11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.

Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.


The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
SWOT analysis: Examples and templates

A SWOT analysis helps you identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for a specific project or your overall business plan. It’s used for strategic planning and to stay ahead of market trends. Below, we describe each part of the SWOT framework and show you how to conduct your own.
Whether you’re looking for external opportunities or internal strengths, we’ll walk you through how to perform your own SWOT analysis, with helpful examples along the way.
What is a SWOT analysis?
A SWOT analysis is a technique used to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for your business or even a specific project. It’s most widely used by organizations—from small businesses and non-profits to large enterprises—but a SWOT analysis can be used for personal purposes as well.
While simple, a SWOT analysis is a powerful tool for helping you identify competitive opportunities for improvement. It helps you improve your team and business while staying ahead of market trends.
What does SWOT stand for?
SWOT is an acronym that stands for:
Opportunities

When analyzed together, the SWOT framework can paint a larger picture of where you are and how to get to the next step. Let’s dive a little deeper into each of these terms and how they can help identify areas of improvement.
Strengths in SWOT refer to internal initiatives that are performing well. Examining these areas helps you understand what’s already working. You can then use the techniques that you know work—your strengths—in other areas that might need additional support, like improving your team’s efficiency .
When looking into the strengths of your organization, ask yourself the following questions:
What do we do well? Or, even better: What do we do best?
What’s unique about our organization?
What does our target audience like about our organization?
Which categories or features beat out our competitors?
Example SWOT strength:
Customer service: Our world-class customer service has an NPS score of 90 as compared to our competitors, who average an NPS score of 70.
Weaknesses in SWOT refer to internal initiatives that are underperforming. It’s a good idea to analyze your strengths before your weaknesses in order to create a baseline for success and failure. Identifying internal weaknesses provides a starting point for improving those projects.
Identify the company’s weaknesses by asking:
Which initiatives are underperforming and why?
What can be improved?
What resources could improve our performance?
How do we rank against our competitors?
Example SWOT weakness:
E-commerce visibility: Our website visibility is low because of a lack of marketing budget , leading to a decrease in mobile app transactions.
Opportunities in SWOT result from your existing strengths and weaknesses, along with any external initiatives that will put you in a stronger competitive position. These could be anything from weaknesses that you’d like to improve or areas that weren’t identified in the first two phases of your analysis.
Since there are multiple ways to come up with opportunities, it’s helpful to consider these questions before getting started:
What resources can we use to improve weaknesses?
Are there market gaps in our services?
What are our business goals for the year?
What do your competitors offer?
Example SWOT opportunities:
Marketing campaign: To improve brand visibility, we’ll run ad campaigns on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Threats in SWOT are areas with the potential to cause problems. Different from weaknesses, threats are external and out of your control. This can include anything from a global pandemic to a change in the competitive landscape.
Here are a few questions to ask yourself to identify external threats:
What changes in the industry are cause for concern?
What new market trends are on the horizon?
Where are our competitors outperforming us?
Example SWOT threats:
New competitor: With a new e-commerce competitor set to launch within the next month, we could see a decline in customers.
SWOT analysis example
One of the most popular ways to create a SWOT analysis is through a SWOT matrix—a visual representation of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The matrix comprises four separate squares that create one larger square.
A SWOT matrix is great for collecting information and documenting the questions and decision-making process . Not only will it be handy to reference later on, but it’s also great for visualizing any patterns that arise.
Check out the SWOT matrix below for a simple example. As you can see, each of the quadrants lists out the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
![business plan group assignment [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
When used correctly and effectively, your matrix can be a great toolkit for evaluating your organization’s strengths and weaknesses.
How to do a SWOT analysis, with examples
A SWOT analysis can be conducted in a variety of ways. Some teams like to meet and throw ideas on a whiteboard, while others prefer the structure of a SWOT matrix. However you choose to make your SWOT analysis, getting creative with your planning process allows new ideas to flow and results in more unique solutions.
There are a few ways to ensure that your SWOT analysis is thorough and done correctly. Let’s take a closer look at some tips to help you get started.
Tip 1: Consider internal factors
Often, strengths and weaknesses stem from internal processes. These tend to be easier to solve since you have more control over the outcome. When you come across internal factors, you can start implementing improvements in a couple of different ways.
Meet with department stakeholders to form a business plan around how to improve your current situation.
Research and implement new tools, such as a project management tool , that can help streamline these processes for you.
Take immediate action on anything that can be changed in 24 hours or less. If you don’t have the capacity, consider delegating these items to others with deadlines.
The way you go about solving internal factors will depend on the type of problem. If it’s more complex, you might need to use a combination of the above or a more thorough problem management process.
Tip 2: Evaluate external factors
External factors stem from processes outside of your control. This includes competitors, market trends, and anything else that’s affecting your organization from the outside in.
External factors are trickier to solve, as you can’t directly control the outcome. What you can do is pivot your own processes in a way that mitigates negative external factors.
You can work to solve these issues by:
Competing with market trends
Forecasting market trends before they happen
Improving adaptability to improve your reaction time
Track competitors using reporting tools that automatically update you as soon as changes occur
While you won’t be able to control an external environment, you can control how your organization reacts to it.
Let’s say, for instance, that you’re looking to compete with a market trend. For example, a competitor introduced a new product to the market that’s outperforming your own. While you can’t take that product away, you can work to launch an even better product or marketing campaign to mitigate any decline in sales.
Tip 3: Hold a brainstorming session
Brainstorming new and innovative ideas can help to spur creativity and inspire action. To host a high impact brainstorming session, you’ll want to:
Invite team members from various departments. That way, ideas from each part of the company are represented.
Be intentional about the number of team members you invite, since too many participants could lead to a lack of focus or participation. The sweet spot for a productive brainstorming session is around 10 teammates.
Use different brainstorming techniques that appeal to different work types.
Set a clear intention for the session.
Tip 4: Get creative
In order to generate creative ideas, you have to first invite them. That means creating fun ways to come up with opportunities. Try randomly selecting anonymous ideas, talking through obviously bad examples, or playing team building games to psych up the team.
Tip 5: Prioritize opportunities
Now, rank the opportunities. This can be done as a team or with a smaller group of leaders. Talk through each idea and rank it on a scale of one through 10. Once you’ve agreed on your top ideas based on team capabilities, competencies, and overall impact, it’s easier to implement them.
Tip 6: Take action
It’s all too easy to feel finished at this stage —but the actual work is just beginning. After your SWOT analysis, you’ll have a list of prioritized opportunities. Now is the time to turn them into strengths. Use a structured system such as a business case , project plan, or implementation plan to outline what needs to get done—and how you plan to do it.
SWOT analysis template
A SWOT analysis template is often presented in a grid format, divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant represents one of the four elements.
Use this free SWOT analysis template to jump-start your team’s strategic planning.
Identify the strengths that contribute to achieving your objectives. These are internal characteristics that give you an advantage. Some examples could be a strong brand reputation, an innovative culture, or an experienced management team.
Next, focus on weaknesses. These are internal factors that could serve as obstacles to achieving your objectives. Common examples might include a lack of financial resources, high operational costs, or outdated technology.
Move on to the opportunities. These are external conditions that could be helpful in achieving your goals. For example, you might be looking at emerging markets, increased demand, or favorable shifts in regulations.
Lastly, let's address threats. These are external conditions that could negatively impact your objectives. Examples include increased competition or potential economic downturns.
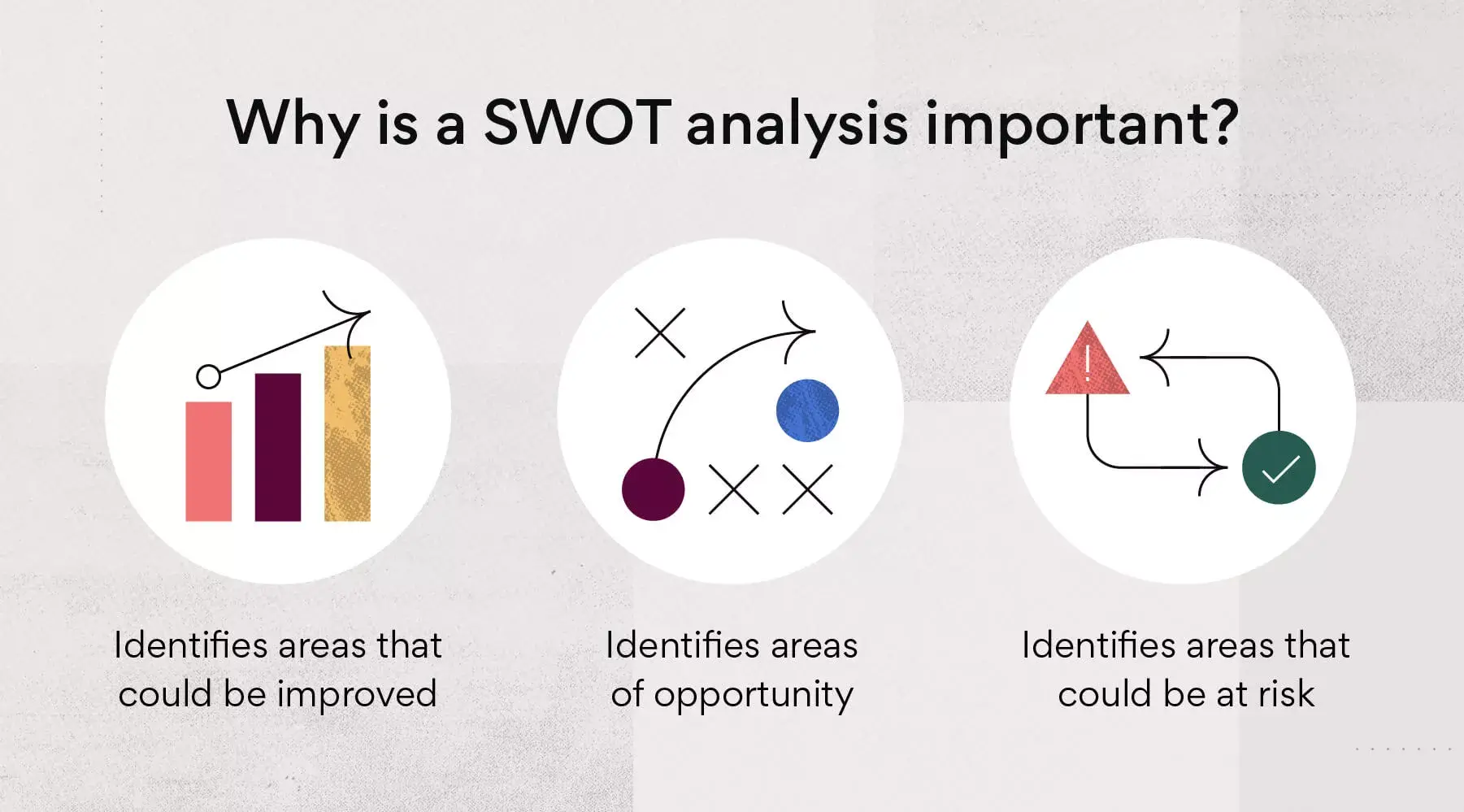
Why is a SWOT analysis important?
A SWOT analysis can help you improve processes and plan for growth. While similar to a competitive analysis , it differs because it evaluates both internal and external factors. Analyzing key areas around these opportunities and threats will equip you with the insights needed to set your team up for success.
A SWOT analysis isn’t only useful for organizations. With a personal SWOT analysis, you can examine areas of your life that could benefit from improvement, from your leadership style to your communication skills. These are the benefits of using a SWOT analysis in any scenario.
1. Identifies areas of opportunity
One of the biggest benefits of conducting an analysis is to determine opportunities for growth. It’s a great starting point for startups and teams that know they want to improve but aren’t exactly sure how to get started.
Opportunities can come from many different avenues, like external factors such as diversifying your products for competitive advantage or internal factors like improving your team’s workflow . Either way, capitalizing on opportunities is an excellent way to grow as a team.
2. Identifies areas that could be improved
Identifying weaknesses and threats during a SWOT analysis can pave the way for a better business strategy.
Ultimately, learning from your mistakes is the best way to excel. Once you find areas to streamline, you can work with team members to brainstorm an action plan . This will let you use what you already know works and build on your company’s strengths.
3. Identifies areas that could be at risk
Whether you have a risk register in place or not, it’s always crucial to identify risks before they become a cause for concern. A SWOT analysis can help you stay on top of actionable items that may play a part in your risk decision-making process.
It may be beneficial to pair your SWOT analysis with a PEST analysis, which examines external solutions such as political, economic, social, and technological factors—all of which can help you identify and plan for project risks .
When should you use a SWOT analysis?
You won’t always need an in-depth SWOT analysis. It’s most useful for large, general overviews of situations, scenarios, or your business.
A SWOT analysis is most helpful:
Before you implement a large change—including as part of a larger change management plan
When you launch a new company initiative
If you’d like to identify opportunities for growth and improvement
Any time you want a full overview of your business performance
If you need to identify business performance from different perspectives
SWOT analyses are general for a reason—so they can be applied to almost any scenario, project, or business.
SWOT analysis: Pros and cons
Although SWOT is a useful strategic planning tool for businesses and individuals alike, it does have limitations. Here’s what you can expect.
The simplicity of SWOT analysis makes it a go-to tool for many. Because it is simple, it takes the mystery out of strategic planning and lets people think critically about their situations without feeling overwhelmed.
For instance, a small bakery looking to expand its operations can use SWOT analysis to easily understand its current standing. Identifying strengths like a loyal customer base, weaknesses such as limited seating space, opportunities like a rising trend in artisanal baked goods, and threats from larger chain bakeries nearby can all be accomplished without any specialized knowledge or technical expertise.
Versatility
Its versatile nature allows SWOT analysis to be used across various domains. Whether it’s a business strategizing for the future or an individual planning their career path, SWOT analysis lends itself well.
For example, a tech start-up in the competitive Silicon Valley landscape could employ SWOT to navigate its pathway to profitability. Strengths might include a highly skilled development team; weaknesses could be a lack of brand recognition; opportunities might lie in emerging markets; and threats could include established tech giants.
Meaningful analysis
SWOT excels in identifying external factors that could impact performance. It nudges organizations to look beyond the present and anticipate potential future scenarios.
A retail company, for example, could use SWOT analysis to identify opportunities in e-commerce and threats from changing consumer behavior or new competitors entering the market. By doing so, the company can strategize on how to leverage online platforms to boost sales and counteract threats by enhancing the customer experience or adopting new technologies.
Subjectivity and bias
The subjective nature of SWOT analysis may lead to biases. It relies heavily on individual perceptions, which can sometimes overlook crucial data or misinterpret information, leading to skewed conclusions.
For example, a manufacturing company might undervalue the threat of new entrants in the market due to an overconfidence bias among the management. This subjectivity might lead to a lack of preparation for competitive pricing strategies, ultimately affecting the company's market share.
Lack of prioritization
SWOT analysis lays out issues but falls short on prioritizing them. Organizations might struggle to identify which elements deserve immediate attention and resources.
For instance, a healthcare provider identifying numerous opportunities for expansion into new services may become overwhelmed with the choices. Without a clear way to rank these opportunities, resources could be spread too thinly or given to projects that do not have as much of an impact, leading to less-than-ideal outcomes.
Static analysis
Since SWOT analysis captures a snapshot at a particular moment, it may miss the evolving nature of challenges and opportunities, possibly leading to outdated strategies. An example could be a traditional retail business that performs a SWOT analysis and decides to focus on expanding physical stores, overlooking the growing trend of e-commerce. As online shopping continues to evolve and gain popularity, the static analysis might lead to investment in areas with diminishing returns while missing out on the booming e-commerce market trend.
SWOT analysis FAQ
What are the five elements of swot analysis.
Traditionally, SWOT stands for its four main elements: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. However, a fifth essential element often overlooked is "actionable strategies." Originally developed by Albert Humphrey, SWOT is more than just a list—it's a planning tool designed to generate actionable strategies for making informed business decisions. This fifth element serves to tie the other four together, enabling departments like human resources and marketing to turn analysis into actionable plans.
What should a SWOT analysis include?
A comprehensive SWOT analysis should focus on the internal and external factors that affect your organization. Internally, consider your strong brand and product line as your strengths, and maybe your supply chain weaknesses. Externally, you'll want to look at market share, partnerships, and new technologies that could either pose opportunities or threats. You should also account for demographics, as it helps in market targeting and segmentation.
How do you write a good SWOT analysis?
Writing an effective SWOT analysis begins with research. Start by identifying your strengths, like a strong brand, and your weaknesses, like a small human resources department. Following that, look outward to find opportunities, possibly in technological advancement, and threats, like fluctuations in market share. Many businesses find it helpful to use a free SWOT analysis template to structure this information. A good SWOT analysis doesn't just list these elements; it integrates them to provide a clear roadmap for making business decisions.
What are four examples of threats in SWOT analysis?
New technologies: Rapid technological advancement can make your product or service obsolete.
Supply chain disruptions: Whether due to natural disasters or geopolitical tensions, an unstable supply chain can seriously jeopardize your operations.
Emerging competitors: New players entering the market can erode your market share and offer alternative solutions to your customer base.
Regulatory changes: New laws or regulations can add costs and complexity to your business, affecting your competitiveness.
How do you use a SWOT analysis?
Once you've completed a SWOT analysis, use the results as a decision-making aid. It can help prioritize actions, develop strategic plans that play to your strengths, improve weaknesses, seize opportunities, and counteract threats. It’s a useful tool for setting objectives and creating a roadmap for achieving them.
Plan for growth with a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis can be an effective technique for identifying key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understanding where you are now can be the most impactful way to determine where you want to go next.
Don’t forget, a bit of creativity and collaboration can go a long way. Encourage your team to think outside of the box with 100+ team motivational quotes .
Related resources
What are story points? Six easy steps to estimate work in Agile
What is a flowchart? Symbols and types explained

How to choose project management software for your team

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
- Productivity
A Quick Guide to the MoSCoW Method Technique
January 12, 2022 - 10 min read
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique used by project and campaign managers to work smarter not harder. In this quick guide, we’ll explain exactly what the MoSCoW method is, how it works, and provide some examples you can use to inform your own analysis. Keep reading to better understand the various categories within the MoSCoW method, as well as an alternative prioritization tool for project managers.
What is the MoSCow method?
The MoSCoW method is a technique used by organizations to communicate the importance and priority of the various requirements being met in various projects. This method is also referred to as MoSCoW prioritization and MoSCoW analysis.
The term MoSCoW is an acronym that refers to the first letter of each of the four priority categories. It uses four categories, which are must-have, should-want, could-have, and will not have. While it’s meant to be used at the start of a project when time is on your side, it can also be adapted to work seamlessly for time constraints .
Software developer Dai Clegg originally created the MoScoW method. Since then, many other leading companies have used it to get their team on the same page, properly distribute resources, and achieve project goals.
How does the MoSCow technique work?
The MoSCoW technique works by allowing teams to include multiple representatives from the organization in their project management discussions. This gives everyone a wider perspective on the organization's operations and where their collective priorities lie.
Before you begin your MoSCoW method, think about which people can provide valuable context for your team. They can help you identify opportunities and threats, and they can help you make better decisions. Once finalized, the MoSCoW method will also force stakeholders to show evidence before they can submit additional work requests mid-project.
Critics of MoSCoW often say that it does not include a comprehensive objective scoring system for all initiatives. This is a common mistake that many teams make. A weighted scoring method will more accurately measure the backlog against a set of predefined benefits and costs.
One of the most challenging aspects of the MoSCoW technique is learning which categories their initiatives should go in. As the manager, you will need to know which of your team's initiatives are “must haves” for their product or which are merely “should haves”.
You may even need to solicit feedback from a different department in order to get greater perspective on your current project prioritization. For example, a marketing department head may have greater insight into which selling points for your upcoming product launch are resonating more with buyers so that you can work on perfecting those components first.
Another key idea about how the MoSCoW technique works is that it’s only effective if you follow it. This means that, once an initiative is placed into a category, the entire team needs to stick to that decision. Many beginner MoSCoW teams end up agreeing that an initiative should have been initiated, but they move on to the next step instead because it feels better or more familiar to them.
Finally, when it comes to making decisions about prioritization, your team will need to have a consistent framework in place before you engage with this technique. A consistent framework for assessing and ranking all initiatives is critical if you want to avoid biases and falling into old patterns.
Your team’s prioritization strategy helps set expectations across the organization. It lets them know that they have made the right decisions and weigh all the factors that go into making those decisions. Don’t be afraid to make your MoSCoW method results available to the rest of your organization if applicable.
Understanding MoSCow prioritization categories
Before the MoSCoW analysis can begin, all participants need to agree on which initiatives will be prioritized. It's important to discuss how to resolve disagreements in order to prevent them from holding up progress during this preparation stage. This can help prevent issues from happening in the first place.
Once the framework has been established, it is time to start identifying the appropriate categories for each project. Here are the definitions and explanations of each of the MoSCoW prioritization categories:
Musts are defined as initiatives that are critical to the success of a project or product. These are usually non-negotiable and can be used to describe specific functionalities or solutions that need to be implemented.
The “must have” category is challenging to define. Before you start, ask yourself if something is truly necessary in this category.
Should have
Although “should have” initiatives are not essential to a product or project, they may add significant value. A “should have” initiative is different from a “must have” initiative, which means it can be scheduled for a future release.
“Could haves” are initiatives that are not necessary to the core of a product. Projects that are placed in the “could have” category are often the first ones to be deprioritized when another project takes longer than expected.
Will not have
The MoSCoW method places several initiatives in a “will not have” category. This method allows you to manage expectations about what will not be included in a release or another timeframe.
Putting initiatives in the “will not have" category can help prevent scope creep . This category shows the team that the project is not a priority at this specific time frame.
Some initiatives are prioritized in the “will not have” group, while others are likely to happen in the future. Some teams then decide to create a subcategory for these initiatives.
How is the MoSCoW method used in project management?
The concept of MoSCoW allows project managers to prioritize tasks that can be done efficiently even when they have limited time. For example, if the team has a tight budget, it can use MoSCoW to determine which initiatives can be completed within those limitations.
This is especially useful for managers juggling more than project or leading cross-functional teams. This is because cross-functional teams are sometimes obligated to another company or department’s priorities. While your team is working on a new product release, another project manager may have them on a tight timeline for another client’s goal.
And, as we all know, things come up throughout the lifespan of a project. Although efficient planning helps teams remain agile, the MoSCoW method can make even the biggest and most unexpected roadblocks more manageable.
MoSCoW examples
This method can be used for nearly any industry or project type because it has to do more with project decision-making than the subject matter itself. Here are a couple of MoSCoW method examples you can use to get started with your first draft:
1. National College of Ireland’s website project
In this example from a lecture on the MoSCoW analysis, Professor Eugene O’Loughlin demonstrates how to use this technique when building a website .
The project goal in this example is to create a platform where users can securely log in and access files. Because of this, the tasks listed under their MoSCoW categories will look different from other standard website creation projects.
For example, while another project may add “have an eye-catching design” to their should-have section, this particular website has added “password retrieval” because it directly applies to their security-oriented goal.
Even if this website project could benefit from a great design, the MoSCoW method helps managers and teams laser focus on completing the highest priority activities first. If they have more time later on, they can potentially add a design improvement task to their “could haves” if they determine the ROI is high enough.
Takeaway: Consider your project holistically when assigning priority. Your goals should be your north star for determining what is or is not truly important, regardless of what conventional wisdom says to do.
2. Slideteam’s Assessing HR Requirements Template
This is one of the MoSCoW examples that shows how many different types of tasks this technique covers. Here, we see storing employee leave history as a must, leave letter printing a should, notifications for pending leave dates a could, and remote access a won’t.
In HR, many of their decisions around prioritization will be made by compliance and legal counsel that they must adhere to. Still, it’s important to define these tasks and their MoSCoW label so that employees understand at a glance that it’s less important to set up leave notifications and more important that they update employment histories in their software.
Takeaway: The MoSCoW method can be used to cover many different aspects of projects including compliance and procedure.
How to undertake a MoSCoW analysis using Wrike
Wrike is a project management software that allows users to strategize how they prioritize their portfolio of projects as well as the tasks within each individual initiative. Using visual tools such as road maps that show what progress will look like from kickoff to completion, managers can easily see which of their chosen MoSCoW analysis configurations work best for achieving their goals.
Wrike also allows you to centralize all of your project planning in one central location. You can view potential resource conflicts across projects, individual task progress statuses, and automate tasks from your should or could have categories that you otherwise wouldn’t have time for.
Ready to get started with the MoSCoW method and Wrike? Sign up for a two-week free trial today.

Maria Waida
Maria is a freelance content writer who specializes in blogging and other marketing materials for enterprise software businesses.
Related articles

An Introduction to Bullet Journal Project Management
Bullet journals are great tools to destress and organize various aspects of project management. In this guide, we’re diving deep into the pros and cons of using this method to organize projects of all kinds. Keep reading to discover what bullet journal project management is and how this practice can boost productivity to new levels. What is a bullet journal? A bullet journal is a customized space to organize all of your personal projects and goals. It can also be used to track deadlines and prioritize tasks. Bullet journaling became popular thanks to the book Getting Things Done, which is about a project management technique that uses a bullet journal to manage different projects efficiently. Bullet journals are often used to create daily, weekly, and monthly project plans. They can also be home to your to-do lists, inspiration boards, and project notes. They’re relaxing to create and relatively easy to maintain. If you have multiple projects to manage, then you may want to use more than one notebook. Or you can swap your physical journal for a professional services management software that has plenty of space for storing digital plans. Software tools are also easy to customize, make collaboration easier, and help with turning the plan into reality through task creation and assignment tools. With Wrike, data from multiple users will automatically sync so that everyone is on the same page with new updates and responsibilities. If you do use a physical journal, using loose leaf paper in a binder will allow you to add pages as you go. This is useful for keeping track of all the data in one place instead of switching to additional notebooks when you run out of room. There are many elegant, decorated bullet journal page layouts out there. Many invest time into making them artistic with drawings, decorative tape, and cut-out images. This isn’t necessary for project management, but it may be a fun activity outside of work. Bullet journals can use several different layouts. The most common is a two-page spread that includes a month-long calendar on one page and a breakdown of goals for that period on the other. The latter will help you keep track of all the dates and commitments that are important to you as you get closer to starting a new project. The two-page spread makes it easy to see where you'll be working most efficiently in the coming weeks. It's ideal for people who manage multiple projects simultaneously. You can also create a view of the next six months within your bullet journal project management layout. This is called a future log. A future log is a calendar that lets you keep track of important events and dates for long-term projects. How do you use a bullet journal in project planning? Projects are essentially collections of notes and tasks that are linked to a common goal. They can be pulled together in a bullet journal for you to easily see all of the work related to that specific project. To start, you’ll need to list out your goals. Create a list that includes every project goal you or your team can think of. Sort them in order of importance. Ideally, these smaller project goals will align with your organization’s big-picture goals. Once you know what you’d like to accomplish, you can begin your bullet journal. Start by breaking down your number one goal into a project action plan. This can span days, weeks, or months. Then, break down your project action plan into individual tasks. Determine what the task is, who will be in charge of getting it done, and when it needs to be completed. After that, you’re ready to use your bullet journal for project planning. Step 1: List out your sections Number your pages if they aren’t already. At the beginning of the bullet journal, write the name of the page on the left side and the page number on the right. Step 2: Add your key You may use symbols and abbreviations throughout your project planning. Put these at the beginning of the journal either after or on the same page as your key. Use color coding to signify which symbols belong to each project if you have more than one. Step 3: Write out your future log A future log is a list of key dates and tasks that aren’t part of your immediate three-to-six month plans but are important to keep in mind. Add this after your key and leave space for other items as they come up. Step 4: Create your calendar This can be in the form of a traditional calendar page. Some people like to hand draw them. However, you can also print, cut out, and paste a blank monthly calendar page into your journal too. Step 5: Track tasks Create sections for monthly, weekly, and daily task lists. You can organize these in a few ways. Some project managers prefer to do it by project or by person. You can also create one massive list with everything you’re personally responsible for so you have it all in one place. Or use a combination of any of these for your various projects. Make sure to check in with your bullet journal weekly and monthly. Note any upcoming or past deadlines. Adjust your task list and schedule for unexpected issues as needed. The benefits of using a bullet journal for work Project managers often have a hard time keeping track of their work activities without losing track of anything along the way. This is one of the reasons why the bullet journal is so useful. Not only does it give you a roadmap of your next projects, but it’s also good for daily use. You can keep track of to-do lists, priorities, and daily reflections. You can also journal about your progress and realign with goals all in the same notebook or tool. You can also rapidly log your thoughts for the day to boost your creativity and clear out emotions that no longer serve the project. Combine your bullet journal for work with your personal goals. It will be easier to prioritize and accurately schedule tasks when you have your entire life laid out in front of you on paper. Another benefit of using a bullet journal for work is that you can either DIY a notebook or use a planner you already have. It’s not so much what you use but how you use it. And bonus: bullet journaling only takes five to 15 minutes a day. Whether it’s reviewing tomorrow’s meetings or crossing off today’s tasks, a bullet journal practice is easy to build into your schedule no matter how busy you are. The disadvantages of using a bullet journal in project management While bullet journaling project management is great for keeping track of key project details, many project managers need a separate system to manage their meetings and reports. Having more than one journal or calendar to manage at one time can be confusing. Add more than one project to the mix, and it may be counterproductive to use a traditional pen and paper bullet journal to accomplish your goals. Another disadvantage of using a bullet journal in project management is your lack of ability to collaborate with others. When writing on paper, you have to either show your team the notebook in person or scan the pages and share them online. Either way, it’s not ideal for large, remote, and/or revolving teams. The other thing to know about bullet journaling before diving in headfirst is that it can be quite time-consuming. If you do a crafty layout with calligraphy and scrapbooking accessories, then it may even take several days to finish. And once you do have your plans laid out, they can be hard to change. Rewriting, erasing, and making more space for things that come up are essential for project planning. For that reason, we suggest using an 11 inch by 7 inch grid lined notebook to give yourself extra space. Also, you can outline headlines and calendars with a pen or marker if you like the look. But stick to pencil for any factual information that is subject to change throughout the lifetime of the project. If you don’t do this now, you may end up having to scrap entire pages and start over later on. Bullet journal alternatives you should consider Bullet journals are fun, unique, and creative. But there are some projects where they just aren’t the best possible option for managing it all. The project may be too complex or too large for a single notebook. There may even be so many updates needed that a physical notebook doesn’t make sense for your project. If you’re facing any of these issues, you can try any of the following bullet journal alternatives: Digital calendar and list app combo Bulletin board, sticky notes, and shared files Project management software Project management software is the top choice for bullet journal alternatives. Not only is it flexible, but it can make project planning more productive. Wrike is the ultimate platform for customizing your own bullet journal project management processes. With over 30 predefined apps you can use to sync all your project data in one place, it's the most versatile platform for managing complex tasks. As a single source of truth for a project, team, and entire organization, project management software offers more advanced features than a simple notebook can. Instead of writing everything down on a few sheets of paper, Wrike acts like a living document. And unlike other digital organization tools, Wrike is specifically built to optimize project performance and success. Wrike's tools are designed to work seamlessly with any team. Anyone who has permission to access the project can share files and tasks quickly and easily. Once uploaded, collaborators can visually edit and obtain files. They’ll also have access to reports and tasks that are simple to understand at a glance without losing the details in the process. This allows all managers to gain visibility across departments and groups. Wrike is the ideal solution for teams that want to grow and operate efficiently with the help of cutting edge technology. For example, Wrike’s Work Intelligence helps you get started with the next generation of work, with AI-powered projects and automation. Wrike also features a streamlined UI that lets you customize its features to work seamlessly with your team. Although bullet journaling allows you to customize your project planning, you’ll be able to get and implement feedback from partners faster with a digital project tool. Here are some other stand out benefits of using a project management software over a physical or digital bullet journal: It’s interactive. For example, Wrike offers Gantt charts that lets users visualize their plans and progress. It’s efficient. Kanban boards make it easy to work seamlessly with Agile teams by creating and sharing whenever needed. It’s faster. Wrike's template library is designed to help you quickly create and manage complex projects. It’s customizable. With custom request forms, you can easily gather details for your intake, assign tasks to the right teams, and dynamically route questions and requests. It’s up to date. Wrike’s calendars are ideal for team members who want to keep up with the latest information. It’s repeatable. Most tasks go through the same steps before they are finished. In a project management solution, you build a path for yours that will automatically assign and notify people when it's ready to begin through Wrike’s Automation Engine. It’s trackable. With timers, approvals, and visual task assignments, you can manage entire teams while streamlining your work. It’s transparent. Get a 360 view across all of your organizations with custom dashboards. It’s syncable. Wrike's 400+ app integrations make it possible to integrate hundreds of apps into one central hub. It’s safe. A digital project management software can safeguard your data by enforcing rules and encryption key ownership. Ready to upgrade your project planning methods and tools? Check out Wrike’s two-week free trial for some more goal-achieving features.

What Is The Pomodoro Technique and How Does it Work?
Endless tasks and expectations from colleagues and employers can make getting things done hard. There’s always something else to add to your to-do list and, as that list grows, it starts to feel like there’s never enough time to do it all. Productivity hacks can seem gimmicky and semi-helpful at best. But what if there was a time management strategy that could help you tackle your to-do list, meet others’ expectations, and help you feel more productive and balanced? That’s where the Pomodoro Technique comes in. This popular time management strategy can help you better plan your workload, overcome distractions, and check tasks off your list. And it doesn’t require working overtime or jamming more work into your day. Instead, it encourages frequent breaks in between stints of work. Perhaps one of the best aspects about it is that it’s easy to use. We’re here to help you make your workdays better and more productive. In this guide, we’re breaking down the Pomodoro method — how to use it, why it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. And don’t worry, we’ll cover what Pomodoro means while we’re at it. Add reading this guide to your list of to-dos for today, and let’s get started. What is the Pomodoro Technique? The Pomodoro Technique is a productivity or time management method created in the early 1990s by Francesco Cirillo. A university student at the time, Cirillo struggled to focus and get his assignments done. Feeling overwhelmed, he realized he needed to try a new way of working and held himself accountable for committing to 10 minutes of focused time while studying. As he committed to the challenge, he found a tomato-shaped timer (you guessed it, Pomodoro is “tomato” in Italian), and the Pomodoro Technique was born. Cirillo wrote an entire book about the Pomodoro Technique, but the gist of it is simple. The method encourages short bursts of manageable chunks of work with breaks built in between. With this method, you work for 25-minutes sessions separated by five-minute breaks. After every four or five Pomodoros (think of these as work sessions), you indulge in a more extended break for 15-20 minutes. With a sense of urgency built into it, the method forces you to think through your to-do list and eliminate distractions while progressing on your tasks for a limited amount of time. And you can eliminate distractions knowing that you have breaks built into your day to look forward to. Let’s start by understanding what exactly the word “Pomodoro” means and where it came from. What does Pomodoro mean? Pomodoro quite literally means “tomato” in Italian. But what does a tomato have to do with time management? Like we mentioned earlier, Cirillo used a tomato-shaped timer to help him manage his focused work time. He later named his famous technique after the tomato-shaped kitchen timer that helped him do his best work. When we talk about the Pomodoro Technique, a Pomodoro also refers to one 25-minute focused work session. You’ll use a timer to work for one Pomodoro. Get it? Don’t worry — we’ll walk you through the nitty-gritty of how to use the Pomodoro Technique next. How to use the Pomodoro Technique One of the best parts of the Pomodoro Technique is that it’s super simple to use without any training. Depending on who you ask, these steps may vary slightly. But that’s one of the best parts about the method — you can customize it. Here’s how Cirillo’s Pomodoro method works: 1. Make a list of the tasks you need to accomplish To make the best use of your Pomodoro sessions, consider starting your day by creating a to-do list and outlining the tasks you need to accomplish. Don’t panic if your list becomes lengthy! Remember, you’re going to split up your work so that it’s more manageable throughout the day. You just need to make a note of what you need to accomplish today. Tip: When you make a list of your tasks, think about how much time you need to complete each task. For example, one task might take you a full 25-minute Pomodoro. Or you might have three short tasks that you can group during one Pomodoro. Write down how many minutes each task will take. That way, you can pair up tasks that will take less than 25-minutes to complete. Your estimations don’t have to be perfect, but you want to avoid having gaps of time to fill or going past time during your Pomodoro sessions. 2. Set a timer for 25 minutes You don’t have to mimic Cirillo exactly and use a tomato-shaped kitchen timer, but to live the complete Pomodoro Technique experience, give a real timer a try. It doesn’t matter if you use a virtual or physical timer; any will do. Here are a few options to choose from when selecting a Pomodoro Technique timer: Pomodoro tomato timer Online tomato timer Focus Keeper app Pomodoro Timer Lite app The timer you use doesn’t need to be overly cumbersome or have any fancy capabilities, so don’t get caught up in the details. Keep it simple to make it most effective. 3. Focus on your tasks until the timer goes off This is the tricky part. Once you’ve set your timer, you need to work on the task or tasks you’ve chosen for 25 minutes without any interruptions throwing you off track. Combating distractions is no easy feat, and it may take practice to nail this step. Tip: If possible, alert those around you when you’re using the Pomodoro method. This can help reduce interruptions and external distractions. If you find yourself with spare time during a Pomodoro and aren’t sure what to focus on, Cirillo recommends taking advantage of the opportunity for overlearning. Use the time to make improvements and tidy up your work, reflect on the tasks you completed, or make a note of what you’ve learned until the timer goes off. Use the 25 minutes as best you can and avoid starting your break early if possible. 4. Enjoy a short break for five minutes You made it! Time is up and you can enjoy a break for five minutes or so. Consider using this time to use the restroom, grab a snack, or fill up your water bottle. Give your eyes a break and try to limit screen time if you can. Get up and stretch your legs or move your body around. Taking care of your well-being will help you stay motivated throughout the remainder of the day. 5. Repeat steps the first four steps Are you getting the hang of it? Rinse and repeat the above steps. After you’ve completed four Pomodoros, skip step four and jump straight to step six. 6. After every four or five Pomodoros, enjoy a more extended break You’ve earned it! Enjoy a longer, restorative break this time. Take 15-20 minutes to rejuvenate yourself. Maybe it’s time for breakfast or lunch. Or perhaps you want to spend a few minutes outside in the sun. Whatever the case may be, use your break wisely and prepare to jump into more Pomodoros after the break. That’s it. The Pomodoro Technique is an easy-to-use system, which means there isn’t much of a learning curve to start using it to your advantage. Does the Pomodoro Technique work? It sounds simple, right? That means you might be asking yourself whether the Pomodoro method truly works or not. Reviews of the method spread amongst the internet suggest that many have seen success when using the technique. One person found that the Pomodoro Technique was a great solution for monotonous tasks on the to-do list. Knowing that they only needed to work on a task for 25 minutes encouraged them to get started on those dreaded, tedious to-do’s. Another person found success using the Pomodoro Technique and later adapted the method to fit their specific needs. The Pomodoro Technique helped them define a practice of self-discipline to expand on and boost productivity. But what is it about the Pomodoro Technique that makes it work? Studies suggest that brief mental breaks help keep you focused. Frequent distractions rob us of productivity at work, but the Pomodoro method helps eliminate distractions for more focus in the workplace. As with any time management strategy, what works best for some may not work well for others. Give the Pomodoro Technique a try and tailor it to your individual needs to ensure it has the most payoff for you. The advantages and disadvantages of the Pomodoro method As with any time management strategy, the Pomodoro Technique has both benefits and drawbacks to consider before experimenting with it. Let’s take a look at both, starting with the advantages. Advantages of the Pomodoro Technique Break the habit of multitasking When you follow the Pomodoro Technique, you’ll break the habit of multitasking. While multitasking might seem like a great way to get more done, it’s distracting and actually hinders your productivity. With the Pomodoro method, your goal is to dedicate your focus to any given task at hand — and save the rest of the items on your to-do list for another Pomodoro. Reduce or prevent feelings of burnout Looking at your neverending to-do list can feel overwhelming and stressful, and working through that list without a strategic plan in place can cause feelings of burnout. The Pomodoro Technique not only encourages frequent breaks but it builds them directly into your schedule for you. You can reduce or prevent stress and burnout by taking full advantage of your breaks when you have them. Reduce procrastination We all procrastinate now and then, but the Pomodoro Technique ignites a sense of urgency in the day, which reduces or eliminates procrastination. There isn’t any time to scroll through your favorite social media platform, grab another snack, stare out the window, or engage in another distraction when you know you only have 25 minutes to complete a task. (Don’t beat yourself up — we’re all guilty of these things!) Disadvantages of the Pomodoro Technique Some tasks take more than 25 minutes The Pomodoro method is said to be beneficial for tasks like writing, coding, and studying. It also comes in handy when needing to work through some monotonous to-dos like cleaning out your inbox or digging into some administrative items. But some tasks are bound to take more than 25 minutes to complete, which means the Pomodoro Technique may not always work for every type of project or task. If you’re in the middle of a project and are in a solid flow state, you might want to keep working past the 25-minute timer mark, which will interrupt all subsequent Pomodoro scheduling. You know your work styles and productivity best, so you’ll be in charge of making the judgment call on whether you need to work past the timer’s buzz. Meetings could interfere with your Pomodoro planning The Pomodoro method sounds particularly beneficial to those who have full control over their schedules. But many career professionals are bound to be interrupted by planned and unexpected meetings. Your meeting schedule could interfere with how you plan your Pomodoros or could interrupt you in the middle of a Pomodoro session. Every time management strategy comes with advantages and disadvantages, and no method is guaranteed to be one-size-fits-all. Since the Pomodoro method is easy and comes without cost, consider giving it a try to see if it works for you. Remember, you can always tweak it to suit you best. How to use Wrike to plan your Pomodoros To set yourself up for success when using the Pomodoro Technique, you’ll want to have a to-do list prepared. A project management tool like Wrike can help you organize your tasks so that you can dive right into your Pomodoros (without wondering what you should start with). With Wrike, you can: Manage and prioritize your work Use templates to organize and break your projects down into manageable tasks Track your time to understand how you’re spending it Manage workloads with resource management capabilities You’re on your way to a more productive workday. Start your free trial of Wrike and begin planning your Pomodoros today.

Moore’s Law and the Productivity Problem
As the year draws to a close, developing strategies for how to be more productive and finish the year off strong is on every team’s mind — regardless of department or industry. According to a study by California-based management platform Redbooth, the month of the year that we are at our most productive is October, followed by November, then September. The fall provides a feeling of a new start for many businesses, with the desire for shiny new productivity tools and aids bringing us back to our school days. But, while a new pencil case or a multi-colored pen can work wonders, today’s organizations are looking to much more sophisticated tools to boost their productivity. Note-taking apps, instant messaging platforms, virtual to-do lists, calendar tools — our desktops are overflowing with software designed to make us our most productive selves. But, with so many conflicting apps clouding our vision, it can often be difficult to get anything done at all. So, why are we so inclined to constantly invest in new technology, believing it will exponentially increase our productivity levels? This concept is commonly referred to as Moore’s Law, and it’s important to understand it if you’re concerned about your team’s or your own productivity levels. What is Moore’s Law? Let’s start off with a simple enough question: what is Moore’s Law? The origins of Moore’s Law lie in IT and computer hardware. It is the principle that the speed and efficiency of a computer can be expected to double every two years, while the cost decreases by half. Moore’s Law is named after Gordon E. Moore, the co-founder of Intel, who made this observation of exponential growth in 1965. You will have no doubt experienced Moore’s Law for yourself over the last decade, as the need to purchase a new phone or laptop normally begins to creep up every two years or so. While the technical capabilities of your gadget will have grown hugely, the price largely remains standard. We then begin to fall into a cycle of purchasing new technology as a habit, stretching our view to include phones, computers, exercise aids, entertainment systems, and, yes, productivity tools. Moore’s Law and endless productivity tools Of course, Moore’s Law has huge benefits for the technologically-driven society that we live in. The standards of the technology that we rely on can even be linked to Moore’s Law. The overarching idea of Moore’s Law — that speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of technology is constantly evolving at a rapid pace — could apply to productivity tools and solutions. The need to update and reinvest in the ever-growing ecosystem of productivity tools and software every few years sees many teams losing themselves to too many apps. In 2015, the average number of cloud applications per company was 73. In 2020, that number had increased to 163. So much so, that 56% of IT executives are now reporting having to use manual spreadsheets to keep track of all their SaaS apps — defeating their productivity goals before they’ve even started. This concept is commonly known as ‘SaaS sprawl,’ a term that refers to the dilemma of an organization’s tech stack being so expansive that it becomes unmanageable and causes visibility problems across departments. $40 billion is estimated to be spent on unused software each year, and the number of apps we are downloading continues to rise. Many teams believe themselves to be more productive than ever, when really, spending so much time flicking between apps, tools, and software stifles creativity and raises burnout to an all-time high. How your team can effectively invest in productivity If your organization has fallen foul to overindulgence in productivity tools and gadgets, don’t worry. There are plenty of ways to empower your teams and teach them how to be more productive without overwhelming themselves with dozens of productivity platforms. Consider toxic productivity The concept of toxic productivity relates to an unattainable desire for increased productivity, at the expense of other priorities, such as family or health. Toxic productivity is a real issue for many teams, especially if both our personal and work devices are overrun with technology that is constantly drawing us back to working mode. Consider whether your team could benefit from a digital detox of work-related technology, and set boundaries for after-hours work communication. Turn your attention to other methods of increasing productivity There are plenty of ways to increase productivity and wellbeing at work that have nothing to do with technology. For example, has your organization invested in a flexible work structure, allowing employees to choose where they work best? Could your business go the extra mile and trial a four-day workweek? Could your employee recognition programs use some extra love? These are all areas to consider when brainstorming how to be more productive across the board. Making the most of all-in-one technology like Wrike Of course, technology will always be a cornerstone of a successful business, and continuing to use productivity tools in some way at work is non-negotiable. But which tools should you invest in? What are the most important features of work management software that can actually increase productivity by up to 40%? Workflow automation: With Wrike’s custom request forms and automated task assignment, your team will never miss important tasks and details because of a cluttered workspace. App integration: Using so many apps can be tiresome and inefficient, with details and updates often being missed by team members. Wrike’s work management includes over 400 app integrations, so the constant context switching can stop. Single source of truth: Trawling through emails and messaging apps to find important documents and updates is time-consuming and frustrating for teams. Keeping everything organized in one centralized hub, where users can comment, edit, and give feedback, is a life-saver for teams who wish to be more productive. Collaborative features: Whether your team works in-office, remotely, or under a hybrid model, breakdowns in communication are one of the most common challenges to successful projects. Wrike’s collaborative features, including @mentions, real-time editing, and email and chat app integrations means that your team all have the same view, no matter where they are. Want to know more about how Wrike can boost your team’s productivity? Try out a free two-week trial today.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
Ukraine war latest: 'Let Ukraine strike back!' - Calls to remove restrictions on use of Western weapons
Ukrainians gather outside the US embassy in Kyiv as part of mounting demands to remove restrictions on the use of Western weapons. Meanwhile, Volodymyr Zelenskyy warns Moscow is amassing more troops on the border and preparing to intensify its invasion on the second front near Kharkiv.
Sunday 26 May 2024 23:45, UK

- Zelenskyy warns Russian troops preparing to intensify attacks on second front
- Number killed rising after Russian attack on DIY store kills more than 40 people | 16 confirmed dead
- Ukrainian boy, 13, takes DNA test to identify father's body
- Eyewitness: Russia producing shells three times faster than Ukraine's allies
- Live reporting by Michael Drummond and (earlier) Brad Young
Vladimir Putin has arrived in Uzbekistan ahead of formal talks on Monday.
The Russian president laid a wreath at a monument to Uzbekistan's independence in the capital, Tashkent.
He is expected to hold formal talks with President Shavkay Mirziyoyev that are expected to focus on deepening the countries' relations.
The pair spoke in what were described by the Kremlin as informal talks on Sunday.
The visit is President Putin's third foreign trip since being inaugurated for a fifth term in May.
He first went to China , where he expressed appreciation for China's proposals for talks to end the Ukraine conflict, and later to Belarus.
For context: Now separated from Russia by Kazakhstan in central Asia, Uzbekistan was once part of the Soviet Union.
However, the invasion of Ukraine is believed to have accelerated a process of reducing Russian influence in the country.
In the two-plus years since February 2022, Uzbekistan has also boosted its relations with the EU.
Fighting continues along the Kharkiv frontline as Russian forces try to overwhelm defenders.
In an update on Sunday evening, Ukraine's armed forces said its troops were seeking to repel attacks and in places have mounted offensives.
The General Staff said on social media: "The Russian aggressor is trying to use superiority in manpower and equipment and air support.
"Ukrainian soldiers are giving battle to the enemy, and in some directions they themselves are carrying out effective assault actions to improve the stability of the defence and restore positions."
Twelve clashes were reported in the direction of Kharkiv, the update said, as well as near the villages of Lyptsi and Ternova.
"The situation is under control," the statement said.
Ukrainians gathered outside the US embassy in Kyiv as part of mounting demands to remove restrictions on where Ukraine can use Western weapons.
Many NATO countries who provide military aid to Ukraine currently do so on the condition that it is not used to strike targets inside Russia.
The US and Germany in particular have been strict on this issue, likely out of concern about escalation with Moscow.
Other countries - the UK and Sweden, for example - have confirmed or suggested that Ukraine can use their weapons to hit targets across the border.
In Kyiv today, activists held up placards saying "let Ukraine strike back" and "remove the restriction".
The US will participate in Volodymyr Zelenskyy's peace summit next month, an official has said.
It comes after the Ukrainian president called on America's President Joe Biden and China's President Xi Jinping to attend the event.
However the US official did not say who would attend or at what level.
The summit, co-hosted by Switzerland, starts on 15 June and, according to President Zelenskyy, 80 countries have already confirmed their attendance.
Battling against the odds, the Ukrainians say they have become skilled at trying to make every round count.
"Often, with just one, two or three shells, we can completely destroy a target," said Senior Lieutenant Kostiantin, an artillery battery commander with the 57th Brigade.
His troops are fighting against a new Russian invasion into the Kharkiv region, in the northeast of Ukraine.
"We have to keep holding the Russians back… and make every metre of land they try to take cost them hundreds of lives."
Watch this report from our defence and security editor, Deborah Haynes :
Crowds of people marched through the Georgian capital, Tblisi, today to mark the country's Independence Day - and also to protest against the government's divisive "foreign agents" law.
The legislation is seen by some as threatening press and civic freedoms and there are concerns it's modelled on laws used by Vladimir Putin in neighbouring Russia.
Hundreds of people walked through the city on Sunday, as the EU anthem played.
Many held white and red Georgian flags, others the blue and yellow of the EU or the stars and stripes of the US.
There was also a military parade in the city centre as part of the celebrations, attended by Georgia's president and prime minister.
The pair are at odds over the "foreign agents" bill after President Salome Zourabichvili vetoed the bill.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy posted on social media congratulating the Georgian people on their Independence Day.
"Both our nations know all too well that freedom and independence are won rather than granted," he said on X.
"I wish the Georgian people to prosper and strengthen their statehood and ties will all other free nations. I also wish magnificent Georgian culture, identity, and hospitality to multiply over the years."
The parents of a Ukrainian girl who died after a Russian missile strike have bid goodbye to their daughter in emotional scenes at her funeral.
Just five years old, Zlata Rostochil was seriously wounded in an attack at the end of April and later died.
Today, her mother Nadiia and father Vyacheslav knelt beside her body during the memorial service in Odesa.
Other mourners stood solemnly behind them holding candles.
Russian forces are making "maximum efforts" to break through Ukraine's defences, amid fighting on the frontline near Kharkiv.
Kyiv's armed forces said there have been 83 clashes with the enemy on Sunday.
"Ukrainian troops are taking measures to maintain positions and destroy the offensive potential of the enemy," the General Staff said in an update on social media.
It said there were "no major changes" in the direction of Kharkiv but Russian troops continue to mount offensives around Vovchansk city and the village of Lyptsi.
Is National Service a good idea?
Rishi Sunak has talked a lot this week about security in Europe and the need to invest in defence - and then he announced that he would bring back National Service.
Our military analyst Sean Bell broke down the announcement on Sky News earlier...
By John Sparks, international correspondent
If the war in Ukraine was fought in the media alone, the Russians would have been repelled months, or even years, ago.
While the Kremlin funds "debate shows" with far-right nationalists spouting historical theories from the 19th century, the Ukrainians fight their corner with slickly-produced content highlighting every aspect of their defence.
Want to see the Ukrainians blowing up Russian tanks? That will be on X.
The petition to send clapped out cars in London to the Ukrainian military? Head to "Insta".
The passionate address where President Volodymyr Zelenskyy speaks from a burnt-out book-making factory, pleading with Joe Biden and Xi Jinping to turn up at a peace summit?
That dropped this morning.
Read more:
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A3: BUSINESS PLAN REPORT (Group Assignment) Prepared by: No. Student Name Student Matrix Number 1 ROSDIAH BINTI ROSLAN 2021246266 2 NURFAZRINA SYZWIN JASRI 2021226986 3 MARKRANDY MARCUS 2021672824 4 DEXTER EARL CHARLES TINDI 2022194629. Prepared for: MADAM RUSIYAH BINTI BANDI. Date of Submission: 01 ST JANUARY 2023. TABLE OF CONTENT
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Rice University's Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51, 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2.
ENT300 BUSINESS PLAN (GROUP ASSIGNMENT) - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. De'Boba is a partnership business located in Miri, Sarawak that plans to sell boba milk tea and other beverages. The business is formed by 4 partners who will take on roles like General Manager and Marketing Manager. The business plan provides details on the partnership ...
And How to Create One. 1. Executive summary. This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Determine how you can best reach potential customers. Evaluate your competition. Your marketing plan must set you apart from your competition, and you can't stand out unless you know your ...
7 4.3 Schedule of Tasks and Responsibilities Position Main Tasks General Manager • To plan, implement and control the overall management of the business. • To supervise daily business operations. • To monitor and motivating staffs. Administrative Manager • To initiates and coordinates goals (planning, organizing, leading, and controlling) to ensure deadlines goals are met.
group assignment ent 300 fundamentals of enterpreneurship assignment topic: business plan prepared for: madam nur hazelen binti mat rusok date of submission: 23 january 2021 prepared by: no. name matric no. group 1. nurul nadiah binti mohd asri 2017366451 d1am1105b 2. wan natasha binti wan naziron 2018409452 d1am1105b ...
Business legal Entity: Partnership Nature of business: Food and Beverages Business address: Lot GF- 20 &21, Ground Floor, Gravitas, Jalan Baru, 13700, Penang Date of commencement: Register on 10 November 2021 and start on 1 January 2022 Factors in selecting the proposed business: Obtain the most popular desire from the community. Introduced the society to a brand-new coffee and pastry.
View ent300-business-plan-group-assignment.pdf from Financial Management MSE4 at CDI College of Business, Technology and Health Care. lOMoARcPSD|15309310 ENT300 - Business PLAN - GROUP
A SWOT analysis is a technique used to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in order to develop a strategic plan or roadmap for your business. While it may sound difficult, it's actually quite simple. Whether you're looking for external opportunities or internal strengths, we'll walk you through how to perform your ...
1. It allowed the entrepreneur to view and evaluate the proposed business venture in an objective, critical and practical manner . The business plan can shows the entrepreneur the potential of the business and it can be a guideline for the business management. 2. The function of a business plan is to convince relevant parties of the investment
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique used in management, business analysis, project management, and software development to reach a common understanding with stakeholders on the importance they place on the delivery of each requirement; it is also known as MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW analysis.. The term MOSCOW itself is an acronym derived from the first letter of each of four ...
View Homework Help - Business Plan Group Assignment from ARCHITECTU 101 at Limkokwing University of Creative Technology, Cyberjaya. BBE2313/BBE3333 / BBUSS2403 BUSINESS PLANNING Department Course
The MoSCoW method is a four-step approach to prioritizing which project requirements provide the best return on investment (ROI). MoSCoW stands for must have, should have, could have and will not have -- the o's make the acronym more pronounceable. A variety of business disciplines use the MoSCoW method.
The MoSCoW method is a technique used by organizations to communicate the importance and priority of the various requirements being met in various projects. This method is also referred to as MoSCoW prioritization and MoSCoW analysis. The term MoSCoW is an acronym that refers to the first letter of each of the four priority categories.
The plan would see 90% channeled through the European Peace Facility fund to buy weapons for Ukraine. The rest would be used for recovery and reconstruction. 19:47:59