step guide to tackling assessments
- Assessment types
- Plan your assessment
- Understand your assessment task
- Writing skills
Formatting and presenting assessments
- Assessments information
- Referencing and plagiarism
- How to reference
- Preparing for exams
- Types of exam questions
- Planning your time for an exam
- Information for sitting exams
- Research ethics for doing research projects
- How your work will be assessed
- How to submit your assessment for marking
- Submitting your work in te reo Māori
- How to request an assessment extension
- Special Consideration for in-course assessments
- Grading scales
- Academic Integrity
- Assessment writing
- Referencing
- Word limits and word count guidelines
- Using AI - Artificial Intelligence services
- Exam dates and venue information
- Exam admittance information and permitted materials
- Information for exam day
- Sitting exams from overseas
- Getting assistance with exams
- Exam reconsiderations, resits and the return of exam papers
- Aegrotat consideration
- Getting your final results
- Te whare tapa whā
- The Fonofale model of health
- Taha tinana – physical wellbeing
- Taha hinengaro – mental wellbeing
- Taha whānau – family, community and social wellbeing
- Taha wairua – spiritual wellbeing
- Free mental health support
- Rainbow learner support
- Applying to graduate
- Attending a graduation ceremony
- Academic transcripts
- Graduation Live Stream
- Tertiary and International Learners Code of Practice
- Complaints and concerns
- Learning Engine LMS
- CPD and training services
- Digital design, video, animation and software development
- Instructional design
- Content licensing
- Digital design, video and animation
Formatting and presenting your assessments correctly is important because many include marks for presentation.
This may include marks for things such as:
- formatting and layout
- APA referencing
- writing style
- grammar and spelling.
Before you start on your assessment:
- check your assessment question, emails from your course leader, and learning materials for how it should be presented
- read the instructions carefully. Make sure you understand them and follow them exactly
- if you're not sure about what’s required contact your course leader.
General guidelines for electronic submissions
- Most assessments should be produced using Microsoft Word.
- You can also submit assessments using: .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx or .rtf.
- if you don’t have Microsoft Word go to My Open Polytechnic to download and access your free version
- if you're not sure about the file type required, contact your course leader.
- Use a clear, readable font, such as Verdana, Calibri, Tahoma or Arial and use the same font throughout.
- Use black text on a white background.
- Avoid coloured backgrounds or text in a colour other than black, unless you have special permission to use them.
- Use 11 or 12 point font for the body of your assessment.
- Use 1.5 spacing and 2.53 cm (1”) wide margins.
- Leave a blank line between paragraphs.
- If the questions are short, leave a blank line between each question. If they are long, start each question on a new page.
- Left-justify your work (also known as left-aligned).
- Use bold for headings.
- Essays don’t usually need subheadings; reports usually do.
Most assessments need a title page, which should include:
- the title and number of the assessment
- the course number and name
- the due date
- your full name and student number.
Centre this information on the page, starting approximately one-third of the way down the page.
- Number and clearly label figures and tables.
- Add numbers as follows: Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Table 2, and so on.
- Put table and figure captions above the table.
- Don't number the items in a reference list.
For more help with figures and tables, check:
Get more help with tables and figures – APA Style website
Headers and footers
Insert a header or footer on each page (except the title page). It should contain:
- your name (last name, first name/s)
- your student number
- the course code
- the assessment number
- page numbers.
Reference list
The reference list comes at the end of the assessment and should start on a new page labelled 'References'.
Need more help with reference lists? Check out the guides below:
Quick referencing APA guidelines (PDF 47 KB; opens in a new window)
Guide to APA referencing (PDF 395.11 KB; opens in a new window)
Appendices are used for information that:
- is too long to include in the body of your assessment
- supplements or complements the information you are providing.
Start each appendix (if applicable) on a new page. If there's just one appendix label it ‘Appendix’ without a number. If there is more than one, label them Appendix A, Appendix B, and so on.
In the main text of your assessment, refer to the Appendix by the label – for example, Appendix A.
Tops and bottoms of pages
Check the top and bottom of your pages to ensure they avoid:
- widows – single lines of text at the top of a page
- orphans – first lines of paragraphs at the bottom of a page
- tombstones – headings or subheadings alone at the bottom of a page
- split lists – lists that are divided between two pages (if possible).
General guidelines for hard copies
Most of the guidelines above also apply to hard copies (printed or handwritten documents).
If your course requires or allows handwritten assessments, be sure to follow the course instructions on presenting handwritten assessments.
Word limits and word count guidelines
Word limits support the development of concise writing skills. Word count guidelines help you to understand the expectation of workload for an assessment.
For more detailed information about these go to:
Word limits and word count guidelines
Got a question?
If you want to talk with someone about formatting and presenting your assessments, contact The Library and Learning Centre | Te Whare Pukapuka Wāhanga Whakapakari Ako.
Contact the Library and Learning Centre
Subject Explorer
School Subjects
Math & Science
Business & Technology
Electives & Health
Board & Administration
Teaching & Learning
Audio/Video Lectures
Books & Documents
Classifieds
Jobs & Resources
Discussions
Language & Literature
Practice Projects for Microsoft Word

Word 9 Table
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with a title and table. The table has two columns that have different font alignment and incluces various fonts. …

Word 8 Formatting Text
In this practice project for Word, students create a document using a different size and color font for the title than the rest of the paragraph. …

Word 7 Bullets
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with two different types of bullets showing points and subpoints. …

Word 6 Letter
In this practice project for Word, students create a letter. Included in the letter is a heading on the right, indented paragraphs, and the closing and signiture near the middle of the document. …

Word 5 Text And Outline
In this practice project for Word, students create a document that contains several paragraphs of text and also includes an outline with key points and subpoints. …

Word 4 Modified Text
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with the heading on the right, a boldfaced, centered title, and indented paragraphs. The document is double-spaced. …
Word 3 Basic Text
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with the heading on the right, a boldfaced title that is centered, and several paragraphs that are indented. …

Word 22 Preset Headings
In this practice project for Word, students create a document using the preset headings to create a title bar. The document has different alignment and font, blanks, and a short outline. …

Word 21 Formatting Options
In this practice project for Word, students create a document that shows some different effects that can be used with the same font. …

Word 20 Numbered List
In this practice project for Word, students create a document that includes a centered title followed by a numbered list. …

Word 2 Heading 2
In this practice project for Word, students create a document that has a centered title, a heading in the upper right corner, and indented paragraphs. …
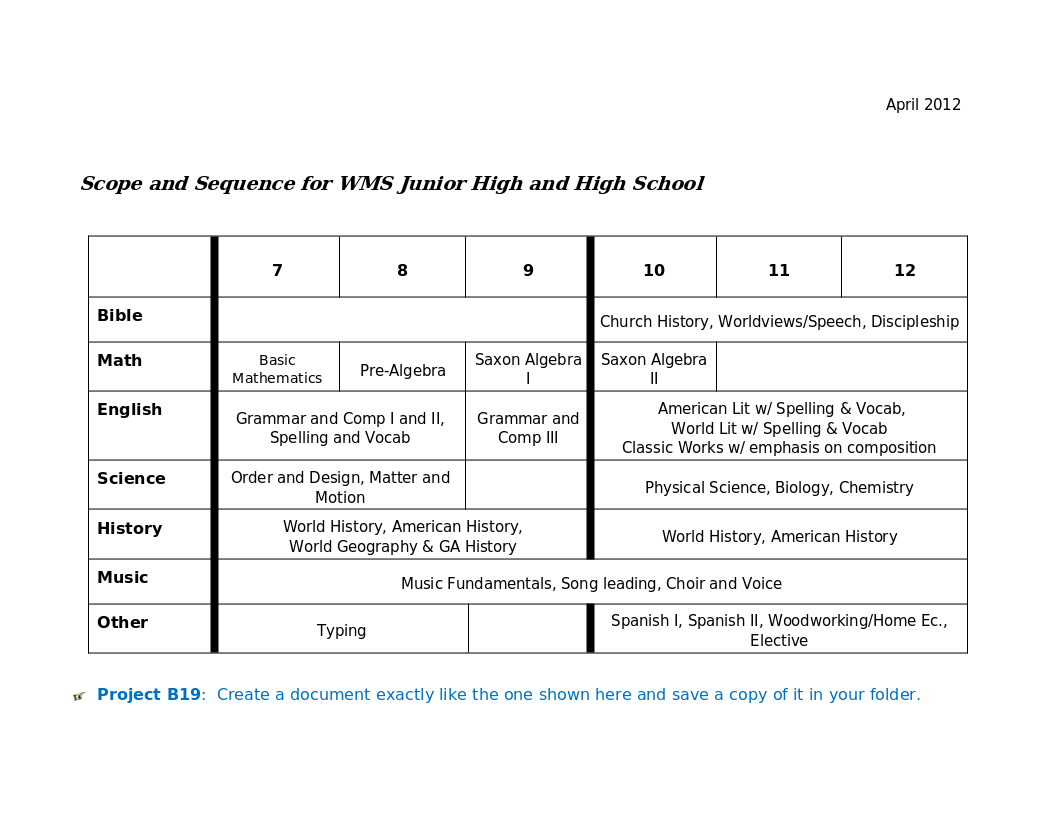
Word 19 Advanced Table
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with a table showing a school schedule. The blocks in the table are different sizes and will take individual work within the blocks to …

Word 18 Columns
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with a header and two colomns. The columns include boldfaced and italic font and different alignment. …

Word 17 Columns
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with two identical columns in landscape orientation. Included in each are indented lines and different alignment and font. …

Word 16 Lesson Notes Handout
In this practice project for Word, students create a document like a student handout. This includes an outline with several levels, blanks for students to write on, and different font. …

Word 15 Lesson Notes
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with a header and two outlines. Students are asked to use the automatic numbering and outlining features in Word. They must use different …
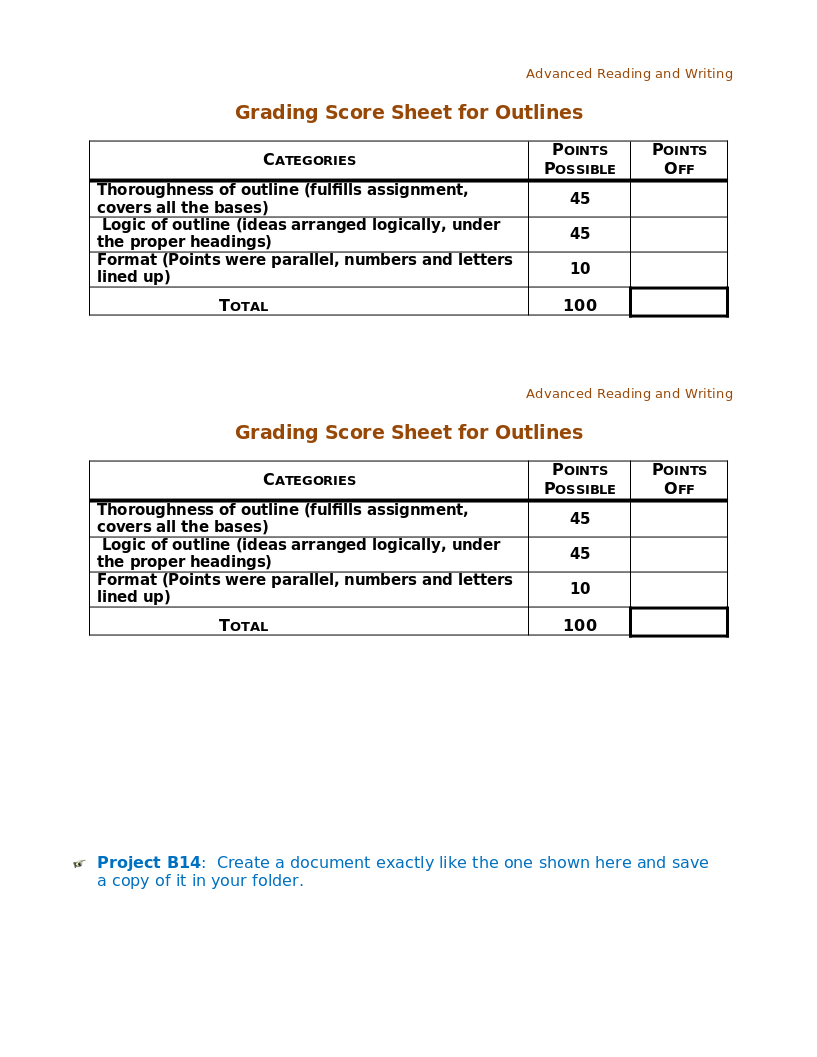
Word 14 Table
In this practice project for Word, students create a scoresheet using a table. Students must use different sizes, colors and styles of font, including different alignment. …

Word 13 Outline
In this practice project for Word, students create an outline using the automatic outline in Word, including many levels of subpoints. …

Word 12 Formatting
In this practice project for Word, students create a document with a centered title in all capitals, the first letter of each word slightly larger than the rest. Throughout the document the font is …

Word 11 Formatting
In this practice project for Word, students create a document similar to a test or quiz. They must include points and subpoints, blanks, boldfaced text, tabs, and spacing. …
Resource Type:
Pass it on:
Leave a Reply
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
Formatting your assignments
Illustrated step-by-step guides to help you understand the formatting and presentation expectations of university assignments.

Introduction
Although formatting your essay, report or dissertation can feel like a lesser priority than the process of research and writing itself, it is an important way to ensure your ideas are given the spotlight through visually accessible, professional presentation. Formatting can be a minefield, especially when you’re formatting at the last minute; it’s important to leave a few days at the end of your essay writing process for working on your formatting, and to spend some time familiarising yourself with the different aspects of formatting.
301 Recommends:
Our Essay Structure and Planning workshop will outline how to analyse your essay question, discuss approaches logically structure all your ideas, help you make your introductions and conclusions more effective, and teach how to link your ideas and ensure all essay content flows logically from the introduction.
Below, you will find some general introductions to the key areas.
Action: know the rules
Because formatting rules can vary greatly depending on your department or assignment, it’s crucial to check the formatting specifications in your assignment description/rubric, and any general departmental presentation standards, as a first port of call. Many referencing systems also have specific rules about how to format your work, so make sure to familiarise yourself with the university library’s referencing guides . Many referencing systems also have more detailed style guides available via their websites.
Formatting key information
Assignment cover sheets .
In some departments, you may be expected to include a cover sheet on the front page of your assignment. This is a page including key information about your assignment, such as your module number, student registration number, essay title, and submission date.
You may be asked to submit a plagiarism declaration and to make your markers aware of any disabilities through the yellow sticker system . If you are asked to include a cover sheet in your assignment, your department should make you aware of where you can access this.
Assignment titles
Place your assignment title at the top of your first page, either centre or left aligned, in bold font. At university, you may be assigned a pre-designed essay title/question, or asked to select from several possible titles. You may also be asked to design your own essay title. Here are some top tips on designing your own title:
- To bring focus to your essay, draft a working title at the essay planning stage. You can come back and review this title in light of your finished essay draft.
- Make sure to use action words in your essay title that reflect the skills your assessors are looking for, both in the assignment description and the marking criteria you have been given. For example, if heavy emphasis is placed on critical analysis, you could use a title like ‘Analyse the effect of…’ See this glossary of essay terms , containing examples that you can use in your own titles.
- The action words you choose can also help you to reflect the structure of the essay in your question. For example, an essay using the action word ‘Discuss’ might use a for/against/conclusion or advantages/disadvantages/conclusion structure, or an essay using the term ‘Analyse’ might break an issue down into parts, e.g. into key themes, to understand its meaning as a whole. Think about the type of essay you want to write: do you want it to be comparative, look at several topics equally, or do you have a clear argument that you want to put forward? You can then create a question that gives you the opportunity to approach the topic from your own perspective.
- Make sure to include the main terminology you are working with in your assignment title.
- Make sure your question has a realistic scope, without being so broad that you cannot answer it within the limitations of your essay. To limit your question, you could include any limiting factors you are working with, such as specific time periods, geographical regions or sub-themes within the overall topic area. For example, in the title ‘Evaluate the proposition that a global monoculture will destroy diversity and difference’, the broad topic of global monoculture is limited down through a specific sub-focus on diversity and difference.
Stating word counts
Depending on the instructions you have been given, you may be asked to state your word count, either on your cover sheet or at the beginning of your essay. If you are asked to include this information, make sure your word count accurately reflects the assessment guidance: for example, are references included in your word count?
Visual clarity
Line spacing .
Most assignment descriptions specify that you should increase the space between each line on the page, from the standard 1.0 spacing to either 1.5 or 2.0 spacing. You are asked to do this to make the essay more visually accessible and easier to read, by breaking up the number of lines on each page.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to line spacing in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Fonts
All non-examination based assignments should be word processed rather than handwritten. Most assignment descriptions will specify that for visual clarity, and to ensure a professional appearance, you should use a plain, sans-serif font such as Arial. For readability, this should be in 11 or 12 point size. Check your departmental or assignment guidance for any specific rules about font choices.
Page numbering, headers and footers
Including page numbers in your assignments makes them more accessible. Depending on the departmental guidance you have been given, you may be asked to include these in either the header or the footer of your essay (the blank space above and below where the text would go on a normal page in a word processor). It may also be helpful to include your registration number and the module code of the essay in the same header or footers that specify the page number.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to adding page numbers and using headers and footers in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Page layout
Margins .
A margin is the amount of blank space on either side of a paragraph in a normal word processor. Traditionally, assignment descriptions specified that the margins should be made wider at the binding edge (the left hand side) of the page, to allow for easier reading of printed essays. However, with the shift to online essays, you might not be asked to do this any more and the default settings on your word processor are likely to be sufficiently wide.
For printed dissertations and theses, you may receive specific guidance about the suitable layout of margins, as these are more likely to be printed: see this university guide on formatting PhD theses .
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to adjusting margins in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Paragraph alignment
Most formatting instructions specify that paragraphs should be lined up in a straight line (aligned) on the left hand edge, but left jagged on the right hand edge (like this page). This is called left alignment, or flush-left style, and should be the default alignment setting for your word processor. This style can be helpful for visual accessibility, but check any specific instructions you have been given by your department to see which style of alignment you have been asked to use.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to adjusting paragraph alignment in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Paragraph indentation
You may be asked to add indents to your paragraphs: an indent is an additional small gap between the margin and the beginning of a paragraph (it makes a ‘dent’ in the first line of your paragraph). Indents are used to provide extra clarification that the reader is starting a new paragraph after finishing the last one: therefore, they should not be used in the first paragraph of your essay. Indents are not always required, and whether you are expected to use them may depend on your referencing style , and any formatting instructions you have been given by your department.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to indenting paragraphs in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Formatting referenced material
Footnotes and endnotes .
Some referencing systems require you to use footnotes or endnotes to format your references (make sure to check the library’s referencing guide to familiarise yourself with the expected format of your referencing style). Inserting a footnote into your word document when you have cited from a source adds a superscript number (a number formatted in a smaller font) to the sentence. It creates a note with a matching number at the bottom of the page you are working on (in the footer), which you can add the reference information to.
Endnotes work in the same way, but instead of appearing at the bottom of the page, the reference list appears at the end of the document.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to manually inserting footnotes and endnotes in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
References and bibliographies
Instead of, or alongside footnotes/endnotes, some referencing systems ask you to include a bibliography and/or a reference list at the end of the essay (make sure to check the library’s referencing guide to familiarise yourself with the expected format of your referencing style). A reference list is a list of all the sources you have directly referred to in the essay, which could be ordered numerically or alphabetically, depending on your referencing style.
A bibliography could be used alongside, or instead of, a reference list, depending on your referencing style; here, you list all the sources you have consulted that have influenced your ideas, whether they are included in the essay or not. The way this is ordered also depends on your referencing style.
If you auto-generate your citations in Microsoft Word or Google Docs, you can auto-generate your bibliography instead of creating it manually: instructions for doing so are in the resource below. If you use a different reference manager, such as Mendeley, Zotero, or Endnote, these have their own specific instructions for auto-generating bibliographies. See the reference management resources offered by the university.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to manually or automatically formatting a bibliography or reference list in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Block quotations
When you need to include a quotation in your essay that is three or more lines long, you can add this as a block quotation. A block quotation appears on a separate line to the other parts of the paragraph, and is indented (i.e. there is a wider gap between a block quotation and the left-hand margin than there is between the rest of the paragraph and the left-hand margin). Block quotations aren’t placed in quotation marks, so the indentation is used to indicate that you are using a quotation.
Check your referencing guide and any departmental guidance to learn more about the specific rules on formatting block quotations in your department. Because they take up large chunks of your word count, and break up the flow of your texts, make sure to use block quotations sparingly: they are especially helpful when you are going to perform close analysis of a large section of text. For more information on different types of quotation and how to use them, see our workshop on paraphrasing and using academic sources.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to formatting block quotations in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Advanced formatting
Headings and contents tables .
Most standard short essays do not include headings, other than the essay title and reference list and/or bibliography. Section headings may be required for some longer or more structured types of academic writing, such as reports; reports often follow a very closely prescribed structure, so it is essential to pay very careful attention to the specific guidelines issued with your brief. Make sure that any system you use for numbering your headings and subheadings is consistently applied throughout the document.
Depending on the advice you have been given, and the length and complexity of a lab report, you may also be required to include a table of contents to help the reader navigate between headings. Contents tables are generally standard practice in longer assignments such as dissertations and theses. Make sure to check any departmental guidance you have been given about formatting reports.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to formatting headings and contents tables in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
301 Recommends: Scientific Writing and Lab Reports Workshop
This workshop will help you to familiarise yourself with some of the specific expectations associated with this assignment format.
Figures and tables
Some kinds of essays, dissertations and reports will require you to make use of figures (pictures, diagrams, and graphs) and tables (any data in a table format). Figures and tables are normally numbered in sequence, e.g. ‘Table 1’, ‘Figure 4’, and are directly referred to in the text according to their number, rather than according to their location on the page (e.g. ‘as shown in Table 2’ rather than ‘as shown below’).
If your text is of dissertation or thesis length, or if your text has several figures, it may also be helpful to include a list of figures immediately after the table of contents. Some referencing guides have specific rules about presenting and referencing tables and figures, so make sure to familiarise yourself with these and carefully read any specific instructions about figures and tables in your assignment brief.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to inserting figures and tables and creating lists of figures/tables in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Top tips for formatting tables and figures:
- Make sure that any tables or figures you use are placed below the paragraph where you refer to them, and that you have directly referred to all figures and tables in the text of the essay.
- The caption for a table usually acts as its title, so this is placed above the table in the document. The caption for a figure is usually placed underneath the figure. Do not include unnecessary additional titles in the graph image itself, if the title is already included in your image caption.
- Make sure to label your captions consistently, choosing between ‘Fig.’ or ‘Figure’ and consistently using either a full stop or a colon after the label (i.e. ‘Figure 1:’ or ‘Fig. 1.’)
- Your caption should clearly and succinctly explain what the figure or table is. If the figure is taken from an external source, you must provide a reference that accurately reflects its copyright status (see these university library guides to inserting and attributing images and figures in university work).
- Make sure to include legends in any charts you use (a key that helps to explain the data in the chart). Any data series you use should be clearly distinguishable from each other (e.g. avoid printing a report with coloured graphs in black and white!) If you are only using one series of data, a legend is not always necessary.
- Make sure tables are clear and easy to read, using sans serif fonts, a readable font size, and avoiding unnecessary use of colour.
- Make sure graphs are clear and easy to read, with clearly and appropriately labelled axes. Be wary of 3D effects that may obscure the clarity of a graph.
- Make sure to avoid presenting the same information in a graph and a table.
- Images and figures in printed essays, such as dissertations and theses, should be large enough for the text and numbers to be legible on the printed copy. Make sure they do not extend beyond the print margins of the document.
301 Recommends: Displaying Data in Graphs and Tables Workshop
This workshop will provide more technical advice on using graphs and tables in your work. See also this Engineering department guidance on formatting graphs and tables in Engineering lab reports.
Appendices
Appendices commonly appear in dissertations, theses, and lab reports. An appendix provides supporting information that gives the reader a better understanding of the essay, but that might be too long, detailed or awkward to insert into the main body of the essay without breaking up its flow. Interview questions or transcripts, sample questionnaires, raw data, figures, photographs, large/complex datasets, and diagrams are all examples of information that could be included in an appendix, if it is relevant to do so.
The reader should be able to understand the essay without reference to this supporting information, as all the most important and relevant information needed to answer the question should be included in the body (i.e., the appendix should not be used to make room for content that doesn’t fit within your word count). Your appendices must be clearly signposted and explained in the body of your report, highlighting any information that is essential for your reader to understand. Do not include any appendices that are not referenced in the text itself.
The appendices should be placed in numerical or alphabetical order, and signposted according to this specific system (e.g. ‘Appendix B indicates that…’) They should be clearly labelled, using headings that match up to the in-text reference. Appendices usually appear at the very end of the assignment, after your references/bibliography. Make sure to list any appendices used in your table of contents; if you have been instructed to do so by your department or within your referencing system, you could include a list of appendices separate to your contents list.
The specific format of the appendix heading, and the reference made to the appendix in the text, depends on your referencing style , so make sure to carefully review this information before you design your appendices.
Download this step-by-step illustrated guide to inserting appendices and creating lists of appendices in Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
Tips and resources
- Use this 301 proofreading checklist to check over your work when you are finished.
- Use the University Library referencing guide for advice about referencing and formatting that is specific to your referencing style. If you need extra clarification about formatting rules, it is often possible to download an extended style guide from the official website for a specific referencing system.
- For further training on referencing, using reference generators, and using images in your work, see the University Library workshop programme .
Related information
Academic Writing
Proofreading
Essay structure and planning
Scientific writing and lab reports
Creating accessible Word documents

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
How to Create Professional Reports and Documents in Microsoft Word
This guide examines the elements of a professional report and reviews the structuring, styling, and finalizing of your document in Microsoft Word.
If Microsoft Office had been a country, it would have been the third most populous country in the world. 1.2 billion people using a single suite of apps is mind-boggling. And, they "speak" 107 languages!
But right now, you and I are speaking in English and we are going to talk about the most popular tool in the Microsoft Office arsenal -- Microsoft Word 2016 .
This document editor is used for writing a variety of documents. From a simple application to the necessary resume. From a plain bucket list to an office memo. We think we can work with Word. But it is when we sit down to write a serious professional report, we discover an important fact.
Professional report writing needs a different set of skills.
So, ask yourself this -- can you make the leap from a single document to a lengthy report? Do you know all the Microsoft Word features that will help manage this large scale document project? Can you collaborate on the work with other team members?
You may be a student, a small business owner, or an office worker...you will need to create a report or a professionally formatted document of some kind. This MakeUseOf guide will help you update your techniques and sharpen your design approach.

In this guide:
Writing a Report -- Introduction | The Report Checklist
Useful Microsoft Word Tools -- Paste Special | Researcher | Freeze Parts of Your Document
Work on the Layout & Design -- Intro | Cover Page | Table of Contents | Header and Footer | Page Numbers | Font Styling | Paragraph Styling | Page Breaks | Styles and Themes | Captions | Quick Parts | Page Borders
References and Collaboration -- Index | Bibliographies | Cross-Referencing | Comments
Finalize Your report -- Signatures | Watermarks | Read Only | Print to PDF
The Next Step -- Conclusion
Writing a Report
Report writing involves research and then publishing the outcome of that analysis. In the professional world, the "look" or appearance of what you publish is paramount. The eye-pleasing final result could burnish your reputation and enhance your personal brand.
The steps below will handhold you through the expert features in Microsoft Word 2016. Spend a lot of time on a plan. Start with these guidelines…
Step 1: Decide the Purpose
Before you begin the report, you must first know why you are writing it in the first place. Reports are of many kinds but they are either meant to inform or persuade. It can be meant for describing a technical process, sharing background information, or demonstrate progress on a project.
Ask yourself – What and Why . This will help you distill the purpose to the one main point and stick to it instead of rambling on with unnecessary details.
Step 2: Identify Your Audience
The second important consideration is to evaluate your audience. Will they be able to understand what you are talking about? Are there different levels of readers who will read the report? The reader's knowledge of the subject will greatly influence the information that you need to include.
Decide on the primary audience and then script the report at the adequate technical level. The secondary audience can be supported with supplemental information at the end of the report.
Step 3: Know Your Topic
You must know what you are talking about. So, research the topic, and include all the relevant information to prove your point. Make sure that you come to a conclusion based on facts and not personal opinion. The information must be correct, current, and well-referenced.
Also use a variety of resources such as journals, newspaper articles, books, websites, brochures, raw data, annual reports, and speeches to help support your point. Just don't stick to Wikipedia.
Step 4: Outline the Report
You have done the research. There's a ton of information that is waiting to be typed and printed. But wait! Don't drown before you enter the water. Prepare the final outline of the report which will be the chart of waypoints to help you navigate from start to finish. The outline is the blueprint. It will give you a bird's eye view of the land and also show you where you need to fill in the details.
The structure of an idea report can include the following elements:
- Executive Summary
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Body of the Report
- Recommendations
- Bibliography and References
Microsoft Word's Document Outline is a powerful feature that can help you organize a document even before you start filling it with research. Take advantage of brainstorming and mind-mapping templates too.
Step 5: Write, Edit, Proofread, and Finish
Once you have structured your report, it is time to fill out the headers with content. I personally find it best to tackle a little bit of each section, and then bulk it up with information. You can do that if you want, or finish each section as you go down the report structure. Make sure you focus on presenting your ideas and using supportive evidence rather than spelling and grammar first. Outline your argument and write a few sentences that cast your main ideas. If you find something worth quoting, quote it.
Once the majority of your text is written, it is now time to read through it and make sure it flows well. Make sure you guide the reader's understanding with transition words such as "This information shows…", "In other words…", "Similarly…" and do highlight relevant and key points.
Finally, spend time to proofread, check for grammar and spelling , and double-check all relevant information and its logical flow. It is best to leave at least one day to check and proofread your work. Don't try to edit it straight after you think you have finished, as you will tend to miss read what you have written. Get some sleep, and proofread it the next day.
The Report Checklist
Before you go and submit or hand in your report that you have worked so hard on, make sure you have done the following:
- Completed the title page with the Title, Your Name, Date, Who the report is for, and a possible description of what the report is about.
- The contents page has appropriate headings and pages numbers are correct.
- Make sure the introduction covers key points, the scope of the report, and the objective it wants to meet.
- You have added captions above tables and below images/graphs.
- Does the content of the report present the information in a clear way, logical, factual, stay on topic, is to the point?
- Does the conclusion state the results, restate main idea's, and does not include any new information?
- Are the headings and sub headings clearly labeled?
- Are quotes relevant, up-to-date, and correctly referenced?
- Have you used page breaks where appropriate?
Now, let's launch Microsoft Word and take you through the features that will help piece together the draft of your report and present it as a professional document.
Useful Microsoft Word Features for Report Writing
Take these as bite-sized tips and master them one by one.
Microsoft Word is a big howitzer with many nuts and bolts. Let's focus on the key skill sets and the tools you will need to plan, prepare, and present the professional report. The Microsoft Word features we will cover below are also productivity shortcuts that will make your job easier.
Tip: Use Microsoft Word 2016's "Tell Me" assistant to learn more about new features in the Office suite.
Let's start with three preliminary tools...
Use Paste Special
For most of us, when we need to copy text or an image into Word, the CTRL+V shortcut does just fine. But sometimes we might want to paste the copied data into another format, such as Excel data as an image. With the Paste Special command you can discard or specify the format when you paste a picture, presentation data, table, or object from any other program into Word.
You will work a lot with Excel tables and charts in a professional document.
If you just copy what you want and click paste, you will notice that it will insert the data as tables. But, if it is a large area of cells you want to paste, and you do not want to edit it, you may want to paste it as an image, with the extra option to edit it.
In Microsoft Excel: Select and highlight the cells that you want to copy > Press CTRL+C.
In Microsoft Word: Go to Home > Paste > Paste Special . Select Paste Special and from the dialog select Microsoft Office Excel Worksheet Object .
You can resize the data as it was an image, and if you double click, you will be able to edit the values. You can change the table or chart and redesign it. And, if you update the data in the chart or table in Excel, you can automatically refresh the chart in Word.
Try the right-click context menu too. The Paste Special menu pops up:
There are more options to import data from Excel into Word . The Microsoft Office Support page also describes them in detail.
Use the Researcher
Yes, there is Google and Wikipedia. But constantly switching from Word to your browser can hamper your productivity. Office 2016 brings in powerful research integration to this grunt work. The Researcher can not only help you find content from within Microsoft Word but also help you quickly add citations. It uses the Bing Knowledge Graph to find the right content to support your document.
Go to Ribbon > References tab and c Choose Researcher . A pane will open on the right with the search options.
Type a keyword for the topic want to search for and press Enter.
The Results pane shows a list of sources you can use in your document. Choose a topic to explore in detail.
Add the topic to your Microsoft Word document with a click on the plus sign on the top-right. You can also click the plus sign on any result to cite the source in your research document. The cite source helps you support your research with web sources and books.
As we will see later, an annotated bibliography is one of the toughest parts of a document. The Researcher is an intelligent assistant who steps in.
Freeze Part of Your Word Document
Let's take for granted that your professional report will be a long and complex work. You can split the Word window into two panes so that you can view two different parts of a document at the same time. It is a valuable time saver when you want to copy and paste parts from one place to another or refer to one part of the document while working in another.
Go to Ribbon > View tab > Split .
To remove the split, click on Remove Split in the same tab.
The Windows group gives you several options to change the way you work with two or more documents. The features are self-explanatory.
To scroll both documents at the same time, click Synchronous Scrolling in the Window group on the View tab. You can also click on View Side by Side to put two parts of the document next to each other.
Tip: Use Split View to display two different layouts – for instance, Print and Outline. Set the split. Then, click in the pane that you want to change, and then select a different layout on the View tab.
Work on the Layout & Design
The presentation of a report is what gets someone to read a report in the first place, and that is why it is crucial that your report is well presented. If you had the choice of four reports to read, what will you choose?
- A hand written report.
- A document printed in black and white.
- A report printed on normal A4 paper in color.
- A report printed in color, with a catchy title page, neatly bounded, and slick?
You will pick up the fourth report because it will pull you towards it by the visual appearance alone.
The front cover is not the only reason. A well-designed report is easier to read. It is also easier to scan when you don't have time to read. That is why you need to spend some time on your headers and footers, and the different styles and themes. In short – the formatting of every element in the report.
Formatting may seem like a difficult chore, but it is a fun exercise that will exercise all your creative muscles. The key takeaways will be the skills you can apply to anything in Microsoft Office going forward. And the time you will save with all the productivity tips learned here.
Microsoft Word 2016 has a wealthy set of features. These are only some of the ways that your report design can stand out from the rest and be professional. So, let's break down the layout and design skills.
This section will cover these features step-by-step:
- Start with a Cover Page
- Make a Table of Contents
- Create Your Header and Footer
- Add Page Numbers
(Format the Content)
- Pick the Right Fonts
- Style the Paragraphs
- Control Page Breaks
- Use Styles and Themes
- Use Quick Parts
- Decorate with Page Borders
1. Start With a Cover Page
The first page is the first point of contact with your reader. It is also your opportunity to make a favorable impression. Don't let your lack of artistic skills be an excuse because Word takes up the job with its in-built gallery of title pages. All you have to do is marry one to the theme of the report.
Microsoft Word 2016 offers you 16 pre-formatted templates and three more on Office.com.
Go to Insert > Pages Group > Cover Page .
The cover page appears at the beginning of the document by default.
As there are only 16 "official" templates on offer, you may find that all your other peers have the same cover page. So, why not customize it, and make it a bit more unique.
You can design a title page (or cover page) in Microsoft Word that can be an original in the stack. Save it as a template or easily change the design on the fly.
2. Make a Table of Contents
Casual readers scan. Good readers scan first and then dive deep. A table of contents provides the waypoints that help both. When it is a long and complicated document, wouldn't you rather check the lay of the land before you head to the section that interests you?
Consider a Table of Contents (TOC) if your document is more than 10 pages long. You should first make sure you don't need to rearrange any pages in your document before creating the TOC.
In Microsoft Word, you don't have to write the entire TOC by hand. There's a Table of Contents automatic tool under the References tab which takes your outline and designs it for you. Also, you can easily keep it updated when you want to change something.
There are also templates you can download and fit it around the nature of the content. For instance, a TOC for a thesis will look different from that of a company's annual report.
We have a complete tutorial on how to create a table of contents page in Word .
The gist of it is this:
Create the outline and use heading styles to organize the hierarchy. Apply the automatic TOC tool to the heading styles. Word 2016 searches for those headings and then inserts the table of contents into your document. Then you can automatically update your TOC if you make changes in your document.
For more hands-on control, you can also use the Manual Table of Contents style. Word inserts placeholder text and you have to insert and format each content in the list.
3. Create Your Header and Footer
Headers and Footers are important in reports as the main purpose is to provide information about the report on every page. They are the common display areas for page numbers. The header of the document should contain the title of the report, and possibly the name of who created it. The title of the current section is helpful.
The footer, on the other hand, should include the page numbers, date of publication, and other administrative information that is required. Do note that some style guides have special guidelines for headers and footers .
Let's start with the header in your document and give it a unique look.
Select Insert , then select either Header or Footer from the group. The built-in gallery shows you several options you can choose from.
The header and footer space is inserted in your document with placeholder text or table. The Header & Footer Tools opens on the Ribbon for other formatting work like the date, time, or picture.
Enter your text and then select Close Header and Footer .
You can start with a blank header and footer. If you have the design skills, use the Header & Footer Tools to design your own. Master the header and footer space if you want to create custom letterheads for your organization. You can use brand elements like company or organization logos at the top and neatly formatted footnotes at the bottom
Let's try with and modify one of the inbuilt headers. I selected Facet from the gallery.
The final look took two minutes to put together with simple text effects and an icon sourced from the Microsoft Office icon gallery.
The header and footer are in place. But, how do you know where you are in the document? Insert page numbers as the next important signpost.
4. Add Page Numbers
Page numbers look best in the footer (unlike in the header as in the image above). You can add a basic page number from the Insert > Page Number button on the Ribbon. You can also add it from the Design tab that appears when you add the header and the footer.
You have a lot of control over page numbers. Choose from a wide range of number formats and customize them to your needs. In this case, we are adding the number to the footer, but you can put them at the top or even at the margins. In this example, I have placed the page number at the bottom left. But, I would like to change the default look and the format.
For example: Using a "Page X of XXX" makes for a better indicator on a long document.
Select the page number. Go to Insert > Quick Parts . From the drop-down menu, select Field . You can also reach the Field dialog from the Header and Footer Design tab.
Choose NumPages from the long list of field names. From the box on the right, you can pick a specific format. I selected the usual 1, 2, 3. Click OK , and the number of the number of pages will appear. Now all you have to do is add your text such as Page X of XXX, and change the look of the numbers with the usual text formatting tools available from the Home tab.
It now looks like this:
Design the look on any page number in your document and Word updates all the remaining automatically. Page numbers are the most common elements in a footer, but it can also hold any other information like the header. From the options in the Insert group, you can add the date and time, document info, pictures, and more to your header or footer.
Next, we're heading into formatting the content.
The visual draw of your professional report comes together with the "beautification" you apply to the content. Formatting is also an essential step for a document that flows well. So, you must focus a lot of energy on picking the right font, paragraph space, and the colors.
Don't worry. Even, the artistically challenged will find this part easy because Microsoft Word comes packaged with default themes and visual styles. Let's start with the most basic element of a document.
5. Pick and Style the Right Font
Your choice of font in a professional Word report not only determines how the text stands out but also how it is printed. You want both for maximum impact.
You can apply a typeface (i.e. the visual look of the font) to either an entire document or to specific parts of a document. All font choices are available from the Home tab. Go to Home > Font .
The default font in Microsoft Word 2016 is Calibri. Look beyond that as you have lots of others to choose from. If you choose Times New Roman, you may be considered lazy, if you choose Windings, well… I don't think I need to explain that. So make sure you choose a font that is easy to read and suits the report. To play it safe, pick from one of these professional-looking Google fonts ; they're available for free.
Tip: Baskerville and Georgia are good alternatives to the over-used Times New Roman
Try different font pairing for the body text and Headings (and Subheadings). Several websites like FontJoy and TypeWolf will help you experiment with font pairings. You can download and use custom fonts too. But remember the thumb-rule -- never use more than three different typefaces in a document.
For that extra bit of pizazz, try a drop cap to enhance your text .
6. Style the Paragraphs
If you want to have your lines double spaced, or single spaced, you need to change the format of the paragraphs. By changing the spacing, you can make a document easier to read or give the impression that it is longer and that you have put more work into it.
To change the paragraph for the whole document, it is best that you select each block of text; otherwise, if you are using headers in your report, they will change too. Another better option is if you customize the particular style you are using to format the paragraph.
To do this, go to Home > Styles . Right click on the style you want to change and select Modify . Click on Format > Paragraph which is at the bottom of the dialog box. Now, change the spacing, indentation, and alignment for the paragraph. Click OK to close the dialogs.
When you want to change a smaller portion of the document , select what you want to change. Right click on the highlighted text and select Paragraph . The same dialog box as above will appear.
7. Control Page Breaks
A page break -- by its very name -- splits a continuous block of text across two pages. Page breaks are important structural elements for long documents. Word automatically inserts a page break at the end of the page. But in a long document, you can place page breaks where you want them.
To insert a manual page break, click Insert > Page Break. (Keyboard shortcut: CTRL + Enter)
A page break looks like this when you click on the Show/Hide command in the Paragraph group .
But what if you want to keep a bunch of lines together on a page or column and not have them separate because of a page break? The layout is in your control. Click the tiny arrow you see in the bottom right of the Paragraph group.
In the Paragraph box, click Line and Page Breaks. Select from these four pagination options:
- Widow/Orphan control places at least two lines of a paragraph at the top or bottom of a page.
- Keep with next prevents breaks between paragraphs you want to stay together.
- Keep lines together prevents page breaks in the middle of paragraphs.
- Page break before adds a page break before a specific paragraph.
We've also shown how to remove page breaks when necessary.
8. Use Styles and Themes
Styles and themes are perhaps two of the more underused features in Microsoft Word . But I think you should use them at every opportunity to save a lot of time.
But what is the difference between a theme and a style? Microsoft says:
Themes provide a quick way to change the overall color and fonts. If you want to change text formatting quickly, Word Styles are the most effective tools.
So, as themes control the general look with color, effects, and fonts – start with a good theme for your document first. Then , use Styles to dig into the specific portions you want to change the appearance for.
For Themes: Go to the Design tab. Pick a theme from the gallery. You can see previews of what the color combination is like.
For Styles: Select the part of the text you want to change. Go to the Styles group on the Home tab. You can see previews of what they look like. Choose the Style that is suitable for your content. For instance, choose a heading style for the headings in your document. Or, a particular style for any quotes. You can also modify an existing style and create new styles from scratch.
9. Captions
Every picture, chart, or illustration needs a caption to clearly describe it. It is a single line of text, usually located below a graphic. Captions are also an important reference when you need to mention them in another place. Many documents omit this small detail.
It is easy to add a caption. Right-click the illustration you want to add a caption to. Select Add Caption .
In the dialog box, add your caption text and configure the remaining options. Captions can be automatically referenced in Word.
10. Use Quick Parts
Professional documents can get repetitive. This is why you should start using Quick Parts for boilerplate content you reuse all the time. For instance, let's say there is a contract clause you include with every document. Or, some introductory information. Instead of repeated copy-paste, save them as Quick Parts and re-use them again and again.
Quick Parts is also a type of building block . You can see the gallery of all reusable blocks of content in the Building Block Organizer .
Save and reuse your own Quick Parts in two steps:
- Select the phrase, sentence, or other portion of your document that you want to save to the gallery.
- Go to Insert > Text group > Quick Parts > Save Selection to Quick Part Gallery . Change the name and add a description if you like. Click OK .
Just as easily, you can re-use the saved snippet of content.
Place your cursor where you want to insert a selection from the Quick Parts Gallery. Go to Insert > Text group > Quick Parts . Then click the sentence, phrase, or other saved selection you want to reuse.
You will notice three other categories in the Quick Parts menu.
AutoText: Word 2016 has retained the old AutoText feature. It works like Quick Parts for any block of text that you use a great deal. Example: A note you want to use with every document.
Document Property: A set of constant properties that you can include with every document. Example: Company name or author.
Fields: These are predefined elements that update automatically. Example: Date, time, page numbers etc.
Remember, entries for document property can sometimes include information you wouldn't want to share with everyone. So, keep a close eye on these fields and remove the hidden personal data whenever required.
11. Decorate With Page Borders
Page borders look good not only on flyers and invitations. If done right, they can add a touch of class to a document. A variety of line styles and widths and art borders are available from the Design menu on the Ribbon.
Go to Design > Page Borders.
In the Borders and Shading box, use the Page Border tab to design your border.
The settings are self-explanatory. Try Shadow or 3-D with the right colors to add a subtle but elegant border. The Art styles with their clip-art borders might be too garish for professional documents.
Use the four corner buttons in the Preview window to select the sides of the page to draw borders. Click these buttons to remove or add borders, as you wish.
Place the cursor on the first page of a document if you want to put a border around only the first page. You can also put borders around certain pages in a section. Place the cursor in the section — either in the first page of that section or in a subsequent page.
References and Collaboration
A Word report can seem like an unmanageable chore. It's like organizing a million piles of hay into neat little stacks. The idea is to know precisely which stack has the pin you are looking for. These features are meant to make it easier.
1. Create an Index
When writing large documents such as a report that contains a lot of information, a contents page may not be enough. An Index should appear at the end of the document, with page numbers to keywords and information in the report. Create an index to help the reader reference the right information with just the page number.
Make an index if your document has more than 20 pages. Microsoft Word 2016 doesn't let the process overwhelm you. It basically has two parts:
- Select the words or information you want to include in the index.
- Place the index at the right place in your document.
You can scroll through the finished document and mark the words or phrases you want to include in the index or mark them as you go along. Either way, select the text you'd like to use as an index entry or click where you want to insert the entry.
1. Click References > Mark Entry .
2. Edit the text in the Mark Index Entry dialog box. You can also add a sub-entry which further defines the main word you used in the index. You can add multiple levels and each appears indented under the main entry.
3. Under Options , you can also create a cross-reference to another main entry. A reader can use this to refer related information elsewhere in the same document.
4. Use the Page number format to decide on the appearance of the page numbers in the index.
5. Click Mark to mark the index entry. To mark this text everywhere it shows up in the document, click Mark All .
6. Repeat the process for all the words and phrases you want to include in the index.
You have now built your index. Insert it at the right place towards the end of the document.
1. Click on the page where you want to insert the index.
2. Click References > Insert Index .
3. The Index dialog box is displayed. Here you can choose to format the text entries, page numbers, tabs, and leader characters.
4. Choose the appearance from the different formats in the list and check the Preview window on the right. Remember, the Preview window doesn't show you actual index. It is just a "simulation" of how it will look like.
5. Click OK . Your Index is now ready.
Sometimes, you may need to add more entries to the index after you have inserted it on the page. Mark the entry and go to References > Update index to include the new mentions.
Also, add a heading for the index because Word doesn't do it automatically.
2. Creating Bibliographies
Your document is almost done. Now, you need to credit all the other research work and ideas which you have referenced in your document. It's time for a bibliography.
A company report might not need a bibliography but an academic paper isn't finished without one. The bibliography is one of the most painstaking jobs in an academic report. You need to have all your citations in order before you sit down to frame the bibliography. Also, decide on the citation style (typically MLA, APA , or Chicago-style ) as per the guidelines of your subject.
Don't hesitate to take advantage of third-party citation and bibliography generators for constructing this section.
But, Microsoft Word 2016 has a complete toolset to make this process as painless as possible. So, go to the point in the document where you would like to place the bibliography. It's good if you have at least one citation to include, but even if you don't, Word 2016 lets you use a placeholder citation and fill in the sources later.
Click References > Bibliography .
Word offers a few bibliography styles that differ only in their heading names. Choose the appropriate style and then insert citations from the button in the Citations & Bibliography group .
The bibliography tool has a few steps to it. For the sake of brevity, I will direct you to the excellent Microsoft Office help page which is a step-by-step guide.
Some academic papers will ask you to create an annotated bibliography . It is a more fleshed out version of a bibliography with a list of citations to journals, books, articles, and other documents followed by a brief paragraph. The paragraph is a description of the source and how it supports your paper.
3. Cross-Referencing
You can use a cross-reference to help the reader navigate through a long document. At any point in a document, you can tell the reader to refer back to a heading, page number, image, chart, footnote, endnote, and paragraph. A cross-reference link is a neat way to connect related information together. The reader just has to click on the link to go that snippet of information.
Here's how you begin:
1. Select the place for the cross-reference and type the text that tells the reader about it. For instance: "Refer to Chart 3 for future trends."
2. Go to Insert > Cross-reference .
3. In the Reference type box, click the drop-down list to select what you want to link to.
4. The options in the Insert Reference to drop-down will change according to your choice above.
5. In the For Which field, go through the choices and tell Word the exact information to link to.
6. Check the Insert as hyperlink box to create the hyperlink for the referenced information.
7. Click on Insert to include the cross-reference in the document.
Remember, our mention of captions? You can make cross-references to equations, figures, graphs, and tables if you used captions below them.
Word cannot create a cross-reference for something that does not exist. Word will let you know about these errors and also update the cross-references automatically when you change the page number or text of the referenced item.
4. Using Comments
A professional report can be a solitary job or you can take the help of a team to prepare the first draft. The humble Comment is one of the most underused tools of a Word document. It is displayed as a rectangular colored balloon in the margin or in the Reviewing Pane.
You can use comments as small "stickies" or self-notes. Leave little notes to yourself in the margins as you write, edit, and revise your way through a report or a manuscript. Be creative – add extra links to other resources, use them for tips and pointers, link to different parts of a document, or set up a feedback link for your readers. And when you finalize, you can easily remove all comments in Word .
Microsoft Word 2016 is also an enhanced collaborative writing tool. Comments play a huge role in communicating feedback across a team. Here's how the comment system works...
1. Highlight the text you want to add a comment to or click at the end of a text block.
2. Go to Insert > Comment . Type your comment in the box. The comments appear in the markup area on the right. The Print Layout view is usually the best way to see the comments alongside the text.
3. Go to the Review tab and see more options for comments. This tab also shows all the controls for tracking changes and comments in a collaborative document. Use the Markup options to display or hide the comments. For instance: No Markup will hide the comments and the markup area on the right.
Finalize Your Report
Once the bulk of your report is completed and saved, it is time to finalize your report. When I say finalize, I don't mean proofread it. That should be done too. Now, you have to take the security measures to protect the report from unauthorized changes and plagiarism.
These security measures will give an extra level of authenticity to your electronic file before you share it.
This section will cover:
- Insert watermarks
- Make the document 'read only'
- Password protect your document
- Print your document to PDF
1. Signatures
You can add text signature for a personal touch to the report. But a simple text signature does not need any authentication. A digital signature is the better way to protect your document from unauthorized access. A digital signature confirms that the document came from the signer and hasn't been tampered in any way.
Let's create a signature line in Microsoft Word 2016.
In the document, place your cursor where you want to create a signature line.
1. Go to Insert > Text group > Signature Line and click Microsoft Office Signature Line .
2. The Signature Setup dialog box is displayed. Fill the fields as indicated. If you are sending the document to someone else for signing, add instructions for the signer in the field reserved for it ( Instructions to the signer ). The signer can also add give the purpose for the signing if the Allow the signer to add comments in the Sign dialog box is checked.
3. Click on OK and the document will now display a placeholder for the signature.
Enter a signature:
When you need to sign a document with a digital signature, go to the signature line and right-click on it.
You will be prompted to sign with a digital ID. If you don't have one, Microsoft will tell you to get one from a signature service partner.
If you don't have a digital ID, you can just insert a textual representation of a signature line . You can use a written signature or an image that doesn't require authentication.
2. Insert Watermarks
A Microsoft Word watermark is a "fake" but still useful visual indicator for the status of the document. For instance, you can use a watermark that says "Drafts" to differentiate it from the final version of the document. Or, use the watermark to suggest the document is "Copyrighted" or "Confidential".
The "Draft" mark is the most common. But, Microsoft Word gives you several other watermarks to choose from.
1. Go to Design > Page Background and choose Watermark . The Watermark button will be enabled in the Print view only.
2. You can choose a picture or a text watermark from the gallery. Both horizontal and diagonal versions are available. The dialog box gives you all the customization options for the final look of the watermark. Try different fonts, layouts, sizes, and colors.
3. You can type your own text in the Text field to create your custom watermark.
4. Choose OK to apply the watermark to your document. Word automatically applies the watermark to every page except the title page.
3. Make Documents "Read Only"
A professional report by its nature should not need to be edited by its readers. Converting the document to a PDF is one way. But, you can also apply a few more restrictions in Microsoft Word and prevent accidental modification or omission of any kind.
There are three ways to protect a document.
First -- Make your document "read only".
This ensures that your document can only be read or copied. It won't prevent anyone from copying the file and making changes to the copy.
1. Go to the File tab > Info > Protect Document > Mark as Final.
2. When readers open a document, a bar on top will prompt readers to treat this document as read only. But, they can click on "Edit Anyway" to open the document in Edit mode.
Second -- Password Protect Your Document.
Protect your document from unwanted edits with a password barrier.
1. Under Protect Document , choose Encrypt with Password . Type a password and click OK .
2. In the Confirm Password box, type the password again, and then click OK . The document will open with the reader prompted for a password.
Microsoft uses the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), 128-bit key length, SHA1 (a cryptographic hashing algorithm which generates an almost unique 160-bit key to replace the plaintext), and CBC (cipher block chaining) to give a hacker a well-deserved headache.
Third -- Restrict Editing.
This control feature helps you as the author decide which parts of the document others can edit and which will be locked out. Think of it as the bouncer who lets the VIPs in but otherwise bars the door for the common folk.
1. Go to Review > Restrict Editing .
2. Under Editing restrictions , check Allow only this type of editing in the document , and make sure the list says No changes (Read only) .
No changes (Read only) is the default restriction type. For a different restriction level for the document, click the menu and select from Tracked changes, Comments, or Filling in forms.
3. To free some sections from the editing blockade, select the sections for editing without restrictions. To select more than one area, click CTRL while selecting the area using the mouse.
4. You can check Everyone under Exceptions (optional) in the Restrict Editing panel. Or, click More users … and allow only specific users to modify the sections. The allowable areas will be marked with square brackets.
5. Click Yes, Start Enforcing Protection .
Now, type a unique password in the box that opens. You have to type it again to confirm it.
The password is optional. But it ensures that no one can just click Stop Protection and edit the document. If you are still paranoid, go ahead and encrypt your Microsoft Word document as we did in the second process above.
4. Print Your Report to PDF
The Portable Document Format comes with many advantages. Not least is its cross-platform compatibility across all computers. Your document is ready and now you need to share it or send it across to be printed. Many professional reports -- for instance, a legal document -- need to retain the format as intended.
Save or convert a copy to PDF. Microsoft Word 2016 does not need any third-party add-ins.
Go to File > Export > Create PDF/XPS .
Remember, your Word document may contain sensitive information that you do not want to be included in the PDF. Remove it before you publish to PDF. In the Publish as PDF or XPS window, choose Options . Then select Document and clear Document properties . Set any other options you want and choose OK .
Browse to where you want to save the file and click on Publish .
The Next Step...
You are close to the finishing line. The report is ready to be handed over to your readers. But there's one last job left.
Turn the pages and make sure (again) that your report is reader-friendly. Approach it with the eye of the reader. Have you organized your thoughts and written persuasively? Does the information flow well with the charts and illustrations? Can they skim through and find the information quickly? Is the text readable? Use the readability score to gauge the readability level of your documents as a final step.
You also might have noticed we didn't cover some aspects of Microsoft Word. For instance, Microsoft Word Tables are an important tool for data display. Or, the power of lists in information management.
Microsoft Word is more than a quarter of a century old, and packed with little features. At MakeUseOf, we have covered every nook and cranny of this beast. So, do use our resources to learn more about this software for free. Each new feature of Microsoft Word learned will make your life easier.
Make Your Report Shine
As author Nathaniel Hawthorne said,
Easy reading is damn hard writing
Isn't this true for professional report writing too? After all, if given a choice, no one may want to read it. Writing a business report and using it to communicate are two different things. Microsoft Word is just a tool -- it's your job to engage.
For some alternatives, check out the best online word processors . And for more help with professional writing, take a look at how to apologize in an email and mean it .
What are the best practices for writing professional business reports? Tell us in the comments.
Templates for college and university assignments
Include customizable templates in your college toolbox. stay focused on your studies and leave the assignment structuring to tried and true layout templates for all kinds of papers, reports, and more..

Keep your college toolbox stocked with easy-to-use templates
Work smarter with higher-ed helpers from our college tools collection. Presentations are on point from start to finish when you start your project using a designer-created template; you'll be sure to catch and keep your professor's attention. Staying on track semester after semester takes work, but that work gets a little easier when you take control of your scheduling, list making, and planning by using trackers and planners that bring you joy. Learning good habits in college will serve you well into your professional life after graduation, so don't reinvent the wheel—use what is known to work!
28+ Best Free Assignment Cover Page Formats for MS Word
What is an assignment cover page, key elements for a comprehensive front page.
- Institution Details: Begin by prominently featuring the name of your school, college, or institute. This establishes credibility and provides context for your assignment.
- Personal Information: Include your own name to indicate authorship and ownership of the assignment. This adds a personal touch and facilitates easy identification.
- Assignment Title: Clearly state the title of your assignment, conveying its purpose and focus. A concise and informative title sets the tone for your work.
- Course Information: Specify the relevant course title or code to indicate the academic context in which your assignment was completed. This assists in proper categorization and organization.
- Instructor’s Name: Acknowledge the teacher or professor who will be evaluating your assignment by including their name. This demonstrates respect and professionalism.
- Due Date: Clearly indicate the deadline or due date for the assignment submission. This ensures timely assessment and helps you stay organized.
What are the basic tips?
- Font style : It is always in the best interest to use bold, simple, and clear text instead of using fancy text fonts and styles. This helps the reader understand things in a better way. Moreover, the usage of pictures behind texts must be avoided as it creates poor visibility for the reader when reading the text printed on it.
- Presentation: Presentation plays an important role in expressing what you need to convey to someone and how you need to communicate it. Presenting the title page in the most effective manner is essential as this leaves an impression on the teacher reading the assignment. It also acts as a decisive tool for the teacher whether or not he/ she interestingly goes through the whole document.
- Spell Check: Before handing over the assignment, one should take a brief review of all the spelling and also look for any grammatical errors.
- Avoid plagiarism: A student must always be honest in what he writes. He should avoid copying material or texts from anywhere.
- Personal detail: One should never forget to mention his/her name. The font size used for writing the name must be bigger so that it makes the name visible to the teacher.
Advantages of an Impressive Assignment Cover Page
- Showcasing Professionalism: By meticulously designing your cover page, you demonstrate a strong commitment to professionalism. This attention to detail reflects positively on your work ethic and sets you apart as a dedicated student.
- Creating a Positive Impression: A well-crafted front page sets the tone for your assignment, capturing the attention of your teacher or professor. It establishes a positive first impression, arousing their interest and encouraging them to delve further into your work.
- Enhancing Visual Appeal: A visually appealing cover page enhances the overall presentation of your assignment. With carefully chosen fonts, colors, and layouts, you create an engaging and aesthetically pleasing introduction that captivates the reader’s attention.
- Communicating Pertinent Information: It provides a concise summary of essential details, such as the assignment title, your name, and the due date. This ensures clarity and facilitates seamless identification and organization of your work.
- Reflecting a Professional Attitude: By dedicating time and effort to creating an impressive cover page, you exemplify a professional attitude towards your academic pursuits. This level of dedication and care leaves a lasting impression on your teacher or professor.
Download Free Cover Page Templates
#1 – best format.

#2 – Assignment Cover Page for Case Study

#3 – Best Design for Critical Review

#4 – For Any Kind of Educational Assignment

Video Tutorial
#5 – essay assignment.

#6 – Syllabus Assignment

#7 – Cover Page For University Assignments

#14 – Cover Page for Business Assignment

#16 – Academic

#17 – Generic Cover Page for any Assignment

#18 – Biology Assignment

#19 – For Chemistry Projects

#20 – Cover Page for Computer Projects

#21 – For Engineering-Related Assignments

#22 – For English Assignment

#23 – For Geography Projects

#24 – Mathematics

#25 – Physics

#26 – Cover Page for School Assignments

#27 – Best for Science Projects

#28 – For Social Study Assignment

Versatile Designs and Layouts for Every Purpose
- Assignment Types: Our templates are designed specifically for different types of assignments, such as case studies, critical reviews, essays, syllabi, and business projects. Each template is tailored to suit the requirements and objectives of its respective assignment type.
- Academic Disciplines: Our collection includes templates suitable for various academic disciplines like biology, chemistry, computer science, engineering, English, geography, mathematics, physics, and social studies. Each template aligns with the themes and aesthetics of its corresponding discipline.
- Purposes: Whether you are a student, educator, or professional, our templates serve multiple purposes. They can be used for university assignments, school projects, research papers, or any academic or professional endeavor that requires a polished cover page.
- Designs, Layouts, and Styles: Our templates offer a diverse range of designs, from minimalistic and clean to visually captivating and sophisticated. You can choose from different layouts that creatively arrange text, images, and graphics. Our templates cater to a variety of styles, ensuring there is something for everyone’s preferences.
User-Friendly Customization: Make It Your Own
- Easy Modifications: We believe in keeping things simple. With just a few clicks, you can effortlessly modify our templates to suit your specific requirements. Change colors, fonts, and layouts with ease, and watch your cover page transform before your eyes.
- Colors and Themes: Infuse it with the perfect color scheme and themes that truly represent your assignment. Our templates offer a wide range of options, so you can find the ideal palette and theme that resonate with your content.
- Font Selection: The right font can make all the difference. Choose from our diverse selection of fonts to enhance the visual appeal and readability. From elegant and professional to modern and bold, we have fonts to suit every style.
- Layout Flexibility: It should reflect your unique presentation style. With our templates, you have the freedom to experiment with different layouts, arranging titles, subtitles, images, and text blocks in a way that best suits your assignment.
Benefits of Using Professionally Designed Templates: Make an Impact with Ease
- Time and Effort Saving: Our professionally designed templates eliminate the need to start from scratch. With pre-designed layouts, styles, and graphics, you can save valuable time and effort in creating visually appealing front pages. Simply customize the template to suit your assignment’s requirements, and you’re ready to impress.
- Consistency and Professionalism: Using our templates ensures consistency in your assignment submissions. The standardized design elements and formatting guidelines help maintain a professional appearance throughout your work. Presenting your assignments with a polished title page enhances the overall quality and credibility of your content.
- Visual Appeal: A visually appealing title page grabs attention and sets the tone for your assignment. Our templates are thoughtfully crafted by design professionals, incorporating aesthetically pleasing elements, color schemes, and typography. By leveraging these designs, you can effortlessly create eye-catching cover pages that captivate your professors or readers.
- Positive Impression: First impressions matter, and a well-designed cover page leaves a positive impact on professors and readers alike. Showcasing your assignment in a professional and visually appealing manner demonstrates your dedication and attention to detail. It sets the stage for an engaging reading experience, encouraging your audience to delve deeper into your work.
- User-Friendly Customization: Our templates are designed to be easily customizable, allowing you to add your personal touch without technical expertise. You can modify text, colors, images, and other elements to align with your assignment’s theme and requirements. This flexibility ensures that your cover page reflects your unique style while maintaining a professional look.
Tips for Maximizing the Impact: Make Your Cover Page Stand Out
- Choose Colors Wisely: Select colors that complement your assignment’s theme and evoke the desired emotions. Vibrant colors can grab attention, while muted tones create a sense of elegance. Maintain consistency with your assignment’s overall design and avoid using too many colors that may distract from the main message.
- Opt for Legible Fonts: Use clear and readable fonts to enhance the accessibility and professionalism of your cover page. Avoid overly decorative or complex fonts that may hinder readability. Opt for fonts that align with your assignment’s tone and maintain consistency throughout the document.
- Incorporate Relevant Graphics: Graphics can enhance the visual appeal of your cover page and reinforce the assignment’s subject matter. Choose images or icons that are directly related to the topic or convey the assignment’s main concept. Ensure that the graphics are high-quality and appropriately sized to maintain clarity.
- Organize Information Effectively: Arrange the information in a logical and visually appealing manner. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break down content and make it easier to read. Highlight key details such as the assignment title, your name, course information, and submission date.
- Maintain Simplicity: While it’s important to make it visually appealing, avoid cluttering it with excessive elements. Keep the design clean and uncluttered, allowing the key information to stand out. Remember, simplicity often has a greater impact than complexity.
- Preview and Proofread: Before finalizing, preview it to ensure that all elements are properly aligned and visually balanced. Proofread the content to eliminate any spelling or grammatical errors. A polished and error-free cover demonstrates your attention to detail and professionalism.
← Previous Article
Next Article →
You may also like

- Mother’s Day Cards
- Doctor Prescription Pad Formats
- Printable ID Cards
- Creative Resume Formats for Freshers
- Modern Resume Templates
- Best Cover Page Formats
- Printable Report Cards
- Business Proposal Templates
- 22 Raffle Ticket Templates
- Free Certificate Templates
Search the database of 10,000+ templates, designs & formats for Microsoft Office.
- Crafted with Love: Free Mother’s Day Cards to Warm Mom’s Heart
- Stand Out from the Crowd: 6+ Free Fact Sheet Templates
- Make Your Mark: Free Printable Dog Name Tags for Every Tail-Wagger!
- 7+ Free Stunning Easter Templates for Joyful Celebrations
- 9+ Free Admit-One Ticket Templates: Flexible and Easy to Edit
- Get Cooking with Style: 8+ Free Customizable Recipe Card Templates
- 11+ Free Mortgage Flyer Templates to Elevate Your Marketing
- Enhance Your Events with 20+ Unique and Free Ticket Voucher Templates
- Relaxation Redefined: Explore Free 8+ Spa Voucher Templates
- 24+ Free Employment Verification Letter Templates
- Free 5+ Best Christmas Wishlist Templates for Joyful Giving
- 5+ Best FREE Wedding Timeline Templates for a Magical Celebration
- Certificates
- Cover Pages
- Educational
- Event Templates
- Invoices & Receipts
- Letterheads
- Office Related
- Personal Use
- 137+ Professional Reports – MS Word & Excel
- 70+ Printable & Editable ID Card Designs
- 59+ Proposal Formats
- 31+ Best Flyer Designs & Formats
- 100+ Cover Page Templates
- 22+ Free Letterhead Designs and Formats
- 24+ Free Resume Designs & for Freshers and Professionals
- 136+ Printable Certificate Templates
- 55+ Quotations & Invoices
- Create FREE PDF Calendar Online
- Microsoft /
Microsoft Word just fixed its default paste option
Now, microsoft word will use the ‘merge formatting’ option by default..
By Emma Roth , a news writer who covers the streaming wars, consumer tech, crypto, social media, and much more. Previously, she was a writer and editor at MUO.
Share this story
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24347780/STK095_Microsoft_04.jpg)
Have you ever pasted text into your beautifully formatted Microsoft Word document, only for it to ruin everything? Well, the days of the should finally be over, as Microsoft Word will now merge the text’s formatting with your document by default.
Unlike the previous “keep source formatting” default, the “merge formatting” option preserves the original bold and underlined text, along with list and table structure. But it also changes the visual aspects of the text, such as font family, size, and color, to match the document you’re working on. That should save you from messing up the formatting of your entire document when pasting in text from another source.

- Google Sheets’ new formatting feature has Excel switchers excited
You could previously choose the “merge formatting” option from Word’s pasting menu, but it wasn’t the default. If you still want to use the “keep source formatting” option as the default, you can change it by heading to File > Options > Advanced > Cut, copy, and paste and then selecting the Pasting from other program drop-down menu. From there, choose Keep Source Formatting .
Last year, Microsoft finally started supporting the Control + Shift + V shortcut , which lets you paste in text without formatting at all.
The Mac vs. PC war is back on
Grand theft auto vi is launching in fall 2025, reddit brings back its old award system — ‘we messed up’, sony’s new playstation pc overlay is a simple start, twitter is officially x.com now.
More from Microsoft
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25449864/2150504820.jpg)
Microsoft’s AI obsession is jeopardizing its climate ambitions
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25449825/65cf71ee2368ff61aaf13de7_1.jpg)
Microsoft announces the Proteus Controller, a gamepad for Xbox gamers with disabilities
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25283724/STK048_XBOX_C.jpg)
Xbox Cloud Gaming now has mouse and keyboard support in 26 games
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25439012/NOTEPAD_CHORUS_LEDE_2040x1360.jpg)
Welcome to Notepad, a newsletter on Microsoft’s era-defining bets

Microsoft Word has finally added the copy and paste feature users have begged for — automatic merge formatting is here at last
Y ears of frustration for Microsoft Word users could finally be at an end after the company announced an update to fix one of its most irritating quirks.
Going forward, the default option when pasting into a Word document from other programs will to be to merge the formatting.
Previously, copying text into a Microsoft Word document from another source was somewhat of a minefield, as depending on its origin, the formatting of said text could be markedly different.
Microsoft Word formatting
Simply copying and pasting a few words into your existing carefully-crafted document was prone to causing an explosion of formatting chaos, with users unable to sync up their fonts or alignment, wasting valuable time on pasting formatting across paragraphs or pages.
Users will be able to check that merge formatting is the default option via the usual Paste Options menu ( File > Options > Advanced > Cut, copy, and paste ) with the ability to try different paste options (as before) with the previous Keep Source Formatting option still available, as well as Paste as Picture and Keep Text Only.
"Paste is one of the top user actions in Word, but it can also take up a lot of time," Ali Forelli, a Product Manager on the Microsoft Word team, wrote in a blog post announcing the change, tongue most likely firmly in cheek
"Do you ever paste content into your document, only to spend countless minutes manually fixing all the formatting of the pasted content? Do you wish you could bring content into your document and have it match the look and feel of the rest of your content?"
Forelli added the change will also mean pasted text keeps formatting from the original source "that has meaning" - for example, if it is in bold or italics, or part of a list or table.
The feature is available now to Word for Windows users running Version 2405 (Build 17624.20000) or later, but isn't on offer for Word for the web or Word for Mac just yet.
Hopefully the move will soon be mirrored by the likes of Google Docs, which does still struggle with copying formatted text. Microsoft did also recently support the Control + Shift + V shortcut, allowing users paste text without zero formatting, and the fact that this latest change comes after years of complaints might suggest big tech is finally listening to its user's biggest gripes after all.
More from TechRadar Pro
- How to download and use Microsoft Word for free
- Stay focused with our list of the best productivity software
- Our pick of the best document editing and management software around

Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Convert Word to PDF [For Students]
To ensure the sharing and security of your documents, instructors or teachers often require essays to be submitted in PDF format. However, finding a reliable conversion tool can be challenging. Many recommended tools either require payment or fail to preserve the formatting adequately. I too faced these issues until I discovered the life-saving tool I'll introduce to you in this article.
When to Convert Word to PDF?
In the academic world, ensuring your work is presented flawlessly is crucial. Converting your Word documents to PDFs offers several advantages:
Professorial Preferences : Many professors prefer submissions in PDF format for your essays, research papers, or thesis/dissertation. The major reason for this is to ensure that the academic style, such as APA or MLA, is maintained without formatting issues. Submitting in a Word document can cause problems because different writing software may interpret the formatting differently. Take Microsoft's recent update, for example, where the official font has been set to Aptos. If your document is in Aptos style and your professor uses a different office suite, there may be an error in the font.
Resume Readiness : For job applications or academic program admissions, a PDF resume maintains a professional appearance. It eliminates formatting inconsistencies that might occur when using different word processing software.
Application Advantage : The same principle applies to any application materials. Converting them to PDFs ensures consistent formatting, regardless of the receiving system. This allows your application to showcase your qualifications flawlessly.
How to Convert Word to PDF [Basic]
To answer the question of "How to Convert Word to PDF ," we will be using the free and powerful WPS Office, an office suite that I use daily for several reasons. One of them is converting PDFs without losing any formatting, providing an easy and complete solution. This is beneficial for students working on their thesis during their studies or preparing their resumes for future job applications. Converting to PDFs in a few easy steps, alongside the common issue faced by Microsoft Word users where bookmarks are not exported, can easily be addressed in WPS Office.
The Easiest Method: Save Word Documents as PDF Using 'Save As
My preferred method for everyday conversion is using the simple 'Save as' feature, where I can ask WPS Writer to save my Word documents in other file formats, be it PDF or another format for some other use. WPS Writer is always my go-to choice. So let's learn how to save a Word document as a PDF by following these simple steps:
Step 1 : Open your resume, job application, or essay document in WPS Writer that you want to convert to PDF.
Step 2 : Click on the "Menu" button at the top left corner of the WPS Writer interface.
Step 3 : In the Menu, select the "Save as" option, then choose the "Other Formats" option from the flyout menu.
Step 4 : The Save as window will appear. Set the file type to "PDF Format (*.pdf)" in the "File Type" field.
Step 5 : Users can also change the file name for their PDF document and adjust the location where they wish to save it. After making all the necessary settings, click on "Save" to convert Word to PDF.
This feature is very similar to the one offered by Microsoft Office, but Microsoft Office doesn't provide a PDF solution in its office suite, whereas WPS Office stays with me throughout the journey after the document has been completed, offering a PDF conversion for free. This makes WPS Office an office suite for students looking to convert Word to PDF with easy solutions.
Convert Your Writing to PDF Containing the Structure
The second method involves advanced conversion of your Word document to PDF to retain the structure of your document, especially for lengthy documents. The problem I found with normally converting Word documents to PDF using Microsoft Word was that there were no bookmarks in the PDF version of my document. To recall what these bookmarks are, you may have used textbooks in PDF form during your academic cycle, so jumping from one section to another with a single click is possible if the bookmarks have been retained in the structure.
Now, let's say your professor is going through your dissertation or thesis, and they want to jump to a section like an exhibit, so with bookmarks, it becomes easier to navigate. Upon learning how to convert Word to PDF using Microsoft Word, I found out that the method was really complex as it involved several steps. But with my free Word to PDF converter , WPS Office, this only involves one single click to get bookmarks. Here is how students can make their PDF navigation easier using the following conversion tool:
Step 1 : Let's open our lengthy Word document in WPS Writer to convert it to PDF.
Step 2 : Now, click on the Menu button located at the top right corner.
Step 3 : In the Menu, click on the "Export to PDF" option for a more enhanced PDF conversion.
Step 4 : In the Export to PDF window, visit the "Advanced Settings" options to change the default settings.
Step 5 : Now, in the Content section of the Advanced Settings window, make sure to check the "Bookmark" checkbox to convert the Word document to PDF, then click on "Confirm".
Step 6 : Upon returning to the Export to PDF window, look for any additional settings such as the file location or change the name of the output PDF, then hit "Export to PDF".
Your academic work has now been converted to PDF with all bookmarks, making it easier for navigation. As soon as you convert your Word document, you get yet another benefit of WPS Office: a dedicated PDF viewer and editor, so no need to download a separate PDF software. WPS Office, a single office suite, is all you need for all your academic endeavors.
Use WPS AI to Polish Your Writing
WPS Office has become a cornerstone for many, offering plenty of effortless solutions that have undoubtedly saved countless hours and improved productivity. Its suite of tools simplifies the writing and document creation process, making it accessible and user-friendly for students and professionals alike. However, where WPS Office truly shines is in its comprehensive PDF tools, which offer an unparalleled level of functionality and versatility.
Here's how students can utilize WPS AI Spell Check to ensure there are no inconsistencies in their academic work before submission:
Step 1 : Go to the Review tab in WPS Writer and click on the "AI Spell Check" button.
Step 2 : This will open WPS AI Spell Check on the right side of the interface.
Step 3 : To ensure you're following the correct formatting of your current academic style, click on "Set Goals".
Step 4 : Now, set your goal by selecting the Domain as "Academic".
Step 5 : Next, simply choose the format of your document. This will ensure that you're correctly following all the guidelines laid out by the academic style you're following.
For students, the scope of WPS AI becomes even more apparent. Not only does it provide invaluable assistance in writing and formatting academic papers, but it also serves as a comprehensive tool for document management and organization. With WPS Office and its AI capabilities at their disposal, students can tackle assignments and projects with confidence, knowing that they have a powerful ally to support them every step of the way.
Here's how students can enhance the quality of their work using WPS AI Writer:
Step 1 : Select the text or section you want to improve using your cursor.
Step 2 : Once the text is selected, right-click to open the context menu.
Step 3 : From the context menu, click on the "WPS AI" icon to enable WPS AI Assistant.
Step 4 : Once WPS AI is activated, a set of options will be displayed in a context menu. Click on "Improve Writing".
Step 5 : WPS AI will process your request and display an improved version of the section. Students can choose to either discard the result or use it in their work.
Students have found a significant source of relief in WPS AI, particularly with its spell check and AI writer functionalities. These tools offer more than just basic corrections; they provide a comprehensive solution for refining content in terms of tone, style, and vocabulary. With WPS AI, students can effortlessly enhance the quality of their writing, ensuring clarity and professionalism in their work.
One of the standout features of WPS AI is its ability to provide summaries and direct answers extracted from PDF documents. This functionality streamlines the research process, allowing students to quickly grasp the main points of complex texts without having to read through them entirely. Also, WPS AI offers the option to shorten or expand content as needed, providing flexibility in tailoring the length and depth of academic papers or other written assignments.
Effortless PDF Workflows with WPS Office
WPS PDF is not like other PDF tools and has made a distinguished name for itself from other free Word to PDF converters in several ways, offering enhanced functionality and reliability, especially when handling multiple documents and preserving formatting:
No Daily Limits : Many free converters impose daily limits on conversions, which can be restrictive when dealing with numerous documents. WPS Office, however, does not have such limitations. This means that users can convert as many documents as needed without worrying about hitting a cap.
Batch PDF Export : The premium version of WPS Office includes a batch PDF export function, which enables users to convert multiple documents simultaneously. This feature is invaluable for streamlining workflow and saving time, particularly in professional settings where efficiency is paramount. For instance, imagine you're compiling a series of reports for a business presentation. With WPS Office's batch PDF export function, you can quickly convert all the reports into PDF format with just a few clicks, ensuring a smooth and polished presentation.
Preservation of Formatting : One of the most common concerns when converting documents to PDF is the risk of format distortion. WPS Office excels in preserving the formatting of documents, ensuring that the converted PDFs retain the same appearance and layout as the original files. For example, when converting a Word document with headings and subheadings to PDF, the bookmarks in the exported PDF file accurately reflect the structure of the document, making it easy for readers to navigate. In contrast, issues with bookmarks and formatting discrepancies have been reported when using other converters, such as Microsoft Word's built-in conversion feature.
Resume Templates : WPS Office offers a wide selection of professionally designed resume templates, making it easy for users to create polished and visually appealing resumes with minimal effort. These templates cover a range of industries and job roles, allowing users to find the perfect design to suit their needs.
Resumes can be effortlessly converted to PDFs using WPS Office's PDF tool, offering the simplest method I've encountered for maintaining formatting consistency and facilitating easy sharing.
Step 1 : Open your resume document in WPS Writer.
Step 2 : Go to the "Student Tools" tab and click on the "Annotate in PDF Format" option in the ribbon.
Step 3 : This will instantly create a PDF of your resume and open it in a new tab within WPS Office.
FAQs about Converting Word to PDF
Q1. why can’t i convert word to pdf.
If you're unable to convert a Word document to PDF, consider the following solutions:
Check if the document is checked out : Ensure that no other user is currently editing or has the document checked out. You need exclusive access to convert it to PDF.
Remove password protection : Make sure the document isn't protected by a password. Password-protected documents can't be opened for conversion, causing conversion failures.
Verify the document size : Check if the file size is within the permissible limits for conversion. Large files may fail to convert properly. For example, Word documents should be smaller than 10 MB (10,485,760 bytes) for successful conversion to PDF. If the file size exceeds this limit, the conversion may fail with an error message indicating that the file size exceeds the maximum allowed size for Word conversions.
Q2. Why was I unable to save Word as a PDF?
You may be unable to save your Word document as a PDF if the app cannot locate your file's contents. To address this issue, follow these steps:
Step 1 : Open the Word document you wish to save as a PDF.
Step 2 : Go to the "File" menu and select "Share".
Step 3 : Choose "Send PDF" to create a PDF version of your document that you can share via email.
Q3. Why should students convert a document to PDF?
For students, converting a document to PDF resolves compatibility issues that may arise when opening files on different computers. Documents containing tables and graphs can sometimes have messy layouts on various devices, but PDFs maintain consistent presentation and readability across desktop computers and mobile devices. It ensures accessibility and allows students to access their documents smoothly, regardless of the device they're using. Whether switching devices or sharing files with others, PDFs provide a reliable format for consistent document viewing.
A Students Solution for PDF Conversions
As a former student, I understand the struggle of finding a reliable PDF tool. However, when I discovered WPS PDF, I knew my search was over. From that moment until now, WPS PDF has catered to all my needs seamlessly. Students will find themselves relying on it time and again. Whether creating PDFs for resumes or submitting essays, converting to PDFs has never been easier with WPS Office. With just one simple step of exporting to PDF, all the problems are solved—and for free. Download WPS Office today to experience its PDF capabilities firsthand.
- 1. How to Use Track Changes in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 2. How to Add Page Numbers in Word for Your Papers? [For Students]
- 3. How to Do Hanging Indent in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 4. How to Check Word Count for Your Essays in Word [For Students]
- 5. How to Insert Degree Symbol in Word [For Students]
- 6. How to Insert Signatures in Word [For Students]
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to set up your assignment formatting in Microsoft Word. Includes: margins, font style and size, line spacing, line indents, header, headings and r...
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5-in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. For paper sections with different alignment and ... Assignment due date. Page number 1 in the top right corner of the page header. The format for the byline depends on whether the paper has one author ...
Instructions: Go to the Format menu, drag down to Style, make sure "Normal" is selected from the list of styles, and click "modify.". In the lower left corner, select the dropdown menu that starts with "Format" and drag down to Paragraph. In the paragraph settings menu that pops up, change the settings for Spacing After to 0pt.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
In this video, we're going to show you the steps on how to format your university assignment/ report on Microsoft Word. In this example, we have a dissertati...
To select a word, double-click it. Word will select to the left and right of the cursor, until it encounters a space character. Triple-click A triple-click selects the current paragraph. Margin+click To select an entire line, move the cursor into the left margin. When you see the insertion pointer turn into an arrow pointer, click.
From keyboard shortcuts to simple, built-in features such as Find and Replace and the automatic table of contents, here are several tips you can use to edit and format your college assignment more efficiently in Microsoft Word. 1. Leave Paragraph Spacing as Your Last Step. Let's first start on the right track.
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
Right-click the text on which you want to base a new style. In the mini toolbar that appears, click Styles, and then click Create a Style. In the Create New Style from Formatting dialog box, give your style a name and click OK. Your new style will now appear in the Styles gallery. Note: If you want your new style to appear in all new Word ...
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments. The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create ...
For a student assignment, you will probably only require a paragraph or sentence on disclosures and acknowledgements. An example author note for a student paper could be: Author Note. This paper was prepared using Bing Copilot to assist with research and ChatGPT to assist with formatting the reference list.
To turn on text wrapping: Right-click (or ctrl-click, on a Mac) on the image and hover over Wrap Text. Select the alignment that best suits your document. You will see a preview as you hover over each option. To change the location of the image in the document, select the image and then hold the Ctrl key.
Select the heading text. Open the Home tab and go to the Styles section of the ribbon menu, at the top right side of the document. Select the heading style you want from the list of styles. For instance, if you're creating a top-level heading, select Heading 1. For subheadings, choose Heading 2 or Heading 3.
Follow the steps below to correctly format your document in current APA style using Microsoft Word. For additional help in formatting your UAGC papers, download our APA template: Template: UAGC Student Paper in APA (Word document) Title Page & Headers. Font Style & Size. Double Spacing.
Fonts. Use a clear, readable font, such as Verdana, Calibri, Tahoma or Arial and use the same font throughout. Use black text on a white background. Avoid coloured backgrounds or text in a colour other than black, unless you have special permission to use them. Use 11 or 12 point font for the body of your assessment.
Word 11 Formatting. ★★★★★. Kendall Myers November 15, 2017. In this practice project for Word, students create a document similar to a test or quiz. They must include points and subpoints, blanks, boldfaced text, tabs, and spacing. …. 1 2.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
Place your assignment title at the top of your first page, either centre or left aligned, in bold font. At university, you may be assigned a pre-designed essay title/question, or asked to select from several possible titles. You may also be asked to design your own essay title. Here are some top tips on designing your own title: To bring focus ...
A quick tutorial on formatting your assignments in the online version of Microsoft Word 365. This is very different in the Desktop version - please see my ot...
In Microsoft Word: Go to Home > Paste > Paste Special. Select Paste Special and from the dialog select Microsoft Office Excel Worksheet Object . You can resize the data as it was an image, and if you double click, you will be able to edit the values. You can change the table or chart and redesign it.
Templates for college and university assignments. Include customizable templates in your college toolbox. Stay focused on your studies and leave the assignment structuring to tried and true layout templates for all kinds of papers, reports, and more. Category. Color. Create from scratch. Show all.
CSC 110: Introduction to Computers Learning Unit 4: Word Assignment - Editing/Formatting Page 2 of 3 Assignment Instructions: 1. Copy and paste the text provided into a Microsoft Word document 2. Make the following changes to the title "Dress for Success." a. Make the font bold b. Center the text horizontally c. hange the font to ...
Created using Microsoft Word, these templates are highly customizable, allowing you to personalize them to suit your specific requirements. Modify them effortlessly to include your own text, images, and formatting. Enhance the visual appeal of your assignments with these professionally crafted cover page templates.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
Coupled with the templates, WPS's seamless PDF conversion feature can convert your documents to PDF in just a click without losing formatting. This is especially useful when submitting assignments, sharing work with classmates, or sending documents to professors or supervisors. WPS PDF. FAQs about Superscript and Subscript in Word for ...
Step 1: So, let's open the document in WPS Writer that we want to print after adjusting the margins. Step 2: Once the document is open, click on the "Menu" button at the top left corner. Step 3: Now, hover over the "Print" option in the menu and then select "Print Preview" from the flyout menu.
Microsoft finally fixed copy and paste in Word. Microsoft is about to make copying and pasting much easier in Word, thanks to a new Merge Formatting option. In a Microsoft 365 Insiders blog post ...
From there, choose Keep Source Formatting. Last year, Microsoft finally started supporting the Control + Shift + V shortcut, which lets you paste in text without formatting at all. Microsoft Word ...
Previously, copying text into a Microsoft Word document from another source was somewhat of a minefield, as depending on its origin, the formatting of said text could be markedly different.
Step 1: Let's open our lengthy Word document in WPS Writer to convert it to PDF. Step 2: Now, click on the Menu button located at the top right corner. Step 3: In the Menu, click on the "Export to PDF" option for a more enhanced PDF conversion. WPS Writer Export to PDF option.