Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Introduction to Computer
- Computer Science


What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic machine that processes raw data and outputs information. An electronic device that takes data as input and transforms it using a set of special instructions known as Programs to produce the desired output. A computer has an internal memory that stores data and instructions that are temporarily awaiting processing, as well as the intermediate result (information) before it is communicated to the recipients via the Output devices
What Does the Computer Require in Order to be Operational?
A Computer requires hardware devices and an operating system in order to be operational.
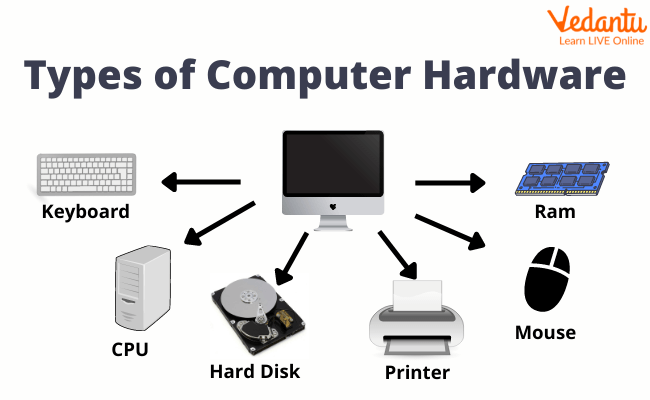
1. Hardware Devices
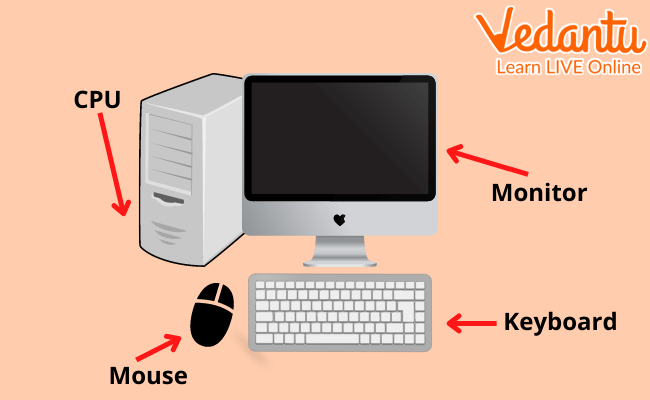
Monitor: It is a big television-like screen. It is an output device where you see what is happening on the computer.
Keyboard: It is an input device. It is a way of giving commands to a computer with the help of keys over it.
Central Processing Unit (CPU): It is a processing unit.It is considered the brain of the computer as it can’t perform any activity without CPU.
Mouse: It is an input device. This is the alternate method for cooperating with your PC. Most mice have two buttons — a right and a left button — and a looking over wheel.
Hardware Devices
2. Operating System (OS)

Operating System
PCs without an OS are precisely similar to TVs without a signal. They will turn on, yet you will be checking a clear screen out without any desire to collaborate with it. The most famous working framework is "Microsoft Windows," and it is used by most PC.
The OS acts as the sensory system of the PC, interfacing the computer processor to all the PC programs. The OS permits you to run other programs, work on projects, and do essentially all the other things that PCs are prepared to do.
There are a wide range of renditions of Microsoft Windows, and a new adaptation is delivered every several years.
How to Operate a Computer
There are three states in which a computer is at any given time.
OFF : This is precisely the exact thing it seems like: The PC is off, and no parts are running or working. The screen is dark (no pictures), there is no "humming" sound from the central processor, and the PC is inert to mouse developments or pressing keys on the keyboard.
ON : When a PC is on, you ought to see pictures on the screen, conceivably hear a "buzzing" commotion coming from the central processor and the pointer on the screen ought to answer when you move the mouse.
Rest Mode : Most PCs have a mode called "Rest," in which the PC is on, yet has expected an energy-productive, insignificant power mode. To "wake" the PC, basically move the mouse around or press the spacebar on the console, and it will "awaken" and return to the identical spot that it was at the point at which it fell asleep.
Signing on Screen
When you turn the PC on, the PC will go through a progression of mechanized undertakings before it is prepared for you to associate with it; this cycle is called "startup." This cycle will endure somewhere in the range of one and two minutes. Assuming the PC is not working accurately, you might see a blunder message during startup.
After you sign on, the PC will show what is known as your work area inside a couple of moments to a couple of moments. Here you will see a computerized portrayal of something almost identical to real-life office space, complete with a work area, documents and record organizers, and a recycling bin.
Features of Computer
Below mentioned are some of the features of a computer..
When executing mathematical computations, a computer works significantly faster and more accurately than a human.
Speed of Computer
Calculations made by computers are always accurate. Data inaccuracy or consistency might lead to errors.
A computer contains internal storage for data called main memory. Data is also stored on removable media like CDs, pen drives, and other types of secondary storage.
Computer Memory
Reliability
When given the same set of data repeatedly, a computer will consistently provide the same output, demonstrating its dependability.
The computer completes every task automatically, that is, without human interaction.

Computer Automation
Drawbacks of Computer
Although using a computer has numerous benefits, there are also risks and drawbacks. If used improperly, computers can cause a number of health problems.
The computer is emotionless.
It can't function alone. It requires somebody to work on it and give it instructions.
The computer must be supplied with each command.
No choice can be made by a computer on its own.
What is a Machine?
A machine is a tool that facilitates our job.
It helps us save time and effort.
Humans are not as productive as machines .
Machine Examples Include the Following:
For enjoyment, people use televisions.

To iron the clothes, use an iron box.
An automobile is used for transportation.
Calling is done on a mobile device.

Mobile Device
Points to Remember
Computer is an electronic machine.
The main components required for a computer are mouse, monitor and keyboard.
The CPU is also known as the “Brain” of the computer.
OS stands for operating system.
The first screen you see when it starts is called the desktop.
Learning by Doing
Choose the correct answer:.
1. Which part of the computer contains the computer's brains?
B. Keyboard
D. All of above
Write True or False
1. Windows, Linux, and Android are examples of Operating devices(True/False)
2. Keyboard is an Input device. (True/False)
Sample Questions
1. Choose the correct statement
A. Computer is an electronic machine
B. It performs arithmetic operation
C. Both A) and B)
2. What is an OS?
Ans: OS stands for operating system.The OS permits you to run other programs, work on projects, and do essentially all the other things that PCs are prepared to do.
3. List various primary parts of the computer.
1. A Motherboard
2. A CPU i.e. Central Processing Unit’
3. RAM i.e. Random Access Memory
5. Hard drives
6. Computer Mouse
The monitor, CPU, keyboard, mouse, printer, sound system, RAM, hard drive, and many other components make up the computer system's hardware. There are various operating systems in computers such as Microsoft Windows, Linux and so on.
FAQs on Introduction to Computer
1. Which OS does Apple use?
An Apple Computer is called a Macintosh (Mac). Its Operating System is OS X while other PCs use windows.
2. Do computers require the Internet to operate?
A computer does not need to access the Internet in order to run properly. The Internet is a way of connecting to other computer users. You can interface with the web utilizing a telephone line, a link association, or by utilizing a remote interfacing gadget (wi-fi). For most home PC clients, this is a paid help, however you can use the Web for free in a few public areas, similar to the library or a café. A PC will actually want to carry out most normal roles (play music, type records, alter pictures) and run programs without a Web association. Notwithstanding, to see a page or send an email, you will require a Web association.
3. What “My Computer is Possessed!” means?
“My Computer is Possessed!” It is a common misconception that computers have “a mind of their own.” In spite of the fact that PCs can play out specific assignments significantly more effectively and quicker than people (like counting, performing numerical computations, and so on), they are, eventually, machines and can't have an independent mind. Any reasonable person would agree that the PC can do nothing that you don't advise it to do.

- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Computer Fundamental Tutorial
This Computer Fundamental Tutorial covers everything from basic to advanced concepts, including computer hardware, software, operating systems, peripherals, etc. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, this tutorial is designed to enhance your computer skills and take them to the next level.

What is Computer?
The computer is a super-intelligent electronic device that can perform tasks, process information, and store data. It takes the data as an input and processes that data to perform tasks under the control of a program and produces the output. A computer is like a personal assistant that follows instructions to get things done quickly and accurately. It has memory to store information temporarily so that the computer can quickly access it when needed.
Prerequisites for Computer Fundamentals
No prerequisites or prior knowledge required to learn computer fundamentals, Hence, this article on Computer Fundamentals is designed for absolute beginners.
Computer Fundamentals Tutorial Index
In the upcoming section you will get a topic wise categories for computer fundamental. So, explore the below section to learn the fundamentals of computer fundamentals.
Introduction To Computer Fundamentals
- What are Computer Fundamentals?
- Importance of Computer Fundamentals in Digital Age
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
- Classification of Computers
- Application area of Computer
History and Evolution of Computers
- History of Computers
- The Origins of Computing
- First Generation – 1940-1956 Vacuum Tubes
- Second Generation – 1956-1963 Transistors
- Third Generation – 1964-1971 Integrated Circuits
- Fourth Generation – 1971-Present Microprocessors
- Fifth Generation – Present and Beyond Artificial Intelligence

Components of a Computer System
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory Units
Input Devices
Output devices.
- LCD Monitor
- LED Monitor
- QWERTY Keyboard
- AZERTY Keyboard
- DVORAK Keyboard
- Trackball Mouse
- Mechanical Mouse
- Optical Mouse
- Wireless Mouse
- Peripherals Devices
Computer Hardware
- Motherboard
- What are the Functions of a CPU?
- Program Execution in the CPU
- Difference Between ALU and CU
- Difference between System Unit and CPU
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- SRAM Full Form
- DRAM Full Form
- Difference between Random Access Memory (RAM) and Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM)
- Similarities of RAM and ROM
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Computer Peripherals (Keyboard, Mouse, Monitor, etc.)
Computer Software
- Introduction to Software
- Types of Software
- Application Software
- System Software
- Utility Software
- What is Keyboard?
- What is Mouse?
- What is a Joystick?
- What is a light pen?
- What is Scanner?
- What is OCR?
- What is barcode reader?
- What is WebCam?
Data Storage and Memory
- What is a Storage Device?
- Types of Data Storage
- Optical Storage
- DVD-ROM Full Form
- DVD-RAM Full Form
- DVD-R Full Form
- DVD-RW Full Form
- Flash Drives
- Memory Cards
- Cloud Storage
Computer Short Cut Key
- Computer Keyboard Shortcut Keys
- Function Keys on keyboard
- Windows Shortcut Keys
- Keyboard Shortcuts for Ubuntu |
- Most Used Shortcuts of Turbo C++
- Important Questions for Computer Keyboard Shortcuts
- Computer Memory
- Register Memory
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
Basics of Operating System
- What is Operating System?
- Evolution of Operating System
- Types of Operating Systems
- Operating System Services
- Functions of Operating System
Computer Security and Privacy
- What is Computer Security?
- Importance of Computer Security
- Common Security Threats
- Network Security Measures (Firewalls, Encryption)
- Access Control
- User Authentication
- Privacy Concerns and Data Protection
Computer Networks and Internet
- Introduction to Computer Networks
- Network Topologies (Star, Bus, Ring)
- Network Protocols (TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP)
- World Wide Web
Introduction to Programming
- What is Programming?
- A Categorical List of programming languages
- Language Processors: Assembler, Compiler and Interpreter
- Variables ( C , C++ , Java )
- Data Types ( C , C++ , Java )
- Operators ( C , C++ , Java )
- Control Structures (Conditionals, Loops)
- Functions and Procedures
Difference Between
- Difference between RAM and ROM
- Difference between Hard Disk and Floppy Disk
- Difference between CD-ROM and Magnetic Disks
- Difference between Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
- Difference between Magnetic Disk and Optical Disk
- Difference between Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD)
- Difference between CD and DVD
- Difference Between Blu-Ray and DVD
- Difference between Application Software and Utility Software
- Difference between Application Software and Operating System
- Difference between System Software and Application Software
- Difference between Barcode and QR Code
Functionalities of Computer
Any digital computer performs the following five operations:
- Step 1 − Accepts data as input.
- Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required.
- Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information.
- Step 4 − Provides the output.
- Step 5 − Have control over all the above four steps
The Evolution of Computers
A journey through the history of computers. We’ll start with the origins of computing and explore the milestones that led to the development of electronic computers.
Applications of Computer Fundamentals
- Software Development: Computer fundamentals are fundamental to software development. Understanding programming languages, algorithms, data structures, and software design principles are crucial for developing applications, websites, and software systems. It forms the basis for creating efficient and functional software solutions.
- Network Administration : Computer fundamentals are essential for network administrators. They help set up and manage computer networks, configure routers and switches, troubleshoot network issues, and ensure reliable connectivity. Knowledge of computer fundamentals enables network administrators to maintain and optimize network performance.
- Cybersecurity : Computer fundamentals are at the core of cybersecurity. Understanding the basics of computer networks, operating systems, encryption techniques, and security protocols helps professionals protect systems from cyber threats. It enables them to identify vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond effectively to security incidents.
- Data Analysis : Computer fundamentals are necessary for data analysis and data science. Knowledge of programming, statistical analysis, and database management is essential to extract insights from large datasets. Understanding computer fundamentals helps in processing and analyzing data efficiently, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : Computer fundamentals provide the foundation for AI and machine learning. Concepts such as algorithms, data structures, and statistical modelling are vital in training and developing intelligent systems. Understanding computer fundamentals allows professionals to create AI models, train them on large datasets, and apply machine learning techniques to solve complex problems.
Understanding computer fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to navigate the digital world confidently. This tutorial Computer fundamental has covered the basics of hardware, software, operating systems, and networking, providing you with a solid foundation. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refresh your knowledge, mastering these core concepts will help you use technology more effectively and prepare you for more advanced studies in computing.
Computer Fundamentals Tutorial – FAQs
Q.1 how long does it take to learn computer fundamentals .
The time required to learn computer fundamentals can vary depending on your prior knowledge and the depth of understanding you aim to achieve. With consistent effort and dedication, one can grasp the basics within a few weeks or months. However, mastering computer fundamentals is an ongoing process as technology evolves.
Q.2 Are computer fundamentals only for technical professionals?
No, computer fundamentals are not limited to technical professionals. They are beneficial for anyone who uses computers in their personal or professional life. Basic computer skills are increasingly essential in various careers and everyday tasks.
Q.3 Can I learn computer fundamentals without any prior technical knowledge?
Absolutely! Computer fundamentals are designed to be beginner-friendly. You can start learning without any prior technical knowledge. There are numerous online tutorials, courses, and resources available that cater to beginners.
Q.4 How can computer fundamentals improve my job prospects?
Computer skills are highly sought after in today’s job market. Proficiency in computer fundamentals can enhance your employability by opening up job opportunities in various industries. It demonstrates your adaptability, problem-solving abilities, and ability to work with digital tools.
Similar Reads
- Computer Subject
Please Login to comment...
Improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

COMMENTS
In the simplest terms, a computer is a machine that accepts some kind of input, performs actions and calculations according to a set of instructions, and returns the result of its calculations. All computers, regard-less of their size, purpose, or type, follow this defi nition.
A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use 1 .
A computer is an electronic machine that processes raw data and outputs information. An electronic device that takes data as input and transforms it using a set of special instructions known as Programs to produce the desired output. A computer has an internal memory that stores data and instructions that are temporarily awaiting processing, as ...
Understanding computer fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to navigate the digital world confidently. This tutorial Computer fundamental has covered the basics of hardware, software, operating systems, and networking, providing you with a solid foundation.
Covers the basics of computer hardware, software, and networking and helps students develop basic skills in using Windows and Microsoft Office, and creating web pages. Students also learn how to use computers safely, and to consider ethical issues related to computer usage.
Welcome to ITE 115 – Introduction to Computer Applications and Concepts. Computers are important tools in nearly every profession, so almost everyone can benefit by knowing how they work and how to use them. In this course, you will learn the basics of computer hardware, software, and networking.
Introduction to Computers 1 and Programming. TOPICS. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Hardware and Software. 1.4 How a Program Works. 1.5 Using Python. 1.3 How Computers Store Data. 1.1. Introduction. of the different ways that people use computers. In school, students use com-puters for tasks such as writing papers, searching for articles, s.
Learn how computer system components, such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices, interact with the operating system. Gain insight into security, hardware, and software relationships. Skills you'll gain
AN INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS. COMPILED BY HOWIE BAUM. WHAT IS A COMPUTER ? A computer is a programmable electronic machine used to store, retrieve, and process data. They are used to type documents, send e-mail, play games, browse the Internet, create presentations, event invitations, and listen to music or watch videos. Chromebook. Laptop. 3.
Introduction to Computing. elopments of the twentieth century. Like the industrial revolution of the nineteenth century, the computer and the information and communication technology built upon it have drastically changed business, culture, government and science, and have touc.