- 7 August 2023

6 Examples of Great Brand Strategy Case Studies
What is brand strategy.
The term brand strategy relates to the methods a brand will use to market its products or services to consumers. It focuses on how they present and position themselves in the market. There are several strategies a brand can use and here are some of the biggest.
Company Name
This is where a brand will focus on marketing their company/brand name as a whole. They don’t focus on any specific element of their brand, services or products. Their goal is to improve brand awareness through marketing their name alone.
Individual Branding
This is where a brand will focus on a specific element of their brand. This could range from an individual product to a service, or even a person. This form of branding moves away from overall brand marketing and narrows its focus towards a specific element.
Attitude Branding
This is where the brand markets the idea or emotion behind their brand rather than the name or product. A brand will align itself with this idea, emotion or feeling and market their association with this factor.
Brand Extension
Brand extension is when a brand markets a sub-brand rather than the overall parent brand. Many big brands are owned by even bigger brands, but they don’t market the larger parent brand.
Private Label
Not all brands or companies create their own products. The term private label refers to products that are produced for multiple brands from one creator. Private labels offer an in-house version of commonly produced products, and a brand can market this as a lower price alternative, for example.
Brand Strategy Case Studies
There are many successful branding case studies we could use to explain each element of a brand strategy. However, we believe these 7 examples help explain the power and benefits of brand strategy well.
Red Bull – Company Brand Name
Red Bull is somewhat of a powerhouse in the world of brand marketing. Their company-based brand marketing strategy is one of the most complete but does require a lot of budget. Running F1 teams and sponsoring extreme sports athletes doesn’t come cheap but it can lead to virality.
What Has Red Bull Done?
Red Bull has always known their target market and have found a way to communicate with them. Their initial brand marketing involved finding out where their target market would hang out and hand out free products: increasing brand awareness and word-of-mouth exposure.
Now, with a much larger budget, they still perform the same style of marketing. They know where their target market will be online or what sports they enjoy and position themselves there. Be it an F1 race or an 18 year old university student looking at skydiving content on YouTube.
What Can We Learn From Red Bull?
Understanding your target market will help you position your brand correctly. Their brand is so well known most will associate it name with their favourite sport before a canned energy drink.
Apple – Individual
Apple has always pushed their products before their brand name. Hosting large expos to launch a new product and advertising their latest phone before looking to raise brand awareness. The ‘Shot on Iphone’ ad campaigns are a great example of their marketing efforts pushing the quality and ability of their products.
What Have Apple Done?
Apple focuses on the consumer within its marketing efforts and aligns this with their product. Their push towards innovation is clear from their slogan ‘Think Different’. They look to expose their product strengths and do this through TV advertising and tech influencers.
What Can We Learn From Apple?
If we’re looking to market an individual part of our brand, like a product, it’s important that we first understand the benefits. By understanding the benefits we can market these and draw attention to the selling factors. Ensuring the individual element embodies the overall brand message.
Air Jordan – Brand Extension
One of the most recognisable brand extensions is Air Jordan. A sub-brand of Nike, Air Jordans have become some of the most successful and sought after shoes in the market. They currently sell somewhere around $5 billion worth of shoes each year.
What Have Air Jordan Done?
Nike aligned their product with an up and coming basketball superstar. They also moved away from the Nike brand name as, at the time, it wasn’t ‘cool’ within the basketball scene. By focusing on the brand extension, Air Jordan, they were able to market it alongside the athlete.
What Can We Learn From Air Jordan?
Brand extensions don’t need to follow the same brand message as the parent brand. They can be unique and move away from what would be expected of the parent brand, giving them freedom to push in other directions to reach a wider potential customer base.
Aldi – Private Label
Aldi is a European supermarket that has found great success with their private label range. In fact, 90% of Aldi’s products are private label and, as the majority of their products are in-house, they’re able to control price and availability. This flexibility gives them an edge over their larger supermarket competitors.
What Have Aldi Done?
Aldi have run a number of brand marketing campaigns, however, their focus on the quality of their private label stands out. The ‘I also like this one’ campaign is a great example of how they compare themselves to others in the industry. Backing it up with consumer data, they are able to stand out as just as good but less expensive.
What Can We Learn From Aldi?
If you’re a private label brand, it’s important to know your strengths and weaknesses. Perform market research to gather relevant data and market using this information. Part of the 4 Ps of marketing is ‘price’, so it’s important to consumers that the price is competitive.
Jeep – Attitude Branding
Jeep brand themselves alongside the idea of adventure. Jeep’s marketing campaigns are all focused around the idea of the car being a tool to achieve adventures. This is a great example of how a brand can align themselves with an idea and brand the idea with the product.
What Have Jeep Done Well?
Jeep have understood their target market and have in some ways built their target market around their products. They have positioned themselves through advertisement and product placements to be recognised alongside an attitude.
What Can We Learn From Jeep?
Marketing and branding doesn’t always have to be about yourself. Branding can be an idea that you and your products envelop. Marketing this idea can associate you with that idea. You are therefore no longer just Jeep, you are the adventure car.
Enhancing a Brand Strategy
Not every brand is the same and not every strategy works for every brand. It’s important to understand who you and who your customers are before you develop a brand strategy. Knowing this will give you the best chance of success when launching a new campaign.
For more help and support in creating a brand strategy for your business or company get in contact with Fellow. You can also view our brand strategy page here.
Drop us a message
Maximum file size: 268.44MB
Recommended Articles
How to develop a brand strategy , how to choose a brand name, how to identify your brand, how to create sustainable packaging design, fellow - creative branding agency in london.
At Fellow we believe the great design reflects ambitious clients. We have a passion for all digital and print designs, not just creative branding. You can view all our services here.
Fellow Studio © 2022
Join our mailing list
Call us on 020 8058 1998 or email [email protected] The Department Store Studios 19 Bellefields Road London, SW9 9UH, United Kingdom
Privacy overview, subscribe to our newsletter.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
Featured Articles

The Power of a Strong Brand Identity: Definition, Importance, and Key Elements

Brand Personality: Definition, Examples, and How to Define Yours

Personal Branding: Why It Matters
Expert interviews.

Green Design: An Introduction by Sustainable Designer Emma Fanning

Luxury Branding: An Introduction by Philippe Mihailovich

Interview With Ken Segall – the Ad Man Who Placed the ‘i’ in iMac
Follow us on instagram.
thebrandingjournal

Receive our Monthly Newsletter
By checking this box, you confirm that you have read and are agreeing to our terms of use regarding the storage of the data submitted through this form.
3 Simple Steps to Boost Your Personal Brand

Elevating Brand Imagery: Lessons from the Detailed Illustrations of the Paris 2024 Olympics Posters

Boosting Efficiency in Brand Naming: Expert Tips for Agencies and Consultants

Sustainability as the ‘Modern Sacred’: Restoring Marketing to the Position of Power
- Case Studies
We love to analyze successful and not so successful brand strategies worldwide and see what we can learn from them. Read our branding case studies here!

- Brand Visual Identity

How to Humanize An EdTech Brand: Insights from EdTutor’s Case Study

Twitter’s Extreme Rebrand to X: A Calculated Risk or Pure Chaos?

Case Study: Visit Estonia

Learning from the Gap Logo Redesign Fail

- Brand Identity
- Brand Positioning
- Branding Strategy
Case Study: BeyondMinds’ Branding Journey

How To Brand a Podcast – “La Poudre” Case Study

Brand Strategy & Visual Identity for Layton Preparatory School in Nigeria

- Brand Image
How Not to Re-Create Another Vegemite Isnack 2.0 Branding Disaster

Etihad Airways’ Rebranding – Has it paid off?
Marketing case study 101 (plus tips, examples, and templates)

Summary/Overview
If you’re familiar with content lines like, “See how our fancy new app saved Sarah 10 hours a week doing payroll,” you’ve encountered a marketing case study. That’s because case studies are one of the most powerful marketing tools, showcasing real-world applications and customer success stories that help build trust with potential customers.
More than 42% of marketers use case studies in their marketing strategy. Let’s face it — we love testimonials and reviews. People love hearing customer stories and experiences firsthand. In fact, 88% of consumers view reviews before making a purchase decision. Case studies work similarly by providing prospective customers with real-life stories demonstrating the brand’s success.
Case studies provide a more in-depth view of how your product solves an existing problem — something potential buyers can relate to and learn from.
In this article, we take a closer look at what marketing case studies are, why they’re important, and how you can use them to improve your content marketing efforts. You’ll also learn the key elements of a successful case study and how to turn a good case study into a great case study.
What is a marketing case study?
A case study is a narrative that documents a real-world situation or example. A marketing case study is a detailed examination and analysis of a specific strategy, initiative, or marketing campaign that a business has implemented. It’s intended to serve as an all-inclusive narrative that documents a real-world business situation and its outcome.
Marketing case studies are tools businesses use to showcase the effectiveness of a particular tool, technique, or service by using a real-world example. Companies often use case studies as sales collateral on websites, email marketing, social media , and other marketing materials. They provide readers with a firsthand look into how your product or service has helped someone else and demonstrate the value of your offering while building trust with potential customers.
Some common key components of a marketing case study include:
- Context: A case study begins by describing the business’s situation or problem. This often includes challenges, opportunities, or objectives.
- Strategy: An outline of the tactics or strategy utilized to address the business’s situation. This includes details such as the target audience, messaging, channels used, and other unique aspects of the approach.
- Implementation: Provide information about how the strategy was implemented, including timeline, resources, and budget.
- Results: This is arguably the most crucial part of a marketing case study. Present the results through data, metrics, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to demonstrate the impact of the strategy. The results section should highlight both qualitative and quantitative data.
- Challenges and Solutions: A great case study not only focuses on the successes but addresses any obstacles faced during the campaign. Make sure to address any challenges and how they were overcome or mitigated.
- Customer Feedback: Including testimonials or quotes from satisfied clients is a great way to add credibility and authenticity to a case study. Choose customer feedback that reinforces the positive outcomes of the strategy taken.
- Visuals: Compelling case studies include visuals such as graphs, charts, images, videos, and infographics to make the information presented more engaging and easier to understand.
- Analysis: An optional way to conclude a case study includes discussing key takeaways, insights, and lessons learned from a campaign.
Case studies can help you connect your product to the customer’s needs by providing a real world examples of success and encouraging conversions.
Benefits of marketing case studies
Some of the key benefits of using case studies in your marketing efforts include the following:
- Building trust and credibility. You build trust and credibility with potential clients or customers by demonstrating real world success stories. In-depth looks at how your products or services have helped other businesses or people achieve success can increase customer loyalty and encourage repeat business.
- Learn best practices. Learn from strategies employed in successful case studies and apply similar approaches to future campaigns.
- Enhancing sales and conversions. By highlighting the real world results your products or services have delivered, case studies can be a powerful tool for boosting sales. They can help demonstrate the value of your offering and persuade your target audience to make a purchase.
- Explain how your business generates results. Case studies are a compelling way to share key takeaways with your target audience and showcase your brand.
- Use them as content marketing material. Use case studies as content for marketing purposes on websites, social media, and beyond.
Case studies can help your business stand out and achieve success. By highlighting the real world results you’ve delivered, you can use case studies to boost sales, build customer loyalty, and compellingly showcase your business.
Tips on how to write an effective marketing case study
Are you ready to write a compelling case study? Get started with these tips.
Develop a clear and compelling headline
You have about 10 seconds to communicate your value proposition to keep customer attention. Whether you’re designing a new landing page or making a long-term plan for your brand’s content marketing strategy , the headline is the most crucial part.
A compelling title should capture readers’ attention and make them want to read more. To craft a compelling headline:
- Understand your audience: Before crafting a headline, ensure you know your target audience — what are their pain points, interests, and needs?
- Highlight the most significant result: Focus on the most impactful result achieved in the case study. What was the primary outcome of the strategy implemented?
- Keep it brief: Keep your headline concise and to the point. Try to keep your headline under 12 words.
- Use action words: Incorporate action verbs such as “achieved,” “transformed,” or “boosted” to convey a sense of accomplishment.
- Include data: Numbers make your headline more credible. For example, if the case study achieved a 75% increase in sales, include that in the headline.
- Emphasize benefits: Focus on the positive changes or advantages the implemented strategy brought to the client or business. Use these as selling points in your headline.
- Make it unique and memorable: Avoid generic phrases to make your headline stand out from the competition.
- Use keywords wisely: Incorporate relevant keywords that align with the case study and your target audience’s search interest to improve search engine visibility through search engine optimization (SEO).
- Consider subheadings: If you cannot fit all the necessary information in a headline, consider adding a subheading to provide additional context or details.
Here are some examples of clear and convincing case study headlines:
- “Achieving a 150% ROI: How [XYZ] Strategy Transformed a Startup”
- “How Optimized SEO Tactics Skyrocketed Sales by 80%”
- “Mastering Social Media: How [ABC] Brand Increased Engagement by 50%”
- “The Power of Personalization: How Tailored Content Quadrupled Conversions”
Write relatable content
Almost 90% of Gen Z and millennial shoppers prefer influencers who they consider relatable. Relatability is part of building trust and connection with your target audience.
When writing your case study, make content that resonates with readers and speaks to their pain points. The best marketing doesn’t just increase conversion rates — it also serves your customers’ needs. To write content that really resonates with your target audience, make sure to:
- Understand your audience: To successfully write relatable content, you first need to understand your target audience — their interests, pain points, and challenges. The more you know about your target audience, the better you can tailor your content to their needs.
- Identify pain points: As mentioned above, identify challenges your target audience may face. Make sure to highlight how the product or service in the case study can effectively address these pain points.
- Tell a story: Create a narrative that follows a standard story arc. Start with a relatable struggle that the customer or business faced and describe its associated emotions.
- Use real customer feedback: Incorporate quotes or testimonials from actual customers or clients. Including authentic voices makes the content more relatable to readers because they can see real people expressing their experiences.
- Use relatable language: Write in a tone to which your audience can relate. Only include overly technical terms if your target audience solely consists of experts who would understand them.
- Use social proof: Mention any recognitions, awards, or industry acknowledgments that may have been received by the customer or business in the case study.
- Encourage engagement: Urge readers to share their own challenges or experiences related to the subject matter of the case study. This is a great way to foster a sense of community.
Outline your strategies with corresponding statistics
Whether you’re showing off the results your marketing team achieved with a new strategy or explaining how your product has helped customers, data and research make it easier to back up claims.
Include relevant statistics in your case study to provide evidence of the effectiveness of your strategies, such as:
- Quantitative data: Use numerical data to quantify results.
- Qualitative data: Use qualitative data, such as customer testimonials, to back up numerical results.
- Comparisons: Compare the post-campaign results with the pre-campaign benchmarks to provide context for the data.
- Case study metrics: Include specific metrics relevant to your industry or campaign if applicable. For example, in e-commerce, common metrics could include customer acquisition cost, average order value, or cart abandonment rate.
By incorporating relatable outcomes — such as cost savings from new automation or customer responsiveness from your new social media marketing campaign — you can provide concrete evidence of how your product or service has helped others in similar situations.
Use multiple formats of representation
People love visuals . It doesn’t matter if it’s an infographic for digital marketing or a graph chart in print materials — we love to see our data and results represented in visuals that are easy to understand. Additionally, including multiple representation formats is a great way to increase accessibility and enhance clarity.
When making a case study, consider including various forms of representation, such as:
- Infographics: Use infographics to condense critical information into a visually appealing, easy-to-understand graphic. Infographics are highly sharable and can be used across marketing channels.
- Charts: Use charts (bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, etc.) to illustrate statistical information such as data trends or comparisons. Make sure to include clear labels and titles for each chart.
- Images: Include relevant photos to enhance the storytelling aspect of your case study. Consider including “before and after” pictures if relevant to your case study.
- Videos: Short videos summarizing a case study’s main points are great for sharing across social media or embedding into your case study.
- Tables: Use tables to help organize data and make it easier for readers to digest.
- Data visualizations: Include data visualizations such as flowcharts or heatmaps to illustrate user journeys or specific processes.
- Screenshots: If your case study involves digital products, include screenshots to provide a visual walkthrough of how the product or service works.
- Diagrams: Use diagrams, such as a flowchart, to explain complex processes, decision trees, or workflows to simplify complicated information.
- Timelines: If your case study involves a timeline of specific events, present it using a timeline graphic.
Use a consistent design style and color scheme to maintain cohesion when incorporating multiple formats. Remember that each format you use should serve a specific purpose in engaging the reader and conveying information.
Get your case study in front of your intended audience
What good is a compelling case study and a killer call to action (CTA) if no one sees it? Once you’ve completed your case study, share it across the appropriate channels and networks your target audience frequents and incorporate it into your content strategy to increase visibility and reach. To get your case study noticed:
- Take advantage of your website. Create a dedicated section or landing page on your website for your case study. If your website has a blog section, consider including it here. Optimize the page for search engines (SEO) by including relevant keywords and optimizing the meta description and headers. Make sure to feature your case study on your homepage and relevant product or service pages.
- Launch email marketing campaigns. Send out the case study to your email subscriber list. Be specific and target groups that would most likely be interested in the case study.
- Launch social media campaigns. Share your case study on your social media platforms. Use eye-catching graphics and engaging captions to draw in potential readers. Consider creating teaser videos or graphics to generate interest.
- Utilize paid promotions. Use targeted social media and search engine ads to reach specific demographics or interests. Consider retargeting ads to re-engage visitors who have previously interacted with your website.
- Issue a press release. If your case study results in a significant industry impact, consider issuing a press release to share the exciting news with relevant media outlets or publications.
- Utilize influencer outreach. Collaborate with influencers who can share your case study with their followers to increase credibility and expand your reach.
- Host webinars and presentations. Discuss the case study findings and insights through webinars or presentations. Promote these events through your various marketing channels and make sure to encourage participation.
- Utilize networking events and conferences. Present your case study at industry-related conferences, trade shows, or networking events. Consider distributing printed or digital copies of the case study to attendees.
- Utilize online communities. Share the case study in relevant online forums and discussion groups where your target audience congregates.
- Practice search engine optimization (SEO). Optimize the SEO elements of your case study to improve organic search ranking and visibility.
Remember, the key to successfully promoting your case study is to tailor your approach to your specific target audience and their preferences. Consistently promoting your case study across multiple channels increases your chances of it reaching your intended audience.
Marketing case study examples
Let’s look at some successful marketing case studies for inspiration.
“How Handled Scaled from Zero to 121 Locations with HubSpot”

Right away, they lead with compelling metrics — the numbers don’t lie. They use two different formats: a well-made video accompanied by well-written text.
The study also addresses customer pain points, like meeting a higher demand during the pandemic.
“How AppSumo grew organic traffic 843% and revenue from organic traffic 340%”

This case study from Omniscient Digital leads with motivating stats, a glowing review sharing a real user experience, and a video review from the AppSumo Head of Content.
The case study information is broken down into clearly marked sections, explaining the benefits to their target audience (startups) and providing plenty of visuals, charts, and metrics to back it up.
“How One Ecommerce Business Solved the Omnichannel Challenge with Bitly Campaigns”

Download this Bitly case study from their site to see the details of how this company made an impact.
Not only is it well designed, but it also tackles customer challenges right away. The most compelling types of case studies serve their audience by showing how the product or service solves their problems.
Bitly nails it by listing obstacles and jumping right into how the brand can help.
Marketing case study template
Use this basic template to better understand the typical structure of a business case study and use it as a starting place to create your own:
Case Study Title
Date: [Date]
Client or Company Profile:
- Client/Company Name: [Client/Company Name]
- Industry: [Industry]
- Location: [Location]
- Client/Company Background: [Brief client or company background information.]
Introduction:
- Briefly introduce the client or company and any necessary context for the campaign or initiative.
- Problem statement: Describe the specific challenge or problem faced by the client or company before implementing the campaign or initiative.
- Strategy: Explain the strategy that was implemented to address the challenge. Include details such as target audience, objectives, goals, and tactics.
- Implementation: Provide a timeline of the strategy’s implementation, including key milestones and other notable considerations taken during execution.
- Outcomes: Present the qualitative and quantitative results achieved through the implemented strategy. Include relevant metrics, statistics, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Comparative data: Compare the post-campaign results to pre-campaign benchmarks or industry standards.
Analysis and Insights:
- Key insights: Summarize insights and lessons learned from the campaign and discuss the campaign's impact on the client or company’s goals.
- Challenges faced: Address any obstacles encountered during the campaign and how they were mitigated or overcome.
Conclusion:
- Conclusion: Summarize the campaign’s overall impact on the client or company. Highlight the value that was delivered by the implemented strategy and the success it achieved.
- Next Steps: Discuss potential follow-up actions, recommendations, or future strategies.
Testimonials:
- Include quotes or testimonials from the clients or customers who benefitted from the campaign.
- Incorporate relevant visuals to illustrate key points, findings, and results.
The above template is a great way to get started gathering your ideas and findings for a marketing case study. Feel free to add additional sections or customize the template to match your requirements.
Craft a compelling marketing case study for your business
Are you ready to make your marketing case study shine? With Adobe Express, you can make high-quality infographics and presentations that take your case studies to the next level.
Choose from our library of designed templates, or make it yourself with powerful tools and a library of ready-to-use graphic elements.
Get started with Adobe Express today to make compelling marketing case studies that engage your audience and drive conversions.
Try Adobe Express today
Ready to create standout content?
Start for free
Explore Related Posts
https://www.adobe.com/express/learn/blog/brand-strategy
https://www.adobe.com/express/learn/blog/marketing-plan
https://www.adobe.com/express/learn/blog/types-of-marketing
5 Big Brand Case Studies Every Marketer Should Know
Updated: October 11, 2022
Published: January 21, 2010
Many big businesses have begun to experiment with social media, and have dived head-first into the world of Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and beyond. While others still remain traditionally skeptical of the new metrics and pull-instead-of-push approach, companies such as Southwest Airlines and Ford have proven the success of incorporating these new platforms into the company culture.

If you're wondering which big brands do it best, here are 5 big brands case studies that every marketer should know:
![brands marketing strategy case study Download Now: Free State of Marketing Report [Updated for 2024]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/b0f73a5e-16e4-41fd-9511-8564efc560a7.png)
Southwest Airlines: Personalize your brand.
Southwest Airlines has effectively used social media to highlight what makes their company unique. From promoting a viral video of a rapping flight attendant on YouTube to informing customers of flight delays on Twitter to uploading customer photos on their blog, Southwest Airlines has developed their image into a friendly, unique, and personable brand , with which customers can build a long-lasting relationship.
Comcast: Serve your customers.
Having an issue with your television connection? Instead of listening to elevator music while on hold indefinitely, tweet about to @ comcastcares . Comcast has discovered a way to respond quickly and directly to customers, especially unhappy ones. The company uses Twitter to monitor customer feedback , reactions, and complaints, and responds within minutes to not-so-favorable posts.
Ford: Resolve emerging issues.
When Ford made an internal error that involved threatening enthusiast sites with lawsuits about copyright infringement, the enraged public quickly made the situation a big deal. The saving factor emerged when Ford’s community manager clarified the story and immediately informed the public via social media. Furthermore, as the company resolved the situation, the public was informed every step of the way, preventing further confusion and frustration .
Starbucks: Request direct feedback.
“My Starbucks Idea” is the popular coffee brand’s consumer portal where customers can submit ideas and vote/comment on other’s thoughts about improving the product(s). In a company where the “experience” compensates for the high prices, it is in Starbucks’ best interest to receive feedback directly from the customers themselves. The corresponding “ Ideas in Action Blog ” is written by Starbucks employees and discusses ideas that are being implemented while responding to other suggestions.
Sun Microsystems: Increase company transparency.
In a world where trade secrets are protected and gaffes are hidden, Jonathan Schwartz, CEO of Sun Microsystems, publishes a CEO blog that addresses company issues and discloses business advancements. By encouraging two-way communication between the head management and employees/customers, Sun Microsystems promotes a culture of transparency and honesty , in which everyone can receive visibility into the company’s actions.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Weird Words in English: 100+ Terms You Need to Know from 2023 and Beyond

10 Examples of Brilliant Healthcare Marketing
![brands marketing strategy case study How to Create a Case Study Video That Converts Leads [Video]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/case-study-video.png)
How to Create a Case Study Video That Converts Leads [Video]

Women Shave Because of Marketers: How the Industry Created Demand for Women's Razors

The Public Apology Letter: 6 Brands That Nailed It

How 6 Little-Known Athletic Brands Are Changing the Face of Fitness

8 of the Weirdest Shark Tank Products That Got Investments

Ben & Jerry, theSkimm & Apple: The Inspiring Stories of 10 Famous Co-Founders

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Case Studies

Why Case Studies are Critical for the Medtech Buyer Persona
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Valueleaf Blog
Home » Marketing Case Studies: Success Blueprints for Brands To Follow
Marketing Case Studies: Success Blueprints for Brands To Follow

Marketing is a dynamic field that constantly develops to meet the ever-changing demands of consumers and the marketplace. These case studies and marketing strategy case studies offer valuable lessons and insights that can inspire and inform your own marketing efforts.
In this blog, we will explore the intriguing world of marketing case studies—stories of innovative campaigns, brilliant strategies, and remarkable successes. From campaigns from industry giants like Apple, Nike, and Coca-Cola, as well as unconventional triumphs like Red Bull’s space jump and Oreo’s real-time marketing.
Let’s begin our journey into the world of marketing excellence.
1. Lay’s: #SmileDekeDekho
Lay’s #SmileDekeDekho Campaign: Spreading Joy, One Smile at a Time
Lay’s, the beloved snack brand, embarked on a heartwarming marketing campaign called #SmileDekeDekho. This campaign was a refreshing departure from traditional advertising strategies and resonated deeply with consumers.
The core concept of the #SmileDekeDekho campaign was to inspire people to share their smiles with others, especially during challenging times when a simple smile could make a world of difference. Lay’s believed that a smile has the power to brighten anyone’s day, and they wanted to spread this positivity far and wide.
Key Highlights:
- Positive Message: Lay’s celebrated the power of smiles in their #SmileDekeDekho campaign, emphasizing the importance of sharing positivity.
- Real People, Real Smiles: Heartwarming TV commercials featured everyday people sharing genuine smiles, making the campaign relatable and heartfelt.
- Social Media Buzz: Lay’s encouraged user-generated content with the hashtag #SmileDekeDekho, driving engagement and creating a sense of community.
- Interactive Billboards: In major cities, billboards detected smiles and played Lay’s jingles, promoting the campaign’s message on the streets.
- Limited Edition Packaging: Special chip packaging with colorful designs spread smiles and contributed to free meals for underprivileged children.
- Memorable Marketing: Lay’s demonstrated how a brand can make a positive difference in society by promoting smiles and joy.
Lay’s #SmileDekeDekho campaign not only showcased smiles but also inspired people to share them, making the world a happier place one smile at a time!
2. Burger King’s “Whopper Detour”
Burger King’s “Whopper Detour”: A Sneaky Marketing Triumph:Burger King’s “Whopper Detour” campaign was nothing short of genius.
It involved a clever ploy: customers were encouraged to order a ‘Whopper’ through the Burger King mobile app while physically being at or near a McDonald’s restaurant.
- Mobile App Integration: Customers were lured to McDonald’s locations via the Burger King app, where they could order a Whopper for just one cent.
- Buzzworthy Promotion: The one-cent Whopper offer generated immense buzz on social media and news outlets, creating a viral sensation.
- Competitive Edge: By targeting a competitor’s locations, Burger King cleverly outmaneuvered the competition and drew customers to their own stores.
- Mobile Ordering : The campaign encouraged the use of the Burger King app, boosting mobile ordering and app downloads.
- Gamification: Customers enjoyed the thrill of “hacking” the system and getting a Whopper for a steal, adding an element of gamification to the promotion.
- Increase in Foot Traffic: The “Whopper Detour” led to a surge in foot traffic to both McDonald’s and Burger King locations.
- Sales Boost: The campaign resulted in a significant boost in sales, showcasing the power of innovative marketing strategies.
Burger King’s “Whopper Detour” campaign not only demonstrated creativity but also showed how technology can be harnessed to drive customer engagement, foot traffic, and sales in the fiercely competitive fast-food industry.
3. Dove’s “Real Beauty” Campaign
Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign is an iconic example of marketing with a powerful message. Instead of showcasing airbrushed models, Dove celebrated women of all shapes, sizes, and backgrounds. Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign broke the beauty industry’s mold by promoting realistic and diverse representations of women.
- Real Women, Real Beauty: The campaign featured real women of different ages, sizes, and backgrounds, challenging traditional beauty standards.
- Body Positivity: Dove encouraged women to embrace their natural beauty, fostering a culture of self-acceptance and body positivity.
- Sketches Experiment: The “Real Beauty Sketches” video experiment went viral, highlighting how women underestimate their own beauty, touching millions worldwide.
- Self-Esteem Workshops: Dove sponsored self-esteem workshops for young girls, emphasizing the importance of confidence and inner beauty.
- Global Reach: The campaign’s messages resonated globally, sparking conversations about redefining beauty standards and promoting inclusivity.
- Social Impact: Dove’s commitment to portraying real beauty contributed to positive societal change, inspiring other brands to follow suit.
- Award-Winning: The campaign received numerous awards for its impactful message and societal contributions.
Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign remains a shining example of a brand empowering women, challenging beauty norms, and promoting self-confidence and authenticity. It has left an indelible mark on the advertising industry and society as a whole.
4. Apple’s “Get a Mac” Campaign: Redefining Brand Personification
In the mid-2000s, Apple launched its iconic “Get a Mac” marketing campaign, revolutionizing the way brands connect with their audience. This campaign featured two contrasting characters: the cool, youthful Mac (played by Justin Long) and the stuffy, outdated PC (played by John Hodgman).
- Personification of Brands: Apple brilliantly personified its products, turning them into relatable, human-like characters. Mac represented innovation and simplicity, while PC symbolized clunky, complex technology.
- Simplicity Wins: The campaign’s core message was clear—Mac computers were user-friendly and hassle-free. This resonated with consumers who valued simplicity in technology.
- Humor as a Weapon: The witty and humorous tone of the ads made them memorable. Viewers enjoyed watching the comical exchanges between Mac and PC, which made the message stick.
- Addressing Pain Points: The campaign smartly addressed common PC user frustrations, like crashes and viruses, positioning Mac as the solution to these problems.
- Cultural Impact: “Get a Mac” became a cultural phenomenon. The simplicity and humor made it not just an advertising campaign but a topic of conversation.
Apple’s “Get a Mac” campaign was a masterclass in branding and marketing . It showcased the power of simplicity, humor, and relatability in winning over consumers and reshaping the way people viewed technology brands.
5. Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” Campaign: Personalization and Connection
Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign, launched in 2011, was a game-changer in the world of marketing. This innovative campaign allowed consumers to personalize Coke bottles with their names, making it a profound example of brand engagement.
- Personalization Revolution: “Share a Coke” went beyond a one-size-fits-all approach. By putting individual names on bottles, Coca-Cola created a sense of ownership and connection.
- Social Media Buzz: The campaign encouraged people to share photos of their personalized bottles on social media, turning customers into brand advocates.
- Inclusivity: It wasn’t just about common names; Coca-Cola included a wide range of names, reflecting diverse cultures and backgrounds.
- Memorable Moments: “Share a Coke” fostered emotional connections by turning ordinary moments into memorable ones, like finding your name on a Coke bottle.
- Global Reach: The campaign was a global phenomenon, spanning more than 80 countries and translated into 35 languages.
Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign showed the power of personalization, inclusivity, and social media in modern marketing. It wasn’t just about selling a beverage; it was about creating moments of connection and turning customers into active participants in the brand’s story.

Red Bull’s Stratos Space Jump: Defying Gravity and Limits
In 2012, Red Bull orchestrated one of the most daring and iconic marketing campaigns in history—the Stratos Space Jump.
This incredible event saw Austrian skydiver Felix Baumgartner ascend to the edge of space in a helium balloon, then free-fall back to Earth, breaking the sound barrier along the way.
- Extreme Adventure: Red Bull’s Stratos Space Jump embodied the brand’s adventurous and daring spirit, appealing to adrenaline junkies and thrill-seekers.
- Scientific Endeavor: The campaign blended entertainment with science, capturing the imagination of people worldwide and showcasing human potential.
- Record-Breaking Feat: Felix Baumgartner set multiple records, including the highest free-fall jump and the first human to break the sound barrier without vehicular assistance.
- Live Streaming: The jump was broadcasted live on the internet, drawing millions of viewers and creating real-time engagement.
- Global Impact: Red Bull’s Stratos Space Jump transcended borders, capturing attention and admiration globally.
This campaign highlighted Red Bull’s commitment to pushing boundaries and embracing extraordinary challenges.
It showcased the brand’s ability to captivate a global audience through a unique blend of extreme sports, science, and live entertainment, leaving an indelible mark in the world of marketing.
Oreo’s Real-Time Marketing: Dunking in Digital Creativity
Oreo, the iconic cookie brand, made marketing history during Super Bowl XLVII in 2013 with its real-time marketing campaign. When a blackout occurred during the game, Oreo seized the moment with a brilliantly quick and witty social media post.
- Timely Creativity: Oreo’s tweet, “You can still dunk in the dark,” within minutes of the blackout, showcased the power of real-time marketing.
- Virality: The tweet went viral instantly, generating thousands of retweets and mentions, and earning Oreo widespread acclaim.
- Cost-Effective: Oreo’s real-time marketing approach was cost-effective compared to traditional Super Bowl advertising, yet it achieved tremendous impact.
- Cultural Relevance: The campaign tapped into a cultural event, demonstrating Oreo’s agility in staying relevant.
- Engagement: It engaged consumers, sparking conversations and cementing Oreo as a brand with a finger on the pulse of pop culture.
Oreo’s real-time marketing success illuminated the path for brands to engage with audiences in real-time, leveraging cultural moments to create memorable and cost-effective campaigns. It showcased the importance of agility, creativity, and timely responses in the digital marketing landscape.
Zomato’s Game-Changing Campaign: Redefining Food Delivery
Zomato, a global food delivery and restaurant discovery platform, launched a groundbreaking marketing campaign that transformed the way people perceived food delivery services.
- Unique Approach: Zomato’s “Ordering in – Eating Out” campaign celebrated the joy of dining out while staying in, offering a fresh perspective on food delivery.
- Cultural Relevance: The campaign resonated with consumers by tapping into the growing trend of ordering food for home enjoyment.
- Engaging Content: Zomato used engaging visuals, user-generated content, and relatable narratives to connect with its audience.
- Interactive Elements: The campaign featured interactive quizzes, contests, and social media challenges, boosting user engagement.
- Global Reach: Zomato’s campaign spanned multiple countries, reflecting its global presence.
Zomato’s “Ordering in – Eating Out” campaign not only captured the essence of evolving food habits but also showcased the brand’s ability to engage with consumers on a personal level. By embracing cultural trends and offering an immersive experience, Zomato redefined the food delivery narrative and solidified its position in the industry.

Starbucks’ Unforgettable Moments Campaign: Savoring More Than Coffee
Starbucks, the global coffee giant, embarked on a heartwarming marketing journey with its “Unforgettable Moments” campaign, blending coffee with genuine human connections.
- Emotional Storytelling: Starbucks went beyond coffee, sharing emotionally resonant stories of real-life customers and baristas.
- Customer Engagement: The campaign encouraged customers to share their personal Starbucks moments, creating a sense of community and engagement.
- Social Media Amplification: User-generated content was featured on Starbucks’ social media platforms to boost your online presence.
- Charitable Component: Starbucks partnered with a charitable organization, underscoring its commitment to making a positive impact.
- Global Presence: The campaign spanned Starbucks locations worldwide, fostering a sense of unity.
Starbucks’ “Unforgettable Moments” campaign demonstrated the brand’s ability to move beyond the transactional nature of business and create meaningful connections with customers. By celebrating the shared moments and experiences, Starbucks reinforced its position as more than just a coffee shop—it became a part of people’s stories and memories.
Times of India’s “Lead India” Campaign: Empowering Tomorrow’s Leaders
The Times of India, one of India’s leading newspapers, launched the “Lead India” campaign, a transformative initiative aimed at shaping the nation’s future by identifying and nurturing exceptional leadership potential.
- Nation-Building Vision: “Lead India” aspired to discover visionary leaders who could drive positive change in the country.
- Pan-India Talent Hunt: The campaign conducted extensive talent searches across India, seeking individuals with leadership qualities.
- Mentorship and Training: Selected leaders received mentorship and training, fostering their growth and impact.
- Social Impact: The campaign encouraged youth participation and social awareness, driving engagement across demographics.
- Media Influence: Times of India leveraged its extensive media presence to reach millions, inspiring them to participate in the nation’s progress.
“Lead India” by the Times of India exemplified the power of media to inspire positive change. By identifying and nurturing leadership potential at the grassroots level, the campaign contributed to shaping a brighter future for India, one empowered leader at a time.
Key Takeaways from Top Marketing Case Studies
Brands we have discussed above have shaped the consumer behaviour and made them the cult classics. It is not just about the product or brand’s position in the market that made a difference. A deep understanding of consumer behaviour, understanding the primary need of the their target audience, has made it possible.
Some other key take aways we can have from these brands are mentioned below:
Emotional Engagement:
Real-time relevance:, global impact:, storytelling:, social impact:, media influence:, innovation:, customer-centric approach:.
These takeaways collectively emphasize the evolving landscape of marketing, highlighting the importance of adaptability, creativity, and a deep understanding of consumer behavior in crafting successful campaigns.
In our exploration of these top marketing case studies, one undeniable truth emerges—marketing is an ever-evolving landscape where creativity, innovation, and a deep understanding of human psychology intersect to create impactful campaigns.
Whether it’s tapping into real-time opportunities, harnessing the power of storytelling, or championing social causes, these campaigns provide a blueprint for modern marketing. They encourage us to push boundaries, think creatively, and embrace the dynamic nature of marketing. With these lessons in mind, we can embark on our marketing endeavors, armed with the knowledge that, in the world of marketing, the possibilities are as limitless as human imagination.
Q. What is a case study for marketing? A. A marketing case study provides a detailed account of the objectives, challenges, tactics, and outcomes, often used to illustrate best practices, lessons learned, and the effectiveness of marketing efforts. Q. What are popular examples of case studies? A. Popular examples of case studies in marketing include Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign, which revitalized brand engagement, and Apple’s product launch strategies, demonstrating the power of product anticipation and brand loyalty. Additionally, Airbnb’s growth through user-generated content and storytelling is another frequently cited case study showcasing the impact of innovative marketing approaches.
Q. Are case studies good for marketing? A. Yes, case studies are highly effective for marketing purposes. They provide tangible evidence of a brand’s success, build credibility, and offer valuable insights to potential customers. Well-crafted case studies can demonstrate a company’s expertise, showcase real-world results, and inspire trust, ultimately influencing purchasing decisions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You may also like

Performance Marketing Vs Growth Marketing

Updated PPC Statistics Insights You Need To Know

Know About The Emerging Technologies That Will Shape Mobile Marketing
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
Case studies: How brands are innovating on YouTube
See how brands are innovating—and driving impact—with their video marketing strategies on YouTube. From targeting techniques, to contextual creative, to six-second video ads, learn how brands are building campaigns that deliver results with these case studies and interviews.
Share this page
How overstock.com created a multipurpose video campaign, how the cdc built an awareness campaign that spurred action, how one travel marketer turned the typical use cases for video and search upside down, inside google marketing: how pixel tested a full-funnel youtube campaign, 4 principles for creating video ads that drive conversions, why your online video strategy should be more than uploading your tv spot, how an insight from search data sparked a beauty brand’s multicultural video campaign, how turner sports brought the world’s largest live pregame show to millions of fans on youtube, how hefty brands cracked the brief for 6-second video ads: 1 successful campaign, 3 viewpoints, 4 principles for building a super bowl campaign without a tv ad, for effective video ads, look beyond demographics to behavior and context, 3 tips for making effective, hyper-relevant video ads at scale, with a few tweaks, you can use the same ad on multiple platforms. clinique shows how it’s done, how duracell created one of the top youtube bumper ads: 1 campaign success story, 3 viewpoints, how l’oréal, a century-old company, uses experimentation to succeed in the digital age, the secret to successful influencer marketing letting go of control, 3 ways to build stories with short-form video ads, how can brands win dads’ loyalty on youtube, 3 ways brands are innovating with youtube bumper ads, inside google marketing: testing a media plan that leads with youtube bumper ads, neutrogena's first digital-centric campaign: 1 campaign success story, 3 viewpoints, how using brand ads in unexpected ways drove higher installs for lyft, budweiser’s world series home run: 1 campaign success story, 3 viewpoints.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Better Way to Map Brand Strategy
- Niraj Dawar
- Charan K. Bagga

Companies have long used perceptual mapping to understand how consumers feel about their brands relative to competitors’, to find gaps in the marketplace, and to develop brand positions. But the business value of these maps is limited because they fail to link a brand’s market position to business performance metrics such as pricing and sales. Other marketing tools measure brands on yardsticks such as market share, growth rate, and profitability but fail to take consumer perceptions into consideration.
In this article, Ivey Business School’s Niraj Dawar and Charan K. Bagga present a new type of map that links a brand’s position to competitors according to its perceived “centrality” (how representative it is of the company) and “distinctiveness” (how much it stands out from other brands) with its business performance along a given metric.
Using the tool, marketers can determine a brand’s current and desired position, predict its marketplace performance, and devise and track marketing strategy and execution.
In-depth examples of the car and beer markets demonstrate the value of this tool to managers of brands in any category.
HBR Reprint R1506G
Figure out where you are on the distinctiveness-centrality spectrum.
Idea in Brief
The problem.
Companies have long used perceptual maps to understand how consumers feel about their brands relative to competitors’ and to develop brand positions. But their business value is limited because they fail to link a brand’s position to market performance metrics. Other marketing tools measure brands on yardsticks such as market share, growth rate, and profitability but fail to take consumer perceptions into consideration.
The Solution
The C-D map links perception and performance in a new way. It shows brands’ relative position in the marketplace according to perceived “centrality” (how representative a brand is of its category) and “distinctiveness” (how well it stands out from other brands). It also captures financial performance along a given metric, such as sales volume or price.
The Implications
Using the tool, marketers can determine a brand’s current and desired position, predict its marketplace performance, and devise and track marketing strategy and execution.
In-depth examples of the car and beer markets demonstrate the value of this tool for managers of brands in any category.
Marketers have always had to juggle two seemingly contradictory goals: making their brands distinctive and making them central in their category. Central brands, such as Coca-Cola in soft drinks and McDonald’s in fast food, are those that are most representative of their type. They’re the first ones to come to mind, and they serve as reference points for comparison. These brands shape category dynamics, including consumer preferences, pricing, and the pace and direction of innovation. Distinctive brands, such as Tesla in cars and Dos Equis in beer, stand out from the crowd and avoid direct competition with widely popular central brands.
- ND Niraj Dawar is a professor of marketing at the Ivey Business School, Canada. He is the author of TILT: Shifting your Strategy from Products to Customers (Harvard Business Review Press, 2013).
- Charan K. Bagga is a visiting assistant professor at Tulane University’s Freeman School of Business.
Partner Center
The Business of Fashion
Agenda-setting intelligence, analysis and advice for the global fashion community.
News & Analysis
- Professional Exclusives
- The News in Brief
- Sustainability
- Direct-to-Consumer
- Global Markets
- Fashion Week
- Workplace & Talent
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Markets
- Newsletters
- Case Studies
- Masterclasses
- Special Editions
- The State of Fashion
- Read Careers Advice
- BoF Professional
- BoF Careers
- BoF Insights
- Our Journalism
- Work With Us
- Read daily fashion news
- Download special reports
- Sign up for essential email briefings
- Follow topics of interest
- Receive event invitations
- Create job alerts
Case Study | The Essential Brand Marketing Guide

- Diana Pearl
Key insights
- After a performance marketing boom in the 2010s, driven by the ubiquitous availability of social and search advertising online, brand marketing is back in the limelight.
- More so than ever, fashion and beauty brand marketing needs to be omnipresent to attract and retain customers, and ultimately boost revenues.
- Insights from a range of brands, including Jacquemus and Coach, show why successful brand marketing requires agility and vision to be relevant with consumers.
Today’s brands need to be more than just a label on a sweater or a logo on a shopping bag.
It’s in part a reflection of the deepening convergence of fashion and beauty with everything from sports to music to pop culture generally, enabling brands to touch so many different aspects of consumers’ lives. In turn, consumers have high expectations of the brands they choose to let into their lives — whether it means aligning around social and political causes or amplifying certain lifestyles or aspirations.
“The brand is where actual value is created, and where customers feel that there’s a value because there’s more to it than just what’s in the box,” said Tiffany Rolfe, global chief creative officer of advertising agency R/GA.
Beauty and fashion products with recognisable, emotionally resonant brand identities behind them, often synonymous with a lifestyle or persona, will stand out. Ralph Lauren’s visual embrace of Americana, from cowboy-style Western to New England prep, for example, permeates every aspect of the brand, from its ad campaigns to its brick-and-mortar stores to its products. That identity has turned it into the quintessential American fashion brand.
ADVERTISEMENT
But how can a brand stand out in today’s fiercely competitive, crowded market, as customers have become choosier about their discretionary purchases? This case study shows how brand marketing holds the key to creating the essence of a brand: by conveying a brand’s values and identity to consumers. It’s not about a one-off runway show or pop-up, rather an ongoing trajectory reshaped over time. Effective brand marketing not only builds an identity, but also creates communities of loyal customers and even opens new markets and other opportunities for business growth.
In some ways, it’s easier to invest in building a brand earlier on in a company’s lifespan — there’s minimal overhead, fewer employees and less oversight on spending. Founders with a strong intuition can execute on their vision and take risks that end up paying off. Take J.Crew: The brand was able to establish itself with its visual-heavy catalogues when it was still a family-run business in the 1980s and 1990s. Once it took on a majority investment, that vision began to falter. (Though it later resurged under the direction of chief executive Mickey Drexler.)
The challenge is to maintain that vision even as other factors begin to play more of a role in a business’ direction. Companies that are under pressure from investors or shareholders to shore up the balance sheet may find themselves de-prioritising brand marketing investments, whose impact isn’t always immediately evident in near-term sales growth. But the strongest brands can see the bigger picture and know that investing in brand marketing is worth the time and cash.
Recent years have seen many brands lose that vision as they prioritised performance marketing. The boom in performance marketing, which began in the early 2010s, was driven by the rise of more novel and cheaper marketing methods, where brands pay for their marketing initiatives based on the results, such as clicks or conversions on social media and search. It was a slam-dunk way for brands to simultaneously acquire customers and build their businesses rapidly. Even today as social media ads become more costly and less effective, performance marketing is critical for fashion and beauty companies.
But as this case study shows, brand marketing too needs to be part of the mix to create closer, longer-lasting connections with customers, regardless of a company’s age or size.
With seemingly endless products to buy, it’s the brand that makes the difference. Consumers will spend upwards of $10,000 on a Chanel bag not because the quality is so superior to its $2,000 counterparts, but because of the strength of the brand.
“When you hear that brand name, you want a clear, focused idea and story to come into your head,” said Allen Adamson, chief executive of marketing agency Metaforce and adjunct professor at New York University’s Stern School of Business.
Companies profiled in this case study are striving for deep, long-lasting connections with customers, as they strategise around in-person and digital events, social media and often old-fashioned advertising on TV, radio and billboards. French luxury label Jacquemus has written the playbook for modern brand building by demonstrating how to bring a brand’s online persona to life offline. The story of another luxury label — heritage brand Coach — shows the importance of evolving and modernising brand identities to remain relevant. And two young brands — Dae Hair and Hill House Home — have proven the power of using community to build a brand in a short amount of time.

Introducing The BoF Brand Magic Index
BoF Insights and Quilt.AI co-created The BoF Brand Magic Index to examine if customers see a brand the same way a brand sees itself. The Index quantifies and ranks 50 global luxury and fashion labels using AI-driven analysis of tens of thousands of social media posts by brands and their customers.
BoF Masterclass | The Essential Brand Marketing Guide
Watch on demand a BoF Professional Masterclass that explores the topic in our Case Study, “The Essential Brand Marketing Guide.”

Diana Pearl is News and Features Editor at The Business of Fashion. She is based in New York and drives BoF’s marketing and media coverage.
- Marketing : Performance Marketing
- Marketing : Celebrity & Influencers
- Marketing : Social Media
- Marketing : Branding
- Simon Porte Jacquemus
- Bastien Daguzan
- Stuart Vevers
- Nell Diamond
- Hill House Home
© 2024 The Business of Fashion. All rights reserved. For more information read our Terms & Conditions

Fashion’s Golden Opportunity With Older Shoppers
Often left out of the picture in a youth-obsessed industry, selling to Gen-X and Baby Boomer shoppers is more important than ever as their economic power grows.


What Fashion PR & Communications Professionals Need to Know Today
This month, BoF Careers provides essential sector insights to help PR & communications professionals decode fashion’s creative landscape.

Revolve Invented Influencer Marketing as We Know It. Now It’s Pulling Back.
The brand’s scaled-back Revolve Festival points to a new direction in its signature influencer marketing approach.

Should Lab-Grown Diamonds Be Labelled? Regulators (Again) Say Yes.
Brands selling synthetic stones should make their provenance clear in marketing, according to the UK’s Advertising Standards Authority.
Subscribe to the BoF Daily Digest
The essential daily round-up of fashion news, analysis, and breaking news alerts.
Our newsletters may include 3rd-party advertising, by subscribing you agree to the Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Our Products
- BoF Insights Opens in new window

Marketing Research
40 case studies in branding.
[Apple: Innovation and Design as Brand Identity]
[Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation]
[Tesla: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry Through Innovation and Sustainability]
[Amazon: Transforming Retail and Beyond]
[Zoom: Connecting the World Through Video Communications]
[Beyond Meat: A Plant-Based Revolution]
[TikTok: A Dance with Global Success]
[Coca-Cola: Quenching the World’s Thirst for Over a Century]
[Netflix: Redefining the Future of Entertainment]
[Airbnb: Disrupting the Hospitality Industry]
[Starbucks: Brewing Success Through Innovation and Responsibility]
[The Walt Disney Company: A Kingdom of Creativity and Innovation]
[McDonald’s: Serving Success with a Side of Innovation]
[Dove (Unilever): Crafting Beauty and Confidence]
[IKEA: A Symphony of Design, Affordability, and Sustainability]
[LEGO: Building Blocks of Innovation and Success]
[Slack: Revolutionizing Workplace Communication]
[Patagonia: A Case Study in Sustainable Business Practices]
[Spotify: Transitioning from music sales to subscription streaming]
[Warby Parker: Disrupting the traditional eyewear market with an online-first approach]
[Allbirds: A Case Study in Sustainable Footwear Innovation]
40.1 Apple : Innovation and Design as Brand Identity
- Introduction:
Apple Inc., known for its revolutionary technology and design, has built its brand on innovation and a unique user experience. What began as a garage startup in 1976 has become one of the world’s most valuable companies. Let’s explore how Apple achieved this success.
- Background:
Founding and Early Years: Founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, Apple started as a computer manufacturer. The launch of the Apple I computer in 1976 marked the company’s debut, and the subsequent Apple II became a significant success.
Rise to Prominence: With the introduction of the Macintosh in 1984, Apple emphasized graphical user interface, leading the way in user-friendly computing. The iPod, iPhone, iPad, and MacBook line have since become iconic products.
- Product Development: Regularly updating products to include the latest technology.
- Software Ecosystem: Creating a seamless software environment that ties different Apple products together.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Sleek and modern design across all products.
- User Experience: Emphasizing intuitive interfaces.
- Apple Ecosystem: The interoperability of products encourages customers to stay within the Apple brand.
- Customer Service: Apple’s customer support, including the Genius Bar in Apple Stores, provides personalized service.
- Store Design: Apple Stores are known for their minimalist design and layout.
- In-Store Experience: Offering hands-on experience with products and one-on-one customer service.
- High Pricing Strategy: Apple’s premium pricing limits accessibility for many consumers.
- Dependence on Key Products: A significant reliance on the iPhone, which generates a large portion of revenue.
- Manufacturing Practices: Criticisms regarding working conditions in factories.
- Environmental Concerns: Issues related to recycling and waste management.
- Cultural Impact and Legacy:
Apple’s marketing has not only sold products but also shaped culture.
Think Different Campaign: This campaign emphasized Apple’s image as a company for creative and unconventional thinkers.
Influence on Music Industry: With the iPod and iTunes, Apple changed how people buy and listen to music.
Smartphone Revolution: The iPhone transformed mobile communication.
- Conclusion:
Apple’s brand is more than just a logo; it’s a symbol of innovation, quality, and a unique customer experience. By consistently focusing on design and innovation, Apple has maintained a strong brand identity that resonates with consumers globally. Its success offers essential insights into how a focus on innovation, design, and customer experience can build a powerful and enduring brand. The company’s challenges and criticisms also provide a nuanced understanding of the complexities of operating at the forefront of technology.
- Further Exploration:
Apple’s Advertising: Analyzing various Apple advertising campaigns over the years.
Competitor Analysis: Understanding how Apple’s branding strategies compare with competitors like Samsung, Google, and Microsoft.
Future Outlook: Speculating on Apple’s future in an ever-changing technology landscape.
This extended case study provides a comprehensive view of Apple’s branding, suitable for students who want to delve deeply into branding’s multifaceted nature. It includes various aspects of branding, marketing, challenges, and impact, allowing for a rich understanding of how a brand can shape not only a company’s success but also influence broader culture and industry trends.
40.2 Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation
Nike, Inc. is a household name synonymous with athleticism, performance, and innovation. Through its creative marketing strategies and commitment to design, Nike has become a leader in the sports apparel industry. This case study will explore Nike’s rise to prominence and the branding strategies that have kept it at the forefront of the sports industry.
- Founding and Early Years: Founded as Blue Ribbon Sports in 1964 by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight, the company changed its name to Nike, Inc. in 1971. The famous swoosh logo and the “Just Do It” slogan became integral parts of the brand’s identity.
- Growth and Expansion: With an initial focus on running shoes, Nike expanded into various sports, including basketball, soccer, and golf, becoming a multi-sport brand.
- Historical Partnerships: Nike’s collaboration with athletes like Michael Jordan led to the creation of the Air Jordan line.
- Global Ambassadors: Associating with top athletes like Serena Williams, Cristiano Ronaldo, and LeBron James.
- Emotional Connection: Creating ads that resonate emotionally with consumers, such as the “Find Your Greatness” campaign.
- Social Commentary: Engaging in cultural conversations, like the Colin Kaepernick campaign.
- Technological Advancements: Such as Nike Air cushioning technology and Flyknit fabric.
- Customization: Allowing consumers to personalize products through the NIKEiD platform.
- Nike Run Clubs: Building a community around the brand through running clubs and apps.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Such as the “Move to Zero” campaign focusing on reducing environmental impact.
- Market Competition: Competition from brands like Adidas and Under Armour.
- Pricing Strategies: Balancing premium pricing with accessibility for a broader audience.
- Labor Practices: Historical criticisms regarding factory working conditions.
- Sustainability Challenges: Managing environmental impacts across the supply chain.
Nike’s influence goes beyond sports apparel.
Influence on Streetwear: Collaborations with designers like Virgil Abloh have made Nike relevant in fashion circles.
Promotion of Women’s Sports: Marketing campaigns focusing on female athletes.
Global Reach: Establishing a presence in various global markets and sports.
Nike’s brand success lies in its ability to intertwine sports, culture, and personal aspiration. Its collaborations with athletes, investment in storytelling, and commitment to innovation have made it a leader in the sports apparel industry. The challenges and criticisms it has faced provide insight into the complexities of maintaining a global brand. Understanding Nike’s branding strategies offers an exciting exploration into how a brand can connect with consumers on multiple levels and across diverse markets.
Analyzing Advertising Campaigns: Students may explore various campaigns to understand how Nike connects with different demographics.
Competitor Analysis: Comparing Nike’s strategies with competitors to understand market dynamics.
Future of Sports Branding: Speculating on the future of branding in the sports industry and how Nike may continue to innovate.
This comprehensive case study provides a deep understanding of Nike’s branding strategies and allows students to appreciate the multifaceted nature of branding in the modern market. The connections between sports, culture, innovation, and marketing weave together to create a compelling story that offers valuable insights for anyone interested in branding, marketing, or the sports industry.
40.3 Tesla: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry Through Innovation and Sustainability
Tesla, Inc. is not just a car manufacturer; it’s a technology company with a mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Founded by a group of engineers, including Elon Musk, who became the public face of the company, Tesla has become a symbol of innovation and environmental responsibility. This case study explores how Tesla achieved this status.
- Founding and Early Years: Founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, and later joined by Elon Musk, JB Straubel, and Ian Wright, Tesla started with a vision to create electric cars that didn’t compromise on performance.
- Road to Success: The launch of the Tesla Roadster in 2008 proved that electric cars could be both stylish and powerful. Subsequent models, including the Model S, Model X, Model 3, and Model Y, diversified the product line.
- Autopilot: Developing self-driving technology.
- Battery Technology: Pioneering advancements in battery efficiency and lifespan.
- Clean Energy Products: Including solar panels and the Powerwall for energy storage.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Efforts to minimize environmental impact in production.
- Online Sales: Bypassing traditional dealerships, selling directly to consumers online.
- Customer Experience: Creating unique showrooms and offering test drives.
- Elon Musk’s Twitter Presence: Utilizing social media to promote and defend the brand.
- Product Launches: Hosting grand events to unveil new products.
- Production Challenges: Meeting demand and managing quality control.
- Market Competition: Growing competition from traditional automakers entering the EV market.
- Labor Practices: Controversies related to factory conditions.
- Autopilot Safety Concerns: Debates over the safety of Tesla’s self-driving technology.
Changing Automotive Industry: Pushing the entire automotive industry towards electric vehicles.
Energy Conversation: Shaping dialogues about renewable energy and climate change.
Stock Market Phenomenon: Tesla’s unique position in the stock market as a technology/automotive company.
Tesla’s brand represents a fusion of technology, sustainability, and luxury. Through innovative products, a focus on environmental responsibility, and disruptive sales models, Tesla has not only built a successful brand but has also changed the landscape of the automotive industry. Analyzing Tesla’s strategies, challenges, and impacts provides valuable insights into how a brand can be a catalyst for industry-wide change.
Comparative Analysis: Understanding how Tesla’s branding strategies differ from traditional automotive brands.
Future of Mobility: Speculating on the future of electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and Tesla’s role in shaping that future.
Global Expansion: Exploring Tesla’s efforts to expand into various global markets, such as China and Europe.
40.4 Amazon: Transforming Retail and Beyond
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, started as an online bookstore and quickly expanded into a vast e-commerce platform that sells virtually everything. Beyond retail, Amazon has also entered cloud computing, entertainment, and even healthcare. This case study will explore Amazon’s diverse business activities and how they’ve contributed to its colossal success.
- Early Years: Started in a garage, focusing on books, before expanding into other categories.
- Global Expansion: Rapid growth into international markets and diversified product offerings.
- Customer Experience: One-click ordering, personalized recommendations, and fast shipping.
- Amazon Prime: Subscription model offering free shipping, video streaming, and more.
- Amazon Marketplace: Allowing third-party sellers to reach Amazon’s vast customer base.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A leading provider of cloud computing services.
- Voice Technology: Introduction of Alexa and Echo smart speakers.
- Amazon Studios: Producing and distributing original content.
- Twitch Acquisition: Engaging the gaming community.
- Whole Foods Acquisition: Entering the brick-and-mortar retail space.
- Amazon Pharmacy: Expanding into the healthcare sector.
- Market Power: Criticisms related to monopolistic practices.
- Tax Practices: Scrutiny over tax strategies and contributions.
- Working Conditions: Concerns over conditions in warehouses and treatment of employees.
- Environmental Impact: Criticisms related to packaging and carbon footprint.
- Changing Retail Landscape: Influencing consumer expectations and competitors’ strategies.
- Innovation Leader: Setting standards in technology, logistics, and customer service.
Amazon’s success story is a testament to innovation, diversification, and relentless focus on customer experience. By continuously expanding into new areas, Amazon has not only transformed retail but also various other industries. Examining Amazon’s strategies, challenges, and cultural impact provides a deep understanding of modern business dynamics and the role of branding in shaping industry landscapes.
Competitive Analysis: Understanding Amazon’s position among global tech giants.
Future Projections: Exploring potential new markets and technologies for Amazon.
Regulatory Landscape: Analyzing potential legal and regulatory challenges.
This extensive case study offers students a multifaceted exploration of one of the world’s most impactful brands. From e-commerce to entertainment, Amazon’s influence is felt across multiple sectors. Understanding its success and challenges provides insights into innovation, strategy, ethics, and the complex dynamics of modern business environments.
40.5 Zoom: Connecting the World Through Video Communications
Zoom Video Communications, known simply as Zoom, played a pivotal role in connecting people during a time of global upheaval. Founded by Eric Yuan in 2011, Zoom quickly rose to prominence as a leading platform for video conferencing, webinars, and collaboration. This case study explores Zoom’s exponential growth, the strategies that propelled it, and the challenges it faced along the way.
- Founding Vision: Eric Yuan, a former Cisco executive, founded Zoom with a mission to make video communication frictionless and reliable.
- Early Growth: Despite entering a competitive market, Zoom differentiated itself through ease of use and robust performance.
- Ease of Use: Simple interface, quick setup, and no user account required for joining meetings.
- Quality and Reliability: Consistent video and audio quality across various devices and internet connections.
- Business and Enterprise Solutions: Offering scalable solutions for organizations of all sizes.
- Education Sector: Customized features for virtual classrooms and administrative meetings.
- Healthcare Integration: Compliance with healthcare regulations for telemedicine use.
- Localization: Tailoring offerings to different regions and languages.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with hardware vendors and integrators for seamless user experience.
- Free Access for Schools: Providing free access to educational institutions during lockdowns.
- Scaling Infrastructure: Rapidly expanding server capacity to handle surging demand.
- Security Enhancements: Addressing early security concerns with significant updates and transparency.
- “Zoombombing” Incidents: Unwanted intrusions into meetings raised questions about security.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Scrutiny over encryption and data handling practices.
- Competing Platforms: Navigating competition from established players like Microsoft and new entrants like Google.
- Sustaining Growth: Challenges in maintaining growth rates as restrictions lift and in-person meetings resume.
- Changing Work Culture: Enabling remote work, hybrid models, and global collaboration.
- Social Connections: Facilitating social interactions, virtual family gatherings, and online events.
- Redefining Communication: Setting new standards for video communication and online engagement.
Zoom’s journey is a compelling study in understanding customer needs, agile adaptation, and effective scaling. From a startup competing against tech giants to becoming a household name, Zoom’s story offers valuable lessons in innovation, strategic planning, crisis management, and ethical considerations. Analyzing Zoom’s branding, growth strategies, challenges, and cultural impact provides rich insights into the dynamics of technology-driven market disruption and the responsibilities that come with rapid success.
Competitive Landscape Analysis: Understanding Zoom’s position in a fast-evolving market.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations: Analyzing Zoom’s response to security and privacy concerns.
Long-term Strategy and Sustainability: Evaluating Zoom’s plans to sustain growth and diversify offerings.
40.6 Beyond Meat: A Plant-Based Revolution
Beyond Meat has become a synonym for the plant-based food movement, leading the way in creating meat alternatives that cater to a growing global demand for sustainable and ethical eating. This case study explores the company’s journey, its innovative products, market strategies, and the broader impact on the food industry.
- Founding Vision: Established by Ethan Brown in 2009, Beyond Meat aimed to address environmental, health, and ethical concerns related to animal agriculture.
- Product Innovation: The development of plant-based meat substitutes that mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of traditional meat.
- Not Just for Vegetarians: Positioning products to appeal to meat-eaters looking to reduce meat consumption.
- Retail and Food Service Partnerships: Collaborations with supermarkets, fast-food chains, and restaurants.
- Celebrity Endorsements: Engaging well-known advocates of plant-based diets, such as Bill Gates and Leonardo DiCaprio.
- Sustainability Messaging: Emphasizing the environmental and health benefits of plant-based foods.
- Adaptation to Local Tastes: Developing products tailored to various global markets and cuisines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex food regulations in different countries.
- Rising Competitors: Facing competition from both traditional food companies and new entrants in the plant-based sector.
- Product Differentiation: Striving to stand out in an increasingly crowded market.
- Taste and Texture Expectations: Meeting consumer expectations for flavors and textures similar to traditional meat.
- Price Barriers: Addressing price competitiveness with animal-based products.
- Transparency in Ingredients: Providing clear information about ingredients and processing methods.
- Life Cycle Analysis: Assessing the full environmental impact of products, from production to consumption.
- Changing Consumer Habits: Influencing a shift in dietary preferences towards plant-based options.
- Industry Collaboration: Collaborations with traditional meat producers and food service providers.
- Impact on Animal Agriculture: Contributing to debates about the sustainability and ethics of conventional meat production.
Beyond Meat’s story represents a transformative moment in the food industry, reflecting a broader cultural shift towards sustainability and conscious consumption. By analyzing Beyond Meat’s product innovation, market strategies, challenges, and cultural impact, students can gain insights into how a company can both lead and adapt to changing consumer values and industry dynamics. This case encourages critical thinking about innovation, branding, competition, ethics, and the interplay between business and societal needs.
Comparative Analysis with Competitors: Examining strategies and approaches of other players in the plant-based food market.
Consumer Behavior Study: Investigating consumer attitudes towards plant-based alternatives.
Sustainability Assessment: Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the sustainability aspects of plant-based foods.
40.7 TikTok: A Dance with Global Success
TikTok, a social media app developed by Chinese tech company ByteDance, has quickly become a sensation, particularly among younger users. This case study examines TikTok’s rapid growth, innovative content delivery, competition, and the complex regulatory landscape it navigates.
- Launch and Growth: TikTok was launched in 2016 and merged with Musical.ly in 2018 to expand its reach in the U.S. market.
- Algorithm Magic: TikTok’s unique algorithm offers personalized content, leading to higher engagement and user retention.
- Short Video Format: Users create engaging 15-second videos with a wide array of editing tools.
- Personalized Feed: The “For You Page” algorithm provides a customized content feed, enhancing user experience.
- Hashtag Challenges: Promoting user-generated content through viral challenges.
- Collaborations and Duets: Enabling collaboration between users to foster community.
- Music and Dance Focus: Strong emphasis on music and dance-related content.
- Influencer Partnerships: Collaborating with youth influencers to drive adoption.
- Local Content Adaptation: Encouraging content that resonates with local cultures and trends.
- Strategic Advertising: Utilizing in-app advertising and partnerships with brands.
- Data Security Issues: Ongoing debates over data privacy and national security.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Challenges related to compliance with international regulations.
- Competing for Attention: A battle with platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, and YouTube.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: Issues related to copyright and content ownership.
- Democratizing Content Creation: Empowering individuals to become content creators.
- Cultural Influence: Fostering global cultural exchange and trends.
TikTok’s story is a fascinating example of how a social media platform can become a global phenomenon through innovative technology, strategic targeting, community engagement, and adaptability to local cultures. This case allows students to explore various aspects of social media business, including algorithms, user engagement, competition, regulation, and cultural impact.
Algorithm Analysis: Delve into how TikTok’s algorithm works and compare it with other platforms.
Regulatory Compliance Study: Investigate TikTok’s compliance with different countries’ regulatory frameworks.
Cultural Impact Research: Explore how TikTok influences and reflects cultural trends across the globe.
40.8 Coca-Cola: Quenching the World’s Thirst for Over a Century
Coca-Cola, founded in 1886, has grown to become one of the world’s leading beverage companies. This case study explores Coca-Cola’s brand legacy, marketing innovations, product diversity, sustainability initiatives, and the challenges and opportunities in an ever-changing global beverage market.
- Founding and Early Years: From a pharmacy concoction to a global brand.
- Iconic Advertising Campaigns: A look at some of Coca-Cola’s most memorable marketing efforts.
- Logo and Packaging: The evolution of Coca-Cola’s iconic logo and bottle design.
- Sponsorships and Partnerships: Coca-Cola’s association with sports events, entertainment, and charities.
- Local Market Adaptation: Customizing products and campaigns to fit regional tastes and cultures.
- Digital Engagement: Leveraging social media and technology for customer engagement.
- Beverage Portfolio: Introduction to Coca-Cola’s diverse product line, including soft drinks, water, and juices.
- Health-Conscious Offerings: Response to changing consumer preferences towards healthier options.
- Water Stewardship: Initiatives to reduce water usage and support community water projects.
- Recycling and Packaging: Commitment to reducing plastic waste through recycling and innovative packaging.
- Market Competition: An overview of competitors like PepsiCo and changing consumer tastes.
- Health and Regulatory Scrutiny: Challenges related to sugar content and obesity concerns.
- Emerging Markets: Strategies and challenges in entering and thriving in new markets.
- Economic Sensitivities: How global economic fluctuations affect sales and operations.
Coca-Cola’s story offers an inspiring journey into the world of branding, marketing, innovation, and corporate responsibility. The brand’s ability to adapt, innovate, and remain socially responsible provides valuable insights for anyone interested in business, marketing, and sustainability.
Marketing Analysis: Investigate how Coca-Cola has maintained its brand appeal over time.
Sustainability Evaluation: Examine Coca-Cola’s efforts in promoting environmental stewardship.
Global Business Study: Analyze Coca-Cola’s strategies in adapting to different cultures and markets.
This student version of the Coca-Cola case study serves as an engaging educational resource for courses related to business, marketing, branding, sustainability, and global commerce. Through exploration, discussion, and critical analysis, students can uncover the multifaceted dynamics that have shaped Coca-Cola’s success and its continued relevance in today’s competitive and evolving marketplace. It invites learners to reflect on the power of branding, the importance of innovation, the challenges of global expansion, and the growing significance of corporate social responsibility in modern business.
40.9 Netflix: Redefining the Future of Entertainment
Netflix, founded in 1997, has transformed from a DVD rental service to a global streaming giant. With over 200 million subscribers worldwide, Netflix has redefined the way people consume entertainment. This case study explores Netflix’s growth, innovation, content strategy, and the challenges it faces in a competitive market.
- Founding and Early Growth: From a mail-order DVD service to streaming pioneer.
- Subscription Model: Introduction of the subscription model that revolutionized content consumption.
- Streaming Technology: Development of cutting-edge streaming technology to deliver content seamlessly.
- Personalized Recommendations: Utilization of algorithms to tailor content suggestions to individual viewers.
- Original Content Creation: Investment in exclusive shows and movies to differentiate from competitors.
- Content Licensing: Acquiring rights to popular shows and movies to broaden the content library.
- Localization Strategy: Adapting content to suit diverse cultural tastes and regulatory requirements.
- Emerging Markets Growth: Expanding into developing regions with unique pricing and content strategies.
- Streaming Wars: Competition with other streaming platforms like Amazon Prime, Disney+, and HBO Max.
- Regulatory and Legal Hurdles: Navigating complex international laws and content regulations.
- Content Piracy Concerns: Efforts to combat unauthorized sharing and illegal streaming of content.
Netflix’s story is a testament to innovation, adaptability, and the power of a customer-centric approach. The lessons drawn from Netflix’s success and ongoing challenges provide valuable insights for those interested in technology, media, marketing, and global business strategy.
Technology Analysis: Investigate how Netflix’s technological advancements have shaped its success.
Content Strategy Evaluation: Examine how Netflix’s original content creation has redefined the entertainment industry.
Global Business Study: Analyze Netflix’s strategies for entering and thriving in diverse global markets.
40.10 Airbnb: Disrupting the Hospitality Industry
Airbnb, established in 2008, has emerged as a disruptive force in the global hospitality industry. This platform connects hosts and travelers, providing unique accommodations and experiences. This case study examines Airbnb’s innovation, growth, and the challenges it faces, providing comprehensive insights for students interested in entrepreneurship, technology, law, and global business.
- Founding Story: How an idea to rent air mattresses turned into a revolutionary business concept.
- Peer-to-Peer Model: Airbnb’s model of connecting hosts with travelers and its impact on traditional lodging.
- Platform Design: Exploration of the user-friendly design, including search functionality, booking process, and communication between hosts and guests.
- Trust and Community Building: Methods of establishing trust through reviews, verification processes, host education, community guidelines, and conflict resolution.
- Revenue Model: Understanding Airbnb’s commission-based revenue model, pricing strategies, and value proposition for hosts and guests.
- Global Growth Strategy: Airbnb’s rapid expansion into various cities and countries, including marketing strategies, partnerships, and local engagement.
- Experiences and Diversification: Introduction of Airbnb Experiences, business travel accommodations, and other extensions of the platform.
- Challenges in Scaling: Examination of the obstacles faced during rapid growth, including maintaining quality, customer support, and local adaptation.
- Local Regulations and Compliance: Encounters with legal issues, zoning laws, city ordinances, and ongoing battles with regulators and the traditional hotel industry.
- Impact on Housing Markets: Exploration of criticisms and studies on Airbnb’s effect on local housing prices, availability, gentrification, and neighborhood dynamics.
- Safety and Liability Concerns: Analysis of safety measures, insurance policies, host responsibilities, and incidents that have raised concerns.
- Sustainable Travel Initiatives: Airbnb’s efforts to promote eco-friendly travel practices, partnerships with local communities, and support for responsible hosting.
- Community Outreach and Disaster Response: Airbnb’s involvement in community development and providing emergency accommodations during natural disasters or crises.
- Brand Identity and Positioning: Examination of Airbnb’s brand evolution, advertising campaigns, social media presence, and efforts to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Strategies for targeting different customer segments and personalizing the user experience through algorithms and data analysis.
Airbnb’s transformation of the hospitality industry offers an in-depth look into technology-driven disruption, entrepreneurial innovation, community engagement, legal complexities, and social impact. The multifaceted nature of Airbnb’s journey provides a rich context for exploring diverse business concepts.
- Further Exploration and Assignments:
Platform Analysis Project: Students analyze Airbnb’s platform functionality, user experience, and technological innovations.
Regulatory Environment Study: Research and debates on the legal and ethical aspects of Airbnb’s operations in different regions.
Global Strategy Simulation: Group exercise to plan Airbnb’s entry into a new market, considering cultural, legal, and market dynamics.
Social Impact Assessment: Critical evaluation of Airbnb’s social responsibility efforts, community impact, and sustainability initiatives.
40.11 Starbucks: Brewing Success Through Innovation and Responsibility
Starbucks, founded in 1971 in Seattle, Washington, has become a global coffee icon, known for its premium quality coffee, unique store ambiance, and commitment to social responsibility. This case study examines Starbucks’ journey from a single store to an international chain, focusing on its strategic decisions, marketing practices, innovations, and challenges.
- Founding and Early Years: How Starbucks transformed from a single store selling quality coffee beans into a global coffeehouse chain.
- Mission and Vision: An examination of Starbucks’ commitment to inspiring and nurturing the human spirit, one cup at a time.
- Retail Innovation: An exploration of Starbucks’ unique store designs, customer experience, and the introduction of the “third place” concept.
- Product Diversification: Starbucks’ expansion into various products, including specialty beverages, food, packaged products, and even non-coffee items.
- Global Expansion: Strategies and challenges in entering new markets across different continents.
- Brand Building and Positioning: How Starbucks built a strong brand that emphasizes quality, community, and ethical sourcing.
- Loyalty Programs: The impact and success of Starbucks’ rewards program in enhancing customer loyalty and retention.
- Digital Engagement: Utilizing mobile apps, social media, and digital marketing to engage customers.
- Ethical Sourcing: Commitment to sourcing ethically produced coffee through fair trade practices and farmer support.
- Environmental Initiatives: Efforts in reducing waste, conserving energy, and promoting reusable products.
- Community Engagement: Investing in local communities through education, volunteerism, and support for local causes.
- Market Saturation: The challenge of maintaining growth amid increasing competition and market saturation.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Navigating cultural differences in global markets and occasional backlashes.
- Economic Factors: Responding to economic downturns and changes in consumer spending habits.
- Mobile Ordering: Implementing mobile ordering and payment systems to enhance convenience.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data to personalize marketing and enhance customer experiences.
- Partnerships with Technology Companies: Collaborations to expand reach and offer new products.
Starbucks’ story offers valuable insights into brand building, global expansion, innovation, social responsibility, and resilience in the face of challenges. Its journey from a single store to a global chain showcases the importance of strategic decision-making, adaptability, and commitment to core values.
Supply Chain Analysis: Investigate Starbucks’ complex supply chain and its approach to ensuring quality and ethical practices.
Competitive Landscape Study: Analyze Starbucks’ competitive positioning and the dynamics of the coffeehouse industry.
Crisis Management Review: Examine Starbucks’ response to various challenges and crises over the years.
40.12 The Walt Disney Company: A Kingdom of Creativity and Innovation
The Walt Disney Company, founded in 1923 by Walt and Roy O. Disney, has grown from a small animation studio to a global entertainment conglomerate. This case study delves into Disney’s storied history, business diversification, technological leadership, and strategies that have made it a symbol of creativity and imagination.
- Founding and Early Success: The birth of Mickey Mouse, the creation of the first synchronized sound and full-color cartoons, and the groundbreaking “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs.”
- Expanding the Magic Kingdom: Disney’s foray into theme parks, beginning with Disneyland in 1955 and followed by a global expansion.
- Diversification: Exploration of Disney’s diversification into various entertainment sectors, including movies, television, theme parks, merchandise, and media networks.
- Content Creation and Distribution: Examination of Disney’s strategies in producing and distributing content through various channels, including streaming services like Disney+.
- Global Expansion: Analysis of Disney’s strategies to enter and thrive in international markets, including China and Europe.
- Brand Building: How Disney built a universally loved brand based on storytelling, characters, and immersive experiences.
- Synergy: Understanding how Disney leverages its characters and stories across multiple business segments.
- Digital Engagement: Exploration of Disney’s digital marketing efforts, social media presence, and engagement with younger audiences.
- Revolutionizing Animation: Disney’s pioneering role in animation technology, including the introduction of CGI.
- Immersive Experiences: The integration of technology in theme parks for personalized and interactive experiences.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Insight into Disney’s acquisitions, including Pixar, Marvel, Lucasfilm, and 21st Century Fox.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Exploration of Disney’s collaborations with other companies to enhance its product offerings and reach.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Disney’s efforts in environmental conservation, community support, and ethical sourcing.
- Content and Cultural Sensitivity: Balancing storytelling with cultural respect and inclusiveness.
- Market Saturation and Competition: Navigating an increasingly competitive media and entertainment landscape.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: Adhering to varying regulations across global markets.
- Pandemic Response: Adaptation and response to the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on various business segments.
The Walt Disney Company’s journey offers a captivating exploration of creativity, innovation, strategic thinking, and adaptability. From pioneering animation to building global theme parks, launching streaming services, and acquiring leading entertainment brands, Disney’s story is a rich lesson in entrepreneurship, marketing, technology, and global business strategies.
Leadership Analysis: Investigate Disney’s leadership strategies and the role of key leaders in shaping the company.
Competitive Landscape Study: Analyze Disney’s competitive positioning and the dynamics of the entertainment industry.
Crisis Management Review: Examine Disney’s response to various challenges, including economic downturns and unexpected crises.
40.13 McDonald’s: Serving Success with a Side of Innovation
McDonald’s is more than just a fast-food chain; it’s a global phenomenon that has shaped the way people eat around the world. Founded in 1940 by Richard and Maurice McDonald, the company has since evolved into a multi-billion-dollar giant with thousands of locations worldwide. This case study examines the key ingredients behind McDonald’s success.
- Founding and Early Growth: A look at McDonald’s beginnings, from a single drive-in to the creation of the Speedee Service System, a precursor to the modern fast-food restaurant.
- Global Expansion: How McDonald’s turned the Golden Arches into an international symbol, adapting to various cultures and tastes.
- Franchising: Exploration of McDonald’s franchising model and how it fueled the company’s rapid growth.
- Menu Innovation: How McDonald’s constantly innovates its menu to meet consumer demands and local preferences.
- Supply Chain Management: Examination of McDonald’s logistical prowess in sourcing and distributing ingredients across the globe.
- Sustainability Efforts: An insight into McDonald’s initiatives to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable practices.
- Iconic Branding: Understanding how the Golden Arches and characters like Ronald McDonald became global icons.
- Advertising and Promotions: A review of memorable ad campaigns and marketing strategies that resonate with various demographics.
- Customer Experience: How McDonald’s focuses on customer satisfaction through services like McDelivery and the recent digital transformation.
- Digital Ordering and Mobile Apps: Exploration of McDonald’s embrace of technology to enhance customer convenience.
- Smart Restaurants: How technology is changing the in-store experience, from kiosks to AI-powered drive-thrus.
- Health Concerns: Analysis of criticisms regarding the nutritional content of McDonald’s food and the company’s response.
- Labor Practices: Discussion of challenges related to employee wages, benefits, and working conditions.
- Competitive Landscape: Examination of the fast-food market competition and how McDonald’s maintains its edge.
- Adaptation to Changing Consumer Preferences: The shift towards healthier options and how McDonald’s is responding.
- Investments in Technology: Future technological innovations that may shape the McDonald’s experience.
- Sustainability Goals: Long-term objectives in minimizing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility.
McDonald’s journey offers a multifaceted case study in entrepreneurship, innovation, marketing, global expansion, and adaptability. From flipping burgers in a single location to flipping the script on fast food worldwide, the company continues to evolve, facing new challenges and seizing opportunities.
40.14 Dove (Unilever): Crafting Beauty and Confidence
Dove, a personal care brand owned by Unilever, has become synonymous with beauty and self-esteem through its innovative products and socially conscious campaigns. This case study invites you to explore Dove’s journey and its commitment to promoting a more inclusive and positive depiction of beauty.
- Dove’s Inception: A look at the brand’s origins in 1957 with the launch of the Dove Beauty Bar.
- Product Portfolio: Overview of Dove’s wide range of personal care products, including body wash, hair care, and skincare.
- The “Real Beauty” Campaign: Examination of Dove’s groundbreaking campaign that challenged conventional beauty standards.
- Customer Engagement: Insights into Dove’s interaction with customers through social media, events, and community outreach.
- Global Expansion: Strategies behind Dove’s growth into various international markets and adaptation to different cultures.
- Research and Development: A look at how Dove constantly innovates its product line through scientific research and consumer insights.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Understanding Dove’s efforts in reducing environmental impact and promoting ethical sourcing.
- Promoting Self-Esteem: Analysis of Dove’s initiatives to enhance self-esteem, particularly among young women, through education and advertising.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: How Dove collaborates with NGOs, influencers, and other stakeholders to amplify social messages.
- Market Competition: Assessment of the competitive landscape and how Dove differentiates itself.
- Advertising Backlash: Discussion of certain advertising missteps and how the brand managed the fallout.
- Trend Adaptation: Exploration of how Dove aligns with emerging beauty and wellness trends.
- Technology Integration: How Dove leverages technology, including AI and data analytics, for product development and personalized experiences.
- Sustainability Goals: Examination of Dove’s long-term commitment to environmental sustainability and ethical practices.
Dove’s journey presents an engaging case study that goes beyond products and marketing to encompass social values, consumer connection, innovation, and global reach. The brand’s commitment to challenging beauty norms and promoting self-esteem has set it apart in a crowded market.
40.15 IKEA: A Symphony of Design, Affordability, and Sustainability
- Founding and Mission: Founded in Sweden in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad, IKEA’s mission is to “create a better everyday life for many people.” It emphasizes affordability, design, and functionality.
- Overview of Offerings: IKEA offers a wide range of home furnishings, including furniture, kitchen appliances, decor, and accessories.
- Global Presence: With over 400 stores in 50 countries, IKEA has become a global leader in the home furnishing industry.
- Product Design and Development: IKEA’s products are known for minimalist design, functionality, and ease of assembly. Collaboration with designers worldwide keeps its offerings fresh and innovative.
- Supply Chain and Manufacturing: A well-integrated supply chain with close relationships to over 1,000 suppliers allows IKEA to maintain low costs while ensuring quality and sustainability.
- Retail Experience: The IKEA in-store experience is distinctive with showrooms, self-service warehouses, and in-store restaurants offering Swedish cuisine.
- Pricing Strategy: IKEA’s cost-conscious approach means designing products from the price tag up, ensuring affordability without compromising on quality.
- Digitalization and E-commerce: With a strong online presence, IKEA provides customers with online shopping options, planning tools, and virtual product previews.
- Advertising Campaigns: IKEA uses creative and often humorous advertising to appeal to a broad customer base, focusing on life improvement and solutions.
- Online Engagement: Digital catalogs, apps, and social media keep IKEA’s audience engaged and provide valuable customer insights.
- In-store Promotions: Seasonal displays and in-store events promote new products and encourage customer interaction.
- Brand Identity and Values: IKEA’s brand emphasizes sustainability, inclusiveness, and accessibility.
- Environmental Practices: Commitment to sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and energy efficiency are core to IKEA’s operations.
- Renewable Energy Projects: IKEA invests in wind and solar energy, aiming to produce as much renewable energy as it consumes in its operations by 2030.
- Social Responsibility: The IKEA Foundation supports initiatives related to children’s education, refugee support, and climate change.
- Sustainable Product Lines: IKEA offers products that promote sustainable living, from energy-efficient appliances to recycled materials.
- Cultural Adaptation: IKEA adapts its product lines and marketing to reflect local tastes, customs, and living conditions.
- Market Entry Strategies: IKEA studies each market carefully, adapting its store format and product selection to local needs.
- Challenges in Different Markets: Navigating regulations, cultural differences, and local competition has posed challenges in some markets.
- Competition and Market Pressures: IKEA faces competition from both traditional furniture stores and online platforms.
- Cultural Missteps: Some global marketing campaigns have been criticized for insensitivity to local cultures.
- Quality Concerns: IKEA’s emphasis on low cost has sometimes led to perceived quality issues.
- Emerging Markets: Expansion into new markets like India and South America presents opportunities and challenges.
- Technological Innovations: IKEA is exploring augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and smart home technologies.
- Sustainability Goals: Commitment to further sustainability through its entire value chain.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: IKEA’s collaboration with designers, tech companies, and even other retailers fuels innovation.
IKEA’s unique blend of design, affordability, sustainability, and global reach has made it a standout brand in the home furnishing industry. The company’s multifaceted approach offers a rich study of modern retail, branding, international business, and corporate responsibility. The complexities and successes of IKEA’s model provide invaluable insights and inspiration for students across various disciplines.
40.16 LEGO: Building Blocks of Innovation and Success
- Founding and History: LEGO was founded in 1932 by Ole Kirk Christiansen in Billund, Denmark. The LEGO brick, as we know it today, was launched in 1958.
- Product Portfolio: Beyond the iconic bricks, LEGO’s products include themed sets, video games, movies, and educational tools.
- Mission and Values: LEGO’s mission is to “Inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow” through creative play and learning.
- Innovation in Design: LEGO constantly innovates its product line, incorporating new themes and licensed partnerships (e.g., Star Wars, Marvel).
- Quality and Precision: The manufacturing process emphasizes precision and quality, ensuring compatibility across generations of LEGO bricks.
- Digital Expansion: LEGO has embraced digital gaming and augmented reality experiences, extending the brand into the digital realm.
- Brand Building: LEGO’s brand revolves around creativity, imagination, learning, and fun.
- Advertising and Promotion: Utilizing various channels, LEGO engages customers through inventive advertising campaigns and social media.
- Community Engagement: LEGO Ideas invites fans to submit and vote on new product ideas. The LEGO community is actively engaged in product development, events, and online forums.
- Retail Experience: LEGO stores offer hands-on experiences with play areas, workshops, and exclusive products.
- Online Shopping: The online store provides an extensive product selection, customization options, and exclusive membership benefits.
- Global Distribution: LEGO products are available in more than 140 countries through various retail channels.
- LEGO Education: Through LEGO Education, the company offers learning solutions that encourage hands-on, playful learning in schools.
- Charitable Activities: The LEGO Foundation supports children’s development and learning through various global initiatives.
- Environmental Sustainability: LEGO is committed to reducing its environmental impact, including the goal to produce all products and packaging with sustainable materials by 2030.
- Market Pressures: Facing competition from both traditional toys and digital games, LEGO has had to continuously innovate and adapt.
- Intellectual Property Issues: LEGO has faced legal challenges around patents and copyrights, particularly concerning the design of its bricks.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns and shifts in consumer behavior have influenced LEGO’s sales and growth strategies.
- Adaptation to Local Markets: LEGO tailors its marketing and product strategies to different cultures and consumer preferences.
- Challenges in Emerging Markets: Entering new markets such as China has presented both opportunities and challenges, including issues related to counterfeiting.
- Technological Innovation: LEGO continues to explore new technologies, such as 3D printing and artificial intelligence.
- Collaborations and Licensing: Partnerships with entertainment franchises and designers fuel creativity and market reach.
- Focus on Adult Fans: LEGO has been expanding its appeal to adult fans through complex sets and themes that cater to various interests.
LEGO’s journey from a small carpentry shop to a global brand is a study in innovation, adaptability, community engagement, and brand stewardship. Its commitment to quality, creativity, and social responsibility offers a multifaceted case study with insights into product development, marketing, sustainability, global business strategy, and more. The story of LEGO inspires aspiring entrepreneurs, marketers, designers, and leaders to think creatively and act with purpose and integrity.
40.17 Slack: Revolutionizing Workplace Communication
- Founding and Background: Launched in 2013 by Stewart Butterfield, Eric Costello, Cal Henderson, and Serguei Mourachov, Slack has quickly become one of the leading tools for team communication.
- Business Model: Slack offers a freemium model where basic features are free, with paid plans for more functionality.
- Key Features: Slack provides channels, direct messaging, file sharing, integrations with other tools, and more to enhance team communication.
- Innovation and Updates: Continual updates and feature enhancements have kept Slack at the forefront of workplace communication tools.
- User-Centric Design: Slack’s interface is designed for ease of use and collaboration, reducing email overload.
- Target Audience: Primarily targeting businesses, both small and large, Slack has also found usage in communities and other groups.
- Growth Strategies: Referral programs, partnerships, and effective content marketing have contributed to Slack’s rapid adoption.
- Customer Engagement: Slack has utilized community engagement, feedback, and customer support to foster loyalty and improve its product.
- Competitors: Major competitors include Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and others offering communication and collaboration tools.
- Differentiation: Slack’s integrations, customization, and user experience have been key differentiators.
- Security Concerns: As with many digital platforms, security and privacy have been challenges, and Slack has implemented measures to ensure data protection.
- Freemium to Premium: The free version attracts users, while additional features and support drive customers to paid plans.
- Enterprise Solutions: Slack’s Enterprise Grid offers solutions tailored to large organizations, including advanced security and administrative features.
- Localization and Cultural Adaptation: Slack has localized its product for various markets and cultures to drive global adoption.
- Challenges in Emerging Markets: Issues such as local compliance, competition, and connectivity can present challenges in various regions.
- Pandemic Response: The shift to remote work during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in Slack usage, adapting to new work patterns.
- Long-term Trends: Remote and hybrid work trends may shape Slack’s future development and market positioning.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Acquiring companies like Rimeto added capabilities to Slack’s portfolio.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with companies like Google, Salesforce, and others have extended Slack’s functionality.
- Salesforce Acquisition: The pending acquisition by Salesforce as of the cut-off knowledge date may significantly shape Slack’s future direction.
- Continued Innovation: Slack continues to explore new features, integrations, and market opportunities.
Slack’s story offers insights into the fast-paced world of technology startups, product development, global expansion, and market competition. Its response to changing work patterns and its strategic acquisitions and partnerships make it a rich subject for study. The lessons from Slack’s journey are relevant to aspiring entrepreneurs, product managers, marketers, and others interested in technology, innovation, and the future of work.
40.18 Patagonia: A Case Study in Sustainable Business Practices
- Background: Patagonia, founded in 1973 by Yvon Chouinard, is an outdoor clothing and gear retailer known for its commitment to environmental sustainability.
- Mission: “Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.”
- Innovation: Patagonia has been a leader in developing sustainable fabrics and materials.
- Quality & Durability: Emphasizing long-lasting products to reduce consumerism.
- Recycling & Repairing: Offering repair services and encouraging recycling of products through programs like “Worn Wear.”
- Transparency: Publicly sharing supply chain information and environmental impacts.
- Activism Marketing: Taking strong stances on environmental and social issues.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with NGOs and community organizations.
- Supply Chain: Focusing on ethical production, fair labor practices, and organic materials.
- Environmental Activism: Regularly donating to environmental causes and supporting conservation efforts.
- B Corp Certification: Patagonia is a certified B Corporation, aligning profit with purpose.
- Profit vs. Purpose: Balancing strong financial growth with a commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
- Investing in Sustainability: Reinvesting profits in sustainable initiatives and environmental causes.
- Market Competition: Navigating a competitive market while maintaining ethical standards.
- Scale and Growth: Balancing growth and scalability with sustainability commitments.
- Greenwashing Accusations: Managing perceptions and criticisms related to authenticity and impact.
- International Expansion: Adapting sustainable practices across diverse markets and cultures.
- Global Partnerships: Collaborating with global organizations to expand environmental initiatives.
- Employee Engagement: Fostering a workplace culture that aligns with company values.
- Leadership and Governance: Maintaining leadership that embodies the brand’s ethos.
- Influencing Other Brands: Patagonia’s practices have influenced other companies to consider sustainability.
- Industry Collaboration: Working with competitors on common goals such as responsible sourcing.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Developing strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- New Market Opportunities: Exploring new product lines and markets while adhering to core values.
Patagonia serves as a compelling example of a company that has successfully integrated sustainability, ethical considerations, and environmental activism into every aspect of its business. From innovative product development to bold marketing strategies and influential industry leadership, Patagonia’s case study offers valuable insights for those interested in business ethics, environmental stewardship, social entrepreneurship, and innovative brand management. The brand’s ongoing challenges and successes provide rich material for analysis and reflection on the future of sustainable business practices.
40.19 Spotify: Transitioning from music sales to subscription streaming
- Background: Spotify, founded in 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon, transformed the way people access and enjoy music.
- Mission: “To unlock the potential of human creativity—by giving a million creative artists the opportunity to live off their art and billions of fans the opportunity to enjoy and be inspired by it.”
- Streaming Model: Spotify’s on-demand streaming model allows users to access millions of songs and podcasts.
- Algorithm & Personalization: The use of algorithms to create personalized playlists and recommendations.
- Freemium Model: Free, ad-supported tier alongside premium subscriptions.
- Revenue Streams: Subscriptions, advertising, and partnerships.
- User Engagement: Innovative playlists like “Discover Weekly” engage users.
- Collaborations: Partnerships with artists, labels, and other brands.
- International Reach: Spotify has expanded to numerous countries, adapting to various markets and regulations.
- Localized Content: Offering content that resonates with local cultures and tastes.
- Market Competitors: Facing competitors like Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music.
- Royalty Disputes: Navigating complex relationships with labels, artists, and rights holders.
- Environmental Footprint: Efforts to reduce carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices.
- Supporting Artists: Initiatives to support emerging artists and creatives.
- New Features: Continual innovation in features and user experience.
- Podcasts and Original Content: Investing in podcasts and original content to diversify offerings.
- Technology Investments: Exploring technologies like AI to enhance user experience.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Transforming the way people consume and interact with music.
- Influence on the Music Industry: Affecting record labels, artists, and music distribution.
Spotify’s rise as a leading music streaming platform offers a multifaceted case study encompassing technology innovation, marketing strategies, global expansion, and industry impact. From navigating complex licensing agreements to crafting personalized user experiences, Spotify’s journey provides valuable insights into digital transformation, competitive strategy, customer engagement, and the future of entertainment. It serves as a valuable example for understanding modern business dynamics in the digital age, including the ongoing challenges and opportunities of operating in a rapidly evolving industry.
40.20 Warby Parker: Disrupting the traditional eyewear market with an online-first approach
- Background: Founded in 2010, Warby Parker aimed to offer designer eyewear at a fraction of the price through a direct-to-consumer model.
- Mission: “To offer designer eyewear at a revolutionary price, while leading the way for socially conscious businesses.”
- Design: In-house design leading to unique and affordable eyewear.
- Home Try-On: A free program allowing customers to try on glasses at home before purchasing.
- Direct-to-Consumer: Selling directly to customers through e-commerce and physical stores, cutting out intermediaries.
- Social Responsibility: “Buy a Pair, Give a Pair” program donates glasses to those in need.
- Digital Marketing: Effective use of social media and content marketing.
- Community Engagement: Building brand loyalty through community events and collaborations.
- Physical Stores: Combining e-commerce with brick-and-mortar stores for an omnichannel experience.
- International Growth: Expanding to Canada and other markets, adapting to local regulations and preferences.
- Traditional Competitors: Competition with traditional eyewear brands and retailers.
- Copycat Brands: Managing competition from similar direct-to-consumer eyewear startups.
- Environmentally Conscious Manufacturing: Commitment to using sustainable materials.
- Carbon Neutrality: Efforts to reduce and offset carbon emissions.
- Virtual Try-On: Use of augmented reality for virtual try-ons via mobile app.
- Telehealth Services: Offering eye exams and prescriptions through telehealth technology.
- Disrupting Traditional Retail: Changing the way people shop for glasses.
- Promoting Social Responsibility: Encouraging other brands to adopt socially responsible practices.
Warby Parker’s innovative approach to eyewear retail has not only disrupted traditional industry practices but also set new standards in customer experience, social responsibility, and sustainability. Through its unique business model, commitment to social causes, and use of technology, Warby Parker has carved out a unique position in the market. The case study of Warby Parker offers valuable insights into how innovative thinking, customer-centric approaches, and ethical business practices can create a strong brand identity and successful business in today’s competitive retail landscape. It’s an exemplary story for understanding modern entrepreneurship, retail strategies, marketing, and social entrepreneurship.
40.21 Allbirds: A Case Study in Sustainable Footwear Innovation
- Background: Allbirds, founded in 2016 by Tim Brown and Joey Zwillinger, aimed to create comfortable and sustainable footwear.
- Mission: “To tread lighter on the planet while making better things people love to wear.”
- Sustainable Materials: Allbirds uses renewable materials like merino wool and eucalyptus fiber.
- Comfort and Design: Combining sustainable materials with comfortable and aesthetically appealing design.
- Direct-to-Consumer: Selling directly to customers to reduce costs and improve accessibility.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring the ethical treatment of animals and workers in the supply chain.
- Storytelling: Emphasizing the brand’s commitment to sustainability and innovative materials.
- Word-of-Mouth: Leveraging satisfied customers as brand advocates.
- International Presence: Expanding into international markets while staying true to the brand’s values.
- Localized Initiatives: Tailoring products and marketing to suit local preferences.
- Market Competitors: Competing with established footwear brands and other sustainable startups.
- Scale and Sustainability: Balancing growth with maintaining eco-friendly practices.
- Carbon Footprint: Measuring and reducing the brand’s carbon footprint.
- Circular Economy: Exploring ways to make footwear more recyclable and sustainable.
- Transparency: Sharing information about the supply chain and material sources.
- Community Engagement: Partnering with organizations for social and environmental causes.
- Research and Development: Continuing to innovate with new materials and product lines.
- Market Expansion: Exploring new markets and consumer segments.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Influencing the way consumers think about sustainable products.
- Inspiring Competitors: Encouraging other brands to prioritize sustainability.
Allbirds’ unique approach to footwear production, blending innovation, comfort, and sustainability, has positioned it as a leader in the sustainable fashion movement. The Allbirds case study provides a valuable window into the world of sustainable business, marketing, and product innovation. By exploring Allbirds’ strategies and challenges, students can gain insights into how a commitment to ethical practices, environmental consciousness, and customer satisfaction can drive success in today’s competitive market. The case offers lessons for those interested in entrepreneurship, sustainable business practices, and ethical consumerism.

Adidas Branding Strategy and Marketing Case Study
Analysis and examples of adidas’ identity, positioning, key messages, tone of voice, brand archetypes, customer benefits, competitors, and marketing content..
Back To The Branding Strategies Homepage

Brand Overview
Business type.
Physical Products
https://adidas.com
Target Customer
Quality-Focused Athletic Wear Consumers
Primary Need ( Job To Be Done )
Use athletic clothing that emphasizes quality and performance
Brand Visual Identity & Content
Primary brand colors, brand typefaces, hero content.

Hero Content Type
Content features people, brand messaging, key messages, benefit or feature focus, tone of voice, brand archetypes.
( Learn More About Brand Archetypes )

Everyperson

Brand Positioning ( Elements of Value )
( Learn More About The Elements of Value )
Aspirational
Self-Actualization

Badge Value

Brand Benefits
Use sports clothing that has been proven and tested at the highest levels of competition
Classic, simple designs that can work for sports and casual settings
Self-actualization using the same brand that athletes at every level trust on a global level
Competition
Key competitors.
Nike , Under Armour, Lululemon, New Balance, Puma, Converse, Allbirds
Get Help Growing Your Brand

Get a 10 page workbook on Purpose, Vision, and Values. Plus resources for Archetypes, Tone, Messaging, and more.
Check your email to confirm your address and receive your workbook!

Warby Parker—an Advertising and Marketing Strategy Case Study
When Warby Parker was founded to take on the $140 billion eyewear industry, their approach needed to boldly convince people why they were the brand to choose the next pair of glasses from. Through their unveiling that Luxottica had a monopolized grip on the worldwide eyewear industry, Warby Parker entered the market as the biggest consumer differentiator brand at that time. What their marketing strategy entailed would propel not just the eyewear upstart but the entire direct-to-consumer (DTC) landscape.
Warby Parker’s value proposition was simple: consumers should be able to conveniently get a good quality pair of glasses for a good price. The emphasis on the convenience factor is perhaps why Warby Parker took off the way they had. Through their Home Try-On program, Warby Parker cut the perceived difficulties of an eCommerce-only business at that point in their lifecycle. Pre-2010, the only real way consumers could purchase glasses would be going in-store to try on a pair and complete the transaction in one go. Warby Parker disrupted that market norm by allowing people to select any five pairs of glasses from their line and have them mailed to try on for five days before sending them back, all free of charge. This “highly delineated offering,” as Dave Gilboa—co-founder and co-CEO of Warby Parker—puts it, is what gave the fledgling company the success to push forward. In this take on Warby Parker’s advertising strategy, we take a closer look at what one of the most celebrated upstarts of the last ten years has done to earn the recognition it deserves.
G & Co. is a world-leading direct-to-consumer agency, empowering consumer goods brands to build enthusiastic audiences, create captivating experiences, and thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
Warby Parker’s Marketing Strategy
To owe all the credit to Warby Parker’s success due to its accessible nature and the irresistible proposal would be mistakenly overlooking its other admirable qualities and perceptive marketing strategies . In fact, it was Warby Parker’s early conviction in marketing that gave way to its rising popularity. One of the three things the DTC brand spent money on in the beginning years was its inventory, its eCommerce storefront, and a public relations firm. And while a PR team may sound trivial to some, the positive press Warby Parker generated due to their early investment was what set it on a trailblazing trajectory.
As part of its launching strategy, Warby Parker was featured in style magazines Vogue and GQ , dubbing them “a line of boutique vintage-inspired frames and lenses for savvy urbanites at a revolutionary price point” and “the Netflix of eyewear.” The press features were so successful that the emergent brand’s expectations were surpassed when their top 15 styles sold out in four weeks and met their first year’s sales targets in three weeks. On top of that, Warby Parker amassed 20,000 customers on a waitlist. While such a long waitlist initially seemed like a difficult logistic problem, the brand quickly turned into a positive component of their customer experience when the company wrote personalized emails to upset customers and apologize and explain the Home Try-On program’s temporary suspension. Warby Parker co-founder Neil Blumenthal would later explain that the incident “set the tone” for how the company would run customer service.

Alongside the unique value proposition, Warby Parker’s press machine was also aided by the brand’s championing of their social entrepreneurship model in the Buy a Pair, Give a Pair program. In every pair bought from the brand, another pair is donated to someone in need through Warby Parker’s partnership with VisionSpring. In 2015, the brand started the Pupils Project, where their coordination with local government agencies, including the Department of Education in New York City and the Department of Health in Baltimore, helps provide vision screenings, eye exams, and glasses-free of charge to students.

While not a key focus of Warby Parker’s advertising strategy, the socially-conscious efforts are nonetheless a bedrock of its founding principles. As Blumenthal put it, “it’s the social mission that drives us...for our 1,800 current employees and for people we’re recruiting, we lead with social mission.” Just because Warby Parker is not as vocal about its initiatives as they are about providing people with great-looking glasses with an exceptional customer experience—which are the most important factors among customers—does not mean their efforts are any less noteworthy than their product placement marketing strategy . In 2019, Warby Parker made headlines when it announced it had distributed five million pairs of glasses to people in more than fifty countries, adding to the supercharged media exposure the DTC eyewear brand has amassed over the years.

Of course, the importance of press-generated coverage is not nearly as crucial to Warby Parker’s marketing strategy now as it had been before. For any DTC business, the brand awareness one garners as Warby Parker did in its GQ and Vogue features is essential in the beginning stages. “In any digitally-native brand, name recognition is what determines the viability of a business,” says Juan Manuel Gonzalez, founder of UI/UX and DTC marketing agency G & Co. Over time, Warby Parker has utilized more word-of-mouth marketing than press as the brand has become one of the most recognizable DTC brands today.

At the core of Warby Parker’s marketing strategy is doubling down on the customer experience. It’s a given that DTC brands will have to take up the mantle of acting as their own manufacturers, distribution partners, and promoters. And Warby Parker has impeccably executed as complete a shopping experience as any consumer can hope for. Through their maintenance of consumer-centric dialogue, Warby Parker’s marketing approach is fertile ground for healthy user-generated content.
In every Home Try-On Kit, Warby Parker encourages recipients to ask their friends and family for their opinion on any of the five frames they’re trying on to make a choice. Additionally, the brand uses the hashtag #WarbyHomeTryOn to bring the decision-making process to social media as well, where more than 50,000 posts under the tag populated social networks and where a Warby Parker representative gives their feedback to home try on recipients on what frames to choose. That also doesn’t count the more personal interaction consumers can opt for, if they choose; only a message away, recipients of the Warby Parker Home Try-On Kit can text the brand and ask for a stylists’ judgment before settling on a pair. Such a twist on the customer experience led to a 50% increase in the likelihood of purchasing a pair of glasses. This kind of ingenuity in terms of convenience and assistance sets Warby Parker apart from the traditional eyewear brand and erodes any doubt early skeptics may have had about the success of a strictly eCommerce company.

And to supplement the responsive customer experience, Warby Parker has since introduced its “Wearing Warby” series. Customers share their heartening stories in the form of a video interview accompanied by a blog post. The series highlights Warby Parker customers whose narrative paints a picture of just how much of an impact the DTC eyewear brand has made in their lives and is a different light than that of influencer marketing done by other direct-to-consumer names. The series is only one facet of a wave of user-generated content that further spurred Warby Parker’s marketing efforts.
In matters dealing more so with levity than marketing, Warby Parker has also played around with the digitally savvy consumer. Their launching of the joke site Warby Barker for April Fool’s Day showcased the brand’s social media game and only endeared them to more people. But a facet of Warby Parker’s advertising is not strictly attributed to generating more conversation through user-generated content with posts under the #WarbyHomeTryOn tag or in sharing customer stories about their journey with a new pair of Warby Parker glasses but because of their very infrastructure.
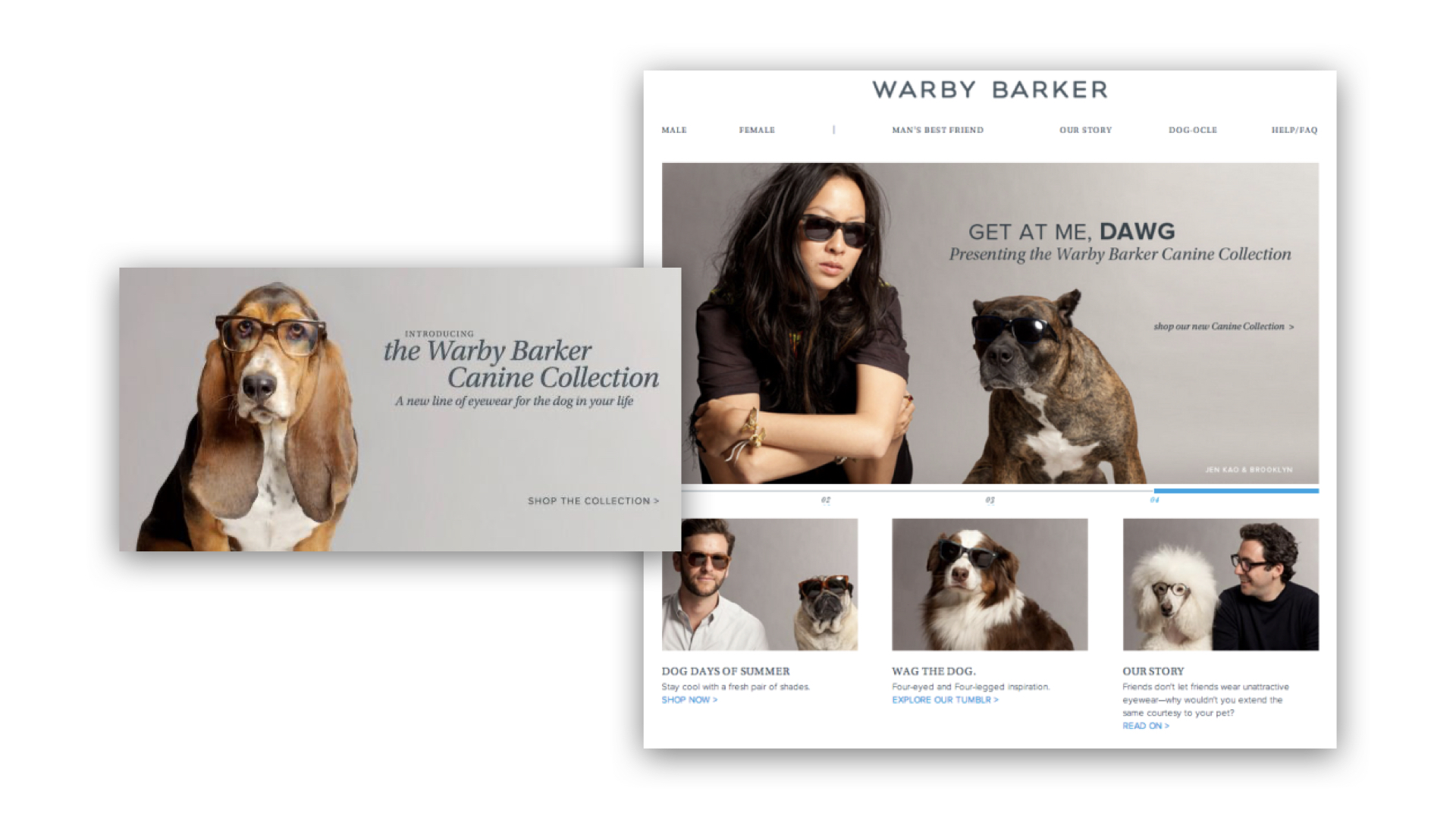
Warby Parker’s eCommerce Strategy
Considering Warby Parker began as a digitally native business, it’s no surprise that the DTC brand has a strengthened online presence. Everything from the eCommerce website to the two mobile app experiences represents a brand on the consumer space’s bleeding edge. Warby Parker has made an app in its own league as a fundamental component to its mobile strategy. Through augmented reality (AR), users can use the official Warby Parker app to virtually try on a pair of their glasses. Additionally, the official app is outfitted with Apple Pay integration and SMS updates for shipping for a seamless purchase process. Warby Parker’s secondary app allows people to renew their prescription using their telehealth service. Users can verify whether their vision has changed by taking an at-home eye exam. Based on unchanged results from the current prescription, Warby Parker will confirm a renewal for $15 and will otherwise recommend a comprehensive eye exam without charging one for using the app.

All this goes to show how digital innovation tied with riding the tide of shifting consumer behaviors towards a more convenient manner positions Warby Parker as a brand primed for continued growth. Their bold embrace of cutting-edge technology as part of its marketing strategy tied Warby Parker as an eyewear name that’s both suited for style and cognizant of how to leverage social media and customer experience together.
For those looking for a guided DTC strategy, G & Co. a trusted partner in the direct-to-consumer space. With a wide breath of experience in the world of marketing and brand strategy, G & Co. provides brands with a comprehensive approach in building and scaling brands.
We invite you to start a journey where your brand’s history and future are turned into a story that connects, captures attention, and converts.
Submit an inquiry to G & Co. on our contact page or click on the blue "Click to Contact Us" button on the bottom right corner of your screen for your convenience. We look forward to hearing from you.
How much does Warby Parker spend on digital marketing and advertising ?
While there are no exact estimates on how much Warby Parker spends on digital marketing and advertising , we can point to their television advertising budget. According to Media Post , Warby Parker reins among the DTC world in TV advertising, spending a reported $10 million in the first quarter of 2020. As recently as 2015, Warby Parker spent $492,000 on paid search keyword rankings from January through June.
What is Warby Parker’s digital strategy?
As a digitally native brand that has only flexed its online muscle in the last few years, Warby Parker’s digital strategy is no doubt one of the most robust in the market today. By differentiating themselves from the rest of the eyewear names while doing it all through an online front and innovating new ways for consumers to interact with products, Warby Parker has excelled, if not outright changed, the dynamic by which DTC brands and their digital strategies are based.
Pioneering virtual try-on and encouraging customers to share how their frames look on social media are only a few examples of many that demonstrate just how capable Warby Parker is at energizing customers and carrying through in every customer interaction.
What is Warby Parker’s customer experience (CX) strategy?
Warby Parker co-founder and co-CEO Neil Blumenthal explained it best when he said, “We’ve created an example of a business that can scale, be profitable, and do good in the world without charging a premium for it.” Going after Luxottica and revealing to the extent that consumers were charged marked-up prices for glasses was a luxury many simply couldn’t bear to put up with. Fortunately, neither did Warby Parker.
The entire value proposition in Warby Parker is to provide great quality glasses at a great price in a convenient manner. If the brand’s $95 frames, dozens of styles, and ease of purchase is any indication of their commitment to that promise, they’ve certainly kept it.
To add on to it, though, Warby Parker has since introduced an AR feature in their mobile app that allows users to virtually try on a frame. Additionally, the Warby Parker prescription check app has simplified the renewal process, making it easier than ever to support customers with their visual needs. There’s also the social initiative in which for every pair of glasses Warby Parker sells, another goes to one of more than 600 million people around the world in need of them. So far, Warby Parker has provided five million pairs of glasses to people through its Buy a Pair, Give a Pair program, and counts its Pupils Project as another solutions-based cause.
What is DTC brand d igital marketing , how is it different?
DTC marketing is different in that direct-to-consumer brands are in charge of everything from the manufacturing process to the distribution and the promotion. There are no intermediary parties that have to greenlight a brand’s idea or approach. And as such, DTC brands have far more freedom in managing their customer experience from the start of the customer journey with the brand awareness stage to post-purchase and retention.
As a DTC advertising agency and DTC marketing agency, we understand strategies come in a variety of different approaches. But almost all of them start with the ideation of their ideal customer profile and how to best communicate to them and provide a rewarding experience they can appreciate. A few examples include pushing out high-quality and engaging content with the intent that it prompts user-generated posts or having a personalized shopping experience that more closely matches a brand’s mission. There truly is no shortage of ways in how DTC brands approach their marketing and advertising strategy to engage and connect with their consumers.
Why is marketing important for any DTC brand?
Given that most DTC brands start from ground one, it is incredibly important that marketing be a crucial part of its business strategy. DTC brands must work to overcome the absence in name recognition traditional brands enjoy. That work largely stems from DTC brands’ use of marketing to establish themselves as the choice for a specific product line.
And because the internet has opened up the accessibility of convenient shopping and brand-building, there are far more tools easily disposable for connecting with people and establishing the consumer-provider relationship. Any great DTC digital agency will tell you this means more businesses than ever before have the same capacity to target consumers and refine their marketing approach. With the relative ease in marketing tools and strategies, brands from all over constantly vie for consumers’ attention. In short, marketing is essential for DTC brands because it is the one way in which they can assure their visibility and turn attention into sales and because it is how they differentiate themselves from the competition.
Why is eCommerce important for DTC brands?
An upstart DTC brand will probably not have the financial depth enterprise businesses or subsidiaries enjoy, nor will they have the retail relationships to rely on having their products stocked on shelves in stores for consumers to pick and choose. Typically, a nouveau DTC brand originates online and builds its business online before expanding to physical stores. It’s why the single most important aspect of any digital front for a DTC brand is their eCommerce store, presence, and strategy.
DTC brands are synonymous with convenience, ease of use, and high quality. It’s through a DTC brand’s eCommerce strategy that these things shine through, delivering a straightforward and enjoyable shopping experience to any customer. As a DTC advertising agency and DTC eCommerce agency, we understand that because they live and breathe online, a DTC brand’s eCommerce strategy is quintessential to its success. Without the restraint that can come with physical stores, direct-to-consumer players relish the flexibility in making their user experience clear-cut and designed to make the purchasing process as simple as possible (or at least that’s the goal).
More Resources
- 2024 Elections and Brands: Business of Fashion x G & Co.
- [VIDEO] The State of Digital Experience in Retail 2024
- The New Consumer Landscape and Work-From-Home Impact | The Retail & Consumer Index
- Retail Trends and Predictions for the U.S. Holiday Season | The Retail & Consumer Index
- Top Retail Market Research Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- eCommerce UX: Essential Design Strategies and Principles
- What is Competitive Intelligence and How Retailers Can Leverage It for a Competitive Advantage
- A Guide to Incorporating Competitive Intelligence in Your eCommerce Strategy
- How to Develop a Competitive Retail Customer Experience Strategy
- What is Retail Analytics + a List of Top 9 Analytics Software Solutions
- How To Perform a Retail Competitor Analysis (With Benefits)
- Top Digital Transformation Agencies & Consulting Firms to Work With - March 2024
- Top Best Retail Consulting Firms to Work With - March 2024
- Top Product Design Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- Top Fashion & Luxury Creative & Media Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- Top Fashion & Luxury Marketing & Advertising Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- Retail Industry Analysis: State of Retail, Outlook, Market Growth
- Top Mobile App Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- Top Shopify Plus Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- Top Digital Product Agencies to Work With - March 2024
- UI/UX Design Deliverables from an eCommerce Agency
- User Experience - UX Resource 2023
- Top 10 Best Performing Brands in 2021 - G & Co. Innovation Index®
- Top Global Retail, Fashion, and Luxury Industry Index 2023: The State of Brands' Digital Performance & Strategy
- LVMH, Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study
- Guide to Luxury Marketing Strategy: A Luxury Marketing Agency’s Take on What Brands Should Know
- Retail and Apparel Benchmark Index 2022: The State of Consumer Brands' Customer Experience
- Luxury eCommerce: Reshaping through Digital in 2023
- Hermès, an eCommerce Case Study
- Guide to Luxury Digital Strategy: A Luxury Digital Agency’s Take on What High-End Brands Should Know
- Louis Vuitton, an eCommerce Case Study
- Luxury Brands in 2023: Digital Marketing and Customer Experience (CX)
- Guide to Luxury Digital Agencies: What to Look for in a Digital Partner
- Louis Vuitton, a Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study
- Kering, a Luxury Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study
- Guide to DTC Marketing Strategy: A DTC Marketing Agency’s Take on What Brands Need to Know
- Gucci, Digital Advertising & Strategy Case Study
- Gucci, an eCommerce Case Study
- Guide to DTC Digital Agencies: What to Look for in a Digital Partner
- Activewear & Athleisure Industry Index 2021: The State of Activewear Brands' Digital Performance & Strategy
- G & Co. IQ Mapping - Benchmarking Brand & Customer Experiences through Data & Strategy
- Five Industries Poised to Win the 2021 Holiday Shopping Season & Beyond
- DTC Digital Marketing: from a DTC Digital Agency
- Fashion and Apparel, and Luxury Brands in 2021: eCommerce and Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Strategy and Insight
- Fashion & Apparel Industry Index 2021: The State of Fashion Brands' Digital Performance & Strategy
- What is DTC Marketing?: A Beginner's Guide to Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
- Fashion & Apparel Brands in 2021: Direct to Consumer (DTC) and User Experience (UX) - Industry Insights & Strategy
- Customer Experience in 2021: What to Learn from the Best Performing Brands in the Fashion, Retail, and Apparel Industry
- Fashion, Apparel, & Luxury: Key Themes for the Industry in 2021 - Digital Insight and Strategy
- Chanel, an eCommerce Case Study
- Customer Experience - CX Survey 2021


Jacquemus Case Study: Marketing Strategy and Fashion Success
- Written by 440 Industries
- November 15, 2023

In the world of fashion, a name that has taken center stage in recent years is Jacquemus. This Jacquemus case study delves into the meteoric rise of this French brand and its innovative marketing strategies.
As we embark on an exploration of sensual minimalism meeting youthful playfulness, you’ll discover how extravagant runway show locations have contributed to the brand’s allure.
The heart of this Jacquemus case study lies in understanding their innovative marketing strategies, including events and pop-ups for audience engagement as well as differentiated product assortment choices. We will also delve into the apparel offering and signature colorways that define their collections.
Furthermore, boutique expansion and collaborations such as with Nike have played a significant role in boosting brand recognition. Memorable fashion moments like tiny bags and gigantic straw hats are just some examples of accessories impact on profit-driving success.
Last but not least, maintaining brand independence has been crucial to Jacquemus’ growth strategy through resisting takeover interest while focusing on collaborations and partnerships instead.
Table of Contents:
Extravagant runway show locations, sensual minimalism meets youthful playfulness, events and pop-ups for audience engagement, differentiated product assortment choices, neutral shades representing simplicity, golden tones reflecting warmth, blue hues capturing coastal vibes, the power of collaboration: breaking new ground together, memorable fashion moments & accessories’ impact: a jacquemus case study, maintaining brand independence: the jacquemus way, what makes jacquemus so successful, is jacquemus an ethical brand, who is jacquemus’ target audience, what is jacquemus’ concept, the rise of jacquemus: sensual minimalism meets youthful playfulness.
Let’s talk about the magic behind Jacquemus, a French fashion label that has taken the world by storm. Founded in 2009 by Simon Porte Jacquemus, this brand is known for its blend of sensual minimalism and youthful freshness. Are you curious to know more?
Jacquemus’ runway shows are nothing short of breathtaking. Their Provence-inspired designs come alive in extravagant locations such as lavender fields and Salt Mountains, creating an unforgettable sun-kissed chic aesthetic. Vogue even described them as “Instagram catnip”.
The brand’s unique style can be summed up in two words: sensual minimalism meets youthful playfulness. This combination results in collections that are both sophisticated and fun – perfect for those who appreciate high-quality design with a touch of whimsy.
A Quick Dive into Their Marketing Strategy:
- Jacquemus Case Study: The brand creates engaging events and pop-ups that keep audiences captivated while making differentiated choices when building their assortment.
- Social Media Presence: With a strong Instagram following , Jacquemus leverages the power of visual storytelling to showcase their designs and connect with their audience.
- Collaborations: By partnering with other brands, designers, and celebrities, Jacquemus maintains its independence while expanding its reach in the fashion world .
So there you have it. A glimpse into the rise of Jacquemus and how they’ve managed to create an iconic brand that resonates with modern consumers who value shareable moments above all else. If you’re interested in learning more about their marketing strategy or want to dive deeper into this Jacquemus case study, check out our comprehensive analysis on 440 Industries .
Innovative Marketing Strategies: The Jacquemus Way
Hey there, fashion enthusiasts.
Let’s dive into the captivating world of Jacquemus and uncover their innovative marketing strategies that keep us all mesmerized.
Are you ready? Let’s go.
Jacquemus knows how to create buzz-worthy events.
Their runway shows in breathtaking locations like lavender fields or Salt Mountains are not only visually stunning but also make a strong statement about their Provence-inspired designs. Do you recall the spectacular 10th-anniversary presentation?
Besides jaw-dropping events, Jacquemus’ product assortment choices play a significant role in their success too.
Instead of blindly following trends, they focus on delivering unique experiences through high-quality products that resonate with modern consumers who value shareable moments above all else (hello Instagram.).
Tips for Adopting the Jacquemus Approach:
- Create memorable experiences: Think outside the box when planning your next event or pop-up. Choose an unconventional location or theme to generate buzz and excitement around your brand.
- Differentiate your product offerings: Don’t be afraid to stand out from competitors by offering something truly unique and exclusive. This will help you build a loyal customer base that appreciates your brand’s distinctiveness.
- Engage with your audience: Use social media to connect with fans, showcase behind-the-scenes content, and encourage user-generated content. This will create a sense of community around your brand while providing valuable insights into what resonates most with your target market.
So there you have it.
The secret sauce behind Jacquemus’ marketing strategy is all about creating unforgettable experiences through innovative events, differentiated product offerings, and genuine audience engagement.
Ready to learn more about the Jacquemus case study? Head over to 440 Industries for more insights.
Happy strategizing.
Apparel Offering & Signature Colorways: The Jacquemus Palette
Let’s talk colors, shall we?
Jacquemus is known for its Provence-inspired minimalism and sun-kissed chic aesthetic, which translates into a beautiful color palette in their apparel offerings.
Ready to dive into the hues that make this brand stand out? Here we go.
Ah, neutrals – the foundation of any wardrobe.
Jacquemus embraces simplicity with neutral shades like beige, cream, and white in their designs.
Their minimalist approach allows these pieces to become versatile staples in your closet while still exuding sophistication and elegance.
Next up: golden tones that bring warmth to your ensemble.
Inspired by the sun-drenched landscapes of southern France, Jacquemus incorporates rich yellows and golds into their collection for an added touch of vibrancy and luxury.
Moving on to cooler shades now.
Drawing inspiration from the Mediterranean coastline, Jacquemus infuses calming blues reminiscent of crystal-clear waters and azure skies into their garments.
These coastal vibes are perfect for channeling effortless style during those warm summer months or dreamy vacation getaways.
- Don’t forget their signature pink colorway.
Last but not least, we have Jacquemus’ iconic pink hue that adds a playful touch to the brand’s sensual minimalism.
This vibrant tint provides a perfect way to make an impact while still keeping true to the brand’s essence and look.
So there you have it – the colors that define Jacquemus and set them apart in the fashion world. Happy styling.
Boutique Expansion & Collaborations: A Winning Combination
Let’s talk about how Jacquemus is making waves in the fashion world.
Their boutique on Avenue Montaigne offers a unique shopping experience, blending accessible items like baseball caps with elevated pieces for those who crave luxury. This diverse range caters to different tastes and budgets while staying true to their Provence-inspired minimalism and sun-kissed chic aesthetic.
But wait, there’s more. Jacquemus has also entered into a multi-year partnership with Nike , further boosting brand awareness through exciting collaborations that push boundaries beyond traditional luxury fashion labels’ expectations.
- Bold move #1: Opening an Avenue Montaigne boutique offering a diverse product range for all types of customers.
- Bold move #2: Partnering with Nike to create innovative designs that solidify their position among industry leaders.
Staying ahead of the competition and capturing consumers’ interest requires collaboration in today’s ever-evolving fashion landscape. Jacquemus understands this well, which is why they’ve teamed up with powerhouse brands like Nike.
How Can You Apply This Strategy?
The Jacquemus case study shows us how boutique expansion combined with strategic collaborations can propel a fashion label into the spotlight. If you’re passionate about fashion and lifestyle, take inspiration from their innovative marketing strategy as you chart your own path to success.
Let’s take a nostalgic voyage, shall we?
Do you remember the iconic Spring/Summer 2018 show featuring tiny bags and gigantic straw hats? Jacquemus sure knows how to make an impression.
Apart from creating memorable moments, handbags have played an essential role in driving profitability for Jacquemus. In fact, they achieved a remarkable operating profit margin of 25% in 2023 – impressive stuff.
At ContentHacker.com, we understand the importance of a strong marketing strategy. And that’s exactly what Jacquemus has in place. By creating unforgettable fashion moments and leveraging the power of accessories, they have successfully captured the attention of their target audience.
So there you have it – memorable moments and accessories that not only make a statement but also drive profitability. To make your fashion label stand out, consider following the lead of Jacquemus and incorporating memorable moments and accessories into your strategy.
Let’s dive into the world of fashion and explore how Simon Porte Jacquemus has managed to maintain brand independence with his eponymous label, Jacquemus.
Despite the fashion industry ‘s rapid evolution, Jacquemus’ Simon Porte has managed to preserve his brand’s identity and creative freedom. However, Simon has achieved this by remaining steadfast in keeping his brand independent, despite being approached by various investors and conglomerates looking for a piece of the pie.
So, how did he do it?
Instead of succumbing to corporate pressures, Jacquemus opts for strategic collaborations and partnerships as a means of growth. For instance, the multi-year partnership with Nike boosts brand awareness while solidifying their position among industry leaders pushing boundaries beyond traditional luxury fashion labels expectations. Additionally, celebrities like Kendall Jenner, Bella Hadid, and more have donned pieces from the French label on red carpets or during off-duty moments, further cementing their influence within the fashion realm. Moreover, Jacquemus creates opportunities for consumers to capture and share their experiences with the brand on social media, further enhancing its presence in the digital space.
In a nutshell, Simon Porte Jacquemus has managed to maintain his label’s independence by sticking to his creative vision and leveraging strategic partnerships that align with the brand’s core values. This approach is working wonders for Jacquemus, as they continue to captivate audiences worldwide with their sun-kissed chic aesthetic and innovative marketing strategies.
FAQs in Relation to Jacquemus Case Study
Jacquemus’ success can be attributed to its unique blend of sensual minimalism and youthful playfulness, innovative marketing strategies, and memorable fashion moments. The brand’s ability to create buzz through extravagant runway shows, audience engagement events, and iconic accessories like tiny bags and oversized straw hats has helped it stand out in the competitive fashion industry. Additionally, maintaining independence allows for creative freedom and strategic collaborations.
While Jacquemus does not openly promote itself as an ethical or sustainable brand, it takes steps towards responsible practices by producing most of its collections in Europe using local artisans. This approach supports regional craftsmanship while reducing carbon emissions from transportation. However, there is limited information available on their supply chain transparency or labor standards.
Jacquemus targets a diverse range of customers who appreciate contemporary design with a touch of whimsy. Its primary audience includes young adults seeking high-quality apparel that combines simplicity with bold statement pieces such as oversized hats or micro handbags. The brand also appeals to those interested in luxury lifestyle products that evoke warmth and coastal vibes.
The concept behind Jacquemus revolves around creating modern yet timeless designs inspired by the founder’s French heritage and Mediterranean upbringing. Sensual minimalism meets playful elements resulting in versatile clothing suitable for various occasions without compromising style or comfort. Signature colorways like neutral shades represent simplicity while golden tones reflect warmth; blue hues capture coastal vibes.
Jacquemus Case Study showcases the success story of a brand that has made its mark in the fashion industry with innovative marketing strategies, unique apparel offerings, and memorable fashion moments. The brand’s signature colorways and expansion into collaborations have also played a significant role in boosting its recognition.
The ability to maintain brand independence while still growing through partnerships is another key takeaway from this case study. By staying devoted to their vision and creating items that strike a chord with their crowd, Jacquemus has become an influential presence in the fashion industry.
Was This Article Helpful?
You're never to cool to learn new things, here are sources for further research.
Please note: 440 Industries is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.
Fashion Marketing
Retail marketing, fashion entrepreneurship, fashion finance.
MORE ARTICLES FROM OUR BLOG

Diesel Case Study: Fashion Industry’s Sustainable Revolution
Explore the Diesel Case Study: fashion industry’s sustainable shift through cleaner engines, innovative campaigns, and Smart Rebels focus.

The OTB Group Case Study: Core Values and Growth Strategies
Discover The OTB Group Case Study, highlighting core values, growth strategies, sustainability efforts, and digital innovation in the fashion world.

Jil Sander Case Study: Fashion Legacy & Adaptations
Explore the Jill Sander Case Study, delving into her minimalist fashion legacy and how creative directors Lucie and Luke Meier adapt to market changes.

Marni Case Study: Bold Fashion and Diverse Collaborations
Explore the Marni Case Study, highlighting bold fashion, diverse collaborations, and innovative digital expansion in this captivating analysis.

440 Industries Disclaimer, Credits and acknowledgements. Privacy Policy
Copyright © 440 industries 2024.
A Successful Brand Repositioning Strategy – Case Study

The challenge
The brand repositioning process, examples of questions included in the study.
The following is a use case based on the actual facts of one of our clients, which will help you get an idea of the usefulness of our smart insights platform. Find out how to conduct a successful brand repositioning and how to define a solid marketing strategy for a new target market.
We place the utmost importance on our client’s privacy and confidentiality, therefore we won’t be disclosing their identity.

A dairy product producer sees their sales plummet due to the underlying financial situation, the massification of their product category, and the little differentiation within it . To face the problem, the company goes for a selective and exclusive strategy based on supporting its ‘healthy’ brands and deprioritizing the rest, halting all investments going into them.
The brand’s target audience in the countries it operates in has always been the mothers of children under 10 years old and its communication has always been focused on the benefits of its products for their health, but after seeing their numbers steadily drop the brand rethinks its communication strategy.
It will need to find out if its target consumers have changed and, if so, what their interests are to approach them effectively.
The brand launches a study to their current target asking them about their purchase intent and consumption habits to find out why their products’ sales have dropped.
The problem comes down to the fact that when mothers go to the supermarket they focus on buying products for the whole family and their priority is to fill the fridge with products offering the best value. If children don’t ask for the brand’s products, their mothers won’t buy them.
On the other hand, if their children ask them for a specific brand, they will. The influence that children have over their parents is known as Pester Power.
In light of the results, the brand decides to center its communication strategy on children and, therefore, must find a way to catch their attention and stay away from the messages it used in the past (focused on health and sports).
To determine the best way to penetrate this new target , the brand launches a second study asking mothers what their children’s lives are like and how they spend their free time. Results show that children’s days are all alike: go to school, do extracurricular activities, do homework, have dinner, sleep, and repeat, making routine their worst enemy.
Based on this information, the brand comes up with a new concept to reach its new market segment and link it to the pain point found in the study. Routine has a prominent place in consumers’ lives, so the brand decides to make it the core of its communication strategy and help them break it.
With its new target (children) in mind and an interesting value proposition in hand (breaking their routine), the brand decides to launch a third study to discover its consumers’ favorite brands and use that information to pinpoint the ideal product to launch and which ones are more in-sync with the brand image.
After studying the results, a brainstorming session is conducted during which a series of collaborations between brands are suggested to create a new product. To check if the co-branding ideas that come up have any potential, a study is carried out via which consumers are asked which brand combinations they find most attractive and wouldn’t hesitate to purchase.
Based on the most noteworthy suggestions, the brand outlines and designs 2 pilot products with which it conducts a new study to determine the interest and purchase intent for them.
- Who eats it at home
- When deciding to buy a product, what does your child consider the most important aspect of it is?
- Which are his/her favorite brands? Choose two of the following brands.
- Do you think your child would like these 2 brands to launch a product together?
- From 0 to 10, how willing would you be to purchase the product resulting from the collaboration?
The brand gets essential insights thanks to the 5 conducted studies and the direct consequences are:
- Online and offline campaign launch to present the new image, far from the family values the brand has in other countries and focused on its new target: children.
- Creation of a fictional character and online content to help break the routine.
- A rewards program for purchasing the brand’s products, giving children a chance to acquire the new fictional character’s merchandise: a mask, an inflatable mattress, etc.
- A new packaging design, with a round and modern shape, leaving no traces of the old brand identity.
- 8 successful advertising spots thanks to the 3 million euros the company is convinced to invest, even after previously cutting ad spend.
- 2 flagship products as a result of the co-branding initiative with the best-suited brands and a two-year innovation pipeline with three more future references.
All of these actions don’t go unnoticed and impact the brand in the form of:
- A boost to the TOP3 of children’s favorite brands.
- +4 percentage points in global market penetration
- Of this increase, 58% is thanks to new consumers of the brand
- + 7 pp in target penetration
- 150% growth in social media (fan base and engagement)
- 3% sales volume increase
- 10% more brand value
- +4 pp of market share
- Revenue from the campaign amounting to 5M€
Finally, to stay in the loop regarding new and upcoming trends that may be of interest to such a dynamic and changing target as children are, and make good use of them to detect potential opportunities , the client decides to launch studies on an ongoing basis (weekly during the first 6 months after the target change).
In conclusion, this case study highlights the effectiveness of a well-crafted brand repositioning strategy that takes into account the evolving needs of the target market. By using real-time insights, marketing professionals can identify pain points and tailor their communication approach accordingly , resulting in increased market penetration, brand value, and revenue. This case study is a testament to the power of smart insights in creating a successful marketing campaign and sustaining long-term growth. As the market landscape continues to evolve, ongoing studies and adaptability will be key to staying ahead of the curve and identifying new opportunities for products or services innovation.

Receive regular updates from Zinklar!
Related articles, cookie policy, privacy overview.
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
9 Top Marketing Trends and Strategies of 2024
Discover the marketing landscape of 2024 with insights on AI integration, short-form video popularity, UGC strategies, and the importance of authentic branding.
![brands marketing strategy case study [Featured image] Inspired Gen Z marketer in light shirt with floral pattern sitting at table in modern cafe typing on laptop while researching new AI tools for marketing](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/5nCFHwt9ZrlSMXyAJPA4dJ/5534b1a350828fdc642ff1e47d6cb8c4/GettyImages-1493933061.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
Because marketing is so closely tied to consumer behavior, no matter what area of marketing you specialize in, the effectiveness of your campaigns is susceptible to cultural ebbs and flows. To optimize your marketing plan for the modern consumer, it can be important to incorporate some trendier elements into your marketing strategy alongside the more tried-and-true efforts.
In this article, we’ll discuss the top marketing trends of 2024, spanning social media marketing, digital marketing, brand marketing, and more.
As you read through these trends, remember to keep your unique consumer base in mind, as not all of these trends will necessarily translate across all audiences. To help figure out who your consumers are and foundational strategies to reach them, try the University of Pennsylvania’s top-rated crash course, Introduction to Marketing .
Top marketing trends of 2024
To identify the top marketing trends, we researched a range of marketing reports and studies across several areas of marketing. Trends worth keeping in mind as you develop your marketing plans are:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is boosting effectiveness and efficiency.
Short-form video content, like TikTok, is driving social strategy.
User-Generated Content (UGC) is increasing brand awareness.
Community efforts and genuine branding encourage consumer trust.
Quality editorial content persists.
Case studies continue to drive brand recognition and sales lead generation .
Search engine changes are shifting search engine optimization (SEO) strategies.
AI-powered chatbots are expanding conversational capabilities.
Personalization is enhancing the user experience.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these trends and the data that informs them.
1. AI boosts effectiveness and efficiency.
The impact of AI advancements spans industries and job functions, and marketing is no exception. According to HubSpot ’s State of Marketing Report 2024, 64 percent of marketers are already using AI and automation, and 38 percent of those who didn’t use AI in 2023 plan to use it in 2024 [ 1 ]. What’s more, consulting firm Gartner predicts that 80 percent of advanced creative roles in marketing will be tasked with using GenAI to enhance their marketing efforts by 2026 [ 2 ].
Two areas where AI is frequently appearing in marketing workflows are content production and marketing analytics.
GenAI for content production
Many marketers use generative AI (GenAI) across different stages of content creation, estimating that they save about three hours of work per piece of content, with 84 percent of those using AI reporting higher efficiency when creating content, 82 percent reporting producing “significantly more” content, and 56 percent reporting increased content performance [ 1 ].
You can use GenAI tools like ChatGPT or Google Gemini to generate content ideas, build briefs and outlines, draft content, or even write complete pieces.
Start advancing your GenAI skills with DeepLearning.AI’s Generative AI for Everyone course. In about six hours, you’ll learn how GenAI works, what it can be used for, and how to start incorporating this technology into your workflow.
Using AI for marketing analytics
Data-driven marketing isn’t a new trend, but the way marketers are getting their data is changing, thanks to AI. According to The Work Innovation Lab’s 2023 report, The State of AI at Work, 30 percent of workers already use AI for data analysis, and 62 percent of workers want to use AI for data analysis [ 3 ].
With the power of AI driving your analytics, you can learn about your target audience, identify trends, predict behaviors, and optimize your marketing campaigns faster and with more accuracy than you may have without AI assistance.
Start advancing your marketing analytics skills with the Meta Marketing Analytics Professional Certificate . You’ll learn how to gather and analyze marketing data, and how to turn your insights into actionable strategies.
2. Short-form video content drives social strategy.
As marketers increasingly target digital-first generations, they’re meeting them where they are: scrolling short-form videos on TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram. According to HubSpot, short-form video is the content type with the highest return on investment (ROI) and is primed to see the most growth in 2024, with 53 percent of marketers planning to increase their investment in TikTok, YouTube Shorts, and Instagram Reels [ 1 ].
Start advancing your TikTok skills with Aptly’s Marketing with TikTok Specialization .
3. UGC increases brand awareness.
User-generated content (UGC) is any type of content that users post about your product on their social media profiles. The content itself may be similar to the type of content you’d see influencers or affiliate partners posting, but unlike those posts, businesses don’t work directly with the users to sponsor or produce the content. It’s more like word-of-mouth marketing, where users create content and share it with their audiences, and then businesses can leverage that content through tactics like social sharing or giveaways.
Traditional influencer marketing and affiliate marketing programs continue to have a place in marketing strategy, but marketing professionals are also increasingly relying on UGC as a cost-effective way to promote brand awareness in a way that feels organic to the typical viewer. According to Gartner, over 80 percent of consumers believe that UGC improves product discovery, brand trust, and experience [ 2 ].
Start advancing your social media marketing skills with the Meta Social Media Marketing Professional Certificate . Here, you’ll learn how to create an authentic brand across various social media platforms and build effective social media campaigns.
4. Community efforts and genuine branding encourage consumer trust.
Authenticity is the third-highest value US consumers identify with, according to Gartner [ 2 ], and nurturing a genuine brand voice is going to become increasingly important as AI-generated content becomes more prevalent in online spaces.
The modern marketer’s response: lean into emotional connections with community-building efforts. A 2024 report from marketing platform TINT found that 70 percent of marketers agree that community building is key for customer retention and that 82 percent of consumers are more likely to purchase new products from a company with an engaging online community [ 4 ].
Start advancing your brand marketing skills with the University of London’s top-rated Brand Management: Aligning Business, Brand and Behaviour course.
5. Quality editorial content persists.
Marketers will continue to invest in editorial content, like blog posts and podcasts, to generate engagement, support conversions, and promote thought leadership. According to HubSpot, 82 percent of marketers surveyed plan to increase or maintain their investment in podcasts and audio content, and 92 percent plan to increase or maintain their investment in blogging in 2024 [ 5 ].
Start advancing your digital marketing skills with the Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate . You’ll explore the fundamentals of digital marketing, ground your performance with analytics, and learn about various marketing channels.
6. Case studies drive brand recognition and sales leads.
More traditional content marketing , like case studies, are typically used to increase brand recognition and drive lead generation, particularly for B2B marketing. In 2024, case studies will continue to show up in marketing strategies. HubSpot found that 26 percent of marketing teams already use case studies in their content marketing strategy, and 87 percent of marketers plan to increase or maintain their investment in case studies [ 5 ].
Start advancing your content marketing skills with Northwestern University’s Content Strategy for Professionals Specialization . Here, you’ll learn about engaging your audience, managing content, and maximizing your impact.
7. Search engine changes shift SEO strategies.
With AI-powered enhancements to popular search engines, Gartner predicts that brands will see a 50 percent decrease in organic search traffic to their websites by 2028 [ 2 ]. Despite the shifting landscape, HubSpot reports that 92 percent of marketers plan to increase or maintain their investment in SEO in 2024 [ 5 ].
In addition to evolving historical strategies, SEO teams are increasingly expanding into video, image, and, in some cases, audio search content, aiming to prioritize a delightful customer experience while capitalizing on all aspects of Google and Bing’s latest developments.
Start advancing your SEO skills with the University of California, Davis’ Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Specialization . You’ll learn SEO fundamentals, how to optimize your website, and some advanced tactics.
8. AI-powered chatbots expand conversational capabilities.
Chatbots and virtual assistants are providing consumers with high-quality answers to common or easily answered questions. With advancements in AI and natural language processing (NLP) technologies, it’s becoming easier for marketers to program and use these tools to increase efficiency without disrupting customer satisfaction. According to HubSpot, 58 percent of marketers plan to increase their investments in chatbots in 2024 [ 1 ].
Learn how to build your own chatbot with IBM’s Building AI Powered Chatbots Without Programming .
9. Personalization enhances user experience.
AI is also enabling personalized experiences, which 96 percent of marketers say leads to repeat business, and 94 percent say increases sales, according to HubSpot [ 1 ]. Machine learning product recommendations or immersive experiences, like augmented reality (AR) features that allow users to “view” physical products in their space, tap into individual consumer preferences to unlock data-driven purchase decisions and increase customer satisfaction.
Still, this is an emerging digital marketing trend. HubSpot notes that while 73 percent of marketers agree that personalization is important, only 35 percent feel that their brand offers a personalized user experience [ 1 ].
Data collection and privacy policies shift targeting strategies
Alongside the interest in personalization, digital marketers are keenly aware of changing data collection and privacy policies that stand to change the way they learn about their audience. As Apple and Google phase out third-party cookies, businesses are exploring first-party data collection methods [ 1 ].
Learn more about data privacy with Northeastern University’s Data Privacy Fundamentals course.
Start advancing your marketing skills today
Learn how to keep up with the latest marketing trends with Coursera. Advance your skills with some of these top marketing Professional Certificates:
With the Meta Marketing Analytics Professional Certificate , you’ll learn how to collect, interpret, and analyze marketing data to optimize your marketing campaigns.
With the Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate , you’ll learn the fundamentals of digital marketing and e-commerce, develop insights with marketing analytics, and use marketing tactics across various channels to grow customer loyalty.
With the Meta Social Media Marketing Professional Certificate , you’ll learn how to establish an online presence for your business, manage social media channels, and create and optimize social advertising campaigns.
Article sources
HubSpot. “ The State of Marketing 2024 , https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/2024%20State%20of%20Marketing%20Report/2024-State-of-Marketing-HubSpot-CXDstudio-FINAL.pdf.” Accessed April 1, 2024.
Gartner. “ Gartner Marketing Predictions 2024 , https://emt.gartnerweb.com/ngw/globalassets/en/marketing/documents/marketing-predictions-for-2024.pdf.” Accessed April 1, 2024.
The Work Innovation Lab by Asana. “ The State of AI at Work , https://asana.com/work-innovation-lab/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/The-State-of-AI-at-Work.pdf.” Accessed April 1, 2024.
TINT. “ State of Community Powered Marketing , https://www.go.tintup.com/hubfs/Downloads/TINT%20-%20State%20of%20Community%20Powered%20Marketing%20-%202024.pdf.” Accessed April 1, 2024.
HubSpot. “ The Top Marketing Trends of 2024 & How They've Changed Since 2023 , https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/marketing-trends.” Accessed April 1, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

- Free Resources

B2B Brand Awareness: Examples both big (integrated, geo-targeted marketing campaign) and small (bootstrapped startup’s new image)
Try this prompt using the Conversion Pro expert assistant in MECLABS AI to get ideas for improving your landing pages and homepage. It's totally FREE to use, for now (MECLABS is MarketingSherpa’s parent organization):
Could you please scan the content on this page and suggest improvements? [paste webpage URL here]
Quick Case Study #1: How software development company increased leads 33% with a non-traditional B2B marketing approach focused on its industry’s geographic concentration
“In this project, for which the SOFTSWISS Marketing Team received recognition at the EGR Marketing Innovations Awards 2023, we employed a creative solution uncommon in the technology industry,” said Valentina Bagniya, CMO, SOFTSWISS .
SOFTSWISS is an international tech product company with 15 years of experience. While the iGaming software provider’s target audience in general is globally dispersed, the team focused this campaign on Malta.
“Despite having a population of less than half a million, Malta's stature as an online gambling leader is notable, especially considering that 10% of the world's online gaming companies are registered and represented there,” she said.
Lest you think this case study only applies to this industry, remember, there are many industries that have a geographic concentration:
- Technology and innovation in Silicon Valley, Tel Aviv, and Bangalore
- Entertainment and film in Hollywood, Bollywood, and Kollywood
- Finance on Wall Street
- Automative in Detroit
- Wine in Bordeaux
- Pharmaceuticals in Basel
- Diamonds in Antwerp
And of course, industry events cause a geographical concentration in certain locations for brief periods as well (another aspect covered in this case study).
BEFORE: Traditional industry approach results in low brand awareness in Malta
In previous marketing communications, the company focused on the rational benefits of the product and used only traditional digital channels.
Creative Sample #1: Example of previously used digital banners highlighting rational brand features

AFTER: Non-traditional B2B campaign strategy with a simple message and eye-catching visuals
The gambling software development company realized that thanks to its industry’s concentration in Malta, it could take approaches that were non-traditional for B2B, and more like the FMCG industry.
“The high concentration of B2B iGaming audiences in Malta and, hence the high affinity of media channels that are typically not very relevant for B2B TA, prompted us to adopt a non-standard approach for B2B in choosing the mix of channels,” she said.
The team launched the campaign in October with an eye on the key industry event of the year – SiGMA Europe 2022 – that was held in November.
Step #1: Channel selection
Competitors limited their non-digital promotion methods to participation in various iGaming events. Which meant the SOFTSWISS team could stand out in channels like OOH advertising, radio, in-mall ads, flight magazines, and airport advertisements.
The choice of channels was based on the below research.
Step #2: Teaser campaign
To stand out even more, the team went with a high-concept branding approach for its teaser campaign that was more typical of B2C brands. The ‘Bringing the Heat’ creative concept was developed, with a message rooted in urban slang, meaning ‘adding power.’
But before they launched that main campaign, the team launched a teaser campaign with similar visuals and coloration – the team chose a hot pepper as the key symbol of the campaign – with the line 'Blazing In.'
Creative Sample #2: Key visual featuring the chilli pepper

“Traditionally, it's understood that B2B and B2C target audiences have different needs and preferences. However, in this campaign, we proceeded from the understanding that regardless of what is being purchased, the final decision is made by a person. And no matter the context in which a person makes a decision, it primarily comes from understanding the value the product provides. Here, not only rational factors or reasons are important but also emotional ones,” she said.
Creative Sample #3: Social media post from Aleksei Trudov excited to see bus advertising for a gambling software provider

Step #3: Main campaign
The team chose five C-level executives from SOFTSWISS to feature in the main campaign, executives that the target audience could then recognize at industry events or around Malta.
Creative sample #4: Key visuals featuring the C-level

The creative campaign also featured below-the-line, in-person experiential activations. For example, the team offered unique ice cream with spicy flavors such as chilli-mango and strawberry chilli (yellow and red, representing the brand colors of SOFTSWISS) near the offices of 29 potential clients for two days, serving 800 people.
Creative sample #5: Below The Line activities

And to target industry experts flying to Malta for the iGaming event, the team had five ad placements at Malta International Airport (OOH billboard, departure, arrivals, baggage areas) and in the in-flight Bizzilla Magazine.
The integrated campaign included PR, with four press and post releases, articles for iGaming media magazines, and podcast interviews.
RESULTS: Growth in brand awareness and target audience engagement
The campaign was meant to be a 360-degree experience that the target audience couldn’t ignore. It achieved the following results:
- Branded keyword clicks increased 104% vs the previous period (before the campaign)
- Leads (using UTM codes to qualify leads from the campaign) increased 33%
- Organic traffic increased 45%
- Nearly all targets were achieved, spending 40% less than the projected budget
Besides the measurable KPIs, the campaign helped SOFTSWISS increase employee loyalty thanks to C-level managers’ role as the main campaign heroes. Competitors inquired about the brains behind the idea and shared photos of the C-level executives, whom they recognized from the billboards and had the opportunity to engage with at the company’s event booth.
“In a young, competitive sector like ours, unique and engaging communication can have a substantial impact. Establishing a compelling creative brand image facilitates the presentation of rational product features, making the brand more attractive and recognizable,” she said.
But what sticks out for a moment in time does not last forever. “In the context of a small Maltese audience, creative content becomes less effective over time as the audience becomes accustomed to and bored with repeatedly seeing the same banners. Planning such campaigns for the short term is recommended,” she said.
And what works in one market, does not work in every market. For instance, in LATAM, the team sees value in partnerships with celebrities and influencers. “Brazilians tend to buy from those they know and trust. It's important to them that the brand is represented by locals. This is also about the emotional connection with the brand,” she said.
Quick Case Study #2: Small remote hiring company grows clients from Facebook advertising while reducing turnover
The previous case study showed the impact of an all-in branding campaign. But even a smaller business that can’t afford a 360-degree campaign can improve results. Let’s take a look at the story of Virtustant, a remove hiring company.
BEFORE – Starting small
When the remote hiring company started, the two partners themselves were the only employees, and the logo looked amateurish.
Creative Sample #6: Remote hiring company logo (before)

“We found the clients by advertising on Facebook with my savings,” said Erik Reid, CEO, Virtustant . The CTA focused on a free consultation.
Creative Sample #7: Facebook ad for remote hiring company (before)

This got the company clients and remote workers, however the turnover rate was high. But they were young and scrappy and dedicated to improving. “We quickly adopted the strategy of ‘the aggregation of marginal gains’ by Sir Dave Brailsford. This is simply to try and grow 1% a day,” Reid said.
One way they tried to grow was by improving their brand image. When I asked Reid if anything specific catalyzed this change, he told me, “There absolutely was a specific moment, and it was when we ran out of money again, due to the high turnover bleed we experienced from both sides of the spectrum. We decided to go through one last round of low-cost work and use the entirety of the result to invest in getting at least one serious company to hire through us.”
AFTER – Rebranding for a more professional identity
The previous logo was heavy and “didn’t bring much to the table in the way of transmitting just how simple our process is.” It also conveyed a traditional sense of procedure, referencing the Greek laurels of victory, while the team considered their methods to be cutting-edge modernist.
So they created a new logo that had a more youthful approach, streamlining the many aspects of their work into one simple, friendly tick without sharp edges. “As comfortable as the couch where you can work from home,” he calls it.
The coloring also changed to represent a work focus, over a formal one, in the way that it brings to mind a traffic cone or construction area, but without the dangers (as working remotely is quite safe).
Creative Sample #8: Remote hiring company logo (after)

They hoped the new, more professional look would attract bigger, more serious clients. Since advertising is still one of the tactics the team uses, here’s an example of the new advertising look. While the message still focused on the lower cost of hiring someone from outside the United States, the CTA changed from a free consultation to a focus on the cost of hiring.
Creative Sample #9 Facebook ad for remote hiring company (after)

RESULTS – Growth and client satisfaction
In all of 2022, the team was able to get nine clients through Facebook ads. In 2024 so far, the international staffing firm has already gotten 11 clients.
And these were higher-quality clients. “We learned that good quality marketing and sales bring a better-quality customer, who is better served by the excellence of the candidates we’ve provided. This leads to recommendations to other companies they are friends with, and when their production grows, they call us back to hire more remote employees. It is a virtuous cycle to focus on those you can perceive as serious leads and not waste time with those who want to lowball,” he said.
This approach has helped the company grow from the original two co-founders to a team of 30.
EPILOGUE – Global team dynamics
In working on this story, Reid also shared with me many lessons about working with a global team, something many marketers and entrepreneurs reading this article do on a daily basis.
For one, the team pivoted from originally recruiting in Asia, which they initially focused on since Reid’s co-founder was working in Asia on a Mandarin teaching project. They found Latin America to be a better fit because the time zones better align with the United States, and there are more native English speakers.
Reid also cautioned that it’s important to understand the culture of workers outside your home market.
“It's important to have a diverse group of individuals who bring a different perspective to the job. However, sometimes the culture of where people are from is not explored enough to know that it will not mesh. America is a very unique country in the way we work, and the ‘grind’ mentality,” he said.
“We have seen many people struggle to enjoy and keep up with the hustle of American work culture.”
This article was distributed through the MarketingSherpa email newsletter .
Related resources
B2B Brand Marketing and Culture: The higher up you go, your priority becomes the people (podcast episode #88)
Strategic Branding For Small Businesses: B2C rebranding and B2B advertising case studies
4 Lessons About B2B Inbound Marketing from a Sunday Morning in the Coffee Shop
Improve Your Marketing
Join our thousands of weekly case study readers.
Enter your email below to receive MarketingSherpa news, updates, and promotions:
Note: Already a subscriber? Want to add a subscription? Click Here to Manage Subscriptions
Get Better Business Results With a Skillfully Applied Customer-first Marketing Strategy

The customer-first approach of MarketingSherpa’s agency services can help you build the most effective strategy to serve customers and improve results, and then implement it across every customer touchpoint.
Get headlines, value prop, competitive analysis, and more.
Marketer Vs Machine

Marketer Vs Machine: We need to train the marketer to train the machine.
Free Marketing Course

Become a Marketer-Philosopher: Create and optimize high-converting webpages (with this free online marketing course)
Project and Ideas Pitch Template

A free template to help you win approval for your proposed projects and campaigns
Six Quick CTA checklists

These CTA checklists are specifically designed for your team — something practical to hold up against your CTAs to help the time-pressed marketer quickly consider the customer psychology of your “asks” and how you can improve them.
Infographic: How to Create a Model of Your Customer’s Mind
You need a repeatable methodology focused on building your organization’s customer wisdom throughout your campaigns and websites. This infographic can get you started.
Infographic: 21 Psychological Elements that Power Effective Web Design

To build an effective page from scratch, you need to begin with the psychology of your customer. This infographic can get you started.
Receive the latest case studies and data on email, lead gen, and social media along with MarketingSherpa updates and promotions.
- Your Email Account
- Customer Service Q&A
- Search Library
- Content Directory:
Questions? Contact Customer Service at [email protected]
© 2000-2024 MarketingSherpa LLC, ISSN 1559-5137 Editorial HQ: MarketingSherpa LLC, PO Box 50032, Jacksonville Beach, FL 32240
The views and opinions expressed in the articles of this website are strictly those of the author and do not necessarily reflect in any way the views of MarketingSherpa, its affiliates, or its employees.
- English English
- தமிழ் தமிழ்
- বাংলা বাংলা
- മലയാളം മലയാളം
- ગુજરાતી ગુજરાતી
- हिंदी हिंदी
- मराठी मराठी
- Business Business
- बिज़नेस बिज़नेस
- Insurance Insurance
The Financial Express
- UP Board 10th 12th Results Live Updates
- Assam 10th Result Live
- TSBSE Live Updates
- LSG vs CSK Live Score
- PSEB 10th Result 2024 Live
- Mutual Funds
- Gold Rate Today
- Top Indices Performance
- Stock Market Stats
- JAC Jharkhand class 10th Results Live
- Lok Sabha Election 2024 Phase 1 Voting Live
- Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim Assembly Elections Live
- UPMSP UP board Result Live Direct Link
- MP Board Result Live
- Loksabha Election
- Budget 2024
- Stock Market Quotes
- Mutual Fund
- Stock Stats
- Top Gainers
- CaFE Invest
- Investing Abroad
- Gold Rate in India
- Silver Rate in India
- Petrol Rate in India
- Diesel Rate in India
- Express Mobility
- Banking & Finance
- Travel & Tourism
- Brand Wagon
- Entertainment
- Web Stories
- Auto Web Stories
- Infographics
- Today’s Paper
- International
- Edits & Columns
- Personal Finance Print
- PRIVACY POLICY
- TERMS AND CONDITIONS

Analysing Zomato’s marketing strategy: a case study of digital success or marketing fail?
By catering specifically to vegetarian customers, the company aimed to capture a niche market and differentiate itself from competitors.

By Bhaskar Majumdar
Zomato recently made waves with its introduction of ‘Pure Veg Mode’ and the subsequent controversy surrounding its colour-coded delivery service. This case presents a compelling study of whether the company’s actions represent digital success or a marketing failure.

The introduction of ‘Pure Veg Mode’ was a bold move by Zomato CEO Deepinder Goyal. By catering specifically to vegetarian customers, the company aimed to capture a niche market and differentiate itself from competitors. However, the decision to use distinctive green attire and delivery boxes for vegetarian orders stirred up a storm of criticism. It’s critical to understand and consider your customers’ choices. However, a step like this is rather extreme.

At first glance, the colour-coded strategy seemed like a savvy marketing tactic. It garnered significant media attention, sparked online debates, and even broke the charts on Google Trends. This suggests a successful execution of digital marketing techniques to create buzz and generate conversation around the brand. However, the backlash that followed painted a different picture. Critics argued that the segregation of delivery riders based on the type of cuisine they deliver was unnecessary and potentially discriminatory. The decision to backtrack and revert to the standard, red-coloured attire for all riders indicates a misstep in Zomato’s marketing strategy. Personally, am not in favour of overt engagement with a particular food preference.
From a marketing perspective, Zomato’s move can be seen as a double-edged sword. On one hand, it succeeded in generating buzz and increasing brand visibility, demonstrating the power of digital marketing in today’s landscape. On the other hand, the negative backlash tarnished the brand’s image and raised questions about the company’s understanding of consumer preferences and sensitivities.
An idea can sound great in the conference room, but when you get it out there, not so much.
Sometimes what you thought was a great idea can go wrong in so many ways. Whether it’s how it’s executed or how it’s perceived, the result can be a complicated mess that can hurt your brand. Today, marketers are exploring new channels and new media. Competition is intense and as you chase after that viral video or trending tweet, marketing fails to happen. Even the biggest, most recognisable brands make them. And these blunders can be incredibly costly.
The timing of the announcement, just before elections, further fueled speculation about the company’s intentions. Some viewed it as a deliberate attempt to capitalise on political discourse surrounding vegetarianism and non-vegetarianism. In today’s digital era, where social media holds considerable sway in moulding public perception, brands must be cognizant of the narratives they propagate and the responses they provoke from their audience. Transparency and openness to feedback stand as fundamental tenets of successful communication strategies. Conversely, I appreciate Deepinder Goyal’s comprehensive elucidation of the rationale behind retracting the decision. This episode also underscores the significance of thorough research preceding business decisions. Whether this was a calculated move, or an oversight remains open to interpretation.
Despite the controversy, Zomato’s case offers valuable lessons for marketers. It highlights the importance of understanding the nuances of consumer behaviour and preferences. While bold initiatives can drive attention and engagement, they also carry inherent risks. Brands must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the potential backlash before implementing such strategies.
Moreover, Zomato’s experience underscores the growing influence of social media in shaping public discourse and perceptions of brands. In today’s digital age, companies must be prepared to navigate the complex landscape of online conversations and respond effectively to feedback from consumers and stakeholders.
Another perspective suggests that Zomato may have accomplished its intended goals – garnering attention and necessary publicity. Although there isn’t empirical evidence to validate success or failure, nor clear logic to support it, the shared economy concept, encompassing companies like Uber, Ola, Zomato, Oyo, and AirBnB, is relatively recent. Within this framework, Zomato and its counterparts are even newer. By engaging in discussions and debates on social media, we inadvertently contribute to the attention and publicity that Zomato sought, indicating a well-considered strategy on their part.
Zomato’s foray into ‘Pure Veg Mode’ serves as a compelling case study of digital marketing success and failure. The interesting thing though is that the markets have liked it. Zomato is outperforming the indices by a margin. While the company succeeded in generating buzz and sparking conversations, the backlash it faced highlights the pitfalls of overlooking consumer sensitivities. Ultimately, brands must tread carefully in their pursuit of attention and engagement in the digital realm.
Follow us on Twitter , Instagram , LinkedIn, Facebook
Get live Share Market updates, Stock Market Quotes , and the latest India News and business news on Financial Express. Download the Financial Express App for the latest finance news.
Related News
Photo gallery.
4 Arvind Kejriwal’s wife Sunita quits govt: What we know so far
6 Dubai floods: Cancelled flights, submerged cars – Heavy rainfall wreaks havoc in desert-city! See pics here
9 Rs 50, Rs 200, Rs 500 and Rs 2000 notes images: Here are the new currency notes released by RBI
Latest News

Elon Musk postpones India trip due to ‘very heavy’ Tesla obligations

Assam HSLC 10th Result 2024 Live Updates: SEBA Assam board Matric results releasing today, get direct link here

Manipur: 3 arrested for shooting near polling booth in Imphal East

Assam HSLC 10th Result 2024: Assam Education Minister busts fake news on exam results announcement

Chai pe Charcha with Easiloan’s Pramod Kathuria Premium Story
Trending topics.
- IPO’s Open and Upcoming 4
- Stock Analysis
- Financial Literacy
- NSE Top Gainers 1145
- NSE Top Losers 1402
- BSE Top Gainers 1879
- BSE Top Losers 2192
- NSE 52-Week High 0
- NSE 52-Week Low 0
- BSE 52-Week High 0
- BSE 52-Week Low 0
- NSE Price Shocker
- NSE Volume Shocker
- BSE Price Shocker
- BSE Volume Shocker
- NSE Sellers
- BSE Sellers
- Silver Rate Today
- Petrol Rate Today
- Diesel Rate Today


Your company may already be a member. View our member list to find out, or create a new account .
Forgot Password?
Content Library
You can search our content library for case studies, research, industry insights, and more.
You can search our website for events, press releases, blog posts, and more.
This Truth Campaign Offers a Masterclass in Authentic Influencer Marketing
April 17, 2024
To combat a rapid rise in youth vaping, the Truth Initiative partnered with a TikTok influencer on her own quitting journey, leveraging her authentic story to create content that would overcome youth distrust of brands and inspire others to give up the harmful habit.
This Is an ANA Member Exclusive
Access to this item is reserved for ANA members only.
Already have an account? The industry's best insights and resources await:
No Account?
Use your business email address to create your free account ; if you're a member through your company, we'll know.
Members can access their benefits as soon as they sign up and log in.
Not a Member?
You can still create a free account to access the latest from our online publication, ANA Magazine , receive content and special event offers through our newsletters, get breaking industry updates, and so much more.
The content you're trying to see is available to:
- ANA Client-Side Marketer Tier Members
- Platinum Tier Members
- Gold Tier Members
- Silver Tier Members
- Individual Members
Discover everything the ANA can do to help drive growth for your organization. Connect with our membership team.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brand Marketing Case Studies. This collection features brands and content creators that used video and other digital tactics to drive innovation, connect with their consumers, and drive brand and business metrics. Learn about best practices, creative executions, and how brands achieved success through digital. Case Study.
A collection of brand strategy and marketing case studies that provide analysis, insights, and examples around visual identity, positioning, tone of voice, key messages, brand archetypes, content, competitors, and more. Join 5,866 folks who receive our latest insights and you'll get immediate access to our 10 page brand strategy workbook!
Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you. Like in the other case study examples, you'll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements. 16. " NetApp ," by Evisort. Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client.
So to help you thrive in times of change, we look back over the past year and bring you stories of three brands that rethought their marketing strategy during the pandemic. First up, a tourism association that optimized its on-site SEO to be ready when the lockdowns lifted. ... And finally, real estate agents that made a 180-degree shift on its ...
Brand Strategy Case Studies. There are many successful branding case studies we could use to explain each element of a brand strategy. However, we believe these 7 examples help explain the power and benefits of brand strategy well. Red Bull - Company Brand Name. Red Bull is somewhat of a powerhouse in the world of brand marketing.
Etihad Airways, established in 2003, is the second largest flag carrier of the United Arab Emirates. They are…. by Ryan Stephen. May 4, 2016. We love to analyze successful and not so successful brand strategies worldwide and see what we can learn from them. Read our branding case studies here!
Here are some examples of clear and convincing case study headlines: "Achieving a 150% ROI: How [XYZ] Strategy Transformed a Startup". "How Optimized SEO Tactics Skyrocketed Sales by 80%". "Mastering Social Media: How [ABC] Brand Increased Engagement by 50%".
Learn about creative marketing strategies through case studies of successful campaigns by top brands. ... Marketing Strategy Case Studies from Leading Brands With Brian Honigman Liked by 628 ...
5 Big Brand Case Studies Every Marketer Should Know. Many big businesses have begun to experiment with social media, and have dived head-first into the world of Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and beyond. While others still remain traditionally skeptical of the new metrics and pull-instead-of-push approach, companies such as Southwest Airlines and ...
Brand Marketing Case Studies Continued. Digital provides today's brand advertisers and content creators with opportunities to tell compelling stories that engage audiences in new, exciting ways. This collection features brands and content creators that used video, display and social to drive innovation and connect with their consumers.
Grow your brand with the best, most actionable hub of free branding guides, articles, templates, case studies, exercises, examples, and original research available anywhere. Our Content Is Featured In: Join 5,866 folks who receive our latest insights and you'll get immediate access to our 10 page brand strategy workbook! Get The Workbook.
That's why in this case study, we'll dig deeper into McDonald's Marketing Strategy from a marketing perspective by going through its marketing strategies, marketing mix, marketing campaigns, and SWOT analysis. So let us start by first learning more about the business model and brand history of McDonald's.
Here are 15 brand strategy case study examples you can get inspired from: 1. PeachyLean by Nick Ó and Cortney Walker. Using the brand roadmap to tell the story and strategy of the brand in the case study. 2. School of American Thanatology by Subtle Design. Reel / Full case study. Using Instagram Reels to preview the project, then breaking down ...
Marketing Case Studies: Success Blueprints for Brands To Follow. Saranya Ramesh. Marketing is a dynamic field that constantly develops to meet the ever-changing demands of consumers and the marketplace. These case studies and marketing strategy case studies offer valuable lessons and insights that can inspire and inform your own marketing efforts.
Case studies: How brands are innovating on YouTube. See how brands are innovating—and driving impact—with their video marketing strategies on YouTube. From targeting techniques, to contextual creative, to six-second video ads, learn how brands are building campaigns that deliver results with these case studies and interviews. Case Study.
Using the tool, marketers can determine a brand's current and desired position, predict its marketplace performance, and devise and track marketing strategy and execution. In-depth examples of ...
In today's hyper-competitive, crowded environment, marketing strategies that make brands stand out and stay culturally relevant need a mix of old and new tactics. BoF's new case study, The Essential Brand Marketing Guide (Getty Images) By. Diana Pearl. 20 September 2023.
40.2 Nike: Building a Global Brand Through Storytelling and Innovation. Introduction: Nike, Inc. is a household name synonymous with athleticism, performance, and innovation. Through its creative marketing strategies and commitment to design, Nike has become a leader in the sports apparel industry. This case study will explore Nike's rise to ...
Hands-on Brand Strategy Help. Transform your best business thinking into an actionable, shareable, growth-oriented guide. Click below to learn about the Brand Guidebook process. Analysis of Adidas' brand strategy, identity, positioning, key messages, tone of voice, brand archetypes, benefits, competitors, and content.
This study examines Apple's marketing strategy from a customer perspective, focusing. on brand image and engagement. Apple has earned a strong brand image in the global market with. its ...
G & Co. is a luxury and DTC digital agency who has worked with Burberryand Outdoor Voices. At the core of Warby Parker's marketing strategy is doubling down on the customer experience. It's a given that DTCbrands will have to take up the mantle of acting as their own manufacturers, distribution partners, and promoters.
A Quick Dive into Their Marketing Strategy: Jacquemus Case Study: The brand creates engaging events and pop-ups that keep audiences captivated while making differentiated choices when building their assortment. Social Media Presence: With a strong Instagram following, Jacquemus leverages the power of visual storytelling to showcase their designs and connect with their audience.
In conclusion, this case study highlights the effectiveness of a well-crafted brand repositioning strategy that takes into account the evolving needs of the target market. By using real-time insights, marketing professionals can identify pain points and tailor their communication approach accordingly, resulting in increased market penetration ...
B2B Case Study #3: Spotify Boosts Advertisements Through "All Ears on You Campaign". Spotify Advertising, a B2B brand within Spotify, sought to educate brands and media buyers about its digital audio advertising product while positioning itself as a media innovator. As a part of the "All Ears on You Campaign" which showcased the ...
6. Case studies drive brand recognition and sales leads. More traditional content marketing, like case studies, are typically used to increase brand recognition and drive lead generation, particularly for B2B marketing.In 2024, case studies will continue to show up in marketing strategies.
B2B Brand Marketing and Culture: The higher up you go, your priority becomes the people (podcast episode #88) Strategic Branding For Small Businesses: B2C rebranding and B2B advertising case studies. 4 Lessons About B2B Inbound Marketing from a Sunday Morning in the Coffee Shop
This case presents a compelling study of whether the company's actions represent digital success or a marketing failure. The introduction of 'Pure Veg Mode' was a bold move by Zomato CEO ...
This Truth Campaign Offers a Masterclass in Authentic Influencer Marketing. April 17, 2024 . To combat a rapid rise in youth vaping, the Truth Initiative partnered with a TikTok influencer on her own quitting journey, leveraging her authentic story to create content that would overcome youth distrust of brands and inspire others to give up the harmful habit.
By Charlotte Rogers 18 Apr 2024. Soft skills around leadership and communication are more important than functional expertise to succeed in marketing, according to a new study. Leadership emerged as the most useful skill for both CMOs and senior marketing leaders, followed by communication, strategic thinking, interpersonal skills and problem ...