Key EBP Nursing Topics: Enhancing Patient Results through Evidence-Based Practice

This article was written in collaboration with Christine T. and ChatGPT, our little helper developed by OpenAI.

Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the use of the best available evidence to inform clinical decision-making in nursing. EBP has become increasingly popular in nursing practice because it ensures that patient care is based on the most current and relevant research. In this article, we will discuss the latest evidence-based practice nursing research topics, how to choose them, and where to find EBP project ideas.

What is Evidence-Based Practice Nursing?
EBP nursing involves a cyclical process of asking clinical questions, seeking the best available evidence, critically evaluating that evidence, and then integrating it with the patient’s clinical experience and values to make informed decisions. By following this process, nurses can provide the best care for their patients and ensure that their practice is informed by the latest research.
One of the key components of EBP nursing is the critical appraisal of research evidence. Nurses must be able to evaluate the quality of studies, including study design, sample size, and statistical analysis. This requires an understanding of research methodology and the ability to apply critical thinking skills to evaluate research evidence.
EBP nursing also involves the use of clinical practice guidelines and protocols, which are evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice. These guidelines have been developed by expert groups and are based on the best available evidence. By following these guidelines, nurses can ensure that their practice is in line with the latest research and can provide the best possible care for their patients.
Finally, EBP nursing involves continuous professional development and a commitment to lifelong learning. Nurses must keep abreast of the latest research and clinical practice guidelines to ensure that their practice is informed by the latest research. This requires a commitment to ongoing learning and professional development, including attending conferences, reading scholarly articles, and participating in continuing education programs.
You can also learn more about evidence-based practice in nursing to gain a deeper understanding of the definition, stages, benefits, and challenges of implementing it.
Medical Studies Overwhelming?
Delegate Your Nursing Papers to the Pros!
Get 15% Discount
+ Plagiarism Report for FREE
How to Choose Evidence-Based Practice Nursing Research Topics
Choosing a science-based topic for nursing practice can be a daunting task, especially if you are new to the field. Here are some tips to help you choose a relevant and interesting EBP topic:
- Look for controversial or debated issues
Look for areas of nursing practice that are controversial or have conflicting evidence. These topics often have the potential to generate innovative and effective research.
- Consider ethical issues
Consider topics related to ethical issues in nursing practice. For example, bereavement care, informed consent , and patient privacy are all ethical issues that can be explored in an EBP project.
- Explore interdisciplinary topics
Nursing practice often involves collaboration with other health professionals such as physicians, social workers, and occupational therapists. Consider interdisciplinary topics that may be useful from a nursing perspective.
- Consider local or regional issues
Consider topics that are relevant to your local or regional healthcare facility. These topics may be relevant to your practice and have a greater impact on patient outcomes in your community.
- Check out the latest research
Review recent research in your area of interest to identify gaps in the literature or areas where further research is needed. This can help you develop a research question that is relevant and innovative.
With these tips in mind, you can expand your options for EBP nursing research topics and find a topic that fits your interests and goals. Remember that patient outcomes should be at the forefront of your research and choose a topic that has the potential to improve treatment and patient outcomes.
Where to Get EBP Project Ideas
There are several sources that nurses can use to get EBP project ideas. These sources are diverse and can provide valuable inspiration for research topics. By exploring these sources, nurses can find research questions that align with their interests and that address gaps in the literature. These include:
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
Look for clinical practice guidelines developed by professional organizations or healthcare institutions. These guidelines provide evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice and can help identify areas where further research is needed.
- Research databases
Explore research databases such as PubMed, CINAHL, and the Cochrane Library to find the latest studies and systematic reviews. These databases can help you identify gaps in the literature and areas where further research is needed.
- Clinical Experts
Consult with clinical experts in your practice area. These experts may have insights into areas where further research is needed or may provide guidance on areas of practice that may benefit from an EBP project.
- Quality Improvement Projects
Review quality improvement projects that have been implemented in your healthcare facility. These projects may identify areas where further research is needed or identify gaps in the literature that could be addressed in an EBP project.
- Patient and family feedback
Consider patient and family feedback to identify areas where further research is needed. Patients and families can provide valuable information about areas of nursing practice that can be improved or that could benefit from further research.
Remember, when searching for ideas for EBP nursing research projects, it is important to consider the potential impact on patient care and outcomes. Select a topic that has the potential to improve patient outcomes and consider the feasibility of the project in terms of time, resources, and access to data. By choosing a topic that matches your interests and goals and is feasible at your institution, you can conduct a meaningful and productive EBP research project in nursing.
Nursing EBP Topics You Can Use in Your Essay
Here are some of the latest evidence-based practice nursing research topics that you can use in your essay or explore further in your own research:
- The impact of telehealth on patient outcomes in primary care
- The use of music therapy to manage pain in post-operative patients
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in reducing stress and anxiety in healthcare workers
- Combating health care-associated infections: a community-based approach
- The impact of nurse-led discharge education on readmission rates for heart failure patients
- The use of simulation in nursing education to improve patient safety
- The effectiveness of early mobilization in preventing post-operative complications
- The use of aromatherapy to manage agitation in patients with dementia
- The impact of nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and outcomes
- The effectiveness of peer support in improving diabetes self-management
- The impact of cultural competence training on patient outcomes in diverse healthcare settings
- The use of animal-assisted therapy in managing anxiety and depression in patients with chronic illnesses
- The effectiveness of nurse-led smoking cessation interventions in promoting smoking cessation among hospitalized patients
- Importance of literature review in evidence-based research
- The impact of nurse-led care transitions on hospital readmission rates for older adults
- The effectiveness of nurse-led weight management interventions in reducing obesity rates among children and adolescents
- The impact of medication reconciliation on medication errors and adverse drug events
- The use of mindfulness-based interventions to manage chronic pain in older adults
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing hospital-acquired infections
- The impact of patient-centered care on patient satisfaction and outcomes
- The use of art therapy to manage anxiety in pediatric patients undergoing medical procedures
- Pediatric oncology: working towards better treatment through evidence-based research
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving medication adherence among patients with chronic illnesses
- The impact of team-based care on patient outcomes in primary care settings
- The use of music therapy to improve sleep quality in hospitalized patients
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing falls in older adults
- The impact of nurse-led care on maternal and infant outcomes in low-resource settings
- The use of acupressure to manage chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting breastfeeding initiation and duration
- The impact of nurse-led palliative care interventions on end-of-life care in hospice settings
- The use of hypnotherapy to manage pain in labor and delivery
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing hospital length of stay for surgical patients
- The impact of nurse-led transitional care interventions on readmission rates for heart failure patients
- The use of massage therapy to manage pain in hospitalized patients
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting physical activity among adults with chronic illnesses
- The impact of technology-based interventions on patient outcomes in mental health settings
- The use of mind-body interventions to manage chronic pain in patients with fibromyalgia
- Optimizing the clarifying diagnosis of stomach cancer
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing medication errors in pediatric patients
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in long-term care settings
- The use of aromatherapy to manage anxiety in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving glycemic control in patients with diabetes
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in emergency department settings
- The use of relaxation techniques to manage anxiety in patients with cancer
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving self-management skills among patients with heart failure
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in critical care settings
- The use of yoga to manage symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting medication safety in community settings
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in home healthcare settings
- The role of family involvement in the rehabilitation of stroke patients
- Assessing the effectiveness of virtual reality in pain management
- The impact of pet therapy on mental well-being in elderly patients
- Exploring the benefits of intermittent fasting on diabetic patients
- The efficacy of acupuncture in managing chronic pain in cancer patients
- Effect of laughter therapy on stress levels among healthcare professionals
- The influence of a plant-based diet on cardiovascular health
- Analyzing the outcomes of nurse-led cognitive behavioral therapy sessions for insomnia patients
- The role of yoga and meditation in managing hypertension
- Exploring the benefits of hydrotherapy in post-operative orthopedic patients
- The impact of digital health applications on patient adherence to medications
- Assessing the outcomes of art therapy in pediatric patients with chronic illnesses
- The role of nutrition education in managing obesity in pediatric patients
- Exploring the effects of nature walks on mental well-being in patients with depression
- The impact of continuous glucose monitoring systems on glycemic control in diabetic patients
The Importance of Incorporating EBP in Nursing Education
Evidence-based practice is not just a tool for seasoned nurses; it’s a foundational skill that should be integrated early into nursing education. By doing so, students learn the mechanics of nursing and the rationale behind various interventions grounded in scientific research.
- Bridging Theory and Practice:
Introducing EBP in the curriculum helps students bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and clinical practice. They learn how to perform a task and why it’s done a particular way.
- Critical Thinking:
EBP promotes critical thinking. By regularly reviewing and appraising research, students develop the ability to discern the quality and applicability of studies. This skill is invaluable in a rapidly evolving field like healthcare.
- Lifelong Learning:
EBP instills a culture of continuous learning. It encourages nurses to regularly seek out the most recent research findings and adapt their practices accordingly.
- Improved Patient Outcomes:
At the heart of EBP is the goal of enhanced patient care. We ensure patients receive the most effective, up-to-date care by teaching students to base their practices on evidence.
- Professional Development:
Familiarity with EBP makes it easier for nurses to contribute to professional discussions, attend conferences, and conduct research. It elevates their professional stature and opens doors to new opportunities.
To truly prepare nursing students for the challenges of modern healthcare, it’s essential to make EBP a core part of their education.
In summary, evidence-based practice nursing is an essential component of providing quality patient care. As a nurse, it is important to stay up to date on the latest research in the field and incorporate evidence-based practices into your daily work. Choosing a research topic that aligns with your interests and addresses a gap in the literature can lead to valuable contributions to the field of nursing.
When it comes to finding EBP project ideas, there are many sources available, including professional organizations, academic journals, and healthcare conferences. By collaborating with colleagues and seeking feedback from mentors, you can refine your research question and design a study that is rigorous and relevant.
The nursing evidence-based practice topics listed above provide a starting point for further exploration and investigation. By studying the effectiveness of various nursing interventions and techniques, we can continue to improve patient outcomes and deliver better care. Ultimately, evidence-based practice nursing is about using the best available research to inform our decisions and provide the highest quality care possible to our patients.
📎 Related Articles
1. Top Nursing Research Topics for Students and Professionals 2. Nursing Debate Topics: The Importance of Discussing and Debating Nursing Issues 3. Mental Health Nursing Research Topics: Inspiring Ideas for Students 4. Top Nursing Argumentative Essay Topics: Engage in Thought-Provoking Debates 5. Top Nursing Topics for Discussion: Engaging Conversations for Healthcare Professionals 6. Exploring Controversial Issues in Nursing: Key Topics and Examples 7. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics for Students: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of content
Crafted with Care:
Nursing Essays!
Precision, Passion, & Professionalism in Every Page.

Best Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Nursing Research Topics and Ideas

We have already explored as much as there is regarding evidence-based nursing in our comprehensive EBP paper-writing guide . A time comes in your nursing school journey, either at basic (ADN, LPN, or BSN) or advanced levels (MSN, DNP, or PhD), when you are required to select a suitable evidence-based practice nursing research topic, research, and write an evidence-based nursing paper, report, or white paper. The process for selecting the topic is more or less the same as when selecting a nursing dissertation topic or topic for a nursing capstone .
You have to go through the instructions, consider an area of nursing specialization that interests you, do some thorough research, reading, and analysis, come up with a few topics, and eliminate and remain with the most suitable topic for your EBP nursing paper. You can locate good EBP project ideas from course materials (readings, handouts, PPTs, and class notes), online blogs and websites (like NurseMyGrade), nursing textbooks, nursing journals and articles, and other online resources.
General, Current, and Latest Evidence-Based Nursing Topics
- Effects of evidence-based practice on the quality and safety of patients
- Attitudes and readiness for Evidence-Based Nursing Practice among newly hired nurses
- Engaging advanced practice nurses in evidence-based practice through an e-monitoring program
- Effectiveness of EBP practice guidelines in preventing adverse events in clinical settings
- The attitudes of nurses toward adhering to clinical guidelines regarding the management of various conditions
- Prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) among surgical patients
- Effectiveness of warming interventions for women undergoing Cesarean Section
- Strategies for managing second-stage labor
- Effects of gum chewing and early mobilization on intestinal mobility after cesarean birth
- Therapeutic use of music in maternity wards post-cesarean section
- Strategies for preparing women for unplanned Cesarean birth
- Effectiveness of hydrotherapy during labor
- Strategies to implement skin-to-skin contact in the OR following Cesarean birth
- Benefits of the EBP Organizational culture and readiness scale
- Transferability, reach, and impact of the EBP Questionnaire
- Barriers and facilitators influencing the implementation of EBP in clinical settings
- Challenges to implementing EBP in healthcare systems
- The beliefs and competencies of medical-surgery nurses on EBP
- Effects of EBP courses on MSN and DNP students' attitudes and beliefs on EBP
- The impacts of gamification on EBP training among nursing students
- Strategies to promote evidence-based nursing practice among nursing students
- The link between knowledge of EBP and nurse job satisfaction
- Impacts of nursing ethics on evidence-based practice
- Strategies to address the implementation gap between practice, research, and knowledge in nursing
- Using social media to promote the dissemination of evidence-based practice
- Strategies for implementing and translating evidence-based practice
- Benefits of frequently training nursing staff on evidence-based practice
- Role of evidence-based practice in modeling professional nursing practice
- Strategies for enhancing utility and understanding of evidence-based practice during undergraduate nursing education
- Knowledge, attitude, beliefs, and use of evidence-based practice among registered pediatric nurses
- Improving the readiness of evidence-based practice in critical care units
- Strategies for improving evidence-based practice among registered nurses (RNs)
- Best strategies for assessing compliance to EBP guidelines for VAP prevention among ICU nurses
- Impacts of EBP guidelines on clinical decision-making
- Challenges in communicating research evidence and translating it to practice
- Effectiveness of SBAR Tool Implementation to advanced communication and collaboration in clinical settings
- Knowledge of EBP and the confidence of newly recruited nurses
- Role of evidence-based practice guidelines in maintaining competence among mental health nurses
- Impacts of teaching advanced evidence-based practice research in doctoral nursing programs
Evidence-Based Topics for Anesthesia
- Primary concerns in the process of extubation in the anesthesia settings
- Perceptions and attitudes of anesthesia professionals on digital anesthesia information management system
- Benefits of nurse anesthetist perioperative dialog
- Causes of high attrition rates and turnover among nurse anesthetists
- Perceptions and attitudes of nurses on automatic dispensing cabinets
- Strategies for translating evidence-based research into anesthesia practice
- Addressing challenges associated with anesthesia in clinical settings
- Causes and solutions to anesthesia-associated mortality and morbidity
- An evidence-based approach to airway management via anesthesia administration
- Attitudes, knowledge, skills, and use of anesthesia teams toward EBP practice in clinical settings
- Why anesthetists are hesitant to implement ERAS guidelines
Related read: How to complete Shadow Health Assessments .
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Evidence-Based Topics
- Improving the quality of cardiovascular care through evidence-based practice
- Addressing social determinants of health as a means of addressing cardiovascular diseases
- Effects of listening to music during cardiac rehabilitation on clinical outcomes
- Effectiveness of physical activity on cardiovascular health
- Role of physical therapists in the management of venous thromboembolism
- Effectiveness of aerobic exercise training in improving aerobic capacity after heart transplant
- Impacts of guarding on the outcomes of the 6-minute walk test
- Role of Mitsungumin 53 in cardiovascular diseases (CVD)
- Effects of autophagy on the cardiovascular system
- The ethics of using embryonic stem cells in cardiovascular research
- Use of telehealth in early detection of anxiety and depression in post-coronary patients
- Effectiveness of indoor allergen reduction in the management of asthma
- Non-invasive technologies for diagnosing coronary artery disease in women
- Impacts of smoking on the lungs of a fetus
- Strategies to address obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease
- The link between consuming fatty animal meat and cardiovascular health
- Benefits of prone positioning for patients with ARDS
- Response of COPD to prophylactic antibiotics
- Evidence-based nursing strategies for the prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury
- Impacts of home monitoring on COPD patients
Complementary and Alternative Medicine Evidence-Based Topics
- The link between probiotics use and diarrhea
- The effectiveness of vitamin C in the prevention of complex regional pain syndrome following wrist fractures
- The link between using essential oils and hypertension
- Effectiveness of cranberry products for the treatment of UTIs
- Effectiveness of botulism toxin in the treatment of restless legs syndrome
- Using therapeutic honey in tropical wound management
- Impacts of scalp cooling on alopecia among cancer patients
- Effects of spiritual beliefs on type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
- Effects of aromatherapy in the management of depression and anxiety
- Non-pharmacologic interventions for treatment-resistant depression among adolescents
Nursing Ethics Evidence-Based Topics
- Effects of abandonment on nursing staff shortage
- Effects of negligence on patient outcomes
- AI ethics awareness, attitudes, and beliefs, and the behavioral intentions of nursing students
- Attitudes and perspectives of nursing faculty on noncompliance with ethics in nursing academic environments
- Application of Nightingale's professionalism among student nurses
- Influence of nursing ethics on clinical decision-making
- Perceptions and awareness of student nurses on social justice in the healthcare system
- Benefits of increased ethical competency of nurses in clinical settings
- Ethical problems of clinical nursing practice
- Factors influencing professionalism in nursing among Registered Nurses
- Information literacy and ethical decision-making among nurses
- The link between clinical dishonesty and perceived clinical stress among nursing students
- Strategies to help nurses handle compassion fatigue
- Ethical perspectives of evidence-based practice
- Influence of laws and Legislation on evidence-based practice
- Moral distress among Registered Nurses
- Barriers and facilitators of addressing nursing research ethics
- Role of nursing ethics in the implementation of evidence-based practice
Family Practice Evidence-Based Topics
- The significance of genetic counseling in diabetes prevention
- Challenges for contraception for women with diabetes
- Management of autism in children
- Diagnosis, treatment, and management of psoriasis
- Using a gluten-free diet to improve outcomes in patients with psoriasis
- The link between psoriasis and cardiovascular diseases
- Impacts of nutritional counseling on the BMI of patients
- Using Metformin over Sulfonylurea for initial treatment of gestational diabetes
- Best ways to diagnose menopause in perimenopausal women
- Dinoprostone vs. vaginal misoprostol in labor induction: which is better?
- Effectiveness of using narcotics to treat patients with chronic daily headaches
- Vitamins and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease
- The link between regular family dinners and obesity in adolescent patients
- Is the Mediterranean diet better for bone health?
- Benefits of self-managed diabetes programs
- Is acupuncture effective in the treatment of allergic rhinitis?
- The link between antibiotic use and acute sinusitis
- Effectiveness of Flu vaccine on prevention of community-acquired pneumonia
- The link between male obesity and infertility
- Lower back pains and NSAIDS
- Seasonal Nasal Irrigation and Seasonal Allergic Reactions: Best management strategies
- Effectiveness of abortive treatment for acute migraine
- Effectiveness of combination treatment for hepatitis C
- Benefits of tailored education for melanoma management
- Genetic testing and obesity
- Treatment and management of atopic dermatitis
Nursing Forensics Evidence-Based Topics
- Strategies to document injuries from domestic violence abuse by forensic nurses
- Perceptions of forensic nurses on victim counseling before post-domestic violence cases
- Stress management and coping strategies in prison settings
- Mental health as a risk factor for sexual assault
- Barriers and challenges to implementing remote sexual assault nurse examiner programs
- Limit setting and de-escalation in forensic mental health units
- The risk factors for domestic minor sex trafficking in the USA
- Benefits of sexual assault nurse examiners practicing trauma-informed care
- Ethical issues involved during forensic nursing investigations
- Strategies for preparing victims of sexual assault to be witnesses in courts of law
- Role of forensic nurses in combating human and sexual trafficking
- The link between sexual assault and suicide
- Strategies to handle compassion fatigue among forensic nurses
- Strategies for emergency contraception administration among the SANE and non-SANE medical providers
- Strategies forensic nurses use to resolve difficulties in supporting offenders with mental health disorders
- Role of forensic nurses in addressing challenges for children in foster care
- Forensic nursing interventions for patients with personality disorders
- Application of telehealth among sexual assault forensic examiners
- Strategies for handling children facing maltreatment from parents
- Interprofessional collaboration to optimize trauma-informed care
- Role of pediatric forensics in clinical settings
- Role of forensic nurses in abortion investigations
- Steps and evidence-based methods for screening children for neglect or abuse
- Strategies for solving burnout among forensic nurses
- Role of forensic nurses in death investigations
- Attitudes of Sexual Assault Nurse Examiners (SANE) toward sexual assault victims
- Methods for promoting resilience, competence, and quality of life of Sexual Assault Nurse Examiners
- Role of correctional nurses in advocating for pregnant women's rights in prison
- An evidence-based approach to suicide risk assessment following sexual assault
Gastroenterology Evidence-Based Topics
- The use of probiotics to treat and manage irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Using behavioral therapy adjunct to drug therapy in the management of urinary incontinence
- Pharmacological strategies for the management of Crohn's disease
- Complementary alternative medicine approaches to the management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Intermittent fasting among obese women and the management of pylori
- Homemade solutions for constipation among pregnant women
Geriatrics or Long-Term Care Evidence-Based Topics
- The effectiveness of the North Dakota Association of director of Nursing Administration (NADONA) /Long-Term Care standards of Practice in managing long-term care facilities
- Strategies to encourage elderly people to age in place
- Methods to improve drug adherence among elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease
- Methods for managing polypharmacy among elderly adults
- Design strategies to address falls for patients aging in place
- Use of technology to address the challenges of elderly adults who choose to age in place
- Benefits of music therapy for patients with Multiple Sclerosis
- Strategies for addressing pressure ulcers among the elderly
- Benefits of teaching self-care practices to elderly patients with long-term in-dwelling catheter
- Using stories to entertain and give hope to elderly patients in long-term care facilities
- Multifactorial approach towards management of falls in long-term care facilities
Hospital-Acquired Infections Evidence-Based Topics
- Effectiveness of hand hygiene in reducing hospital-acquired infections
- Strategies to prevent blood contamination and infection during transfusion
- The value of Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection Bundle Compliance in preventing CLABSI
- Impacts of implementing central nervous catheter bundle in reducing central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI)
- The knowledge and attitudes of nurses on evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infections
- Benefits of governments supporting nursing homes in infection management
- How effective are leadership rounds in reducing healthcare-associated infections?
- Knowledge, beliefs, and attitude of newly graduated nurses on infection prevention and control
- Evidence-based strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia
- Perceptions of NICU nurses regarding measures to prevent HAIs
- The role of chlorhexidine gluconate bathing in preventing HAIs
- Importance of communication networks in the management of infections in ICUs
- Strategies to reduce catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs)
- The perspectives and experiences of patients on HAIs
- Nurse-led quality improvement interventions to reduce hospital-acquired infections in the NICU
- Using a multimodal approach to institute hand hygiene
- The correlation between hospital length of stay and acquiring infections
- Evidence-based strategies to prevent nosocomial infections in clinical settings
- Value of e-learning for preventing healthcare-associated infections
- Impacts of nurse burnout and shortage on HAIs
- Core components of an infection prevention and control program for a nursing home
- Leadership skills of the APRNs and prevention of HAIs
- The motivations of healthcare workers to reduce HAIs
- Hand hygiene knowledge and beliefs among newly recruited nurses
- Impacts of hospital design on HAIs
- Overcrowding in the ER and hospital-acquired infections
- Effects of training on nurses' knowledge and skills in indwelling urinary catheters in preventing CAUTIs
- Low rates of Influenza vaccination among nurses and HAIs
- Role of environmental cleaning in the control of HAIs
- Green cleaning and HAIs
- Compliance with Chlorhexidine wipes to prevent Hospital-acquired infections
- The knowledge of nurses of the WHO Five Moments of Hand hygiene and HAIs in the Operating rooms
Nursing Education Evidence-Based Topics
- Effectiveness of situated e-learning on medical and nursing education
- Benefits of cultural competence training among nurses on the patient satisfaction
- Experiences and attitudes of student nurses on formal preceptor programs
- The effectiveness of using virtual and augmented reality in nursing education
- Strategies to attract, train, and retain student nurses until retirement
- The application of gamification in nursing training
- Should nurses be taught basic coding concepts?
- Inclusion of LGBTQ student nurses in clinical settings
- The use of social media to facilitate learning among nursing students
- Benefits of introducing students to reflective nursing practice
- Benefits of e-learning for nursing education
- Online nursing programs as a means to prepare nurses for leadership roles
- The nurse training pipeline is an essential aspect of addressing nurse shortages
- Discrimination among nurse student acceptance of some programs/nursing schools
- Factors affecting the progress of nursing students in the USA
- Should the nursing career be ubiquitous globally?
- Student nurses should join professional organizations that advocate for their rights
- Steps to improve collaboration and teamwork among nurse students
Pain Management Evidence-Based Topics
- Effectiveness of ERAS in postoperative pain management
- Non-pharmacological methods and perceived barriers in pain management by nurses
- Psychological and behavioral pain management strategies in pediatric oncology departments
- Mindfulness mediation as a strategy for chronic pain management
- Impacts of relaxation techniques for pain management during labor
- The efficacy of cannabis-based medicines for pain management
- Use of music therapy during labor
- Impacts of massage therapy on cancer pain management
- The effectiveness of craniosacral therapy for chronic pain management
- Effectiveness of manual therapy vs. exercise therapy in the management of adult neck-pain
- Non-pharmacological pain management approaches for cancer patients
- Music-induced analgesia in chronic pain management
- The effectiveness of transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation for cancer pain
- The efficacy of acupuncture in the management of postoperative pain
- The application of cannabinoids in pain management
- Acupressure for pain management during labor
Pediatrics Evidence-Based Topics
- Practical strategies for preventing failure to rescue obstetric patients
- Effectiveness of neonatal pain management via oral sucrose
- Benefits of nutritional assessment and intervention in a pediatric oncology unit
- Strategies to manage inguinal hernias in children
- Impacts of clinical settings appearance on the anxiety of kids in cancer care facilities
- Evidence-based strategies for the management of the acute phase of Kawasaki disease
- Strategies to address diabetes ketoacidosis among pediatric patients
- The use of virtual reality in managing anxiety among pediatric patients
- The use of probiotics in the prevention of diarrhea among children
- The efficiency of using gastronomy tubes among pediatric patients
- Best strategies to treat and manage infant colic
- Management of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) among neonates and children
- Strategies parents can use to cope during acute pediatric hospitalizations
- Strategies to address childhood constipation
- Strategies to prevent SIDS during breastfeeding
- The safety of corticosteroids in young children with acute respiratory conditions
- Management of hospital-acquired venous thromboembolism in pediatric patients
- Efficacy of insertion and maintenance bundles in preventing central-line associated bloodstream infections in critically ill pediatric patients
- Prevalent and management strategies for burnout among pediatric nurses
- The efficacy of magnesium supplementation in addressing postoperative arrhythmias after cardiopulmonary bypass among pediatric patients
As we come to the End of this Article '
You can select a topic among the ones we have listed above or get inspired to select a topic whose research direction interests you. If you need unique topics, kindly place a one-page order and get 3-4 topics researched, suggested, and listed by an expert based on your preferences.
Nobody understands evidence-based nursing practice more than our online nursing writers. Through the years, we have helped students at the ADN, BSN, MSN, DNP, and Ph.D. nursing levels access unique and exciting evidence-based topics. What's more, if you need help writing an evidence-based practice paper (report, term paper, change project, thesis, research paper, or dissertation), our astute writers can help you. You will get a 100% original, well-formatted (in APA or Harvard format), and edited paper that meets your rubric requirements.
Struggling with
Related Articles

How to Make SOAP Notes for a Nursing Class Assignment

How to Write a Quality Improvement (QI) Report | An Ultimate Guide

Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas About Healthcare
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
Sharing health evidence you can trust

Evidence for Nursing: new evidence and resources – January 2022
The latest evidence and resources for nurses and clinical support staff. You can either scroll through this page or click on any of the links below to jump to the relevant section.
Please note, unlike the rest of our blogs, our Evidence for Nursing: new evidence and resources blogs will not be updated.
Bronchiolitis
- Care of the newborn, including preterm infants
Cervical screening – encouraging uptake
Communication for adults with an artificial airway, de-implementation of low value health care , delirium prevention, dietary salt for people with chronic kidney disease, heparin injections: slow versus fast delivery, intrauterine insemination, life-threatening conditions and emergency care, patient questionnaires, perioperative non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids) for women having breast surgery, preventing surgical site infection, reducing medication errors, rehabilitation after hip fracture, respiratory syncytial virus (rsv) infection in children, smoking cessation, vaccination uptake, vegan diet for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease, venous leg ulcers.
- Opportuntities and events
This year, Cochrane is continuing to produce new and updated reviews in response to the pandemic . We have blogged about many of them and this blog COVID-19 evidence: a Cochrane round-up brings together a large collection of evidence and resources, starting from when this evidence was first being produced in spring 2020. Like the reviews themselves, all our blogs are updated to reflect new evidence.
There is a Cochrane news item about Ivermectin: Cochrane’s most talked about review so far, ever. Why?
The impact of measures intended to prevent or reduce the spread of Covid-19 in long-term care facilities have been explored in Non‐pharmacological measures implemented in the setting of long‐term care facilities to prevent SARS‐CoV‐2 infections and their consequences: a rapid review . There is evidence that a number of strategies may reduce the number of infections and related outcomes Outcomes are measures of health (for example quality of life, pain, blood sugar levels) that can be used to assess the effectiveness and safety of a treatment or other intervention (for example a drug, surgery, or exercise). In research, the outcomes considered most important are ‘primary outcomes’ and those considered less important are ‘secondary outcomes’. , but more robust evidence is needed. You can read more in the news item Can non-pharmacological measures prevent or reduce Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infections in long term care facilities? and there are a number of related Cochrane Clinical Answers (see reference list).
Cochrane Special Collections
Cochrane Special Collections assemble Cochrane Reviews on important topics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. They are developed with experts from our global Cochrane network. They are based on World Health Organization interim guidance, and continuously updated. You can find Coronavirus (COVID-19) Special Collections here .
Cochrane Podcasts
Cochrane COVID-19 Podcasts offer short summaries of Cochrane COVID-19 reviews from the authors themselves. A good way to hear the latest Cochrane evidence in under 5 minutes each.
Cochrane Clinical Answers
Cochrane Clinical Answers (CCAs) provide a readable, digestible, clinically-focused entry point to rigorous research from Cochrane Reviews Cochrane Reviews are systematic reviews. In systematic reviews we search for and summarize studies that answer a specific research question (e.g. is paracetamol effective and safe for treating back pain?). The studies are identified, assessed, and summarized by using a systematic and predefined approach. They inform recommendations for healthcare and research. . They are designed to be actionable and to inform point-of-care decision-making. Each CCA contains a clinical question, a short answer, and data Data is the information collected through research. for the outcomes from the Cochrane Review deemed most relevant to practising healthcare professionals.
You can find Cochrane Clinical Answers related to COVID-19 here.
A new Cochrane Review Parenteral versus enteral fluid therapy for children hospitalised with bronchiolitis (December 2021) with evidence from two studies, with fewer than 1000 hospitalised infants, highlights the need for an expanded evidence-base to inform practice.
As things stand, the authors find that enteral tube feeding probably reduces local complications compared with IV fluid administration. They also find that there was probably a higher rate The speed or frequency of occurrence of an event, usually expressed with respect to time. For instance, a mortality rate might be the number of deaths per year, per 100,000 people. of success in inserting a feeding tube on first try compared to an intravenous catheter, and probably a lower rate of switching method of fluid delivery.
This is one of the reviews included in our blog Bronchiolitis: evidence and guidance for practice .
- The Cochrane Review Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in people with cancer was updated in 2021.
- It is included in this Evidently Cochrane blog – Bringing harmony to the hospital: music therapies revisited .
- Podcast: Can music interventions benefit people with cancer?

Care of the newborn, including preterm infants
Avoidance of bottles in establishing breastfeeds in preterm infants.
The authors of the Cochrane Review Avoidance of bottles during the establishment of breastfeeds in preterm infants (October 2021) have concluded:
“Avoiding the use of bottles when preterm infants need supplementary feeds probably increases the extent of any breastfeeding at discharge, and may improve any and full breastfeeding (exclusive) up to six months postdischarge. Most of the evidence demonstrating benefit was for cup feeding. Only one study An investigation of a healthcare problem. There are different types of studies used to answer research questions, for example randomised controlled trials or observational studies. used a tube feeding strategy. We are uncertain whether a tube alone approach to supplementing breastfeeds improves breastfeeding outcomes.”

This review has been added to two existing Evidently Cochrane blogs:
- “ Yummy, yummy in my tummy, getting big with milk from mummy. Getting preterm babies feeding orally – a roundup of current evidence ”
- “ Breastfeeding: a round-up of Cochrane evidence ”
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For preterm infants, does avoidance of bottles during establishment of breast‐feeding help to increase the extent and duration of breast‐feeding?
Corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
A Cochrane Review Early (< 7 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants (October 2021) has been updated. From high-certainty The certainty (or quality) of evidence is the extent to which we can be confident that what the research tells us about a particular treatment effect is likely to be accurate. Concerns about factors such as bias can reduce the certainty of the evidence. Evidence may be of high certainty; moderate certainty; low certainty or very-low certainty. Cochrane has adopted the GRADE approach (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) for assessing certainty (or quality) of evidence. Find out more here: https://training.cochrane.org/grade-approach evidence, the review authors have found that systemic postnatal corticosteroids, in the regimens used, have had “significant short‐term and long‐term effects ‐ both beneficial and harmful”.
They conclude that “Early systemic postnatal corticosteroid treatment Something done with the aim of improving health or relieving suffering. For example, medicines, surgery, psychological and physical therapies, diet and exercise changes. (started during the first six days after birth) prevents BPD [bronchopulmonary dysplasia] and the combined outcome of mortality death or BPD. However, it increases risks of gastrointestinal perforation, cerebral palsy, and the combined outcome of mortality or cerebral palsy. Most beneficial and harmful effects are related to early treatment with dexamethasone, rather than to early treatment with hydrocortisone, but early hydrocortisone may prevent mortality, whereas early dexamethasone does not.”
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For preterm infants with evolving or established bronchopulmonary dysplasia, what are the effects of systemic corticosteroids administered within eight days after birth?
The Cochrane Review Late (≥ 7 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants (November 2021) has also been updated. There is high-certainty evidence that “late systemic postnatal corticosteroid treatment (started at seven days or more after birth) reduces the risks of mortality and BPD, and the combined outcome of mortality or BPD, without evidence of increased cerebral palsy. ” But the authors note that there is limited evidence on long-term outcomes, including possible neurodevelopment harms.
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For preterm infants with evolving or established bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), what are the effects of late (≥ 7 days) systemic corticosteroids (CSs)?
CPAP for preterm infants
The authors of a Cochrane Review Nasal continuous positive airway pressure levels for the prevention of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants (November 2021) conclude: “There are insufficient data from randomized Randomization is the process of randomly dividing into groups the people taking part in a trial. One group (the intervention group) will be given the intervention being tested (for example a drug, surgery, or exercise) and compared with a group which does not receive the intervention (the control group). trials Clinical trials are research studies involving people who use healthcare services. They often compare a new or different treatment with the best treatment currently available. This is to test whether the new or different treatment is safe, effective and any better than what is currently used. No matter how promising a new treatment may appear during tests in a laboratory, it must go through clinical trials before its benefits and risks can really be known. to guide nasal CPAP level selection in preterm infants, whether provided as initial respiratory support or following extubation from invasive mechanical ventilation. We are uncertain as to whether low or moderate‐high nasal CPAP levels improve morbidity illness or harm and mortality in preterm infants.”
There is also a Cochrane Clinical Answer Can prophylactic nasal continuous positive airway pressure help to prevent morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants? for the review Prophylactic or very early initiation of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for preterm infants (October 2021).
Enteral zinc supplementation for preterm neonates
The Cochrane Review Enteral zinc supplementation for prevention of morbidity and mortality in preterm neonates (February 2021) found that “Enteral supplementation of zinc in preterm infants compared to no supplementation or placebo An intervention that appears to be the same as that which is being assessed but does not have the active component. For example, a placebo could be a tablet made of sugar, compared with a tablet containing a medicine. may moderately decrease mortality and probably improve short‐term weight gain and linear growth, but may have little or no effect on common morbidities of prematurity. There are no data to assess the effect of zinc supplementation on long‐term neurodevelopment.”
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the benefits and harms of enteral zinc supplementation for preterm neonates?
Opioid withdrawal in newborn infants
The Cochrane Review Opioid treatment for opioid withdrawal in newborn infants was updated in July 2021 with new trials added and conclusions changed.
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For newborn infants with opioid withdrawal, how does morphine compare with methadone, buprenorphine, phenobarbital, and chlorpromazine?
Preventing bronchopulmonary dysplasia
The Cochrane Review Late (≥ 7 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants (November 2021) has been updated with more evidence that shows a reduction in mortality at all ages from treatment with late systemic corticosteroids. The evidence for most outcomes is high-certainty. The authors note, however that “the methodological quality of studies determining long‐term outcomes is limited, and no studies were powered The power of a trial is the chance that it will correctly detect a real effect of an intervention being tested (for example a drug, surgery, or exercise). Studies with more participants will have greater power. to detect increased rates of important adverse long‐term neurodevelopmental outcomes.”
Surfactant administration for preterm infants with or at risk A way of expressing the chance of an event taking place, expressed as the number of events divided by the total number of observations or people. It can be stated as ‘the chance of falling were one in four’ (1/4 = 25%). This measure is good no matter the incidence of events i.e. common or infrequent. of respiratory distress syndrome
Cochrane Clinical Answer: How does surfactant administration via thin catheter (S‐TC) compare with surfactant administration through an endotracheal tube (S‐ETT) for preterm infants with or at risk of respiratory distress syndrome?
Tube feeding preterm and low birth weight infants
The Cochrane Review Monitoring of gastric residual volume during enteral nutrition (September 2021) concludes that “The evidence is very uncertain about the effect of GRV on clinical outcomes including mortality, pneumonia, vomiting, and length of hospital stay.”
Cochrane Clinical Answers:
- For preterm or very low birth weight infants, how does slow advancement compare with fast advancement of enteral feed volumes?
- How do high‐ and standard‐volume fortified enteral feeds compare for improving outcomes in preterm or low birthweight infants?
- How does continuous nasogastric milk feeding compare with intermittent bolus milk feeding for preterm infants?
- What are the effects of push versus gravity for intermittent bolus gavage tube feeding of premature and low birth weight infants?
The Cochrane Review Interventions targeted at women to encourage the uptake of cervical screening (September 2021) has found that the use of invitation letters probably increases the uptake of cervical screening. Lay health worker involvement amongst ethnic minority populations may increase screening coverage. Uncertainty remains about the effects of most strategies to promote uptake.
The Cochrane Review Interventions to enable communication for adult patients requiring an artificial airway with or without mechanical ventilator support (October 2021) has highlighted a lack of evidence to guide practice on choice of communication aid and when to use them.
Chronic A health condition marked by long duration, by frequent recurrence over a long time, and often by slowly progressing seriousness. For example, rheumatoid arthritis. non‐invasive ventilation
The Cochrane Review Chronic non‐invasive ventilation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease was published in August 2021. The authors concluded: “Regardless of the timing of initiation, chronic NIV [non-invasive ventilation] improves daytime hypercapnia. In addition, in stable COPD, survival seems to be improved and there might be a short term HRQL [health-related quality of life] benefit. In people with persistent hypercapnia after a COPD exacerbation, chronic NIV might prolong admission‐free survival without a beneficial effect on HRQL.”
Integrated disease management
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the effects of integrated disease management (IDM) interventions for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
In the Evidently Cochrane blog Choosing health care wisely when resources are scarce Selena Ryan-Vig describes the first in a new series of Cochrane Special Collections which brings together examples of treatments and health care which – despite being costly and time-consuming – research suggests could be unhelpful to patients, or even harmful.

You can also read more in this Cochrane Editorial Making wise choices about low‐value health care in the COVID‐19 pandemic
A new podcast series looks at initiatives to wind back the medical excess that is causing harm to people and the planet. You can find out more on this page: Cochrane Sustainable Healthcare joins forces with the BMJ to explore new ways to make health systems healthier.
Delirium is common in hospitalised patients. The authors of a Cochrane Review on Non‐pharmacological interventions for preventing delirium in hospitalised non‐ICU patients (November 2021) have concluded:
- “There is moderate‐certainty evidence regarding the benefit of multicomponent non‐pharmacological interventions for the prevention of delirium in hospitalised adults, estimated to reduce incidence The number of new occurrences of something in a population over a particular period of time, e.g. the number of cases of a disease in a country over one year. by 43% compared to usual care.
- We found no evidence of an effect on mortality.
- There is emerging evidence that these interventions may reduce hospital length of stay, with a trend towards reduced delirium duration, although the effect on delirium severity remains uncertain.”
- What are the effects of multi‐domain interventions for prevention of dementia and cognitive decline?
- Can palliative care interventions improve outcomes for people with advanced dementia?
Cochrane Author Somebody responsible for preparing and, in the case of Cochrane Reviews, keeping up-to-date a systematic review. The term ‘reviewer’ is also sometimes used to refer to an external peer reviewer, or referee. Q&A: Ketamine as a treatment for depression.
The authors of a Cochrane Review Altered dietary salt intake for people with chronic kidney disease (June 2021) found high-certainty evidence that salt reduction reduced blood pressure in people with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and albuminuria in people with earlier stage CKD in the short‐term. They state that “if such reductions could be maintained long‐term, this effect may translate to clinically significant Clinical significance is the practical importance of an effect (e.g. a reduction in symptoms); whether it has a real genuine, palpable, noticeable effect on daily life. It is not the same as statistical significance. For instance, showing that a drug lowered the heart rate by an average of 1 beat per minute would not be clinically significant, as it is unlikely to be a big enough effect to be important to patients and healthcare providers. reductions in CKD progression and cardiovascular events. Research into the long‐term effects of sodium‐restricted diet for people with CKD is warranted.”
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the effects of altered dietary salt intake for adults with chronic kidney disease?
A recently updated Special Collection: Influenza: evidence from Cochrane Reviews.
Cochrane Review: Slow versus fast subcutaneous heparin injections for prevention of bruising and site pain intensity (June 2021)
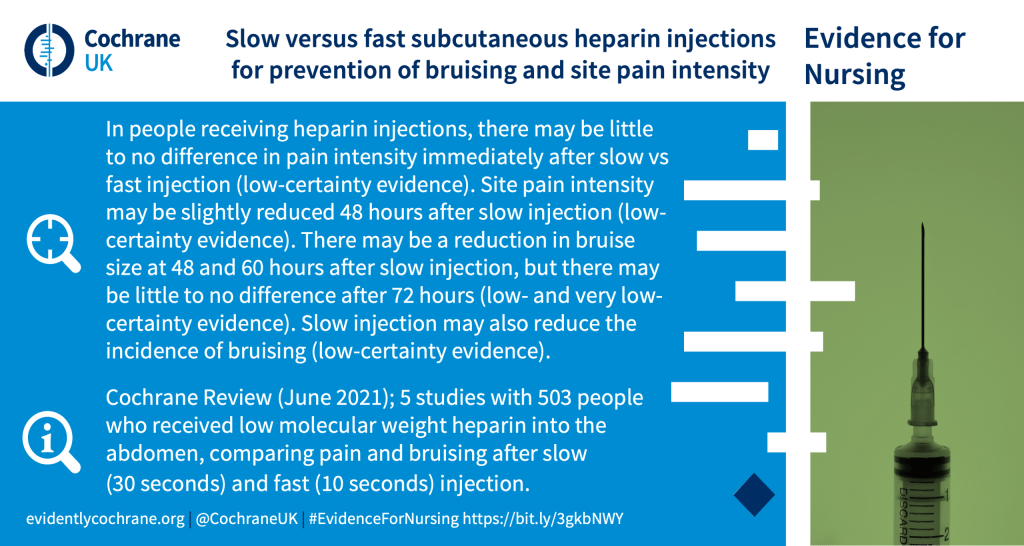
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For people receiving subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) injections, how does a slow injection compare with a fast injection?
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For women with subfertility, how does double intrauterine insemination (IUI) compare with single IUI in stimulated cycles?
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the benefits and harms of interventions to increase patient and family involvement in the escalation of care for community health and hospital settings?
Using patient questionnaires for improving clinical management and outcomes – an interview with Cochrane review author Christopher Gibbons about their recent Cochrane Review to find out whether healthcare workers who receive information from questionnaires completed by their patients give better health care and whether their patients have better health.
The authors of a Cochrane Review on Perioperative systemic nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in women undergoing breast surgery (November 2021) conclude that “Low‐certainty evidence suggests that NSAIDs may reduce postoperative pain, nausea and vomiting, and postoperative opioid use. However, there was very little evidence to indicate whether NSAIDs affect the rate of breast hematoma or bleeding from any location within 90 days of breast surgery, the need for blood transfusion and incidence of other side effects compared to placebo or other analgesics.”
Cochrane Clinical Answer: Does preoperative hair removal reduce postoperative surgical site infection?
A Cochrane Review Reducing medication errors for adults in hospital settings (November 2021) concludes that “Compared to usual care, medication reconciliation, electronic prescribing systems, barcoding and feedback to professionals may reduce adverse drug events or medication errors, or both. Nonetheless, the best modalities to deliver these interventions, and the effect of other interventions, are less clear.”
Care and rehabilitation after hip fracture surgery are increasingly in the hands of a multidisciplinary team, and this was explored in a Cochrane Review Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for older people with hip fractures (updated November 2021). There is now evidence that, in hospital settings, rehabilitation after hip fracture surgery delivered by a multidisciplinary team and supervised by an appropriate medical specialist, probably results in fewer cases of ‘poor outcome’. It may also reduce the number of people with poor mobility at 12 months. Its effects (if any) on other outcomes, such as long-term hip-related pain, quality of life, and activities of daily living pain, are uncertain. The impact of supported discharge and multidisciplinary home rehabilitation is also unclear.
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the benefits and harms of multidisciplinary rehabilitation (MDR) for older people with hip fracture?
This is one of several reviews included in our blog After hip fracture: how best to help people get back on their feet .

A Cochrane Review Palivizumab for preventing severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in children (November 2021) has found that prophylaxis with palivizumab:
- reduces hospitalisation due to RSV infection
- reduces the number of wheezing days at one year’s follow‐up
- probably results in little to no difference in mortality or adverse events
- probably results in a slight reduction in hospitalisation due to respiratory‐related illness at two years’ follow‐up
- may result in a large reduction in RSV infection at two years’ follow‐up.
E-cigarettes
The Cochrane Review Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation was updated in September 2021.
Here is a summary of the review:

Cochrane Clinical Answer: How effective and safe are electronic cigarettes (ECs) for smoking cessation?
Preventing weight gain
- Cochrane Clinical Answer: Does varenicline or nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) help prevent weight gain after smoking cessation?
- Podcast: Interventions for preventing weight gain after smoking cessation.
Strategies to improve smoking cessation rates in primary care
The Cochrane Review Strategies to improve smoking cessation rates in primary care (September 2021) has found that providing adjunctive counseling by an allied health professional, cost‐free smoking cessation medications, and tailored printed materials as part of smoking cessation support in primary care probably increases the number of people who achieve smoking cessation.
Reducing sedentary behaviour
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For people with stroke, what are the effects of interventions to reduce sedentary behavior?
Screening for dysphagia
A new Cochrane Review Screening for aspiration risk associated with dysphagia in acute stroke has been published and reveals an evidence gap. The authors conclude “we were unable to identify a tool that could accurately identify everyone with food and drink entering their airway, as well as detect all those who definitely did not.”
Factors influencing parents’ and carers’ decisions on routine vaccinations
The Cochrane news item What factors influence parents’ and carers’ decisions on routine vaccinations for their children? looks at a new Cochrane Review on this topic. The key messages are:
- “Many factors influence parents’ vaccination views and practices, including those related to individual perceptions, social relationships, and the wider social and political context in which parents live.
- When parents make decisions about vaccination for their children, they are often communicating not just what they think about vaccines, but also who they are, what they value, and with whom they identify.”
From the news item you can jump to the full review and a short implementation guide related to it.
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What factors influence parents’ and informal caregivers’ views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination?
Interventions to increase uptake of human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B vaccines
Cochrane Clinical Answer: Which interventions improve vaccination uptake among adolescents?
Cochrane Clinical Answer: What are the effects of a vegan dietary pattern for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
Cochrane Clinical Answer: For people with venous leg ulcers, what are the effects of compression bandages?
Opportunities and events
On this page, Important Cochrane Links , you can find opportunities to get involved, including how to join Cochrane, find volunteer tasks, or jump into the Cochrane Library.
Hundreds of health leaders and experts met on October 14 to recommend the international community urgently mount stronger evidence-based responses to global health emergencies. Recordings from this event are now available on this page: Cochrane Convenes recordings available: the world must learn from pandemic lessons to avoid future catastrophes.
Please note that this page includes a round-up of materials mainly published within the last two months, and is not updated after it’s posted.
References (pdf)
Join in the conversation on Twitter with @SarahChapman30 and @CochraneUK or leave a comment on the blog.
Please note, we cannot give medical advice and do not publish comments that link to individual pages requesting donations or to commercial sites, or appear to endorse commercial products. We welcome diverse views and encourage discussion but we ask that comments are respectful and reserve the right to not publish any we consider offensive. Cochrane UK does not fact check – or endorse – readers’ comments, including any treatments mentioned.
Sarah and Selena have nothing to disclose.
- #EvidenceForNursing
- breast surgery
- bronchiolitis
- care of the newborn
- cervical cancer
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- communication
- emergency care
- EvidenceFor
- heparin injections
- hip fracture
- smoking cessation
- surgical site infection
- vaccination
- venous leg ulcers

About Sarah Chapman and Selena Ryan-Vig
Sarah and Selena are Cochrane UK’s Knowledge Brokers. Their role involves sharing evidence in accessible ways with those who could find it helpful for their health decision-making, and encouraging engagement with it through social media. Sarah trained and worked as a nurse, has degrees in History from the Universities of Oxford and Reading, and worked in health services research before joining Cochrane UK in 2007. She is a recent cochlear implant recipient (2021) and is a Patient Ambassador for the COACH Trial, a randomised controlled trial of cochlear implantation versus hearing aids in adults with severe hearing loss. Sarah tweets @SarahChapman30. Selena has a psychology degree from the University of Bath and has previously worked for a national charity that provides support for young women. With a colleague, Selena delivers interactive sessions to students from Years 10 to 13 to teach about evidence-based practice and to encourage critical thinking, particularly around healthcare claims made in the media.
is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Evidently Cochrane
What is Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing? (With Examples, Benefits, & Challenges)

Are you a nurse looking for ways to increase patient satisfaction, improve patient outcomes, and impact the profession? Have you found yourself caught between traditional nursing approaches and new patient care practices? Although evidence-based practices have been used for years, this concept is the focus of patient care today more than ever. Perhaps you are wondering, “What is evidence-based practice in nursing?” In this article, I will share information to help you begin understanding evidence-based practice in nursing + 10 examples about how to implement EBP.
What Is Evidence-Based Practice In Nursing?
When was evidence-based practice first introduced in nursing, who introduced evidence-based practice in nursing, what is the difference between evidence-based practice in nursing and research in nursing, what are the benefits of evidence-based practice in nursing, top 5 benefits to the patient, top 5 benefits to the nurse, top 5 benefits to the healthcare organization, 10 strategies nursing schools employ to teach evidence-based practices, 1. assigning case studies:, 2. journal clubs:, 3. clinical presentations:, 4. quizzes:, 5. on-campus laboratory intensives:, 6. creating small work groups:, 7. interactive lectures:, 8. teaching research methods:, 9. requiring collaboration with a clinical preceptor:, 10. research papers:, what are the 5 main skills required for evidence-based practice in nursing, 1. critical thinking:, 2. scientific mindset:, 3. effective written and verbal communication:, 4. ability to identify knowledge gaps:, 5. ability to integrate findings into practice relevant to the patient’s problem:, what are 5 main components of evidence-based practice in nursing, 1. clinical expertise:, 2. management of patient values, circumstances, and wants when deciding to utilize evidence for patient care:, 3. practice management:, 4. decision-making:, 5. integration of best available evidence:, what are some examples of evidence-based practice in nursing, 1. elevating the head of a patient’s bed between 30 and 45 degrees, 2. implementing measures to reduce impaired skin integrity, 3. implementing techniques to improve infection control practices, 4. administering oxygen to a client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd), 5. avoiding frequently scheduled ventilator circuit changes, 6. updating methods for bathing inpatient bedbound clients, 7. performing appropriate patient assessments before and after administering medication, 8. restricting the use of urinary catheterizations, when possible, 9. encouraging well-balanced diets as soon as possible for children with gastrointestinal symptoms, 10. implementing and educating patients about safety measures at home and in healthcare facilities, how to use evidence-based knowledge in nursing practice, step #1: assessing the patient and developing clinical questions:, step #2: finding relevant evidence to answer the clinical question:, step #3: acquire evidence and validate its relevance to the patient’s specific situation:, step #4: appraise the quality of evidence and decide whether to apply the evidence:, step #5: apply the evidence to patient care:, step #6: evaluating effectiveness of the plan:, 10 major challenges nurses face in the implementation of evidence-based practice, 1. not understanding the importance of the impact of evidence-based practice in nursing:, 2. fear of not being accepted:, 3. negative attitudes about research and evidence-based practice in nursing and its impact on patient outcomes:, 4. lack of knowledge on how to carry out research:, 5. resource constraints within a healthcare organization:, 6. work overload:, 7. inaccurate or incomplete research findings:, 8. patient demands do not align with evidence-based practices in nursing:, 9. lack of internet access while in the clinical setting:, 10. some nursing supervisors/managers may not support the concept of evidence-based nursing practices:, 12 ways nurse leaders can promote evidence-based practice in nursing, 1. be open-minded when nurses on your teams make suggestions., 2. mentor other nurses., 3. support and promote opportunities for educational growth., 4. ask for increased resources., 5. be research-oriented., 6. think of ways to make your work environment research-friendly., 7. promote ebp competency by offering strategy sessions with staff., 8. stay up-to-date about healthcare issues and research., 9. actively use information to demonstrate ebp within your team., 10. create opportunities to reinforce skills., 11. develop templates or other written tools that support evidence-based decision-making., 12. review evidence for its relevance to your organization., bonus 8 top suggestions from a nurse to improve your evidence-based practices in nursing, 1. subscribe to nursing journals., 2. offer to be involved with research studies., 3. be intentional about learning., 4. find a mentor., 5. ask questions, 6. attend nursing workshops and conferences., 7. join professional nursing organizations., 8. be honest with yourself about your ability to independently implement evidence-based practice in nursing., useful resources to stay up to date with evidence-based practices in nursing, professional organizations & associations, blogs/websites, youtube videos, my final thoughts, frequently asked questions answered by our expert, 1. what did nurses do before evidence-based practice, 2. how did florence nightingale use evidence-based practice, 3. what is the main limitation of evidence-based practice in nursing, 4. what are the common misconceptions about evidence-based practice in nursing, 5. are all types of nurses required to use evidence-based knowledge in their nursing practice, 6. will lack of evidence-based knowledge impact my nursing career, 7. i do not have access to research databases, how do i improve my evidence-based practice in nursing, 7. are there different levels of evidence-based practices in nursing.
• Level One: Meta-analysis of random clinical trials and experimental studies • Level Two: Quasi-experimental studies- These are focused studies used to evaluate interventions. • Level Three: Non-experimental or qualitative studies. • Level Four: Opinions of nationally recognized experts based on research. • Level Five: Opinions of individual experts based on non-research evidence such as literature reviews, case studies, organizational experiences, and personal experiences.
8. How Can I Assess My Evidence-Based Knowledge In Nursing Practice?

Evidence Based Nursing Practice
- Articles & Journals
- Searching the Literature
Contact the Library
All Mayo staff with LAN IDs and passwords can use Document Delivery to receive copies of journal articles and book chapters.
If you require additional assistance, please contact the Library .
Evidence Based Practice Resources
- Mayo Clinic Evidence Based Practice

Systems - integration of evidence with patient records Summaries - practice guidelines found via Clinical Key & UpToDate Synopses of Syntheses - focused journals: Evidence-Based Nursing , Evidence-Based Medicine , ACP Journal Club Syntheses - m eta-analyses, systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses found through Cochrane , CINAHL , PubMed Synopses of Single Studies - focused journals: Evidence-Based Nursing , Evidence-Based Medicine , ACP Journal Club Single Studies - CINAHL , PubMed
- See McMaster University Nursing 6S Pyramid for additional details
Nursing Research Journals
Log-in to Current Awareness to get contents pages delivered to your e-mail!
- Current Awareness - Nursing Research Journals
Recent Articles from the CINAHL Database
- Next: Books >>
- Last Updated: Nov 20, 2023 3:07 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.mayo.edu/evidencebasednursing
- Request An Appointment
- Pay a Bill or Get an Estimate
- For Referring Providers
- Pediatric Care
- Cancer Center
- Carver College of Medicine
- Find a Provider
- Share Your Story
- Health Topics
- Educational Resources & Support Groups
- Clinical Trials
- Medical Records
- Info For... Directory
Evidence-Based Practice Resources
As global experts with decades of experience in evidence-based practice (EBP) processes and implementation, University of Iowa Health Care offers individuals and organizations opportunities to learn from time-tested, user-friendly products and programs.
From the trusted Iowa Model to action-oriented tools, these resources are available to help you apply EBP to your practice and improve outcomes.
If you are interested in a tailored program to meet your organization’s needs, please contact us for a consultation.
Evidence-based practice events
- Advanced Evidence-Based Practice Institute
- National Evidence-Based Practice Conference
- Tailored Programs and Presentations
- Nursing continuing education offered by University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics
Evidence-based practice resources for purchase
- Evidence-Based Practice in Action Book
- EBP to Go ® : Accelerating Evidence-Based Practice
- Evidence-Based Practice Staff Nurse Internship
- Online EBP Course
Evidence-based practice complimentary resources
- Iowa Implementation for Sustainability Framework ©
- The Iowa Model Revised: EBP to Promote Excellence in Health Care ©
- Evidence-Based Practice in Action tools
Additional resources
- Implementation Strategies for Evidence-Based Practice ©
- Dissemination of Nursing Knowledge: Tips and Resources
- Evidence-Based Nursing Practice Self-Efficacy Scale ©
- Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Survey ©
- WellMe in 3 ©
Additional resources for nurses
Looking for more information about a nursing career with UI Health Care? View our resource pages to learn more.
- Benefits of Being a Nurse
- Nursing Orientation
- Nurse Residency Program
- Experienced Nurse Fellowship Program
- Professional Practice Model
- Nursing Research
- Evidence-Based Practice
- Application Tips
- Application Resource Center

Join our team
UI Health Care is always looking for dedicated nurses to join our team. Don’t wait—apply today to launch a meaningful career at Iowa’s top hospital.

Locations and Offices
Nursing evidence-based practice and research.

This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Brechin A. Introducing critical practice. In: Brechin A, Brown H, Eby MA (eds). London: Sage/Open University; 2000
Introduction to evidence informed decision making. 2012. https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/45245.html (accessed 8 March 2022)
Cullen L, Adams SL. Planning for implementation of evidence-based practice. JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration. 2012; 42:(4)222-230 https://doi.org/10.1097/NNA.0b013e31824ccd0a
DiCenso A, Guyatt G, Ciliska D. Evidence-based nursing. A guide to clinical practice.St. Louis (MO): Mosby; 2005
Implementing evidence-informed practice: International perspectives. In: Dill K, Shera W (eds). Toronto, Canada: Canadian Scholars Press; 2012
Dufault M. Testing a collaborative research utilization model to translate best practices in pain management. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2004; 1:S26-S32 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2004.04049.x
Epstein I. Promoting harmony where there is commonly conflict: evidence-informed practice as an integrative strategy. Soc Work Health Care. 2009; 48:(3)216-231 https://doi.org/10.1080/00981380802589845
Epstein I. Reconciling evidence-based practice, evidence-informed practice, and practice-based research: the role of clinical data-mining. Social Work. 2011; 56:(3)284-288 https://doi.org/10.1093/sw/56.3.284
Implementation research: a synthesis of the literature. 2005. https://tinyurl.com/mwpf4be4 (accessed 6 March 2022)
Graham ID, Logan J, Harrison MB Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map?. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2006; 26:(1)13-24 https://doi.org/10.1002/chp.47
Greenhalgh T, Robert G, Bate P, MacFarlane F, Kyriakidou O. Diffusion of innovations in health service organisations. A systematic literature review.Malden (MA): Blackwell; 2005
Greenhalgh T, Howick J, Maskrey N. Evidence based medicine: a movement in crisis?. BMJ. 2014; 348 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g3725
Haynes RB, Devereaux PJ, Guyatt GH. Clinical expertise in the era of evidence-based medicine and patient choice. BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine. 2002; 7:36-38 https://doi.org/10.1136/ebm.7.2.36
Hitch D, Nicola-Richmond K. Instructional practices for evidence-based practice with pre-registration allied health students: a review of recent research and developments. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2017; 22:(4)1031-1045 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-016-9702-9
Jerkert J. Negative mechanistic reasoning in medical intervention assessment. Theor Med Bioeth. 2015; 36:(6)425-437 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11017-015-9348-2
McSherry R, Artley A, Holloran J. Research awareness: an important factor for evidence-based practice?. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2006; 3:(3)103-115 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2006.00059.x
McSherry R, Simmons M, Pearce P. An introduction to evidence-informed nursing. In: McSherry R, Simmons M, Abbott P London: Routledge; 2002
Implementing excellence in your health care organization: managing, leading and collaborating. In: McSherry R, Warr J (eds). Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2010
Melnyk BM, Fineout-Overholt E, Stillwell SB, Williamson KM. Evidence-based practice: step by step: the seven steps of evidence-based practice. AJN, American Journal of Nursing. 2010; 110:(1)51-53 https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000366056.06605.d2
Implementing evidence-based practices: six ‘drivers’ of success. Part 3 in a Series on Fostering the Adoption of Evidence-Based Practices in Out-Of-School Time Programs. 2007. https://tinyurl.com/mu2y6ahk (accessed 8 March 2022)
Muir-Gray JA. Evidence-based healthcare. How to make health policy and management decisions.Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1997
Nevo I, Slonim-Nevo V. The myth of evidence-based practice: towards evidence-informed practice. British Journal of Social Work. 2011; 41:(6)1176-1197 https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcq149
Newhouse RP, Dearholt S, Poe S, Pugh LC, White K. The Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-based Practice Rating Scale.: The Johns Hopkins Hospital: Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing; 2005
Nursing and Midwifery Council. The Code. 2018. https://www.nmc.org.uk/standards/code (accessed 7 March 2022)
Nutley S, Walter I, Davies HTO. Promoting evidence-based practice: models and mechanisms from cross-sector review. Research on Social Work Practice. 2009; 19:(5)552-559 https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731509335496
Reed JE, Howe C, Doyle C, Bell D. Successful Healthcare Improvements From Translating Evidence in complex systems (SHIFT-Evidence): simple rules to guide practice and research. Int J Qual Health Care. 2019; 31:(3)238-244 https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzy160
Rosswurm MA, Larrabee JH. A model for change to evidence-based practice. Image J Nurs Sch. 1999; 31:(4)317-322 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.1999.tb00510.x
Rubin A. Improving the teaching of evidence-based practice: introduction to the special issue. Research on Social Work Practice. 2007; 17:(5)541-547 https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731507300145
Shlonsky A, Mildon R. Methodological pluralism in the age of evidence-informed practice and policy. Scand J Public Health. 2014; 42:18-27 https://doi.org/10.1177/1403494813516716
Straus SE, Tetroe J, Graham I. Defining knowledge translation. CMAJ. 2009; 181:(3-4)165-168 https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.081229
Titler MG, Everett LQ. Translating research into practice. Considerations for critical care investigators. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2001; 13:(4)587-604 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5885(18)30026-1
Titler MG, Kleiber C, Steelman V Infusing research into practice to promote quality care. Nurs Res. 1994; 43:(5)307-313 https://doi.org/10.1097/00006199-199409000-00009
Titler MG, Kleiber C, Steelman VJ The Iowa model of evidence-based practice to promote quality care. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2001; 13:(4)497-509 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5885(18)30017-0
Ubbink DT, Guyatt GH, Vermeulen H. Framework of policy recommendations for implementation of evidence-based practice: a systematic scoping review. BMJ Open. 2013; 3:(1) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001881
Wang LP, Jiang XL, Wang L, Wang GR, Bai YJ. Barriers to and facilitators of research utilization: a survey of registered nurses in China. PLoS One. 2013; 8:(11) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081908
Warren JI, McLaughlin M, Bardsley J, Eich J, Esche CA, Kropkowski L, Risch S. The strengths and challenges of implementing EBP in healthcare systems. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2016; 13:(1)15-24 https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12149
Webber M, Carr S. Applying research evidence in social work practice: Seeing beyond paradigms. In: Webber M (ed). London: Palgrave; 2015
Evidence-based practice vs. evidence-based practice: what's the difference?. 2014. https://tinyurl.com/2p8msjaf (accessed 8 March 2022)
Evidence-informed practice: simplifying and applying the concept for nursing students and academics
Elizabeth Adjoa Kumah
Nurse Researcher, Faculty of Health and Social Care, University of Chester, Chester
View articles · Email Elizabeth Adjoa
Robert McSherry
Professor of Nursing and Practice Development, Faculty of Health and Social Care, University of Chester, Chester
View articles
Josette Bettany-Saltikov
Senior Lecturer, School of Health and Social Care, Teesside University, Middlesbrough
Paul van Schaik
Professor of Research, School of Social Sciences, Humanities and Law, Teesside University, Middlesbrough

Background:
Nurses' ability to apply evidence effectively in practice is a critical factor in delivering high-quality patient care. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is recognised as the gold standard for the delivery of safe and effective person-centred care. However, decades following its inception, nurses continue to encounter difficulties in implementing EBP and, although models for its implementation offer stepwise approaches, factors, such as the context of care and its mechanistic nature, act as barriers to effective and consistent implementation. It is, therefore, imperative to find a solution to the way evidence is applied in practice. Evidence-informed practice (EIP) has been mooted as an alternative to EBP, prompting debate as to which approach better enables the transfer of evidence into practice. Although there are several EBP models and educational interventions, research on the concept of EIP is limited. This article seeks to clarify the concept of EIP and provide an integrated systems-based model of EIP for the application of evidence in clinical nursing practice, by presenting the systems and processes of the EIP model. Two scenarios are used to demonstrate the factors and elements of the EIP model and define how it facilitates the application of evidence to practice. The EIP model provides a framework to deliver clinically effective care, and the ability to justify the processes used and the service provided by referring to reliable evidence.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) was first mentioned in the literature by Muir-Gray, who defined EBP as ‘an approach to decision-making in which the clinician uses the best available evidence in consultation with the patient to decide upon the option which suits the patient best’ (1997:97). Since this initial definition was set out in 1997, EBP has gained prominence as the gold standard for the delivery of safe and effective health care.
There are several models for implementing EBP. Examples include:
- Rosswurm and Larrabee's (1999) model
- The Iowa model ( Titler et al, 2001 )
- Collaborative research utilisation model ( Dufault, 2004 ); DiCenso et al's (2005) model
- Greenhalgh et al's (2005) model
- Johns Hopkins Nursing model ( Newhouse et al, 2005 )
- Melnyk et al's (2010) model.
Although a comprehensive review of these models is beyond the scope of this article, a brief assessment reveals some commonalities among them. These include a) asking or selecting a practice question, b) searching for the best evidence, c) critically appraising and applying the evidence, d) evaluating the outcome(s) of patient care delivery, and e) disseminating the outcome(s).
Regardless of the benefits of EBP, and the existence of multiple EBP models intended to facilitate the application of evidence into practice, health professionals, including nurses, continue to struggle to implement it effectively ( Ubbink et al, 2013 ). Critics of EBP have questioned its validity ( Rubin, 2007 ; Nevo and Slonim-Nevo, 2011 ); the best practice and setting to support its use ( Nutley et al, 2009 ); its failure to address the complexity of health and health care, as well as the patient's context ( Muir-Gray, 1997 ; Reed et al, 2019 ), and its mechanistic approach ( Epstein, 2009 ; Jerkert, 2015 ). Some of these criticisms are outlined below.
For example, previous studies have reported the barriers health professionals face to successfully implement EBP. Ubbink et al (2013) conducted a systematic review to determine nurses' and doctors' views on knowledge, attitudes, skills, barriers, and behaviour required to implement EBP. The review included 31 studies from 17 countries: eight from North America and 11 from Europe. The results revealed that organisational and individual barriers prevent uptake of EBP among nurses and doctors. These barriers included the lack of material and human resources, and lack of support from managers and leaders; individual barriers included knowledge deficit regarding EBP, time and workload ( Ubbink et al, 2013 ). Researchers such as Hitch and Nicola-Richmond (2017) and Warren et al (2016) found similar barriers to implementing EBP reported by health professionals.
Effective and consistent implementation of EBP in healthcare settings depends on complex interdependent factors, such as the characteristics of an organisation (eg the internal and external healthcare environment, and organisational structures and values); the EBP intervention (eg reduction of hospital-acquired infections); and the attitudes of the individual practitioner towards EBP ( Titler and Everett, 2001 ; Cullen and Adams, 2012 ). Yet, existing approaches of EBP have been ineffective in facilitating its implementation ( Greenhalgh et al, 2014 ).
Consequently, authors such as Cullen and Adams (2012) and Greenhalgh et al (2014) have called for a resurgence of the concept, especially concerning the components of EBP associated with involving patients in decision-making, and with expert judgement and experience. Greenhalgh et al (2014:3) consider it is time to return to implementing ‘real EBP’, where person-centred care is the priority, and health professionals and their patients ‘are free to make appropriate care decisions that may not match what best evidence seems to suggest’. Nonetheless, researchers including McSherry et al (2002) , Epstein (2009) and Nevo and Slonim-Nevo (2011) have proposed an alternative, holistic approach to the application of evidence into practice, termed evidence-informed practice (EIP).
Journey towards evidence-informed practice
The problems with the uptake and effective implementation of EBP led to the emergence of the EIP concept. This concept is based on the premise that healthcare practice should, as a matter of principle, be informed by, rather than based on, evidence ( Nevo and Slonim-Nevo, 2011 ). This implies that other forms of evidence (for example, patient experiences, the nurse's expertise and experiences), not just the ‘research evidence’, should be considered in applying evidence in practice.
McSherry et al (2002) defined EIP as the assimilation of professional judgment and research evidence regarding the efficiency of interventions. This definition was further elaborated as an approach to patient care where:
‘Practitioners are encouraged to be knowledgeable about findings coming from all types of studies and to use them in an integrative manner, taking into consideration clinical experience and judgment, clients' preferences and values, and context of the interventions.’
Nevo and Slonim-Nevo (2011:18)
It has been over two decades since EIP emerged in the literature, however, primary research on the concept has been limited. Hence, although the term EIP has gained momentum in recent times, the methods needed to implement it effectively are not widely known ( McSherry, 2007 ; Woodbury and Kuhnke, 2014 ). While some proponents of EIP (eg Epstein 2011 ; Webber and Carr 2015 ) have identified significant differences between EBP and EIP, most researchers (eg Ciliska, 2012 ; Shlonsky and Mildon, 2014 ) have used the terms interchangeably.
Ciliska (2012) , for instance, developed an evidence-informed decision making (EIDM) module, but referred to the steps of EBP (ie Ask, Acquire, Appraise, Integrate, Adapt, Apply, Analyse) as the processes to be followed in implementing EIDM. Ciliska (2012) explained that the term EIDM was adopted to signify that other types of evidence are useful in clinical decision-making and to attempt to get beyond the criticisms of EBP. This notwithstanding, the author maintained the existing process for implementing EBP. Similarly, Shlonsky and Mildon (2014) used the terms EBP and EIP interchangeably, as they consistently referred to an EBP approach as EIP. Examples include referring to the steps of EBP as ‘the steps of EIP’ ( Shlonsky and Mildon, 2014:3 ) and referring to Haynes et al's (2002) expanded EBP model as a ‘revised EIP model’ ( Shlonsky and Mildon, 2014:2 ).
Another term that is often used interchangeably with EIP is ‘knowledge translation’. This term has been explored extensively. For example, the Canadian Institute of Health Research (CIHR) has adopted knowledge translation to signify the use of high-quality research evidence to make informed decisions ( Straus et al, 2009 ). The CIHR ( Graham et al, 2006 ) developed a ‘knowledge to action’ model intended to integrate the creation and application of knowledge. The model acknowledges the non-linear process of applying evidence in practice, where each stage is influenced by the next, as well as the preceding, stage. In a typical clinical setting, the actual process of applying evidence in practice is not linear, as acknowledged by the proponents of EBP, but cyclical and interdependent. Ciliska (2012) linked Graham et al's (2006) model to the components of evidence-informed decision-making. According to Ciliska (2012:7) , the knowledge-to-action model ‘fits with the steps of evidence-informed decision-making’. However, like EBP, the term ‘knowledge translation’, differs significantly from the EIP concept because it focuses on the ‘research evidence’ in decision-making.
The apparent confusion surrounding EIP is due to inadequate information about its components and the methods involved in implementing the concept. To foster a culture of EIP among health professionals, they must first be made aware of the actual components of the concept and the strategies involved in its successful implementation. The following section uses case scenarios to provide a description of the factors and elements of the EIP model and defines how it facilitates the application of evidence into clinical nursing practice.
Systems thinking
The clinical setting within which nurses work is a complex system made up of several interdependent and inter-related parts. Problems with healthcare delivery and management must therefore be perceived as a consequence of the exchanges between elements of the systems, instead of an outcome or the malfunctioning of a particular element. This, McSherry and Warr (2010) , have referred to as ‘systems thinking’.
Effective implementation of EIP demands an understanding of the various parts of the system that come together to aid the application of evidence in practice.
The evidence-informed practice model
The original model.
The earliest version of the evidence-informed practice model is depicted in Figure 1 . This was developed specifically for nurses and was originally named ‘the evidence-informed nursing model’. The model presented in Figure 1 was developed through PhD research conducted by Robert McSherry (2007) , with the aim to explore, through a mixed-methods study design, why the use of research as evidence in support of clinical nursing practice remains problematic. Study participants were registered nurses practising in a hospital trust located in north-east England.
The results of McSherry's (2007) study showed that, to effectively apply evidence in clinical nursing practice, nurses needed to be informed of, and be able to interact with, several key elements. The evidence-informed nursing model was developed as an alternative framework for facilitating the application of evidence in clinical nursing practice and was grounded in the principles and practices of systems thinking. This is because, primarily, the model provided an integrated process to applying evidence into practice, consisting of:
- A clearly defined input; to encourage nurses to use evidence in practice
- Throughput; facilitation of the processes associated with the elements
- Output; improved standards of professional practice
The revised model
The evidence-informed nursing model has been adapted to the evidence-informed practice model. The new model ( Figure 2 ) is adapted in several ways. First, it has been modified to be all-inclusive, so it could be applied to any health profession. Second, the model has been simplified to show the interconnectedness of the various factors and elements that enable a professional to use evidence in support of their clinical decision-making. Third, the model demonstrates the ongoing complexity that health professionals find themselves working in, in the quest to apply evidence to clinical practice. Last, the EIP model incorporates the principles and components of EBP, which is particularly evident in the EIP cycle (the throughput phase of the model).
The factors and elements of the EIP model ( Figure 2 ) are explored in more detail below with reference to two scenarios, which are used to apply the EIP model to clinical nursing practice within both a scientific and the wider context within which nursing care takes place.
The first factor of the EIP model is ‘Factor 1. Drivers for evidence-informed practice’ ( Figure 2 ). In order for nurses to enhance patient care and experiences, along with improving their knowledge and skills of the patient's condition and associated signs and symptoms, they need to be aware of what EIP is, what it involves, and the principles required to make it happen. Applying the scenarios, it is essential that the nurse understands and can identify the key elements that drive successful implementation of the EIP concept. This is referred to as the drivers for EIP, which are illustrated in Figure 3 and discussed below.
Drivers for EIP
Staff selection.
Recruiting, interviewing and redeploying existing staff or hiring new staff are part of the staff selection process ( Dill and Shera, 2012 ). The importance of this driver is to identify personnel who qualify to implement the EIP programme or model. Additionally, it aims at selecting individuals within the organisation (for example coaches, supervisors, and trainers), who will ensure that the required organisational changes to support nurses in the effective implementation of EIP are done.
In-service training or pre-service
Training on EIP programmes involves activities that are related to offering instruction, providing specialist information or skills development in a structured manner to nurses and other key healthcare staff involved in the EIP programme. Nurses, as well as other members of staff, must learn when, how, where, and with whom to use new approaches and skills in applying evidence to practice ( Metz et al, 2007 ).
Coaching, supervision and mentoring
The coaching and mentoring approach enables new skills to be introduced to nurses on the ward with the support of a coach. The duty of a coach is to offer expert information and support, together with encouragement, opportunities and advice to practise and apply skills that are specific to the EIP programme. Effective implementation of human service interventions (such as EIP) requires changes in behaviour at administrative, supervisory and practitioner levels ( Dill and Shera, 2012 ). Coaching and mentoring are the main ways to bring about a change in behaviour for staff who have been successfully involved in the beginning stage of the implementation process and throughout the life of the EIP programme.
Systems-level partnership
This refers to the improvement of partnerships with the broader and immediate systems to ensure access to required funds, and institutional and human resources necessary to support nurses' work. The immediate systems-level partnership refers to working with individuals or organisations that directly influence healthcare delivery (for example, nurses and doctors).
Partnerships within the broader system, on the other hand, refer to policymakers, funders or other organisations that may support the EIP programme, but are not directly involved in delivering health care. A variety of activities may be conducted as part of the development of systems-level partnerships to aid the implementation of EIP. These may include fundraising activities to support the implementation of EIP programmes, as well as the use of external coaches and consultants to assist with mentoring, technical assistance and training on an ongoing basis.
Internal management support
This involves activities that are associated with establishing processes and structures within an EIP programme to enhance effective implementation of the programme. This is necessary in order to inform healthcare decision-making as well as keep staff organised and focussed on desired care outcomes ( Fixsen et al, 2005 ). Instances of internal management support include the formation of institutional structures and processes, the allocation of resources to support selection of suitable staff, and administrative support for efficient training.
Staff performance and programme evaluation
This involves evaluation of staff performance and the overall EIP programme to determine whether the objectives of the programme have been achieved. To do this effectively, it is important to evaluate the outcomes of the above-defined drivers, in particular, staff selection, in-service training, as well as coaching and mentoring. This will offer managers and stakeholders insight about the effectiveness of staff selection, training, and mentoring in facilitating the application of evidence into clinical practice ( Dill and Shera, 2012 ).
Elements of the EIP model
The first element of the EIP model is professional accountability, depicted as an ‘input’ in Figure 2 . This is an essential part of a nurse's roles and responsibilities and is reaffirmed in the nursing Code ( Nursing and Midwifery Council, 2018 ) of professional practice, the contract of employment and job description. In both case scenarios involving Mitchell and Yvonne ( Box 1 ), professional accountability is evident on several fronts: the nurse must establish a caring, compassionate and therapeutic relationship with the patients by involving and engaging them in shared decision-making regarding all aspects of their care, treatments, and interventions; the nurse is accountable and answerable to the patient and his or her professional colleagues throughout the patient's journey.
Box 1.Patient scenariosScenario 1Yvonne, aged 31, is admitted to the emergency medical unit following a visit to her GP for a non-healing wound to her right big toe. The GP also reported that Yvonne has had a recurring sore throat, extreme tiredness and a low white blood cell count.The GP requested an urgent investigation of these symptoms. Yvonne was placed in a side room for precaution.Scenario 2Mitchell, aged 58, arrives in the emergency department complaining of severe chest pain. He is diaphoretic (sweating excessively) and says his pain is radiating down his left arm and up into his jaw, and he adds that he feels nauseated. A few minutes after admission, he suffers a cardiac arrest.He is resuscitated and transferred to the intensive care unit. He is intubated, is placed on a ventilator and has a central line catheter in place.
Throughput: the evidence-informed practice cycle
The EIP cycle (located in the ‘throughput’ of Figure 2 ) involves the processes or methods through which nurses apply evidence in support of their decision-making in clinical nursing practice. This often occurs in a clinical nursing environment that is complex, constantly changing, and involves numerous members of the multidisciplinary team, patients and their family. Effective communication (verbal and written) is essential for ensuring that the various elements are interchanging, interconnecting and communicating between, and with, each other. For example, the case of Yvonne in scenario 1 ( Box 1 ) can be used as an example to underline the importance of good communication. It is important to explain to the patient and her family the reason for nursing her in a side room rather than the main ward. In this situation, avoiding and preventing cross-infection is essential to safeguard Yvonne from harm.
To ensure the EIP cycle proceeds effectively requires that the nurse (the health professional) acts as the conduit for the interplay between the different elements of the model (ie Element 2: informed decision-making; Element 3: research awareness; Element 4: application of knowledge; and Element 5: evaluation). These elements will be further explored.
Element 2. Informed decision-making
This involves two-way communication between the nurse and the patient(s), and is critical in ensuring there is a robust relationship (honesty, openness, transparency) founded on the principles of person-centred care ( McSherry and Warr, 2010 ). It reaffirms the ethical principle of a patient's right to make an informed decision about what is suitable for them, and takes into account their beliefs, values, priorities and personal circumstances. In case scenario 2, applying the EIP model, the critical care nurse will be expected to involve Mitchell's (the patient's) relatives, medical staff and other members of the healthcare team in making decisions about, for example, ventilator management and care of the central line catheter. However, decision-making in an intensive care unit can be complex, and some of the decisions may involve the nurse only. Similarly, applying the EIP model in case scenario 1, the nurse will be expected to communicate with the patient (Yvonne), carers and colleagues about the importance of hand hygiene, wound care and the importance of using precautions to avoid hospital-acquired infections when caring for the patient.
In both case scenarios, the nurse must endeavour to involve the patient/family members in the process of decision-making by providing them with timely, appropriate and relevant information needed to make often complex and life-changing decisions.
Element 3. Research awareness
This element refers to motivating practitioners to acquire skills and knowledge, as well as to conceptualise what research and evidence involves and the significance they have in improving standards of healthcare practice ( McSherry et al, 2006 ). Research awareness is reliant on the nurse's attitudes towards research, the acquisition of knowledge and confidence about the value of research to practice, and on having supportive managers and colleagues.
This element of the EIP cycle, contained within the model, incorporates three of the steps (Research awareness) of EBP: ask a clinical question, search the literature for research evidence to answer the question, and critically appraise the evidence obtained). Although the nurse is not required to be a researcher to implement the EIP model effectively, they must be knowledgeable about relevant databases and search engines (such as Medline and Google), as well as critical appraisal tools, in order to be able to include high-quality research evidence when making patient care decisions.
However, the EIP model acknowledges the fact that research evidence may not always be readily available, and nurses may not have the necessary hardware and software in the care environment to enable them to search for research evidence. Hence, recommendations by Greenhalgh et al (2014) led to inclusion, within the EIP model, of nurses as critical thinkers and doers which, therefore, allows them to make appropriate care decisions based on patient preferences and actions, the clinical state, clinical setting and circumstances, and advocates that nurses apply their own knowledge, expertise and clinical experiences in clinical decision-making, which may not necessarily match what the research evidence seems to suggest.
With reference to scenario 2 (and similarly for scenario 1), to adhere to the EIP model the nurse would take the following steps:
- Update his/her knowledge about Mitchell's clinical presentation
- Search Medline for research evidence on ‘chest pain’, and ‘cardiac arrest’ and its associated symptoms. Based on the number of articles obtained, the nurse reads the titles and abstracts, and then, the full text of selected articles to exclude irrelevant articles. The remaining articles are then critically appraised to include the best research evidence in patient care decisions.
In situations where the above steps are not possible, the model advocates that the nurse endeavours to make the best care decisions possible based on patient preferences, clinical state, context and circumstances, and the nurse's own expertise and experience, as well as the experience of the patient and family members where possible.
Element 4. Application of knowledge
This is a complex element that requires the gathering and assimilation of various sources of information, evidence, quality and standards, and policy and guidance, to support the nurse's decision-making in clinical practice. In relation to both scenarios, the nurse would need to:
- Apply knowledge acquired from the patients (Mitchell and Yvonne), along with information from their relatives
- Apply evidence from reviewing the findings from research
- Take into account information gleaned from engaging with the multidisciplinary team
- Ensure they follow recommended local and national guidance and policy on the management of each patient's condition.
It is imperative that the nurse is experienced, knowledgeable, and competent in order to make the most appropriate care decisions together with the patient, the family and the wider multidisciplinary team. To do this effectively, the nurse requires certain personal attributes, it is also important for the organisation within which the nurse works to have specific institutional characteristics. Institutional features include culture, education and training, and workload/skill mix, whereas personal characteristics include improved confidence, attitude, understanding and behaviour towards the application of evidence into practice.
Element 5. Evaluation
This element of the EIP cycle within the model measures the effects of decision-making and actions of the nurse on care outcomes and in creating an optimal care environment. In both scenarios, the nurse would need to periodically evaluate specific processes and outcomes of care. For example, with regards to scenario 2, this would include:
- Monitoring how Mitchell is performing on the ventilator
- Taking the necessary infection prevention precautions to avoid the development of infections related to the insertion of a central line and transmission of hospital-acquired infection
- Monitoring improvement in Mitchell's general wellbeing.
Depending on the outcome of the evaluation, Mitchell's care plan would be either revised or continued.
Element 6. Conditions affecting research utilisation
Research utilisation involves critically appraising research findings, disseminating, and using the knowledge obtained from research to cause changes in an existing healthcare practice ( Titler et al, 1994 ). The conditions that affect research utilisation are grouped into five domains ( Wang et al, 2013 ):
- The process involved in utilising research findings
- Accessibility to research
- The quality of research
- The knowledge and attitudes of the nurse (health professional) regarding the use of research findings
- The organisation within which the findings of research are to be implemented.
In the two scenarios ( Box 1 ), the nurse needs to be aware of the potential barriers to research utilisation and identify ways to overcome these in order to effectively apply evidence to healthcare practice. In addition, the clinical environment within which nurses work must provide sufficient support in order to enhance the effective and consistent application of evidence to practice. Nurses must be supported to acquire the necessary knowledge, skills, and understanding needed to practise safely (ie competently and confidently). In addition, the resources necessary to obtain research evidence, such as IT (computers and internet), must be readily available in the clinical setting for easy access to information.
Factor 2 (Output). Critical thinker and doer, the professional nurse
To ensure that nurses inform their decisions with the best available evidence, it is imperative that they have a sound understanding and knowledge of what constitutes the EIP model ( Figure 2 ). Successfully engaging with the various factors and elements of this model will lead to the desired outcome—that of a professional who is a critical thinker and doer, a professional nurse who, as argued by Brechin (2000:44) , is ‘knowledgeable and skilled, yet welcomes alternative ideas and belief systems, appreciating and respecting alternative views’. In this context, it is about creating a caring and compassionate environment in which excellence in nursing practice occurs. This can only be exemplified by ensuring that decisions and actions are based on the best available evidence.
The benefits of the EIP model for the nurse, patient and family are that it simplifies a highly complex series of systems and processes pertaining to how evidence is used to support decisions made in clinical practice. The EIP model simply illustrates the why, the how and the sequencing of getting evidence into clinical practice. It also complements the evidence-based movement by offering a holistic systems-based approach to facilitating the application of evidence into clinical practice.
EIP is a holistic integrated approach to applying evidence into practice, which incorporates the steps of EBP within its system and processes. In other words, EBP is a subset of the EIP model, made explicit within the EIP cycle. Thus, EIP is neither an alternative to, nor a replacement for, EBP. The EIP model provides a framework for nurses (indeed all health practitioners) to deliver clinically effective care and enable them to justify the processes used and the service provided by referring to reliable evidence. Using two scenarios, this article demonstrated how the EIP model can be applied to clinical nursing practice. Future initiatives should focus on developing EIP educational interventions and determining the effects of such interventions on healthcare students' knowledge of, and attitudes towards, the application of evidence to practice.
- Two main concepts have been associated with the application of evidence into practice: evidence-based practice (EBP) and evidence-informed practice (EIP)
- The main feature that distinguishes EIP from EBP is the processes used in implementing the concepts
- EIP provides the mechanisms or processes to follow in implementing EBP
- EIP is not a substitute or replacement for EBP. EIP is an integrated approach to applying evidence to practice, which incorporates the steps of EBP in its processes
CPD reflective questions
- Make a list of the challenges you encounter in implementing EBP
- Use the same list and indicate how these challenges prevent you from using evidence to support your nursing clinical decisions and actions in practice
- How does viewing health and healthcare delivery as a complex system impact on your patient care?
- Make a list of the drivers that are encouraging you to support your clinical nursing decisions and actions with evidence
- Using your own experience to date and the information presented in the text, make a list of why and how you think evidence-informed practice forms part of your professional accountability and professional registration

College of Nursing
In this section, research and evidence translation.
The College of Nursing is committed to promoting the synthesis and implementation of Evidence Based Practice (EBP) among our students, our graduates, and our clinical partners. Our DNP students undertake significant projects over the course of their DNP studies in one of three areas: 1) original research where evidence is needed on an important clinical topic, 2) synthesis of existing evidence where there is a need to bring together empirical research and determine best practice, and 3) translation of evidence into practice with clinical partners using implementation science.
To improve patient care, our work is informed the JBI model of EBP which is a comprehensive model that depicts the evolution from discovery of new evidence to eventual global adoption of best practices.
Use the links below to discover timely resources to inform care and practice, and increase efficiencies.
View DNP Projects from Team 23


Master of Science in Nursing Leadership
- Professional Organizations for Nurses
- MSN 6500: Leadership Roles
- MSN 6502: Contemporary Concepts
- MSN 6608: Evidence Based Practice
- MSN 6609 & 6610 - Pathophysiology, Pharmacology & Physical Assessment
- MSN 6612 & 6613: Nurse Executive This link opens in a new window
- MSN 6646: Philosophy and Ethics
- MSN 7350: Forensic Nursing Clinical & Legal Implications
- MSN 7710: Integrative Pathophysiology, Pharmacology & Physical Assessment
- MSN 7741: Politics and Policy in Healthcare
- MSN 7750: Teaching and Learning in Nursing
- HEL 8501: Nurse Leaders in Higher Education This link opens in a new window
- MSN 8705 & 8706: Nursing Leadership Capstone
- MSN 8900: Nurse Leadership Portfolio
- APA Citation Help
- Booked Up in the College of Health Professions
- Evidence Based Practice
PICO for Clinical Questions
Healthcare professionals sometimes use the pico or picot format to develop keywords for searching of clinical questions where:.
P - Patient or Population or Problem
I - Intervention or prognostic factor of interest
C - Comparison to intervention
O - Outcome of interest
T - Time (sometimes included)
For more information about forming and using a PICO question to search, please see the American Journal of Nursing article below.
- Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question: A Key Step in Evidence-Based Practice (2010).
Evaluating Evidence
- EBP Form for Evaluating the Literature
Information about Practicing EBP
- Evidence Based Practice Step by Step The purpose of these 18 articles from the American Journal of Nursing is to give nurses the knowledge and skills they need to implement EBP consistently, one step at a time.
- Glossary of EBM Terms BMJ Best Practice
- Glossary of Evidence-based Terms Not a comprehensive glossary but it outlines some of the key terms that should be understood in relation to Evidence-Based practice. From the Centre for Evidence Based Medicine (University of Oxford)
Evidence Based Practice for Nurses
Learn more about EBP and building EBP skills . Click on the title to view the journal article.
- Yoo, J. Y., Kim, J. H., Kim, J. S., Kim, H. L., & Ki, J. S. (2019). Clinical nurses' beliefs, knowledge, organizational readiness and level of implementation of evidence-based practice: the first step to creating an evidence-based practice culture. Plos O
- Bridges, E.J. (2015). Research at the bedside: It makes a difference. American Journal of Critical Care, 24(4): 283-289.
- Hellier, S., Cline, T. (2016). Factors that affect nurse practitioners' implementation of evidence-based practice. Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners, 28, 612-621.
Searching Licensed Resources for Clincial Evidence
Searchable Open Access Resources
- National Guideline Clearinghouse Public resource for evidence-based clinical practice guidelines.
- Cochrane Library High quality evidence for health care decision making. This is the open-access version so is not completely full text, but many systematic reviews are freely available.
- PubMed Clinical Queries Specialized PubMed searches designed to connect clinicians to evidence-based literature. Results display available systematic reviews as well as research articles arranged by 5 clinical areas--Etiology, Diagnosis, Prognosis, Clinical prediction guidelines, & Therapy.
- PubMed Provides information for consumers and clinicians on prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions and specializes in reviews of clinical effectiveness research, with easy-to-read summaries for consumers as well as full technical reports. Clinical guides are available on the Contents tab.
- NLM Resources for Informing Comparative Effectiveness The purpose of the search strategies presented here is to help inform discussions on or relating to comparative effectiveness by providing retrieval of a full-range of studies on the efficacy-effectiveness-effectiveness in the "real world" continuum
- DARE (Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects) Focused primarily on systematic reviews that evaluate the effects of health care interventions and the delivery and organization of health services. The database also includes reviews of the wider determinants of health such as housing, transport, and social care where these impact directly on health, or have the potential to impact on health.
- TRIP Database A clinical search engine designed to allow users to quickly and easily find and use high-quality research evidence to support their practice and/or care. Offers the ability to filter by several options including evidence-based synopses, systematic reviews, primary research, and controlled trials.
- AHRQ (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality) Guidelines and Recommendations Includes links to the National Guideline Clearinghouse, the U.S. Preventative Services Task Force, the Guide to Preventative Services, and an archive of guidelines published by AHRQ between 1992 and 1996.
- << Previous: Booked Up in the College of Health Professions
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 10:17 AM
- Guide URL: https://libguides.wilmu.edu/MSN

- How it works
Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Evidence-based Practice Nursing Dissertation Topics
Published by Owen Ingram at January 3rd, 2023 , Revised On August 16, 2023
Nurses provide daily clinical care to patients based on evidence-based practices. This article encourages you to consider a career as an EBP nurse to contribute to the healthcare industry and look at the various evidence-based nursing dissertation topics for your thesis paper.
Evidence-based practice nursing involves integrating the use of the best available evidence into the care of patients. The subject is not new and has been around for several decades. It is now becoming a career option for many healthcare professionals. Evidence-based practice nursing improves patient outcomes, reduces costs, and enhances a hospital’s reputation.
Evidence-based practice nursing incorporates four fundamental principles:
The use of the best available evidence to make decisions about care for patients with specific health problems;
- The ability to recognise gaps in knowledge about how to provide safe and effective patient care;
- The ability to identify potential barriers that may interfere with implementing evidence-based practices; and
- The ability to translate research findings into clinical practice guidelines and other practical resources
Possible Evidence-Based Practice Nursing Issues
EBP includes many studies, including those of low methodological quality, to inform clinical decision-making in each care area. In other words, it incorporates the best research evidence into clinical decision-making to treat a patient on time. It is best to use a clearly defined decision tree or matrix based on a previous literature review when performing EBP.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is becoming increasingly important in nursing as the role evolves. EBP expertise is expected of nurse practitioners (NPs), certified nurse midwives (CNMs), and certified registered nurse anaesthetists (CRNAs). Nurses must prepare for the changes the profession is undergoing.
Care providers in this field are encouraged to apply their knowledge and expertise. In addition, you gain experience and confidence in your judgment. Due to this, more emphasis is placed on what works in practice than on what doesn’t. By teaching best practices, nurses can become leaders in their field by challenging their beliefs and experiences.
- Child Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Dementia Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Midwifery Dissertation Topics
- Palliative Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Mental Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Nursing Dissertation Topics
Evidence-Based Nursing Dissertation Topics
Topic:1 reducing falls in combative dementia patients.
Research Aim: Studying all the preventive measures to protect dementia patients from accidental falls and injuries with severe cognitive impairments.
Topic:2 Palliative oxygen usage: nasal cannula vs masks
Research Aim: Understanding the importance of the nasal canal for high flow rates of oxygen for those with breathing difficulties.
Topic:3 Early care of intoxicated patients
Research Aim: Studying the management of intoxicated patients admitted to intensive care units because of causative diseases, mortality issues and others.
Topic:4 Delirium Prevention
Research Aim: Learning the sensitivity of the topic of delirium and finding ways to prevent it with the help of sensory impairment, regular continence, hydration and others.
Topic:5 Choosing the correct catheter size of IVs
Research Aim: Measuring the accurate vessel size with respect to the length of the catheter for reducing dislodgement.
Topic:6 Reducing CAUTI's (Catheter acquired UTI)
Research Aim: Studying the intervention and the use of chlorhexidine mixture to treat the catheter associated with urinary tract infections with special tricks and techniques.
Topic:7 Alternative interventions to SOB for COPD patients
Research Aim: Differentiating between the pharma-logical and non-pharmacological interventions to treat breathlessness through different medical procedures.
Topic:8 Effect of visiting hours on patient outcomes
Research Aim: Studying the horrendous effect of visiting hours on patient outcomes because of the visiting policies made years ago.
Topic:9 Reducing pressure ulcerations
Research Aim: Finding out all the possible ways to reduce pressure ulcerations with the help of common practices like hydration, moisturisation, using skin Protestants and others.
Topic:10 Offering pain medication for hospitalised patients
Research Aim: Search for useful ways to improve pain management for hospitalized patients with acute needs to be fulfilled
Topic:11 Nonpharmacologic intervention for pain
Research Aim: Understanding the meaning of nonpharmacological pain management with different educational and psychological hypnosis conditions.
Topic:12 Discharge on heart failure and readmission rates
Research Aim: Learning different insights on the discharge education program for patients suffering from serious health problems like heart failure and terms and policies for readmission.
Topic:13 NPO status and hypoglycemic rates
Research Aim: Understanding the need of hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients and injecting into the patient’s blood glucose.
Topic:14 Ambulations after surgery
Research Aim:
Studying different body systems and the role of ambulation to get the blood system flow smoothly throughout the body after surgery or any medical procedure.
Topic:15 Reducing HAP And VAP for medical treatments
Research Aim: Understanding the difference between hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-acquired pneumonia with their respective treatments through antibiotics and other medical procedures.
I/O Example
To become an Evidence-based practice nurse, you need to be able to:
- Understand the importance of evidence-based practice
- Develop a clear understanding of the clinical decision-making process and how it relates to nursing research and evidence-based practice.
- Use principles from evidence-based practice to make decisions about patient care.
- Recognize potential problems in applying evidence-based practice and be able to respond appropriately.
You will also need to gain hands-on experience in a clinical setting in order to become an evidence-based practice nurse.
A nurse who practices evidence-based practice can earn $53,000 annually. In the United States, this is the average wage for nurses, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
A registered nurse’s average salary in 2014 was $58,790. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, registered nurses have earned an average of $51,230 over the past five years.
It is a rewarding and fulfilling career to work in evidence-based nursing. Nurses can make a significant impact on their patients’ lives through this field. There is a high demand for nurses with strong clinical skills and an understanding of evidence-based practice in today’s nursing market.
If you need help with the complete dissertation writing process, you may want to additionally read about our proposal writing service and the full dissertation writing service .
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find evidence based practice nursing dissertation topics.
For evidence-based practice nursing dissertation topics:
- Identify healthcare gaps.
- Review clinical problems.
- Explore recent research.
- Focus on patient outcomes.
- Consider innovations.
- Choose a topic with available data and relevance.
You May Also Like
The study of cognitive psychology focuses on how the brain processes and stores information. The underlying mechanisms are investigated using experimental methods, computer modeling, and neuropsychology.
Here is a list of Linguistic dissertation topics to help you choose the one studies any one as per your requirements.
Find the most unique and interesting dissertation topic ideas for translation studies to help you in your translation dissertation/ thesis.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Family Nurse Pracitioner (DNP)
Graduates will deliver evidence-based direct patient care at an advanced practice level to individuals across the lifespan in primary care settings, and will translate evidence based research and guidelines to transform practice. Graduates are prepared to work collaboratively with rural communities to reduce health disparities.
Certification
Graduates are eligible for certification as a family nurse practitioner from either the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) or the American Academy of Nurse Practitioner Certification Board (AANPCB).
Course Requirements
Program coursework is delivered online. Select classes may require on-campus visits. We can help you tailor your plan to meet your needs. Interested applicants are advised to contact us to discuss options.
Available curriculum plans for the Doctor of Nursing Practice Family Nurse Practitioner:
- Bachelor's to DNP Family Nurse Practitioner (if you have a B.S.N. and want to obtain a DNP as a FNP)
- Master's to DNP Family Nurse Practitioner (if you have your M.S. in nursing and want to obtain a DNP as a FNP)
Are you ready to take the next step?
- Admission Requirements

DNP Project List

Faculty Research Areas

Wondering about funding?
- See funding options.
Let's Talk
Our Nursing Student Services team is ready to help you find a path to meet your nursing goals. Fill out this online form and our staff will get back to you as soon as possible to answer your questions.
Virtual View of SDSU Nursing
Learn more about SDState's nursing program, faculty, learning facilities and more wherever you are.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Navigating the maze of self-management in primary glaucoma: insights from a qualitative study
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Mona Khurana 1 ,
- Rajiv Raman 2
- 1 Sankara Nethralaya , Chennai , Tamil Nadu , India
- 2 Shri Bhagwan Mahavir Vitreoretinal Services , Sankara Nethralaya , Chennai , Tamil Nadu , India
- Correspondence to Dr Rajiv Raman, Shri Bhagwan Mahavir Vitreoretinal Services, Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, 600006, India; rajivpgraman{at}gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2024-103956
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- Ophthalmology
- Primary Care Nursing
Commentary on: Hua Y, Lu H, Dai J, et al . Self-management challenges and support needs among patients with primary glaucoma: a qualitative study. BMC nursing . 2023 Nov 14;22(1):426.
Implications for practice and research
Healthcare professionals should provide personalised and comprehensive support, addressing the medical, emotional and social challenges faced by patients with primary glaucoma.
Further research is needed to explore the effectiveness of tailored self-management support programmes in improving the quality of life and treatment outcomes for patients with glaucoma.
Glaucoma is a chronic disease characterised by progressive visual field defects. It is the most common cause of irreversible blindness and is associated with a decrease in quality of life. 1 Most studies in literature look at specific challenges faced by patients with glaucoma like adherence to medications, driving or depression. 2–4 There is a paucity of literature shedding light on the various aspects of the self-management challenges faced by patients with glaucoma on a day-to-day basis. The study by Hua et al 5 addresses this gap by exploring the self-management challenges and support needs of patients with primary glaucoma, providing valuable insights for improving patient-centred care and informing future interventions.
The study population had participants of different ages and genders. Both patients with primary open-angle and patients with angle-closure glaucoma were included. However, the severity of glaucoma was unclear. Majority of the patients had received education up to junior high school or less (75%) and most were married (70%). The study revealed that patients with primary glaucoma face challenges in becoming knowledgeable about their condition, managing negative emotions, adapting to daily life changes and resuming social activities. They expressed a need for personalised health information, shared decision-making and support in using mobile medical technologies. Additionally, patients highlighted the importance of social support, psychological support, and guidance in symptom monitoring and self-management.
The study by Hua et al provides valuable insights into the self-management challenges and support needs of patients with primary glaucoma. The findings underscore the importance of personalised and comprehensive support that addresses not only the medical aspects of glaucoma management but also the emotional and social challenges faced by patients. Healthcare professionals should be equipped to provide tailored education and counselling that empowers patients to actively participate in their care and make informed decisions about their treatment.
The study highlights the potential of mobile health technologies in facilitating communication between patients and healthcare providers and in supporting long-term follow-up and self-management. As the use of digital health tools continues to grow, further research is needed to evaluate their effectiveness in improving outcomes for patients with glaucoma and to ensure their accessibility and usability for diverse patient populations.
The emphasis on social support, including family, peers and financial assistance, in the study is particularly noteworthy. The role of family members and peers in supporting self-management behaviours and providing emotional support can be crucial for patients’ well-being and adherence to treatment. 7 Healthcare providers should consider involving patients’ support networks in education and intervention efforts and advocate for policies that address the financial barriers to accessing glaucoma care.
One limitation of the study is its single-centre design, which may limit the generalisability of the findings to broader populations of patients with glaucoma. Additionally, the study’s focus on inpatients may not fully capture the self-management challenges and support needs of patients managing their condition in an outpatient or community setting. Further studies on patients with different severity of glaucoma will be helpful. Methods to avoid biases during the study can be included.
In conclusion, the study by Hua et al contributes to our understanding of the multifaceted nature of self-management in glaucoma and highlights the need for holistic, patient-centred approaches to support patients in navigating the challenges of living with this chronic condition.
- Wong TY , et al
- Berchuck S ,
- Mukherjee S , et al
- Muñoz B, EE ,
- Jampel HD , et al
- Ramulu PY ,
- Munoz B , et al
- Dai J , et al
- Shtein RM ,
- Newman-Casey PA ,
- Herndon L , et al
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
2024 KSPAN Spring Conference
Webinar/Online
Saturday, April 27, 2024 at 8:30am ET - 12:00pm ET This event has ended.
Nursing: Past, Present, Future
Attachments
Additional information.
At our Spring Conference we want to celebrate the unsung heroes that made nursing a profession. By understanding how nurses can actively participate in research and evidence-based practice, we can make changes and improvements for our patients. These changes will help those we serve achieve optimal outcomes. Our profession has been the most trusted profession 23 of the last 24 years. By uniting with one voice, we can advocate for changes in healthcare that will directly benefit those we serve.
Event Agenda
Access restricted.
If you are a registered attendee to this event, you can log in to your account to access handouts.

COMMENTS
Here are some of the latest evidence-based practice nursing research topics that you can use in your essay or explore further in your own research: ... The nursing evidence-based practice topics listed above provide a starting point for further exploration and investigation. By studying the effectiveness of various nursing interventions and ...
Editor's choice. Evidence for Nurse Education. Health promotion and public health. Mental health. Nursing issues. Pain management. Research made simple. Women's Health and Midwifery. Discover the key topics collections published by Evidence-Based Nursing.
Impacts of nursing ethics on evidence-based practice. Strategies to address the implementation gap between practice, research, and knowledge in nursing. Using social media to promote the dissemination of evidence-based practice. Strategies for implementing and translating evidence-based practice. Benefits of frequently training nursing staff on ...
Evidence-Based Nursing systematically searches a wide range of international healthcare journals applying strict criteria for the validity of research and relevance to best nursing practice. Content is critically appraised and the most relevant articles are summarised into succinct expert commentaries, focusing on the papers` key findings and implications for nursing practice.
Evidence-based practice is now widely recognized as the key to improving healthcare quality and patient outcomes. Although the purposes of nursing research (conducting research to generate new knowledge) and evidence-based nursing practice (utilizing best evidence as basis of nursing practice) seem quite different, an increasing number of research studies have been conducted with the goal of ...
Evidence-based practice in nursing involves providing holistic, quality care based on the most up-to-date research and knowledge rather than traditional methods, advice from colleagues, or personal beliefs. Nurses can expand their knowledge and improve their clinical practice experience by collecting, processing, and implementing research findings.
It is defined as "The nursing professional development (NPD) practitioner integrates scholarship, evidence, and research findings into practice" (p. 104). There is often confusion between quality improvement, evidence-based practice, and research. A seminal article by Shirey and colleagues. [2] differentiated these three topics.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the process of collecting, processing, and implementing research findings to improve clinical practice, the work environment, or patient outcomes. According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), nursing interventions should be practical, methodical decisions based on EBP research studies.
Research studies show that evidence-based practice (EBP) leads to higher quality care, improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and greater nurse satisfaction than traditional approaches to care. 1-5 Despite these favorable findings, many nurses remain inconsistent in their implementation of evidence-based care. Moreover, some nurses, whose education predates the inclusion of EBP in the ...
Models of Evidence-Based Practice. Multiple models of EBP are available and have been used in a variety of clinical settings. 16-36 Although review of these models is beyond the scope of this chapter, common elements of these models are selecting a practice topic (e.g., discharge instructions for individuals with heart failure), critique and syntheses of evidence, implementation, evaluation ...
EBP is a process used to review, analyze, and translate the latest scientific evidence. The goal is to quickly incorporate the best available research, along with clinical experience and patient preference, into clinical practice, so nurses can make informed patient-care decisions ( Dang et al., 2022 ). EBP is the cornerstone of clinical practice.
Practice: Topics for researchers and practitioners. Vanessa Antunes 1. Associate Editor. Keywords: nursing research, evidence-based healthcare, nurses, developing nursing. skills, evidence-based ...
Evidence-Based Nursing should therefore be exceptionally useful, and its target audience of practitioners is a refreshing move in the right direction. The worlds of researchers and practitioners have been separated by seemingly impenetrable barriers for too long. 4. Tiptoeing in the wake of the movement for evidence-based medicine, however, we ...
Nursing Care and Research Foster Evidence-Based Practice. Pursuit of knowledge leads to improvements in patient care. For Cleveland Clinic nurses, evidence-based practice (EBP) is much more than a buzz phrase. It is ingrained in everything they do, from training at The Stanley Shalom Zielony Institute for Nursing Excellence to delivering care ...
This nursing research course reviews evidence-based practice and introduces the importance of evidence-based research to improve clinical practice. Students will develop and be evaluated on skills such as identifying, reading, and comprehending scholarly research, strategies to evaluate the quality of research and evidence, and to determine ...
With a colleague, Selena delivers interactive sessions to students from Years 10 to 13 to teach about evidence-based practice and to encourage critical thinking, particularly around healthcare claims made in the media. Evidence for Nursing: new evidence and resources - January 2022 by Sarah Chapman and Selena Ryan-Vig.
Top 5 Benefits To The Nurse. 1. Evidence-based practice in nursing provides nurses with scientifically supported research to help them make well-educated decisions. 2. EBP in nursing helps nurses stay up-to-date about new nursing interventions and protocols used in patient care. 3.
Systems - integration of evidence with patient records. Summaries - practice guidelines found via Clinical Key & UpToDate. Synopses of Syntheses - focused journals: Evidence-Based Nursing, Evidence-Based Medicine , ACP Journal Club. Syntheses - m eta-analyses, systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses found through Cochrane, CINAHL, PubMed.
Our nurses here at UI Hospitals & Clinics are known for application-focused evidence-based practice at the point of care. ... Health Topics Educational Resources & Support Groups COVID-19 ... Nursing Evidence-Based Practice and Research T100 General Hospital (GH) 1-319-384-9098 [email protected] ...
The Iowa Model Revised: Evidence‐Based Practice to Promote Excellence in Health Care uses an algorithm to guide evidence‐based practice processes from identification of a trigger to integrating and sustaining a practice change (Buckwalter et al., 2017). The conduct of research is included in the Iowa Model as a strategy to be used when ...
Nursing research contributes significantly to generate scientific knowledge as too for evidence-based clinical practice. However, the reality experienced in clinical contexts does not accompany the production of scientific evidence, which means there is still a significant gap between theory and practice. The increasing differentiation and empowerment of nurses enhances the relevance of ...
The problems with the uptake and effective implementation of EBP led to the emergence of the EIP concept. This concept is based on the premise that healthcare practice should, as a matter of principle, be informed by, rather than based on, evidence (Nevo and Slonim-Nevo, 2011). This implies that other forms of evidence (for example, patient experiences, the nurse's expertise and experiences ...
Our DNP students undertake significant projects over the course of their DNP studies in one of three areas: 1) original research where evidence is needed on an important clinical topic, 2) synthesis of existing evidence where there is a need to bring together empirical research and determine best practice, and 3) translation of evidence into ...
Research can help improve patients' outcomes as well as nurses' professional lives, National Institute of Nursing Research director says at UND. Shannon Zenk, director of the National Institute of Nursing Research, sat down for a freside chat with College of Nursing & Professional Disciplines dean Maridee Shogren on April 19.
CINAHL Complete provides easy access to 1,400 top nursing and allied health journals with full text dating back to 1937 and information for more than 50 nursing specialties, including speech language pathology, nutrition, general health and medicine, along with evidence-based care sheets, research instruments and quick lessons.
A nurse who practices evidence-based practice can earn $53,000 annually. In the United States, this is the average wage for nurses, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. A registered nurse's average salary in 2014 was $58,790. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, registered nurses have earned an average of $51,230 over the past ...
1. Introduction. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is defined as "clinical decision-making that considers the best available evidence; the context in which the care is delivered; client preference; and the professional judgment of the health professional" [] (p. 2).EBP implementation is recommended in clinical settings [2,3,4,5] as it has been attributed to promoting high-value health care ...
Graduates will deliver evidence-based direct patient care at an advanced practice level to individuals across the lifespan in primary care settings, and will translate evidence based research and guidelines to transform practice. Graduates are prepared to work collaboratively with rural communities to reduce health disparities. Certification Graduates are eligible for certification as a family ...
Methods. The study used a descriptive phenomenological approach which is often used in nursing research.6 This technique is based on patients' own lived experiences to determine their needs for support. It answers the 'what' and 'how' questions.6 The study was conducted in a purposive sample of patients with glaucoma in the inpatient department of a single centre.
Topic. Nursing: Past, Present, Future. Attachments. 2024 KSPAN Spring Conference Brochure (290 KB) Additional Information. At our Spring Conference we want to celebrate the unsung heroes that made nursing a profession. By understanding how nurses can actively participate in research and evidence-based practice, we can make changes and ...