
39 Different Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay (Rated)

The phrase “In conclusion …” sounds reductive, simple and … well, just basic.
You can find better words to conclude an essay than that!
So below I’ve outlined a list of different ways to say in conclusion in an essay using a range of analysis verbs . Each one comes with an explanation of the best time to use each phrase and an example you could consider.
Read Also: How to Write a Conclusion using the 5C’s Method
List of Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
The following are the best tips I have for to say in conclusion in an essay.
1. The Weight of the Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 10/10
Overview: This is a good concluding phrase for an evaluative essay where you need to compare two different positions on a topic then conclude by saying which one has more evidence behind it than the other.
You could also use this phrase for argumentative essays where you’ve put forward all the evidence for your particular case.
Example: “The weight of the evidence suggests that climate change is a real phenomenon.”
2. A Thoughtful Analysis would Conclude…
My Rating: 9/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in either an argumentative essay or a comparison essay. As an argument, it highlights that you think your position is the most logical.
In a comparison essay, it shows that you have (or have intended to) thoughtfully explore the issue by looking at both sides.
Example: “A thoughtful analysis would conclude that there is substantial evidence highlighting that climate change is real.”
Related Article: 17+ Great Ideas For An Essay About Yourself
3. A Balanced Assessment of the Above Information…
Overview: This phrase can be used to show that you have made a thoughtful analysis of the information you found when researching the essay. You’re telling your teacher with this phrase that you have looked at all sides of the argument before coming to your conclusion.
Example: “A balanced assessment of the above information would be that climate change exists and will have a strong impact on the world for centuries to come.”
4. Across the Board…
My Rating: 5/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in a less formal context such as in a creative discussion but would leave it out of a formal third-person essay. To me, the phrase comes across as too colloquial.
Example: “Across the board, there are scientists around the world who consistently provide evidence for human-induced climate change.”
5. Logically…
My Rating: 7/10
Overview: This phrase can be used at the beginning of any paragraph that states out a series of facts that will be backed by clear step-by-step explanations that the reader should be able to follow to a conclusion.
Example: “Logically, the rise of the automobile would speed up economic expansion in the United States. Automobiles allowed goods to flow faster around the economy.
6. After all is Said and Done…
Overview: This is a colloquial term that is more useful in a speech than written text. If you feel that the phrase ‘In conclusion,’ is too basic, then I’d also avoid this term. However, use in speech is common, so if you’re giving a speech, it may be more acceptable.
Example: “After all is said and done, it’s clear that there is more evidence to suggest that climate change is real than a hoax.”
7. All in All…
Overview: ‘All in all’ is a colloquial term that I would use in speech but not in formal academic writing. Colloquialisms can show that you have poor command of the English language. However, I would consider using this phrase in the conclusion of a debate.
Example: “All in all, our debate team has shown that there is insurmountable evidence that our side of the argument is correct.”
8. All Things Considered…
My Rating: 6/10
Overview: This term is a good way of saying ‘I have considered everything above and now my conclusion is..’ However, it is another term that’s more commonly used in speech than writing. Use it in a high school debate, but when it comes to a formal essay, I would leave it out.
Example: “All things considered, there’s no doubt in my mind that climate change is man-made.”
9. As a Final Note…
My Rating: 3/10
Overview: This phrase gives me the impression that the student doesn’t understand the point of a conclusion. It’s not to simply make a ‘final note’, but to summarize and reiterate. So, I would personally avoid this one.
Example: “As a final note, I would say that I do think the automobile was one of the greatest inventions of the 20 th Century.”
10. As Already Stated…
My Rating: 2/10
Overview: I don’t like this phrase. It gives teachers the impression that you’re going around in circles and haven’t organized your essay properly. I would particularly avoid it in the body of an essay because I always think: “If you already stated it, why are you stating it again?” Of course, the conclusion does re-state things, but it also adds value because it also summarizes them. So, add value by using a phrase such as ‘summarizing’ or ‘weighing up’ in your conclusion instead.
Example: “As already stated, I’m going to repeat myself and annoy my teacher.”
11. At present, the Best Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 8/10
Overview: In essays where the evidence may change in the future. Most fields of study do involve some evolution over time, so this phrase acknowledges that “right now” the best evidence is one thing, but it may change in the future. It also shows that you’ve looked at the latest information on the topic.
Example: “At present, the best evidence suggests that carbon dioxide emissions from power plants is the greatest influence on climate change.”
12. At the Core of the Issue…
Overview: I personally find this phrase to be useful for most essays. It highlights that you are able to identify the most important or central point from everything you have examined. It is slightly less formal than some other phrases on this list, but I also wouldn’t consider it too colloquial for an undergraduate essay.
Example: “At the core of the issue in this essay is the fact scientists have been unable to convince the broader public of the importance of action on climate change.”
13. Despite the shortcomings of…
Overview: This phrase can be useful in an argumentative essay. It shows that there are some limitations to your argument, but , on balance you still think your position is the best. This will allow you to show critical insight and knowledge while coming to your conclusion.
Often, my students make the mistake of thinking they can only take one side in an argumentative essay. On the contrary, you should be able to highlight the limitations of your point-of-view while also stating that it’s the best.
Example: “Despite the shortcomings of globalization, this essay has found that on balance it has been good for many areas in both the developed and developing world.”
14. Finally…
My Rating: 4/10
Overview: While the phrase ‘Finally,’ does indicate that you’re coming to the end of your discussion, it is usually used at the end of a list of ideas rather than in a conclusion. It also implies that you’re adding a point rather that summing up previous points you have made.
Example: “Finally, this essay has highlighted the importance of communication between policy makers and practitioners in order to ensure good policy is put into effect.”
15. Gathering the above points together…
Overview: While this is not a phrase I personally use very often, I do believe it has the effect of indicating that you are “summing up”, which is what you want out of a conclusion.
Example: “Gathering the above points together, it is clear that the weight of evidence highlights the importance of action on climate change.”
16. Given the above information…
Overview: This phrase shows that you are considering the information in the body of the piece when coming to your conclusion. Therefore, I believe it is appropriate for starting a conclusion.
Example: “Given the above information, it is reasonable to conclude that the World Health Organization is an appropriate vehicle for achieving improved health outcomes in the developing world.”
17. In a nutshell…
Overview: This phrase means to say everything in the fewest possible words. However, it is a colloquial phrase that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.”
18. In closing…
Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for ‘In conclusion’ and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay. Make sure you follow-up by explaining your position based upon the weight of evidence presented in the body of your piece
Example: “In closing, there is ample evidence to suggest that liberalism has been the greatest force for progress in the past 100 years.”
19. In essence…
Overview: While the phrase ‘In essence’ does suggest you are about to sum up the core findings of your discussion, it is somewhat colloquial and is best left for speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In essence, this essay has shown that cattle farming is an industry that should be protected as an essential service for our country.”
20. In review…
Overview: We usually review someone else’s work, not our own. For example, you could review a book that you read or a film you watched. So, writing “In review” as a replacement for “In conclusion” comes across a little awkward.
Example: “In review, the above information has made a compelling case for compulsory military service in the United States.”
21. In short…
Overview: Personally, I find that this phrase is used more regularly by undergraduate student. As students get more confident with their writing, they tend to use higher-rated phrases from this list. Nevertheless, I would not take grades away from a student for using this phrase.
Example: “In short, this essay has shown the importance of sustainable agriculture for securing a healthy future for our nation.”
22. In Sum…
Overview: Short for “In summary”, the phrase “In sum” sufficiently shows that you are not coming to the moment where you will sum up the essay. It is an appropriate phrase to use instead of “In conclusion”.
But remember to not just summarize but also discuss the implications of your findings in your conclusion.
Example: “In sum, this essay has shown the importance of managers in ensuring efficient operation of medium-to-large enterprises.”
23. In Summary…
Overview: In summary and in sum are the same terms which can be supplemented for “In conclusion”. You will show that you are about to summarize the points you said in the body of the essay, which is what you want from an essay.
Example: “In summary, reflection is a very important metacognitive skill that all teachers need to master in order to improve their pedagogical skills.”
24. It cannot be conclusively stated that…
Overview: While this phrase is not always be a good fit for your essay, when it is, it does show knowledge and skill in writing. You would use this phrase if you are writing an expository essay where you have decided that there is not enough evidence currently to make a firm conclusion on the issue.
Example: “It cannot be conclusively stated that the Big Bang was when the universe began. However, it is the best theory so far, and none of the other theories explored in this essay have as much evidence behind them.”
25. It is apparent that…
Overview: The term ‘ apparent ’ means that something is ‘clear’ or even ‘obvious’. So, you would use this word in an argumentative essay where you think you have put forward a very compelling argument.
Example: “It is apparent that current migration patterns in the Americas are unsustainable and causing significant harm to the most vulnerable people in our society.”
26. Last but not least…
Overview: The phrase “last but not least” is a colloquial idiom that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing. Furthermore, when you are saying ‘last’, you mean to say you’re making your last point rather than summing up all your points you already made. So, I’d avoid this one.
Example: “Last but not least, this essay has highlighted the importance of empowering patients to exercise choice over their own medical decisions.”
27. Overall…
My Rating: 7.5/10
Overview: This phrase means ‘taking everything into account’, which sounds a lot like what you would want to do in an essay. I don’t consider it to be a top-tier choice (which is why I rated it 7), but in my opinion it is perfectly acceptable to use in an undergraduate essay.
Example: “Overall, religious liberty continues to be threatened across the world, and faces significant threats in the 21 st Century.”
28. The above points illustrate…
Overview: This phrase is a good start to a conclusion paragraph that talks about the implications of the points you made in your essay. Follow it up with a statement that defends your thesis you are putting forward in the essay.
Example: “The above points illustrate that art has had an overwhelmingly positive impact on humanity since the renaissance.”
29. The evidence presented in this essay suggests that…
Overview: I like this phrase because it highlights that you are about to gather together the evidence from the body of the essay to put forward a final thesis statement .
Example: “The evidence presented in this essay suggests that the democratic system of government is the best for securing maximum individual liberty for citizens of a nation.”
30. This essay began by stating…
Overview: This phrase is one that I teach in my YouTube mini-course as an effective one to use in an essay conclusion. If you presented an interesting fact in your introduction , you can return to that point from the beginning of the essay to provide nice symmetry in your writing.
Example: “This essay began by stating that corruption has been growing in the Western world. However, the facts collected in the body of the essay show that institutional checks and balances can sufficiently minimize this corruption in the long-term.”
31. This essay has argued…
Overview: This term can be used effectively in an argumentative essay to provide a summary of your key points. Follow it up with an outline of all your key points, and then a sentence about the implications of the points you made. See the example below.
Example: “This essay has argued that standardized tests are damaging for students’ mental health. Tests like the SATs should therefore be replaced by project-based testing in schools.”
32. To close…
Overview: This is a very literal way of saying “In conclusion”. While it’s suitable and serves its purpose, it does come across as being a sophomoric term. Consider using one of the higher-rated phrases in this list.
Example: “To close, this essay has highlighted both the pros and cons of relational dialectics theory and argued that it is not the best communication theory for the 21 st Century.”
33. To Conclude…
Overview: Like ‘to close’ and ‘in summary’, the phrase ‘to conclude’ is very similar to ‘in conclusion’. It can therefore be used as a sufficient replacement for that term. However, as with the above terms, it’s just okay and you could probably find a better phrase to use.
Example: “To conclude, this essay has highlighted that there are multiple models of communication but there is no one perfect theory to explain each situation.”
34. To make a long story short…
My Rating: 1/10
Overview: This is not a good phrase to use in an academic essay. It is a colloquialism. It also implies that you have been rambling in your writing and you could have said everything more efficiently. I would personally not use this phrase.
Example: “To make a long story short, I don’t have very good command of academic language.”
35. To Sum up…
Overview: This phrase is the same as ‘In summary’. It shows that you have made all of your points and now you’re about to bring them all together in a ‘summary’. Just remember in your conclusion that you need to do more than summarize but also talk about the implications of your findings. So you’ll need to go beyond just a summary.
Example: “In summary, there is ample evidence that linear models of communication like Lasswell’s model are not as good at explaining 21 st Century communication as circular models like the Osgood-Schramm model .”
36. Ultimately…
Overview: While this phrase does say that you are coming to a final point – also known as a conclusion – it’s also a very strong statement that might not be best to use in all situations. I usually accept this phrase from my undergraduates, but for my postgraduates I’d probably suggest simply removing it.
Example: “Ultimately, new media has been bad for the world because it has led to the spread of mistruths around the internet.”
37. Undoubtedly…
Overview: If you are using it in a debate or argumentative essay, it can be helpful. However, in a regular academic essay, I would avoid it. We call this a ‘booster’, which is a term that emphasizes certainty. Unfortunately, certainty is a difficult thing to claim, so you’re better off ‘hedging’ with phrases like ‘It appears’ or ‘The best evidence suggests’.
Example: “Undoubtedly, I know everything about this topic and am one hundred percent certain even though I’m just an undergraduate student.”
38. Weighing up the facts, this essay finds…
Overview: This statement highlights that you are looking at all of the facts both for and against your points of view. It shows you’re not just blindly following one argument but being careful about seeing things from many perspectives.
Example: “Weighing up the facts, this essay finds that reading books is important for developing critical thinking skills in childhood.”
39. With that said…
Overview: This is another phrase that I would avoid. This is a colloquialism that’s best used in speech rather than writing. It is another term that feels sophomoric and is best to avoid. Instead, use a more formal term such as: ‘Weighing up the above points, this essay finds…’
Example: “With that said, this essay disagrees with the statement that you need to go to college to get a good job.”
Do you Need to Say Anything?
Something I often tell my students is: “Can you just remove that phrase?”
Consider this sentence:
- “In conclusion, the majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
Would it be possible to simply say:
- “ In conclusion, The majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
So, I’d recommend also just considering removing that phrase altogether! Sometimes the best writing is the shortest, simplest writing that gets to the point without any redundant language at all.
How to Write an Effective Conclusion
Before I go, I’d like to bring your attention to my video on ‘how to write an effective conclusion’. I think it would really help you out given that you’re looking for help on how to write a conclusion. It’s under 5 minutes long and has helped literally thousands of students write better conclusions for their essays:
You can also check out these conclusion examples for some copy-and-paste conclusions for your own essay.
In Conclusion…
Well, I had to begin this conclusion with ‘In conclusion…’ I liked the irony in it, and I couldn’t pass up that chance.
Overall, don’t forget that concluding an essay is a way to powerfully summarize what you’ve had to say and leave the reader with a strong impression that you’ve become an authority on the topic you’re researching.
So, whether you write it as a conclusion, summary, or any other synonym for conclusion, those other ways to say in conclusion are less important than making sure that the message in your conclusion is incredibly strong.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
List of 50 "In Conclusion" Synonyms—Write Better with ProWritingAid

Alex Simmonds

Table of Contents
Why is it wrong to use "in conclusion" when writing a conclusion, what can i use instead of "in conclusion" for an essay, what are some synonyms for "in conclusion" in formal writing, what are some synonyms for "in conclusion" in informal writing, what is another word for "in conclusion", what should a conclusion do in an article or paper.
The final paragraphs of any paper can be extremely difficult to get right, and yet they are probably the most important. They offer you a chance to summarize the points you have made into a neat package and leave a good impression on the reader.
Many people choose to start the last paragraph with the phrase in conclusion , but this has its downsides.
Firstly, you should only use it once. Any more than that and your essay will sound horribly repetitive. Secondly, there is the question of whether you should even use the phrase at all?

Though it’s okay to use in conclusion in a speech or presentation, when writing an essay it comes across as stating the obvious. The phrase will come across as a bit unnecessary or "on the nose."
Its use in an essay is clichéd, and there are far cleaner and more elegant ways of indicating that you are going to be concluding the paper. Using in conclusion might even irritate and alienate your audience or readers.
Thankfully, there are hundreds of synonyms available in the English language which do a much better (and much more subtle) job of drawing a piece of writing to a close.
The key is to choose ones which suit the tone of the paper. Here we will look at both formal options for an essay or academic paper, and informal options for light-hearted, low key writing, or speeches.

If you are writing an academic essay, a white paper, a business paper, or any other formal text, you will want to use formal transitional expressions that successfully work as synonyms for in conclusion .
The following are some suggestions you could use:
As has been demonstrated
A simple way of concluding all your points and summarizing everything you have said is to confidently state that those points have convincingly proven your case:
As the research has demonstrated , kids really do love chocolate.
As all the above points have demonstrated , Dan Brown really was the most technically gifted writer of the 20th Century.
As has been demonstrated in this paper , the side-effects of the vaccine are mild in comparison to the consequences of the virus.
As has been shown
This is another way of saying as has been demonstrated , but perhaps less scientific and more literary. As has been shown would work well in literature, history, or philosophy essays.
For example:
As has been shown above , the First World War and industrialization were the drivers for a new way of seeing the world, reflected in Pound’s poetry.
In the final analysis
This is a great expression to use in your conclusion, since it’s almost as blunt as in conclusion , but is a more refined and far less clichéd way of starting the concluding paragraph.
Once you have finished your argument and started drawing things to a close, using in the final analysis allows you to tail nicely into your last summation.
In the final analysis , there can be little doubt that Transformers: Dark of the Moon represents a low point in the history of cinema.

Along with let’s review , this is short and blunt way of announcing that you intend to recap the points you have made so far, rather than actually drawing a conclusion.
It definitely works best when presenting or reading out a speech, but less well in an essay or paper.
However, it does work effectively in a scientific paper or if you wish to recap a long train of thought, argument, or sequence before getting to the final concluding lines.
To review , of the two groups of senior citizens, one was given a placebo and the other a large dose of amphetamines.

Another phrase you could consider is in closing . This is probably better when speaking or presenting because of how double-edged it is. It still has an in conclusion element to it, but arguably it could also work well when drawing an academic or scientific paper to a conclusion.
For example, it is particularly useful in scientific or business papers where you want to sum up your points, and then even have a call to action:
In closing then, it is clear that as a society, we all need to carefully monitor our consumption of gummy bears.
Or in an academic paper, it offers a slightly less blunt way to begin a paragraph:
In closing , how do we tie all these different elements of Ballard’s writing together?
Perhaps the most similar expression to in conclusion is in summary . In summary offers a clear indication to the reader that you are going to restate the main points of your paper and draw a conclusion from those points:
In summary , Existentialism is the only philosophy that has any real validity in the 21st century.
In summary , we believe that by switching to a subscription model...
On top of those previously mentioned, here are some other phrases that you can use as an alternative to in conclusion :
To summarize
Overall, it may be said
Taking everything into account
On the whole
In general, it can be said that
With this in mind
Considering all this
Everything considered
As a final observation
Considering all of the facts
For the most part
In light of these facts
When it comes to finishing up a speech, a light-hearted paper, blog post, or magazine article, there are a couple of informal phrases you can use rather than in conclusion :
In a nutshell
The phrase in a nutshell is extremely informal and can be used both in speech and in writing. However, it should never be used in academic or formal writing.
It could probably be used in informal business presentations, to let the audience know that you are summing up in a light-hearted manner:
In a nutshell , our new formula Pro Jazzinol shampoo does the same as our old shampoo, but we get to charge 20% more for it!
You can also use it if you want to get straight to the point at the end of a speech or article, without any fluff:
In a nutshell , our new SocialShocka app does what it says on the tin—gives you an electric shock every time you try to access your social media!
At the end of the day
This is a pretty useful expression if you want to informally conclude an argument, having made all your points. It basically means in the final reckoning or the main thing to consider is , but said in a more conversational manner:
At the end of the day , he will never make the national team, but will make a good living as a professional.
At the end of the day , the former President was never destined to unite the country…

Long story short
Another informal option when replacing in conclusion is to opt for to make a long story short —sometimes shortened to long story short .
Again, this is not one you would use when writing an academic or formal paper, as it is much too conversational. It’s a phrase that is far better suited to telling a joke or story to your friends:
Long story short , Billy has only gone and started his own religion!
Would you ever use it in writing? Probably not, except for at the end of friendly, low-key presentations:
Long story short , our conclusion is that you are spending far too much money on after work company bowling trips.
And possibly at the end of an offbeat magazine article or blog post:
Long story short , Henry VIII was a great king—not so great a husband though!
Other "In Conclusion" Synonyms for Informal Writing
You can use any of the synonyms in this article when writing informally, but these are particularly useful when you want your writing to sound conversational:
By and large
On a final note
Last but not least
For all intents and purposes
The bottom line is
To put it bluntly
To wrap things up
To come to the point
To wind things up

Instead of opting for one of the above expressions or idioms, there are several different singular transition words you can use instead. Here are a couple of examples:
The perfect word to tell the reader you are reaching the end of your argument. Lastly is an adverb that means "at the end" or "in summary." It is best used when you are beginning your conclusion:
Lastly , with all the previous points in mind, there is the question of why Philip K Dick was so fascinated with alternate history?
But can also be used at the very end of your conclusion too:
Lastly then, we are left with Eliot’s own words on his inspiration for "The Waste Land."
Finally does exactly the same job as lastly . It lets the reader know that you are at the final point of your argument or are about to draw your conclusion:
Finally , we can see from all the previous points that...
Another word that can be used at beginning of the conclusion is the adverb ultimately . Meaning "in the end" or "at the end of the day," it can be used as a conclusion to both informal and formal papers or articles:
Ultimately , it comes down to whether one takes an Old Testament view of capital punishment or...
It can also be used in more survey, scientific, or charity appeal style articles as a call to action of some sort:
Ultimately , we will all need to put some thought into our own carbon footprints over the next couple of years.
A good word to conclude a scientific, or survey style paper is overall . It can be used when discussing the points, arguments or results that have been outlined in the paper up until that point.
Thus, you can say:
Overall , our survey showed that most people believe you should spread the cream before you add the jam, when eating scones.
Other Transition Words to Replace "In Conclusion"
Here are a few transition word alternatives to add to your arsenal:
Considering
Essentially
Principally
Summarizing
Pro tip: You should use transition words throughout your essay, paper, or article to guide your reader through your ideas towards your conclusion. ProWritingAid’s Transitions Report tells you how many transition words you’ve used throughout your document so you can make sure you’re supporting your readers’ understanding.
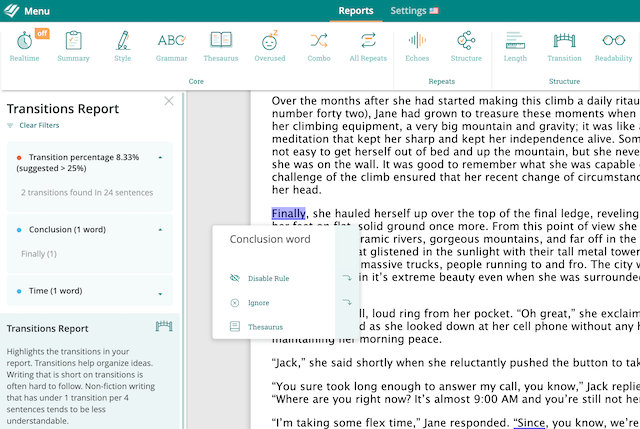
It’ll also tell you what type of transitions you’ve used. If there are no conclusion words in your writing, consider using one of the synonyms from this article.
Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account to try the Transitions Report.
One of the most effective ways of finishing up a piece of writing is to ask a question, or return to the question that was asked at the beginning of the paper using. This can be achieved using how , what , why , or who .
This is sometimes referred to as the "so what?" question. This takes all your points and moves your writing (and your reader) back to the broader context, and gets the reader to ask, why are these points important? Your conclusion should answer the question "so what?" .

To answer that, you circle back to the main concept or driving force of the essay / paper (usually found in the title) and tie it together with the points you have made, in a final, elegant few sentences:
How, then, is Kafka’s writing modernist in outlook?
Why should we consider Dickens’ work from a feminist perspective?
What, then , was Blake referring to, when he spoke of mind forged manacles?
In Conclusion
There are plenty of alternatives for drawing an effective and elegant close to your arguments, rather than simply stating in conclusion .
Whether you ask a question or opt for a transition expression or a single transition word, just taking the time to choose the right synonyms will make all the difference to what is, essentially, the most important part of your paper.
Want to improve your essay writing skills?
Use prowritingaid.
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you’re losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much.
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Alex Simmonds is a freelance copywriter based in the UK and has been using words to help people sell things for over 20 years. He has an MA in English Lit and has been struggling to write a novel for most of the last decade. He can be found at alexsimmonds.co.uk.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Conclusions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of conclusions, offer strategies for writing effective ones, help you evaluate conclusions you’ve drafted, and suggest approaches to avoid.
About conclusions
Introductions and conclusions can be difficult to write, but they’re worth investing time in. They can have a significant influence on a reader’s experience of your paper.
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. Such a conclusion will help them see why all your analysis and information should matter to them after they put the paper down.
Your conclusion is your chance to have the last word on the subject. The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Your conclusion can go beyond the confines of the assignment. The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings.
Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or appreciate your topic in personally relevant ways. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest your reader, but also enrich your reader’s life in some way. It is your gift to the reader.
Strategies for writing an effective conclusion
One or more of the following strategies may help you write an effective conclusion:
- Play the “So What” Game. If you’re stuck and feel like your conclusion isn’t saying anything new or interesting, ask a friend to read it with you. Whenever you make a statement from your conclusion, ask the friend to say, “So what?” or “Why should anybody care?” Then ponder that question and answer it. Here’s how it might go: You: Basically, I’m just saying that education was important to Douglass. Friend: So what? You: Well, it was important because it was a key to him feeling like a free and equal citizen. Friend: Why should anybody care? You: That’s important because plantation owners tried to keep slaves from being educated so that they could maintain control. When Douglass obtained an education, he undermined that control personally. You can also use this strategy on your own, asking yourself “So What?” as you develop your ideas or your draft.
- Return to the theme or themes in the introduction. This strategy brings the reader full circle. For example, if you begin by describing a scenario, you can end with the same scenario as proof that your essay is helpful in creating a new understanding. You may also refer to the introductory paragraph by using key words or parallel concepts and images that you also used in the introduction.
- Synthesize, don’t summarize. Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points, but don’t simply repeat things that were in your paper. Instead, show your reader how the points you made and the support and examples you used fit together. Pull it all together.
- Include a provocative insight or quotation from the research or reading you did for your paper.
- Propose a course of action, a solution to an issue, or questions for further study. This can redirect your reader’s thought process and help them to apply your info and ideas to their own life or to see the broader implications.
- Point to broader implications. For example, if your paper examines the Greensboro sit-ins or another event in the Civil Rights Movement, you could point out its impact on the Civil Rights Movement as a whole. A paper about the style of writer Virginia Woolf could point to her influence on other writers or on later feminists.
Strategies to avoid
- Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as “in conclusion,” “in summary,” or “in closing.” Although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as wooden and trite in writing.
- Stating the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion.
- Introducing a new idea or subtopic in your conclusion.
- Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes.
- Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of an analytical paper.
- Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper.
Four kinds of ineffective conclusions
- The “That’s My Story and I’m Sticking to It” Conclusion. This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can’t think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a pioneer in American education, proving that education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
- The “Sherlock Holmes” Conclusion. Sometimes writers will state the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion. You might be tempted to use this strategy if you don’t want to give everything away too early in your paper. You may think it would be more dramatic to keep the reader in the dark until the end and then “wow” them with your main idea, as in a Sherlock Holmes mystery. The reader, however, does not expect a mystery, but an analytical discussion of your topic in an academic style, with the main argument (thesis) stated up front. Example: (After a paper that lists numerous incidents from the book but never says what these incidents reveal about Douglass and his views on education): So, as the evidence above demonstrates, Douglass saw education as a way to undermine the slaveholders’ power and also an important step toward freedom.
- The “America the Beautiful”/”I Am Woman”/”We Shall Overcome” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion usually draws on emotion to make its appeal, but while this emotion and even sentimentality may be very heartfelt, it is usually out of character with the rest of an analytical paper. A more sophisticated commentary, rather than emotional praise, would be a more fitting tribute to the topic. Example: Because of the efforts of fine Americans like Frederick Douglass, countless others have seen the shining beacon of light that is education. His example was a torch that lit the way for others. Frederick Douglass was truly an American hero.
- The “Grab Bag” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion includes extra information that the writer found or thought of but couldn’t integrate into the main paper. You may find it hard to leave out details that you discovered after hours of research and thought, but adding random facts and bits of evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting case study for masculinity in the American South. He also offers historians an interesting glimpse into slave resistance when he confronts Covey, the overseer. His relationships with female relatives reveal the importance of family in the slave community.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. New York: Dover.
Hamilton College. n.d. “Conclusions.” Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://www.hamilton.edu//academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/conclusions .
Holewa, Randa. 2004. “Strategies for Writing a Conclusion.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated February 19, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/acadwrite/conclude.html.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Essay Conclusion

4-minute read
- 1st October 2022
Regardless of what you’re studying, writing essays is probably a significant part of your work as a student . Taking the time to understand how to write each section of an essay (i.e., introduction, body, and conclusion) can make the entire process easier and ensure that you’ll be successful.
Once you’ve put in the hard work of writing a coherent and compelling essay, it can be tempting to quickly throw together a conclusion without the same attention to detail. However, you won’t leave an impactful final impression on your readers without a strong conclusion.
We’ve compiled a few easy steps to help you write a great conclusion for your next essay . Watch our video, or check out our guide below to learn more!
1. Return to Your Thesis
Similar to how an introduction should capture your reader’s interest and present your argument, a conclusion should show why your argument matters and leave the reader with further curiosity about the topic.
To do this, you should begin by reminding the reader of your thesis statement. While you can use similar language and keywords when referring to your thesis, avoid copying it from the introduction and pasting it into your conclusion.
Try varying your vocabulary and sentence structure and presenting your thesis in a way that demonstrates how your argument has evolved throughout your essay.
2. Review Your Main Points
In addition to revisiting your thesis statement, you should review the main points you presented in your essay to support your argument.
However, a conclusion isn’t simply a summary of your essay . Rather, you should further examine your main points and demonstrate how each is connected.
Try to discuss these points concisely, in just a few sentences, in preparation for demonstrating how they fit in to the bigger picture of the topic.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Show the Significance of Your Essay
Next, it’s time to think about the topic of your essay beyond the scope of your argument. It’s helpful to keep the question “so what?” in mind when you’re doing this. The goal is to demonstrate why your argument matters.
If you need some ideas about what to discuss to show the significance of your essay, consider the following:
- What do your findings contribute to the current understanding of the topic?
- Did your findings raise new questions that would benefit from future research?
- Can you offer practical suggestions for future research or make predictions about the future of the field/topic?
- Are there other contexts, topics, or a broader debate that your ideas can be applied to?
While writing your essay, it can be helpful to keep a list of ideas or insights that you develop about the implications of your work so that you can refer back to it when you write the conclusion.
Making these kinds of connections will leave a memorable impression on the reader and inspire their interest in the topic you’ve written about.
4. Avoid Some Common Mistakes
To ensure you’ve written a strong conclusion that doesn’t leave your reader confused or lacking confidence in your work, avoid:
- Presenting new evidence: Don’t introduce new information or a new argument, as it can distract from your main topic, confuse your reader, and suggest that your essay isn’t organized.
- Undermining your argument: Don’t use statements such as “I’m not an expert,” “I feel,” or “I think,” as lacking confidence in your work will weaken your argument.
- Using generic statements: Don’t use generic concluding statements such as “In summary,” “To sum up,” or “In conclusion,” which are redundant since the reader will be able to see that they’ve reached the end of your essay.
Finally, don’t make the mistake of forgetting to proofread your essay ! Mistakes can be difficult to catch in your own writing, but they can detract from your writing.
Our expert editors can ensure that your essay is clear, concise, and free of spelling and grammar errors. Find out more by submitting a free trial document today!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.

6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Change will not be effected, say some others, unless individual actions raise the necessary awareness.
While a reader can see the connection between the sentences above, it’s not immediately clear that the second sentence is providing a counterargument to the first. In the example below, key “old information” is repeated in the second sentence to help readers quickly see the connection. This makes the sequence of ideas easier to follow.
Sentence pair #2: Effective Transition
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change.
You can use this same technique to create clear transitions between paragraphs. Here’s an example:
Some experts argue that focusing on individual actions to combat climate change takes the focus away from the collective action required to keep carbon levels from rising. Other experts argue that individual actions are key to raising the awareness necessary to effect change. According to Annie Lowery, individual actions are important to making social change because when individuals take action, they can change values, which can lead to more people becoming invested in fighting climate change. She writes, “Researchers believe that these kinds of household-led trends can help avert climate catastrophe, even if government and corporate actions are far more important” (Lowery).
So, what’s an individual household supposed to do?
The repetition of the word “household” in the new paragraph helps readers see the connection between what has come before (a discussion of whether household actions matter) and what is about to come (a proposal for what types of actions households can take to combat climate change).
Sometimes, transitional words can help readers see how ideas are connected. But it’s not enough to just include a “therefore,” “moreover,” “also,” or “in addition.” You should choose these words carefully to show your readers what kind of connection you are making between your ideas.
To decide which transitional word to use, start by identifying the relationship between your ideas. For example, you might be
- making a comparison or showing a contrast Transitional words that compare and contrast include also, in the same way, similarly, in contrast, yet, on the one hand, on the other hand. But before you signal comparison, ask these questions: Do your readers need another example of the same thing? Is there a new nuance in this next point that distinguishes it from the previous example? For those relationships between ideas, you might try this type of transition: While x may appear the same, it actually raises a new question in a slightly different way.
- expressing agreement or disagreement When you are making an argument, you need to signal to readers where you stand in relation to other scholars and critics. You may agree with another person’s claim, you may want to concede some part of the argument even if you don’t agree with everything, or you may disagree. Transitional words that signal agreement, concession, and disagreement include however, nevertheless, actually, still, despite, admittedly, still, on the contrary, nonetheless .
- showing cause and effect Transitional phrases that show cause and effect include therefore, hence, consequently, thus, so. Before you choose one of these words, make sure that what you are about to illustrate is really a causal link. Novice writers tend to add therefore and hence when they aren’t sure how to transition; you should reserve these words for when they accurately signal the progression of your ideas.
- explaining or elaborating Transitions can signal to readers that you are going to expand on a point that you have just made or explain something further. Transitional words that signal explanation or elaboration include in other words, for example, for instance, in particular, that is, to illustrate, moreover .
- drawing conclusions You can use transitions to signal to readers that you are moving from the body of your argument to your conclusions. Before you use transitional words to signal conclusions, consider whether you can write a stronger conclusion by creating a transition that shows the relationship between your ideas rather than by flagging the paragraph simply as a conclusion. Transitional words that signal a conclusion include in conclusion , as a result, ultimately, overall— but strong conclusions do not necessarily have to include those phrases.
If you’re not sure which transitional words to use—or whether to use one at all—see if you can explain the connection between your paragraphs or sentence either out loud or in the margins of your draft.
For example, if you write a paragraph in which you summarize physician Atul Gawande’s argument about the value of incremental care, and then you move on to a paragraph that challenges those ideas, you might write down something like this next to the first paragraph: “In this paragraph I summarize Gawande’s main claim.” Then, next to the second paragraph, you might write, “In this paragraph I present a challenge to Gawande’s main claim.” Now that you have identified the relationship between those two paragraphs, you can choose the most effective transition between them. Since the second paragraph in this example challenges the ideas in the first, you might begin with something like “but,” or “however,” to signal that shift for your readers.
- picture_as_pdf Transitions

Conclusion transition words: Phrases for summarizing and ending
Transition words help us structure our thoughts and guide the reader or listener through what we are saying. When it’s time to summarize your message or end a paragraph, conclusion transition words let you signal this closing.
It’s good to know some synonyms for ‘in conclusion’ and ‘to conclude’, because although these are good examples of concluding words, they can get repetitive.
Our comprehensive list of transition words for conclusion and summary should give you all the inspiration you need, whether you are writing an essay or speech, or just want to become more confident forming an argument. These signal words can also be helpful for restating ideas, drawing attention to key points as you conclude.
We have included plenty of examples of how you can use these transition words for concluding paragraphs or sentences, so by the end of this article, you should be clear on how to use them properly.

Conclusion transition words with examples
We have grouped these summarizing and concluding transition words according to how and where they can be used. For example, some should only be used when forming a final conclusion, whereas others can be used to summarize sections mid-way through your speech or writing.
First, let’s be clear about the difference between a summary and a conclusion .
Summary vs conclusion
A conclusion comes at the end of a speech, chapter, or piece of text, and it brings together all of the points mentioned. A summary, however, can be placed anywhere (even at the beginning). A summary gives a brief outline of the main points but is not as in-depth as a conclusion.
If you are giving a presentation or writing a blog, you may wish to summarize the main points in your introduction so that people know what you are going to cover. You could also summarize a section part-way through before moving on to another angle or topic.
In contrast, the conclusion always comes at the end, and you should only use specific conclusion transition words as you are drawing to a close.
Transition words for conclusion paragraphs
Let’s begin with some discourse markers that signal you are moving to the concluding paragraph in your presentation, speech, essay, or paper. These can all be used to start a conclusion paragraph.
- In conclusion
- To conclude
- We can conclude that
- Given these points
- In the final analysis
- As can be seen
- In the long run
- When all is said and done
- I’ll end by
- As we draw to a close
The last three on this list, the ‘closing’ transition words, would generally only be used in spoken discourse.
Some transition words for order and sequencing should also help with structuring what you want to say, including the ending.
Example conclusion sentences
The following sentences show how to use conclusion words correctly:
- In conclusion , we can say that plan A will be of greater benefit to the company.
- When all is said and done , it’s clear that we should steer clear of this investment strategy.
- Given these points , I believe the trial was a great success.
- I’ll end by reminding you all that this experiment was just the beginning of a much larger project.
- To wrap up , let’s look at how this learning can be applied.
- In the long run , we will make more profit by investing heavily in new machinery.
- Having analyzed seven of our competitors in detail, we can conclude that our content marketing strategy should be updated.
Transition words for summary
The following summary transition words may be used as part of a conclusion paragraph, but they are especially helpful for concisely drawing together several points.
- To summarize
- On the whole
- Generally speaking
- All things considered
- In a nutshell (informal)
- In any case
Note that although you can insert summary transition words anywhere, the specific phrases ‘In summary’, ‘To summarize’ and ‘To sum up’ are generally only used at the end, similar to conclusion phrases.
Example summary sentences
- In brief , this presentation is going to cover the pros and cons of the device and how we can apply this to our own product development.
- This new technology is, in a word , revolutionary.
- All things considered , we found that Berlin was a great city for a weekend break.
- To summarize , we can say that Shakespeare’s writing continues to have a global influence.
- We can say that the combustion engine was, on the whole , a good invention.
- In any case , we should put the necessary precautions in place.
- Generally speaking , girls are more thoughtful than boys.
Transition words to end a paragraph
You may wish to add ending transition words in the final sentence of a paragraph to conclude the ideas in that section of text, before moving on to another point.
Here are some transition words to conclude a paragraph:
- This means that
- With this in mind
- By and large
- For the most part
Note that some of these could equally be used to begin a new paragraph, so long as that paragraph is summarizing the points previously mentioned.
Cause and effect transition words could also be helpful in this context.
Examples of transition words for the end of a paragraph
- Jamie is a vegan and Sheryl has a lot of allergies. This means that we should be careful which restaurant we choose.
- The weather forecast said it would rain this afternoon. With this in mind , should we postpone our hike?
- Each of the students has their own opinion about where to go for the field trip. Ultimately , though, it’s the teacher who will decide.
Restating points as you conclude
Conclusion transition words can also signal that you are restating a point you mentioned earlier. This is common practice in both writing and speaking as it draws the reader or listener’s attention back to something you want them to keep in mind. These are, therefore, also examples of transition words for emphasizing a point .
Here are some helpful transition words for concluding or summarizing by restating points:
- As mentioned previously
- As stated earlier
- As has been noted
- As shown above
- As I have said
- As I have mentioned
- As we have seen
- As has been demonstrated
You may switch most of these between the passive and active voice, depending on which is most appropriate. For example, ‘As has been demonstrated’ could become ‘As I have demonstrated’ and ‘As shown above’ could become ‘As I have shown’.
Example sentences to restate a point in conclusion or summary
- As I stated earlier , the only way we can get meaningful results from this survey is by including at least a thousand people.
- As has been demonstrated throughout this conference, there are exciting things happening in the world of neuroscience.
- As shown by this study, the trials have been promising.
If you were researching these transition words for concluding an essay, you might find it helpful to read this guide to strong essay conclusions . Of course, there are many ways to use summary transition words beyond essays. They may be a little formal for casual conversation, but they certainly can be used in speech as part of a presentation, debate, or argument.
Can you think of any other concluding words or phrases that should be on this list? Leave a comment below to share them!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and site URL in my browser for next time I post a comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
33 Transition Words and Phrases
Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one.
Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that “this follows logically from the preceding” include accordingly, therefore, and consequently . Words that mean “in addition to” include moreover, besides, and further . Words that mean “contrary to what was just stated” include however, nevertheless , and nonetheless .
as a result : THEREFORE : CONSEQUENTLY
The executive’s flight was delayed and they accordingly arrived late.
in or by way of addition : FURTHERMORE
The mountain has many marked hiking trails; additionally, there are several unmarked trails that lead to the summit.
at a later or succeeding time : SUBSEQUENTLY, THEREAFTER
Afterward, she got a promotion.
even though : ALTHOUGH
She appeared as a guest star on the show, albeit briefly.
in spite of the fact that : even though —used when making a statement that differs from or contrasts with a statement you have just made
They are good friends, although they don't see each other very often.
in addition to what has been said : MOREOVER, FURTHERMORE
I can't go, and besides, I wouldn't go if I could.
as a result : in view of the foregoing : ACCORDINGLY
The words are often confused and are consequently misused.
in a contrasting or opposite way —used to introduce a statement that contrasts with a previous statement or presents a differing interpretation or possibility
Large objects appear to be closer. Conversely, small objects seem farther away.
used to introduce a statement that is somehow different from what has just been said
These problems are not as bad as they were. Even so, there is much more work to be done.
used as a stronger way to say "though" or "although"
I'm planning to go even though it may rain.
in addition : MOREOVER
I had some money to invest, and, further, I realized that the risk was small.
in addition to what precedes : BESIDES —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
These findings seem plausible. Furthermore, several studies have confirmed them.
because of a preceding fact or premise : for this reason : THEREFORE
He was a newcomer and hence had no close friends here.
from this point on : starting now
She announced that henceforth she would be running the company.
in spite of that : on the other hand —used when you are saying something that is different from or contrasts with a previous statement
I'd like to go; however, I'd better not.
as something more : BESIDES —used for adding information to a statement
The city has the largest population in the country and in addition is a major shipping port.
all things considered : as a matter of fact —used when making a statement that adds to or strengthens a previous statement
He likes to have things his own way; indeed, he can be very stubborn.
for fear that —often used after an expression denoting fear or apprehension
He was concerned lest anyone think that he was guilty.
in addition : ALSO —often used to introduce a statement that adds to and is related to a previous statement
She is an acclaimed painter who is likewise a sculptor.
at or during the same time : in the meantime
You can set the table. Meanwhile, I'll start making dinner.
BESIDES, FURTHER : in addition to what has been said —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
It probably wouldn't work. Moreover, it would be very expensive to try it.
in spite of that : HOWEVER
It was a predictable, but nevertheless funny, story.
in spite of what has just been said : NEVERTHELESS
The hike was difficult, but fun nonetheless.
without being prevented by (something) : despite—used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
Notwithstanding their youth and inexperience, the team won the championship.
if not : or else
Finish your dinner. Otherwise, you won't get any dessert.
more correctly speaking —used to introduce a statement that corrects what you have just said
We can take the car, or rather, the van.
in spite of that —used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
I tried again and still I failed.
by that : by that means
He signed the contract, thereby forfeiting his right to the property.
for that reason : because of that
This tablet is thin and light and therefore very convenient to carry around.
immediately after that
The committee reviewed the documents and thereupon decided to accept the proposal.
because of this or that : HENCE, CONSEQUENTLY
This detergent is highly concentrated and thus you will need to dilute it.
while on the contrary —used to make a statement that describes how two people, groups, etc., are different
Some of these species have flourished, whereas others have struggled.
NEVERTHELESS, HOWEVER —used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way
It was pouring rain out, yet his clothes didn’t seem very wet.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 more grammar terms you used to know: special verb edition, point of view: it's personal, 31 useful rhetorical devices, grammar & usage, more words you always have to look up, 'fewer' and 'less', 7 pairs of commonly confused words, more commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, great big list of beautiful and useless words, vol. 4, 9 other words for beautiful, why jaywalking is called jaywalking, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.
Your Best College Essay
Maybe you love to write, or maybe you don’t. Either way, there’s a chance that the thought of writing your college essay is making you sweat. No need for nerves! We’re here to give you the important details on how to make the process as anxiety-free as possible.

What's the College Essay?
When we say “The College Essay” (capitalization for emphasis – say it out loud with the capitals and you’ll know what we mean) we’re talking about the 550-650 word essay required by most colleges and universities. Prompts for this essay can be found on the college’s website, the Common Application, or the Coalition Application. We’re not talking about the many smaller supplemental essays you might need to write in order to apply to college. Not all institutions require the essay, but most colleges and universities that are at least semi-selective do.
How do I get started?
Look for the prompts on whatever application you’re using to apply to schools (almost all of the time – with a few notable exceptions – this is the Common Application). If one of them calls out to you, awesome! You can jump right in and start to brainstorm. If none of them are giving you the right vibes, don’t worry. They’re so broad that almost anything you write can fit into one of the prompts after you’re done. Working backwards like this is totally fine and can be really useful!
What if I have writer's block?
You aren’t alone. Staring at a blank Google Doc and thinking about how this is the one chance to tell an admissions officer your story can make you freeze. Thinking about some of these questions might help you find the right topic:
- What is something about you that people have pointed out as distinctive?
- If you had to pick three words to describe yourself, what would they be? What are things you’ve done that demonstrate these qualities?
- What’s something about you that has changed over your years in high school? How or why did it change?
- What’s something you like most about yourself?
- What’s something you love so much that you lose track of the rest of the world while you do it?
If you’re still stuck on a topic, ask your family members, friends, or other trusted adults: what’s something they always think about when they think about you? What’s something they think you should be proud of? They might help you find something about yourself that you wouldn’t have surfaced on your own.
How do I grab my reader's attention?
It’s no secret that admissions officers are reading dozens – and sometimes hundreds – of essays every day. That can feel like a lot of pressure to stand out. But if you try to write the most unique essay in the world, it might end up seeming forced if it’s not genuinely you. So, what’s there to do? Our advice: start your essay with a story. Tell the reader about something you’ve done, complete with sensory details, and maybe even dialogue. Then, in the second paragraph, back up and tell us why this story is important and what it tells them about you and the theme of the essay.
THE WORD LIMIT IS SO LIMITING. HOW DO I TELL A COLLEGE MY WHOLE LIFE STORY IN 650 WORDS?
Don’t! Don’t try to tell an admissions officer about everything you’ve loved and done since you were a child. Instead, pick one or two things about yourself that you’re hoping to get across and stick to those. They’ll see the rest on the activities section of your application.
I'M STUCK ON THE CONCLUSION. HELP?
If you can’t think of another way to end the essay, talk about how the qualities you’ve discussed in your essays have prepared you for college. Try to wrap up with a sentence that refers back to the story you told in your first paragraph, if you took that route.
SHOULD I PROOFREAD MY ESSAY?
YES, proofread the essay, and have a trusted adult proofread it as well. Know that any suggestions they give you are coming from a good place, but make sure they aren’t writing your essay for you or putting it into their own voice. Admissions officers want to hear the voice of you, the applicant. Before you submit your essay anywhere, our number one advice is to read it out loud to yourself. When you read out loud you’ll catch small errors you may not have noticed before, and hear sentences that aren’t quite right.
ANY OTHER ADVICE?
Be yourself. If you’re not a naturally serious person, don’t force formality. If you’re the comedian in your friend group, go ahead and be funny. But ultimately, write as your authentic (and grammatically correct) self and trust the process.
And remember, thousands of other students your age are faced with this same essay writing task, right now. You can do it!

7 Best Ways to Shorten an Essay
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: May 14, 2024
Are you removing a lot of words and paragraphs from your essay but still not seeing the word count budge? Whether you’re meeting a strict word count or refining your message, reducing your essay’s length without sacrificing content quality can be challenging.
Luckily, besides just aiming for the minimum word count, there are some pretty simple solutions, like using artificial intelligence, conducting thorough research, and trimming unnecessary words. But there’s more.
In this guide, we’ll unpack some practical tips to help you make your essay concise and impactful. Time to make every word count!
7 Best Ways To Shorten an Essay
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the best ways you can shorten your essay:
1. Use Artificial intelligence
When we talk about academic writing, artificial intelligence (AI) can be a game changer, especially when it comes to reducing the length of your essays.
Tools like Smodin can help make your content more concise while enhancing overall quality. AI can help you shorten your essay through the following methods:
- Automated rewriting : AI rewriting tools can reformulate existing content to make it more straightforward while maintaining the original meaning.
- Sentence simplification : Algorithms can analyze your sentences and suggest simpler alternatives, helping eliminate redundant information and reduce word count.
- Research assistance : Certain platforms have AI-powered research tools that allow you to quickly gather the most relevant information. This ensures that every word in your essay contributes to your argument without unnecessary fillers.
- Plagiarism check : Ensuring your essay is plagiarism-free is crucial. For example, Smodin’s plagiarism detection tools help you identify and replace copied content with original, concise expressions.
- Instant feedback : Receive real-time suggestions on how to streamline your text, focusing on the essentials to effectively communicate your message.
- Reference generation : Automatically generate and insert citations in the correct format, which helps save you time while maintaining the academic integrity of your essay and keeping it short.
2. Identify Unnecessary Words and Remove Them
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to shorten your essay is by identifying and eliminating unnecessary words.
This approach helps decrease word count and sharpens your arguments, making your writing more compelling. You can identify and remove extra words by doing the following:
- Spot wordy phrases : Often, phrases can be condensed without losing meaning. For example, the phrase “due to the fact that” can be replaced with “because.” Be on the lookout for wordy phrases that increase word count needlessly.
- Remove unnecessary prepositional phrases : Prepositional phrases can be redundant or add unnecessary detail. Evaluate whether these phrases add value or just extra words. Cutting them can make sentences more direct.
- Avoid redundancies : Redundant pairs like “absolutely essential” or “future plans” can be reduced to one word without losing informational value.
- Trim excess adjectives and adverbs : Adjectives and adverbs can make writing better but can also lead to over-description. Use them sparingly, especially when they don’t contribute additional meaning to the nouns and verbs they modify.
- Fewer words; more impact : Aim for brevity by using fewer words to express the same idea. This will help to reduce the word count while making your writing more impactful and clear.
3. Tighten Sentence Structure
Tightening your sentence structure is crucial for making your essay more concise and readable. Use active voice to make your writing clearer and more dynamic. This is especially important in academic writing, where you have to get to the point quickly.
In academic essays, shifting from passive voice to active voice can shorten and strengthen your sentences. For example, instead of writing, “The experiment was conducted by the students,” you can say, “The students conducted the experiment.” This reduces the number of words and places the action directly with the subject, making your sentences more direct.
Combining two separate sentences into one can streamline your ideas and reduce redundancies. Look for opportunities where sentences can be merged without losing their significance. For example, “He wrote the book. It became a bestseller.” can be rephrased as “He wrote the book, which became a bestseller.”
Also, avoid unnecessary qualifiers and modifiers that don’t add substantial information. Sentences often become bogged down with these extras, making them cluttered and long.
4. Conduct Thorough Research
When writing essays, extensive research can make the final output a lot shorter. Effective research helps you gather precise information that’s relevant to your topic. This means you’ll write more directly and avoid needless elaboration. Here’s how you can conduct research effectively:
- Define the scope of your research : Determine what information is essential to the argument. This initial step will help you focus your research efforts and prevent irrelevant data.
- Identify key sources : Begin with scholarly databases and academic journals that offer peer-reviewed articles. These sources provide credible, authoritative information that can be crucial for academic writing.
- Use precise keywords : When searching for information, use specific keywords related to your essay topic. Precision here will help find the most relevant articles and studies, reducing time spent on unnecessary reading.
- Evaluate sources : Assess the relevance and reliability of each source. Check the publication date to ensure the information is current and relevant to your topic.
- Take notes efficiently : As you research, jot down important points, quotes, and references. Organize these notes according to the sections in your essay to make writing faster.
- Synthesize information : Combine information from multiple sources to build a strong argument. This will allow you to write comprehensively and with fewer words, as each sentence carries more weight.
5. Improve Your Paragraph Structure
Streamlining paragraphs can make your essay shorter and more digestible for the reader. With a well-structured paragraph, you can focus on a single idea supported by concise statements.
Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that clearly states the main idea. This sentence sets the direction and tone, letting the reader know what to expect. It also helps ensure that every following sentence relates directly to the main idea.
Condense supporting information by merging ideas that logically coexist within a single sentence or phrase. After that, evaluate each sentence for its contribution to the paragraph’s main idea. Remove any information that is repeated or goes into too much detail.
Focus on providing evidence and explanations that directly support the main point. You should also end each paragraph with a sentence that reinforces the main idea and potentially links to the next paragraph. This creates smooth transitions and keeps the essay focused and cohesive.
6. Refine the Introduction and Conclusion
These sections frame your essay and influence how your arguments are perceived. Here are some ways to keep them concise yet effective.
Introduction
The introduction should be engaging and concise, clearly stating the purpose and scope of your essay. Begin with a hook that grabs the reader’s attention, followed by background information that sets the context. Incorporate your thesis statement early on, ideally at the end of the intro.
The conclusion needs to reinforce the thesis. Summarize key points in the essay and show how they support the thesis. Provide a final thought that leaves the reader with something to ponder.
Also, remember to keep it tight – the conclusion isn’t a place for introducing new ideas. It should wrap up the ones you presented and prompt the reader to pose their own questions.
7. Edit and Proofread
Keep your essay concise and error-free by allocating ample time for editing and proofreading. These processes scrutinize your work at different levels, from the overall structure to word choices and punctuation. Here’s how you can go about it:
Start by reading through your entire paper to get a feel for its flow and coherence. Check if all paragraphs support your thesis statement and if section transitions are smooth. This will help you spot areas where the argument might be weak, or wording could be clearer.
Focus next on paragraph structure. Ensure each paragraph sticks to one main idea and that all sentences directly support the idea. Remove any repetitive or irrelevant sentences that don’t add value.
Then, look for clarity and style. Replace complex words with simpler alternatives to maintain readability. Keep your tone consistent throughout the paper. Adjust the sentence length and structure to enhance the flow and make it more engaging.
Proofreading
Proofreading comes after editing. The focus here is catching typing errors, grammatical mistakes, and inconsistent formatting. It’s always best to proofread with fresh eyes, so consider taking a break before this step.
Use tools like spell checkers, but don’t rely solely on them. Read your essay aloud or have someone else review it. Hearing the words can help you catch errors you may have missed.
Lastly, check for punctuation errors and ensure all citations and references are formatted according to the required academic style. This and all of the above are areas in which AI can help get the job done with speed and precision.
Why You Might Need to Shorten Your Essay
Ever heard the expression “less is more”? When it comes to academic writing, it normally is. Keeping your essays concise offers several benefits:
- Enhances clarity : A shorter essay forces you to focus on the main points and critical arguments, reducing the risk of going off-topic. This clarity makes your writing more impactful and easier for the reader to follow.
- Meets word limits : Many academic assignments have a maximum word count. Learning to express your thoughts concisely helps you stay within these limits without sacrificing essential content.
- Saves time : For both the writer and the reader, shorter essays take less time to write, revise, and read. This efficiency is especially valuable in academic settings where time is usually limited.
- Increases engagement : Readers are more likely to stay engaged with a document that gets to the point quickly. Lengthy texts can deter readers, especially if the content has unnecessary words or redundant points.
- Improves writing skills : Shortening essays helps refine your writing skills. You become better at identifying and eliminating fluff, focusing instead on what really adds value to your paper.
Overall, adopting a more succinct writing style helps you meet academic requirements and polish your communication skills.
Why Use Smodin To Shorten an Essay
Using AI-powered platforms like Smodin to shorten your essay is both the simplest and the least time-consuming method available. Here’s why you should probably make Smodin your go-to essay shortener:
- Efficiency : Smodin eases the editing process, using advanced algorithms to quickly identify areas where content can be condensed without losing meaning.
- Accuracy : With its powerful AI, Smodin ensures that the essence of your essays stays intact while getting rid of unnecessary words, making your writing more precise.
- Ease of use : Smodin is user-friendly, making it accessible even to those who aren’t the most tech-savvy. Its easy-to-grasp interface allows for seamless navigation and operation.
Smodin’s offerings
- Rewriter : Available in over 50 languages, this tool helps rewrite text to be more concise.
- Article Writer : Assists in drafting articles that are crisp and to the point.
- Plagiarism and Auto Citation : Ensures your essay is original and correctly cited, which is crucial in academic writing.
- Language Detection : Identifies the language of the text, ensuring the right adjustments are made for clarity.
All these tools and more are what make Smodin an excellent choice for academics looking to reduce the length of their essays.
Final Thoughts
Word counts can be a real headache, especially when you need to say a lot with a little. Thankfully, by identifying unnecessary words, tightening your sentences, and using tools like Smodin, you can make your essay concise without losing its meaning. Remember, a shorter essay doesn’t just meet word limits; and it’s clear, more compelling, and more likely to keep your reader engaged.
Keep it short, keep it sweet, and make every word count! Get started for free right now with Smodin.
- Free Tools for Students
- Harvard Referencing Generator
Free Harvard Referencing Generator
Generate accurate Harvard reference lists quickly and for FREE, with MyBib!
🤔 What is a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style.
It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing style.
The generated references can be copied into a reference list or bibliography, and then collectively appended to the end of an academic assignment. This is the standard way to give credit to sources used in the main body of an assignment.
👩🎓 Who uses a Harvard Referencing Generator?
Harvard is the main referencing style at colleges and universities in the United Kingdom and Australia. It is also very popular in other English-speaking countries such as South Africa, Hong Kong, and New Zealand. University-level students in these countries are most likely to use a Harvard generator to aid them with their undergraduate assignments (and often post-graduate too).
🙌 Why should I use a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator solves two problems:
- It provides a way to organise and keep track of the sources referenced in the content of an academic paper.
- It ensures that references are formatted correctly -- inline with the Harvard referencing style -- and it does so considerably faster than writing them out manually.
A well-formatted and broad bibliography can account for up to 20% of the total grade for an undergraduate-level project, and using a generator tool can contribute significantly towards earning them.
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's Harvard Referencing Generator?
Here's how to use our reference generator:
- If citing a book, website, journal, or video: enter the URL or title into the search bar at the top of the page and press the search button.
- Choose the most relevant results from the list of search results.
- Our generator will automatically locate the source details and format them in the correct Harvard format. You can make further changes if required.
- Then either copy the formatted reference directly into your reference list by clicking the 'copy' button, or save it to your MyBib account for later.
MyBib supports the following for Harvard style:
🍏 What other versions of Harvard referencing exist?
There isn't "one true way" to do Harvard referencing, and many universities have their own slightly different guidelines for the style. Our generator can adapt to handle the following list of different Harvard styles:
- Cite Them Right
- Manchester Metropolitan University (MMU)
- University of the West of England (UWE)

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Find anything you save across the site in your account

In the campus protests over the war in Gaza, language and rhetoric are—as they have always been when it comes to Israel and Palestine—weapons of mass destruction.
By Zadie Smith
A philosophy without a politics is common enough. Aesthetes, ethicists, novelists—all may be easily critiqued and found wanting on this basis. But there is also the danger of a politics without a philosophy. A politics unmoored, unprincipled, which holds as its most fundamental commitment its own perpetuation. A Realpolitik that believes itself too subtle—or too pragmatic—to deal with such ethical platitudes as thou shalt not kill. Or: rape is a crime, everywhere and always. But sometimes ethical philosophy reënters the arena, as is happening right now on college campuses all over America. I understand the ethics underpinning the protests to be based on two widely recognized principles:
There is an ethical duty to express solidarity with the weak in any situation that involves oppressive power.
If the machinery of oppressive power is to be trained on the weak, then there is a duty to stop the gears by any means necessary.
The first principle sometimes takes the “weak” to mean “whoever has the least power,” and sometimes “whoever suffers most,” but most often a combination of both. The second principle, meanwhile, may be used to defend revolutionary violence, although this interpretation has just as often been repudiated by pacifistic radicals, among whom two of the most famous are, of course, Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King, Jr . In the pacifist’s interpretation, the body that we must place between the gears is not that of our enemy but our own. In doing this, we may pay the ultimate price with our actual bodies, in the non-metaphorical sense. More usually, the risk is to our livelihoods, our reputations, our futures. Before these most recent campus protests began, we had an example of this kind of action in the climate movement. For several years now, many people have been protesting the economic and political machinery that perpetuates climate change, by blocking roads, throwing paint, interrupting plays, and committing many other arrestable offenses that can appear ridiculous to skeptics (or, at the very least, performative), but which in truth represent a level of personal sacrifice unimaginable to many of us.
I experienced this not long ago while participating in an XR climate rally in London. When it came to the point in the proceedings where I was asked by my fellow-protesters whether I’d be willing to commit an arrestable offense—one that would likely lead to a conviction and thus make travelling to the United States difficult or even impossible—I’m ashamed to say that I declined that offer. Turns out, I could not give up my relationship with New York City for the future of the planet. I’d just about managed to stop buying plastic bottles (except when very thirsty) and was trying to fly less. But never to see New York again? What pitiful ethical creatures we are (I am)! Falling at the first hurdle! Anyone who finds themselves rolling their eyes at any young person willing to put their own future into jeopardy for an ethical principle should ask themselves where the limits of their own commitments lie—also whether they’ve bought a plastic bottle or booked a flight recently. A humbling inquiry.
It is difficult to look at the recent Columbia University protests in particular without being reminded of the campus protests of the nineteen-sixties and seventies, some of which happened on the very same lawns. At that time, a cynical political class was forced to observe the spectacle of its own privileged youth standing in solidarity with the weakest historical actors of the moment, a group that included, but was not restricted to, African Americans and the Vietnamese. By placing such people within their ethical zone of interest, young Americans risked both their own academic and personal futures and—in the infamous case of Kent State—their lives. I imagine that the students at Columbia—and protesters on other campuses—fully intend this echo, and, in their unequivocal demand for both a ceasefire and financial divestment from this terrible war, to a certain extent they have achieved it.
But, when I open newspapers and see students dismissing the idea that some of their fellow-students feel, at this particular moment, unsafe on campus, or arguing that such a feeling is simply not worth attending to, given the magnitude of what is occurring in Gaza, I find such sentiments cynical and unworthy of this movement. For it may well be—within the ethical zone of interest that is a campus, which was not so long ago defined as a safe space, delineated by the boundary of a generation’s ethical ideas— it may well be that a Jewish student walking past the tents, who finds herself referred to as a Zionist, and then is warned to keep her distance, is, in that moment, the weakest participant in the zone. If the concept of safety is foundational to these students’ ethical philosophy (as I take it to be), and, if the protests are committed to reinserting ethical principles into a cynical and corrupt politics, it is not right to divest from these same ethics at the very moment they come into conflict with other imperatives. The point of a foundational ethics is that it is not contingent but foundational. That is precisely its challenge to a corrupt politics.
Practicing our ethics in the real world involves a constant testing of them, a recognition that our zones of ethical interest have no fixed boundaries and may need to widen and shrink moment by moment as the situation demands. (Those brave students who—in supporting the ethical necessity of a ceasefire—find themselves at painful odds with family, friends, faith, or community have already made this calculation.) This flexibility can also have the positive long-term political effect of allowing us to comprehend that, although our duty to the weakest is permanent, the role of “the weakest” is not an existential matter independent of time and space but, rather, a contingent situation, continually subject to change. By contrast, there is a dangerous rigidity to be found in the idea that concern for the dreadful situation of the hostages is somehow in opposition to, or incompatible with, the demand for a ceasefire. Surely a ceasefire—as well as being an ethical necessity—is also in the immediate absolute interest of the hostages, a fact that cannot be erased by tearing their posters off walls.
Part of the significance of a student protest is the ways in which it gives young people the opportunity to insist upon an ethical principle while still being, comparatively speaking, a more rational force than the supposed adults in the room, against whose crazed magical thinking they have been forced to define themselves. The equality of all human life was never a self-evident truth in racially segregated America. There was no way to “win” in Vietnam. Hamas will not be “eliminated.” The more than seven million Jewish human beings who live in the gap between the river and the sea will not simply vanish because you think that they should. All of that is just rhetoric. Words. Cathartic to chant, perhaps, but essentially meaningless. A ceasefire, meanwhile, is both a potential reality and an ethical necessity. The monstrous and brutal mass murder of more than eleven hundred people, the majority of them civilians, dozens of them children, on October 7th, has been followed by the monstrous and brutal mass murder (at the time of writing) of a reported fourteen thousand five hundred children. And many more human beings besides, but it’s impossible not to notice that the sort of people who take at face value phrases like “surgical strikes” and “controlled military operation” sometimes need to look at and/or think about dead children specifically in order to refocus their minds on reality.
To send the police in to arrest young people peacefully insisting upon a ceasefire represents a moral injury to us all. To do it with violence is a scandal. How could they do less than protest, in this moment? They are putting their own bodies into the machine. They deserve our support and praise. As to which postwar political arrangement any of these students may favor, and on what basis they favor it—that is all an argument for the day after a ceasefire. One state, two states, river to the sea—in my view, their views have no real weight in this particular moment, or very little weight next to the significance of their collective action, which (if I understand it correctly) is focussed on stopping the flow of money that is funding bloody murder, and calling for a ceasefire, the political euphemism that we use to mark the end of bloody murder. After a ceasefire, the criminal events of the past seven months should be tried and judged, and the infinitely difficult business of creating just, humane, and habitable political structures in the region must begin anew. Right now: ceasefire. And, as we make this demand, we might remind ourselves that a ceasefire is not, primarily, a political demand. Primarily, it is an ethical one.
But it is in the nature of the political that we cannot even attend to such ethical imperatives unless we first know the political position of whoever is speaking. (“Where do you stand on Israel/Palestine?”) In these constructed narratives, there are always a series of shibboleths, that is, phrases that can’t be said, or, conversely, phrases that must be said. Once these words or phrases have been spoken ( river to the sea, existential threat, right to defend, one state, two states, Zionist, colonialist, imperialist, terrorist ) and one’s positionality established, then and only then will the ethics of the question be attended to (or absolutely ignored). The objection may be raised at this point that I am behaving like a novelist, expressing a philosophy without a politics, or making some rarefied point about language and rhetoric while people commit bloody murder. This would normally be my own view, but, in the case of Israel/Palestine, language and rhetoric are and always have been weapons of mass destruction.
It is in fact perhaps the most acute example in the world of the use of words to justify bloody murder, to flatten and erase unbelievably labyrinthine histories, and to deliver the atavistic pleasure of violent simplicity to the many people who seem to believe that merely by saying something they make it so. It is no doubt a great relief to say the word “Hamas” as if it purely and solely described a terrorist entity. A great relief to say “There is no such thing as the Palestinian people” as they stand in front of you. A great relief to say “Zionist colonialist state” and accept those three words as a full and unimpeachable definition of the state of Israel, not only under the disastrous leadership of Benjamin Netanyahu but at every stage of its long and complex history, and also to hear them as a perfectly sufficient description of every man, woman, and child who has ever lived in Israel or happened to find themselves born within it. It is perhaps because we know these simplifications to be impossible that we insist upon them so passionately. They are shibboleths; they describe a people, by defining them against other people—but the people being described are ourselves. The person who says “We must eliminate Hamas” says this not necessarily because she thinks this is a possible outcome on this earth but because this sentence is the shibboleth that marks her membership in the community that says that. The person who uses the word “Zionist” as if that word were an unchanged and unchangeable monolith, meaning exactly the same thing in 2024 and 1948 as it meant in 1890 or 1901 or 1920—that person does not so much bring definitive clarity to the entangled history of Jews and Palestinians as they successfully and soothingly draw a line to mark their own zone of interest and where it ends. And while we all talk, carefully curating our shibboleths, presenting them to others and waiting for them to reveal themselves as with us or against us—while we do all that, bloody murder.
And now here we are, almost at the end of this little stream of words. We’ve arrived at the point at which I must state clearly “where I stand on the issue,” that is, which particular political settlement should, in my own, personal view, occur on the other side of a ceasefire. This is the point wherein—by my stating of a position—you are at once liberated into the simple pleasure of placing me firmly on one side or the other, putting me over there with those who lisp or those who don’t, with the Ephraimites, or with the people of Gilead. Yes, this is the point at which I stake my rhetorical flag in that fantastical, linguistical, conceptual, unreal place—built with words—where rapes are minimized as needs be, and the definition of genocide quibbled over, where the killing of babies is denied, and the precision of drones glorified, where histories are reconsidered or rewritten or analogized or simply ignored, and “Jew” and “colonialist” are synonymous, and “Palestinian” and “terrorist” are synonymous, and language is your accomplice and alibi in all of it. Language euphemized, instrumentalized, and abused, put to work for your cause and only for your cause, so that it does exactly and only what you want it to do. Let me make it easy for you. Put me wherever you want: misguided socialist, toothless humanist, naïve novelist, useful idiot, apologist, denier, ally, contrarian, collaborator, traitor, inexcusable coward. It is my view that my personal views have no more weight than an ear of corn in this particular essay. The only thing that has any weight in this particular essay is the dead. ♦
New Yorker Favorites
The day the dinosaurs died .
What if you started itching— and couldn’t stop ?
How a notorious gangster was exposed by his own sister .
Woodstock was overrated .
Diana Nyad’s hundred-and-eleven-mile swim .
Photo Booth: Deana Lawson’s hyper-staged portraits of Black love .
Fiction by Roald Dahl: “The Landlady”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Ruth Margalit

By Keeanga-Yamahtta Taylor

By Jay Caspian Kang

By Susan B. Glasser

'In Praise of Laziness and Other Essays' book review: Chronicle of Masterly Inactivity
E clectic and freewheeling are two words that best describe Indrajit Hazra’s latest, In Praise of Laziness and Other Essays. The author’s adjective of choice for his new collection, however, is themeless; because, as he explains in the introduction to the book, it is the result of his “job at the papers” that kept him “tethered to that kind of rubbish”.
It comprises 12 literary pieces, including a story and two recipes by his grandmothers. But, the most entertaining and insightful essay of the lot is the titular one, where the writer offers his “encomium to laziness”. Being lazy is considered a vice, particularly in today’s relentless, productivity-obsessed era. A meditation on laziness, however, is far from counterintuitive in the current post-pandemic burnout age, making Hazra’s essay timely, relevant and thought-provoking.
From invoking the Ramayana’s Kumbhakarna and sharing Mark Twain’s writing to establish that what Huckleberry Finn felt was “the beauty of the laze” to taking a leaf from Milan Kundera’s thoughts on slowness, Hazra effortlessly underlines how action is linked with “greatness” and laziness is labelled an “anti-social activity”. But, he argues, being lazy “is not the first refuge of the scoundrel.” Instead, “it seeks to take leave from both justice and injustice alike”.
Interestingly, much like his approach towards laziness, Hazra’s writing too is a departure from deterministic positions, for he’s interested in deliberation, though often at the cost of irritating the reader. This is reflected in the essay titled, Why I Am Not a Miso Soup. Recalling what had happened in Lille, France, he writes: “So there I was, Rimbaudelaired to my gills and quivering to my tits facing the query, ‘Are you a miso soup?’ which, to be fair, came with the pretext (or is it context?) that I had a habit of killing off/maiming the female characters in my novels.”
Seemingly written in his defense, this essay, which informs the reader why the author is not a misogynist, begins with notes on casual drinking, and is peppered with random information and thoughts, making it an unappetising read. Though cocksure men rarely pay heed, the least Hazra could have done is not defend himself.
Whatever he may or may not be, Hazra’s writing is certainly not lazy. It’s courageous to pull off a collection like this, touching an array of sensitive issues with humour and ease. Becoming Adult: Mr Finn and Dashorothi-Babu is the principal example. Here, the author revisits the death of “his first-ever friend” Rana, a slow-learner compared to his peers, and juxtaposes it with fictional characters Huck and Dashorothi. By using contemporary labels like “special” used mostly for the differently-abled, Hazra elevates the standard of literary meditation on grief and loss. There’s another essay on death—“public deaths” to be precise: Everybody Loves a Good Mourning. In all its seriousness, one can’t help but laugh at this sentence: “The death of a person is serious business”.
Then, in A Man of the Great Indoors, Hazra deliberates on nation-building. “I could have easily titled this essay ‘an investigation into nationalism’,” he writes. But he didn’t, because that would be “hoodwinking the reader”. And rightly so, because whatever has been written on this undiscussed and undisclosed emergency worldwide—hypernationalism—is limiting and terribly unexciting to read. Offering a consideration that nation is a Dantean circle, Hazra invokes Dunbar’s Number—“the number of people with whom one can maintain stable social relationships”—to underline the fact that in a Benedictine sense, the “closest model to the nation” is the social-networking giant Meta (formerly Facebook). This Man’s Place Is Not in the Kitchen is another case in point. Writing why “kitchen, for me, remains a sinkhole”, he once again champions defamiliarising the familiar and vice versa. This smart collection, however, will be appreciated in parts like all novel attempts.
In Praise of Laziness and Other Essays
By: Indrajit Hazra
Publisher: Yoda Press x
Simon &Schuster
Price: Rs 399


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Example: "In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.". 18. In closing…. My Rating: 7/10. Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for 'In conclusion' and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Other Transition Words to Replace "In Conclusion" Here are a few transition word alternatives to add to your arsenal: Briefly. Obviously. Considering. Therefore. Thus. Essentially. Indeed. Principally. Summarizing. Altogether. Pro tip: You should use transition words throughout your essay, paper, or article to guide your reader through your ...
Restate your thesis: remind readers of your main point. Reiterate your supporting points: remind readers of your evidence or arguments. Wrap everything up by tying it all together. Write a clincher: with the last sentence, leave your reader with something to think about. For many, the conclusion is the most dreaded part of essay writing.
Overall, It Can Be Said…. To recap an idea at the end of a critical or descriptive essay, you can use this phrase at the beginning of the concluding paragraph. "Overall" means "taking everything into account," and it sums up your essay in a formal way. You can use "overall" on its own as a transition signal, or you can use it as ...
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
1. Return to Your Thesis. Similar to how an introduction should capture your reader's interest and present your argument, a conclusion should show why your argument matters and leave the reader with further curiosity about the topic. To do this, you should begin by reminding the reader of your thesis statement.
Topic #5: Explain how to write an essay conclusion. Essay conclusions are pretty simple once you know the framework. It all boils down to three main parts: a transition from the last body paragraph, a summary of the thesis statement and main points of the essay, and a closing statement that wraps everything up. If all students knew this simple ...
Also read: How to Write a Thesis Statement. 2. Tying together the main points. Tying together all the main points of your essay does not mean simply summarizing them in an arbitrary manner. The key is to link each of your main essay points in a coherent structure. One point should follow the other in a logical format.
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
Option 4: End on an action. Ending on an action can be a strong way to wrap up your essay. That might mean including a literal action, dialogue, or continuation of the story. These endings leave the reader wanting more rather than wishing the essay had ended sooner. They're interesting and can help you avoid boring your reader.
If you're looking for good conclusion starters to finish your piece strongly, look no further. Find examples of great ways to begin your conclusion here. ... Essays; Good Conclusion Starters for Final Paragraphs By Mary Gormandy White, M.A. , Staff Writer . Updated July 19, 2022 Image Credits.
It's true: there are other ways to say "in conclusion" that don't feel as trite. Can't think of any? Find 57 different words and phrases right here.
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
explaining or elaborating. Transitions can signal to readers that you are going to expand on a point that you have just made or explain something further. Transitional words that signal explanation or elaboration include in other words, for example, for instance, in particular, that is, to illustrate, moreover. drawing conclusions.
In short. In essence. On balance. Overall. In any case. In effect. Note that although you can insert summary transition words anywhere, the specific phrases 'In summary', 'To summarize' and 'To sum up' are generally only used at the end, similar to conclusion phrases.
See how to write a good conclusion for a project, essay or paper to get the grade. Strong conclusion examples pave the way for the perfect paper ending. See how to write a good conclusion for a project, essay or paper to get the grade. ... But that begs the question, is Huggies the best in leak protection among all brands? That would take a bit ...
Pin. In Conclusion Meaning "In conclusion" is a transitional phrase used to indicate that you are approaching the end of your writing.It serves to summarize the main points or indicate a final thought or opinion. Using synonyms for "in conclusion" can help maintain your reader's interest and offer a sense of variety and sophistication in your writing.
For example, transition words like therefore show a cause-and-effect relationship, while transition words like in conclusion introduce a summary or wrap-up. Often, conjunctive adverbs work well as transition words. ... However, most essay transition words work best at the beginning of a sentence, where they can more effectively bridge the gap ...
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
By Nell Freudenberger. May 14, 2024. Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn't supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or ...
So, what's there to do? Our advice: start your essay with a story. Tell the reader about something you've done, complete with sensory details, and maybe even dialogue. Then, in the second paragraph, back up and tell us why this story is important and what it tells them about you and the theme of the essay. THE WORD LIMIT IS SO LIMITING.
2. Identify Unnecessary Words and Remove Them. One of the simplest yet most effective ways to shorten your essay is by identifying and eliminating unnecessary words. This approach helps decrease word count and sharpens your arguments, making your writing more compelling. You can identify and remove extra words by doing the following: Spot wordy ...
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style. It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing ...
In the campus protests over the war in Gaza, language and rhetoric are—as they have always been when it comes to Israel and Palestine—weapons of mass destruction. By Zadie Smith. May 5, 2024 ...
A majority of prospective MBA students, 56%, say they should be allowed to use AI to help them write admissions essays, but they also say there should be guidelines and restrictions, according to a new survey from Manhattan Prep and Kaplan. Only 18% of the more than 300 prospective MBA students surveyed said the use of AI should be unrestricted.
E clectic and freewheeling are two words that best describe Indrajit Hazra's latest, In Praise of Laziness and Other Essays. The author's adjective of choice for his new collection, however ...