
5 Expository Essay Examples (Full Text with Citations)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
- Video Overview
- Quick Example
- Formatting Guide
An expository essay attempts to explain a topic in-depth, demonstrating expert knowledge and understanding.
This form of essay is structured around the clear, factual presentation of information, devoid of the writer’s personal opinions or arguments.
The primary goal is to inform or explain rather than persuade.
Unlike an argumentative essay, which is built around defending a particular point of view with evidence and persuasion, an expository essay maintains a neutral stance, focusing on delivering straightforward facts and explanations.
An example of expository writing could be an article explaining the process of photosynthesis.
The article would systematically describe each stage of how plants convert sunlight into energy, detailing the role of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
It would explain the sequence of reactions – first, second, third, fourth, fifth – that occur and the importance of each step in supporting the life of the plant.
An expository essay generally follows this essay format:

- A) To persuade the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint
- B) To inform or explain a topic clearly
- C) To present the writer’s personal opinions and arguments
- D) To entertain the reader with creative writing
- A) An expository essay uses creative storytelling techniques
- B) An expository essay remains neutral and avoids personal opinions
- C) An expository essay focuses on persuading the reader with evidence
- D) An expository essay prioritizes the writer’s personal experiences
Expository Essay Examples
#1 impacts of technology on education.
955 words | 4 Pages | 15 References

Thesis Statement: “The integration of technology in education represents a complex and critical area of study crucial for understanding and shaping the future of educational practices.”
#2 Impacts of Globalization on Education
1450 words | 5 Pages | 9 References

Thesis Statement: “This essay examines the profound and multifaceted effects of globalization on education, exploring how technological advancements and policy reforms have transformed access to, delivery of, and perceptions of education.”
#3 The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Interpersonal Relationships
1211 Words | 5 Pages | 22 References

Thesis Statement: “The central thesis is that EI, defined as the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions, is a crucial determinant of success and well-being.”
#4 The Future of Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact
870 words | 4 Pages | 20 References

Thesis Statement: “The essay posits that although renewable energy sources hold immense promise for a sustainable future, their full integration into the global energy grid presents significant challenges that must be addressed through technological innovation, economic investment, and policy initiatives.”
#5 The Psychology Behind Consumer Behavior
1053 words | 4 Pages | 17 References

Thesis Statement: “The thesis of this essay is that consumer behavior is not merely a product of rational decision-making; it is deeply rooted in psychological processes, both conscious and subconscious, that drive consumers’ choices and actions.”
How to Write an Expository Essay

Unlike argumentative or persuasive essays, expository essays do not aim to convince the reader of a particular point of view.
Instead, they focus on providing a balanced and thorough explanation of a subject.
Key characteristics of an expository essay include:
- Clarity and Conciseness
- Structured Organization (Introduction, Body, Conclusion)
- Objective Tone
- Evidence-Based (Cite academic sources in every body paragraph)
- Objective thesis statement (see below)
- Informative purpose (Not argumentative)
You can follow my expository essay templates with AI prompts to help guide you through the expository essay writing process:

How to write a Thesis Statement for an Expository Essay
An expository thesis statement doesn’t make an argument or try to persuade. It uses ‘is’ rather than ‘ought’ statements.
Take these comparisons below. Note how the expository thesis statements don’t prosecute an argument or attempt to persuade, while the argumentative thesis statements clearly take a side on an issue:
💡 AI Prompt for Generating Sample Expository Thesis Statements An expository essay’s thesis statement should be objective rather than argumentative. Write me five broad expository thesis statement ideas on the topic “[TOPIC]”.
Go Deeper: 101 Thesis Statement Examples
Differences Between Expository and Argumentative Essays
Expository and argumentative essays are both common writing styles in academic and professional contexts, but they serve different purposes and follow different structures.
Here are the key differences between them:
- Expository Essay : The primary purpose is to explain, describe, or inform about a topic. It focuses on clarifying a subject or process, providing understanding and insight.
- Argumentative Essay : The goal is to persuade the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific action. It’s about presenting a stance and supporting it with evidence and logic.
- Expository Essay : It maintains a neutral and objective tone. The writer presents information factually and impartially, without expressing personal opinions or biases.
- Argumentative Essay : It often adopts a more assertive, persuasive, and subjective tone. The writer takes a clear position and argues in favor of it, using persuasive language.
- Expository Essay : The reader is expected to gain knowledge, understand a process, or become informed about a topic. There’s no expectation for the reader to agree or disagree.
- Argumentative Essay : The reader is encouraged to consider the writer’s viewpoint, evaluate arguments, and possibly be persuaded to adopt a new perspective or take action.
Go Deeper: Expository vs Argumentative Essays
Ready to Write your Essay?

Take action! Choose one of the following options to start writing your expository essay now:
Read Next: Process Essay Examples

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write an Expository Essay
#scribendiinc
Does Expository Writing Have You Confused?
Maybe you find yourself on this page because your instructor asked you to write an expository essay, and you aren't exactly sure what's expected of you—if so, you've certainly found the right place. Expository writing, or exposition, is a type of discourse used to describe, explain, define, inform, or clarify. It literally means "to expose." Exposition can be found in writing or oral discourse, but for the sake of this article, we'll stick with expository writing.
You are likely familiar with expository writing already, even if the name sounds unfamiliar. Common examples include newspaper articles, how-to manuals, and assembly instructions. Expository writing is also the most frequent type of academic writing !
Present the facts, and only the facts
If you are asked to write an expository essay, then you are essentially being asked to present the facts; there is no place for bias or opinion in expository writing. In a way, this makes writing simple—it is a matter of gathering and presenting the facts about a certain topic.
Something important to keep in mind when writing exposition is that you should not assume your readers have any knowledge of the topic; don't gloss over basic or important details, even if you think they're common knowledge.
When writing expository essays, it is best to use third person narration, although second person is acceptable in some instances, such as for instructions—or articles on expository writing.
Characteristics of expository writing
There are a few characteristics of expository writing you should remember when crafting an expository essay. The first is to keep a tight focus on the main topic, avoiding lengthy tangents, wordiness, or unrelated asides that aren’t necessary for understanding your topic.
In the same vein, be sure to pick a topic that is narrow, but not so narrow that you have a hard time writing anything about it (for example, writing about ice cream would be too broad, but writing about ice cream sold at your local grocery store between 5:00 and 5:15 pm last Saturday would be too narrow).
You must also be sure to support your topic, providing plenty of facts, details, examples, and explanations, and you must do so in an organized and logical manner. Details that can support your expository writing include:
- Comparisons
- Descriptive details
- Definitions
- Charts and graphs
Formatting an expository essay
The typical format for an expository essay in school is the traditional five-paragraph essay. This includes an introduction and a conclusion, with three paragraphs for the body of the paper. Most often, these three paragraphs are limited to one subtopic each.
This is the basic essay format, but expository writing does not need to be limited to five paragraphs. No matter how long your essay is, be sure your introduction includes your thesis statement and that the paper is based on facts rather than opinions. And, as with all good essay writing , make sure to connect your paragraphs with transitions.
Methods for writing an expository essay
There are a few different methods for writing an expository essay. These include:
- Compare and contrast
- Cause and effect
- Problem and solution
- Extended definition
Generally, you will want to pick one method for each piece of expository writing. However, you may find that you can combine a few methods. The important thing is to stay focused on your topic and stick to the facts.
Now that you have a clearer understanding of expository writing, you're ready to write your essay. One final tip: be sure to give yourself plenty of time for the writing process. After you've completed your first draft, let your paper sit for a few days—this lets you return to it with fresh eyes. If you'd like a second opinion, our essay editors are always available to help.
Image source: picjumbo_com/Pixabay.com
Let’s Make an Impact on Your Reader
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

Five Habits to Avoid in Your Academic Writing

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How to Write an Expository Essay
Published by Grace Graffin at August 17th, 2021 , Revised On July 26, 2023
Expository means “to describe or explain something” . It is related to the words ‘exposition’, ‘expound’, and ‘expose’ – to explain or reveal the meaning, to lay open, speak one’s mind.
Whenever there is a need to gather research and describe an idea, a topic , or a process clearly and logically, it is done in the form of an expository essay .
An expository essay requires the writer to take a balanced approach to the subject matter rather than justifying a particular point of view.
Expository essays are assigned to students to evaluate their subject knowledge and composition skills. When compared with argumentative essays , they involve a lot less research.
Definition of Expository Essay
“The expository essay is the type of essay that involves an investigation of an idea or topic, appraises relevant supporting evidence material, and presents an argument in a clear and concise manner. ”
When to Write an Expository Essay
Your school or university could assign an expository essay to you as coursework or as part of an online exam.
However, the guidelines may or may not clearly state that your assignment is an expository essay. If that is the case, then look for keywords like ‘explain’, ‘describe’, ‘define’, etc., to be sure that what has been asked for is an expository essay.
You might even be asked to explain and emphasise a particular concept or term. Writing a simple definition will not be enough because you will be expected to explore the ideas in detail.
Writing an Expository Essay
An expository essay should not be based on your personal experiences and opinions. It rather takes an objective approach. You will be expected to explain the topic in a balanced way without any personal bias.
Make sure to avoid the first and second person (“I” and “You”) when writing an expository essay.
How to Structure an Expository Essay
The structure and format of your expository essay assignment will depend on your school’s guidelines and the topic you are investigating. However, it is always a good idea to develop an outline for your essay before starting to work.
The Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Approach
An expository essay will require you to take the five-paragraph essay approach: an introductory paragraph , a main body paragraph , and a concluding paragraph . This is often referred to as the hamburger style of the essay because, like a hamburger, it contains five main parts: the introduction and conclusion being the bun that encapsulates everything.
Rationale and Thesis Statement
Start your essay with a rationale and thesis, also known as the thesis statement , so your readers know what you set out to achieve in your expository essay assignment. Ensure the thesis statement is narrow enough to follow the guidelines in the assignment brief. If the thesis statement is weak and too broad, you will struggle to produce a flawless expository essay.
The Framework
Construct a framework, so you know what elements will constitute the basis of your essay.
Expository Essay Introduction
Like other essay types , an expository essay begins with an introduction , including a hook, background to the topic, and a thesis statement. Once you have grabbed the readers’ interest, it will be easier to get them to read the remaining essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will i need the skill of expository writing after i finish my studies.
It depends on what you are studying for. While you might or might not write any more expository essays after your formal education has ended, the skill will be very useful in certain careers, such as business reports, journalism, and in scientific and technical writing.
How does an expository essay differ from an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is usually longer and requires more research. It starts with a claim about something that will need supporting evidence. And both sides of the argument need to be discussed. In an expository essay, there is no requirement to make an original argument and defend/support it.
What is the purpose of expository essays?
This style of essay is necessary when you have to showcase your knowledge on a given subject, or your ability to gather research on one and present your findings.
How long is an expository essay?
There is no fixed length but an expository essay could be part of an exam, in which case it might only be 1,000 words or less. They are usually shorter than argumentative essays . It can depend on the subject under discussion. You will likely be given instructions on the required word count.
Are there different types of expository essay?
There are six different types of expository essay, each with a different purpose.
The six types are:
Process essay – describing a task, a method, how to complete something Cause and effect essay – why something happened and its effects Problem-solution essay – provide analysis of problems and their solutions Compare and contrast essay – describe the similarities and differences between two subjects Definition essay – define the topic in detail and explain the how, what, and why Classification essay – separate the topic’s categories and define them in detail
When you are assigned your essay, you should be able to distinguish which of these approaches you are required to take.
You May Also Like
Before you totally lose your mind here let’s see whether the broken argument in an essay needs to be dumped or just neatly reworked and fixed.
Here are some tips on writing the main body paragraphs of an essay to help you correctly plan and organize the most critical part of your academic essay.
Identifying the causes and reasons why so many students struggle with essay writing can help students avoid these mistakes and write a perfect essay.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
- How It Works
- Order an essay
- College essay
- Admission essay
- Research paper
- Dissertation
How to Write an Expository Essay: Simple Guide
Expository essay writing might be difficult, but it can be made much easier with the correct advice. This guide will take you step-by-step through the entire process, from explaining what an expository essay is to writing a coherent and impactful composition.
What Is Expository Essay Writing?
An expository essay is an academic writing that aims to provide factual information, describe a specific topic, or offer a comprehensive explanation of a particular concept. It is notable for its strict adherence to objectivity, refraining from presenting the writer’s personal opinions, emotions, or biases. Key features of an essay include an informative focus, impartiality, educational nature, structured format, well-defined paragraphs, transitional devices, conclusive recap, absence of personal bias, proper citation and references, and a balanced, evidence-based account of the subject matter.
It aims to inform and educate the reader by providing detailed information and insights.
A Step-By-Step Guide to Writing an Excellent Expository Essay
Crafting an essay is a challenging yet fulfilling task that requires a systematic approach. This article will guide you through the expository essay writing process, from selecting a compelling topic to conducting thorough research, writing an expository essay introduction, and meticulously revising your final draft. Regardless of your experience or familiarity with the subject matter, this guide will assist you in every phase of the writing process. By following these structured steps, you will gain confidence in your essay-writing abilities and ensure your essay is well-organized, informative, and engaging. So, dive into the world of essay writing and unlock the art of crafting an impactful, well-structured, and informative essay.
Steps to Writing an Expository Essay
An expository essay serves as a vehicle for providing objective, informative, and detailed explanations or descriptions of a chosen subject, empowering readers with comprehensive knowledge and helping them gain a deeper understanding of the topic or concept presented.
Essential steps to writing an expository essay ensure a well-structured and informative piece of writing. These steps include selecting a relevant topic, conducting thorough research, creating an outline, writing the introduction, composing body paragraphs, using transition words, citing sources, writing the conclusion, revising and editing, seeking feedback, conducting a final proofread, formatting according to instructor or institution guidelines, and performing a last review before submitting.
- Choose a topic that is engaging for your audience.
- Research thoroughly by gathering information from reputable sources such as books, academic journals, websites, and interviews. Take notes and keep track of your sources for proper citation.
- Develop a structured outline that organizes your essay into sections, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Write an engaging introduction that includes a hook, provides context for the topic, and presents a clear thesis statement.
- Compose body paragraphs, starting with a clear topic sentence, followed by supporting evidence, examples, and analysis. Use transitional words and phrases to maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas.
- Cite sources properly, following a consistent citation style like APA, MLA, or Chicago.
- Summarize the main points of the expository essay and provide a concise recap of key takeaways.
- Revise and edit your content for clarity, coherence, and grammar.
- Format your essay according to instructor or institution guidelines, paying attention to formatting, font size, margins, and any additional style instructions.
Following these simple steps, you will write a well-structured and informative expository essay that effectively conveys your message and engages your audience.
How Do You Choose Expository Essay Topics?
Choosing a topic is crucial as it sets the stage for the entire research process and generates interest. A well-chosen topic can make the writing process smoother and more enjoyable, while a poorly chosen one can lead to frustration and a lackluster essay.
Before choosing a topic, consider your target audience and their level of knowledge and interest in the subject. Ensure your chosen topic has sufficient research material, especially for expository essays that rely on factual information and evidence. Brainstorming and narrowing down your list of ideas, concepts, or subjects can help you find the perfect topic.
Expository Essay Prompts
Expository essay prompts cover various subjects and themes, such as education, technology, health and wellness, environment, history, literature, social issues, science, economy, travel and culture, and more. Expository essay topics can cover a wide range of subjects, including the impact of climate change on polar ice caps, the history of ancient Egypt, the psychological effects of bullying on adolescents, the process of DNA replication, the Industrial Revolution and its impact on urbanization, the benefits of a balanced diet for health, the influence of Shakespeare on modern literature, and the causes and effects of air pollution in urban areas.
Selecting the topic for your expository essay is a critical first step in the writing process, impacting the depth of your research, the quality of your writing, and the level of interest generated.
Expository Essay Tips for Good Research
Research is a crucial aspect of crafting an expository essay, as it provides the necessary information to inform and engage the audience. To conduct effective research, one should consider various sources, including books, academic journals, websites, interviews, and surveys. Citation management tools like Zotero or EndNote can help organize references and citations, making citations more manageable.
Critical evaluation of sources is essential, assessing their credibility, reliability, and bias. Taking detailed notes on vital information, quotes, data, and thoughts is also necessary for easy reference during the writing process.
Expository Essay Structure
Just as an architect methodically develops a blueprint before beginning building, a writer must craft a solid structure for their essay to ensure its clarity and effectiveness. Expository essay structure aims to enlighten, clarify, or describe a subject.
How to write an expository essay outline?
An expository essay outline is a crucial tool for any writer, as it helps plan, organize, and systematically present thoughts. It provides clarity, coherence, and logical flow, preventing veering off track and saving time by creating a coherent draft without constant revisions.
To create an effective outline, follow these steps:
- Identify your purpose and audience. Tailor your outline to suit your objectives and readers.
- Choose a suitable format. Outlines can take various formats, such as alphanumeric, decimal, or mind maps. Select a design that aligns with your writing style and the complexity of your work.
- Begin with main points: List the primary issues or sections you want to cover, such as critical topics or arguments. Subdivide the content into subpoints or subtopics, providing more detailed information, explanations, or evidence that support the main point.
- Use a consistent structure: Maintain a consistent design throughout your outline, such as using Roman numerals for main points.
- Include supporting evidence: Make notes of the evidence, examples, quotations, or data you plan to incorporate under each sub point to ensure well-supported content.
- Maintain a logical flow: Check that your outline follows a logical progression, creating a coherent narrative. If the order seems disjointed, consider reorganizing your resume.
An outline is an invaluable tool for any expository essay writer, helping to plan, organize, and present thoughts systematically.
How to write an expository essay introduction?
An expository essay introduction is a crucial aspect of essay writing, serving as a bridge between readers and the content of the essay. It plays a pivotal role in achieving several objectives: engagement, context, and the thesis statement. To create an inviting introduction, follow these steps:
- Attract your readers with a captivating hook that sparks their curiosity.
- Contextualize your topic by explaining the background and importance of the case.
- Introduce your statement, which should be clear, specific, and forward-looking.
An inviting introduction is a critical skill in essay writing, as it serves as the gateway to your essay, welcoming your readers and setting the tone for the journey ahead.
By following these steps, you can create an engaging and engaging introduction that sets the stage for your essay’s content and makes it a valuable resource for your readers.
How to write an expository essay thesis statement?
The expository essay thesis statement is a crucial element in an essay, serving as the core idea that guides the reader and provides clarity.
To craft a well-crafted statement, start by analyzing the assignment, defining the main idea, considering the audience, preparing specific and concise information, and utilizing impactful language. This will help align the thesis statement with the assignment’s expectations and ensure that all arguments and evidence support the central idea.
An effective statement should not only state facts but also present an opinion, argument, or perspective, establishing a solid foundation for the analysis and development of the essay. It is essential to choose a powerful and precise language for the thesis statement, avoid ambiguity, and use impactful language to capture readers’ attention.
How to write expository essay body paragraphs?
Crafting effective expository essay body paragraphs is crucial for a successful essay. They are the foundation of your paper, where your ideas come to life, your arguments take shape, and your evidence is presented. Body paragraphs are essential for development, structure, unity, and transition. To create engaging and effective body paragraphs, follow these steps:
- Craft a compelling topic sentence: Start each paragraph with a clear and engaging topic sentence that sets the stage for what follows.
- Present supporting evidence: Provide relevant, reliable evidence that reinforces the main point of the paragraph.
- Elaborate and analyze the evidence: Explain the significance of the evidence and how it connects to your main argument.
- Choose words with impact: Use clear and impactful language without unnecessary jargon or convoluted sentences.
- Maintain focus and unity: Ensure all sentences in the paragraph contribute to the central point.
- Use seamless transitions: Use transitional words and phrases to connect ideas and create a seamless flow between paragraphs.
Crafting engaging body paragraphs is essential for a successful essay.
How to write an expository essay conclusion?
The conclusion of an expository essay is a crucial aspect of the article as it serves as the last impression on the reader. To create a compelling decision, follow these steps:
- Rephrase your thesis statement to emphasize its core argument.
- Summarize with precision: Condense your ideas into concise statements, connecting each summary directly to your thesis.
- Elevate to a broader context: Share the implications of your findings or the relevance of your topic beyond the essay.
- The art of closure, not introduction: Avoid introducing new information or arguments and synthesize what you’ve already presented in the essay’s body.
- Offer a parting thought: End with a thought-provoking statement or insight that resonates with your readers.
- Maintain consistency: Keep the tone and style of your conclusion consistent with the rest of the essay, maintaining the same level of professionalism and academic rigor throughout.
- Avoid repetition: Use fresh language to maintain reader engagement while reiterating your thesis and summarizing your main points.
- Craft a memorable closing line: Create a memorable and impactful closing line that resonates with your readers.
In conclusion, crafting a compelling expository essay conclusion is a powerful opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers.
Transition Words in Expository Writing
Transition words in expository writing serve as navigational tools that guide readers through the exposition. They establish connections between concepts, making it clear how different ideas relate to one another, ensuring a logical and smooth flow in the writing. These words are instrumental in organizing thoughts and creating a structured and easily understandable essay.
There are various types of transition words, such as addition transitions, contrast transitions, cause and effect transitions, sequence transitions, clarification transitions, illustration transitions, and summary transitions. For instance, “furthermore,” “moreover,” “in addition,” and “likewise” indicate that you are presenting supplementary details.
Contrast transitions are essential for highlighting differences or opposing ideas: words like “however,” “on the other hand,” “in contrast,” and “conversely” draw attention to shifts in thought. Cause and effect transitions are crucial when explaining causes and their effects. Sequence transitions are indispensable for arranging steps or events in chronological order.
Clarification transitions help clarify or restate a point using words like “in other words,” “to clarify,” “in essence,” or “that is.” Illustration transitions help provide examples or illustrate ideas. Like, “for instance,” “for example,” “such as,” and “to illustrate” are frequently employed in this context.
Summary transitions signal the end of your discussion. For instance, “In conclusion,” “to sum up,” “in summary,” or “overall.”
Transition words are the unseen guides that lead readers through the intricate landscape of expository writing, facilitating understanding, enhancing organization, and emphasizing crucial points.
Writing Skills Needed for Writers
The art of clarity is crucial in crafting a solid expository essay. This involves embracing simplicity in language and sentence structure, avoiding convoluted sentences, and aiming for a universally understandable writing style. Research skills are essential for effective expository writing, as is organization and a well-structured structure. Mastering proper citation and referencing is necessary for academic integrity. Finally, the consistency of tone, style, and formatting contributes to the overall readability and professionalism of the work.
Expository essay format
The choice of font and size is crucial for the readability and visual appeal of expository essays. Opt for a standard and easily readable font such as Calibri, Times New Roman, Arial, or Garamond, and use a 12-point font size for the main text. This size balances readability and conserving space, ensuring your text is legible without appearing oversized.
Formatting your text alignment and spacing can significantly impact the visual structure of your essay. Text alignment should be left-justified, providing a clean and professional look. Double-spacing is the standard for most academic papers, providing ample room for readers to make annotations and comments. Paragraph indentation should begin with a 0.5-inch indentation or use the “Tab” key to visually separate paragraphs and enhance the essay’s readability. Maintain one-inch margins on all sides of your paper to frame your text neatly and prevent it from appearing cramped or spreading too far to the edge of the page.
Headings and subheadings can be beneficial for organizing and guiding the reader. Use a consistent formatting style for titles, such as bold, larger font size, or italics, and establish a clear hierarchy for multiple levels of headings. Align headings to the left for a clean and organized appearance.
Expository Writing Tips to Make the Essay Interesting
Writing an expository essay involves more than just providing information; it also involves holding readers’ interest, stimulating their thought processes, and creating a lasting impression. Your work can be a fascinating adventure, whether delving deeply into a subject, clarifying a complicated idea, or bringing a topic to light. Now, let’s provide some tips and tricks to make your writing more captivating and informative. These expository essay techniques capture readers’ attention, engage their minds, and leave a lasting impression.
To create an engaging essay, follow these tips:
- Choose an intriguing angle: Choose a unique perspective that piques readers’ curiosity.
- Craft a captivating opening: Start with an attention-grabbing hook, such as a surprising fact, thought-provoking question, or vivid anecdote.
- Tell a story: Weave storytelling elements into your expository writing, using personal stories or relatable anecdotes to make complex topics more accessible and relatable.
- Create a mental journey: Guide your readers through your essay like a journey, using vivid language and descriptive imagery.
- Embrace the power of analogies: Compare complex concepts to familiar objects or experiences to make them more understandable.
- Spark curiosity with questions: Pose thought-provoking questions throughout your essay, engaging readers’ minds and encouraging more profound thinking.
- Break it down with lists: Use lists to break down very complex ideas into easily digestible chunks.
- Use the rule of three: Present ideas, examples, or arguments in sets of three to make content more memorable and impactful.
- Engage the senses: Appeal to the reader’s senses by describing how things look, sound, smell, taste, or feel.
- Explore the ‘So What’ factor: Challenge the significance of each point to keep your writing focused on what truly matters.
- Use relatable analogies: Relate your topic to everyday experiences and objects your readers can quickly grasp.
- Emphasize the ‘Why’ and ‘How:’ Explain not only ‘what’ but also ‘why’ and ‘how.’
- Create a personal connection: Share personal anecdotes or experiences related to your topic.
- Be conversational: Write in a friendly, approachable tone.
- End with a Call to Action: Conclude your essay by motivating readers to take action.
Remember, the goal is to make your words come alive on the page.
Expository Essay Checklist to Ease Your Writing Struggles
Once your expository essay is complete, use this checklist to ensure it meets high standards of clarity and professionalism.
- Have you considered your target audience’s expectations, interests, and level of knowledge?
- Have you researched extensively using dependable sources, such as books, scholarly publications, trustworthy websites, and interviews?
- Is your writing simple and direct, free of technical terms and jargon that can confuse readers?
- Have you evaluated and assessed the data, elucidating its relevance to your thesis?
- Have you employed transitional words and phrases to make your article flow naturally and logically?
- Have you written the essay in a consistent tone and style?
- Does your opening offer background information on your article and a hook to draw the reader in?
- Do the arguments in your body paragraphs have a transparent organization, analysis, and supporting data?
- Does your conclusion substantially impact, reiterate your argument, and briefly summarize your key points?
- Have you given your topic some thought and made a connection to a larger context to determine its relevance and significance?
- Does the conclusion of your article provide the reader with a provocative realization or moment of reflection?
- Have you ensured that every quote or idea you use is correctly attributed to prevent unintentional plagiarism?
By going over these aspects, you can ensure that your writing skills are on top and essay is compelling and influential
Argumentative Essay Introduction
In essay writing, the toughest part is always starting it. Most students agree: when you get the introduction paragraph right, you become much more confident about writing the rest of the paper. And, when it comes to more specific academic… Read More

How to Write a Conclusion for an Argumentative Essay: Outline and Examples
Writing a conclusion for an argumentative essay can be a breaking point for most students. This section is critical to your academic project because it guides your paper to a safe landing. Failing to pay special attention to this part… Read More
How to Write an Essay on a Book
Book essay writing is an omnipresent assignment imposed by many professors, especially if you are dealing with literature constantly. An essay on a book is usually a way for your teacher to get proof that you gained something from analyzing… Read More
Essay Papers Writing Online
Get the ultimate guide on writing an expository essay – step-by-step tips and examples.

Are you grappling with the challenge of composing a compelling expository essay? Look no further, as this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential tools and techniques to effectively convey your ideas and captivate your readers. By employing powerful writing strategies and supplementing your work with concrete examples and real-life anecdotes, you will unlock the true potential of your explanatory essay.
Begin your writing journey by harnessing the power of clarity and conciseness. Structuring your essay with a logical flow will allow your readers to effortlessly follow your thought process and grasp your central ideas. Employing strong transitions between paragraphs and employing cohesive language will ensure a seamless reading experience. Additionally, honing your analytical skills and supporting your claims with factual evidence will lend credibility to your work while fostering a deep understanding of the topic.
Furthermore, incorporating vivid examples and engaging anecdotes will breathe life into your expository essay, making your content relatable and memorable. By utilizing descriptive language and the art of storytelling, you will create a lasting impact in the minds of your readers. Whether it is a personal experience, a historical event, or a scientific study, weaving in these narratives will amplify the effectiveness and persuasiveness of your essay, leaving a lasting imprint on your audience.
Mastering the Art of Crafting a Compelling Expository Composition: Pointers and Illustrations

An in-depth exploration of the fundamentals behind composing an impactful expository essay can serve as an invaluable tool in your academic and professional endeavors. By harnessing the power of language, analysis, and evidence, you can construct a persuasive and enlightening piece of writing that will captivate your readers. Let us embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of crafting an exquisite expository essay.
1. Avoid monotony: Deliver your ideas in a fresh, stimulating manner to enthrall your audience. Strive to maintain a captivating narrative flow by skillfully employing synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and metaphors. This will invigorate your writing and make it truly memorable.
2. Be concise yet comprehensive: Accomplish the delicate balance of being succinct without sacrificing the clarity and depth of your exposition. Remember to select your words wisely, presenting each idea concisely while ensuring it is thorough and complete.
3. Provide evidence: Back up your statements with solid evidence and well-researched examples. Citing credible sources, such as reputable studies, expert opinions, and statistical data, will add credibility and weight to your arguments, making them more persuasive and powerful.
4. Organize your thoughts: Structure your essay in a logical and coherent manner, ensuring that each idea flows seamlessly into the next. Utilize transitional words and phrases to guide your readers through the different sections of your essay, enabling them to follow your line of reasoning effortlessly.
5. Cater to your audience: Tailor your language, tone, and examples to suit the preferences and background of your intended audience. Use relatable and engaging references to convey your message effectively and establish a connection with your readers.
6. Emphasize clarity: Clarity is key when it comes to expository writing. Avoid excessive jargon, convoluted sentences, and ambiguous expressions. Instead, strive for lucidity and precision, ensuring that your readers can easily grasp the main points of your essay.
7. Show don’t tell: Instead of merely stating information, aim to vividly illustrate your ideas through anecdotes, case studies, and real-life examples. This will make your essay more relatable and memorable, enabling your readers to form a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
8. Revise and refine: Do not underestimate the importance of the revision process. Review your essay meticulously, focusing on grammar, clarity, and coherence. Eliminate redundancies, enhance sentence structure, and refine your vocabulary to elevate the quality and impact of your writing.
By equipping yourself with these essential guidelines and examples, you are well-prepared to embark on your expository essay writing journey. Remember, mastering the art of crafting a compelling expository composition requires practice and perseverance. Let your ideas flow, embrace creativity, and allow your words to inspire, educate, and leave an indelible mark in the minds of your readers.
The Significance of an Expository Article
When it pertains to written compositions, the significance of an expository article cannot be underestimated. This type of writing piece serves a crucial purpose in communicating information, presenting facts, and explaining ideas in a clear and concise manner. By utilizing objective analysis, evidence-based reasoning, and logical arguments, an expository essay provides readers with a deeper understanding of a subject matter.
Unlike other forms of writing, an expository essay focuses on informing rather than persuading or entertaining. It acts as a reliable source of knowledge, offering readers an opportunity to broaden their horizons and gain new insights. Whether used in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay serves as a valuable tool for conveying information accurately and objectively.
Furthermore, an expository essay aids in building critical thinking and analytical skills. Through the process of researching and organizing information, the writer develops the ability to evaluate sources, discern facts from opinions, and present arguments based on logical reasoning. This type of writing encourages readers to question assumptions, analyze evidence, and draw their own conclusions.
Moreover, mastering the art of composing an expository essay equips individuals with essential communication skills that are applicable in various aspects of life. By learning how to present complex ideas in a clear and coherent manner, one becomes an effective communicator across different fields and disciplines. Whether it be writing research papers, reports, or even delivering presentations, the skills acquired from writing an expository essay are invaluable in expressing ideas persuasively and engaging an audience.
In conclusion, the importance of an expository essay lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive and objective understanding of a subject matter. By offering factual information, logical arguments, and clear explanations, this type of writing contributes to the development of critical thinking skills and effective communication. Whether in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay plays a vital role in disseminating knowledge and fostering intellectual growth.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience
In order to create a compelling and impactful expository essay, it is important to have a clear understanding of the purpose and audience of your writing.
The purpose of an expository essay is to explain or inform the reader about a specific topic or idea. Unlike other types of essays, the main goal is to provide a balanced analysis and present factual information in a clear and concise manner. The purpose may vary depending on the specific assignment or context, but it is important to always keep the purpose in mind when writing an expository essay.
Equally important is knowing your audience. Understanding who will be reading your essay will help you tailor your writing style, tone, and level of complexity to effectively communicate your ideas. Consider the background knowledge, interests, and beliefs of your audience to ensure that your essay is accessible and engaging.
- Start by identifying the demographic characteristics of your audience, such as age, education level, and background.
- Consider their prior knowledge on the topic. Are they familiar with the subject matter, or do you need to provide additional context?
- Think about their potential biases or preconceived notions. Are there any potential challenges or objections you need to address?
By understanding the purpose and audience of your expository essay, you can craft a well-written and relevant piece that effectively communicates your ideas and engages your readers.
Choosing the Right Topic and Gathering Information
One of the crucial steps in writing an outstanding expository essay is selecting a compelling topic and gathering relevant information. The topic should be interesting, relevant, and align with the purpose of your essay. It’s important to choose a topic that you are passionate about and have a good understanding of, as it will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and easier.
Start by brainstorming different ideas and concepts that you find intriguing. Consider your personal experiences, hobbies, or areas of expertise that you would like to explore further. You can also look for inspiration from current events, popular trends, or societal issues that grab your attention. Once you have a list of potential topics, narrow it down to the one that has enough depth and scope for exploration.
Once you have chosen a topic, it’s time to gather information to support your thesis statement and provide evidence for your claims. Start by conducting thorough research using various sources such as books, scholarly articles, reputable websites, and interviews with experts in the field. Take notes and keep track of the sources you use for referencing purposes.
By choosing the right topic and gathering relevant information, you lay the foundation for a well-researched and compelling expository essay. Take the time to explore different ideas, conduct thorough research, and organize your findings effectively. Remember, a well-chosen topic and solid information will make your essay engaging and informative for your readers.
Structuring Your Expository Essay

When it comes to composing an expository essay, the way you structure your piece is crucial. Organizing your thoughts and ideas in a clear and logical manner will not only make your writing more coherent and easy to follow, but it will also help you effectively convey your message to the readers.
One effective way to structure your expository essay is to use the traditional five-paragraph format. This format consists of an introduction paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall development of your essay.
The introduction paragraph is where you grab the attention of your readers and provide them with a brief overview of what your essay will be about. It should include a strong thesis statement that clearly states your main argument or point of view.
The body paragraphs are where you present your evidence, provide supporting details, and analyze your topic. Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea or aspect of your topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point, and then provide examples, facts, or explanations to support your argument.
In the conclusion paragraph, you should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information or arguments in this section. Instead, focus on leaving a lasting impression on your readers and reinforcing the main ideas discussed throughout your essay.
Remember to use appropriate transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas. Examples of transitional phrases include “firstly,” “in addition, “finally,” and “on the other hand,” among others.
By following a well-structured approach, you can effectively organize your expository essay and make it engaging and informative for your readers. Take the time to plan your essay, identify your main points, and arrange them in a logical order. With a clear structure, your expository essay will be a powerful piece of writing that effectively conveys your ideas.
Enhancing Clarity and Coherence
Creating a clear and coherent expository essay requires skillful use of language and organization. By carefully selecting words and arranging ideas logically, you can ensure that your essay is easy to understand and follow.
Word Choice: One of the most effective ways to enhance clarity is through thoughtful word choice. Consider using precise and specific language to convey your ideas. Instead of using general terms, opt for more descriptive words that accurately depict the information you are presenting.
Logical Organization: Coherence in your essay can be achieved through proper organization. Present your ideas in a logical progression, ensuring that each paragraph flows smoothly into the next. Use transitional words and phrases to connect your thoughts and guide the reader through your essay.
Consistent Structure: To enhance clarity and coherence, maintain a consistent structure throughout your essay. Use a clear introduction to outline your main points and a strong conclusion to summarize your findings. Each body paragraph should focus on a single topic and provide sufficient evidence and examples to support your claims.
Effective Transitions: Transitions are essential in ensuring a cohesive flow between ideas and paragraphs. Use transitional words and phrases such as “however,” “in addition,” and “furthermore” to link your ideas and create a smooth transition between different sections of your essay.
Eliminating Ambiguity: To enhance clarity, it is crucial to eliminate any ambiguity or confusion from your writing. Be precise in your language and avoid using vague terms or jargon. Make sure your ideas are clearly articulated and leave no room for misinterpretation.
Proofreading: Finally, closely edit and proofread your essay for clarity and coherence. Look for any unclear sentences or confusing phrases and revise them for greater clarity. Ensure that your ideas are presented in a logical and coherent manner, leaving no room for confusion.
By enhancing clarity and coherence in your expository essay, you can effectively communicate your ideas and engage your readers. Thoughtful word choice, logical organization, consistent structure, effective transitions, and careful proofreading all play important roles in creating a clear and coherent essay that will leave a lasting impact.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
How to Write an Expository Essay: Definition, Outline, Writing Tips, and Examples

In the realm of academic writing, this type of essay stands as a beacon of clarity, demanding writers to illuminate a subject with precision and objectivity. Whether you're a seasoned essayist or a student embarking on your first exploration of this genre, mastering the art of expository writing is a valuable skill that transcends disciplines. This form of essay invites you to delve into expository essay topics, dissect their intricacies, and present your findings in a straightforward manner.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the terrain of expository writing, unraveling the techniques and strategies that transform a mere composition into a beacon of insight. From understanding the fundamental principles to honing your ability to craft a compelling thesis, join us on a journey that promises to demystify the process of writing, empowering you to articulate ideas with clarity and purpose. Or, you can get our essay writing help and take care of other important tasks set for today.
What Is an Expository Essay
An expository essay is a form of academic writing that aims to elucidate, clarify, and present a balanced analysis of a particular topic or idea. Unlike other essay types that may delve into personal opinions or narratives, the expository essay emphasizes objectivity and factual accuracy. The primary objective is to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of the chosen subject, exploring its various facets, presenting evidence, and ensuring a logical progression of ideas.
.webp)
According to an expository essay definition, this genre requires the writer to delve into research, organize information systematically, and deliver a coherent and informative piece that educates the reader on the chosen topic. Whether investigating a scientific concept, historical event, or literary work, it serves as a vehicle for conveying knowledge in a concise, lucid manner.
Expository Essay Examples
An expository essay example serves as a valuable tool for students, offering a concrete illustration of the structure, style, and depth expected in this genre of writing. By studying examples, students gain insights into effective thesis formulation, organizing ideas within paragraphs, and integrating supporting evidence to bolster arguments.
Additionally, examples showcase how to balance factual accuracy and engaging prose, providing a model for clear and concise communication. Students can draw inspiration from the content and presentation of well-crafted expository essays, honing their own skills in research, analysis, and effective expression. By the way, we have an interesting autobiography example , so check it out!
Example 1: “The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence”
This expository essay explores the multifaceted evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), examining its historical roots, contemporary applications across various industries, and the consequential societal impact. It provides a comprehensive overview of AI's journey from philosophical debates and early computational developments to its current role as a transformative force in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and entertainment. Additionally, the essay addresses ethical considerations surrounding the widespread adoption of AI, including concerns related to job displacement, privacy, and responsible development. Ultimately, it navigates the complex landscape of artificial intelligence, shedding light on its remarkable advancements and its challenges to our ever-changing society.
Example 2: “The Benefits of Outdoor Education for Children”
This essay highlights the advantages of outdoor education for children, emphasizing its positive impacts on their physical, mental, and social development. It argues that outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and team sports not only promote physical health by encouraging movement and reducing sedentary behavior but also contribute to mental well-being by providing a respite from everyday stressors and fostering a connection with nature. Furthermore, it suggests that exposure to outdoor environments cultivates environmental awareness and a sense of stewardship among children.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Need some help with your homework?
Get help from our expository essay writing service ! Leave us a notice and we'll make your tasks asap.
Types of Expository Essay
Expository essays come in several distinct types, each serving a unique purpose and requiring specific approaches to convey information effectively. One common categorization includes:
- Descriptive Expository Essay. This type focuses on painting a vivid picture of a subject, using sensory details to engage the reader's imagination. It aims to create a clear and sensory-rich portrayal of a person, place, object, or experience.
- Process Expository Essay. Here, the writer breaks down a complex process or procedure into manageable steps, providing a detailed and sequential explanation. This type of essay is instructional, guiding readers through a series of actions to achieve a specific outcome.
- Comparison and Contrast Expository Essay. This form involves analyzing similarities and differences between two or more subjects, offering insights into their shared characteristics or divergent qualities. It requires a careful examination of the chosen elements to highlight their relationships.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. Focused on exploring the reasons behind an occurrence and its subsequent consequences, this type delves into the cause-and-effect relationships within a given topic. Writers elucidate the connections between actions and outcomes, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Problem and Solution Expository Essay. Addressing real-world issues, this essay type identifies a specific problem, analyzes its root causes, and proposes viable solutions. It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, compelling readers to consider alternative approaches to challenges.
- Definition Expository Essay. This essay seeks to clarify and explain the meaning of a particular term, concept, or idea. Writers provide a comprehensive definition, often including examples and illustrations to ensure readers grasp the essence of the subject.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. This type of essay examines the reasons behind a particular phenomenon or event and explores its subsequent effects. It aims to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship, allowing readers to comprehend the interconnected elements of the topic.
Understanding these diverse types of essays empowers writers to choose the most suitable approach for effectively conveying information and achieving their communicative goals. Our experts can rewrite essay that you already did according to any of the above-mentioned types.
Expository Essay Topics
Selecting compelling expository essay topics requires thoughtful consideration of both personal interest and the potential engagement of the intended audience. Start by identifying subjects that genuinely captivate your curiosity or align with your expertise, as this enthusiasm will naturally infuse vigor into your writing. Additionally, assess the topic's relevance in the broader context, ensuring it addresses contemporary issues or timeless themes.
Consider the audience's interests, aiming for subjects that resonate with their experiences or evoke a sense of shared relevance. Striking a balance between uniqueness and accessibility is key—opt for topics that allow you to offer fresh perspectives while ensuring there is ample research material available. Ultimately, the best topics seamlessly blend your passion, the audience's interests, and the broader significance of the chosen subject, ensuring a captivating and informative exploration for both writer and reader alike. Here are expository essay ideas from our writers for your inspiration:
.webp)
- The influence of art on human emotions.
- Exploring the life cycle of a star.
- Tips for sustainable living in urban areas.
- The impact of social media on political awareness.
- How to cultivate a positive mindset in challenging times.
- The history and cultural significance of tattoos.
- The process of recycling electronic waste.
- Benefits of incorporating meditation into daily routines.
- The role of laughter in maintaining mental health.
- Understanding the psychology of decision-making.
- The impact of fashion on individual expression.
- Tips for effective conflict resolution in relationships.
- The science behind the sense of taste.
- The significance of biodiversity in ecosystems.
- Exploring the history of traditional folk music.
- How to foster a sense of community in a neighborhood.
- The benefits of learning a musical instrument.
- The evolution of communication technologies.
- The process of seed germination in plants.
- Tips for creating a productive home office space.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job markets.
- Understanding the concept of emotional intelligence.
- The benefits of practicing gratitude daily.
- The history and cultural importance of tea.
- How to develop effective public speaking skills.
- Exploring the world of virtual reality technology.
- The significance of water purification methods.
- Tips for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
- The process of making sustainable food choices.
- The role of literature in shaping societal norms.
Expository Essay Outline
An outline for expository essay is a structured plan that serves as a roadmap for organizing the main ideas and supporting details of the essay in a logical and coherent manner. While the specific structure may vary based on the assignment or preferences, a typical outline generally includes the following components, beginning with how to start an expository essay:
.webp)
Expository Essay Introduction
- Hook or attention-grabbing statement.
- Background information on the topic.
- Clear thesis statement that presents the main idea.
Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Topic sentence for each paragraph, presenting a main point or supporting idea.
- Supporting evidence, facts, or examples to illustrate and explain the topic sentence.
- Analysis or interpretation of the evidence to connect it back to the thesis.
Expository Essay Conclusion
- Restatement of the thesis in different words.
- Summary of the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Concluding thoughts or insights, possibly suggesting implications or future considerations.
Transitions
- Smooth transitions between paragraphs to ensure a cohesive flow of ideas.
- Clear connections between sentences and paragraphs to guide the reader through the essay.
Revising and Editing
- Space for notes on areas that may need revision or improvement.
- Consideration of clarity, coherence, and overall effectiveness.
By creating an expository essay outline, a college essay writer can organize their thoughts, ensure a logical progression of ideas, and maintain a clear and concise structure. This framework helps writers stay focused on the main purpose of the essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a particular subject – while providing a roadmap for readers to follow and comprehend the information presented.
How to Write an Expository Essay Step by Step
Writing an expository essay involves a systematic process that ensures clarity, coherence, and effectiveness in conveying information. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an expository essay:
Choose a Topic
- Select a topic that interests you and aligns with the purpose of an expository essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a subject.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant and credible information to support your chosen topic.
- Utilize reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and reliable websites.
Create an Outline
- Develop a clear and organized outline that includes the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Each section should have a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence of the essay.
Write the Introduction
- Start with an attention-grabbing hook that relates to your topic.
- Provide background information and context, leading to a concise and focused thesis statement that outlines the main idea.
Develop Body Paragraphs
- Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point.
- Support the topic sentence with evidence, facts, or examples.
- Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs, using transitions to guide the reader.
Provide Evidence
- Support your points with credible evidence and examples.
- Ensure that each piece of evidence directly relates to the topic sentence and supports the overall thesis of the essay.
Analyze and Interpret
- After presenting evidence, analyze and interpret it.
- Explain the significance of the evidence and how it relates to your thesis.
- This step helps to ensure that your audience understands the relevance of the information presented.
Write the Conclusion
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs without introducing new information.
- Restate the thesis in different words and offer concluding insights or implications related to the topic.
Revise and Edit
- Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency.
- Check for grammatical errors and awkward phrasing, ensuring a smooth flow of ideas.
- Consider feedback from others or take a break before revising to gain a fresh perspective.
- Carefully proofread your essay to catch any remaining errors, typos, or issues.
- Pay attention to grammar and punctuation.
By following these steps, you can systematically approach the writing process and create a well-organized and informative expository essay. Remember to stay focused on the purpose of informing, explaining, or analyzing the chosen topic throughout the entire writing process.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to write an expository essay offers students several important advantages. First off, it helps them express their thoughts clearly and organize ideas effectively, skills that are useful not only in academics but also in various professional situations where clear communication is key.
Moreover, writing expository essays improves critical thinking as students practice analyzing information, connecting ideas, and presenting well-supported arguments. This skill is valuable in everyday decision-making and problem-solving scenarios.
Additionally, the process of crafting such essays enhances research abilities, teaching students how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively. Overall, mastering expository writing equips students with practical, transferable skills that can positively impact their academic and professional pursuits. You can use our research paper service to cope with assignments better and faster.
Want to Ace Your Expository Writing?
Your wish is our command - order now and experience the excellence of our expert writers!
What are the Different Types of Expository Essays?
What is the most important part of the expository essay structure, what is the main idea in expository writing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
%20(1).webp)

Expository Essay
Expository essay generator.

An expository essay is a quintessential part of academic writing that delves into explaining or clarifying a topic in a comprehensive manner. This type of essay requires the writer to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. Discovering exemplary essay examples can greatly enhance understanding and mastery of this style. Here, we provide a complete guide with examples to empower students and educators in crafting effective expository essays

Download Expository Essay Bundle
In school, it is an unavoidable truth that you will be asked to write something about a topic which sometimes you are so eager to finish. There are also times when you feel like you do not want to write anything at all. Well, that is just normal. We all go through those times.One of the things that we do in school is essay writing . As we all know, it is never an easy job to write especially college essays . However, having the right disposition and enthusiasm makes it all so easy. By the time you start to write, all those ideas keep coming and you wouldn’t realize you’re already done.
What is an expository essay?
An expository essay is a genre of writing that investigates an idea, evaluates evidence, expounds on the idea, and sets forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This type of essay requires the writer to define a topic, use examples, statistics, and facts to explain it to the reader. Expository essays are factual and devoid of the writer’s opinions, focusing instead on delivering straightforward information and analysis on a subject. Their primary purpose is to educate or explain, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic to the reader.
Structure of an Expository Essay
It typically consists of five paragraphs, but the length can vary depending on the depth of the topic. Here’s a breakdown of the traditional structure:
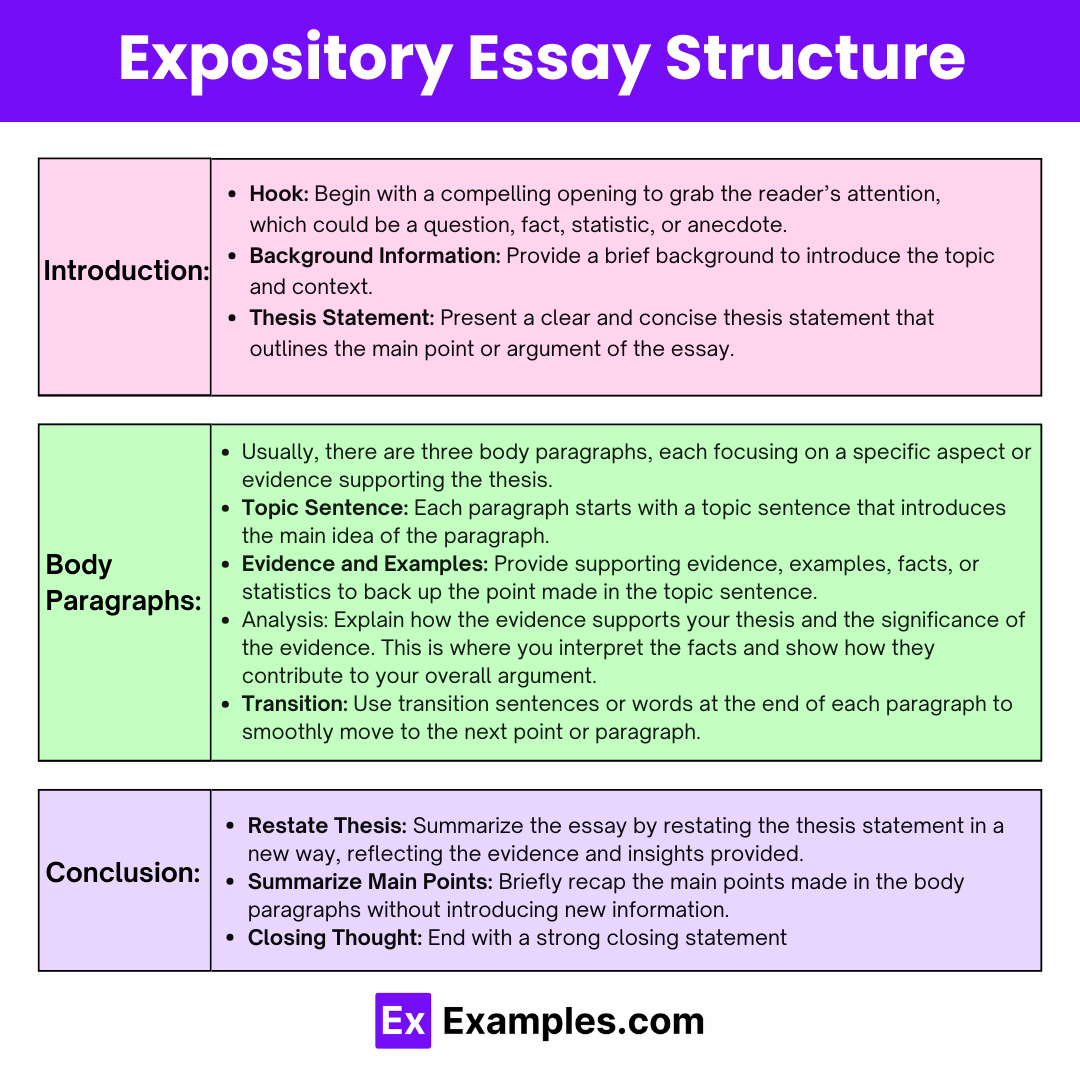
Download This Image
Introduction:
Hook: Begin with a compelling opening to grab the reader’s attention, which could be a question, fact, statistic, or anecdote. Background Information: Provide a brief background to introduce the topic and context. Thesis Statement: Present a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main point or argument of the essay.
Body Paragraphs:
Usually, there are three body paragraphs, each focusing on a specific aspect or evidence supporting the thesis. Topic Sentence: Each paragraph starts with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Evidence and Examples: Provide supporting evidence, examples, facts, or statistics to back up the point made in the topic sentence. Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your thesis and the significance of the evidence. This is where you interpret the facts and show how they contribute to your overall argument. Transition: Use transition sentences or words at the end of each paragraph to smoothly move to the next point or paragraph.
Conclusion:
Restate Thesis: Summarize the essay by restating the thesis statement in a new way, reflecting the evidence and insights provided. Summarize Main Points: Briefly recap the main points made in the body paragraphs without introducing new information. Closing Thought: End with a strong closing statement that reinforces the importance of the topic or provides a call to action or thought-provoking statement to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The primary purpose of expository writing is to explain, inform, or describe. It aims to present a balanced and objective explanation of a topic, process, or concept, based on facts without the writer’s personal opinions influencing the content.
- Educate Readers: It provides readers with a thorough understanding of a subject through clear, concise, and informative content.
- Clarify Complex Ideas: By breaking down complicated subjects into more manageable parts, it helps readers grasp difficult concepts or processes.
- Enhance Critical Thinking: Encourages readers to think critically about the subject matter as they process the information presented.
- Improve Research Skills: Involves researching and presenting facts, which cultivates research and analytical skills in both the writer and the reader.
- Present Objective Analysis: Offers an unbiased perspective, allowing readers to form their own opinions based on the presented facts.
How Do You Write an Expository Essay
Writing an expository essay involves a clear, focused approach that communicates information to the reader in a concise and effective manner. Follow these steps to write a compelling expository essay:
Choose a Topic: Select a topic that is interesting, manageable, and relevant to your assignment’s requirements. It should be broad enough to write about but narrow enough to cover comprehensively in your essay. Conduct Research: Gather information from credible sources to thoroughly understand your topic. Note down important facts, statistics, and examples that will help you explain your topic clearly. Create a Thesis Statement: Develop a clear thesis statement that outlines the main point or argument of your essay. This statement will guide the direction of your essay and inform the reader about your focus. Outline Your Essay: Organize your thoughts and research into an outline. Structure your essay into an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. This will help you maintain a logical flow when writing. Write the First Draft: Using your outline as a guide, write the first draft of your essay. Focus on getting your ideas down; you can refine and edit your work in subsequent drafts. Revise and Edit: Review your essay for clarity and coherence. Ensure each paragraph effectively supports your thesis and that your argument flows logically.Check for grammatical errors, punctuation, and spelling. Ensure that your language is clear, concise, and free of jargon. Cite Your Sources: Properly cite all the sources you used to gather information. This will add credibility to your essay and prevent plagiarism. Finalize Your Essay: Make any necessary revisions based on your review and feedback from others, if available.Ensure your essay meets the assignment criteria and is polished and professional.
Expository Essay Samples
- Essay on Internet
- Essay on Cyber Crime
- Essay on Road Safety
- Essay on National Disaster
- Essay on Floods
- Essay on Education Rules
- Essay on Politics
- Essay on World War 1
- Essay on Cold war
- Essay on Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Expository Essay Examples
[/ns_col] free download [/ns_row] college expository essay.

Free Download

Fee Download
Essay Format

Short Expository Essay

Expository Essay Sample

Expository Education

College Expository

Basic Expository Essay

High School Expository Essay

Types of Expository Essays
Expository essays are a fundamental aspect of expository writing , encompassing various forms that cater to different academic requirements and personal expressions. Each type serves a unique purpose and requires a specific approach to effectively convey information and ideas.
- Definition Essay This type of essay explores the meaning of a concept or term. It goes beyond the basic dictionary definition, providing deeper insights and personal interpretations. Ideal for exploring abstract concepts, a Definition Essay encourages critical thinking and analytical skills.
- Classification Essay In a Classification Essay, objects or ideas are sorted into categories. This form of essay is particularly useful for organizing complex information into more digestible sections, making it easier for the reader to understand and analyze the topic.
- Process Essay Also known as a “How-To” essay, the Process Essay outlines the steps required to complete a task or procedure. It is sequential and detailed, ensuring the reader can follow along and understand each stage of the process.
- Comparison and Contrast Essay This essay type examines the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It’s a powerful tool for analysis, helping students develop critical thinking by evaluating various aspects of the subjects being compared.
- Cause and Effect Essay The Cause and Effect Essay delves into the reasons behind a specific event or situation (the cause) and its outcomes (the effect). It’s essential in academic settings for developing a student’s ability to establish logical connections and reason systematically.
- Problem and Solution Essay This essay identifies a problem and proposes one or more solutions. It not only encourages critical thinking but also fosters creativity and problem-solving skills as students explore viable solutions to real-world issues.
Each of these types of expository essays serves as a tool for students and educators to explore and convey complex ideas and information. From high school essays to more advanced academic essays, the ability to effectively write various types of expository essays is a valuable skill in educational development. Whether it’s a personal essay reflecting on individual experiences or a concept essay explaining abstract ideas, mastering these forms equips students with the capability to communicate effectively and think critically
- Tips to Write an Expository Essay
- Choose a Topic That Interests You
- Conduct Thorough Research
- Create a Detailed Outline
- Craft a Strong Thesis Statement
- Use Clear and Concise Language
- Incorporate Evidence and Examples
- Analyze the Evidence
- Follow a Logical Structure
- Write in the Third Person
- Keep Your Writing Objective
- Revise for Clarity and Cohesion
- Edit for Grammar and Spelling Mistakes
- Seek Feedback from Peers or Teachers
- Practice Writing Regularly
Guidelines to Write Expository Essay
Some people find expository writing harder than descriptive writing . Probably because it is at times difficult to present an idea and expand it so the readers can get a grasp of it. Here are a few guidelines you can use.
- Do an intensive research. Oftentimes, the problem with expository writers is that they don’t have enough points to present for the idea. Do your research.
- Widen your vocabulary. It is easier to write when you have the right words to use. You don’t have to browse your dictionary from time to time.
- Design a method. Be a little creative. There may be some methods that people use to write but it is still better if you have one for your own.
Benefits of Expository Essay
Essay writing provides a lot of benefits to students in the academe. Not only it gives them credits from their teachers, it also boosts their confidence in expressing their ideas.
Expository essays provide a better understanding of a certain topic. We cannot avoid that at times, there are things that are presented vaguely making us question what it really means. Expository essay conclusion explains it logically so we can grasp the its true meaning.
Another benefit is expository essays present a fair and balanced analysis of the idea. It eliminates writer’s opinions and emotions just like in a persuasive writing .
When Should You Write an Expository Essay?
- In Academic Assignments: Expository essays are commonly assigned in academic settings to assess students’ understanding and ability to explain complex concepts clearly.
- For Standardized Tests: Many standardized tests include expository writing sections that require candidates to organize and express their thoughts on a given topic.
- When Explaining Processes: Whenever there’s a need to describe how something works or the steps in a process, an expository essay format is ideal for providing clear instructions.
- To Clarify Concepts: Use an expository essay to break down difficult concepts or ideas into understandable parts for educational purposes or to inform a general audience.
- In Professional Settings: Professionals might write expository essays in the form of reports, manuals, or proposals to convey information or explain procedures within a company.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Define an expository essay and its main objective
Outline the structure of a standard expository essay.
Describe the process of selecting a topic for an expository essay.
Explain the importance of research in expository essay writing.
Analyze the role of the thesis statement in expository essays
Discuss the differences between expository and narrative essays
Examine techniques for developing paragraphs in expository essays
Explain how to effectively conclude an expository essay
Describe methods for maintaining objectivity in expository writing
Analyze the impact of audience on expository essay content
How to Write a Personal Narrative Essay
by Sue Weems | 0 comments
Learning how to write a personal narrative essay is a core skill in most middle and high school writing classes, but narrative essays are great practice for so much more! If you've ever wanted to nail an assignment, an interview, or just be a more interesting person, this practice is for you!

As an award-winning teacher, I always begin my courses with a personal narrative essay, whether I'm teaching beginning composition to college freshmen or English to eighth graders.
Why? Because you know the most about yourself and your own experience. Most students find they don't know what to write about when they get assigned an essay. A personal narrative doesn't require any research.
Plus, learning to tell a story about yourself and your experiences is so valuable for more than school assignments. Let's break down this type of essay, so you can learn to write a terrific one.
What is a personal narrative essay?
At the most basic level, this kind of creative writing essay recounts a personal experience with a point or lesson. it is not your entire life story, but a small slice of life that was significant.
The goal of a personal narrative is to entertain and sometimes to share wisdom or offer tribute to someone who's made a significant impact on you.
These essays are often compelling narratives of human experience, but they don't have to be about a flashy, newsworthy moment. Any life event or experience that changed you or helped you understand yourself or the world in a new way can be a terrific topic!
Why learn to write a personal narrative?
The first question I always address when I assign this type of essay is why it's even something you need to learn. At first glance, students question whether or not learning to write about themselves really matters. But it does!
Sure, you want to do well on your school assignments, and it's helpful to know that college essay applications require one or more types of personal essay for admissions.
But beyond your educational goals, learning to tell a focused story about yourself will serve you well in cover letters, interviews, and even an author biography.
Additionally, the personal narrative essay is a staple of memoir writing. If you're hoping to write a memoir, a shorter essay is perfect practice for the type of storytelling skills you need to produce a book length memoir. (And it's the type of writing you would likely produce to promote a memoir once your book is published!)
What are the key elements of a personal essay?
I tell students you need a story from your life that recounts a meaningful experience. It will be a personal experience with one central idea.
You'll likely need all the elements of good storytelling, like a main character (that will be you!) with a goal, conflict, action, a crisis, and a choice or epiphany that results in change. You'll want to use vivid details, a setting, and some dialogue when appropriate.
So here's your (very short!) personal narrative checklist:
a story from your life (think one scene or one focused experience)
the one sentence lesson or wisdom you learned from that experience
If you need help figuring out a story or deciding which one to choose, let's discuss what makes for a great essay topic.
How to choose a personal narrative topic
Many students don't feel they have anything to write about. They claim to have a boring life and can't possibly have lived anything worth an entire essay.
They're wrong.
Your life is worth writing about because you're you. No one else has had the exact same experience you have–not even if you grew up in the same household.
No one has your voice. And only you can articulate what made an encounter life-altering.
Sometimes you will get a list of narrative essay topics to choose from. Other times you have to develop your own from a life event or life lesson. But either way, you can create a short list of ideas based on the moments that matter most for you. Here are some ideas to get you started:
Tell about a moment that left a mark. It can be a physical mark, like a scar or an emotional mark—positive or negative. Think about the activity you love most. Make a list of the three most memorable moments doing that activity (could be when you first started, a time you were successful or failed, etc.) When was a time you won or lost (or felt you did), but the experience was as gratifying as the outcome?
Whatever you choose, make it something that you care about that showcases your personality, voice, or strengths. For a full set of possible personal narrative writing prompts, check out our article here.
How to start a personal narrative
Once you have an idea about the story you want to tell, along with the statement of what it meant to you (the lesson or wisdom you learned), you're ready to begin writing.
Some assignments will ask you to write an introduction. If they require it, then write one. It might start with something related to the prompt or the lesson you learned.
For example, if the prompt is “Write a personal narrative about a favorite childhood memory,” you can use words from the prompt to begin your essay. “One of my favorite childhood memories happened in [time and setting] when I learned about the [hint at lesson].”
I prefer to jump in with the story and grab the reader from the first line. In this case, it will begin more like a story, where your first job is to show us a character in a setting with a problem.
The wind whipped my coat open on the middle school activity field. It was January and if the group of kids swinging on the soccer goal post was any indication, no teachers were on duty yet. “Come play with us on the goal!,” my friend Katie shouted, as she lifted another student to grab the bar.
Notice how an opening like this is straightforward. We know where we are (middle school activity field in winter)and what the initial problem is (friends inviting me to swing on a goal that's likely against the rules).
How to organize a personal narrative essay in 8 steps
When you tell the story, you can use a simple structure to guide the writing and then finish with the lesson. Here are eight steps to guide you:
- Begin with a character (that's you!) in a setting with a problem.
- Expand by helping us see who else is there and why (use sensory details here!).
- Then show us how you try (and possibly fail) to solve the problem or reach the goal.
- Repeat the try/fail cycle as needed, and remember to tell the story using dialogue where appropriate and details to make the scene vivid to readers.
- Build to a crisis point–the moment when a decision is presented (think about what you stand to gain and lose and the cost of either choice).
- The climax is the choice or high point–show what you chose or what happened.
- The denouement is what happened as a result of your choice in the climax.
- Finish by using a few sentences to explain the significance of the experience.
How to end a personal essay
You don't have to summarize the story or repeat the lesson over and over as you finish. Connect the story to the lesson or epiphany or significance, then turn toward the purpose of the essay.
Let's say you wrote about a person who inspired you–maybe a coach from your soccer team who stayed after one game to show you how to do something you'd failed at over and over. You could close your essay with a sentence or two about what the coach taught and why it still matters today.
Coach Wall taught me so much more than dribbling that day. She taught me what it meant to persevere and showed me that failure didn't have to be final. As I approach new situations that feel overwhelming at first today, I often think back to Coach Wall and that phrase she taught me: “It's hard because it's new. Keep at it.”
Write your own personal essay
Whether you're writing for school, family, or personal fun, practicing a personal narrative is valuable storytelling practice. These are the stories our parents and grandparents tell us around the table. They are the stories we tell each other as friends.
Learn to tell a great personal story and enjoy the connections you make.
What are your best tips for personal narrative? Share in the comments .
Set the timer for fifteen minutes . Choose one of the prompts above and collect your list of ideas, including a story and lesson for each. With the time left, start writing one of the stories.
When finished, share in the Pro Practice Workshop and leave feedback for a few other writers.
Sue Weems is a writer, teacher, and traveler with an advanced degree in (mostly fictional) revenge. When she’s not rationalizing her love for parentheses (and dramatic asides), she follows a sailor around the globe with their four children, two dogs, and an impossibly tall stack of books to read. You can read more of her writing tips on her website .

Work with Sue Weems?
Award-winning instructor and writer of 20+ years, book coach, and editor. Sue Weems specializes in working with Children's, Memoir, Middle Grade, Mystery, Nonfiction, Romance, and Thriller books. Sound like a good fit for you?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Essay Writing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource begins with a general description of essay writing and moves to a discussion of common essay genres students may encounter across the curriculum. The four genres of essays (description, narration, exposition, and argumentation) are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres, also known as the modes of discourse, have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these genres and students’ need to understand and produce these types of essays. We hope these resources will help.
The essay is a commonly assigned form of writing that every student will encounter while in academia. Therefore, it is wise for the student to become capable and comfortable with this type of writing early on in her training.
Essays can be a rewarding and challenging type of writing and are often assigned either to be done in class, which requires previous planning and practice (and a bit of creativity) on the part of the student, or as homework, which likewise demands a certain amount of preparation. Many poorly crafted essays have been produced on account of a lack of preparation and confidence. However, students can avoid the discomfort often associated with essay writing by understanding some common genres.
Before delving into its various genres, let’s begin with a basic definition of the essay.
What is an essay?
Though the word essay has come to be understood as a type of writing in Modern English, its origins provide us with some useful insights. The word comes into the English language through the French influence on Middle English; tracing it back further, we find that the French form of the word comes from the Latin verb exigere , which means "to examine, test, or (literally) to drive out." Through the excavation of this ancient word, we are able to unearth the essence of the academic essay: to encourage students to test or examine their ideas concerning a particular topic.
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.
The purpose of an essay is to encourage students to develop ideas and concepts in their writing with the direction of little more than their own thoughts (it may be helpful to view the essay as the converse of a research paper). Therefore, essays are (by nature) concise and require clarity in purpose and direction. This means that there is no room for the student’s thoughts to wander or stray from his or her purpose; the writing must be deliberate and interesting.
This handout should help students become familiar and comfortable with the process of essay composition through the introduction of some common essay genres.
This handout includes a brief introduction to the following genres of essay writing:
- Expository essays
- Descriptive essays
- Narrative essays
- Argumentative (Persuasive) essays

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to approach an expository essay. An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn't about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person ("I" or "you"). The structure of your expository essay will ...
An expository essay is an essay that communicates factual information. Broadly, this type of writing is known as expository writing. Expository essays rely on different structures to communicate their positions, like compare and contrast, process essays, and analyzing cause and effect. Expository writing is one of the four main types of writing ...
An expository essay is a genre of writing that explores and explains a specific topic in a logical and straightforward manner. The main goals of expository writing are to inform the reader, explain a subject, or describe a topic in a way that is accessible and comprehensible. You're not trying to confuse or overwhelm a reader with all of your ...
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Argumentative Essay: The goal is to persuade the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific action. It's about presenting a stance and supporting it with evidence and logic. Tone and Approach: Expository Essay: It maintains a neutral and objective tone.
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Learning how to write a good expository essay is an academic writing skill that lays the foundation for the type of expository writing that's necessary for numerous professions. Explore.
Step One: Research Your Topic. An expository essay starts with research. You need to understand the topic before you write about it. You also need to understand what points the reader needs to know to comprehend the subject. The internet has been outstanding in terms of helping people get access to information.
Formatting an expository essay. The typical format for an expository essay in school is the traditional five-paragraph essay. This includes an introduction and a conclusion, with three paragraphs for the body of the paper. Most often, these three paragraphs are limited to one subtopic each. This is the basic essay format, but expository writing ...
Writing an Expository Essay. An expository essay should not be based on your personal experiences and opinions. It rather takes an objective approach. You will be expected to explain the topic in a balanced way without any personal bias. Make sure to avoid the first and second person ("I" and "You") when writing an expository essay.
1. Read Your Essay Prompt. Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following: Define and explain a concept or theory. Compare and contrast two ideas. Examine a problem and propose a solution. Describe a cause and effect relationship. Explain a step-by-step process.
2. Body paragraph. After understanding how to start an expository essay the next step is to construct substantial body paragraphs. Each body paragraph in an expository essay consists of a topic sentence, its explanation, and a transition statement. A single idea should be introduced in each paragraph.
2. Select a Topic and Narrow Down the Focus. Begin by choosing a topic that captivates your interest. Let's say you're intrigued by renewable energy sources. Focus your essay on a specific aspect, like the efficacy of solar power in mitigating environmental impact, ensuring a manageable and insightful exploration. 3.
Emphasize the 'Why' and 'How:' Explain not only 'what' but also 'why' and 'how.'. Create a personal connection: Share personal anecdotes or experiences related to your topic. Be conversational: Write in a friendly, approachable tone. End with a Call to Action: Conclude your essay by motivating readers to take action.
Cater to your audience: Tailor your language, tone, and examples to suit the preferences and background of your intended audience. Use relatable and engaging references to convey your message effectively and establish a connection with your readers. 6. Emphasize clarity: Clarity is key when it comes to expository writing.
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an expository essay: Choose a Topic. Select a topic that interests you and aligns with the purpose of an expository essay - to inform, explain, or analyze a subject. Conduct Research. Gather relevant and credible information to support your chosen topic.
An expository essay asks for a critical explanation of a specific idea, theory, or topic. Our expert tips can help you write a well-structured and informative piece.
To write an effective expository essay, research needs to be conducted on the topic to find credible sources. Then, the findings should be presented along with their own analysis to explain the research and the connections between the sources. Every essay will have three parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
de: the topic of the essay.the writer's position, opinio. , or approach to the topic.the main ideas that will develop and supp. rt the writer's position.Also note the following about the thesis statement: It appears at the end of the introductory paragraph and, in short essays, i.
Types of Expository Essays. Expository essays are a fundamental aspect of expository writing, encompassing various forms that cater to different academic requirements and personal expressions.Each type serves a unique purpose and requires a specific approach to effectively convey information and ideas.
Additionally, the personal narrative essay is a staple of memoir writing. If you're hoping to write a memoir, a shorter essay is perfect practice for the type of storytelling skills you need to produce a book length memoir. (And it's the type of writing you would likely produce to promote a memoir once your book is published!)
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.