- Reconstructive Procedures

Transfeminine Bottom Surgery
Feminizing genital surgery.
The goal of transfeminine bottom surgery, or feminizing genital surgery, is to reconstruct the male genitalia into female genitalia.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Consultation
- Questions to Ask
- Risks and Safety
- Preparation
- Procedure Steps
- Glossary of Terms
- Choosing a Plastic Surgeon
What results should I expect after transfeminine bottom surgery?
The final results of transfeminine bottom surgery can help alleviate the feelings of gender dysphoria that some individuals may experience.
Over time, the new vagina will settle into position and the scar lines will improve, although they'll never disappear completely. There are trade-offs, but most transwomen feel these are small compared to the large improvement in their quality of life and the ability to look and feel like a woman.
The prostate gland is not removed from your body during the procedure. Although the amount of prostate growth as a result of estrogen therapy is small, the risk of developing prostate cancer is not zero. Careful monitoring of prostate health through exam is essential to your long-term health.
When you go home, if you experience shortness of breath, chest pains, or unusual heartbeats, seek medical attention immediately. Should any of these complications occur, you may require hospitalization and additional treatment.
The practice of medicine and surgery is not an exact science. Although good results are expected, there is no guarantee. In some situations, it may not be possible to achieve optimal results with a single surgical procedure and another surgery may be necessary.
Following your physician's instructions is key to the success of your surgery. It is important that the surgical incisions are not subjected to excessive force, abrasion, or motion during the time of healing. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for yourself.
Find Your Surgeon
On the blog.

Facial feminization surgery is a combination of procedures designed to soften the facial features and feminize the face. There are many procedures that are available to feminize the face.
- Boosted by positive cultural changes, gender affirmation procedures are soaring Kaitlin Clark
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons releases first-ever facial, breast/chest and genital data for gender affirmation procedures Kaitlin Clark
On The Vlog
Patient care center, before & after photos.
Video Gallery
3d animations, patient safety.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, male-to-female gender-affirming surgery: 20-year review of technique and surgical results.

- 1 Serviço de Urologia, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
- 2 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
- 3 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Purpose: Gender dysphoria (GD) is an incompatibility between biological sex and personal gender identity; individuals harbor an unalterable conviction that they were born in the wrong body, which causes personal suffering. In this context, surgery is imperative to achieve a successful gender transition and plays a key role in alleviating the associated psychological discomfort. In the current study, a retrospective cohort, we report the 20-years outcomes of the gender-affirming surgery performed at a single Brazilian university center, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications. During this period, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty.
Results: Results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18–61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The most commons minor postoperative complications were granulation tissue (20.5 percent) and introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and the major complications included urethral meatus stenosis (20.5 percent) and hematoma/excessive bleeding (8.9 percent). A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation. One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Conclusions: Findings confirm that it is a safety procedure, with a low incidence of serious complications. Otherwise, in our series, there were a high level of functionality of the neovagina, as well as subjective personal satisfaction.
Introduction
Transsexualism (ICD-10) or Gender Dysphoria (GD) (DSM-5) is characterized by intense and persistent cross-gender identification which influences several aspects of behavior ( 1 ). The terms describe a situation where an individual's gender identity differs from external sexual anatomy at birth ( 1 ). Gender identity-affirming care, for those who desire, can include hormone therapy and affirming surgeries, as well as other procedures such as hair removal or speech therapy ( 1 ).
Since 1998, the Gender Identity Program (PROTIG) of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA), Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil has provided public assistance to transsexual people, is the first one in Brazil and one of the pioneers in South America. Our program offers psychosocial support, health care, and guidance to families, and refers individuals for gender-affirming surgery (GAS) when indicated. To be eligible for this surgery, transsexual individuals must have been adherent to multidisciplinary follow-up for at least 2 years, have a minimum age of 21 years (required for surgical procedures of this nature), have a positive psychiatric or psychological report, and have a diagnosis of GD.
Gender-affirming surgery (GAS) is increasingly recognized as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity, with growing societal acceptance ( 2 ). At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty (PIV), with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. Studies have demonstrated that GAS for the management of GD can promote improvements in mental health and social relationships for these patients ( 2 – 5 ). It is therefore imperative to understand and establish best practice techniques for this patient population ( 2 ). Although there are several studies reporting the safety and efficacy of gender-affirming surgery by penile inversion vaginoplasty, we present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
Patients and Methods
Subjects and study setup.
This is a retrospective cohort study of Brazilian transgender women who underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty between January of 2000 and March of 2020 at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil. The study was approved by our institutional medical and research ethics committee.
At our institution, gender-affirming surgery is indicated for transgender women who are under assistance by our program for transsexual individuals. All transsexual women included in this study had at least 2 years of experience as a woman and met WPATH standards for GAS ( 1 ). Patients were submitted to biweekly group meetings and monthly individual therapy.
Between January of 2000 and March of 2020, a total of 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty. The surgical procedures were performed by two separate staff members, mostly assisted by residents. A retrospective chart review was conducted recording patient demographics, intraoperative and postoperative complications, reoperations, and secondary surgical procedures. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Hormonal Therapy
The goal of feminizing hormone therapy is the development of female secondary sex characteristics, and suppression/minimization of male secondary sex characteristics.
Our general therapy approach is to combine an estrogen with an androgen blocker. The usual estrogen is the oral preparation of estradiol (17-beta estradiol), starting at a dose of 2 mg/day until the maximum dosage of 8 mg/day. The preferred androgen blocker is spironolactone at a dose of 200 mg twice a day.
Operative Technique
At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty, with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. For more details, we have previously published our technique with a step-by-step procedure video ( 6 ). All individuals underwent intestinal cleansing the evening before the surgery. A first-generation cephalosporin was used as preoperative prophylaxis. The procedure was performed with the patient in a dorsal lithotomy position. A Foley catheter was placed for bladder catheterization. A inverted-V incision was made 4 cm above the anus and a flap was created. A neovaginal cavity was created between the prostate and the rectum with blunt dissection, in the Denonvilliers space, until the peritoneal fold, usually measuring 12 cm in extension and 6 cm in width. The incision was then extended vertically to expose the testicles and the spermatic cords, which were removed at the level of the external inguinal rings. A circumferential subcoronal incision was made ( Figure 1 ), the penis was de-gloved and a skin flap was created, with the de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening ( Figure 2 ). The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle were bluntly dissected away from the penile shaft ( Figure 3 ) as well as the urethra, which included a portion of the bulbospongious muscle ( Figure 4 ). The corpora cavernosa was excised up to their attachments at the symphysis pubis and ligated. The neoclitoris was shaped and positioned in the midline at the level of the symphysis pubis and sutured using interrupted 5-0 absorbable suture. The corpus spongiosum was reduced and the urethra was shortened, spatulated, and placed 1 cm below the neoclitoris in the midline and sutured using interrupted 4-0 absorbable suture. The penile skin flap was inverted and pulled into the neovaginal cavity to become its walls ( Figure 5 ). The excess of skin was then removed, and the subcutaneous tissue and the skin were closed using continuous 3-0 non-absorbable suture ( Figure 6 ). A neo mons pubis was created using a 0 absorbable suture between the skin and the pubic bone. The skin flap was fixed to the pubic bone using a 0 absorbable suture. A gauze impregnated with Vaseline and antibiotic ointment was left inside the neovagina, and a customized compressive bandage was applied ( Figure 7 —shows the final appearance after the completion of the procedures).
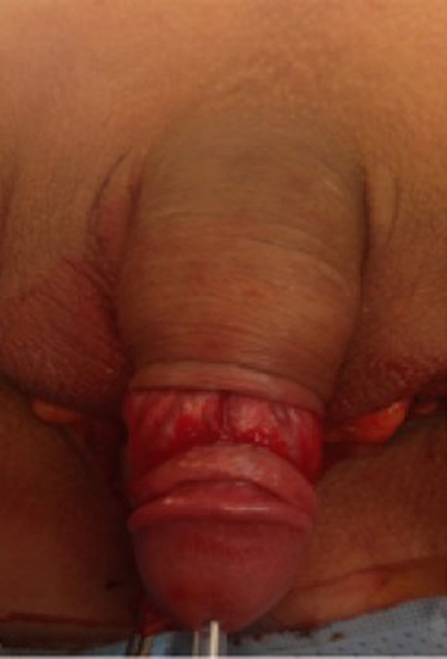
Figure 1 . The initial circumferential subcoronal incision.
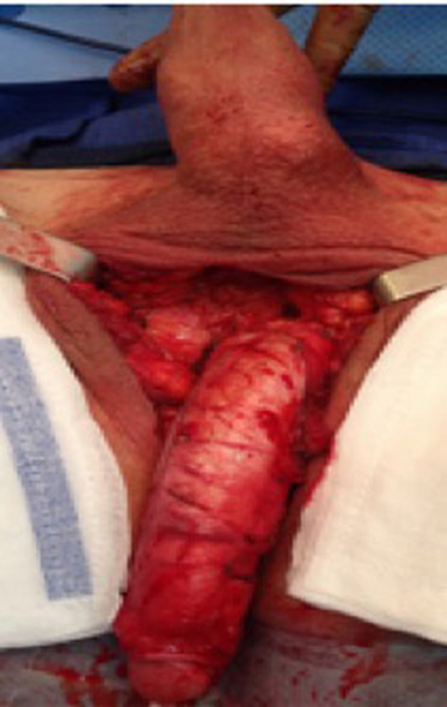
Figure 2 . The de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening.
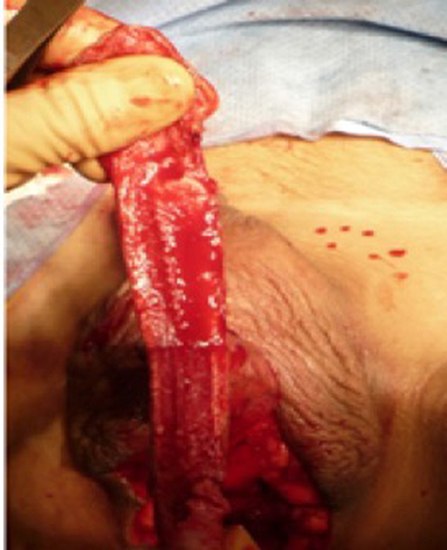
Figure 3 . The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle dissected away from the penile shaft.
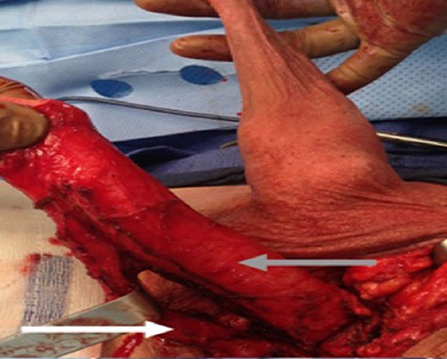
Figure 4 . The urethra dissected including a portion of the bulbospongious muscle. The grey arrow shows the penile shaft and the white arrow shows the dissected urethra.
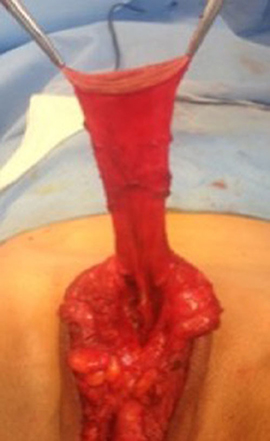
Figure 5 . The inverted penile skin flap.
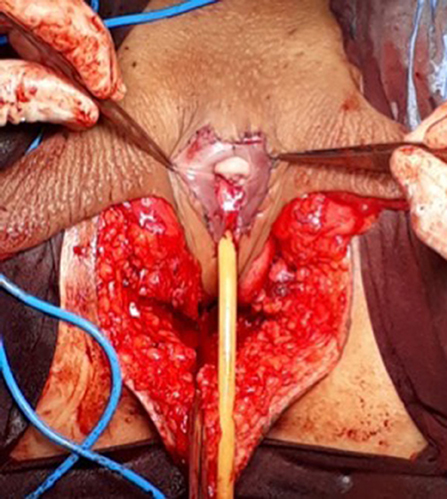
Figure 6 . The neoclitoris and the urethra sutured in the midline and the neovaginal cavity.
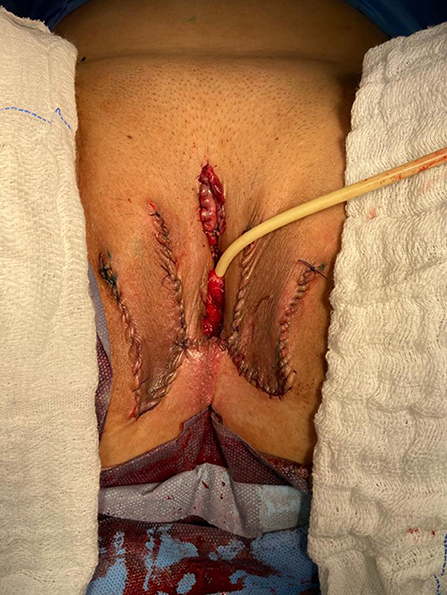
Figure 7 . The final appearance after the completion of the procedures.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
The patients were usually discharged within 2 days after surgery with the Foley catheter and vaginal gauze packing in place, which were removed after 7 days in an ambulatorial attendance.
Our vaginal dilation protocol starts seven days after surgery: a kit of 6 silicone dilators with progressive diameter (1.1–4 cm) and length (6.5–14.5 cm) is used; dilation is done progressively from the smallest dilator; each size should be kept in place for 5 min until the largest possible size, which is kept for 3 h during the day and during the night (sleep), if possible. The process is performed daily for the first 3 months and continued until the patient has regular sexual intercourse.
The follow-up visits were performed 7 days, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12 months after surgery ( Figure 8 ), and included physical examination and a quality-of-life questionnaire.
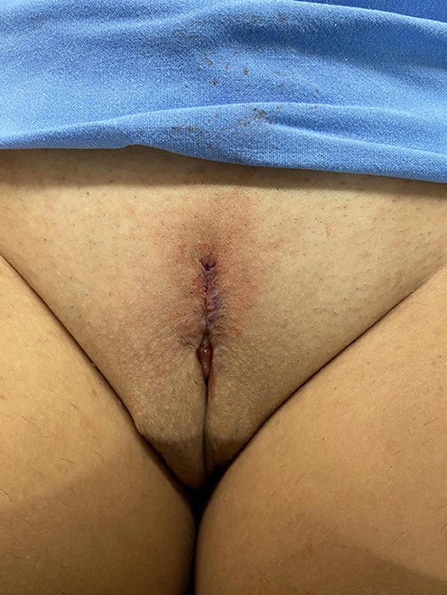
Figure 8 . Appearance after 1 month of the procedure.
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using Statistical Product and Service Solutions Version 18.0 (SPSS). Outcome measures were intra-operative and postoperative complications, re-operations. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the study outcomes. Mean values and standard deviations or median values and ranges are presented as continuous variables. Frequencies and percentages are reported for dichotomous and ordinal variables.
Patient Demographics
During the period of the study, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty, performed by two staff surgeons, mostly assisted by residents ( Table 1 ). The average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years). There was no significant increase or decrease in the ages of patients who underwent SRS over the study period (Fisher's exact test: P = 0.065; chi-square test: X 2 = 5.15; GL = 6; P = 0.525). The average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h). The average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The majority of patients were white (88.3 percent). The most prevalent patient comorbidities were history of tobacco use (15 percent), human immunodeficiency virus infection (13 percent) and hypertension (10.7 percent). Other comorbidities are listed in Table 1 .
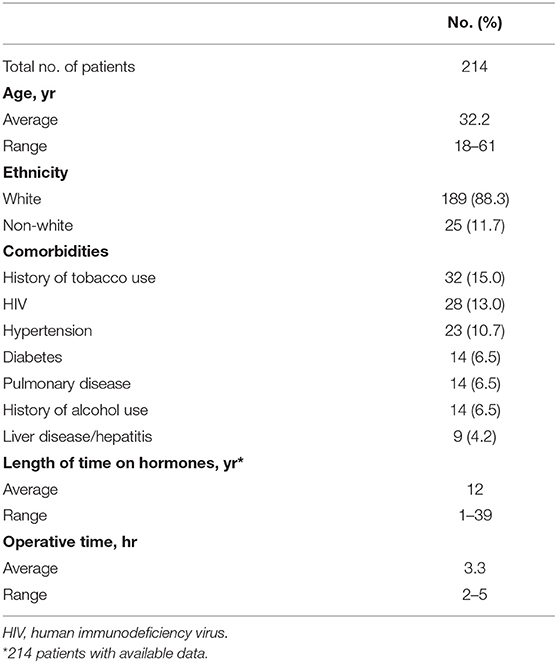
Table 1 . Patient demographics.
Multidisciplinary follow-up was comprised of 93.45% of patients following up with a urologist and 59.06% of patients continuing psychiatric follow-up, median follow-up time of 16 and 9.3 months after surgery, respectively.
Postoperative Results
The complications were classified according to the Clavien-Dindo score ( Table 2 ). The most common minor postoperative complications (Grade I) were granulation tissue (20.5 percent), introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and wound dehiscence (12.6 percent). The major complications (Grade III-IV) included urethral stenosis (20.5 percent), urethral fistula (1.9 percent), intraoperative rectal injury (1.9 percent), necrosis (primarily along the wound edges) (1.4 percent), and rectovaginal fistula (0.9 percent). A total of 17 patients required blood transfusion (7.9 percent).
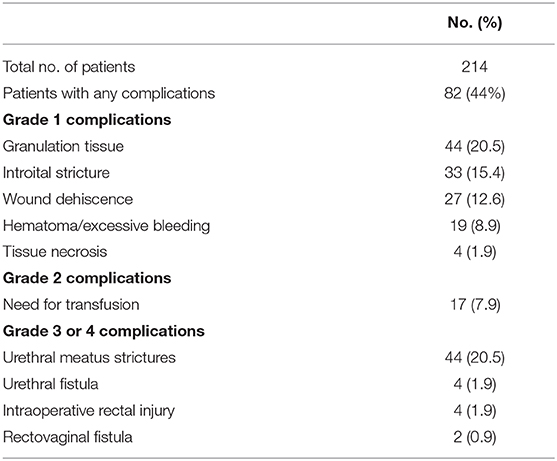
Table 2 . Complications after penile inversion vaginoplasty.
A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual vaginal intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Penile inversion vaginoplasty is the gold-standard in gender-affirming surgery. It has good functional outcomes, and studies have demonstrated adequate vaginal depths ( 3 ). It is recognized not only as a cosmetic procedure, but as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity ( 2 ). We present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
The mean age of transsexual women who underwent GAS in our study was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years), which is lower than the mean age of patients in studies found in the literature. Two studies indicated that the mean ages of patients at time of GAS were 36.7 years and 41 years, respectively ( 4 , 5 ). Another study reported a mean age at time of GAS of 36 years and found there was a significant decrease in age at the time of GAS from 41 years in 1994 to 35 years in 2015 ( 7 ). According to the authors, this decrease in age is associated with greater tolerance and societal approval regarding individuals with GD ( 7 ).
There was no grade IV or grade V complications. Excessive bleeding noticed postoperatively occurred in 19 patients (8.9 percent) and blood transfusion was required in 17 cases (7.9 percent); all patients who required blood transfusions were operated until July 2011, and the reason for this rate of blood transfusion was not identified.
The most common intraoperative complication was rectal injury, occurring in 4 patients (1.9 percent); in all patients the lesion was promptly identified and corrected in 2 layers absorbable sutures. In 2 of these patients, a rectovaginal fistula became evident, requiring fistulectomy and colonic transit deviation. This is consistent with current literature, in which rectal injury is reported in 0.4–4.5 percent of patients ( 4 , 5 , 8 – 13 ). Goddard et al. suggested carefully checking for enterotomy after prostate and bladder mobilization by digital rectal examination ( 4 ). Gaither et al. ( 14 ) commented that careful dissection that closely follows the urethra along its track from the central tendon of the perineum up through the lower pole of the prostate is critical and only blunt dissection is encouraged after Denonvilliers' fascia is reached. Alternatively, a robotic-assisted approach to penile inversion vaginoplasty may aid in minimizing these complications. The proposed advantages of a robotic-assisted vaginoplasty include safer dissection to minimize the risk of rectal injury and better proximal vaginal fixation. Dy et al. ( 15 ) has had no rectal injuries or fistulae to date in his series of 15 patients, with a mean follow-up of 12 months.
In our series, we observed 44 cases (20.5 percent) of urethral meatus strictures. We credit this complication to the technique used in the initial 5 years of our experience, in which the urethra was shortened and sutured in a circular fashion without spatulation. All cases were treated with meatal dilatation and 11 patients required surgical correction, being performed a Y-V plastic reconstruction of the urethral meatus. In the literature, meatal strictures are relatively rare in male-to-female (MtF) GAS due to the spatulation of the urethra and a simple anastomosis to the external genitalia. Recent systematic reviews show an incidence of five percent in this complication ( 16 , 17 ). Other studies report a wide incidence of meatal stenosis ranging from 1.1 to 39.8 percent ( 4 , 8 , 11 ).
Neovagina introital stricture was observed in 33 patients (15.4 percent) in our study and impedes the possibility of neovaginal penetration and/or adversely affects sexual life quality. In the literature, the reported incidence of introital stenosis range from 6.7 to 14.5 percent ( 4 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 11 – 13 ). According to Hadj-Moussa et al. ( 18 ) a regimen of postoperative prophylactic dilation is crucial to minimize the development of this outcome. At our institution, our protocol for vaginal dilation started seven days after surgery and was performed three to four times a day during the first 3 months and was continued until the individual had regular sexual intercourse. We treated stenosis initially with dilation. In case of no response, we propose a surgical revision with diamond-shaped introitoplasty with relaxing incisions. In recalcitrant cases, we proposed to the patient a secondary vaginoplasty using a full-thickness skin graft of the lower abdomen.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients were classified as having a “functional vagina,” characterized as the capacity to maintain satisfactory sexual vaginal intercourse, since the mean neovaginal depth was not measured. In a review article, the mean neovaginal depth ranged from 10 to 13.5 cm, with the shallowest neovagina depth at 2.5 cm and the deepest at 18 cm ( 17 ). According to Salim et al. ( 19 ), in terms of postoperative functional outcomes after penile inversion vaginoplasty, a mean percentage of 75 percent (range from 33 to 87 percent) patients were having vaginal intercourse. Hess et al. found that 91.4% of patients who responded to a questionnaire were very satisfied (34.4%), satisfied (37.6%), or mostly satisfied (19.4%) with their sexual function after penile inversion vaginoplasty ( 20 ).
Poor cosmetic appearance of the vulva is common. Amend et al. reported that the most common reason for reoperation was cosmetic correction in the form of mons pubis and mucosa reduction in 50% of patients ( 16 ). We had no patient regrets about performing GAS, although 36 patients (16.8 percent) were reoperated due to cosmetic issues. Gaither et al. propose in order to minimize scarring to use a one-stage surgical approach and the lateralization of surgical scars to the groin ( 14 ). Frequently, cosmetic issues outcomes are often patient driven and preoperative patient education is necessary ( 14 ).
Analyzing the quality of life, in 2016, our health care group (PROTIG) published a study assessing quality of life before and after gender-affirming surgery in 47 patients using the diagnostic tool 100-item WHO Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL-100) ( 21 ). The authors found that GAS promotes the improvement of psychological aspects and social relations. However, even 1 year after GAS, MtF persons continue to report problems in physical and difficulty in recovering their independence. In a systematic review and meta-analysis of QOL and psychosocial outcomes in transsexual people, researchers verified that sex reassignment with hormonal interventions more likely corrects gender dysphoria, psychological functioning and comorbidities, sexual function, and overall QOL compared with sex reassignment without hormonal interventions, although there is a low level of evidence for this ( 22 ). Recently, Castellano et al. assessed QOL in 60 Italian transsexuals (46 transwomen and 14 transmen) at least 2 years after SRS using the WHOQOL-100 (general QOL score and quality of sexual life and quality of body image scores) to focus on the effects of hormonal therapy. Overall satisfaction improved after SRS, and QOL was similar to the controls ( 23 ). Bartolucci et al. evaluated the perception of quality of sexual life using four questions evaluating the sexual facet in individuals with gender dysphoria before SRS and the possible factors associated with this perception. The study showed that approximately half the subjects with gender dysphoria perceived their sexual life as “poor/dissatisfied” or “very poor/very dissatisfied” before SRS ( 24 ).
Our study has some limitations. The total number of operated patients is restricted within the long follow-up period. This is due to a limitation in our health system, which allows only 1 sexual reassignment surgery to be performed per month at our institution. Neovagin depth measurement was not performed routinely in the follow-up of operated patients.
Conclusions
The definitive treatment for patients with gender dysphoria is gender-affirming surgery. Our series demonstrates that GAS is a feasible surgery with low rates of serious complications. We emphasize the high level of functionality of the vagina after the procedure, as well as subjective personal satisfaction. Complications, especially minor ones, are probably underestimated due to the nature of the study, and since this is a surgical population, the results may not be generalizable for all transgender MTF individuals.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GM: conception and design, data acquisition, data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, review of the literature, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. ML and TR: conception and design, data interpretation, drafting the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. DS, KS, AF, AC, PT, AG, and RC: conception and design, data acquisition and data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, and review of the literature. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos (FIPE - Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos) of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Coleman E, Bockting W, Botzer M, Cohen-Kettenis P, DeCuypere G, Feldman J, et al. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-non-conforming people, version 7. Int J Transgend. (2012) 13:165–232. doi: 10.1080/15532739.2011.700873
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Massie JP, Morrison SD, Maasdam JV, Satterwhite T. Predictors of patient satisfaction and postoperative complications in penile inversion vaginoplasty. Plast Reconstruct Surg. (2018) 141:911–921. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004427
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Pan S, Honig SC. Gender-affirming surgery: current concepts. Curr Urol Rep . (2018) 19:62. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0809-9
4. Goddard JC, Vickery RM, Qureshi A, Summerton DJ, Khoosal D, Terry TR. Feminizing genitoplasty in adult transsexuals: early and long-term surgical results. BJU Int . (2007) 100:607–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07017.x
5. Rossi NR, Hintz F, Krege S, Rübben H, Vom DF, Hess J. Gender reassignment surgery – a 13 year review of surgical outcomes. Eur Urol Suppl . (2013) 12:e559. doi: 10.1016/S1569-9056(13)61042-8
6. Silva RUM, Abreu FJS, Silva GMV, Santos JVQV, Batezini NSS, Silva Neto B, et al. Step by step male to female transsexual surgery. Int Braz J Urol. (2018) 44:407–8. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2017.0044
7. Aydin D, Buk LJ, Partoft S, Bonde C, Thomsen MV, Tos T. Transgender surgery in Denmark from 1994 to 2015: 20-year follow-up study. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:720–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.01.012
8. Perovic SV, Stanojevic DS, Djordjevic MLJ. Vaginoplasty in male transsexuals using penile skin and a urethral flap. BJU Int. (2001) 86:843–50. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00934.x
9. Krege S, Bex A, Lümmen G, Rübben H. Male-to-female transsexualism: a technique, results and long-term follow-up in 66 patients. BJU Int. (2001) 88:396–402. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.2001.02323.x
10. Wagner S, Greco F, Hoda MR, Inferrera A, Lupo A, Hamza A, et al. Male-to-female transsexualism: technique, results and 3-year follow-up in 50 patients. Urol International. (2010) 84:330–3. doi: 10.1159/000288238
11. Reed H. Aesthetic and functional male to female genital and perineal surgery: feminizing vaginoplasty. Semin PlasticSurg. (2011) 25:163–74. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1281486
12. Raigosa M, Avvedimento S, Yoon TS, Cruz-Gimeno J, Rodriguez G, Fontdevila J. Male-to-female genital reassignment surgery: a retrospective review of surgical technique and complications in 60 patients. J Sex Med. (2015) 12:1837–45. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12936
13. Sigurjonsson H, Rinder J, Möllermark C, Farnebo F, Lundgren TK. Male to female gender reassignment surgery: surgical outcomes of consecutive patients during 14 years. JPRAS Open. (2015) 6:69–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2015.09.003
14. Gaither TW, Awad MA, Osterberg EC, Murphy GP, Romero A, Bowers ML, et al. Postoperative complications following primary penile inversion vaginoplasty among 330 male-to-female transgender patients. J Urol. (2018) 199:760–5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.10.013
15. Dy GW, Sun J, Granieri MA, Zhao LC. Reconstructive management pearls for the transgender patient. Curr. Urol. Rep. (2018) 19:36. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0795-y
16. Amend B, Seibold J, Toomey P, Stenzl A, Sievert KD. Surgical reconstruction for male-to-female sex reassignment. Eur Urol. (2013) 64:141–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.12.030
17. Horbach SER, Bouman MB, Smit JM, Özer M, Buncamper ME, Mullender MG. Outcome of vaginoplasty in male-to-female transgenders: a systematic review of surgical techniques. J Sex Med . (2015) 12:1499–512. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12868
18. Hadj-Moussa M, Ohl DA, Kuzon WM. Feminizing genital gender-confirmation surgery. Sex Med Rev. (2018) 6:457–68.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.11.005
19. Salim A, Poh M. Gender-affirming penile inversion vaginoplasty. Clin Plast Surg. (2018) 45:343–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2018.04.001
20. Hess J, Rossi NR, Panic L, Rubben H, Senf W. Satisfaction with male-to-female gender reassignment surgery. DtschArztebl Int. (2014) 111:795–801. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2014.0795
21. Silva DC, Schwarz K, Fontanari AMV, Costa AB, Massuda R, Henriques AA, et al. WHOQOL-100 before and after sex reassignment surgery in brazilian male-to-female transsexual individuals. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:988–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.03.370
22. Murad MH, Elamin MB, Garcia MZ, Mullan RJ, Murad A, Erwin PJ, et al. Hormonal therapy and sex reassignment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of quality of life and psychosocial outcomes. Clin Endocrinol . (2010) 72:214–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03625.x
23. Castellano E, Crespi C, Dell'Aquila C, Rosato R, Catalano C, Mineccia V, et al. Quality of life and hormones after sex reassignment surgery. J Endocrinol Invest . (2015) 38:1373–81. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0398-0
24. Bartolucci C, Gómez-Gil E, Salamero M, Esteva I, Guillamón A, Zubiaurre L, et al. Sexual quality of life in gender-dysphoric adults before genital sex reassignment surgery. J Sex Med . (2015) 12:180–8. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12758
Keywords: transsexualism, gender dysphoria, gender-affirming genital surgery, penile inversion vaginoplasty, surgical outcome
Citation: Moisés da Silva GV, Lobato MIR, Silva DC, Schwarz K, Fontanari AMV, Costa AB, Tavares PM, Gorgen ARH, Cabral RD and Rosito TE (2021) Male-to-Female Gender-Affirming Surgery: 20-Year Review of Technique and Surgical Results. Front. Surg. 8:639430. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.639430
Received: 17 December 2020; Accepted: 22 March 2021; Published: 05 May 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Moisés da Silva, Lobato, Silva, Schwarz, Fontanari, Costa, Tavares, Gorgen, Cabral and Rosito. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gabriel Veber Moisés da Silva, veber.gabriel@gmail.com
This article is part of the Research Topic
Gender Dysphoria: Diagnostic Issues, Clinical Aspects and Health Promotion
Long-term Outcomes After Gender-Affirming Surgery: 40-Year Follow-up Study
Affiliations.
- 1 From the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
- 2 School of Medicine.
- 3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
- 4 Department of Urology.
- 5 Department of Psychiatry and Neurobehavioral Sciences, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA.
- PMID: 36149983
- DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003233
Background: Gender dysphoria is a condition that often leads to significant patient morbidity and mortality. Although gender-affirming surgery (GAS) has been offered for more than half a century with clear significant short-term improvement in patient well-being, few studies have evaluated the long-term durability of these outcomes.
Methods: Chart review identified 97 patients who were seen for gender dysphoria at a tertiary care center from 1970 to 1990 with comprehensive preoperative evaluations. These evaluations were used to generate a matched follow-up survey regarding their GAS, appearance, and mental/social health for standardized outcome measures. Of 97 patients, 15 agreed to participate in the phone interview and survey. Preoperative and postoperative body congruency score, mental health status, surgical outcomes, and patient satisfaction were compared.
Results: Both transmasculine and transfeminine groups were more satisfied with their body postoperatively with significantly less dysphoria. Body congruency score for chest, body hair, and voice improved significantly in 40 years' postoperative settings, with average scores ranging from 84.2 to 96.2. Body congruency scores for genitals ranged from 67.5 to 79 with free flap phalloplasty showing highest scores. Long-term overall body congruency score was 89.6. Improved mental health outcomes persisted following surgery with significantly reduced suicidal ideation and reported resolution of any mental health comorbidity secondary to gender dysphoria.
Conclusion: Gender-affirming surgery is a durable treatment that improves overall patient well-being. High patient satisfaction, improved dysphoria, and reduced mental health comorbidities persist decades after GAS without any reported patient regret.
Copyright © 2022 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
- Follow-Up Studies
- Gender Dysphoria* / surgery
- Sex Reassignment Surgery*
- Transgender Persons* / psychology
- Transsexualism* / psychology
- Patient Care & Health Information
- Tests & Procedures
- Feminizing surgery
Feminizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Feminizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to increase the size of the breasts. That procedure also is called breast augmentation. Bottom surgery can involve removal of the testicles, or removal of the testicles and penis and the creation of a vagina, labia and clitoris. Facial procedures or body-contouring procedures can be used as well.
Not everybody chooses to have feminizing surgery. These surgeries can be expensive, carry risks and complications, and involve follow-up medical care and procedures. Certain surgeries change fertility and sexual sensations. They also may change how you feel about your body.
Your health care team can talk with you about your options and help you weigh the risks and benefits.
Products & Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Available Sexual Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Why it's done
Many people seek feminizing surgery as a step in the process of treating discomfort or distress because their gender identity differs from their sex assigned at birth. The medical term for this is gender dysphoria.
For some people, having feminizing surgery feels like a natural step. It's important to their sense of self. Others choose not to have surgery. All people relate to their bodies differently and should make individual choices that best suit their needs.
Feminizing surgery may include:
- Removal of the testicles alone. This is called orchiectomy.
- Removal of the penis, called penectomy.
- Removal of the testicles.
- Creation of a vagina, called vaginoplasty.
- Creation of a clitoris, called clitoroplasty.
- Creation of labia, called labioplasty.
- Breast surgery. Surgery to increase breast size is called top surgery or breast augmentation. It can be done through implants, the placement of tissue expanders under breast tissue, or the transplantation of fat from other parts of the body into the breast.
- Plastic surgery on the face. This is called facial feminization surgery. It involves plastic surgery techniques in which the jaw, chin, cheeks, forehead, nose, and areas surrounding the eyes, ears or lips are changed to create a more feminine appearance.
- Tummy tuck, called abdominoplasty.
- Buttock lift, called gluteal augmentation.
- Liposuction, a surgical procedure that uses a suction technique to remove fat from specific areas of the body.
- Voice feminizing therapy and surgery. These are techniques used to raise voice pitch.
- Tracheal shave. This surgery reduces the thyroid cartilage, also called the Adam's apple.
- Scalp hair transplant. This procedure removes hair follicles from the back and side of the head and transplants them to balding areas.
- Hair removal. A laser can be used to remove unwanted hair. Another option is electrolysis, a procedure that involves inserting a tiny needle into each hair follicle. The needle emits a pulse of electric current that damages and eventually destroys the follicle.
Your health care provider might advise against these surgeries if you have:
- Significant medical conditions that haven't been addressed.
- Behavioral health conditions that haven't been addressed.
- Any condition that limits your ability to give your informed consent.
Like any other type of major surgery, many types of feminizing surgery pose a risk of bleeding, infection and a reaction to anesthesia. Other complications might include:
- Delayed wound healing
- Fluid buildup beneath the skin, called seroma
- Bruising, also called hematoma
- Changes in skin sensation such as pain that doesn't go away, tingling, reduced sensation or numbness
- Damaged or dead body tissue — a condition known as tissue necrosis — such as in the vagina or labia
- A blood clot in a deep vein, called deep vein thrombosis, or a blood clot in the lung, called pulmonary embolism
- Development of an irregular connection between two body parts, called a fistula, such as between the bladder or bowel into the vagina
- Urinary problems, such as incontinence
- Pelvic floor problems
- Permanent scarring
- Loss of sexual pleasure or function
- Worsening of a behavioral health problem
Certain types of feminizing surgery may limit or end fertility. If you want to have biological children and you're having surgery that involves your reproductive organs, talk to your health care provider before surgery. You may be able to freeze sperm with a technique called sperm cryopreservation.
How you prepare
Before surgery, you meet with your surgeon. Work with a surgeon who is board certified and experienced in the procedures you want. Your surgeon talks with you about your options and the potential results. The surgeon also may provide information on details such as the type of anesthesia that will be used during surgery and the kind of follow-up care that you may need.
Follow your health care team's directions on preparing for your procedures. This may include guidelines on eating and drinking. You may need to make changes in the medicine you take and stop using nicotine, including vaping, smoking and chewing tobacco.
Because feminizing surgery might cause physical changes that cannot be reversed, you must give informed consent after thoroughly discussing:
- Risks and benefits
- Alternatives to surgery
- Expectations and goals
- Social and legal implications
- Potential complications
- Impact on sexual function and fertility
Evaluation for surgery
Before surgery, a health care provider evaluates your health to address any medical conditions that might prevent you from having surgery or that could affect the procedure. This evaluation may be done by a provider with expertise in transgender medicine. The evaluation might include:
- A review of your personal and family medical history
- A physical exam
- A review of your vaccinations
- Screening tests for some conditions and diseases
- Identification and management, if needed, of tobacco use, drug use, alcohol use disorder, HIV or other sexually transmitted infections
- Discussion about birth control, fertility and sexual function
You also may have a behavioral health evaluation by a health care provider with expertise in transgender health. That evaluation might assess:
- Gender identity
- Gender dysphoria
- Mental health concerns
- Sexual health concerns
- The impact of gender identity at work, at school, at home and in social settings
- The role of social transitioning and hormone therapy before surgery
- Risky behaviors, such as substance use or use of unapproved hormone therapy or supplements
- Support from family, friends and caregivers
- Your goals and expectations of treatment
- Care planning and follow-up after surgery
Other considerations
Health insurance coverage for feminizing surgery varies widely. Before you have surgery, check with your insurance provider to see what will be covered.
Before surgery, you might consider talking to others who have had feminizing surgery. If you don't know someone, ask your health care provider about support groups in your area or online resources you can trust. People who have gone through the process may be able to help you set your expectations and offer a point of comparison for your own goals of the surgery.
What you can expect
Facial feminization surgery.
Facial feminization surgery may involve a range of procedures to change facial features, including:
- Moving the hairline to create a smaller forehead
- Enlarging the lips and cheekbones with implants
- Reshaping the jaw and chin
- Undergoing skin-tightening surgery after bone reduction
These surgeries are typically done on an outpatient basis, requiring no hospital stay. Recovery time for most of them is several weeks. Recovering from jaw procedures takes longer.
Tracheal shave
A tracheal shave minimizes the thyroid cartilage, also called the Adam's apple. During this procedure, a small cut is made under the chin, in the shadow of the neck or in a skin fold to conceal the scar. The surgeon then reduces and reshapes the cartilage. This is typically an outpatient procedure, requiring no hospital stay.
Top surgery
- Breast augmentation incisions
As part of top surgery, the surgeon makes cuts around the areola, near the armpit or in the crease under the breast.
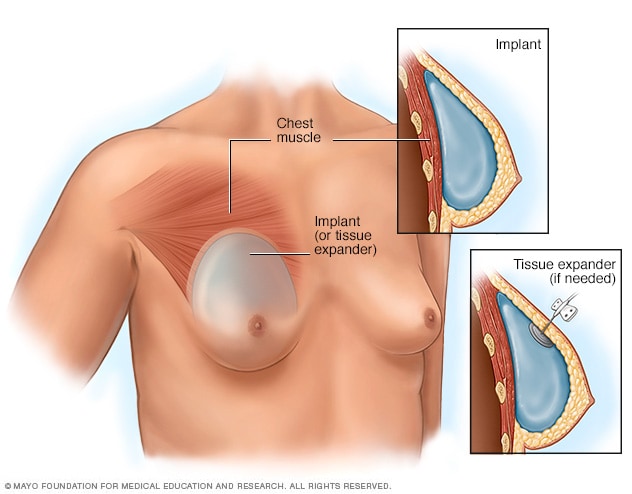
- Placement of breast implants or tissue expanders
During top surgery, the surgeon places the implants under the breast tissue. If feminizing hormones haven't made the breasts large enough, an initial surgery might be needed to have devices called tissue expanders placed in front of the chest muscles.
Hormone therapy with estrogen stimulates breast growth, but many people aren't satisfied with that growth alone. Top surgery is a surgical procedure to increase breast size that may involve implants, fat grafting or both.
During this surgery, a surgeon makes cuts around the areola, near the armpit or in the crease under the breast. Next, silicone or saline implants are placed under the breast tissue. Another option is to transplant fat, muscles or tissue from other parts of the body into the breasts.
If feminizing hormones haven't made the breasts large enough for top surgery, an initial surgery may be needed to place devices called tissue expanders in front of the chest muscles. After that surgery, visits to a health care provider are needed every few weeks to have a small amount of saline injected into the tissue expanders. This slowly stretches the chest skin and other tissues to make room for the implants. When the skin has been stretched enough, another surgery is done to remove the expanders and place the implants.
Genital surgery
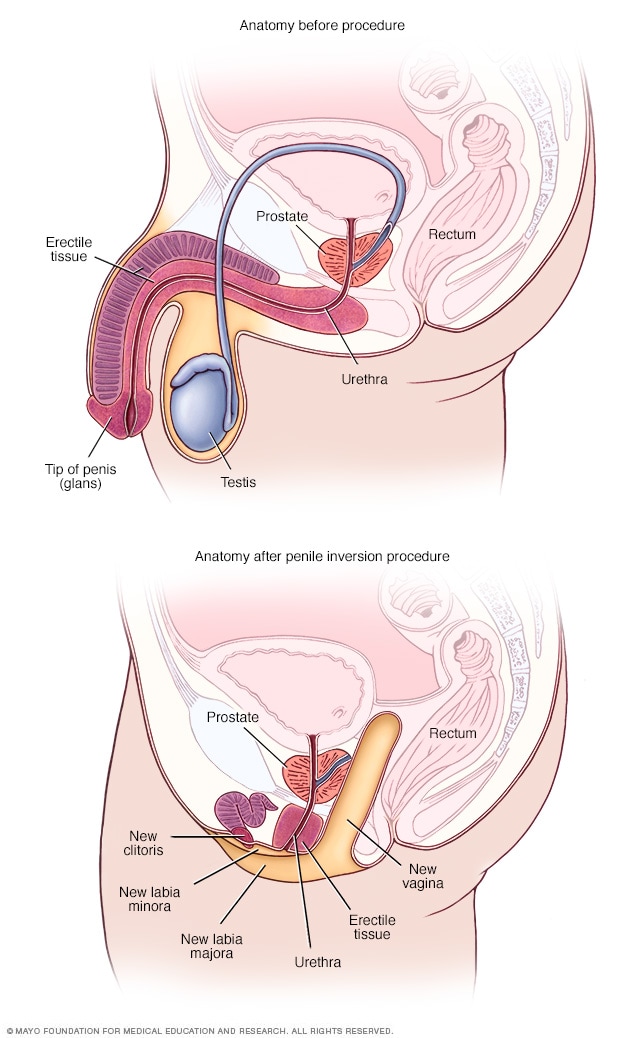
- Anatomy before and after penile inversion
During penile inversion, the surgeon makes a cut in the area between the rectum and the urethra and prostate. This forms a tunnel that becomes the new vagina. The surgeon lines the inside of the tunnel with skin from the scrotum, the penis or both. If there's not enough penile or scrotal skin, the surgeon might take skin from another area of the body and use it for the new vagina as well.
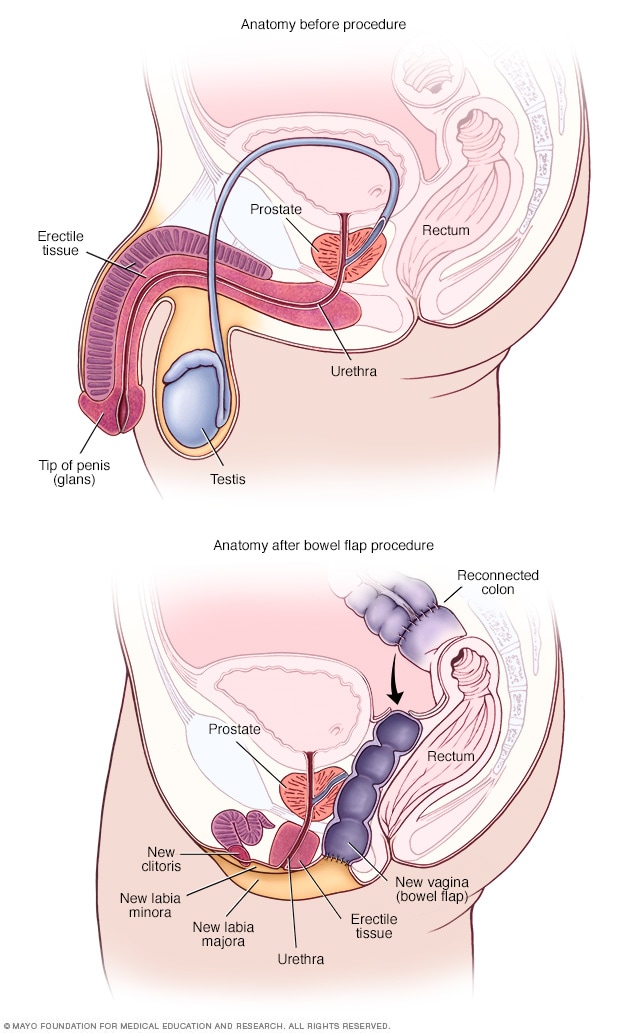
- Anatomy before and after bowel flap procedure
A bowel flap procedure might be done if there's not enough tissue or skin in the penis or scrotum. The surgeon moves a segment of the colon or small bowel to form a new vagina. That segment is called a bowel flap or conduit. The surgeon reconnects the remaining parts of the colon.
Orchiectomy
Orchiectomy is a surgery to remove the testicles. Because testicles produce sperm and the hormone testosterone, an orchiectomy might eliminate the need to use testosterone blockers. It also may lower the amount of estrogen needed to achieve and maintain the appearance you want.
This type of surgery is typically done on an outpatient basis. A local anesthetic may be used, so only the testicular area is numbed. Or the surgery may be done using general anesthesia. This means you are in a sleep-like state during the procedure.
To remove the testicles, a surgeon makes a cut in the scrotum and removes the testicles through the opening. Orchiectomy is typically done as part of the surgery for vaginoplasty. But some people prefer to have it done alone without other genital surgery.
Vaginoplasty
Vaginoplasty is the surgical creation of a vagina. During vaginoplasty, skin from the shaft of the penis and the scrotum is used to create a vaginal canal. This surgical approach is called penile inversion. In some techniques, the skin also is used to create the labia. That procedure is called labiaplasty. To surgically create a clitoris, the tip of the penis and the nerves that supply it are used. This procedure is called a clitoroplasty. In some cases, skin can be taken from another area of the body or tissue from the colon may be used to create the vagina. This approach is called a bowel flap procedure. During vaginoplasty, the testicles are removed if that has not been done previously.
Some surgeons use a technique that requires laser hair removal in the area of the penis and scrotum to provide hair-free tissue for the procedure. That process can take several months. Other techniques don't require hair removal prior to surgery because the hair follicles are destroyed during the procedure.
After vaginoplasty, a tube called a catheter is placed in the urethra to collect urine for several days. You need to be closely watched for about a week after surgery. Recovery can take up to two months. Your health care provider gives you instructions about when you may begin sexual activity with your new vagina.
After surgery, you're given a set of vaginal dilators of increasing sizes. You insert the dilators in your vagina to maintain, lengthen and stretch it. Follow your health care provider's directions on how often to use the dilators. To keep the vagina open, dilation needs to continue long term.
Because the prostate gland isn't removed during surgery, you need to follow age-appropriate recommendations for prostate cancer screening. Following surgery, it is possible to develop urinary symptoms from enlargement of the prostate.
Dilation after gender-affirming surgery
This material is for your education and information only. This content does not replace medical advice, diagnosis and treatment. If you have questions about a medical condition, always talk with your health care provider.
Narrator: Vaginal dilation is important to your recovery and ongoing care. You have to dilate to maintain the size and shape of your vaginal canal and to keep it open.
Jessi: I think for many trans women, including myself, but especially myself, I looked forward to one day having surgery for a long time. So that meant looking up on the internet what the routines would be, what the surgery entailed. So I knew going into it that dilation was going to be a very big part of my routine post-op, but just going forward, permanently.
Narrator: Vaginal dilation is part of your self-care. You will need to do vaginal dilation for the rest of your life.
Alissa (nurse): If you do not do dilation, your vagina may shrink or close. If that happens, these changes might not be able to be reversed.
Narrator: For the first year after surgery, you will dilate many times a day. After the first year, you may only need to dilate once a week. Most people dilate for the rest of their life.
Jessi: The dilation became easier mostly because I healed the scars, the stitches held up a little bit better, and I knew how to do it better. Each transgender woman's vagina is going to be a little bit different based on anatomy, and I grew to learn mine. I understand, you know, what position I needed to put the dilator in, how much force I needed to use, and once I learned how far I needed to put it in and I didn't force it and I didn't worry so much on oh, did I put it in too far, am I not putting it in far enough, and I have all these worries and then I stress out and then my body tenses up. Once I stopped having those thoughts, I relaxed more and it was a lot easier.
Narrator: You will have dilators of different sizes. Your health care provider will determine which sizes are best for you. Dilation will most likely be painful at first. It's important to dilate even if you have pain.
Alissa (nurse): Learning how to relax the muscles and breathe as you dilate will help. If you wish, you can take the pain medication recommended by your health care team before you dilate.
Narrator: Dilation requires time and privacy. Plan ahead so you have a private area at home or at work. Be sure to have your dilators, a mirror, water-based lubricant and towels available. Wash your hands and the dilators with warm soapy water, rinse well and dry on a clean towel. Use a water-based lubricant to moisten the rounded end of the dilators. Water-based lubricants are available over-the-counter. Do not use oil-based lubricants, such as petroleum jelly or baby oil. These can irritate the vagina. Find a comfortable position in bed or elsewhere. Use pillows to support your back and thighs as you lean back to a 45-degree angle. Start your dilation session with the smallest dilator. Hold a mirror in one hand. Use the other hand to find the opening of your vagina. Separate the skin. Relax through your hips, abdomen and pelvic floor. Take slow, deep breaths. Position the rounded end of the dilator with the lubricant at the opening to your vaginal canal. The rounded end should point toward your back. Insert the dilator. Go slowly and gently. Think of its path as a gentle curving swoop. The dilator doesn't go straight in. It follows the natural curve of the vaginal canal. Keep gentle down and inward pressure on the dilator as you insert it. Stop when the dilator's rounded end reaches the end of your vaginal canal. The dilators have dots or markers that measure depth. Hold the dilator in place in your vaginal canal. Use gentle but constant inward pressure for the correct amount of time at the right depth for you. If you're feeling pain, breathe and relax the muscles. When time is up, slowly remove the dilator, then repeat with the other dilators you need to use. Wash the dilators and your hands. If you have increased discharge following dilation, you may want to wear a pad to protect your clothing.
Jessi: I mean, it's such a strange, unfamiliar feeling to dilate and to have a dilator, you know to insert a dilator into your own vagina. Because it's not a pleasurable experience, and it's quite painful at first when you start to dilate. It feels much like a foreign body entering and it doesn't feel familiar and your body kind of wants to get it out of there. It's really tough at the beginning, but if you can get through the first month, couple months, it's going to be a lot easier and it's not going to be so much of an emotional and uncomfortable experience.
Narrator: You need to stay on schedule even when traveling. Bring your dilators with you. If your schedule at work creates challenges, ask your health care team if some of your dilation sessions can be done overnight.
Alissa (nurse): You can't skip days now and do more dilation later. You must do dilation on schedule to keep vaginal depth and width. It is important to dilate even if you have pain. Dilation should cause less pain over time.
Jessi: I hear that from a lot of other women that it's an overwhelming experience. There's lots of emotions that are coming through all at once. But at the end of the day for me, it was a very happy experience. I was glad to have the opportunity because that meant that while I have a vagina now, at the end of the day I had a vagina. Yes, it hurts, and it's not pleasant to dilate, but I have the vagina and it's worth it. It's a long process and it's not going to be easy. But you can do it.
Narrator: If you feel dilation may not be working or you have any questions about dilation, please talk with a member of your health care team.
Research has found that that gender-affirming surgery can have a positive impact on well-being and sexual function. It's important to follow your health care provider's advice for long-term care and follow-up after surgery. Continued care after surgery is associated with good outcomes for long-term health.
Before you have surgery, talk to members of your health care team about what to expect after surgery and the ongoing care you may need.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Feminizing surgery care at Mayo Clinic
- Tangpricha V, et al. Transgender women: Evaluation and management. https://www.uptodate.com/ contents/search. Accessed Aug. 16, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Surgical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Coleman E, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. International Journal of Transgender Health. 2022; doi:10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
- AskMayoExpert. Gender-affirming procedures (adult). Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- Nahabedian, M. Implant-based breast reconstruction and augmentation. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Medical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Ferrando C, et al. Gender-affirming surgery: Male to female. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Doctors & Departments
- Care at Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What to Know About Metoidioplasty (Bottom Surgery)
- Who Qualifies?
- Surgical Techniques
- Neophallus Function
- Surgery Follow-Up
- Where to Have Surgery
Metoidioplasty , or "bottom surgery," is a gender-affirming surgical procedure that involves creating a neophallus (new penis) from a hormonally enlarged clitoris . Transgender men and transmasculine people assigned female at birth (AFAB) may elect for a metoidioplasty if they want their genital appearance to align with their gender identity.
In contrast to the more complex phalloplasty that involves several surgeries, metoidioplasty offers a more straightforward phallic reconstruction in one procedure.
During a metoidioplasty, a surgeon cuts the ligaments that connect the clitoris to the pubic bone to release the clitoris and create a penis with erogenous (sexual) sensations. It may also include additional steps, such as urethral lengthening and scrotoplasty (forming a scrotum), to enhance the appearance and functionality of the neophallus.
This article explores metoidioplasty surgical techniques, the recovery process, and what to expect post-surgery.
CarlosDavid.org / Getty Images
Who Qualifies for Metoidioplasty Surgery?
Metoidioplasty is a gender-affirming (sex-reassignment) surgery for transgender men assigned female at birth. According to the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey, about 4% of trans men have undergone the procedure, while another 53% expressed a desire to undergo metoidioplasty in the future.
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) developed the criteria for gender reaffirmation surgeries to ensure optimal physical and psychological outcomes for those pursuing bottom (genital) surgeries. The eligibility criteria for metoidioplasty include the following:
- Ongoing and well-documented gender dysphoria
- The ability to make informed decisions and provide consent for treatment
- Being 18 years of age or older
- Medical or mental health concerns are well-managed (if applicable)
- At least 12 consecutive months of gender-affirming testosterone therapy
- Living as a male or masculine-presenting person for at least one year in all settings (e.g., work, school, with family members and community)
Though it is not required, regular visits with a mental health or other medical professional are highly recommended before undergoing a metoidioplasty.
Metoidioplasty Surgical Techniques
People can choose a few different metoidioplasty surgical techniques depending on their preferences. Other procedures can occur simultaneously (e.g., hysterectomy) if desired.
Simple Release Metoidioplasty
In the simple release procedure, ligaments attached to the pubic bone are cut and released, and the clitoris is separated from surrounding tissue to enhance the position and visibility of the clitoris. The labia minora are wrapped around the clitoris to create the glans (head) of the newly formed penis.
Ring Metoidioplasty
Similar to the simple release, this technique involves releasing the clitoral ligaments to lengthen the clitoris. This procedure also involves lengthening the urethra using a flap of tissue from the vaginal wall and labia minora. This procedure gives trans men a micropenis with more girth and the ability to stand while urinating.
Belgrade (Full) Metoidioplasty
The Belgrade technique, or full metoidioplasty, involves the removal of the vagina (vaginectomy) and releasing the clitoris to lengthen and straighten the clitoris. The urethra is lengthened using vaginal tissue and buccal mucosa (inner cheek) skin grafts. The penis is reconstructed with the remaining clitoral and labial skin to give it more girth.
Then, the labia minor flaps are joined to create a scrotum (scrotoplasty), and testicular implants may be inserted into the newly created scrotum. A penile pump or vacuum is recommended three weeks post-surgery to lengthen the neophallus and prevent retraction.
Simultaneous Procedures
In addition to metoidioplasty, some trans men may opt for additional procedures performed at the same time to achieve their desired outcomes. These procedures may include:
- Hysterectomy : Removal of the uterus
- Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy : Removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes
- Vaginectomy : Removal of the vagina and surrounding tissues
- Scrotoplasty : Forms a new scrotum; testicular implants may be placed to give the appearance of natural testicles
- Erectile implant : A device is placed inside the neophallus to help achieve erections
Metoidioplasty vs. Phalloplasty
Metoidioplasty and phalloplasty are surgical options for transgender men seeking gender-affirming genital reconstruction. Metoidioplasty involves using existing genital tissue, such as the hormonally enlarged clitoris, to create a neophallus. It usually results in a smaller but functional neophallus.
Phalloplasty involves constructing a neophallus using various techniques, including grafting tissue from other body parts. This procedure can provide a larger and more visually realistic phallus but is more complex and may require multiple stages. The choice between metoidioplasty and phalloplasty depends on individual preferences, desired outcomes, and considerations such as surgical risk, recovery time, and aesthetic goals.
Risks to Understand Before Metoidioplasty
While metoidioplasty is generally considered safe, like any surgical intervention, it carries certain risks. Before undergoing metoidioplasty, discuss the risks with a healthcare provider to gain a comprehensive understanding and make an informed decision.
Potential risks include:
- Urethral stricture or stenosis : Narrowing of the urethral passage, leading to difficulty with urination and potential obstruction of urine flow. Sometimes, urine flow may be blocked entirely, requiring surgery to correct the problem.
- Urethral fistula : An abnormal connection or passageway between the urethra and the skin or surrounding tissues. This can result in urine leakage or an abnormal opening along the neophallus.
- Sensation changes : The newly formed penis may have decreased or loss of sensation or feel hypersensitive and tender.
Function of Neophallus Post-Bottom Surgery
Trans men who have undergone metoidioplasty report high levels of satisfaction with the procedure's results, both in appearance and function.
While a neophallus created through metoidioplasty is usually considered a micropenis (1–4 inches), erections and orgasms are achieved by nearly all who have undergone the procedure. Penetrative sex may or may not be possible. Urinating while standing is possible for most men after metoidioplasty.
Metoidioplasty Recovery Period
The recovery period following metoidioplasty depends on the specific surgical technique and can vary from person to person. Most people can expect one week of bed rest immediately following the procedure and gradually resume their activities within about six weeks.
Initially, there will be discomfort, swelling, and bleeding in the genital region, which will gradually subside over time. You may also experience:
- Bruising in the genital area that spreads from the belly down to the legs
- Itching and short, sharp, shooting sensations as the area heals
- Numbness at or near the incision sites, which can persist for months
- Scarring on the genitals that will first appear red or pink and fade over time
Metoidioplasty Follow-Up (and Asking for Help)
You will need assistance and support during the follow-up period after metoidioplasty, as the recovery process can involve discomfort, limited mobility, and restricted activity. You will need a caretaker for at least a week or two after the procedure—someone who can help with daily tasks such as meal preparation, household chores, and running errands.
Your surgeon may restrict certain activities, such as driving, sex, and heavy lifting. You may need help with transportation to follow-up appointments for about six weeks. Most people can resume their normal activities within six weeks post-surgery. Still, getting the OK from a healthcare provider is important to ensure you are properly healed and to lower the risk of complications.
Where to Have Metoidioplasty Surgery
Specialized surgeons with experience in transgender healthcare often perform metoidioplasty surgery. The procedure is usually carried out in a hospital or surgical center with the necessary tools and equipment for the surgery. It is essential to choose a reputable medical facility that is experienced in transgender surgeries and maintains a supportive and inclusive environment.
When considering where to have metoidioplasty surgery, start by asking a mental health professional or another healthcare provider for referrals and recommendations of surgeons who specialize in the procedure. They can provide information and guidance on the options available to you.
Researching and gathering information about the surgeon's qualifications, experience, and success rates, as well as reading reviews or testimonials from other people who have undergone metoidioplasty at the facility, can also help you select the most suitable location for the surgery. Open communication with healthcare providers can ensure that all your questions and concerns are addressed before deciding where to have metoidioplasty surgery.
Metoidioplasty is a gender-affirming surgery for trans-male people assigned female at birth (AFAB). The procedure involves releasing the clitoral ligaments and utilizing the hormonally enlarged clitoris to create a neophallus (new penis).
There are a few different metoidioplasty techniques. Sometimes, people undergo simultaneous procedures, such as hysterectomy and vaginectomy. Metoidioplasty is considered a safe, effective procedure that results in a 1–4 inch functional penis that gives trans men the opportunity to align their physical characteristics with their gender identity.
Djordjevic ML, Stojanovic B, Bizic M. Metoidioplasty: Techniques and outcomes . Transl Androl Urol . 2019;8(3):248-253. doi:10.21037/tau.2019.06.12
Kjölhede A, Cornelius F, Huss F, Kratz G. Metoidioplasty and groin flap phalloplasty as two surgical methods for the creation of a neophallus in female-to-male gender-confirming surgery: A retrospective study comprising 123 operated patients . JPRAS Open . 2019;22:1-8. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2019.07.003
Stojanovic B, Bencic M, Bizic M, Djordjevic ML. Metoidioplasty in gender affirmation: A review . Indian J Plast Surg . 2022;55(2):156-161. doi:10.1055/s-0041-1740081
National Center for Transgender Equality. Injustice at every turn: a report of the national transgender discrimination survey .
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender nonconforming people .
Heston AL, Esmonde NO, Dugi DD 3rd, Berli JU. Phalloplasty: techniques and outcomes . Transl Androl Urol . 2019;8(3):254-265. doi:10.21037/tau.2019.05.05
Alberta Medical Association. Metoidioplasty .
Bordas N, Stojanovic B, Bizic M, et al. Metoidioplasty: Surgical options and outcomes in 813 cases . Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) . 2021;12:760284. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.760284
TransCare BC. Provincial Health Services Authority. Metoidioplasty .
Michigan Medicine: University of Michigan. What to expect: Metoidioplasty at Michigan Medicine .
TransHealthCare. Metoidioplasty - list of surgeons in the USA .
By Lindsay Curtis Curtis is a writer with over 20 years of experience focused on mental health, sexual health, cancer care, and spinal health.

Dr. Alter’s Before and After IMAGE GALLERY
Female procedures.

LABIAPLASTY (Labia Minora Reduction)

CLITORAL HOOD REDUCTION WITH/WITHOUT CLITOROPEXY

LABIA MAJORA REMODELING

COMBINATION FEMALE GENITAL SURGERIES

REVISION OF BOTCHED LABIAPLASTIES

CLITORIS REDUCTION

PUBIC LIPOSUCTION

PUBIC MONS LIFT

INTERSEX & COMPLEX FEMALE RECONSTRUCTION
Male procedures.

BURIED/HIDDEN PENIS CORRECTIVE SURGERY – ADULT
Buried/hidden penis corrective surgery – child, penoscrotal webbing, scrotum reduction, male genital reconstruction, penis enlargement reconstruction, congenital penile curvature, gender confirmation procedures.

MALE TO FEMALE GENDER CONFIRMATION SURGERY

MALE-TO-FEMALE SEX REASSIGNMENT REVISIONS
Female-to-male chest contouring, female to male metaidoioplasty, gender confirmation breast augmentations, cosmetic procedures.

ABDOMINOPLASTY
Breast augmentation, breast reconstruction & breast reduction, liposuction, patient-first policy.
Dr. Alter and the entire team are dedicated to providing every patient with exceptional individualized care—from consultation to recovery. We take the time to learn about your concerns, goals, and desires, so we can build a plan that addresses your concerns and gets you the results you deserve.
Thoughts & Insights

5 Labiaplasty Benefits You Should Know About


Is Your Penis Curved? How Much Is Too Much?

Have You Thought About Your Sexual Wellness Today?

Top Vaginal Rejuvenation Treatments for Moms
Our locations.
BEVERLY HILLS
NEW YORK CITY
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Article Information
Error bars represent 95% CIs. GAS indicates gender-affirming surgery.
Percentages are based on the number of procedures divided by number of patients; thus, as some patients underwent multiple procedures the total may be greater than 100%. Error bars represent 95% CIs.
eTable. ICD-10 and CPT Codes of Gender-Affirming Surgery
eFigure. Percentage of Patients With Codes for Gender Identity Disorder Who Underwent GAS
Data Sharing Statement
See More About
Sign up for emails based on your interests, select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Get the latest research based on your areas of interest.
Others also liked.
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Wright JD , Chen L , Suzuki Y , Matsuo K , Hershman DL. National Estimates of Gender-Affirming Surgery in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(8):e2330348. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30348
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
National Estimates of Gender-Affirming Surgery in the US
- 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, New York
- 2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles
Question What are the temporal trends in gender-affirming surgery (GAS) in the US?
Findings In this cohort study of 48 019 patients, GAS increased significantly, nearly tripling from 2016 to 2019. Breast and chest surgery was the most common class of procedures performed overall; genital reconstructive procedures were more common among older individuals.
Meaning These findings suggest that there will be a greater need for clinicians knowledgeable in the care of transgender individuals with the requisite expertise to perform gender-affirming procedures.
Importance While changes in federal and state laws mandating coverage of gender-affirming surgery (GAS) may have led to an increase in the number of annual cases, comprehensive data describing trends in both inpatient and outpatient procedures are limited.
Objective To examine trends in inpatient and outpatient GAS procedures in the US and to explore the temporal trends in the types of GAS performed across age groups.
Design, Setting, and Participants This cohort study includes data from 2016 to 2020 in the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample and the National Inpatient Sample. Patients with diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder, transsexualism, or a personal history of sex reassignment were identified, and the performance of GAS, including breast and chest procedures, genital reconstructive procedures, and other facial and cosmetic surgical procedures, were identified.
Main Outcome Measures Weighted estimates of the annual number of inpatient and outpatient procedures performed and the distribution of each class of procedure overall and by age were analyzed.
Results A total of 48 019 patients who underwent GAS were identified, including 25 099 (52.3%) who were aged 19 to 30 years. The most common procedures were breast and chest procedures, which occurred in 27 187 patients (56.6%), followed by genital reconstruction (16 872 [35.1%]) and other facial and cosmetic procedures (6669 [13.9%]). The absolute number of GAS procedures rose from 4552 in 2016 to a peak of 13 011 in 2019 and then declined slightly to 12 818 in 2020. Overall, 25 099 patients (52.3%) were aged 19 to 30 years, 10 476 (21.8%) were aged 31 to 40, and 3678 (7.7%) were aged12 to 18 years. When stratified by the type of procedure performed, breast and chest procedures made up a greater percentage of the surgical interventions in younger patients, while genital surgical procedures were greater in older patients.
Conclusions and Relevance Performance of GAS has increased substantially in the US. Breast and chest surgery was the most common group of procedures performed. The number of genital surgical procedures performed increased with increasing age.
Gender dysphoria is characterized as an incongruence between an individual’s experienced or expressed gender and the gender that was assigned at birth. 1 Transgender individuals may pursue multiple treatments, including behavioral therapy, hormonal therapy, and gender-affirming surgery (GAS). 2 GAS encompasses a variety of procedures that align an individual patient’s gender identity with their physical appearance. 2 - 4
While numerous surgical interventions can be considered GAS, the procedures have been broadly classified as breast and chest surgical procedures, facial and cosmetic interventions, and genital reconstructive surgery. 2 , 4 Prior studies 2 - 7 have shown that GAS is associated with improved quality of life, high rates of satisfaction, and a reduction in gender dysphoria. Furthermore, some studies have reported that GAS is associated with decreased depression and anxiety. 8 Lastly, the procedures appear to be associated with acceptable morbidity and reasonable rates of perioperative complications. 2 , 4
Given the benefits of GAS, the performance of GAS in the US has increased over time. 9 The increase in GAS is likely due in part to federal and state laws requiring coverage of transition-related care, although actual insurance coverage of specific procedures is variable. 10 , 11 While prior work has shown that the use of inpatient GAS has increased, national estimates of inpatient and outpatient GAS are lacking. 9 This is important as many GAS procedures occur in ambulatory settings. We performed a population-based analysis to examine trends in GAS in the US and explored the temporal trends in the types of GAS performed across age groups.
To capture both inpatient and outpatient surgical procedures, we used data from the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample (NASS) and the National Inpatient Sample (NIS). NASS is an ambulatory surgery database and captures major ambulatory surgical procedures at nearly 2800 hospital-owned facilities from up to 35 states, approximating a 63% to 67% stratified sample of hospital-owned facilities. NIS comprehensively captures approximately 20% of inpatient hospital encounters from all community hospitals across 48 states participating in the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), covering more than 97% of the US population. Both NIS and NASS contain weights that can be used to produce US population estimates. 12 , 13 Informed consent was waived because data sources contain deidentified data, and the study was deemed exempt by the Columbia University institutional review board. This cohort study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology ( STROBE ) reporting guideline.
We selected patients of all ages with an International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision ( ICD-10 ) diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder or transsexualism ( ICD-10 F64) or a personal history of sex reassignment ( ICD-10 Z87.890) from 2016 to 2020 (eTable in Supplement 1 ). We first examined all hospital (NIS) and ambulatory surgical (NASS) encounters for patients with these codes and then analyzed encounters for GAS within this cohort. GAS was identified using ICD-10 procedure codes and Common Procedural Terminology codes and classified as breast and chest procedures, genital reconstructive procedures, and other facial and cosmetic surgical procedures. 2 , 4 Breast and chest surgical procedures encompassed breast reconstruction, mammoplasty and mastopexy, or nipple reconstruction. Genital reconstructive procedures included any surgical intervention of the male or female genital tract. Other facial and cosmetic procedures included cosmetic facial procedures and other cosmetic procedures including hair removal or transplantation, liposuction, and collagen injections (eTable in Supplement 1 ). Patients might have undergone procedures from multiple different surgical groups. We measured the total number of procedures and the distribution of procedures within each procedural group.
Within the data sets, sex was based on patient self-report. The sex of patients in NIS who underwent inpatient surgery was classified as either male, female, missing, or inconsistent. The inconsistent classification denoted patients who underwent a procedure that was not consistent with the sex recorded on their medical record. Similar to prior analyses, patients in NIS with a sex variable not compatible with the procedure performed were classified as having undergone genital reconstructive surgery (GAS not otherwise specified). 9
Clinical variables in the analysis included patient clinical and demographic factors and hospital characteristics. Demographic characteristics included age at the time of surgery (12 to 18 years, 19 to 30 years, 31 to 40 years, 41 to 50 years, 51 to 60 years, 61 to 70 years, and older than 70 years), year of the procedure (2016-2020), and primary insurance coverage (private, Medicare, Medicaid, self-pay, and other). Race and ethnicity were only reported in NIS and were classified as White, Black, Hispanic and other. Race and ethnicity were considered in this study because prior studies have shown an association between race and GAS. The income status captured national quartiles of median household income based of a patient’s zip code and was recorded as less than 25% (low), 26% to 50% (medium-low), 51% to 75% (medium-high), and 76% or more (high). The Elixhauser Comorbidity Index was estimated for each patient based on the codes for common medical comorbidities and weighted for a final score. 14 Patients were classified as 0, 1, 2, or 3 or more. We separately reported coding for HIV and AIDS; substance abuse, including alcohol and drug abuse; and recorded mental health diagnoses, including depression and psychoses. Hospital characteristics included a composite of teaching status and location (rural, urban teaching, and urban nonteaching) and hospital region (Northeast, Midwest, South, and West). Hospital bed sizes were classified as small, medium, and large. The cutoffs were less than 100 (small), 100 to 299 (medium), and 300 or more (large) short-term acute care beds of the facilities from NASS and were varied based on region, urban-rural designation, and teaching status of the hospital from NIS. 8 Patients with missing data were classified as the unknown group and were included in the analysis.
National estimates of the number of GAS procedures among all hospital encounters for patients with gender identity disorder were derived using discharge or encounter weight provided by the databases. 15 The clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients undergoing GAS were reported descriptively. The number of encounters for gender identity disorder, the percentage of GAS procedures among those encounters, and the absolute number of each procedure performed over time were estimated. The difference by age group was examined and tested using Rao-Scott χ 2 test. All hypothesis tests were 2-sided, and P < .05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc).
A total of 48 019 patients who underwent GAS were identified ( Table 1 ). Overall, 25 099 patients (52.3%) were aged 19 to 30 years, 10 476 (21.8%) were aged 31 to 40, and 3678 (7.7%) were aged 12 to 18 years. Private insurance coverage was most common in 29 064 patients (60.5%), while 12 127 (25.3%) were Medicaid recipients. Depression was reported in 7192 patients (15.0%). Most patients (42 467 [88.4%]) were treated at urban, teaching hospitals, and there was a disproportionate number of patients in the West (22 037 [45.9%]) and Northeast (12 396 [25.8%]). Within the cohort, 31 668 patients (65.9%) underwent 1 procedure while 13 415 (27.9%) underwent 2 procedures, and the remainder underwent multiple procedures concurrently ( Table 1 ).
The overall number of health system encounters for gender identity disorder rose from 13 855 in 2016 to 38 470 in 2020. Among encounters with a billing code for gender identity disorder, there was a consistent rise in the percentage that were for GAS from 4552 (32.9%) in 2016 to 13 011 (37.1%) in 2019, followed by a decline to 12 818 (33.3%) in 2020 ( Figure 1 and eFigure in Supplement 1 ). Among patients undergoing ambulatory surgical procedures, 37 394 (80.3%) of the surgical procedures included gender-affirming surgical procedures. For those with hospital admissions with gender identity disorder, 10 625 (11.8%) of admissions were for GAS.
Breast and chest procedures were most common and were performed for 27 187 patients (56.6%). Genital reconstruction was performed for 16 872 patients (35.1%), and other facial and cosmetic procedures for 6669 patients (13.9%) ( Table 2 ). The most common individual procedure was breast reconstruction in 21 244 (44.2%), while the most common genital reconstructive procedure was hysterectomy (4489 [9.3%]), followed by orchiectomy (3425 [7.1%]), and vaginoplasty (3381 [7.0%]). Among patients who underwent other facial and cosmetic procedures, liposuction (2945 [6.1%]) was most common, followed by rhinoplasty (2446 [5.1%]) and facial feminizing surgery and chin augmentation (1874 [3.9%]).
The absolute number of GAS procedures rose from 4552 in 2016 to a peak of 13 011 in 2019 and then declined slightly to 12 818 in 2020 ( Figure 1 ). Similar trends were noted for breast and chest surgical procedures as well as genital surgery, while the rate of other facial and cosmetic procedures increased consistently from 2016 to 2020. The distribution of the individual procedures performed in each class were largely similar across the years of analysis ( Table 3 ).
When stratified by age, patients 19 to 30 years had the greatest number of procedures, 25 099 ( Figure 2 ). There were 10 476 procedures performed in those aged 31 to 40 years and 4359 in those aged 41 to 50 years. Among patients younger than 19 years, 3678 GAS procedures were performed. GAS was less common in those cohorts older than 50 years. Overall, the greatest number of breast and chest surgical procedures, genital surgical procedures, and facial and other cosmetic surgical procedures were performed in patients aged 19 to 30 years.
When stratified by the type of procedure performed, breast and chest procedures made up the greatest percentage of the surgical interventions in younger patients while genital surgical procedures were greater in older patients ( Figure 2 ). Additionally, 3215 patients (87.4%) aged 12 to 18 years underwent GAS and had breast or chest procedures. This decreased to 16 067 patients (64.0%) in those aged 19 to 30 years, 4918 (46.9%) in those aged 31 to 40 years, and 1650 (37.9%) in patients aged 41 to 50 years ( P < .001). In contrast, 405 patients (11.0%) aged 12 to 18 years underwent genital surgery. The percentage of patients who underwent genital surgery rose sequentially to 4423 (42.2%) in those aged 31 to 40 years, 1546 (52.3%) in those aged 51 to 60 years, and 742 (58.4%) in those aged 61 to 70 years ( P < .001). The percentage of patients who underwent facial and other cosmetic surgical procedures rose with age from 9.5% in those aged 12 to 18 years to 20.6% in those aged 51 to 60 years, then gradually declined ( P < .001). Figure 2 displays the absolute number of procedure classes performed by year stratified by age. The greatest magnitude of the decline in 2020 was in younger patients and for breast and chest procedures.
These findings suggest that the number of GAS procedures performed in the US has increased dramatically, nearly tripling from 2016 to 2019. Breast and chest surgery is the most common class of procedure performed while patients are most likely to undergo surgery between the ages of 19 and 30 years. The number of genital surgical procedures performed increased with increasing age.
Consistent with prior studies, we identified a remarkable increase in the number of GAS procedures performed over time. 9 , 16 A prior study examining national estimates of inpatient GAS procedures noted that the absolute number of procedures performed nearly doubled between 2000 to 2005 and from 2006 to 2011. In our analysis, the number of GAS procedures nearly tripled from 2016 to 2020. 9 , 17 Not unexpectedly, a large number of the procedures we captured were performed in the ambulatory setting, highlighting the need to capture both inpatient and outpatient procedures when analyzing data on trends. Like many prior studies, we noted a decrease in the number of procedures performed in 2020, likely reflective of the COVID-19 pandemic. 18 However, the decline in the number of procedures performed between 2019 and 2020 was relatively modest, particularly as these procedures are largely elective.
Analysis of procedure-specific trends by age revealed a number of important findings. First, GAS procedures were most common in patients aged 19 to 30 years. This is in line with prior work that demonstrated that most patients first experience gender dysphoria at a young age, with approximately three-quarters of patients reporting gender dysphoria by age 7 years. These patients subsequently lived for a mean of 23 years for transgender men and 27 years for transgender women before beginning gender transition treatments. 19 Our findings were also notable that GAS procedures were relatively uncommon in patients aged 18 years or younger. In our cohort, fewer than 1200 patients in this age group underwent GAS, even in the highest volume years. GAS in adolescents has been the focus of intense debate and led to legislative initiatives to limit access to these procedures in adolescents in several states. 20 , 21
Second, there was a marked difference in the distribution of procedures in the different age groups. Breast and chest procedures were more common in younger patients, while genital surgery was more frequent in older individuals. In our cohort of individuals aged 19 to 30 years, breast and chest procedures were twice as common as genital procedures. Genital surgery gradually increased with advancing age, and these procedures became the most common in patients older than 40 years. A prior study of patients with commercial insurance who underwent GAS noted that the mean age for mastectomy was 28 years, significantly lower than for hysterectomy at age 31 years, vaginoplasty at age 40 years, and orchiectomy at age 37 years. 16 These trends likely reflect the increased complexity of genital surgery compared with breast and chest surgery as well as the definitive nature of removal of the reproductive organs.
This study has limitations. First, there may be under-capture of both transgender individuals and GAS procedures. In both data sets analyzed, gender is based on self-report. NIS specifically makes notation of procedures that are considered inconsistent with a patient’s reported gender (eg, a male patient who underwent oophorectomy). Similar to prior work, we assumed that patients with a code for gender identity disorder or transsexualism along with a surgical procedure classified as inconsistent underwent GAS. 9 Second, we captured procedures commonly reported as GAS procedures; however, it is possible that some of these procedures were performed for other underlying indications or diseases rather than solely for gender affirmation. Third, our trends showed a significant increase in procedures through 2019, with a decline in 2020. The decline in services in 2020 is likely related to COVID-19 service alterations. Additionally, while we comprehensively captured inpatient and ambulatory surgical procedures in large, nationwide data sets, undoubtedly, a small number of procedures were performed in other settings; thus, our estimates may underrepresent the actual number of procedures performed each year in the US.
These data have important implications in providing an understanding of the use of services that can help inform care for transgender populations. The rapid rise in the performance of GAS suggests that there will be a greater need for clinicians knowledgeable in the care of transgender individuals and with the requisite expertise to perform GAS procedures. However, numerous reports have described the political considerations and challenges in the delivery of transgender care. 22 Despite many medical societies recognizing the necessity of gender-affirming care, several states have enacted legislation or policies that restrict gender-affirming care and services, particularly in adolescence. 20 , 21 These regulations are barriers for patients who seek gender-affirming care and provide legal and ethical challenges for clinicians. As the use of GAS increases, delivering equitable gender-affirming care in this complex landscape will remain a public health challenge.
Accepted for Publication: July 15, 2023.
Published: August 23, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30348
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2023 Wright JD et al. JAMA Network Open .
Corresponding Author: Jason D. Wright, MD, Division of Gynecologic Oncology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, 161 Fort Washington Ave, 4th Floor, New York, NY 10032 ( [email protected] ).
Author Contributions: Dr Wright had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Wright, Chen.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Wright.
Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors.
Statistical analysis: Wright, Chen.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Wright, Suzuki.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Wright reported receiving grants from Merck and personal fees from UpToDate outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 2 .
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Keelee MacPhee, M.D.
Transgender Surgery & Plastic Surgery
TRANSGENDER SURGERY COSMETIC PLASTIC SURGERY BOARD CERTIFIED
MTF Vaginoplasty
In male-to-female sex reassignment, the trans woman may choose to undergo vaginoplasty – the inversion of the penis to create a vagina – as part of her physical transition. This procedure can result in a fully sensate neovagina.
Dr. MacPhee performs this reconstructive procedure by disassembling the penis and utilizing the inverted penile and scrotal skin flap and urethral flap to construct a new vulva, clitoris and vagina. The blood and nerve supplies are preserved to provide sensation, and the urethra is used to create the mucosal part of the vagina that provides additional sensitivity and wetting. The remaining penile and scrotal tissue are used to form the clitoral hood and labia.
The depth and diameter of the neovagina may be limited due the narrowness of the male pelvis. At the time of surgery, a stent is put in place to form vaginal dimensions, and the patient will need to dilate the vagina following surgery, frequently at first and tapering over time. A typical post-op protocol will involve dilating three times a day for 50 minutes each time for the first year. After that, maintenance dilation will be necessary for life. View MTF genital reconstruction results in our Photo Gallery.
Dr. MacPhee also performs orchiectomy, scrotal skin removal and limit-depth vaginoplasty procedures as alternatives to full MTF genital reconstruction .
PHOTO GALLERY

We are grateful for our many patients who are willing to share their experiences and results. Click … Read More >
MEET DR. MACPHEE

A highly skilled Plastic & Reconstructive surgeon in practice for more than 17 years, Dr. Keelee … Read More >
TRANSGENDER SURGERY

Dr. Keelee MacPhee has been performing gender affirming surgery since 2005 and is grateful for the … Read More >
READ OUR BLOG

Tune into our blog for recent news about GRS and the latest trends in cosmetic surgery procedures … Read More >
- About Dr. MacPhee
- Office Environment
- Surgery Hospitals
- Blog / News
- Photo Gallery
- Patient Forms
- Price Transparency
- Referring Therapists
- Referring Physicians

Graphic Medical Content
Content May be Inappropriate for Younger Audiences
Are you over 18 years of age?
- FIND A PROVIDER
I'm a Candidate
I'm a Provider
Log In / Sign Up
I'm a candidate
Provider login
I'm a provider
List your practice
FTM Gender Confirmation: Genital Construction
The specifics, the takeaway.
Download the app
As part of a transgender individual’s transition, genital reassignment surgery alters female genitalia into male genitalia.
Written By: Erin Storm, PA-C
Published: October 07, 2021
Last updated: February 18, 2022
- Procedure Overview
- Ideal Candidate
- Side Effects
- Average Cost
thumbs-up Pros
- Can Help Complete A Gender Affirmation Journey
thumbs-down Cons
- Potentially Cost Prohibitive
Invasiveness Score
Invasiveness is graded based on factors such as anesthesia practices, incisions, and recovery notes common to this procedure.
Average Recovery
Application.
Surgical Procedure
$ 50000 - $ 100000
What is a female to male (FTM) gender reassignment surgery?
Female to male (FTM) gender reassignment surgery is also known as sex reassignment surgery (SRS), genital construction, and generally as gender confirmation surgery. These plastic surgery procedures are used by transgender patients to remove and alter female genitalia into traditional male genitalia.
Plastic surgeons will usually perform a hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy to remove the uterus and ovaries. A vaginoplasty or vaginectomy will close the vagina, the erectile tissue of the clitoris is released and with the mons portion of the pubic area a neo-phallus is created (phalloplasty or metoidioplasty). The labia majora then become the scrotum (scrotoplasty), bilateral testicular implants are placed, and finally the urethra is lengthened through the newly created penile tissue.
Typically gender reassignment surgery is performed as a last step in a transgender individuals transition journey. Guidelines on standards of care from The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) state candidates must have letters of recommendation from their mental health professional and healthcare provider, have been living full time as a man for one year, and have completed one year of hormonal therapy to be eligible.
Information on facial masculinization surgeries, top surgeries (like a mastectomy), and other female to male gender affirming surgeries as part of a gender transition for transmen can be found in our comprehensive guide to FTM gender affirmation solutions .
What concerns does a FTM gender reassignment surgery treat?
- Transmasculine Bottom Surgery & Genital Construction : Female to male gender reassignment surgery creates male genitalia that are aesthetically authentic and functional.
Who is the ideal candidate for a FTM gender reassignment surgery?
The ideal candidate for FTM gender reassignment surgery is a transgender man seeking to complete his physical embodiment of his gender identity. This reconstructive genital surgery creates functioning male genitalia. FTM gender reassignment surgery is not recommended for those who have not been on hormone therapy for one year, have not been living full time as a man for one year, do not have letters of recommendation from their mental health provider and physician, children under the age of 18, and those with certain chronic medical conditions.
What is the average recovery associated with a FTM gender reassignment surgery?
Most patients experience four to six weeks of recovery time following a FTM gender reassignment surgery. Patients can expect bruising, swelling, and tenderness following the procedure. A urinary catheter is typically used for two to three weeks.
What are the potential side effects of a FTM gender reassignment surgery?
Possible side effects following a FTM gender reassignment surgery include bleeding, swelling, bruising, incision site infection, altered sensation, difficulty urinating due to strictures, difficulty with sexual function, prolonged edema, and complications from anesthesia or the procedure.
What can someone expect from the results of a FTM gender reassignment surgery?
The results of FTM gender reassignment surgery are permanent. This procedure creates functional male genitalia and removes all female genitalia.
What is the average cost of a FTM gender reassignment surgery?
What to expect.
A FTM gender reassignment surgery creates male genitalia. Here is a quick guide for what to expect before, during, and after a FTM gender reassignment surgery:
Before Surgery
- Prophylactic antibiotics or antivirals may be prescribed
- Stop taking blood thinning medications two weeks prior to surgery. Blood thinners may include, Advil, Tylenol, Aspirin, and prescription anticoagulants
- Stop smoking four weeks prior to the procedure and continue cessation for four weeks post op
- No alcohol two days prior to the procedure
- Do not eat or drink six hours before
During Surgery
- General anesthesia
- A hysterectomy, oophorectomy, and vaginoplasty are performed
- The clitoris is released from suspensory ligaments
- The neo-phallus and scrotum are created with existing tissues
- Testicular implants are placed - The urethra is lengthened
Immediately After Surgery
- Swelling, bruising, and tenderness
1 - 30 Days After Treatment & Beyond
- Resume most activities after a few days
- Swelling typically resolves within a few weeks
- Avoid strenuous activity for two to four weeks
- Remove urinary catheter after two to three weeks
Result Notes
- Results are permanent
- Proper aftercare will ensure optimal results
- Any revisions needed are typically not performed until six months after the initial procedure
Gender confirmation surgeries for transgender individuals are an important component of transgender health and in creating an embodied gender identity. Gender reassignment surgery allows transgender men who feel it is a part of their transition to more fully embrace their gender identity.
To learn more about our content creation practices, visit our Editorial Process page .
Source List
AEDIT uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons Gender Confirmation Surgeries plasticsurgery.org
- Karel E Y Claes Chest Surgery for Transgender and Gender Nonconforming Individuals PubMed.gov ; 2018-07-02
Related Procedures

FTM Gender Confirmation Solutions

Adam’s Apple Enhancement

FTM Gender Confirmation: Facial Masculinization

FTM Gender Confirmation: Transmasculine Top & Bottom Surgeries
View all procedures
Learn More About FTM Gender Confirmation: Genital Construction in The AEDITION

Gender Transitioning And Skincare: Taking Care Of Your Changing Face
Side effects of hormone therapy often show up on the skin in the form of acne, pigmentation, and uneven skin texture. Here’s what you need to know about the most common skin concerns and treatment options.

Everything You Need To Know About Clavicle Surgery
Clavicle (a.k.a. collarbone) surgery is growing in popularity among patients seeking to change the length and prominence of the bone, enhance their décolleté, and improve the overall proportion of the body.

Finding The Right Plastic Surgeon, Dermatologist, Or Cosmetic Dentist
When considering a cosmetic procedure, it is so important to find the right doctor for you.
Discover more articles

‘Try on’ aesthetic procedures and instantly visualize possible results with AEDIT and our patented 3D aesthetic simulator.
Find Top Aesthetic Providers Near You
Providers by locations.
- Alpharetta, GA Providers
- Bay Harbor Islands, FL Providers
- Chevy Chase, MD Providers
- Fall River, MA Providers
- Glenview, IL Providers
- Lone Tree, CO Providers
- Metairie, LA Providers
- Minneapolis, MN Providers
- More Locations
- New Haven, CT Providers
- Newport Beach, CA Providers
- Scottsdale, AZ Providers
- Southfield, MI Providers
- Springdale, AR Providers
- Washington, DC Providers
Providers by Specialties
- Cosmetic Dentistry Providers
- Cosmetic Dermatology Providers
- Cosmetic Surgery Providers
- Dermatologic Surgery Providers
- Dermatology Providers
- Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Providers
- General Surgery Providers
- Hair Restoration Surgery Providers
- Head and Neck Surgery Providers
- Medspa Providers
- More Procedures
- Oculoplastic Surgery Providers
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Providers
- Vaginal Rejuvenation Providers
Providers by Procedures
- Acne Scar Treatment Providers
- Acne Treatment Providers
- Birthmark Removal Providers
- Blepharoplasty Providers
- Botox Providers
- Brow Lift Providers
- Buccal Fat Removal (Cheek Reduction) Providers
- Cheek Augmentation (Cheek Implants) Providers
- Cheek Surgery Providers
- Chemical Peels Providers
- Chin Surgery (Mentoplasty) Providers
- Dental Treatments Providers
- Dermabrasion Treatment Providers
- Dermal Fillers & Injectables Providers
- More Specialties

Results of gender reassignment surgery

Vaginoplasty

Buttock augmentation

Facial feminiZation

BREAST AUGMENTATION

Phalloplasty

Post-phalloplasty aesthetics

Metaidoioplasty
Do you need more information about gender affirmation surgery ? Do you have questions about a sex reassignment surgery ?
(18 years in Spain)
Are you 18 years or older?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Semin Plast Surg
- v.25(3); 2011 Aug

Aesthetic and Functional Genital and Perineal Surgery: Male
Sex reassignment surgery in the female-to-male transsexual, stan j. monstrey.
1 Department of Plastic Surgery, Ghent University Hospital, Gent, Belgium
Peter Ceulemans
Piet hoebeke.
2 Department of Urology, Ghent University Hospital, Gent, Belgium
In female-to-male transsexuals, the operative procedures are usually performed in different stages: first the subcutaneous mastectomy which is often combined with a hysterectomy-ovarectomy (endoscopically assisted). The next operative procedure consists of the genital transformation and includes a vaginectomy, a reconstruction of the horizontal part of the urethra, a scrotoplasty and a penile reconstruction usually with a radial forearm flap (or an alternative). After about one year, penile (erection) prosthesis and testicular prostheses can be implanted when sensation has returned to the tip of the penis. The authors provide a state-of-the-art overview of the different gender reassignment surgery procedures that can be performed in a female-to-male transsexual.
Transsexual patients have the absolute conviction of being born in the wrong body and this severe identity problem results in a lot of suffering from early childhood on. Although the exact etiology of transsexualism is still not fully understood, it is most probably a result of a combination of various biological and psychological factors. As to the treatment, it is universally agreed that the only real therapeutic option consists of “adjusting the body to the mind” (or gender reassignment) because trying to “adjust the mind to the body” with psychotherapy has been shown to alleviate the severe suffering of these patients. Gender reassignment usually consists of a diagnostic phase (mostly supported by a mental health professional), followed by hormonal therapy (through an endocrinologist), a real-life experience, and at the end the gender reassignment surgery itself.
As to the criteria of readiness and eligibility for these surgical interventions, it is universally recommended to adhere to the Standards of Care (SOC) of the WPATH (World Professional association of Transgender Health) 1 . It is usually advised to stop all hormonal therapy 2 to 3 weeks preoperatively.
The two major sex reassignment surgery (SRS) interventions in the female-to-male transsexual patients that will be addressed here are (1) the subcutaneous mastectomy (SCM), often combined with a hysterectomy/ ovariectomy; and (2) the actual genital transformation consisting of vaginectomy, reconstruction of the fixed part of the urethra (if isolated, metoidioplasty), scrotoplasty and phalloplasty. At a later stage, a testicular prostheses and/or erection prosthesis can be inserted.
SUBCUTANEOUS MASTECTOMY
General principles.
Because hormonal treatment has little influence on breast size, the first (and, arguably, most important) surgery performed in the female-to-male (FTM) transsexual is the creation of a male chest by means of a SCM. This procedure allows the patient to live more easily in the male role 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 and thereby facilitates the “real-life experience,” a prerequisite for genital surgery.
The goal of the SCM in a FTM transsexual patient is to create an aesthetically pleasing male chest, which includes removal of breast tissue and excess skin, reduction and proper positioning of the nipple and areola, obliteration of the inframammary fold, and minimization of chest-wall scars. 4 , 5 Many different techniques have been described to achieve these goals and most authors agree that skin excess , not breast volume, is the factor that should determine the appropriate SCM technique. 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 Recently, the importance of the skin elasticity has also been demonstrated and it is important to realize that in this patient population, poor skin quality can be exacerbated when the patient has engaged in years of “breast binding” (Fig. 1 ). 6

(A,B) Result of long-term “breast binding.”
In the largest series to date, Monstrey et al 6 described an algorithm of five different techniques to perform an aesthetically satisfactory SCM (Fig. 2 ). Preoperative parameters to be evaluated include breast volume, degree of excess skin, nipple-areola complex (NAC) size and position, and skin elasticity.

Algorithm for choosing appropriate subcutaneous mastectomy technique.
Regardless of the technique, it is extremely important to preserve all subcutaneous fat when dissecting the glandular tissue from the flaps. This ensures thick flaps that produce a pleasing contour. Liposuction is only occasionally indicated laterally, or to attain complete symmetry at the end of the procedure. Postoperatively, a circumferential elastic bandage is placed around the chest wall and maintained for a total of 4 to 6 weeks.
The semicircular technique (Fig. 3 ) is essentially the same procedure as that described by Webster in 1946 7 for gynecomastia. It is useful for individuals with smaller breasts and elastic skin. A sufficient amount of glandular tissue should be left in situ beneath the NAC to avoid a depression. The particular advantage of this technique is the small and well-concealed scar which is confined to (the lower half of) the nipple-areola complex. The major drawback is the small window through which to work, making excision of breast tissue and hemostasis more challenging.

Semicircular technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.
In cases of smaller breasts with large prominent nipples, the transareolar technique (Fig. 4 ) is used. This is similar to the procedure described by Pitanguy in 1966 8 and allows for subtotal resection and immediate reduction of the nipple. The resulting scar traverses the areola horizontally and passes around the upper aspect of the nipple.

Transareolar technique. (A,B) Incisions and scar; (C) preoperative; (D) postoperative.
The concentric circular technique (Fig. 5 ) is similar to that described by Davidson in 1979. 9 It is used for breasts with a medium-sized skin envelope (B cup), or in the case of smaller breasts with poor skin elasticity. The resulting scar will be confined to the circumference of the areola. The concentric incision can be drawn as a circle or ellipse, enabling deepithelialization of a calculated amount of skin in the vertical or horizontal direction. 4 , 5 Access is gained via an incision in the inferior aspect of the outer circle leaving a wide pedicle for the NAC. A purse-string suture is placed and set to the desired areolar diameter (usually 25–30 mm). The advantage of this technique is that it allows for reduction and/or repositioning of the areola, where required, and for the removal of excess skin.

Concentric circular technique. (A) incisions; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.
The extended concentric circular technique (Fig. 6 ) is similar to the concentric circular technique, but includes one or two additional triangular excisions of skin and subcutaneous tissue lateral and/ or medial. This technique is useful for correcting skin excess and wrinkling produced by large differences between the inner and outer circles. The resulting scars will be around the areola, with horizontal extensions onto the breast skin, depending on the degree of excess skin.

Extended concentric circular technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative preoperative; (C) postoperative.
The free nipple graft technique (Fig. 7 ) has been proposed by several authors for patients with large and ptotic breasts. 2 , 3 , 10 , 11 , 12 It consists of harvesting the NAC as a full-thickness skin graft; amputating the breast; and grafting the NAC onto its new location on the chest wall. Our preference is to place the incision horizontally 1 to 2 cm above the inframammary fold, and then to move upwards laterally below the lateral border of the pectoralis major muscle. The placement of the NAC usually corresponds to the 4th or 5th intercostal space. Clinical judgment is most important, however, and we always sit the patient up intraoperatively to check final nipple position. The advantages of the free nipple graft technique are easy chest contouring, excellent exposure and more rapid resection of tissue, as well as nipple reduction, areola resizing, and repositioning. The disadvantages are the long residual scars, NAC pigmentary and sensory changes, and the possibility of incomplete graft take.

Free nipple graft technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.
Complications
Postoperative complications include hematoma (most frequent, despite drains and compression bandages), (partial) nipple necrosis, and abscess formation. This underscores the importance of achieving good hemostasis intraoperatively. Smaller hematomas and seromas can be evacuated through puncture, but for larger collections surgical evacuation is required.
Another not infrequent complication consists of skin slough of the NAC, which can be left to heal by conservative means. The exceptional cases of partial or total nipple necrosis may require a secondary nipple reconstruction. Even in the patients without complications, ~25% required an additional procedure to improve the aesthetic results. The likelihood of an additional aesthetic correction should be discussed with the patient in advance. 13 Tattoo of the areola may be performed for depigmentation.
The recommendations of the authors are summarized in their algorithm (Fig. 2 ), which clearly demonstrates that a larger skin envelope and a less elastic skin will require progressively a longer-incision technique. The FTM transsexual patients are rightfully becoming a patient population that is better informed and more demanding as to the aesthetic outcomes.
Finally, it is important to note that there have been reports of breast cancer after bilateral SCM in this population 14 , 15 , 16 because in most patients the preserved NAC and the always incomplete glandular resection leave behind tissue at risk of malignant transformation.
PHALLOPLASTY
In performing a phalloplasty for a FTM transsexual, the surgeon should reconstruct an aesthetically appealing neophallus, with erogenous and tactile sensation, which enables the patient to void while standing and have sexual intercourse like a natural male, in a one-stage procedure. 17 , 18 The reconstructive procedure should also provide a normal scrotum, be predictably reproducible without functional loss in the donor area, and leave the patient with minimal scarring or disfigurement.
Despite the multitude of flaps that have been employed and described (often as Case Reports), the radial forearm is universally considered the gold standard in penile reconstruction. 17 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28
In the largest series to date (almost 300 patients), Monstrey et al 29 recently described the technical aspects of radial forearm phalloplasty and the extent to which this technique, in their hands approximates the criteria for ideal penile reconstruction.
For the genitoperineal transformation (vaginectomy, urethral reconstruction, scrotoplasty, phalloplasty), two surgical teams operate at the same time with the patient first placed in a gynecological (lithotomy) position. In the perineal area, a urologist may perform a vaginectomy, and lengthen the urethra with mucosa between the minor labiae. The vaginectomy is a mucosal colpectomy in which the mucosal lining of the vaginal cavity is removed. After excision, a pelvic floor reconstruction is always performed to prevent possible diseases such as cystocele and rectocele. This reconstruction of the fixed part of the urethra is combined with a scrotal reconstruction by means of two transposition flaps of the greater labia resulting in a very natural looking bifid scrotum.
Simultaneously, the plastic surgeon dissects the free vascularized flap of the forearm. The creation of a phallus with a tube-in-a-tube technique is performed with the flap still attached to the forearm by its vascular pedicle (Fig. 8A ). This is commonly performed on the ulnar aspect of the skin island. A small skin flap and a skin graft are used to create a corona and simulate the glans of the penis (Fig. 8B ).

(A–D) Phallic reconstruction with the radial forearm flap: creation of a tube (urethra) within a tube (penis).
Once the urethra is lengthened and the acceptor (recipient) vessels are dissected in the groin area, the patient is put into a supine position. The free flap can be transferred to the pubic area after the urethral anastomosis: the radial artery is microsurgically connected to the common femoral artery in an end-to-side fashion and the venous anastomosis is performed between the cephalic vein and the greater saphenous vein (Fig. 8C ). One forearm nerve is connected to the ilioinguinal nerve for protective sensation and the other nerve of the arm is anastomosed to one of the dorsal clitoral nerves for erogenous sensation. The clitoris is usually denuded and buried underneath the penis, thus keeping the possibility to be stimulated during sexual intercourse with the neophallus.
In the first 50 patients of this series, the defect on the forearm was covered with full-thickness skin grafts taken from the groin area. In subsequent patients, the defect was covered with split-thickness skin grafts harvested from the medial and anterior thigh (Fig. 8D ).
All patients received a suprapubic urinary diversion postoperatively.
The patients remain in bed during a one-week postoperative period, after which the transurethral catheter is removed. At that time, the suprapubic catheter was clamped, and voiding was begun. Effective voiding might not be observed for several days. Before removal of the suprapubic catheter, a cystography with voiding urethrography was performed.
The average hospital stay for the phalloplasty procedure was 2½ weeks.
Tattooing of the glans should be performed after a 2- to 3-month period, before sensation returns to the penis.
Implantation of the testicular prostheses should be performed after 6 months, but it is typically done in combination with the implantation of a penile erection prosthesis. Before these procedures are undertaken, sensation must be returned to the tip of the penis. This usually does not occur for at least a year.
The Ideal Goals of Penile Reconstruction in FTM Surgery
What can be achieved with this radial forearm flap technique as to the ideal requisites for penile reconstruction?
A ONE-STAGE PROCEDURE
In 1993, Hage 20 stated that a complete penile reconstruction with erection prosthesis never can be performed in one single operation. Monstrey et al, 29 early in their series and to reduce the number of surgeries, performed a (sort of) all-in-one procedure that included a SCM and a complete genitoperineal transformation. However, later in their series they performed the SCM first most often in combination with a total hysterectomy and ovariectomy.
The reason for this change in protocol was that lengthy operations (>8 hours) resulted in considerable blood loss and increased operative risk. 30 Moreover, an aesthetic SCM is not to be considered as an easy operation and should not be performed “quickly” before the major phalloplasty operation.
AN AESTHETIC PHALLUS
Phallic construction has become predictable enough to refine its aesthetic goals, which includes the use of a technique that can be replicated with minimal complications. In this respect, the radial forearm flap has several advantages: the flap is thin and pliable allowing the construction of a normal sized, tube-within-a-tube penis; the flap is easy to dissect and is predictably well vascularized making it safe to perform an (aesthetic) glansplasty at the distal end of the flap. The final cosmetic outcome of a radial forearm phalloplasty is a subjective determination, but the ability of most patients to shower with other men or to go to the sauna is the usual cosmetic barometer (Fig. 9A-C ).

(A–C) Late postoperative results of radial forearm phalloplasties.
The potential aesthetic drawbacks of the radial forearm flap are the need for a rigidity prosthesis and possibly some volume loss over time.
TACTILE AND EROGENOUS SENSATION
Of the various flaps used for penile reconstruction, the radial forearm flap has the greatest sensitivity. 1 Selvaggi and Monstrey et al. always connect one antebrachial nerve to the ilioinguinal nerve for protective sensation and the other forearm nerve with one dorsal clitoral nerve. The denuded clitoris was always placed directly below the phallic shaft. Later manipulation of the neophallus allows for stimulation of the still-innervated clitoris. After one year, all patients had regained tactile sensitivity in their penis, which is an absolute requirement for safe insertion of an erection prosthesis. 31
In a long-term follow-up study on postoperative sexual and physical health, more than 80% of the patients reported improvement in sexual satisfaction and greater ease in reaching orgasm (100% in practicing postoperative FTM transsexuals). 32
VOIDING WHILE STANDING
For biological males as well as for FTM transsexuals undergoing a phalloplasty, the ability to void while standing is a high priority. 33 Unfortunately, the reported incidences of urological complications, such as urethrocutaneous fistulas, stenoses, strictures, and hairy urethras are extremely high in all series of phalloplasties, as high as 80%. 34 For this reason, certain (well-intentioned) surgeons have even stopped reconstructing a complete neo-urethra. 35 , 36
In their series of radial forearm phalloplasties, Hoebeke and Monstrey still reported a urological complication rate of 41% (119/287), but the majority of these early fistulas closed spontaneously and ultimately all patients were able to void through the newly reconstructed penis. 37 Because it is unknown how the new urethra—a 16-cm skin tube—will affect bladder function in the long term, lifelong urologic follow-up was strongly recommended for all these patients.
MINIMAL MORBIDITY
Complications following phalloplasty include the general complications attendant to any surgical intervention such as minor wound healing problems in the groin area or a few patients with a (minor) pulmonary embolism despite adequate prevention (interrupting hormonal therapy, fractioned heparin subcutaneously, elastic stockings). A vaginectomy is usually considered a particularly difficult operation with a high risk of postoperative bleeding, but in their series no major bleedings were seen. 30 Two early patients displayed symptoms of nerve compression in the lower leg, but after reducing the length of the gynecological positioning to under 2 hours, this complication never occurred again. Apart from the urinary fistulas and/or stenoses, most complications of the radial forearm phalloplasty are related to the free tissue transfer. The total flap failure in their series was very low (<1%, 2/287) despite a somewhat higher anastomotic revision rate (12% or 34/287). About 7 (3%) of the patients demonstrated some degree of skin slough or partial flap necrosis. This was more often the case in smokers, in those who insisted on a large-sized penis requiring a larger flap, and also in patients having undergone anastomotic revision.
With smoking being a significant risk factor, under our current policy, we no longer operate on patients who fail to quit smoking one year prior to their surgery.
NO FUNCTIONAL LOSS AND MINIMAL SCARRING IN THE DONOR AREA
The major drawback of the radial forearm flap has always been the unattractive donor site scar on the forearm (Fig. 10 ). Selvaggi et al conducted a long-term follow-up study 38 of 125 radial forearm phalloplasties to assess the degree of functional loss and aesthetic impairment after harvesting such a large forearm flap. An increased donor site morbidity was expected, but the early and late complications did not differ from the rates reported in the literature for the smaller flaps as used in head and neck reconstruction. 38 No major or long-term problems (such as functional limitation, nerve injury, chronic pain/edema, or cold intolerance) were identified. Finally, with regard to the aesthetic outcome of the donor site, they found that the patients were very accepting of the donor site scar, viewing it as a worthwhile trade-off for the creation of a phallus (Fig. 10 ). 38 Suprafascial flap dissection, full thickness skin grafts, and the use of dermal substitutes may contribute to a better forearm scar.

(A,B) Aspect of the donor site after a phalloplasty with a radial forearm flap.
NORMAL SCROTUM
For the FTM patient, the goal of creating natural-appearing genitals also applies to the scrotum. As the labia majora are the embryological counterpart of the scrotum, many previous scrotoplasty techniques left the hair-bearing labia majora in situ, with midline closure and prosthetic implant filling, or brought the scrotum in front of the legs using a V-Y plasty. These techniques were aesthetically unappealing and reminiscent of the female genitalia. Selvaggi in 2009 reported on a novel scrotoplasty technique, which combines a V-Y plasty with a 90-degree turning of the labial flaps resulting in an anterior transposition of labial skin (Fig. 11 ). The excellent aesthetic outcome of this male-looking (anteriorly located) scrotum, the functional advantage of fewer urological complications and the easier implantation of testicular prostheses make this the technique of choice. 39

Reconstruction of a lateral looking scrotum with two transposition flaps: (A) before and (B) after implantation of testicular prostheses.
SEXUAL INTERCOURSE
In a radial forearm phalloplasty, the insertion of erection prosthesis is required to engage in sexual intercourse. In the past, attempts have been made to use bone or cartilage, but no good long-term results are described. The rigid and semirigid prostheses seem to have a high perforation rate and therefore were never used in our patients. Hoebeke, in the largest series to date on erection prostheses after penile reconstruction, only used the hydraulic systems available for impotent men. A recent long-term follow-up study showed an explantation rate of 44% in 130 patients, mainly due to malpositioning, technical failure, or infection. Still, more than 80% of the patients were able to have normal sexual intercourse with penetration. 37 In another study, it was demonstrated that patients with an erection prosthesis were more able to attain their sexual expectations than those without prosthesis (Fig. 12 ). 32

(A,B) Phalloplasty after implantation of an erection prosthesis.
A major concern regarding erectile prostheses is long-term follow-up. These devices were developed for impotent (older) men who have a shorter life expectancy and who are sexually less active than the mostly younger FTM patients.
Alternative Phalloplasty Techniques
Metaidoioplasty.
A metoidioplasty uses the (hypertrophied) clitoris to reconstruct the microphallus in a way comparable to the correction of chordee and lengthening of a urethra in cases of severe hypospadias. Eichner 40 prefers to call this intervention “the clitoris penoid.” In metoidioplasty, the clitoral hood is lifted and the suspensory ligament of the clitoris is detached from the pubic bone, allowing the clitoris to extend out further. An embryonic urethral plate is divided from the underside of the clitoris to permit outward extension and a visible erection. Then the urethra is advanced to the tip of the new penis. The technique is very similar to the reconstruction of the horizontal part of the urethra in a normal phalloplasty procedure. During the same procedure, a scrotal reconstruction, with a transposition flap of the labia majora (as previously described) is performed combined with a vaginectomy.
FTM patients interested in this procedure should be informed preoperatively that voiding while standing cannot be guaranteed, and that sexual intercourse will not be possible (Fig. 13 ).

Results of a metoidioplasty procedure.
The major advantage of metoidioplasty is the complete lack of scarring outside the genital area. Another advantage is that its cost is substantially lower than that of phalloplasty. Complications of this procedure also include urethral obstruction and/or urethral fistula.
It is always possible to perform a regular phalloplasty (e.g., with a radial forearm flap) at a later stage, and with substantially less risk of complications and operation time.
FIBULA FLAP
There have been several reports on penile reconstruction with the fibular flap based on the peroneal artery and the peroneal vein. 27 , 41 , 42 It consists of a piece of fibula that is vascularized by its periosteal blood supply and connected through perforating (septal) vessels to an overlying skin island at the lateral site of the lower leg. The advantage of the fibular flap is that it makes sexual intercourse possible without a penile prosthesis. The disadvantages are a pointed deformity to the distal part of the penis when the extra skin can glide around the end of fibular bone, and that a permanently erected phallus is impractical.
Many authors seem to agree that the fibular osteocutaneous flap is an optimal solution for penile reconstruction in a natal male. 42
NEW SURGICAL DEVELOPMENTS: THE PERFORATOR FLAPS
Perforator flaps are considered the ultimate form of tissue transfer. Donor site morbidity is reduced to an absolute minimum, and the usually large vascular pedicles provide an additional range of motion or an easier vascular anastomosis. At present, the most promising perforator flap for penile reconstruction is the anterolateral thigh (ALT) flap. This flap is a skin flap based on a perforator from the descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery, which is a branch from the femoral artery. It can be used both as a free flap 43 and as a pedicled flap 44 then avoiding the problems related to microsurgical free flap transfer. The problem related to this flap is the (usually) thick layer of subcutaneous fat making it difficult to reconstruct the urethra as a vascularized tube within a tube. This flap might be more indicated for phallic reconstruction in the so-called boys without a penis, like in cases of vesical exstrophy (Fig. 14 ). However, in the future, this flap may become an interesting alternative to the radial forearm flap, particularly as a pedicled flap. If a solution could be found for a well-vascularized urethra, use of the ALT flap could be an attractive alternative to the radial forearm phalloplasty. The donor site is less conspicuous, and secondary corrections at that site are easier to make. Other perforator flaps include the thoracodorsal perforator artery flap (TAP) and the deep inferior epigastric perforator artery flap (DIEP). The latter might be an especially good solution for FTM patients who have been pregnant in the past. Using the perforator flap as a pedicled flap can be very attractive, both financially and technically.

Penile reconstruction with a pedicled anterolateral thigh flap. (A) Preoperative and (B) postoperative results.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach
Gender reassignment, particularly reassignment surgery, requires close cooperation between the different surgical specialties. In phalloplasty, the collaboration between the plastic surgeon, the urologist, and the gynecologist is essential. 45 The actual penile reconstruction is typically performed by the plastic and reconstructive surgeon, and the contribution of the gynecologist, who performs a hysterectomy and a BSO (preferably through a minimal endoscopic access in combination with SCM), should not be underestimated.
However, in the long term, the urologist's role may be the most important for patients who have undergone penile reconstruction, especially because the complication rate is rather high, particularly with regard to the number of urinary fistulas and urinary stenoses. The urologist also reconstructs the fixed part of the urethra. He or she is likely the best choice for implantation and follow-up of the penile and/or testicular prostheses. They must also address later sequelae, including stone formation. Moreover, the surgical complexity of adding an elongated conduit (skin-tube urethra) to a biological female bladder, and the long-term effects of evacuating urine through this skin tube, demand lifelong urological follow-up.
Therefore, professionals who unite to create a gender reassignment program should be aware of the necessity of a strong alliance between the plastic surgeon, the urologist, mental health professional and the gynecologist. In turn, the surgeons must commit to the extended care of this unique population, which, by definition, will protract well into the future.
- Meyer W J, III, Bockting W O, Cohen-Kettenis P, et al. The Standards of Care for Gender Identity Disorders, 6th Version. J Psychol Human Sex. 2002; 13 :1–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindsay W RN. Creation of a male chest in female transsexuals. Ann Plast Surg. 1979; 3 (1):39–46. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eicher W. Transsexualismus. Vol. 1992. Stuttgart: Fisher Verlag; pp. 120–123. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bloem J J. Chest wall contouring for female-to-male transsexuals: Amsterdam experience. Ann Plast Surg. 1995; 34 (1):59–66. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Kesteren P J van. Chest-wall contouring in female-to-male transsexuals: basic considerations and review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995; 96 (2):386–391. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Monstrey S, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, et al. Chest-wall contouring surgery in female-to-male transsexuals: a new algorithm. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 121 (3):849–859. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webster J P. Mastectomy for gynecomastia through a semicircular intra-areolar incision. Ann Surg. 1946; 124 :557–575. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pitanguy I. Transareolar incision for gynecomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966; 38 (5):414–419. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson B A. Concentric circle operation for massive gynecomastia to excise the redundant skin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979; 63 (3):350–354. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kluzák R. Sex conversion operation in female transsexualism. Acta Chir Plast. 1968; 10 (3):188–198. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoopes J E. Surgical construction of the male external genitalia. Clin Plast Surg. 1974; 1 (2):325–334. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kenney J G, Edgerton M T. Reduction mammoplasty in gender dysphoria. Abstract presented at the 11th Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association; septerber20–23, 1989; Cleveland, Ohio.
- Beer G M, Budi S, Seifert B, Morgenthaler W, Infanger M, Meyer V E. Configuration and localization of the nipple-areola complex in men. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 108 (7):1947–1952. discussion 1953. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symmers W S. Carcinoma of breast in trans-sexual individuals after surgical and hormonal interference with the primary and secondary sex characteristics. BMJ. 1968; 2 (5597):83–85. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Secreto G, Toniolo P, Berrino F, et al. Increased androgenic activity and breast cancer risk in premenopausal women. Cancer Res. 1984; 44 (12 Pt 1):5902–5905. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burcombe R J, Makris A, Pittam M, Finer N. Breast cancer after bilateral subcutaneous mastectomy in a female-to-male trans-sexual. Breast. 2003; 12 (4):290–293. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert D A, Horton C E, Terzis J K, Devine C J, Jr, Winslow B H, Devine P C. New concepts in phallic reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1987; 18 (2):128–136. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bouman F G, de Graaf F H, Bloem J J. Construction of the neophallus in female-to-lake transsexuals: the Amsterdam experience. J Urol. 1993; 6 :1463–1468. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang T S, Hwang W Y. Forearm flap in one-stage reconstruction of the penis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984; 74 (2):251–258. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, De Graaf F H. Addressing the ideal requirements by free flap phalloplasty: some reflections on refinements of technique. Microsurgery. 1993; 14 (9):592–598. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fang R H, Kao Y S, Ma S, Lin J T. Phalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals using free radial osteocutaneous flap: a series of 22 cases. Br J Plast Surg. 1999; 52 (3):217–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Biemer E. Penile construction by the radial arm flap. Clin Plast Surg. 1988; 15 (3):425–430. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koshima I, Tai T, Yamasaki M. One-stage reconstruction of the penis using an innervated radial forearm osteocutaneous flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 1986; 3 (1):19–26. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyer R, Daverio P J. One-stage phalloplasty without sensory deprivation in female transsexuals. World J Urol. 1987; 5 :9–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Upton J, Mutimer K L, Loughlin K, Ritchie J. Penile reconstruction using the lateral arm flap. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1987; 32 (2):97–101. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harashina T, Inoue T, Tanaka I, Imai K, Hatoko M. Reconstruction of penis with free deltoid flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1990; 43 (2):217–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadove R C, Sengezer M, McRoberts J W, Wells M D. One-stage total penile reconstruction with a free sensate osteocutaneous fibula flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 92 (7):1314–1323. discussion 1324–1325. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santanelli F, Scuderi N. Neophalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals with the island tensor fasciae latae flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 105 (6):1990–1996. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, et al. Penile reconstruction: is the radial forearm flap really the standard technique? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 124 (2):510–518. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weyers S, Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, et al. Two-stage versus one-stage sex reassignment surgery in female-to-male transsexual individuals. Gynecol Surg. 2006; 3 :190–194. [ Google Scholar ]
- Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, Ceulemans P, T'Sjoen G, De Cuypere G, Hoebeke P. Genital sensitivity after sex reassignment surgery in transsexual patients. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 58 (4):427–433. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Cuypere G, T'Sjoen G, Beerten R, et al. Sexual and physical health after sex reassignment surgery. Arch Sex Behav. 2005; 34 (6):679–690. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bout C A, Bloem J J, Megens J A. Phalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals: what do our patients ask for? Ann Plast Surg. 1993; 30 (4):323–326. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vriens J P, Acosta R, Soutar D S, Webster M H. Recovery of sensation in the radial forearm free flap in oral reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 98 (4):649–656. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Felici N, Felici A. A new phalloplasty technique: the free anterolateral thigh flap phalloplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59 (2):153–157. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matti B A, Matthews R N, Davies D M. Phalloplasty using the free radial forearm flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1988; 41 (2):160–164. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, et al. Impact of sex reassignment surgery on lower urinary tract function. Eur Urol. 2005; 47 (3):398–402. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, et al. Donor-site morbidity of the radial forearm free flap after 125 phalloplasties in gender identity disorder. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118 (5):1171–1177. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoebeke P, de Cuypere G, Ceulemans P, Monstrey S. Obtaining rigidity in total phalloplasty: experience with 35 patients. J Urol. 2003; 169 (1):221–223. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eicher W. Surgical Treatment of Female-to-Male Transsexuals. In: Echer W, editor. Plastic Surgery in the Sexually Handicapped. Vol. 1989. Berlin: Springer; pp. 106–112. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Winters H A, Lieshout J Van. Fibula free flap phalloplasty: modifications and recommendations. Microsurgery. 1996; 17 (7):358–365. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sengezer M, Oztürk S, Deveci M, Odabaşi Z. Long-term follow-up of total penile reconstruction with sensate osteocutaneous free fibula flap in 18 biological male patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 114 (2):439–450. discussion 451–452. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Felici N. Phalloplasty with Free Anterolateral Thigh Flap. Paper presented the XIX Biennial Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association (HBIGDA); April 6–9, 2005; Bologna, Italy.
- Ceulemans P. The Pedicled Anterolateral Thigh Flap (ALT) Perforator Flap: A New Technique for Phallic Reconstruction. Paper presented at the XIV Biennial Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association (HBIGDA); April 6–9, 2005; Bologna, Italy.
- Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Dhont M, et al. Surgical therapy in transsexual patients: a multi-disciplinary approach. Acta Chir Belg. 2001; 101 (5):200–209. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
German parliament votes to make it easier for people to legally change their name and gender
German lawmakers have approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records.
Demonstrators protest demanding a law to protect the rights of the transgender community outside of the parliament Bundestag building in Berlin, Friday, Apri 12, 2024. German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. (AP Photo/Ebrahim Noroozi)
- Copy Link copied
A demonstrator holds a fan during a protest demanding a law to protect the rights of the transgender community outside of the parliament Bundestag building in Berlin, Friday, April 12, 2024. German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. (AP Photo/Ebrahim Noroozi)
Demonstrators protest demanding a law to protect the rights of the transgender community outside of the parliament Bundestag building in Berlin, Friday, April 12, 2024. German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. (AP Photo/Ebrahim Noroozi)
A Demonstrator protests demanding a law to protect the rights of the transgender community outside of the parliament Bundestag building in Berlin, Friday, Apri 12, 2024. German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. (AP Photo/Ebrahim Noroozi)
A demonstrator protests demanding a law to protect the rights of the transgender community outside of the parliament Bundestag building in Berlin, Friday, Apri 12, 2024. German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. (AP Photo/Ebrahim Noroozi)
BERLIN (AP) — German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records.
The “self-determination law,” one of several social reforms that Chancellor Olaf Scholz’s liberal-leaning coalition government pledged when it took office in late 2021, is set to take effect on Nov. 1.
Germany, the European Union’s most populous nation, follows several other countries in making the change. Parliament’s lower house, the Bundestag, approved it by 374 votes to 251 with 11 abstentions.
The German legislation will allow adults to change their first name and legal gender at registry offices without further formalities. They will have to notify the office three months before making the change.
The existing “transsexual law,” which dates back four decades, requires individuals who want to change gender on official documents to first obtain assessments from two experts “sufficiently familiar with the particular problems of transsexualism” and then a court decision.
Since that law was drawn up, Germany’s top court has struck down other provisions that required transgender people to get divorced and sterilized, and to undergo gender-transition surgery.
“For over 40 years, the ‘transsexual law’ has caused a lot of suffering ... and only because people want to be recognized as they are,” Sven Lehmann, the government’s commissioner for queer issues, told lawmakers. “And today we are finally putting an end to this.”
The new legislation focuses on individuals’ legal identities. It does not involve any revisions to Germany’s rules for gender-transition surgery.
The new rules will allow minors 14 years and older to change their name and legal gender with approval from their parents or guardians; if they don’t agree, teenagers could ask a family court to overrule them.
In the case of children younger than 14, parents or guardians would have to make registry office applications on their behalf.
After a formal change of name and gender takes effect, no further changes would be allowed for a year. The new legislation provides for operators of, for example, gyms and changing rooms for women to continue to decide who has access.
Nyke Slawik, a transgender woman elected to parliament in 2021 for the Greens, one of the governing parties, recounted her experience of going through the current system a decade ago. She said she had had enough of being asked “is that your brother’s ID?” when she had to identify herself.
“Two years, many conversations with experts and one district court process later, it was done — the name change went through, and I was nearly 2,000 euros ($2,150) poorer,” she told lawmakers. “As trans people, we repeatedly experience our dignity being made a matter for negotiation.”
The mainstream conservative opposition faulted the legislation for what it described as a lack of safeguards against abuse and a lack of protection for young people. Conservative lawmaker Susanne Hierl complained that the government is “ignoring the justified concerns of many women and girls.”
“You want to satisfy a loud but very small group and, in doing so, are dividing society,” Hierl said.
Martin Reichardt of the far-right Alternative for Germany blasted what he called “ideological nonsense.”
Justice Minister Marco Buschmann said in a statement that “there are numerous precautions against possibilities of abuse, however improbable they may be.” He insisted that the new law takes into account the interests of the whole of society and said “much less will change with this law than some say.”
Among others, Denmark, Norway, Finland and Spain already have similar legislation.
In the U.K., the Scottish parliament in 2022 passed a bill that would allow people aged 16 or older to change the gender designation on identity documents by self-declaration. That was vetoed by the British government, a decision that Scotland’s highest civil court upheld in December .
In other socially liberal reforms, Scholz’s government has legalized the possession of limited amounts of cannabis; eased the rules on gaining German citizenship and ended restrictions on holding dual citizenship; and ended a ban on doctors “advertising” abortion services. Same-sex marriage was already legalized in 2017.

COMMENTS
Research consistently shows that people who choose gender affirmation surgery experience reduced gender incongruence and improved quality of life. Depending on the procedure, 94% to 100% of people report satisfaction with their surgery results. Gender-affirming surgery provides long-term mental health benefits, too.
The final results of transfeminine bottom surgery can help alleviate the feelings of gender dysphoria that some individuals may experience. Over time, the new vagina will settle into position and the scar lines will improve, although they'll never disappear completely. There are trade-offs, but most transwomen feel these are small compared to ...
Results: results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18 to 61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 hours (range, 2 to 5 hours); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range, 1-39). ... sexual function, and overall QOL compared with sex reassignment without ...
Body congruency score for chest, body hair, and voice improved significantly in 40 years' postoperative settings, with average scores ranging from 84.2 to 96.2. Body congruency scores for genitals ranged from 67.5 to 79 with free flap phalloplasty showing highest scores. Long-term overall body congruency score was 89.6.
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.. Often used to refer to vaginoplasty, sex reassignment surgery can also more broadly refer to other gender-affirming ...
Gender affirming surgery can be used to create a vulva and vagina. It involves removing the penis, testicles and scrotum. During a vaginoplasty procedure, tissue in the genital area is rearranged to create a vaginal canal (or opening) and vulva (external genitalia), including the labia. A version of vaginoplasty called vulvoplasty can create a ...
Overview. Feminizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Feminizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to increase the size of the breasts. That procedure also is called breast augmentation.
Metoidioplasty is a gender-affirming (sex-reassignment) surgery for transgender men assigned female at birth. According to the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey, about 4% of trans men have undergone the procedure, while another 53% expressed a desire to undergo metoidioplasty in the future.
Featured Expert: Fan Liang, M.D. Phalloplasty is surgery for masculinizing gender affirmation. Phalloplasty is a multistaged process that may include a variety of procedures, including: Creating the penis. Lengthening the urethra so you are able to stand to urinate. Creating the tip (glans) of the penis. Creating the scrotum.
MALE-TO-FEMALE SEX REASSIGNMENT REVISIONS. by altermd. altermd March 2, 2020. BEFORE & AFTER Gender Confirmation. FEMALE-TO-MALE CHEST CONTOURING. by altermd. ... results you deserve. Schedule Your Consultation Today. Thoughts & Insights. Labiaplasty January 24, 2024. 5 Labiaplasty Benefits You Should Know About.
Patients with diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder, transsexualism, or a personal history of sex reassignment were identified, and the performance of GAS, including breast and chest procedures, genital reconstructive procedures, and other facial and cosmetic surgical procedures, were identified. ... Results A total of 48 019 patients ...
Gender-affirming surgery is a surgical procedure, or series of procedures, that alters a person's physical appearance and sexual characteristics to resemble those associated with their identified gender.The phrase is most often associated with transgender health care and intersex medical interventions, although many such treatments are also pursued by cisgender and non-intersex individuals.
MTF Vaginoplasty. In male-to-female sex reassignment, the trans woman may choose to undergo vaginoplasty - the inversion of the penis to create a vagina - as part of her physical transition. This procedure can result in a fully sensate neovagina. Dr. MacPhee performs this reconstructive procedure by disassembling the penis and utilizing the ...
In addition to cross-sex hormone therapy, gender-affirming surgery (GAS)—formerly known as sex-reassignment surgery (SRS)—aims to surgically align physical characteristics with one's identity. These surgical interventions target sex-specific physical characteristics such as genitals (e.g., vaginoplasty), chest (e.g., mastectomy), face ...
During this period, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty. Results: Results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18-61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2-5 h); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1-39).
Results from studies imply that sex reassignment surgery on the one hand has positive effects in terms of partial aspects of quality of life, such as mental health, sexuality, and life satisfaction, and, on the other hand, on quality of life overall. Because of the studies' high dropout rates (12-77%; median 56%), the results should be ...
A 2018 study found that 94-100% of participants who had undergone gender-affirming surgery reported satisfaction with the surgical results, with the variance depending on the type of procedure.
Löwenberg ( 19) also found a correlation between satisfaction with surgery and satisfaction with aesthetic appearance of the external genitalia. In our study, almost all patients (98.2%) were satisfied with the gender reassignment surgery process ( n = 50, 45.5% "very satisfied"; n = 33, 30% "satisfied"; n = 25, 22.7% "mostly ...
The results of FTM gender reassignment surgery are permanent. This procedure creates functional male genitalia and removes all female genitalia. What is the average cost of a FTM gender reassignment surgery? FTM gender reassignment surgery costs generally exceed $50,000. The actual cost of a surgical procedure will be dependent on location ...
Results of gender reassignment surgery. Knowing the before and after of a surgery or treatment performed by the IM GENDER team is important so as to have a clear idea of the results. Vaginoplasty. Buttock augmentation . Facial feminiZation. MASTECTOMY. BREAST AUGMENTATION . Phalloplasty .
By Valerie Richardson - The Washington Times - Monday, April 8, 2024. A landmark Dutch study found that most adolescents ultimately outgrow their gender confusion, fueling the growing unease over ...
The authors provide a state-of-the-art overview of the different gender reassignment surgery procedures that can be performed in a female-to-male transsexual. Keywords: Genital ... Transsexual patients have the absolute conviction of being born in the wrong body and this severe identity problem results in a lot of suffering from early childhood ...
The Report on sex change, signed by paediatrician Dr Hilary Cass, has 32 recommendations Photo: Expansion Politica . Following Research, British Government Makes Known Frightening Results of ...
Updated 6:58 AM PDT, April 12, 2024. BERLIN (AP) — German lawmakers on Friday approved legislation that will make it easier for transgender, intersex and nonbinary people to change their name and gender in official records. The "self-determination law," one of several social reforms that Chancellor Olaf Scholz's liberal-leaning ...