If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Course: 8th grade > Unit 5
- Use Pythagorean theorem to find area of an isosceles triangle
- Use Pythagorean theorem to find perimeter
- Use Pythagorean theorem to find area
- Pythagorean theorem word problem: carpet
- Pythagorean theorem word problem: fishing boat
Pythagorean theorem word problems
- Pythagorean theorem in 3D
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4

Free Mathematics Tutorials
- Math Problems
- Algebra Questions and Problems
- Graphs of Functions, Equations, and Algebra
- Free Math Worksheets to Download
- Analytical Tutorials
- Solving Equation and Inequalities
- Online Math Calculators and Solvers
- Free Graph Paper
- Math Software
- The Applications of Mathematics in Physics and Engineering
- Exercises de Mathematiques Utilisant les Applets
- Calculus Tutorials and Problems
- Calculus Questions With Answers
- Free Calculus Worksheets to Download
- Geometry Tutorials and Problems
- Online Geometry Calculators and Solvers
- Free Geometry Worksheets to Download
- Trigonometry Tutorials and Problems for Self Tests
- Free Trigonometry Questions with Answers
- Free Trigonometry Worksheets to Download
- Elementary Statistics and Probability Tutorials and Problems
- Mathematics pages in French
- About the author
- Primary Math
- Middle School Math
- High School Math
- Free Practice for SAT, ACT and Compass Math tests
Pythagorean Theorem and Problems with Solutions
Explore some simple proofs of the Pythagorean theorem and its converse and use them to solve problems. Detailed solutions to the problems are also presented.
POPULAR PAGES
privacy policy

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.1: The Pythagorean Theorem
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 35449

- David Arnold
- College of the Redwoods
Pythagoras was a Greek mathematician and philosopher, born on the island of Samos (ca. 582 BC). He founded a number of schools, one in particular in a town in southern Italy called Crotone, whose members eventually became known as the Pythagoreans. The inner circle at the school, the Mathematikoi, lived at the school, rid themselves of all personal possessions, were vegetarians, and observed a strict vow of silence. They studied mathematics, philosophy, and music, and held the belief that numbers constitute the true nature of things, giving numbers a mystical or even spiritual quality.
Today, nothing is known of Pythagoras’s writings, perhaps due to the secrecy and silence of the Pythagorean society. However, one of the most famous theorems in all of mathematics does bear his name, the Pythagorean Theorem.
Prior to revealing the contents of the Pythagorean Theorem, we pause to provide the definition of a right triangle and its constituent parts.
Right Triangle
A triangle with one right angle (90 ◦ ) is called a right triangle . In the figure below, the right angle is marked with a little square.

The side of the triangle that is directly opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse . The sides of the triangle that include the right angle are called the legs of the right triangle.
Now we can state one of the most ancient theorems of mathematics, the Pythagorean Theorem .
Pythagorean Theorem
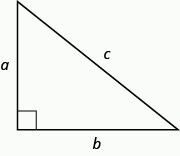
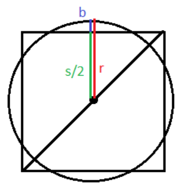
Let \(c\) represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and let a and b represent the lengths of its legs, as pictured in the image that follows.

The relationship involving the legs and hypotenuse of the right triangle, given by
\[a^2 + b^2 = c^2,\nonumber \]
is called the Pythagorean Theorem .
Here are two important observations.
Observations Regarding the Hypotenuse
Two important facts regarding the hypotenuse of the right triangle are:
- The hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle and lies directly opposite the right angle.
- In the Pythagorean equation \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), the hypotenuse lies by itself on one side of the equation.
The Pythagorean Theorem can only be applied to right triangles.
Let’s look at a simple application of the Pythagorean Theorem.
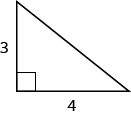
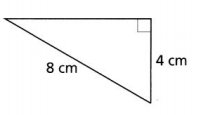
The legs of a right triangle measure 3 and 4 meters, respectively. Find the length of the hypotenuse.
Let’s follow the Requirements for Word Problem Solutions .
1. Set up a Variable Dictionary . Let c represent the length of the hypotenuse, as pictured in the following sketch.
2. Set up an Equation . The Pythagorean Theorem says that
\[a^2 + b^2 = c^2.\nonumber \]
In this example, the legs are known. Substitute 4 for a and 3 for b (3 for a and 4 for b works equally well) into the Pythagorean equation.
\[4^2 + 3^2 = c^2\nonumber \]
3. Solve the Equation .
\[ \begin{aligned} 4^2 + 3^2 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ The Pythagorean equation.}} \\ 16 + 9 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 4^2 = 16 \text{ and } 3^2 = 9.} \\ 25 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Add: } 16+9=25.} \\ 5 = c~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
Technically, there are two answers to c 2 = 25, i.e., c = −5 or c = 5. However, c represents the hypotenuse of the right triangle and must be nonnegative. Hence, we must choose c = 5.
4. Answer the Question . The hypotenuse has length 5 meters.
5. Look Back . Do the numbers satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem? The sum of the squares of the legs should equal the square of the hypotenuse. Let’s check.
\[\begin{aligned} 4^2 + 3^2 = 5^2 \\ 16 + 9 = 25 \\ 25 = 25 \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
All is well!
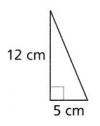
The legs of a right triangle measure 5 and 12 feet, respectively. Find the length of the hypotenuse.
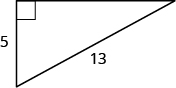
Given the following right triangle, find the length of the missing side.

Note that the hypotenuse (across from the right angle) has length 13. This quantity should lie on one side of the Pythagorean equation all by itself. The sum of the squares of the legs go on the other side. Hence,
\[5^2 + x^2 = 13^2\nonumber \]
Solve the equation for x .
\[ \begin{aligned} 25+x^2 = 169 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 5^2 = 25 \text{ and } 13^2 = 169.} \\ 25 + x^2 -25 = 169 - 25 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Subtract 25 from both sides.}} \\ x^2 = 144 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Simplify both sides.}} \\ x= 12 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root of 144.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
The hypotenuse of a right triangle measures 25 centimeters. One leg of the right triangle measures 24 centimeters. Find the length of the remaining leg.
7 centimeters
Perfect squares are nice, but not required.
Given the following right triangle, find the exact length of the missing side.

Note that the hypotenuse (across from the right angle) has length 12. This quantity should lie on one side of the Pythagorean equation all by itself. The sum of the squares of the legs go on the other side. Hence,
\[x^2 + 7^2 = 12^2\nonumber \]
\[ \begin{aligned} x^2 + 49 = 144 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 7^2 = 49 \text{ and } 12^2 = 144.} \\ x^2 + 49-49 = 144 - 49 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Subtract 49 from both sides.}} \\ x^2 = 95 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Simplify both sides.}} \\ x = \sqrt{95} ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root of 95.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
Hence, the exact length of the missing side is \(\sqrt{95}\).
The hypotenuse and one leg of a right triangle measure 9 and 7 inches, respectively. Find the length of the remaining leg.
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
Important Observation
Any attempt to use your calculator to approximate 95 in Example 3 would be an error as the instructions asked for an exact answer.
Sometimes an approximate answer is desired, particularly in applications.
Ginny want to create a vegetable garden in the corner of her yard in the shape of a right triangle. She cuts two boards of length 8 feet which will form the legs of her garden. Find the length of board she should cut to form the hypotenuse of her garden, correct to the nearest tenth of a foot.
We follow the Requirements for Word Problem Solutions .
1. Set up a Variable Dictionary . We begin with a labeled sketch. Let x represent the length of the unknown hypotenuse.

2. Set Up an Equation . The hypotenuse is isolated on one side of the Pythagorean equation.
\[x^2 = 8^2 + 8^2\nonumber \]
\[ \begin{aligned} x^2 = 8^2 + 8^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ The Pythagorean equation.}} \\ x^2 = 64 + 64 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 8^2 = 64 \text{ and } 8^2 = 64.} \\ x^2 = 128 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Add: } 64 + 64 = 128.} \\ x = \sqrt{128} ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
4. Answer the Question . The exact length of the hypotenuse is \(\sqrt{128}\) feet, but we’re asked to find the hypotenuse to the nearest tenth of a foot. Using a calculator, we find an approximation for \(\sqrt{128}\).
\[\sqrt{128} \approx 11.313708499\nonumber \]
To round to the nearest tenth, first identify the rounding and test digits.

The test digit is less than five. So we leave the rounding digit alone and truncate. Therefore, correct to the nearest tenth of a foot, the length of the hypotenuse is approximately 11.3 feet.
5. Look Back . The sum of the squares of the legs is
\[ \begin{aligned} 8^2 + 8^2 = 64 + 64 \\ = 128. \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
The square of the hypotenuse is
\[(11.3)^2 = 127.69\nonumber \]
These are almost the same, the discrepancy due to the fact that we rounded to find an approximation for the hypotenuse.
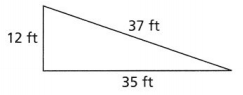
A 15 foot ladder leans against the wall of a building. The base of the ladder lies 5 feet from the base of the wall. How high up the wall does the top of the ladder reach? Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a foot.
In Exercises 1-16, your solutions should include a well-labeled sketch.
1. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 15 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 25 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
2. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 7 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 25 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
3. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 12 meters and 16 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
4. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 9 meters and 12 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
5. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 13 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 22 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
6. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 6 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
7. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 2 meters and 21 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
8. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 7 meters and 8 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
9. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 12 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 19 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
10. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 5 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 10 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
11. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 meters and 8 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
12. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 5 meters and 12 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
13. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 6 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 10 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
14. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 9 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
15. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 meters and 22 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
16. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 9 meters and 19 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
In Exercises 17-24, your solutions should include a well-labeled sketch.
17. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 3 meters and 18 meters. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
18. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 10 feet and 16 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
19. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 2 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 17 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
20. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 4 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 12 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
21. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 15 feet and 18 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
22. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 feet and 13 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
23. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 4 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 8 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
24. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 3 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
25. Greta and Fritz are planting a 13-meter by 18-meter rectangular garden, and are laying it out using string. They would like to know the length of a diagonal to make sure that right angles are formed. Find the length of a diagonal. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
26. Markos and Angelina are planting an 11- meter by 19-meter rectangular garden, and are laying it out using string. They would like to know the length of a diagonal to make sure that right angles are formed. Find the length of a diagonal. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
27. The base of a 24-meter long guy wire is located 10 meters from the base of the telephone pole that it is anchoring. How high up the pole does the guy wire reach? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
28. The base of a 30-foot long guy wire is located 9 feet from the base of the telephone pole that it is anchoring. How high up the pole does the guy wire reach? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
29. Hiking Trail. A hiking trail runs due south for 8 kilometers, then turns west for about 15 kilometers, and then heads northeast on a direct path to the starting point. How long is the entire trail?
30. Animal Trail. An animal trail runs due east from a watering hole for 12 kilometers, then goes north for 5 kilometers. Then the trail turns southwest on a direct path back to the watering hole. How long is the entire trail?
31. Upper Window. A 10-foot ladder leans against the wall of a house. How close to the wall must the bottom of the ladder be in order to reach a window 8 feet above the ground?
32. How high? A 10-foot ladder leans against the wall of a house. How high will the ladder be if the bottom of the ladder is 4 feet from the wall? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
1. 20 meters
3. 20 meters
5. √315 meters
7. \(\sqrt{445}\) meters
9. \(\sqrt{217}\) meters
11. 10 meters
13. 8 meters
15. \(\sqrt{520}\) meters
17. 18.25 meters
19. 16.9 meters
21. 23.43 feet
23. 6.93 meters
25. 22.20 meters
27. 21.82 meters
29. 40 kilometers
Word problems on Pythagorean Theorem
Learn how to solve different types of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem .
Pythagoras Theorem can be used to solve the problems step-by-step when we know the length of two sides of a right angled triangle and we need to get the length of the third side.
Three cases of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem :
Case 1: To find the hypotenuse where perpendicular and base are given.
Case 2: To find the base where perpendicular and hypotenuse are given.
Case 3: To find the perpendicular where base and hypotenuse are given.
Word problems using the Pythagorean Theorem:
1. A person has to walk 100 m to go from position X in the north of east direction to the position B and then to the west of Y to reach finally at position Z. The position Z is situated at the north of X and at a distance of 60 m from X. Find the distance between X and Y.
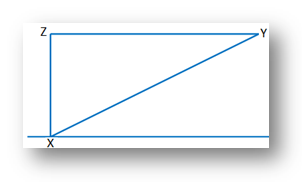
⇒ 200x = 10000 + 3600
⇒ 200x = 13600
⇒ x = 13600/200
Therefore, distance between X and Y = 68 meters.
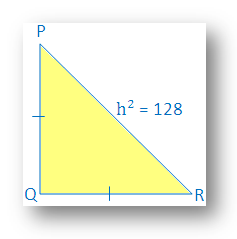
Therefore, length of each side is 8 cm.
Using the formula solve more word problems on Pythagorean Theorem.
3. Find the perimeter of a rectangle whose length is 150 m and the diagonal is 170 m.
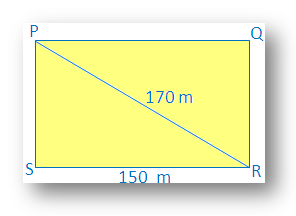
In a rectangle, each angle measures 90°.
Therefore PSR is right angled at S
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get
⇒ PS = √6400
Therefore perimeter of the rectangle PQRS = 2 (length + width)
= 2 (150 + 80) m
= 2 (230) m
= 460 m
4. A ladder 13 m long is placed on the ground in such a way that it touches the top of a vertical wall 12 m high. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the bottom of the wall.
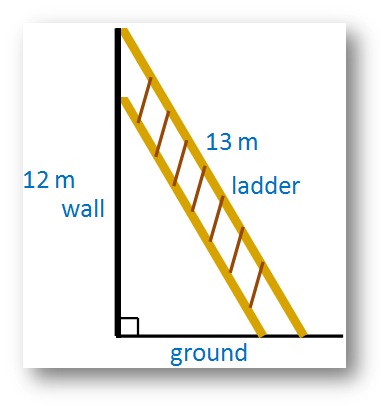
Let the required distance be x meters. Here, the ladder, the wall and the ground from a right-angled triangle. The ladder is the hypotenuse of that triangle.
According to Pythagorean Theorem,
Therefore, distance of the foot of the ladder from the bottom of the wall = 5 meters.
5. The height of two building is 34 m and 29 m respectively. If the distance between the two building is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
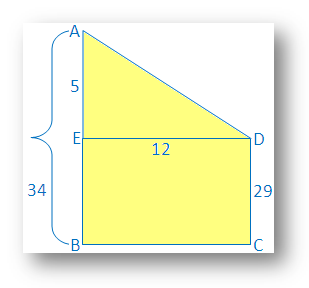
The vertical buildings AB and CD are 34 m and 29 m respectively.
Draw DE ┴ AB
Then AE = AB – EB but EB = BC
Therefore AE = 34 m - 29 m = 5 m
Now, AED is right angled triangle and right angled at E.
⇒ AD = √169
Therefore the distance between their tops = 13 m.
The examples will help us to solve various types of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem.
Congruent Shapes
Congruent Line-segments
Congruent Angles
Congruent Triangles
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Side Side Side Congruence
Side Angle Side Congruence
Angle Side Angle Congruence
Angle Angle Side Congruence
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Pythagorean Theorem
Proof of Pythagorean Theorem
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems 8th Grade Math Practice From Word problems on Pythagorean Theorem to HOME PAGE
New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
Worksheet on Word Problems on Division | Division Word Problems
Apr 08, 24 02:58 PM
Word Problems on Division | Examples on Word Problems on Division
Apr 08, 24 12:46 PM
Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Number | Long Division |Worksheet Answer
Apr 08, 24 11:08 AM

Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers | Dividing Larger Numbers
Apr 08, 24 01:22 AM

Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers | Worksheet with Answer
Apr 07, 24 02:54 PM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
Math teaching support you can trust

resources downloaded

one-on-one tutoring sessions

schools supported
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities
Engage your students with our ready-to-go packs of no-prep games and activities for a range of abilities across Kindergarten to Grade 5!
15 Pythagorean Theorem Practice Problems For 8th Grade
Beki christian.
Pythagorean Theorem practice problems involve using the relationship between the sides of a right triangle to calculate missing side lengths in triangles. The Pythagorean Theorem is introduced in 8th grade and is used to solve a variety of problems across high school.
Here, you’ll find a selection of Pythagorean Theorem questions that demonstrate the different types of questions students are likely to encounter in 8th grade.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
How to answer pythagorean theorem questions, pythagorean theorem in real life, pythagorean theorem in 8th grade, pythagorean theorem practice problems.
The Pythagorean Theorem is the geometric theorem that states that the square of the hypotenuse (longest side) of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides of the triangle.
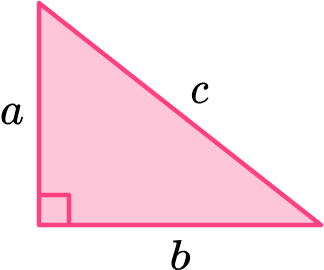
This can be written as a^2+b^2=c^2 for a triangle labeled like this:
15 Pythagoras Theorem Practice Problems
Wish you could have the 15 Pythagoras Theorem questions from this blog in a ready-to-go worksheet? We've done just that!
1 – Label the sides of the triangle a , b , and c . Note that the hypotenuse, the longest side of a right triangle, is opposite the right angle and will always be labeled .
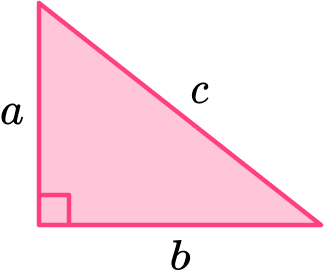
2 – Write down the formula and substitute the values>
3 – Calculate the answer. You may be asked to give your answer in an exact form or round to a given degree of accuracy, such as a certain number of decimal places or significant figures.
Pythagorean Theorem has many real-life uses, including in architecture and construction, navigation and surveying.
Pythagorean Theorem is usually introduced in middle school, as it is a part of the 8th grade Common Core Math Standards.
The emphasis in middle school is on students being able to:
- Explain the Pythagorean Theorem;
- Use the theorem to solve mathematical and real-world problems – with both 2D and 3D figures;
- Use the theorem to calculate the distance between two points on a coordinate grid.
The process for solving any Pythagoras Theorem problem always begins by identifying the relevant right-angled triangle and labeling the sides a , b , c. If there is not a diagram in the question, it can be helpful to draw one.
Where necessary, round your answers to 3 significant figures.
1. A ship sails 6 \, km East and then 8 \, km North. Find the ship’s distance from its starting point.
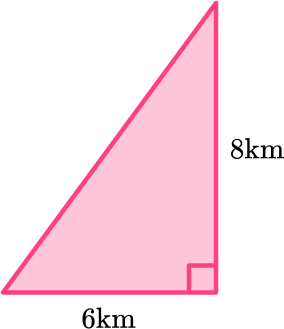
The ship is 10 kilometers from its starting point.
2. A ladder is 5 \, m long. The base of the ladder is 3 \, m from the base of a vertical wall. How far up the wall does the ladder reach?
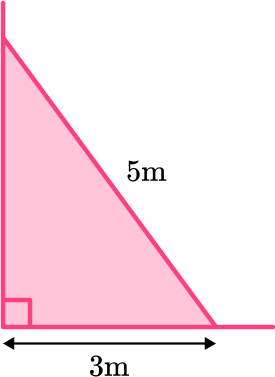
The ladder reaches 4 meters up the wall.
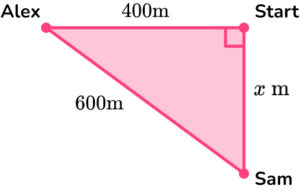
3. Alex and Sam start from the same point. Alex walks 400 meters west. Sam walks x meters south, until they are 600 \, m apart from each other. How far does Sam walk?
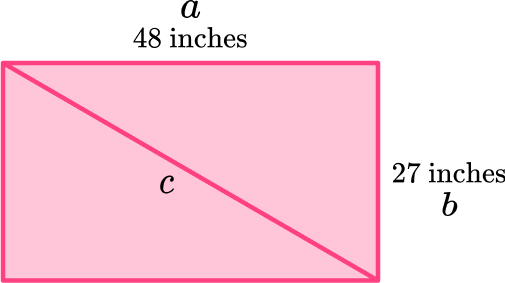
4. A television’s size is the measurement from the upper left hand corner of the television to the bottom right hand corner. Find the size of this television.

39.7 inches
55.1 inches
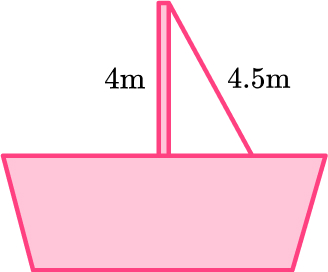
5. The pole of a sailing boat is supported by a rope from the top of the pole to an anchor point on the deck. The pole is 4 \, m long and the rope is 4.5 \, m long. Calculate the distance from the base of the pole to the anchor point of the rope on the deck.
6. Work out the length of the diagonal of a square with 8 \, cm sides.
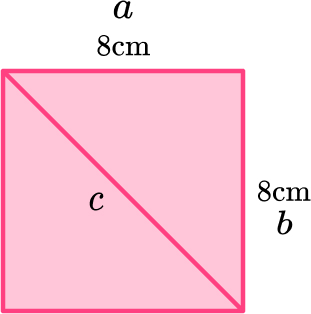
The diagonal of the square has a length of 11.3 centimeters.
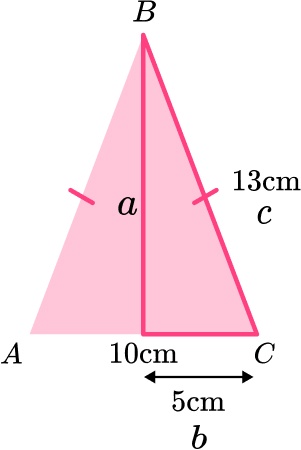
7. ABC is an isosceles triangle.
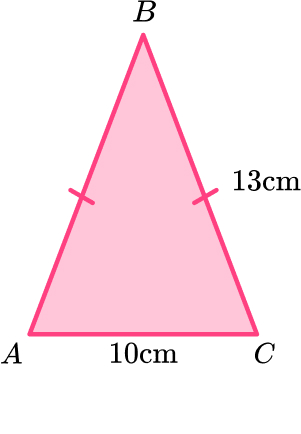
Work out the height of the triangle.
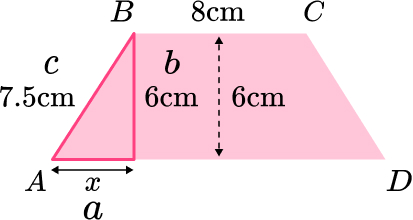
8. ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid.
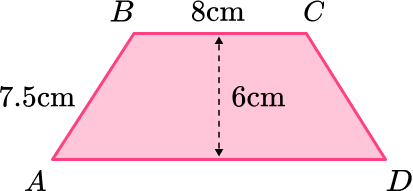
Work out the length of AD.
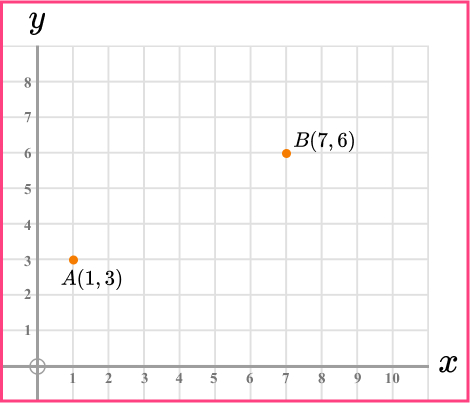
9. Here is a cm square grid. Calculate the distance between the points A and B.
10. Which is a right angled triangle?
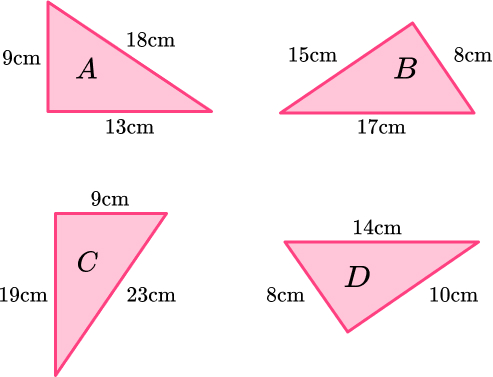
Not a right angled triangle because Pythagorean Theorem doesn’t work.
Right angled triangle because Pythagorean Theorem works.
11. PQRS is made from two right angled triangles.
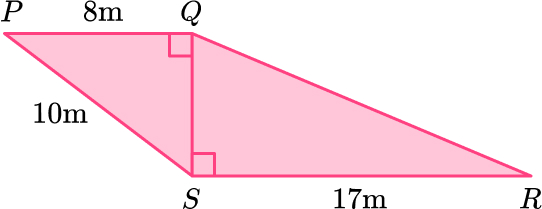
Work out the length of QR.
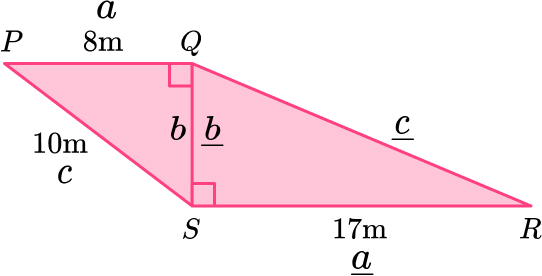
Triangle \text{PQS:}
Triangle \text{QRS}
12. Here is a pattern made from right angled triangles. Work out the length x.
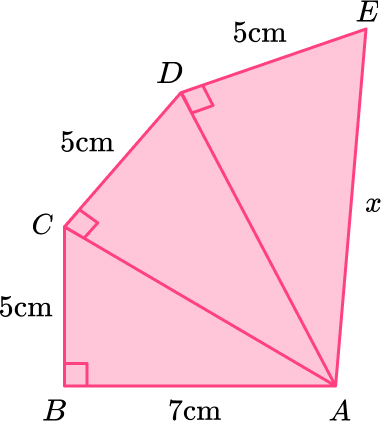
Triangle \text{ABC:}
Triangle \text{ACD:}
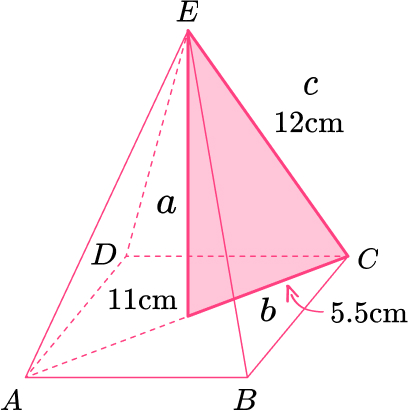
13. Here is a pyramid.
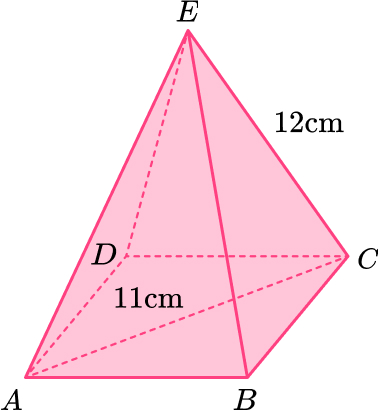
Work out the height of the pyramid.
14. Here is a cuboid.
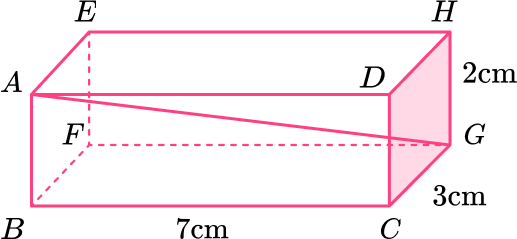
Work out the length AG.
Give your answer in its exact form.
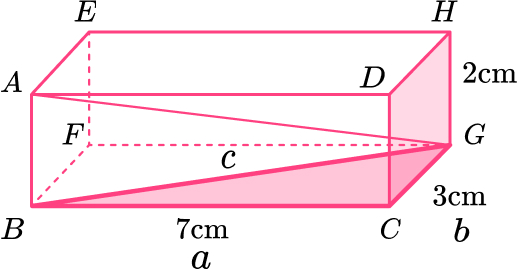
Length of \text{BG:}
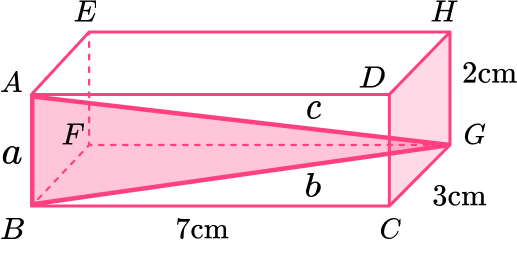
Length of \text{AG:}
15. Here is a right angled triangle.
Form an equation and use it to work out the value of x.
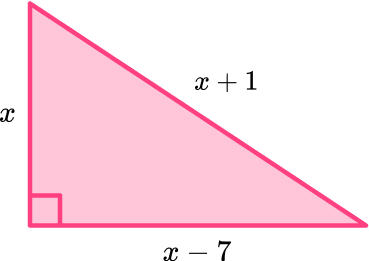
x=4 \, or \, x=12
x cannot be 4 as you can’t have a negative side length so x=12
In middle school, students…
- prove the Pythagorean Theorem;
- use the Pythagorean Theorem with trigonometric ratios to solve problems;
- use the Pythagorean Theorem in proofs.
Pythagoras Theorem may feature in questions alongside other topics, such as trigonometry, circle theorems or algebra.
The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate a missing length in a right triangle . If you have a right angled triangle and you know two of the lengths, label the sides of the triangle a,b and c (c must be the hypotenuse – the longest side). Pythagorean Theorem is a^2+b^2=c^2. Substitute the values you know into Pythagorean Theorem and solve to find the missing side.
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side. If you know the lengths of the other two sides, you can find the length of the hypotenuse by squaring the two shorter sides, adding those values together and then taking the square root. By doing this you are finding c in a^2+b^2=c^2
If your triangle is a right triangle and you know two of the sides, you can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side. To do this, label the sides a , b and c (with c being the hypotenuse – the longest side). Substitute the values you know into a^2+b^2=c^2 and solve to find the missing side.
Looking for more Pythagorean theorem math questions?
- Ratio questions
- Algebra questions
- Probability questions
- Trigonometry questions
- Venn diagram questions
- Long division questions
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
The content in this article was originally written by former UK Secondary teacher Beki Christian and has since been revised and adapted for US schools by elementary and middle school teacher Kathleen Epperson.
Math Games for 6th Graders [FREE]
On the lookout to make your math lessons fun and interactive while building math skills? Try our 6 printable math games for 6th graders.
Playable in pairs, teams or a whole class, our accompanying instructions and printable resources make preparation a breeze!
Privacy Overview
Module 11: Geometry
Using the pythagorean theorem to solve problems, learning outcomes.
- Use the pythagorean theorem to find the unknown length of a right triangle given the two other lengths
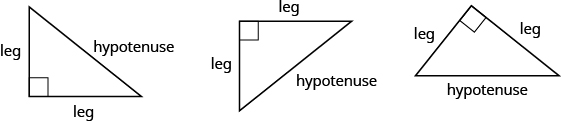
The Pythagorean Theorem is a special property of right triangles that has been used since ancient times. It is named after the Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras who lived around [latex]500[/latex] BCE.
Remember that a right triangle has a [latex]90^\circ [/latex] angle, which we usually mark with a small square in the corner. The side of the triangle opposite the [latex]90^\circ [/latex] angle is called the hypotenuse, and the other two sides are called the legs. See the triangles below.
In a right triangle, the side opposite the [latex]90^\circ [/latex] angle is called the hypotenuse and each of the other sides is called a leg.
The Pythagorean Theorem
In any right triangle [latex]\Delta ABC[/latex],
[latex]{a}^{2}+{b}^{2}={c}^{2}[/latex]
where [latex]c[/latex] is the length of the hypotenuse [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]b[/latex] are the lengths of the legs.
To solve problems that use the Pythagorean Theorem, we will need to find square roots. In Simplify and Use Square Roots we introduced the notation [latex]\sqrt{m}[/latex] and defined it in this way:
[latex]\text{If }m={n}^{2},\text{ then }\sqrt{m}=n\text{ for }n\ge 0[/latex]
For example, we found that [latex]\sqrt{25}[/latex] is [latex]5[/latex] because [latex]{5}^{2}=25[/latex].
We will use this definition of square roots to solve for the length of a side in a right triangle.
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the longer leg.
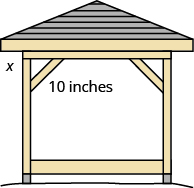
Kelvin is building a gazebo and wants to brace each corner by placing a [latex]\text{10-inch}[/latex] wooden bracket diagonally as shown. How far below the corner should he fasten the bracket if he wants the distances from the corner to each end of the bracket to be equal? Approximate to the nearest tenth of an inch.
In the following video we show two more examples of how to use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve application problems.
- Question ID 146918, 146916, 146914, 146913. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Solve Applications Using the Pythagorean Theorem (c only). Authored by : James Sousa (mathispower4u.com). Located at : https://youtu.be/2P0dJxpwFMY . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]

enVision Math Common Core Grade 8 Answer Key Topic 7 Understand And Apply The Pythagorean Theorem
Practice with the help of enVision Math Common Core Grade 8 Answer Key Topic 7 Understand and Apply the Pythagorean Theorem regularly and improve your accuracy in solving questions.
enVision Math Common Core 8th Grade Answers Key Topic 7 Understand And Apply The Pythagorean Theorem
Topic Essential Question How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems? Answer: The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate the steepness of slopes of hills or mountains. A surveyor looks through a telescope toward a measuring stick a fixed distance away, so that the telescope’s line of sight and the measuring stick form a right angle.
3-ACT MATH OOO


Topic 7 enVision STEM Project
Topic 7 GET READY!
Review What You Know!
Vocabulary Choose the best term from the box to complete each definition. cube root diagonal isosceles triangle perimeter right triangle square root
Question 1. The __________ of a number is a factor that when multiplied by itself gives the number. Answer: We know that, The “Square root” of a number is a factor that when multiplied by itself gives the number Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the best term to complete the given definition is a “Square root”
Question 2. A _________ is a line segment that connects two vertices of a polygon and is not the side. Answer: We know that, A “Diagonal” is a line segment that connects two vertices of a polygon and is not the side Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the best term to complete the given definition is a “Diagonal”
Question 3. The _________ of a figure is the distance around it. Answer: We know that, The “Perimeter” of a figure is the distance around it Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the best term to complete the given definition is the “Perimeter”
Question 4. A ___________ is a triangle with one right angle. Answer: We know that, A “Right triangle” is a triangle with one right angle Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the best term to complete the given definition is a “Right angle”
Simplify Expressions with Exponents
Simplify the expression. Question 5. 3 2 + 4 2 Answer: The given expression is: 3 2 + 4 2 So, 3 2 + 4 2 = (3 × 3) + (4 × 4) = 9 + 16 = 25
Question 6. 2 2 + 5 2 Answer: The given expression is: 2 2 + 5 2 So, 2² + 5 2 = (2 × 2) + (5 × 5) = 4 + 25 = 29
Question 7. 10 2 – 8 2 Answer: The given expression is: 10 2 – 8 2 So, 10 2 – 8 2 = (10 × 10) – (8 × 8) = 100 – 64 = 36
Square Roots
Determine the square root. Question 8. \(\sqrt {81}\) Answer: The given expression is: \(\sqrt{81}\) Hence, \(\sqrt{81}\) = 9
Question 9. \(\sqrt {144}\) Answer: The given expression is: \(\sqrt{144}\) Hence, \(\sqrt{144}\) = 12
Question 10. \(\sqrt {225}\) Answer: The given expression is: \(\sqrt{225}\) Hence, \(\sqrt{225}\) = 15
Distance on a Coordinate Plane
Language Development
Topic 7 MID-TOPIC CHECKPOINT
Question 1. Vocabulary How are the hypotenuse and the legs of a right triangle related? Lesson 7-1 Answer: The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse. The sides adjacent to the right angle are called legs
Question 2. Given that ∆QPR has side lengths of 12.5 centimeters, 30 centimeters, and 32.5 centimeters, proves ∆QPR is a right triangle. Lesson 7-2 Answer: It is given that ∆QPR has side lengths of 12.5 centimeters, 30 centimeters, and 32.5 centimeters Now, We know that, According to the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, If c² = a² + b², then, the triangle is a right triangle So, (32.5)² = (12.5)² + 30² 1,056.25 = 156.25 + 900 1,056.25 = 1,056.25 So, The condition c² = a² + b² is true for the given side lengths of a triangle Hence, from the above, We can conclude that ΔQPR is a right triangle
Question 3. Ella said that if she knows the lengths of just two sides of any triangle, then she can find the length of the third side by using the Pythagorean Theorem. Is Ella correct? Explain. Lesson 7-1 Answer: Ella said that if she knows the lengths of just two sides of any triangle, then she can find the length of the third side by using the Pythagorean Theorem. Now, We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the hypotenuse a and b are the legs Now, If we know a and b, then we can find c If we know b and c, then we can find a If we know a and c, then we can find b Hence, from the above, We can conclude that Ella is correct
Question 6. Select all the sets of lengths that could represent the sides of a right triangle. Lesson 7-2 ☐ 5 cm, 10 cm, 15 cm ☐ 7 in., 14 in., 25 in. ☐ 13 m, 84 m, 85 m ☐ 5 ft, 11 ft, 12 ft ☐ 6ft, 9 ft, \(\sqrt {117}\) ft Answer: Let the given options be named as A, B, C, D, and E Now, We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the hypotenuse and has the longest length a and b are the legs So, A) 15² = 5² + 10² 225 = 25 + 100 225 ≠ 125 B) 25² = 7² + 14² 625 = 49 + 196 625 ≠ 245 C) 85² = 84² + 13² 7,225 = 7,056 + 169 7,225 = 7,225 D) 12² = 11² + 5² 144 = 121 + 25 144 ≠ 146 E) (\(\sqrt{117}\))² = 6² + 9² 117 = 36 + 81 17 = 117 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the side lengths present in options C and E represent the side lengths of a right triangle
Topic 7 MID-TOPIC PERFORMANCE TASK
Javier is standing near a palm tree. He holds an electronic tape measure near his eyes and finds the three distances shown.
PART A Javier says that he can now use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height of the tree. Explain. Use vocabulary terms in your explanation. Answer: It is given that Javier says that he can now use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height of the tree Now, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. The sides of this triangle have been named Perpendicular (The height of the tree), Base, and Hypotenuse.
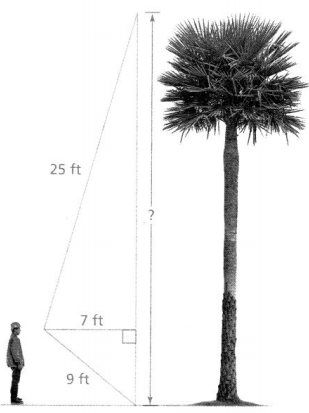
PART C Javier moves backward so that his horizontal distance from the palm tree is 3 feet greater. Will the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree also be 3 feet greater? Explain. Answer: Yes it will be greater, he is moving back 3 feet so what you are doing is taking the leg (a²) and multiplying it by 3. Once you do, you see triangle 1 has double and so did triangle 2. Triangle 2 was originally 5.6 (rounded to 6) then went up to 26.1. Triangle 1 was originally 24 and went up to 74.7 (or 75) Step-by-step explanation: For Triangle 1 (when multiplied by 3): We know that, a² + b² = c² 7² + b² = 27² 49 + b² = 729 b² = 680 b = \(\sqrt{680}\) b = 26.1 ft For Triangle 2: We know that, a² + b² = c² 7² + b² =75² b² = 5576 b = \(\sqrt{5,576}\) b = 74.7 ft
PART D Could Javier change his horizontal distance from the tree so that the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree is only 20 feet? Explain. Answer: Yes, Javier can change his horizontal distance from the tree so that the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree is only 20 feet by moving forward 5 ft
Lesson 7.3 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to Solve Problems
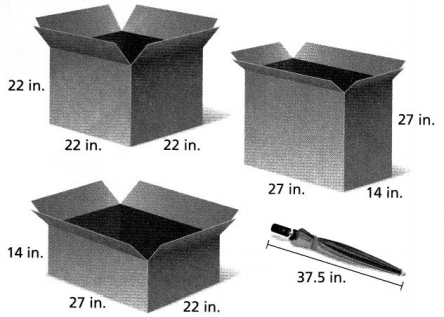
Make Sense and Persevere How will the umbrella fit inside any of the boxes? Answer: We know that, The box is a 3-d figure So, To fit the whole umbrella in the box, we have to put it in a diagonal manner i.e., like the hypotenuse of a right triangle
Focus on math practices Construct Arguments Tim says that the diagonal of any of the boxes will always be longer than the sides. Is Tim correct? Explain. Answer: We know that, If we consider a square or any 2-d figure or any 3-d figure that consists of 1 right angle, then, the diagonal will divide a figure into 2 right triangles We know that, We can apply the Pythagorean Theorem for any right triangle We know that, In a right triangle, The hypotenuse is the longest side We know that, The hypotenuse in a right triangle is considered as a diagonal in a figure that consists of 1 right angle Hence, from the above, We can conclude that Tim is correct
Essential Question What types of problems can be solved using the Pythagorean Theorem? Answer: The Pythagorean theorem is a way of relating the leg lengths of a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse, which is the side opposite the right angle. Even though it is written in these terms, it can be used to find any of the sides as long as you know the lengths of the other two sides
What is the length of the diagonal, d, of a rectangle with length 19 feet and width 17 feet? leg 2 + leg 2 = hypotenuse 2 ______ 2 + _______ 2 = d 2 ______ + _______ = d 2 _______ = d 2 ________ ≈ d Answer: It is given that a rectangle has a length of 19 feet and a width of 17 feet Now, We know that, In a rectangle, If a diagonal is drawn, then it divides the rectangle into 2 right angles So, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, d² = a² + b² Where, d is the diagonal or hypotenuse a and b are the lengths of the legs So, d²= 19² + 17² d² = 361 + 289 d² = 650 d = \(\sqrt{650}\) d = 25.4 ft Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the length of the diagonal is: 25.4 ft
Convince Me! If the rectangle were a square, would the process of finding the length of the diagonal change? Explain. Answer: We know that, For any figure i.e., either 2-d figure or 3-d figure with 1 right angle, the diagonal will divide that figure into 2 right angles We know that, We will use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of any unknown side in the right triangle Hence, from the above, We can conclude that even if the rectangle were a square, the process of finding the length of the diagonal will not change
Do You Understand? Question 1. Essential Question What types of problems can be solved using the Pythagorean Theorem? Answer: The Pythagorean theorem is a way of relating the leg lengths of a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse, which is the side opposite the right angle. Even though it is written in these terms, it can be used to find any of the sides as long as you know the lengths of the other two sides
Question 2. Look for Structure How is using the Pythagorean Theorem in a rectangular prism similar to using it in a rectangle? Answer: We know that, The rectangular prism and the rectangle have at least 1 right angle We know that, If a 3-d or 2-d figure has 1 right angle, then the diagonal of that figure divides the figure into the right triangles So, If we have the right triangle, then we can use the Pythagorean Theorem irrespective of the overall shape of the figure
Question 3. Construct Arguments Glen found the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle using \(\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\). Gigi used \(\sqrt{(a+b)^{2}}\). Who is correct? Explain. Answer: It is given that Glen found the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle using \(\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\). Gigi used \(\sqrt{(a+b)^{2}}\). Now, We know that, We can use the Pythagorean Theorem only for the right triangles The condition for a triangle to become the right triangle is: Hypotenuse² = Side² + Side² c² = a² + b² Hence, from the above, We can conclude that Glen is correct
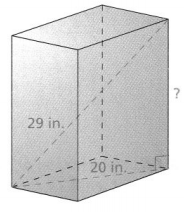
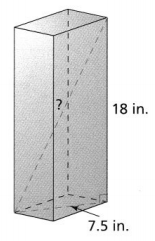
Question 5. A box-shaped like a right rectangular prism measures 5 centimeters by 3 centimeters by 2 centimeters. What is the length of the interior diagonal of the prism to the nearest hundredth? Answer: It is given that A box-shaped like a right rectangular prism measures 5 centimeters by 3 centimeters by 2 centimeters. So, The dimensions of a rectangular prism is: 5 cm × 3 cm × 2 cm So, The length of the rectangular prism is: 5 cm The width of the rectangular prism is: 3 cm The height of the rectangular prism is: 2 cm Now, We know that, The length of the diagonal of the prism = \(\sqrt{Length^{2} + Width^{2} + Height^{2}}\) So, The length of the diagonal of the rectangular prism = \(\sqrt{5^{2} + 3^{2} + 2^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{25 + 9 + 4}\) = \(\sqrt{38}\) = 6.16 cm Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the length of the interior diagonal of the rectangular prism is: 6.16 cm
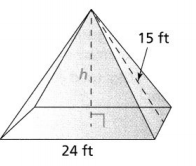
Question 9. A stainless steel patio heater is shaped like a square pyramid. The length of one side of the base is 19.8 inches. The slant height is 92.8 inches. What is the height of the heater? Round to the nearest tenth of an inch. Answer: It is given that A stainless steel patio heater is shaped like a square pyramid. The length of one side of the base is 19.8 inches. The slant height is 92.8 inches Now, We know that, The slant height is nothing but a length of the diagonal Now, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the slant height a is the length of the base of the steel patio heater b is the height of the heater So, (92.8)² = (19.8)² + b² b² = 8,611.84 – 392.04 c² = 8,219.8 c = \(\sqrt{8,219.8}\) c = 90.6 inches Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the height of the heater is: 90.6 inches
Question 10. Reasoning What is the measurement of the longest line segment in a right rectangular prism that is 16 centimeters long, 9 centimeters wide, and 7 centimeters tall? Round to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. Answer: It is given that A right rectangular prism is 16 centimeters long, 9 centimeters wide, and 7 centimeters tall So, The dimensions of a right rectangular prism are: 16 cm × 9 cm × 7 cm So, The length of the right rectangular prism is: 16 cm The width of the right rectangular prism is: 9 cm The height of the right rectangular prism is: 7 cm We know that, The longest line segment in any 2-d or 3-d figure is a “Diagonal” Now, We know that, The length of the diagonal of the right rectangular prism = \(\sqrt{Length^{2} + Width^{2} + Height^{2}}\) So, The length of the diagonal of the right rectangular prism = \(\sqrt{16^{2} + 9^{2} + 7^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{256 + 49 + 81}\) = \(\sqrt{386}\) = 19.64 cm Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the length of the longest line segment in the right rectangular prism is: 19.64 cm
Question 13.
The corner of a room where two walls meet the floor should be at a right angle. Jeff makes a mark along each wall. One mark is 3 inches from the corner. The other is 4 inches from the corner. How can Jeff use the Pythagorean Theorem to see if the walls form a right angle? Answer: It is given that The corner of a room where two walls meet the floor should be at a right angle. Jeff makes a mark along each wall. One mark is 3 inches from the corner. The other is 4 inches from the corner. Now, To see whether the walls form a right angle or not, We have to see whether the length along the walls is greater than the lengths of the marks from the corners Now, We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the length along the walls a is the length of one mark from the corner b is the length of another mark from the corner So, c² = 3² + 4² c² = 9 + 16 c² = 25 c = \(\sqrt{25}\) c = 5 So, From the above value, We can observe that c > a and c > b Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the walls form a right angle
Assessment Practice
Lesson 7.4 Find Distance in the Coordinate
B. Jim says that the marked yellow paths show the shortest path to the tent. Write an expression to represent this and find the distance Jim walks from the haunted mansion to the clown tent. Answer: From part (a), We know that, The coordinates of the haunted house are: (500, 1,500), The coordinates of the clown tent are: (2,000, 500) Now, We know that The linear equation in the slope-intercept form is: y = mx + b Where, m is the slope b is the initial value (or) y-intercept Now, Compare the given points with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, Slope (m) = y 2 – y 1 / x 2 – x 1 So, Slope (m) = \(\frac{500 – 1,500}{2,000 – 500}\) Slope (m) = –\(\frac{1,000}{1,500}\) Slope (m) = –\(\frac{2}{3}\) So, The equation in the slope-intercept form is: y = –\(\frac{2}{3}\)x + b So, 3y = -2x + 3b Now, Substitute (500, 1,500) or (2,000, 500) in the above equation So, 1,500 = -4000 + 3b 3b = 5,500 So, The equation that represents the shortest path to the tent is: 3y = -2x + 5,500 Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the haunted mansion and the clown tent = \(\sqrt{(2,000 – 500)^{2} + (500 – 1,500)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1,500^{2} + 1,000^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{2,250,000 + 1,000,000}\) = 1,802.77 feet Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The equation that represents the shortest path to the clown tent is: 3y = -2x + 5,500 The distance between the haunted mansion and the clown tent is: 1,802.77 feet
Focus on math practices Construct Arguments Why is the distance between two nonhorizontal and nonvertical points always greater than the horizontal or vertical distance? Answer: Let us consider a coordinate plane Now, When we draw either a horizontal line or the vertical line, We can observe that the length will be constant But, When we draw non-vertical and non-horizontal lines, We can observe that the lengths are unknown and not constant Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the distance between two nonhorizontal and nonvertical points always greater than the horizontal or vertical distance
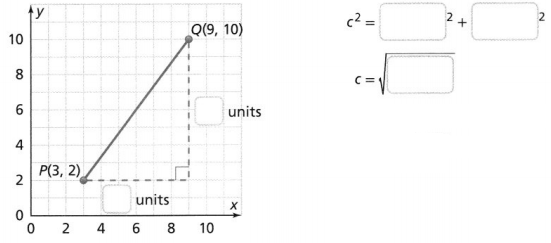
Essential Question How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points? Answer: We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the hypotenuse a and b are the side lengths or lengths of the legs Now, Graphically, The terms of the Pythagorean Theorem can be expressed as: c is the distance between two points a and b are the points So, c = \(\sqrt{a^{2} + b^{2}}\)
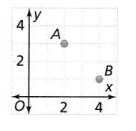
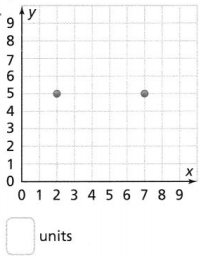
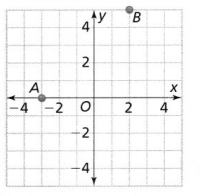
Try It! Find the perimeter of ∆ABC with vertices (2, 5), (5, -1), and (2, -1). Answer: It is given that ∆ABC with vertices (2, 5), (5, -1), and (2, -1) Now, The names of the vertices are: A (2, 5), B (5, -1), and C (2, -1) We know that, The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of all the side lengths of a triangle Now, Compare the given points with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, In ∆ABC, AB and BC are the side lengths Ac is the hypotenuse Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points A and B = \(\sqrt{(5 – 2)^{2} + (-1 – 5)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{3^{2} + 6^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{9 + 36}\) = 6.70 units The distance between the points B and C (BC) = \(\sqrt{(2 – 5)^{2} + (-1 + 1)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{3^{2} + 0^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{9 + 0}\) = 3 units The distance between the points A and C (AC) = \(\sqrt{(2 – 2)^{2} + (-1 – 5)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0^{2} + 6^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0 + 36}\) = 6 units So, The perimeter of ∆ABC = AB + BC + AC = 6 + 3 + 6.70 = 15.7 units Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the perimeter of ∆ABC is about 15.7 units
What are the coordinates, to the nearest tenth, of the third vertex in an isosceles triangle that has one side length of 2 and two side lengths of 5, with vertices at (1, 0) and (1, 2)? The third vertex is in the first quadrant. Answer: It is given that An isosceles triangle that has one side length of 2 and two side lengths of 5, with vertices at (1, 0) and (1, 2) Now, Let the third vertex be (x, y) Now, The given vertices are: A (1, 0), B (1, 2), and C (x, y) It is also given that BC = 2 units, and AC = 5 units We know that, An isosceles triangle has any 2 equal side lengths Now, Compare the given points with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points A and B = \(\sqrt{(2 – 0)^{2} + (1 – 1)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{2^{2} + 0^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4 + 0}\) = 4 units The distance between the points B and C = \(\sqrt{(x – 1)^{2} + (y – 2)^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, BC² = (x – 1)² + (y – 2)² The distance between the points A and C = \(\sqrt{(x – 1)^{2} + (y – 0)^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, BC² = (x – 1)² + y² So, (x – 1)² + (y – 2)² = 4 —– (1) (x – 1)² + y² = 25 —— (2) So, From eq (1) and eq (2), 25 – y² + (y – 2)² = 4 -y² + y² – 4y + 4 = -21 -4y = -25 y = \(\frac{25}{4}\) So, (x – 1)² = |25 – (\(\frac{25}{4}\))²| x = \(\frac{19}{4}\) Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the third vertex is: (\(\frac{19}{4}\), \(\frac{25}{4}\))

Do You Understand? Question 1. Essential Question How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points? Answer: We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a² + b² Where, c is the hypotenuse a and b are the side lengths or lengths of the legs Now, Graphically, The terms of the Pythagorean Theorem can be expressed as: c is the distance between two points a and b are the points So, c = \(\sqrt{a^{2} + b^{2}}\)
Question 2. Model with Math Can you use a right triangle to represent the distance between any two points on the coordinate plane? Explain. Answer: Derived from the Pythagorean Theorem, the distance formula is used to find the distance between two points in the plane. We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, a²+b²=c² where, a and b are the lengths of the legs adjacent to the right angle c is the length of the hypotenuse.
Question 3. Generalize How does the fact that the points are on opposite sides of the y-axis affect the process of finding the distance between the two points? Answer: The fact that the points are on opposite sides of the y-axis affects the process of finding the distance between the two points because We need to find the distance between the two points by adding the distances from each of them to the y-axis.
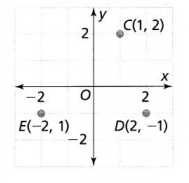
Question 4. Find the distance between points C and D. Round to the nearest hundredth. Answer: Compare the points C and D with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points C and D = \(\sqrt{(2 – 1)^{2} + (-1 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1^{2} + 3^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1 + 9}\) = 3.16 units Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the distance between points C and D is: 3.16 units
Question 5. Find the perimeter of ∆CDE. Answer: We know that, The “Perimeter” is defined as the sum of all the side lengths So, The perimeter of ∆CDE = CD + DE + CE So, The distance between the points C and D = \(\sqrt{(2 – 1)^{2} + (-1 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1^{2} + 3^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1 + 9}\) = 3.16 units The distance between the points D and E = \(\sqrt{(-2 – 2)^{2} + (1 + 1)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4^{2} + 2^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{16 + 4}\) = 4.47 units The distance between the points C and E = \(\sqrt{(-2 – 1)^{2} + (1 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{3^{2} + 1^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1 + 9}\) = 3.16 units So, The perimeter of ∆CDE = 3.16 + 4.47 + 3.16 = 10.79 units Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the perimeter of ∆CDE is: 10.79 units
Question 6. Point B is plotted on the coordinate plane above the x-axis. ∆BDE is equilateral. What are the coordinates of point B to the nearest hundredth? Answer: It is given that Point B is plotted on the coordinate plane above the x-axis. ∆BDE is equilateral. Now, Let the unknown vertex be B (x, y) So, The given points are: B (x, y), D (2, -1), and E (-2, 1) It is given that ΔBDE is equilateral So, BD = DE = EB BD² = DE² = EB² Now, Compare the given points with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points B and D = \(\sqrt{(x – 2)^{2} + (y – 1)^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, BD² = (x – 2)² + (y + 1)² The distance between the points D and E = \(\sqrt{(1 + 1)^{2} + (-2 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{2^{2} + 4^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4 + 16}\) = 4.47 units The distance between the points E and B = \(\sqrt{(x + 2)^{2} + (y – 1)^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, EB² = (x + 2)² + (y – 1)² Now, (x – 2)² + (y + 1)² = 4.47 —- (1) (x + 2)² + (y – 1)² = (x – 2)² + (y + 1)² x² + 2x + 4 + y² + 1 – 2y = x² + 4 – 4x + y² + 1 + 2y 2x + 4 + 1 – 2y = 4 – 4x + 1 + 2y 6x + 5 = 4y + 5 6x = 4y 3x = 2y x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)y Now, From eq (1), x² + 4 – 4x + y² + 1 + 2y = 4.47 x² + y² -4x + 2y = -0.47 (\(\frac{2}{3}\)y)² + y² – 4 (\(\frac{2}{3}\))y + 2y = -0.47 4y² + 15y + 4.23 = 0 So, y = -0.30 (or) y = -3.44 So, x = \(\frac{2}{3}\) (-0.30) (or) x = \(\frac{2}{3}\) (-3.44) x = -0.2 (or) x = -2.29 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the coordinates of point B are: (-0.2, -0.30) or (-2.29, -3.44)
Question 9. Determine whether the triangle is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. Answer: We know that, On the basis of the side lengths, Scalene Triangle – All the side lengths are different Equilateral Triangle – All the side lengths are the same Isosceles Triangle – Any two of the side lengths are the same So, From Exercise 8, We can observe that all the side lengths are different Hence, from the above, We can conclude that ΔPQR is a scalene Triangle
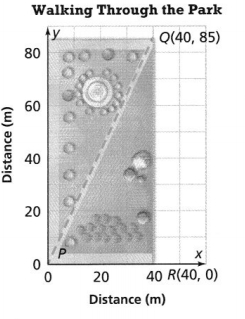
b. What is the total length of your walk in the park? Round to the nearest tenth of a meter. Answer: We know that, The total length is nothing but the “Perimeter” So, The perimeter of the given triangle = PQ + QR + PR Now, The distance between the points P and Q = \(\sqrt{(40 – 0)^{2} + (85 – 0)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{40^{2} + 85^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1,600 + 7,225}\) = 93.9 m The distance between the points Q and R = \(\sqrt{(40 – 40)^{2} + (85 – 0)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0^{2} + 85^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0 + 7,225}\) = 85 m The distance between the points P and R = \(\sqrt{(40 – 0)^{2} + (0 – 0)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0^{2} + 40^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{0 + 1,600}\) = 40 m So, The total length of your walk in the park = PQ + QR + PR = 93.9 + 85 + 40 = 218.9 meters Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the total length of your walk in the park is: 218.9 meters
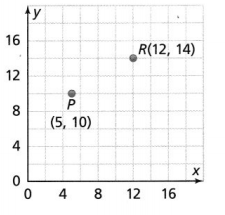
Question 12. Use Structure Point B has coordinates (2, 1). The x-coordinate of point A is -10. The distance between point A and point B is 15 units. What are the possible coordinates of point A? Answer: It is given that Point B has coordinates (2, 1). The x-coordinate of point A is -10. The distance between point A and point B is 15 units Now, Let the coordinates of A be: (x, y) = (-10, y) Now, Compare the points A and B with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points A and B = \(\sqrt{(-10 – 2)^{2} + (y – 1)^{2}}\) 15 = \(\sqrt{12^{2} + (y – 1)^{2}}\) 15 = \(\sqrt{144 + (y – 1)^{2}}\) Now, Squaring on both sides So, 144 + (y – 1)² = 225 (y 1)² = 225 – 144 (y – 1)² = 81 y – 1 = \(\sqrt{81}\) y – 1 = 9 (or) y – 1 = -9 y = 9 + 1 (or) y = -9 + 1 y = 10 (or) y = -8 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the possible coordinates of A are: (-10, 10), and (-10, -8)
Question 13. Higher-Order Thinking ∆EFG and ∆HIJ have the same perimeter and side lengths. The coordinates are E(6, 2), F(9, 2), G(8, 7), H(0, 0), and I(0, 3). What are the possible coordinates of point J? Answer: It is given that ∆EFG and ∆HIJ have the same perimeter and side lengths. The coordinates are E(6, 2), F(9, 2), G(8, 7), H(0, 0), and I(0, 3) So, According to the side lengths, EF = HI, FG = IJ, and GE = JH So, EF² = HI², FG²= JI², and GE² = JH² Now, Let the unknown vertex be J (x, y) Now, Compare the given points with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points E and F = \(\sqrt{(9 – 6)^{2} + (2 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{3^{2} + 0^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{9 + 0}\) = 3 units The distance between the points F and G = \(\sqrt{(8 – 9)^{2} + (7 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1^{2} + 5^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{1 + 25}\) = 5.09 units The distance between the points G and E = \(\sqrt{(8 – 6)^{2} + (7 – 2)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{2^{2} + 5^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4 + 25}\) = 5.38 units Now, The distance between the points H and I = \(\sqrt{(0 – 0)^{2} + (3 – 0)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{3^{2} + 0^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{9 + 0}\) = 3 units The distance between the points I and J = \(\sqrt{(x – 0)^{2} + (y – 3)^{2}}\) 5.09 = \(\sqrt{x^{2} + (y – 3)^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, x² + (y – 3)² = 25.90 units The distance between the points J and H = \(\sqrt{(x – 0)^{2} + (y – 0)^{2}}\) 5.38 = \(\sqrt{x^{2} + y^{2}}\) Squaring on both sides So, x² + y² = 28.94 units Now, 28.94 – y² + (y – 3)² = 25.90 y² + 9 – 6y – y² = 25.90 – 28.94 9 – 6y = -3.04 -6y = -3.04 – 9 6y = 12.04 y = 2 Now, Substitute the value of y in eq 2 x² + 4 = 28.94 x² = 24.94 x = 4.99 (or) x = -4.99 Hence, from the baove, We can conclude that the missing vertex is: J (4.99, 2) or J (-4.99, 2)
b. Explain why there can be different possibilities for the coordinates for point J. Answer:
Question 15. Find the distance, in units, between A(1, 5) and B(5.5, 9.25). Round to the nearest tenth. Answer: The given points are: A (1, 5), and B (5.5, 9.25) Now, Compare the points A and B with (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ) Now, We know that, The distance between two points = √(x 2 – x 1 ) + (y 2 – y 1 )² So, The distance between the points A and B = \(\sqrt{(9.25 – 5)^{2} + (5.5 – 1)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4.25^{2} + 4.5^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{18.06 + 20.25}\) = 6.2 units Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the distance between points A and B is: 6.2 units
Topic 7 REVIEW
Topic Essential Question How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems? Answer: Step 1: Draw a right triangle and then read through the problems again to determine the length of the legs and the hypotenuse. Step 2: Use the Pythagorean Theorem (a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ) to write an equation to be solved. Step 3: Simplify the equation by distributing and combining like terms as needed.
Vocabulary Review
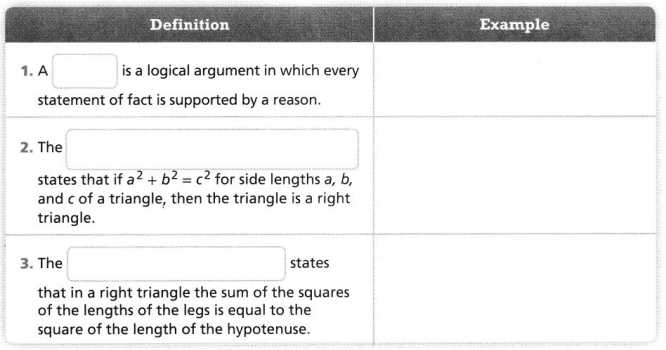
Complete each definition and then provide an example of each vocabulary word. Vocabulary The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem hypotenuse leg proof Pythagorean Theorem
Concepts and Skills Review
Quick Review The Pythagorean Theorem states that, in a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs, a and b, is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse, c. So, a 2 + b 2 = c 2 .
Example Find the length of the hypotenuse of a triangle with legs of 7 meters and 24 meters. Answer: Substitute 7 for a and 24 for b. Then solve for c. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 49 + 576 = c 2 \(\sqrt {625}\) = C The length of the hypotenuse is 25 meters.
Quick Review For a triangle with side lengths a, b, and c, if a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , then the triangle is a right triangle by the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Example Is a triangle with side lengths of 8 m, 15 m, and 17 m a right triangle? Explain. Answer: Substitute 8 for a, 15 for b, and 17 for c. a 2 + b 2 \(\underline{\underline{?}}\) c 2 8 2 + 15 2 \(\underline{\underline{?}}\) 17 2 289 = 289 ✓ Because a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 2. A triangle has side lengths of 1.5 inches, 2 inches, and 3 inches. Is the triangle a right triangle? Explain. Answer: It is given that A triangle has side lengths of 1.5 inches, 2 inches, and 3 inches Now, We know that, According to the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, If c² = a² + b² then, the given triangle is a right triangle We know that, The longest side is the hypotenuse So, Now, 3² = (1.5)² + 2² 9 = 2.25 + 4 9 = 6.25 So, The condition c² = a² + b² is false Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the given triangle is not a right triangle
Question 3. A triangle has side lengths of 9 feet, 40 feet, and 41 feet. Is the triangle a right triangle? Explain Answer: It is given that A triangle has side lengths of 9 feet, 40 feet, and 41 feet Now, We know that, According to the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, If c² = a² + b² then, the given triangle is a right triangle We know that, The longest side is the hypotenuse So, Now, 41² = 40² + 9² 1,681 = 1,600 + 81 1,681 = 1,681 So, The condition c² = a² + b² is true Hence, from the above, We can conclude that the given triangle is a right triangle
Quick Review The Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find unknown side lengths of an object that is shaped like a right triangle. It also can be used to find diagonal measures in certain two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects.
Practice Question 1. A basketball court is in the shape of a rectangle that is 94 feet long and 50 feet wide. What is the length of a diagonal of the court? Round to the nearest tenth. Answer: It is given that A basketball court is in the shape of a rectangle that is 94 feet long and 50 feet wide We know that, By drawing a diagonal in the rectangle, it will become 2 right triangles The diagonal will be the hypotenuse of the right triangle Now, We know that, According to the Pythagorean Theorem, c² = a²+ b² Where, c is the length of the diagonal a and b are the side lengths So, c² = 94²+ 50² c²= 8,836 + 2,500 c² = 11,336 c = \(\sqrt{11,336}\) c = 106.4 feet hence, from the above, We can conclude that the length of the diagonal is: 106.4 feet
Lesson 7.4 Find Distance in the Coordinate Plane
Quick Review The Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find the distance between any two points on the coordinate plane.
Topic 7 Fluency Practice
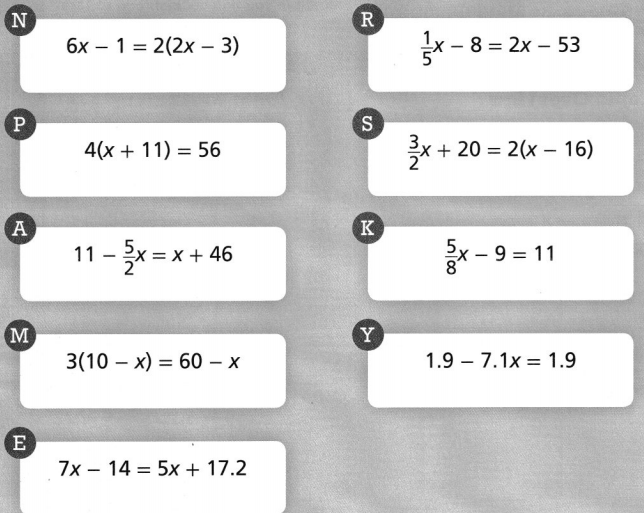
Riddle Rearranging Solve each equation. Then arrange the answers in order from least to greatest. The letters will spell out the answer to the riddle below.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean Theorem
One has to learn the concepts if he/she wants to become a master in maths. The fundamentals in Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean theorem will help you to learn the subject. You need to practice from the beginning itself. We will help you to achieve your dreams by providing simple methods to solve the problems in an easy manner. Download Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean Theorem free pdf to help you to gain a grip over the subject.
Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean Theorem will help you to complete your homework in time without any mistakes. The main aim of the ccssmathanswers.com site is to provide quick and simple methods to all the students of 8th grade. The solutions to all the questions in Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean Theorem are prepared by the math experts. Tap the links and practice the problems provided in the HMH Go Math 8th Grade Solution Key Chapter 12 The Pythagorean Theorem.
Chapter 12- Lesson 1:
Guided Practice – The Pythagorean Theorem – Page No. 378
12.1 independent practice – the pythagorean theorem – page no. 379, focus on higher order thinking – the pythagorean theorem – page no. 380.
Chapter 12- Lesson 2:
Guided Practice – Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem – Page No. 384
12.2 independent practice – converse of the pythagorean theorem – page no. 385, converse of the pythagorean theorem – page no. 386.
Chapter 12- Lesson 3:
Guided Practice – Distance Between Two Points – Page No. 390
12.3 independent practice – distance between two points – page no. 391, distance between two points – page no. 392, ready to go on – model quiz – page no. 393, selected response – mixed review – page no. 394.
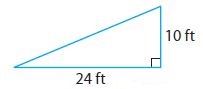
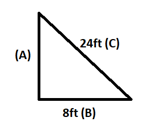
Answer: The length of the hypotenuse is 26 feet.
Explanation: According to Pythagorean Theorem, we shall consider values of a = 24ft, b = 10ft. Therefore c = √(a 2 +b 2 ) c = √(24 2 + 10 2 ) = √(576 + 100) = √676 = 26ft

Answer: 1700 inches.
Explanation: Here we consider the length of the diagonal across the bottom of the box as d. Therefore, according to Pythagorean Theorem W 2 + l 2 = d 2 40 2 + 10 2 = d 2 1600 + 100 = d 2 1700 = d 2
Question 2. b. Find the length from a bottom corner to the opposite top corner to the nearest tenth. Will the fishing rod fit? ________ inches
Answer: 42.42 inches.
Explanation: We denote by r, the length from the bottom corner to the opposite top corner. We use our Pythagorean formula to find r. h 2 + s 2 = r 2 10 2 + 1700 = r 2 100 + 1700 = r 2 1800 = r 2 , r = √1800 => 42.42 inches
ESSENTIAL QUESTION CHECK-IN
Question 3. State the Pythagorean Theorem and tell how you can use it to solve problems.
Answer: Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the sum of squares of the legs a and b is equal to the square of the hypotenuse c. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 We can use it to find the length of a side of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known.
Find the length of the missing side of each triangle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
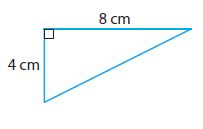
Answer: 8.9 cm.
Explanation: According to Pythagorean theorem we consider values of a = 4cm, b = 8cm. c 2 = a 2 + b 2 = 4 2 + 8 2 = 16 + 64 c 2 = 80, c= √80 => 8.944 After rounding to nearest tenth value c= 8.9cm
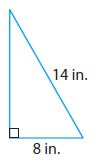
Answer: 11.5 in.
Explanation: According to Pythagorean theorem we consider values of b = 8in, c= 14in c 2 = a 2 + b 2 14 2 = a 2 + 8 2 196 = a 2 + 64 a 2 = 196 – 64 a = √132 => 11.4891 a = 11.5 in
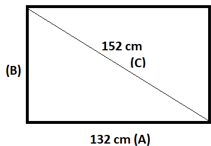
Question 6. The diagonal of a rectangular big-screen TV screen measures 152 cm. The length measures 132 cm. What is the height of the screen? ________ cm
Answer: 75.4 cm
Question 7. Dylan has a square piece of metal that measures 10 inches on each side. He cuts the metal along the diagonal, forming two right triangles. What is the length of the hypotenuse of each right triangle to the nearest tenth of an inch? ________ in.
Answer: 14.1in.
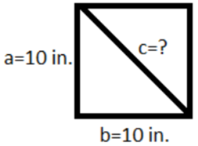
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we have: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 10 2 + 10 2 = c 2 100 + 100 = c 2 200 = c 2 We are told to round the length of the hypotenuse of each right triangle to the nearest tenth of an inch, therefore: c = 14.1in
Question 8. Represent Real-World Problems A painter has a 24-foot ladder that he is using to paint a house. For safety reasons, the ladder must be placed at least 8 feet from the base of the side of the house. To the nearest tenth of a foot, how high can the ladder safely reach? ________ ft
Answer: 22.6 ft.
Explanation: Consider the below diagram. Length of the ladder C = 24ft, placed at a distance from the base B = 8ft, let the safest height be A.
By using Pythagorean Theorem: C 2 = A 2 + B 2 24 2 = A 2 + 8 2 576 = A 2 + 64 A 2 = 576 – 64 => 512 A = √512 => 22.627 After rounding to nearest tenth, value of A = 22.6ft
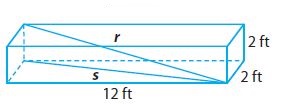
Answer: The longest flagpole (in whole feet) that could be shipped in this box is 12 feet.
Explanation: From the above diagram we have to find the value of r, which gives us the length longest flagpole that could be shipped in the box. Where width w = 2ft, height h = 2ft and length l = 12ft.
First find s, the length of the diagonal across the bottom of the box. w 2 + l 2 = s 2 2 2 + 12 2 = s 2 4 + 144 = s 2 148 = s 2 We use our expression for s to find r, since triangle with sides s, r, and h also form a right-angle triangle. h 2 + s 2 = r 2 2 2 + 148 = r 2 4 + 148 = r 2 152 = r 2 r = 12.33ft.
Question 10. Sports American football fields measure 100 yards long between the end zones, and are 53 \(\frac{1}{3}\) yards wide. Is the length of the diagonal across this field more or less than 120 yards? Explain. ____________
Answer: The diagonal across this field is less than 120 yards.
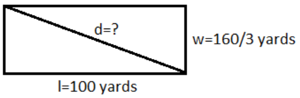
We are given l = 100 and w = 53 = . If we denote with d the diagonal of the field, using the Pythagorean Theorem, we have: l 2 + w 2 = d 2 100 2 + (160/3) 2 = d 2 10000 + (25600/9) = d 2 9*10000 + 9*(25600/9) = 9* d 2 90000 + 25600 = 9 d 2 (115600/9) = d 2 (340/9) = d 2 d = 113.3 Hence the diagonal across this field is less than 120 yards.
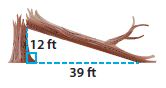
Answer: The total height of the tree was 52.8ft
Explanation:

Question 12. Multistep Main Street and Washington Avenue meet at a right angle. A large park begins at this corner. Joe’s school lies at the opposite corner of the park. Usually Joe walks 1.2 miles along Main Street and then 0.9 miles up Washington Avenue to get to school. Today he walked in a straight path across the park and returned home along the same path. What is the difference in distance between the two round trips? Explain. ________ mi
Answer: Joe walks 1.2 miles less if he follows the straight path across the park.
Explanation: Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we find the distance from his home to school following the straight path across the park: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 1.2 2 + 0.9 2 = c 2 1.44 + 0.81 = c 2 2.25 = c 2 1.5 = c Therefore, the distance of Joe’s round trip following the path across the park is 3 miles ( d home-school + d school-home = 1.5 + 1.5). Usually, when he walks along Main Street and Washington Avenue, the distance of his round trip is 4.2 miles ( d home-school + d school-home = (1.2 + 0.9) + (0.9+1.2)). As we can see, Joe walks 1.2 miles less if he follows the straight path across the park.
Question 13. Analyze Relationships An isosceles right triangle is a right triangle with congruent legs. If the length of each leg is represented by x, what algebraic expression can be used to represent the length of the hypotenuse? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: c = x√ 2
Explanation: From the Pythagorean Theorem, we know that if a and b are legs and c is the hypotenuse, then a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . In our case, the length of each leg is represented by x, therefore we have: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 x 2 + x 2 = c 2 2x 2 = c 2 c = x√ 2

Answer: Each corner of the burger sticks out 0.57 inches from the bun.
Explanation: Frist, we need to find the radius r of the circular bun. We know that its area A is 16 square inches, therefore:
A = πr 2 16 = 3.14*r 2 r 2 = (16/3.14) r = 2.26
Then, we need to find the side s of the square hamburger. We know that its area A is 16 square inches, therefore: A = s 2 16 = s 2 s = 4 Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we have to find diagonal d of the square hamburger: s 2 + s 2 = d 2 4 2 + 4 2 = d 2 16 + 16 = d 2 32 = d 2 d = 5.66 To find how far does each corner of the burger stick out from the bun, we denote this length by a and we get: a = (d/2) – r => (5.66/2) – 2.26 a = 0.57. Therefore, Each corner of the burger sticks out 0.57 inches from the bun.
Question 14. b. How far does each bun stick out from the center of each side of the burger? ________ in
Answer: Each bun sticks out 0.26 inches from the center of each side of the burger.
We found that r = 2.26 and s = 4. To find how far does each bun stick out from the center of each side of the burger, we denote this length by b and we get: b = r – (s/2) = 2.26 – (4/2) b = 0.26 inches.
Question 14. c. Are the distances in part a and part b equal? If not, which sticks out more, the burger or the bun? Explain.
Answer: The distances a and b are not equal. From the calculations, we found that the burger sticks out more than the bun.
Answer: The length of Lashandra’s triangle is 8 units, 6 units, 10 units.
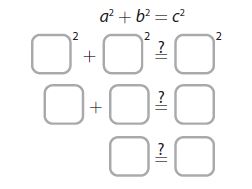
Answer: Lashandra’s triangle is right angled triangle as it satisfied Pythagorean theorem
Explanation: Verifying with Pythagorean formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2 8 2 + 6 2 = 10 2 64 + 36 =100 100 = 100.
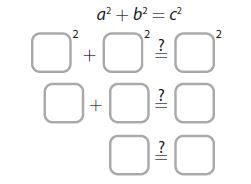
Answer: The given triangle is not a right-angled triangle
Explanation: Verifying with Pythagorean formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 16 2 81 + 144 = 256 225 ≠ 256. Hence given dimensions are not from the right angled triangle.
Question 3. The marketing team at a new electronics company is designing a logo that contains a circle and a triangle. On one design, the triangle’s side lengths are 2.5 in., 6 in., and 6.5 in. Is the triangle a right triangle? Explain. _______
Answer: It is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 2.5, b = 6 and c= 6.5 Verifying with Pythagorean formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2 2.5 2 + 6 2 = 6.5 2 6.25 + 36 = 42.25 42.25 = 42.25. Hence it is a right-angled triangle.
Question 4. How can you use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to tell if a triangle is a right triangle?
Answer: Knowing the side lengths, we substitute them in the formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , where c contains the biggest value. If the equation holds true, then the given triangle is a right triangle. Otherwise, it is not a right triangle.
Tell whether each triangle with the given side lengths is a right triangle.
Question 5. 11 cm, 60 cm, 61 cm ______________
Answer: Since 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 11, b = 60 and c= 61 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 121 + 3600 = 3721 3721 = 3721. Since 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 6. 5 ft, 12 ft, 15 ft ______________
Answer: Since 5 2 + 12 2 ≠ 15 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 5, b = 12 and c= 15 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 25 + 144 = 225 169 ≠ 225. Since 5 2 + 12 2 ≠ 15 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 7. 9 in., 15 in., 17 in. ______________
Answer: Since 9 2 + 15 2 ≠ 17 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 9, b = 15 and c= 17 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 9 2 + 15 2 = 17 2 81 + 225 = 225 306 ≠ 225. Since 9 2 + 15 2 ≠ 17 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 8. 15 m, 36 m, 39 m ______________
Answer: Since 15 2 + 36 2 = 39 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 15, b = 36 and c= 39 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 15 2 + 36 2 = 39 2 225 + 1296 = 1521 1521 = 1521. Since 15 2 + 36 2 = 39 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 9. 20 mm, 30 mm, 40 mm ______________
Answer: Since 20 2 + 30 2 ≠ 40 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 20, b = 30 and c= 40 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 20 2 + 30 2 = 40 2 400 + 900 = 1600 1300 ≠ 1600. Since 20 2 + 30 2 ≠ 40 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 10. 20 cm, 48 cm, 52 cm ______________
Answer: Since 20 2 + 48 2 = 52 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 20, b = 48 and c= 52 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 20 2 + 48 2 = 52 2 400 + 2304 = 2704 2704 = 2704. Since 20 2 + 48 2 = 52 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 11. 18.5 ft, 6 ft, 17.5 ft ______________
Answer: Since 6 2 + 17.5 2 = 18.5 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 6, b = 17.5 and c= 18.5 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 6 2 + 17.5 2 = 18.5 2 36 + 306.25 = 342.25 342.5 = 342.25. Since 6 2 + 17.5 2 = 18.5 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 12. 2 mi, 1.5 mi, 2.5 mi ______________
Answer: Since 2 2 + 1.5 2 = 2.5 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 2, b = 1.5 and c= 2.5 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 2 2 + 1.5 2 = 2.5 2 4 + 2.25 = 6.25 6.25 = 6.25. Since 2 2 + 1.5 2 = 2.5 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 13. 35 in., 45 in., 55 in. ______________
Answer: Since 35 2 + 45 2 ≠ 55 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 35, b = 45 and c= 55 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 35 2 + 45 2 = 55 2 1225 + 2025 = 3025 3250 ≠ 3025. Since 35 2 + 45 2 ≠ 55 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 14. 25 cm, 14 cm, 23 cm ______________
Answer: Since 14 2 + 23 2 ≠ 25 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 14, b = 23 and c= 25 (longest side) Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 14 2 + 23 2 = 25 2 196 + 529 = 625 725 ≠ 625. Since 14 2 + 23 2 ≠25 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 15. The emblem on a college banner consists of the face of a tiger inside a triangle. The lengths of the sides of the triangle are 13 cm, 14 cm, and 15 cm. Is the triangle a right triangle? Explain. ________
Answer: Since 13 2 + 14 2 ≠ 15 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 13, b = 14 and c= 15 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 13 2 + 14 2 = 15 2 169 + 196 = 225 365 ≠ 225. Since 13 2 + 14 2 ≠ 15 2 , the triangle is not a right-angled triangle.
Question 16. Kerry has a large triangular piece of fabric that she wants to attach to the ceiling in her bedroom. The sides of the piece of fabric measure 4.8 ft, 6.4 ft, and 8 ft. Is the fabric in the shape of a right triangle? Explain. ________
Answer: The triangular piece of fabric that Kerry has is in the shape of a right angle since it follows the Pythagorean theorem.
Explanation: Let a = 4.8, b = 6.4 and c= 8 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 4.8 2 + 6.4 2 = 8 2 23.04 + 40.96 = 64 64 = 64. Since 4.8 2 + 6.4 2 = 8 2 , the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 17. A mosaic consists of triangular tiles. The smallest tiles have side lengths 6 cm, 10 cm, and 12 cm. Are these tiles in the shape of right triangles? Explain. ________
Answer: Since 6 2 + 10 2 ≠ 12 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the tiles are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 6, b = 10 and c= 12 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 6 2 + 10 2 = 12 2 36 + 100 = 144 136 ≠ 144. Since 6 2 + 10 2 ≠ 12 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the tiles are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Answer: The rope has formed a right-angled triangle because the length of its sides follows Pythagorean Theorem.
Explanation: The knots are evenly placed at equal distances The lengths in terms of knots are a=4 knots, b = 3knots, c = 5 knots Therefore a 2 + b 2 = c 2 4 2 + 3 2 = 5 2 16+9 = 25 25 = 25. Hence rope has formed a right-angled triangle because the length of its sides follows Pythagorean Theorem.
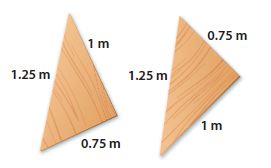
Answer: Since it was proved that both can form a right-angled triangle, we can form a rectangle by joining them.
Explanation: Given both triangles are identical, if both are right-angled triangles then we can surely join to form a rectangle. Let’s consider a = 0.75, b= 1 and c=1.25. By using converse Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 0.75 2 + 1 2 = 1.25 2 0.5625 + 1 = 1.5625 1.5625 = 1.5625. Since it was proved that both can form right angled triangle, we can form a rectangle by joining them.
Question 20. Critique Reasoning Shoshanna says that a triangle with side lengths 17 m, 8 m, and 15 m is not a right triangle because 17 2 + 8 2 = 353, 15 2 = 225, and 353 ≠ 225. Is she correct? Explain _______
Answer: She is not right, A triangle with sides 15, 8, and 17 is a right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Lets consider a =15, b= 8 and c = 17 (which is long side) We will verify by using converse Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 15 2 + 8 2 = 17 2 225 + 64 = 289 289 = 289. Since the given dimensions satisfied Pythagorean Theorem, we can say it is a right-angled triangle. In the given above statement what Shoshanna did was c 2 + b 2 = a 2 , which is not the correct definition of the Pythagorean Theorem.
FOCUS ON HIGHER ORDER THINKING
Question 21. Make a Conjecture Diondre says that he can take any right triangle and make a new right triangle just by doubling the side lengths. Is Diondre’s conjecture true? Test his conjecture using three different right triangles. _______
Answer: Yes, Diondre’s conjecture is true. By doubling the sides of a right triangle would create a new right triangle.
Explanation: Given a right triangle, the Pythagorean Theorem holds. Therefore, a 2 + b 2 = c 2 If we double the side lengths of that triangle, we get: (2a) 2 + (2b) 2 = (2c) 2 4a 2 + 4b 2 = 4c 2 4(a 2 + b 2 ) = 4c 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 As we can see doubling the sides of a right triangle would create a new right triangle.We can test that by using three different right triangles.
The triangle with sides a = 6, b = 8 and c = 10 is a right triangle. We double its sides and check if the new triangle is a right triangle. After doubling value of a = 12, b = 16 and c = 20. 12 2 + 16 2 = 20 2 144 + 256 = 400 400 = 400 Hence proved! Since 12 2 + 16 2 = 20 2 , the new triangle is a right triangle by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
The triangle with sides a = 3, b = 4 and c = 5 is a right triangle. We double its sides and check if the new triangle is a right triangle. After doubling value of a = 6, b = 8 and c = 10. 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 36 + 64 = 100 100 = 100 Hence proved! Since 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 , the new triangle is a right triangle by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
The triangle with sides a = 12, b = 16 and c = 20 is a right triangle. We double its sides and check if the new triangle is a right triangle. After doubling value of a = 24, b = 32 and c = 40. 24 2 + 32 2 = 40 2 576 + 1024 = 1600 1600 = 1600 Hence proved! Since 24 2 + 32 2 = 40 2 , the new triangle is a right triangle by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Question 22. Draw Conclusions A diagonal of a parallelogram measures 37 inches. The sides measure 35 inches and 1 foot. Is the parallelogram a rectangle? Explain your reasoning. _______
Answer: Since 12 2 + 35 2 = 37 2 , the triangle is right triangle. Therefore, the given parallelogram is a rectangle.
Explanation: A rectangle is a parallelogram where the interior angles are right angles. To prove if the given parallelogram is a rectangle, we need to prove that the triangle formed by the diagonal of the parallelogram and two sides of it, is a right triangle. Converting all the values into inches, we have a = 12, b = 35 and c = 37. Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we have: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 12 2 + 35 2 = 37 2 144 + 1225 = 1369 1369 = 1369. Since 12 2 + 35 2 = 37 2 , the triangle is right triangle. Therefore, the given parallelogram is a rectangle.
Question 23. Represent Real-World Problems A soccer coach is marking the lines for a soccer field on a large recreation field. The dimensions of the field are to be 90 yards by 48 yards. Describe a procedure she could use to confirm that the sides of the field meet at right angles.
Answer: To confirm that the sides of the field meet at right angles, she could measure the diagonal of the field and use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. If a 2 + b 2 = c 2 (where a = 90, b = 48 and c is the length of the diagonal), then the triangle is right triangle. This method can be used for every corner to decide if they form right angles or not.
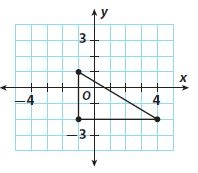
Answer: The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle to the nearest tenth is 5.8 units.
Explanation: From the above figure let’s take Length of the vertical leg = 3 units Length of the horizontal leg = 5 units let length of the hypotenuse = c By using Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 c 2 = 3 2 + 5 2 c 2 = 9 +25 c = √34 => 5.830. Therefore Length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle to the nearest tenth is 5.8 units.
Question 2. Find the distance between the points (3, 7) and (15, 12) on the coordinate plane. _______ units
Answer: Distance between points on the coordinate plane is 13
Explanation: So (x 1 , y 1 ) = (3,7) and (x 2 , y 2 ) = (15, 12) distance formula d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 d = √(15 -3) 2 + √(12 – 7) 2 d = √12 2 + 5 2 d = √144 + 25 d = √169 => 13 Therefore distance between points on the coordinate plane is 13.
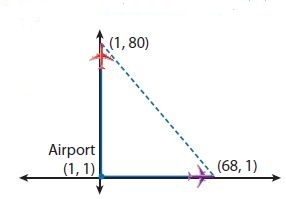
Answer: The distance between the two planes is 103.6 miles.
Explanation: Length of the vertical d v = √(80 -1) 2 + √(1-1) 2 = √79 2 => 79. Length of the horizontal d h = √(68 -1) 2 + √(1-1) 2 = √67 2 => 67. Distance between the two planes D = √(79 2 + 67 2 ) = √(6241+4489) => √10730 = 103.5857 => 103.6 miles.
Question 4. Describe two ways to find the distance between two points on a coordinate plane.
Explanation: We can draw a right triangle whose hypotenuse is the segment connecting the two points and then use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of that segment. We can also the Distance formula to find the length of that segment.
For example, plot three points; (1,2), (20,2) and (20,12)
Using the Pythagorean Theorem:
The length of the horizontal leg is the absolute value of the difference between the x-coordinates of the points (1,2) and (20,2). |1 – 20| = 19 The length of the horizontal leg is 19.
The length of the vertical leg is the absolute value of the difference between the y-coordinates of the points (20,2) and (20,12). |2 – 12| = 10 The length of the vertical leg is 10.
Let a = 19, b = 10 and let c represent the hypotenuse. Find c. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 19 2 + 10 2 = c 2 361 + 100 = c 2 461 = c 2 distance is 21.5 = c
Using the Distance formula: d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 The length of the horizontal leg is between (1,2) and (20,2). d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(20 -1) 2 + √(2-2) 2 = √(19) 2 + √(0) 2 = √361 => 19 The length of the vertical leg is between (20,2) and (20,12). d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(20 -20) 2 + √(12-2) 2 = √(0) 2 +√(10) 2 = √100 => 10 The length of the diagonal leg is between (1,2) and (20,12). d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(20 -1) 2 + √(12-2) 2 = √(19) 2 + √(10) 2 = √(361+100) => √461 = 21.5
Answer: The length of the longest side of the metal triangle to the nearest tenth is 7.8 units.
Explanation: From the above figure let’s take Length of the vertical leg = 6 units Length of the horizontal leg = 5 units let length of the hypotenuse = c By using Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 c 2 = 6 2 + 5 2 c 2 = 36 +25 c = √61 => 7.8 Therefore Length of the longest side of the metal triangle to the nearest tenth is 7.8 units.
Question 6. When a coordinate grid is superimposed on a map of Harrisburg, the high school is located at (17, 21) and the town park is located at (28, 13). If each unit represents 1 mile, how many miles apart are the high school and the town park? Round your answer to the nearest tenth. _______ miles
Answer: The high school and the town park are 13.6 miles apart.
Explanation: The coordinates of the high school are said to be (17,21), where as the coordinates of the park are (28,13). In a coordinate plane, the distance d between the points (17,21) and (28,13) is:
d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(28 -17) 2 + √(13-21) 2 = √(11) 2 + √(-8) 2 = √(121+64) => √185 = 13.6014
Rounding the answer to the nearest tenth: d = 13.6. Taking into consideration that each unit represents 1 mile, the high school and town park are 13.6 miles apart.
Answer: The diagonal ET is about 10.63 units long.
Explanation: Taking into consideration the triangle TRE, the length of the vertical leg (ER) is 8 units. The length of the horizontal leg (RT) is 7 units. Let a = 8 and b =7. Let c represent the length of the hypotenuse, the diagonal ET. We use the Pythagorean Theorem to find c. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 c 2 = 8 2 + 7 2 c 2 = 64 +49 c = √113 => 10,63. The diagonal ET is about 10.63 units long.
Question 7. b. How can you use the Distance Formula to find the length of \(\overline { ET } \) ? Show that the Distance Formula gives the same answer.
Answer: The diagonal ET is about 10.63 units long. As we can see the answer is the same as the one we found using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Explanation: Using the distance formula, in a coordinate plane, the distance d between the points E(-3,4) and T(4, -4) is: d= √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(4 – (-3)) 2 + √(- 4 – 4) 2 = √(7) 2 + √(-8) 2 = √(49+64) => √113 = 10.63. The diagonal ET is about 10.63 units long. As we can see the answer is the same as the one we found using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Question 8. Multistep The locations of three ships are represented on a coordinate grid by the following points: P(- 2, 5), Q(- 7, – 5), and R(2, – 3). Which ships are farthest apart?
Answer: Ships P and Q are farthest apart
Explanation: Distance Formula: In a coordinate plane, the distance d between two points (x 1 ,y 1 ) and (x 2 ,y 2 ) is:
The distance d 2 between the two points Q(-7,-5) and R(2,-3) is: d 3 = √( x R – x Q ) 2 + √( y R – y Q ) 2 = √(2 – (-7)) 2 + √(- 3 – 5) 2 = √(9) 2 + √(2) 2 = √(81+4) => √85 = 9.22
The distance d 3 between the two points P(-2,5) and R(2,-3) is: d 3 = √( x R – x P ) 2 + √( y R – y P ) 2 = √(2 – (-2)) 2 + √(- 3 – 5) 2 = √(4) 2 + √(-8) 2 = √(16+64) => √80 = 8.94. As we can see, the greatest distance is d 1 11.8, which means that ships P and Q are farthest apart.
Question 9. Make a Conjecture Find as many points as you can that are 5 units from the origin. Make a conjecture about the shape formed if all the points 5 units from the origin were connected.
Answer: (0,5), (3,4), (4,3),(5,0),(4,-3),(3,-4),(0,-5),(-3,-4),(-4,-3),(-5,0),(-4,3),(-3,4).
Explanation: Some of the points that are 5 units away from the origin are: (0,5), (3,4), (4,3),(5,0),(4,-3),(3,-4),(0,-5),(-3,-4),(-4,-3),(-5,0),(-4,3),(-3,4) etc, If all the points 5 units away from the origin are connected, a circle would be formed.
Answer: Considering each unit represents 1 foot, the motion detector, and peacock are 33.5 feet apart. Since the motion detector has a maximum range of 34 feet, it means that it will sense the motion of the peacock’s feathers.
Explanation: The coordinates of the motion detector are said to be (0,25), whereas the coordinates of the peacock are (30,10). In a coordinate plane, the distance d between the points (0,25) and (30,10) is: d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(30 – 0) 2 + √(10 – 25) 2 = √(30) 2 + √(-15) 2 = √(900+225) => √1125. Rounding answer to the nearest tenth: d = 33.5 feet. Considering each unit represents 1 foot, the motion detector and peacock are 33.5 feet apart. Since the motion detector has a maximum range of 34 feet, it means that it will sense the motion of the peacock’s feathers.
Answer: 7.1 units.
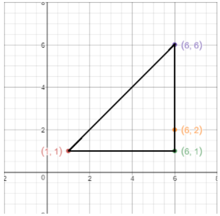
One leg of an isosceles right triangle has endpoints (1,1) and (6,1), which means that the leg is 5 units long. Since the triangle is isosceles, the other leg should be 5 units long too, therefore the endpoints of the second leg that passes through the point (6,2) are (6,1) and (6,6). In the coordinate plane, the length of the hypotenuse is the distance d between the points (1,1) and (6,6). d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(6 – 1) 2 + √(6 – 1) 2 = √(5) 2 + √(5) 2 = √(25+25) => √50. Rounding answer to nearest tenth: d = 7.1. The hypotenuse is around 7.1 units long.
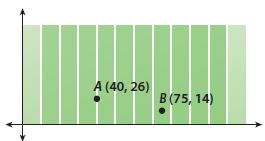
Answer: The distance between point A and B is 37 yards
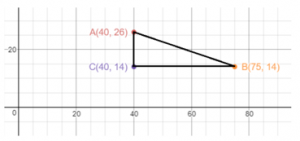
12.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Find the length of the missing side.
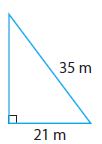
Answer: Length of missing side is 28m
Explanation: Lets consider value of a = 21 and c = 35. Using Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 21 2 + b 2 = 35 2 441 + b 2 = 1225 b 2 = 784 => b = √784 = 28. Therefore length of missing side is 28m.
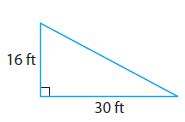
Answer: Length of missing side is 34ft
Explanation: Let’s consider value of a = 16 and b = 30. Using Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 16 2 + 30 2 = c 2 256 + 900 = c 2 c 2 = 1156 => c = √1156 = 34. Therefore length of missing side is 34ft.
12.2 Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
Question 3. 11, 60, 61 ____________
Answer: Since 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 11, b = 60 and c= 61 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 121 + 3600 = 3721 3721 = 3721 Since 11 2 + 60 2 = 61 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle. Question 4. 9, 37, 40 ____________
Answer: Since 9 2 + 37 2 ≠ 40 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 9, b = 37 and c= 40 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 9 2 + 37 2 = 40 2 81 + 1369 = 1600 1450 ≠ 3721. Since 9 2 + 37 2 ≠ 40 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Question 5. 15, 35, 38 ____________
Answer: Since 15 2 + 35 2 ≠ 38 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 15, b = 35 and c= 38 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 15 2 + 35 2 = 38 2 225 + 1225 = 1444 1450 ≠ 1444 Since 15 2 + 35 2 ≠ 38 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are not in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Question 6. 28, 45, 53 ____________
Answer: Since 28 2 + 45 2 = 53 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 28, b = 45 and c= 53 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 28 2 + 45 2 = 53 2 784 + 2025 = 2809 2809 = 2809 Since 28 2 + 45 2 = 53 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle. Question 7. Keelie has a triangular-shaped card. The lengths of its sides are 4.5 cm, 6 cm, and 7.5 cm. Is the card a right triangle? ____________
Answer: Since 4.5 2 + 6 2 = 7.5 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle.
Explanation: Let a = 4.5, b = 6 and c= 7.5 Using the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 4.5 2 + 6 2 = 7.5 2 20.25 + 36 = 56.25 56.25= 56.25 Since 4.5 2 + 6 2 = 7.5 2 , by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, we say that the given sides are in the shape of right-angled triangle.
12.3 Distance Between Two Points
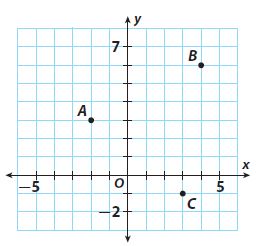
Question 8. A and B ________ units
Answer: Distance between A and B is 6.7 units
Explanation: A= (-2,3) and B= (4,6)
Distance between A and B is d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(4 – (-2) 2 + √(6 – 3) 2 = √(6) 2 + √(3) 2 = √(36+9) => √45 = 6.7 units
Question 9. B and C ________ units
Answer: Distance between B and C is 7.07 units
Explanation: B= (4,6) and C= (3,1)
Distance between B and C is d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(4 – 3) 2 + √(6 – (-1)) 2 = √(1) 2 + √(7) 2 = √(1+49) => √50 = 7.07 units
Question 10. A and C ________ units
Answer: Distance between A and C is 6.403 units
Explanation: A= (-2,3) and C= (3, -1)
Distance between A and C is d = √( x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + √( y 2 – y 1 ) 2 = √(3 – (-2) 2 + √(-1 – 3) 2 = √(5) 2 + √(-4) 2 = √(25+16) => √41 = 6.403 units
ESSENTIAL QUESTION
Question 11. How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-world problems?
Answer: We can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of a side of a right triangle when we know the lengths of the other two sides. This application is usually used in architecture or other physical construction projects. For example, it can be used to find the length of a ladder, if we know the height of the wall and distance on the ground from the wall of the ladder.
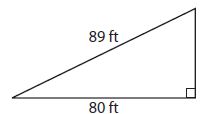
Explanation: Given a= 80 ft b= ? c= 89 ft As a 2 +b 2 =c 2 80 2 +b 2 = 89 2 6,400+b 2 = 7,921 b 2 = 7,921-6,400 b= √1,521 b= 39 ft.
Question 2. Which relation does not represent a function? Options: A. (0, 8), (3, 8), (1, 6) B. (4, 2), (6, 1), (8, 9) C. (1, 20), (2, 23), (9, 26) D. (0, 3), (2, 3), (2, 0)
Explanation: The value of X is the same for 2 points and 2 values of Y [(2, 3), (2, 0)]. The value of X is repeated for a function to exist, no two points can have the same X coordinates.
Question 3. Two sides of a right triangle have lengths of 72 cm and 97 cm. The third side is not the hypotenuse. How long is the third side? Options: A. 25 cm B. 45 cm C. 65 cm D. 121 cm
Explanation: Given a= 72 cm b= ? c= 97 cm As a 2 +b 2 =c 2 72 2 +b 2 = 97 2 5,184+b 2 = 9,409 b 2 = 9,409-5,184 b= √4,225 b= 65 cm.
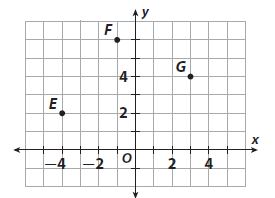
Explanation: Given F= (-1,6) =(x1,y1). G= (3,4) = (x2,y2). The difference between F&G points is d= √(x2-x1) 2 + (y2-y1) 2 = √(3 – (-1)) 2 + (4 – 6) 2 = √(4) 2 + (-2) 2 = √16+4 = √20 = 4.471 = 4.5 units.
Question 5. A flagpole is 53 feet tall. A rope is tied to the top of the flagpole and secured to the ground 28 feet from the base of the flagpole. What is the length of the rope? Options: A. 25 feet B. 45 feet C. 53 feet D. 60 feet
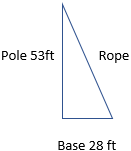
Question 6. Which set of lengths are not the side lengths of a right triangle? Options: A. 36, 77, 85 B. 20, 99, 101 C. 27, 120, 123 D. 24, 33, 42
Explanation: Check if side lengths in option A form a right triangle. Let a= 36, b= 77, c= 85 By Pythagorean theorem a 2 +b 2 =c 2 36 2 +77 2 = 85 2 1,296+ 5,929= 7,225 7,225= 7,225 As 36 2 +77 2 = 85 2 the triangle is a right triangle.
Check if side lengths in option B form a right triangle. Let a= 20, b= 99, c= 101 By Pythagorean theorem a 2 +b 2 =c 2 20 2 +99 2 = 101 2 400+ 9,801= 10,201 10,201= 10,201 As 20 2 +99 2 = 101 2 the triangle is a right triangle.
Check if side lengths in option B form a right triangle. Let a= 27, b= 120, c= 123 By Pythagorean theorem a 2 +b 2 =c 2 27 2 +120 2 = 123 2 729+ 14,400= 15,129 15,129= 15,129 As 27 2 +120 2 = 123 2 the triangle is a right triangle.
Check if side lengths in option B form a right triangle. Let a= 27, b= 120, c= 123 By Pythagorean theorem a 2 +b 2 =c 2 24 2 +33 2 = 42 2 576+ 1,089= 1,764. 1,665= 1,764 As 24 2 +33 2 is not equal to 42 2 the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 7. A triangle has one right angle. What could the measures of the other two angles be? Options: A. 25° and 65° B. 30° and 15° C 55° and 125° D 90° and 100°
Explanation: The sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180 <A+<B+<C= 180° <A+<B+ 90°= 180° <A+<B= 180°-90° <A+<B= 90, here we will verify with the given options. 25°+65°= 90° So, the measure of the other two angles are 25° and 65°
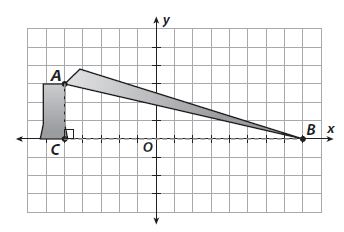
Answer: 13.34 m.
Explanation: A= (-5,3) B= (8,0) Distance between A & B is D= √{8-(-5) 2 + (0-3) 2 = √(13) 2 + (-3) 2 = √169+9 = √178 = 13.34 m.
Question 8. b. What was the height of the tree before it fell? _______ meters
Answer: 16.3 m.
Explanation: Length of the broken part= 13.3 m Length of vertical part= 3 m Total Length = 13.3 m + 3 m = 16.3 m.
Final Words
In addition to the exercise problems, we have provided the solutions for the review questions. So all the students are requested to test your knowledge and solve the problems provided at the end of this chapter. Refer HMH Go Math Grade 8 Answer Keu and try to score the highest marks in the exams. Hope you liked the explanations provided in this chapter. Stay tuned to get the solutions according to the list of the chapters of all the grades.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

The Pythagorean Theorem
Related Videos
Pythagorean Theorem- Color By Number

Description
Introducing "Colorful Pythagoras: A Color by Answer Practice Activity!" Engage your students in a fun and interactive way to reinforce their understanding of the Pythagorean theorem with our exciting Color by Answer practice activity. Designed with both educational value and artistic flair in mind, this activity is perfect for classroom use or at-home learning. Features:
- Nine Engaging Questions: Students will tackle nine thought-provoking questions that require them to apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the lengths of the legs and the hypotenuse of right triangles. Each question presents a unique scenario, keeping students challenged and engaged throughout the activity.
- Visual Learning: Our color-by-answer format combines the thrill of problem-solving with the satisfaction of coloring. As students solve each question correctly, they will be rewarded with a corresponding color code, allowing them to bring a delightful bird house picture to life.
- Reinforcement of Concepts: By practicing with real-world applications of the Pythagorean theorem, students deepen their understanding of geometric principles while honing their problem-solving skills. This activity serves as a valuable review tool for classroom instruction or individual study.
- Bulletin Board Ready: Once completed, the vibrant bird house picture serves as a beautiful showcase of students' mastery of the Pythagorean theorem. Teachers can proudly display these colorful creations on bulletin boards to celebrate their students' achievements and showcase their mathematical prowess.
How to Use:
- Distribute the activity sheets to your students along with coloring materials.
- Students will solve each Pythagorean theorem question and identify the correct answer.
- Using the provided color key, students will color the corresponding sections of the bird house picture based on their answers.
- As students progress through the activity, they will gradually reveal the full-color image of the bird house, demonstrating their understanding of the Pythagorean theorem in a visually captivating way.
- Reinforces understanding of the Pythagorean theorem through hands-on practice.
- Encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Fosters creativity and artistic expression through coloring.
- Provides an opportunity for interactive learning and engagement.
- Creates a visually appealing display for classroom or bulletin board decoration.
Ignite your students' enthusiasm for geometry while reinforcing essential mathematical concepts with our "Colorful Pythagoras" activity. Watch as they proudly showcase their colorful creations, demonstrating their mastery of the Pythagorean theorem with confidence and flair!
*Nine Pythagorean Theorem Questions
*Bird house Picture
*Example Key
Please leave feedback on my product! Thank you for your purchase!
Other Related Materials:
- Pythagorean Theorem- Real Life Town Project
Follow Me on Social Media
▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ Easy As Pi Learning ◀ ◀ ◀ ◀ ◀ ◀
Terms of Use:
By purchasing this product, you agree not to share, resell, copy, or alter this product in any way. You agree not to share without the purchase of multiple licenses. All sales are final. Clip Art is not included as a separate file and is included as part of the background.
© 2024 Easy As Pi Learning Incorporated
Questions & Answers
Easy as pi learning incorporated.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Pythagorean Theorem Calculate 4+
Pythagorean theorem calculator, kantaben gorasiya, designed for ipad, screenshots, description.
Unlock the power of the Pythagorean Theorem with our intuitive and versatile Pythagorean Theorem Calculator app. Whether you're a student tackling geometry problems, a math enthusiast, or a professional in need of quick triangular solutions, this app is your ultimate companion. Key Features: Effortless Triangle Solving: Solve for any missing side or angle in a right triangle with ease. Our calculator makes complex calculations a breeze, saving you time and effort. Interactive Triangle Visualisation: Visualize triangles dynamically as you input values, helping you understand the theorem better and ensuring accuracy in your calculations. Step-by-Step Solutions: Get a detailed breakdown of how each calculation is performed, perfect for learning and teaching the Pythagorean Theorem. Who Can Benefit: Students: Ace your geometry classes by understanding and applying the Pythagorean Theorem confidently. Teachers: Use this tool to teach the Pythagorean Theorem effectively with interactive visualizations and step-by-step solutions. Professionals: Solve real-world problems that involve right triangles, whether in architecture, engineering, or any field where accurate measurements are crucial. Why Choose Our App: Our Pythagorean Theorem Calculator is designed to simplify your math journey. Whether you're learning, teaching, or applying this fundamental concept, our user-friendly interface and powerful features ensure that you have the right tool at your fingertips. Download the Pythagorean Theorem Calculator app today and start unlocking the mysteries of right triangles effortlessly. Mathematics has never been this accessible and enjoyable!
Version 1.1
improved user flow
App Privacy
The developer, Kantaben Gorasiya , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Not Collected
The developer does not collect any data from this app.
Privacy practices may vary based on, for example, the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- Developer Website
- App Support
- Privacy Policy

Family Sharing
Up to six family members can use this app with family sharing enabled., more by this developer.
28 days Excercise challenge
Bible Quiz & Answers
Speak English Fluently 2023
Lose Belly Fat in just 7 days
English Conversion Practice
HOLY QURAN (القرآن الكريم)
You Might Also Like
Quadrilateral Calculator
Geometry Calculator Plus
Unit Converter Deluxe
Concrete Calculator Pro Metric
Steel Bending Calculator
Bending Sheet Metal

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A simple equation, Pythagorean Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite to the right angle triangle) is equal to the sum of the other two sides. Following is how the Pythagorean equation is written: a²+b²=c². In the aforementioned equation, c is the length of the hypotenuse while the length of the other two sides ...
Here's the Pythagorean Theorem formula for your quick reference. Note: drawings not to scale. Problem 1: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 2: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 3: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 4: The legs of a right triangle ...
Part is an alternate interior angle to a 45° angle, and part is an alternate interior angle to a 35° angle. I can use those measures to add because the angles are congruent. 4. m∠x = 70° − 30° = 40° The angle marked 70° and the angles marked x and 30° are alternate interior angles and therefore congruent.
Solve the word problems. Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Answer Key Level 1: S1 Score : Printable Math Worksheets @ www.mathworksheets4kids.com Name : Mark is on his way home from work. He drives 35 miles due North and then 42 miles due West. Find the shortest distance he can cover to reach home early. 1) Joshua won a laptop in a school ...
Learn. Test your understanding of Pythagorean theorem with these NaN questions. The Pythagorean theorem describes a special relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Even the ancients knew of this relationship. In this topic, we'll figure out how to use the Pythagorean theorem and prove why it works.
Determine the length of BC. Problem 5. Given a right triangle ABC, \displaystyle \angle C = 90 ^ {\circ} ∠C = 90∘, in which AC=8, BC=15. Determine the length of AB. Problem 6. A company must stretch a cable from the top of a tower that is 25 meters high to a point 50 meters away from the base of the tower. Calculate the length of the cable.
This second Pythagorean theorem word problems worksheet with answers will focus on more challenging math problems involving right triangles. The sample questions found on this worksheet involve problems where the hypotenuse is given, and the missing side is one of the other two side lengths. Since you are working with 2-step equations, you will ...
Pythagorean theorem word problems. Steve is turning half of his backyard into a chicken pen. His backyard is a 24 meter by 45 meter rectangle. He wants to put a chicken wire fence that stretches diagonally from one corner to the opposite corner. How many meters of fencing will Steve need?
According to the definition of the Pythagorean theorem, the formula would be written as: c 2 = a 2 + b 2. When a triangle has a right-angle, we can use the sum of the squares of each leg of the triangle to find the squared value of the hypotenuse. It can be rearranged to find the length of any of the sides. The Pythagorean Theorem has so many ...
Find the missing side of each triangle. Leave your answers in simplest radical form. 5) x 13 yd 15 yd 2 14 yd 6) 8 km x 16 km 8 3 km Find the missing side of each right triangle. Side c is the hypotenuse. Sides a and b are the legs. Leave your answers in simplest radical form. 7) a = 11 m, c = 15 m 2 26 m 8) b = 6 yd, c = 4 yd 10 yd-1-
Solution to Problem 2. We use the converse of the Pythagorean theorem to solve this problem. a) (2 , 3 , 4) : 4 is the length of the longest side. 2 2 + 3 2 = 13. 4 2 = 16. since 2 2 + 3 2 is NOT EQUAL to 4 2, (2 , 3 , 4) are not the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. b) (12 , 16 , 20) : 20 is the longest side.
Pythagorean Theorem Problems Worksheets. This Pythagorean Theorem Problems Worksheet will produce problems for practicing solving the lengths of right triangles. You may choose the type of numbers and the sides of the triangle. This worksheet is a great resources for the 6th Grade, 7th Grade, and 8th Grade.
©K 12 p0W1y29 yK qu BtaE ZSMoyf0t swNaxr 0eF 2L 7LiCR. 1 S RAulMl6 yrki ZgPh HtZss 2r0e vs Ze zrQvxe vd P.U u JMfa odNeC lw 7i6tHhe gI EnqfziInsi rt 8eC cP Or Te L- yA Dllg 0eVbhrMaT. k Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Key Vocabulary theorem, p. 236 legs, p. 238 hypotenuse, p. 238 Pythagorean Theorem, p. 238 Study Tip In a right triangle, the legs are the shorter sides and the hypotenuse is always the longest side. EXAMPLE 1 Finding the Length of a Hypotenuse Find the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 Write the Pythagorean Theorem. 52 ...
Pythagorean Theorem. Let \(c\) represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and let a and b represent the lengths of its legs, as pictured in the image that follows. The relationship involving the legs and hypotenuse of the right triangle, given by \[a^2 + b^2 = c^2,\nonumber \] is called the Pythagorean Theorem.
Worksheet #1 - Word Problems Pythagorean Theorem Directions: Solve by drawing a picture, identifying a, b, and c, and applying the Pythagorean Theorem. Do not forget to give your answer with units and show ALL your work to receive full credit. 1. Two sides of a right triangle are 8 inches and 12 inches. a.
Word problems using the Pythagorean Theorem: 1. A person has to walk 100 m to go from position X in the north of east direction to the position B and then to the west of Y to reach finally at position Z. The position Z is situated at the north of X and at a distance of 60 m from X. Find the distance between X and Y. Solution:
How to answer Pythagorean Theorem questions. 1 - Label the sides of the triangle a, b, and c. Note that the hypotenuse, the longest side of a right triangle, is opposite the right angle and will always be labeled. 2 - Write down the formula and substitute the values>. a^2+b^2=c^2 a2 +b2 = c2. 3 - Calculate the answer.
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse. Solution. Step 1. Read the problem. Step 2. Identify what you are looking for. the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle. Step 3. Name.
1. A swimmer starts at a point on the shore and swims 200 meters due east. Then, the swimmer turns and swims 300 meters due north. What is the shortest distance for the swimmer to return to the starting point to the nearest metre? a 2 + b 2 = c. 2. 2 200 + 300 = c. 2 2 Therefore the shortest distance. c 300 m is approximately 114 m.
Lesson 7.3 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to Solve Problems. Quick Review The Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find unknown side lengths of an object that is shaped like a right triangle. It also can be used to find diagonal measures in certain two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects. Example
Answer: The length of the hypotenuse is 26 feet. Explanation: According to Pythagorean Theorem, we shall consider values of a = 24ft, b = 10ft. Therefore c = √ (a 2 +b 2) c = √ (24 2 + 10 2) = √ (576 + 100) = √676 = 26ft. Question 2. Mr. Woo wants to ship a fishing rod that is 42 inches long to his son.
Module 12: The Pythagorean Theorem Answer Key. The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that helps us solve problems involving right triangles. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two ...
The Pythagorean Theorem has many practical applications, such as in construction, engineering, and physics, where calculating distances and solving geometric problems are essential. Understanding the Pythagorean Theorem allows us to determine unknown side lengths of right triangles and is the basis for trigonometry, a branch of mathematics that ...
As students progress through the activity, they will gradually reveal the full-color image of the bird house, demonstrating their understanding of the Pythagorean theorem in a visually captivating way. Benefits: Reinforces understanding of the Pythagorean theorem through hands-on practice. Encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills ...
Read reviews, compare customer ratings, see screenshots and learn more about Pythagorean Theorem Calculate. Download Pythagorean Theorem Calculate and enjoy it on your iPhone, iPad and iPod touch.