
Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), computer speech recognition or speech-to-text, is a capability that enables a program to process human speech into a written format.
While speech recognition is commonly confused with voice recognition, speech recognition focuses on the translation of speech from a verbal format to a text one whereas voice recognition just seeks to identify an individual user’s voice.
IBM has had a prominent role within speech recognition since its inception, releasing of “Shoebox” in 1962. This machine had the ability to recognize 16 different words, advancing the initial work from Bell Labs from the 1950s. However, IBM didn’t stop there, but continued to innovate over the years, launching VoiceType Simply Speaking application in 1996. This speech recognition software had a 42,000-word vocabulary, supported English and Spanish, and included a spelling dictionary of 100,000 words.
While speech technology had a limited vocabulary in the early days, it is utilized in a wide number of industries today, such as automotive, technology, and healthcare. Its adoption has only continued to accelerate in recent years due to advancements in deep learning and big data. Research (link resides outside ibm.com) shows that this market is expected to be worth USD 24.9 billion by 2025.
Explore the free O'Reilly ebook to learn how to get started with Presto, the open source SQL engine for data analytics.
Register for the guide on foundation models
Many speech recognition applications and devices are available, but the more advanced solutions use AI and machine learning . They integrate grammar, syntax, structure, and composition of audio and voice signals to understand and process human speech. Ideally, they learn as they go — evolving responses with each interaction.
The best kind of systems also allow organizations to customize and adapt the technology to their specific requirements — everything from language and nuances of speech to brand recognition. For example:
- Language weighting: Improve precision by weighting specific words that are spoken frequently (such as product names or industry jargon), beyond terms already in the base vocabulary.
- Speaker labeling: Output a transcription that cites or tags each speaker’s contributions to a multi-participant conversation.
- Acoustics training: Attend to the acoustical side of the business. Train the system to adapt to an acoustic environment (like the ambient noise in a call center) and speaker styles (like voice pitch, volume and pace).
- Profanity filtering: Use filters to identify certain words or phrases and sanitize speech output.
Meanwhile, speech recognition continues to advance. Companies, like IBM, are making inroads in several areas, the better to improve human and machine interaction.
The vagaries of human speech have made development challenging. It’s considered to be one of the most complex areas of computer science – involving linguistics, mathematics and statistics. Speech recognizers are made up of a few components, such as the speech input, feature extraction, feature vectors, a decoder, and a word output. The decoder leverages acoustic models, a pronunciation dictionary, and language models to determine the appropriate output.
Speech recognition technology is evaluated on its accuracy rate, i.e. word error rate (WER), and speed. A number of factors can impact word error rate, such as pronunciation, accent, pitch, volume, and background noise. Reaching human parity – meaning an error rate on par with that of two humans speaking – has long been the goal of speech recognition systems. Research from Lippmann (link resides outside ibm.com) estimates the word error rate to be around 4 percent, but it’s been difficult to replicate the results from this paper.
Various algorithms and computation techniques are used to recognize speech into text and improve the accuracy of transcription. Below are brief explanations of some of the most commonly used methods:
- Natural language processing (NLP): While NLP isn’t necessarily a specific algorithm used in speech recognition, it is the area of artificial intelligence which focuses on the interaction between humans and machines through language through speech and text. Many mobile devices incorporate speech recognition into their systems to conduct voice search—e.g. Siri—or provide more accessibility around texting.
- Hidden markov models (HMM): Hidden Markov Models build on the Markov chain model, which stipulates that the probability of a given state hinges on the current state, not its prior states. While a Markov chain model is useful for observable events, such as text inputs, hidden markov models allow us to incorporate hidden events, such as part-of-speech tags, into a probabilistic model. They are utilized as sequence models within speech recognition, assigning labels to each unit—i.e. words, syllables, sentences, etc.—in the sequence. These labels create a mapping with the provided input, allowing it to determine the most appropriate label sequence.
- N-grams: This is the simplest type of language model (LM), which assigns probabilities to sentences or phrases. An N-gram is sequence of N-words. For example, “order the pizza” is a trigram or 3-gram and “please order the pizza” is a 4-gram. Grammar and the probability of certain word sequences are used to improve recognition and accuracy.
- Neural networks: Primarily leveraged for deep learning algorithms, neural networks process training data by mimicking the interconnectivity of the human brain through layers of nodes. Each node is made up of inputs, weights, a bias (or threshold) and an output. If that output value exceeds a given threshold, it “fires” or activates the node, passing data to the next layer in the network. Neural networks learn this mapping function through supervised learning, adjusting based on the loss function through the process of gradient descent. While neural networks tend to be more accurate and can accept more data, this comes at a performance efficiency cost as they tend to be slower to train compared to traditional language models.
- Speaker Diarization (SD): Speaker diarization algorithms identify and segment speech by speaker identity. This helps programs better distinguish individuals in a conversation and is frequently applied at call centers distinguishing customers and sales agents.
A wide number of industries are utilizing different applications of speech technology today, helping businesses and consumers save time and even lives. Some examples include:
Automotive: Speech recognizers improves driver safety by enabling voice-activated navigation systems and search capabilities in car radios.
Technology: Virtual agents are increasingly becoming integrated within our daily lives, particularly on our mobile devices. We use voice commands to access them through our smartphones, such as through Google Assistant or Apple’s Siri, for tasks, such as voice search, or through our speakers, via Amazon’s Alexa or Microsoft’s Cortana, to play music. They’ll only continue to integrate into the everyday products that we use, fueling the “Internet of Things” movement.
Healthcare: Doctors and nurses leverage dictation applications to capture and log patient diagnoses and treatment notes.
Sales: Speech recognition technology has a couple of applications in sales. It can help a call center transcribe thousands of phone calls between customers and agents to identify common call patterns and issues. AI chatbots can also talk to people via a webpage, answering common queries and solving basic requests without needing to wait for a contact center agent to be available. It both instances speech recognition systems help reduce time to resolution for consumer issues.
Security: As technology integrates into our daily lives, security protocols are an increasing priority. Voice-based authentication adds a viable level of security.
Convert speech into text using AI-powered speech recognition and transcription.
Convert text into natural-sounding speech in a variety of languages and voices.
AI-powered hybrid cloud software.
Enable speech transcription in multiple languages for a variety of use cases, including but not limited to customer self-service, agent assistance and speech analytics.
Learn how to keep up, rethink how to use technologies like the cloud, AI and automation to accelerate innovation, and meet the evolving customer expectations.
IBM watsonx Assistant helps organizations provide better customer experiences with an AI chatbot that understands the language of the business, connects to existing customer care systems, and deploys anywhere with enterprise security and scalability. watsonx Assistant automates repetitive tasks and uses machine learning to resolve customer support issues quickly and efficiently.

The SpeakWrite Blog
Ultimate guide to speech recognition technology (2023).
- April 12, 2023
Learn about speech recognition technology—how speech to text software works, benefits, limitations, transcriptions, and other real world applications.

Whether you’re a professional in need of more efficient transcription solutions or simply want your voice-enabled device to work smarter for you, this guide to speech recognition technology is here with all the answers.
Few technologies have evolved rapidly in recent years as speech recognition. In just the last decade, speech recognition has become something we rely on daily. From voice texting to Amazon Alexa understanding natural language queries, it’s hard to imagine life without speech recognition software.
But before deep learning was ever a word people knew, mid-century were engineers paving the path for today’s rapidly advancing world of automatic speech recognition. So let’s take a look at how speech recognition technologies evolved and speech-to-text became king.
What Is Speech Recognition Technology?
With machine intelligence and deep learning advances, speech recognition technology has become increasingly popular. Simply put, speech recognition technology (otherwise known as speech-to-text or automatic speech recognition) is software that can convert the sound waves of spoken human language into readable text. These programs match sounds to word sequences through a series of steps that include:
- Pre-processing: may consist of efforts to improve the audio of speech input by reducing and filtering the noise to reduce the error rate
- Feature extraction: this is the part where sound waves and acoustic signals are transformed into digital signals for processing using specialized speech technologies.
- Classification: extracted features are used to find spoken text; machine learning features can refine this process.
- Language modeling: considers important semantic and grammatical rules of a language while creating text.
How Does Speech Recognition Technology Work?
Speech recognition technology combines complex algorithms and language models to produce word output humans can understand. Features such as frequency, pitch, and loudness can then be used to recognize spoken words and phrases.
Here are some of the most common models for speech recognition, which include acoustic models and language models . Sometimes, several of these are interconnected and work together to create higher-quality speech recognition software and applications.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
“Hey, Siri, how does speech-to-text work?”
Try it—you’ll likely hear your digital assistant read a sentence or two from a relevant article she finds online, all thanks to the magic of natural language processing.
Natural language processing is the artificial intelligence that gives machines like Siri the ability to understand and answer human questions. These AI systems enable devices to understand what humans are saying, including everything from intent to parts of speech.
But NLP is used by more than just digital assistants like Siri or Alexa—it’s how your inbox knows which spam messages to filter, how search engines know which websites to offer in response to a query, and how your phone knows which words to autocomplete.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are one of the most powerful AI applications in speech recognition. They’re used to recognize patterns and process large amounts of data quickly.
For example, neural networks can learn from past input to better understand what words or phrases you might use in a conversation. It uses those patterns to more accurately detect the words you’re saying.
Leveraging cutting-edge deep learning algorithms, neural networks are revolutionizing how machines recognize speech commands. By imitating neurons in our brains and creating intricate webs of electrochemical connections between them, these robust architectures can process data with unparalleled accuracy for various applications such as automatic speech recognition.
Hidden Markov Models (HMM)
The Hidden Markov Model is a powerful tool for acoustic modeling, providing strong analytical capabilities to accurately detect natural speech. Its application in the field of Natural Language Processing has allowed researchers to efficiently train machines on word generation tasks, acoustics, and syntax to create unified probabilistic models.
Speaker Diarization
Speaker diarization is an innovative process that segments audio streams into distinguishable speakers, allowing the automatic speech recognition transcript to organize each speaker’s contributions separately. Using unique sound qualities and word patterns, this technique pinpoints conversations accurately so every voice can be heard.
The History of Speech Recognition Technology
It’s hard to believe that just a few short decades ago, the idea of having a computer respond to speech felt like something straight out of science fiction. Yet, Fast-forward to today, and voice-recognition technology has gone from being an obscure concept to becoming so commonplace you can find it in our smartphones.
But where did this all start? First, let’s take a look at the history of speech recognition technology – from its uncertain early days through its evolution into today’s easy-to-use technology.
Speech recognition technology has existed since the 1950s when Bell Laboratory researchers first developed systems to recognize simple commands . However, early speech recognition systems were limited in their capabilities and could not identify more complex phrases or sentences.
In the 1980s, advances in computing power enabled the development of better speech recognition systems that could understand entire sentences. Today, speech recognition technology has become much more advanced, with some systems able to recognize multiple languages and dialects with high accuracy.
Timeline of Speech Recognition Programs
- 1952 – Bell Labs researchers created “Audrey,” an innovative system for recognizing individual digits. Early speech recognition systems were limited in their capabilities and could not identify more complex phrases or sentences.
- 1962 – IBM shook the tech sphere in 1962 at The World’s Fair, showcasing a remarkable 16-word speech recognition capability – nicknamed “Shoebox” —that left onlookers awestruck.
- 1980s – IBM revolutionized the typewriting industry in the 1980s with Tangora , a voice-activated system that could understand up to 20,000 words. Advances in computing power enabled the development of better speech recognition systems that could understand entire sentences.
- 1996 – IBM’s VoiceType Simply Speaking application recognized 42,000 English and Spanish words.
- 2007 – Google launched GOOG-411 as a telephone directory service, an endeavor that provided immense amounts of data for improving speech recognition systems over time. Now, this technology is available across 30 languages through Google Voice Search .
- 2017 – Microsoft made history when its research team achieved the remarkable goal of transcribing phone conversations utilizing various deep-learning models.
How is Speech Recognition Used Today?
Speech recognition technology has come a long way since its inception at Bell Laboratories.
Today, speech recognition technology has become much more advanced, with some systems able to recognize multiple languages and dialects with high accuracy and low error rates.
Speech recognition technology is used in a wide range of applications in our daily lives, including:
- Voice Texting: Voice texting is a popular feature on many smartphones that allow users to compose text messages without typing.
- Smart Home Automation: Smart home systems use voice commands technology to control lights, thermostats, and other household appliances with simple commands.
- Voice Search: Voice search is one of the most popular applications of speech recognition, as it allows users to quickly
- Transcription: Speech recognition technology can transcribe spoken words into text fast.
- Military and Civilian Vehicle Systems: Speech recognition technology can be used to control unmanned aerial vehicles, military drones, and other autonomous vehicles.
- Medical Documentation: Speech recognition technology is used to quickly and accurately transcribe medical notes, making it easier for doctors to document patient visits.
Key Features of Advanced Speech Recognition Programs
If you’re looking for speech recognition technology with exceptional accuracy that can do more than transcribe phonetic sounds, be sure it includes these features.
Acoustic training
Advanced speech recognition programs use acoustic training models to detect natural language patterns and better understand the speaker’s intent. In addition, acoustic training can teach AI systems to tune out ambient noise, such as the background noise of other voices.
Speaker labeling
Speaker labeling is a feature that allows speech recognition systems to differentiate between multiple speakers, even if they are speaking in the same language. This technology can help keep track of who said what during meetings and conferences, eliminating the need for manual transcription.
Dictionary customization
Advanced speech recognition programs allow users to customize their own dictionaries and include specialized terminology to improve accuracy. This can be especially useful for medical professionals who need accurate documentation of patient visits.
If you don’t want your transcript to include any naughty words, then you’ll want to make sure your speech recognition system consists of a filtering feature. Filtering allows users to specify which words should be filtered out of their transcripts, ensuring that they are clean and professional.
Language weighting
Language weighting is a feature used by advanced speech recognition systems to prioritize certain commonly used words over others. For example, this feature can be helpful when there are two similar words, such as “form” and “from,” so the system knows which one is being spoken.
The Benefits of Speech Recognition Technology
Human speech recognition technology has revolutionized how people navigate, purchase, and communicate. Additionally, speech-to-text technology provides a vital bridge to communication for individuals with sight and auditory disabilities. Innovations like screen readers, text-to-speech dictation systems, and audio transcriptions help make the world more accessible to those who need it most.
Limits of Speech Recognition Programs
Despite its advantages, speech recognition technology still needs to be improved.
- Accuracy rate and reliability – the quality of the audio signal and the complexity of the language being spoken can significantly impact the system’s ability to accurately interpret spoken words. For now, speech-to-text technology has a higher average error rate than humans.
- Formatting – Exporting speech recognition results into a readable format, such as Word or Excel, can be difficult and time-consuming—especially if you must adhere to professional formatting standards.
- Ambient noise – Speech recognition systems are still incapable of reliably recognizing speech in noisy environments. If you plan on recording yourself and turning it into a transcript later, make sure the environment is quiet and free from distractions.
- Translation – Human speech and language are difficult to translate word for word, as things like syntax, context, and cultural differences can lead to subtle meanings that are lost in direct speech-to-text translations.
- Security – While speech recognition systems are great for controlling devices, you don’t always have control over how your data is stored and used once recorded.
Using Speech Recognition for Transcriptions
Speech recognition technology is commonly used to transcribe audio recordings into text documents and has become a standard tool in business and law enforcement. There are handy apps like Otter.ai that can help you quickly and accurately transcribe and summarize meetings and speech-to-text features embedded in document processors like Word.
However, you should use speech recognition technology for transcriptions with caution because there are a number of limitations that could lead to costly mistakes.
If you’re creating an important legal document or professional transcription , relying on speech recognition technology or any artificial intelligence to provide accurate results is not recommended. Instead, it’s best to employ a professional transcription service or hire an experienced typist to accurately transcribe audio recordings.
Human typists have an accuracy level of 99% – 100%, can follow dictation instructions, and can format your transcript appropriately depending on your instructions. As a result, there is no need for additional editing once your document is delivered (usually in 3 hours or less), and you can put your document to use immediately.
Unfortunately, speech recognition technology can’t achieve these things yet. You can expect an accuracy of up to 80% and little to no professional formatting. Additionally, your dictation instructions will fall on deaf “ears.” Frustratingly, they’ll just be included in the transcription rather than followed to a T. You’ll wind up spending extra time editing your transcript for readability, accuracy, and professionalism.
So if you’re looking for dependable, accurate, fast transcriptions, consider human transcription services instead.
Is Speech Recognition Technology Accurate?
The accuracy of speech recognition technology depends on several factors, including the quality of the audio signal, the complexity of the language being spoken, and the specific algorithms used by the system.
Some speech recognition software can withstand poor acoustic quality, identify multiple speakers, understand accents, and even learn industry jargon. Others are more rudimentary and may have limited vocabulary or may only be able to work with pristine audio quality.
Speaker identification vs. speech recognition: what’s the difference?
The two are often used interchangeably. However, there is a distinction. Speech recognition technology shouldn’t be confused with speech identification technology, which identifies who is speaking rather than what the speaker has to say.
What type of technology is speech recognition?
Speech recognition is a type of technology that allows computers to understand and interpret spoken words. It is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses algorithms to recognize patterns in audio signals, such as the sound of speech. Speech recognition technology has been around for decades.
Is speech recognition AI technology?
Yes, speech recognition is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses algorithms to recognize patterns in audio signals, such as the sound of speech. Speech recognition technology has been around for decades, but it wasn’t until recently that systems became sophisticated enough to accurately understand and interpret spoken words.
What are examples of speech recognition devices?
Examples of speech recognition devices include virtual assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri. Additionally, many mobile phones and computers now come with built-in voice recognition software that can be used to control the device or issue commands. Speech recognition technology is also used in various other applications, such as automated customer service systems, medical transcription software, and real-time language translation systems.
See How Much Your Business Could Be Saving in Transcription Costs
With accurate transcriptions produced faster than ever before, using human transcription services could be an excellent decision for your business. Not convinced? See for yourself! Try our cost savings calculator today and see how much your business could save in transcription costs.

Explore FAQs
Discover blogs, get support.

- 800-756-7828
- 7164 Beechmont Avenue, Cincinnati, OH 45230
Dolbey and Company, Inc.
Dolbey Speech Recognition Solutions

The Ultimate Guide to Speech Recognition
In this ‘Ultimate Guide to Speech Recognition’, we’ll provide a brief overview of speech recognition and its importance, explore the various types and applications of speech recognition, then look towards the future.
Click any of the boxes below to jump directly to that section. You can also download a full version of the guide as a PDF , complete with additional insights, charts, and tips & tricks.
Table of Contents
PART ONE
Speech Recognition Overview
What is speech recognition.
Speech recognition is a method of translating speech to text through artificial intelligence. Speech recognition software is able to convert live or recorded audio of spoken language into text nearly instantaneously.
How speech recognition is used today
Speech recognition has rapidly become more accessible, to the point where ‘smart’ devices don’t seem as smart without some form of speech recognition.
For many, speech recognition has become so ingrained in their daily routine that asking Siri for directions or getting Alexa to play a song comes naturally. Smart devices – more specifically virtual assistants on smart devices – are among the most common uses for speech recognition today.
In the Microsoft® 2019 Voice Report , 72% of respondents indicated they have used a digital assistant like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, or Cortana. The use of digital assistants is likely to continue rising over time as they become more accurate and can perform more functions.
Aside from personal use, speech recognition is widely used to boost productivity in work environments. The healthcare, education, business, legal, law enforcement, and entertainment industries all benefit from speech recognition for transcription and work automation.
Speech Recognition vs. Voice Recognition
The main difference between speech recognition and voice recognition is that, for any given audio where spoken language can be heard, speech recognition identifies the words being used, whereas voice recognition identifies the speaker.
Voice recognition is generally used as a security measure for unlocking devices, but can also be used for personalization.
Speech recognition and voice recognition are sometimes used interchangeably to mean the same thing (converting speech to text), but there are slight differences between the two.
The history of speech recognition
Speech recognition is a relatively new technology, and one that continues to improve each decade. Sound recording was first made possible with the Dictaphone in 1907 . Roughly 50 years later, in 1952, the first speech recognition technology emerged. This technology was named Audrey, built by Bell Labs – and it was able to recognize speech for single digits from zero to nine.
Development for speech recognition technology took major leaps nearly every decade. 10 years after Audrey was created, IBM demonstrated their own speech recognition device: Shoebox . Shoebox was also able to recognize single digits from zero to nine, but it could also recognize a few English command words, such as “plus” and “minus”.
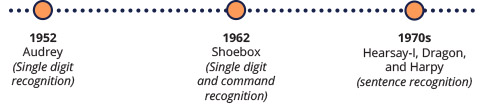
The next leaps in speech technology were largely the result of research at Carnegie Mellon University, where three systems – Hearsay-I, Dragon, and Harpy – were developed. Harpy was created with learnings from the two prior models (Hearsay-I and Dragon) and was the most advanced speech recognition system to date. Harpy had a limited vocabulary but was able to recognize sentences. The Dragon system has continued development and was later acquired by Nuance Communications to become one of the most widely used professional speech recognition options today.
Speech recognition continued to develop as more elements of speech were analyzed. During and beyond the 1980s, speech recognition models were able to recognize more words and even reference context and grammar to improve recognition accuracy.
The greatest improvements to speech recognition technology today were made alongside two major technological advancements: PCs and mobile phones. PCs and mobile phones allowed for more applications of speech recognition for personal use, expanding the possibilities of speech recognition and driving further improvements.
How speech recognition accuracy is measured
Speech recognition accuracy is measured by word error rate. Word errors can either occur from an unrecognized word or phrase, an incorrectly recognized word or phrase, or a contextually incorrect word or phrase.
There are several instances where words or phrases will be entirely unrecognizable or incorrectly recognized by speech recognition software. Some of the most common causes are a mumbled or muffled dictation or proper nouns outside of the speech engine’s dictionary. Speech recognition software generally has two courses of action in a case like this – either return a phonetically similar word/phrase or, in the case of virtual assistants like Siri, prompt the dictator to try again.
A contextually incorrect word might be recognizing ‘colon’ as the punctuation mark (:) rather than the organ, or recognizing ‘to’ as the number ‘2’. There are various other cases and examples of incorrect contextual recognition which all can contribute to a higher word error rate.
Some remedies for incorrect recognition are machine learning and specialized speech recognition. A healthcare-specific speech recognition solution might be able to better handle the ‘colon’ example from earlier. It would also better handle healthcare terminology, such as medications, where general-purpose speech recognition might struggle.
Accuracy is a key factor in determining speech recognition proficiency, but return time should also be considered. Return time is the amount of time it takes for the speech recognition software to recognize and transcribe speech into text. Highly accurate speech recognition that takes more time to transcribe than a human might not be as useful as 95% accuracy with a return time of a few seconds.

Industries that use speech recognition
Speech recognition is used in a variety of industries, including healthcare, education, legal, law enforcement, business, and entertainment. We cover this in more detail in part four.
Two main functions of speech recognition – speech-to-text and voice commands – can add efficiency in nearly any profession, especially those that deal in computer work.
In any job that involves a lot of typing, like some positions in the fields listed above, speech-to-text can save time as a supporting software or even as a substitute for typing. The average typing speed is only 41 words per minute (wpm), while the average conversational speaking speed is triple that at 120 wpm.
Those in a role that involves typing daily will often have above-average typing speeds, but only the most skilled typists can even come close to the average speaking speed.
Speech recognition is also heavily relied upon in customer service (especially for business), where a virtual assistant guides a caller through a menu of options.

Want a version of this guide to keep on your computer?
Download a full version of this guide for more insights.
Download the guide
The Importance of Speech Recognition
There are two key benefits of speech recognition:
- Time savings
- Higher accessibility
Time savings and overall efficiency are a large part of why speech recognition has been adopted in so many industries.
Speech recognition is mutually beneficial for businesses and employees because it leads to more automation, and as a result, higher efficiency.
People speak faster than they type and that alone can be a source of huge time savings.
As soon as you start incorporating voice-enabled shortcuts (either with virtual assistants or dedicated speech recognition software), you can save even more time.
It also saves time in activities outside of work. The less time you spend manually typing or navigating on a device, the more time you have for everything else.
Speech recognition offers accessibility. With the proper equipment, it can be used without a keyboard or mouse. This gives speech technology a leg up over traditional data entry and can lead to further efficiency.
Speech recognition also offers accessibility for personal tasks with virtual assistants. Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa make it easy to write down a note, play music, or make a call from your car or in your home. With the help of a voice assistant, you might be able to better multi-task, stay organized, and get away from your phone.
Why doesn’t everyone use speech recognition?
Even with accuracy rates of 95%+, there is some reluctance to completely rely on speech recognition. 5% may not seem like much, but when dealing with numbers or recording valuable information, any mistake can be detrimental.
Most recognized text will still need some level of review. This is still faster than manually typing in most cases, but some individuals and organizations are still hesitant towards speech recognition.
As speech recognition technology continues to make advancements, each benefit will be further amplified. That means more time saved and even greater accessibility. With these improvements, reluctance towards speech recognition will also likely decrease.
Types of Speech Recognition
Speech recognition has become integrated with phones, cars, and nearly any device connected to the internet. With such a wide range of applications, it’s only natural that different types and uses for speech recognition have arisen.
The core functionality of speech recognition is the same across all applications: recognize words, phrases, and numbers. But, for each application of speech recognition, the objective is slightly different and more might be requested from the speech recognition software.
For example, some software might transcribe recognized words to text (think speech-to-text) while another might simply use the recognition to perform an action (think virtual assistant).
Most speech recognition that we’re familiar with today falls under the umbrella of Automated Speech Recognition (ASR). An even more advanced subcategory of ASR Is natural language processing (NLP). The virtual assistants that we’re familiar with often incorporate NLP to more accurately recognize speech.
Most popular speech recognition software
The most popular speech recognition software is often free. Google’s speech-to-text tool, speech-to-text on operating systems like Mac and Windows ® , and virtual assistants are all built-in features with high accuracy and functionality. There are limitations for these free options, but they’re convenient and often do a good enough job (depending on what they’re being used for).
Let’s take a deeper look at the technology behind some of these major speech platforms because their inner workings are more connected than you might expect.
Free speech recognition software
Siri is arguably the most common form of speech recognition today, because it comes pre-installed on the most prominent smartphone on the market – the iPhone ® . Siri was introduced in 2011 with the iPhone ® 4S , making it not only the most popular modern virtual assistant, but the first.
Siri’s voice engine was developed by Nuance Communications who, if you’ll remember, acquired one of the earliest speech recognition systems: Dragon.
Recently, Microsoft ® purchased Nuance Communications for $19.7 billion. Microsoft ® has its own virtual assistant, Cortana, which is available on Microsoft ® phones and devices that operate on Windows ® . This purchase could mean two of the most popular virtual assistants – and several of the most trusted paid speech recognition solutions – would be powered by the same (or similar) voice engines.
The third virtual assistant of note is Amazon’s Alexa. Alexa is powered by Amazon’s own voice recognition engine and comes pre-installed on nearly all modern Amazon devices, including tablets, speakers, smartphones, and streaming devices.
Google has both speech-to-text tool built directly into their search engine and a virtual assistant that comes paired with Google devices. Google’s speech-to-text tool works on mobile and desktop devices with any operating system within their search engine. The tool is also available within Google Chrome in their word processing software, Google Docs. Much like Amazon, Google offers several smart devices with its own virtual assistant.
Paid speech recognition software
Free speech recognition software is dominated by some of the biggest names in technology and is advancing quickly. However, free software isn’t always suited for professional work, which is definitely the case with speech recognition.
Some of the more advanced use cases for speech recognition, such as healthcare dictation, legal and law transcription, and data entry, require speech recognition built for that purpose. Healthcare speech recognition will operate differently from legal speech recognition, for example.
Although the major players in the free speech recognition market still have some stake in professional speech recognition (especially with the recent Microsoft ® purchase of Nuance Communications), there are a few different companies at the top of the paid market.
Nuance Communications is likely the biggest name in the paid speech market with its suite of Dragon products, built for the previously mentioned industries (healthcare, law enforcement, and legal) as well as a general-purpose paid solution: Dragon NaturallySpeaking.
Within the healthcare market, there are two other major speech recognition vendors: Dolbey and 3M.
Amazon Transcribe is also built with Amazon’s speech recognition engine with a pricing model based on seconds of audio transcribed. The pricing and design for this software make it ideal for clients that need large quantities of audio transcribed on a consistent basis.
Amazon also has software intended for the healthcare industry with Amazon Transcribe Medical.
IBM Watson is an incredibly accurate speech recognition platform designed for enterprises. IBM Watson can be used for simple speech-to-text, but it can also be used to transcribe calls from call centers or as the speech engine that behind virtual assistants on support calls.
Get a copy to share with your friends
Download the full version of this guide for more insights.
Applications of Speech Recognition
As we’ve explored, some of the most common applications of speech recognition are virtual assistants, devices that can recognize your voice, and speech-to-text.
Some of the more niche, but equally important, applications of speech recognition are translation and custom voice commands.
Google Translate is an excellent example of speech recognition for translation; with support for over 100 languages , users can speak into their device’s microphone and easily get a translation for their preferred language. Google has implemented a conversational translation feature for the Google Translate app, which allows people speaking two different languages to more easily communicate. Google will pick up on the language and speaker, then translate to the other language being spoken.
With the wide set of applications for speech recognition at work (which we’ll go into in just a minute), efficiency has become one of the driving factors for improvements and feature updates to speech recognition software. A key addition to speech recognition in the past few decades is custom voice commands. With voice commands, an end user can order their device to perform an action or series of actions with just a word or phrase.
For example, someone might build a ‘start my day’ command on their computer, which would open a series of applications they need to start their day – maybe the weather app, their email inbox, and the homepage of a news site. As soon as this these commands are applied to work or any sort of repetitive task, they can be a huge timesaver, made even more accessible by voice activation.
Speech recognition for work
Speech recognition is used to make work more efficient or to take over work responsibilities in several industries, but especially in healthcare, law enforcement, business, legal, entertainment, and education.
The primary use for speech recognition in healthcare is to streamline the documentation process. Physicians that interact with patients must record notes for the patient visit to provide a status update and guide towards next steps. These notes are what make up documentation, which is a standard process for physicians. Healthcare specialties that don’t involve direct interaction with patients also require some level of reporting.
The documentation process became more involved with the introduction of electronic health records. Some early approaches were writing notes or dictating directly into a voice recorder, then having a third party convert those notes into a more legible version. Transcriptionists are still relatively common in the medical practice, but speech recognition has proven to be a more efficient approach.
Law Enforcement
Law enforcement is similar to healthcare in that encounters must be recorded. Incident forms and police reports must be completed as a standard procedure.
Completing this paperwork can be overwhelming, but is made more manageable with speech recognition. Law enforcement professionals can record their notes either from a mobile device, at home, or in the office with the use of speech recognition. This can clear up time that would otherwise be spent doing paperwork for other work responsibilities or personal time.
Speech recognition for business is generally used for three purposes: customer service, transcription, and data entry.
Many large businesses now use digital operators that effectively work the same as a virtual assistant. These operators assist callers as they navigate through an option menu with their voice. Speech recognition has completely changed customer service and can allow businesses to reduce their staff and save money.
Meeting transcription is another common application for speech recognition in business. Instead of frantically jotting down notes, speech recognition can simply transcribe a full meeting. More advanced solutions are even able to separate the transcription by who is talking, combining the power of voice recognition and speech recognition.
Data entry can be optimized or even automated with the use of speech recognition. Many solutions are able to handle large numerical values which can be quicker and more reliable than manual entry – but the key benefit of speech recognition for data entry is the use of voice commands to run functions or macros in database and data processing tools. You can more quickly run queries or perform repetitive functions with a simple voice command, making data entry more efficient and accessible.
Speech recognition can assist in filling documents in preparation for court proceedings and building court transcripts.
Several documents need to be prepared for court, including memos and briefs. These documents take quite a bit of time to prepare manually – which is why the task is often allocated to paralegals or legal scribes. Instead of allocating the work to another person, it can instead be expedited through speech recognition.
Speech recognition is also making its mark on court transcripts. You’ve almost certainly seen court reporting in practice, whether it’s in a courtroom or on TV – someone typing quickly on a device transcribing dialogue within the courtroom. It’s a tough job that requires keen attention, a legal vocabulary, and fast typing speeds. Court reporters are also in short supply , but the demand continues to rise.
Some courts now utilize speech typing, which involves the court reporter repeating dialogue directly into a speech device as it is spoken. As speech recognition technology develops, we may see software that utilizes both speech and voice recognition that recognizes speech and separates recognized text based on the speaker.
Entertainment
One key factor of modern televised or digital entertainment, especially live broadcasts, is closed captioning. Closed captioning is generally provided by a stenographer or generated by automatic speech recognition.
Live broadcasting is fast-paced and requires fast, accurate stenographers. As with legal speech recognition, finding stenographers for this type of work is becoming more of a challenge. Speech recognition is an affordable alternative.
Although speech recognition for closed captioning is more readily available than stenographers, it must reach a similar level of accuracy and speed. This can be difficult to match for live broadcasts, which is why closed captioning speech recognition tends to be more expensive.
Closed captioning can be equally important for recorded videos. In education, speech recognition can be used to transcribe videos. In fact, with so much educational content on YouTube, speech recognition is already being used heavily – YouTube videos can receive automated closed captioning with technology that continues to improve. Some educators and those in other fields have started uploading videos to YouTube for quick, free transcription.
Speech recognition can also be used for lecture transcription, which can be a useful way to keep notes.
The Future of Speech Recognition
As speech recognition technology continues to develop, it will only become more ingrained in our daily lives. Technology that improves efficiency catches the eye of businesses and makes its way into our personal lives.
Speech recognition will only become more compelling as accuracy continues to improve and more uses for speech recognition are developed. Speech and voice recognition technology is already advanced, but improvements to accuracy and speed will take it to the next level.
The next frontier is speech recognition accuracy approaching, or maybe even surpassing human accuracy in transcription. Is that even possible? It remains to be seen.
Although there were leaps in accuracy for the past several decades, progress has slowed and improving average accuracy by even a fraction of a percent is a major milestone.
But many of the ideas that once seemed futuristic have already been realized – we have speech recognition in cars, at home, and even in the palm of our hand. We’ll certainly continue to see improvements in speech recognition accuracy, but how far can we move that needle?
It might not be too far-fetched to believe that speech recognition will one day surpass human accuracy, but it also might simply not happen.
The future of speech recognition is exciting – and as speech technology develops, our lives might see more major shifts in the way we do things. Keep an eye out for new applications of speech recognition and watch as one of the most universal technologies continues to grow.
Now that you have a better understanding of speech recognition, get out there and start improving your efficiency in your work and daily life.
Download the guide:
Discover more speech recognition insghts and keep a full version of the guide saved to your desktop. We'll also send you a copy directly to your inbox.
" * " indicates required fields
- Category: Speech Recognition

Posted by Brian Gaysunas
Marketing Manager
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- > Artificial Intelligence
Automatic Speech Recognition: Types and Examples
- Yashoda Gandhi
- Mar 02, 2022
.jpg)
Voice assistants such as Google Home, Amazon Echo, Siri, Cortana, and others have become increasingly popular in recent years. These are some of the most well-known examples of automatic speech recognition (ASR).
This type of app starts with a clip of spoken audio in a specific language and converts the words spoken into text. As a result, they're also called Speech-to-Text algorithms.
Apps like Siri and the others mentioned above, of course, go even further. They not only extract the text but also interpret and comprehend the semantic meaning of what was said, allowing them to respond to the user's commands with answers or actions.
Automatic Speech Recognition
ASR (Automated speech recognition) is a technology that allows users to enter data into information systems by speaking rather than punching numbers into a keypad. ASR is primarily used for providing information and forwarding phone calls.
In recent years, ASR has grown in popularity among large corporation customer service departments. It is also used by some government agencies and other organizations. Basic ASR systems recognize single-word entries such as yes-or-no responses and spoken numerals.
This enables users to navigate through automated menus without having to manually enter dozens of numerals with no margin for error. In a manual-entry situation, a customer may press the wrong key after entering 20 or 30 numerals at random intervals in the menu and abandon the call rather than call back and start over. This issue is virtually eliminated with ASR.
Natural Language Processing, or NLP for short, is at the heart of the most advanced version of currently available ASR technologies. Though this variant of ASR is still a long way from realizing its full potential, we're already seeing some impressive results in the form of intelligent smartphone interfaces like Apple's Siri and other systems used in business and advanced technology.
Even with a "accuracy" of 96 to 99 percent , these NLP programs can only achieve these kinds of results under ideal circumstances, such as when humans ask them simple yes or no questions with a small number of possible responses based on selected keywords.
Also Read | A Step Towards Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
How to carry out Automatic Speech Recognition ?
We’ve listed three significant ways for automatic speech recognition.
Old fashioned way
With ARPA funding in the 1970s, a team at Carnegie Melon University developed technology that could generate transcripts from context-specific speech, such as voice-controlled chess, chart-plotting for GIS and navigation, and document management in the office environment.
These types of products had one major flaw: they could only reliably convert speech to text for one person at a time. This is due to the fact that no two people speak in the same way. In fact, even if the same person speaks the same sentence twice, the sounds are mathematically different when recorded and measured!
Two mathematical realities for silicon brains, the same word to our human, meat-based brains! These ASR-based, personal transcription tools and products were revolutionary and had legitimate business uses, despite their inability to transcribe the utterances of multiple speakers.
Frankenstein approach
In the mid-2000s, companies like Nuance, Google, and Amazon realized that by making ASR work for multiple speakers and in noisy environments, they could improve on the 1970s approach.
Rather than having to train ASR to understand a single speaker, these Franken-ASRs were able to understand multiple speakers fairly well, which is an impressive feat given the acoustic and mathematical realities of spoken language. This is possible because these neural-network algorithms can "learn on their own" when given certain stimuli.
However, slapping a neural network on top of older machinery (remember, this is based on 1970s techniques) results in bulky, complex, and resource-hungry machines like Back-to-the-DeLorean Future's or my college bicycle: a franken-bike that worked when the tides and winds were just right, usually except when it didn't.
While clumsy, the mid-2000s hybrid approach to ASR works well enough for some applications; after all, Siri isn't supposed to answer any real-world data questions.
End to end Deep Learning
The most recent method, end-to-end deep learning ASR, makes use of neural networks and replaces the clumsy 1970s method. In essence, this new approach allows you to do something that was unthinkable even two years ago: train the ASR to recognize dialects, accents, and industry-specific word sets quickly and accurately.
It's a Mr. Fusion bicycle, complete with rusted bike frames and ill-fated auto brands. Several factors contribute to this, including breakthrough math from the 1980s, computing power/technology from the mid-2010s, big data, and the ability to innovate quickly.
It's crucial to be able to experiment with new architectures, technologies, and approaches. Legacy ASR systems based on the franken-ASR hybrid are designed to handle "general" audio rather than specialized audio for industry, business, or even academic purposes.To put it another way, they provide generalized speech recognition and cannot realistically be trained to improve your speech data.
Also Read | Speech Analytics
Types of ASR
The two main types of Automatic Speech Recognition software variants are directed dialogue conversations and natural language conversations.
Detecting a direct dialogue speech
Directed Dialogue conversations are a much less complicated version of ASR at work, consisting of machine interfaces that instruct you to respond verbally with a specific word from a limited list of options, forming their response to your narrowly defined request. Directed conversation Automated telephone banking and other customer service interfaces frequently use ASR software.
Analyze natural language conversation
Natural Language Conversations (the NLP we discussed in the introduction) are more advanced versions of ASR that attempt to simulate real conversation by allowing you to use an open-ended chat format with them rather than a severely limited menu of words. One of the most advanced examples of these systems is the Siri interface on the iPhone.
Applications of ASR
Where continuous conversations must be tracked or recorded word for word, ASR is used in a variety of industries, including higher education, legal, finance, government, health care, and the media.
In legal proceedings, it's critical to record every word, and court reporters are in short supply right now. ASR technology has several advantages, including digital transcription and scalability.
ASR can be used by universities to provide captions and transcriptions in the classroom for students with hearing loss or other disabilities. It can also benefit non-native English speakers, commuters, and students with a variety of learning needs.
ASR is used by doctors to transcribe notes from patient meetings or to document surgical procedures.
Media companies can use ASR to provide live captions and media transcription for all of their productions.
Businesses use ASR for captioning and transcription to make training materials more accessible and to create more inclusive workplaces.
Also Read | Hyper Automation
Advantages of ASR over Traditional Transcriptions
We’ve listed some advantages of ASR over Traditional Transcriptions below :
ASR machines can help improve caption and transcription efficiencies, in addition to the growing shortage of skilled traditional transcribers.
In conversations, lectures, meetings, and proceedings, the technology can distinguish between voices, allowing you to figure out who said what and when.
Because disruptions among participants are common in these conversations with multiple stakeholders, the ability to distinguish between speakers can be very useful.
Users can train the ASR machine by uploading hundreds of related documents, such as books, articles, and other materials.
The technology can absorb this vast amount of data faster than a human, allowing it to recognize different accents, dialects, and terminology with greater accuracy.
Of course, in order to achieve the near-perfect accuracy required, the ideal format would involve using human intelligence to fact-check the artificial intelligence that is being used.
Automatic Speech Recognition Systems (ASRs) can convert spoken words into understandable text.
Its application to air traffic control and automated car environments has been studied due to its ability to convert speech in real-time.
The Hidden Markov model is used in feature extraction by the ASR system for air traffic control, and its phraseology is based on the commands used in air applications.
Speech recognition is used in the car environment for route navigation applications.
Also Read | Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence
Automatic Speech Recognition vs Voice Recognition
The difference between Voice Recognition and Automatic Speech Recognition (the technical term for AI speech recognition, or ASR) is how they process and respond to audio.
You'll be able to use voice recognition with devices like Amazon Alexa or Google Dot. It listens to your voice and responds in real-time. Most digital assistants use voice recognition, which has limited functionality and is usually limited to the task at hand.
ASR differs from other voice recognition systems in that it recognizes speech rather than voices. It can accurately generate an audio transcript using NLP, resulting in real-time captioning. ASR isn't perfect; in fact, even under ideal conditions, it rarely exceeds 90%-95 percent accuracy . However, it compensates for this by being quick and inexpensive.
In essence, ASR is a transcription of what someone said, whereas Voice Recognition is a transcription of who said it. Both processes are inextricably linked, and they are frequently used interchangeably. The distinctions are subtle but noticeable.
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Scope of Managerial Economics
Different Types of Research Methods

Latest Comments
jasonbennett355
Omg I Finally Got Helped !! I'm so excited right now, I just have to share my testimony on this Forum.. The feeling of being loved takes away so much burden from our shoulders. I had all this but I made a big mistake when I cheated on my wife with another woman and my wife left me for over 4 months after she found out.. I was lonely, sad and devastated. Luckily I was directed to a very powerful spell caster Dr Emu who helped me cast a spell of reconciliation on our Relationship and he brought back my wife and now she loves me far more than ever.. I'm so happy with life now. Thank you so much Dr Emu, kindly Contact Dr Emu Today and get any kind of help you want.. Via Email [email protected] or Call/WhatsApp cell number +2347012841542 Https://web.facebook.com/Emu-Temple-104891335203341
Speech Recognition: Definition, Importance and Uses

Transkriptor 2024-01-17
Speech recognition, known as voice recognition or speech-to-text, is a technological development that converts spoken language into written text. It has two main benefits, these include enhancing task efficiency and increasing accessibility for everyone including individuals with physical impairments.
The alternative of speech recognition is manual transcription. Manual transcription is the process of converting spoken language into written text by listening to an audio or video recording and typing out the content.
There are many speech recognition software, but a few names stand out in the market when it comes to speech recognition software; Dragon NaturallySpeaking, Google's Speech-to-Text and Transkriptor.
The concept behind "what is speech recognition?" pertains to the capacity of a system or software to understand and transform oral communication into written textual form. It functions as the fundamental basis for a wide range of modern applications, ranging from voice-activated virtual assistants such as Siri or Alexa to dictation tools and hands-free gadget manipulation.
The development is going to contribute to a greater integration of voice-based interactions into an individual's everyday life.

What is Speech Recognition?
Speech recognition, known as ASR, voice recognition or speech-to-text, is a technological process. It allows computers to analyze and transcribe human speech into text.
How does Speech Recognition work?
Speech recognition technology works similar to how a person has a conversation with a friend. Ears detect the voice, and the brain processes and understands.The technology does, but it involves advanced software as well as intricate algorithms. There are four steps to how it works.
The microphone records the sounds of the voice and converts them into little digital signals when users speak into a device. The software processes the signals to exclude other voices and enhance the primary speech. The system breaks down the speech into small units called phonemes.
Different phonemes give their own unique mathematical representations by the system. It is able to differentiate between individual words and make educated predictions about what the speaker is trying to convey.
The system uses a language model to predict the right words. The model predicts and corrects word sequences based on the context of the speech.
The textual representation of the speech is produced by the system. The process requires a short amount of time. However, the correctness of the transcription is contingent on a variety of circumstances including the quality of the audio.
What is the importance of Speech Recognition?
The importance of speech recognition is listed below.
- Efficiency: It allows for hands-free operation. It makes multitasking easier and more efficient.
- Accessibility: It provides essential support for people with disabilities.
- Safety: It reduces distractions by allowing hands-free phone calls.
- Real-time translation: It facilitates real-time language translation. It breaks down communication barriers.
- Automation: It powers virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, streamlining many daily tasks.
- Personalization: It allows devices and apps to understand user preferences and commands.

What are the Uses of Speech Recognition?
The 7 uses of speech recognition are listed below.
- Virtual Assistants. It includes powering voice-activated assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Transcription services. It involves converting spoken content into written text for documentation, subtitles, or other purposes.
- Healthcare. It allows doctors and nurses to dictate patient notes and records hands-free.
- Automotive. It covers enabling voice-activated controls in vehicles, from playing music to navigation.
- Customer service. It embraces powering voice-activated IVRs in call centers.
- Educatio.: It is for easing in language learning apps, aiding in pronunciation, and comprehension exercises.
- Gaming. It includes providing voice command capabilities in video games for a more immersive experience.
Who Uses Speech Recognition?
General consumers, professionals, students, developers, and content creators use voice recognition software. Voice recognition sends text messages, makes phone calls, and manages their devices with voice commands. Lawyers, doctors, and journalists are among the professionals who employ speech recognition. Using speech recognition software, they dictate domain-specific information.
What is the Advantage of Using Speech Recognition?
The advantage of using speech recognition is mainly its accessibility and efficiency. It makes human-machine interaction more accessible and efficient. It reduces the human need which is also time-consuming and open to mistakes.
It is beneficial for accessibility. People with hearing difficulties use voice commands to communicate easily. Healthcare has seen considerable efficiency increases, with professionals using speech recognition for quick recording. Voice commands in driving settings help maintain safety and allow hands and eyes to focus on essential duties.
What is the Disadvantage of Using Speech Recognition?
The disadvantage of using speech recognition is its potential for inaccuracies and its reliance on specific conditions. Ambient noise or accents confuse the algorithm. It results in misinterpretations or transcribing errors.
These inaccuracies are problematic. They are crucial in sensitive situations such as medical transcribing or legal documentation. Some systems need time to learn how a person speaks in order to work correctly. Voice recognition systems probably have difficulty interpreting multiple speakers at the same time. Another disadvantage is privacy. Voice-activated devices may inadvertently record private conversations.
What are the Different Types of Speech Recognition?
The 3 different types of speech recognition are listed below.
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Speaker-Dependent Recognition (SDR)
- Speaker-Independent Recognition (SIR)
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is one of the most common types of speech recognition . ASR systems convert spoken language into text format. Many applications use them like Siri and Alexa. ASR focuses on understanding and transcribing speech regardless of the speaker, making it widely applicable.
Speaker-Dependent recognition recognizes a single user's voice. It needs time to learn and adapt to their particular voice patterns and accents. Speaker-dependent systems are very accurate because of the training. However, they struggle to recognize new voices.
Speaker-independent recognition interprets and transcribes speech from any speaker. It does not care about the accent, speaking pace, or voice pitch. These systems are useful in applications with many users.
What Accents and Languages Can Speech Recognition Systems Recognize?
The accents and languages that speech recognition systems can recognize are English, Spanish, and Mandarin to less common ones. These systems frequently incorporate customized models for distinguishing dialects and accents. It recognizes the diversity within languages. Transkriptor, for example, as a dictation software, supports over 100 languages.
Is Speech Recognition Software Accurate?
Yes, speech recognition software is accurate above 95%. However, its accuracy varies depending on a number of things. Background noise and audio quality are two examples of these.
How Accurate Can the Results of Speech Recognition Be?
Speech recognition results can achieve accuracy levels of up to 99% under optimal conditions. The highest level of speech recognition accuracy requires controlled conditions such as audio quality and background noises. Leading speech recognition systems have reported accuracy rates that exceed 99%.
How Does Text Transcription Work with Speech Recognition?
Text transcription works with speech recognition by analyzing and processing audio signals. Text transcription process starts with a microphone that records the speech and converts it to digital data. The algorithm then divides the digital sound into small pieces and analyzes each one to identify its distinct tones.
Advanced computer algorithms aid the system for matching these sounds to recognized speech patterns. The software compares these patterns to a massive language database to find the words users articulated. It then brings the words together to create a logical text.
How are Audio Data Processed with Speech Recognition?
Speech recognition processes audio data by splitting sound waves, extracting features, and mapping them to linguistic parts. The system collects and processes continuous sound waves when users speak into a device. The software advances to the feature extraction stage.
The software isolates specific features of the sound. It focuses on phonemes that are crucial for identifying one phoneme from another. The process entails evaluating the frequency components.
The system then starts using its trained models. The software combines the extracted features to known phonemes by using vast databases and machine learning models.
The system takes the phonemes, and puts them together to form words and phrases. The system combines technology skills and language understanding to convert noises into intelligible text or commands.
What is the best speech recognition software?
The 3 best speech recognition software are listed below.
Transkriptor
- Dragon NaturallySpeaking
- Google's Speech-to-Text
However, choosing the best speech recognition software depends on personal preferences.

Transkriptor is an online transcription software that uses artificial intelligence for quick and accurate transcription. Users are able to translate their transcripts with a single click right from the Transkriptor dashboard. Transkriptor technology is available in the form of a smartphone app, a Google Chrome extension, and a virtual meeting bot. It is compatible with popular platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet which makes it one of the Best Speech Recognition Software.
Dragon NaturallySpeaking allows users to transform spoken speech into written text. It offers accessibility as well as adaptations for specific linguistic languages. Users like software’s adaptability for different vocabularies.

Google's Speech-to-Text is widely used for its scalability, integration options, and ability to support multiple languages. Individuals use it in a variety of applications ranging from transcription services to voice-command systems.
Is Speech Recognition and Dictation the Same?
No, speech recognition and dictation are not the same. Their principal goals are different, even though both voice recognition and dictation make conversion of spoken language into text. Speech recognition is a broader term covering the technology's ability to recognize and analyze spoken words. It converts them into a format that computers understand.
Dictation refers to the process of speaking aloud for recording. Dictation software uses speech recognition to convert spoken words into written text.
What is the Difference between Speech Recognition and Dictation?
The difference between speech recognition and dictation are related to their primary purpose, interactions, and scope. Itss primary purpose is to recognize and understand spoken words. Dictation has a more definite purpose. It focuses on directly transcribing spoken speech into written form.
Speech Recognition covers a wide range of applications in terms of scope. It helps voice assistants respond to user questions. Dictation has a narrower scope.
It provides a more dynamic interactive experience, often allowing for two-way dialogues. For example, virtual assistants such as Siri or Alexa not only understand user requests but also provide feedback or answers. Dictation works in a more basic fashion. It's typically a one-way procedure in which the user speaks and the system transcribes without the program engaging in a response discussion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Transkriptor stands out for its ability to support over 100 languages and its ease of use across various platforms. Its AI-driven technology focuses on quick and accurate transcription.
Yes, modern speech recognition software is increasingly adept at handling various accents. Advanced systems use extensive language models that include different dialects and accents, allowing them to accurately recognize and transcribe speech from diverse speakers.
Speech recognition technology greatly enhances accessibility by enabling voice-based control and communication, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with physical impairments or motor skill limitations. It allows them to operate devices, access information, and communicate effectively.
Speech recognition technology's efficiency in noisy environments has improved, but it can still be challenging. Advanced systems employ noise cancellation and voice isolation techniques to filter out background noise and focus on the speaker's voice.
Speech to Text
Convert your audio and video files to text
Audio to Text
Video Transcription
Transcription Service
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
Contact Information
© 2024 Transkriptor
From Talk to Tech: Exploring the World of Speech Recognition

What is Speech Recognition Technology?
Imagine being able to control electronic devices, order groceries, or dictate messages with just voice. Speech recognition technology has ushered in a new era of interaction with devices, transforming the way we communicate with them. It allows machines to understand and interpret human speech, enabling a range of applications that were once thought impossible.
Speech recognition leverages machine learning algorithms to recognize speech patterns, convert audio files into text, and examine word meaning. Siri, Alexa, Google's Assistant, and Microsoft's Cortana are some of the most popular speech to text voice assistants used today that can interpret human speech and respond in a synthesized voice.
From personal assistants that can understand every command directed towards them to self-driving cars that can comprehend voice instructions and take the necessary actions, the potential applications of speech recognition are manifold. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities are endless.
How do Speech Recognition Systems Work?
speech to text processing is traditionally carried out in the following way:
Recording the audio: The first step of speech to text conversion involves recording the audio and voice signals using a microphone or other audio input devices.
Breaking the audio into parts: The recorded voice or audio signals are then broken down into small segments, and features are extracted from each piece, such as the sound's frequency, pitch, and duration.
Digitizing speech into computer-readable format: In the third step, the speech data is digitized into a computer-readable format that identifies the sequence of characters to remember the words or phrases that were most likely spoken.
Decoding speech using the algorithm: Finally, language models decode the speech using speech recognition algorithms to produce a transcript or other output.
To adapt to the nature of human speech and language, speech recognition is designed to identify patterns, speaking styles, frequency of words spoken, and speech dialects on various levels. Advanced speech recognition software are also capable of eliminating background noises that often accompany speech signals.
When it comes to processing human speech, the following two types of models are used:
Acoustic Models
Acoustic models are a type of machine learning model used in speech recognition systems. These models are designed to help a computer understand and interpret spoken language by analyzing the sound waves produced by a person's voice.
Language Models
Based on the speech context, language models employ statistical algorithms to forecast the likelihood of words and phrases. They compare the acoustic model's output to a pre-built vocabulary of words and phrases to identify the most likely word order that makes sense in a given context of the speech.
Applications of Speech Recognition Technology
Automatic speech recognition is becoming increasingly integrated into our daily lives, and its potential applications are continually expanding. With the help of speech to text applications, it's now becoming convenient to convert a speech or spoken word into a text format, in minutes.
Speech recognition is also used across industries, including healthcare , customer service, education, automotive, finance, and more, to save time and work efficiently. Here are some common speech recognition applications:
Voice Command for Smart Devices
Today, there are many home devices designed with voice recognition. Mobile devices and home assistants like Amazon Echo or Google Home are among the most widely used speech recognition system. One can easily use such devices to set reminders, place calls, play music, or turn on lights with simple voice commands.
Online Voice Search
Finding information online is now more straightforward and practical, thanks to speech to text technology. With online voice search, users can search using their voice rather than typing. This is an excellent advantage for people with disabilities and physical impairments and those that are multitasking and don't have the time to type a prompt.
Help People with Disabilities
People with disabilities can also benefit from speech to text applications because it allows them to use voice recognition to operate equipment, communicate, and carry out daily duties. In other words, it improves their accessibility. For example, in case of emergencies, people with visual impairment can use voice commands to call their friends and family on their mobile devices.
Business Applications of Speech Recognition
Speech recognition has various uses in business, including banking, healthcare, and customer support. In these industries, voice recognition mainly aims at enhancing productivity, communication, and accessibility. Some common applications of speech technology in business sectors include:
Speech recognition is used in the banking industry to enhance customer service and expedite internal procedures. Banks can also utilize speech to text programs to enable clients to access their accounts and conduct transactions using only their voice.
Customers in the bank who have difficulties entering or navigating through complicated data will find speech to text particularly useful. They can simply voice search the necessary data. In fact, today, banks are automating procedures like fraud detection and customer identification using this impressive technology, which can save costs and boost security.
Voice recognition is used in the healthcare industry to enhance patient care and expedite administrative procedures. For instance, physicians can dictate notes about patient visits using speech recognition programs, which can then be converted into electronic medical records. This also helps to save a lot of time, and correct data is recorded in the best way possible with this technology.
Customer Support
Speech recognition is employed in customer care to enhance the customer experience and cut expenses. For instance, businesses can automate time-consuming processes using speech to text so that customers can access information and solve problems without speaking to a live representative. This could shorten wait times and increase customer satisfaction.
Challenges with Speech Recognition Technology
Although speech recognition has become popular in recent years and made our lives easier, there are still several challenges concerning speech recognition that needs to be addressed.
Accuracy may not always be perfect
A speech recognition software can still have difficulty accurately recognizing speech in noisy or crowded environments or when the speaker has an accent or speech impediment. This can lead to incorrect transcriptions and miscommunications.
The software can not always understand complexity and jargon
Any speech recognition software has a limited vocabulary, so it may struggle to identify uncommon or specialized vocabulary like complex sentences or technical jargon, making it less useful in specific industries or contexts. Errors in interpretation or translation may happen if the speech recognition fails to recognize the context of words or phrases.
Concern about data privacy, data can be recorded.
Speech recognition technology relies on recording and storing audio data, which can raise concerns about data privacy. Users may be uncomfortable with their voice recordings being stored and used for other purposes. Also, voice notes, phone calls, and recordings may be recorded without the user's knowledge, and hacking or impersonation can be vulnerable to these security breaches. These things raise privacy and security concerns.
Software that Use Speech Recognition Technology
Many software programs use speech recognition technology to transcribe spoken words into text. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Nuance Dragon.
Amazon Transcribe.
Google Text to Speech
Watson Speech to Text
To sum up, speech recognition technology has come a long way in recent years. Given its benefits, including increased efficiency, productivity, and accessibility, its finding applications across a wide range of industries. As we continue to explore the potential of this evolving technology, we can expect to see even more exciting applications emerge in the future.
With the power of AI and machine learning at our fingertips, we're poised to transform the way we interact with technology in ways we never thought possible. So, let's embrace this exciting future and see where speech recognition takes us next!
What are the three steps of speech recognition?
The three steps of speech recognition are as follows:
Step 1: Capture the acoustic signal
The first step is to capture the acoustic signal using an audio input device and later pre-process the motion to remove noise and other unwanted sounds. The movement is then broken down into small segments, and features such as frequency, pitch, and duration are extracted from each piece.
Step 2: Combining the acoustic and language models
The second step involves combining the acoustic and language models to produce a transcription of the spoken words and word sequences.
Step 3: Converting the text into a synthesized voice
The final step is converting the text into a synthesized voice or using the transcription to perform other actions, such as controlling a computer or navigating a system.
What are examples of speech recognition?
Speech recognition is used in a wide range of applications. The most famous examples of speech recognition are voice assistants like Apple's Siri, Amazon's Alexa, and Google Assistant. These assistants use effective speech recognition to understand and respond to voice commands, allowing users to ask questions, set reminders, and control their smart home devices using only voice.
What is the importance of speech recognition?
Speech recognition is essential for improving accessibility for people with disabilities, including those with visual or motor impairments. It can also improve productivity in various settings and promote language learning and communication in multicultural environments. Speech recognition can break down language barriers, save time, and reduce errors.
You should also read:

Understanding Speech to Text in Depth

Top 10 Speech to Text Software in 2024

How Speech Recognition is Changing Language Learning

RingCX: An AI-First Contact Centre that Simplifies Smarter Customer Experiences
Get Intelligent, omnichannel capabilities with RingCX, tailored to your businesses, and at a fraction of the costs of other enterprise contact centre solutions
Voice Recognition
Share this Post on:
Evaluating enterprise telephony for Microsoft Teams

Voice recognition will be a key part of the future of communication. Whether it’s asking Alexa the time or navigating a business phone system, you’ll have encountered it before.
Many businesses are adopting this new way of working, whether to improve their own internal processes or upgrade their customer service systems. Despite this, speech recognition is still relatively new, and many people remain sceptical about what it does and how it can be used.
In this guide, we’ll discuss what voice recognition is, where you can use it, what benefits it has, and why you should be using it if you’re a business owner.
What is voice recognition?
Thanks to modern technology, it’s now possible for computer software to understand speech. This software can listen to what you say, and interpret it to a digitised version that reads and analyses.
So, how does it do this? Through artificial intelligence and machine learning. Large amounts of data are used to create an algorithm which can be developed over time. The AI then learns from this data and identifies patterns. It looks at previous input and captures what you’re saying. It even gets to understand how you speak, for example, your use of regional language.
Voice recognition means that your mobile device, smart speakers, or computer can listen to what you’re saying. This increased functionality can be useful when you need help around the house, like asking your Amazon Alexa what the weather will be like today to see if you need an umbrella before you head to work. It can also be used to dictate notes when you haven’t got the time or means physically to write it down.

Many businesses also use it to improve their customer service. Callers can respond to certain questions, and be directed to the right agent for their problem. That’s the technology that RingCentral voice recognition brings. This improves the first call resolution rate and makes sure your agents don’t have to forward calls to other departments. It’s great for the customers who get their problem solved quickly and efficiently, and great for the business to increase productivity and take on more calls.
How voice recognition works
So, how does voice recognition work? Well, it uses technology to evaluate the biometrics of your voice. That includes the frequency and flow of your voice, as well as your accent. Every word you speak is broken up into segments of several tones. This is then digitised and translated to create your own unique voice template.
Artificial intelligence , deep learning, and machine learning are the forces behind speech recognition. Artificial intelligence is used to understand the colloquialisms, abbreviations, and acronyms we use. Machine learning then pieces together the patterns and develops from this data using neural networks.
This technology can be used for a variety of systems, some more complex than others. For example, if you’ve ever called your mobile phone provider’s contact centre, you may be greeted with a menu powered by voice recognition. To get directed to the correct department, you need to select an option. This can be done by saying the number or using the keypad.
But voice recognition can do so much more than this. Take Alexa, for example. This clever home helper can answer questions, play music, and turn off the lights in your home all through the power of your voice.
Uses of voice recognition
As it stands, 72% of people who use voice search devices claim they have become part of their daily routines. Technology advances rapidly that sometimes the next “big thing” gets overshadowed by another new development. But as more people become comfortable talking into their phone and smart hub, the more this trend is set to catch on.
It’s not just for personal use, either. As industries and businesses jump on board, the trend of using voice recognition is only a matter of time before that number increases. A growing number of businesses adopt voice recognition systems to help them with efficiency and accuracy when it comes to customer service.
Here are some of the main uses of voice recognition thus far:
Speech recognition technology can be used in various ways. Many industries are now utilising voice recognition to help with everyday processes. For example, the law industry has benefited greatly from voice recognition. Lawyers use it for dictating important meetings that they can then transcribe into documents. This not only saves them time but ensures all information is accurately recorded.
It also helps in regular, everyday activities. Many of us have smartphones or home hub devices that also have a virtual assistant, and you can dictate your shopping list, daily tasks, and just about anything you want to make a note of. It’s easier, and often more productive than writing it down yourself.

Accessibility
Voice recognition can also be used in reverse, that is, instead of speech-to-text, you can translate text-to-speech. Some platforms, such as Dragon Professional from Nuance, offer this feature. Many people who have speech and sight problems, for example, those with disabilities or speech impediments, find it useful. It can also be used in the education sector for this reason.
Purchases using voice command
Over 55% of customers have purchased a product from an eCommerce website using speech recognition. And, as more people get comfortable with voice recognition technology, this number could grow.
Advantages and disadvantages of voice recognition
Although many people see voice recognition as part of our future, there are some drawbacks to consider. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of voice recognition:
- It can help to increase productivity in many businesses, such as in healthcare industries.
- It can capture speech much faster than you can type
- You can use text-to-speech in real-time.
- The software can spell the same ability as any other writing tool.
- Helps those who have problems with speech or sight
Disadvantages
- Voice data can be recorded, which some fear could impact privacy.
- The software can struggle with vocabulary, particularly if there are specialist terms.
- It can misinterpret words if you don’t speak clearly – take a look at Youtube’s auto-captions!
Examples of systems with voice recognition
Automated phone systems.
In the workplace, automated phone systems are becoming more common. Take the RingCentral Office, for example. This cloud-based phone platform includes an IVR (interactive voice response) feature . When a customer calls, the machine uses automatic speech recognition to understand what the customer is saying. It can then direct them to voicemail, to an extension number, and even to external numbers. You can have up to 250 menus enabled at any time, which is ideal for large global businesses.
Google Voice
If you say “Hey Google” into your Android device, the Google Voice assistant is there to help. Like Cortana and Apple’s Siri, you can ask it to search for various topics, but this one directs users to Google’s search engine. This also works with ‘Google Next’, the latest smart speaker from Google. What’s more, you can accurately convert text-to-speech using an API powered by Google technology.
Digital assistant
Many smart devices have their own digital assistant. If you have an Apple device, you’ve likely heard of ‘Siri’. Siri is a personal assistant that can recognise your voice. You can ask Siri to search a question for you, send a text to someone, and even play your favourite song. Other digital assistants include Alexa, Cortana, and Bixby, to name a few.
Car Bluetooth
Having car Bluetooth is not only convenient but also a step-up in safety. Where drivers may have been tempted to send a text behind the wheel, they can now connect to their car via Bluetooth and send a text hands-free using speech recognition.
What are voice recognition systems?
Some voice recognition systems work differently to others, depending on the software used to develop them. Here are some examples of different voice recognition systems:
1. Speaker dependent system
These systems are dependent on knowledge of the speaker’s voice. And machine learning is a key part of this because it analyses data and recognises user patterns. Thanks to this technology, smart hubs can understand phrases and words that the person uses. In other words, they are trained by the user. That also means that the system is more accurate to the person’s voice; it’s used to hearing.
2. Speaker independent system
A speaker-independent system can recognise words from a wide range of contexts and understand words regardless of who is speaking. They understand a range of speech patterns, fluctuations, and tones. Most systems designed for phone calls will be speaker-independent.
3. Discrete speech recognition
When it comes to discrete speech recognition, the user has to be more careful about phrase sentences. They need to pause between words for the software to understand.
4. Continuous speech recognition
This recognises how we would speak normally, meaning you don’t need to pause between each word for it to understand what you’re saying. Tools designed for transcribing will make use of this kind of voice recognition.
5. Natural language
A natural language voice recognition system is one that we are mostly used to. It uses natural language processing (NLP). NLP is another branch of artificial intelligence that allows computers to interpret and learn natural human language. It allows the computer to understand our natural way of talking, including fluctuations and accents. That’s why your home smart hub can answer questions and conversationally respond to you.
Voice recognition software
Due to the advancements in voice recognition software, there are various types on the market hoping to compete with one another, such as:
Windows Speech Recognition
It’s not just on our smartphones and smart devices where we can use voice recognition. It’s also available on PCs and Laptops. Those with Microsoft Windows can use their version of a speech recognition system to navigate their way around the user interface. You can dictate onto a document, open up apps, and use short commands to activate keyboard shortcuts.
Dictation on a Mac
Apple Mac’s have their own speech recognition systems. Like the Windows speech recognition software, users can open applications, navigate their way around their Mac using only their voice, and send emails and texts through their iPhone when synced.
Google Speech Recognition
Google speech recognition can work for anyone with access to Google and a working microphone. The search engine has its own transcription software for users of any smart device to dictate into Google Docs.
Dragon Individual Professional
This software is useful for those who want to use their voice more when working on their PC or laptop. You can send emails, texts, fill forms, and even create reports with this useful tool. It’s used by many businesses to increase productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
How does RingCentral’s solution support voice recognition?
RingCentral’s solution supports the growing demand for voice recognition. The cloud-based software can be used on office phones and smart devices, so you can stay connected wherever you are. This is particularly useful when you need to access work technology from home.
Multi-level IVR
You can set up multi-level IVR which provides customers with an automated phone menu. Set your company’s main number to dial through to an auto-receptionist. Users can then say or press the option they require from a series of questions set up by you. This can then ring externally to one of the team members who can take the call remotely.
It’s ideal for reducing wait times and improving call routing because customers are directed to the best agent for their issues, reducing the frustration that comes from being put through to someone who can’t solve your problem. When this happens, it’s not only frustrating for the customer who may need to be transferred several times, but it also means each agent’s call time is taken up. With RingCentral’s effective call routing feature , you’ll be put through the right person the first time around.
Here are some key reasons why businesses love RingCentral’s voice recognition technology:
- Users don’t need to press buttons, they can speak directly to the auto-machine
- You can set up over 250 menus at any one time.
- It can reduce customer waiting times.
- It ensures the customer’s call is directed to the best agent to resolve the issue.
- You can integrate it with a third-party payment gateway to allow for IVR payments
Originally published Feb 18, 2021, updated Mar 13, 2024
Sam O’Brien is the Director of Digital and Growth for EMEA at RingCentral, a Global VoIP, video conferencing and call centre software provider. Sam has a passion for innovation and loves exploring ways to collaborate more with dispersed teams. He has written for websites such as G2 and Hubspot . Here is his LinkedIn .
Related Terms
Interactive voice response (ivr), call centre agent, automatic call distribution (acd).
Collaboration
Small Business

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), computer speech recognition or speech-to-text, is a capability that enables a program to process human speech into a written format. While speech recognition is commonly confused with voice recognition, speech recognition focuses on the translation of speech from a verbal ...
Speech recognition. Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also known as automatic speech recognition ( ASR ), computer speech recognition or ...
The variety of speech recognition software available caters to different needs and uses. 12 types of speech recognition are listed below. Speaker-Dependent Speech Recognition: Speaker-Dependent Speech Recognition systems learn and adapt to the unique voice characteristics of an individual user. Speaker-Independent Speech Recognition: Speaker ...
Speech recognition is a type of technology that allows computers to understand and interpret spoken words. It is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses algorithms to recognize patterns in audio signals, such as the sound of speech. Speech recognition technology has been around for decades.
Development for speech recognition technology took major leaps nearly every decade. 10 years after Audrey was created, IBM demonstrated their own speech recognition device: Shoebox. Shoebox was also able to recognize single digits from zero to nine, but it could also recognize a few English command words, such as “plus” and “minus”.
Automatic Speech Recognition vs Voice Recognition . The difference between Voice Recognition and Automatic Speech Recognition (the technical term for AI speech recognition, or ASR) is how they process and respond to audio. You'll be able to use voice recognition with devices like Amazon Alexa or Google Dot.
Voice recognition also known as speech recognition or speaker recognition, enables users to dictate commands to a computer to get things done. The computing system interprets and converts oral commands into tangible actions. like drawing curtains, dimming lights, voice typing and so on. Voice recognition, also known as “speech to text,” is ...
The importance of speech recognition is listed below. Efficiency: It allows for hands-free operation. It makes multitasking easier and more efficient. Accessibility: It provides essential support for people with disabilities. Safety: It reduces distractions by allowing hands-free phone calls.
Speech recognition technology has ushered in a new era of interaction with devices, transforming the way we communicate with them. It allows machines to understand and interpret human speech, enabling a range of applications that were once thought impossible. Speech recognition leverages machine learning algorithms to recognize speech patterns ...
Voice recognition software. Due to the advancements in voice recognition software, there are various types on the market hoping to compete with one another, such as: Windows Speech Recognition; It’s not just on our smartphones and smart devices where we can use voice recognition. It’s also available on PCs and Laptops.