- En español – ExME
- Em português – EME

Case-control and Cohort studies: A brief overview
Posted on 6th December 2017 by Saul Crandon

Introduction
Case-control and cohort studies are observational studies that lie near the middle of the hierarchy of evidence . These types of studies, along with randomised controlled trials, constitute analytical studies, whereas case reports and case series define descriptive studies (1). Although these studies are not ranked as highly as randomised controlled trials, they can provide strong evidence if designed appropriately.
Case-control studies
Case-control studies are retrospective. They clearly define two groups at the start: one with the outcome/disease and one without the outcome/disease. They look back to assess whether there is a statistically significant difference in the rates of exposure to a defined risk factor between the groups. See Figure 1 for a pictorial representation of a case-control study design. This can suggest associations between the risk factor and development of the disease in question, although no definitive causality can be drawn. The main outcome measure in case-control studies is odds ratio (OR) .
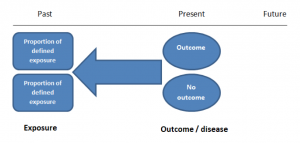
Figure 1. Case-control study design.
Cases should be selected based on objective inclusion and exclusion criteria from a reliable source such as a disease registry. An inherent issue with selecting cases is that a certain proportion of those with the disease would not have a formal diagnosis, may not present for medical care, may be misdiagnosed or may have died before getting a diagnosis. Regardless of how the cases are selected, they should be representative of the broader disease population that you are investigating to ensure generalisability.
Case-control studies should include two groups that are identical EXCEPT for their outcome / disease status.
As such, controls should also be selected carefully. It is possible to match controls to the cases selected on the basis of various factors (e.g. age, sex) to ensure these do not confound the study results. It may even increase statistical power and study precision by choosing up to three or four controls per case (2).
Case-controls can provide fast results and they are cheaper to perform than most other studies. The fact that the analysis is retrospective, allows rare diseases or diseases with long latency periods to be investigated. Furthermore, you can assess multiple exposures to get a better understanding of possible risk factors for the defined outcome / disease.
Nevertheless, as case-controls are retrospective, they are more prone to bias. One of the main examples is recall bias. Often case-control studies require the participants to self-report their exposure to a certain factor. Recall bias is the systematic difference in how the two groups may recall past events e.g. in a study investigating stillbirth, a mother who experienced this may recall the possible contributing factors a lot more vividly than a mother who had a healthy birth.
A summary of the pros and cons of case-control studies are provided in Table 1.
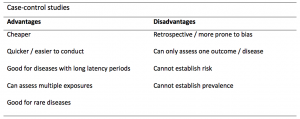
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of case-control studies.
Cohort studies
Cohort studies can be retrospective or prospective. Retrospective cohort studies are NOT the same as case-control studies.
In retrospective cohort studies, the exposure and outcomes have already happened. They are usually conducted on data that already exists (from prospective studies) and the exposures are defined before looking at the existing outcome data to see whether exposure to a risk factor is associated with a statistically significant difference in the outcome development rate.
Prospective cohort studies are more common. People are recruited into cohort studies regardless of their exposure or outcome status. This is one of their important strengths. People are often recruited because of their geographical area or occupation, for example, and researchers can then measure and analyse a range of exposures and outcomes.
The study then follows these participants for a defined period to assess the proportion that develop the outcome/disease of interest. See Figure 2 for a pictorial representation of a cohort study design. Therefore, cohort studies are good for assessing prognosis, risk factors and harm. The outcome measure in cohort studies is usually a risk ratio / relative risk (RR).
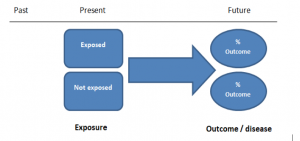
Figure 2. Cohort study design.
Cohort studies should include two groups that are identical EXCEPT for their exposure status.
As a result, both exposed and unexposed groups should be recruited from the same source population. Another important consideration is attrition. If a significant number of participants are not followed up (lost, death, dropped out) then this may impact the validity of the study. Not only does it decrease the study’s power, but there may be attrition bias – a significant difference between the groups of those that did not complete the study.
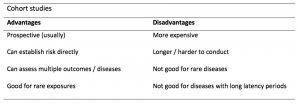
Cohort studies can assess a range of outcomes allowing an exposure to be rigorously assessed for its impact in developing disease. Additionally, they are good for rare exposures, e.g. contact with a chemical radiation blast.
Whilst cohort studies are useful, they can be expensive and time-consuming, especially if a long follow-up period is chosen or the disease itself is rare or has a long latency.
A summary of the pros and cons of cohort studies are provided in Table 2.
The Strengthening of Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Statement (STROBE)
STROBE provides a checklist of important steps for conducting these types of studies, as well as acting as best-practice reporting guidelines (3). Both case-control and cohort studies are observational, with varying advantages and disadvantages. However, the most important factor to the quality of evidence these studies provide, is their methodological quality.
- Song, J. and Chung, K. Observational Studies: Cohort and Case-Control Studies . Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.  2010 Dec;126(6):2234-2242.
- Ury HK. Efficiency of case-control studies with multiple controls per case: Continuous or dichotomous data . Biometrics . 1975 Sep;31(3):643–649.
- von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies.  Lancet 2007 Oct;370(9596):1453-14577. PMID: 18064739.
Saul Crandon
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
No Comments on Case-control and Cohort studies: A brief overview
Very well presented, excellent clarifications. Has put me right back into class, literally!
Very clear and informative! Thank you.
very informative article.
Thank you for the easy to understand blog in cohort studies. I want to follow a group of people with and without a disease to see what health outcomes occurs to them in future such as hospitalisations, diagnoses, procedures etc, as I have many health outcomes to consider, my questions is how to make sure these outcomes has not occurred before the “exposure disease”. As, in cohort studies we are looking at incidence (new) cases, so if an outcome have occurred before the exposure, I can leave them out of the analysis. But because I am not looking at a single outcome which can be checked easily and if happened before exposure can be left out. I have EHR data, so all the exposure and outcome have occurred. my aim is to check the rates of different health outcomes between the exposed)dementia) and unexposed(non-dementia) individuals.
Very helpful information
Thanks for making this subject student friendly and easier to understand. A great help.
Thanks a lot. It really helped me to understand the topic. I am taking epidemiology class this winter, and your paper really saved me.
Happy new year.
Wow its amazing n simple way of briefing ,which i was enjoyed to learn this.its very easy n quick to pick ideas .. Thanks n stay connected
Saul you absolute melt! Really good work man
am a student of public health. This information is simple and well presented to the point. Thank you so much.
very helpful information provided here
really thanks for wonderful information because i doing my bachelor degree research by survival model
Quite informative thank you so much for the info please continue posting. An mph student with Africa university Zimbabwe.
Thank you this was so helpful amazing
Apreciated the information provided above.
So clear and perfect. The language is simple and superb.I am recommending this to all budding epidemiology students. Thanks a lot.
Great to hear, thank you AJ!
I have recently completed an investigational study where evidence of phlebitis was determined in a control cohort by data mining from electronic medical records. We then introduced an intervention in an attempt to reduce incidence of phlebitis in a second cohort. Again, results were determined by data mining. This was an expedited study, so there subjects were enrolled in a specific cohort based on date(s) of the drug infused. How do I define this study? Thanks so much.
thanks for the information and knowledge about observational studies. am a masters student in public health/epidemilogy of the faculty of medicines and pharmaceutical sciences , University of Dschang. this information is very explicit and straight to the point
Very much helpful
Subscribe to our newsletter
You will receive our monthly newsletter and free access to Trip Premium.
Related Articles

Cluster Randomized Trials: Concepts
This blog summarizes the concepts of cluster randomization, and the logistical and statistical considerations while designing a cluster randomized controlled trial.

Expertise-based Randomized Controlled Trials
This blog summarizes the concepts of Expertise-based randomized controlled trials with a focus on the advantages and challenges associated with this type of study.

An introduction to different types of study design
Conducting successful research requires choosing the appropriate study design. This article describes the most common types of designs conducted by researchers.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Case control studies.
Steven Tenny ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Mary R. Hoffman .
Affiliations
Last Update: March 27, 2023 .
- Introduction
A case-control study is a type of observational study commonly used to look at factors associated with diseases or outcomes. [1] The case-control study starts with a group of cases, which are the individuals who have the outcome of interest. The researcher then tries to construct a second group of individuals called the controls, who are similar to the case individuals but do not have the outcome of interest. The researcher then looks at historical factors to identify if some exposure(s) is/are found more commonly in the cases than the controls. If the exposure is found more commonly in the cases than in the controls, the researcher can hypothesize that the exposure may be linked to the outcome of interest.
For example, a researcher may want to look at the rare cancer Kaposi's sarcoma. The researcher would find a group of individuals with Kaposi's sarcoma (the cases) and compare them to a group of patients who are similar to the cases in most ways but do not have Kaposi's sarcoma (controls). The researcher could then ask about various exposures to see if any exposure is more common in those with Kaposi's sarcoma (the cases) than those without Kaposi's sarcoma (the controls). The researcher might find that those with Kaposi's sarcoma are more likely to have HIV, and thus conclude that HIV may be a risk factor for the development of Kaposi's sarcoma.
There are many advantages to case-control studies. First, the case-control approach allows for the study of rare diseases. If a disease occurs very infrequently, one would have to follow a large group of people for a long period of time to accrue enough incident cases to study. Such use of resources may be impractical, so a case-control study can be useful for identifying current cases and evaluating historical associated factors. For example, if a disease developed in 1 in 1000 people per year (0.001/year) then in ten years one would expect about 10 cases of a disease to exist in a group of 1000 people. If the disease is much rarer, say 1 in 1,000,0000 per year (0.0000001/year) this would require either having to follow 1,000,0000 people for ten years or 1000 people for 1000 years to accrue ten total cases. As it may be impractical to follow 1,000,000 for ten years or to wait 1000 years for recruitment, a case-control study allows for a more feasible approach.
Second, the case-control study design makes it possible to look at multiple risk factors at once. In the example above about Kaposi's sarcoma, the researcher could ask both the cases and controls about exposures to HIV, asbestos, smoking, lead, sunburns, aniline dye, alcohol, herpes, human papillomavirus, or any number of possible exposures to identify those most likely associated with Kaposi's sarcoma.
Case-control studies can also be very helpful when disease outbreaks occur, and potential links and exposures need to be identified. This study mechanism can be commonly seen in food-related disease outbreaks associated with contaminated products, or when rare diseases start to increase in frequency, as has been seen with measles in recent years.
Because of these advantages, case-control studies are commonly used as one of the first studies to build evidence of an association between exposure and an event or disease.
In a case-control study, the investigator can include unequal numbers of cases with controls such as 2:1 or 4:1 to increase the power of the study.
Disadvantages and Limitations
The most commonly cited disadvantage in case-control studies is the potential for recall bias. [2] Recall bias in a case-control study is the increased likelihood that those with the outcome will recall and report exposures compared to those without the outcome. In other words, even if both groups had exactly the same exposures, the participants in the cases group may report the exposure more often than the controls do. Recall bias may lead to concluding that there are associations between exposure and disease that do not, in fact, exist. It is due to subjects' imperfect memories of past exposures. If people with Kaposi's sarcoma are asked about exposure and history (e.g., HIV, asbestos, smoking, lead, sunburn, aniline dye, alcohol, herpes, human papillomavirus), the individuals with the disease are more likely to think harder about these exposures and recall having some of the exposures that the healthy controls.
Case-control studies, due to their typically retrospective nature, can be used to establish a correlation between exposures and outcomes, but cannot establish causation . These studies simply attempt to find correlations between past events and the current state.
When designing a case-control study, the researcher must find an appropriate control group. Ideally, the case group (those with the outcome) and the control group (those without the outcome) will have almost the same characteristics, such as age, gender, overall health status, and other factors. The two groups should have similar histories and live in similar environments. If, for example, our cases of Kaposi's sarcoma came from across the country but our controls were only chosen from a small community in northern latitudes where people rarely go outside or get sunburns, asking about sunburn may not be a valid exposure to investigate. Similarly, if all of the cases of Kaposi's sarcoma were found to come from a small community outside a battery factory with high levels of lead in the environment, then controls from across the country with minimal lead exposure would not provide an appropriate control group. The investigator must put a great deal of effort into creating a proper control group to bolster the strength of the case-control study as well as enhance their ability to find true and valid potential correlations between exposures and disease states.
Similarly, the researcher must recognize the potential for failing to identify confounding variables or exposures, introducing the possibility of confounding bias, which occurs when a variable that is not being accounted for that has a relationship with both the exposure and outcome. This can cause us to accidentally be studying something we are not accounting for but that may be systematically different between the groups.
The major method for analyzing results in case-control studies is the odds ratio (OR). The odds ratio is the odds of having a disease (or outcome) with the exposure versus the odds of having the disease without the exposure. The most straightforward way to calculate the odds ratio is with a 2 by 2 table divided by exposure and disease status (see below). Mathematically, we can write the odds ratio as follows. See Figure. Case-Control Studies Odds Ratio.
Odds ratio = [(Number exposed with disease)/(Number exposed without disease) ]/[(Number not exposed to disease)/(Number not exposed without disease) ]
This can be rewritten as:
Odds ratio = [ (Number exposed with disease) x (Number not exposed without disease) ] / [ (Number exposed without disease ) x (Number not exposed with disease) ]
The odds ratio tells us how strongly the exposure is related to the disease state. An odds ratio of greater than one implies the disease is more likely with exposure. An odds ratio of less than one implies the disease is less likely with exposure and thus the exposure may be protective. For example, a patient with a prior heart attack taking a daily aspirin has a decreased odds of having another heart attack (odds ratio less than one). An odds ratio of one implies there is no relation between the exposure and the disease process.
Odds ratios are often confused with Relative Risk (RR), which is a measure of the probability of the disease or outcome in the exposed vs unexposed groups. For very rare conditions, the OR and RR may be very similar, but they are measuring different aspects of the association between outcome and exposure. The OR is used in case-control studies because RR cannot be estimated; whereas in randomized clinical trials, a direct measurement of the development of events in the exposed and unexposed groups can be seen. RR is also used to compare risk in other prospective study designs.
- Issues of Concern
The main issues of concern with a case-control study are recall bias, its retrospective nature, the need for a careful collection of measured variables, and the selection of an appropriate control group. [3] These are discussed above in the disadvantages section.
- Clinical Significance
A case-control study is a good tool for exploring risk factors for rare diseases or when other study types are not feasible. Many times an investigator will hypothesize a list of possible risk factors for a disease process and will then use a case-control study to see if there are any possible associations between the risk factors and the disease process. The investigator can then use the data from the case-control study to focus on a few of the most likely causative factors and develop additional hypotheses or questions. Then through further exploration, often using other study types (such as cohort studies or randomized clinical studies) the researcher may be able to develop further support for the evidence of the possible association between the exposure and the outcome.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Case-control studies are prevalent in all fields of medicine from nursing and pharmacy to use in public health and surgical patients. Case-control studies are important for each member of the health care team to not only understand their common occurrence in research but because each part of the health care team has parts to contribute to such studies. One of the most important things each party provides is helping identify correct controls for the cases. Matching the controls across a spectrum of factors outside of the elements of interest take input from nurses, pharmacists, social workers, physicians, demographers, and more. Failure for adequate selection of controls can lead to invalid study conclusions and invalidate the entire study.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Case-Control Studies Odds Ratio. The figure shows a 2x2 table with calculations for the odds ratio and a 95% confidence interval for it. Contributed by S Tenny, MD, MPH, MBA
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Connor Kerndt declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Mary Hoffman declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Kerndt CC, Hoffman MR. Case Control Studies. [Updated 2023 Mar 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Epidemiology Of Study Design. [StatPearls. 2024] Epidemiology Of Study Design. Munnangi S, Boktor SW. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Risk factors for Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV-positive subjects in Uganda. [AIDS. 1997] Risk factors for Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV-positive subjects in Uganda. Ziegler JL, Newton R, Katongole-Mbidde E, Mbulataiye S, De Cock K, Wabinga H, Mugerwa J, Katabira E, Jaffe H, Parkin DM, et al. AIDS. 1997 Nov; 11(13):1619-26.
- Review The epidemiology of classic, African, and immunosuppressed Kaposi's sarcoma. [Epidemiol Rev. 1991] Review The epidemiology of classic, African, and immunosuppressed Kaposi's sarcoma. Wahman A, Melnick SL, Rhame FS, Potter JD. Epidemiol Rev. 1991; 13:178-99.
- Review Improving Methods for Analyzing Data from Case-Only Studies [ 2022] Review Improving Methods for Analyzing Data from Case-Only Studies Mostofsky E, Ngo LH, Mittleman MA. 2022 Feb
Recent Activity
- Case Control Studies - StatPearls Case Control Studies - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Case Series and Case Reports
- First Online: 21 August 2024
Cite this chapter

- Peter D. Fabricant MD, MPH 2
183 Accesses
Summary take-home points for case series and case reports:
Case series may be prospective or retrospective and are essentially single cohort observational studies.
Case series and case reports differ based on the number of study participants evaluated. Typically, case series have five or more patients included, while case reports have fewer than five patients.
Case series and case reports are classified as “level IV” evidence. This is the least rigorous level of evidence (except for expert opinion narratives).
Case series and case reports frequently use descriptive methodology without comparative statistics.
Despite the low level of evidence, case series and case reports comprise important works. They are ideal for reporting rare outcomes or complications, disseminating early clinical results from a new treatment technique, or piloting data to design and power prospective studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
McLaren SH, Dayan PS, Fenster DB, et al. Novel coronavirus infection in febrile infants aged 60 days and younger. Pediatrics. 2020;146:e20201550. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-1550 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Atallah R, Li JJ, Lu W, et al. Osseointegrated transtibial implants in patients with peripheral vascular disease: a multicenter case series of 5 patients with 1-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:1516–23. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.16.01295 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA
Peter D. Fabricant MD, MPH
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Peter D. Fabricant MD, MPH .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Fabricant, P.D. (2024). Case Series and Case Reports. In: Practical Clinical Research Design and Application. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-58380-3_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-58380-3_12
Published : 21 August 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-58379-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-58380-3
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Study Design 101: Case Control Study
- Case Report
- Case Control Study
- Cohort Study
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Practice Guideline
- Systematic Review
- Meta-Analysis
- Helpful Formulas
- Finding Specific Study Types
A study that compares patients who have a disease or outcome of interest (cases) with patients who do not have the disease or outcome (controls), and looks back retrospectively to compare how frequently the exposure to a risk factor is present in each group to determine the relationship between the risk factor and the disease.
Case control studies are observational because no intervention is attempted and no attempt is made to alter the course of the disease. The goal is to retrospectively determine the exposure to the risk factor of interest from each of the two groups of individuals: cases and controls. These studies are designed to estimate odds.
Case control studies are also known as "retrospective studies" and "case-referent studies."
- Good for studying rare conditions or diseases
- Less time needed to conduct the study because the condition or disease has already occurred
- Lets you simultaneously look at multiple risk factors
- Useful as initial studies to establish an association
- Can answer questions that could not be answered through other study designs
Disadvantages
- Retrospective studies have more problems with data quality because they rely on memory and people with a condition will be more motivated to recall risk factors (also called recall bias).
- Not good for evaluating diagnostic tests because it's already clear that the cases have the condition and the controls do not
- It can be difficult to find a suitable control group
Design pitfalls to look out for
Care should be taken to avoid confounding, which arises when an exposure and an outcome are both strongly associated with a third variable. Controls should be subjects who might have been cases in the study but are selected independent of the exposure. Cases and controls should also not be "over-matched."
Is the control group appropriate for the population? Does the study use matching or pairing appropriately to avoid the effects of a confounding variable? Does it use appropriate inclusion and exclusion criteria?
Fictitious Example
There is a suspicion that zinc oxide, the white non-absorbent sunscreen traditionally worn by lifeguards is more effective at preventing sunburns that lead to skin cancer than absorbent sunscreen lotions. A case-control study was conducted to investigate if exposure to zinc oxide is a more effective skin cancer prevention measure. The study involved comparing a group of former lifeguards that had developed cancer on their cheeks and noses (cases) to a group of lifeguards without this type of cancer (controls) and assess their prior exposure to zinc oxide or absorbent sunscreen lotions.
This study would be retrospective in that the former lifeguards would be asked to recall which type of sunscreen they used on their face and approximately how often. This could be either a matched or unmatched study, but efforts would need to be made to ensure that the former lifeguards are of the same average age, and lifeguarded for a similar number of seasons and amount of time per season.
Real-life Examples
Boubekri, M., Cheung, I., Reid, K., Wang, C., & Zee, P. (2014). Impact of windows and daylight exposure on overall health and sleep quality of office workers: a case-control pilot study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine : JCSM : Official Publication of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 10 (6), 603-611. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.3780
This pilot study explored the impact of exposure to daylight on the health of office workers (measuring well-being and sleep quality subjectively, and light exposure, activity level and sleep-wake patterns via actigraphy). Individuals with windows in their workplaces had more light exposure, longer sleep duration, and more physical activity. They also reported a better scores in the areas of vitality and role limitations due to physical problems, better sleep quality and less sleep disturbances.
Togha, M., Razeghi Jahromi, S., Ghorbani, Z., Martami, F., & Seifishahpar, M. (2018). Serum Vitamin D Status in a Group of Migraine Patients Compared With Healthy Controls: A Case-Control Study. Headache, 58 (10), 1530-1540. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.13423
This case-control study compared serum vitamin D levels in individuals who experience migraine headaches with their matched controls. Studied over a period of thirty days, individuals with higher levels of serum Vitamin D was associated with lower odds of migraine headache.
Related Formulas
- Odds ratio in an unmatched study
- Odds ratio in a matched study
Related Terms
A patient with the disease or outcome of interest.
Confounding
When an exposure and an outcome are both strongly associated with a third variable.
A patient who does not have the disease or outcome.
Matched Design
Each case is matched individually with a control according to certain characteristics such as age and gender. It is important to remember that the concordant pairs (pairs in which the case and control are either both exposed or both not exposed) tell us nothing about the risk of exposure separately for cases or controls.
Observed Assignment
The method of assignment of individuals to study and control groups in observational studies when the investigator does not intervene to perform the assignment.
Unmatched Design
The controls are a sample from a suitable non-affected population.
Now test yourself!
1. Case Control Studies are prospective in that they follow the cases and controls over time and observe what occurs.
a) True b) False
2. Which of the following is an advantage of Case Control Studies?
a) They can simultaneously look at multiple risk factors. b) They are useful to initially establish an association between a risk factor and a disease or outcome. c) They take less time to complete because the condition or disease has already occurred. d) b and c only e) a, b, and c
Evidence Pyramid - Navigation
- Meta- Analysis
- Case Reports
- << Previous: Case Report
- Next: Cohort Study >>

- Last Updated: Sep 25, 2023 10:59 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/studydesign101

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2962
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unlike most other studies, a retrospective study collects data that have been previously collected for some other reason than research (Hess, 2004). 2. Terminology Note. In epidemiology (i.e. in clinical studies), "case-control" and "retrospective study" are used synonymously.
A case series is a retrospective, noncomparative investigation that evaluates a group of patients with a known medical condition, disease state, exposure, or who have undergone a similar procedure. Case series is one of the most common studies performed in medical research and provides the foundation for many more rigorous research studies.
Matched Case-Control Study Summary A retrospective study uses existing data that have been recorded for reasons other than research. A retrospective case series is the description of a group of cases with a new or unusual disease or treatment. With a case-control study, cases with and without the condition of interest are identified,
The retrospective case-control study is an important research strategy encountered in the medical literature, and if carefully executed, can be an invaluable source of clinical information. Unfortunately, the retrospective viewpoint of case-control studies—looking "backwards" from an outcome event to an earlier exposure—is accompanied ...
Case-control studies are retrospective. They clearly define two groups at the start: one with the outcome/disease and one without the outcome/disease. They look back to assess whether there is a statistically significant difference in the rates of exposure to a defined risk factor between the groups. See Figure 1 for a pictorial representation ...
As a retrospective, descriptive study, case series are a relatively high-yield study in terms of generating new hypotheses from existing clinical data. Compared to design and execution of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), case series are a relatively cost-effective and less labor-intensive approach to identifying clinical correlations and ...
Retrospective cohort and case-control studies are similar but generally have differing goals. Cohort designs typically assess known risk factors and how they affect outcomes at different times. Case-control studies evaluate a particular incident, and it is an exploratory design to identify potential risk factors.
A case-control study is a type of observational study commonly used to look at factors associated with diseases or outcomes.[1] ... The main issues of concern with a case-control study are recall bias, its retrospective nature, the need for a careful collection of measured variables, and the selection of an appropriate control group. These are ...
Case series (comprising five or more patients) and case reports (fewer than five patients) are the result of prospective or retrospective reporting of a single cohort of patients. Unlike comparative cohort studies, case series and case reports have few patients and a single cohort, so they do not typically include comparative statistical analyses.
These studies are designed to estimate odds. Case control studies are also known as "retrospective studies" and "case-referent studies." Advantages. Good for studying rare conditions or diseases; Less time needed to conduct the study because the condition or disease has already occurred; Lets you simultaneously look at multiple risk factors