
Call us @ 08069405205


Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

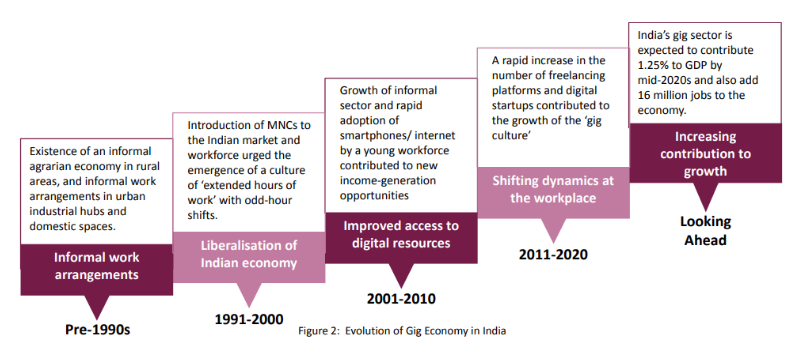
Gig economy
Syllabus: Indian Economy and related issues
Context: The recent strike by Zomato-owned Blinkit delivery agents has once again brought to the forefront the issues plaguing the gig economy in the country.
Background: The strikes began when Blinkit slashed the minimum payout per delivery to Rs 15 per delivery from Rs 25.
The gig economy in India:

- According to the NITI Aayog estimates, nearly 23.5 million workers will be engaged in the gig economy by 2029 .
Issues faced by gig workers:
- Minimum wages,
- Overtime pay,
- Medical leave, and
- A statutorily bound resolution of employer-employee disputes.
- Whether gig workers should be categorised as ‘employees’ or as ‘independent contractors’ ?
- In India , employees are entitled to a host of benefits under the Minimum Wages Act 1948, EPF Act 1952 and the Payment of Bonus Act 1965.
- Similarly, contract labourers are governed under the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act 1970 and are entitled to benefits under the EPF.
- However, gig workers display characteristics of both employees and independent contractors → as a result fall outside the ambit of statutory benefits.
What is the proposed law for gig workers? In keeping with the National Commission on Labour’s recommendation to consolidate central labour laws, the Ministry of Labour and Employment introduced the Code on Social Security 2020.
Salient provisions in the Code on Social Security 2020:
- It brings gig workers within the ambit of labour laws for the first time.
- I t distinguishes between such workers and employees .
- It stipulates that Central and State Governments must frame suitable social security schemes for gig workers .
- A social security fund for gig workers, to which Gig employers must contribute 1-2% of their annual turnover → to be used for the aforementioned schemes.
- It also mandates the compulsory registration of all gig workers to avail of benefits under these schemes.
- It also envisages the constitution of a National Social Security Board by the Central government to monitor the implementation of such schemes.
- Out of the four new labour codes proposed, gig work finds reference only in the Code on Social Security .
- Hence, they cannot create legally recognised unions and access a national minimum wage that applies to all forms of employment.
- Gig workers are excluded from the category of ‘unorganised workers’ or ‘wage workers’.
- Gig workers also remain excluded from accessing the specialised redressal mechanism against their employers.
- They also do not have the right to collective bargaining – a fundamental principle of modern labour law.
- All the above leads to the violation of their fundamental rights under Articles 14 and 21 and comes within the meaning of forced labour under Article 23.
Can judicial intervention be expected? A petition demanding that gig workers or platform workers be declared as ‘unorganised workers’ so that they come under the purview of the Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008, is pending in the SC of India.
Best practices:
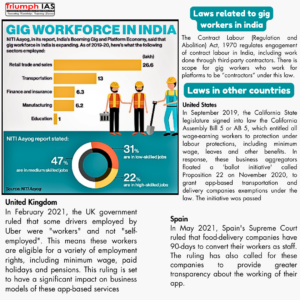
- In 2021, the UK Supreme Court classified Uber drivers as ‘workers’ under the UK Employment Rights Act 1996.
- Germany’s Temporary Employment Act provides for equal pay and equal treatment of gig workers.
- Singapore has also proposed legislative changes to extend work injury insurance and pension coverage to such workers.
Way ahead for India:
- The Labour Codes need to be implemented as soon as possible.
- For this, State governments should frame rules as soon as possible.
Insta Links:
Mains Links:
How globalization has led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased in formalization detrimental to the development of the country? (UPSC 2016)

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

- Pre Cum Mains Foundation Courses
- GS + CSAT Pre cum Main Foundation Course
- GS Pre cum Main Foundation Course
- GS + CSAT + Optional
- GS + Optional
- Prelims Courses
- Current Affairs Course for CSE 2025
- CSAT Course
- Current Affairs for Prelims (CAP)-2024
- Mains Courses
- Mains Advance Course (MAC)
- Essay Course Cum Test Series
- First Step — NCERT Based Course
- Optional Foundation Courses
- Mathematics
- Anthropology
- Political Science and International Relations (PSIR)
- Optional Advance Courses (Optional Through Questions)
- Civil Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Interview Guidance Programme / Personality Test Training Program
- GS + CSAT Postal Courses
- Current Affairs Magazine – Annual Subscription
- GS+CSAT Postal Study Course
- First Step Postal Course
- Postal Study Course for Optional Subjects
- Prelims Test Series for CSE 2024 (Offline/Online)
- General Studies
- GS Mains Test Series for CSE 2024
- Mains Test Series (Optional)
- Paarth PSIR
- PSIR Answer Writing Program
- PSIR PRO Plus Test Series
- Mathematics Year Long Test Series (MYTS) 2024
- Indian Economic Services
- Anubhav (All India Open Mock Test)
- Prelims (GS + CSAT)
- Headlines of the Day
- Daily Current Affairs
- Editorial Analysis
- Monthly MCQ Compilation
- Monthly Current Affairs Magazine
- Previous Year Papers
- Down to Earth
- Kurukshetra
- Union Budget
- Economic Survey
- NIOS Study Material
- Beyond Classroom
- Indian Economy
Gig Economy: Advantages, Challenges & Driving Factors

The gig economy refers to an economic system characterized by flexible work arrangements, where labor and resources are exchanged through digital platforms that facilitate connections between buyers and sellers. Instead of hiring full-time employees, organizations in this type of setup rely on independent contractors and freelancers for temporary work.
Advantages of the Gig Economy
Disadvantages of the gig economy, who works in the gig economy.
According to an OECD paper, the main motives for working in the gig economy are generating additional income and having work flexibility.
- Free agents: These individuals actively choose independent work as their primary source of income.
- Casual earners: They engage in independent work by choice to supplement their income from other sources.
- Reluctant: These workers primarily rely on independent work for their livelihood but would prefer traditional employment if given the opportunity.
- Financially strapped: They engage in supplemental independent work out of necessity, often due to financial constraints.
Factor Driving the Growth of the Gig Economy
The gig sector is driven by several key factors that have shaped its growth and popularity:
- Changing Work Approach: The younger generation, particularly millennials, have a different perspective on careers. They prioritize finding work that aligns with their passions and interests rather than settling for traditional career paths that may not fulfill their inner desires.
- Business Models: In the gig economy, different compensation models are employed, such as fixed-fee, time-based, work output-based, and quality-driven models. While fixed-fee arrangements are most common, the time-based model is also prevalent.
- The emergence of a Start-up Culture: India’s start-up ecosystem has witnessed significant growth, leading to a rise in gig employment. Start-ups, in order to minimize fixed costs, hire contractual freelancers for non-core activities.
- Rising Demand for Contractual Employees : Multinational corporations (MNCs) are increasingly embracing flexible hiring options, especially for specialized projects, as a means to reduce operational expenses, particularly in the aftermath of the pandemic. This trend has contributed significantly to the gig culture in India.
The gig sector is here to stay as it provides a new opportunity to work flexibly and earn using different online platforms. It has been driven by the need for location-independent work, changing career aspirations, and various compensation models. These factors have collectively fueled the growth and prominence of the gig economy in India.
But still, there exists a number of challenges including lack of proper benefits, chances of exploitation of workers, etc. India needs to develop proper legislation in order to safeguard the needs of both organizations as well as workers.
What is an Example of a Gig Economy?
An example of this type of platform in India is Swiggy, which is a food delivery service. Swiggy connects customers with delivery partners ( gig workers ) who pick up food orders from restaurants and deliver them to the customers’ locations. The gig workers have the flexibility to choose their working hours and earn income per delivery.
What is Another Name for the Gig Economy?
Another name for the gig economy is the “freelance economy” or the “on-demand economy.” These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the same concept of temporary and flexible work arrangements facilitated by digital platforms.
What is Platform vs Gig Economy?
The platform economy and gig economy are closely related but have some distinctions. The gig economy specifically refers to the labor market where independent workers engage in short-term or freelance work. It focuses on the workforce aspect.
On the other hand, the platform economy refers to the broader economic system in which digital platforms act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers, service providers, or workers. The platform economy encompasses not only gig work but also various other types of online transactions and interactions facilitated by platforms.
What are the Features of the Gig Economy?
The key features of Gig economy the include:
– Flexibility : Gig workers have the freedom to choose when, where, and how much they work – Independent contractor status : Gig workers are usually considered independent contractors rather than traditional employees. – Digital platforms : These platforms facilitate the matching of gig workers with available gigs and often handle payment transactions. – Task-based work : Instead of long-term employment, gig workers typically engage in specific tasks, projects, or assignments. – Uncertain income and job security : The gig economy offers flexibility but often comes with income variability and less stability compared to traditional employment.
What is the Gig Economy in India?
The gig economy in India refers to an economic system where temporary, flexible, and freelance work arrangements are prevalent.
It involves individuals, often referred to as gig workers, taking up short-term projects or tasks on a contractual basis rather than being traditional employees of a company. These workers are usually connected to employers or clients through digital platforms or online marketplaces.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Financial market: meaning, classification, roles & more, capital market: meaning, structure, instruments, roles & more, instruments of capital market, money market: meaning, structure, instruments, roles & more, securities and exchange board of india (sebi), banking system in india: structure, types & more, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Featured Post
Overview of the NITI Aayog Report on Gig and Platform Economy
Important facts given in the NITI Aayog report titled ‘India’s Booming Gig and Platform Economy ’ are given below:
- According to the Report, the gig economy employed more than 7.5 million people in 2020–21.
- In the following eight years, the number of workers employed will increase to 23.5 million workers, accounting for 4.1% of all Indians’ means of subsistence.
- The Report states that at the moment, medium-skilled occupations make up about 47% of gig work, high-skilled jobs make up about 22%, and low-skilled employment make up about 31%.
- Women are more likely to work in platform positions after getting their education and getting married, according to a survey done in urban areas of India.
- In India, the female labour force participation has remained low, ranging from 16 to 23 percent in recent years.
- The labour force participation percentage for persons with disabilities, who make up 2.11 to 10% of the population in India, is 36% .
- The participation of the two demographic groups in the labour force has been hampered by structural impediments like access to education and a lack of skills .
- As per the Report, platform companies empower workers to monetise their idle assets when and where they want — a benefit lacking in traditional employment sectors — offer flexibility and choice of labour to all workers in general, and women in particular, according to the report, making them an appealing opportunity for both groups.
- The Report suggests businesses to implement old age or retirement plans, as well as additional insurance coverage for contingencies like injury sustained at work that could result in loss of job and income.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gig Economy
The gig economy has its advantages and disadvantages. These are given below:
- It makes the work more adaptable to the requirements of the employee and the employer.
- It promotes a flexible lifestyle.
Disadvantages
- As the employees are frequently employed by businesses on a contractual basis , they mostly do not receive allowances like paid sick, housing and travel expenses, provident fund etc.
- Some platform gig workers may receive low wages and there is lack of job security .
- There may be no scope for upward mobility within the firm or institution.
- There is unequal gender participation in such platforms.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Win up to 100% Scholarship
- UPSC Online
- UPSC offline and Hybrid
- UPSC Optional Coaching
- UPPCS Online
- BPSC Online
- MPSC Online
- MPPSC Online
- WBPSC Online
- OPSC Online
- UPPCS Offline Coaching
- BPSC Offline Coaching
- UPSC Test Series
- State PSC Test Series
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- SUBJECT WISE CURRENT AFFAIRS
- DAILY EDITORIAL ANALYSIS
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS QUIZ
- Daily Prelims(MCQs) Practice
- Daily Mains Answer Writing
- Free Resources

- Offline Centers
- NCERT Notes
- UDAAN Notes
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Prelims PYQs
- UPSC Mains PYQs
- Prelims Preparation

Gig Economy in India
Context: Recently, Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Bill, 2023 was passed by Rajasthan Assembly.
About Gig Economy:
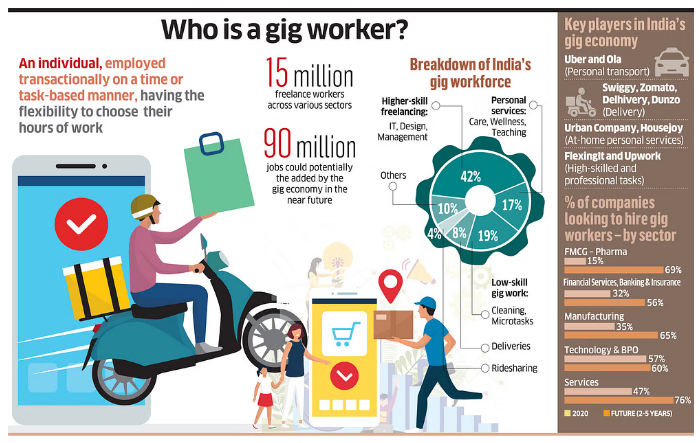
- A gig economy is a labor market that relies on independent contractors and freelancers rather than full-time permanent employees.
- Platform-based: They use online apps or digital platforms to find and perform work, such as ride-hailing, food delivery, e-commerce, online freelancing , etc.
- Non-platform-based gig workers : They work outside the traditional employer-employee relationship, such as casual wage workers and own-account workers in sectors like construction, domestic work, agriculture, etc.
- For Workers: Gig economy can provide more flexibility, autonomy, income opportunities, skill development, and inclusion.
- For Employers : It can enable access to a large and diverse pool of talent, lower fixed costs, higher scalability, and better customer satisfaction.
- For Customers : It can offer more choice, convenience, quality, and affordability.
Gig Economy in India:
- Prospect: According to a report by NITI Aayog, the platform-based gig economy in India has grown rapidly in recent years, driven by factors such as demographic dividend, urbanisation, digitalisation, and consumer demand.
- The report also projects that the platform-based gig economy in India can create up to 56 million new jobs by 2029-30, adding up to 1.3% to India’s GDP in the long run.
- The report suggests that the non-platform-based gig economy in India can create up to 34 million new jobs by 2029-30.
- According to a report by Nasscom , the gig economy is expected to contribute around 1.25% to India’s GDP by 2025, with the potential to create 90 million jobs.
- Pillar of Strength: Gig economy has proven its resilience and potential in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, by continuing to unlock jobs in the millions and keeping communities connected.
Need of Gig Economy in India:
- Employment Opportunity : India as a developing country is faced with the challenge of providing employment opportunities to all. Gig economy has expanded the availability of jobs and improved labour force participation.
- Catering demand of low Skilled: At present, about 47 per cent of the gig work is in medium-skilled jobs, about 22 per cent in high skilled, and about 31 per cent in low-skilled jobs.
- Many millennials value flexibility and work-life balance and are drawn to the gig economy because of the opportunities it provides.
- Youth participation in the Gig economy has seen an 8-fold increase between 2019-2022.
- Women’s participation in the gig economy has increased from 18% to 36%.
- Catering to Retired Persons: Due to the flexibility that contract work offers, many people after retirement start working for themselves.
- Democratization of Jobs: The gig and platform sector has low-entry barriers and hence holds enormous potential for job creation in India.
- Technological Disruption: Tech advancements, particularly in AI, robotics, and data analytics, have eliminated workplace limitations. Tech integration in the gig economy can boost productivity and improve gig workers’ living standards.
- Last Mile Delivery : It has revolutionized the last-mile delivery industry, making it more accessible, affordable, and efficient.
- Remote Working : Telecommunications have made work more dynamic, allowing individuals to collaborate regardless of where they are geographically located .
- Start-Up Culture: Gig workers can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional employees, as they can be hired on a project-by-project basis, without the need to provide benefits or other forms of compensation.
Steps taken to Promote Gig Economy in India:
- Code on Social Security, 2020 , the gig workers are provided with recognition as a new occupational category.
- Dedicated Social Security Fund to extend Social Security benefits to gig workers.
- State Government Initiatives: Karnataka government has announced for gig workers an accident and life insurance cover of Rs 4 lakh for which it will entirely bear the cost of the annual premium.
- Defines Gig Worker: Person who performs work or participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of the traditional employer-employee relationshi p and who works on a contract that results in a given rate of payment, based on terms and conditions laid down in such contract and includes all piece-rate work.
- Registration: It seek to register all gig workers and aggregators in the state, facilitate guarantee of social security to gig workers, and give them an opportunity to air any grievances.
- State government will maintain a database of the gig workers and generate a unique ID for every one of them.
- Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers Welfare Board: It will have two members each from gig workers and aggregators to be nominated by the state government besides two civil servants.
- Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers Social Security and Welfare Fund: For the benefit of registered gig workers. Welfare fees will be charged from aggregators.
- Penalties on Aggregators: State government may impose a fine which may extend up to Rs 5 lakh for the first contravention and up to Rs 50 lakh for subsequent contraventions.
Concern Associated with Gig Economy:
- I ncrease in Voluntary Unemployment: It has led to an increase in voluntary unemployment as some workers prefer the flexibility and autonomy of gig work over traditional employment.
- It often means that workers have to make themselves available any time gigs come up, regardless of their other needs , and must always be on the hunt for the next gig.
- Job insecurity: Gig workers in India often lack job security, as they are typically engaged on a project or assignment basis , rather than as permanent employees.
- Income instability: Gig workers in India may experience fluctuations in income due to the irregular and unpredictable nature of gig work.
- Lack of formalization: Many gig workers in India operate in the informal sector, which can limit their ability to access credit, government support programs, and other resources.
- Gig workers d o not have access to social security benefits such as health insurance, retirement benefits, and paid leave.
- Unequal bargaining power: Gig workers in India may lack the bargaining power to negotiate fair compensation and working conditions, particularly when they are competing against a large pool of other workers on digital platforms.
- Training and upskilling : Many gig workers lack the necessary skills to perform their work effectively. Gig workers often have limited opportunities for upskilling and career advancement.
- Social stigma: Gig work is still viewed by some in India as a temporary or low-paying option, which can result in social stigma and lack of recognition for the work done by gig workers.
- Payments, Incentives, and Growth Models: Absence of a minimum wage guarantee makes workers susceptible to financial vagaries during crises/disasters
- Workplace Conditions & Interaction: Lack of appropriate forums that capture concerns of gig-workers and help platforms to understand the challenges and problem-solve
Way Forward:
- These include coverage for medical costs, hospitalization, preventive care services such as regular health check-ups and vaccinations, as well as paid leaves for workers.
- Platform businesses can provide certifications, allowing workers to progress better in their careers.
- This can protect the rights of gig workers and help curb labour disputes.
- Adopt gender-inclusive language and imagery to normalize participation of women platform gig-workers enabling platforms to expand markets and attract more women customers.
- R ecognise the varied nature of platform work to design equitable schemes.
- A llow augmentation of social security through innovative financing mechanisms.
- I ncorporate, while designing schemes, the specific interests of platforms, factoring the impact on job creation, platform businesses and workers.
- S upport workers to subscribe to government schemes and welfare programmes through widespread awareness campaigns.
- E nsure benefits are readily accessible to workers.
- Incentivising ‘platformization’: To accelerate ‘platformisation’ i.e., give impetus for more platform businesses by starting a program called ‘Platform India’ along the lines of the government’s earlier Start Up India initiative.
Conclusion:
- The increasing demand for gig workers and the rise in participation of gig workers, especially the youth and women indicate that the gig economy in India is gaining popularity.
- According to a report by the International Labour Organization (ILO), India is the second-largest gig economy in the world, with around 56% of all gig workers in the Asia-Pacific region working in India.
- The gig economy is predicted to be a significant building block in achieving India’s aim to become a $5 trillion economy by 2025 . This would help in bridging the income and unemployment gap.
- Greater collaboration between the government, employers, and workers’ organizations is needed to ensure that gig workers are able to enjoy their rights and access the benefits they are entitled to.
News Source: The Hindu
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.

- Recent Post
- Related Post
- Most Viewed Post

Effects of Climate Change on Mental Health
MEDITECH STACKATHON 2024
Celebrities Liable for Products in Misleading Ads in India, ...
Role of Wildlife Corridors in Tiger Conservation
Promotion of Regional language by utilization of Primers
Crispr-cas9 gene editing clinical trial treating cases of in..., social stock exchange, prime- minister’s egypt state visit, shanan power project, msp hike and its impact, natural rubber production in india: status, government initi..., latest comments, recent editorial.
Chinese President Xi Jinping in Europe, a Divided ...
Progress on Global Plastics Treaty
Rules for a New Dawn for the Indian Legal Industry
India-Nepal Relations: Territorial Disputes and Ge...
Mullaperiyar Dam Row
Online Gaming Sector in India
Popular current affairs
Celebrities Liable for Products in Misleading Ads ...
Promotion of Regional language by utilization of P...
CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing Clinical Trial treating c...
Our Courses

THE MOST LEARNING PLATFORM
Learn From India's Best Faculty
Our Initiatives
Beginner’s roadmap, quick links.

PW-Only IAS came together specifically to carry their individual visions in a mission mode. Infusing affordability with quality and building a team where maximum members represent their experiences of Mains and Interview Stage and hence, their reliability to better understand and solve student issues.
Subscribe our Newsletter
Sign up now for our exclusive newsletter and be the first to know about our latest Initiatives, Quality Content, and much more.
Contact Details
G-Floor,4-B Pusha Road, New Delhi, 110060
- +91 9920613613
- [email protected]
Download Our App
Biginner's roadmap, suscribe now form, fill the required details to get early access of quality content..
Join Us Now
(Promise! We Will Not Spam You.)
CURRENT AF.
<div class="new-fform">
Select centre Online Mode Hybrid Mode PWonlyIAS Delhi (ORN) PWonlyIAS Delhi (MN) PWonlyIAS Lucknow PWonlyIAS Patna Other
Select course UPSC Online PSC ONline UPSC + PSC ONLINE UPSC Offline PSC Offline UPSC+PSC Offline UPSC Hybrid PSC Hybrid UPSC+PSC Hybrid Other
</div>


Gig Economy: Challenges and Future Prospects of Online Delivery Workers in India | An In-depth Analysis | Sociology Optional for UPSC Civil Services Examination | Triumph IAS
Table of Contents
Online Delivery Workers(Gig Workers)
(relevant for sociology optional for civil services examination).
Paper 1: Unit-6 Work and Economic Life: Formal and Informal Organization of Work
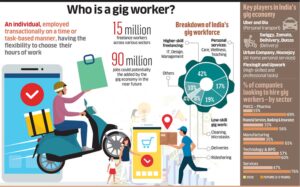
Online Delivery Workers Data
- A NITI Aayog study estimated that in 2020−21, 77 lakh workers were engaged in the gig economy. The gig workforce is expected to expand to 2.35 crore workers by 2029−30.
- In 2019−20, 10 lakh people were working as delivery executives. Out of these, women constituted 67,900 workers till June 2019.
Work Conditions
- On contract paper, food delivery platforms term the delivery workers as “independent contractors” or “delivery partners.” This kind of classification, compounded by the lack of legal security and conceptual ambiguity, is forcing such workers to work almost 12 hours or more per day and on less than prescribed minimum wage. Hence, they are not considered as traditional “employees.” Consequently, these workers do not benefit from labour rights as guaranteed in the labour laws of the country .
- The Fair Work India Ratings (2022) speak of the declining earnings and deteriorating working conditions of delivery labourers. The report has evaluated and rated the working conditions of 12 food delivery platforms in India. Of these, Swiggy and Zomato were found to have a poor record.
- The rapidly burgeoning gig workforce is ushering in a new economic revolution, delivery workers face acute exploitation in many aspects. It commences from the phase of recruitment itself, wherein workers are burdened to incur all expenses of transportation facilities and gadgets without compensation at any stage of service. Moreover, all popular food delivery platforms charge `1,500−`2,000 as security deposit from each newly joining worker. Thus, delivery workers start their first working day with debt, resembling modern debt bondage.
- There are other major aspects of the delivery platform work that directly affects their well-being . The living and working conditions of delivery workers in India exemplify the fact that they are forced to compromise with their mental and physical health to eke out a barely sustainable wage
- Resurging working class consciousness: Delivery workers across India face acute exploitation and are deprived of basic labour rights, the recent struggle carried out by Zomato and Swiggy workers in Kerala resembles the resurging working class consciousness among them.
- Asymmetry of Information: These online platforms function on the basis of asymmetry of information which converts to unequal distribution of power between the delivery workers, customers and online food chains. Delivery workers do not know how they get orders, how their ratings drop and how the overall system works. Therefore, delivery workers are forced to work without possessing the right to information about their basic labour rights.
Women Delivery Workers
- Late and less entry of Women: Recruitment of women workforce had started in 2016, for the first time, in India. Though the number of women in the workforce has increased from 40,000 in 2018, it has not reached even one-third of the total workforce of delivery executives . Late and less entry of women workers as delivery partners indicates different variables associated with access to work and workplace outside their house.
- Gender-based subordination : The work of delivery partners demands certain basic requirements, for example, a motorcycle, scooter or bicycle with a driving license.
- It is observed that all the women workers belong to economically downtrodden families . In that context, “ getting permission” from the “family and society” to work in a public space can be a matter of concern for many women..
- The working patterns of these food delivery partners are to make movements to different locations to collect and deliver food. In this process, access and use of hygienic washrooms and maintenance of menstrual hygiene becomes a few major conce rns.
- It is observed that women delivery partners are not given work after 6 pm to maintain their safety. According to Zomato, entry of women workers as delivery partners needs different sets of initiatives and working patterns. The concern regarding safety become another layer of gender-based subordination.
- The flexibility of work time and income pattern is another significant issue shared by women workers.
Few Steps Taken
- New Labour Code and Delivery Workers
- Labour laws pertaining to gig workers are covered only under the Code on Social Security, 2020. Section 2(35) in Chapter I of the code elucidates a gig worker as “a person who participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of a traditional employer–employee relationship.” Though the code precisely discerns the delivery workers from regular and non-employee classes of workers, it lacks clarity as to who exactly a gig worker is.
- Section 2(26) in Chapter I of the Code on Social Security defines an “employee” as “a person employed on wages by an establishment, either directly or through a contractor to do any skilled, semi-skilled, unskilled or any other work, whether the terms of employment be expressed or implied.”
- On a positive note, the code mandates provision of provident fund, gratuity, insurance employee compensation and maternity benefits.
- It assigns the union and state governments to frame adequate social security schemes on matters relating to accident insurance, life and disability cover, old age protection, maternity benefits , etc.
- It puts an obligation on the delivery workers to contribute 1%−2% of their annual turnover into the Central State Funds which may be used for carrying out the welfare measures.
- Zomato mentioned four major initiatives taken by the company for the “safety” of the women delivery partners . It includes access to safety related education and tools, contactless deliveries by default, extended support from restaurant partners, safety handy emergency call button (SOS) and dedicated support to use washrooms in public spaces.
- The formation of All India Gig Workers Union has become a platform for the women delivery workers to make their voice heard by the authority.
Way Forward:
- The need of the hour is to consider food delivery partners as labourers and they have to be brought under the purview of the organised and formal sector.
- There should be a legal and administrative framework to keep the aggregator companies under the purview of the labour laws in the country . Such efforts would compel the gig economy unicorns to categorise workers as full-time employees.
- Labour class consciousness among delivery workers in India would also play a pivotal role in strengthening their unity to fight pay cuts and other benefits.
- The recent resurging labour consciousness and strikes of Meituan delivery workers in China, Talabat food delivery workers in Dubai and online delivery workers in South Korea under the Parcel Delivery Workers’ Solidarity Union for better wage, better working conditions and social security provisions , can be seen as a catalyst factor in accelerating resistance of delivery workers in India against acute exploitative policies of online giant food delivery platforms.
Reference: Economic Political Weekly
Related Blogs …

To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
Gig Economy, Online Delivery Workers, Labour Laws, Gender Disparity, Work Conditions, India, Labour Class Consciousness, Zomato, Swiggy, Social Security, Gig Workers Union, Gig Economy, Online Delivery Workers, Labour Laws, Gender Disparity, Work Conditions, India, Labour Class Consciousness, Zomato, Swiggy, Social Security, Gig Workers Union
Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose T he Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “ which optional subject is the best? ” and “ which optional subject is the most scoring? ” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher , is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains , which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“ A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers. ”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional , you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey , potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher . Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎 www.triumphias.com
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- TRP for UPSC Personality Test
- Interview Mentorship Programme – 2023
- Daily News & Analysis
- Daily Current Affairs Quiz
- Baba’s Explainer
- Dedicated TLP Portal
- 60 Day – Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – 2024
- English Magazines
- Hindi Magazines
- Yojana & Kurukshetra Gist
- PT20 – Prelims Test Series
- Gurukul Foundation
- Gurukul Advanced – Launching Soon
- Prelims Exclusive Programme (PEP)
- Prelims Test Series (AIPTS)
- Integrated Learning Program (ILP) – 2025
- Connect to Conquer(C2C) 2024
- TLP Plus – 2024
- TLP Connect – 2024
- Public Administration FC – 2024
- Anthropology Foundation Course
- Anthropology Optional Test Series
- Sociology Foundation Course – 2024
- Sociology Test Series – 2023
- Geography Optional Foundation Course
- Geography Optional Test Series – Coming Soon!
- PSIR Foundation Course
- PSIR Test Series – Coming Soon
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – Prelims Crash Course
- CTI (COMMERCIAL TAX INSPECTOR) Test Series & Video Classes
- Monthly Magazine
Baba’s Explainer – Niti Aayog’s report on India’s gig economy
- July 15, 2022
Economics , Governance

- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy & challenges
Context: In a report titled ‘India’s Booming Gig and Platform Economy’, government think-tank Niti Aayog has made suggestions on Gig Economy.
- A gig economy is a free market system in which organisations hire or contract workers for a short span of time. Simply put, the positions are temporary to meet the company’s requirements by having short-term engagements.
- According to the Code on Social Security, 2020 (India), “A gig worker is a person who performs work or participates in work arrangements and earns from such activities, outside of the traditional employer-employee relationship.”
- Platform workers are those whose work is based on online software apps or digital platforms.
- Non-platform gig workers are generally casual wage workers and own-account workers in the conventional sectors, working part-time or full time.
- At present, about 47 per cent of the gig work is in medium skilled jobs, about 22 per cent in high skilled, and about 31 per cent in low skilled jobs.
- The survey also stated that digital platforms played a significant role in discovering job seekers and job providers in the absence of middlemen.
- According to the Boston Consulting Group’s report, in India, over 15 million workers are employed as gig workers across the industries. The number is projected to rise by over 24 million in the near-medium term and to 90 million in the long term.
- An ASSOCHAM report reveals, that the gig sector has the potential to grow to the US $455 billion at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17% by 2024.
- The Indian gig economy has the potential to add 25% to the Indian Gross Domestic Product (GDP ) and provide over 90 million jobs in the non-farm sectors of India.
- While in 2020-21, the gig workforce constituted 2.6% of the non-agricultural workforce or 1.5% of the total workforce in India, by 2029-30, gig workers are expected to form 6.7% of the non-agricultural workforce or 4.1% of the total livelihood workforce in India
- When you’re working in the gig economy you can decide the jobs you’re applying to or taking, which platforms you’re joining, where you’re working from and under what schedule.
- Companies aren’t hiring someone for a long period and with all the privileges of a fixed-term employee (like paid vacations or health insurance, as is the case in some countries). This allows them not only to save money but also to get the best person on board for a short time.
- Furthermore, businesses also save time with long recruitment and selection processes. This allows them to be more agile and better respond to the market’s unpredictabilities.
- Thanks to firms that are based on gig workers, transactions costs for consumers are lower, all types of products are delivered everywhere, almost at any time, and the idea of convenience is now at a whole new level.
- Jobs from the gig economy are an extraordinary opportunity to lift up the unemployed and thus addresses the unemployment problem in an economy.
- At the same time, they allow people to specialize in what they do best, making them feel more engaged and ultimately raising their productivity.
- So from a point of view of artists or creatives starting a career, it’s a good way to making a living while dedicating time to make their art and build up a career.
The benefits of the gig economy are decentralized and affect different actors, from workers to businesses and consumers. However, when it comes to its disadvantages, they rely mostly on workers.
- Traditional jobs often provide employees with a lot of protections and perks like bonuses, paid holidays, insurance, travel and housing allowances, and provident fund savings
- However, independent workers don’t benefit from any of this as they’re just performing temporary works. They need to handle their own retirement plan and health insurance and use their own car and fuel.
- Moreover, paid vacations or sick days are over. Independent workers are paid per assignment and they’ll only get all their money once the job is over and delivered. So if they’re not working, they’re not being paid.
- Low wages, bait-and-switch incentives, Opaque payout calculations, commission deductions, and constant surveillance on aggregator platforms have all contributed to massive demonstrations by gig workers against the aggregators’ service conditions.
- A worker must be sufficiently skilled. Unless a person is exceptionally gifted, his bargaining power is bound to be limited.
- A gig-economy employee will have to upgrade his skills on his own at his own cost While companies routinely invest in training employees.
- Lack of possibility for upward mobility within an organisation has triggered protests from workers at companies like Swiggy, Zomato, Ola, Uber etc.
- It is largely unregulated which results in less job security and nominal benefits. In another word, it is an extension of India’s informal or unorganised labour, which is yet to be reformed by the government
- India has protected workers through heavy-handed industrial regulation and labour laws, which suit the factory floor. They are irrelevant, insufficient, and ineffective in addressing disputes that originate on these platforms.
- There are already far more potential online independent workers than there are jobs, and the demand-supply mismatch will only worsen over time, lowering wages.
- A large component of delivery platform’s cost is gig worker fees. An analysis of the grievances suggests that many are linked to the way gig work is assigned, performed and rewarded – all of which are decided by Machine Learning (ML) algorithms that try to cut costs & maximise profits.
- Being an independent worker, depending on the type of job, can be very lonely. This is especially true for designers, developers or copywriters working on their laptop from home. They can be spending a whole week working at home without real-life interactions.
- Companies that operate by the gig economy’s principles are posing a big challenge to the previously established businesses. For instance, Airbnb is putting the hotel’s industry on notice, and the same happens with Uber and the taxi industry.
- Traditional players are lobbying with government bodies to bring in level playing legislations so as to protect the interest of existing players.
- Given the electoral weight that these traditional players command, government regulations may lead to additional conditions on such gig principled based businesses. Such conditions can increase the costs and blunt their competitive edge.
- According to the Code on Wages, 2019, a universal minimum wage and floor wage should be provided to all organised and unorganised sectors, including gig workers.
- The SS Code also defines an unorganised sector worker as one who works in the unorganised sector and is not covered by the provisions of the Industrial Relations Act, 1947. Consequently, both gig workers and platform workers are also covered by the definition of unorganised sector worker.
- The definitions of gig worker, platform worker and unorganised sector worker are overlapping and confusing.
- As the Code envisions different social security schemes for each of these categories of workers, there is a lack of clarity about what scheme will apply to whom, potentially leading to challenges at the stage of implementation.
- SS Code adopts a welfare-based approach towards social security and places an obligation on the union and state governments, rather than rights-based approach.
- A Platform India initiative, built on the pillars of accelerating platformization by simplification and handholding, funding support and incentives, skill development, and social financial inclusion, like the immensely successful Startup India initiative, may be introduced.
- Access to institutional credit may be enhanced through financial products specifically designed for platform workers and those interested to set-up their own platforms.
- Venture capital funding, grants and loans from banks and other funding agencies should be provided to platform businesses of all sizes at the pre-revenue and early-revenue stages.
- Platform-led models of skilling and job creation need to be promoted for the gig and platform sector.
- Platforms can collaborate with the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, and the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) to nurture skilled workers and micro-entrepreneurship
- Platform businesses can undertake partnerships with Civil Society Organizations (CSOs) to enable different sections of workers such as women workers and PwDs to take up employment opportunities in the platform sector through skill development, access to finance and assets.
- Women led-platforms or platforms that encourage recruitment of women employees and those with disabilities should be incentivized.
- On the lines of measures introduced to mitigate the challenges posed by the Covid-19 pandemic by platforms businesses, measures for paid sick leave, health insurance may be adopted by platforms for all the workers they engage, round the year.
- Undertake a separate enumeration exercise to estimate the size of the gig economy, and identify the characteristic features of gig workers
- During enumerations (census, PLFS, NSS or otherwise), capture the different occupations an individual might be performing, including whether or not they are a gig worker.
- During enumerations, collect information to identify gig workers. This could include questions on the nature of contract between worker and job creator, use of technology in work, etc
- R ecognise the varied nature of platform work to design equitable schemes.
- A llow augmentation of social security through innovative financing mechanisms.
- I ncorporate, while designing schemes, the specific interests of platforms, factoring the impact on job creation, platform businesses and workers.
- S upport workers to subscribe to government schemes and welfare programmes through widespread awareness campaigns.
- E nsure benefits are readily accessible to workers
Mains Practice Question – The rapidly burgeoning gig workforce is ushering in a new economic revolution globally. Critically analyse.
Note: Write answers to this question in the comment section.
For a dedicated peer group, Motivation & Quick updates, Join our official telegram channel – https://t.me/IASbabaOfficialAccount
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Explainer Videos, Strategy Sessions, Toppers Talks & many more…

- Gig Economy UPSC , What is Gig Economy?
Related Posts :
Upsc quiz – 2022 : iasbaba’s daily current affairs quiz 15th july 2022, global gender gap index.
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –9th May 2024
- [DAY 58] 60 DAY RAPID REVISION (RaRe) SERIES for UPSC Prelims 2024 – ECONOMY, CURRENT AFFAIRS & CSAT TEST SERIES!
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 9th May 2024
- [RESULTS] UPSC Indian Forest Service (IFoS) Final Results 2023 Declared
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –8th May 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 8th May 2024
- [DAY 57] 60 DAY RAPID REVISION (RaRe) SERIES for UPSC Prelims 2024 – ECONOMY, CURRENT AFFAIRS & CSAT TEST SERIES!
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –7th May 2024
- [DAY 56] 60 DAY RAPID REVISION (RaRe) SERIES for UPSC Prelims 2024 – GEOGRAPHY, CURRENT AFFAIRS & CSAT TEST SERIES!
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 7th May 2024
Don’t lose out on any important Post and Update. Learn everyday with Experts!!
Email Address
Search now.....
Sign up to receive regular updates.
Sign Up Now !

- UPSC IAS Exam Pattern
- UPSC IAS Prelims
- UPSC IAS Mains
- UPSC IAS Interview
- UPSC IAS Optionals
- UPSC Notification
- UPSC Eligibility Criteria
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Results
- UPSC Cut-Off
- UPSC Calendar
- Documents Required for UPSC IAS Exam
- UPSC IAS Prelims Syllabus
- General Studies 1
- General Studies 2
- General Studies 3
- General Studies 4
- UPSC IAS Interview Syllabus
- UPSC IAS Optional Syllabus

Gig Workers and the Gig Economy – UPSC Economy Notes
The rise of gig workers and the gig economy marks a fundamental shift in the traditional employment landscape, redefining the way individuals engage in work and businesses operate. Gig workers, often referred to as independent contractors, freelancers, or on-demand workers, participate in short-term, flexible arrangements to provide services or complete tasks for various clients or platforms. This phenomenon has gained momentum with the proliferation of digital platforms and technological advancements, offering individuals autonomy over their schedules and diverse opportunities to generate income. As the gig economy continues to expand, it presents both opportunities and challenges, reshaping labor dynamics, socioeconomic structures, and policy frameworks globally. Understanding the complexities and implications of this evolving paradigm is essential in navigating its impact on workers, businesses, and society at large.
Table of Contents
Gig Economy:
- Definition: The gig economy is a free and global market where companies and independent workers (contractors) establish short-term and on-demand professional relationships that are both flexible and skill-based.
Gig Worker:
- Definition: Gig workers are individuals engaged “on demand” by companies for short-term contracts or freelance work, rather than full-time positions. Examples include Zomato delivery personnel and Uber drivers.
Data and Facts:
- The gig workforce has seen a 13% increase in overall hiring intent by employment type.
- NITI Aayog estimates that there are currently over 7.5 million gig workers in India, projected to reach 25 million by 2030.
- Approximately 60% of new employment is attributed to the gig economy.
- India’s Gig Economy is anticipated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17%, reaching $455 billion by 2023 (ASSOCHAM).
Reasons for Gig Worker Preference:
- Gig Economy provides flexible work hours without attendance restrictions.
- Opportunities for low-skilled workers due to project-based or less time-consuming jobs.
- Students can acquire skills and experience before entering full-time employment.
- Employment opportunities for both young and retired individuals.
- Women can earn independently and take career breaks without sacrificing employment.
Challenges Associated with Gig Economy:
- Gig workers may have weakened bargaining power.
- Some gig workers may face challenges related to wages falling below the minimum wage.
- Concerns about hampering inclusive growth.
- Limited access to finance, technology, and markets.
- Low labor productivity may be a challenge.
- Gig workers may lack safety nets and benefits, making them vulnerable.
- Gig economy dynamics may worsen poverty conditions.
- Certain marginalized groups may be disproportionately affected.
- Challenges in obtaining credible data for targeted government schemes related to gig workers.
Conclusion:
- While the gig economy offers flexibility and opportunities, addressing associated challenges is crucial to ensure fair labor practices, inclusivity, and social security for gig workers.

1. What exactly is the gig economy?
Answer: The gig economy refers to a labor market characterized by short-term, freelance, or temporary work engagements, often facilitated by online platforms or apps. Individuals, known as gig workers, perform tasks or projects on a flexible basis, rather than being employed full-time by a single employer.
2. Who are gig workers?
Answer: Gig workers are independent contractors, freelancers, or temporary workers who provide services or complete tasks on a per-project or gig basis. They encompass a diverse range of professions, including ride-sharing drivers, freelance writers, graphic designers, and delivery couriers.
3. What are the benefits of gig work for workers?
Answer: Gig work offers flexibility, allowing individuals to choose when, where, and how much they work. It can provide opportunities for supplemental income, accommodate varied schedules, and enable workers to pursue multiple income streams. Additionally, gig work can offer autonomy and independence, allowing individuals to control their workload and work environment.
4. What are the challenges faced by gig workers?
Answer: Gig workers often lack traditional employment benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. They may face income instability due to fluctuating demand for their services and variable pay rates. Additionally, gig workers may experience challenges related to job security, lack of workplace protections, and difficulty accessing social safety nets.
5. How is the gig economy evolving in response to regulatory and societal changes?
Answer: Regulatory scrutiny and public discourse surrounding the gig economy have prompted discussions about labor rights, worker classification, and social protections for gig workers. Some jurisdictions have implemented or proposed regulations to provide gig workers with benefits such as minimum wage guarantees, sick leave, and unemployment insurance. Meanwhile, technological advancements continue to shape the gig economy, influencing the types of services offered, the platforms used, and the nature of gig work itself.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here
- Currency Depreciation and its effects – UPSC Economy Notes
- National Highways Development Project (NHDP) – UPSC Economy Notes
- National Income – Economy for UPSC
- Official Unemployment Estimates – UPSC Economy Notes
Edukemy Team
Payment banks in india: an overview – upsc economy notes, sdrs as global reserve currency – upsc economy notes, infrastructure debt funds (idf) – upsc economy notes, internationalization of the rupee – upsc economy notes, consumer price index + new cpi series 2015 – upsc..., gst and federalism – upsc economy notes, types of unemployment – upsc economy notes, non-tariff barriers (ntbs) – upsc economy notes, foreign direct investment (fdi) – upsc economy notes, priority sector lending – upsc economy notes, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies Got it
Keep me signed in until I sign out
Forgot your password?
A new password will be emailed to you.
Have received a new password? Login here


Home > Daily-current-affairs
Daily-current-affairs / 27 Dec 2021
Gig Economy : Daily Current Affairs

Relevance: GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Key phrases: Gig worker, temporary, freelancing, social security code 2019, GRM
Why in News?
- The surge in demand for gig workers, particularly in the shared services and logistics segments, in the aftermath of the pandemic led to mushrooming of job discovery platforms specifically targeting this area.
What is Gig Economy?
- As per the World Economic Forum, gig economy is defined by its focus on workforce participation and income generation via “gigs”, single projects or tasks for which a worker is hired.
- Gig economy” refers to a general workforce environment in which short-term engagements, temporary contracts, and independent contracting is commonplace. It’s also referred to as the “freelancer economy,” “agile workforce,” “sharing economy,” or “independent workforce.”
- The gig economy is made up of three main components:
Independent workers paid by the gig (i.e., a task or a project) as opposed to those workers who receive a salary or hourly wage. Consumers who need a specific service, for example, a ride to their next destination, or a particular item delivered; and Companies that connect the worker to the consumer in a direct manner, including app-based technology platforms.
Gig Economy in India
- The COVID-19 pandemic has altered the way businesses operate as many companies have realised the advantages of remote working on stressed cash flows. The pandemic-induced remote working has blurred the age-old scepticism over the efficiency and dependability of contractual or part-time employees, with companies increasingly looking to hire gig workers.
- As per a report by ASSOCHAM, India’s gig sector is expected to increase to US$455 billion at a CAGR of 17% by 2024 and has the potential to expand at least 2x the pre-pandemic estimates. In another estimate, India is likely to have 350 million gig jobs by 2025, presenting a huge opportunity for job seekers to capitalise and adapt to the changing work dynamics.
- At present, India has a pool of ~15 million freelance workers staffed in projects across IT, HR and designing. In addition, India’s workforce is growing by ~4 million people annually. And as most of them are young millennials, they are showing an increasing preference for gig contracts. This trend is expected to significantly impact gig economy in the near future.
Key Drivers for Gig Economy:
- Unconventional work approach by millennials: Hectic lifestyles of employees in private sectors have created a negative perception of full-time employment among millennials. Factors such as growth opportunities, flexibility, better work-life balance and option to not acquire a college degree are encouraging millennials to opt for freelancing opportunities as opposed to corporate work culture.
- Emergence of a start-up culture: The start-up ecosystem in India has been developing rapidly. For start-ups, hiring full-time employees leads to high fixed costs and therefore, contractual freelancers are hired for non-core activities. Start-ups are also looking at hiring skilled technology freelancers (on a per project basis) in areas such as engineering, product, data science and ML to bolster their tech platforms.
- MNCs are hiring contractual employees: MNCs are adopting flexi-hiring options, especially for niche projects, to reduce operational expenses after the pandemic. This trend is significantly contributing to the gig culture in India.
- Rise in freelancing platforms: Rise in freelancing platforms has also aided in the development of the gig economy. Many home-grown platforms such as Upwork, Truelancer and Guru provide access to high-skilled freelancers. The number of freelancing platforms has significantly increased—from 80 in 2009 to 330 in 2021. These platforms boast of a clientele comprising not only start-ups, but also Fortune 500 companies.
- Business Models: Gig employees work on various compensation models such as fixed-fee (decided during contract initiation), time & effort, actual unit of work delivered and quality of outcome. The fixed-fee model is the most prevalent; however, time & effort model comes a close second.
- Impact of Covid-19: According to the survey, India stands to lose ~135 million jobs because of the pandemic and this is likely to push the full-time workforce towards the gig economy. Moreover, many laid-off employees are focusing on developing skills to avail freelance job opportunities and become a part of this burgeoning economy.
Challenges faced by gig-workers in India:
- The main issue with the gig economy workers in India is no clear employment relationship. Most of the time, it is the ambiguity around the rights of workers and the responsibilities of platforms that allows businesses to treat their gig workers as employees in terms of the control they exert upon them, but without any employee entitlements like insurance, medical benefits, employees’ provident fund, bonus or gratuity, etc.
- No employment stability and heavy workload
- Low payment and Wages: According to gig workers in India, the low payment often pushes them to work longer than 8 hours and work on all days of the week.
- There is no proper Grievance Redressal Mechanism available to gig workers to solve their genuine problems.
Code on Social Security 2019
- To further aid these gig workers, the government passed the ‘Code on Social Security’ , which will provide workers with life and disability cover, accidental insurance, health & maternity benefits old age protection and others.
- Under this code, the central and state governments will primarily fund social security measures, with a nominal contribution (1-2% of their annual turnover) by the aggregator. Also, the contribution made by the aggregator/platform will not exceed 5% of the amount payable to gig and platform workers.
- In addition, the code proposed to establish a ‘National Social Security Board’, which will supervise and formulate schemes for the well-being of gig and platform workers.
Way Forward:
- The gig economy has been on the rise and is expected to beat the pre-pandemic estimates due the expected influx of gig workers transitioning from full-time employment.
- While the government has taken the initial steps to ensure social security of gig workers, the ‘Code on Social Security’ needs to be fine-tuned. For example, the option to deduct 5% from the amount payable to gig workers should be voluntary (based upon income brackets). As most gig workers, especially delivery executives and drivers, are already facing declining income levels due to COVID-19, such deductions would not be amenable.
- Further, all platform workers should be offered mandatory coverage under the Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana . This can be facilitated through the employer companies and will ensure employee protection; thus, guaranteeing a sustainable gig economy.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Question:
Q. The pandemic-led boom in demand for gig workers, who is the gig worker? What are the challenges faced by gig-workers in India? Do gig workers have any social security in India? Illustrate.
Click Here for Daily Current Affairs MCQ Quiz
For Any Query Contact us
Recent Article

Get in Touch
Social links.
Connect with social account.
Test Series

635, Ground Floor, Main Road, Dr. Mukherjee Nagar, Delhi 110009
Dhyeya IAS © 2024 | All rights reserved | Made by WNT / Sitemap.xml

Enquiry Now

UPSC SUPER SIMPLIFIED
Your Goals. Our Mission.
Gig Economy

The gig economy refers to a labor market characterized by the prevalence of short-term contracts or freelance work, as opposed to permanent jobs. Gig economy workers are typically engaged as independent contractors and are not entitled to the benefits that traditional employees receive.
Examples of Gig Economy
1. Ride-Hailing: Companies like Uber and Ola provide ride-hailing services which allow individuals to sign up to be drivers and transport passengers.
2. Delivery Services: Companies like Amazon allow individuals to sign up to be delivery drivers and deliver packages.
3. Virtual Assistants: Companies like Fancy Hands allow individuals to sign up to provide virtual assistance to businesses.
4. Freelance Writing: Companies like Textbroker and Upwork allow individuals to sign up to provide freelance writing services.
5. House Cleaning: Companies like Urban clap allow individuals to sign up to provide house cleaning services.
India and the gig economy
India has been one of the leading countries in the world to embrace the gig economy. The gig economy in India has seen tremendous growth in the past few years, with more and more people opting for freelance work and flexible working hours. India has seen a surge in the number of freelancers and gig workers, with more than 6 million people employed in gig jobs in 2019.
The gig economy has opened new avenues for self-employment and enabled people to take control of their own careers and financial destinies. From software developers to content writers, the gig economy in India has become an attractive alternative for many to traditional employment. The government of India has also introduced various reforms to promote the gig economy and has even set up a dedicated department for the gig economy. With the continuing growth of the gig economy in India, it is likely to become an even more important part of the Indian economy in the future.
Benefits of the Gig Economy
1. Flexibility: The gig economy offers individuals the ability to work when they want and where they want. This allows workers to set their own hours, take on as much or as little work as they want, and manage their own schedules.
2. Variety: The gig economy provides workers with a wide variety of opportunities to choose from. This allows workers to explore different types of work and to develop a range of skills.
3. Lower commitment: Gig economy jobs are often short-term or project-based, meaning that workers have lower commitment levels and can more easily switch between jobs.
4. Access to new markets: The gig economy has opened up new markets for workers, allowing them to access jobs that would have previously been unavailable to them. This can include jobs in different countries or even jobs that require special skills or qualifications.
5. Increased income potential: The gig economy provides workers with the opportunity to make more money per hour than they would in a traditional job. This is because workers can set their own rates and work as much as they want.
Challenges of the Gig Economy
1. Lack of job security: The gig economy does not provide workers with the same level of job security as a traditional job. This means that workers may need to find alternative sources of income if their gigs dry up.
2. Uncertainty: The gig economy can be unpredictable, and workers may not always know where their next job is coming from or how much money they will make from it.
3. Lack of benefits: Gig economy jobs do not usually offer benefits such as health insurance or paid time off.
4. Tax implications: The gig economy can create tax implications for workers, who may need to pay more in taxes than they would in a traditional job.
5. Limited job opportunities: The gig economy is still in its infancy, and there may not be enough job opportunities available in certain markets.
The gig economy is an ever-growing labor market that provides individuals with an opportunity to work flexible hours and earn money on their own terms. While there are many benefits to the gig economy, such as increased income potential and flexibility, there are also some challenges, such as a lack of job security and tax implications. It is important for individuals to be aware of the pros and cons of the gig economy before entering into it.
1 thought on “Gig Economy”
History of gig economy and information related to gig economy data,the publisher and data also supports this article otherwise it’s nice Thanks to publisher
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- Exam Details
- Current Affairs

- State PSC Exams
Gig Economy Meaning in India & Platforms – What is? | UPSC

Behind every exam, there is a lot of struggle and hard work involved. Further, when we talk about the IAS exam, the first that comes to our mind is the syllabus. Surely, it is one of the toughest exams, and one needs to invest time and effort to clear the exam. To assist you with the exam, we cover all the essential topics for the exam. Therefore, in this article, you will get all information related to the Gig Economy in India, Gig Economy platforms, meaning, and other essential details. So, read the complete article and learn more about the Gig Economy for the IAS exam preparations.
Impact – Gig Economy

Introduction
To begin with, the Gig economy is a free market in which temporary positions are common, and companies contract with independent workers for short period engagements. According to the Boston Consulting Group, India’s gig workforce comprises 15 million workers employed across industries. As we have mentioned, this topic is essential to understand for the IAS main exam. In addition, it will help you to score for the GS papers. Below understand all the things like Gig Economy meaning and other related things.
Gig Economy Meaning
As mentioned earlier, the Gig economy is a free market system. Further, according to of Boston Consulting Group. It says India’s gig workforce comprises 15 million workers employed across industries such as software, shared services, and professional services. Besides, it is estimated that 56% of new employment in India is being generated by Gig economy companies, consists both the blue-collar and white-collar workforce.
Get the complete information of the UPSC and the IAS exam. Read More . Before applying for the IAS exam, one must know all the things related to it. So go through the links and learn about the vital things.
Why it is important?
Let us understand why Gig Economy is essential from the below points.
- In the first place, with the digital age there is no need for workers sit at one place as the job can be done from anywhere. Therefore, employers can select the best talent available for a project without location constraint.
- With the presentbgenerations you will find different attitudes to careers. Further, they know which type of work is suitable for them rather than having careers that may not satisfy their urgers.
- Also, all kind of jobs offers you with the job training.

Requirements
Further, the code mandates compulsory registration of both gig and platform workers on an online portal. It is essential to register to get all benefits. Below we have mentioned the essential points on the same.
- One must be between 16 and 60 years of age
- Further, one must worked for not less than ninety days during the preceding twelve years.
- Further, Gig worker or platform worker must make an application for registration along with the documents.
- Accidental insurance
- Life and disability cover
- Old age protection
- Health and maternity benefits
- Further, platforms can claim the benefits that are provided under Social Security Code but cannot claim labour rights.
Pros and Cons
Talking about the pros, it offers workers flexibility, and one can choose to work for various organizations simultaneously. Further, it provides an opportunity for workers to understand their skills in an area. Besides, freelancers writers can try part-time jobs.

Further, with cons, workers may suffer from inconsistent pay and a lack of stability in job tenure. Even though they get the flexibility of work, they may find difficulty with work hours, pricing, etc. Also, they are denied the benefits offered to their regular workers, like health insurance, paid leaves, etc.
- In the first place, there is a need for skilled workers. Further, various companies invest money in training employees. A gig woker will have to upgrade his skills on his own at his own cost.
- Further, the Gig Economy is unregulated in nature. It means workers have little job security and few benefits.
- Besides, there is a mismatch of demand and supply. This may get worse over time.
Issues Related
Further, there is no guarantee of benefits. Besides, platforms workers are now eligible for maternity benefits, life and disability cover, old age protection, employment injury benefits, etc. Besides, there is no fixed responsibility as the code states that provisions of basic welfare measures.
Importance of Gig Platform Workers
The Gig Economy is the new concept in India, and gig and platform workers have become a significant part of the economy.
The covid-19 gave realization that gig and the platform workers play a major role as delivery drivers and agents. Further, these workers helped in various platforms during the pandemic. They helped all get the necessities to reach people at their homes. Besides, with increasing urbanization, this sector has high growth potential.
We all are aware of the covid-19 impact all over the world. Due to this, businesses got affected, and people were looking for an income source to sustain themselves. Further, the number of Gig workers has grown over the years. It has shown growth in internet companies like Zomato, Swiggy, Uber, Ola, Urban Company, etc. However, it also created new business models to cater to the growing demand requirements. Further, Gig workers provide for a universal minimum wage.
Collar Jobs
- Blue Collar Worker – He belongs to the working class, who performs manual labor and earns an hourly wage.
- White Collar Worker – He is a salaried professional, referring to general office workers and management.
- Gold Collar Worker – these are the workers who are highly skilled and knowledgeable people. Example – Lawyers, doctors, research, etc.
- Grey Collar Worker is the balance of employed people not classified as white or blue-collar. Examples – Police officers, health care professionals, Security Guards, etc.
- Green Collar Workers – these are the people who work in the environmental sectors of the economy. Examples – people who work for solar panels, Greenpeace, World Wide Fund for nature, etc.
- Pink Collar Worker – these are the people who are often women’s work and are often low-paid.
- Scarlet Collar Worker – these people work in the pornography industry.
- Red Collar Worker – these are government workers.
- Open Collar Worker – these are the workers who work from home, especially via the internet.
As a whole, we can say that there is a need for more clarity. To ensure social security, measures are provided to workers. Further, there is also a need for socio-legal acknowledgment.
Conclusion – Gig Economy
The above article gives you details of the Gig Economy, meaning, platforms in India. Further, we have covered all the requirements, challenges, effects, and issues related to India’s Gig economy. Besides, it is one of the vital concepts for the UPSC exam. When we talk about the IAS exam, many things are to be taken care of. Further, in the IAS exam, you will find three-round. In the IAS prelims, there are two papers, and in the IAS main exam. Finally, there will be an interview round. One needs to go through all stages of the IAS exam. Then, to get the best results in the exam, one must study from the standard books. We have added all details on the IAS exam. You can check here for more information. Click Here
Also, find other IAS exam study materials here . To know about the question pattern and other details, one must go through the previous year’s question papers. It will help you understand questions, patterns, marks, trending topics, and other details. Also, you go through some essential exam tips that will help you score good marks in the exam. Finally, try to refer to give mock tests, and it will help you understand your skills well. One needs to visit the official site to get the latest updates on the exam. Good Luck with your exams. It is normal to get tense, but instead, try to make the proper plan and prepare for the exam.

FAQs – Gig Economy
The general workforce environment includes short-term employment, contractual jobs, and independent contractors.
Some of the best jobs are 1. Delivery Driver. 2. Writer/Editor. 3. Accounting 4. Software Developer/IT Consultant. 5. Health and Safety Worker.
Examples of the Gig economy are ride-hailing, food delivery, and holiday rental apps.
Editor’s Note | Gig Economy
After reading the above article, you will get details of the Gig Economy meaning, platforms in India, and Gig Economy Platforms. Further, it is a must for the IAS aspirants to know about these concepts as a part of the IAS exam syllabus. We have covered the necessary details to help you with your exam preparations. As we mention in our article, try to maintain a separate book to write all the essential points. Then, you can study the same during the exam. The above article helps you by providing the necessary details and revising concepts. Revision is the essential thing. You will also find the vital links that will help you with the IAS exam preparations. We wish you Good Luck with the exams.
Suhas Yathiraj Ly Lalinakere – Paralympics | IAS with Disability
Attorney general of india – present or current & first – who appoints, related posts.

- G7 Countries List or Members | G7 Summit & Headquarters

- Make in India – Made in India Logo | Project & Scheme

- Nitrogen Cycle – What is? – Explain | Diagram & Drawing

- World War 2 – Second (2nd) World War – II | Date

- Kashi Vishwanath Temple or Mandir or Dham | Banaras Corridor

Attorney General of India - Present or Current & First - Who Appoints?
Recent posts.
- Best IAS Coaching in Mumbai – Top 5 UPSC Classes in Mumbai
- President of India – Rashtrapati – Who is? & Current Salary
Browse by Category
- Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission (APPSC)
- Assam Public Service Commission (APSC)
- Bihar Public Service Commission (BPSC)
- Chhattisgarh Public Service Commission (CGPSC)
- Cut Off Marks
- Economics Books
- Editorial Articles
- Eligibility Criteria
- Essay Writing
- Ethics Books
- Exam Pattern
- Geography Books
- Gujarat Public Service Commission (GPSC)
- Haryana Public Service Commission (HPSC)
- Himachal Pradesh Public Service Commission (HPPSC)
- Hindi Medium
- History Books
- IAS & IPS Officers
- IAS Exam (CSE)
- Indian Polity
- Jammu and Kashmir Public Service Commission (JKPSC)
- Jharkhand Public Service Commission (JPSC)
- Karnataka Public Service Commission (KPSC)
- Kerala Public Service Commission (KPSC)
- Kurukshetra Magazine
- Madhya Pradesh Public Service Commission (MPPSC)
- Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC)
- Mains General Studies
- Mains Syllabus
- Mathematics
- NCERT Books
- Notification
- Odisha Public Service Commission (OPSC)
- Offline Coaching
- Online Application
- Online Coaching
- Optional Subjects
- Prelims Books
- Prelims Exam
- Prelims General Studies
- Prelims Syllabus
- Press Information Bureau (PIB)
- Public Administration
- Punjab Public Service Commission (PPSC)
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC)
- State Public Service Commission
- Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC)
- The Indian Express
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC CSE Subjects
- UPSC Current Affairs
- UPSC Exam Details
- UPSC Interview Process
- UPSC Question Papers
- UPSC Strategy
- UPSC Study Material
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Test Series
- UPSC Training
- Uttar Pradesh Public Service Commission (UPPSC)
- Uttarakhand Public Service Commission (UKPSC)
- West Bengal Public Service Commission (WBPSC)
- Yojana Magazine
Browse by Tags
© 2021 IAS BABU JI - One-Stop Solution for UPSC Exam Aspirants
Are you sure want to unlock this post?
Are you sure want to cancel subscription.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Labour market reform
Self-employment, the gig economy and the National Minimum Wage
This is a paper on understanding the similarities between gig work and low-paid work, and whether NLW impacts what form of work individuals decide to take up.
PDF , 194 KB , 11 pages
The short paper stands apart from the main stream of the LPC’s work on low-paid employment, but offers insights into different kinds of work. This note draws principally on conversations held with individuals working in the following sectors: food delivery, private hire, parcel delivery, nannying and yoga teaching. We found it a useful exercise to speak to these individuals, and we hope this report will be of interest to other parties we engage with.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Our Centers Delhi Bhubaneswar Lucknow
- UPSC Mains Previous Year Questions
- Examine the role of ‘Gig Economy’ in the proce
Examine the role of ‘Gig Economy’ in the process of empowerment of women in India. (150 Words)
- Subject Indian Society
- Define gig economy in brief. ( 25 words)
- Discuss how gig economy is affecting process of women empowerment in India. ( 100 words)
- Conclude your answer. ( 25 words)

Verifying, please be patient.
Our Centers
DELHI (Karol Bagh)
GS SCORE, 1B, Second Floor, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Get directions on Google Maps
BHUBANESWAR (Jaydev Vihar)
GS SCORE, Plot No.2298, Jaydev Vihar Square, Near HCG Day Care, BBSR - 751013
LUCKNOW (Aliganj)
GS SCORE, 2nd Floor, B-33, Sangam Chauraha, Sector H, Aliganj, Lucknow, UP - 226024

© 2024 IAS SCORE. All Rights Reserved
Welcome to our secure login portal. Access your account with ease.

- Using Password
Not registered yet? register here!
Welcome to our secure register portal. For a brighter future, register now and unlock endless learning opportunities.
User Register
Already have an account? Login
Oops, forgot your password? Don't worry, we've got you covered. Reset it here
Lost your login details? No problem! forgot your password in just a few clicks
Forgot Password
Verify your mobile number, you have successfully logged in.
Join Us on WhatsApp

COMMENTS
The gig economy can serve up to 90 million jobs in the non-farm sectors in India with a potential to add 1.25% to the GDP over the "long term". As India moves towards its stated goal of becoming a USD 5 trillion economy by 2025, the gig economy will be a major building block in bridging the income and unemployment gap.
The gig economy in India: According to the NITI Aayog estimates, nearly 23.5 million workers will be engaged in the gig economy by 2029. Gig worker. Gig workers refer to workers outside of the traditional employer-employee relationship. There are two groups of gig workers - platform workers and non-platform workers. Platform workers.
A gig economy is a labor market that relies on independent contractors and freelancers rather than full-time permanent employees. The Code on Wages, 2019 provides for universal minimum wage and floor wage across organised and unorganised sectors, including gig workers. The Code on Social Security, 2020 recognises gig workers as a new ...
Gig Economy finds its relevance in the economy section, and descriptive-type questions on this topic can be asked in the GS Papers as well. Aspirants can go through the best UPSC Economics Books, and study material to prepare Gig Economy UPSC Notes for effective preparation. Gig Economy UPSC Questions
1. Lack of Benefits: Gig economy organizations typically do not provide benefits to their workers, as independent contractors are not considered full-fledged employees. 2. Personal Expenses: Workers in this setup may be responsible for covering their own expenses, such as gas used while driving for delivery platforms like Swiggy. 3.
According to the Report, the gig economy employed more than 7.5 million people in 2020-21. In the following eight years, the number of workers employed will increase to 23.5 million workers, accounting for 4.1% of all Indians' means of subsistence. The Report states that at the moment, medium-skilled occupations make up about 47% of gig ...
A gig economy is a free market system in which organisations hire independent workers for short-term assignments. During UPSC preparation, it is critical to learn how to take short notes, especially in the context of the Mains exam. Without intensive study and the preparation and regular revision of one's own notes, one cannot expect to ...
The report suggests that the non-platform-based gig economy in India can create up to 34 million new jobs by 2029-30. Economic Contribution: In 2020, ASSOCHAM projected that India's gig economy would rise at a compound annual growth rate of 17% to $455 billion by 2023. ... Download UPSC Mains 2023 Question Papers PDF ...
Paper 1: Unit-6 Work and Economic Life: Formal and Informal Organization of Work. Online Delivery Workers Data. A NITI Aayog study estimated that in 2020−21, 77 lakh workers were engaged in the gig economy. The gig workforce is expected to expand to 2.35 crore workers by 2029−30. In 2019−20, 10 lakh people were working as delivery executives.
A gig economy is a free market system in which organisations hire or contract workers for a short span of time. Simply put, the positions are temporary to meet the company's requirements by having short-term engagements. According to the Code on Social Security, 2020 (India), "A gig worker is a person who performs work or participates in ...
For economy-. As per a BCG report, the gig economy has the potential to serve up to 90 million jobs, add up to 1.25% to India's GDP. Enable India to harness demographic dividend, which is estimated to be around 65%, and average age of India is 28 years. Gig economy and female empowerment -. Flexi jobs make it easy for females to handle dual ...
Objective: To present comprehensive perspectives and recommendations on the gig-platform economy in India. The Indian gig workforce is expected to expand to 23.5 million workers by 2029-30, a near 200 per cent jump from 7.7 million now. Gig workers will form 4.1 per cent of the total workforce in India by FY30, from 1.5 per cent now.
NITI Aayog estimates that there are currently over 7.5 million gig workers in India, projected to reach 25 million by 2030. Approximately 60% of new employment is attributed to the gig economy. India's Gig Economy is anticipated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17%, reaching $455 billion by 2023 (ASSOCHAM).
A gig economy is a free market system in which temporary positions are common and organisations contract with independent workers for short-term engagements. According to a report by Boston Consulting Group, India's gig workforce comprises 15 million workers employed across industries such as software, shared services and professional services.
The gig economy has been on the rise and is expected to beat the pre-pandemic estimates due the expected influx of gig workers transitioning from full-time employment. While the government has taken the initial steps to ensure social security of gig workers, the 'Code on Social Security' needs to be fine-tuned.
Gig Economy. December 23, 2022 by Dr. Gaurav J. Sontake. The gig economy refers to a labor market characterized by the prevalence of short-term contracts or freelance work, as opposed to permanent jobs. Gig economy workers are typically engaged as independent contractors and are not entitled to the benefits that traditional employees receive.
— NITI Aayog pitched for incentives to draw more women into the gig economy in its report, 'India's Booming Gig and Platform Economy'. — In an attempt to increase the participation of women in the gig economy, the NITI Aayog has proposed fiscal incentives like tax breaks or startup grants for companies with about one-third of their ...
The Gig Economy is the new concept in India, and gig and platform workers have become a significant part of the economy. The covid-19 gave realization that gig and the platform workers play a major role as delivery drivers and agents. Further, these workers helped in various platforms during the pandemic.
This is a paper on understanding the similarities between gig work and low-paid work, and whether NLW impacts what form of work individuals decide to take up. Self-employment, the gig economy and ...
Examine the role of 'Gig Economy' in the process of empowerment of women in India. (150 Words) Subject. Indian Society. Year. 2021. Approach: Define gig economy in brief. ( 25 words) Discuss how gig economy is affecting process of women empowerment in India. ( 100 words) Conclude your answer. ( 25 words)
Explained The India-Nepal Border issue. Syllabus: Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance. Mains Examination: GS-II: India and its neighbourhood relations. What's the ongoing story- Nepal's cabinet last week decided to put a map on its Rs 100 currency note showing certain areas administered by India in Uttarakhand as part of its territory, provoking ...
Delhi has emerged as the top destination for migrant workers joining India's tech-enabled gig economy, pushing startup capital Bengaluru to a distant second spot.. A gig economy is a free market system in which temporary positions are common and organizations contract with independent workers for short-term engagements.; An estimated 56% of new employment in India is being generated by the ...