Amazon is introducing new tech to monitor shoppers in its grocery stores and share data with advertisers
- Amazon has new data tracking in its physical grocery stores to mine data on shoppers' habits.
- The company announced its Store Analytics, which will offer brands aggregated data, in a blog post .
- It will include logs on how many shoppers put a product back instead of purchasing it in-store.

Amazon has launched a new data tracking program for its physical grocery stores to mine data on shoppers' behavior, the company announced in a blog post on Wednesday .
Store Insights, rolled out to all Amazon Go and Amazon Fresh stores with the Dash Cart or Just Walk Out technology in the US, will feed data back to brands on shoppers' interests – similar to data collection on e-commerce sites. The data collection and analytics aims to provide brands insights and feedback on their promotions and advertising strategies, the company said.
Individual or disaggregated data will not be shared and customers are able to opt out of the service on the Store Insights website, according to Amazon. Data will be "stored in a secure zone in the cloud," the blog post said.
Related stories
Data tracked by the site will include how often products are taken off shelves and subsequently purchased either during the same store visit, or later on Amazon's website.
Amazon's cashierless stores themselves operate through a complex system of shopper surveillance , including AI-powered cameras that follow shoppers and weight sensors on carts. Amazon has made major investments in its cashierless stores in the US and has plans for global expansion in 2022 and 2023, according to internal documents seen by Insider .
But Amazon has also come up against privacy scandals in the past. The company's delivery van surveillance cameras closely monitor workers down to their hand movements and facial expressions, which made some workers feel paranoid.
In December, shareholders asked Amazon to audit its productivity quotas and worker surveillance systems.
Amazon did not immediately respond to Insider's request for comment.

Watch: Amazon wants to open 3,000 cashier-less grocery stores — and they'll have a major advantage over their competitors
- Main content
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

UPDATED 10:00 EDT / JANUARY 30 2020
How Amazon is solving big-data challenges with data lakes

GUEST COLUMN by Werner Vogels
Back when Jeff Bezos filled orders in his garage and drove packages to the post office himself, crunching the numbers on costs, tracking inventory and forecasting future demand was relatively simple. Fast-forward 25 years, Amazon’s retail business has more than 175 fulfillment centers worldwide with more than 250,000 full-time associates shipping millions of items per day.
Amazon’s worldwide financial operations team has the incredible task of tracking all of that data (think petabytes). At Amazon’s scale, a miscalculated metric, such as cost per unit, or delayed data can have a huge impact (think millions of dollars). The team is constantly looking for ways to get more accurate data faster.
That’s why, in 2019, they had an idea: Build a data lake that can support one of the largest logistics networks on the planet. It would later become known internally as the Galaxy data lake. The Galaxy data lake was built in 2019 and now all the various teams are working on moving their data into it.
A data lake is a centralized secure repository that allows you to store, govern, discover and share all of your structured and unstructured data at any scale. Data lakes don’t require a predefined schema, so you can process raw data without having to know what insights you might want to explore in the future. The following figure shows the key components of a data lake:
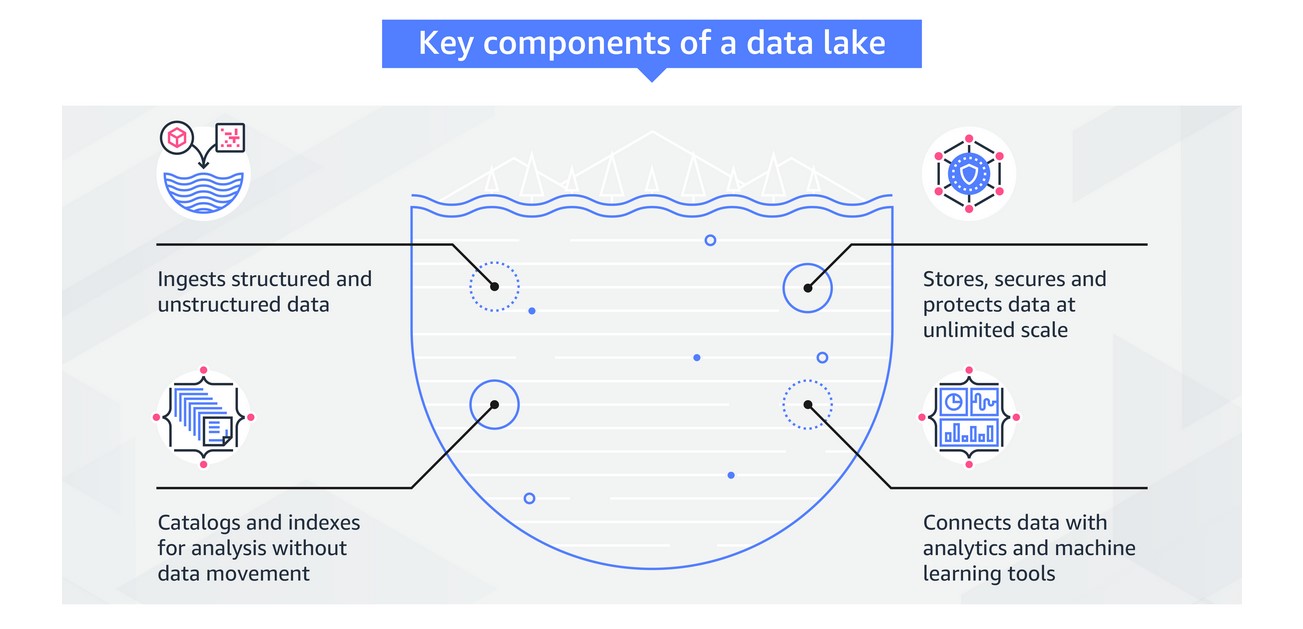
The challenges of big data
The challenges Amazon has faced with big data are similar to the challenges many other companies face: data silos, difficulty analyzing diverse datasets, data controllership, data security and incorporating machine learning. Let’s take a closer look at these challenges and see how a data lake can help solve them.
Breaking down silos
A major reason companies choose to create data lakes is to break down data silos. Having pockets of data in different places, controlled by different groups, inherently obscures data. This often happens when a company grows fast and/or acquires new businesses. In the case of Amazon, it has been both.
To expand internationally and create new shipping programs quickly (for example, free same-day delivery or Amazon Fresh ), most operations planning teams have been in control of their own data and technology. As a result, data is stored in different places and in different ways. This approach allows each team to tackle problems, respond to customer needs and innovate faster.
However, it’s harder to make sense of the data at an organizational and companywide level. It requires manual data collection from many different sources. With so many teams operating independently, we lose efficiencies that could be achieved by solving problems together.
It’s also difficult to get granular details from the data, because not everybody has access to the various data repositories. For smaller queries, you could share a cut of the data in a spreadsheet. But challenges arise when data exceeds the capacity of a spreadsheet, which often happens at larger companies. In some cases, you could share a higher-level summary of the data, but then you’re really not getting the full picture.
A data lake solves this problem by uniting all the data into one central location. Teams can continue to function as nimble units, but all roads lead back to the data lake for analytics. No more silos.
Analyzing diverse datasets
Another challenge of using different systems and approaches to data management is that the data structures and information vary. For example, Amazon Prime has data for fulfillment centers and packaged goods, while Amazon Fresh has data for grocery stores and food.
Even shipping programs differ internationally. For example, different countries sometimes have different box sizes and shapes. There’s also an increasing amount of unstructured data coming from “internet of things” devices such as sensors on fulfillment center machines.
What’s more, different systems may also have the same type of information, but it’s labeled differently. For example, in Europe, the term used is “cost per unit,” but in North America, the term used is “cost per package.” The date formats of the two terms are different. In this instance, a link needs to be made between the two labels so people analyzing the data know it refers to the same thing.
If you wanted to combine all of this data in a traditional data warehouse without a data lake, it would require a lot of data preparation and export, transform and load or ETL operations. You would have to make tradeoffs on what to keep and what to lose and continually change the structure of a rigid system.
Data lakes allow you to import any amount of data in any format because there is no predefined schema. You can even ingest data in real time. You can collect data from multiple sources and move it into the data lake in its original format. You can also build links between information that might be labeled differently but represents the same thing.
Moving all your data to a data lake also improves what you can do with a traditional data warehouse. You have the flexibility to store highly structured, frequently accessed data in a data warehouse, while also keeping up to exabytes of structured, semistructured and unstructured data in your data lake storage.
Managing data access
With data stored in so many locations, it’s difficult both to access all of it and to link to external tools for analysis. Amazon’s operations finance data are spread across more than 25 databases, with regional teams creating their own local version of datasets. That means more than 25 access management credentials for some people. Many of the databases require access management support to do things such as change profiles or reset passwords. In addition, audits and controls must be in place for each database to ensure that nobody has improper access.
With a data lake, it’s easier to get the right data to the right people at the right time. Instead of managing access for all the different locations in which data is stored, you only have to worry about one set of credentials. Data lakes have controls that allow authorized users to see, access, process or modify specific assets. Data lakes help ensure that unauthorized users are blocked from taking actions that would compromise data confidentiality and security.
Data is also stored in an open format, which makes it easier to work with different analytic services. The open format also makes it more likely for the data to be compatible with tools that don’t even exist yet. Various roles in your organization, such as data scientists, data engineers, application developers and business analysts, can access data with their choice of analytic tools and frameworks.
In short, you’re not locked in to a small set of tools, and a broader group of people can make sense of the data.
Accelerating machine learning
A data lake is a powerful foundation for machine learning and artificial intelligence), because they thrive on large, diverse datasets. Machine learning uses statistical algorithms that learn from existing data, a process called training, to make decisions about new data, a process called inference.
During training, patterns and relationships in the data are identified to build a model. The model allows you to make intelligent decisions about data it hasn’t encountered before. The more data you have the better you can train your machine learning models, resulting in improved accuracy.
One of the biggest responsibilities of Amazon’s worldwide operations finance team is planning and forecasting operating costs and capital expenditure for Amazon’s supply chain, which includes the entire transportation network, hundreds of fulfillment centers, sort centers, delivery stations, Whole Foods locations, Fresh pick-up points and more.
They help answer important high-level questions such as “How many packages will we ship next year?” and “How much will we spend on salaries?” They also address very specific questions, such as “How many boxes of each size do we need next month in Tampa, Florida?”

The more accurate your forecast is, the better. If you estimate too low or too high, it can have negative consequences that affect your customers and your bottom line.
For example, at Amazon, if we forecast demand too low, warehouse workers at a fulfillment center might not have enough supplies or there might not be enough drivers, which could lead to packages being delayed, more calls to customer service, orders being cancelled and loss of customer trust. If we forecast too high, you could have inventory and boxes sitting around taking up valuable space in a warehouse. This situation means there’s less room for products that are higher in demand.
Most organizations, like Amazon, spend a lot of time trying to predict the future. Luckily, machine learning can improve forecasts. Last year, the Amazon operations finance team did a test. They took a subset of their forecasts and compared their traditional manual process against Amazon Forecast , a fully managed service that uses machine learning to deliver highly accurate forecasts. In this trial run, the forecasts completed by Forecast were 67% more accurate on average than the forecasts completed by the manual process.
By moving all the data to a data lake, Amazon’s operations finance team can combine datasets to train and deploy more accurate models. Training machine learning models with more relevant data increases the accuracy of forecasting. In addition, it frees employees who were performing this task manually to work on more strategic projects, such as analyzing the forecasts to drive operations improvements in the field.
Using the right tools: Galaxy on AWS
Amazon’s retail business uses some technology that predates the creation of Amazon Web Services, which started in 2006. To become more scalable, efficient, performant and secure, many workloads in Amazon’s retail business have moved to AWS over the last decade. The Galaxy data lake is a critical component of a larger big-data platform known internally as Galaxy. The figure below shows some of the ways Galaxy relies on AWS and some of the AWS services it uses:
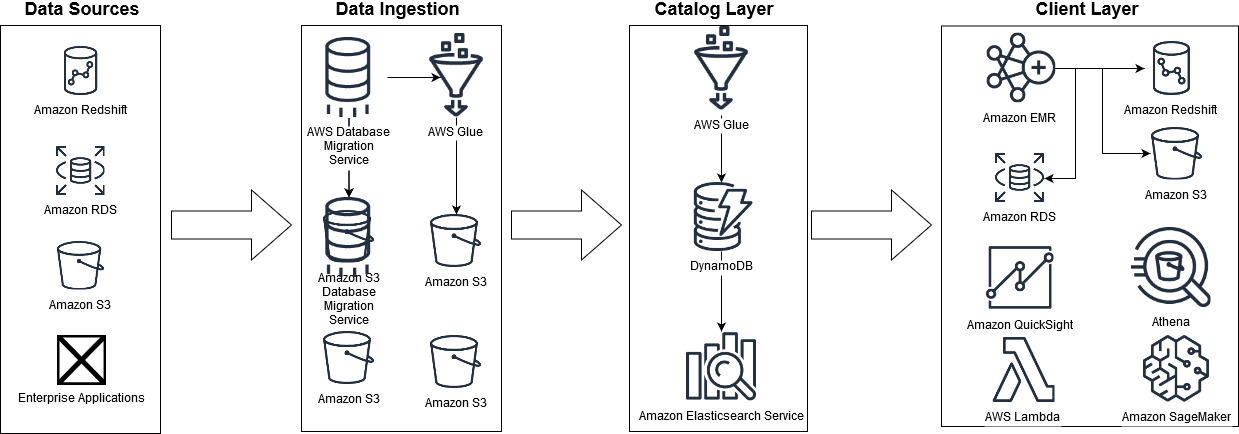
The Galaxy data lake is built on Amazon’s Simple Storage Service or S3 , an object storage service. Some data is also housed on Amazon proprietary file-based data stores, Andes and Elastic Data eXchange, both of which are service layers on top of Amazon S3. Some other data sources are data warehouse Amazon Redshift , Amazon Relational Database Service or RDS , and enterprise applications.
AWS Glue , a fully managed ETL service that makes it easy for you to prepare and load data for analytics, and AWS Database Migration Service or DMS are used to onboard the various data sets to Amazon S3. Galaxy combines metadata assets from multiple services, including Amazon Redshift, Amazon RDS and the AWS Glue Data Catalog, into a unified catalog layer built on Amazon DynamoDB , a key-value and document database. Amazon Elasticsearch Service or ES is used to enable faster search queries on the catalog.
After the data has been catalogued, or onboarded, various services are used at the client layer. For example, Amazon Athena , an interactive query service, for ad hoc exploratory queries using standard SQL; Amazon Redshift, a service for more structured queries and reporting; and Amazon SageMaker , for machine learning.
AWS Lake Formation
The Amazon team created the Galaxy data lake architecture from the ground up. They had to develop many of the components manually over months, which is similar to how other companies have had to do this in the past. In August 2019, AWS released a new service called AWS Lake Formation .
It allows you to streamline the data lake creation process and build a secure data lake in days instead of months. Lake Formation helps you collect and catalog data from databases and object storage, move the data into your new Amazon S3 data lake, clean and classify your data using machine learning algorithms, and secure access to your sensitive data.
By storing data in a unified repository in open-standards-based data formats, data lakes allow you to break down silos, use a variety of analytics services to get the most insights from your data and cost-effectively grow your storage and data processing needs over time.
For Amazon’s financial operations team, the Galaxy data lake will provide an integrated experience for its worldwide users. The infrastructure for Galaxy was built in 2019, and now the various database systems are moving into the data lake. The teams using the tool now are already seeing its benefits, citing the removal of manual processes and clunky spreadsheets, an increase in productivity and more time available for value-added analysis.
Werner Vogels is chief technology officer of Amazon.com. He wrote this guest column for SiliconANGLE. He also writes about building scalable distributed systems on his blog All Things Distributed . There’s more on AWS data lakes and analytics here and here .
Featured photo: pixel2013/Pixabay ; images: Amazon
A message from john furrier, co-founder of siliconangle:, your vote of support is important to us and it helps us keep the content free., one click below supports our mission to provide free, deep, and relevant content. , join our community on youtube, join the community that includes more than 15,000 #cubealumni experts, including amazon.com ceo andy jassy, dell technologies founder and ceo michael dell, intel ceo pat gelsinger, and many more luminaries and experts..
Like Free Content? Subscribe to follow.
LATEST STORIES

PitchBook: US venture capital deal activity hits five-year low in Q1 2024
Browser-based IDE startup Replit debuts generative AI coding assistant

Lowe's looks to Nvidia and AI to improve its retail operations

Top musicians ask for protection against AI, calling it ‘an assault on human creativity’

AWS Deadline Cloud is a new, dedicated service for cloud-based VFX rendering

Intel's stock falls after it reveals its nascent foundry business lost $7B in fiscal 2023
EMERGING TECH - BY DUNCAN RILEY . 5 HOURS AGO
AI - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 7 HOURS AGO
AI - BY ZEUS KERRAVALA . 7 HOURS AGO
AI - BY JAMES FARRELL . 8 HOURS AGO
CLOUD - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 9 HOURS AGO
INFRA - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 9 HOURS AGO
Blog > Unveiling Amazon’s Data Analytics Mastery: A Case Study
Unveiling Amazon’s Data Analytics Mastery: A Case Study
12 September , 2023
June 30th, 2023

De-Normalization and Data Integration
Unlocking the full potential of data analytics, security issues and challenges.

- inadequate security measures
- the use of untrustworthy networks
- misconfigurations in server setups.

Add a Comment
Related articles.

List of 10 best paying jobs in India
29 September , 2023

What to Expect if You Choose a Career in Business Analytics ?
3 April , 2023

How to ace an interview

Business Analytics Career : Everything You Need to Know

Digital Marketing Tips You Need to Know to Land the Best Job

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Inside Amazon’s Growth Strategy
If the key to success is focus, why does Amazon work?
- Apple Podcasts
Since Amazon started as an online retailer in 1994, it has expanded into streaming, cloud computing, content creation, and even groceries. But traditional business strategy tells us that the key to success is focus. So, why does Amazon work?
“I think in Amazon’s case, everything is very tightly connected. If you remove one part, the whole becomes less,” says Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta . “That’s the key question: are the pieces fitting together nicely, or they just happen to be another business because it’s profitable?”
Gupta has studied Amazon’s growth strategy and he tells Cold Call host Brian Kenny how Amazon looks beyond traditional industry boundaries to define their competitors and why connecting products and services with their customers is at the core of their strategy.
Key episode topics include: business models, growth strategy, operations and supply chain management, innovation, technology and analytics, online retail, customer-centricity, customer experience, competitive strategy.
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR Cold Call episode: If the Key to Business Success Is Focus, Why Does Amazon Work? (May 2019)
- Find more episodes of Cold Call .
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR On Strategy , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock new ways of doing business. Amazon started as an online retailer back in 1994. Since then, it has expanded into streaming, cloud computing, content creation, and even groceries. But if traditional business strategy tells us that the key to success is focus – why does Amazon work ? Today, we bring you a conversation with Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta – who has studied Amazon’s growth strategy. You’ll learn how Amazon builds its business around its customers — rather than its products and services. You’ll also learn how they look beyond traditional industry boundaries to define their competitors – and why connecting products and services with their customers is at the core of their strategy. This episode originally aired on Cold Call in May 2019. Here it is.
BRIAN KENNY: In the world of computer science, Jon Wainwright is kind of a big deal. A pioneer of computer languages, he was the principle architect of both Script 5 and Manuscript. What makes Jon a legend has nothing to do with programming. Let me explain. On April 3, 1995, Jon was in need of some work-related reading material. So, he fired up his T1 modem and navigated the fledgling internet to the beta version of a new online bookstore. With the click of a mouse, he became the very first customer to make a purchase on Amazon.com. Fluid Concepts and Creative Analogies, the book he purchased, never became a best seller. But Amazon took off like a rocket ship and hasn’t slowed down since. With a market cap larger than all other retailers combined, including Walmart, Amazon owns 49% of all online sales. In the time it takes me to read this introduction, the company will earn over 300,000 dollars. Will we ever see the likes of it again? Today, we’ll hear from professor Sunil Gupta, about his case entitled, “Amazon in 2017.” I’m your host Brian Kenny. You’re listening to Cold Call, part of the HBR Presents network. Sunil Gupta is an expert in the area of digital technology and its impact on consumer behavior and firm strategy. He is the author of the recently published, Driving Digital Strategy, a guide to re-imagining your business. This case is the perfect stepping off point to cover some of the ideas in that book, Sunil. Thank you for joining me today.
SUNIL GUPTA: Thank you for having me.
BRIAN KENNY: This is your second spin I think on Cold Call. We appreciate you coming back.
SUNIL GUPTA: I enjoy doing this.
BRIAN KENNY: Good, as long as it’s not too painful for you. I like having you here. I’ve had an opportunity to read the book. The case I think is really kind of a great foundational piece to launch into some of the ideas. I’m going to assume anybody listening to this podcast has purchased something on Amazon or watched something on Amazon Prime. I had forgotten about their modest beginnings and just how much they’ve grown and expanded and changed. The case was a great reminder of that. We’ll get into some of that. Let me start by asking you, just to set it up for us. What led you to write the case?
SUNIL GUPTA: As you said, everybody knows Amazon. At the same time, Amazon has become quite complex. I mean, they have gone into businesses that defy imagination. That raises the question, is Amazon spreading itself too thin? Are they an online retailer? Are they video producers? Are they now making movies? In strategy, we learn, everybody should focus. Obviously Jeff Bezos missed that class.
BRIAN KENNY: He didn’t come to HBS by the way.
SUNIL GUPTA: You sort of start wondering as to, what is the magic behind this? What is the secret sauce that makes Amazon such a huge success? The market gap almost touched a trillion dollars a few months ago.
BRIAN KENNY: Insane.
SUNIL GUPTA: That was the reason why I thought A, everybody knows about it, and B, it’s hugely successful and C, his business model seems to defy logic.
BRIAN KENNY: The case we know by the title takes place in 2017. Maybe you can just start us off by setting it up. How does the case open up?
SUNIL GUPTA: At that point in time, Amazon had just bought Whole Foods, which was very counterintuitive because Amazon has been an online player. So why is it getting into offline business? That was against his grain as an online player. The second thing is food is a very low margin category. You sort of say, Amazon is a technology company, its stock is going to stratosphere. Why buy a low margin business that Amazon actually had been trying Amazon Fresh for 10 years and hasn’t succeeded? Why don’t they give up? That was a starting point. But of course, the case describes all the other 20 different things that they have done in the last 20 years and asked the question, what is Amazon up to?
BRIAN KENNY: Amazon and Jeff Bezos are sort of synonymous. He’s a cult of personality there, kind of like Steve Jobs was with Apple. Jeff’s been in the news a lot lately for other reasons, you know, personal reasons. He is still obviously, probably one of the best known CEOs in the world. What’s he like as a leader?
SUNIL GUPTA: I don’t know him personally. Based on the research that I’ve done, he certainly is very customer obsessed. He’s focused on customer. He always says, “You start with the customer and work backwards.” He still takes evidently calls on the call center. The culture is very entrepreneurial, but also very heart driven. I mean, the idea for example of Amazon Prime evidently didn’t come from Jeff Bezos, it came from a low person in the organization. He’s quick to adapt the ideas if he sees some merit in it. It’s almost a 25-year-old company that still works like a startup.
BRIAN KENNY: Was the original concept for Amazon … I mean, I know he sold books originally. Was it ever really a book company?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think it started more as an online retailer. Book was an easy thing because everybody knows exactly what you’re buying. It’s no concern about the quality. His premise in the online store was a very clear value proposition of three things. One was convenience that you can shop in your pajamas, so we don’t have to fight the traffic of Boston or Los Angeles. The second was infinite variety. I don’t have the constraint of a physical store. Even if I have Walmart, which is a huge store, I can only stock so many things. As a result, you only have the top sellers. In Amazon, I can have the long tail of any product if you will. The third was price. It was cheaper, simply because I don’t have fixed costs of the brick and mortar store. I can reduce the cost structure and therefore I can be cheaper. Those were the three key value propositions. That’s how it started. The idea was, I’ll start with books and then move on to electronics and other things. But then of course, it moved far beyond being an online retailer.
BRIAN KENNY: This gets into some of the ideas in your book. I was really intrigued in the book about the notion of what kind of business are we in? Just that question alone. At face value, it looked like Amazon was a retailer. They went in directions that nobody could have imagined. The case really goes into some of a litany of all the things they tried.
SUNIL GUPTA: Right. Again, the purpose of the case was to illustrate as to how these are all connected. From a distance they look completely disconnected and completely lack of focus. Let’s start with how the concept evolved. The first thing was, as I said was online retailer. Very soon it became a marketplace. Now, what is a marketplace? They basically allow third party sellers also to sell on the Amazon platform, which is distinct from a traditional retailer. Walmart doesn’t allow me to set up shop within Walmart, but Amazon allows me to do that. Now, why would they do that? Simply because it increases the variety that they can sell on the platform. Therefore, consumers are quite happy with the variety of the product they can get on Amazon. Amazon gets commission without having the inventory and the capital cost. Perhaps the most important thing of becoming a platform is it creates what we call the network effects. If there are lots of products, everything I can buy is available on Amazon. More consumers are likely to go there. Because there are more consumers, more sellers are likely to go there. It just feeds in itself. More consumers mean more sellers, more sellers mean more consumers, and it becomes a virtual cycle. That’s why there is only one Amazon. Even if I start an online retail, which is in many ways better than Amazon, nobody’s coming to gupta.com, because buyers and sellers are not there. That became the next phase, change from online retailer to marketplace. Then it went into AWS, and you sort of say, “Well, how can it go into a technology company and compete with IBM and Microsoft?” It was competing with Walmart before.
BRIAN KENNY: That’s the web services division.
SUNIL GUPTA: That’s the web services. In fact, at that point in time, Wall Street was very down on that. They said, “What is Bezos thinking?” The idea again, if you think about it, it was very simple. Amazon was building this technology for its own purpose. And then, they started giving this technology, using this technology for the third party sellers, who were selling on its platform.
BRIAN KENNY: Let me just interrupt for a second. That’s a marked, a marked change in direction. They had always been a consumer platform. Now they’re in a business-to-business play. I bet a lot of consumers don’t even know about Amazon Web Services.
SUNIL GUPTA: Correct. Again, not in a traditional sense saying, “This is my market.” That’s simply saying, “I have this capability. There’s a demand for this capability. Can I do it?” Part of that was opportunistic also. If you remember in 2001, the dot.com bubble crashed. If you’re a B2C company, you hedge your bets and get into B2B business. Part of that may have been luck. That was, again, a change of direction. And then, Amazon started producing hardware, Kindle, and now competing with Apple. You sort of say, why is an online retailer getting into hardware production? If you think a little bit about it, the answer is very easy. Kindle was designed to sell eBooks as people move from buying the hard copy books to downloading the eBooks. The Kindle is the classic razor and blade strategy. I sell razors cheap in order to make money on the blades. I’m not making that much money Kindle, but I’m making money on eBooks, which is very different from Apple’s strategy. Apple actually makes money on devices, but Amazon is not making money on devices, or at least not making huge money on devices. Similarly, it moved into online streaming of the video content and suddenly became a competition on Netflix. You sort of say, “Why is a retailer becoming a competition on Netflix?” Again, if you think a little about it, the answer becomes clear. As you and I moved on to not buying DVDs, but actually streaming the stuff, that’s what Netflix did. They used to send the DVDs to us.
BRIAN KENNY: I remember that. I still have a couple.
SUNIL GUPTA: Amazon is very good in sort of moving with the customer. If the customer moved from buying books to eBooks, I move in that direction. If customers move from buying DVDs to streaming, I move in that direction. Now, can Amazon do it? Of course, they can. They have AWS. Netflix is one of the largest customers.
BRIAN KENNY: Are they leading or following? Are they creating a market? In the beginning it seemed like they created something entirely new. Now, are they anticipating, or are they just sort of reacting to what’s happening?
SUNIL GUPTA: No, it’s a combination of both. In some ways they are actually following the consumer behavior and say consumers are moving to a streaming and move with that. They were not the first ones. Netflix actually started the streaming thing. Then, they sort of come up with it. If you think about it, Amazon became not only distributing third party content on videos, but now they have Amazon Studio. I mean, they are making movies, and the competition now becomes Hollywood instead of Walmart. You sort of say, “What has gone wrong with Jeff Bezos? Why is he making movies?” Movies are pretty expensive business and highly risky. The key to that is to understand the purpose of the movies. The purpose of the movies is to hook the consumers from Amazon Prime. If you remember, Amazon Prime started with 79 dollars per year. The benefit at that time was two-day free shipping. Now, you and I are smart enough to sort of do the math in our heads saying, how many shipments do we expect next year, and is 79 dollars worth it or not? Bezos does not want you to do that math. He basically says, “Oh, by the way, I’ll throw in some free content, some free music, some free unique movies.” Now you can’t do the calculation. Why does he care about Prime? Right now, Amazon has about one hundred million Prime customers globally. Let’s say I get an average 100 dollars per year, that’s 10 billion dollars in my pocket before I open the store.
BRIAN KENNY: Right.
SUNIL GUPTA: The research also shows that Amazon Prime customers buy three to four times more than non-Prime customers. I mean, if you’re a Prime customer, you don’t even price shop.
BRIAN KENNY: Once you’re Prime, you’ve got to justify being a member. You buy everything on Amazon.
SUNIL GUPTA: Exactly. Your purchase increases. You become price sensitive, which is fantastic. In fact Jeff Bezos has gone public and say that every time we win a Golden Globe award for our content, we sell more shoes. The purpose of creating their own content is not to make money on the content. This is another different razor to sell you more shoes. Once you understand that, what looks like disparate business is actually extremely tied together.
BRIAN KENNY: It all comes right back to the core. They haven’t always had good ideas. Have they had some misses along the way too?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think the biggest failure was Fire phone.
BRIAN KENNY: Remind us what that was?
SUNIL GUPTA: Amazon launched their own phone. They were obviously very late in the market. iPhone was already there. Samsung had done very good. You have two major players, if not many others, who are very well established. Consumers love their iPhones. The question of course was, why is Amazon launching the phone? What are the odds of success? Clearly the odds of success were low. The reason to launch it was they didn’t want to be beholden to the iPhone or the Googles of the world. They know that the world is moving towards mobile, in terms of shopping, certainly in emerging markets, everybody’s moving to mobile shopping. If tomorrow Apple or Google sort of restrict the Amazon use, or availability of Amazon, because they’re all competing with each other now. It becomes a challenge. To Amazon’s credit, I mean, it’s true for all innovations. Not all innovations succeed. You’ve got to take a shot. If you think about it, all the technology and thought process that got into Fire phone, was not completely a waste. That went into Echo. Now Alexa is a big hit.
BRIAN KENNY: They’re a market leader in that in that. Let’s talk a little bit about the ideas that underlie his Amazon case. I think it starts with knowing what business you’re in. Your book addresses this. I think I know we’re in the education space here at Harvard Business School. Should we be thinking about other businesses?
SUNIL GUPTA: You’re right. The bigger question that Amazon case raises is: how do you define what business you are in? Most of us tend to define business by the traditional industry boundaries. If I’m a bank, I’m in banking and other banks are my competition. I think industry boundaries are getting blurred today. Amazon can get into banking. I have lots of customers, I can start giving loans to small and medium enterprises.
BRIAN KENNY: They know a lot about those customers.
SUNIL GUPTA: They know a lot about customers. The key asset is now customers and data, and not the product and services that you offer. Once you know about customers, you can do lots of different things. One thing is, I would say is the industry boundaries are getting blurred. You need to think about not competition, but what do customers want. Do I have capabilities to serve that? The second thing is the traditional definition of where competitive advantage comes from is changing. What I learned, in doing my MBA class many years ago, we used to read Michael Porter’s competitive strategy stuff. If I were to simplify and summarize what I learned in competitive strategy was competitive advantage comes from making your product better or cheaper. Differentiation or cost leadership, which makes sense. If you think about it, it’s very much product-focused. I think in today’s world, competitive advantage comes from connecting products and connecting customers. The Kindle and eBooks is an example of connecting products, multiple products right? Making movies of Amazon and selling more shoes is connecting products. Razor and blade have been around forever. I think what is different today is razor and blade could be in completely different industries. Movies and shoes. The other side is connecting customers. We are in a network economy. That’s why there is only one Facebook, or one WhatsApp. If you are the only person on Facebook, what’s the value of Facebook? Not much, unless you love yourself. As more and more people get onto Facebook, the value of Facebook increases. It’s not about improving product. Without changing product, Facebook value increases. I think in this connected world that we live in, it’s about connecting products and connecting consumers.
BRIAN KENNY: We’ve got a lot of listeners out there. Many of whom are probably leading firms of one kind or another. How do they even go about exploring redefining their business?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think again, you need to think about what is your key asset? Everything starts with the consumer. In the Amazon case, you move with the consumer to some extent. I asked the same of a company for a medical device manufacturer. I said, “Who’s your competition?” The typical answer is: the other medical devices. Medical business is now becoming a lot about data. Google is getting into that. Apple. iPhone is becoming a medical device. Suddenly you have a very different kind of player getting into this thing. When I say, “What business are you in?” You need to think about who might actually get into that business and that changes the whole picture.
BRIAN KENNY: Why is Amazon so good at engaging customers?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think it comes from the culture of being customer obsessed, that no matter what the customer is right. They deliver on that promise. I mean, the level of convenience that customers expect from companies has changed. It used to be, if a company delivers a product within a week, that was considered good. Now, if you don’t deliver on the same day it just seems awful. They’ve raised the bar in everything. Of course, they’re using technology very effectively, whether it’s in their warehousing, whether now they’re investing in drones. I think they’re still a 25-year-old startup.
BRIAN KENNY: That’s another point that I wanted to touch upon. They’re able to adapt their supply chain it seems almost effortlessly to whatever business direction they move in. Is it possible for another entry to come into this space and scale in the same way that Amazon has? Is this a once-in-a-lifetime type thing?
SUNIL GUPTA: That’s a tough question. I think Amazon, it’s not that they’re adapting supply chain for everything, right? For example, I don’t think Amazon supply chain is ready for delivering frozen food yet. If I have a supply chain to ship you electronics, I can use the same supply chain to ship you prescription medication. That opens up another billion dollar, several billion dollar market. If I call myself an online retailer, I will never think of prescription drug delivery. If I think of my capabilities, I have the warehouse to deliver electronics and books. Why can’t I deliver your prescription medication? That opens up completely different businesses.
BRIAN KENNY: What are the kind of pitfalls that you need to be careful of, as you start to move into adjacent markets?
SUNIL GUPTA: I think definitely the big challenge is: how far do you go? On one hand it’s good to expand the business scope because the industry boundaries are getting blurred. The danger is do you lose focus? The classic challenge of losing focus. There’s a balance. I think in Amazon’s case, if you notice, everything is very tightly connected. If you remove one part, the whole becomes less. That’s the key question: are the pieces fitting together nicely, or they just happen to be another business because it’s profitable?
BRIAN KENNY: We’ve done a couple of cases on Cold Call that touch on the organizational impact of firms that move into new businesses. Some of them are examples of where it’s benefitted the employees. In other cases, it seems to have disrupted the culture in negative ways. How do you see this playing out at Amazon? Does it impact them in any way?
SUNIL GUPTA: If you look at Amazon, it has grown the top line 20, 25% every quarter without fail, except for one quarter in 2001. Right now, it’s in 2019, their sales are 232 billion. I don’t know that many companies, which grow at that rate, even when they’re over 200 billion. I think, if you’re on a winning team, that as an employee, it has to energize you. If you are in a culture which encourages experimentation and innovation, it has to excite you. At the same time, I’m sure it’s a very demanding culture, and there have been reports about how demanding the culture of Amazon is. It probably is not for everybody. For the people who are innovative, who are entrepreneurial, who want to be on a winning team, I’m sure it’s an exciting place.
BRIAN KENNY: There are sort of shades of Apple there. I mean, I think Apple had the same reputation. You’ve discussed this case in class with students.
SUNIL GUPTA: Oh, many students.
BRIAN KENNY: What are sort of the top line things that surprise you as you discuss it?
SUNIL GUPTA: The nice thing about this case is, everybody knows Amazon as a consumer. Everybody has shopped at Amazon. It’s very easy case. In fact, it’s a very short case that I give, at the opening of most sessions. People see it as very surface level. They sort of don’t realize the deep insights that comes out. As a three page case, you sort of say, I will be done in ten minutes, but then you peel the layers of the onion. That was a shocking thing to them, as to how you peel the layers of the onion and how you see the connection across different things. Why did Amazon buy Whole Foods? It makes no sense. Why did they get into AWS? It makes no sense. When you start un-peeling that layer, you see the connection as to why Amazon is doing all these different things. I think that’s the “A-ha” moment that comes across.
BRIAN KENNY: Much more on that in your book. How’s the book doing?
SUNIL GUPTA: Book is doing great.
BRIAN KENNY: Great.
SUNIL GUPTA: Fabulous. It was released in August. I’ve been going around on tour for many, different parts of the world.
BRIAN KENNY: I bet you can buy it on Amazon.
SUNIL GUPTA: You can certainly buy it on Amazon.
BRIAN KENNY: That’s great. Sunil, thanks for joining us today.
SUNIL GUPTA: Thank you very much Brian.
HANNAH BATES: That was Harvard Business School professor Sunil Gupta – in conversation with Brian Kenny on Cold Call . If you liked this episode and want to hear more of Harvard Business School’s legendary case studies in podcast form – search for Cold Call wherever you get your podcasts. We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about business strategy from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review. We’re a production of the Harvard Business Review – if you want more articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, be sure to subscribe to HBR at HBR.org. This episode was produced by Anne Saini, Ian Fox, and me, Hannah Bates. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener. See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about business models.
- Growth strategy
- Operations and supply chain management
Partner Center

Big Data Use Case: How Amazon uses Big Data to drive eCommerce revenue

Amazon is no stranger to big data. In this big data use case, we’ll look at how Amazon is leveraging data analytic technologies to improve products and services and drive overall revenue.
Big data has changed how we interact with the world and continue strengthening its hold on businesses worldwide. New data sets can be mined, managed, and analyzed using a combination of technologies.
These applications leverage the fallacy-prone human brain with computers. If you can think of applications for machine learning to predict things, optimize systems/processes, or automatically sequence tasks – this is relevant to big data.
Amazon’s algorithm is another secret to its success. The online shop has not only made it possible to order products with just one mouse click, but it also uses personalization data combined with big data to achieve excellent conversion rates.
On this page:
Amazon and Big data
Amazon’s big data strategy, amazon collection of data and its use, big data use case: the key points.
The fascinating world of Big Data can help you gain a competitive edge over your competitors. The data collected by networks of sensors, smart meters, and other means can provide insights into customer spending behavior and help retailers better target their services and products.
RELATED: Big Data Basics: Understanding Big Data
Machine Learning (a type of artificial intelligence) processes data through a learning algorithm to spot trends and patterns while continually refining the algorithms.
Amazon is one of the world’s largest businesses, estimated to have over 310 million active customers worldwide. They recently accomplished transactions that reached a value of $90 billion. This shows the popularity of online shopping on different continents. They provide services like payments, shipping, and new ideas for their customers.
Amazon is a giant – it has its own clouds. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers individuals, companies, and governments cloud computing platforms . Amazon became interested in cloud computing after its Amazon Web Services was launched in 2003.
Amazon Web Services has expanded its business lines since then. Amazon hired some brilliant minds in the field of analytics and predictive modeling to aid in further data mining of Amazon’s massive volume of data that it has accumulated. Amazon innovates by introducing new products and strategies based on customer experience and feedback.
Big Data has assisted Amazon in ascending to the top of the e-commerce heap.
Amazon uses an anticipatory delivery model that predicts the products most likely to be purchased by its customers based on vast amounts of data.
This leads to Amazon assessing your purchase pattern and shipping things to your closest warehouse, which you may use in the future.
Amazon stores and processes as much customer and product information as possible – collecting specific information on every customer who visits its website. It also monitors the products a customer views, their shipping address, and whether or not they post reviews.
Amazon optimizes the prices on its websites by considering other factors, such as user activity, order history, rival prices, product availability, etc., providing discounts on popular items and earning a profit on less popular things using this strategy. This is how Amazon utilizes big data in its business operations.
Data science has established its preeminent place in industries and contributed to industries’ growth and improvement.
RELATED: How Artificial Intelligence Is Used for Data Analytics
Ever wonder how Amazon knows what you want before you even order it? The answer is mathematics, but you know that.
You may not know that the company has been running a data-gathering program for almost 15 years now that reaches back to the site’s earliest days.
In the quest to make every single interaction between buyers and sellers as efficient as possible, getting down to the most minute levels of detail has been essential, with data collection coming from a variety of sources – from sellers themselves and customers with apps on their phones – giving Amazon insights into every step along the way.
Voice recording by Alexa
Alexa is a speech interaction service developed by Amazon.com. It uses a cloud-based service to create voice-controlled smart devices. Through voice commands, Alexa can respond to queries, play music, read the news, and manage smart home devices such as lights and appliances.
Users may subscribe to an Alexa Voice Service (AVS) or use AWS Lambda to embed the system into other hardware and software.
You can spend all day with your microphone, smartphone, or barcode scanner recording every interaction, receipt, and voice note. But you don’t have to with tools like Amazon Echo.
With its always-on Alexa Voice Service, say what you need to add to your shopping list when you need it. It’s fast and straightforward.
Single click order
There is a big competition between companies using big data. Using big data, Amazon realized that customers might prefer alternative vendors if they experience a delay in their orders. So, Amazon has created Single click ordering.
You need to mention the address and payment method by this method. Every customer is given a time of 30 minutes to decide whether to place the order or not. After that, it is automatically determined.
Persuade Customers
Persuasive technology is a new area at Amazon. It’s an intersection of AI, UX, and the business goal of getting customers to take action at any point in the shopping journey.
One of the most significant ways Amazon utilizes data is through its recommendation engine. When a client searches for a specific item, Amazon can better anticipate other items the buyer may be interested in.
Consequently, Amazon can expedite the process of convincing a buyer to purchase the product. It is estimated that its personalized recommendation system accounts for 35 percent of the company’s annual sales.
The Amazon Assistant helps you discover new and exciting products, browse best sellers, and shop by department—there’s no place on the web with a better selection of stuff. Plus, it automatically notifies you when price drops or items you’ve been watching get marked down, so customers get the best deal possible.
Price dropping
Amazon constantly changes the price of its products by using Big data trends. On many competitor sites, the product’s price remains the same.
But Amazon has created another way to attract customers by constantly changing the price of the products. Amazon continually updates prices to deliver you the best deals.
Customers now check the site constantly that the price of the product they want can be low at any time, and they can buy it easily.
Shipping optimization
Shipping optimization by Amazon allows you to choose your preferred carrier, service options, and expected delivery time for millions of items on Amazon.com. With Shipping optimization by Amazon, you can end surprises like unexpected carrier selection, unnecessary service fees, or delays that can happen with even standard shipping.
Today, Amazon offers customers the choice to pick up their packages at over 400 U.S. locations. Whether you need one-day delivery or same-day pickup in select metro areas, Prime members can choose how fast they want to get their goods in an easy-to-use mobile app.
RELATED: Amazon Supply Chain: Understanding how Amazon’s supply chain works
Using shipping partners makes this selection possible, allowing Amazon to offer the most comprehensive selection in the industry and provide customers with multiple options for picking up their orders.
To better serve the customer, Amazon has adopted a technology that allows them to receive information from shoppers’ web browsing habits and use it to improve existing products and introduce new ones.
Amazon is only one example of a corporation that uses big data. Airbnb is another industry leader that employs big data in its operations; you can also review their case study. Below are four ways big data plays a significant role in every organization.
1. Helps you understand the market condition: Big Data assists you in comprehending market circumstances, trends, and wants, as well as your competitors, through data analysis.
It helps you to research customer interests and behaviors so that you may adjust your products and services to their requirements.
2. It helps you increase customer satisfaction: Using big data analytics, you may determine the demographics of your target audience, the products and services they want, and much more.
This information enables you to design business plans and strategies with the needs and demands of customers in mind. Customer satisfaction will grow immediately if your business strategy is based on consumer requirements.
3. Increase sales: Once you thoroughly understand the market environment and client needs, you can develop products, services, and marketing tactics accordingly. This helps you dramatically enhance your sales.
4. Optimize costs: By analyzing the data acquired from client databases, services, and internet resources, you may determine what prices benefit customers, how cost increases or decreases will impact your business, etc.
You can determine the optimal price for your items and services, which will benefit your customers and your company.
Businesses need to adapt to the ever-changing needs of their customers. Within this dynamic online marketplace, competitive advantage is often gained by those players who can adapt to market changes faster than others. Big data analytics provides that advantage.
RELATED: Top 5 Big Data Privacy Issues Businesses Must Consider
However, the sheer volume of data generated at all levels — from individual consumer click streams to the aggregate public opinions of millions of individuals — provides a considerable barrier to companies that would like to customize their offerings or efficiently interact with customers.

James joined BusinessTechWeekly.com in 2018, following a 19-year career in IT where he covered a wide range of support, management and consultancy roles across a wide variety of industry sectors. He has a broad technical knowledge base backed with an impressive list of technical certifications. with a focus on applications, cloud and infrastructure.
Deep Web vs Dark Web vs Shadow Web: What are the differences?
Measuring Training ROI: Techniques and Tools for Effective Evaluation
Securing your Organization with a Business Firewall
Optimizing Development: Implementing an Efficient DevOps Workflow
The Pros and Cons of Chatbots for Online Customer Service
What are the risks of dropshipping, and how do you avoid them?
The Integration of Digital Business Models: The Amazon Case Study
- First Online: 21 May 2022
Cite this chapter

- Carlo Bagnoli 10 ,
- Andrea Albarelli 11 ,
- Stefano Biazzo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3373-2964 12 ,
- Gianluca Biotto 13 ,
- Giuseppe Roberto Marseglia 14 ,
- Maurizio Massaro ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6461-2709 15 ,
- Matilde Messina 13 ,
- Antonella Muraro 16 &
- Luca Troiano 17
Part of the book series: Future of Business and Finance ((FBF))
1872 Accesses
5 Altmetric
The final chapter involves the description of the Amazon case study. The intention is to reconnect the various categorizations illustrated in the previous chapter to a real-world example for the purpose of presenting a successful case of business disruption as Amazon is known to have disrupted retail. The analysis aims at highlighting the fact that Amazon combines all the business model frameworks described in the preceding chapters as well as investigating their coexistence within a single organization.
The present chapter also explains a few methodologies which have been developed in order to guide companies through the process of disrupting their existing business models and facilitating the shift towards an innovative framework. Digital technologies can ease the above-mentioned transition as firms are required to select the technological advancements enabling them to accomplish particular organizational goals.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Stone, B. (2014). Vendere tutto. Jeff Bezos e l’era di Amazon . Hoepli.
Google Scholar
Forbes. (2021). Amazon non è immortale. E il declino potrebbe essere già cominciato . https://forbes.it/2021/10/04/amazon-non-immortale-potrebbe-avere-gia-iniziato-declino/
Bishop, T. (2013). Bezos: 3D printing “exciting” but not disruptive for Amazon in short term . GeekWire.
Battistella, C., Biotto, G., & De Toni, A. F. (2021). From design driven innovation to meaning strategy. Management Decision, 50 (4), 718–743.
Article Google Scholar
Bagnoli, C., et al. (2018). Business Model 4.0. I modelli di business vincenti per le imprese italiane nella quarta rivoluzione industriale . Edizioni Ca’ Foscari.
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Management, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Venice, Italy
Carlo Bagnoli
Department of Environmental Sciences, Informatics and Statistics, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Mestre, Venice, Italy
Andrea Albarelli
Department of Management and Engineering, University of Padua, Padua, Italy
Stefano Biazzo
Strategy Innovation S.r.l., Venice, Italy
Gianluca Biotto & Matilde Messina
University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy
Giuseppe Roberto Marseglia
Maurizio Massaro
Avanade Italy S.r.l., Milan, Italy
Antonella Muraro
Zeb Consulting S.r.l., Milan, Italy
Luca Troiano
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carlo Bagnoli .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Bagnoli, C. et al. (2022). The Integration of Digital Business Models: The Amazon Case Study. In: Digital Business Models for Industry 4.0. Future of Business and Finance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97284-4_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97284-4_4
Published : 21 May 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-97283-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-97284-4
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- > Big Data
How Amazon uses Big Data?
- Ritesh Pathak
- Nov 03, 2020
- Updated on: May 06, 2021
.jpg)
Amazon is a well-known name to all of us. It is among the leading e-Commerce platforms. Apart from offering online shopping, Amazon serves us with its different services like Amazon Pay, Amazon Pantry, Amazon Web Services (AWS) , and many more. For a company like Amazon, the amount of data collected on a regular basis is very big. To manage such large amounts of data companies leverage big data technology.
For any company, one of the most valuable assets is its customer base because it is the customer who turns a company into a brand, and if a company fails to meet the expectations of its customers, that probably leads to its decline.
Big data is a technology that helps in the management of large amounts of data . In today’s times when almost everything has become digital, data collection is also being digitized. Data for a company refers to every crucial information the company possesses about its customers, market insights, and even its competitors’ marketing strategies. All these data are analyzed and worked upon to form strategies accordingly.
Amazon leverages its data via its recommendation engine. Everytime a user searches for a specific product, this data helps the platform to guess what else the user can have interest in. This in turn allows Amazon to enhance their procedure of convincing the consumer into purchasing it.
Amazon collects individual data regarding each of its customers as they make use of the website. Additionally to what the customer purchases, Amazon also keeps track of what items were viewed, the shipping address of the users and the reviews left by the user. Big Data has greatly played a role in making Amazon a leading e-commerce platform. The inventory is tracked through the manufacturers for ensuring that the orders are executed fast. Big Data enables the warehouse nearest to the user to be chosen, reducing the shipping expenses considerably.
So, in this blog, we will discuss the use of Big Data in Amazon. We will look at the ways it is doing it. At first, we should briefly recall big data analytics.
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data is a term that is applied to datasets whose size or type is way complex than traditional data sets and is beyond the ability of traditional relational databases to capture, manage, and process with efficiency. Nowadays, since the introduction of new technologies like Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things , mobile applications, and the web, the amount and complexity of data has increased.
Now, talking about Big Data Analytics , it means to analyze diverse and large data sets that are structured, semi-structured, and unstructured with the help of advanced analytics techniques. Analysis of big data allows analysts, researchers, and business users to make better and faster decisions using data that was previously inaccessible or unusable.
Now, having understood the relevant terms, we should move to the main part of the blog i.e. how Amazon uses big data analytics?
5 Ways in which Amazon Uses Big Data for Monitoring
Amazon is a leader in collecting, storing, processing and analyzing personal information from every customer as a means of determining how customers are spending their money. The company uses predictive analytics for targeted marketing which helps them in increasing customer satisfaction and get loyalty in return. Let’s have a look at how they do it?
Alexa Voice Recordings
Amazon offers virtual assistants such as Echo and Echo Show, which include a camera as well as speakers. We use it for several purposes like getting weather updates, daily news, or ordering shampoo and these are all a voice command away.
However, we may not realize that these audio recordings are being uploaded to Amazon’s servers. The company says that these voice files help make the Alexa experience better. It helps by enabling better speech recognition from a diverse group of customers and hence accurate message processing as well as functioning.
Amazon’s Alexa- a smart home solution
However, for some customers, this may be a privacy concern. For such customers, who are not comfortable with their voice recordings being stored in the cloud, they can delete them one by one or by data range, using the Alexa enabled assistant.
Personalized Recommendation System
Amazon is a leader in using a comprehensive, collaborative filtering engine (CFE). The company follows the concept of behavioral analytics . It analyzes the purchasing patterns of the customers from the previously purchased items, items in the shopping cart or on their wishlist, the products reviewed and rated by them, to most searched products.
This information is then used to recommend additional products that other customers purchased when buying those same items. For example, if a customer adds a mobile phone to its shopping cart, mobile cases are recommended for purchase.
In this way, Amazon’s big data uses the power of suggestion to encourage impulsive purchases from a customer and further enhance the whole shopping experience. This seems to pretty much work for the company as it generates 35% of its annual sales using this method.
One-Click Ordering
Since there is so much competition out there, Big data shows that a customer starts looking for alternatives if there is a delay in the delivery period. This compelled Amazon to come up with something like One-Click ordering. One-Click ordering is a patented feature that is automatically enabled when a person places its first order and enters a shipping address and a payment method. If someone chooses One-Click ordering, he/she has 30 minutes to decide on the purchase. After that, the product is automatically charged via the added payment method and shipped to the added address.
Anticipatory Shipping Model
Amazon's licensed anticipatory delivery model additionally utilizes large information for anticipating the items a customer is probably going to buy, when he/she may get them, and where he/she may require the items. The things are shipped off a neighborhood circulation focus or stockroom so they will be prepared for transportation once the customer requests them.
Amazon utilizes prescient examination to expand its item deals and net revenues while diminishing its conveyance time and general expenses.
Book Recommendations from Kindle Highlighting
After acquiring Goodreads in 2013, Amazon integrated the social networking service of roughly 25 million users with some Kindle functions. This enabled the users to highlight words and notes and also to share them among their peers as a means to discuss the book. The company benefited from this in a way that it could regularly monitor the highlighted words in Kindle to know about the interest of the readers. They further used this data to recommend ebooks to their customers and also to enhance the reading experience.
So, these were the ways in which Amazon uses big data to monitor us. Now, we will look at some ways they implement it.
Referred blog: Big Data Applications
“In retail, while things like the size of the catalogue, advertising and other stuff might play a role in success, at Amazon, I think success is largely technology driven,” - Werner Vogels, Chief Technology Officer, Amazon
How Amazon implements big data ?
After collecting crucial information about the consumers, Amazon uses those insights to better serve them. Let’s see how?

Supply Chain Optimization
When it comes to increasing efficiency, Supply Chain Optimization is the best way to achieve it. Amazon wants to fulfill the orders quickly and to achieve this feat the company connects with the manufacturers and tracks their inventories. Amazon’s big data analyzes the available data and locates the closest warehouse to a customer/vendor to reduce the shipping costs. Additionally, graph theory helps in deciding the best delivery schedule, route, and product groupings which further reduces the shipping expenses.
Recommended blog - Supply Chain Management
Price Optimization
Big Data is also used to manage the prices of products to attract more customers and eventually increase the net profit. Before Big Data was used in price optimization, products’ prices remained unchanged irrespective of the frequency on the website. Now, prices change frequently. One of the reasons is because big data platforms assess a person’s willingness to buy.
Prices are set according to your activity on the website, competitors’ pricing, product availability, item preferences, order history, expected profit margin, and other factors. Product prices generally change every 10 minutes as big data is updated and analyzed. As a result, Amazon typically offers discounts on best-selling items and earns larger profits on less popular items. This benefited the company in increasing their annual income by 143% from 2016 to 2019, according to a report .
To screen purchases and return requests for signs of fraud
Being a leader in the e-commerce market, there remains a risk of retail fraud with the company. To avoid this, the company collects thousands of historical and real-time data points on every order and uses machine learning algorithms to find transactions with an elevated likelihood of being fraudulent.
Because of Amazon's proactive methodology, and huge information calculations changed to address exact issues, the organization can likewise examine dubious bring requests back.
For instance, if enormous information shows an individual has returned a bizarrely high amount of products in the course of recent months, the organization may explore further. In 2018, some long-term clients announced getting restricted for making what Amazon esteemed an excessive number of returns.
To encourage people to buy more with each order
Amazon’s product recommendations are the most familiar application of big data to its users and, as it is mentioned above, they also use it to collect insights. Later, it is made to work by presenting users with related items based on things already in their carts and previously purchased products.
Personalized shopping experience on Amazon
With the arrival of Amazon Personalize, the organization facilitated developers with a simple-to-utilize and profoundly versatile stage that offers proposals to clients across almost any area. Different organizations could take advantage of Amazon's innovation for their clients, giving them stock choices going from garments, food and that's only the tip of the iceberg.
At the point when Amazon can effectively engage clients with customized picks and make them need to spend more, organization benefits rise and individuals get the recognition that Amazon is where they can purchase basically anything they may require.
To change and modify physical stores
Amazon Go, the brand's cashier-less accommodation store brand, likewise vigorously depends on information to work. Sensors identify which things individuals get to purchase, and cameras guarantee customers don't prevail with shoplifting endeavors. Despite the fact that the organization has not really expounded on the information it gathers about Amazon Go customers and why, it's feasible the firm would utilize the information to improve its stores.
Recommended blog - Hive Big Data
For instance, if cameras indicated individuals with child buggies experienced difficulty exploring the walkways, Amazon may make them more extensive. Then again, if deals that demonstrated vegetarian amicable things sell particularly quickly in a particular locale, it may arrange a greater amount of those items to coordinate client needs.
So, these were the ways in which Amazon is collecting and implementing big data to drive more customer traffic. The process of data collection starts right from the moment a person navigates the website. Nowadays, we can see it happening so often. We search for a product on the platform and its ads start to come before us at every possible place.
Technology is changing the dynamics of everything and businesses are no exception. Amazon is a giant in the e-commerce platform and now we know the reason, wise use of technology.
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Scope of Managerial Economics
Different Types of Research Methods
Latest Comments
magretpaul6
I recently recovered back about 145k worth of Usdt from greedy and scam broker with the help of Mr Koven Gray a binary recovery specialist, I am very happy reaching out to him for help, he gave me some words of encouragement and told me not to worry, few weeks later I was very surprise of getting my lost fund in my account after losing all hope, he is really a blessing to this generation, and this is why I’m going to recommend him to everyone out there ready to recover back their lost of stolen asset in binary option trade. Contact him now via email at [email protected] or WhatsApp +1 218 296 6064.
It's really good article, I got here i am expecting points. Thank you Visit our socks online shopping website www.eazybuy.com
10 Real World Data Science Case Studies Projects with Example
Top 10 Data Science Case Studies Projects with Examples and Solutions in Python to inspire your data science learning in 2023.

BelData science has been a trending buzzword in recent times. With wide applications in various sectors like healthcare , education, retail, transportation, media, and banking -data science applications are at the core of pretty much every industry out there. The possibilities are endless: analysis of frauds in the finance sector or the personalization of recommendations on eCommerce businesses. We have developed ten exciting data science case studies to explain how data science is leveraged across various industries to make smarter decisions and develop innovative personalized products tailored to specific customers.

Walmart Sales Forecasting Data Science Project
Downloadable solution code | Explanatory videos | Tech Support
Table of Contents
Data science case studies in retail , data science case study examples in entertainment industry , data analytics case study examples in travel industry , case studies for data analytics in social media , real world data science projects in healthcare, data analytics case studies in oil and gas, what is a case study in data science, how do you prepare a data science case study, 10 most interesting data science case studies with examples.

So, without much ado, let's get started with data science business case studies !
With humble beginnings as a simple discount retailer, today, Walmart operates in 10,500 stores and clubs in 24 countries and eCommerce websites, employing around 2.2 million people around the globe. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2021, Walmart's total revenue was $559 billion showing a growth of $35 billion with the expansion of the eCommerce sector. Walmart is a data-driven company that works on the principle of 'Everyday low cost' for its consumers. To achieve this goal, they heavily depend on the advances of their data science and analytics department for research and development, also known as Walmart Labs. Walmart is home to the world's largest private cloud, which can manage 2.5 petabytes of data every hour! To analyze this humongous amount of data, Walmart has created 'Data Café,' a state-of-the-art analytics hub located within its Bentonville, Arkansas headquarters. The Walmart Labs team heavily invests in building and managing technologies like cloud, data, DevOps , infrastructure, and security.

Walmart is experiencing massive digital growth as the world's largest retailer . Walmart has been leveraging Big data and advances in data science to build solutions to enhance, optimize and customize the shopping experience and serve their customers in a better way. At Walmart Labs, data scientists are focused on creating data-driven solutions that power the efficiency and effectiveness of complex supply chain management processes. Here are some of the applications of data science at Walmart:
i) Personalized Customer Shopping Experience
Walmart analyses customer preferences and shopping patterns to optimize the stocking and displaying of merchandise in their stores. Analysis of Big data also helps them understand new item sales, make decisions on discontinuing products, and the performance of brands.
ii) Order Sourcing and On-Time Delivery Promise
Millions of customers view items on Walmart.com, and Walmart provides each customer a real-time estimated delivery date for the items purchased. Walmart runs a backend algorithm that estimates this based on the distance between the customer and the fulfillment center, inventory levels, and shipping methods available. The supply chain management system determines the optimum fulfillment center based on distance and inventory levels for every order. It also has to decide on the shipping method to minimize transportation costs while meeting the promised delivery date.
Here's what valued users are saying about ProjectPro

Gautam Vermani
Data Consultant at Confidential

Graduate Research assistance at Stony Brook University
Not sure what you are looking for?
iii) Packing Optimization
Also known as Box recommendation is a daily occurrence in the shipping of items in retail and eCommerce business. When items of an order or multiple orders for the same customer are ready for packing, Walmart has developed a recommender system that picks the best-sized box which holds all the ordered items with the least in-box space wastage within a fixed amount of time. This Bin Packing problem is a classic NP-Hard problem familiar to data scientists .
Whenever items of an order or multiple orders placed by the same customer are picked from the shelf and are ready for packing, the box recommendation system determines the best-sized box to hold all the ordered items with a minimum of in-box space wasted. This problem is known as the Bin Packing Problem, another classic NP-Hard problem familiar to data scientists.
Here is a link to a sales prediction data science case study to help you understand the applications of Data Science in the real world. Walmart Sales Forecasting Project uses historical sales data for 45 Walmart stores located in different regions. Each store contains many departments, and you must build a model to project the sales for each department in each store. This data science case study aims to create a predictive model to predict the sales of each product. You can also try your hands-on Inventory Demand Forecasting Data Science Project to develop a machine learning model to forecast inventory demand accurately based on historical sales data.
Get Closer To Your Dream of Becoming a Data Scientist with 70+ Solved End-to-End ML Projects
Amazon is an American multinational technology-based company based in Seattle, USA. It started as an online bookseller, but today it focuses on eCommerce, cloud computing , digital streaming, and artificial intelligence . It hosts an estimate of 1,000,000,000 gigabytes of data across more than 1,400,000 servers. Through its constant innovation in data science and big data Amazon is always ahead in understanding its customers. Here are a few data analytics case study examples at Amazon:
i) Recommendation Systems
Data science models help amazon understand the customers' needs and recommend them to them before the customer searches for a product; this model uses collaborative filtering. Amazon uses 152 million customer purchases data to help users to decide on products to be purchased. The company generates 35% of its annual sales using the Recommendation based systems (RBS) method.
Here is a Recommender System Project to help you build a recommendation system using collaborative filtering.
ii) Retail Price Optimization
Amazon product prices are optimized based on a predictive model that determines the best price so that the users do not refuse to buy it based on price. The model carefully determines the optimal prices considering the customers' likelihood of purchasing the product and thinks the price will affect the customers' future buying patterns. Price for a product is determined according to your activity on the website, competitors' pricing, product availability, item preferences, order history, expected profit margin, and other factors.
Check Out this Retail Price Optimization Project to build a Dynamic Pricing Model.
iii) Fraud Detection
Being a significant eCommerce business, Amazon remains at high risk of retail fraud. As a preemptive measure, the company collects historical and real-time data for every order. It uses Machine learning algorithms to find transactions with a higher probability of being fraudulent. This proactive measure has helped the company restrict clients with an excessive number of returns of products.
You can look at this Credit Card Fraud Detection Project to implement a fraud detection model to classify fraudulent credit card transactions.
New Projects
Let us explore data analytics case study examples in the entertainment indusry.
Ace Your Next Job Interview with Mock Interviews from Experts to Improve Your Skills and Boost Confidence!
Netflix started as a DVD rental service in 1997 and then has expanded into the streaming business. Headquartered in Los Gatos, California, Netflix is the largest content streaming company in the world. Currently, Netflix has over 208 million paid subscribers worldwide, and with thousands of smart devices which are presently streaming supported, Netflix has around 3 billion hours watched every month. The secret to this massive growth and popularity of Netflix is its advanced use of data analytics and recommendation systems to provide personalized and relevant content recommendations to its users. The data is collected over 100 billion events every day. Here are a few examples of data analysis case studies applied at Netflix :
i) Personalized Recommendation System
Netflix uses over 1300 recommendation clusters based on consumer viewing preferences to provide a personalized experience. Some of the data that Netflix collects from its users include Viewing time, platform searches for keywords, Metadata related to content abandonment, such as content pause time, rewind, rewatched. Using this data, Netflix can predict what a viewer is likely to watch and give a personalized watchlist to a user. Some of the algorithms used by the Netflix recommendation system are Personalized video Ranking, Trending now ranker, and the Continue watching now ranker.
ii) Content Development using Data Analytics
Netflix uses data science to analyze the behavior and patterns of its user to recognize themes and categories that the masses prefer to watch. This data is used to produce shows like The umbrella academy, and Orange Is the New Black, and the Queen's Gambit. These shows seem like a huge risk but are significantly based on data analytics using parameters, which assured Netflix that they would succeed with its audience. Data analytics is helping Netflix come up with content that their viewers want to watch even before they know they want to watch it.
iii) Marketing Analytics for Campaigns
Netflix uses data analytics to find the right time to launch shows and ad campaigns to have maximum impact on the target audience. Marketing analytics helps come up with different trailers and thumbnails for other groups of viewers. For example, the House of Cards Season 5 trailer with a giant American flag was launched during the American presidential elections, as it would resonate well with the audience.
Here is a Customer Segmentation Project using association rule mining to understand the primary grouping of customers based on various parameters.
Get FREE Access to Machine Learning Example Codes for Data Cleaning , Data Munging, and Data Visualization
In a world where Purchasing music is a thing of the past and streaming music is a current trend, Spotify has emerged as one of the most popular streaming platforms. With 320 million monthly users, around 4 billion playlists, and approximately 2 million podcasts, Spotify leads the pack among well-known streaming platforms like Apple Music, Wynk, Songza, amazon music, etc. The success of Spotify has mainly depended on data analytics. By analyzing massive volumes of listener data, Spotify provides real-time and personalized services to its listeners. Most of Spotify's revenue comes from paid premium subscriptions. Here are some of the examples of case study on data analytics used by Spotify to provide enhanced services to its listeners:
i) Personalization of Content using Recommendation Systems
Spotify uses Bart or Bayesian Additive Regression Trees to generate music recommendations to its listeners in real-time. Bart ignores any song a user listens to for less than 30 seconds. The model is retrained every day to provide updated recommendations. A new Patent granted to Spotify for an AI application is used to identify a user's musical tastes based on audio signals, gender, age, accent to make better music recommendations.
Spotify creates daily playlists for its listeners, based on the taste profiles called 'Daily Mixes,' which have songs the user has added to their playlists or created by the artists that the user has included in their playlists. It also includes new artists and songs that the user might be unfamiliar with but might improve the playlist. Similar to it is the weekly 'Release Radar' playlists that have newly released artists' songs that the listener follows or has liked before.
ii) Targetted marketing through Customer Segmentation
With user data for enhancing personalized song recommendations, Spotify uses this massive dataset for targeted ad campaigns and personalized service recommendations for its users. Spotify uses ML models to analyze the listener's behavior and group them based on music preferences, age, gender, ethnicity, etc. These insights help them create ad campaigns for a specific target audience. One of their well-known ad campaigns was the meme-inspired ads for potential target customers, which was a huge success globally.
iii) CNN's for Classification of Songs and Audio Tracks
Spotify builds audio models to evaluate the songs and tracks, which helps develop better playlists and recommendations for its users. These allow Spotify to filter new tracks based on their lyrics and rhythms and recommend them to users like similar tracks ( collaborative filtering). Spotify also uses NLP ( Natural language processing) to scan articles and blogs to analyze the words used to describe songs and artists. These analytical insights can help group and identify similar artists and songs and leverage them to build playlists.
Here is a Music Recommender System Project for you to start learning. We have listed another music recommendations dataset for you to use for your projects: Dataset1 . You can use this dataset of Spotify metadata to classify songs based on artists, mood, liveliness. Plot histograms, heatmaps to get a better understanding of the dataset. Use classification algorithms like logistic regression, SVM, and Principal component analysis to generate valuable insights from the dataset.
Explore Categories
Below you will find case studies for data analytics in the travel and tourism industry.
Airbnb was born in 2007 in San Francisco and has since grown to 4 million Hosts and 5.6 million listings worldwide who have welcomed more than 1 billion guest arrivals in almost every country across the globe. Airbnb is active in every country on the planet except for Iran, Sudan, Syria, and North Korea. That is around 97.95% of the world. Using data as a voice of their customers, Airbnb uses the large volume of customer reviews, host inputs to understand trends across communities, rate user experiences, and uses these analytics to make informed decisions to build a better business model. The data scientists at Airbnb are developing exciting new solutions to boost the business and find the best mapping for its customers and hosts. Airbnb data servers serve approximately 10 million requests a day and process around one million search queries. Data is the voice of customers at AirBnB and offers personalized services by creating a perfect match between the guests and hosts for a supreme customer experience.
i) Recommendation Systems and Search Ranking Algorithms
Airbnb helps people find 'local experiences' in a place with the help of search algorithms that make searches and listings precise. Airbnb uses a 'listing quality score' to find homes based on the proximity to the searched location and uses previous guest reviews. Airbnb uses deep neural networks to build models that take the guest's earlier stays into account and area information to find a perfect match. The search algorithms are optimized based on guest and host preferences, rankings, pricing, and availability to understand users’ needs and provide the best match possible.
ii) Natural Language Processing for Review Analysis
Airbnb characterizes data as the voice of its customers. The customer and host reviews give a direct insight into the experience. The star ratings alone cannot be an excellent way to understand it quantitatively. Hence Airbnb uses natural language processing to understand reviews and the sentiments behind them. The NLP models are developed using Convolutional neural networks .
Practice this Sentiment Analysis Project for analyzing product reviews to understand the basic concepts of natural language processing.
iii) Smart Pricing using Predictive Analytics
The Airbnb hosts community uses the service as a supplementary income. The vacation homes and guest houses rented to customers provide for rising local community earnings as Airbnb guests stay 2.4 times longer and spend approximately 2.3 times the money compared to a hotel guest. The profits are a significant positive impact on the local neighborhood community. Airbnb uses predictive analytics to predict the prices of the listings and help the hosts set a competitive and optimal price. The overall profitability of the Airbnb host depends on factors like the time invested by the host and responsiveness to changing demands for different seasons. The factors that impact the real-time smart pricing are the location of the listing, proximity to transport options, season, and amenities available in the neighborhood of the listing.
Here is a Price Prediction Project to help you understand the concept of predictive analysis which is widely common in case studies for data analytics.
Uber is the biggest global taxi service provider. As of December 2018, Uber has 91 million monthly active consumers and 3.8 million drivers. Uber completes 14 million trips each day. Uber uses data analytics and big data-driven technologies to optimize their business processes and provide enhanced customer service. The Data Science team at uber has been exploring futuristic technologies to provide better service constantly. Machine learning and data analytics help Uber make data-driven decisions that enable benefits like ride-sharing, dynamic price surges, better customer support, and demand forecasting. Here are some of the real world data science projects used by uber:
i) Dynamic Pricing for Price Surges and Demand Forecasting
Uber prices change at peak hours based on demand. Uber uses surge pricing to encourage more cab drivers to sign up with the company, to meet the demand from the passengers. When the prices increase, the driver and the passenger are both informed about the surge in price. Uber uses a predictive model for price surging called the 'Geosurge' ( patented). It is based on the demand for the ride and the location.
ii) One-Click Chat
Uber has developed a Machine learning and natural language processing solution called one-click chat or OCC for coordination between drivers and users. This feature anticipates responses for commonly asked questions, making it easy for the drivers to respond to customer messages. Drivers can reply with the clock of just one button. One-Click chat is developed on Uber's machine learning platform Michelangelo to perform NLP on rider chat messages and generate appropriate responses to them.
iii) Customer Retention
Failure to meet the customer demand for cabs could lead to users opting for other services. Uber uses machine learning models to bridge this demand-supply gap. By using prediction models to predict the demand in any location, uber retains its customers. Uber also uses a tier-based reward system, which segments customers into different levels based on usage. The higher level the user achieves, the better are the perks. Uber also provides personalized destination suggestions based on the history of the user and their frequently traveled destinations.
You can take a look at this Python Chatbot Project and build a simple chatbot application to understand better the techniques used for natural language processing. You can also practice the working of a demand forecasting model with this project using time series analysis. You can look at this project which uses time series forecasting and clustering on a dataset containing geospatial data for forecasting customer demand for ola rides.
Explore More Data Science and Machine Learning Projects for Practice. Fast-Track Your Career Transition with ProjectPro
7) LinkedIn
LinkedIn is the largest professional social networking site with nearly 800 million members in more than 200 countries worldwide. Almost 40% of the users access LinkedIn daily, clocking around 1 billion interactions per month. The data science team at LinkedIn works with this massive pool of data to generate insights to build strategies, apply algorithms and statistical inferences to optimize engineering solutions, and help the company achieve its goals. Here are some of the real world data science projects at LinkedIn:
i) LinkedIn Recruiter Implement Search Algorithms and Recommendation Systems
LinkedIn Recruiter helps recruiters build and manage a talent pool to optimize the chances of hiring candidates successfully. This sophisticated product works on search and recommendation engines. The LinkedIn recruiter handles complex queries and filters on a constantly growing large dataset. The results delivered have to be relevant and specific. The initial search model was based on linear regression but was eventually upgraded to Gradient Boosted decision trees to include non-linear correlations in the dataset. In addition to these models, the LinkedIn recruiter also uses the Generalized Linear Mix model to improve the results of prediction problems to give personalized results.
ii) Recommendation Systems Personalized for News Feed
The LinkedIn news feed is the heart and soul of the professional community. A member's newsfeed is a place to discover conversations among connections, career news, posts, suggestions, photos, and videos. Every time a member visits LinkedIn, machine learning algorithms identify the best exchanges to be displayed on the feed by sorting through posts and ranking the most relevant results on top. The algorithms help LinkedIn understand member preferences and help provide personalized news feeds. The algorithms used include logistic regression, gradient boosted decision trees and neural networks for recommendation systems.
iii) CNN's to Detect Inappropriate Content
To provide a professional space where people can trust and express themselves professionally in a safe community has been a critical goal at LinkedIn. LinkedIn has heavily invested in building solutions to detect fake accounts and abusive behavior on their platform. Any form of spam, harassment, inappropriate content is immediately flagged and taken down. These can range from profanity to advertisements for illegal services. LinkedIn uses a Convolutional neural networks based machine learning model. This classifier trains on a training dataset containing accounts labeled as either "inappropriate" or "appropriate." The inappropriate list consists of accounts having content from "blocklisted" phrases or words and a small portion of manually reviewed accounts reported by the user community.
Here is a Text Classification Project to help you understand NLP basics for text classification. You can find a news recommendation system dataset to help you build a personalized news recommender system. You can also use this dataset to build a classifier using logistic regression, Naive Bayes, or Neural networks to classify toxic comments.
Get confident to build end-to-end projects
Access to a curated library of 250+ end-to-end industry projects with solution code, videos and tech support.
Pfizer is a multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in New York, USA. One of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally known for developing a wide range of medicines and vaccines in disciplines like immunology, oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Pfizer became a household name in 2010 when it was the first to have a COVID-19 vaccine with FDA. In early November 2021, The CDC has approved the Pfizer vaccine for kids aged 5 to 11. Pfizer has been using machine learning and artificial intelligence to develop drugs and streamline trials, which played a massive role in developing and deploying the COVID-19 vaccine. Here are a few data analytics case studies by Pfizer :
i) Identifying Patients for Clinical Trials
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are used to streamline and optimize clinical trials to increase their efficiency. Natural language processing and exploratory data analysis of patient records can help identify suitable patients for clinical trials. These can help identify patients with distinct symptoms. These can help examine interactions of potential trial members' specific biomarkers, predict drug interactions and side effects which can help avoid complications. Pfizer's AI implementation helped rapidly identify signals within the noise of millions of data points across their 44,000-candidate COVID-19 clinical trial.
ii) Supply Chain and Manufacturing
Data science and machine learning techniques help pharmaceutical companies better forecast demand for vaccines and drugs and distribute them efficiently. Machine learning models can help identify efficient supply systems by automating and optimizing the production steps. These will help supply drugs customized to small pools of patients in specific gene pools. Pfizer uses Machine learning to predict the maintenance cost of equipment used. Predictive maintenance using AI is the next big step for Pharmaceutical companies to reduce costs.
iii) Drug Development
Computer simulations of proteins, and tests of their interactions, and yield analysis help researchers develop and test drugs more efficiently. In 2016 Watson Health and Pfizer announced a collaboration to utilize IBM Watson for Drug Discovery to help accelerate Pfizer's research in immuno-oncology, an approach to cancer treatment that uses the body's immune system to help fight cancer. Deep learning models have been used recently for bioactivity and synthesis prediction for drugs and vaccines in addition to molecular design. Deep learning has been a revolutionary technique for drug discovery as it factors everything from new applications of medications to possible toxic reactions which can save millions in drug trials.
You can create a Machine learning model to predict molecular activity to help design medicine using this dataset . You may build a CNN or a Deep neural network for this data analyst case study project.
Access Data Science and Machine Learning Project Code Examples
9) Shell Data Analyst Case Study Project
Shell is a global group of energy and petrochemical companies with over 80,000 employees in around 70 countries. Shell uses advanced technologies and innovations to help build a sustainable energy future. Shell is going through a significant transition as the world needs more and cleaner energy solutions to be a clean energy company by 2050. It requires substantial changes in the way in which energy is used. Digital technologies, including AI and Machine Learning, play an essential role in this transformation. These include efficient exploration and energy production, more reliable manufacturing, more nimble trading, and a personalized customer experience. Using AI in various phases of the organization will help achieve this goal and stay competitive in the market. Here are a few data analytics case studies in the petrochemical industry:
i) Precision Drilling
Shell is involved in the processing mining oil and gas supply, ranging from mining hydrocarbons to refining the fuel to retailing them to customers. Recently Shell has included reinforcement learning to control the drilling equipment used in mining. Reinforcement learning works on a reward-based system based on the outcome of the AI model. The algorithm is designed to guide the drills as they move through the surface, based on the historical data from drilling records. It includes information such as the size of drill bits, temperatures, pressures, and knowledge of the seismic activity. This model helps the human operator understand the environment better, leading to better and faster results will minor damage to machinery used.
ii) Efficient Charging Terminals
Due to climate changes, governments have encouraged people to switch to electric vehicles to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. However, the lack of public charging terminals has deterred people from switching to electric cars. Shell uses AI to monitor and predict the demand for terminals to provide efficient supply. Multiple vehicles charging from a single terminal may create a considerable grid load, and predictions on demand can help make this process more efficient.
iii) Monitoring Service and Charging Stations
Another Shell initiative trialed in Thailand and Singapore is the use of computer vision cameras, which can think and understand to watch out for potentially hazardous activities like lighting cigarettes in the vicinity of the pumps while refueling. The model is built to process the content of the captured images and label and classify it. The algorithm can then alert the staff and hence reduce the risk of fires. You can further train the model to detect rash driving or thefts in the future.
Here is a project to help you understand multiclass image classification. You can use the Hourly Energy Consumption Dataset to build an energy consumption prediction model. You can use time series with XGBoost to develop your model.
10) Zomato Case Study on Data Analytics
Zomato was founded in 2010 and is currently one of the most well-known food tech companies. Zomato offers services like restaurant discovery, home delivery, online table reservation, online payments for dining, etc. Zomato partners with restaurants to provide tools to acquire more customers while also providing delivery services and easy procurement of ingredients and kitchen supplies. Currently, Zomato has over 2 lakh restaurant partners and around 1 lakh delivery partners. Zomato has closed over ten crore delivery orders as of date. Zomato uses ML and AI to boost their business growth, with the massive amount of data collected over the years from food orders and user consumption patterns. Here are a few examples of data analyst case study project developed by the data scientists at Zomato:
i) Personalized Recommendation System for Homepage
Zomato uses data analytics to create personalized homepages for its users. Zomato uses data science to provide order personalization, like giving recommendations to the customers for specific cuisines, locations, prices, brands, etc. Restaurant recommendations are made based on a customer's past purchases, browsing history, and what other similar customers in the vicinity are ordering. This personalized recommendation system has led to a 15% improvement in order conversions and click-through rates for Zomato.
You can use the Restaurant Recommendation Dataset to build a restaurant recommendation system to predict what restaurants customers are most likely to order from, given the customer location, restaurant information, and customer order history.
ii) Analyzing Customer Sentiment
Zomato uses Natural language processing and Machine learning to understand customer sentiments using social media posts and customer reviews. These help the company gauge the inclination of its customer base towards the brand. Deep learning models analyze the sentiments of various brand mentions on social networking sites like Twitter, Instagram, Linked In, and Facebook. These analytics give insights to the company, which helps build the brand and understand the target audience.
iii) Predicting Food Preparation Time (FPT)
Food delivery time is an essential variable in the estimated delivery time of the order placed by the customer using Zomato. The food preparation time depends on numerous factors like the number of dishes ordered, time of the day, footfall in the restaurant, day of the week, etc. Accurate prediction of the food preparation time can help make a better prediction of the Estimated delivery time, which will help delivery partners less likely to breach it. Zomato uses a Bidirectional LSTM-based deep learning model that considers all these features and provides food preparation time for each order in real-time.
Data scientists are companies' secret weapons when analyzing customer sentiments and behavior and leveraging it to drive conversion, loyalty, and profits. These 10 data science case studies projects with examples and solutions show you how various organizations use data science technologies to succeed and be at the top of their field! To summarize, Data Science has not only accelerated the performance of companies but has also made it possible to manage & sustain their performance with ease.
FAQs on Data Analysis Case Studies
A case study in data science is an in-depth analysis of a real-world problem using data-driven approaches. It involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to extract insights and solve challenges, offering practical insights into how data science techniques can address complex issues across various industries.
To create a data science case study, identify a relevant problem, define objectives, and gather suitable data. Clean and preprocess data, perform exploratory data analysis, and apply appropriate algorithms for analysis. Summarize findings, visualize results, and provide actionable recommendations, showcasing the problem-solving potential of data science techniques.

About the Author

ProjectPro is the only online platform designed to help professionals gain practical, hands-on experience in big data, data engineering, data science, and machine learning related technologies. Having over 270+ reusable project templates in data science and big data with step-by-step walkthroughs,
© 2024
© 2024 Iconiq Inc.
Privacy policy
User policy
Write for ProjectPro
Amazon Business Case Study [2024]: In-depth Analysis
![amazon data analytics case study Amazon Business Case Study [2024]: In-depth Analysis](https://www.upgrad.com/__khugblog-next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd14b9ctw0m6fid.cloudfront.net%2Fugblog%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2019%2F07%2FBlog_FI_July_upGrads-Knowledge-base.png&w=1920&q=75)
How does an online book retailer become a behemoth dominating the global e-commerce industry? The 28-year-old history of Amazon’s growth is a masterclass in building a successful business strategy that has revolutionised the retail experience forever! The company has achieved eponymous status with a global presence and diversified business. No wonder its sales are expected to reach an astounding USD 746.22 billion with a valuation of USD 2 trillion in 2024! From being an online bookseller headquartered in a garage to becoming the second most valuable brand in the world , the saga of this global brand is a case study in all the leading business schools.
So what is the secret behind the explosive success of Amazon? This article provides a comprehensive case study of Amazon and its winning business strategy.
Study Product Management Courses online from the World’s top Universities. Earn Masters, Executive PGP, or Advanced Certificate Programs to fast-track your career.
Glimpsing Back: A Brief History of Amazon
With a small team, the budding company made headway in the book-selling market by offering a wide virtual selection of books compared to brick-and-mortar stores with doorstep delivery. With a user-friendly interface, easy-to-search engine, and focus on creating a ‘virtual community,’ the business grew by leaps and bounds. The emphasis on customer choice, experience, and convenience serves the company well even today.

The name was aspirational with a nod to the largest river in the world- Bezos’ Amazon sought to be the largest e-commerce bookseller in the world. By July 1995, Amazon was marketing itself as the “Earth’s Biggest Bookstore,” selling over one million titles to all 50 states in the US and across 45 countries . It provided stiff competition to brick-and-mortar giants like Barnes and Noble and Borders.
The company went public with its IPO in 1997 ; since then, there has been no looking back. Since its listing, the company has significantly diversified its offering by including music, electronics, toys, kitchen utensils, clothes, and more on its e-commerce site. From the Earth’s Biggest Bookstore, Amazon shifted its tagline to “Books, Music and More.” The company expanded to Germany and the United Kingdom by purchasing online bookstores, thus increasing its revenue. At its core, the company established a dynamic, efficient, and successful distribution and logistical model that helped capture a global market.
The year 1999 marked two critical moments for Amazon. First, the company patents the “1-Click” technology allowing users to purchase a product with one click. Second, it launches the 3rd party seller marketplace to allow third-party sellers to sell their produce through Amazon. These measures exponentially increased the sales on the platform. The company’s success put Bezos on the map as he received the prestigious accolade of the “Time’s Person of the Year” in 1999 at 35 years of age.
The company survived the dot-com bubble burst and got only stronger. In 2003, the company took a momentous step by launching Amazon Web Services , a web-hosting business, that marked its arrival into the tech business. It provides cloud computing services to individual developers, companies, and governments through the platform’s IT infrastructure. The strategic shift from an e-commerce platform to a tech company was instrumental in Amazon’s diversification strategy and revenue generation.
The company took further measures to develop brand loyalty through its Amazon Prime program in 2005. Prime membership has since expanded its services significantly and is one of the most valuable assets for the company today. It reshaped consumer expectations and experiences of shopping across the world.
Amazon has been on a path of extensive acquisition and alliance . From the online shoe retailer Zappos to the robotics company Kiva Systems and the grocery delivery service Whole Foods- each acquisition captured pre-existing markets and distribution networks of the acquired assets. With every move, the company strategically entered new markets, removed competitive businesses by acquiring them, made distribution and logistics more efficient, and improved consumer experience. These moves catapulted the company to a 1 trillion dollar valuation in 2018. The company’s profits surged during the pandemic as Bezos’ hourly wealth increased by USD 11.7 million . The following year, Bezos stepped down as the CEO and found his replacement in Andy Jassy, the CEO of Amazon Web Services.
Now that we know the history of Amazon, its business strategy becomes easier to decipher. Before we unravel its key business strategies, let’s look at its many businesses.
Amazon and its Diversified Business Model
A case study of Amazon is incomplete without an understanding of the many businesses that it has a foot in. Here are the diverse businesses that help Amazon generate revenues from multiple streams and have made it a leader in the global market.
Online retail store
Amazon began as an online seller of books, and it continues its operations as an e-commerce site. Today the site offers a variety of products for the best prices to the consumer’s doorsteps. With an easy-to-use interface, easy return policy, “1-Click” buying, customer reviews, and suggestions, the e-commerce site knits an unrivalled retail experience.
Amazon Marketplace
Amazon opened its platform to third-party sellers who could leverage its large customer base to sell products. It brings a diversity of products to the retailer without holding inventory. Amazon would, in turn, charge the sellers a percentage of their revenue as a commission fee. It is estimated that third-party sellers generate a gross merchandise value (GMV) of USD 300 billion for the platform.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon’s cloud platform offers individual developers, start-ups, established businesses, and governments a range of cloud computing services through its IT infrastructure. It is the fastest-growing business segment for the brand clocking a global net revenue of USD 80.1 billion in 2022.
Amazon Prime
Amazon’s member subscription service offers numerous membership benefits ranging from access to digital video and music streaming, audiobook and ebook platforms, free delivery, exclusive deals, Prime Day access, and much more. The company’s global net revenue from its subscription services stood at USD 35.22 billion in 2022.
Amazon revealed in 2022 that the advertising wing of the company had generated a revenue of USD 31.2 billion the preceding year. The company offers custom advertising solutions to customers and campaign placements across multiple channels like Fire TV placements, Amazon physical stores, the brand’s homepage, and customised destination pages.
Physical stores
Amazon made an entry into the brick-and-mortar business with the establishment of a physical bookstore in Seattle in 2015. The company has since expanded its physical presence with Amazon Go, Amazon Fresh, Amazon Go Grocery, Whole Foods Market, and Amazon Style. It has sought to transform the real-world shopping experience with its “Just Walk Out Shopping’ experience.
Breaking Down Amazon’s Business Strategy
Amazon’s business strategy has been innovative and forward-thinking from the get-go. Its path-breaking business model has inspired many but retains its uniqueness in execution. At its core, the company has maintained its customer-centric ethos, where its customers comprise three sets: retail customers, seller customers, and developer customers.
For a comprehensive case study of Amazon , let’s take a closer look at the secret recipe behind its success.
Customer Obsession
The company proudly proclaims that it aims to be the “Earth’s most customer-centric company.” Since its inception, Amazon has won over the trust and loyalty of its customers by perfecting its marketing mix by offering “a comprehensive selection of products, low prices, fast and free delivery, easy-to-use functionality, and timely customer service.” As Amazon’s customer base and usage expands exponentially, the company has worked towards optimising user experience through continuous assessment and feedback mechanisms.
Diversification
Amazon has kept up with the emerging demands of the market with growth potential in the long term. Its future-oriented vision has helped the company grow by leaps and bounds by venturing into new businesses that have added to its revenue streams. From cloud computing services to OTT services and subscription-based benefits, Amazon has reinvented what a diversified business looks like.
Expansion through partnerships and acquisitions
Amazon has continually acquired and partnered with businesses to expand its customer base, enter new markets, diversify its product offerings, eliminate competition, and gain distribution and logistical networks. From IMDB and The Washington Post to Twitch and Pillpack, Amazon has bought companies across multiple categories to gain a foothold in their markets and operations. It has helped the company scale up its functions rapidly across the globe.
Technologically-driven innovations
Initially, Amazon was written off as it was started by “computer guys” who knew nothing about selling books. However, it was a focus on innovative technology that the company grew into a tech giant dominating the e-commerce space. Whether it is the 1-Click technology, SEO, user interface, cloud computing services, Just Walk Out technology, or its e-devices, the company has optimised customer experience by leveraging technology.
Data-based metrics
Amazon has consistently relied on metrics to assess, strategise, and grow its business. Data is an invaluable currency left behind with every click by the customer. The company has effectively and efficiently amassed these data into actionable insights to improve user experience, build and improve products and services, and develop successful marketing strategies.
Marketing strategy
A comprehensive marketing strategy has been central to Amazon’s brand-building exercise. With the right marketing mix, the brand has become a household name. Its name and logo are recognisable anywhere in the world. A continual push to diversify its portfolio, competitive pricing policy, expanding its operations, and consistent promotions through multiple channels have been integral to achieving this global status.
Explore our Popular Management Courses
Amazon, the second-most valuable company in the world, has been almost three decades in the making. Every step and misstep has been strategic and guided by the principles of: “customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking.” This case study of Amazon has sought to highlight its history, business model, and business strategies that have gone into the making of the behemoth. Ultimately, the company is a product of the management of Jeff Bezos and Amazon’s leadership.
Top Management Skills to Learn
Do you want to learn the tricks of the trade that makes the brightest management minds tick?
Leap into the sphere of management with upGrad!
The Advanced General Management Program by upGrad will guide you in the right direction in your management journey. Learn from the world-class faculty from one of India’s premier B-schools- Institute of Management Technology (IMT), Ghaziabad. The program offers a comprehensive syllabus covering subjects like Business Growth Strategies, Leadership, Structured Thinking and Problem Solving, and Project Management skills. The 11-month course offers 1:1 mentoring and placement assistance, too.
Enrol now to unleash your potential!
Our Top Management Articles
You can also check out our free courses offered by upGrad in Management, Data Science, Machine Learning, Digital Marketing, and Technology. All of these courses have top-notch learning resources, weekly live lectures, industry assignments, and a certificate of course completion – all free of cost!

Jitesh Goel
Something went wrong
Our Trending Product Management Courses
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management
- PG Program in Management
Our Popular Product Management Course

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Jeff Bezos has held the position of Founder and CEO of the company. However, he inherited the position of the Executive Chairman of Amazon after resigning as the CEO of the company in 2021.
Amazon launched in India in June 2013. Initially starting its operations to serve Indians with books, films, TV shows and subscription-based services, the company further expanded its wings to become one of the leading shopping destinations for Indians.
The most important focal point of Amazon’s business strategy is its customers (retail customers, sellers, and developers) and building a customer-centric company.
Related Programs View All
Certification
16 Hrs Live Expert-Led Sessions
14 Case Studies, 3 Mock Tests
View Program

Master's Degree
Dual Credentials

Job Assistance
16+ Hrs Expert-Led Sessions
5 Simulation Exams, 8 Mock Tests
24 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Earn 24 PDUs and 24 SEUs
36 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Premium 2000+ Question Bank
32 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Earn 32 PDUs and SEUs

Complimentary On-Demand Course
1 Year SAFe® Community Membership
88 Hours On-Demand Learning
100% Exam-Pass Guarantee
16 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Earn 16 PDUs and 16 SEUs

AACSB accredited
Training by Top-Notch SPCs

3 Day Leadership Summit in Dubai

Ivy League School

Executive PG Program
Offline Campus Experience
PG Certification
6-10.5 Months
2500+ Students Enrolled

EQUIS & AMBA Accredited

Executive Coaching
Simulations, 5 Mock Tests
Instructor Led Model
16-Hrs Live Expert-Led Sessions
Earn 16 SEUs and 16 PDUs
16+ Hrs Expert-Led Training

AMBA, AACSB & NIRF Accreditation
24+ Hrs Expert-Led Sessions
Simulation Exams, 24 PDUs
35 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
35 PD Hrs, 35 CDUs & 35 PDUs
24-Hrs Live Expert-Led Sessions
Activities and Case Studies
8+ Hrs Expert-Led Sessions
Interactive Sessions, Activities
36+ Expert-Led Training
5 Simulation Exams, Projects
21 Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Earn 21 CDUs and 21 PDUs
2-Day Live Expert-led Training
Simulations, 4 Mock Tests
16 Hours of Instructor-Led Sessions
Simulation Exams and Mock Tests
Earn 16 PDUs and 16 SEUs
24-Hrs Live Expert-Led Training
Earn 24 SEUs and 24 PDUs
Explore Free Courses
Learn more about the education system, top universities, entrance tests, course information, and employment opportunities in Canada through this course.
Advance your career in the field of marketing with Industry relevant free courses
Build your foundation in one of the hottest industry of the 21st century
Master industry-relevant skills that are required to become a leader and drive organizational success
Build essential technical skills to move forward in your career in these evolving times
Get insights from industry leaders and career counselors and learn how to stay ahead in your career
Kickstart your career in law by building a solid foundation with these relevant free courses.
Stay ahead of the curve and upskill yourself on Generative AI and ChatGPT
Build your confidence by learning essential soft skills to help you become an Industry ready professional.
Learn more about the education system, top universities, entrance tests, course information, and employment opportunities in USA through this course.
Suggested Blogs
![amazon data analytics case study Project Manager Salary in India in 2024 [For Freshers & Experienced]](https://www.upgrad.com/__khugblog-next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd14b9ctw0m6fid.cloudfront.net%2Fugblog%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2020%2F07%2F684.png&w=3840&q=75)
by Dilip Guru
24 Jan 2024
25 Sep 2023

24 Sep 2023
![amazon data analytics case study Average Product Manager Salary in India in 2024 [For Freshers & Experienced]](https://www.upgrad.com/__khugblog-next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd14b9ctw0m6fid.cloudfront.net%2Fugblog%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2019%2F07%2FBlog_FI_July_upGrads-Career-advice.png&w=3840&q=75)
by Jitesh Goel
19 Sep 2023

by Keerthi Shivakumar
18 Sep 2023

12 Sep 2023
28 Aug 2023

08 Jul 2023

- Kindle Store
- Kindle eBooks
Promotions apply when you purchase
These promotions will be applied to this item:
Some promotions may be combined; others are not eligible to be combined with other offers. For details, please see the Terms & Conditions associated with these promotions.
Buy for others
Buying and sending ebooks to others.
- Select quantity
- Buy and send eBooks
- Recipients can read on any device
These ebooks can only be redeemed by recipients in the US. Redemption links and eBooks cannot be resold.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Data Analytics Case Studies Kindle Edition
"Data Analytics Case Studies" is a book that provides practical examples of how data analytics can be used in various industries and settings to solve real-world problems. The book includes 8 case studies from a wide range of industries, including healthcare, chemical, finance, and food & beverages.
The case studies presented in the book cover a variety of topics, such as predictive modeling, text analytics, machine learning, and data visualization. Each case study includes a detailed description of the problem being addressed, the data sources used, the analytical techniques employed, and the results and insights gained from the analysis.
The book is designed to help readers understand the potential of data analytics in various fields and to provide guidance on how to approach similar problems. It also provides insights into the challenges and limitations of using data analytics in real-world settings.
Overall, "Data Analytics Case Studies" is a valuable resource for data analysts, business leaders, and anyone interested in understanding how data analytics can be used to solve complex problems and drive business outcomes.
- Print length 53 pages
- Language English
- Sticky notes On Kindle Scribe
- Publication date February 21, 2023
- Reading age 15 - 18 years
- File size 7134 KB
- Page Flip Enabled
- Word Wise Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting Enabled
- See all details

Product details
- ASIN : B0BWL8GC5R
- Publication date : February 21, 2023
- Language : English
- File size : 7134 KB
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Enabled
- Sticky notes : On Kindle Scribe
- Print length : 53 pages
- #1,017 in Education Research (Kindle Store)
- #3,088 in Research Reference Books
- #3,173 in 90-Minute Education & Reference Short Reads
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A big data analysis case study of amazon. Big data is one of the advanced technologies mainly used for evaluating and integrating the collected data in the companies. The use of big data is ...
Amazon has new data tracking in its physical grocery stores to mine data on shoppers' habits. The company announced its Store Analytics, which will offer brands aggregated data, in a blog post. It ...
AWS Payments is part of the AWS Commerce Platform (CP) organization that owns the customer experience of paying AWS invoices. It helps AWS customers manage their payment methods and payment preferences, and helps customers make self-service payments to AWS. The Machine Learning, Data and Analytics (MLDA) team at AWS Payments enables data-driven ...
The Galaxy data lake is a critical component of a larger big-data platform known internally as Galaxy. The figure below shows some of the ways Galaxy relies on AWS and some of the AWS services it ...
Scalable data lakes. AWS-powered data lakes, supported by the unmatched availability of Amazon S3, can handle the scale, agility, and flexibility required to combine different data and analytics approaches. Build and store your data lakes on AWS to gain deeper insights than with traditional data silos and data warehouses allow.
Hearst Data Analytics Case Study. Hearst Corporation, headquartered in New York City, is one of the largest media and information companies in the world. The company owns 15 daily and 36 weekly newspapers and more than 300 popular magazines worldwide, including Cosmopolitan, Esquire, and O, The Oprah Magazine.
Behind their success lies a sophisticated data analytics infrastructure that drives personalised recommendations, enhances customer experience, and optimises operations. In this case study, we explore how Amazon utilises data analysis in research and other verticals to create a seamless shopping experience for millions of customers worldwide.
Use cases. Simplify Data Analytics at scale. Automated Data Analytics on AWS simplifies the management and analysis of data, providing an end-to-end platform used for ingesting, transforming, governing, and querying datasets, from a range of different data sources, using an intuitive standalone user interface. This enables analysts to easily ...
This case study delves into an in-depth analysis of Amazon sales data to unearth insights that could revolutionize how businesses view their sales strategy and customer engagement. The Dataset
Publication date: July 26, 2021 (Document revisions) This whitepaper helps architects, data scientists, and developers understand the big data analytics options available in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud. It provides an overview of services, including: Ideal usage patterns. Cost model. Performance.
Gupta has studied Amazon's growth strategy and he tells Cold Call host Brian Kenny how Amazon looks beyond traditional industry boundaries to define their competitors and why connecting products ...
In this big data use case, we'll look at how Amazon is leveraging data analytic technologies to improve products and services and drive overall revenue. Big data has changed how we interact with the world and continue strengthening its hold on businesses worldwide. New data sets can be mined, managed, and analyzed using a combination of ...
Amazon represents indeed a successful example of algorithmic business as it is powered by data and algorithms and as it learnt from its mistakes and its experiments operating on a strategic and organizational level, as an advanced machine learning system, both when the priorities for Bezos included dimensional growth and building up a competitive critical mass (Get Big Fast strategy) and when ...
By migrating its big data environment to Amazon EMR, Autodesk has improved the service's reliability, performance, and cost efficiency. "By migrating to Amazon EMR, we reduced costs by 30 percent," says Anitha Matta, engineering manager of platform infrastructure at Autodesk. "And we achieved this cost reduction while significantly ...
Our business case study explores Amazon's revenue model and culture of customer metrics, history of Amazon.com and marketing objectives. In the final quarter of 2022, Amazon reported net sales of over $149.2 billion. This seasonal spike is typical of Amazon's quarterly reporting, but the growth is undeniable as this was the company's highest ...
Amazon's big data analyzes the available data and locates the closest warehouse to a customer/vendor to reduce the shipping costs. Additionally, graph theory helps in deciding the best delivery schedule, route, and product groupings which further reduces the shipping expenses. Recommended blog - Supply Chain Management.
Here are a few data analytics case study examples at Amazon: i) Recommendation Systems. Data science models help amazon understand the customers' needs and recommend them to them before the customer searches for a product; this model uses collaborative filtering. Amazon uses 152 million customer purchases data to help users to decide on ...
Amazon.com: Data Analytics Case Study - Open University Learning Analytics Dataset: using KNIME, Python and SAS Viya eBook : Tan, Jessica: Kindle Store
In order to meet its growing needs, Amazon's consumer business decided to migrate the Oracle data warehouse to an AWS-based solution. The new data lake solution uses a variety of AWS services to deliver performance and reliability at exabyte scale for data processing, streaming, and analytics. The company used Amazon Simple Storage Service ...
The company has achieved eponymous status with a global presence and diversified business. No wonder its sales are expected to reach an astounding USD 746.22 billion with a valuation of USD 2 trillion in 2024! From being an online bookseller headquartered in a garage to becoming the second most valuable brand in the world, the saga of this ...
Kindle Edition. "Data Analytics Case Studies" is a book that provides practical examples of how data analytics can be used in various industries and settings to solve real-world problems. The book includes 8 case studies from a wide range of industries, including healthcare, chemical, finance, and food & beverages.
Another company, Netflix, used its subscriber data and real-time data analytics to transform into a global streaming company, as its revenues rose from $3.2 billion in 2011 to $33.7 billion by 2023.
Coca-Cola Andina Builds Data Lake on AWS, Increases Analytics Productivity by 80% for More Data-Driven Decision-Making. Coca-Cola Andina allowed both the company itself and its customers to make decisions based on reliable data, promoting joint growth of the entire ecosystem, maintaining its competitive advantage, and increasing the company's ...
The non-tectonic deformation caused by hydrological loads is an important influencing factor in GNSS vertical displacement. Limited by the temporal and spatial resolution of global models and model errors, the hydrological load results calculated by traditional methods are difficult to meet the high temporal and spatial resolution requirements of small to medium-scale regions. This paper ...
Organizations of all sizes across all industries are transforming their businesses and delivering on their missions every day using AWS. Contact our experts and start your own AWS journey today. Learn how organizations of all sizes use AWS to increase agility, lower costs, and accelerate innovation in the cloud.