- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects

How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
Introduction, general overviews.
- Experimental Research
- Quasi-Experimental Research
- Hierarchical Linear Modeling
- Survey Research
- Assessment and Measurement
- Qualitative Research Methodologies
- Program Evaluation
- Research Syntheses
- Implementation
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Action Research in Education
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Educational Assessment
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Grounded Theory
- Literature Reviews
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Mixed Methods Research
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Narrative Research in Education
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Science and Education Research
- Statistical Assumptions
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- English as an International Language for Academic Publishing
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- History of Education in Europe
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Methodologies for Conducting Education Research by Marisa Cannata LAST REVIEWED: 15 December 2011 LAST MODIFIED: 15 December 2011 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0061
Education is a diverse field and methodologies used in education research are necessarily diverse. The reasons for the methodological diversity of education research are many, including the fact that the field of education is composed of a multitude of disciplines and tensions between basic and applied research. For example, accepted methods of systemic inquiry in history, sociology, economics, and psychology vary, yet all of these disciplines help answer important questions posed in education. This methodological diversity has led to debates about the quality of education research and the perception of shifting standards of quality research. The citations selected for inclusion in this article provide a broad overview of methodologies and discussions of quality research standards across the different types of questions posed in educational research. The citations represent summaries of ongoing debates, articles or books that have had a significant influence on education research, and guides to those who wish to implement particular methodologies. Most of the sections focus on specific methodologies and provide advice or examples for studies employing these methodologies.
The interdisciplinary nature of education research has implications for education research. There is no single best research design for all questions that guide education research. Even through many often heated debates about methodologies, the common strand is that research designs should follow the research questions. The following works offer an introduction to the debates, divides, and difficulties of education research. Schoenfeld 1999 , Mitchell and Haro 1999 , and Shulman 1988 provide perspectives on diversity within the field of education and the implications of this diversity on the debates about education research and difficulties conducting such research. National Research Council 2002 outlines the principles of scientific inquiry and how they apply to education. Published around the time No Child Left Behind required education policies to be based on scientific research, this book laid the foundation for much of the current emphasis of experimental and quasi-experimental research in education. To read another perspective on defining good education research, readers may turn to Hostetler 2005 . Readers who want a general overview of various methodologies in education research and directions on how to choose between them should read Creswell 2009 and Green, et al. 2006 . The American Educational Research Association (AERA), the main professional association focused on education research, has developed standards for how to report methods and findings in empirical studies. Those wishing to follow those standards should consult American Educational Research Association 2006 .
American Educational Research Association. 2006. Standards for reporting on empirical social science research in AERA publications. Educational Researcher 35.6: 33–40.
DOI: 10.3102/0013189X035006033
The American Educational Research Association is the professional association for researchers in education. Publications by AERA are a well-regarded source of research. This article outlines the requirements for reporting original research in AERA publications.
Creswell, J. W. 2009. Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches . 3d ed. Los Angeles: SAGE.
Presents an overview of qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods research designs, including how to choose the design based on the research question. This book is particularly helpful for those who want to design mixed-methods studies.
Green, J. L., G. Camilli, and P. B. Elmore. 2006. Handbook of complementary methods for research in education . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Provides a broad overview of several methods of educational research. The first part provides an overview of issues that cut across specific methodologies, and subsequent chapters delve into particular research approaches.
Hostetler, K. 2005. What is “good” education research? Educational Researcher 34.6: 16–21.
DOI: 10.3102/0013189X034006016
Goes beyond methodological concerns to argue that “good” educational research should also consider the conception of human well-being. By using a philosophical lens on debates about quality education research, this article is useful for moving beyond qualitative-quantitative divides.
Mitchell, T. R., and A. Haro. 1999. Poles apart: Reconciling the dichotomies in education research. In Issues in education research . Edited by E. C. Lagemann and L. S. Shulman, 42–62. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Chapter outlines several dichotomies in education research, including the tension between applied research and basic research and between understanding the purposes of education and the processes of education.
National Research Council. 2002. Scientific research in education . Edited by R. J. Shavelson and L. Towne. Committee on Scientific Principles for Education Research. Center for Education. Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
This book was released around the time the No Child Left Behind law directed that policy decisions should be guided by scientific research. It is credited with starting the current debate about methods in educational research and the preference for experimental studies.
Schoenfeld, A. H. 1999. The core, the canon, and the development of research skills. Issues in the preparation of education researchers. In Issues in education research . Edited by E. C. Lagemann and L. S. Shulman, 166–202. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Describes difficulties in preparing educational researchers due to the lack of a core and a canon in education. While the focus is on preparing researchers, it provides valuable insight into why debates over education research persist.
Shulman, L. S. 1988. Disciplines of inquiry in education: An overview. In Complementary methods for research in education . Edited by R. M. Jaeger, 3–17. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association.
Outlines what distinguishes research from other modes of disciplined inquiry and the relationship between academic disciplines, guiding questions, and methods of inquiry.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender, Power and Politics in the Academy
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Native American Studies
- Nonformal and Informal Environmental Education
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.147.128.134]
- 185.147.128.134
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
Research Methods and Methodologies in Education
- Robert Coe - Durham University, UK
- Michael Waring - University of Leeds, UK
- Larry V Hedges - Northwestern University, USA
- Laura Day Ashley - University of Birmingham, UK
- Description
The #1 resource for carrying out educational research as part of postgraduate study.
High-quality educational research requires careful consideration of every aspect of the process. This all-encompassing textbook written by leading international experts gives students and early career researchers a considered overview of principles that underpin research, and key qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods for research design, data collection and analysis.
This third edition includes four new chapters:
- Disseminating your research
- Data science and computational research methods
- Observational methods
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
Plus a new Research essentials feature that highlights key ‘must-haves’ or misconceptions relating to each methodological approach, research design or analytical tool discussed.
This is essential reading for postgraduate students on education courses and early career researchers looking to sharpen their research practice.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
Logically structured, clear and informative. This book has significant chapter on Academic ethics which will be essential not only for BA students but for PhD and early research career as well
This book covers a wide range of issues in relation to educational research - there is something in there for all my students. Each chapter is short and to the point.
Research Methods and Methodologies in Education is a book I have used repeatedly since teaching Research on Foundation degree and BA top up
This book is beneficial for doctoral students because it provides clear and concise details on the steps to performing scholarly research designs. I am highly recommending this book for my courses.
Preview this book
Sample materials & chapters.
Sample Chapter
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, related products.

- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Curriculum, instruction, and pedagogy article, research methods in teacher education: meaningful engagement through service-learning.

- 1 Department of Education and Centre for Teacher Education, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 2 Ecological Economics & RCE Vienna, Vienna University of Economics and Business, Vienna, Austria
- 3 Centre for Teacher Education, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Competence in research methods is a major contribution to (future) teachers’ professionalism. In the pedagogical approach presented here, which we call the Teaching Clinic, we combine service-learning and design-based research to create meaningful learning engagements. We present two cases to illustrate the objectives, processes, and outcomes of the service-learning projects and reflect about both in terms of learning and service outcomes. This includes discussions of how this pedagogical approach led to motivation and engagement, how principles of transfer of training are obeyed, and what this means quite generally for school-university relationships.
Introduction
Research skills, such as the knowledge and skills necessary to pose clear (scientific) questions, to critically review the literature, and to collect, analyze, and interpret data, are important to navigate the complexity of daily life. This is also true for teachers, where research skills and increasingly seen as important elements of professionalism ( Amirova et al., 2020 ) and the establishment of evidence-based teaching practices ( Burke et al., 2005 ). In this article, we aim to present case studies of a pedagogical approach that helps in increasing the perceived relevance of discussing methodological issues within teacher education ( Davidson and Palermo, 2015 ): the Teaching Clinic (TC).
TCs are designed as semester-long courses in which teachers in training (now “students”) collaborate with practicing teachers (now “teachers”) on pedagogical innovations in the teachers’ classrooms through design-based research ( Bakker, 2018 ). They can be seen as instances of service learning in the domain of teacher education ( Stoecker, 2016 ). TCs tackle the combined needs of students, such as the wish for more formal experiences directly in the school-context and obtaining well-transferable competences and knowledge, and teachers, who may want a more direct access to state-of-the-art knowledge and support in implementing pedagogical innovations.
The objective of this article is to present the pedagogical approach taken in the TC and to explore its outcomes in terms of research competence and service through the accounts of stakeholders to the TC. Specifically, we present two exemplary projects that were conducted within the TC and showcase the reflections from students, teachers, and the course facilitators.
Context and Frameworks
The Teaching Clinic (TC) is a course for Master students in a teacher education curriculum at an Austrian university. Established teachers submit research questions about current professional challenges. These questions are then picked up by students, who conceptualize and execute research projects to find evidence based solutions.
The primary objective of doing research at this very local and practical level is to instill a scientific mindset in the students. Research skills are increasingly seen as tools of the professional practice; not as something confined to academic research. Importantly, this perspective is not only shared with the students that work on the projects, but also with the teachers that submit them. In that sense, the TC is about the transfer from university to practice (see also the current debate about “Third Mission”; Schober et al., 2016 ).
In terms of research methods, two secondary objectives of the format exist. First, the TC presents a clear purpose, and, therefore, motivation, to apply research methods. Second, the students apply research methods in a context that is almost identical to the context of their later work. This facilitates the transfer from the training context to the subsequent professional work as teachers ( Blume et al., 2010 ; Quesada-Pallarès and Gegenfurtner, 2015 ).
Main Pedagogical Approach: Service-Learning
The main pedagogical frame used to conduct the TC was service-learning ( Sotelino-Losada et al., 2021 ). There are numerous definitions of service-learning, but perhaps the most cited is the one formulated by Bringle and Hatcher (1995) , who define service-learning as a
“...course-based, credit-bearing educational experience in which students (a) participate in an organized service activity that meets identified community needs and (b) reflect on the service activity in such a way as to gain further understanding of course content, a broader appreciation of the discipline, and an enhanced sense of personal values and civic responsibility” (p. 212).
Service-learning is an experience-based learning approach ( Biberhofer and Rammel, 2017 ) that combines learning objectives with community service and emphasizes individual development and social responsibility through providing a service for others; service situations are viewed as learning settings and opportunities for public engagement ( Forman and Wilkinson, 1997 ). According to Furco (1996) , the key lies in the equal benefit for providers (TC: students) and recipients (TC: teachers). The TC could also be discussed from the perspective of transformative learning ( Mezirow and Taylor, 2009 ), as the learning goal of the seminar is not about pure knowledge acquisition, but about “building the capacity of students as agents of change” ( Biberhofer and Rammel, 2017 , p. 66). The TC provides a rather open learning environment, in which students engage in an open dialogue with each other, with the teachers, and the course facilitator, who does not necessarily possess the necessary subject-matter expertize but provides feedback and guidance throughout this process of dialectic inquiry.
Useful Methodological Lens: Design-Based Research and Action Research
As stipulated above, the main objective of the TC is to implement research projects at a local level in the teaching context. One methodological perspective that is very well adapted to this aim is design-based research (DBR). DBR is a research approach that claims to overcome “the gap between educational practice and theory, because it aims both at developing theories about domain-specific learning and the means that are designed to support that learning” ( Bakker and Van Eerde, 2015 , p. 430). In DBR, the design of learning environments proceeds in a reflective and cyclic process simultaneous to the testing or development of theory. The design includes the selection and creation of interventions which is done in cooperation with practitioners, while holding only little control of the situation. This research approach aims to explain and advise on ways of teaching and learning that proved to be useful and to develop theories that can be of predictive nature for educational practice. Because of its interventionist nature, researchers conducting this type of research are often referred to as “didactical engineers” ( Anderson and Shattuck, 2012 ; Bakker and Van Eerde, 2015 ).
In the TC, we use DBR as a methodological frame to set up the projects. On a micro level, different projects feature very different data (e.g., video recordings, surveys among pupils, interviews, texts, etc.) and methods (e.g., field experiments, statistical analyses, content analysis, etc.). The students need to decide which ones to use, get appropriate data, and run the analysis.
In this section, we present how TCs are a useful context for becoming teachers to develop research competences. Since this is the very first discussion about TCs, we use case studies to explore the outcomes of this pedagogical format. The case studies presented here contain reflections of students, teachers, and course facilitators based on a set of guiding questions in the direction of research methods and service-learning. Specifically, two independent TC projects will be presented. The first project focused on implementing concepts of Education for Sustainable Development (EDS) in the context of socio-economically disadvantaged classes in the field of Science, Mathematics, Engineering, and Technology (STEM). A team of two students and two teachers collaborated to further develop and evaluate lesson plans based on classroom experience, pupils’ feedback, and expert knowledge. The second project focused on improving the feedback strategies in response to students’ writing in language classrooms. Using an experimental research design, a team of four students generated data to allow for the evidence-based improvement of personal feedback and marking strategies.
Both projects will be reflected from the angles of multiple stakeholders; the team of authors of this article include a Master student, a teacher, and a researcher (and facilitator of the course). This reflects the nature of the TC as a learning experience that is co-created by multiple stakeholders; the participating students are not just learners, but also co-researchers and pedagogical co-designers (see Bovill et al., 2016 ). In the context of this publication students not only helped by providing additional reflections and data (see Case 1), but also by taking the position as a co-author (Case 2 was written by a student of the project; the course facilitator, an experienced researcher and first author of this text, provided feedback but otherwise did not interfere in the writing process; for student faculty-student co-authoring also see Abbott et al., 2021 ). For each case, we will first describe the objectives as laid out by the submitting teacher(s), the methodological process to find answers to the questions posed, and the final outcomes as reported back to the teacher(s).
Case 1: Education for Sustainable Development for Socio-Economically Disadvantaged Classes in the Prevocational School Sector (Teacher’s View)
This first case about Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) for socio-economically disadvantaged classes in the prevocational school sector is presented from the point of view of the teacher (who submitted the problem to the TC).
The relevance of the global educational environment for social fields of action was already taken up by the United Nations (UN) before the turn of the millennium and led to the years 2005–2014 being declared the World Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (WDESD) ( Combes, 2005 ). In the German-speaking countries, the Orientation framework for the learning area “ Global Development ” serves as an essential contribution to explicit didactics for ESD in the secondary education sector ( Schreiber and Siege, 2016 ).
This pedagogical concept was used by the students to support two teachers at a prevocational school in implementing ESD didactics into Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) lessons. The aim of the curriculum was to help low-income pupils at a vulnerable prevocational school location to develop highly demanded competences in the field of STEM professions.
Another objective was to strengthen the students’ sense of responsibility for society and environment in alignment with the bottom-up drive of the “FridaysforFuture” movement. The starting point for the research needs in schools was a study conducted by the German Federal Environment Agency, which asked whether environmental protection as a motive is useful for addressing young people’s motivation to enter STEM professions more successfully than before ( Örtl, 2017 ). The results of the study imply, among other aspects, that STEM didactics have close links to ESD and that synergetic overlaps in this area seem to be a promising approach for STEM lessons at prevocational schools.
Throughout the TC, promising learning formats in STEM lessons were tested in iterative cycles of implementation, evaluation, and adjustment in the sense of DBR at the chosen school site. Here, learning journals produced by students for different learning formats in STEM lessons on the topic “Renewable Energies” and “Climate Change” served as the primary data to create a scientifically and empirically driven curriculum for motivating students to pursue STEM professions (see Figure 1 ).
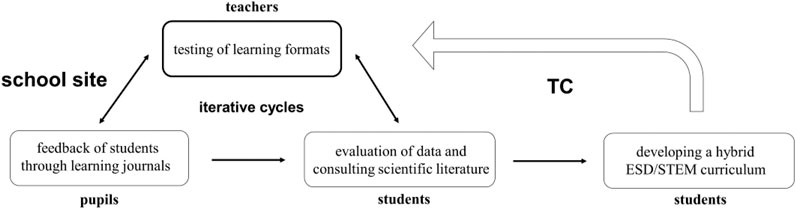
FIGURE 1 . Overview over the work process in Case 1.
The method of structured qualitative content analysis ( Mayring, 2014 ) was used to search for indicators that make learning formats subjectively interesting for students. The students were required to document steps and problems that occurred during the implementation and evaluate the learning opportunities on an ordinal scale from one to five after completion of the learning journal. The underlying learning formats include problem-centered films, concrete technical tasks (programming, mechanics, construction, electronics, and applied computer science), external workshops and lectures with companies from the technology sector.
After an initial review of the data, implications for the indicator “perceived as subjectively interesting by the students” could be concluded. The finding showed that individual isolated learning opportunities on the topic of climate change do not necessarily lead to the desired effect of students showing intrinsic motivation to acquire relevant professional skills for finding solutions.
Based on these interim results, the TC students consulted the scientific literature, which allowed for contextualization of socially relevant and scientific-technical dimensions in the acquisition of competencies in the sense of ESD. The framework for this approach was provided by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BWZ) and the German Conference of Ministers of Education and Cultural Affairs (KMK) ( Schreiber and Siege, 2016 ).
Through the continuous cycles of the DBR approach using different learning formats in ongoing school lessons, the students were able to develop a hybrid ESD/STEM curriculum step by step by evaluating the data material. Decisive input for the concrete lesson plans was derived from the indicators identified through the structured content analysis according to Mayring (2014) , which were perceived by the students as subjectively interesting and motivating. Due to COVID-19-related school closures, it was not possible to complete an annual curriculum. Nevertheless, a total of 16 lessons that met the requirements of the research assignment based on the identified indicators were designed. The curriculum created through the cooperation of school and TC now serves as a preliminary study and basis for a fully empirical main study, which is to be carried out at several school locations after the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic. The results of the qualitative preliminary study were used by the students in the final step to formulate hypotheses for the main study in accordance with the underlying research question following Mayring (2014) methodological approach.
In addition to the general results of the qualitative preliminary study, various positive effects on the stakeholders could be identified in the present case as a result of the service-learning offering. The question chosen in the case study whether environmental protection issues can contextually contribute to motivating young people in STEM classes to take an interest in related professions could not be fully answered. However, the DBR approach has served to identify those indicators based on different learning formats that were rated as subjectively interesting and motivating for students. As a pedagogical and didactic core concept, the approach of the “Recognize- Evaluate- Act”-principle from the Orientation framework for the learning area “ Global Development ” ( Schreiber and Siege, 2015 ) turned out to be particularly promising. Furthermore, a concrete further research assignment for the TC could be derived from the results to initiate a fully comprehensive empirical study based on pre-formulated hypotheses.
The TC research semester was described by the students as an eye-opening experience between university teaching and practical school experience. In this case, the service-learning project enabled the Master students to implement theoretically learned scientific methods in a practical way within the school environment. The scholarly exposure to ESD content along with instructional development using STEM learning opportunities gave the Master students a holistic view into practice-based teaching and learning research.
“The exchange, especially the feedback, with teaching staff at a preparatory vocational school with difficult socio-economic conditions was far more informative and practically relevant to me than most frontal lectures at the university. In addition to the practical and school-relevant part of the research semester, the TC together with ESD principles was an enriching support for me to be able to conduct current educationally relevant research in a scientifically and methodologically correct way. The balance between the cornerstones of school practice, TC and the final research work has given me a new perspective and understanding of the profession of a teacher and the different places of work.” (Student)
Furthermore, the underlying DBR approach has been identified as a promising approach for adapting hybrid ESD-STEM learning formats and teaching contents to determine successful learning effects with students.
The service-learning concept offered freed up additional resources for instructional development that would have been difficult to implement during the regular school year due to administrative duties and other teacher commitments. This gave teachers the opportunity not only to get ideas for lesson design, but also to further develop their own teaching based on sound and up-to-date scientific methodology. Learnings reportedly included new ways “to inspire the students with new approaches and to show them that STEM cannot be purely theoretical, but that it is important for them and society.”
Through the joint development of the curriculum, it was possible to link subject-related STEM lessons with social relevance, which often seems intangible for students, especially in STEM subjects. Teachers attributed great importance to this interconnection in identifying students' ability to explore, reflect, and critically evaluate scientific content from multiple perspectives.
“Experiencing values such as sustainability, environmental awareness and solidarity […] provide a good basis for developing into independent and responsible personalities.” (Teacher)
Particularly the context of teaching at a socially vulnerable school site suggests a value-oriented attitude and precise concept of learning formats next to topics that are relevant to the realities of the young people’s lives.
The composition of the student body in the underlying pre-vocational preparation school class showed a high degree of heterogeneity in terms of country of origin and socio-economic status. 90% of the students had a first language other than German and the vast majority could be classified as belonging to a deprivileged class of the population. The empowerment of being able to work on a curriculum for their future career led to increased motivation for the lessons, which could be seen in the underlying learning journals. The motivation was also reflected in an increased learning curve in STEM-related subject knowledge. Moreover, students’ involvement with environmental and social issues of the 21st century led to an observable increased interest in technical and scientific career profiles.
Case 2: Effective Feedback (Student’s View)
The second case shall illustrate the student’s perspective and is written by a student of the TC. The project had been carried out in the summer term 2020 and was conducted by a team of four students. The collaboration took place in a school in Vienna with two teachers and two lower-secondary classes of theirs.
At the beginning of the TC, we were confronted with a common problem of teachers: An English and a German teacher reported that they spend much time correcting their pupils’ assignments while suspecting that their pupils did not use the feedback for their own progress. In close exchange with the teachers and after an initial evaluation of the problem, we formulated a project goal: an invention should be set to counteract this problem and improve the situation for both learners and teachers.
As a first step, a thorough literature review was necessary to find appropriate strategies to tackle the problem. There exists a plethora of publications about feedback strategies; to narrow down our focus, we opted for the “minimal marking” approach because this strategy directly addresses both issues voiced by the teachers. As Hyland (1990) puts it very precisely:
Many teachers find marking to be a tedious and unrewarding chore. While it is a crucial aspect of the classroom writing process, our diligent attention and careful comments only rarely seem to bring about improvements in subsequent work (p. 279).
Besides Hyland (1990) , also Haswell (1983) dedicated a publication to the same issue. Both suggested minimal marking as a solution to reduce the teacher’s workload by simultaneously increasing the positive effect of the feedback. The basic principle of minimal marking is that instead of detailed feedback, only a cross or a check is set beside the line in which the mistake occurred; subsequently, it is the pupil’s task to correct his/her own text by identifying the mistakes and correcting it using prior knowledge or a dictionary (p. 600). Thus, the pupil receives as minimal information as necessary and is encouraged to edit the text independently ( Haswell, 1983 , p. 601). Through this approach, pupils shall be enabled to edit their texts without much support of the teacher or other adults, which shall help them to develop essential writing skills. This method is considered especially effective because it requires the pupil to act on the feedback received by the teacher ( Hyland, 1990 , p. 279). Although this approach is still applied nowadays ( McNeilly, 2014 ), it has received little attention in research. Due to this research gap and our personal interest in the topic as future language teachers, we ventured out to explore the effects of minimal marking on (a) learner’s mistake awareness, (b) the time teachers spend on giving feedback and (c) the quality as perceived by pupils and teachers.
To answer these research questions, we chose a set of methods consisting of quantitative and qualitative tools (see Figure 2 ). The procedure can be described as the following: Pupils of both classes were divided in an experimental group and a control group. Then all pupils of one class were asked to write a text in response to the same task. Teachers gave feedback using their traditional method, in which they indicate every mistake and write a short comment to each one, among the control group and using the minimal marking strategy to give feedback on the texts of the experimental group. Both teachers measured the time they needed to correct every single text. Then the pupils got their texts back and edited them. Then the edited texts were collected again. Discovered and undiscovered mistakes were counted and analyzed in the texts of both groups. Time spent on correction was analyzed for each group and juxtaposed. The pupils were asked for their opinion after the experiment through an online survey which consisted of closed and open questions. Finally, the teachers shared their experience in a narrative interview, which was also conducted online.
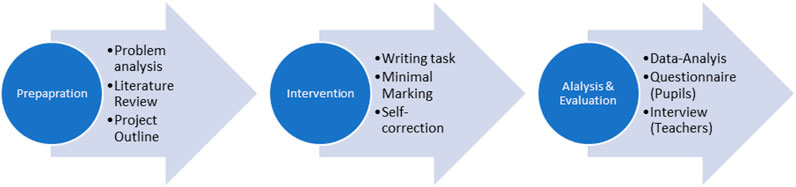
FIGURE 2 . Experimental setup of case 2.
Although the results of this small-scale study were not statistically significant, some interesting insights could be gained. Although an increased mistake awareness among pupils could not be proved with the number of mistakes occurring in the first and second text, an increased mistake awareness can be inferred from the pupil’s answers given in the questionnaire. Several pupils highlighted the positive aspects of the minimal marking approach and considered it as (really) helpful; one of the learners summarized: “I thought more about my mistakes than I usually do and, hence, I could improve my writing skills. It was more difficult to find the mistakes, but it also helped me to get better” (translated by the authors).
Regarding the time spent for correction, an advantage of the minimal marking approach could only be detected in one of both classes. The German teacher reported an average correction time of 3:14 (first round) and 2:12 (second round) per text using the traditional method and an average time of 1:39 (first round) and 1:14 (second round) per text using the minimal marking approach. The English teacher measured similar times for both feedback strategies. Limiting factors, such as the small sample size of the project and the pupils’ unfamiliarity with the new method, need to be kept in mind when conclusions are drawn. However, this only highlights the need for further research about the effects of this specific feedback method.
Probably the most promising outcomes can be reported about the attitudes of teachers and pupils. Both teachers described the collaboration between them and the students as enriching and both want to continue the collaboration with the university. Additionally, they reported an increased interest in action research for themselves but also among their colleagues. Through the questionnaire we could also observe a positive attitude toward the experiment among pupils, which gives reason for further projects in class and to further incorporate pupils in research. And finally, we students were able to develop a deeper understanding of teacher professionalism and a more positive attitude toward the application of research in teaching. Additionally, all members of the team were convinced that they wanted to apply this method as teachers in their future practice.
As outlined above, the objectives of the pedagogical/didactical concept of the TC are to create a highly effective (co-creative) learning environment for teachers in training while at the same time delivering valuable service to practice.
Reflections on Learning
Several themes of learning emerged in the cases above. The opportunity to combine own learning with delivering a service was described as important. Being of service to someone matters and enhances the motivation of students to engage also with the methodological parts of the course. The ESD case confirms the findings of Biberhofer and Rammel (2017) derived in the context of their two-semester “Sustainability Challenge”, which has been successfully executed since 2010. Participation in real life problems increases intrinsic motivation to investigate solutions (and to apply the methods needed to carry out this investigation). The master students who carried out the minimal marking project pointed out that this collaboration enabled them to apply research methods in an authentic environment and, thus, rendered them more meaningful. Additionally, this project allowed them to engage with research methods in a demanding but motivating manner which is a frequently neglected part in teacher education. The project enabled them to practice teaching methods and evaluate them through scientific methods in a systematic way; this led to a better understanding of the vital symbiosis between research and practical teaching ( Paran, 2017 ). The exploratory case studies presented in this paper cannot give an in-depth account of the learnings processes and outcomes. Future research could seek to further explore the impact of service-learning approaches to the students’ motivation (cf. Medina and Gordon, 2014 ; Huber, 2015 ).
There are some indications that the course had a positive impact on the students’ future professionalism as teachers and their scientific attitude. In the ESD case, students’ engagement with the dimensions of ecological and social justice (which are integral components of ESD) was evident primarily at two levels. On the one hand, the professional engagement with ESD led to the desire to make its impact on students measurable through scientific methodologies. On the other hand, a reframing in the sense of transformative learning ( Mezirow and Taylor, 2009 ) about the subjective role perception as a teacher for shaping an sustainable worldview for future generations of pupils could be observed. The master students of the minimal marking project considered the collaboration with already practicing teachers as especially helpful. Firstly, this special constellation allowed them to gain practical experience besides the obligatory practicum and benefit from the teachers’ experience. Secondly, the conduction within the university context required them to combine academic research and practical teaching. This supported them in their professional development as teachers because it made them realize the importance of research methods in evidence-based teaching ( Paran, 2017 ).
Basically, having learned and experienced how to utilize research methods not just for the purpose of “pure research”, but framing it as a practice of evidence-based teaching, is expected to make teachers perform better in an increasingly VUCA (volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous; Johansen and Euchner, 2013 ; LeBlanc, 2018 ) world. The COVID-19 pandemic is a case in point here. While all teachers needed to react to the changing context, not all did so in a thoughtful and effective manner ( Hodges et al., 2020 ). Different levels of professionalism and of having a scientific mindset could be a major factor in this equation. As described above, increasing this mindset was the primary objective of the course format and we hypothesize that this is an important ingredient to foster teachers’ lifelong learning ( Bakkenes et al., 2010 ; Hoekstra and Korthagen, 2011 ).
An important strategy to increase the learning outcomes for students used in the TC is to work directly in the context that the knowledge should later be applied in. Put differently, the Master students support one individual overcoming a teaching-related challenge. This similarity of contexts aids the transfer of the learnings and helps to make them more applicable ( Blume et al., 2010 ; Burns, 2008 ). Additionally, the learning process is highly social, including peers, the course facilitator(s), and the teachers. Previous research indicates that this social dimension may additionally increase the odds of “successful” learning ( Daniel et al., 2013 ; Penuel et al., 2012 ). In the ESD case, confirmation of the success of the underlying ESD/STEM concept for increasing young people’s enthusiasm for STEM careers was a transformational realization for the teachers and master’s students in the collaborative learning process. Similarly, the minimal marking group reported an unprecedented feeling of responsibility in comparison with other university courses. Because of the knowledge that their collaborating teachers and their students profited from the project, the students’ work felt meaningful and important. Simultaneously, this environment enabled them to gain experience in research methods and practical teaching which would not be possible without this unique course format.
On the other hand, students gained practical experience in non-university organizations during their studies. In the feedback, the students commented on both, gaining experience from the school context in cooperation with the teachers and the methodological and research-oriented support by the TC itself. The work at local school sites additionally motivates the students to further develop their pedagogical and didactic knowledge in a practical setting based on current school challenges. Furthermore, the interaction of the scientific approach together with the practical school experiences enables the students to internalize their own values for contemporary teaching for their future role as teachers themselves.
Reflections on Service
The teachers involved in the projects described above reported high satisfaction with the project results and an increased interest in research even extending to their colleagues. Teachers valued the opportunity to develop and improve their teaching formats and methods based on evidence and through scientific methods. Through the collaboration with students, time-consuming research could be outsourced, and the desired role of the teacher researcher could be fulfilled despite time constraints.
As shown in Figure 1 of the ESD case, the clear division of roles with clear lines of communication and distributions of action items was a major advantage in the creation and implementation of the ESD/STEM curriculum. The well-structured method of the DBR approach throughout the semester allowed for proper planning at each point in time for the scarce time resources of the various stakeholders involved during the school year. The teachers engaged in the minimal marking project also reported an increased interest in research and collaboration with the university which further extended among their colleagues. At the end of the project, they expressed their wish to continue collaboration with students of next courses to further improve their teaching. This illustrates the positive influence on the teachers’ attitude toward research and even a potential multiplying factor of the teaching clinic on teachers beyond the active participants.
Finally, the TC can function as a promising channel to maintain communication between teachers and research ( Paran, 2017 ). The collaboration between teachers working in the field and university may lead to the identification of new research gaps on the one side and more evidence-based teaching on the other. Introducing teachers to the concept of evidence-based teaching in early stages of their education may have a positive effect on their attitude toward research in teaching and be the key to the development of a professional role teacher as researcher ( Paran, 2017 ). This illustrates the close interconnections between research at university, teacher education and practicing teachers and their potential to profit from collaboration with each other.
Other Outcomes
The TC aims to create value in terms of enhancing university social responsibility ( Vasilescu et al., 2010 ). Universities play an important role in addressing global challenges, such as growing socio-economic differences, the climate crisis, or the current COVID-19 pandemic. Irrespective of the specific disciplines, the concept of university social responsibility suggests that universities should not limit themselves to research and teaching, but should commit to solving economic, social, and ecological problems. Universities play a central role in raising students’ awareness of social responsibility to help them develop into social personalities ( Bokhari, 2017 ). In that sense, special attention must be paid to teacher education for its promise of achieving multiplication effects that will eventually reach all educational levels. The principle of “Third Mission” provides a key point of reference in this context, which emphasizes the targeted use of scientific findings to deal with a wide range of societal challenges and proposes the transfer of technologies and innovations to non-academic institutions ( Schober et al., 2016 ).
The systematic approach at hand uses a university research service to address concrete issues in the local field of schooling. The benefit lies in the possibility of merging education theory with socially relevant topics from multiple perspectives. The TC initiates a sustainable circular process, which facilitates the generation of a mutual learning curve for the university system and the school system by instrumentalizing research on an evidence-based level. Thereby, the TC acts as a door opener for practice researchers with access to the otherwise difficult to access compulsory school system.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
DF designed the didactical concept and has written the conceptual part of this article. UH and KM were stakeholders to the two case studies presented in the article. Both have collected data for their case-study and offered their own reflections. All authors contributed to the overall discussion.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbott, L., Andes, A., Pattani, A., and Mabrouk, P. A. (2021). An Authorship Partnership with Undergraduates Studying Authorship in Undergraduate Research Experiences. Teaching and Learning Together in Higher Education 1 (32).
Google Scholar
Amirova, A., Iskakovna, J. M., Zakaryanovna, T. G., Nurmakhanovna, Z. T., and Elmira, U. (2020). Creative and research competence as a factor of professional training of future teachers: Perspective of learning technology. Wjet 12 (4), 278–289. doi:10.18844/wjet.v12i4.5181
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anderson, T., and Shattuck, J. (2012). Design-Based Research. Educ. Res. 41 (1), 16–25. doi:10.3102/0013189X11428813
Bakkenes, I., Vermunt, J. D., and Wubbels, T. (2010). Teacher learning in the context of educational innovation: Learning activities and learning outcomes of experienced teachers. Learn. Instruct. 20 (6), 533–548. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.09.001
Bakker, A. (2018). Design research in education: A practical guide for early career researchers . Abingdon, UK: Routledge . doi:10.4324/9780203701010
CrossRef Full Text
Bakker, A., and Van Eerde, D. (2015). “An introduction to design-based research with an example from statistics education”, in Approaches to qualitative research in mathematics education . Springer , 429–466. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9181-6_16
Biberhofer, P., and Rammel, C. (2017). Transdisciplinary learning and teaching as answers to urban sustainability challenges. Ijshe 18 (1), 63–83. doi:10.1108/IJSHE-04-2015-0078
Blume, B. D., Ford, J. K., Baldwin, T. T., and Huang, J. L. (2010). Transfer of Training: A Meta-Analytic Review. J. Manag. 36 (4), 1065–1105. doi:10.1177/0149206309352880
Bokhari, A. A. H. (2017). Universities‟ Social Responsibility (USR) and Sustainable Development: A Conceptual Framework. Ijems 4 (12), 8–16. doi:10.14445/23939125/IJEMS-V4I12P102
Bovill, C., Cook-Sather, A., Felten, P., Millard, L., and Moore-Cherry, N. (2016). Addressing potential challenges in co-creating learning and teaching: overcoming resistance, navigating institutional norms and ensuring inclusivity in student-staff partnerships. High Educ. 71 (2), 195–208. doi:10.1007/s10734-015-9896-4
Bringle, R. G., and Hatcher, J. A. (1995). A Service-Learning Curriculum for Faculty. Michigan Journal of Community Service Learning 2 (1), 112–122.
Burke, L. E., Schlenk, E. A., Sereika, S. M., Cohen, S. M., Happ, M. B., and Dorman, J. S. (2005). Developing research competence to support evidence-based practice. J. Professional Nursing 21 (6), 358–363. doi:10.1016/j.profnurs.2005.10.011
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Burns, J. Z. (2008). Informal learning and transfer of learning: How new trade and industrial teachers perceive their professional growth and development. Career Techn. Educ. Res. 33, 3–24. doi:10.5328/cter33.1.3
Combes, B. P. Y. (2005). The United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005-2014): Learning to Live Together Sustainably. Appl. Environ. Educ. Commun. 4 (3), 215–219. doi:10.1080/15330150591004571
Daniel, G. R., Auhl, G., and Hastings, W. (2013). Collaborative feedback and reflection for professional growth: Preparing first-year pre-service teachers for participation in the community of practice. Asia-Pac. J. Teacher Educ. 41 (2), 159–172. doi:10.1080/1359866X.2013.777025
Davidson, Z. E., and Palermo, C. (2015). Developing Research Competence in Undergraduate Students through Hands on Learning. J. Biomed. Educ. 2015, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2015/306380
Forman, S. G., and Wilkinson, L. C. (1997). Educational policy through service learning: Preparation for citizenship and civic participation. Innov. High Educ. 21 (4), 275–286. doi:10.1007/BF01192276
Furco, A. (1996). Service-Learning: A balanced approach to experiential education , 7
Haswell, R. H. (1983). Minimal Marking. College English 45 (6), 600–604. doi:10.2307/377147
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T., and Bond, A. (2020). The Difference Between Emergency Remote Teaching and Online Learning. EDUCAUSE Quarterly 15.
Hoekstra, A., and Korthagen, F. (2011). Teacher Learning in a Context of Educational Change: Informal Learning Versus Systematically Supported Learning. J. Teacher Educ. 62 (1), 76–92. doi:10.1177/0022487110382917
Huber, A. M. (2015). Diminishing the Dread: Exploring service learning and student motivation. Ijdl 6 (1). doi:10.14434/ijdl.v6i1.13364
Hyland, K. (1990). Providing productive feedback. ELT J. 44 (4), 279–285. doi:10.1093/elt/44.4.279
Johansen, B., and Euchner, J. (2013). Navigating the VUCA World. Res.-Technol. Manag. 56 (1), 10–15. doi:10.5437/08956308X5601003
LeBlanc, P. J. (2018). Higher Education in a VUCA World. Change Magazine Higher Learn. 50 (3–4), 23–26. doi:10.1080/00091383.2018.1507370
Mayring, P. (2014). Qualitative content analysis. doi:10.4135/9781446282243
McNeilly, A. (2014). Minimal Marking: A Success Story. cjsotl-rcacea 5 (1). doi:10.5206/cjsotl-rcacea.2014.1.7
Medina, A., and Gordon, L. (2014). Service Learning, Phonemic Perception, and Learner Motivation: A Quantitative Study. Foreign Language Annals 47 (2), 357–371. doi:10.1111/flan.12086
Mezirow, J., and Taylor, E. W. (2009). Transformative learning in practice: Insights from community, workplace, and higher education . John Wiley & Sons .
Örtl, E. (2017). MINT the gap – Umweltschutz als Motivation für technische Berufsbiographien? Umweltbundesamt . https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/mint-the-gap-umweltschutz-als-motivation-fuer
Paran, A. (2017). 'Only connect': researchers and teachers in dialogue. ELT J. 71 (4), 499–508. doi:10.1093/elt/ccx033
Penuel, W. R., Sun, M., Frank, K. A., and Gallagher, H. A. (2012). Using social network analysis to study how collegial interactions can augment teacher learning from external professional development. Am. J. Educ. 119 (1), 103–136. doi:10.1086/667756
Quesada-Pallarès, C., and Gegenfurtner, A. (2015). Toward a unified model of motivation for training transfer: A phase perspective. Zeitschrift Für Erziehungswissenschaft 18 (S1), 107–121. doi:10.1007/s11618-014-0604-4
Schober, B., Brandt, L., Kollmayer, M., and Spiel, C. (2016). Overcoming the ivory tower: Transfer and societal responsibility as crucial aspects of the Bildung-Psychology approach. Eur. J. Dev. Psychol. 13 (6), 636–651. doi:10.1080/17405629.2016.1231061
J.-R. Schreiber, and H. Siege (2015). Orientierungsrahmen für den Lernbereich Globale Entwicklung [rientation Framework for the Learning Area Global Development , p. 468.
J.-R. Schreiber, and H. Siege (2015). in Curriculum Framework: Education for Sustainable Development . Engagement Global gGmbH . 2nd edn.
Sotelino-Losada, A., Arbués-Radigales, E., García-Docampo, L., and González-Geraldo, J. L. (2021). Service-Learning in Europe. Dimensions and Understanding From Academic Publication. Front. Educ. 6. doi:10.3389/feduc.2021.604825
Stoecker, R. (2016). Liberating service learning and the rest of higher education civic engagement . Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press .
Vasilescu, R., Barna, C., Epure, M., and Baicu, C. (2010). Developing university social responsibility: A model for the challenges of the new civil society. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2 (2), 4177–4182. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.660
Keywords: service-learning, design-based research, research methods, teacher education, engagement
Citation: Froehlich DE, Hobusch U and Moeslinger K (2021) Research Methods in Teacher Education: Meaningful Engagement Through Service-Learning. Front. Educ. 6:680404. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.680404
Received: 14 March 2021; Accepted: 05 May 2021; Published: 18 May 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Froehlich, Hobusch and Moeslinger. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dominik E. Froehlich, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Teaching and Learning Research Methods: Fostering Research Competence Among Students
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.

Imperial academic wins €2.4m European funding to improve solar harvesting tech

Meningococcal vaccine is cost effective at protecting men against gonorrhoea

Shape-shifting cancer cell discovery reveals potential skin cancer drug targets
- Centre for Higher Education Research and Scholarship
- Research and Innovation
Educational research methods

Use the sections below to find out more about planning and executing educational research.
The nature of educational research.
Important principles to think about when considering educational research

Before you start
Planning and preparation for a successful project
Before you start continued
Approaches and paradigms in educational research.
This section is currently being developed, check back soon
Methods in educational research
Practical introductions to methods that you might use
2 colour column ed research landing page 3
Analysing and writing up your research.
How to draw robust conclusions from your data and present it appropriately
Networks, funding and further resources
Sharing and disseminating your research within the wider education community
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide
Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methods
Definition:
Research Methods refer to the techniques, procedures, and processes used by researchers to collect , analyze, and interpret data in order to answer research questions or test hypotheses. The methods used in research can vary depending on the research questions, the type of data that is being collected, and the research design.
Types of Research Methods
Types of Research Methods are as follows:
Qualitative research Method
Qualitative research methods are used to collect and analyze non-numerical data. This type of research is useful when the objective is to explore the meaning of phenomena, understand the experiences of individuals, or gain insights into complex social processes. Qualitative research methods include interviews, focus groups, ethnography, and content analysis.
Quantitative Research Method
Quantitative research methods are used to collect and analyze numerical data. This type of research is useful when the objective is to test a hypothesis, determine cause-and-effect relationships, and measure the prevalence of certain phenomena. Quantitative research methods include surveys, experiments, and secondary data analysis.
Mixed Method Research
Mixed Method Research refers to the combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. This approach aims to overcome the limitations of each individual method and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic. This approach allows researchers to gather both quantitative data, which is often used to test hypotheses and make generalizations about a population, and qualitative data, which provides a more in-depth understanding of the experiences and perspectives of individuals.
Key Differences Between Research Methods
The following Table shows the key differences between Quantitative, Qualitative and Mixed Research Methods
Examples of Research Methods
Examples of Research Methods are as follows:
Qualitative Research Example:
A researcher wants to study the experience of cancer patients during their treatment. They conduct in-depth interviews with patients to gather data on their emotional state, coping mechanisms, and support systems.
Quantitative Research Example:
A company wants to determine the effectiveness of a new advertisement campaign. They survey a large group of people, asking them to rate their awareness of the product and their likelihood of purchasing it.
Mixed Research Example:
A university wants to evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching method in improving student performance. They collect both quantitative data (such as test scores) and qualitative data (such as feedback from students and teachers) to get a complete picture of the impact of the new method.
Applications of Research Methods
Research methods are used in various fields to investigate, analyze, and answer research questions. Here are some examples of how research methods are applied in different fields:
- Psychology : Research methods are widely used in psychology to study human behavior, emotions, and mental processes. For example, researchers may use experiments, surveys, and observational studies to understand how people behave in different situations, how they respond to different stimuli, and how their brains process information.
- Sociology : Sociologists use research methods to study social phenomena, such as social inequality, social change, and social relationships. Researchers may use surveys, interviews, and observational studies to collect data on social attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors.
- Medicine : Research methods are essential in medical research to study diseases, test new treatments, and evaluate their effectiveness. Researchers may use clinical trials, case studies, and laboratory experiments to collect data on the efficacy and safety of different medical treatments.
- Education : Research methods are used in education to understand how students learn, how teachers teach, and how educational policies affect student outcomes. Researchers may use surveys, experiments, and observational studies to collect data on student performance, teacher effectiveness, and educational programs.
- Business : Research methods are used in business to understand consumer behavior, market trends, and business strategies. Researchers may use surveys, focus groups, and observational studies to collect data on consumer preferences, market trends, and industry competition.
- Environmental science : Research methods are used in environmental science to study the natural world and its ecosystems. Researchers may use field studies, laboratory experiments, and observational studies to collect data on environmental factors, such as air and water quality, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Political science : Research methods are used in political science to study political systems, institutions, and behavior. Researchers may use surveys, experiments, and observational studies to collect data on political attitudes, voting behavior, and the impact of policies on society.
Purpose of Research Methods
Research methods serve several purposes, including:
- Identify research problems: Research methods are used to identify research problems or questions that need to be addressed through empirical investigation.
- Develop hypotheses: Research methods help researchers develop hypotheses, which are tentative explanations for the observed phenomenon or relationship.
- Collect data: Research methods enable researchers to collect data in a systematic and objective way, which is necessary to test hypotheses and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Analyze data: Research methods provide tools and techniques for analyzing data, such as statistical analysis, content analysis, and discourse analysis.
- Test hypotheses: Research methods allow researchers to test hypotheses by examining the relationships between variables in a systematic and controlled manner.
- Draw conclusions : Research methods facilitate the drawing of conclusions based on empirical evidence and help researchers make generalizations about a population based on their sample data.
- Enhance understanding: Research methods contribute to the development of knowledge and enhance our understanding of various phenomena and relationships, which can inform policy, practice, and theory.
When to Use Research Methods
Research methods are used when you need to gather information or data to answer a question or to gain insights into a particular phenomenon.
Here are some situations when research methods may be appropriate:
- To investigate a problem : Research methods can be used to investigate a problem or a research question in a particular field. This can help in identifying the root cause of the problem and developing solutions.
- To gather data: Research methods can be used to collect data on a particular subject. This can be done through surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, and more.
- To evaluate programs : Research methods can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a program, intervention, or policy. This can help in determining whether the program is meeting its goals and objectives.
- To explore new areas : Research methods can be used to explore new areas of inquiry or to test new hypotheses. This can help in advancing knowledge in a particular field.
- To make informed decisions : Research methods can be used to gather information and data to support informed decision-making. This can be useful in various fields such as healthcare, business, and education.
Advantages of Research Methods
Research methods provide several advantages, including:
- Objectivity : Research methods enable researchers to gather data in a systematic and objective manner, minimizing personal biases and subjectivity. This leads to more reliable and valid results.
- Replicability : A key advantage of research methods is that they allow for replication of studies by other researchers. This helps to confirm the validity of the findings and ensures that the results are not specific to the particular research team.
- Generalizability : Research methods enable researchers to gather data from a representative sample of the population, allowing for generalizability of the findings to a larger population. This increases the external validity of the research.
- Precision : Research methods enable researchers to gather data using standardized procedures, ensuring that the data is accurate and precise. This allows researchers to make accurate predictions and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Efficiency : Research methods enable researchers to gather data efficiently, saving time and resources. This is especially important when studying large populations or complex phenomena.
- Innovation : Research methods enable researchers to develop new techniques and tools for data collection and analysis, leading to innovation and advancement in the field.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Methods in Education. Assignment Guidance. The assignment for the RME unit will normally be a plan for a small-scale educational enquiry. If you are near to completing your five units, this assignment can be used to develop a plan for your dissertation study. If you are closer to the start of your five units, you may not be ready to ...
7.5 Ethics in Focus: Beneficence and Random Assignment ... "Research Methods for Education is an excellent textbook that covers information on educational research design including qualitative, quantitative, and action research in education. It provides great information which is easy to understand for students to learn and instructors to teach.
Research Methods in Education. L. Cohen, Lawrence Manion, K. Morrison. Published 1980. Education. Introduction Part 1. The Context of Educational Research: 1. The Nature of Inquiry Part 2. Planning Educational Research: 2. The Ethics of Educational and Social Research 3.
11/06 Day 11. Mixed methods approaches ± Mixed methods, multi-methods, and action research Assignment 2, RQ 7 11/13 Day 12. Mixed methods continued and other research approaches Assignment 3 11/20 Day 13. Other research approaches continued and summary review 11/27 Thanksgiving Break 12/04 Day 14.
Assignments Research 2.0: Research Media and Technologies Day 4 F2F #10 - #12 Readings (Text & Topics #6) & Assignments Research Media and Technologies Research Methods and Methodologies Day 5 F2F #10 - #12 First Assignment Due Research Media and Technologies Research Methods and Methodologies Data Collection, Coding, Analysis & Visualization
EDUC 500: Educational Research Methods Lecture Notes University of British Columbia Stephen Petrina (2014) 2 Etymology, History and Philosophy of Research 1. Etymology and Semantics a. Etymology i. Research: Etymologically, research derives from the Italian ricercare and French recherche, meaning to seek out or to search intensively with particular
Generating a research topic, ontology, epistemology, axiology; Knowledge & power: Introduction to research methodologies; Qualitative and quantitative research. Activity: Artifacts Activity: Fill Library Research Backgrounder. Text: chpt. 1 Fill out research backgrounder for the library lab. Return to the instructor.
Presents an overview of qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods research designs, including how to choose the design based on the research question. This book is particularly helpful for those who want to design mixed-methods studies. Green, J. L., G. Camilli, and P. B. Elmore. 2006. Handbook of complementary methods for research in education.
This all-encompassing textbook written by leading international experts gives students and early career researchers a considered overview of principles that underpin research, and key qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods for research design, data collection and analysis. This third edition includes four new chapters: Plus a new Research ...
The Handbook of Critical Theoretical Research Methods in Education by Cheryl E. Matias (Editor) Call Number: Online. ISBN: 9780429056963. Publication Date: 2021-05-12. An Introduction to Grounded Methodology for Emerging Educational Researchers by Simon Hayhoe. Call Number: Online. ISBN: 9780367854393.
The prioritized research agenda from American Academy of Physician Assistants includes 20 research topics within four areas: value, roles, workforce, and education (Fang, 2012). Thus, it may be important to provide a foundation and instill excitement for research among pre-professional health undergraduate students.
In the pedagogical approach presented here, which we call the Teaching Clinic, we combine service-learning and design-based research to create meaningful learning engagements. We present two cases ...
3 Centre for Teacher Education, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria. Competence in research methods is a major contribution to (future) teachers' professionalism. In the pedagogical approach presented here, which we call the Teaching Clinic, we combine service-learning and design-based research to create meaningful learning engagements.
Education journals. Applying for ethical approval of educational research. Educational research methods. The nature of educational research. Before you start. Rationale and potential impact of your research. Your research question. Identifying literature. Practical considerations.
Education: Research methods are used in education to understand how students learn, how teachers teach, and how educational policies affect student outcomes. Researchers may use surveys, experiments, and observational studies to collect data on student performance, teacher effectiveness, and educational programs. ... Assignment - Types ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Research in education is use of the methods of scientific analysis to produce information, needed to make improvements in educational planning, decision making, teaching and. learning, curriculum ...
Appraise research methods (e.g. such as qualitative, quantitative, single-case designs, action research, and outcome-based research) Reading(s) Readings located in Lesson 4 Assignment(s) Forum 4: Statistics (Complete section three- Method section of Research Paper and submit for review- if you want feedback, no grade) Week 5: Research methods ...
Research contribute Type seek to test, to improved. #1: Foundational of systems or learning processes. Research. in methodologies and/o technologies of teaching provides or education the fundamental that will influence and infor outcomes. and may knowledge development in contexts. research and innovations of.
This course will introduce you to the major aspects of research methods in education. During the course, you will learn about what research is all about: parts of research that deal with the identification and ... Assignment File will be available from the web CT OLE in due course Presentation Schedule. In addition, you must obtain the set ...
Assignment 1 Plan. Research methods assessment. Assignment 1: Interviews and focus groups advantages and disadvantages: (The learning curve by Mansell, Ian) - Focus groups explore the interactions between participants - Particularly used in health and social care area - Defined as 'simply a discussion in which a small group of people under the guidance of a facilitator or moderator, talk ...
Page 9 of 32 14. Footer/ header 15. Bullets and numbering 16. The assignment should be printed on one sides of paper. 17. MS PowerPoint should be used as the medium for the presentation along with the standard cover page in the first slide, assessment criteria, table of content, content, reference list at the end (All references and citation shall use Harvard Referencing Style).
Abstract. In all educational levels, teachers assign their students with different activities to practice and reinforce what they have learnt. Further, assignments are valuable educational tools ...