

Why Students Don’t Do Homework (And What You Can Do About It)

Homework provides supplementary learning opportunities for students, helping to reinforce topics and concepts covered in the classroom. However, many students fail to complete the homework assigned to them. And that raises the question: why don’t students do their homework?
Some of the most common reasons why students don’t complete homework include not understanding the assignment’s instructions, an overabundance of homework, and feelings of disinterest and apathy toward the homework’s importance. After-school activities can also impact homework completion.
This article will explore why students fail to complete their homework and discuss ways teachers can increase homework completion rates.
Table of Contents
What Happens When Students Don’t Do Homework?
Students face multiple consequences when they fail to complete homework. The most common ones being an adverse effect on academic performance, a lack of understanding of future topics, and a worsening student-teacher relationship.
Academic Performance Suffers
Depending on your classroom grading policies, homework can account for as little as 1% or as much as 25% of a student’s overall grade . School districts can impose some control over these grading policies, but many public schools allow teachers to set the percentage.
Educators who prefer to assign more worth to homework can find that students’ grades and overall academic performance quickly suffer when their students fail to submit at-home assignments.
Decreasing grades can be highly discouraging for students and contribute to a lack of self-confidence. The situation can also become problematic for teachers.
Teachers Can Lose Their Jobs
School administrators can fire or decide not to renew the contracts for teachers whose students aren’t succeeding academically. For example, in 2019, a teacher in Port St. Lucie, Florida , was fired for giving her students zeros after they failed to complete homework assignments, which went against the school’s “no zero” policy.
School board members and administrators often judge a teacher’s performance by their students’ grades and academic performance. When grades and test scores plummet, some schools resort to dismissing the teacher, often without exploring the factors contributing to the lower-than-expected attainment to which homework can be linked to.
Future Course Topics Become More Challenging
School subjects become increasingly more complex over time .
For example, once elementary students have mastered the alphabet, they’re taught how to spell simple words. After that, they advance to writing basic sentences and reading aloud.
But if students never master the first phase (learning the alphabet), future learning related to writing and reading becomes harder to grasp. Similarly, students who fail to complete assigned homework will struggle to cope with future course topics and learning objectives.
Without immediate intervention to help students catch up with the course material and remain on pace with their peers, students can begin to fail their classes. They can also become reluctant to attend school and may even develop a dislike or distrust of educators.
Student-Teacher Relationships Worsen
When teachers chastise their students for underperforming on homework assignments or failing to submit completed homework, the relationship between students and teachers suffers.
Students can begin to resent homework and the teachers that assign at-home assignments. As a consequence, students’ in-class performance suffers because students have a negative emotional response to a teacher’s presence or teaching style.
Some students may also purposely disengage during lessons or act out in retaliation, causing classroom disruptions .
Naturally, this behavior only degrades teacher-student relationships further, making it more challenging for instructors to help their students achieve their fullest academic potential.
Reasons Why Students Don’t Do Homework
Failing to complete and turn in homework can have long-lasting implications for students and teachers. This begs the question: Why don’t students do their homework?
There’s no easy answer to this question because there are many reasons why students are unable to or choose not to do homework.
But it’s crucial that educators explore the potential reasons why students don’t complete homework assignments. Doing so offers insight that can help teachers improve the homework completion rate and provides a glimpse into the challenges many students face when attempting to complete at-home assignments.
Let’s discuss the most prevalent reasons why students don’t do homework.
The Assignment’s Instructions Are Unclear or Overly Complicated
Sometimes, students don’t do homework because they don’t know how to. The assignment’s instructions may be vague, or students might need more time and instruction to grasp the concepts being tested.
When faced with an assignment that seems undoable due to a lack of information or confusing guidelines, many students will simply opt to ignore the task and move on.
After all, students often have multiple homework assignments each school day, resulting in an at-home workload that can feel extremely overwhelming, bringing us to the next item on the list.
Students Feel Overwhelmed With the Amount of Homework
The average amount of time that students spend completing homework each night varies depending on their grade level and teachers’ preferences.
Some studies report that students spend as little as one hour per night on homework, while others maintain that the average is just under three hours . But some students report spending up to nine hours working on at-home assignments each night!
Regardless, stress related to homework is a common issue among students, and it’s often associated with the amount of homework assigned.
Suppose we consider it like this: the average school day spans six to seven hours. Spending several more hours working on assignments at home can make students feel stressed, mentally exhausted, and unable to pursue their favorite after-school hobbies and activities.
Students Lack the Resources Required to Complete Homework
Not all schools and school districts receive the same level of financial support, leaving some students with few resources.
For example, some students might be prohibited from bringing home textbooks because the school cannot afford to provide one to each student. Others might have limited access to the internet at home or school.
This comparative lack of resources (called education inequity ) can significantly impact a child’s ability to complete homework, especially when take-home assignments are based on textbook questions or require reference material only accessible online or from local library books.
Assignments Are Repetitive and Time-Consuming
One of the primary benefits of homework is that it can help reinforce concepts learned in the classroom. Homework can also offer an opportunity for students to practice the new skills and concepts they’ve learned, keeping them fresh in their minds.
But imagine this: you’ve just learned how to solve basic single-variable algebraic equations , and you’re now given a set of 50 such equations to complete at home.
While you may complete the first few problems without complaint, by the time you’ve finished a few dozen, you’re probably ready to move on to other topics and equations.
Students may only partially complete their homework when assignments are repetitive. Tasks that are both repetitive and time-consuming might get neglected altogether, as students’ after-school time is precious and often limited.
After-School Activities Are Restricting Students’ Time
Extra-curricular activities are a crucial part of life for many students. These activities can also help increase students’ chances of being accepted into specific universities or college degree programs.
But these activities can reduce the time students have to complete homework. Finding the balance between enriching after-school activities and the free time to complete homework can be challenging, even for the most organized and time-conscious students.
Managing free time can also contribute to students’ stress and anxiety regarding schoolwork, negatively impacting academic performance.
Students Don’t Believe the Homework Is Relevant
Often, homework tends to be the least significant part of a student’s final grade, with exams, tests, and quizzes typically holding more weight.
For this reason, students may focus more on preparing for tests and quizzes. Homework that seems irrelevant to upcoming test material is particularly prone to be ignored by students.
Assignments with supplementary information that won’t appear on tests or quizzes might soon become frustrating for students, leading to a total abandonment of any attempt to complete at-home assignments.
Teachers who declare that homework holds minimal weight regarding a student’s final grade might also experience a lack of completed homework assignments.
If students understand that homework is only worth 10% or less of their final grade, they know their true focus should be on test-taking and quizzes. Even if a student completes zero homework for a class, so long as they perform well on the higher-weight tasks, they can still earn a decent overall grade.
There’s a Lack of Constructive Feedback on Completed Homework Assignments
Making mistakes is part of the learning process. But it’s impossible to learn from mistakes when errors aren’t explained.
Students that feel their homework doesn’t help them master specific concepts or skills can begin to feel disillusioned with doing at-home assignments. That’s why constructive feedback for homework assignments is essential.
For example, a student receives a grade for a spelling homework assignment. But instead of finding the correct spelling written next to the words they’ve misspelled, they only see “X” marks in red pen , indicating wrong answers.
While teachers might expect or request students to look up the misspelled words using a dictionary or a spell-checking device, some students might not have access to these resources at home.
In this scenario, students can remain uncertain about why they got specific answers wrong and thus be unable to learn from their mistakes, resulting in disillusionment toward homework.
Parents Aren’t Available or Capable of Assisting With Homework
Students who struggle with their homework might turn to their parents for assistance. But some parents are unable or unwilling to assist their children with at-home tasks.
While this reaction certainly isn’t true of all parents, these attitudes can leave students feeling more frustrated than before. They can also cause a general feeling of apathy toward homework.
A lack of support or engagement from parents can also contribute to poor mental health, another issue that can contribute to problems with completing homework.
Issues Outside of School
Every child deserves a happy and stable home, but not all students are fortunate enough to have supportive family members and a safe home environment.
Students struggling to cope with problems at home can struggle with schoolwork, both in and after class. The burden of unfavorable at-home conditions can cause or contribute to significant mental health concerns , resulting in reduced academic performance and an inability to complete homework.
Unfortunately, declining grades and pressure related to homework can contribute to student anxiety and stress, creating a feedback loop that only worsens academic performance.
However, there are several things teachers can do to help students turn things around and complete homework more frequently and confidently.
What Can Teachers Do?
To avoid homework-related problems, teachers should set aside time during class to clarify the instructions and address any misconceptions related to homework assignments. Reducing the workload also increases students’ chances to complete their tasks and allows teachers more time to provide constructive feedback. Finally, teachers should ensure that homework is relevant and engaging if they want to boost the homework completion rate.
Discuss Homework Assignments During Class
One of the most common reasons students fail to complete homework is a lack of understanding of how to complete the assignment.
For example, worksheet instructions can be confusing or unclear, or students might need clarification about how to approach a new homework activity.
Teachers can reduce confusion regarding homework instructions by setting aside some time during class to discuss and explain the assignment. This small change can help clarify what you expect from your students and help them approach the work more confidently.
Teachers often sacrifice a few minutes at the end of the lesson to review the homework instructions. But avoid holding students after the bell , as this could have a knock-on effect on other classes or subjects.
Set Aside Part of In-Class Time for Homework
Although it might seem counterintuitive to allow students to work on homework while in the classroom, doing so can provide opportunities for teachers to engage with students on a one-on-one basis.
When students have questions or concerns about specific parts of a homework assignment, they can discuss those issues with you in class. Not only is this beneficial for students, but it can also offer teachers insight into what types of assignments are confusing or engaging to students.
Setting aside in-class time for homework can also reduce a student’s overall at-home workload, thus decreasing stress associated with school.
Be Patient With Students and Allow for Late Turn-In
Because some students may be struggling with issues outside their control, such as mental health concerns or family problems, educators should practice patience when dealing with a lack of submitted homework.
For example, instead of asking, “Why haven’t you turned in your homework assignment?” teachers can ask, “Would you be able to complete this if you had an extra day to work on it?”
Although accepting late assignments can result in completed tasks being returned later than expected, it can also reassure students that their work is appreciated and valued. The same can be said for providing in-depth feedback on homework assignments.
Provide Feedback When Returning Completed Homework
When a student receives a graded homework assignment and sees they’ve gotten a few items wrong, their first question is generally, “Why was this marked incorrect?”
If homework lacks comments, students can struggle to understand what information they’re misunderstanding. As a result, they can begin to feel frustrated or apathetic about their schoolwork.
Providing detailed feedback on an individual basis can be time-consuming for teachers, but it’s a fantastic way to help students perform better on in-class and at-home assignments. Besides, teachers can assign fewer homework assignments to reduce the workload for both themselves and their students.
Reduce or Eliminate Assigned Homework
Most public schools in the United States don’t require teachers to give their students homework.
Although it’s often recommended, teachers are the ones who create course syllabi and assign grade percentages to academic tasks like exams, quizzes, group projects, and homework assignments.
Consequently, they can choose to eliminate or significantly reduce homework loads. This option can be particularly beneficial for elementary school students and teachers.
After all, homework assignments given to elementary-aged children can have negative consequences, including strained parent-child relationships, increased stress levels, and a bleak outlook on education.
But reducing or getting rid of homework altogether can also be a beneficial change for older students.
For example, Scott Anderson, a high school mathematics teacher from Wisconsin, decided to eliminate homework and focus more on completing tests and quizzes. This change placed a stronger focus on learning and mastering concepts.
This no-homework policy may be unconventional, but it could also help students boost their academic performance without increasing their stress levels.
Final Thoughts
When students fail to complete their homework, their grades can suffer. They can also struggle to understand more complex course topics that build on information covered in the homework, leading to a cycle of declining academic performance and increasing apathy or frustration.
There are several reasons why students don’t do homework. Complicated directions, an excessive homework workload, and apathy towards homework can all contribute to a lack of homework completion.
Fortunately, teachers can adapt homework assignments to meet students’ needs, thus increasing homework completion rates.
- Moms: Florida Teacher Fired For Failing Students Who Didn’t Submit Their Work
- Three Penny Press: Students spend three times longer on homework than average, survey reveals
- University of San Diego: Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students
- Suicide Prevention Resource Center: Consequences of Student Mental Health Issues
- National Education Association: A High School Teacher Scrapped Homework. Here’s What Happened Next
- The Herald: Should homework count toward grades? A district wonders
Related posts:
- How To Deal With Students Who Won’t Stop Talking (20 Top Tips)
- How To Deal With Angry Elementary Students (13 Top Tips)
- How Would Students Describe You as a Teacher? (7 Answers to Give)
- How Do I Become A Teacher In California?
- Why Do Teachers Not Use Red Pens Anymore?
Thanks for reading the article - we hope that your teaching query has been answered with helpful information and insightful advice. Feel free to share this article with friends and let’s help the Teacher How community grow!
Recent Posts
TeacherHow.com Expands Educational Reach with Acquisition of MontessoriOnMars.com
Teacherhow.com, a leading online website committed to empowering those concerned with education, proudly announces the acquisition of MontessoriOnMars.com, an inspirational platform dedicated to the...
How Do Kindergarten Teachers Stay Calm?
Kindergarten teachers spend many hours of the day with twenty or so very young children. Children who are just starting to learn social and self-management skills through unaccustomed boundaries set...
Learn American English Online
UPDATED DAILY
Listen and repeat:
Next: Watch this video
did + not + main verb
Click here to take a quiz on the present tense
Click here to take a quiz on the past tense
Next: Lesson Four commands in English

- All Lessons
- business english
- comprehension
- culture & tips
- expressions
- pronunciation

Write a Dialogue Between a Teacher and a Student who has Not done his Homework or Assignment
In this article, I will cover how to write a dialogue writing between a teacher and a student who has not done his homework or assignment.

Sample Conversation 1
Teacher: Good morning All!. Please submit yesterday’s homework.
Students: Good morning sir!
Teacher: Please submit your homework! All those who have not completed the homework please stand up.
(Rahul stands up)
Teacher: Rahul! Tell me.Why did you not complete your homework yesterday?
Rahul: Sir actually I was not able to do my homework as I was busy the whole day.
Teacher: But why Rahul? This is the fourth time this week that your homework is incomplete.
Rahul: I know sir I am really sorry. Actually, My father is very sick and he is in the hospital due to which I did not get enough time to do my homework.
Teacher: Oh, I see. That is very bad. It’s okay Rahul. You can complete your homework when your father is better. I hope he gets better soon.
Rahul: Thank you sir.
Sample Conversation 2
(Two students are conversing in the classroom where the teacher overhears their conversation)
Student1: I hate it when Ms Banerjee gives us homework! It’s so unnecessary.
Student2: I know! It is so annoying.
Teacher: I think you kids have misunderstood the purpose of homework.
Students: Oh, we didn’t see your teacher.
Teacher: You see homework teaches you responsibility. It is meant to inculcate small values in your life. Kittu, have you watched all the marvel films?
Student1: I’ve watched them so many times that I can narrate the dialogues to you.
Teacher: Exactly! Repeated revision of your favourite movies means that you know them as well as the back of your hand. Repeated learning of difficult topics helps you understand them better.
Students: I didn’t realize how beneficial homework actually could be! Thank you, teacher. We will never think of homework as a burden.
Sample Conversation 3
Student: Let me tell you what happened to my assignment.
Teacher: OK, go ahead- what is the excuse this time?
Student: Actually, I did it, but then it got lost.
Teacher: Could you have gotten it done at another time?
Student: Yes, I could.
Teacher: This is nothing new. Why don’t you do your assignment? These are so important for your understanding.
Student: I try so hard to finish them on time but I always end up taking more time than estimated. I never finish assignments on time.
Teacher: I know it’s hard to juggle classes, assignments and social life. But these assignments are the first step toward achieving a work-life balance. Keep trying! Don’t give up.
Student: I’ll make it up early next week.
Teacher: Don’t let it happen again.
Student: I’ll try.
Teacher: That will solve it then. Let’s work hard to not let it happen again.
Sample Conversation 4
Teacher: Where is your homework, Gunu?
Gunu: I had some doubts about the assignment. I didn’t understand some of the questions.
Teacher: Why didn’t you clarify your doubts with me then?
Gunu: Sorry Madam.
Teacher: Gunu, I am tired of these constant excuses. I cannot entertain your reasons every day.
Gunu: Sorry Madam! This will not happen again.
Teacher: Well, next time you have any doubts come and meet me in the staff room so that we can work on them. You’ll only waste time if you don’t ask your doubts.
Gunu: Thank you, ma’am. I will clear all my doubts before submission.
Teacher: I’ll need you to solve the assignment on my desk tomorrow then. Meet me after class with your doubts.
Gunu: Thank you so much.
There you have it: Dialogue writing between a teacher and a student who has not done his homework or assignment.
I hope these examples are cleared your doubts.
Do let me know if you have any doubts or topic suggestions for me by leaving a quick comment below.
How to Write a Conversation or Dialogue In-depth Video:
More from English Compositions
- Madhyamik English Writing Suggestion 2022 [With PDF]
- [FREE PDF] From The Diary Of Anne Frank MCQs | CBSE Class 10 English Chapter 4 [TERM 1]
- Short Essay on Importance of Homework [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- [FREE PDF] Two Stories about Flying MCQs | CBSE Class 10 English Chapter 3 [TERM 1]
- Anchoring Script For Seminar [With PDF]
- Short Essay On A Busy Railway Station [100, 200, 400 Words] With Pdf
- Anchoring Script for Quiz Competition [With PDF]
- Report Writing on Annual Sports Day Celebration in Your School [2023]
- Report Writing on Road Safety Week [2023 Updated]
- Anchoring Script for Republic Day [With PDF]
- Anchoring Script for Sports Day [With PDF]
- Anchoring Script for Retirement Function [With PDF]
- Used to — Exercise 1
- 1. I / cry / a lot in my childhood. I used to cry a lot in my childhood.
- 2. you / have / many toys? Did you use to have many toys?
- 3. we / not / complain / much. We didn’t use to complain much.
- 4. your granny / bake / pies? Did your granny use to bake pies?
- 5. Nick / argue / with his parents. Nick used to argue with his parents.
- 6. we / get / to work by car. We used to get to work by car.
- 7. the students / not / do / so much homework. The students didn’t use to do so much homework.
- 8. your friend / work / as a flight attendant? Did your friend use to work as a flight attendant?
- 9. they / explain / every mistake to us. They used to explain every mistake to us.
- 10. Samantha / not / help / people. Samantha didn’t use to help people.
- Used to — Exercise 2
- Used to — Exercise 3
- Used to — Jumbled words
- Used to, Get used to, Be used to
- Used to, Get used to, Be used to — Exercise 2

How To Handle A Student Who Doesn’t Do Homework?

Affiliate Disclaimer
As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.
If you’ve been teaching for any length of time, you know that there are students who don’t do their homework.
This is not always a sign of laziness, apathy, or lack of interest in the subject matter. It may just be that they didn’t understand the assignment and/or were too busy to complete it.
Regardless of the reason, these students will need some extra attention and guidance if you want them to succeed academically.
A personal touch is usually the best approach. In other words, don’t hesitate to talk to your students face-to-face about their homework problems. They will appreciate your interest and show a willingness to improve because you care enough about them as an individual to find a solution.
If these students want to improve their grades, your guidance will simplify the learning process and help them experience the satisfaction of doing well in school.
I hope this article helps you manage your students who don’t do homework!
Why Some Students Don’t Do Their Homework?
This is a question often asked by young and veteran teachers alike. The following list contains common reasons why students don’t complete their homework, as well as ideas on how to make sure that such situations never occur in your classroom.
1) What’s the Point?
Sometimes, students simply don’t see a point in doing their homework. This may be because the subject is boring, or monotonous – or it could be because it’s impossible to comprehend. Ensuring that students have a solid understanding of the material before moving on to the next topic will help eliminate this issue. In addition, if you find yourself instructing something that lacks value, it may be time to rethink your approach.
2) Too Many Homework Assignments
This is often the most common issue students face. Teachers who fail to recognize that their students are carrying too much of a workload can create unbearable conditions that lead to laziness and failure. If you’re finding yourself sending home a large amount of work every night, you should strongly consider revising your approach. It’s much better to focus on a small number of assignments and ensure they’re completed correctly, rather than overwhelming students with too many tasks.
3) Lack of Self-Motivation
Many students don’t do their homework because they lack motivation and self-discipline. In situations such as these, it’s important to remember that you can’t force a student to complete their work – but there are ways for you to motivate them. The key is making the endeavor rewarding and worth their time – this could be through rewards or points systems.
4) Intellectual Disability
Sometimes students don’t do their homework because they’re struggling to keep up. This can be due to a variety of reasons (e.g., medical conditions, learning disabilities, etc.) If you suspect that your students are facing issues like these, you must take immediate action at the appropriate time.
5) Lack of Parental Involvement
Sometimes, parents fail to support their child’s education. This lack of involvement can significantly affect the student, who may then find it difficult to complete homework tasks without parental guidance. You should give students enough space to do their work, but you should also be supportive in helping them when they need help.
6) Poor Planning
Students can underestimate the amount of time it will take to complete their homework. When this happens, they might put off starting work until the last minute – or simply give up altogether. You should always keep an eye on how much time has passed since your students were given their task, so you can notify them if it’s becoming overdue. In addition, you should encourage your students to start work early, so they have sufficient time to complete it.
7) Illness
When students become ill, they may struggle to control their behavior and focus on homework. If your class falls victim to a bug, you should allow individuals to take the necessary time off without anxiety or pressure. The same goes for injuries – any situations where students are bedridden should be handled with appropriate care.
8) Bad Timing
Sometimes, students don’t do their homework due to bad timing. This could be because they’ve only just returned home from school and haven’t had enough time to rest. It’s important that you give your students ample time to unwind before starting any work, so they can retain their focus.
9) Distractions at Home
Modern homes contain a multitude of distractions that can affect the way students work. In addition to these, students may also have distracted siblings or relatives – making it hard for them to concentrate on tasks given by the teacher. You should always provide plenty of space and seclusion when working on academic tasks.
10) The Task is Too Challenging
It’s possible that students are attempting to complete assignments that are just too difficult for them. If this happens, you should consider revising the difficulty of your work until all of your students feel comfortable completing it.
11) Poorly Organized
Similar to planning issues, poorly organized students can struggle when it comes to completing their homework. You should work closely with your students to ensure they have the best tools for completing assignments.
12) Disinterest
There are some students who just aren’t interested in what you’re teaching them. This could mean that they refuse to complete their work or it may prevent them from retaining information. You should try and engage all of your students in your lessons so they remain interested and invested.
In conclusion, there are several reasons why some students don’t do their homework. The main causes include a lack of planning, ill health, and excessive or poorly organized tasks. You should always monitor your classes to make sure they’re completing work effectively and without difficulty.
How Should Handle Students Who Don’t Do Their Homework?
For a new teacher, handling a student who doesn’t do their homework can be a difficult task. It could throw off the rest of your lesson plans that you have been working on all day or week. You have to find a way to deal with it without showing favoritism and giving out punishments for those who don’t complete their work.
This can be a very delicate situation especially if several children don’t complete their homework.
1. Let them know the importance of doing their work
One of the first steps to take when a student does not complete their work is letting them know the importance of doing so. You can tell students that it is important to do their work, so they will be prepared for the next school day.
2. Give them a warning
Giving out a simple warning would be an ideal approach when handling students who have not completed their work. This means letting them know of any consequences or possible punishments that can be given if they do not complete their homework.
3. Let them know what your role is as a teacher
Another very effective way to deal with students who don’t do their work is by informing them of what the teacher’s role is in the classroom. By explaining this, you are letting them know that you are not responsible for their education. You are there to help them when needed and direct them in the right direction.
4. Give students who don’t do their work another opportunity
After letting students know what consequences they will face if they don’t complete their work, you can give them an opportunity to turn it in the next day or the following class period. This is a very effective way of dealing with students who did not complete their homework because it lets them have another chance to do so.
5. Give consequences for students who don’t complete their work
The most common consequence that you can give out when a student does not do their schoolwork is giving them detention or some other form of punishment. This can be a difficult thing to do because you have to find a way of disciplining students without jeopardizing your relationship with students or other teachers.
6. Have the parent call the student’s teacher
If a student does not turn in homework more than two times and they continue to not complete their work for several weeks, you can give the student’s parent a call. This can be an effective way of notifying parents about their child’s lack of schoolwork and lack of studying at home.
7. Talk to the student after class or during lunch
If you feel as if it is appropriate, you can talk to the student outside of the classroom setting, during lunch, or after school. This is an approach you can take when dealing with students who continuously do not complete their homework. By talking to them outside of the classroom, it makes it easier to handle situations that may arise during class periods.
8. Give student work to another classmate
Another successful way of handling students who don’t do their work is to give them school work that is given to other students. For example, you can give out extra credit questions or assignments that are completed by other students if they do not complete their work.
9. Make an announcement about the homework policy
Announcing what your classroom’s policy for homework is can be helpful because it lets everyone know what to expect for the upcoming weeks or months. You can also use this chance to remind students of your classroom rules and procedures.
10. Make sure homework is not repeatedly an issue
Make sure that you are aware of how often homework becomes an issue in your classroom. If it happens all the time, then there may be something wrong with how you are handing out homework. It may be a good idea to have students complete homework during the first week of school so you can see if there becomes an issue or not.
Final Thought
It can be frustrating when students don’t do their homework. There are a variety of approaches for handling this issue, but the most important thing is to identify what will work best with your personality and teaching style. In this blog post, we’ve provided ten different ways you can address students who consistently turn in incomplete schoolwork or neglect it altogether. Don’t forget that it may take some time before you find out which approach works best for both you and your students! Check out more articles here.
Image by mathgun from Pixabay
About the author
Latest posts
Enhancing classroom communication with visual aids.
As a teacher, I’ve noticed that students often lose interest quickly. However, when I use visual aids in my lessons, the classroom becomes much more engaging. I want to share with you 15 effective ways that visual aids have made learning more exciting. These tools, which include interactive whiteboards and detailed mind maps, do more…
Boosting Student Participation: 13 Communication Tips for Success
As an educator, my goal is to find effective ways to increase student participation in the classroom. It’s important to understand that communication plays a crucial role in engaging students. In this article, I will share 13 communication tips that have proven to be successful in creating a positive classroom environment and fostering open dialogue…
Why Is Empathy Essential for Effective Classroom Communication?
Empathy is really important when we talk with our students. When we understand how they feel, it helps remove barriers and makes learning easier. Empathy builds trust, makes the classroom a supportive place, and gets students truly involved. When we pay attention to each student’s specific situation and treat them with respect, we’re doing more…

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.
#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.

#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2022 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2021 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2020 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2019 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2018 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2017 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
College Minor: Everything You Need to Know
14 fascinating teacher interview questions for principals, tips for success if you have a master’s degree and can’t find a job, 14 ways young teachers can get that professional look, which teacher supplies are worth the splurge, 8 business books every teacher should read, conditional admission: everything you need to know, college majors: everything you need to know, 7 things principals can do to make a teacher observation valuable, 3 easy teacher outfits to tackle parent-teacher conferences, 21 ways to support students who have trouble finishing homework tasks.

Are you looking for ways to support students who have trouble finishing homework tasks? If so, keep reading.
1. Urge the learner to create an understanding of the consequences of their behavior by writing down or talking through problems that may happen due to their failure to finish homework tasks (e.g., if they do not finish the homework task , their grade may drop, then they may not be able to take part in extracurricular learning activities ).
2. Give the learner a book bag, backpack, etc., to take homework tasks and learning materials to and from home.
3. Give a reinforcing learning experience at the beginning of the day/class period, contingent upon the conclusion and return of homework tasks .
4. Get the learner to organize tasks by dividing them into small segments. Get the learner to set deadlines and reward themselves after finishing each segment of the task.
5. Get the learner to create a chart to follow that will let them finish all tasks.
6. Create an environmental setting for the classroom that promotes optimal individual performance (e.g., quiet room, background music, fresh air, etc.).
7. Urge the parents to make positive remarks about school and the importance of finishing homework.
8. Give time at school for homework conclusion when the learner cannot be successful in performing tasks at home.
9. Indicate what is to be done for the conclusion of the homework task (e.g., indicate definite starting and stopping points, indicate the minimum requirements, etc.).
10. Get the learner to question any directions, explanations, or instructions not grasped.
11. Let logical consequences happen for failure to finish homework tasks (e.g., learners who do not finish their homework will not take part in more desirable learning activities ).
12. Give the learner written instructions for doing homework tasks .
13. Provide the parents with information appropriate for them to help the learner with homework (e.g., what the tasks are and Learning Interventions: Strategies to help with the tasks).
14. Urge the learner to reward themselves (e.g., a ten-minute break, speak briefly with a relative, telephone a friend, etc.) for concentrating on a task for a specific length of time.
15. Let the learner perform a highly desirable task when homework has been turned in to the teacher.
16. Get the learner to place notes in highly visible areas (e.g., refrigerator door, bathroom door, front door, etc.) to remind the learner to return homework tasks to school.
17. Let the learner perform alternative homework tasks . As the learner shows success, slowly present more components of the regular homework task until the tasks are routinely performed and returned to school.
18. Make sure the learner knows that homework tasks not finished and turned in to the teacher will have to be finished during other times (e.g., break time, leisure time, before/after school, etc.).
19. Complete a few problems of the homework task with the learner to serve as a model and start the learner on the task.
20. Get the learner to enlist the help of a relative, friend, etc., to remind them of homework tasks .
21. Consider using an education app to help the student sharpen their organizational skills. Click here to view a list of apps that we recommend .
Fellowships: Everything Your Need to Know
Perennialism: everything you need to know.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

Student Learning: What You Need to Know Before Creating Your Lesson Plan

10 Tips for Preventing Summer Slide

Will “school choice on steroids” get a boost under a Trump administration?
9 challenges our students face in school today part iv: violence.

21 Strategies to Help Students Who Have Trouble Completing Assignments Independently

Switch your high school classroom to flexible seating

Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
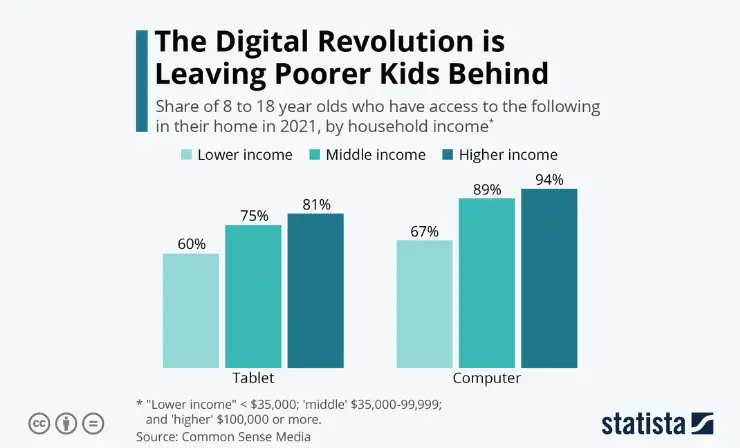
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- Exploring the Evidence: 7 Comprehensive Reasons Why School Should Start Later for Enhanced Student Well-being and Academic Success - February 15, 2024
- Why Students Should Learn a Second Language for Future Success: Exploring the 7 Benefits - February 12, 2024
- 9 Reasons Why Teachers Should Accept Late Work: Balancing Discipline and Flexibility in Education - January 31, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- English Only
All the students didn't do the homework
- Thread starter ravaravaaaaaaaaa
- Start date Jul 16, 2022
ravaravaaaaaaaaa
Senior member.
- Jul 16, 2022
So, today we were asked to submit our hw. It turns out that no one did the hw(homework) . One of my friends stood and told 'All the students didn't do hw' I think it's wrong He should have used 'none of the students ' instead. Am i right?
Yes. None of the students/us did the homework .
"'All of the students didn't do the homework" is not "wrong," although "None of..." is probably more natural.
The Newt said: "'All of the students didn't do the homework" is not "wrong," although "None of..." is probably more natural. Click to expand...
All of the students didn't (do something) = none of the students did (do something). And generally speaking, we are far more likely to use the second form.
JulianStuart
heypresto said: All of the students didn't (do something) = none of the students did (do something). And generally speaking, we are far more likely to use the second form. Click to expand...
Le Gallois bilingue
“All the students didn’t do their homework” might work.
ravaravaaaaaaaaa said: I think 'not' means the rest of the sentence is false. So here, the fact that all did homework is only false Click to expand...
English Basics
Conversation between teacher and student who has not done his homework
This blog post looks at a conversation between a teacher and a student who has not done homework.
Sample Conversation between teacher and student who has not done his homework – 1
Teacher: Good morning, John. Can I see your homework today?
Student: Good morning, Mrs. Smith. I’m sorry, I haven’t finished it yet.
Teacher: Why not?
Student: I had some unexpected things to take care of yesterday and couldn’t get to it.
Teacher: That’s not a good excuse, John. You should have prioritized your homework.
Student: I know. I’m sorry. Can I have a little more time to finish it?
Teacher: I’m afraid not. Homework is due at the start of class. You should have taken care of it last night.
Student: Yes, you’re right. I understand. I’ll make sure to get it done on time next time.
Teacher: I hope so. In the meantime, you’ll have to stay after class to complete it and receive a zero for today’s homework.
Student: Yes, Mrs. Smith. Thank you for understanding. I’ll make sure to get it done.
Sample Conversation between teacher and student who has not done his homework – 2
Teacher: Hi, Sarah. Can I see your homework for today?
Student: Hi, Mrs. Brown. I’m sorry, but I didn’t do it.
Student: I had trouble understanding the assignment and didn’t want to turn in something wrong.
Teacher: I see. Well, you should have come to me for help. I’m here to support you.
Student: I know, and I’m sorry. I should have asked for your help earlier.
Teacher: It’s okay, Sarah. We can work on it together now. Do you have your textbook and notes with you?
Student: Yes, I do.
Teacher: Great. Let’s sit down and go over the assignment together. I’ll explain anything you’re having trouble with, and you can ask me questions.
Student: Thank you, Mrs. Brown. I appreciate it.
Teacher: No problem, Sarah. That’s what I’m here for. Let’s get started.
Related posts:
- Conversation between Professor and Student about God
- How do you write dialogue between a teacher and a student?
- Restorative Conversation between Teacher and Student
- Conversation between Professor and Student about Robotics
- Conversation between Teacher and Student in Staff Room
- Conversation between Teacher and Student on Public Speaking
- Conversation between teacher and student about assignment
- Conversation between teacher and student after long time
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are several reasons why students don't do homework. Complicated directions, an excessive homework workload, and apathy towards homework can all contribute to a lack of homework completion. Fortunately, teachers can adapt homework assignments to meet students' needs, thus increasing homework completion rates.
The verb "do" is a helping verb. We add it to the simple form of a verb to make questions and negatives in the present tense and the past tense. I don't work on the weekend. (present tense negative). He didn't like to go to the store when he was younger. (past tense negative). They didn't have any money last week. (past tense negative.)
For "does" and "doesn't" you forgot the pronoun "it.". Example: 'It ( (the toaster)) doesn't ususally work. It does sometimes work after I whack it a bit.'. I suggest a dding the nonpersonal pronoun "it" to this lecture — as well as the use of non-pronoun subjects with "do," "does," etc.
Advertisement In this article, I will cover how to write a dialogue writing between a teacher and a student who has not done his homework or assignment. Sample Conversation 1 Teacher: Good morning All!. Please submit yesterday's homework. Students: Good morning sir! Advertisement Teacher: Please submit your homework! All those who have not completed the homework… Read More »
5. Nick / argue / with his parents. Nick used to argue with his parents. 6. we / get / to work by car. We used to get to work by car. 7. the students / not / do / so much homework. The students didn't use to do so much homework.
Here are 6 research-backed reasons for why students resist homework- plus tips to help overcome them. 6 Reasons Students Don't Do Their Homework-And What You Can Do About It. Fact #1 The homework takes too long to complete. In a study of over 7000 students (average age of 13), questionnaires revealed that when more than 60 minutes of ...
17. Praise those students who finish their tasks at school during the time given. 18. Send home only one homework task at a time. As the learner shows success finishing tasks at home, slowly increase the number of homework tasks sent home. 19. Show the tasks in the most attractive and exciting manner possible. 20.
2. Give them a warning. Giving out a simple warning would be an ideal approach when handling students who have not completed their work. This means letting them know of any consequences or possible punishments that can be given if they do not complete their homework. 3. Let them know what your role is as a teacher.
You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you've got SAT studying to do. It's just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you're reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time. 5.
A few more tips on giving homework. 1. Always show that you notice if it is done or not, even if it is a quick glance over the shoulder and "Good" or a slight frown. 2. Recycle the language of the homework in class, e.g. checking it straight off and using that language in the warmer for the rest of the class. 3.
Palo Alto, CA: Stanford University Press. Bennett S., Kalish N. (2006). The case against homework: How homework is hurting children and what parents can do about it. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press. Brown S., Vaughan C. (2009). Play: How it shapes the brain, opens imagination, and invigorates the soul.
19. Complete a few problems of the homework task with the learner to serve as a model and start the learner on the task. 20. Get the learner to enlist the help of a relative, friend, etc., to remind them of homework tasks. 21. Consider using an education app to help the student sharpen their organizational skills.
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
USA / EEUU. English - US. Jul 16, 2022. #8. ravaravaaaaaaaaa said: I think 'not' means the rest of the sentence is false. So here, the fact that all did homework is only false. " Not all of the students did their homework" means that some did not do it, but that presumably others did. "All of the students didn't do the homework" could ...
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
Here are nine reasons kids don't finish their reading homework. 1. They read slowly. Kids read at different paces. Your child may read more slowly than classmates. This doesn't mean your child isn't as smart as other kids. But it may mean your child needs shorter reading assignments, more time, or extra support.
We use did and didn't (NOT was/wasn't or were/weren't) as the auxiliary verb in negatives and questions in past simple. We didn't eat at 6. We weren't eat at 6. Did you do your homework? Were you do your homework? We do NOT use did or didn't in past simple negatives or questions when the main verb is be. They weren't happy. They ...
Homework is due at the start of class. You should have taken care of it last night. Student: Yes, you're right. I understand. I'll make sure to get it done on time next time. Teacher: I hope so. In the meantime, you'll have to stay after class to complete it and receive a zero for today's homework. Student: Yes, Mrs. Smith.
A student didn't do the homework because they "couldn't afford" the book . I had a student send me an essay-length email because they didn't think it was right that I assigned questions from our textbook in the homework this week. For context, I don't use the book questions in all of the assignments, because I like to write my own. ...
Homework is not a countable noun, so you have to say: the homework assignment. their homework. your homework. So you might say: Please stand up if you have not done your homework. Please stand up if you have not done the homework assignment. Anyone who has not done their homework, please stand up.
Three students didn't do _____ English homework. 2.I have a car._____ car is white. 3. We have a dog_____ name is Pancho. 4. Nancy is from England _____ husband is from Australia. 5. Freddy and Nodia go to a high school, _____ little brother goes to primary school. 6. Mr. O'Neil has a boat. _____ boat is very old. 7.
Brazil. Current Location. Brazil. Mar 15, 2019. #1. Before starting to correct the homework, I'd say a teacher would ask the students: "Have you done the homework, guys", rather than "Did you do the homework" (at least, in British English).
A. 1_ Three students didn't do..... English homework. B. 2_ I have a car. ..... car is white. C. 3_These are my teachers. ..... Names are Gisela and Maria Jose. D. 4_Norma is from England. ..... husband is from Australia. E. 5_We are Betty and Barbara and this is .....favorite book. .....title is Twilight