My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

In this article:
Problem-Solution Outline
Problem-solution examples, criminal justice, environment, relationships, teen issues.
What to include in your problem-solution speech or essay?
Problem-solution papers employ a nonfiction text structure, and typically contain the following elements:
Introduction: Introduce the problem and explain why the audience should be concerned about it.
Cause/Effect : Inform the audience on what causes the problem. In some cases, you may also need to take time to dispel common misconceptions people have about the real cause.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Thesis Statement: The thesis typically lays out the problem and solution in the form of a question and answer. See examples below.
Solution : Explain the solution clearly and in detail, your problem-solving strategy, and reasons why your solution will work. In this section, be sure to answer common objections, such as “there is a better solution,” “your solution is too costly,” and “there are more important problems to solve.”
Call to Action: Summarize the problem and solution, and paint a picture of what will happen if your final solution is adopted. Also, let the reader know what steps they should take to help solve the problem.
These are the most used methods of developing and arranging:
Problem Solution Method Recommended if you have to argue that there is a social and current issue at stake and you have convince the listeners that you have the best solution. Introduce and provide background information to show what is wrong now.
List the best and ideal conditions and situations. Show the options. Analyze the proper criteria. And present your plan to solve the not wanted situation.
Problem Cause Solution Method Use this pattern for developing and identifying the source and its causes.
Analyze the causes and propose elucidations to the causes.
Problem Cause-Effect Method Use this method to outline the effects of the quandary and what causes it all. Prove the connection between financial, political, social causes and their effects.
Comparative Advantage Method Use this organizational public speaking pattern as recommendation in case everyone knows of the impasse and the different fixes and agrees that something has to be done.
Here are some examples of problems you could write about, with a couple of potential solutions for each one:
Marriage Problem: How do we reduce the divorce rate?
Solution 1: Change the laws to make it more difficult for couples to divorce.
Solution 2: Impose a mandatory waiting period on couples before they can get married.
Environmental Problem: What should we do to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Solution 1: Use renewable energy to fuel your home and vehicles.
Solution 2: Make recycling within local communities mandatory.
Technical Problem: How do we reduce Windows error reporting issues on PCs?
Solution 1: Learn to use dialogue boxes and other command prompt functions to keep your computer system clean.
Solution 2: Disable error reporting by making changes to the registry.
Some of the best problems to write about are those you have personal experience with. Think about your own world; the town you live in, schools you’ve attended, sports you’ve played, places you’ve worked, etc. You may find that you love problem-solution papers if you write them on a topic you identify with. To get your creativity flowing, feel free to browse our comprehensive list of problem-solution essay and paper topics and see if you can find one that interests you.
Problem-Solution Topics for Essays and Papers
- How do we reduce murder rates in the inner cities?
- How do we stop police brutality?
- How do we prevent those who are innocent from receiving the death penalty?
- How do we deal with the problem of gun violence?
- How do we stop people from driving while intoxicated?
- How do we prevent people from texting while driving?
- How do we stop the growing child trafficking problem?
- What is the best way to deal with domestic violence?
- What is the best way to rehabilitate ex-cons?
- How do we deal with the problem of overcrowded prisons?
- How do we reduce binge drinking on college campuses?
- How do we prevent sexual assaults on college campuses?
- How do we make college tuition affordable?
- What can students do to get better grades in college?
- What is the best way for students to effectively balance their classes, studies, work, and social life?
- What is the best way for college students to deal with a problem roommate?
- How can college students overcome the problem of being homesick?
- How can college students manage their finances more effectively?
- What is the best way for college students to decide on a major?
- What should be done about the problem of massive student loan debts?
- How do we solve the global debt crisis?
- How do we keep countries from employing child labor?
- How do we reduce long-term unemployment?
- How do we stop businesses from exploiting consumers?
- How do we reduce inflation and bring down the cost of living?
- How do we reduce the home foreclosure rate?
- What should we do to discourage consumer debt?
- What is the best way to stimulate economic growth?
- How do we lower the prime cost of manufacturing raw materials?
- How can book retailers deal with rising bookseller inventory costs and stay competitive with online sellers?
- How do we prevent kids from cheating on exams?
- How do we reduce the illiteracy rate?
- How do we successfully integrate English as a Second Language (ESL) students into public schools?
- How do we put an end to the problem of bullying in schools?
- How do we effectively teach students life management skills?
- How do we give everyone access to a quality education?
- How do we develop a system to increase pay for good teachers and get rid of bad ones?
- How do we teach kids to problem solve?
- How should schools deal with the problem of disruptive students?
- What can schools do to improve reading comprehension on standardized test scores?
- What is the best way to teach sex education in public schools?
- How do we teach students to recognize a noun clause?
- How do we teach students the difference between average speed and average velocity?
- How do we teach math students to use sign charts?
- How can we make public education more like the Webspiration Classroom?
- How do we stop pollution in major population centers?
- How do we reduce the negative effects of climate change?
- How do we encourage homeowners to lower their room temperature in the winter to reduce energy consumption?
- What is the best way to preserve our precious natural resources?
- How do we reduce our dependence on fossil fuels?
- What is the best way to preserve the endangered wildlife?
- What is the best way to ensure environmental justice?
- How can we reduce the use of plastic?
- How do we make alternative energy affordable?
- How do we develop a sustainable transportation system?
- How can we provide quality health care to all our citizens?
- How do we incentivize people to stop smoking?
- How do we address the growing doctor shortage?
- How do we curb the growing obesity epidemic?
- How do we reduce dependence on prescription drugs?
- How do we reduce consumption of harmful substances like phosphoric acid and acetic acid?
- How can we reduce the number of fatal hospital errors?
- How do we handle the health costs of people living longer?
- How can we encourage people to live healthier lifestyles?
- How do we educate consumers on the risk of laxatives like magnesium hydroxide?
- How do we end political corruption?
- How do we address the problem of election fraud?
- What is the best way to deal with rogue nations that threaten our survival?
- What can our leaders do to bring about world peace?
- How do we encourage students to become more active in the political process?
- What can be done to encourage bipartisanship?
- How can we prevent terrorism?
- How do we protect individual privacy while keeping the country safe?
- How can we encourage better candidates to run for office?
- How do we force politicians to live by the rules they impose on everyone else?
- What is the best way to get out of a bad relationship?
- How do we prevent cyberbullying?
- What is the best solution for depression?
- How do you find out where you stand in a relationship?
- What is the best way to help people who make bad life choices?
- How can we learn to relate to people of different races and cultures?
- How do we discourage humans from using robots as a substitute for relationships?
- What is the best way to deal with a long-distance relationship?
- How do we eliminate stereotypical thinking in relationships?
- How do you successfully navigate the situation of dating a co-worker?
- How do we deal with America’s growing drug problem?
- How do we reduce food waste in restaurants?
- How do we stop race and gender discrimination?
- How do we stop animal cruelty?
- How do we ensure that all citizens earn a livable wage?
- How do we end sexual harassment in the workplace?
- How do we deal with the water scarcity problem?
- How do we effectively control the world’s population?
- How can we put an end to homelessness?
- How do we solve the world hunger crisis?
- How do we address the shortage of parking spaces in downtown areas?
- How can our cities be made more bike- and pedestrian-friendly?
- How do we balance the right of free speech and the right not to be abused?
- How can we encourage people to use public transportation?
- How do we bring neighborhoods closer together?
- How can we eliminate steroid use in sports?
- How do we protect players from serious injuries?
- What is the best way to motivate young athletes?
- What can be done to drive interest in local sports?
- How do players successfully prepare for a big game or match?
- How should the revenue from professional sports be divided between owners and players?
- What can be done to improve local sports venues?
- What can be done to ensure parents and coaches are not pushing kids too hard in sports?
- How can student athletes maintain high academic standards while playing sports?
- What can athletes do to stay in shape during the off-season?
- How do we reduce teen pregnancy?
- How do we deal with the problem of teen suicide?
- How do we keep teens from dropping out of high school?
- How do we train teens to be safer drivers?
- How do we prevent teens from accessing pornography on the Internet?
- What is the best way to help teens with divorced parents?
- How do we discourage teens from playing violent video games?
- How should parents handle their teens’ cell phone and social media use?
- How do we prepare teens to be better workers?
- How do we provide a rational decision-making model for teens?
- How do we keep companies from mining our private data online and selling it for profit?
- How do we prevent artificial intelligence robots from taking over society?
- How do we make high-speed internet accessible in rural areas?
- How do we stop hackers from breaking into our systems and networks?
- How do we make digital payments more secure?
- How do we make self-driving vehicles safer?
- What is the best way to improve the battery life of mobile devices?
- How can we store energy gleaned from solar and wind power?
- What is the best way to deal with information overload?
- How do we stop computer makers from pre-installing Internet Explorer?
Compare and Contrast Speech [Topics and Examples]
Proposal Speech [Tips + 10 Examples]
1 thought on “Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]”
This is very greatfull Thank u I can start doing my essay
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
80+ Problem Solution Speech Topics
A problem/solution speech takes the approach of highlighting an issue with the intent to provide solutions. It is a two-phase approach where first the speaker lays out the problem and explains the importance. Secondly, a variety of solutions are provided to tackle the said issue. The best solutions are those that can be actively applied.
The first problem to tackle is picking a topic. It is a good idea to pick something topical but then again, the world just supplies so many options that it can be overwhelming.
When you are assigned to write a problem-solution essay or research paper, choosing a good topic is the first dilemma you need to work out.
The world is full of issues that need to be resolved. However, it is not sufficient to simply pick a subject because it is topical. Ideally, you should pick a subject that is important to you on some level as well. Speaking about an issue you care about brings out an irreplicable passion that people are sure to respond to. If you’re still confused, we have included a wide variety of topics so that you can pick one that calls out to you.
Let’s get started!

Table of Contents
- Introduction:
- Thesis Statement:
- Cause/Effect:
- Call to Action:
Problem Solution Method
Comparative advantage method, social issues, environment, relationships, wrapping up, problem/solution speech outline.
Before we jump into the topics, it can be handy to understand the speech structure of a problem-solution speech. Understanding how to approach a speech script can have an effect on the topic you pick. Oftentimes, we are confident we can speak about a subject but once we begin the draft, we realize we don’t actually have that much to say.
So take a good look at what elements you need to include in your problem/solution speech:
Introduction:
The introduction is a key part of any speech. This is where you will try to grab the audience’s attention, establish the problem statement, and highlight your key points. It is in your introduction that you will need to explain why the presented issue is an issue. The objective is to convince the audience that the problem at hand is one that requires attention.
If you need help with effective attention-grabbers, you can browse our article on 12 Effective Attention-Grabbers for your speech .
Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is where you will present the problem you are about to tackle. Typically the problem is laid out in the form of a question. You will also be talking about your stance on the presented problem.
Cause/Effect:
Before you launch into giving solutions after highlighting the problem, you need to explain the gravity of the problem at hand. You can do so by explaining what negative consequences occur due to said problem. The more you personalize the effects, the more likely you are to capture their attention.
Solution:
Once you talk about all the negative impacts of the presented problem, it is time to give the audience the solutions. Explain all the solutions step-by-step and talk about the evidence why the said solution will work. Make sure not to give solutions that are too vague. If there are common misconceptions about the solutions, address them as well. Discuss both pros and cons of the proposed solutions and explain why the pros outweigh the cons.
Call to Action:
The most important part of a problem/solution type speech is the call to action. This is when you encourage the audience to take the necessary steps to solve the problem. You can do so by painting a picture of the expected results of your proposed solutions. Don’t end on a vague note that sounds like “Together, we can.” Instead, give actionable steps, such as “I encourage each and every one of you to go home and separate your recycling trash.”
Problem/Solution Presentation Techniques
There is more than one way to present a problem/solution model. You might want to look into these techniques to switch up your speaking style.
The classic take is best used for taking a stance against a social or current issue. In such a case, you will highlight a known issue and suggest probable solutions for it. You can approach this method by informing the audience about the issue, a brief history, all geared to explain why the topic is a problem in the first place.
Follow that up by describing an ideal condition without the said issue. Once you create a tempting picture, offer up more than one solution that is applicable to the situation. Explain the hurdles and how they can be overcome. Make sure it is clear that you’ve thought about the problem from both sides of the issue.
Comparative advantage models are useful when tackling a problem that seems to be at an impasse. It is when an issue is well known and has multiple fixes with their own group of supporters. Here, you can take a comparative approach to show the pros and cons of all the different solutions. The key difference is that the general consensus is already there about the importance of tackling the problem, but only the correct solution needs to be selected.
Problem-Solution Speech Topics
Here is our extensive list of problem/solution speech topics:
- Adopting dogs is more ethical than getting a new puppy.
- How education can solve generational poverty.
- Tackling anxiety by adopting a pet.
- Ebooks over books to save the environment.
- One-child policy: unethical but effective.
- Donating as a solution to fight global poverty.
- Do your part, go vegan to fight world hunger.
- Keep wikipedia alive for free information with donations.
- Kindness can begin with a compliment.
- What can we do to ensure government sanctions against companies using child labor?
- Sorting out your waste and what it can do for the environment.
- The necessary switch to bicycles to tackle pollution.
- Why encouraging volunteering at an early age can produce better citizens.
- High time to make the switch to solar and wind energy.
- Self-driving cars are the future of road safety.
- Bike lanes and bike laws enhance traffic safety.
- Effective gun sales management can help reduce reckless deaths.
- Normalize selling colored dolls in all shapes and sizes to promote confidence in children.
- How data became the new oil?
- How to stay private in an increasingly social world?
- Why is high-speed internet still not considered a basic need for rural areas?
- Ethical hacking and why is there a draw to it?
- Digital payments and how to guarantee security.
- Change your passwords. Why your data is in danger!
- Self-driving vehicles, should we handover 100% of the control?
- Have lithium batteries on mobile phones already reached their peak?
- How can technology promote the use of renewable energy?
- How to keep up with the overwhelming news cycle?
- How can we destigmatize video game addiction?
- How can we shift education to a virtual platform?
- How to smoothen the transition from home-schooling to college.
- What are some new methods to tackle the rampant cheating on exams?
- How can we reduce the illiteracy rate?
- It’s high time to end bullying in schools.
- How to normalize homesickness as a problem and tackle it?
- Education is not enough, students need life management skills.
- Is accessibility to quality education sufficient currently?
- How can we guarantee sufficient pay for quality teachers?
- How can problem-solving be taught in schools?
- Is detention an effective solution for disruptive students?
- How you can help your suicidal friend.
- Are we doing enough to improve standardized test score results?
- Effective ways to increase attention in class.
- How can we make sex education mandatory in public schools?
- Creative ways to get students to love maths.
- Does looking at the stars stimulate brain activity?
- How can we tackle the growing obesity epidemic?
- How spending time outdoors can boost your mood.
- The Pomodoro Technique and why it works for productivity.
- Can meditation be the answer to growing stress?
- Can we incentivize smokers to give up smoking?
- How to increase responsibility for fatal hospital errors?
- Fitness apps and how it can benefit health.
- How augmented reality glasses can be a gamechanger for people with disabilities.
- How does taking baths reduce stress and anxiety?
- Burnout: the need to go offline.
- Better posture to tackle back pain.
- Does reading out loud help improve critical thinking?
- Child obesity: a preventable evil.
- Encouraging more greens to help children improve their memory.
- How global pollution can be tackled locally.
- Climate change. Why it is too late and what can still be done.
- Does lower room temperature really help reduce energy consumption?
- How to do our part in preserving natural resources?
- Is it time to stop depending on fossil fuels?
- How to preserve wildlife from going extinct?
- Are current environmental laws sufficient to keep it protected?
- Improving public transport to reduce the number of private cars.
- How can we upgrade our transportation to be more sustainable?
- Why hunting should be illegal in any circumstances.
- It is high time to replace plastic. What are our options?
- Is it enough to make alternative energy affordable?
- Signs of a toxic relationship.
- How to pull yourself out of an emotionally abusive relationship.
- Should parents be allowed to control teens’ social media accounts?
- How to manage expectations in a relationship?
- Recognize negative people and take active steps to avoid them.
- How to help domestic violence victims?
- Why it is pointless to try changing someone.
- How to say “no” in a way that they listen?
- How to maintain a work-life balance in today’s world.
- Why couples counseling needs to stop being taboo.
- Is it possible to bridge the gap across different races and cultures?
- How technology is capitalizing on the growing need for human contact.
- Long-distance relationships. Can you make it work?
- Modern-day relationships and how expectations have changed.
A problem/solution speech is a great topic as it falls under the informational category. As such, it is much easier to capture the audience’s attention. In terms of delivery, make sure you sell the problem before handing out the solution. Following the above outline and tips paired with your amazing content, we are sure you will be able to win over any audience with ease. Make sure you do your research well and triple-check your sources. All that is left to do is practice. See you on the stage!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter Sixteen – Speaking to Persuade
On the first day of class, your instructor provided you a “lay of the land.” They introduced you to course documents, the syllabus, and reading materials.
“It’s important that you read your textbook,” they likely shared. “The material will allow you to dive deeper into the course material and, even if you don’t initially realize its importance, the reading material will build throughout the semester. The time spent reading will be worth it because without that knowledge, it will be difficult to complete assignments and receive full credit. The time spent reading will benefit you after you leave for the semester, too, and you’ll have critical thinking skills that will permeate your life out of the classroom.” Sound familiar?
This is persuasion. Your instructor is persuading you that reading the textbook is a good idea—that it’s an action you should take throughout the semester. As an audience member, you get to weigh the potential benefits of reading the textbook in relation to the consequences. But if your instructor has succeeded in their persuasive attempt, you will read the book because they have done a good job of helping you to conclude in favor of their perspective.
Your instructor may have even gone a step further, introducing themselves and including their credentials, such as degrees earned, courses taught, years of teaching, books published, etc. That sounds like what Aristotle called ethos , right? This is another key to persuasion, which we will discuss further in Chapter 17.
Persuasion is everywhere. We are constantly inundated with ideas, perspectives, politics, and products that are requesting our attention. Persuasion is often positively paired with ideas of encouragement, influence, urging, or logic. Your instructors, for example, are passionate about the subject position and want you to succeed in the class. Sadly, persuasion can also be experienced as manipulation, force, lack of choice, or inducement. You might get suspicious if you think someone is trying to persuade you. You might not appreciate someone telling you to change your viewpoints.
In this chapter, we explore persuasive speaking and work through best practices in persuasion. Because persuasion is everywhere, being critical and aware of persuasive techniques will allow you to both ethically persuade audiences and evaluate arguments when others attempt to persuade you. We’ll start with the basics by answering the question, “what is persuasion?”
Introducing Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is “the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions” (Lucas, 2015, p. 306). Persuasion is important in all communication processes and contexts—interpersonal, professional, digital—and it’s something that you do every day. Convincing a friend to go see the latest movie instead of staying in to watch TV; giving your instructor a reason to give you an extension on an assignment; writing a cover letter and resume and going through an interview for a job—all of these and so many more are examples of persuasion. In fact, it is hard to think of life without the everyday give-and-take of persuasion. In each example listed, Lucas’s definition of persuasion is being implemented: you are asking a person or group to agree with your main idea.
When using persuasion in a public speech, the goal is to create, change, or reinforce a belief or action by addressing community problems or controversies. Remember that public speaking is a long-standing type of civic engagement; when we publicly speak, we are participating in democratic deliberation. Deliberatio n , or the process of discussing feasible choices that address community problems, is important in resolving community concerns because it allows all perspectives to be considered. Persuasive speaking means addressing a public controversy and advocating for a perspective that the speaker hopes the audience will adopt. If the issue isn’t publicly controversial – if everyone agrees or if there are not multiple perspectives – you are not persuading. You’re informing.
So, what’s a public controversy? Public controversies are community disputes that affect a large number of people. Because they involve a large number of people, public controversies often have multiple perspectives, leading to public deliberation and debate to resolve each dispute.
We experience public controversies daily. Through our social media feeds, we continuously scroll past shared articles, comments, or posts that provide different perspectives on community problems and potential solutions. You might, for example, join your local neighborhood (or dorm) Facebook group where neighbors share information and collaborate on solutions to specific problems facing the community. Each problem has consequences for different neighbors, and Facebook allows a space to deliberate and organize to address community priorities. They are controversial, however, because not all neighbors agree what which problems should be solved first or what those solutions are.
Sadly, there is no shortage of public controversies, and advocating for solutions to key community problems can feel overwhelming.
“How do I figure out one controversy to speak out about?” you may wonder.
Identify public controversies by listening and engaging with your community. What issues are affecting them? What are priorities? Once you’re able to locate a key community dispute, ask yourself:
- What is it? What is the problem? Are there more than 1? Is this the key problem or are there other hidden issues?
- What is the impact? What will happen if the problem is not resolved?
- Who’s affected? Who’s being affected or implicated by this problem? Who are the audiences or stakeholders affected? Are the stakeholders a part of my formal audience?
- What can solve it? Are there suggested solutions?
Controversies arise when a community experiences a problem, so your job is to decipher the breadth and depth of that problem. It’s impossible to address all issues in one speech, so researching and prioritizing are key to identifying what advocacy you find most urgent. For any controversy that you can address in a persuasive speech, keep context and power in mind.
Your public speaking context always informs what’s possible to accomplish during a speech. Remember, the public speaking context refers to both the physical space and cultural context.
The physical context will influence how much information you can provide to your audience. In other words, “Do I have time to talk about this issue?” “What is the most essential information to cover in a limited timeframe?” The broader cultural context can help you in situating your advocacy alongside other community conversations. What else is happening? Have other communities experienced this problem?
As persuasive speakers, you are attempting to influence an audience. What you select and how you present that information will alter how audiences understand the world, and that’s a pretty powerful thought. When you select an advocacy that addresses a public controversy, you are asking the audience to trust your perspective. To uphold that trust, it’s key to examine who is empowered or disempowered by our perspective.
When you’re considering a position toward a public controversy, you might ask, who’s empowered or disempowered by this problem? Who’s left out of the research? How are communities being represented? What am I assuming about those communities? Who is affected by my advocacy?
We can be well-meaning in our advocacies, especially when we select a persuasive insight based on our own experience. We become passionate about issues that we have seen, and that’s OK! Such passion can also, however, mean that we represent information in ways that are stereotypical or lead to the disempowerment of others.
If your city, for example, is deciding where to place a landfill, you may advocate against the plant being placed in your neighborhood. That advocacy, on face, makes sense!
“This will reduce our property values and just be plain stinky,” you might argue.
When we think about the issue reflexively and with power in mind, however, we may find that landfills are much more likely to be placed in neighborhoods that are predominant people of color (Massey, 2004). Advocating against placing the plant in your home may inadvertently mean the plant is placed in more vulnerable neighborhoods. Those neighbors become disempowered in your attempt to empower your own community.
In this example, practicing reflexivity might include asking: What are the potential solutions? What options do I have to avoid disempowering groups? Using sound research skills, considering other alternatives or perspectives, and listening can be mechanisms to answer these inquiries
There are no easy answers, but we are confident that you can select advocacies that are meaningful and worthwhile.
Formulating Persuasive Propositions
Once you feel comfortable and confident about a controversial issue that is ethical, timely and contextually relevant, you will need to identify what type of persuasive proposition that you’ll use in your speech. There are three types of persuasive propositions: propositions of fact, value, or policy. Each type will require different approaches and may have different persuasive outcomes for your audience.
Propositions of Fact
Propositions of fact answer the question, “is this true?” Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. There is not a sense of what is morally right and wrong or what should be done about the issue, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. Imagine these questions as true or false.
These propositions are not facts like “the chemical symbol for water is H20” or “Barack Obama won the presidency in 2008.” Propositions or claims of fact are advocacies with evidence on different sides and/or spark disagreement. Imagine that you are a lawyer in the courtroom arguing if something is true or false, with evidence. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald working alone.
- Coal exacerbates global warming.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
- Granting tuition tax credits to the parents of children who attend private schools will perpetuate educational inequity.
- Watching violence on television causes violent behavior in children.
- William Shakespeare did not write most of the plays attributed to him.
- John Doe committed the crime of which he is accused.
Notice that no values—good or bad—are explicitly mentioned. The point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement, not its inherent value. Your goal is to persuade the audience to update their understanding or belief about the topic in question. Because you are likely not asking the audience to overtly act, it’s necessary to embed arguments that highlight how or why this factual information is meaningful for them or how the factual statement resolves a public controversy.
Propositions of fact are meaningful persuasive claims when new evidence or scientific observations arise that your audience may not know. Facts, statistics, definitions, or expert testimony are common evidence types for these propositions.
Propositions of Value
Propositions of value argue that something is good/bad or right/wrong. When the proposition has a word such as good, bad, best, worst, just, unjust, ethical, unethical, moral, immoral, advantageous or disadvantageous, it is a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Homeschooling is more beneficial for children than traditional schooling.
- The War in Iraq was not justified.
- The United States is not the greatest country on earth.
- Capital punishment is morally wrong.
- White supremacy is wrong.
- Running is the best form of exercise.
- A vegan diet is the healthiest one for adults.
Communication is a key vehicle in understanding values because communication is how communities collectively determine what is right or wrong. Because values are culturally situated and not universal, as a speaker, you must ground and describe what value or moral judgement you’re utilizing. If a war is unjustified, what makes a war “just” or “justified” in the first place? What makes a form of transportation “best” or “better” than another? Isn’t that a matter of personal approach? For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “most stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.”
Effective propositions of value rely on shared beliefs held by your audience. Developing confidence about your audience will allow you to determine what value systems they rely on and how your proposition relies on similar belief systems. We’ll talk more about appealing to your audience below.

Propositions of Policy
Policy propositions identify a solution to correct the problem. These propositions call for a change in policy (including those in a government, community, or school) or call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior.
Speeches with propositions of policy try to instigate the audience to act immediately, in the long-term, or alter their perspective on an issue. A few examples include:
- Our state should require mandatory recertification of lawyers every ten years.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- The state of Georgia should require drivers over the age of 75 to take a vision test and present a certificate of good health from a doctor before renewing their licenses.
- Wyeth Daniels should be the next governor of the state.
- The Supreme Court should rule that migrant detention centers are unconstitutional.
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them.
Many policy propositions advocate for a solution through a specific organization or government agency. In the examples above, the federal government, the state, and the Supreme Court are all listed as relevant actors to resolve the problem.
Alternatively, you could advocate for your audience to make specific behavioral changes that lead to solutions. If you’re addressing the consequences of climate change in your local community, do solutions require government or non-profit action? Could your audience make in-roads to reducing the negative effects of climate change alone? Thorough research will assist you in determining what actors – organizations or your audience—are best suited to implement your policy solution.
Policy propositions commonly embed a specific call-to-action. What should the audience do if they are persuading by your perspective? What actions can and should they take that can support your policy proposition? This can include “call your senator” (though more specificity is often helpful), but your call-to-action should be crafted with audience adaptation and information in mind.

Burns Library, Boston College – Maya Angelou – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Organizing Persuasive Propositions
Organization plays a key role in comprehending an argument. While we have previously discussed organization, in this section, we discuss organizing persuasive speeches with a focus on propositions of policy.
Once you’ve identified your main argument, ask, “what organizational pattern best suits my argument?”
For propositions of fact or value, you might select a categorical organization. Essentially that means that you will have two to four discrete, separate arguments in support of the proposition. For example:
Proposition of Fact: Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- Solar energy reduces power bills.
- Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
- Solar energy works when the power grid goes down.
For propositions of policy, the problem-solution organization pattern is commonly used. We do not typically feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. As the saying goes, “If it ain’t broke, why fix it?” In a problem-solution pattern, you can spend ample and organized time outlining the consequences to inaction, i.e. the problem.
Although a simple problem-solution organization is permissible for a speech of actuation, you will probably do well to utilize the more detailed format called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
This format, designed by Alan Monroe (1951), is based on John Dewey’s reflective thinking process to consider audience listening patterns. This is one of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010). Each step is described below and fully developed following:
- Attention . This is the introduction, where the speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed, a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
- Need. Here the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their family, or their community. The harm or need can be physical, financial, emotional, educational, or social. It will have to be supported by evidence. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
- Visualization. According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization could include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
- Action . In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take as soon as possible to move toward solving the problem. Whereas the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action step gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
The more concrete you can make the action step, the better. Research shows that people are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want students to be vaccinated against the chicken pox virus (after establishing that it is a key public controversy), you can give them directions to and hours for a clinic or health center where vaccinations at a free or discounted price can be obtained.
Now that we have discussed Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Introduction (Attention): Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
Main Points:
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
Conclusion (Action): In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. We add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is some kind of magic persuasive bullet. At the same time, research does support organized messages being perceived as more persuasive, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Before we continue with the potential barriers to persuasive speaking, consider this TEDEd talk: How to Use Rhetoric to Get What You Want .
Barriers to Effective Persuasi ve Speaking
Persuasive speaking can provide opportunities to advocate for important community solutions. But persuasion is really difficult, and there are often barriers to effectively persuading our audience to change their beliefs or act in a new way.
Persuasion is hard because we have a bias against change. As much as we hear statements like “The only constant is change” or “Variety is the spice of life,” the evidence from research and from our personal experience shows that, in reality, we do not like change. Recent risk aversion research, for example, found that humans are concerned more with what we lose than what we gain. Change is often seen as a loss of something rather than a gain of something else, and that’s stressful. We do not generally embrace things that bring us stress.
Given our aversion to change, audiences often go out of their way to protect their beliefs, attitudes, and values. We (as audience members) selectively expose ourselves to messages that we already agree with, rather than those that confront or challenge us. This selective exposure is especially seen in choices of mass media that individuals listen to, watch, and read. Not only do we selectively expose ourselves to information, but we also selectively attend to, perceive, and recall information that supports our existing viewpoints (referred to a s elective recall ).
This principle led Leon Festinger (1957) to form the theory of cognitive dissonance , which states, among other ideas, that when we are confronted with conflicting information or viewpoints, we reach a state of dissonance, or tension between ideas and beliefs. It often occurs when we’re presented information that’s out of line with our values or experiences. This state can be very uncomfortable, and we will do things to get rid of the dissonance and maintain “consonance.” We don’t want to accept that our beliefs may be wrong or inconsistent; we want to remain harmonious.
In a sense, not changing can outweigh very logical reasons to change. For example, you probably know a friend who will not wear a seatbelt in a car. You can say to your friend, “Don’t you know that the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (2009) says, and I quote, ‘1,652 lives could be saved, and 22,372 serious injuries avoided each year on America’s roadways if seat belt use rates rose to 90 percent in every state’?” What will your friend probably say, even though you have cited a credible source?
They will come up with some reason for not wearing it, even something as dramatic as “I knew a guy who had a cousin who was in an accident and the cop said he died because he was wearing his seatbelt.” They may even say, “Well I am a good driver, so you only need seat belts if you’re driving poorly.” You may have had this conversation, or one like it. Their argument may be less dramatic, such as “I don’t like how it feels” or “I don’t like the government telling me what to do in my car.” For your friend, the argument for wearing a seat belt is not as strong as the argument against it, at least at this moment. Ideally, at least for a public speaker, the dissonance is relieved or resolved by being persuaded (changed) to a new belief, attitude, or behavior.
So, what is a speaker to do to overcome these barriers? We suggest making reasonable requests, articulating the benefits or consequences, and answering oppositional arguments.
Make Reasonable Requests
Setting reasonable persuasive goals is the first way to meet audience resistance. Since we resist change, we do not make many large or major changes in our lives. We do, however, make smaller, concrete, step-by-step or incremental changes every day. Over time these small shifts can eventually result in a significant amount of persuasion. Aim small, especially within a time constraint, and work to find future room to build.
Focus on Benefits and Consequences
When problems aren’t resolved, there are consequences. When problems are resolved, there are positive benefits for the community. Because you are asking the audience to change something, they must view the benefits of acting as worth the stress of the change. A speaker should be able to engage the audience at the level of needs, wants, and values as well as logic and evidence.
Identify the benefits, advantages, or improvements that would happen for the audience members who enacted your advocacy. If you do good audience analysis, you know that audiences are asking, “What’s in it for me?” “Why do I need this?”
Alternatively, you could outline the short and long-term consequences of inaction and detail how the problem would negatively affect the audience and/or their community. In other words, you’re identifying what would occur if the audience did nothing, if they choose not to act. Using Monroe’s Motivated Sequences can assist in organizing these arguments.
Answer Oppositional Arguments
During a persuasive speech, audience members are holding a mental dialogue, and they are thinking through rebuttals or oppositional arguments to your advocacy. These mental dialogues could be called the “yeah-buts”—the audience members are saying in their minds, “Yeah, I see what you are arguing, but—”. Reservations can be very strong, since, again, our human bias is to be loss averse and not to change our actions or beliefs.
If you’re advocating a claim that humans are the primary cause of climate change, your audience may think, “yeah, but these consequences won’t happen for a long time,” or “yeah, but we have time to resolve these problems.”
As a speaker, address these! Refute the arguments that may prohibit your audience from changing.
It’s common to call oppositional arguments “misconceptions,” “myths,” or “mistaken ideas” that are widely held about the proposition. You may answer oppositional arguments around climate change by saying, “One common misconception about climate change is that we won’t see the negative impacts for decades. A recent study determined that consequences are already upon us.”
After acknowledging oppositional arguments and seeking to refute or rebut the reservations, you must also provide evidence for your refutation. Ultimately, this will show your audience that you are aware of both sides of the issue you are presenting and make you a more credible speaker.
Additionally, keep in mind that you may be asking your audience for passive agreement or immediate action. Each is described below.
Gain Passive Agreement
When we attempt to gain the passive agreement of our audiences, our goal is to get our audiences to agree with what we are saying and our specific policy without asking the audience to do anything to enact the policy. For example, maybe your speech is on why the Federal Communications Commission should regulate violence on television like it does foul language (i.e., no violence until after 9 p.m.). Your goal as a speaker is to get your audience to agree that it is in our best interest as a society to prevent violence from being shown on television before 9 p.m., but you are not seeking to have your audience run out and call their senators or congressmen or even sign a petition. Often the first step in larger political change is simply getting a massive number of people to agree with your policy perspective.
Let’s look at a few more passive agreement claims:
- Racial profiling of individuals suspected of belonging to known terrorist groups is a way to make America safer.
- Requiring American citizens to “show their papers” is a violation of democracy and resembles tactics of Nazi Germany and communist Russia.
- Colleges and universities should voluntarily implement a standardized testing program to ensure student learning outcomes are similar across different institutions.
In each of these claims, the goal is to sway one’s audience to a specific attitude, value, or belief, but not necessarily to get the audience to enact any specific behaviors.
Gain Immediate Action
The alternative to passive agreement is immediate action, or persuading your audience to start engaging in a specific behavior. Many passive agreement topics can become immediate action-oriented topics as soon as you tell your audience what behavior they should engage in (e.g., sign a petition, call a senator, vote). While it is much easier to elicit passive agreement than to get people to do something, you should always try to get your audience to act and do so quickly. A common mistake that speakers make is telling people to enact a behavior that will occur in the future. The longer it takes for people to engage in the action you desire, the less likely it is that your audience will engage in that behavior.
Here are some examples of good claims with immediate calls to action:
- College students should eat more fruit, so I am encouraging everyone to eat the apple I have provided you and start getting more fruit in your diet.
- Teaching a child to read is one way to ensure that the next generation will be stronger than those that have come before us, so please sign up right now to volunteer one hour a week to help teach a child to read.
- The United States should reduce its nuclear arsenal by 20 percent over the next five years. Please sign the letter provided encouraging the president to take this necessary step for global peace. Once you’ve signed the letter, hand it to me, and I’ll fax it to the White House today.
Each of these three examples starts with a basic claim and then tags on an immediate call to action. Remember, the faster you can get people to engage in a behavior the more likely they actually will.
- Lucas, S. E. (2019). The Art of Public Speaking ( 13th edition) Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
- German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
- Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
- Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
- https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-stretching-his-legs-9623853/
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
- This chapter adapted from Stand up, Speak out. Stand up, Speak out by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted, and Speak out, Call in. Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Principles of Public Speaking Copyright © 2022 by Katie Gruber is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Persuasive Speaking
Learning objectives.
- Explain how claims, evidence, and warrants function to create an argument.
- Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic.
- Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience’s orientation to the proposition.
- Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy.
- Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don’t often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we’ll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Foundation of Persuasion
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis. Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim. The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence. One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the US Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people shouldn’t do things they know are unsafe.
Figure 11.2 Components of an Argument
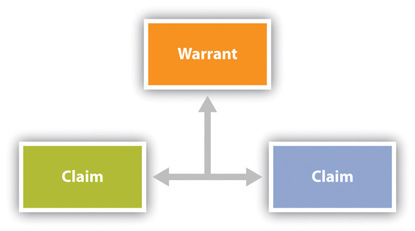
The quality of your evidence often impacts the strength of your warrant, and some warrants are stronger than others. A speaker could also provide evidence to support their claim advocating for a national ban on texting and driving by saying, “I have personally seen people almost wreck while trying to text.” While this type of evidence can also be persuasive, it provides a different type and strength of warrant since it is based on personal experience. In general, the anecdotal evidence from personal experience would be given a weaker warrant than the evidence from the national research report. The same process works in our legal system when a judge evaluates the connection between a claim and evidence. If someone steals my car, I could say to the police, “I’m pretty sure Mario did it because when I said hi to him on campus the other day, he didn’t say hi back, which proves he’s mad at me.” A judge faced with that evidence is unlikely to issue a warrant for Mario’s arrest. Fingerprint evidence from the steering wheel that has been matched with a suspect is much more likely to warrant arrest.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence. If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.
Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
As with any speech, topic selection is important and is influenced by many factors. Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial, and have important implications for society. If your topic is currently being discussed on television, in newspapers, in the lounges in your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it’s a current topic. A persuasive speech aimed at getting audience members to wear seat belts in cars wouldn’t have much current relevance, given that statistics consistently show that most people wear seat belts. Giving the same speech would have been much more timely in the 1970s when there was a huge movement to increase seat-belt use.
Many topics that are current are also controversial, which is what gets them attention by the media and citizens. Current and controversial topics will be more engaging for your audience. A persuasive speech to encourage audience members to donate blood or recycle wouldn’t be very controversial, since the benefits of both practices are widely agreed on. However, arguing that the restrictions on blood donation by men who have had sexual relations with men be lifted would be controversial. I must caution here that controversial is not the same as inflammatory. An inflammatory topic is one that evokes strong reactions from an audience for the sake of provoking a reaction. Being provocative for no good reason or choosing a topic that is extremist will damage your credibility and prevent you from achieving your speech goals.
You should also choose a topic that is important to you and to society as a whole. As we have already discussed in this book, our voices are powerful, as it is through communication that we participate and make change in society. Therefore we should take seriously opportunities to use our voices to speak publicly. Choosing a speech topic that has implications for society is probably a better application of your public speaking skills than choosing to persuade the audience that Lebron James is the best basketball player in the world or that Superman is a better hero than Spiderman. Although those topics may be very important to you, they don’t carry the same social weight as many other topics you could choose to discuss. Remember that speakers have ethical obligations to the audience and should take the opportunity to speak seriously.
You will also want to choose a topic that connects to your own interests and passions. If you are an education major, it might make more sense to do a persuasive speech about funding for public education than the death penalty. If there are hot-button issues for you that make you get fired up and veins bulge out in your neck, then it may be a good idea to avoid those when speaking in an academic or professional context.

Choose a persuasive speech topic that you’re passionate about but still able to approach and deliver in an ethical manner.
Michael Vadon – Nigel Farage – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Choosing such topics may interfere with your ability to deliver a speech in a competent and ethical manner. You want to care about your topic, but you also want to be able to approach it in a way that’s going to make people want to listen to you. Most people tune out speakers they perceive to be too ideologically entrenched and write them off as extremists or zealots.
You also want to ensure that your topic is actually persuasive. Draft your thesis statement as an “I believe” statement so your stance on an issue is clear. Also, think of your main points as reasons to support your thesis. Students end up with speeches that aren’t very persuasive in nature if they don’t think of their main points as reasons. Identifying arguments that counter your thesis is also a good exercise to help ensure your topic is persuasive. If you can clearly and easily identify a competing thesis statement and supporting reasons, then your topic and approach are arguable.
Review of Tips for Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
- Not current. People should use seat belts.
- Current. People should not text while driving.
- Not controversial. People should recycle.
- Controversial. Recycling should be mandatory by law.
- Not as impactful. Superman is the best superhero.
- Impactful. Colleges and universities should adopt zero-tolerance bullying policies.
- Unclear thesis. Homeschooling is common in the United States.
- Clear, argumentative thesis with stance. Homeschooling does not provide the same benefits of traditional education and should be strictly monitored and limited.
Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to directly influence the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important. If possible, poll your audience to find out their orientation toward your thesis. I read my students’ thesis statements aloud and have the class indicate whether they agree with, disagree with, or are neutral in regards to the proposition. It is unlikely that you will have a homogenous audience, meaning that there will probably be some who agree, some who disagree, and some who are neutral. So you may employ all of the following strategies, in varying degrees, in your persuasive speech.
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to further reinforce their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment so they are more likely to follow through on the action.
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral in regards to your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they don’t see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement.
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To effectively persuade, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who doesn’t appear prepared or doesn’t present well-researched and supported information. Don’t give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely, but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience.

Build common ground with disagreeable audiences and acknowledge areas of disagreement.
Chris-Havard Berge – Shaking Hands – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives.
Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy. A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done. Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
- Proposition of fact. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases related to human activity.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong .
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered.
“Getting Critical”
Persuasion and Masculinity
The traditional view of rhetoric that started in ancient Greece and still informs much of our views on persuasion today has been critiqued for containing Western and masculine biases. Traditional persuasion has been linked to Western and masculine values of domination, competition, and change, which have been critiqued as coercive and violent (Gearhart, 1979).
Communication scholars proposed an alternative to traditional persuasive rhetoric in the form of invitational rhetoric. Invitational rhetoric differs from a traditional view of persuasive rhetoric that “attempts to win over an opponent, or to advocate the correctness of a single position in a very complex issue” (Bone et al., 2008). Instead, invitational rhetoric proposes a model of reaching consensus through dialogue. The goal is to create a climate in which growth and change can occur but isn’t required for one person to “win” an argument over another. Each person in a communication situation is acknowledged to have a standpoint that is valid but can still be influenced through the offering of alternative perspectives and the invitation to engage with and discuss these standpoints (Ryan & Natalle, 2001). Safety, value, and freedom are three important parts of invitational rhetoric. Safety involves a feeling of security in which audience members and speakers feel like their ideas and contributions will not be denigrated. Value refers to the notion that each person in a communication encounter is worthy of recognition and that people are willing to step outside their own perspectives to better understand others. Last, freedom is present in communication when communicators do not limit the thinking or decisions of others, allowing all participants to speak up (Bone et al., 2008).
Invitational rhetoric doesn’t claim that all persuasive rhetoric is violent. Instead, it acknowledges that some persuasion is violent and that the connection between persuasion and violence is worth exploring. Invitational rhetoric has the potential to contribute to the civility of communication in our society. When we are civil, we are capable of engaging with and appreciating different perspectives while still understanding our own. People aren’t attacked or reviled because their views diverge from ours. Rather than reducing the world to “us against them, black or white, and right or wrong,” invitational rhetoric encourages us to acknowledge human perspectives in all their complexity (Bone et al., 2008).
- What is your reaction to the claim that persuasion includes Western and masculine biases?
- What are some strengths and weaknesses of the proposed alternatives to traditional persuasion?
- In what situations might an invitational approach to persuasion be useful? In what situations might you want to rely on traditional models of persuasion?
Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Earlier, in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , we discussed recency and primacy, and in this chapter we discussed adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition. These concepts can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first and is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action.

Putting your strongest argument last can help motivate an audience to action.
Celestine Chua – The Change – CC BY 2.0.
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
As was mentioned in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , the cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that lead to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
Persuasive Speech Thesis Statements by Organizational Pattern
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that shouldn’t be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action. If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. We already learned about the five steps of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but we will review them here with an example:
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly US Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
Key Takeaways
- Arguments are formed by making claims that are supported by evidence. The underlying justification that connects the claim and evidence is the warrant. Arguments can have strong or weak warrants, which will make them more or less persuasive.
- Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial (but not inflammatory), and important to the speaker and society.
- When audience members agree with the proposal, focus on intensifying their agreement and moving them to action.
- When audience members are neutral in regards to the proposition, provide background information to better inform them about the issue and present information that demonstrates the relevance of the topic to the audience.
- When audience members disagree with the proposal, focus on establishing your credibility, build common ground with the audience, and incorporate counterarguments and refute them.
- Propositions of fact focus on establishing that something “is or isn’t” or is “true or false.”
- Propositions of value focus on persuading an audience that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.”
- Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done.
- Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic. Then do the same thing for persuasive messages you may receive.
- To help ensure that your persuasive speech topic is persuasive and not informative, identify the claims, evidence, and warrants you may use in your argument. In addition, write a thesis statement that refutes your topic idea and identify evidence and warrants that could support that counterargument.
- Determine if your speech is primarily a proposition of fact, value, or policy. How can you tell? Identify an organizational pattern that you think will work well for your speech topic, draft one sentence for each of your main points, and arrange them according to the pattern you chose.
Bone, J. E., Cindy L. Griffin, and T. M. Linda Scholz, “Beyond Traditional Conceptualizations of Rhetoric: Invitational Rhetoric and a Move toward Civility,” Western Journal of Communication 72 (2008): 436.
Gearhart, S. M., “The Womanization of Rhetoric,” Women’s Studies International Quarterly 2 (1979): 195–201.
Ryan, K. J., and Elizabeth J. Natalle, “Fusing Horizons: Standpoint Hermenutics and Invitational Rhetoric,” Rhetoric Society Quarterly 31 (2001): 69–90.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Persuasive
11.6 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Monroe’s motivated sequence.
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. Monroe’s motivated sequence is a technique for organizing persuasive speeches that inspire people to take action and functions t o help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole”.
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods.
We wanted to add this side-note because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step, in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. A strong attention-getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t quickly know your topic, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step, the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is. Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution. Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem. Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step, in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast. The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step, in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief. When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing distinct main points in a clear manner is the problem-cause-solution speech pattern. The problem-cause-solution organizational pattern organizes the argument by describing a problem, identifying what you believe is causing the problem, and then recommend a solution to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade a civic group to support a citywide curfew for individuals under the age of eighteen
Main Points
- Demonstrate that vandalism and violence among youth are having a negative effect on our community.
- Show how vandalism and violence among youth go up after 10:00 p.m. in our community.
- Explain how instituting a mandatory curfew at 10:00 p.m. would reduce vandalism and violence within our community.
In this speech, the speaker wants to persuade people to pass a new curfew for people under eighteen. To help persuade the civic group members, the speaker first shows that vandalism and violence are problems in the community. Once the speaker has shown the problem, the speaker then explains to the audience that the cause of this problem is youth outside after 10:00 p.m. Lastly, the speaker provides the mandatory 10:00 p.m. curfew as a solution to the vandalism and violence problem within the community. The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution.
While these two patterns are recognized as persuasive speech patterns, you can use any organizational pattern to structure your argument. In addition to Monroe’s Motivated Sequence and Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern of organization, you can apply any of the organizational patterns introduced in the Speech Preparation chapter. For example, you may choose to use a topical organizion to express reasons for enacting a policy change. You may choose a spatial arrangement of gun laws by geographical locations to persuade an audience for legislation. You may look at how marine life is being affected by pollution and focus on the causal relationship. Lastly, you may compare and contrast the current health care reform to the Affordable Care Act introduced under President Obama.
Introduction to Public Communication by Indiana State University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

17.3 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole.” German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods. Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138. We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table 17.1 "Monroe’s Motivated Sequence" lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table 17.1 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step First step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker attempts to get his or her audience’s attention. , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 "Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively" , a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step Second step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.

Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step Third step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step Fourth step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker asks his or her audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast. Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman. The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step Fifth step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker asks for an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table 17.2 "Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist" also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table 17.2 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
- Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.
Module 10: Persuasive Speaking
Structure of a persuasive speech, learning objectives.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of an informative speech is to explain whereas the primary purpose of a persuasive speech is to advocate the audience adopt a point of view or take a course of action. A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence.
We can classify persuasive speeches into three broad categories:
- The widely used pesticide Atrazine is extremely harmful to amphibians.
- All house-cats should be kept indoors to protect the songbird population.
- Offshore tax havens, while legal, are immoral and unpatriotic .
The organizational pattern we select and the type of supporting material we use should support the overall argument we are making.
The informative speech organizational patterns we covered earlier can work for a persuasive speech as well. In addition, the following organization patterns are especially suited to persuasive speeches (these are covered in more detail in Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech):
- Causal : Also known as cause-effect, the causal pattern describes some cause and then identifies what effects resulted from the cause. This can be a useful pattern to use when you are speaking about the positive or negative consequences of taking a particular action.
- Problem-solution : With this organizational pattern, you provide two main points. The first main point focuses on a problem that exists and the second details your proposed solution to the problem. This is an especially good organization pattern for speeches arguing for policy changes.
- Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then explains the causes of the problem, and lastly proposes a solution to the problem.
- Comparative advantage : A speaker compares two or more things or ideas and explains why one of the things or ideas has more advantages or is better than the other.
- Monroe’s motivated sequence : An organizational pattern that is a more elaborate variation of the problem-cause-solution pattern. We’ll go into more depth on Monroe’s motivated sequence on the next page.
- Structure of a Persuasive Speech. Authored by : Mike Randolph with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

We use cookies to provide our clients with the best possible experience. If You continue to use this site, you agree with our cookie policy. Read more »
- Academic Guidance
- Essay Examples
- Essay Topics
- How To Write
- Other Articles
- Research and Sources
- Synonym Explorations
- Writing Tips
Problem Solution Speech Topics Ideas

Problem solution speech topics ideas should be aimed at fulfilling two aims of problem-solving:
- To convey a specific problem you have chosen to reflect on;
- To provide persuasive solutions to it.
How to Choose a Problem and Make the Essay Interesting
The matter of selecting a problem for discussion and critical analysis directly depends on the type of target audience you will present a paper. For instance, if the audience consists of people belonging to a specific profession or research area, then, before designing a problem-solution speech outline, it would be logical to come up with a topic connected with their area of research or the scope of their interest. There are also cases when the audience selects the topic of presentation or speech for you beforehand. If it is a general audience, then it is prudent to select topics that are controversial, appealing to the general public, or that are rather challenging, such as environmental concerns and threats, ethical dilemmas, financial aspects, crime rates in the community, international problems and challenges, and so on. With these tips in mind, you will definitely provide the best proposal speech ever.
Another method to come up with the right entertainment speech ideas is to ask the event organizer to gather ideas from the audience regarding what topics they would love to hear about and further discuss.
On the whole, whatever method of topic selection you choose, the most important thing is to make sure you have sufficient evidence and clear illustrative examples to reflect on the topic in-depth and provide convincing arguments. In any case, if you are lost among the ideas for the topic discussion, opt for one of your personal experience speech ideas.
Whatever method you use to select your problem topic, ensure that you have clear examples, convincing facts, or credible data that supports your position on the matter.
How to Find Solutions
The solutions and recommendations that you put forward should be practical and resourceful. Besides, it should be clear how exactly they can be applied to the real case you are discussing. As you are contemplating how the solution will be effective, keep in mind that your audience will be involved in their own reflection on the topic as well. So, make sure you are persuasive enough.
How to Provide Proper Support for Your Argument
Supporting examples can be related to your personal experience with the help of which you can make the argument stronger and more convincing. When critically analyzing the topic, make sure you know how much the audience knows about it. If much information is left to be explained, interpreted, and so on, make sure you do it. If there is a need to provide background information to make everything clear, then do it as well.
On the contrary, if the audience comprises experts in the scope of research you have focused on, they will surely expect more originality and novelty from you. Therefore, make sure you provide adequate problem-solving examples for your proposal paper. Generally known standard information won’t be the best option.
If the listeners are complete novices to the topic, then try to introduce them to the topic gradually. When it comes to solutions, make sure they are more related to tried and tested principles and approaches. If you are delivering a speech to an audience that is not well-versed in the topic of your proposal essay, then it is recommended to provide a detailed and clear discussion wherein you provide a solution right after each problem you mention.
Problem-solution articles can also have such a structure where you provide the causes of the issue prior to the discussion of solutions. This strategy comes in handy as concentrating on the underlying cause assists in providing more solid support for the explanations, thus providing more reliability and credibility to the solutions.
Moreover, your personal viewpoint on the central issue should be presented in the process of proposing a solution. This way, your speech will be more convincing in that you will share your experience with the people who listen to you.
Concluding your problem/solution speech, make sure you provide a brief synopsis of the core issues, particularly solutions as your audience should remember them particularly well.
The Best Problem Solution Speech Topics for College Students
Professors frequently assign problem-solution speech topics for college students either for written assignments or oral presentations. Regardless of the type of speech topics for college that you have been assigned, you need to select a topic that is of particular interest to you and your target audience. Only when you demonstrate originality in the choice of your topic will you stand out as an original speaker/ writer and will thus be more appreciated by your professor and the audience. When you want just to provide an overview of the problem, then you have to search among the list of good informative speech topics for college students. Still, when you need to demonstrate your skills in critical and analytical writing, it is recommended to organize the essay as a persuasive one.
From the persuasive writing prompts enlisted below, try to select the one that you are well versed in and that aroused the greatest deal of interest in you. Only with these two basic criteria kept in mind will you be able to provide a successfully written problem-solution persuasive paper.
A List of Problem Cause Solution Persuasive Speech Topics for College Students
The list of problem-cause solution persuasive speech topics provided below will help you come up with interesting research ideas for your speech. Take a look at the numerous options for social issues and other problems in society to write about.
- The problem of spying and media leaks in international and domestic communications.
- How to ensure local food movement support? Will it have a positive impact on the local entrepreneurship?
- The restrictions on the exploitation of the Antarctic resources should be maintained and the Antarctic should be viewed as a preserved place merely devoted to science.
- Media marketed for youths and teens convey immoral and unethical ideas.
- The FBI should keep the self-proclaimed militia under scrutiny.
- Tax incentives should be introduced for adopting children internationally.
- Foreign help to dictatorships should be eradicated by the government.
- Online learning can be equaled to classroom education in terms of its effectiveness and accessibility.
- In-vitro fertilization should be prohibited.
- The issue of minors getting tattoos should be more controlled by legal institutions: minors should either be accompanied by their guardians or be given written consent from them.
- Dependence on ACT and SAT scores during admissions should be abolished.
- Surveillance cameras should record all trials in court.
- Student-athletes representing their educational establishment in competitions should be given scholarships to cover at least partial college expenses.
- All students should be encouraged to enroll in foreign language courses and speaking clubs.
- Usage of technological advancement in teaching.
- Beauty contests in schools and colleges should be banned.
- Staffed flights into space are far more expensive than unstaffed research missions.
- Students should not be harshly encouraged or pushed to participate in sports competitions.
- The federal government should adopt a law that standardizes trunk release systems in new transport.
- Race, ethnicity, and gender equality should be supported in politics.
- Mobile phone usage, texting, and Internet use in the classroom prevent students from being involved in the studying process and lower their attention span.
- The usage of paperback textbooks should be eradicated and changed into e-book usage.
- College students should be more cautious and prudent when posting controversial or personal information online.
- The acute immigration problem will hardly ever be solved by constructing the border fence.
- Cyber-attacks pose threats internationally.
- Recycling should be encouraged worldwide.
- The contemporary taxation system does not fairly treat lower-income and middle-income population groups.
- Media advertisements targeted at children population should be banned by the government.
- Oil companies should get disaster control before engaging in offshore drilling.
- Feminists’ standpoint devalues family and motherhood.
- The problem of identity theft is extremely aggravated and the community should pay attention to it.
- Girls should be prohibited from participating in football and wrestling competitions.
- Social networks do not interfere with school education.
- Networks in educational establishments should have special filters to prevent students from accessing inappropriate material.
- The pressing need for school system reform.
- Advertisements engaging children should be restricted at the government level.
- Fast food restaurants should initiate the campaign of publicly displaying calories next to each meal.
- The government should release churches from tax incentives.
- Patients suffering from chronic mental diseases should be preserved in “halfway houses” instead of mental hospitals.
- The government should not allow the allocation of billboards on interstate highways.
- Weapons should not be sold internationally across the countries.
- Marriage should not be allowed before school graduation.
- The role of the United Nations internationally.
- The role of art and music therapy in patients’ rehabilitation.
- Educated people should work as tutors of literacy on a voluntary basis in third-world countries.
- People molesting children should be restricted from the right to adopt.
- Psychologists and psychiatrists should witness and testify in the court of law representing the non-guilty-by-reason-of-insanity.
- Security should be increased in motels and hotels as a means to guarantee security for all its residents regardless of their income.
- The National Health Insurance Program is supposed to provide basic health care for all US citizens independent of their income.
- The construction and building of venues before the Olympic Games should be banned by UNESCO as it harms a lot.
Evidently, the argument topics list entails current issues that are taking place in the contemporary world. To submit a successful paper, make sure to conduct in-depth research on your selected topic and create an impressive paper that will last in memory for a long.
Problem Solution Speech on the Topic of Policy Advocacy
The question of policy persuasive speech topics remains extremely acute for students because frequently they do not know where to start after they have read numerous essay samples. Particularly, students may be confused about the way of organizing information for a speech. To ease the task of writing a properly structured speech paper, check out the following recommended way of paper organization for a policy advocacy speech.
I. Introduction
Attention-grabber: you might provide some controversial fact, relate to personal experience, provide shocking/ impressive statistics, use a rhetorical question or a dramatic quote, etc. (all these devices are used for capturing attention from the target audience);
Relation to the audience: Pinpoint to how the issue under discussion relates to the target audience. Do it either implicitly or explicitly, but regardless of the option you choose, make sure the listeners understand their relation to the topic. If you have chosen to focus on a problem seriously affecting people, express your point of view on how exactly the problem influences the audience.
Credibility of the problem: Emphasize the problem’s significance and why it is worth others’ attention. Provide one or more reasons to make the audience understand why you have decided to speak on this subject area.
Preview: Provide a brief synopsis (overview) of the paper. You need to provide sufficient background information on the topic, especially if the audience is not well-versed in it. For example, you might briefly describe the problem in a few words and then switch over to focusing on the possible solutions.
II. Body: The Problem Identification and Solution Proposal
Identify the problem: Develop a paragraph where you provide an overview of the central problem. Appeal to ratio and emotion, as it is preferable to engage the reader both on an intellectual and emotional level. There are two recommended ways of problem identification and development – qualitative and quantitative.
According to the qualitative approach, you have to present argumentation for the claims that answer the following questions:
- What makes me indifferent about the problem? Or why should I actually care?
- How am I affected by the problem?
- How serious is the issue under discussion?
To help readers understand the problem in depth, make sure to provide examples from your personal experience or provide real-life examples related to other people. This data will not make the statistics too narrow but will add more appealing details to demonstrate how serious the issue is.
According to the quantitative approach, the arguments and support you provide should be related to such questions:
- How large is the problem?
- How much is it widespread and what is the problem scope?
When a writer investigates the scope of the problem, the larger it is – the less detailed evidence is required.
Focus on the causes: The causes of the problem should be closely examined: provide ample evidence, examples, and recent study results. Keep in mind that not every topic requires developing the problem’s causes. Still, if you think that the causes you provide will make the audience more susceptible to trusting your viewpoint. Such an approach is used when there exist multiple opinions on causes.
Put forward the solution: When investigating the possible solution(s), make sure to organize the information in the following way:
- Provide a plan: First and foremost, pinpoint the exact change in policy, law, or campaign you are suggesting. Briefly describe the step (the introduction of the new law, implementation of the new program, short synopsis of the program, etc.). The main aim at this point is to make the audience understand the kind of change you are suggesting.
- Provide supporting argumentation and evidence for the suggested solutions: You should clearly pinpoint how the solution will eliminate the ongoing risks or threats caused by the pending problem. Make sure that you link supporting evidence to the plan.
Provide credible expert evidence that clearly highlights the ways the solution would reduce the burning issue: When citing outside sources and specific examples/ materials researched by scholars, make sure you tell the audience about the credentials of the researchers. Your target audience should be sure that the information you rely on can be trusted and that is it believable overall. If you provide information that even you don’t know by whom it was put forward, then your paper will have no expert value.
Results of the study: If the research included some experimental study that aimed at supporting your solution, make sure you discuss the results and interpret them properly. Provide a brief synopsis of how many people took part in the experiment/ interview/ sociological study and what the results indicate.
Empirical evidence and pilot studies: With the help of such supporting evidence, you will emphasize that the problem has solutions related to real-life events and experiences. You might also pinpoint how small changes in the localities might affect the problem in a large-scale area. Such supporting evidence is really beneficial as it indicates that the effects happened in real surroundings with real people rather than in a laboratory environment.
Personal or peer testimony: It is not recommended to use this evidence as a priority as it is rather weak on its own. Still, if you add this evidence together with the other aforementioned types, it can significantly add up to the paper’s credibility.
Address general disadvantages: When coming up with a policy change, keep in mind that it can solve the existing problem as well as create a new one. Therefore, it is advisable to outline the potential disadvantages of the problem after you have discussed its benefits and positive effects. To make your position strong, make sure to refute the counter-arguments because when you just ignore the negative aspects, the audience will not accept or perceive your solution.
III. Conclusion
Provide a short review of the persisting problem and suggested ways out. Make sure you provide a call for action at the end of the conclusive paragraph, where you provide encouraging information that will make the audience remember your paper.
- Review of the problem and solution
- Closing thought to encourage the audience to remember the speech.
Problem Solution Topics for Your Perfect Speech
The problem solution speech topics that you will find below will help you choose, identify, and organize the way of presenting your essay. As you select the topic, you will research it properly in order to persuade the audience that a particular problem exists and that it is possible to come up with solutions to it. Moreover, you will learn how to convince the audience and make them accept your viewpoint and maybe even change their previously existing biases regarding the issue. Before you start the topic selection process, make sure you are well aware of the core elements that are necessary in such a type of writing. Check them out:
- Indicate the problem and mention specifically what factors make it an actual problem. Provide sufficient background information, pinpoint to the problem’s significance, and let the audience understand the scope of the problem and its overall effect. Make sure you appeal to reasoning and emotion: let the audience understand the needs so that it is convinced by the information you provide.
- Advocate for a solution and provide a detailed plan on how it can be applied in practice.
- Visualize the practical aspect of your solution. Demonstrate how the solutions will come in handy in improving the situation. Emphasize on their practical aspect and general effectiveness. Pay attention to a brief discussion of alternatives with which you do not agree. State how they are impractical and problematic. To put it briefly, you need to highlight the counterarguments and refute them.
- Call to action. Convince the audience to accept your position on the change implementation of the proposed policy or campaign. Or provide an implicit call to action, wherein you make a hint on the policy change.
How to Choose a Proper Problem Solution Speech Topic
If you have been invited to deliver a speech to the public, first of all, find out who your target audience comprises in terms of professional and personal interests. Despite the solid experience you might have about the research area, the audience may not find interest in your topic if it is not adjacent to their scope of interest. Therefore, be cautious when coming up with the topic of your speech or presentation. If the type of your speech has to be structured in the form of a problem-solution paper, then make sure to identify the burning issue, investigate questions and opinions concerning it, and also identify the controversy behind the issue.
When thinking of which topic might be interested in writing about, ask yourself the following questions:
- What would you like to talk about (here choose more than one option).
- How do you think – will your potential audience like the topic of your choice? Explain your viewpoint.
- How long do you plan to talk? Is your chosen topic sufficient for this type of presentation?
- What are your personal opinions and biases regarding the problem?
- Which topic are you most interested in? Which topic would be easy to talk about?
- After you have explored the professional realms of your listeners, think of the most topical problems pertaining to the topic.
- Think of whether you can provide personal experience examples or share your personal goals.
List of Speech Topics for Problem-Solution Presentation
Business area: work surroundings; career goals; bankruptcy; corporate ethics; abuse in marketing.
Teaching and education: peer pressure at school; cheating during exams; online learning versus classroom learning; education at home; sex education at school; internship opportunities.
Environmental aspects: climate change; global warming; alternative sources of energy; depletion of natural resources.
Nourishment and health: food labeling; diets and how to maintain healthy eating; problems of mentally ill people; health care in third-world countries; being vegetarian.
Politics and global issues: spying; international threats; problems with overpopulation.
Legislation and issues in the court of law: punishment for child molesters; drunk driving; frequency of juvenile aggression and delinquency; immigration and fence borders; tax incentives on church property.
Social problems: dealing with the homeless; sexual abuse; domestic violence; the effect of divorce on families; peer pressure; bullying; self-esteem; wage levels; teen drinking; gambling; discrimination on racial, ethnic, and gender backgrounds.
So far, you have a brief list of possible problem-solving essay topics. You may choose some of them for discussion or maybe they will inspire you to choose some other topic to reflect on. To properly develop the topics, make sure to examine them more closely and find some adjacent areas to them. Also thoroughly examine the dimensions of each topic investigation.
Ask yourself the following questions:
- What aspects of the problem have already been researched? Why have some been omitted?
- How could one describe the existing obstacles to solving the problem?
- How long does the problem persist?
- What are the costs needed for problem-solving?
- Will the problem aggravate if no measures are taken?
- Should the problem be immediately addressed?
- Has your target audience in particular been affected by your selected problem? In what way?
- What supporting evidence could you provide to emphasize the importance of the problem?
- What argumentation can you provide to demonstrate that your solutions are right and worth attention?
- What facts/ figures/ supporting evidence could help the target audience understand the issue more comprehensively?
Working on the Solution
- Write down all potential and alternative solutions. Keep in mind various aspects, merits, and features that could convince the audience to accept your standpoint. Investigate figures and facts; provide illustrations and real-life examples as support for your solutions. Do it consistently, step-by-step for each of the proposed solutions.
- Choose the most important and effective solution to the existing problem. Pinpoint to how your solution plan can be applied in practice. Refer to outside sources; cite credible sources; consult sources written by experts in their field of study.
- Devise a step-by-step implementation plan for each of the suggested solutions. Recommend specific procedures. Investigate the cost, effect, and necessary actions.
- Call to action; time and place.
- Other required constituents for the implementation of the plan.
If your listeners comprise people from different educational backgrounds or various professional spheres, then the decisive factor for choosing the topic should lie in choosing the topic that is most topical for the majority. Another option is to come up with a topic that presumably meets the needs of the bulk of the audience. If all of your listeners are well aware of the problem, then pay more attention to the fact of how much the topic is workable and reasonable. If you want to provide counter-arguments for the change policy campaign, then focus on the probable limitations and drawbacks of the policy.
How to Provide an Outline for a Problem Solution Speech
Below you will find the most appropriate methods for developing problem-solution topics:
- Problem Solution Method
This strategy is advisable if you have chosen a contemporary social problem and have to convince the audience that your solution is the best one among those that have been previously provided. As such, provide a proper introduction where you entail sufficient background information in order to pinpoint the problem’s significance. Afterward, list the most appropriate situations and conditions that might serve as supporting evidence for justifying your position. Present a clearly defined plan for solving the problem.
- Problem Cause Solution Method
This strategy is the most appropriate for solution topics. Here you need to single out the problem and investigate its causes. Further, you have to provide a critical analysis of the causes and put forward adequate solutions.
- Problem Cause-Effect Method
This strategy comes in handy when outlining the aftermath of your problem-cause topic.
- Comparative Advantage Method
You need to compare and contrast the identified solutions to the problem outlined.
- Place an order
- About Writology
- How it Works
- Buy Custom Essays
- Nursing Writing Services
- Do My Assignment
- Buy a Letter of Recommendation
- Buy Research Papers

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 3: Preparing for Your First Speech
Patterns of Organization: Persuasive Speeches
Cause/effect pattern.
If the specific purpose mentions words such as “causes,” “origins,” “roots of,” “foundations,” “basis,” “grounds,” or “source,” it is a causal order; if it mentions words such as “effects,” “results,” “outcomes,” “consequences,” or “products,” it is effect order. If it mentions both, it would of course be cause/effect order. This example shows a cause/effect pattern:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the causes and effects of schizophrenia.
I. Schizophrenia has genetic, social, and environmental causes.
II. Schizophrenia has educational, relational, and medical effects. It should be noted, however, that a specific purpose like this example is very broad and probably not practical for your class speeches; it would be better to focus on just causes or effects, or even just one type of cause
(such as genetic causes of schizophrenia) or one type of effect (relational or social). These two examples show a speech that deals with causes only and effects only, respectively.
Specific Purpose: To explain to my fellow Biology 1107 students the origin of the Ebola epidemic in Africa in 2014.
I. The outbreak began in March 2014 in Guinea with the death of one-year-old child who played in a tree with infected bats.
II. The virus next spread to Sierra Leone and Liberia.
III. In Fall of 2014 it spread to the U.S. and Europe by travelers from Liberia.
Specific Purpose: To describe to my classmates the effects of a diagnosis of autism on a child’s life.
I. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s educational plan.
II. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s social existence.
III. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s family relationships.
Problem-Solution Pattern
The problem-solution pattern will be explored in more depth in the chapter on Persuasive Speaking because that is where it is used the most. Then, we will see that there are variations on it. The principle behind problem-solution pattern is that if you explain a problem to an audience, you should not leave them hanging without solutions. Problems are discussed for understanding and to do something about them.
Additionally, when you want to persuade someone to act, the first reason is usually that something is wrong! Even if you wanted your friends to go out to get some dinner, and they have recently eaten, you will probably be less successful because there is no problem for them—they are not hungry. Then you would have to come up with a new problem, such as you will miss their presence, which they may or may not see as a problem for them.
In another real-life example, let’s say you want the members of the school board to provide more funds for music at the three local high schools in your county. What is missing because music or arts are not funded? What is the problem ?
Specific Purpose: To persuade the members of the school board to take action to support the music program at the school.
I. There is a problem with eliminating extracurricular music pro- grams in high schools.
A. Students who do not have extracurricular music in their lives have lower SAT scores.
B. Schools that do not have extracurricular music programs have more gang violence and juvenile delinquency.
II. The solution is to provide $200,000 in the budget to sustain extra- curricular music in our high schools.
A. $120,000 would go to bands.
B. $80,000 would go to choral programs.
Of course, this is a simple outline and you would need to provide evidence to support the arguments, but it shows how problem-solution works.
Psychologically, it makes more sense to use problem-solution rather than solution-problem. The audience will be more motivated to listen if you address needs, deficiencies, or problems in their lives rather than giving them solutions first.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
A variation of the problem-solution pattern, and one that sometimes re- quires more in-depth exploration of an issue, is the “problem-cause-solution” pattern. If you were giving a speech on future extinction of certain animal species, it would be insufficient to just explain that numbers of species are about to become extinct. Your second point would logically have to explain the cause behind this happening. Is it due to climate change, some type of pollution, encroachment on habitats, disease, or some other rea- son? In many cases, you can’t really solve a problem without first identify- ing what caused the problem. This is similar to the organizational pattern called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence (German, Gronbeck, Ehninger & Monroe, 2012), which will be fully explained in Chapter 13. The Mon-
roe’s Motivated Sequence requires a discussion of cause to create a logical speech.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the age to obtain a driver’s license in the state of Georgia should be raised to 18.
I. There is a problem in this country with young drivers getting into serious automobile accidents leading to many preventable deaths.
II. One of the primary causes of this is younger drivers’ inability to remain focused and make good decisions due to incomplete brain development.
III. One solution that will help reduce the number of young drivers involved in accidents would be to raise the age for obtaining a driver’s license to 18.
Some Additional Principles of Organization
It is possible that you may use more than one of these organizational pat- terns within a single speech. For example, the main points of your speech could be one organizational pattern and the subpoints a different one. In the spatial example above about the Native American nations of Georgia, the subpoints might be chronological (emphasizing their development over time), or they could be topical (explaining aspects of their culture).
You should also note that in all of the examples to this point (which have been kept simple for the purpose of explanation), each main point is relatively equal in emphasis; therefore, the time spent on each should be equal as well. While you are not obliged to spend exactly the same amount of time on each main point, the time spent (and the importance of the main point) should be about the same. You would not want your first Main Point to be 30 seconds long, the second one to be 90 seconds, and the third 3 minutes. For example:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the rules of baseball.
I. Baseball has rules about equipment.
II. Baseball has rules about numbers of players.
III. Baseball has rules about play.
Main Point II is not really equal in importance to the other two. There is a great deal you could say about the equipment and even more about the rules of play, but the number of players would take you about ten seconds to say. If Main Point II were “Baseball has rules about the positions on the field,” that would make more sense and be closer in level of importance to the other two.
To give another example, let’s say you want to give a commemorative (or tribute) speech about a local veteran whom you admire.
I. James Owens is an admirable person because he earned the Silver Star in the Korean War.
II. James Owens is an admirable person because he served our com- munity as a councilman for 25 years.
III. James Owens is an admirable person because he rescued five pup- pies that were abandoned in his backyard.
Although Main Point III is a good thing to do, it’s really not equal to Main Points I and II in importance or in the amount of time you would need to spend on it.
Earlier in the chapter, we said that organizing a speech involves grouping, labeling, and ordering. Let’s address labeling here . You will also notice that in most of the examples so far, the main points are phrased using a similar sentence structure. For example, “The first chamber in the blood flow is…” “The second chamber in the blood flow is…” This simple repetition of sentence structure is called parallelism , a technique useful for speakers and helpful for the audience in remembering information. It is not absolutely necessary to use it and will not always be relevant, but par- allelism should be used when appropriate and effective.
In relation to the way each main point is written, notice that they are full grammatical sentences, although sometimes short and simple. For purposes of preparation, this is a good habit, and your instructor will probably require you to write your main points in full sentences. Your instructor may also expect you to write your subpoints in complete sentences as well, but he or she will discuss that with you.
Finally, in the way you phrase the main points, be sure they are adequate labeled and clearly explain your content. Students are often tempted to write main points as directions to themselves, “Talking about the health department” or “Mention the solution.” This is not helpful for you, nor will your instructor be able to tell what you mean by those phrases. “The health department provides many services for low-income residents” says something we can all understand.
We have included examples of outlines at the ends of chapters 12, 13, and We have tried to give examples of different kinds of formats, but individual instructors prefer specific format for outlines. Your instructor should give you examples of how they want the outline to be developed and for- matted, and you should follow their directions.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian

48 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, Problem-Solution, Comparative Advantages
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.
Organizing Persuasive Speeches

Previously in this text, we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Below are the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed, a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic. If this sounds familiar, it should! The attention step uses the same elements as an introduction for any speech: The attention getter, relevance, credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. This will be your first main point. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. This will be your second main point. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker responds to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. This will be your third main point. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break the action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
This step will be your conclusion. Again, it will have the same elements as a conclusion you would use for any speech.
Application
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Below is a checklist that contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
The following video further details Monroe’s Motivated Sequence outlining each component and providing examples to provide an in-depth understanding of the organizational pattern.
For Future Reference | How to organize this in an outline |
Introduction: Attention Step
Main Point #1: Need Step
Main Point #2: Satisfaction Step
Main Point #3: Visualization Step
Conclusoin: Action Step
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.3: Organizing Persuasive Speeches
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 79749
Learning Objectives
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the parts of a Problem-Cause-Solution speech.
- Explain the parts of a Cause-Effect-Solution speech.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
Organizing Persuasive Speeches

Steven Lilley – Engaged – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Problem-Cause-Solution, Cause-Effect-Solution, and Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
Problem-Cause-Solution
One format for organizing a persuasive speech is the Problem-Cause-Solution format. In this organizational pattern, you would provide evidence to show that a problem exists, explain what is causing the problem to persist, and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point should address the problem, one main point should address the cause of the problem, and one main point should address the solution. In the first main point addressing the problem , you should clearly state what the problem is, make the significance of the problem clear by providing evidence and statistics, and finally document the harms of the problem. You should be able to explain to your audience the ultimate impact of the problem. In the second main point addressing the cause , you should explain what is causing the problem, why it continues to exist, and why it hasn't already been solved. Note that you are explaining the cause of the problem not what the problem causes . This section of your speech should get to the root of the problem. Finally, in the third main point addressing the solution , you should state the solution, explain how the solution works, and explain the practicality and desirability of the problem. The solution should clearly connect to both the problem and the causes of the problem that you discussed earlier in your speech.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
Main Points:
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Cause-Effect Solution
An alternate version of the Problem-Cause-Solution pattern is the Cause-Effect-Solution pattern. In this organizational pattern, you would start by explaining what is causing the problem, then describe the negative effects of the problem, and finally, propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. Generally, one main point should address the cause of the problem, one main point should address the effects of the problem, and one main point should address the solution. The first main point should address the cause of the problem. Just as before, the main point addressing the cause should explain what is causing the problem, why it continues to exist, and why it hasn't already been solved. Remember that you are explaining the cause of the problem not what the problem causes . In the second main point addressing the effect of the problem, you should describe the negative outcomes of the problem, elaborate on what will happen if the problem continues to exist, and describe the ultimate impact of the problem. You should be trying to describe the worst-case-scenario for your audience here and show them what will ultimately happen if this problem continues to go unsolved. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have more than one cause that leads to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. Finally, in the third main point addressing the solution , you should state the solution, explain how the solution works, and explain the practicality and desirability of the problem. The solution should clearly connect to the causes of the problem and solve for the effects of the problem that you discussed earlier in your speech.
- Demonstrate hate speech led to confrontations and violence on campus.
- Explore the impact of the confrontations and violence on the student body.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have explained that the cause of the problem is the hate speech used by various groups on campus, you then demonstrate to your audience the effects of the unnecessary confrontations and violence. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence” lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 “Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively”, a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table \(\PageIndex{2}\) “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist” also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table \(\PageIndex{2}\) Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Problem-Cause-Solution, Cause-Effect-Solution, and Monroe’s Motivated Sequence. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- The Problem-Cause-Solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The Cause-Effect-Solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining what is causing the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what they see as the ultimate impact of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how they persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
Learn how to write a problem-solution speech or essay with this guide. Find a list of topics, an outline structure, and examples for different categories.
A problem/solution speech takes the approach of highlighting an issue with the intent to provide solutions. It is a two-phase approach where first the speaker lays out the problem and explains the importance. Secondly, a variety of solutions are provided to tackle the said issue. The best solutions are those that can be actively applied.
5 Steps. •. • Need: demonstrate the problem and a need for change. • Satisfaction: provide a solution. •. for complex problems described by topic. Visualization: use vivid imagery to show the benefits of the solution. • Action: tell the audience to take action. Attention: gain attention of your audience.
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
Problem-Cause-Solution. Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution. Psychological A further way to organize your main ideas within a speech is through a psychological speech pattern in which "a" leads to "b" and "b" leads to ...
Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe's Motivated Sequence. Exercises Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic.
In persuasive speeches, speakers make an argument to their audience. Here are four primary ways to organize a persuasive speech: Problem-solution • Speaker identifies a specific problem and offer a specific solution • Solution should be the most effective • Solution should resolve the problem outlined in the speech Problem-cause-solution
The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution. While these two patterns are recognized as persuasive speech patterns, you can use any organizational pattern to structure your argument.
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
Learn how to structure a persuasive speech with different organizational patterns, such as problem-solution, problem-cause-solution, and causal. Find out how to use supporting evidence and reasons to advocate your point of view or course of action.
Problem-Cause-Solution. One format for organizing a persuasive speech is the Problem-Cause-Solution format. In this organizational pattern, you would provide evidence to show that a problem exists, explain what is causing the problem to persist, and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action.
A List of Problem Cause Solution Persuasive Speech Topics for College Students. The list of problem-cause solution persuasive speech topics provided below will help you come up with interesting research ideas for your speech. Take a look at the numerous options for social issues and other problems in society to write about.
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. ... The most common type of outline organizations for speeches with propositions of policy is problem-solution or problem-cause-solution. Typically we do not feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need ...
DYAD Persuasive Speech Outline; Cause-Effect Outline; Preview text. 1 PROBLEM/CAUSE/SOLUTION OUTLINE Name: Session: CMST 1110-(Section #) Title of your Speech: Organizational Pattern: Problem/Cause/Solution General Purpose: (To persuade) Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience to (title of your speech) in (# of main points). ...
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern. A variation of the problem-solution pattern, and one that sometimes re- quires more in-depth exploration of an issue, is the "problem-cause-solution" pattern. If you were giving a speech on future extinction of certain animal species, it would be insufficient to just explain that numbers of species are about ...
In this video, you'll watch my college student's powerful persuasive speech on the sustainability of life. ****For public-speaking training videos: This vide...
First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular ...
Persuasive Speech Outline: Problem-Cause-Solution Format I. Introduction: A. Attention Getter: B. Audience Relevance: C. Credibility: D. Thesis and Preview:
Persuasive argumentation: Writers must present persuasive arguments to convince readers of the urgency of the issue and the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed solutions. Action-oriented approach: The ultimate goal of this writing is to inspire action and change, whether at the individual, community, or policy level.
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
View Pers Outline Template.docx from COMM 1500 at Clemson University. Name: _ Persuasive Speech Outline Template [Problem-Cause-Solution] Introduction I. II. III. IV. V. Attention
Problem-Cause-Solution. One format for organizing a persuasive speech is the Problem-Cause-Solution format. In this organizational pattern, you would provide evidence to show that a problem exists, explain what is causing the problem to persist, and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action.