

Health Case Studies
(29 reviews)
Glynda Rees, British Columbia Institute of Technology
Rob Kruger, British Columbia Institute of Technology
Janet Morrison, British Columbia Institute of Technology
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: BCcampus
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Jessica Sellars, Medical assistant office instructor, Blue Mountain Community College on 10/11/23
This is a book of compiled and very well organized patient case studies. The author has broken it up by disease patient was experiencing and even the healthcare roles that took place in this patients care. There is a well thought out direction and... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
This is a book of compiled and very well organized patient case studies. The author has broken it up by disease patient was experiencing and even the healthcare roles that took place in this patients care. There is a well thought out direction and plan. There is an appendix to refer to as well if you are needing to find something specific quickly. I have been looking for something like this to help my students have a base to do their project on. This is the most comprehensive version I have found on the subject.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
This is a book compiled of medical case studies. It is very accurate and can be used to learn from great care and mistakes.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
This material is very relevant in this context. It also has plenty of individual case studies to utilize in many ways in all sorts of medical courses. This is a very useful textbook and it will continue to be useful for a very long time as you can still learn from each study even if medicine changes through out the years.
Clarity rating: 5
The author put a lot of thought into the ease of accessibility and reading level of the target audience. There is even a "how to use this resource" section which could be extremely useful to students.
Consistency rating: 5
The text follows a very consistent format throughout the book.
Modularity rating: 5
Each case study is individual broken up and in a group of similar case studies. This makes it extremely easy to utilize.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is very organized and the appendix is through. It flows seamlessly through each case study.
Interface rating: 5
I had no issues navigating this book, It was clearly labeled and very easy to move around in.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
I did not catch any grammar errors as I was going through the book
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This is a challenging question for any medical textbook. It is very culturally relevant to those in medical or medical office degrees.
I have been looking for something like this for years. I am so happy to have finally found it.
Reviewed by Cindy Sun, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 1/7/23
Interestingly, this is not a case of ‘you get what you pay for’. Instead, not only are the case studies organized in a fashion for ease of use through a detailed table of contents, the authors have included more support for both faculty and... read more
Interestingly, this is not a case of ‘you get what you pay for’. Instead, not only are the case studies organized in a fashion for ease of use through a detailed table of contents, the authors have included more support for both faculty and students. For faculty, the introduction section titled ‘How to use this resource’ and individual notes to educators before each case study contain application tips. An appendix overview lists key elements as issues / concepts, scenario context, and healthcare roles for each case study. For students, learning objectives are presented at the beginning of each case study to provide a framework of expectations.
The content is presented accurately and realistic.
The case studies read similar to ‘A Day In the Life of…’ with detailed intraprofessional communications similar to what would be overheard in patient care areas. The authors present not only the view of the patient care nurse, but also weave interprofessional vantage points through each case study by including patient interaction with individual professionals such as radiology, physician, etc.
In addition to objective assessment findings, the authors integrate standard orders for each diagnosis including medications, treatments, and tests allowing the student to incorporate pathophysiology components to their assessments.
Each case study is arranged in the same framework for consistency and ease of use.
This compilation of eight healthcare case studies focusing on new onset and exacerbation of prevalent diagnoses, such as heart failure, deep vein thrombosis, cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease advancing to pneumonia.
Each case study has a photo of the ‘patient’. Simple as this may seem, it gives an immediate mental image for the student to focus.
Interface rating: 4
As noted by previous reviewers, most of the links do not connect active web pages. This may be due to the multiple options for accessing this resource (pdf download, pdf electronic, web view, etc.).
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
A minor weakness that faculty will probably need to address prior to use is regarding specific term usages differences between Commonwealth countries and United States, such as lung sound descriptors as ‘quiet’ in place of ‘diminished’ and ‘puffers’ in place of ‘inhalers’.
The authors have provided a multicultural, multigenerational approach in selection of patient characteristics representing a snapshot of today’s patient population. Additionally, one case study focusing on heart failure is about a middle-aged adult, contrasting to the average aged patient the students would normally see during clinical rotations. This option provides opportunities for students to expand their knowledge on risk factors extending beyond age.
This resource is applicable to nursing students learning to care for patients with the specific disease processes presented in each case study or for the leadership students focusing on intraprofessional communication. Educators can assign as a supplement to clinical experiences or as an in-class application of knowledge.
Reviewed by Stephanie Sideras, Assistant Professor, University of Portland on 8/15/22
The eight case studies included in this text addressed high frequency health alterations that all nurses need to be able to manage competently. While diabetes was not highlighted directly, it was included as a potential comorbidity. The five... read more
The eight case studies included in this text addressed high frequency health alterations that all nurses need to be able to manage competently. While diabetes was not highlighted directly, it was included as a potential comorbidity. The five overarching learning objectives pulled from the Institute of Medicine core competencies will clearly resonate with any faculty familiar with Quality and Safety Education for Nurses curriculum.
The presentation of symptoms, treatments and management of the health alterations was accurate. Dialogue between the the interprofessional team was realistic. At times the formatting of lab results was confusing as they reflected reference ranges specific to the Canadian healthcare system but these occurrences were minimal and could be easily adapted.
The focus for learning from these case studies was communication - patient centered communication and interprofessional team communication. Specific details, such as drug dosing, was minimized, which increases longevity and allows for easy individualization of the case data.
While some vocabulary was specific to the Canadian healthcare system, overall the narrative was extremely engaging and easy to follow. Subjective case data from patient or provider were formatted in italics and identified as 'thoughts'. Objective and behavioral case data were smoothly integrated into the narrative.
The consistency of formatting across the eight cases was remarkable. Specific learning objectives are identified for each case and these remain consistent across the range of cases, varying only in the focus for the goals for each different health alterations. Each case begins with presentation of essential patient background and the progress across the trajectory of illness as the patient moves from location to location encountering different healthcare professionals. Many of the characters (the triage nurse in the Emergency Department, the phlebotomist) are consistent across the case situations. These consistencies facilitate both application of a variety of teaching methods and student engagement with the situated learning approach.
Case data is presented by location and begins with the patient's first encounter with the healthcare system. This allows for an examination of how specific trajectories of illness are manifested and how care management needs to be prioritized at different stages. This approach supports discussions of care transitions and the complexity of the associated interprofessional communication.
The text is well organized. The case that has two levels of complexity is clearly identified
The internal links between the table of contents and case specific locations work consistently. In the EPUB and the Digital PDF the external hyperlinks are inconsistently valid.
The grammatical errors were minimal and did not detract from readability
Cultural diversity is present across the cases in factors including race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, family dynamics and sexual orientation.
The level of detail included in these cases supports a teaching approach to address all three spectrums of learning - knowledge, skills and attitudes - necessary for the development of competent practice. I also appreciate the inclusion of specific assessment instruments that would facilitate a discussion of evidence based practice. I will enjoy using these case to promote clinical reasoning discussions of data that is noticed and interpreted with the resulting prioritizes that are set followed by reflections that result from learner choices.
Reviewed by Chris Roman, Associate Professor, Butler University on 5/19/22
It would be extremely difficult for a book of clinical cases to comprehensively cover all of medicine, and this text does not try. Rather, it provides cases related to common medical problems and introduces them in a way that allows for various... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
It would be extremely difficult for a book of clinical cases to comprehensively cover all of medicine, and this text does not try. Rather, it provides cases related to common medical problems and introduces them in a way that allows for various learning strategies to be employed to leverage the cases for deeper student learning and application.
The narrative form of the cases is less subject to issues of accuracy than a more content-based book would be. That said, the cases are realistic and reasonable, avoiding being too mundane or too extreme.
These cases are narrative and do not include many specific mentions of drugs, dosages, or other aspects of clinical care that may grow/evolve as guidelines change. For this reason, the cases should be “evergreen” and can be modified to suit different types of learners.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is written in very accessible language and avoids heavy use of technical language. Depending on the level of learner, this might even be too simplistic and omit some details that would be needed for physicians, pharmacists, and others to make nuanced care decisions.
The format is very consistent with clear labeling at transition points.
The authors point out in the introductory materials that this text is designed to be used in a modular fashion. Further, they have built in opportunities to customize each cases, such as giving dates of birth at “19xx” to allow for adjustments based on instructional objectives, etc.
The organization is very easy to follow.
I did not identify any issues in navigating the text.
The text contains no grammatical errors, though the language is a little stiff/unrealistic in some cases.
Cases involve patients and members of the care team that are of varying ages, genders, and racial/ethnic backgrounds
Reviewed by Trina Larery, Assistant Professor, Pittsburg State University on 4/5/22
The book covers common scenarios, providing allied health students insight into common health issues. The information in the book is thorough and easily modified if needed to include other scenarios not listed. The material was easy to understand... read more
The book covers common scenarios, providing allied health students insight into common health issues. The information in the book is thorough and easily modified if needed to include other scenarios not listed. The material was easy to understand and apply to the classroom. The E-reader format included hyperlinks that bring the students to subsequent clinical studies.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The treatments were explained and rationales were given, which can be very helpful to facilitate effective learning for a nursing student or novice nurse. The case studies were accurate in explanation. The DVT case study incorrectly identifies the location of the clot in the popliteal artery instead of in the vein.
The content is relevant to a variety of different types of health care providers and due to the general nature of the cases, will remain relevant over time. Updates should be made annually to the hyperlinks and to assure current standard of practice is still being met.
Clear, simple and easy to read.
Consistent with healthcare terminology and framework throughout all eight case studies.
The text is modular. Cases can be used individually within a unit on the given disease process or relevant sections of a case could be used to illustrate a specific point providing great flexibility. The appendix is helpful in locating content specific to a certain diagnosis or a certain type of health care provider.
The book is well organized, presenting in a logical clear fashion. The appendix allows the student to move about the case study without difficulty.
The interface is easy and simple to navigate. Some links to external sources might need to be updated regularly since those links are subject to change based on current guidelines. A few hyperlinks had "page not found".
Few grammatical errors were noted in text.
The case studies include people of different ethnicities, socioeconomic status, ages, and genders to make this a very useful book.
I enjoyed reading the text. It was interesting and relevant to today's nursing student. There are roughly 25 broken online links or "pages not found", care needs to be taken to update at least annually and assure links are valid and utilizing the most up to date information.
Reviewed by Benjamin Silverberg, Associate Professor/Clinician, West Virginia University on 3/24/22
The appendix reviews the "key roles" and medical venues found in all 8 cases, but is fairly spartan on medical content. The table of contents at the beginning only lists the cases and locations of care. It can be a little tricky to figure out what... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The appendix reviews the "key roles" and medical venues found in all 8 cases, but is fairly spartan on medical content. The table of contents at the beginning only lists the cases and locations of care. It can be a little tricky to figure out what is going on where, especially since each case is largely conversation-based. Since this presents 8 cases (really 7 with one being expanded upon), there are many medical topics (and venues) that are not included. It's impossible to include every kind of situation, but I'd love to see inclusion of sexual health, renal pathology, substance abuse, etc.
Though there are differences in how care can be delivered based on personal style, changing guidelines, available supplies, etc, the medical accuracy seems to be high. I did not detect bias or industry influence.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Medications are generally listed as generics, with at least current dosing recommendations. The text gives a picture of what care looks like currently, but will be a little challenging to update based on new guidelines (ie, it can be hard to find the exact page in which a medication is dosed/prescribed). Even if the text were to be a little out of date, an instructor can use that to point out what has changed (and why).
Clear text, usually with definitions of medical slang or higher-tier vocabulary. Minimal jargon and there are instances where the "characters" are sorting out the meaning as well, making it accessible for new learners, too.
Overall, the style is consistent between cases - largely broken up into scenes and driven by conversation rather than descriptions of what is happening.
There are 8 (well, again, 7) cases which can be reviewed in any order. Case #2 builds upon #1, which is intentional and a good idea, though personally I would have preferred one case to have different possible outcomes or even a recurrence of illness. Each scene within a case is reasonably short.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
These cases are modular and don't really build on concepts throughout. As previously stated, case #2 builds upon #1, but beyond that, there is no progression. (To be sure, the authors suggest using case #1 for newer learners and #2 for more advanced ones.) The text would benefit from thematic grouping, a longer introduction and debriefing for each case (there are learning objectives but no real context in medical education nor questions to reflect on what was just read), and progressively-increasing difficulty in medical complexity, ethics, etc.
I used the PDF version and had no interface issues. There are minimal photographs and charts. Some words are marked in blue but those did not seem to be hyperlinked anywhere.
No noticeable errors in grammar, spelling, or formatting were noted.
I appreciate that some diversity of age and ethnicity were offered, but this could be improved. There were Canadian Indian and First Nations patients, for example, as well as other characters with implied diversity, but there didn't seem to be any mention of gender diverse or non-heterosexual people, or disabilities. The cases tried to paint family scenes (the first patient's dog was fairly prominently mentioned) to humanize them. Including more cases would allow for more opportunities to include sex/gender minorities, (hidden) disabilities, etc.
The text (originally from 2017) could use an update. It could be used in conjunction with other Open Texts, as a compliment to other coursework, or purely by itself. The focus is meant to be on improving communication, but there are only 3 short pages at the beginning of the text considering those issues (which are really just learning objectives). In addition to adding more cases and further diversity, I personally would love to see more discussion before and after the case to guide readers (and/or instructors). I also wonder if some of the ambiguity could be improved by suggesting possible health outcomes - this kind of counterfactual comparison isn't possible in real life and could be really interesting in a text. Addition of comprehension/discussion questions would also be worthwhile.
Reviewed by Danielle Peterson, Assistant Professor, University of Saint Francis on 12/31/21
This text provides readers with 8 case studies which include both chronic and acute healthcare issues. Although not comprehensive in regard to types of healthcare conditions, it provides a thorough look at the communication between healthcare... read more
This text provides readers with 8 case studies which include both chronic and acute healthcare issues. Although not comprehensive in regard to types of healthcare conditions, it provides a thorough look at the communication between healthcare workers in acute hospital settings. The cases are primarily set in the inpatient hospital setting, so the bulk of the clinical information is basic emergency care and inpatient protocol: vitals, breathing, medication management, etc. The text provides a table of contents at opening of the text and a handy appendix at the conclusion of the text that outlines each case’s issue(s), scenario, and healthcare roles. No index or glossary present.
Although easy to update, it should be noted that the cases are taking place in a Canadian healthcare system. Terms may be unfamiliar to some students including “province,” “operating theatre,” “physio/physiotherapy,” and “porter.” Units of measurement used include Celsius and meters. Also, the issue of managed care, health insurance coverage, and length of stay is missing for American students. These are primary issues that dictate much of the healthcare system in the US and a primary job function of social workers, nurse case managers, and medical professionals in general. However, instructors that wish to add this to the case studies could do so easily.
The focus of this text is on healthcare communication which makes it less likely to become obsolete. Much of the clinical information is stable healthcare practice that has been standard of care for quite some time. Nevertheless, given the nature of text, updates would be easy to make. Hyperlinks should be updated to the most relevant and trustworthy sources and checked frequently for effectiveness.
The spacing that was used to note change of speaker made for ease of reading. Although unembellished and plain, I expect students to find this format easy to digest and interesting, especially since the script is appropriately balanced with ‘human’ qualities like the current TV shows and songs, the use of humor, and nonverbal cues.
A welcome characteristic of this text is its consistency. Each case is presented in a similar fashion and the roles of the healthcare team are ‘played’ by the same character in each of the scenarios. This allows students to see how healthcare providers prioritize cases and juggle the needs of multiple patients at once. Across scenarios, there was inconsistency in when clinical terms were hyperlinked.
The text is easily divisible into smaller reading sections. However, since the nature of the text is script-narrative format, if significant reorganization occurs, one will need to make sure that the communication of the script still makes sense.
The text is straightforward and presented in a consistent fashion: learning objectives, case history, a script of what happened before the patient enters the healthcare setting, and a script of what happens once the patient arrives at the healthcare setting. The authors use the term, “ideal interactions,” and I would agree that these cases are in large part, ‘best case scenarios.’ Due to this, the case studies are well organized, clear, logical, and predictable. However, depending on the level of student, instructors may want to introduce complications that are typical in the hospital setting.
The interface is pleasing and straightforward. With exception to the case summary and learning objectives, the cases are in narrative, script format. Each case study supplies a photo of the ‘patient’ and one of the case studies includes a link to a 3-minute video that introduces the reader to the patient/case. One of the highlights of this text is the use of hyperlinks to various clinical practices (ABG, vital signs, transfer of patient). Unfortunately, a majority of the links are broken. However, since this is an open text, instructors can update the links to their preference.
Although not free from grammatical errors, those that were noticed were minimal and did not detract from reading.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Cultural diversity is visible throughout the patients used in the case studies and includes factors such as age, race, socioeconomic status, family dynamics, and sexual orientation. A moderate level of diversity is noted in the healthcare team with some stereotypes: social workers being female, doctors primarily male.
As a social work instructor, I was grateful to find a text that incorporates this important healthcare role. I would have liked to have seen more content related to advance directives, mediating decision making between the patient and care team, emotional and practical support related to initial diagnosis and discharge planning, and provision of support to colleagues, all typical roles of a medical social worker. I also found it interesting that even though social work was included in multiple scenarios, the role was only introduced on the learning objectives page for the oncology case.
Reviewed by Crystal Wynn, Associate Professor, Virginia State University on 7/21/21
The text covers a variety of chronic diseases within the cases; however, not all of the common disease states were included within the text. More chronic diseases need to be included such as diabetes, cancer, and renal failure. Not all allied... read more
The text covers a variety of chronic diseases within the cases; however, not all of the common disease states were included within the text. More chronic diseases need to be included such as diabetes, cancer, and renal failure. Not all allied health care team members are represented within the case study. Key terms appear throughout the case study textbook and readers are able to click on a hyperlink which directs them to the definition and an explanation of the key term.
Content is accurate, error-free and unbiased.
The content is up-to-date, but not in a way that will quickly make the text obsolete within a short period of time. The text is written and/or arranged in such a way that necessary updates will be relatively easy and straightforward to implement.
The text is written in lucid, accessible prose, and provides adequate context for any jargon/technical terminology used
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned at different points within the course. Each case can be divided into a chronic disease state unit, which will allow the reader to focus on one section at a time.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The topics in the text are presented in a logical manner. Each case provides an excessive amount of language that provides a description of the case. The cases in this text reads more like a novel versus a clinical textbook. The learning objectives listed within each case should be in the form of questions or activities that could be provided as resources for instructors and teachers.
Interface rating: 3
There are several hyperlinks embedded within the textbook that are not functional.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. More examples of cultural inclusiveness is needed throughout the textbook. The cases should be indicative of individuals from a variety of races and ethnicities.
Reviewed by Rebecca Hillary, Biology Instructor, Portland Community College on 6/15/21
This textbook consists of a collection of clinical case studies that can be applicable to a wide range of learning environments from supplementing an undergraduate Anatomy and Physiology Course, to including as part of a Medical or other health... read more
This textbook consists of a collection of clinical case studies that can be applicable to a wide range of learning environments from supplementing an undergraduate Anatomy and Physiology Course, to including as part of a Medical or other health care program. I read the textbook in E-reader format and this includes hyperlinks that bring the students to subsequent clinical study if the book is being used in a clinical classroom. This book is significantly more comprehensive in its approach from other case studies I have read because it provides a bird’s eye view of the many clinicians, technicians, and hospital staff working with one patient. The book also provides real time measurements for patients that change as they travel throughout the hospital until time of discharge.
Each case gave an accurate sense of the chaos that would be present in an emergency situation and show how the conditions affect the practitioners as well as the patients. The reader gets an accurate big picture--a feel for each practitioner’s point of view as well as the point of view of the patient and the patient’s family as the clock ticks down and the patients are subjected to a number of procedures. The clinical information contained in this textbook is all in hyperlinks containing references to clinical skills open text sources or medical websites. I did find one broken link on an external medical resource.
The diseases presented are relevant and will remain so. Some of the links are directly related to the Canadian Medical system so they may not be applicable to those living in other regions. Clinical links may change over time but the text itself will remain relevant.
Each case study clearly presents clinical data as is it recorded in real time.
Each case study provides the point of view of several practitioners and the patient over several days. While each of the case studies covers different pathology they all follow this same format, several points of view and data points, over a number of days.
The case studies are divided by days and this was easy to navigate as a reader. It would be easy to assign one case study per body system in an Anatomy and Physiology course, or to divide them up into small segments for small in class teaching moments.
The topics are presented in an organized way showing clinical data over time and each case presents a large number of view points. For example, in the first case study, the patient is experiencing difficulty breathing. We follow her through several days from her entrance to the emergency room. We meet her X Ray Technicians, Doctor, Nurses, Medical Assistant, Porter, Physiotherapist, Respiratory therapist, and the Lab Technicians running her tests during her stay. Each practitioner paints the overall clinical picture to the reader.
I found the text easy to navigate. There were not any figures included in the text, only clinical data organized in charts. The figures were all accessible via hyperlink. Some figures within the textbook illustrating patient scans could have been helpful but I did not have trouble navigating the links to visualize the scans.
I did not see any grammatical errors in the text.
The patients in the text are a variety of ages and have a variety of family arrangements but there is not much diversity among the patients. Our seven patients in the eight case studies are mostly white and all cis gendered.
Some of the case studies, for example the heart failure study, show clinical data before and after drug treatments so the students can get a feel for mechanism in physiological action. I also liked that the case studies included diet and lifestyle advice for the patients rather than solely emphasizing these pharmacological interventions. Overall, I enjoyed reading through these case studies and I plan to utilize them in my Anatomy and Physiology courses.
Reviewed by Richard Tarpey, Assistant Professor, Middle Tennessee State University on 5/11/21
As a case study book, there is no index or glossary. However, medical and technical terms provide a useful link to definitions and explanations that will prove useful to students unfamiliar with the terms. The information provided is appropriate... read more
As a case study book, there is no index or glossary. However, medical and technical terms provide a useful link to definitions and explanations that will prove useful to students unfamiliar with the terms. The information provided is appropriate for entry-level health care students. The book includes important health problems, but I would like to see coverage of at least one more chronic/lifestyle issue such as diabetes. The book covers adult issues only.
Content is accurate without bias
The content of the book is relevant and up-to-date. It addresses conditions that are prevalent in today's population among adults. There are no pediatric cases, but this does not significantly detract from the usefulness of the text. The format of the book lends to easy updating of data or information.
The book is written with clarity and is easy to read. The writing style is accessible and technical terminology is explained with links to more information.
Consistency is present. Lack of consistency is typically a problem with case study texts, but this book is consistent with presentation, format, and terminology throughout each of the eight cases.
The book has high modularity. Each of the case studies can be used independently from the others providing flexibility. Additionally, each case study can be partitioned for specific learning objectives based on the learning objectives of the course or module.
The book is well organized, presenting students conceptually with differing patient flow patterns through a hospital. The patient information provided at the beginning of each case is a wonderful mechanism for providing personal context for the students as they consider the issues. Many case studies focus on the problem and the organization without students getting a patient's perspective. The patient perspective is well represented in these cases.
The navigation through the cases is good. There are some terminology and procedure hyperlinks within the cases that do not work when accessed. This is troubling if you intend to use the text for entry-level health care students since many of these links are critical for a full understanding of the case.
There are some non-US variants of spelling and a few grammatical errors, but these do not detract from the content of the messages of each case.
The book is inclusive of differing backgrounds and perspectives. No insensitive or offensive references were found.
I like this text for its application flexibility. The book is useful for non-clinical healthcare management students to introduce various healthcare-related concepts and terminology. The content is also helpful for the identification of healthcare administration managerial issues for students to consider. The book has many applications.
Reviewed by Paula Baldwin, Associate Professor/Communication Studies, Western Oregon University on 5/10/21
The different case studies fall on a range, from crisis care to chronic illness care. read more
The different case studies fall on a range, from crisis care to chronic illness care.
The contents seems to be written as they occurred to represent the most complete picture of each medical event's occurence.
These case studies are from the Canadian medical system, but that does not interfere with it's applicability.
It is written for a medical audience, so the terminology is mostly formal and technical.
Some cases are shorter than others and some go in more depth, but it is not problematic.
The eight separate case studies is the perfect size for a class in the quarter system. You could combine this with other texts, videos or learning modalities, or use it alone.
As this is a case studies book, there is not a need for a logical progression in presentation of topics.
No problems in terms of interface.
I have not seen any grammatical errors.
I did not see anything that was culturally insensitive.
I used this in a Health Communication class and it has been extraordinarily successful. My studies are analyzing the messaging for the good, the bad, and the questionable. The case studies are widely varied and it gives the class insights into hospital experiences, both front and back stage, that they would not normally be able to examine. I believe that because it is based real-life medical incidents, my students are finding the material highly engaging.
Reviewed by Marlena Isaac, Instructor, Aiken Technical College on 4/23/21
This text is great to walk through patient care with entry level healthcare students. The students are able to take in the information, digest it, then provide suggestions to how they would facilitate patient healing. Then when they are faced with... read more
This text is great to walk through patient care with entry level healthcare students. The students are able to take in the information, digest it, then provide suggestions to how they would facilitate patient healing. Then when they are faced with a situation in clinical they are not surprised and now how to move through it effectively.
The case studies provided accurate information that relates to the named disease.
It is relevant to health care studies and the development of critical thinking.
Cases are straightforward with great clinical information.
Clinical information is provided concisely.
Appropriate for clinical case study.
Presented to facilitate information gathering.
Takes a while to navigate in the browser.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
Text lacks adequate representation of minorities.
Reviewed by Kim Garcia, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 11/16/20
The book has 8 case studies, so obviously does not cover the whole of medicine, but the cases provided are descriptive and well developed. Cases are presented at different levels of difficulty, making the cases appropriate for students at... read more
The book has 8 case studies, so obviously does not cover the whole of medicine, but the cases provided are descriptive and well developed. Cases are presented at different levels of difficulty, making the cases appropriate for students at different levels of clinical knowledge. The human element of both patient and health care provider is well captured. The cases are presented with a focus on interprofessional interaction and collaboration, more so than teaching medical content.
Content is accurate and un-biased. No errors noted. Most diagnostic and treatment information is general so it will remain relevant over time. The content of these cases is more appropriate for teaching interprofessional collaboration and less so for teaching the medical care for each diagnosis.
The content is relevant to a variety of different types of health care providers (nurses, radiologic technicians, medical laboratory personnel, etc) and due to the general nature of the cases, will remain relevant over time.
Easy to read. Clear headings are provided for sections of each case study and these section headings clearly tell when time has passed or setting has changed. Enough description is provided to help set the scene for each part of the case. Much of the text is written in the form of dialogue involving patient, family and health care providers, making it easy to adapt for role play. Medical jargon is limited and links for medical terms are provided to other resources that expound on medical terms used.
The text is consistent in structure of each case. Learning objectives are provided. Cases generally start with the patient at home and move with the patient through admission, testing and treatment, using a variety of healthcare services and encountering a variety of personnel.
The text is modular. Cases could be used individually within a unit on the given disease process or relevant sections of a case could be used to illustrate a specific point. The appendix is helpful in locating content specific to a certain diagnosis or a certain type of health care provider.
Each case follows a patient in a logical, chronologic fashion. A clear table of contents and appendix are provided which allows the user to quickly locate desired content. It would be helpful if the items in the table of contents and appendix were linked to the corresponding section of the text.
The hyperlinks to content outside this book work, however using the back arrow on your browser returns you to the front page of the book instead of to the point at which you left the text. I would prefer it if the hyperlinks opened in a new window or tab so closing that window or tab would leave you back where you left the text.
No grammatical errors were noted.
The text is culturally inclusive and appropriate. Characters, both patients and care givers are of a variety of races, ethnicities, ages and backgrounds.
I enjoyed reading the cases and reviewing this text. I can think of several ways in which I will use this content.
Reviewed by Raihan Khan, Instructor/Assistant Professor, James Madison University on 11/3/20
The book contains several important health issues, however still missing some chronic health issues that the students should learn before they join the workforce, such as diabetes-related health issues suffered by the patients. read more
The book contains several important health issues, however still missing some chronic health issues that the students should learn before they join the workforce, such as diabetes-related health issues suffered by the patients.
The health information contained in the textbook is mostly accurate.
I think the book is written focusing on the current culture and health issues faced by the patients. To keep the book relevant in the future, the contexts especially the culture/lifestyle/health care modalities, etc. would need to be updated regularly.
The language is pretty simple, clear, and easy to read.
There is no complaint about consistency. One of the main issues of writing a book, consistency was well managed by the authors.
The book is easy to explore based on how easy the setup is. Students can browse to the specific section that they want to read without much hassle of finding the correct information.
The organization is simple but effective. The authors organized the book based on what can happen in a patient's life and what possible scenarios students should learn about the disease. From that perspective, the book does a good job.
The interface is easy and simple to navigate. Some links to external sources might need to be updated regularly since those links are subject to change that is beyond the author's control. It's frustrating for the reader when the external link shows no information.
The book is free of any major language and grammatical errors.
The book might do a little better in cultural competency. e.g. Last name Singh is mainly for Sikh people. In the text Harj and Priya Singh are Muslim. the authors can consult colleagues who are more familiar with those cultures and revise some cultural aspects of the cases mentioned in the book.
The book is a nice addition to the open textbook world. Hope to see more health issues covered by the book.
Reviewed by Ryan Sheryl, Assistant Professor, California State University, Dominguez Hills on 7/16/20
This text contains 8 medical case studies that reflect best practices at the time of publication. The text identifies 5 overarching learning objectives: interprofessional collaboration, client centered care, evidence-based practice, quality... read more
This text contains 8 medical case studies that reflect best practices at the time of publication. The text identifies 5 overarching learning objectives: interprofessional collaboration, client centered care, evidence-based practice, quality improvement, and informatics. While the case studies do not cover all medical conditions or bodily systems, the book is thorough in conveying details of various patients and medical team members in a hospital environment. Rather than an index or glossary at the end of the text, it contains links to outside websites for more information on medical tests and terms referenced in the cases.
The content provided is reflective of best practices in patient care, interdisciplinary collaboration, and communication at the time of publication. It is specifically accurate for the context of hospitals in Canada. The links provided throughout the text have the potential to supplement with up-to-date descriptions and definitions, however, many of them are broken (see notes in Interface section).
The content of the case studies reflects the increasingly complex landscape of healthcare, including a variety of conditions, ages, and personal situations of the clients and care providers. The text will require frequent updating due to the rapidly changing landscape of society and best practices in client care. For example, a future version may include inclusive practices with transgender clients, or address ways medical racism implicitly impacts client care (see notes in Cultural Relevance section).
The text is written clearly and presents thorough, realistic details about working and being treated in an acute hospital context.
The text is very straightforward. It is consistent in its structure and flow. It uses consistent terminology and follows a structured framework throughout.
Being a series of 8 separate case studies, this text is easily and readily divisible into smaller sections. The text was designed to be taken apart and used piece by piece in order to serve various learning contexts. The parts of each case study can also be used independently of each other to facilitate problem solving.
The topics in the case studies are presented clearly. The structure of each of the case studies proceeds in a similar fashion. All of the cases are set within the same hospital so the hospital personnel and service providers reappear across the cases, giving a textured portrayal of the experiences of the various service providers. The cases can be used individually, or one service provider can be studied across the various studies.
The text is very straightforward, without complex charts or images that could become distorted. Many of the embedded links are broken and require updating. The links that do work are a very useful way to define and expand upon medical terms used in the case studies.
Grammatical errors are minimal and do not distract from the flow of the text. In one instance the last name Singh is spelled Sing, and one patient named Fred in the text is referred to as Frank in the appendix.
The cases all show examples of health care personnel providing compassionate, client-centered care, and there is no overt discrimination portrayed. Two of the clients are in same-sex marriages and these are shown positively. It is notable, however, that the two cases presenting people of color contain more negative characteristics than the other six cases portraying Caucasian people. The people of color are the only two examples of clients who smoke regularly. In addition, the Indian client drinks and is overweight, while the First Nations client is the only one in the text to have a terminal diagnosis. The Indian client is identified as being Punjabi and attending a mosque, although there are only 2% Muslims in the Punjab province of India. Also, the last name Singh generally indicates a person who is a Hindu or Sikh, not Muslim.
Reviewed by Monica LeJeune, RN Instructor, LSUE on 4/24/20
Has comprehensive unfolding case studies that guide the reader to recognize and manage the scenario presented. Assists in critical thinking process. read more
Has comprehensive unfolding case studies that guide the reader to recognize and manage the scenario presented. Assists in critical thinking process.
Accurately presents health scenarios with real life assessment techniques and patient outcomes.
Relevant to nursing practice.
Clearly written and easily understood.
Consistent with healthcare terminology and framework
Has a good reading flow.
Topics presented in logical fashion
Easy to read.
No grammatical errors noted.
Text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
Good book to have to teach nursing students.
Reviewed by april jarrell, associate professor, J. Sargeant Reynolds Community College on 1/7/20
The text is a great case study tool that is appropriate for nursing school instructors to use in aiding students to learn the nursing process. read more
The text is a great case study tool that is appropriate for nursing school instructors to use in aiding students to learn the nursing process.
The content is accurate and evidence based. There is no bias noted
The content in the text is relevant, up to date for nursing students. It will be easy to update content as needed because the framework allows for addition to the content.
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Framework and terminology is consistent throughout the text; the case study is a continual and takes the student on a journey with the patient. Great for learning!
The case studies can be easily divided into smaller sections to allow for discussions, and weekly studies.
The text and content progress in a logical, clear fashion allowing for progression of learning.
No interface issues noted with this text.
No grammatical errors noted in the text.
No racial or culture insensitivity were noted in the text.
I would recommend this text be used in nursing schools. The use of case studies are helpful for students to learn and practice the nursing process.
Reviewed by Lisa Underwood, Practical Nursing Instructor, NTCC on 12/3/19
The text provides eight comprehensive case studies that showcase the different viewpoints of the many roles involved in patient care. It encompasses the most common seen diagnoses seen across healthcare today. Each case study comes with its own... read more
The text provides eight comprehensive case studies that showcase the different viewpoints of the many roles involved in patient care. It encompasses the most common seen diagnoses seen across healthcare today. Each case study comes with its own set of learning objectives that can be tweaked to fit several allied health courses. Although the case studies are designed around the Canadian Healthcare System, they are quite easily adaptable to fit most any modern, developed healthcare system.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
Overall, the text is quite accurate. There is one significant error that needs to be addressed. It is located in the DVT case study. In the study, a popliteal artery clot is mislabeled as a DVT. DVTs are located in veins, not in arteries. That said, the case study on the whole is quite good. This case study could be used as a learning tool in the classroom for discussion purposes or as a way to test student understanding of DVTs, on example might be, "Can they spot the error?"
At this time, all of the case studies within the text are current. Healthcare is an ever evolving field that rests on the best evidence based practice. Keeping that in mind, educators can easily adapt the studies as the newest evidence emerges and changes practice in healthcare.
All of the case studies are well written and easy to understand. The text includes several hyperlinks and it also highlights certain medical terminology to prompt readers as a way to enhance their learning experience.
Across the text, the language, style, and format of the case studies are completely consistent.
The text is divided into eight separate case studies. Each case study may be used independently of the others. All case studies are further broken down as the focus patient passes through each aspect of their healthcare system. The text's modularity makes it possible to use a case study as individual work, group projects, class discussions, homework or in a simulation lab.
The case studies and the diagnoses that they cover are presented in such a way that educators and allied health students can easily follow and comprehend.
The book in itself is free of any image distortion and it prints nicely. The text is offered in a variety of digital formats. As noted in the above reviews, some of the hyperlinks have navigational issues. When the reader attempts to access them, a "page not found" message is received.
There were minimal grammatical errors. Some of which may be traced back to the differences in our spelling.
The text is culturally relevant in that it includes patients from many different backgrounds and ethnicities. This allows educators and students to explore cultural relevance and sensitivity needs across all areas in healthcare. I do not believe that the text was in any way insensitive or offensive to the reader.
By using the case studies, it may be possible to have an open dialogue about the differences noted in healthcare systems. Students will have the ability to compare and contrast the Canadian healthcare system with their own. I also firmly believe that by using these case studies, students can improve their critical thinking skills. These case studies help them to "put it all together".
Reviewed by Melanie McGrath, Associate Professor, TRAILS on 11/29/19
The text covered some of the most common conditions seen by healthcare providers in a hospital setting, which forms a solid general base for the discussions based on each case. read more
The text covered some of the most common conditions seen by healthcare providers in a hospital setting, which forms a solid general base for the discussions based on each case.
I saw no areas of inaccuracy
As in all healthcare texts, treatments and/or tests will change frequently. However, everything is currently up-to-date thus it should be a good reference for several years.
Each case is written so that any level of healthcare student would understand. Hyperlinks in the text is also very helpful.
All of the cases are written in a similar fashion.
Although not structured as a typical text, each case is easily assigned as a stand-alone.
Each case is organized clearly in an appropriate manner.
I did not see any issues.
I did not see any grammatical errors
The text seemed appropriately inclusive. There are no pediatric cases and no cases of intellectually-impaired patients, but those types of cases introduce more advanced problem-solving which perhaps exceed the scope of the text. May be a good addition to the text.
I found this text to be an excellent resource for healthcare students in a variety of fields. It would be best utilized in inter professional courses to help guide discussion.
Reviewed by Lynne Umbarger, Clinical Assistant Professor, Occupational Therapy, Emory and Henry College on 11/26/19
While the book does not cover every scenario, the ones in the book are quite common and troublesome for inexperienced allied health students. The information in the book is thorough enough, and I have found the cases easy to modify for educational... read more
While the book does not cover every scenario, the ones in the book are quite common and troublesome for inexperienced allied health students. The information in the book is thorough enough, and I have found the cases easy to modify for educational purposes. The material was easily understood by the students but challenging enough for classroom discussion. There are no mentions in the book about occupational therapy, but it is easy enough to add a couple words and make inclusion simple.
Very nice lab values are provided in the case study, making it more realistic for students.
These case studies focus on commonly encountered diagnoses for allied health and nursing students. They are comprehensive, realistic, and easily understood. The only difference is that the hospital in one case allows the patient's dog to visit in the room (highly unusual in US hospitals).
The material is easily understood by allied health students. The cases have links to additional learning materials for concepts that may be less familiar or should be explored further in a particular health field.
The language used in the book is consistent between cases. The framework is the same with each case which makes it easier to locate areas that would be of interest to a particular allied health profession.
The case studies are comprehensive but well-organized. They are short enough to be useful for class discussion or a full-blown assignment. The students seem to understand the material and have not expressed that any concepts or details were missing.
Each case is set up like the other cases. There are learning objectives at the beginning of each case to facilitate using the case, and it is easy enough to pull out material to develop useful activities and assignments.
There is a quick chart in the Appendix to allow the reader to determine the professions involved in each case as well as the pertinent settings and diagnoses for each case study. The contents are easy to access even while reading the book.
As a person who attends carefully to grammar, I found no errors in all of the material I read in this book.
There are a greater number of people of different ethnicities, socioeconomic status, ages, and genders to make this a very useful book. With each case, I could easily picture the person in the case. This book appears to be Canadian and more inclusive than most American books.
I was able to use this book the first time I accessed it to develop a classroom activity for first-year occupational therapy students and a more comprehensive activity for second-year students. I really appreciate the links to a multitude of terminology and medical lab values/issues for each case. I will keep using this book.
Reviewed by Cindy Krentz, Assistant Professor, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 6/15/19
The book covers eight case studies of common inpatient or emergency department scenarios. I appreciated that they had written out the learning objectives. I liked that the patient was described before the case was started, giving some... read more
The book covers eight case studies of common inpatient or emergency department scenarios. I appreciated that they had written out the learning objectives. I liked that the patient was described before the case was started, giving some understanding of the patient's background. I think it could benefit from having a glossary. I liked how the authors included the vital signs in an easily readable bar. I would have liked to see the labs also highlighted like this. I also felt that it would have been good written in a 'what would you do next?' type of case study.
The book is very accurate in language, what tests would be prudent to run and in the day in the life of the hospital in all cases. One inaccuracy is that the authors called a popliteal artery clot a DVT. The rest of the DVT case study was great, though, but the one mistake should be changed.
The book is up to date for now, but as tests become obsolete and new equipment is routinely used, the book ( like any other health textbook) will need to be updated. It would be easy to change, however. All that would have to happen is that the authors go in and change out the test to whatever newer, evidence-based test is being utilized.
The text is written clearly and easy to understand from a student's perspective. There is not too much technical jargon, and it is pretty universal when used- for example DVT for Deep Vein Thrombosis.
The book is consistent in language and how it is broken down into case studies. The same format is used for highlighting vital signs throughout the different case studies. It's great that the reader does not have to read the book in a linear fashion. Each case study can be read without needing to read the others.
The text is broken down into eight case studies, and within the case studies is broken down into days. It is consistent and shows how the patient can pass through the different hospital departments (from the ER to the unit, to surgery, to home) in a realistic manner. The instructor could use one or more of the case studies as (s)he sees fit.
The topics are eight different case studies- and are presented very clearly and organized well. Each one is broken down into how the patient goes through the system. The text is easy to follow and logical.
The interface has some problems with the highlighted blue links. Some of them did not work and I got a 'page not found' message. That can be frustrating for the reader. I'm wondering if a glossary could be utilized (instead of the links) to explain what some of these links are supposed to explain.
I found two or three typos, I don't think they were grammatical errors. In one case I think the Canadian spelling and the United States spelling of the word are just different.
This is a very culturally competent book. In today's world, however, one more type of background that would merit delving into is the trans-gender, GLBTQI person. I was glad that there were no stereotypes.
I enjoyed reading the text. It was interesting and relevant to today's nursing student. Since we are becoming more interprofessional, I liked that we saw what the phlebotomist and other ancillary personnel (mostly different technicians) did. I think that it could become even more interdisciplinary so colleges and universities could have more interprofessional education- courses or simulations- with the addition of the nurse using social work, nutrition, or other professional health care majors.
Reviewed by Catherine J. Grott, Interim Director, Health Administration Program, TRAILS on 5/5/19
The book is comprehensive but is specifically written for healthcare workers practicing in Canada. The title of the book should reflect this. read more
The book is comprehensive but is specifically written for healthcare workers practicing in Canada. The title of the book should reflect this.
The book is accurate, however it has numerous broken online links.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The content is very relevant, but some links are out-dated. For example, WHO Guidelines for Safe Surgery 2009 (p. 186) should be updated.
The book is written in clear and concise language. The side stories about the healthcare workers make the text interesting.
The book is consistent in terms of terminology and framework. Some terms that are emphasized in one case study are not emphasized (with online links) in the other case studies. All of the case studies should have the same words linked to online definitions.
Modularity rating: 3
The book can easily be parsed out if necessary. However, the way the case studies have been written, it's evident that different authors contributed singularly to each case study.
The organization and flow are good.
Interface rating: 1
There are numerous broken online links and "pages not found."
The grammar and punctuation are correct. There are two errors detected: p. 120 a space between the word "heart" and the comma; also a period is needed after Dr (p. 113).
I'm not quite sure that the social worker (p. 119) should comment that the patient and partner are "very normal people."
There are roughly 25 broken online links or "pages not found." The BC & Canadian Guidelines (p. 198) could also include a link to US guidelines to make the text more universal . The basilar crackles (p. 166) is very good. Text could be used compare US and Canadian healthcare. Text could be enhanced to teach "soft skills" and interdepartmental communication skills in healthcare.
Reviewed by Lindsey Henry, Practical Nursing Instructor, Fletcher on 5/1/19
I really appreciated how in the introduction, five learning objectives were identified for students. These objectives are paramount in nursing care and they are each spelled out for the learner. Each Case study also has its own learning... read more
I really appreciated how in the introduction, five learning objectives were identified for students. These objectives are paramount in nursing care and they are each spelled out for the learner. Each Case study also has its own learning objectives, which were effectively met in the readings.
As a seasoned nurse, I believe that the content regarding pathophysiology and treatments used in the case studies were accurate. I really appreciated how many of the treatments were also explained and rationales were given, which can be very helpful to facilitate effective learning for a nursing student or novice nurse.
The case studies are up to date and correlate with the current time period. They are easily understood.
I really loved how several important medical terms, including specific treatments were highlighted to alert the reader. Many interventions performed were also explained further, which is great to enhance learning for the nursing student or novice nurse. Also, with each scenario, a background and history of the patient is depicted, as well as the perspectives of the patient, patients family member, and the primary nurse. This really helps to give the reader a full picture of the day in the life of a nurse or a patient, and also better facilitates the learning process of the reader.
These case studies are consistent. They begin with report, the patient background or updates on subsequent days, and follow the patients all the way through discharge. Once again, I really appreciate how this book describes most if not all aspects of patient care on a day to day basis.
Each case study is separated into days. While they can be divided to be assigned at different points within the course, they also build on each other. They show trends in vital signs, what happens when a patient deteriorates, what happens when they get better and go home. Showing the entire process from ER admit to discharge is really helpful to enhance the students learning experience.
The topics are all presented very similarly and very clearly. The way that the scenarios are explained could even be understood by a non-nursing student as well. The case studies are very clear and very thorough.
The book is very easy to navigate, prints well on paper, and is not distorted or confusing.
I did not see any grammatical errors.
Each case study involves a different type of patient. These differences include race, gender, sexual orientation and medical backgrounds. I do not feel the text was offensive to the reader.
I teach practical nursing students and after reading this book, I am looking forward to implementing it in my classroom. Great read for nursing students!
Reviewed by Leah Jolly, Instructor, Clinical Coordinator, Oregon Institute of Technology on 4/10/19
Good variety of cases and pathologies covered. read more
Good variety of cases and pathologies covered.
Content Accuracy rating: 2
Some examples and scenarios are not completely accurate. For example in the DVT case, the sonographer found thrombus in the "popliteal artery", which according to the book indicated presence of DVT. However in DVT, thrombus is located in the vein, not the artery. The patient would also have much different symptoms if located in the artery. Perhaps some of these inaccuracies are just typos, but in real-life situations this simple mistake can make a world of difference in the patient's course of treatment and outcomes.
Good examples of interprofessional collaboration. If only it worked this way on an every day basis!
Clear and easy to read for those with knowledge of medical terminology.
Good consistency overall.
Broken up well.
Topics are clear and logical.
Would be nice to simply click through to the next page, rather than going through the table of contents each time.
Minor typos/grammatical errors.
No offensive or insensitive materials observed.
Reviewed by Alex Sargsyan, Doctor of Nursing Practice/Assistant Professor , East Tennessee State University on 10/8/18
Because of the case study character of the book it does not have index or glossary. However it has summary for each health case study outlining key elements discussed in each case study. read more
Because of the case study character of the book it does not have index or glossary. However it has summary for each health case study outlining key elements discussed in each case study.
Overall the book is accurately depicting the clinical environment. There are numerous references to external sites. While most of them are correct, some of them are not working. For example Homan’s test link is not working "404 error"
Book is relevant in its current version and can be used in undergraduate and graduate classes. That said, the longevity of the book may be limited because of the character of the clinical education. Clinical guidelines change constantly and it may require a major update of the content.
Cases are written very clearly and have realistic description of an inpatient setting.
The book is easy to read and consistent in the language in all eight cases.
The cases are very well written. Each case is subdivided into logical segments. The segments reflect different setting where the patient is being seen. There is a flow and transition between the settings.
Book has eight distinct cases. This is a great format for a book that presents distinct clinical issues. This will allow the students to have immersive experiences and gain better understanding of the healthcare environment.
Book is offered in many different formats. Besides the issues with the links mentioned above, overall navigation of the book content is very smooth.
Book is very well written and has no grammatical errors.
Book is culturally relevant. Patients in the case studies come different cultures and represent diverse ethnicities.
Reviewed by Justin Berry, Physical Therapist Assistant Program Director, Northland Community and Technical College, East Grand Forks, MN on 8/2/18
This text provides eight patient case studies from a variety of diagnoses, which can be utilized by healthcare students from multiple disciplines. The cases are comprehensive and can be helpful for students to determine professional roles,... read more
This text provides eight patient case studies from a variety of diagnoses, which can be utilized by healthcare students from multiple disciplines. The cases are comprehensive and can be helpful for students to determine professional roles, interprofessional roles, when to initiate communication with other healthcare practitioners due to a change in patient status, and treatment ideas. Some additional patient information, such as lab values, would have been beneficial to include.
Case study information is accurate and unbiased.
Content is up to date. The case studies are written in a way so that they will not be obsolete soon, even with changes in healthcare.
The case studies are well written, and can be utilized for a variety of classroom assignments, discussions, and projects. Some additional lab value information for each patient would have been a nice addition.
The case studies are consistently organized to make it easy for the reader to determine the framework.
The text is broken up into eight different case studies for various patient diagnoses. This design makes it highly modular, and would be easy to assign at different points of a course.
The flow of the topics are presented consistently in a logical manner. Each case study follows a patient chronologically, making it easy to determine changes in patient status and treatment options.
The text is free of interface issues, with no distortion of images or charts.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. Patients are represented from a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds
This book would be a good addition for many different health programs.
Reviewed by Ann Bell-Pfeifer, Instructor/Program Director, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 5/21/18
The book gives a comprehensive overview of many types of cases for patient conditions. Emergency Room patients may arrive with COPD, heart failure, sepsis, pneumonia, or as motor vehicle accident victims. It is directed towards nurses, medical... read more
The book gives a comprehensive overview of many types of cases for patient conditions. Emergency Room patients may arrive with COPD, heart failure, sepsis, pneumonia, or as motor vehicle accident victims. It is directed towards nurses, medical laboratory technologists, medical radiology technologists, and respiratory therapists and their roles in caring for patients. Most of the overview is accurate. One suggestion is to provide an embedded radiologist interpretation of the exams which are performed which lead to the patients diagnosis.
Overall the book is accurate. Would like to see updates related to the addition of direct radiography technology which is commonly used in the hospital setting.
Many aspects of medicine will remain constant. The case studies seem fairly accurate and may be relevant for up to 3 years. Since technology changes so quickly in medicine, the CT and x-ray components may need minor updates within a few years.
The book clarity is excellent.
The case stories are consistent with each scenario. It is easy to follow the structure and learn from the content.
The book is quite modular. It is easy to break it up into cases and utilize them individually and sequentially.
The cases are listed by disease process and follow a logical flow through each condition. They are easy to follow as they have the same format from the beginning to the end of each case.
The interface seems seamless. Hyperlinks are inserted which provide descriptions and references to medical procedures and in depth definitions.
The book is free of most grammatical errors. There is a place where a few words do not fit the sentence structure and could be a typo.
The book included all types of relationships and ethnic backgrounds. One type which could be added is a transgender patient.
I think the book was quite useful for a variety of health care professionals. The authors did an excellent job of integrating patient cases which could be applied to the health care setting. The stories seemed real and relevant. This book could be used to teach health care professionals about integrated care within the emergency department.
Reviewed by Shelley Wolfe, Assistant Professor, Winona State University on 5/21/18
This text is comprised of comprehensive, detailed case studies that provide the reader with multiple character views throughout a patient’s encounter with the health care system. The Table of Contents accurately reflected the content. It should... read more
This text is comprised of comprehensive, detailed case studies that provide the reader with multiple character views throughout a patient’s encounter with the health care system. The Table of Contents accurately reflected the content. It should be noted that the authors include a statement that conveys that this text is not like traditional textbooks and is not meant to be read in a linear fashion. This allows the educator more flexibility to use the text as a supplement to enhance learning opportunities.
The content of the text appears accurate and unbiased. The “five overarching learning objectives” provide a clear aim of the text and the educator is able to glean how these objectives are captured into each of the case studies. While written for the Canadian healthcare system, this text is easily adaptable to the American healthcare system.
Overall, the content is up-to-date and the case studies provide a variety of uses that promote longevity of the text. However, not all of the blue font links (if using the digital PDF version) were still in working order. I encountered links that led to error pages or outdated “page not found” websites. While the links can be helpful, continued maintenance of these links could prove time-consuming.
I found the text easy to read and understand. I enjoyed that the viewpoints of all the different roles (patient, nurse, lab personnel, etc.) were articulated well and allowed the reader to connect and gain appreciation of the entire healthcare team. Medical jargon was noted to be appropriate for the intended audience of this text.
The terminology and organization of this text is consistent.
The text is divided into 8 case studies that follow a similar organizational structure. The case studies can further be divided to focus on individual learning objectives. For example, the case studies could be looked at as a whole for discussing communication or could be broken down into segments to focus on disease risk factors.
The case studies in this text follow a similar organizational structure and are consistent in their presentation. The flow of individual case studies is excellent and sets the reader on a clear path. As noted previously, this text is not meant to be read in a linear fashion.
This text is available in many different forms. I chose to review the text in the digital PDF version in order to use the embedded links. I did not encounter significant interface issues and did not find any images or features that would distract or confuse a reader.
No significant grammatical errors were noted.
The case studies in this text included patients and healthcare workers from a variety of backgrounds. Educators and students will benefit from expanding the case studies to include discussions and other learning opportunities to help develop culturally-sensitive healthcare providers.
I found the case studies to be very detailed, yet written in a way in which they could be used in various manners. The authors note a variety of ways in which the case studies could be employed with students; however, I feel the authors could also include that the case studies could be used as a basis for simulated clinical experiences. The case studies in this text would be an excellent tool for developing interprofessional communication and collaboration skills in a variety healthcare students.
Reviewed by Darline Foltz, Assistant Professor, University of Cincinnati - Clermont College on 3/27/18
This book covers all areas listed in the Table of Contents. In addition to the detailed patient case studies, there is a helpful section of "How to Use this Resource". I would like to note that this resource "aligns with the open textbooks... read more
This book covers all areas listed in the Table of Contents. In addition to the detailed patient case studies, there is a helpful section of "How to Use this Resource". I would like to note that this resource "aligns with the open textbooks Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care and Anatomy and Physiology: OpenStax" as noted by the authors.
The book appears to be accurate. Although one of the learning outcomes is as follows: "Demonstrate an understanding of the Canadian healthcare delivery system.", I did not find anything that is ONLY specific to the Canadian healthcare delivery system other than some of the terminology, i.e. "porter" instead of "transporter" and a few french words. I found this to make the book more interesting for students rather than deter from it. These are patient case studies that are relevant in any country.
The content is up-to-date. Changes in medical science may occur, i.e. a different test, to treat a diagnosis that is included in one or more of the case studies, however, it would be easy and straightforward to implement these changes.
This book is written in lucid, accessible prose. The technical/medical terminology that is used is appropriate for medical and allied health professionals. Something that would improve this text would to provide a glossary of terms for the terms in blue font.
This book is consistent with current medical terminology
This text is easily divided into each of the 6 case studies. The case studies can be used singly according to the body system being addressed or studied.
Because this text is a collection of case studies, flow doesn't pertain, however the organization and structure of the case studies are excellent as they are clear and easy to read.
There are no distractions in this text that would distract or confuse the reader.
I did not identify any grammatical errors.
This text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way and uses patients and healthcare workers that are of a variety of races, ethnicities and backgrounds.
I believe that this text would not only be useful to students enrolled in healthcare professions involved in direct patient care but would also be useful to students in supporting healthcare disciplines such as health information technology and management, medical billing and coding, etc.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
Case Study #1: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Learning Objectives
- Patient: Erin Johns
- Emergency Room
Case Study #2: Pneumonia
- Day 0: Emergency Room
- Day 1: Emergency Room
- Day 1: Medical Ward
- Day 2: Medical Ward
- Day 3: Medical Ward
- Day 4: Medical Ward
Case Study #3: Unstable Angina (UA)
- Patient: Harj Singh
Case Study #4: Heart Failure (HF)
- Patient: Meryl Smith
- In the Supermarket
- Day 0: Medical Ward
Case Study #5: Motor Vehicle Collision (MVC)
- Patient: Aaron Knoll
- Crash Scene
- Operating Room
- Post Anaesthesia Care Unit (PACU)
- Surgical Ward
Case Study #6: Sepsis
- Patient: George Thomas
- Sleepy Hollow Care Facility
Case Study #7: Colon Cancer
- Patient: Fred Johnson
- Two Months Ago
- Pre-Surgery Admission
Case Study #8: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Patient: Jamie Douglas
Appendix: Overview About the Authors
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Health Case Studies is composed of eight separate health case studies. Each case study includes the patient narrative or story that models the best practice (at the time of publishing) in healthcare settings. Associated with each case is a set of specific learning objectives to support learning and facilitate educational strategies and evaluation.
The case studies can be used online in a learning management system, in a classroom discussion, in a printed course pack or as part of a textbook created by the instructor. This flexibility is intentional and allows the educator to choose how best to convey the concepts presented in each case to the learner.
Because these case studies were primarily developed for an electronic healthcare system, they are based predominantly in an acute healthcare setting. Educators can augment each case study to include primary healthcare settings, outpatient clinics, assisted living environments, and other contexts as relevant.
About the Contributors
Glynda Rees teaches at the British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT) in Vancouver, British Columbia. She completed her MSN at the University of British Columbia with a focus on education and health informatics, and her BSN at the University of Cape Town in South Africa. Glynda has many years of national and international clinical experience in critical care units in South Africa, the UK, and the USA. Her teaching background has focused on clinical education, problem-based learning, clinical techniques, and pharmacology.
Glynda‘s interests include the integration of health informatics in undergraduate education, open accessible education, and the impact of educational technologies on nursing students’ clinical judgment and decision making at the point of care to improve patient safety and quality of care.
Faculty member in the critical care nursing program at the British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT) since 2003, Rob has been a critical care nurse for over 25 years with 17 years practicing in a quaternary care intensive care unit. Rob is an experienced educator and supports student learning in the classroom, online, and in clinical areas. Rob’s Master of Education from Simon Fraser University is in educational technology and learning design. He is passionate about using technology to support learning for both faculty and students.
Part of Rob’s faculty position is dedicated to providing high fidelity simulation support for BCIT’s nursing specialties program along with championing innovative teaching and best practices for educational technology. He has championed the use of digital publishing and was the tech lead for Critical Care Nursing’s iPad Project which resulted in over 40 multi-touch interactive textbooks being created using Apple and other technologies.
Rob has successfully completed a number of specialist certifications in computer and network technologies. In 2015, he was awarded Apple Distinguished Educator for his innovation and passionate use of technology to support learning. In the past five years, he has presented and published abstracts on virtual simulation, high fidelity simulation, creating engaging classroom environments, and what the future holds for healthcare and education.
Janet Morrison is the Program Head of Occupational Health Nursing at the British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT) in Burnaby, British Columbia. She completed a PhD at Simon Fraser University, Faculty of Communication, Art and Technology, with a focus on health information technology. Her dissertation examined the effects of telehealth implementation in an occupational health nursing service. She has an MA in Adult Education from St. Francis Xavier University and an MA in Library and Information Studies from the University of British Columbia.
Janet’s research interests concern the intended and unintended impacts of health information technologies on healthcare students, faculty, and the healthcare workforce.
She is currently working with BCIT colleagues to study how an educational clinical information system can foster healthcare students’ perceptions of interprofessional roles.
Contribute to this Page
- McMaster University Health Sciences Library
Medicine - Undergraduate
- Case Scenarios
- Students from a Non-Science Background
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Clinical Skills
- Drugs & Natural Products
- EBM & JAMA Evidence
- PICO: writing a searchable question
- Black & Indigenous Health Resources
- Research Support - Book a Consult
- Landmark Papers
- Student Wellness

Case Studies & Scenarios

- Johns Hopkins Medicine- Case Studies
- Case Studies for Fellows (American Society of Hematology)
- LITFL Clinical Cases Dedicated to Emergency Medicine and Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine Cases Canadian medical education podcast
- NEJM Clinical Cases
- Springer Clinical Cases series A catalogue search
- << Previous: LMCC Prep
- Next: Anatomy & Physiology >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 2:14 PM
- URL: https://hslmcmaster.libguides.com/medicine_UGM

Address Information
McMaster University 1280 Main Street West HSC 2B Hamilton, Ontario Canada L8S 4K1
Contact Information
Phone: (905) 525-9140 Ext. 22327
Email: [email protected]
Make A Suggestion
Website Feedback
Search with any image
Unsupported image file format.
Image file size is too large..
Drag an image here
- Medical Books
Sorry, there was a problem.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

250 Cases in Clinical Medicine 4th Edition
- Ideal for use in the ward.
- Each of the 250 cases presents a disease or topic which is covered consistently to address:? salient features ? history ? examination ? diagnosis ? questions covering investigations and differentiations ? advanced-level questions ? management.
New to this edition:
- Over 350 new images
- Enhanced advanced-level questions
- Many more tables
- ISBN-10 0702033863
- ISBN-13 978-0702033865
- Edition 4th
- Publisher Saunders
- Publication date April 3, 2012
- Language English
- Dimensions 4.25 x 1.5 x 7.25 inches
- Print length 928 pages
- See all details

Editorial Reviews
From reviews of the previous edition:
‘This book is just fantastic, not just for MRCP but for all those who really want to learn how to quickly formulate a diagnosis and management plan for the patients.’
‘This book is the most useful guide that money can buy for the final exams in the current MBChB undergraduate course. It covers important areas of clinical medicine in a question-based format and highlights classical scenarios. … This is a must buy for any undergraduate medical student!’
‘Excellent preparation for finals as well the MRCP. …A must-have before MRCP PACES.’
‘Excellent text, very thorough and often contains a lot more info than needed for approaching finals, but if you ignore all the advanced stuff then it's very good for preparing you for vivas. Lots of questions that can come up in PACES and how to answer them.’
‘This book is a great clinical book. Most questions that come up in clinical skills you will find it in this book. The book is a must during the period that the young doctor or student is on the wards, It covers important areas of clinical medicine in a question-based format and highlights classical scenarios.’
Product details
- Publisher : Saunders; 4th edition (April 3, 2012)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 928 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0702033863
- ISBN-13 : 978-0702033865
- Item Weight : 1.55 pounds
- Dimensions : 4.25 x 1.5 x 7.25 inches
- #552 in General (Books)
- #976 in Internal Medicine (Books)
- #1,255 in Medical Test Preparation
About the author
R. r. baliga.
Discover more of the author’s books, see similar authors, read author blogs and more
Customer reviews
| 2 star | 0% | |
Our goal is to make sure every review is trustworthy and useful. That's why we use both technology and human investigators to block fake reviews before customers ever see them. Learn more
We block Amazon accounts that violate our community guidelines. We also block sellers who buy reviews and take legal actions against parties who provide these reviews. Learn how to report
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
250 Cases in Clinical Medicine
- 6th Edition - May 26, 2023
- Authors: Eirini Kasfiki, Ciaran W P. Kelly
- Language: English
- Paperback ISBN: 9780323937863 9 7 8 - 0 - 3 2 3 - 9 3 7 8 6 - 3
- eBook ISBN: 9780323938136 9 7 8 - 0 - 3 2 3 - 9 3 8 1 3 - 6
This unique book presents a wealth of information on common presentations and illnesses, presented as medical case studies. It is useful for exam preparation, as a quick re… Read more

Purchase options
Limited Offer
Save 50% on book bundles
Immediately download your ebook while waiting for your print delivery. no promo code is needed..

Institutional subscription on ScienceDirect
This unique book presents a wealth of information on common presentations and illnesses, presented as medical case studies. It is useful for exam preparation, as a quick reference guide for working doctors, and as an interesting read for all those interested in medicine.
250 Clinical Cases covers a wide variety of conditions, providing in-depth insights into the most relevant topics, classified by system. Cases are accompanied by common viva voce examination questions as well as more advanced level questions that will help the reader develop a deeper understanding.
Now in its sixth edition, the book has been fully updated to reflect current evidence and relevance for working doctors. It will help everyone, from medical students to consultants, to find the hidden clinical gems and historical background they need to achieve true clinical excellence.
- 250 clinical cases in print – provides a comprehensive overview of all relevant topics
- Conversational and accessible style – suitable for medical students
- Based on the latest evidence – provides an ideal quick reference guide
- ‘Ward round’ type question and answer section - ideal for exam preparation
- Cases alphabetised by system for easy navigation
- Easily portable size – fits into any medical bag
- An enhanced eBook version is included with purchase. The eBook allows you to access all the text, figures and references, with the ability to search, customize your content, make notes and highlights, and have content read aloud
- Instructions for online access
- Cover image
- Table of Contents
- Any screen. Any time. Anywhere
- Acknolwedgements
- Section I: Respiratory Cases
- Chapter 1. Respiratory Case
- Instruction
- Salient Features
- Chapter 2. Asthma
- CHAPTER 3. Bronchiectasis
- Further Information
- CHAPTER 4. Cystic Fibrosis
- CHAPTER 5. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- CHAPTER 6. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Examination
- CHAPTER 7. Cor Pulmonale
- CHAPTER 8. Cough
- CHAPTER 9. Fever
- CHAPTER 10. Collapsed Lung
- CHAPTER 11. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
- CHAPTER 12. Bronchogenic Carcinoma
- CHAPTER 13. Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Section II: Cardiology Cases
- CHAPTER 14. Cardiovascular Case
- CHAPTER 15. Aortic Regurgitation
- CHAPTER 16. Aortic Stenosis
- CHAPTER 17. Mixed Aortic Valve Disease
- CHAPTER 18. Mitral Regurgitation
- CHAPTER 19. Mitral Stenosis
- CHAPTER 20. Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Chapter 21. Mixed Mitral Valve Disease
- Chapter 22. Mixed Mitral and Aortic Valve Disease
- Chapter 23. Prosthetic Heart Valves
- Chapter 24. Tricuspid Regurgitation
- CHAPTER 25. Pulmonary Stenosis
- Chapter 26. Atrial Septal Defect
- Chapter 27. Ventricular Septal Defect
- Chapter 28. Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Chapter 29. Ebstein's Anomaly
- Chapter 30. Fallot's Tetralogy
- CHAPTER 31. Dextrocardia
- CHAPTER 32. Eisenmenger Syndrome
- CHAPTER 33. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- CHAPTER 34. Congestive Cardiac Failure
- CHAPTER 35. Constrictive Pericarditis
- CHAPTER 36. Weight Loss
- Section III: Abdominal Cases
- CHAPTER 37. Abdominal Case
- CHAPTER 38. Swallowing Difficulties
- CHAPTER 39. Diarrhoea
- CHAPTER 40. Crohn's Disease
- CHAPTER 41. Abdominal Mass
- CHAPTER 42. Ascites
- CHAPTER 43. Cirrhosis of the Liver
- CHAPTER 44. Jaundice
- CHAPTER 45. Hepatomegaly
- CHAPTER 46. Splenomegaly
- CHAPTER 47. Haemochromatosis
- CHAPTER 48. Wilson Disease
- CHAPTER 49. Felty Syndrome
- Section IV: Renal Cases
- CHAPTER 50. Unilateral Palpable Kidney
- CHAPTER 51. Polycystic Kidney Disease
- CHAPTER 52. Nephrotic Syndrome
- CHAPTER 53. Transplanted Kidney
- CHAPTER 54. Hypertension
- Section V: Haematology Cases
- CHAPTER 55. Anaemia
- CHAPTER 56. Bruising
- CHAPTER 57. Multiple Myeloma
- CHAPTER 58. Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- CHAPTER 59. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
- CHAPTER 60. Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
- CHAPTER 61. Acute Leukaemia
- CHAPTER 62. Lymphadenopathy
- Section VI: Rheumatology Cases
- CHAPTER 63. Rheumatology Case
- CHAPTER 64. Ankylosing Spondylitis
- CHAPTER 65. Charcot Arthropathy
- CHAPTER 66. Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
- CHAPTER 67. Gout
- CHAPTER 68. Osteoarthritis
- CHAPTER 69. Psoriatic Arthritis
- CHAPTER 70. Rheumatoid Hands
- CHAPTER 71. Dermatomyositis—Proximal Muscle Weakness
- Chapter 72. Scleroderma
- Chapter 73. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- CHAPTER 74. Small-vessel ANCA-associated vasculitis
- Section VII: Endocrinology Cases
- CHAPTER 75. Acromegaly
- Chapter 76. Hypopituitarism (Simmonds Disease)
- Chapter 77. Endocrinology Case
- Chapter 78. Graves Disease
- Chapter 79. Orbitopathy
- Chapter 80. Multinodular Goitre
- CHAPTER 81. Hypothyroidism
- CHAPTER 82. Hypoparathyroidism
- CHAPTER 83. Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- CHAPTER 84. Addison Disease
- CHAPTER 85. Cushing Syndrome
- CHAPTER 86. Carcinoid Syndrome
- CHAPTER 87. Gynaecomastia
- CHAPTER 88. Falls—Osteoporosis
- CHAPTER 89. Obesity
- CHAPTER 90. Type 1 Diabetes
- CHAPTER 91. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- CHAPTER 92. Diabetic Foot
- Neuropathic Foot
- Ischaemic Foot
- Neuropathic and Ischaemic Foot Presenting Together
- Section VIII: Eye Cases for Internal Medicine
- CHAPTER 93. The Eye Case
- Examination of the Eye
- Clinicopathologic Correlations of Retinal Haemorrhages and Exudates
- CHAPTER 94. Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- CHAPTER 95. Cataracts
- CHAPTER 96. Cholesterol Embolus in the Fundus
- CHAPTER 97. Diabetic Retinopathy
- CHAPTER 98. Hypertensive Retinopathy
- CHAPTER 99. Optic Atrophy
- CHAPTER 100. Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- CHAPTER 101. Papilloedema
- CHAPTER 102. Retinal Detachment
- CHAPTER 103. Retinal Vein Occlusion
- CHAPTER 104. Retinitis Pigmentosa
- CHAPTER 105. Subhyaloid Haemorrhage
- CHAPTER 106. Vitreous Opacities
- Section IX: Dermatology Cases for Internal Medicine
- CHAPTER 107. Acanthosis Nigricans
- CHAPTER 108. Acne Vulgaris
- CHAPTER 109. Alopecia Areata
- CHAPTER 110. Arterial Leg Ulcer
- CHAPTER 111. Arteriovenous Fistula
- CHAPTER 112. Atopic Dermatitis—Eczema
- CHAPTER 113. Bullous Eruption
- CHAPTER 114. Mycosis Fungoides (Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma)
- CHAPTER 115. Dermatitis Herpetiformis
- CHAPTER 116. Eruptive Xanthomata
- CHAPTER 117. Erythema Ab Igne
- CHAPTER 118. Erythema Multiforme
- CHAPTER 119. Erythema Nodosum
- CHAPTER 120. Fungal Nail Disease
- CHAPTER 121. Hairy Leukoplakia
- CHAPTER 122. Henoch–Schönlein Purpura
- CHAPTER 123. Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome)
- CHAPTER 124. Herpes Simplex
- CHAPTER 125. Herpes Zoster Syndrome (Shingles)
- CHAPTER 126. Ichthyosis
- CHAPTER 127. Lichen Planus
- CHAPTER 128. Lichen Simplex
- CHAPTER 129. Lipodystrophy
- CHAPTER 130. Lupus Pernio
- CHAPTER 131. Maculopapular Rash
- CHAPTER 132. Malignant Melanoma
- CHAPTER 133. Molluscum Contagiosum
- CHAPTER 134. Nail Changes
- CHAPTER 135. Necrobiosis Lipoidica
- CHAPTER 136. Neurofibromatosis
- CHAPTER 137. Onycholysis
- CHAPTER 138. Palmar Xanthomata
- Chapter 139. Peutz–Jeghers Syndrome
- CHAPTER 140. Phlebitis Migrans
- CHAPTER 141. Pretibial Myxoedema
- CHAPTER 142. Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
- CHAPTER 143. Psoriasis
- CHAPTER 144. Purpura
- CHAPTER 145. Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- CHAPTER 146. Raynaud's Phenomenon
- CHAPTER 147. Rosacea
- CHAPTER 148. Seborrhoeic Dermatitis
- CHAPTER 149. Sturge–Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis)
- CHAPTER 150. Tuberous Sclerosis (Bourneville or Pringle Disease)
- Chapter 151. Urticaria
- Chapter 152. Urticaria Pigmentosa
- Chapter 153. Venous Ulcer
- Chapter 154. Vitiligo
- Chapter 155. Xanthelasma
- CHAPTER 156. Xanthomata
- Section X: Neurology and Elderly Care Medical Cases
- Chapter 157. Neurology Case
- Examination of the Cranial Nerves
- Neurological Examination of the Upper Limbs
- Neurological Examination of the Lower Limbs
- Approach to a Myopathic Patient
- CHAPTER 158. Headache
- CHAPTER 159. Memory Loss
- CHAPTER 160. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
- Differential Diagnosis
- CHAPTER 161. Abnormal Gait
- CHAPTER 162. Argyll Robertson Pupil
- CHAPTER 163. Muscular Dystrophy
- CHAPTER 164. Spastic Paraplegia
- CHAPTER 165. Bitemporal Hemianopia
- CHAPTER 166. Brown-Séquard Syndrome
- CHAPTER 167. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- CHAPTER 168. Central Scotoma
- CHAPTER 169. Cerebellar Syndrome
- CHAPTER 170. Cerebellar Dysarthria
- CHAPTER 171. Cerebellopontine Angle Tumour
- CHAPTER 172. Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease (Peroneal Muscular Atrophy)
- CHAPTER 173. Chorea
- Patient 1: Sydenham’s Chorea
- Patient 2: Huntington Disease
- CHAPTER 174. Lateral Popliteal Nerve Palsy, L4, L5 (Common Peroneal Nerve Palsy)
- CHAPTER 175. Expressive Dysphasia
- CHAPTER 176. Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy (Landouzy–Déjérine Syndrome)
- CHAPTER 177. Friedreich's Ataxia
- CHAPTER 178. Hemiballismus
- CHAPTER 179. Hemiplegia
- CHAPTER 180. Homonymous Hemianopia
- CHAPTER 181. Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
- CHAPTER 182. Jerky Nystagmus
- CHAPTER 183. Limb-Girdle Dystrophy
- CHAPTER 184. Motor Neurone Disease
- CHAPTER 185. Multiple Sclerosis
- CHAPTER 186. Multiple System Atrophy
- CHAPTER 187. Myasthenia Gravis
- CHAPTER 188. Myotonia Congenita
- CHAPTER 189. Myotonic Dystrophy
- CHAPTER 190. Parkinson Disease
- CHAPTER 191. Peripheral Neuropathy
- CHAPTER 192. Proximal Myopathy
- CHAPTER 193. Pseudobulbar Palsy
- CHAPTER 194. Ptosis and Horner Syndrome
- CHAPTER 195. Radial Nerve Palsy
- CHAPTER 196. Seventh Cranial Nerve Palsy
- Lower Motor Neurone Type
- CHAPTER 197. Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy
- CHAPTER 198. Syringomyelia
- CHAPTER 199. Tetraplegia
- CHAPTER 200. Third Cranial Nerve Palsy
- Chapter 201. Tremor
- Chapter 202. Deformity of a Lower Limb
- Chapter 203. Ulnar Nerve Palsy
- Chapter 204. Wallenberg Syndrome (Lateral Medullary Syndrome)
- Chapter 205. Wasting of the Small Muscles of the Hand
- Chapter 206. Long Thoracic Neuropathy
- Chapter 207. Anxiety
- Chapter 208. Back Pain
- Chapter 209. Pruritus
- Chapter 210. Speech Disturbance
- CHAPTER 211. Unsteadiness
- Section XI: Acute Internal Medical Cases
- CHAPTER 212. Absent Radial Pulse
- CHAPTER 213. Confusion
- CHAPTER 214. Acute Kidney Injury
- CHAPTER 215. Acute Pancreatitis
- CHAPTER 216. Anaphylaxis
- CHAPTER 217. Chest Pain—Angina
- CHAPTER 218. Cauda Equina Syndrome
- CHAPTER 219. Cellulitis
- CHAPTER 220. Coarctation of Aorta
- CHAPTER 221. Deep Vein Thrombosis
- CHAPTER 222. Gallop Rhythm
- CHAPTER 223. Guillain–Barré Syndrome
- CHAPTER 224. Hyperkalaemia
- CHAPTER 225. Hypernatraemia
- CHAPTER 226. Hypokalaemia
- CHAPTER 227. Hyponatraemia
- CHAPTER 228. Melaena
- CHAPTER 229. Paracetamol Overdose
- CHAPTER 230. Pericardial Rub
- CHAPTER 231. Pleural Effusion
- CHAPTER 232. Sepsis
- CHAPTER 233. Consolidation
- CHAPTER 234. Pulmonary Embolism
- CHAPTER 235. Jugular Venous Pulse
- Chapter 236. Seizures
- Chapter 237. Painful Knee Joint
- Chapter 238. Slow Pulse Rate
- Chapter 239. Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Chapter 240. Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Spinal Cord
- CHAPTER 241. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
- CHAPTER 242. Syncope
- CHAPTER 243. The Pregnant Patient
- CHAPTER 244. Central Line Insertion
- CHAPTER 245. Chest Drain Insertion for Spontaneous (Nontraumatic) Pneumothorax
- CHAPTER 246. Emergency Synchronized Direct Current Cardioversion
- CHAPTER 247. Knee Arthrocentesis
- CHAPTER 248. Lumbar Puncture
- CHAPTER 249. Therapeutic Abdominal Paracentesis
- CHAPTER 250. Temporary External Pacing
- Bibliography
- No. of pages : 976
- Language : English
- Edition : 6
- Published : May 26, 2023
- Imprint : Elsevier
- Paperback ISBN : 9780323937863
- eBook ISBN : 9780323938136
Eirini Kasfiki
Ciaran w p. kelly.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.

- Need Help ?
- Free Shipping *
- Secure Payment
- Direct from Elsevier
- Europe (ENG) (€)
- Germany (€)
- Latin America ($)
- Middle East ($)
- Create an Account
- Compare Products
- Bestsellers
- Digital Subscriptions
Shop by Category
- Internal Medicine
250 Cases in Clinical Medicine, 6th Edition
This unique book presents a wealth of information on common presentations and illnesses, presented as medical case studies. It is useful for exam preparation, as a quick reference guide for working doctors, and as an interesting read for all those interested in medicine.
- Share to receive a discount off your next order
- Share on Twitter
VitalSource Bookshelf gives you access to content when, where, and how you want. When you read an eBook on VitalSource Bookshelf, enjoy such features as:
- Access online or offline, on mobile or desktop devices.
- Bookmarks, highlights and notes sync across all your devices.
- Smart study tools such as note sharing and subscription, review mode, and Microsoft OneNote integration.
- Search and navigate content across your entire Bookshelf library.
- Interactive notebook and read-aloud functionality.
- Look up additional information online by highlighting a word or phrase.
- Self-assessment by system
- Interesting medical emergency presentations
- Procedures for the core medical curriculum
- Topics updated for clinical relevance
- Multiple choice questions replaced with open answer questions
- 250 clinical cases in print – provides a comprehensive overview of all relevant topics
- Conversational and accessible style – suitable for medical students
- Based on the latest evidence – provides an ideal quick reference guide
- ‘Ward round’ type question and answer section - ideal for exam preparation
- Cases alphabetised by system for easy navigation
- Easily portable size – fits into any medical bag
- An enhanced eBook version is included with purchase. The eBook allows you to access all the text, figures and references, with the ability to search, customize your content, make notes and highlights, and have content read aloud
| ISBN Number | 9780323937863 |
|---|---|
| Main Author | By Eirini V. Kasfiki, MBChB, MRCP (UK), PGDipME, FHEA and Ciaran W P. Kelly, BA, BAO, MB BCh (Hons), PGCME, MRCS (ENT), MRCGP |
| Copyright Year | 2024 |
| Edition Number | 6 |
| Format | Book |
| Trim | 152w x 229h |
| Illustrations | Approx. 266 illustrations (134 in full color) |
| Imprint | Elsevier |
| Page Count | 976 |
| Publication Date | 4 Sep 2023 |
| Stock Status | IN STOCK |
Related Products
Edited by Joseph P Iannotti

Alan R. Crossman

Edited by Joseph Iannotti
Edited by David A. Kaminsky
Roger Smith
William F. Young

Marios Loukas

Edited by Roshan Patel
* Elsevier is a leading publisher of health science books and journals, helping to advance medicine by delivering superior education, reference information and decision support tools to doctors, nurses, health practitioners and students. With titles available across a variety of media, we are able to supply the information you need in the most convenient format.
Copyright © 2024, its licensors, and contributors.
All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
For problems or suggestions regarding this site, please visit our Support Hub .
- General & Introductory Medical Science
- Medical Sciences Special Topics

Medical Short Cases for Medical Students
ISBN: 978-0-632-05729-0
February 2001
Wiley-Blackwell

M. Afzal Mir , Robert E. J. Ryder , E. Anne Freeman
Robert E. J. Ryder is the author of Medical Short Cases for Medical Students, published by Wiley. M. Afzal Mir is the author of Medical Short Cases for Medical Students, published by Wiley.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- MXN - Mexican Peso

- 01865 844 640
- Free Delivery
- Secure Payment
- Direct from Elsevier
- Europe (ENG) (€)
- Germany (€)
- Latin America ($)
- Create an Account
- Compare Products
- Bestsellers
Shop by Category
- Medicine and Surgery
- General Medicine
Clinical Cases in Internal Medicine, 1st Edition
View a sample chapter
- Share to receive a discount off your next order
- Share on Twitter
- More than 50 clinical cases , covering the core undergraduate medicine curriculum
- Case discussions using a logical and scientific approach to help students achieve their own diagnoses
- Model answers for comparison, to improve learning outcomes
- Summary of fundamental points for examination revision
- Useful up-to-date resources
- Short-answer and multiple-choice questions to test knowledge
- Diagrams and tables to deepen understanding and consolidate essential concepts
- Includes an Enhanced eBook version with purchase. The enhanced eBook allows the end user to access all of the text, figures, and references from the book on a variety of devices
| ISBN Number | 9780702080494 |
|---|---|
| Author Information | By Samy A. Azer, MB, BCh, MSc Medicine, PhD (Syd), MEd (NSW), FACG, MPH (NSW) |
| Copyright Year | 2022 |
| Edition Number | 1 |
| Format | Book |
| Format Size | 191w x 235h |
| Imprint | Elsevier |
| Page Count | 476 |
| Publication Date | 17-05-2022 |
| Stock Status | IN STOCK |

VitalSource eBooks for practitioners and students

Bring it with you - The Bookshelf app allows you to access books on your laptop, tablet or mobile, so your ebooks go where ever you are - online or offline.

Take notes - Highlight, bookmark and take notes and highlights automatically stay in sync no matter where you make them.

Listen to eBooks - When you need to go screenless, the Text-to-speech tool will read your book aloud.

Powerful search - The searching capabilities allow you to search keywords through all your eBooks, the entire Bookshelf Library and well as on Wikipedia.

Ecological - Manage your environmental impact with paperless books.
How to read your VitalSource eBooks
- Purchase your VitalSource eBook on the Elsevier Health site
- Download VitalSource Bookshelf , the best app for smarter reading, studying, and learning
- Redeem your redeption code you received via email, and download your eBook
- Access your VitalSource eBook on any laptop, tablet, or smartphone device with VitalSource Bookshelf

Copyright © 2024, its licensors, and contributors.
All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Cookies are used by this site. To decline or learn more, visit our Cookies page. Cookie Settings
The Best Books for Medical Students
Table of contents.

| We’ve been there, and we get it. Lecturio’s Medical School Survival Guide is packed with tips and advice for every step of medical school. Take it with you and walk your path with confidence. |
You might think there isn’t a lot of time for or value in reading non-academic books for leisure, but think again! Books are a great way of finding a new perspective when you can’t experience it firsthand. While there is value in interpersonal interactions, words have the power to move people in a totally different way.
So in this article, I’ll talk about books– books that have given medical students the push they need to be the best doctors they can be. In no particular order, I selected these books based on their writing, relevance, how in-depth of a view it gives of the medical profession, and maybe a bit of my personal taste, as an aspiring doctor and self-proclaimed bookworm.
#1: When Breath Becomes Air by Paul Kalanithi
“There is a moment, a cusp, when the sum of gathered experience is worn down by the details of living. We are never so wise as when we live in this moment.”
In the last year of his neurosurgical residency, Kalanithi battles a terminal illness and ponders the meaning of life. As he tries to make the most of the time he has left, he balances his life as a doctor, patient, and husband. Despite the book being published posthumously and its generally gloomy theme, it has moments of hope and inspiration as the author loses the life he thought he’d have and replaces it with something even more meaningful.
This book is a personal favorite of mine, and I put it here at the top of the list for a reason. As a future doctor, you need to learn not only what it means to be a physician, but also what it means to be a patient. In this brief yet meaningful memoir, Kalanithi gives an in-depth view of both — and the struggle between the two.
Kalanithi, as a literature major, immerses you in a story about hope and grief in such as way that you can’t help but put yourself in his shoes. You wonder what you would prioritize at the end of everything and what it would mean to be your own patient. In the face of your own mortality, you’re in the best position to see the bigger picture. If you’re looking for a novel that reminds you what you’re doing all this for or what exactly you’re dedicating your life to, look no further than When Breath becomes Air .
#2: House of God by Samuel Shem
“Every intern makes mistakes. The important thing is neither to make the same mistake twice nor to make a whole bunch of mistakes all at once.”
There is no rule book or manual for being a medical intern in a hospital — sometimes you have to make it up as you go along. In Shem’s House of God , their interns follow their own survival guide passed down from the wisdom of their seniors. The story follows the interns of the House of God (a pseudonym for a fictional hospital) as they traverse the grueling and degrading challenge of being a junior doctor.
I put this here because while the novel is satricial, it’s still loosely based on actual experiences of interns in hospitals. Although a real hospital usually has fewer blurred lines and borderline-negligent rules, it still follows that being a junior doctor is difficult and it’s easy to feel lost. Different doctors will tell you to follow different rules, and it’s up to you to decide what’s best for your patients.
The book overall is a great read, especially if you’re an intern looking for some laughs when resting from your duty hours. It’s so well-known that some of the language is even used in pop culture and by some doctors. But take note: you might also find the haunting truth that maybe the satire isn’t all that far from reality.
#3: The Diving Bell and the Butterfly by Jean-Dominique Bauby
“For pleasure, I have to turn to the vivid memory of tastes and smells, an inexhaustible reservoir of sensations. Once, I was a master at recycling leftovers. Now I cultivate the art of simmering memories.”
This memoir follows the life of the former Editor-in-Chief of the French magazine Elle as he wakes up from a 20-week coma to Locked-in Syndrome, a rare neurological condition in which a person is almost completely paralyzed but their cognitive function and memories remain intact. With only acute awareness and what’s left of his motor function, he tells of his physical, emotional, and mental struggles with his condition, and the memories he holds on to for strength. This book was written by Bauby, who could only communicate through blinking. It took 200,000 blinks and 10 months to “write” before Bauby eventually died of pneumonia.
It’s one thing to diagnose and treat patients, but it’s another to put yourself in their shoes. The way Bauby describes his experience is vivid and impactful, using his years of literary prowess to make you feel the tornado of emotions that one feels when faced with a severely debilitating disease. What feelings do our patients have when robbed of their body’s basic functions? What does it mean to live when the wonders of medicine have not only prolonged survival, but also the agony of living with disease?
If you’re looking for a book to help you understand your patients better, especially those with disabilities, you might want to try this book. It’s important for a doctor to understand the impact of disease on an individual to help decide the next best course of action. While you may find the book tragic, it can be moving and empowering as it makes evident the perseverance and true strength of the human mind.
#4: Being Mortal: Medicine and What Matters in the End by Atul Gawande
“We’ve been wrong about what our job is in medicine. We think our job is to ensure health and survival. But really it is larger than that. It is to enable well-being.”
Gawande has written quite a few books about medicine and patient care. This particular one tackles a topic that I think all students should consider: the end of life. Being Mortal shares the reflections and personal stories of patients undergoing hospice care or struggling with terminal illness.
Health care in our older years can be financially and emotionally exhausting. That’s because as we get older, we are left with memories and some regrets about the life we’ve lived. As a future doctor, it’s important to understand that you will see many patients (and their families) in a day, but for them, these are pivotal moments in their lives. That fact matters as much as any treatment you can give.
If you’re looking for a book to help you come to terms with these aspects of your patient’s lives or to prepare yourself for the inevitable, this book does the job. At the end of life, where theoretical and standard practices may fall short for your patients, empathy becomes your greatest tool in improving their quality of life. I would also recommend Gawande’s other books about medicine as well.
#5: This Is Going To Hurt: Secret Diaries of a Junior Doctor by Adam Kay
“So I told them the truth: the hours are terrible, the pay is terrible, the conditions are terrible; you’re underappreciated, unsupported, disrespected and frequently physically endangered. But there’s no better job in the world.”
For years, the idea of being a doctor has always been followed with some prestige. Who doesn’t think that saving lives on a regular basis is cool as heck? Well, it’s not as glamorous as people make it out to be. In Kay’s collection of diary entries, he paints a messy yet honest picture of his journey as a medical trainee. Under the humorous tone of the book, Kay is faced with grueling work and traumatic events– the harsh and inescapable reality of being a doctor.
I chose this book because it challenges the view of how people see doctors against what it actually is like to be one. Many people believe doctors to be something more than human. They expect doctors to know everything, because it’s terrifying to believe that they could be wrong. Because of this, many — and even some of us doctors — forget that we’re human. We want time for ourselves and the people we love. We want breaks from the heavy pressure of medicine. But despite the compassionate nature of the job, it’s rare we find it for ourselves.
If you’re looking for a book that doesn’t pull punches about what it’s like to be a doctor, but with a tinge of humor, you might want to try this one. It takes real talent to communicate the difficulties while also getting a few laughs. You may think that it’ll turn you off from medicine because of how harsh it sounds, but if you’re entering this career for the right reasons, it’ll take more than this book to stop you.
A Final Word
While your textbooks are important, narrative books are definitely something to include in your reading. They’re entertainers, companions, and mentors. You can read them for leisure and feel like you’ve grown as a person afterwards. You can feel awful one moment and feel inspired the next. There were a lot of times when I read through these books and finally felt like I was understood and my problems were validated. It’s like magic in the form of words that you can bring with you anywhere.
So if you find yourself looking for inspiration, motivation, or a new perspective, try some narrative books. You might think you won’t have time for it, but I encourage you to make time, because you’re going to need help in those times you feel stuck. I know it worked for me when I needed my passion for medicine reignited in my darkest hours. With the right mood, an open mind, and a deep love for medicine, it’ll work for you too.

Bianca is a medical intern at the Ateneo School of Medicine and Public Health in the Philippines. She is a BS Psychology graduate, currently working on her double degrees in MD and MBA.
If it was easy, everyone would do it.
Medical school is a challenge, but it is manageable with proven strategies and good planning.
Get inside advice for every step of medical school in Lecturio’s Survival Guide video course for medical students.
Further Reading
Finding the Sweet Spot: Cushing’s Syndrome vs Adrenal Insufficiency

How to Study Microbiology
How to Effectively Use Lecturio Concept Pages
- Data Privacy
- Terms and Conditions
- Legal Information
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Get Your Free Medical School Survival Guide
Learn the Best-kept Secrets to Succeed at Med School with Doc Ossareh
User Reviews
Get premium to test your knowledge.
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all content & features
Get Premium to watch all videos
Verify your email now to get a free trial.
Create a free account to test your knowledge
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all contents and features—including Lecturio’s Qbank with up-to-date board-style questions.

- Advanced Life Support
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious disease
- Intensive care
- Palliative Care
- Respiratory
- Rheumatology
- Haematology
- Endocrine surgery
- General surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Ophthalmology
- Plastic surgery
- Vascular surgery
- Abdo examination
- Cardio examination
- Neurolo examination
- Resp examination
- Rheum examination
- Vasc exacmination
- Other examinations
- Clinical Cases
- Communication skills
- Prescribing

Clinical cases

Epigastric pain case study with questions and answers

Low urine output case study with questions and answers
Hyperglycaemia case study with questions and answers, breast lump case study with questions and answers.

Constipation case study with questions and answers

Headache case study with questions and answers

Rectal bleeding case study with questions and answers

Flank pain case study with questions and answers
Confusion case study with questions and answers.

Euthanasia case study with questions and answers

Clinical Cases
A collection of interactive clinical case scenarios aligned with UK Medical Licensing Assessment (MLA) presentations . Each scenario allows you to work through history taking , investigations , diagnosis and management . You might also be interested in our bank of 1000+ OSCE Stations .

Painful Hand – OSCE Case

Dizziness and Nausea – OSCE Case

Paediatric Rash – OSCE Case
Pain on Inspiration – OSCE Case

Vaginal Discharge – OSCE Case
Cough, Chest Pain and Fever – OSCE Case

Breathlessness and Acute Rash – OSCE Case
Wheezy Child – OSCE Case

Episode of Facial Weakness – OSCE Case

Lethargic Child – OSCE Case

Headache and Neck Pain – OSCE Case
Acute abdominal pain – osce case.

Other pages
- Product Bundles 🎉
- Join the Team 🙌
- Institutional Licence 📚
- OSCE Station Creator Tool 🩺
- Create and Share Flashcards 🗂️
- OSCE Group Chat 💬
- Newsletter 📰
- Advertise With Us
Join the community

Have a browse through the In2Med Shop, featuring hand-picked products by the In2Med team boost your clinical examination skills.
Special Offers
Stethoscopes
Accessories
Digital Stethoscopes
Investigations
Check out my notes on investigations you need to know as a junior doctor, including Chest X-rays, CT heads, blood tests and more. Just click on a topic to start learning today.
Chest X-Ray
Blood Tests
Arterial Blood Gas
Haematology
Clinical Examinations
Have a look through my collection of clinical examination summaries to help you ace your medical school OSCEs. And what’s more, they are completely free! Just click on a topic to start learning today.
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Peripheral Vascular
Diabetic Foot
Cranial Nerve
Upper Limb Neuro
Lower Limb Neuro
Parkinson’s
- Applying to Med School
- For Medical Students
Pharmacology
Learning the pharmacology is one of the hardest parts of medical school. Check out my notes on pharmacology – click on each topic to learn about mechanisms of action, uses and side effects of each drug class.
Cardiovascular Drugs
Neurology Drugs
Endocrine Drugs
Antibiotics
Gynae Drugs
Respiratory Drugs
Renal Drugs
Haematology Drugs
Psychopharmacology
Medicine Notes
Check out my collection of free medicine notes to help you ace your medical school exams. Just click on a topic to start learning today!
Dermatology
Endocrinology
Gastrointestinal
Gynaecology
History Taking
Infectious Diseases
Musculoskeletal
Paediatrics
Renal-Urinary
Clinical Cases
Practice thinking of differentials, interpreting investigations and diagnosing conditions to answer these clinical cases.
Jaundice during pregnancy
Bloody diarrhoea and frequency, palpitations, achy leg in a child.
Check out these helpful articles written by myself and friends to discover the bigger picture of life at medical school.
How to Break Bad News
How i use flashcards to study medicine efficiently, how to write a medical cv, how to get involved in research and medical academia.

If you fancy a challenge, have a go a these pathology cases. Practice thinking of key differentials, interpreting investigations and applying your knowledge to answer these clinical cases.
by Ankit @ In2Med
by Dr Abhirami Gautham
by Dr Alex Tindale
by Dr Amol Joshi
Abnormal Pharmacology and Nausea
Difficulty urinating, fall in a paediatric patient, shortness of breath, watery diarrhoea and fatigue, radiating chest pain, severe headache and vomiting, excessively tired and sleepy, abdominal pain and vomiting, painless loss of vision, unilateral tinnitus and vertigo, fever in a returning traveller, persistent cough in a smoker, polyuria and loss of appetite, vomiting with tinnitus, crying baby with acute distress, fatigued and vomiting, check out my brand new revision guide .
Ace your medical exams with The Revision Guide to Core Clinical Medicine!
If you've found my notes useful, you'll love my latest creation: a powerhouse revision guide crafted specifically for medical students.
This indispensable resource covers the essentials of eight core specialties, guiding you through everything from pharmacology and investigations to nailing down diagnoses and managing conditions

Subscribe to my weekly newsletter!
Discover the secrets to success in medical school!
Sign up to my weekly newsletter and join the thousands of students to receive a medicine brain teaser and tips on how I succeeded at medical school, directly to your inbox.
Thanks for signing up!
Privacy Policy Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
Download my free OSCE summaries booklet!
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Get the Reddit app
r/medicine is a virtual lounge for physicians and other medical professionals from around the world to talk about the latest advances, controversies, ask questions of each other, have a laugh, or share a difficult moment. This is a highly moderated subreddit. Please read the rules carefully before posting or commenting.
Medical Student here, I'm looking for a large library of case studies to work through. Any suggestions?
I'm looking for a large amount of case studies to work/read through concern common presenting complaints. Can anyone point me in the right direction?
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Without cookies your experience may not be seamless.

- Clinical Cases for Pediatric Medical Students and Residents
In this Book

- Ruth Worthington
- Published by: Michigan State University Press
- View Citation
Table of Contents

- Title, Copyright, Dedication
- pp. vii-viii
- Acknowledgments
- Notes on Content
- pp. xiii-xiv
- Case 1. Newborn Out-of-Hospital Delivery
- Case 2. Three-Month-Old with a Cold
- Case 3. Six-Month-Old with a Skin Lesion
- Case 4. Seventeen-Month-Old with Fever and Rash
- Case 5. Two-Year-Old with a Spreading Rash
- Case 6. Four-Year-Old with a Rash
- Case 7. Five-Year-Old Drowning Victim
- Case 8. Twelve-Year-Old in for a Sports Physical
- Case 9. Twelve-Year-Old Involved in a Motor Vehicle Accident
- Case 10. Thirteen-and-a-Half-Year-Old with Single Testicle
- Case 11. Fourteen-Year-Old with Excessive Bleeding
- Case 12. Sixteen-Year-Old with Turner Syndrome
- Case 13. Seventeen-Year-Old in for a Sports Physical
- Case 14. Two Seventeen-Year-Olds Hit by Lightning
- Case 15. Newborn with Cyanosis
- Case 16. Newborn with an Abnormal Screen
- Case 17. Two-Month-Old with Vaccination Issues
- pp. 103-110
- Case 18. Fifteen-Month-Old with Constipation
- pp. 111-119
- Case 19. Eighteen-Month-Old with Vomiting
- pp. 120-136
- Case 20. Eight-Year-Old Refugee Intake
- pp. 137-158
- Case 21. Nine-Year-Old with Headache and Dizziness
- pp. 159-172
- Case 22. Eleven-Year-Old with Enuresis
- pp. 173-185
- Case 23. Fifteen-Year-Old with a Neck Mass
- pp. 186-200
- Case 24. Sixteen-Year-Old in for a Sports Physical
- pp. 201-216
- Case 25. Twenty-One-Year-Old and Twenty-Six-Year-Old with Seizures
- pp. 217-233
- Case 26. Two-Month-Old with Cyanosis
- pp. 234-270
- Case 27. Three-Year-Old with Fatigue
- pp. 271-281
- Case 28. Four-and-a-Half-Year-Old with Vomiting
- pp. 282-318
- Case 29. Five-Year-Old with a Sore Throat
- pp. 319-357
- Case 30. Fourteen-Year-Old with Vaginal Bleeding
- pp. 358-381
- Case 31. Fifteen-Year-Old with Delayed Puberty
- pp. 382-421
- Case 32. Sixteen-Year-Old with Abdominal Pain
- pp. 422-447
- Case 33. Two-Year-Old with Chest Pain
- pp. 448-485
- Case 34. Eight-Year-Old with Chest Pain
- pp. 486-526
- Case 35. Twelve-Year-Old with Chest Pain
- pp. 527-562
- Case 36. Seventeen-Year-Old with Chest Pain
- pp. 563-606
- Credits for Additional Images
- pp. 607-608
Additional Information
Project muse mission.
Project MUSE promotes the creation and dissemination of essential humanities and social science resources through collaboration with libraries, publishers, and scholars worldwide. Forged from a partnership between a university press and a library, Project MUSE is a trusted part of the academic and scholarly community it serves.

2715 North Charles Street Baltimore, Maryland, USA 21218
+1 (410) 516-6989 [email protected]
©2024 Project MUSE. Produced by Johns Hopkins University Press in collaboration with The Sheridan Libraries.
Now and Always, The Trusted Content Your Research Requires

Built on the Johns Hopkins University Campus

Medical Student Core
Finally! One set of books for all of medical school. The Core comprehensively presents and clearly explains the material you’re expected to learn in med school—and makes learning it easier.
- Entire digital Core, carefully created according to the USMLE exam outline
- All Preview | Review questions
- (digital Core only) Automatic updates as new content is released
- Digital StudyWise guide
- Personal Trainer access
Couldn't load pickup availability
Products are non-refundable. A 30-day free trial is available for you to experience the Core prior to purchase.

Flip through a sample from the Musculoskeletal System section
Med students love the core.

@mo2medicine

@madeittomedicine

@locd.med.monsta
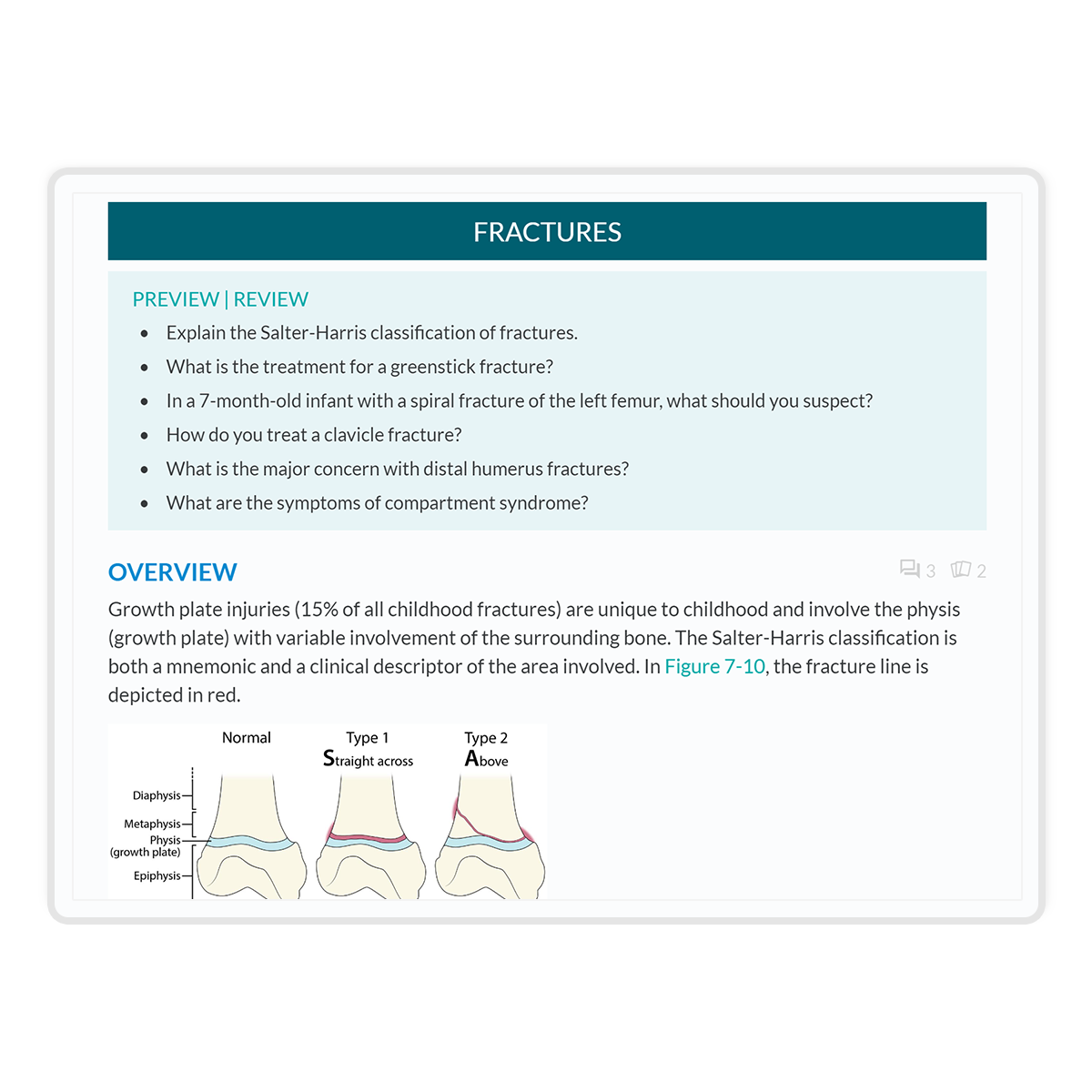
Preview | Review questions
Thousands of built-in questions
Questions appear at the beginning of each main topic to prime your brain for the concepts you'll be learning and for later review. Answers are highlighted in the text.

1,320 medical images and figures
Visualize complicated concepts
Explanations are further clarified with scans, x-rays, photos, and 860+ exquisitely-drawn figures.
Instant search results
Easily find what you're looking for
Quickly search in any topic or section, or across the entire digital Core. Take notes while you read, tie them to content you want to revisit.

clinical pearls
Crack open clinical pearls
See how basic science concepts are applied clinically.
interlinked Q&As
Prep for Step exams while you learn
With a single click, you can easily move between topics in the digital Core and related Step 1 or Step 2 questions.
Qbank+ sold separately.
Access the entire Musculoskeletal System section for free
All Core and Qbank+ questions
Unlimited access for 30 days
Get 30-day access to the entire Musculoskeletal System section of the Student Study Strong System (includes the Core, Q&As, and Personal Trainer). No credit card required.
By starting a free trial, you agree to our terms of use .

Study strong system
Bundle & save $600
Get the full integrated Study Strong System. Learn medicine AND prep for exams at the same time.
Affordable options for residency programs
One of our Program Partners will work with you 1-on-1 to meet your specific learning and budget goals.
Student Core FAQs
Five full-color books to flip through, highlight, and write in will arrive on your doorstep with a beautiful shelf case for easy display. The books are yours to keep. Use the index to flip to the section you’re looking for. Use these books in internet deserts.
Our Digital Core flies through space and lands in your MedStudy account. View instant search results to quickly and easily find what you need. Use Digital Core on every device with internet access. The content is directly interlinked to Q&As (purchase separately). Digital Core receives ongoing updates.
The digital Core receives ongoing updates.
MedStudy has over 30 years of expertise in helping doctors prepare for—and ace—their boards.
We're known for making learning medicine easier, and it all started with the conversational writing style in our Core.
We believe that combining science-based learning techniques with extremely focused content ensures you efficiently store the most important information in your long-term memory. That makes it easier to sail through your boards with flying colors—and makes you a better clinician.
From basic science to clinical knowledge, the casual and concise content in this Core covers all medical knowledge you must master —and makes learning it easier.
This Core covers every item in the USMLE exam content outline for. Step 1 and Step 2 exams.
In this Core, there are over 1,000 unique Preview | Review questions (with answers highlighted in the text) at the beginning of each main topic. These questions are based on the most exam-relevant info.
Customer Reviews
I loved the Student Core books! They were easily digestible and broken down by subject, which made it easier to take just one book with me each day, instead of lugging around a 700-page medical book. It also made it easier to look up topics, I’d just pull the book I needed and go.
What makes this product valuable for medical students is that you have some of the very best experts, folks teach for a living, and who've taken all that experience about what's important and distilled it down into one volume. Really, every piece of information in the Student Core is golden.
The student products are not mere lists of facts. These are true review textbooks written with the purpose of ensuring students truly understand and enjoy learning the high-yield information they contain.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
Prepare for the MCAT® Exam
New section.
Preparing for the MCAT® exam takes time and dedication. Balancing your preparation with an already busy schedule can be a challenge. The AAMC has resources and practice products to help you no matter where you are in the preparation process.
- MCAT Official Prep Hub
- Register for the MCAT Exam
- Get Your Test Scores
Learn more about the new MCAT® Prep enhancements for the upcoming testing year.

Discover the complete list of foundational concepts, content categories, skills, and disciplines you will need to know for test day. We also offer the outline as a course in the MCAT Official Prep Hub , with links to free open access resources covering the same content.

Learn about the free AAMC MCAT® Official Prep resources that the AAMC offers to help you study.

Get answers to your questions about MCAT® registration, scores, and more.
The AAMC Fee Assistance Program assists those who, without financial assistance, would be unable to take the MCAT exam or apply to medical schools that use the AMCAS. The benefits include discounted fees, free MCAT Official Prep products, and more.
Get a comprehensive overview of all MCAT Official Prep products, including pricing information and key features.
Learn about available resources to help you as you advise your students.
The AAMC offers bulk order purchasing for quantities of 10 or more MCAT Official Prep products.
- Open access
- Published: 22 July 2022
Nursing students’ use of social media in their learning: a case study of a Canadian School of Nursing
- Catherine M. Giroux ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1352-8501 1 &
- Katherine A. Moreau ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5955-1689 2
BMC Nursing volume 21 , Article number: 195 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
7 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Social media has diverse applications for nursing education. Current literature focuses on how nursing faculty use social media in their courses and teaching; less is known about how and why nursing students use social media in support of their learning.
The purpose of this study was to explore how nursing students use social media in their learning formally and informally.
This exploratory qualitative case study of a Canadian School of Nursing reports on the findings of interviews ( n = 9) with nursing students to explore how they use social media in their learning. Data were analyzed using a combined deductive and inductive coding approach, using three cycles of coding to facilitate category identification.
Results and conclusions
The findings demonstrate that participants use social media for formal and informal learning and specifically, as a third space to support their learning outside of formal institutional structures. Social media plays a role in the learning activities of nursing students studying both face-to-face and by distance. Accordingly, social media use has implications for learning theory and course design, particularly regarding creating space for student learning communities.
Peer Review reports
Social media are online platforms that allow users to connect with other users, curate lists of connections, and interact with each other within the same online platform [ 1 ]. They have applications for both formal and informal learning in health professions education (HPE). Formal learning refers to planned educational experiences, such as courses or assignments [ 2 ] whereas informal learning refers to what is learned through extracurricular activities [ 3 , 4 ]. With social media, formal learning may include such activities as using YouTube videos in class, while informal learning may involve students scrolling through Twitter and finding relevant learning content on their leisure time. Within the HPE literature, social media have been shown to facilitate electronic communication, networking, and real-time collaboration [ 5 , 6 ]. They have also assumed key educational and communicative roles during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Furthermore, they continue to allow individuals to engage in independent, informal learning on their own terms and in places of formal education, work, or broader social circles [ 10 ]. Several studies demonstrated how social media can be used to facilitate clinical and professional performance tasks, question-and-answer sessions, and the exploration of complex topics collaboratively; social media can also provide professional learning opportunities and facilitate networking with international practitioners [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 ]. Moreover, instructors have used Twitter to provide students with formative feedback in assessment, stimulate reflection and sharing, share daily learning goals, hold journal clubs, notify students of recent topical publications, and orient learners to clinical sites and educational rotations [ 15 , 16 , 17 ]. The literature suggests that the connections that students make using social media can translate to opportunities for mentorship and scholarship [ 18 ]. Moreover, social media may also engage geographically dispersed individuals to create or share content, collaborate in groups, and ultimately form a virtual community [ 19 , 20 ].
Within the nursing education literature, social media is well described as a tool selected by faculty for diverse formal teaching and learning purposes. For instance, several studies described using blogging to facilitate reflections as a teaching strategy for topics such as cultural competence, empathy, the therapeutic relationship, transitions to practice, and self-care [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. The feedback system of the blogging interface provided students with opportunities to practice their reflection and problem-solving skills [ 26 , 27 ]. Some studies used social media to simulate patient encounters or transition experiences for nurses [ 25 , 28 , 29 ]. For example, Thomas et al. used a blog to simulate a new nurse who had just transitioned to practice; the blog was written from the new nurse’s perspective to help final year nursing students consider issues of delegating and supervising, adapting to change, risk and quality management, and legal and ethical issues as they prepared to transition to practice [ 25 ]. Students had to read the blog and post responses. Other studies focused on using Facebook or YouTube as collaborative and interactive tools to help nursing students prepare for examinations like the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX) [ 30 , 31 , 32 ]. Still, issues of professionalism arose in the nursing education literature, with some studies noting concerns about students’ online behaviour and potential implications for their reputations and licensure [ 5 , 33 ]. A 2021 narrative review found that learning about digital professionalism concepts as they relate to social media influenced how students behaved online [ 34 ]. Despite these potential professionalism implications, social media appears to be an effective tool to support formal learning in nursing education. A 2018 systematic review explored the effectiveness of using social media in nursing and midwifery education [ 35 ]. The authors found that the collaborative, interactive, and semi-synchronous nature of social media platforms may support knowledge and skill acquisition in nursing students.
Much of the extant undergraduate nursing education literature explores how social media is used in formal learning, specifically from the perspectives of the faculty who select the platforms to suit specific assignments or learning goals. Studies that focus on undergraduate students’ use of social media tended to explore specific platforms used and data analytics (i.e., hashtags used, number of views or shares). Less is known about how and why undergraduate nursing students themselves select social media platforms as an adjunct to their formal and informal learning activities. Thus, this exploratory qualitative case study aimed to address how and why undergraduate nursing students use social media to support their learning.
Theoretical considerations
Social learning theories like social constructivism are appropriate for framing studies involving social media because they view learning as an active and collaborative process [ 36 , 37 , 38 ]. Social constructivism is based on three assumptions: (1) meanings are constructed by humans as they engage with the world they are interpreting; (2) humans engage with their world and make sense of it based on their historical and social perspectives; and (3) the basic generation of meaning is social, arising from the interaction with a human community [ 36 ]. Social constructivism claims knowledge is acquired when subjective meanings are created in interaction with others, drawing on material from previous experiences to guide learning [ 36 , 37 , 38 ]. This study was informed by social constructivism, which influenced our research questions, data collection instruments, and approaches to data analysis.
Research design
The objective of this study was to explore how students at one Canadian School of Nursing used social media to support their learning. We addressed this objective through an exploratory qualitative single case study. Yin [ 39 ] describes a case study as an empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon in depth within its real-world context even when the boundaries between the context and phenomenon may not be evident. Case studies comprise an all-encompassing method, which influences the logic of design, data collection techniques, and approaches to data analyses. Case study research is particularly useful for answering how and why questions; single case studies are appropriate for cases that are critical, unusual, revelatory, and longitudinal [ 39 ]. Our study site represented a critical case since the variety of program delivery methods and modalities were critically aligned with social constructivism. The study site also represented an unusual case, with four distinct program options – including a distance program – for students to achieve a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BScN) degree. This was a unique program in Canada at the time of the study. The study site did not have any social media policies published to their public-facing website during the time of the study, nor did they have any public-facing references to using social media formally in their programs published on their website.
Case study site and participants
This study took place at a small, relatively northern, Canadian university with a student population of approximately 5,090 students [ 40 ]. The School of Nursing, which includes 1191 students, offers four distinct, English-language, options for students to complete their BScN degree. These options include: 1) a standard four-year direct-entry nursing program; 2) an onsite Registered Practical Nurse (RPN) to BScN bridging program for students who previously obtained an RPN diploma and who are looking to subsequently obtain their BScN degree; 3) a part-time blended learning RPN to BScN bridging program for students currently working as RPNs who are looking to obtain their BScN; and 4) a second entry accelerated program for students who previously obtained an undergraduate degree. Only two of the nursing programs occur at the case study site itself. The second entry program is held in a large city to the south of the case study site. Additionally, students who partake in the RPN to BScN bridging program through blended learning live geographically dispersed throughout the province in which the case study site is located. Given the different program options, the participants in this study consisted of a mixture of face-to-face students and distance students. Additionally, due to the nature of the program options, some participants had pursued their nursing program as their first degree while others were already working as RPNs and had returned to school to obtain their BScN degree.
Participant recruitment and data collection
Participants were purposively recruited from a previous study, which consisted of a digital artifact collection that explored what content nursing students shared to their Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram accounts related to learning [ 41 ]. The twenty-four nursing students who participated in our previous study were contacted by email and invited to participate in this qualitative case study exploring how and why nursing students use social media to support their learning. These students were identified as potential participants because they had confirmed using social media for learning and thus, would be information-rich interviewees for the present study. All potential participants were provided with a Participant Information Letter and Informed Consent form. The data for this study were collected using semi-structured interviews. All interviews were conducted virtually via Zoom in the Fall of 2019, using a semi-structured interview guide that had been developed based on the research questions, our theoretical framework, and the literature (refer to Additional file 1 : Appendix). Prior to using the interview guide, it was piloted with two registered nurses. This pilot involved conducting two mock interviews and debriefing the interview guide with the participants to discuss the feasibility and appropriateness of the interview questions. The average interview length was 32 min, with the shortest being 21 min and the longest being 44 min long. We piloted the interview guide with two registered nurses prior to commencing the study. Each interview was audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Interview participation was incentivized with a $20 gift card to a local coffee chain.
Data analysis
We took a combined deductive and inductive approach to coding and analyzing the interview transcripts. We sought to achieve theoretical sufficiency, which is the stage at which codes and categories manage new data without requiring further modification [ 42 ]. To do this, we conducted three cycles of coding in MAXQDA (v.18.2). In the first cycle, a preliminary codebook − which was informed by our research question, theoretical framework, and the literature − facilitated descriptive and process coding [ 43 ]. In the second cycle of coding, we each independently inductively coded the data using both process coding and in vivo coding (i.e., using the participants’ own words) and compared and discussed our coding. In the third cycle of coding, we grouped these summaries into categories, themes, or constructs [ 43 ]. A combination of matrices and networks visually displayed the data and facilitated category identification [ 43 , 44 ].
Reflexivity and trustworthiness
Neither author is a Registered Nurse nor is affiliated with the case study site. Both authors have expertise in conducting educational research within the health professions and were involved in the study conceptualization, data collection, and analysis. We also took steps to ensure that our analyses were credible, dependable, confirmable, and transferable [ 45 , 46 ]. To establish credibility, we engaged in member-checking, wherein we provided the participants a copy of their interview transcripts so that they could ensure that their statements were accurately represented during transcription [ 45 , 47 ]. We also engaged in peer debriefing. In terms of dependability, each of us inductively coded the data, compared our coding, and discussed and resolved any inconsistencies. In addition, we used audit trails as a strategy to ensure confirmability. These audit trails documented each of our decisions made during the research process and would allow an independent auditor to follow our steps and decisions to establish the same conclusions about the data. Lastly, through purposeful sampling and information-rich interviewees, we were able to obtain thick descriptions of how and why the students use social media to support their learning. We also included detailed descriptions of our research processes. This level of description allows others to judge the contextual similarity and transferability of our study findings.
Ethical considerations
The interviews received formal institutional ethical approval (S-08–18-921) and approval from the study site (101916) in August 2019. We reviewed the informed consent form with each participant prior to commencing the interview and addressed any questions that they had. All participants verbally consented to participate in an interview and participants’ consent was recorded using Zoom video conference software, in accordance with our research ethics board approval.
Nine nursing students ( n = 9) participated in the individual interviews. All participants were female and ranged in age from 18 to 49. Five participants attended classes online in a blended program format that occurred by distance and four participants attended classes face-to-face. The findings demonstrate that participants used social media in numerous ways for both formal and informal learning purposes. Table 1 provides a thematic overview of how the nursing student participants use social media in support of their learning.
Formal learning
Participants reported using social media for a variety of purposes pertaining to formal learning. Table 2 provides exemplary participant quotes outlining their experiences using social media for formal learning purposes.
Sharing and clarifying course content
Several participants reported using social media to share content related to their courses and to clarify course content. Participant 7 explained how “when it comes to having, like, a large quantity of information, I think Facebook’s a better platform for that. Um, you’re able to share different links, you’re able to share pictures, videos, news articles, almost anything, it seems now”. Two participants (Participants 05 and 07) shared contrasting experiences with using social media formally in their distance classes to clarify course concepts. In this instance, a professor had shared YouTube videos in the course. While Participant 7 appreciated the inclusion of videos, Participant 5 found this approach to be lazy, especially since the professor did not create the videos but rather included videos that, according to Participant 5, students would likely search for on their own to assist their learning.
Supplementing university services
Eight participants indicated that Facebook was a good platform to supplement or highlight existing university services. Participant 5 explained how, as a distance student, they used Facebook to learn about the services available to students, like the university’s tutoring service, which Participant 5 found helpful for statistics. Participant 6 described how they used Facebook specifically for sharing course resources, since that platform might be easier at times than the typical learning management system.
Assignments and exams
The participants described using social media as a mechanism to complete their course assignments and to study for course exams and the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX). Social media appeared to be involved in the process of completing assignments; it also appeared to be the product of some assignments. Participant 5 described how “any group projects that we have to do would, which in an online program seems a little silly to me to do group projects but, um, we’d have to find a way to collaborate and it was often over Facebook or that sort of thing”. Participant 1 described creating a social media campaign for their community health class to help parents access vision care for their school-age children. Participant 3 shared how they found posts about how to pass the NCLEX the first time shared to social media and Participant 2 explained how they use social media to review for their course exams by dividing course content up amongst a small group of students and sharing review notes and summaries online. Participant 2 also described using social media platforms like Reddit to understand the patient experience based on what patients choose to share to these sites.
Informal learning
Participants indicated that they used social media for diverse informal learning purposes. Table 3 provides an overview of participants’ experiences using social media for informal learning.

Creating community
By far, students shared the value of social media for connecting with peers and the nursing community most frequently. Four participants spoke about how social media promotes connection between distance students. Participant 3 shared how social media “gives you that camaraderie that you’re missing in a classroom environment”. Four out of the five students who identified as an online student cited Facebook groups as being an important mechanism for connecting with their classmates who were spread throughout the province. One participant explained how “there is a group online, uh, [School Name] distance ed students so I use that quite a bit, um, just to get information on classes, um, what to expect from different professors, etc.” Five participants shared how social media helped them combat isolation in their learning. Participant 2 emphasized the importance of social media for connecting distance students, which was important since they did not have the same opportunities to meet their classmates face-to-face. Participant 1 described how participating in Facebook groups helped enhance both the academic and social aspects of their face-to-face learning experience. Participant 4 explained how “we find it’s been really useful, or even like finding little things, like finding rides to clinical and stuff like that. Like obviously not all of us can afford vehicles and stuff like that so just by helping each other out”. In fact, every participant who identified as a face-to-face student ( n = 4) spoke about the importance of Facebook groups to their learning experience since they contributed to building community and sharing resources.
Similarly, six participants shared how social media connected them with the broader nursing community, outside of their programs and university. Participant 6 described how social media could connect people across the country with experts in the field and the resources they have created. Participant 9 explained how social media could be used to “take my learning outside of the avenues that can be addressed and presented within a program or any program, really. So, it allows you to kind of step outside of that, see what’s happening with other people, how they’re learning…” Participant 1 described how social media allows them to connect with the nursing community on both social and academic levels through sharing memes and experiences on platforms like Instagram and Facebook. Participant 3 shared how social media “probably gives a good, like, um, a good alternative perspective on things, other than the teacher’s”.
‘Behind the scenes’ knowledge sharing
While the participants often spoke about content that was publicly available to them on social media, they also shared how they used social media for informal learning purposes in private or ‘behind the scenes’ ways. Five nursing students reported using social media to buy, sell, and share PDF versions of textbooks. Participant 5 shared how “people share PDFs of textbooks and all that sort of stuff, so it’s definitely saved me several hundred dollars”. Two participants expressed how they prefer social media to textbooks. Participant 9 described how their professors are “not the biggest towards textbooks because they said that the second they are printed they are out of date because of how fast information is changing within healthcare”. In this sense, Participant 9 found social media to be a helpful way to stay up to date with information that textbooks did not provide.
Similarly, three participants described using social media to discuss which professors were the best for each class. Participant 2 explained how “we often talk about which professors are the best for specific courses and so those classes tend to fill up really fast”. Participant 5 described how they use social media to ask questions about the university, share their perceptions of certain professors, and discuss which classes should or should not be taken at the same time. While eight of the nine interview participants actively participated in social media groups, three participants shared that the absence of faculty members in the social media groups could be problematic. Participant 2 suggested using more of the collaborative tools available on the university’s learning management system to eliminate some of the need for the social media groups and better include the faculty members. Participant 5 also found the absence of faculty members in the social media groups to be a problem and recommended involving faculty members in the private groups to correct misinformation and answer questions.
Scaffolding knowledge
In addition to sharing resources, three students indicated that the Facebook groups were essential for giving and receiving support throughout their nursing programs. Similarly, five nursing students shared how they use social media to review their clinical skills. Three participants used social media to review IV insertion. Participant 7 described how “I use Instagram, I follow someone, she, her, her tag is IV Queen or something like that, but she gives a lot of intravenous tips on how to insert IVs and how to care for them”. Participant 3 also described using YouTube videos to review IV compatibility. Participant 1 shared how they used YouTube to practice for their IV therapy lab. Participant 1 also described how “we have used some YouTube videos and tutorials and stuff in our labs where we’re able to view, like, for example just last week we were learning about central lines, um, so we looked at a video about how to do the dressing change for a central line”. Participant 1 also described how they use YouTube to learn about skills like ambulating patients prior to starting their surgical rotation so that they would understand what they were about to do on the rotation.
Why use social media
The study participants presented several reasons to use social media in support of their formal and informal learning activities; similarly, they also presented several reasons to be cautious of using social media for these purposes. Table 4 presents an overview of exemplary participant quotations presented thematically.
Credibility and relevance of sources
Seven participants discussed the credibility and relevance of the sources they found on social media. Participant 7 indicated that they find their friends and followers on social media do not tend to share a lot of content that “I don’t consider real, like the fake news, but it’s a lot of more credible sources, like major journal articles and stuff like that”. Participant 4 expressed that students are taking a risk in depending on social media rather than on their books and their notes. Other students, like Participant 6, emphasized the importance of developing critical thinking skills and being able to filter social media posts so that they could appropriately determine which sources were accurate or credible. Participant 8 indicated that relying on social media links provided by course professors was helpful since “you know if the instructors are posting those videos, then you know that they’re credible sources.”
Professors and professionalism
All nine nursing students shared how their professors, programs, and the importance of professionalism influenced their use of social media. Four participants shared that, perhaps with the exception of YouTube videos, their professors did not use social media in their teaching and discouraged its use by nursing students. Participant 6 explained that “social media is kind of shunned a lot in nursing because of that whole idea of don’t post anything, don’t share your clinical experiences and don’t, you know, breach privacy.” In some instances, participants reported that their professors did not use social media in their teaching but encouraged students to use it to complete course assignments, like learning portfolios. Participant 4 shared that “[the professors] really like the idea of us working together on things and utilizing each other to keep on track”, especially as it related to support during clinical placements.” Other participants described their professors incorporating podcasts, videos, and Reddit into their courses, which encouraged their use of social media for learning. Still, several participants expressed concerns related to professionalism on social media. Participant 3 explained how “I definitely avoid posting about like, things that involve substance use. I feel like there’s added pressure on people in certain, in various professions like healthcare and police that you should avoid because you’re supposed to uphold a certain image of the profession.”
Convenience and accessibility
Several participants discussed the convenience of social media. Two participants shared how it was easier for communication purposes than other methods (i.e., emails, calls, texts). Other participants described how social media provided a central repository for resources that could be easily accessed by classmates. However, Participants 3 and 5 highlighted some challenges to accessibility because of using social media for learning, notably poor internet connection and lack of transcriptions or alternative formats.
Engagement and distraction
Four participants shared how they found social media to be an engaging platform for learning in their nursing education. Participant 4 explained how social media helps highlight major class concepts in a variety of formats, which can be helpful for different learners. Several participants spoke about growing up with social media and how their previous experiences motivated them to use it as a tool to support their nursing education. Participant 6 explained how “I kind of grew up with technology and grew up with social media that I just know how to use it and know how to access it and don’t have a problem filtering out what I don’t need.” Despite how participants felt about social media’s potential for engagement, they also found it potentially distracting. This was a common theme amongst both face-to-face and distance students. Participant 2 described ending up in a “Facebook vortex, where I end up being on it for 2 h, not necessarily on that [program specific] group.”
The nursing student participants described multiple ways of using social media to support their learning. None of the students in this study described using social media for the same creative formal experiences as those published by Thomas et al. [ 25 ] wherein a course instructor developed a simulated student on Facebook for nursing students to interact with online. However, a couple of students outlined their experiences being required to use sites like Reddit to learn about the patient experience. Additionally, some participants described how they used social media to develop patient-oriented health advocacy campaigns for healthcare organizations, effectively demonstrating how social media is being used in their formal nursing education. The ways in which the nursing students use social media to support their formal learning demonstrate social media’s collaborative capacity for knowledge and information exchange for both on-campus and distance students [ 6 , 48 , 49 ]. The study participants used social media creatively to support their formal education; for instance, participants referenced program-specific Facebook groups where they could collectively decide on questions that they needed to ask their professors in class. This finding is consistent with that of Junco et al. [ 50 ], where they found social media to be a low-stress method for students to ask questions of their peers and educators.
Informally, participants indicated using social media to refresh their clinical skills before applying them in lab settings or during clinical rotations. While the findings of this study do not directly touch on the use of social media at the point-of-care, studies like that conducted by Hay et al. [ 51 ] demonstrate social media’s potential utility for enhanced clinical learning and patient safety. In this study, two participants described how they use social media, specifically YouTube videos, to help with patient education at the bedside. Moreover, the participants indicated that they took a cautious approach to using social media in their formal and informal learning out of concern for professionalism implications. Several students indicated that they had been warned about the repercussions of unprofessional online behaviour and had adjusted their behaviour accordingly. This finding is similar to that of a previous conducted narrative review by O’Connor et al. [ 34 ] that found that students were likely to change what content they shared using social media after learning about issues of professionalism.
Importantly, the participants in this study appeared to use social media as a third space. Aaen and Dalsgaard [ 52 ] describe the ‘third space’ as being one that emerges in boundaries or overlaps across spheres; they explain that third spaces emerge from a need for discourses that are unavailable or cannot be filled in existing settings. Participants described creating their own Facebook groups for their classes, cohorts, study groups, clinical groups, and programs. The students explained that faculty members were not present in their Facebook groups, although they did sometimes encourage students to join the groups to stay up to date on information. The participants shared that they used the groups to fill gaps in their education. Others described using the Facebook groups to create a sense of community they felt was missing in their distance learning. In fact, this study found that nursing students use social media in their education in several ways that are often hidden or ‘behind the scenes’. Aaen and Dalsgaard [ 52 ] found that Facebook formed a ‘third space’ that combined elements of academic, personal, and social communication that does not typically take place within conventional university structures or spaces. The findings of this study are similar in the sense that the nursing student participants used social media as a mechanism to collaborate, communicate, teach, and learn when traditional university avenues were unavailable to them.
This study has implications for learning theory in connected teaching and learning. Learning theories – and thus, approaches to teaching – have moved from behaviourist to constructivist in the age of technology [ 53 ]. Indeed, social learning theories like connectivism [ 54 ], Communities of Practice [ 55 ], and social constructivism [ 36 ] can reflect the realities of connected teaching and learning because they focus on collective learning and knowing in both physical and digital spaces. In the present study, social constructivism, specifically Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development, is evident in the participants’ use of social media for formal and informal learning purposes. Vygotsky [ 56 ] defines the Zone of Proximal Development as “the distance between the actual development level as determined by independent problem solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem solving under adult guidance or in collaboration with capable peers” (p. 86). The participants in this study described using online social media groups to share information about course requirements, assignment information, and exam tips. Social media also appeared to be a method for students to consolidate, share, and engage in their learning as part of a larger social process. Several participants described experiences of scaffolding learning for their peers either within their own cohort or in cohorts behind them using social media groups. Scaffolding is a key component of Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development and has applications for online course design; technical scaffolding allows learners to experience just-in-time instruction and be provided with resources to solve problems and generate new learning and understanding collaboratively online [ 57 ]. Thus, the online learning environment should provide learners with the resources, tools, and supports they need to build their own knowledge; scaffolding fades as learners develop their own knowledge and expertise [ 53 ].
Implications for nursing education policy and practice
This study demonstrates that nursing students are using social media in their educational practices both formally and informally. This use of social media has implications for teaching and learning in nursing education. Faculty members must consider the purposes for which nursing students are using social media, especially informally. One finding of this study suggested that nursing students turned to social media to fill perceived gaps – both academic and social – in their learning experience. If faculty members and schools of nursing are aware that social media is being used by nursing students for formal and informal teaching and learning purposes, it can be leveraged to achieve specific competencies and learning objectives. Based on this study, we have highlighted recommendations for nursing education policy and practice.
At the policy level, professional and appropriate social media communication could be included as an educational competency in nursing education programs, if not already stated in guiding curriculum frameworks. The purpose of this recommendation is not to discourage social media use but rather to develop competent online communicators who are equipped to use social media for teaching, learning, advocacy, and knowledge translation purposes. At the institution level, increased training for both faculty members and students on digital literacies, identifying credible online sources, and managing misinformation could help ensure faculty and students feel equipped to use digital tools like social media effectively in their teaching and learning. Finally, at the course level, some participants valued using social media to extend their learning while others were more reluctant to use it; thus, approaching the use of social media with flexibility and allowing for choice is essential. Providing optional opportunities to extend learning may help encourage participation on social media and help students discover how social media platforms can be used as learning tools informally within the nursing profession.
Limitations and future directions
This exploratory qualitative case study included individual semi-structured interviews with nursing students from one Canadian School of Nursing. Despite incentivizing interview participation, we were only able to recruit 9 of the 24 possible participants. It is also probable that those who participated were more interested in social media than those who did not participate. The interviews consisted of self-reported data from the perspectives of the participants. Although participants spoke about how their professors used social media in their courses, the professors’ perspectives were not included in this study, leaving a potential imbalance and area for future research. Moreover, our small qualitative sample did not allow for a stratified analysis based on the program delivery method. This type of analysis would be interesting to conduct with a larger, quantitative dataset. Lastly, while the interview guide included questions about the nursing student participants’ experiences using social media, it did not include questions about their cultural backgrounds. In future, it would be interesting to explore how students’ culture backgrounds influence how and why they use of social media.
Conclusions
The nursing students in this study described and demonstrated using social media to support their formal and informal learning. The participants also used social media as a third space, one that is separate from the traditional confines of the university. Within this space, participants merged their personal and academic discussions to collaborate, share resources, mentor one another, and connect with nursing experts and professional institutions. This use of social media has implications for teaching and learning in nursing education, especially regarding learning theory, scaffolding, and online course design.
Availability of data and materials
Due to the qualitative case study nature of this research, the data generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available to maintain the anonymity of the study participants. Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Boyd dm, Ellison NB. Social network sites: definition, history, and scholarship. J Comput Mediat Commun. 2007;13(1):210–30.
Article Google Scholar
Thomas P, Kern D, Hughes M, Chen B. Curriculum development for medical education: a six-step approach. 3rd ed. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press; 2016.
Google Scholar
Edmunds A, Nickel J, Badley K. Curriculum: designing meaningful learning experiences. In: Educational foundations in Canada. Don Mills, ON: Oxford University Press; 2015. p. 69–117.
Gofton W, Regehr G. What we don’t know we are teaching: unveiling the hidden curriculum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:20–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Duke V, Anstey A, Carter S, Gosse N, Hutchens K, Marsh J. Social media in nurse education: utilization and E-professionalism. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;57:8–13.
Ventola C. Social media and healthcare professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2014;39(7):491–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lu D, Ruan B, Lee M, Yilmaz Y, Chan TM. Good practices in harnessing social media for scholarly discourse, knowledge translation, and education. Perspect Med Educ. 2021;10(1):23–32.
Gottlieb M, Dyer S. Information and Disinformation: Social Media in the COVID-19 Crisis. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(7):640–1.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Merchant R, Lurie N. Social media and emergency preparedness in response to novel Coronavirus. JAMA. 2020;323(20):2011–2.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bell F. Connectivism: Its place in theory-informed research and innovation in technology enabled learning. Int Rev Res Open Dist Learn. 2011;12(3):98–118.
Cohn RJ, Plack MM. A cloud with a silver lining: helping students learn about professionalism. Teach Learn Med. 2017;29(3):304–12.
Craig J, Wong R. Student perceptions of the use and value of wiki technology for the creation and dissemination of an orthopedic physical therapy assignment. Journal of Physical Therapy Education. 2013;27(1):70–6.
Erardi L, Hartmann K. Blogs, wikis, and podcasts: Broadening our connections for communication, collaboration, and continuing education. OT Pract. 2008;13(9):CE1–8.
Guckian J, Utukuri M, Asif A, Burton O, OAdeyoju J, Oumeziane A, et al. Social media in undergraduate medical education: a systematic review. Med Educ. 2021;55(11):1227–41.
Forgie SE, Duff JP, Ross S. Twelve tips for using twitter as a learning tool in medical education. Med Teach. 2013;35(1):8–14.
Kind T, Patel P, Lie D, Chretien K. Twelve tips for using social media as a medical educator. Med Teach. 2014;36(4):284–90.
Minter D, Geha R, Manesh R, et al. The future comes early for medical educators. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36:1400–3.
Pereira I, Cunningham A, Moreau K, Sherbino J, Jalali A. Thou shalt not tweet unprofessionally: an appreciative inquiry into the professional use of social media. Postgrad Med J. 2015;91(1080):561–4.
Comp G, Dyer S, Gottlieb M. Is TikTok the next social media frontier for medicine? AEM Educ Train. 2021;5(3):1–4.
Sherbino J. The social media summit in health professions education. Postgrad Med J. 2015;91(1080):542–3.
Arbour M, Kaspar RW, Teall AM. strategies to promote cultural competence in distance education. J Transcult Nurs. 2015;26(4):436–40.
Chu SKW, Chan CKK, Tiwari AFY. Using blogs to support learning during internship. Comput Educ. 2012;58(3):989–1000.
Garrity M, Jones K, VanderZwan K, de la Rocha A, Epstein I. Integrative review of blogging: implications for nursing education. J Nurs Educ. 2014;53(7):395–401.
Reed SJ, Edmunds D. Use of a blog in an undergraduate nursing leadership course. Nurse Educ Pract. 2015;15(6):537–42.
Thomas CM, Bertram E, Allen R. Preparing for transition to professional practice: creating a simulated blog and reflective journaling activity. Clin Simul Nurs. 2012;8(3):e87–95.
Chu LF, Erlendson MJ, Sun JS, Clemenson AM, Martin P, Eng RL. Information technology and its role in anaesthesia training and continuing medical education. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2012;26(1):33–53.
Reed KS. Bags and blogs: creating an ostomy experience for nursing students. Rehabil Nurs. 2012;37(2):62–5.
Gunberg Ross J. Integration of social media into nursing education. In: Pennsylvania Nurse. 2015. p. 4–10.
Ross JG, Beckmann B, Goumas C. baccalaureate nursing students’ perceptions of the use of a facebook case study as a teaching strategy. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2019;40(3):174–5.
Morales K. Active learning strategies to enhance nursing students’ knowledge of pharmacology. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2017;38(2):100–2.
Tower M, Latimer S, Hewitt J. Social networking as a learning tool: nursing students’ perception of efficacy. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(6):1012–7.
May O, Wedgeworth M, Bigham A. Technology in nursing education: youtube as a teaching strategy. J Pediatr Nurs. 2013;28(4):408–10.
Basevi R, Reid D. Ethical guidelines and the use of social media and text messaging in healthcare: A review of the literature. N Z J Physiother. 2014:68–80.
O’Connor S, Zhang M, Honey M, Lee JJ. Digital professionalism on social media: a narrative review of the medical, nursing, and allied health education literature. Int J Med Inf. 2021;153: 104514.
O’Connor S, Jolliffe S, Stanmore E, Renwick L, Booth R. Social media in nursing and midwifery education: a mixed study systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(10):2273–89.
Creswell J. Research design: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Ltd.; 2003.
Dewey J. Democracy and education: An introduction to the philosophy of education. USA: Feather Trail Press; 1916.
Reich K. Constructivism: diversity of approaches and connections with pragmatism. In: Hickman L, Neubert S, Reich K, editors. John Dewey: between pragmatism and constructivism. New York, NY: Fordham University Press; 2009. p. 39–66.
Chapter Google Scholar
Yin R. Case study research: Design and methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2014.
Universities Canada. 2019 full-time and part-time fall enrolment at Canadian universities. 2019. Available from:. https://www.univcan.ca/universities/facts-and-stats/enrolment-by-university/ .
Giroux CM, Moreau KA. A Qualitative Exploration of the Teaching- and Learning-Related Content Nursing Students Share to Social Media. Can J Nurs Res. 2021:8445621211053113.
Varpio L, Ajjawi R, Monrouxe LV, O’Brien BC, Rees CE. Shedding the cobra effect: problematising thematic emergence, triangulation, saturation and member checking. Med Educ. 2017;51(1):40–50.
Miles M, Huberman A, Saldana J. Qualitative data analysis: a methods sourcebook. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2014.
Creswell J, Plano Clark V. Designing and conducting mixes methods research. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: SAGE; 2018.
Guba E. Criteria for assessing the trustworthiness of naturalistic inquiries. Education and Communicational Technology Journal. 1981;29(2):75–91.
Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE; 1985.
Book Google Scholar
Creswell J, Plano Clark V. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2011.
D’Souza K, Henningham L, Zou R, Huang J, O’Sullivan E, Last J, et al. Attitudes of health professional educators toward the use of social media as a teaching tool: global cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. 2017;3(2).
Giordano C, Giordano C. Health professions students’ use of social media. J Allied Health. 2011;40(2):78–81.
PubMed Google Scholar
Junco R, Elavsky C, Heiberger G. Putting twitter to the test: assessing outcomes for student collaboration, engagement and success. Br J Edu Technol. 2013;44(2):273–87.
Hay B, Carr P, Dawe L, Clark-Burg K. “iM ready to learn”: undergraduate nursing students knowledge, preferences, and practice of mobile technology and social media. Comput Inform Nurs. 2017;35(1):8–17.
Aaen J, Dalsgaard C. Student facebook groups as a third space: between social life and schoolwork. Learn Media Technol. 2016;41(1):160–86.
Flynn L, Jalali A, Moreau KA. Learning theory and its application to the use of social media in medical education. Postgrad Med J. 2015;91(1080):556–60.
Siemens G. Connectivism: learning theory or pastime for the self-amused? elearnspace: everything elearning. 2006.
Wenger E. Communities of practice: learning, meaning, and identity. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 1998.
Vygotsky L. Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1978.
Lau K. Computer-based teaching module design: principles derived from learning theories. Med Educ. 2014;48(3):247–54.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, University of Ottawa, 145 Jean-Jacques Lussier Pvt, OttawaOttawa, ON, K1N 9A7, Canada
Catherine M. Giroux
Faculty of Education, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
Katherine A. Moreau
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
C. G. and K. M. were equally responsible for conceptualizing the study, conducting data collection and analysis, writing the main manuscript text and reviewing the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Catherine M. Giroux .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study received formal ethical approval from the University of Ottawa Social Sciences and Humanities Research Ethics Board (S-08–18-921) and approval from the study site (101916) in August 2019. We reviewed the informed consent form with each participant prior to commencing the interview and addressed any questions that they had. All participants verbally consented to participate in an interview and participants’ consent was recorded using Zoom video conference software, in accordance with our REB approval from the University of Ottawa Social Sciences and Humanities REB (S-08–18-921). We followed Tri-Council ethics guidelines. Our reporting aligns with the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) checklist.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: appendix..
Semi-Structured Interview Guide.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Giroux, C.M., Moreau, K.A. Nursing students’ use of social media in their learning: a case study of a Canadian School of Nursing. BMC Nurs 21 , 195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-00977-0
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2021
Accepted : 06 July 2022
Published : 22 July 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-00977-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Nursing students
- Social media
- Social constructivism
- Third space
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Defining the Role of Authors and Contributors
Page Contents
- Why Authorship Matters
- Who Is an Author?
- Non-Author Contributors
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Assisted Technology
1. Why Authorship Matters
Authorship confers credit and has important academic, social, and financial implications. Authorship also implies responsibility and accountability for published work. The following recommendations are intended to ensure that contributors who have made substantive intellectual contributions to a paper are given credit as authors, but also that contributors credited as authors understand their role in taking responsibility and being accountable for what is published.
Editors should be aware of the practice of excluding local researchers from low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) from authorship when data are from LMICs. Inclusion of local authors adds to fairness, context, and implications of the research. Lack of inclusion of local investigators as authors should prompt questioning and may lead to rejection.
Because authorship does not communicate what contributions qualified an individual to be an author, some journals now request and publish information about the contributions of each person named as having participated in a submitted study, at least for original research. Editors are strongly encouraged to develop and implement a contributorship policy. Such policies remove much of the ambiguity surrounding contributions, but leave unresolved the question of the quantity and quality of contribution that qualify an individual for authorship. The ICMJE has thus developed criteria for authorship that can be used by all journals, including those that distinguish authors from other contributors.
2. Who Is an Author?
The ICMJE recommends that authorship be based on the following 4 criteria:
- Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; AND
- Drafting the work or reviewing it critically for important intellectual content; AND
- Final approval of the version to be published; AND
- Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
In addition to being accountable for the parts of the work done, an author should be able to identify which co-authors are responsible for specific other parts of the work. In addition, authors should have confidence in the integrity of the contributions of their co-authors.
All those designated as authors should meet all four criteria for authorship, and all who meet the four criteria should be identified as authors. Those who do not meet all four criteria should be acknowledged—see Section II.A.3 below. These authorship criteria are intended to reserve the status of authorship for those who deserve credit and can take responsibility for the work. The criteria are not intended for use as a means to disqualify colleagues from authorship who otherwise meet authorship criteria by denying them the opportunity to meet criterion #s 2 or 3. Therefore, all individuals who meet the first criterion should have the opportunity to participate in the review, drafting, and final approval of the manuscript.
The individuals who conduct the work are responsible for identifying who meets these criteria and ideally should do so when planning the work, making modifications as appropriate as the work progresses. We encourage collaboration and co-authorship with colleagues in the locations where the research is conducted. It is the collective responsibility of the authors, not the journal to which the work is submitted, to determine that all people named as authors meet all four criteria; it is not the role of journal editors to determine who qualifies or does not qualify for authorship or to arbitrate authorship conflicts. If agreement cannot be reached about who qualifies for authorship, the institution(s) where the work was performed, not the journal editor, should be asked to investigate. The criteria used to determine the order in which authors are listed on the byline may vary, and are to be decided collectively by the author group and not by editors. If authors request removal or addition of an author after manuscript submission or publication, journal editors should seek an explanation and signed statement of agreement for the requested change from all listed authors and from the author to be removed or added.
The corresponding author is the one individual who takes primary responsibility for communication with the journal during the manuscript submission, peer-review, and publication process. The corresponding author typically ensures that all the journal’s administrative requirements, such as providing details of authorship, ethics committee approval, clinical trial registration documentation, and disclosures of relationships and activities are properly completed and reported, although these duties may be delegated to one or more co-authors. The corresponding author should be available throughout the submission and peer-review process to respond to editorial queries in a timely way, and should be available after publication to respond to critiques of the work and cooperate with any requests from the journal for data or additional information should questions about the paper arise after publication. Although the corresponding author has primary responsibility for correspondence with the journal, the ICMJE recommends that editors send copies of all correspondence to all listed authors.
When a large multi-author group has conducted the work, the group ideally should decide who will be an author before the work is started and confirm who is an author before submitting the manuscript for publication. All members of the group named as authors should meet all four criteria for authorship, including approval of the final manuscript, and they should be able to take public responsibility for the work and should have full confidence in the accuracy and integrity of the work of other group authors. They will also be expected as individuals to complete disclosure forms.
Some large multi-author groups designate authorship by a group name, with or without the names of individuals. When submitting a manuscript authored by a group, the corresponding author should specify the group name if one exists, and clearly identify the group members who can take credit and responsibility for the work as authors. The byline of the article identifies who is directly responsible for the manuscript, and MEDLINE lists as authors whichever names appear on the byline. If the byline includes a group name, MEDLINE will list the names of individual group members who are authors or who are collaborators, sometimes called non-author contributors, if there is a note associated with the byline clearly stating that the individual names are elsewhere in the paper and whether those names are authors or collaborators.
3. Non-Author Contributors
Contributors who meet fewer than all 4 of the above criteria for authorship should not be listed as authors, but they should be acknowledged. Examples of activities that alone (without other contributions) do not qualify a contributor for authorship are acquisition of funding; general supervision of a research group or general administrative support; and writing assistance, technical editing, language editing, and proofreading. Those whose contributions do not justify authorship may be acknowledged individually or together as a group under a single heading (e.g. "Clinical Investigators" or "Participating Investigators"), and their contributions should be specified (e.g., "served as scientific advisors," "critically reviewed the study proposal," "collected data," "provided and cared for study patients," "participated in writing or technical editing of the manuscript").
Because acknowledgment may imply endorsement by acknowledged individuals of a study’s data and conclusions, editors are advised to require that the corresponding author obtain written permission to be acknowledged from all acknowledged individuals.
Use of AI for writing assistance should be reported in the acknowledgment section.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Assisted Technology
At submission, the journal should require authors to disclose whether they used artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technologies (such as Large Language Models [LLMs], chatbots, or image creators) in the production of submitted work. Authors who use such technology should describe, in both the cover letter and the submitted work in the appropriate section if applicable, how they used it. For example, if AI was used for writing assistance, describe this in the acknowledgment section (see Section II.A.3). If AI was used for data collection, analysis, or figure generation, authors should describe this use in the methods (see Section IV.A.3.d). Chatbots (such as ChatGPT) should not be listed as authors because they cannot be responsible for the accuracy, integrity, and originality of the work, and these responsibilities are required for authorship (see Section II.A.1). Therefore, humans are responsible for any submitted material that included the use of AI-assisted technologies. Authors should carefully review and edit the result because AI can generate authoritative-sounding output that can be incorrect, incomplete, or biased. Authors should not list AI and AI-assisted technologies as an author or co-author, nor cite AI as an author. Authors should be able to assert that there is no plagiarism in their paper, including in text and images produced by the AI. Humans must ensure there is appropriate attribution of all quoted material, including full citations.
Next: Disclosure of Financial and Non-Financial Relationships and Activities, and Conflicts of Interest
Keep up-to-date Request to receive an E-mail when the Recommendations are updated.
Subscribe to Changes
- Open access
- Published: 05 June 2024
Experiences of medical students and faculty regarding the use of long case as a formative assessment method at a tertiary care teaching hospital in a low resource setting: a qualitative study
- Jacob Kumakech 1 ,
- Ian Guyton Munabi 2 ,
- Aloysius Gonzaga Mubuuke 3 &
- Sarah Kiguli 4
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 621 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
148 Accesses
Metrics details
Introduction
The long case is used to assess medical students’ proficiency in performing clinical tasks. As a formative assessment, the purpose is to offer feedback on performance, aiming to enhance and expedite clinical learning. The long case stands out as one of the primary formative assessment methods for clinical clerkship in low-resource settings but has received little attention in the literature.
To explore the experiences of medical students and faculty regarding the use of the Long Case Study as a formative assessment method at a tertiary care teaching hospital in a low-resource setting.
Methodology
A qualitative study design was used. The study was conducted at Makerere University, a low-resource setting. The study participants were third- and fifth-year medical students as well as lecturers. Purposive sampling was utilized to recruit participants. Data collection comprised six Focus Group Discussions with students and five Key Informant Interviews with lecturers. The qualitative data were analyzed by inductive thematic analysis.
Three themes emerged from the study: ward placement, case presentation, and case assessment and feedback. The findings revealed that students conduct their long cases at patients’ bedside within specific wards/units assigned for the entire clerkship. Effective supervision, feedback, and marks were highlighted as crucial practices that positively impact the learning process. However, challenges such as insufficient orientation to the long case, the super-specialization of the hospital wards, pressure to hunt for marks, and inadequate feedback practices were identified.
The long case offers students exposure to real patients in a clinical setting. However, in tertiary care teaching hospitals, it’s crucial to ensure proper design and implementation of this practice to enable students’ exposure to a variety of cases. Adequate and effective supervision and feedback create valuable opportunities for each learner to present cases and receive corrections.
Peer Review reports
The long case serves as an authentic assessment method for evaluating medical students’ competence in clinical tasks [ 1 ]. This form of assessment requires students to independently spend time with patients taking their medical history, conducting physical examinations, and formulating diagnosis and management plans. Subsequently, students present their findings to senior clinicians for discussion and questioning [ 2 , 3 ]. While developed countries increasingly adopt simulation-based assessments for formative evaluation, logistical challenges hinder the widespread use of such methods in developing countries [ 4 ]. Consequently, the low-resource countries heavily rely on real patient encounters for formative assessment. The long case is one such method predominantly used as a primary formative assessment method during clinical clerkship and offers a great opportunity for feedback [ 5 ]. The assessment grounds students’ learning into practice by providing them with rich opportunities to interact with patients and have the feel of medical practice. The long case thus bridges the gap between theory and practice, immersing students in the real tasks of a physician [ 1 ]. The complexity of clinical scenarios and the anxiety associated with patient encounters may not be well replicated in simulation-based assessments because diseases often have atypical presentations not found in textbooks. Assessment methods should thus utilize authentic learning experiences to provide learners with applications of learning that they would expect to encounter in real life [ 6 ]. This requires medical education and the curriculum to focus attention on assessment because it plays a significant role in driving learning [ 7 ]. The long case thus remains crucial in medical education as one of the best ways of preparing for practice. It exposes the student repeatedly to taking medical history, examining patients, making clinical judgments, deciding treatment plans, and collaborating with senior clinicians.
The long case, however, has faced significant criticism in the medical education literature due to perceived psychometric deficiencies [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Consequently, many universities have begun to adopt assessment methods that yield more reliable and easily defensible results [ 2 ] due to concerns over the low reliability, generalizability, and validity of the long case, coupled with rising litigations and student appeals [ 11 , 12 ]. Despite these shortcomings, the long case remains an educationally valuable assessment tool that provides diagnostic feedback essential for the learning process during clinical clerkship [ 13 ]. Teachers can utilize long-case results to pinpoint neglected areas or teaching deficiencies and align with course outcomes.
However, there is a paucity of research into the long case as a formative assessment tool. A few studies conducted in developed countries highlighted its role in promoting a holistic approach to patient care, fostering students’ clinical skills, and a driving force for students to spend time with patients [ 2 , 13 ], . There is a notable absence of literature on the use of long case as a formative assessment method in low-resource countries, and no published work is available at Makerere University where it has been used for decades. This underscores the importance of conducting research in this area to provide insight into the effectiveness, challenges, and potentials for improvement. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the experiences of medical students and faculty regarding the utilization of the long case as a formative assessment method within the context of a tertiary care teaching hospital in a low-resource setting.
Study design
This was an exploratory qualitative study.
Study setting
The research was conducted at Makerere University within the Department of Internal Medicine. The Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBChB) degree at Makerere University is a five-year program with the first two years for pre-clinical (biomedical Sciences) course and the last three years dedicated to clinical clerkship. Medical students do Internal Medicine clerkships in third- and fifth-year at the two tertiary teaching hospitals namely; Mulago and Kiruddu National Referral Hospitals. The students are introduced to the long case in third-year as Junior Clerks and later in the fifth-year as Senior Clerks. During clerkship, students are assigned to various medical wards, where they interact with patients, take medical history from them, perform physical examinations, and develop diagnosis and management plans. Subsequently, students present their long cases to lecturers or postgraduate students, often in the presence of their peers, followed by feedback and comprehensive case discussions. Students are afforded ample time to prepare and present their cases during ward rounds, at their discretion. The students are formatively assessed and a mark is awarded on a scale of one to ten in the student’s logbook. Each student is required to make a minimum of ten long cases over the seven weeks of clerkship.
Study participants
The study participants were third- and fifth-year medical students who had completed junior and senior clerkship respectively, as well as lecturers who possessed at least five years of experience with the long case. The participants were selected through purposive sampling. The sample size for the study was determined by data saturation.
Data collection
Data were collected through Focus Group Discussions (FGDs) and Key Informant Interviews (KIIs). A total of 36 medical students participated in FGDs, reflecting on their experiences with the long case. Five faculty members participated in individual KIIs. The students were mobilized by their class representative and a brief recruitment presentation was made at the study site while the lecturers were approached via email and telephone invitation.
Six FGDs were conducted, three for junior clerks and three for senior clerks. Each FGD comprised of 5–7 participants with balanced male and female gender representation. Data saturation was achieved by the fifth FGD, at which point no additional new information emerged. A research assistant proficient in qualitative research methods moderated the FGDs. The discussions lasted between 55 min and 1 h 10 min and were audio recorded. The Principal Investigator attended all the FGDs to document interactions and record his perspectives and non-verbal cues of participants.
Semi-structured KIIs were used to collect data from Internal Medicine faculty. Five KIIs were conducted, and data saturation was achieved by the fourth interview, at which point no new theme emerged. The Principal Investigator conducted the KIIs via Zoom. Each interview lasted between 25 and 50 min and all were audio recorded. A research assistant proficient in qualitative methods attended all the Zoom meetings. The data collected were securely stored on a hard drive and Google Drive with password protection to prevent unauthorized access.
Data analysis
Data analysis was done through inductive thematic analysis method. Following each FGD or KII session, the data collection team listened to the recordings to familiarize themselves with the data and develop general ideas regarding the participants’ perspectives. The data were transcribed verbatim by the researchers to generate text data. Two separate transcripts were generated by the Principal Investigator and a research assistant. The transcripts were then compared and manually reviewed by the research team to compare the accuracy with the audio recordings. After transcript harmonization, data cleaning was done for both FGDs and KIIs transcripts.
The transcribed data from both FGDs and KIIs underwent inductive thematic analysis as aggregated data. This involved initial line-by-line coding, followed by focused coding where the relationships between initial codes were explored and similar codes were grouped. Throughout the analysis, the principle of constant comparison was applied, where emerging codes were compared for similarities and differences.
Study results
Socio-demographics.
A total of 36 medical students participated in the FGDs, comprising 18 junior clerks and 19 senior clerks. The participants were aged between 21 and 25 years except two participants who were aged above 25 (30 and 36 years old). Among the third-year students, there were 10 male and 9 female participants while the fifth-year student comprised of 8 male and 10 female participants.
Five lecturers participated in the Key Informant Interviews, three of whom were females and two male participants. They were aged between 40 and 50 years, and all had over 10 years of experience with the long case. The faculty members included one consultant physician, one associate professor, two senior lecturers, and one lecturer.
Themes that emerged
Three themes emerged from the study: ward placement, case presentations, and case assessment and feedback.
Themes | Codes |
|---|---|
Theme 1; ward placement | Allocation to specific ward, specialization of the wards, orientation on the ward, and exposure to other ward |
Theme 2; case presentation | Variation in the mode of presentation, limited observation of skills, and unreliable presence of lecturers. |
Theme 3; case assessment and feedback | Marks awarded for the long case, case write-up, marks as motivators, pressure to hunt for mark Feedback is given to the student, feedback to the lecturer, limitations of the feedback practice |
Theme 1: Ward placement
The study findings disclosed that medical students are assigned to specific wards for the duration of their clerkship. The specialization of medical wards was found to significantly restrict students’ exposure to limited disease conditions found only in their allocated ward.
With the super-specialization of the units, there is some bias on what they do learn; if a particular group is rotating on the cardiology unit, they will obviously have a bias to learn the history and physical exam related to cardiovascular disease (KII 1).
The students, particularly junior clerks, expressed dissatisfaction with the lack of proper and standardized orientation to the long case on the wards. This deficiency led to wastage of time and a feeling of being unwelcome in the clerkship.
Some orient you when you reach the ward but others you reach and you are supposed to pick up on your own. I expect orientation, then taking data from us, what they expect us to do, and what we expect from them, taking us through the clerkship sessions (FGD 4 Participant 1).
Students’ exposure to cases in other wards poses significant challenges; the study found that as some lecturers facilitate visits to different wards for scheduled teaching sessions, others don’t, resulting in missed learning opportunities. Additionally, some lecturers leave the burden on students’ personal initiative to explore cases in other wards.
We actually encourage them to go through the different specialties because when you are faced with a patient, you will not have to choose which one to see and not to see (KII 4).
Imagine landing on a stroke patient when you have been in the infectious disease ward or getting a patient with renal condition when you have been in the endocrinology ward can create problems (FGD 6 Participant 3).
Theme 2 Case presentation
Medical students present their long case to lecturers and postgraduate students. However, participants revealed variations among lecturers regarding their preferences on how they want students to present their cases. While some prefer to listen to the entire history and examination, others prefer only a summary, and some prefer starting from the diagnosis.
The practice varies depending on the lecturer, as everyone does it their own way. There are some, who listen to your history, examination, and diagnosis, and then they go into basic discussion of the case; others want only a summary. Some lecturers come and tell you to start straight away from your diagnosis, and then they start treating you backward (FGD 6 Participant 3).
The students reported limited observation of their skills due a little emphasis placed by examiners on physical examination techniques, as well as not providing the students with the opportunity to propose treatment plans.
When we are doing these physical examinations on the ward no one is seeing you. You present your physical examination findings, but no one saw how you did it. You may think you are doing the right thing during the ward rotations, but actually your skills are bad (FGD 4 Participant 6).
They don’t give us time to propose management plans. The only time they ask for how you manage a patient is during the summative long case, yet during the ward rotation, they were not giving us the freedom to give our opinion on how we would manage the patient.(FGD 2Participant 6).
Supervision was reportedly dependent on the ward to which the student was allocated. Additionally, the participants believe that the large student-to-lecturer ratio negatively affects the opportunity to present.
My experience was different in years three and five. In year three, we had a specialist every day on the ward, but in year five, we would have a specialist every other day, sometimes even once a week. When I compare year five with year three, I think I was even a better doctor in year three than right now (FGD 1 Participant 1).
Clinical training is like nurturing somebody to behave or conduct themselves in a certain way. Therefore, if the numbers are large, the impacts per person decrease, and the quality decreases (KII 5).
Theme C: Case assessment and feedback
The study found that a student’s long case is assessed both during the case presentation on the ward and through the case write-up, with marks awarded accordingly.
They present to the supervisor and then also write it up, so at a later time you also mark the sheet where they have written up the cases; so they are assessed at presentation and write up (KII 2).
The mark awarded was reportedly a significant motivator for students to visit wards and clerk patients, but students also believe that the pressure to hunt for marks tends to override the goal of the formative assessment.
Your goal there is to learn, but most of us go with the goal of getting signatures; signature-based learning. The learning, you realize probably comes on later if you have the individual morale to go and learn (FGD 1 participant 1).
Feedback is an integral part of any formative assessment. While students receive feedback from lecturers, the participants were concerned about the absence of a formal channel for soliciting feedback from students.
Of course, teachers provide feedback to students because it is a normal part of teaching. However, it is not a common routine to solicit feedback about how teaching has gone. So maybe that is something that needs to be improved so that we know if we have been effective teachers (KII 3).
Whereas the feedback intrigues students to read more to compensate for their knowledge gap, they decried several encounters with demeaning, intimidating, insulting, demotivating, and embarrassing feedback from assessors.
Since we are given a specific target of case presentation we are supposed to make in my training , if I make the ten, I wouldn’t want to present again. Why would I receive other negative comments for nothing? They truly have a personality effect on the student, and students feel low self-esteem (FGD 1, Participant 4).
This study aimed to investigate the experiences of medical students and faculty regarding the use of the long case as a formative assessment method at a tertiary care teaching hospital in a low-resource setting. This qualitative research provides valuable insights into the current practices surrounding the long case as a formative assessment method in such a setting.
The study highlighted the patient bedside as the primary learning environment for medical students. Bedside teaching plays a crucial role in fostering the development of skills such as history-taking and physical examination, as well as modeling professional behaviors and directly observing learners [ 14 , 15 ]. However, the specialization of wards in tertiary hospitals means that students may not be exposed to certain conditions found in other wards. This lack of exposure can lead to issues of case specificity, which has been reported in various literature as a cause of low reliability and generalizability of the long case [ 16 , 17 ]. Participants in the study expressed feeling like pseudo-specialists based on their ward allocations. This is partly attributed to missing scheduled teachings and poor management of opportunities to clerk and present patients on other wards. Addressing these challenges is essential for enhancing the effectiveness of the long case as a formative assessment method in medical education.
Proper orientation at the beginning of a clerkship is crucial for clarifying the structure and organization, defining students’ roles, and providing insights into clinical supervisors’ perspectives [ 18 ]. However, the study revealed that orientation into the long case was unsatisfactory, resulting in time wastage and potentially hindering learning. Effective orientation requires dedicated time and should involve defining expectations and goals, as well as guiding students through the steps of history-taking and physical examination during the initial weeks of the rotation. Contrary to this ideal approach, the medical students reported being taken through systemic examinations when the clerkship was nearing its end, highlighting a significant gap in the orientation process. Proper orientation is very important since previous studies have also documented the positive impact of orientation on student performance [ 19 ]. Therefore, addressing the shortcomings in orientation practices identified in this study is essential for optimizing learning outcomes and ensuring that students are adequately prepared to engage in the long case.
There was reportedly a significant variation in the way students present their long cases, with some lecturers preferring only a case summary, while others expect a complete presentation or begin with a diagnosis. While this diversity in learning styles may expose students to both familiar and unfamiliar approaches, providing a balance of comfort and tension [ 20 ], it’s essential for students to first be exposed to familiar methods before transitioning to less familiar ones to expand their ability to use diverse learning styles. The variation observed in this context may be attributed to time constraints, as lecturers may aim to accommodate the large number of students within the available time. Additionally, a lack of standardized practices could also contribute to this variation. Therefore, there is a pressing need for standardized long-case practices to ensure a consistent experience for students and to meet the desired goals of the assessment. Standardizing the long case practice would not only provide a uniform experience for students but also enhance the reliability, validity, and perception of fairness of the assessment [ 9 , 21 ]. It would ensure that all students are evaluated using the same criteria, reducing potential biases and disparities in grading. Additionally, standardized practices facilitate better alignment with learning objectives and promote more effective feedback mechanisms [ 22 ].
Related to the above, students reported limited observation of skills and little emphasis placed on them to learn physical examination techniques. This finding resonates with the research conducted by Abdalla and Shorbagi in 2018, where many students reported a lack of observation during history-taking and physical examination [ 23 ]. The importance of observation is underscored by the fact that students often avoid conducting physical examinations, as highlighted in Pavlakis & Laurent’s study among postgraduate trainees in 2001 [ 24 ]. This study sheds more light on the critical role of observation in forcing medical students to master clinical assessment and practical skills. The study also uncovered that students are rarely given the opportunity to propose management plans during case presentations, which hampers their confidence and learning of clinical decision-making. These findings likely stem from the large student-to-lecturer ratio and little attention given to these aspects of the long case during the planning of the assessment method. The result is students not receiving the necessary guidance and support to develop their clinical and decision-making skills. Therefore, addressing these issues by putting more emphasis on observation of student-patient interaction, management plan, and having a smaller student group is vital to ensure that medical students receive comprehensive training and are adequately prepared for their future roles as physicians.
The study found that the marks awarded for the long case serve as the primary motivator for students. This finding aligns with previous research indicating that the knowledge that each long case is part of assessment drives students to perform their duties diligently [ 2 , 25 ]. It underscores the crucial role that assessment plays in driving learning processes. However, the pressures to obtain marks and signatures reportedly hinder students’ engagement in learning. This could be attributed to instances where some lecturers relax on supervision or are absent, leaving students to struggle to find someone to assess them. Inadequate supervision by attending physicians has been identified in prior studies as one of the causes of insufficient clinical experience [ 26 ], something that need to be dealt with diligently. While the marks awarded are a motivating factor, it is essential to understand other underlying motivations of medical students to engage in the long case and their impact on the learning process.
Feedback is crucial for the long case to fulfill its role as an assessment for learning. The study participants reported that feedback is provided promptly as students present their cases. This immediate feedback is essential for identifying errors and learning appropriate skills to enhance subsequent performance. However, the feedback process appears to be unilateral, with students receiving feedback from lecturers but lacking a structured mechanism for providing feedback themselves. One reason for the lack of student feedback may be a perceived intimidating approach from lecturers which discourages students from offering their input. It is thus important to establish a conducive environment where students feel comfortable providing feedback without fear of negative repercussions. The study underscores the significance of feedback from students in improving the learning process. This aligns with the findings of Hattie and Timperley (2007), who emphasized that feedback received from learners contributes significantly to improvements in student learning [ 27 ]. Therefore, it is essential to implement strategies to encourage and facilitate bidirectional feedback between students and lecturers in the context of the long case assessment. This could involve creating formal channels for students to provide feedback anonymously or in a structured format, fostering open communication, and addressing any perceived barriers to feedback exchange [ 28 ]. By promoting a culture of feedback reciprocity, educators can enhance the effectiveness of the long case as an assessment tool.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the long case remains a cornerstone of formative assessment during clerkship in many medical schools, particularly in low-resource countries. However, its effectiveness is challenged by limitations such as case specificity in tertiary care hospitals, which can affect the assessment’s reliability and generalizability. The practice of awarding marks in formative assessment serves as a strong motivator for students but also creates tension, especially when there is inadequate contact with lecturers. This can lead to a focus on hunting for marks at the expense of genuine learning. Thus adequate supervision and feedback practices are vital for ensuring the success of the long case as an assessment for learning.
Furthermore, there is a need to foster standardized long case practice to ensure that scheduled learning activities are completed and that all students clerk and present patients with different conditions from various wards. This will promote accountability among both lecturers and students and ensure a consistent and uniform experience with the long case as an assessment for learning, regardless of the ward a student is assigned.
Data availability
The data supporting the study results of this article can be accessed from the Makerere University repository, titled “Perceptions of Medical Students and Lecturers of the Long Case Practices as Formative Assessment in Internal Medicine Clerkship at Makerere University,” available on DSpace. The identifier is http://hdl.handle.net/10570/13032 . Additionally, the raw data are securely stored with the researchers in Google Drive.
Dare AJ, Cardinal A, Kolbe J, Bagg W. What can the history tell us? An argument for observed history-taking in the trainee intern long case assessment. N Z Med J. 2008;121 1282:51–7.
Google Scholar
Tey C, Chiavaroli N, Ryan A. Perceived educational impact of the medical student long case: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):1–9.
Article Google Scholar
Jayasinghe R. Mastering the Medical Long Case. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009.
Martinerie L, Rasoaherinomenjanahary F, Ronot M, Fournier P, Dousset B, Tesnière A, Mariette C, Gaujoux S, Gronnier C. Health care simulation in developing countries and low-resource situations. J Continuing Educ Health Professions. 2018;38(3):205–12.
van der Vleuten C. Making the best of the long case. Lancet (London England). 1996;347(9003):704–5.
Reeves TC, Okey JR. Alternative assessment for constructivist learning environments. Constructivist Learn Environments: Case Stud Instructional Des. 1996;191:202.
Biggs J. What the student does: teaching for enhanced learning. High Educ Res Dev. 1999;18(1):141.
Michael A, Rao R, Goel V. The long case: a case for revival? Psychiatrist. 2013;37(12):377–81.
Benning T, Broadhurst M. The long case is dead–long live the long case: loss of the MRCPsych long case and holism in psychiatry. Psychiatr Bull. 2007;31(12):441–2.
Burn W, Brittlebank A. The long case: the case against its revival: Commentary on… the long case. Psychiatrist. 2013;37(12):382–3.
Norcini JJ. The death of the long case? Bmj 2002;324(7334):408–9.
Pell G, Roberts T. Setting standards for student assessment. Int J Res Method Educ. 2006;29(1):91–103.
Masih CS, Benson C. The long case as a formative Assessment Tool–views of medical students. Ulster Med J. 2019;88(2):124.
Peters M, Ten Cate O. Bedside teaching in medical education: a literature review. Perspect Med Educ. 2014;3(2):76–88.
Wölfel T, Beltermann E, Lottspeich C, Vietz E, Fischer MR, Schmidmaier R. Medical ward round competence in internal medicine–an interview study towards an interprofessional development of an Entrustable Professional Activity (EPA). BMC Med Educ. 2016;16(1):1–10.
Wilkinson TJ, Campbell PJ, Judd SJ. Reliability of the long case. Med Educ. 2008;42(9):887–93.
Sood R. Long case examination-can it be improved. J Indian Acad Clin Med. 2001;2(4):252–5.
Atherley AE, Hambleton IR, Unwin N, George C, Lashley PM, Taylor CG. Exploring the transition of undergraduate medical students into a clinical clerkship using organizational socialization theory. Perspect Med Educ. 2016;5:78–87.
Owusu GA, Tawiah MA, Sena-Kpeglo C, Onyame JT. Orientation impact on performance of undergraduate students in University of Cape Coast (Ghana). Int J Educational Adm Policy Stud. 2014;6(7):131–40.
Vaughn L, Baker R. Teaching in the medical setting: balancing teaching styles, learning styles and teaching methods. Med Teach. 2001;23(6):610–2.
Olson CJ, Rolfe I, Hensley. The effect of a structured question grid on the validity and perceived fairness of a medical long case assessment. Med Educ. 2000;34(1):46–52.
Jensen-Doss A, Hawley KM. Understanding barriers to evidence-based assessment: clinician attitudes toward standardized assessment tools. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2010;39(6):885–96.
Abdalla ME, Shorbagi S. Challenges faced by medical students during their first clerkship training: a cross-sectional study from a medical school in the Middle East. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2018;13(4):390–4.
Pavlakis N, Laurent R. Role of the observed long case in postgraduate medical training. Intern Med J. 2001;31(9):523–8.
Teoh NC, Bowden FJ. The case for resurrecting the long case. BMJ. 2008;336(7655):1250–1250.
Mulindwa F, Andia I, McLaughlin K, Kabata P, Baluku J, Kalyesubula R, Kagimu M, Ocama P. A quality improvement project assessing a new mode of lecture delivery to improve postgraduate clinical exposure time in the Department of Internal Medicine, Makerere University, Uganda. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(2):e001101.
Hattie J, Timperley H. The power of feedback. Rev Educ Res. 2007;77(1):81–112.
Weallans J, Roberts C, Hamilton S, Parker S. Guidance for providing effective feedback in clinical supervision in postgraduate medical education: a systematic review. Postgrad Med J. 2022;98(1156):138–49.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research was supported by the Fogarty International Centre of the National Institute of Health under award number 1R25TW011213. The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Medicine, Department of Paediatrics & Child Health, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Jacob Kumakech
School of Biomedical Sciences, Department of Anatomy, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Ian Guyton Munabi
School of Medicine, Department of Radiology, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Aloysius Gonzaga Mubuuke
School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics & Child Health, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Sarah Kiguli
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JK contributed to the conception and design of the study, as well as the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. He also drafted the initial version of the work and approved the submitted version. He agrees to be personally accountable for his contribution and to ensure that any questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even those in which he was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated and resolved, with the resolution documented in the literature.IMG contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. He also made major corrections to the first draft of the manuscript and approved the submitted version. He agrees to be personally accountable for his contribution and to ensure that any questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even those in which he was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated and resolved, with the resolution documented in the literature.MA contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. He made major corrections to the first draft of the manuscript and approved the submitted version. He agrees to be personally accountable for his contribution and to ensure that any questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even those in which he was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated and resolved, with the resolution documented in the literature.SK made major corrections to the first draft and the final corrections for the submitted version of the work. She agrees to be personally accountable for her contribution and to ensure that any questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even those in which she was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated and resolved, with the resolution documented in the literature.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jacob Kumakech .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Ethical approval to conduct the study was obtained from the Makerere University School of Medicine Research and Ethics Committee, with ethics ID Mak-SOMREC-2022-524. Informed consent was obtained from all participants using the Mak-SOMREC informed consent form.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kumakech, J., Munabi, I.G., Mubuuke, A.G. et al. Experiences of medical students and faculty regarding the use of long case as a formative assessment method at a tertiary care teaching hospital in a low resource setting: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ 24 , 621 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05589-7
Download citation
Received : 04 April 2024
Accepted : 22 May 2024
Published : 05 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05589-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Formative assessment
- Medical education
- Low-resource setting
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Skip to main content
Update your browser for the best possible experience
As of January 1st, 2020, Internet Explorer (versions 11 and below) is no longer supported by Evolve. To get the best possible experience using Evolve, we recommend that you use another web browser. For HESI iNet users click here .

- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

Elektrostal
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.

Elektrostal , city, Moscow oblast (province), western Russia . It lies 36 miles (58 km) east of Moscow city. The name, meaning “electric steel,” derives from the high-quality-steel industry established there soon after the October Revolution in 1917. During World War II , parts of the heavy-machine-building industry were relocated there from Ukraine, and Elektrostal is now a centre for the production of metallurgical equipment. Pop. (2006 est.) 146,189.

- Bahasa Indonesia
- Eastern Europe
- Moscow Oblast
Elektrostal
Elektrostal Localisation : Country Russia , Oblast Moscow Oblast . Available Information : Geographical coordinates , Population, Altitude, Area, Weather and Hotel . Nearby cities and villages : Noginsk , Pavlovsky Posad and Staraya Kupavna .
Information
Find all the information of Elektrostal or click on the section of your choice in the left menu.
- Update data
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Oblast |
Elektrostal Demography
Information on the people and the population of Elektrostal.
| Elektrostal Population | 157,409 inhabitants |
|---|---|
| Elektrostal Population Density | 3,179.3 /km² (8,234.4 /sq mi) |
Elektrostal Geography
Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal .
| Elektrostal Geographical coordinates | Latitude: , Longitude: 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East |
|---|---|
| Elektrostal Area | 4,951 hectares 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) |
| Elektrostal Altitude | 164 m (538 ft) |
| Elektrostal Climate | Humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification: Dfb) |
Elektrostal Distance
Distance (in kilometers) between Elektrostal and the biggest cities of Russia.
Elektrostal Map
Locate simply the city of Elektrostal through the card, map and satellite image of the city.
Elektrostal Nearby cities and villages
Elektrostal Weather
Weather forecast for the next coming days and current time of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Sunrise and sunset
Find below the times of sunrise and sunset calculated 7 days to Elektrostal.
| Day | Sunrise and sunset | Twilight | Nautical twilight | Astronomical twilight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 June | 02:43 - 11:25 - 20:07 | 01:43 - 21:07 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 9 June | 02:42 - 11:25 - 20:08 | 01:42 - 21:08 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 10 June | 02:42 - 11:25 - 20:09 | 01:41 - 21:09 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 11 June | 02:41 - 11:25 - 20:10 | 01:41 - 21:10 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 12 June | 02:41 - 11:26 - 20:11 | 01:40 - 21:11 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 13 June | 02:40 - 11:26 - 20:11 | 01:40 - 21:12 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
| 14 June | 02:40 - 11:26 - 20:12 | 01:39 - 21:13 | 01:00 - 01:00 | 01:00 - 01:00 |
Elektrostal Hotel
Our team has selected for you a list of hotel in Elektrostal classified by value for money. Book your hotel room at the best price.
| Located next to Noginskoye Highway in Electrostal, Apelsin Hotel offers comfortable rooms with free Wi-Fi. Free parking is available. The elegant rooms are air conditioned and feature a flat-screen satellite TV and fridge... | from | |
| Located in the green area Yamskiye Woods, 5 km from Elektrostal city centre, this hotel features a sauna and a restaurant. It offers rooms with a kitchen... | from | |
| Ekotel Bogorodsk Hotel is located in a picturesque park near Chernogolovsky Pond. It features an indoor swimming pool and a wellness centre. Free Wi-Fi and private parking are provided... | from | |
| Surrounded by 420,000 m² of parkland and overlooking Kovershi Lake, this hotel outside Moscow offers spa and fitness facilities, and a private beach area with volleyball court and loungers... | from | |
| Surrounded by green parklands, this hotel in the Moscow region features 2 restaurants, a bowling alley with bar, and several spa and fitness facilities. Moscow Ring Road is 17 km away... | from | |
Elektrostal Nearby
Below is a list of activities and point of interest in Elektrostal and its surroundings.
Elektrostal Page
| Direct link | |
|---|---|
| DB-City.com | Elektrostal /5 (2021-10-07 13:22:50) |

- Information /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#info
- Demography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#demo
- Geography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#geo
- Distance /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist1
- Map /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#map
- Nearby cities and villages /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist2
- Weather /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#weather
- Sunrise and sunset /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#sun
- Hotel /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#hotel
- Nearby /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#around
- Page /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#page
- Terms of Use
- Copyright © 2024 DB-City - All rights reserved
- Change Ad Consent Do not sell my data

40 Facts About Elektrostal
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 01 Jun 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy , materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes , offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development .
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy , with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Elektrostal's fascinating history, vibrant culture, and promising future make it a city worth exploring. For more captivating facts about cities around the world, discover the unique characteristics that define each city . Uncover the hidden gems of Moscow Oblast through our in-depth look at Kolomna. Lastly, dive into the rich industrial heritage of Teesside, a thriving industrial center with its own story to tell.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is a book compiled of medical case studies. It is very accurate and can be used to learn from great care and mistakes. ... The way that the scenarios are explained could even be understood by a non-nursing student as well. The case studies are very clear and very thorough. Interface rating: 5 The book is very easy to navigate, prints well ...
It will help everyone, from medical students to consultants, to find the hidden clinical gems and historical background they need to achieve true clinical excellence. Key Features. 250 clinical cases in print - provides a comprehensive overview of all relevant topics; Conversational and accessible style - suitable for medical students
Discover seven books every medical student should read that show you the good, the bad and the ugly written by the people who know. ... These case studies are part of the reason this book became so popular and medical students will enjoy this as it shows the strong, fascinating link between medicine and psychology.
AccessMedicine Case Files Collection This link opens in a new window AccessMedicine's Case Files Collection from McGraw-Hill Education offers the best-selling Case Files content in an interactive format. Updated regularly, this comprehensive case collection helps students learn and apply basic science and clinical medicine concepts in the context of realistic patient cases.
This is a 2023-2024 edition and 8.5 x 11 inch updated, medical workbook and text. It is an extraordinary resource for studying Internal Medicine. It is an excellent tool for studying for National Boards (Medicine, Recredentialing, PANCE) at any level and there are over 200 topical questions and answers in over 15 categories included.
It covers important areas of clinical medicine in a question based format and highlights classical scenarios. The questions raised are classical of examiners in the long and short case examinations. This is a must buy for any undergraduate medical student!!!''The book is a must during the period that the young doctor or student is on the wards.
Description. This unique book presents a wealth of information on common presentations and illnesses, presented as medical case studies. It is useful for exam preparation, as a quick reference guide for working doctors, and as an interesting read for all those interested in medicine. 250 Clinical Cases covers a wide variety of conditions ...
This unique book presents a wealth of information on common presentations and illnesses, presented as medical case studies. It is useful for exam preparation, as a quick reference guide for working doctors, and as an interesting read for all those interested in medicine. 250 Clinical Cases covers a wide variety of conditions, providing in-depth insights into the most relevant topics ...
This book is intended to help medical students with their preparations for medical short case examinations, and through this process enhance the depth and breadth of their knowledge of clinical medicine as well as their clinical skills. Though particularly useful to students sitting their final clinical exams, it will also be of interest to more junior students, particularly those who face ...
Book. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine International Edition. Edited by Ian D Penman. US$48.99. ADD TO CART. This useful new book enables students to apply the theoretical knowledge gained in their medicine classes to clinical cases. Students will improve their diagnostic skills as they are taken simply and logically through the ...
Gawande has written quite a few books about medicine and patient care. This particular one tackles a topic that I think all students should consider: the end of life. Being Mortal shares the reflections and personal stories of patients undergoing hospice care or struggling with terminal illness.
Headache case study with questions and answers - for doctors and medical students exams, finals and OSCEs.
Each scenario allows you to work through history taking, investigations, diagnosis and management. You might also be interested in our bank of 1000+ OSCE Stations. A collection of interactive medical and surgical OSCE cases (clinical case scenarios) to put your history, examination, investigation, diagnostic and management skills to the test.
Best Books for Medical Students A list of the best books for medical students (or anyone else!) that want to gain a better insight into medical ethics as well as the lives of patients and their doctors. ... A Case of Culture: How Cultural Brokers Bridge Divides in Healthcare. reply | flag. message 6: by Snigdha (new) Feb 05, 2022 10:55AM. reply ...
Clinical Cases. If you fancy a challenge, have a go a these pathology cases. Practice thinking of key differentials, interpreting investigations and applying your knowledge to answer these clinical cases.
Otherwise, I struggle to think of much that's good for free. Again, the BMJ does a weekly case study, aimed at junior doctors, which is normally good. I think that's usually outside their pay wall. Otherwise, I'd try to pick up a textbook of case studies from your medical schools library - they're probably your best bet.
The thirty-six cases presented in this volume are the pedagogic result of the author's years working in a pediatrics medical setting. These cases include scenarios that aim to help students improve such skills as evaluating clinical presentations, formulating differential diagnoses, determining appropriate work-ups and interpreting their results, and producing working diagnoses and ...
OnRounds: 1000 Internal Medicine Pearls. OnRounds is a book specifically designed and written to assist and prepare medical students and junior residents. Internal Medicine can make any student quiver in nervousness and anxiety. This book can help ease those nerves a bit.
The Core comprehensively presents and clearly explains the material you're expected to learn in med school—and makes learning it easier. What's included. Format. Print Core Digital Core. Notes. Set of 20 books, shelf case, and Personal Trainer. $699.00. 4 interest-free installments, or from $63.09/mo with.
Learn about the free AAMC MCAT ® Official Prep resources that the AAMC offers to help you study. Learning through practice is key when it comes to the MCAT ® exam. Prepare for the exam with AAMC MCAT Official Prep products written by the test developers. Get answers to your questions about MCAT ® registration, scores, and more.
Browse journals and books at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature ... Applications and Case Studies. Book • 2022. Abrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage Fracturing ... Book • 1966. Abridged Science for High School Students. The Nuclear Research Foundation School Certificate ...
Only two of the nursing programs occur at the case study site itself. The second entry program is held in a large city to the south of the case study site. Additionally, students who partake in the RPN to BScN bridging program through blended learning live geographically dispersed throughout the province in which the case study site is located.
The following recommendations are intended to ensure that contributors who have made substantive intellectual contributions to a paper are given credit as authors, but also that contributors credited as authors understand their role in taking responsibility and being accountable for what is published. Editors should be aware of the practice of ...
The long case is used to assess medical students' proficiency in performing clinical tasks. As a formative assessment, the purpose is to offer feedback on performance, aiming to enhance and expedite clinical learning. The long case stands out as one of the primary formative assessment methods for clinical clerkship in low-resource settings but has received little attention in the literature.
16-week instructor-led training course. Two-year AAPC membership. Denials Management & Appeals Reference Guide. Three practice tests. Two certification exam attempts ($499 if purchased separately) 50% off + FREE certification exam expires June 28th. $2,495 (a $4,990 value) Enroll now. This entry-level, medical billing course ensures you receive ...
Evolve is a one-stop online portal for healthcare educators and students to access and purchase all of their Elsevier digital teaching & learning materials
Elektrostal, city, Moscow oblast (province), western Russia.It lies 36 miles (58 km) east of Moscow city. The name, meaning "electric steel," derives from the high-quality-steel industry established there soon after the October Revolution in 1917. During World War II, parts of the heavy-machine-building industry were relocated there from Ukraine, and Elektrostal is now a centre for the ...
Elektrostal Geography. Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal. Elektrostal Geographical coordinates. Latitude: 55.8, Longitude: 38.45. 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East. Elektrostal Area. 4,951 hectares. 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) Elektrostal Altitude.
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
Main page; Contents; Current events; Random article; About Wikipedia; Contact us; Donate; Pages for logged out editors learn more