Business Plan Templates
Free Download
.png)
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business. Available as an interactive PDF or a Google Docs template.

With this business plan template, you'll be able to:
- Write a company description that sells your story
- Plan for the future: lay out goals and metrics for success
- Describe your product line in detail and plan for how to stand out from competitors
- Consider any legal formalities that require attention when starting your business
- Put together necessary financial projections to make a strong start
- Create your buyer persona and determine your product/marketing fit

Build A Business Plan That Works
Available as a one-page interactive PDF and a full template on both Google Docs and Microsoft Word!
Whether you’re starting a business or drafting a formalized document with your current business goals, it’s important to clearly defi ne the scope of all aspects of the venture — from mission, to target customers, to fi nances, and beyond.
When just starting out, it can be tempting to think of a business plan as simply your company’s name and a description of your product or service. But in reality, planning a business involves thinking through a lot more details.
In this business plan template we’ll guide you through the steps of writing company and product descriptions, setting sales and marketing goals and plans, and thinking through legal and fi nancial logistics. We've included a plain text, designed , and completed example version of this template.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do you write a business plan.
A business plan is a formal written document that you can use to identify the purpose of your company, make important decisions about your future and help grow your company. HubSpot's free business plan templates provides guidance to establishing your company mission, customer research, competition, and a business strategy to profitability.
Why do I need to fill out the information requested?
We will always keep your personal information safe..
We ask for your information in exchange for a valuable resource in order to (a) improve your browsing experience by personalizing the HubSpot site to your needs; (b) send information to you that we think may be of interest to you by email or other means; (c) send you marketing communications that we think may be of value to you. You can read more about our privacy policy here .
Where can I get a free business plan template?
HubSpot's Free Business Plan Templates are the best way to create a professional, thorough business plan. The templates include instructions and everything you need to know about starting your company.
Is this really free?
Absolutely.
Just sharing some free knowledge that we hope you’ll find useful. Keep us in mind next time you have marketing questions!
What are the basic format of a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that outlines the company's goals, strategy and implementation. The format of the plan varies depending on the type of organization (e.g., for-profit or nonprofit) and size, but most plans share some common features such as an overview, executive summary, and financial information.
What is the best business plan template?
A great business plan template clearly defines the scope of the venture -- from mission, to target customers, to finances, and beyond. HubSpot's business plan template will guide you through the steps of writing company and product descriptions, setting sales and marketing goals and plans, and thinking through legal and financial logistics.
What is needed to start a business?
If you're thinking about starting a business, you'll need to do some research first. You can't just start a business without doing any market research. Market research will tell you if there's an opportunity to turn your idea into a successful business. After that, write your business plan so that you know how much money and time it will take for the project to succeed. Use HubSpot's free business plan template today!
Set yourself up for success with this business plan template
Download the free business plan template.
All fields are required.
Easily create great, effective landing pages for free
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
- Corporations
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
How to Start a Charter Boat Business: The Complete 12-Step Guide
Step 1: Write a Business Plan

- Sizes and types of boats you plan on leasing or buying
- Destinations
- Preferred clientele
- Services offered (fishing equipment rental shop, parasailing, jet ski rentals, etc.)
- Price of services
- Where you’re going to be docking your boat
- If you need to build a dock
- How you plan to market your business
Step 2: Mentorship

Step 3: Licensing
- A current copy of the boat’s registration is required when a vessel is being designated on a license.
- An angler permit specifying the maximum number of persons who may fish from the charter boat per trip. Only a person who holds a salmon charter license may hold an angler permit.
- A non-salmon charter license is required if you accept a fee to take a person fishing for shellfish and fish other than salmon or albacore tuna.
- A food fish guide license is required if you accept a fee to take a person fishing for salmon, sturgeon, or other food fish species in freshwater rivers and streams.
Step 4: Target Market

Step 5: Have a Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- EMOTIONAL CONNECTION: An excellent USP imprints itself on the minds of your prospects so when they need the kind of service you provide, they’ll automatically think of you.
- INCREASED REVENUE: If you communicate a strong USP to customers, you'll invariably boost your revenue.
- LOYAL CUSTOMERS: When your USP delivers a compelling value proposition, you won’t only get customers to buy something from you today, but you’ll win them over for life.
How to Create a USP

- Analyze data from social media marketing campaigns
- Talk directly to your customers
- Talk to your customer service team
Step 6: Name Your Business
Brainstorming, check for availability, register with state authorities.

Step 7: Choose a Business Structure
Partnership.

Step 8: Secure Funding
- BOOTSTRAPPING: Bootstrapping refers to scraping together your own financial reserves. This could include accumulated savings, credit cards, and home equity lines.
- FRIENDS AND FAMILY: One of the best sources of startup funding is friends and family. If you have a rich uncle who always wanted you to start your own business, now is the perfect time to see if he’ll loan you the money. He’ll probably give it to you with little-to-no interest.
- CROWDFUNDING: You can try using the internet to raise small amounts of money from a large number of people. This is known as crowdfunding, and it’s the way many companies get funded these days. Try sites such as AngelList or Crowdfunder .
- TAKE OUT A LOAN: You might qualify for a traditional bank loan. An encouraging sign for small business owners is that banks seem to have a renewed interest in helping out small businesses. In addition to your local bank, Bank of America and Wells Fargo are two banks you might want to try.
Ongoing Expenses
Step 9: docking your fleet.

Renting a Slip
Water traffic, step 10: hire your crew.

Hiring Fishing Charter Employees
Step 11: insurance.
- Damage to your vessel
- Injury to your guests or employees
- Liability coverage
Step 12: Market Your Business

Marketing Channels
The 21 Best Cleaning Franchises to Own in 2024
General Cleaning Industry Overview
How much does a cleaning franchise make.
- How Much Does It Cost to Start a Cleaning Franchise?
- The UpFlip Cleaning Blueprint
Residential Cleaning Franchises
- Commercial Cleaning Franchises
Specialty Cleaning Franchises
- Commercial Cleaning Services : Commonly referred to as janitorial cleaning, these services made over $90 billion in 2022 and are expected to grow to $96.1 Billion by 2028. This segment of the industry averages 6.9% profit.
- Residential Cleaning Services: The housekeeping, maids, and gardening industry made over $30 billion last year and is expected to grow to $33 billion by 2028. This industry has a nearly 52% profit margin.
- Specialty Cleaning Services: This is a catchall for other services like carpet cleaning, upholstery cleaning, power washing, and window washing. These add up to around $10 billion in revenue, and profits vary.
How Much Does a Cleaning Franchise Cost?

- Local market potential
- Reputation of the brand
- Size of the zone
- Corporate greed
- Master vs. Service franchise
- Assistance that the corporate office provides
Can I Buy a Cleaning Franchise Under $1,000?
- UpFlip Cleaning Business Blueprint
- Stratus Building Solutions
- Anago Cleaning Systems
The UpFlip Cleaning Business Blueprint
- A 10-Module Course
- Your Own Website and SEO
- Marketing and Sales Scripts
- Google Local Service Ads Templates
- A Guide to Booking Airbnb Clients
- Software to Provide Reviews
- Mentoring While You Start and Run Your Cleaning Business

- Two Maids (and a Mop)
- You’ve Got Maids
- Merry Maids
#1. The Maids: Top Ranked Cleaning Company by Entrepreneur

- Initial License Fee : $12.5K
- Additional Fees at Signing : $32K to $80K
- Other Startup Costs : $10K to $33K
- 3 Months Operating Expenses : $22K to $39K
- Total Expenses : $76K to $165K
- Royalty Fees : 3.9% to 6.9%
- Advertising : 2%
#2. Two Maids: Best Employee Pay Model
- Pay for Performance: Employees get paid based on performance instead of hourly pay, incentivizing the best performers.
- Guidance with Systems: The company is highly focused on creating the right systems for you to succeed.
- Initial Franchise Fee : $19,950
- Initial Investment : $83,140 to $123,890
- Net Worth Requirement : $200,000
- Cash Requirement : $51,140
- Royalty Fees : 4-7%
- Ad Royalty : 2%
#3. You've Got Maids: Best for High-Value Residential Clients

- Initial Franchise Fee : $7,000
- Initial Investment : $36K to $108K
- Cash Requirement : $40K to $100K
- Royalty Fees : 2.99% to 5.99%
- Ad Royalty : $75/week
#4. Molly Maid: Most Cleaning Franchise Options
- Initial Franchise Fee : $14,900
- Initial Investment : $127K to $185K
- Net Worth Requirement : $250,000
- Cash Requirement : $65,000
- Royalty Fees : 3% to 6.5%
- Ad Royalty : $104/week
- Window Genie: Window washing is another type of cleaning franchise you could start. Learn more about how to start a window cleaning business.
- Dryer Vent Wizard : Gas dryer vents are the number one cause of house fires. Dryer Vent Wizard’s specialized services can save people's lives.
- Shelf Genie : Perfect if you want to offer home organization services.
- Grounds Guys : Landscaping is cleaning the outside, but if you want to do landscaping go talk to the guys at Augusta Lawn Care Services and tell them the UpFlip team says hi.
#5. Merry Maids
- Initial Franchise Fee : $37,500 to $51,500
- Initial Investment : $50K to $100K
- Royalty Fees : 5% to 7%
- Ad Royalty : 1.3%
#6. Maid Right

- The Grout Medic : Grout cleaning and repair franchise
- Renew Crew : Pressure washing franchise
- Kitchen Wise & Closet Wise : Home organization services
- Initial Franchise Fee : $65,000
- Initial Investment : $103K to $148K
- Cash Requirement : $50K
- Royalty Fee : 6%
Commercial Cleaning Services Franchises
- Vanguard Cleaning Systems
#1. Jan-Pro: Best Commercial Cleaning Franchise Under $50K
- Initial Franchise Fee: $2K to $4.5K
- Initial Investment: $4.8K to $58K
- Royalty: 10%
- Ad Royalty: 1%
#2. Jani-King: Largest Global Franchise Cleaning Company

- Initial Franchise Fee : Not Disclosed
- Initial Investment : $20K to $52K
- Net Worth Requirement : Not Disclosed
- Cash Requirement : Not Disclosed
- Royalty Fees : Not Disclosed
- Ad Royalty : Not Disclosed
#3. Coverall: Most Focused on A Positive Work Environment
- Initial Franchise Fee : $16K to $41K
- Initial Investment : $18K to $52K
- Royalty Fee : 5%
#4. Stratus Building Solutions: Lowest Cost Cleaning Franchising
- Janitorial Services Franchises
- Stratus Master Franchises
- Initial Franchise Fee : $3,600 to $69,000
- Initial Investment : $4,600 to $79,000
- Net Worth Requirement : $5K to $40K
- Cash Requirement : $2K to $20K
- Royalty Fees : 5%
- Ad Royalty : 1%
#5. Vanguard Cleaning Systems

- Initial Franchise Fee : $5K
- Initial Investment : $6K to $37K
- Net Worth Requirement : $50K and $250K
- Cash Requirement : $7K and $45K
- Royalty Fees : 11.5%
- Ad Royalty : N/A
#6. Anago Cleaning Systems: Easiest to Get Approved Cleaning Franchise
- Initial Franchise Fee : $5K to $31K for Units; $98K for Master franchises
- Initial Investment : $11K to 61K Units; $219K to $339K Master
- Net Worth Requirement : $31K
- Cash Requirement : $1K
- Royalty Fees : 10%

- Aire-Master of America
- College Hunks Hauling Junk
- ServiceMaster Clean
- TruBlue Total House Care
#1. Aire-Master of America: Most Unique Cleaning Services Franchise
- Initial Franchise Fee : $30K to $100K
- Initial Investment : $45K to $170K
- Net Worth Requirement : $20K
#2. Oxi Fresh Carpet Cleaning: Best Carpet Cleaning Franchise
- Initial Franchise Fee : $42,000
- Initial Investment : $48K to $78K
- Royalty Fees : $395 monthly
- Ad Royalty : 3% [/su_note]
#3. College Hunks Hauling Junk: Best Name (The Uniforms Don’t Match It, Though)

- Initial Franchise Fee: $45K to $75 K
- Initial Investment : Not Disclosed
- Net Worth Requirement : $200K
- Cash Requirement : $75K
- Royalty Fees : 7%
#4. ServiceMaster Clean
- Initial Franchise Fee: $32,500
- Initial Investment : $90K
- Net Worth Requirement : $100K
#5. PuroClean: Most Disclosive Cleaning Franchises

#6. TruBlue Total House Care: Most Diverse Skill Set Needed

- Total Investment: $65,050 to $91,400
- Franchise Fee: $44,900
- Minimum Liquid Capital: $50,000
You Might Also Want to Check Out
- Home Cleaning Centers of America
- Sears Maid Services
- Home Clean Heroes
Contact the Franchise That Works for You
- Start my own cleaning business from scratch.
- Start my cleaning business with a course.
- Contact a franchise. Tell us in the comments which one!
How to Become an Entrepreneur in 13 Steps
Want to be your own boss and quit your day job?
We’ve got you covered with our guide to connect entrepreneurs with their goals. We’ll show you how to become an entrepreneur with advice from five business owners who have turned their ideas into multi-million dollar businesses and opened up even more opportunities.
How to become an entrepreneur
Becoming an entrepreneur requires wearing many hats. You’ll have all kinds of responsibilities, including marketing, human relations, inventory, legal compliance, and more. You’ll want to follow these steps to join the ranks of successful entrepreneurs:
- Identify your passion and expertise.
- Generate and validate business ideas.
- Create a business plan.
- Develop necessary skills.
- Network with successful entrepreneurs.
- Consider the legal structure.
- Secure funding.
- Create a minimum viable product (MVP).
- Build a brand and online presence.
- Market your business.
- Provide exceptional customer service.
- Manage finances and operations.
- Scale your business.
Read from start to finish to learn all about becoming an entrepreneur, from identifying a good business idea to building a brand. Or click on any of the links above to jump straight to the section you need to learn more about right now.

Identify your passion and expertise
To become an entrepreneur, you need to find the intersection of what you’re good at, what makes money, and what people will pay you to do. Start by writing down your hobbies, skills, and experiences. Here’s an example of what mine look like:
As you can see, my combination of skills, hobbies, and work experience hints that I need to be doing something that uses lots of skills and covers a variety of industries. Writing for UpFlip fits that bill.
Also write down things you don’t want to do or would find inconvenient. For instance, if you’re not a morning person, you might not want to start a construction company.
Try writing yours down and see if you learn something about yourself. You can also take an interest and aptitude test to find businesses you might do extraordinarily well in.
Next, you’ll want to find a business idea to pursue.
Generate and validate business ideas
Next, you’ll want to come up with a business idea that fits well with your life.
We have a vast selection of ideas for you to consider when you decide to start a business. We’ve got you covered for a side business , companies that generate passive income , or a business idea that requires eCommerce .
Check out some ideas from Paul Akers:
After you’ve listed businesses you are interested in starting, it’s time to conduct market research to determine whether there's a demand for your product or service. You’ll want to research information like:
- How much does the industry make?
- What is the growth forecast?
- What are the emerging trends?
- Who are the market players?
- How much does the average business make?
- How many employees does the average business need?
Check out our blog about market research to learn more.
You’ll want to save your answers, and where you got them, because you’ll need them for the next step.
Create a business plan
A well-structured business plan helps you clarify your goals and strategies. Outline your business concept, target market, competition, marketing strategy, and financial projections.
Small business owners have different ways of writing a business plan . Some just write a one-page business plan to keep themselves on track, while others write a 100-page plan and pursue venture capital money or loans.
It’s important to note that the majority of successful entrepreneurs have a business plan. You should also be flexible, as 93% of Harvard graduates who chose to become an entrepreneur pivoted from their original strategy to increase success.
Check out our interview with Mike Andes to learn how he writes a business plan.
Develop necessary skills
Entrepreneurs need skills like:
Communication
Problem-solving, persistence.
Consider taking courses, reading books, or attending workshops to develop these skills.
Making something out of nothing requires creativity. Just like an artist with a blank canvas, a successful entrepreneur will take an idea and paint a picture with their business plan.

Successful businesses are teams, and the business owner is the coach. In today’s world, the old model where you could abuse your employees and they’d stay doesn’t work.
A successful entrepreneur looks to find people with aligned interests and empower them to achieve their goals while helping the company achieve its goals.
SessionLab has a great blog on exercises aspiring entrepreneurs can do to improve their leadership skills .
Successful entrepreneurs know how to communicate. You’ll have to talk to customers, investors, and employees. Everyone has different ways of communicating, and with all the lines of communication available, learning how to communicate with each stakeholder can be a challenge.
Email, video conferencing, in-person, and other methods are consistently used, and each of them has its own challenges. Try some of these exercises to build communication skills .

Many entrepreneurs struggle with this element of starting a business. You can always outsource, but it helps to have a solid understanding of marketing, and particularly digital marketing.
There are tons of free certifications you can take to learn about marketing. Some of my favorites are:
- HubSpot Digital Marketing Certification: This covers SEO, website speed, social media, email marketing, and paid ads. Take it through HubSpot Academy .
- Google Certifications: You can get certified on Google Analytics 4 and Google Ads through Skillshop .
While you don’t have to have these certifications, successful entrepreneurs need to understand the “language” of the people they supervise.
The point of a business is to make money. It will be hard to be a successful entrepreneur without a basic understanding of accounting.
Consider taking a course or two so you can better discuss your financial strategies with a certified public accountant.
Successful entrepreneurs are good at solving problems. Some ways to improve your problem-solving skills include:
- Practicing puzzles and brain teasers regularly
- Engaging in critical thinking activities and games
- Reading business books

One of my favorite quotes is from John Maxwell: “Change is inevitable. Growth is optional.”
You’ll deal with constant change on your path to become an entrepreneur. Employees will come and go, and market trends will evolve, but will you?
If you aren’t adaptable, you’ll probably find running your own business tedious. Many entrepreneurs spend most of their days jumping from one task to another and need to know how to shift gears.
The best way to learn adaptability is to go through trials and tribulations. When something challenges you, take a minute, center yourself, and ask why it evokes a response. Once you understand the emotional response, tackle the problem.
A new business venture rarely becomes immediately successful. It can take years for entrepreneurs to find the right combination of product, pricing, and marketing strategies to get the market interested in what it creates.
The best you can do is learn from your mistakes and keep moving forward.
For inspiration, read about Thomas Edison’s persistence when creating the lightbulb.
Murphy’s Law states that what can go wrong will go wrong.
A successful entrepreneur needs to be prepared for things to go wrong when they own a business. How quickly they gain composure and find a way to fix it will dramatically impact their success.
Network with successful entrepreneurs

Connect with other entrepreneurs, join business associations, and attend networking events. A support network can provide valuable advice, mentorship, and potential partnerships.
We’re creating a mentorship program that will help you network with other successful entrepreneurs. Sign up for our newsletter to be one of the first to join.
Consider the legal structure
You’ll need to choose a legal structure for your business. It’s best to consult with a lawyer or legal advisor to understand the implications of the different business structures, but the most common business structures are:
- Limited liability companies
Sole proprietorship

The business owner and the business are the same entity, which means if someone sues your business, they could take your personal assets.
Limited liability company (LLC)
An LLC makes your business a separate entity and provides liability protection—as long as you have a separate bank account, do not personally cause an incident, and do not sign away the protection (beware: lenders try to get you to).
LLCs require less paperwork and compliance work than a corporation, too.
Corporation

A corporation also offers liability protection and also the issuance of shares, but there are numerous compliance issues that may occur.
Learn more in our blog about business structures .
Secure funding
You’ll need money to become a successful entrepreneur. That doesn’t mean it has to be your money, but it’s easier to build a successful business if it is your money.
To fund a business you’ll need to:
- Create a five-year budget.
- Establish how much money you need to follow the budget.
- Decide how to fund the business.
Create a five-year budget
A key step to becoming an entrepreneur is calculating how much money you’ll need to make before your business becomes profitable.
Early-stage companies can become successful within a few months, depending on the business model, but Tesla took 17 years to have a profitable year.
Your financial projections should be made with the following figures in mind:
- How much you need to maintain your lifestyle
- Your current startup funds
- The reasonably expected revenue
- Expenses associated with the small business
We’ve created a startup cost estimator to help you establish how much you’ll need to make to break even.
Establish how much money you need to follow the budget

Once you have a budget, you need to establish whether you have the money or need to find funding. The funding you’ll need for the small business needs to be high enough to cover you through the time when the business model is not making an operating profit.
You may also want to add wiggle room because many businesses fail when they run out of money. Assuming an additional 20% should cover unexpected expenses.
Decide how to fund the business
You can get business funds from numerous sources, including:
Personal savings
Potential business partners, venture capitalists, angel investors, small business investment company (sbic) financing, crowdfunding.
Let’s discuss how to become an entrepreneur using each of these funding sources.
Many entrepreneurs start by self funding. This is the most common way to start a small business. You might use your own money from working, savings accounts, or rollover business start-ups (ROBS).
A ROBS allows a business owner to own company shares with their retirement account. The small business then has funds and doesn’t pay a penalty for early withdrawals.
When you become an entrepreneur, it may be beneficial to have a partner.
Business leaders will often want additional sources of revenue and agree to be a business partner and mentor to other people. Whether the partner is a silent partner or active in the business model can be negotiated.
Venture capital firms look for startup entrepreneurs who have ideas that could make them millions or billions of dollars.
The firms help promising business models get the funds they need to make it through the startup grind, and they effectively manage these businesses until the company qualifies to go public. The venture capitalists gain massive wealth in the process.
Learn how Keith McCall raised millions of dollars for Pollen Systems through venture capital firms.
Angel investors are similar to venture capitalists, but there are some major differences:
- Angel investors do not manage others’ funds, while venture capital companies do.
- Venture capitalists tend to invest in more established companies than angel investors.
- An angel investor tends to invest less than a venture capital firm.
- Venture capital tends to be less hands on than angel investors.
You can take out personal loans or small business loans to become an entrepreneur, but unless the company is an online business with a business model that is likely to scale, you may find it difficult to get funding until after you don’t really need it.
You can learn more about small business loans on the Small Business Administration’s (SBA) website .
The SBA also licenses SBICs. They’re a cross between venture capitalists and banks, where they offer both debt and equity options. For every dollar the SBIC provides you, the Small Business Administration provides two.
Learn more about SBICs here .
Another way to start an entrepreneurial career is crowdfunding, which is when new entrepreneurs list offerings to potential investors on a website in exchange for debt, equity, rewards, or donations.
Check out our interview with Jason Hernandez. He started Pooch Selfie by fundraising on Kickstarter.
Create a minimum viable product (MVP)
An MVP is a basic version of your product or service that allows you to test the market and gather feedback. This might be a prototype of a physical product that people test before mass production, or it might be a less sophisticated version of the intended software.
You’ll want to follow these steps to create an MVP:
- Define your idea and objectives: Clearly articulate your product idea and identify the core problem it solves or value it provides users.
- Identify key features: Determine the features that are essential to addressing the core problem or delivering the primary value proposition. Avoid adding unnecessary features at this stage.
- Prioritize features: Rank the identified features based on their importance. Focus on the must-have features that are critical for the MVP's functionality.
- Design user interface (UI) and user experience (UX): Create a basic design for the user interface. It should be intuitive and user-friendly. You can use wireframes or mockups to visualize the layout.
- Select the technology stack: Choose the appropriate technology and tools for development. Consider factors like programming language, frameworks, and databases.
- Build the MVP: Develop the basic version of your product with the selected features. Keep the development process lean and focused on the core functionality.
- Test and assure quality: Thoroughly test the MVP to identify and fix any bugs or issues. Ensure that the product functions reliably.
- Launch the MVP: Make the MVP accessible to a small group of early users. This could be through a closed beta test or a limited release to a select audience.
- Gather user feedback: Encourage users to provide feedback on their experience with the MVP. This feedback is invaluable for refining and improving the product.
- Analyze metrics and user behavior: Use analytics tools to track user interactions, engagement, and other relevant metrics. This data will help you understand how users are using the MVP.
- Iterate and refine: Based on the feedback and data gathered, make necessary improvements and iterate on the MVP. Focus on enhancing existing features and possibly adding new ones.
- Continue testing and iterating: Keep testing and iterating based on user feedback and data. Continue to refine the product to meet user needs and expectations.
- Scale and expand: Once you have a solid foundation and a validated product, you can start thinking about scaling and adding more features to meet broader market demands.
Remember, the key to a successful MVP is to keep it simple, focused, and aligned with solving a specific problem or delivering a clear value proposition. It's about learning from real user interactions and using that knowledge to guide the development of your product.
Learn more in our blog on product development .
Build a brand and online presence

After you spend money creating your product, it’s time to build your brand. You’ll need to complete the following tasks to build a winning brand:
- Design a logo.
- Create a website.
- Create social media accounts.
- Get packaging for any physical products.
- Design uniforms, building, and vehicle signs (if applicable).
- Write your brand guidelines.
Design a logo
Your logo can be basic or elaborate. Most companies try to keep at or below three colors and want the logo to help explain what they do.
MaidThis is an online business that focuses on booking Airbnb and home cleaning jobs. Hear how Neel made the logo and has turned the remote cleaning business into a $2M per year company.
Create a website
Entrepreneurial success normally relies on digital marketing, and the center of any digital marketing strategy should be your website. It’s where new customers find you after typing something relevant into a search engine.
Learn more in our blog on website creation .
Create social media accounts
You’ll probably want to at least have a small presence on every popular social media platform. Make sure your business’s profile fits its company culture.
You’ll want to research best practices for each one and start building a following. We’ll talk about that more in the marketing section.
As you gain traction on several platforms, you can focus on the ones that help you get more satisfied customers.
Get packaging for any physical products
Companies selling physical products need to have packaging that matches the brand image they want to portray.
Check out Packlane’s blog about custom packaging to get your creative juices flowing.
Design uniforms, building, and vehicle signs (if applicable)
Many local businesses find success, and part of what plays into that success is how they use their vehicles, buildings, and uniforms to convey a brand message.
Mike Andes started a lawn care business that is one of Entrepreneur’s top 500 franchises. He discusses elements of branding in the video below.
Write your brand guidelines
Your brand guidelines will provide information to employees and marketers about how to use your brand assets. Check out the brand guideline example below.
Market your business
Develop a marketing strategy to promote your business. You should include:
Content marketing
Social media marketing.
- Search engine optimization
Email marketing
Advertising.
A profitable business focuses on finding ways to bring people to its website. Content marketing focuses on creating content that people will remember and find useful—and hopefully develop a positive relationship with your brand in turn.
You’ll want to share all the content you create on social media platforms. You want to use that content to encourage actions, including:
- Following your page
- Going to your website
- Providing an email or phone number
- Downloading a useful product
- Buying a product
- Leaving a review
- Referring friends
Notice that each of these steps is building a closer relationship with your audience and will help you get closer to your goal of becoming a profitable business.
Not all entrepreneurs have the patience to go through this process on their own. You may find it easier to hire a marketing team with experience in your product category if you are hoping to be an overnight success.
Search engine optimization (SEO)

SEO works amazingly alongside content marketing and social media marketing.
The goal with SEO is to identify the intent and questions that search engine users have, then provide them the information they want to know. When you successfully help answer questions better than other websites, you may rank higher in the search results.
You can use software like Semrush and SurferSEO to identify the best strategy for answering searchers’ questions and ranking highly in search engine results.
After you have collected a person’s email, you can use email marketing tools like MailChimp to separate people into email lists and automate when you send them emails.
This helps you keep your customers and followers informed about new developments in the company and can increase their lifetime value.
Paid advertising still has a place in marketing, but it is extremely costly if you don’t narrow your target market.
For instance, just by narrowing their ads to people who live in New York City, local businesses can get nearly 40 times better results than if they allow the ads to be shown nationally, and almost 1,000 times better results than if they showed globally.
Given New York City has over eight times the population of most U.S. cities, that means you can market to almost any city for less than $4,000.
Reduce your target market even further, and you can start making it so locals think about your company when they need the service you offer.
Provide exceptional customer service

Providing exceptional customer service is crucial for building customer loyalty and a positive reputation for your business. Here are some steps you can take to deliver outstanding customer service:
- Understand your customers’ needs: Take the time to truly understand what your customers are looking for. Listen actively to their concerns, questions, and feedback.
- Be responsive: Respond to customer inquiries, messages, and feedback promptly. This shows that you value their time and are committed to assisting them.
- Practice active listening: Pay close attention to what your customers are saying. This helps you address their specific needs and concerns more effectively.
- Empathize and show understanding: Put yourself in the customer's shoes and understand their perspective. Acknowledge their feelings, frustrations, or excitement.
- Maintain a positive attitude: Stay positive, even when dealing with challenging or difficult situations. A positive attitude can help diffuse tension and create a more pleasant interaction.
- Personalize interactions: Use the customer's name, refer to previous interactions, and tailor your responses to their specific situation. This shows that you value them as an individual.
- Provide clear and accurate information: Ensure the information you provide is accurate and easy to understand. Avoid jargon that the customer may not be familiar with.
- Go the extra mile: Take initiative to exceed customer expectations. This could be by offering additional assistance, providing special discounts, or offering solutions beyond what was initially requested.
- Admit mistakes and take responsibility: If your business makes a mistake, acknowledge it, apologize, and take steps to rectify the situation. Customers appreciate honesty and transparency.
- Follow up and follow through: After providing assistance, follow up with the customer to ensure that their issue was resolved to their satisfaction. This demonstrates your commitment to their well-being.
- Provide multi-channel support: Offer various communication channels, such as phone, email, chat, and social media. This allows customers to reach out in the way that is most convenient for them.
- Solicit feedback: Ask customers for feedback about their experience. Use this information to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
- Train your customer service team: If you have a team, ensure they are well-trained in customer service skills and have a thorough understanding of your products or services.
- Monitor and measure customer service performance: Use metrics and customer satisfaction surveys to evaluate the effectiveness of your customer service efforts, and make improvements as needed.
- Foster a customer-centric culture: Ensure that everyone in your organization understands the importance of exceptional customer service and is committed to delivering it consistently.
Remember, exceptional customer service is an ongoing effort that requires dedication and a customer-centric mindset. By prioritizing your customers' needs and consistently delivering high-quality service, you can build strong, lasting relationships with your customer base.
Manage finances and operations
Keep track of your finances, manage cash flow, and ensure you have efficient operational processes in place. Most companies use QuickBooks to manage their finances.

Scale your business

Once you've established a solid foundation, consider ways to grow and expand. This could involve hiring more employees , entering new markets, or offering additional products or services. Check out our blog about how to grow a business .
Remember, becoming an entrepreneur is a journey that requires continuous learning and adaptability. Stay open to new ideas, seek feedback, and never stop refining your business.
Become a successful entrepreneur: Start your own business
Now you know how to become an entrepreneur. We’ve discussed everything from choosing an idea to finding funding and building your brand.
Want instant access to business models that work? Skip the formal education and join our global community of young entrepreneurs by taking one of our online courses. Learn more here .
What kinds of businesses do you want to start?
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
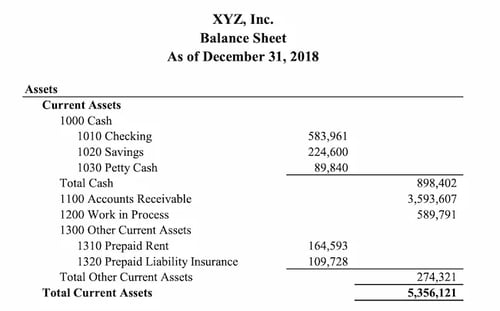
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
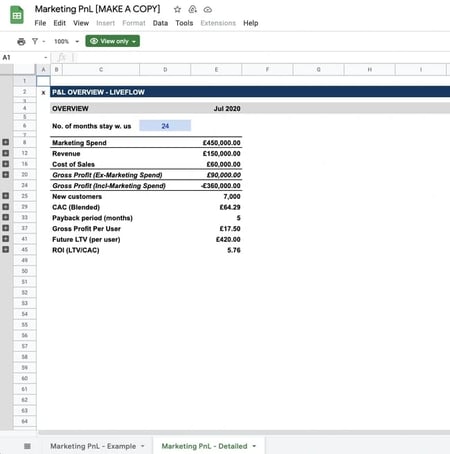
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
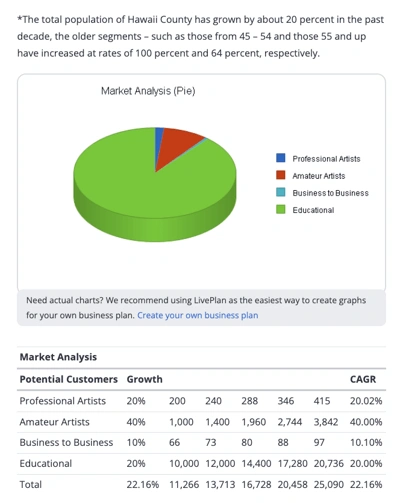
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![latest business plan format How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![latest business plan format 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![latest business plan format The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Powerful business plan templates
Plan for the future, no matter what your business plans are or the size of your business with these designs and templates. whether it's just one big project or an entire organization's worth of dreams, these templates will keep you and your company on track from ideation to completion..

Put your ideas to work with simple templates for every business plan
Every successful business took a lot of planning to get there, and these templates will be cornerstones of your future success. Whether you're looking to attract new business, pitch your services or reimagine your company, with these simple, customizable templates at your fingertips you can turn complexity into something tangible. These templates can become marketing assets or simply remain internal touchpoints for your team. And as your dreams change, you'll always have this template to refer to – it's easy to change what exists on paper. If you're a small business, focusing on your niche can help you dominate in your field, and you can forge a plan to figure out exactly what that niche might be and how to target your ideal customer . When it's time to share your vision with stakeholders, craft a presentation that outlines your plan succinctly and with style. Let these templates from Microsoft Designer be your partner in business strategy for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and self-employed
- Business finance and support
Write a business plan
Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan.
Business plan templates
Download a free business plan template on The Prince’s Trust website.
You can also download a free cash flow forecast template or a business plan template on the Start Up Loans website to help you manage your finances.
Business plan examples
Read example business plans on the Bplans website.
How to write a business plan
Get detailed information about how to write a business plan on the Start Up Donut website.
Why you need a business plan
A business plan is a written document that describes your business. It covers objectives, strategies, sales, marketing and financial forecasts.
A business plan helps you to:
- clarify your business idea
- spot potential problems
- set out your goals
- measure your progress
You’ll need a business plan if you want to secure investment or a loan from a bank. Read about the finance options available for businesses on the Business Finance Guide website.
It can also help to convince customers, suppliers and potential employees to support you.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Small Business Resources is now the Center for Business Empowerment.
Suggested Keywords
Center for Business Empowerment
How to write an effective business plan in 11 steps (with workbook)
February 02, 2023 | 14 minute read
Writing a business plan is a powerful way to position your small business for success as you set out to meet your goals. Landmark studies suggest that business founders who write one are 16% more likely to build viable businesses than those who don’t and that entrepreneurs focused on high growth are 7% more likely to have written a business plan. 1 Even better, other research shows that owners who complete business plans are twice as likely to grow their business successfully or obtain capital compared with those who don’t. 2
The best time to write a business plan is typically after you have vetted and researched your business idea. (See How to start a business in 15 steps. ) If conditions change later, you can rewrite the plan, much like how your GPS reroutes you if there is traffic ahead. When you update your plan regularly, everyone on your team, including outside stakeholders such as investors, will know where you are headed.
What is a business plan?
Typically 15-20 pages long, a business plan is a document that explains what your business does, what you want to achieve in the business and the strategy you plan to use to get there. It details the opportunities you are going after, what resources you will need to achieve your goals and how you will define success.
Why are business plans important?
Business plans help you think through barriers and discover opportunities you may have recognized subconsciously but have not yet articulated. A business plan can also help you to attract potential lenders, investors and partners by providing them with evidence that your business has all of the ingredients necessary for success.
What questions should a business plan answer?
Your business plan should explain how your business will grow and succeed. A great plan will provide detailed answers to questions that a banker or investor will have before putting money into the business, such as:
- What products or services do you provide?
- Who is your target customer?
- What are the benefits of your product and service for customers?
- How much will you charge?
- What is the size of the market?
- What are your marketing plans?
- How much competition does the business face in penetrating that market?
- How much experience does the management team have in running businesses like it?
- How do you plan to measure success?
- What do you expect the business’s revenue, costs and profit to be for the first few years?
- How much will it cost to achieve the goals stated in the business plan?
- What is the long-term growth potential of the business? Is the business scalable?
- How will you enable investors to reap the rewards of backing the business? Do you plan to sell the business to a bigger company eventually or take it public as your “exit strategy”?
How to write a business plan in 11 steps
This step-by-step outline will make it easier to write an effective business plan, even if you’re managing the day-to-day demands of starting a new business. Creating a table of contents that lists key sections of the plan with page numbers will make it easy for readers to flip to the sections that interest them most.
- Use our editable workbook to capture notes and organize your thoughts as you review these critical steps. Note: To avoid losing your work, please remember to save this PDF to your desktop before you begin.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is your opportunity to make a great first impression on investors and bankers. It should be just as engaging as the enthusiastic elevator pitch you might give if you bumped into a potential backer in an elevator.
In three to five paragraphs, you’ll want to explain what your business does, why it will succeed and where it will be in five years. The executive summary should include short descriptions of the following:
- Business concept. What will your business do?
- Goals and vision. What do you expect the business to achieve, both financially and for other key stakeholders, such as the community?
- Product or service. What does your product or service do — and how is it different from those of competitors?
- Target market. Who do you expect to buy your product or service?
- Marketing strategy. How will you tell people about your product or service?
- Current revenue and profits. If your business is pre-revenue, offer sales projections.
- Projected revenue and profits. Provide a realistic look at the next year, as well as the next three years, ideally.
- Financial resources needed. How much money do you need to borrow or raise to fund your plan?
- Management team. Who are the company’s leaders and what relevant experience will they contribute?
2. Business overview
Here is where you provide a brief history of the business and describe the product(s) or service(s) it offers. Make sure you describe the problem you are attempting to solve, for whom you will solve it (your customers) and how you will solve it. Be sure to describe your business model (such as direct-to-consumer sales through an online store) so readers can envision how you will make sales. Also mention your business structure (such as a sole proprietorship , general partnership, limited partnership or corporation) and why it is advantageous for the business. And be sure to provide context on the state of your industry and where your business will fit into it.
3. Business goals and vision
Explain what you hope to achieve in the business (your vision) as well as its mission and value proposition. Most founders judge success by the size to which they grow the business using measures such as revenue or number of employees. Your goals may not be solely financial. You may also wish to provide jobs or solve a societal problem. If that’s the case, mention those goals as well.
If you are seeking outside funding, explain why you need the money, how you will put it to work to grow the business and how you expect to achieve the goals you have set for the business. Also explain your exit strategy—that is, how you would enable investors to cash out, whether that means selling the business or taking it public.
4. Management and organization
Many investors say they bet on the team behind a business more than the business idea, trusting that talented and experienced people will be capable of bringing sound business concepts to life. With that in mind, make sure to provide short bios of the key members of your management team (including yourself) that emphasize the relevant experience each individual brings, along with their special talents and industry recognition. Many business plans include headshots of the management team with the bios.
Also describe more about how your organization will be structured. Your company may be a sole proprietorship, a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation in one or more states.
If you will need to hire people for specific roles, this is the place to mention those plans. And if you will rely on outside consultants for certain roles — such as an outsourced CFO — be sure to make a note of it here. Outside backers want to know if you’ve anticipated the staffing you need.
5. Service or product line
A business will only succeed if it sells something people want or need to buy. As you describe the products or services you will offer, make sure to explain what benefits they will provide to your target customers, how they will differ from competing offerings and what the buying cycle will likely be so it is clear that you can actually sell what you are offering. If you have plans to protect your intellectual property through a copyright or patent filing, be sure to mention that. Also explain any research and development work that is underway to show investors the potential for additional revenue streams.
6. Market/industry analysis
Anyone interested in providing financial backing to your business will want to know how big your company can potentially grow so they have an idea of what kind of returns they can expect. In this section, you’ll be able to convey that by explaining to whom you will be selling and how much opportunity there is to reach them. Key details to include are market size; a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis ; a competitive analysis; and customer segmentation. Make it clear how you developed any projections you’ve made by citing interviews or research.
Also describe the current state of the industry. Where is there room for improvement? Are most companies using antiquated processes and technology? If your business is a local one, what is the market in your area like? Do most of the restaurants where you plan to open your café serve mediocre food? What will you do better?
In this section, also list competitors, including their names, websites and social media handles. Describe each source of competition and how your business will address it.
7. Sales and marketing
Explain how you will spread the word to potential customers about what you sell. Will you be using paid online search advertising, social media promotions, traditional direct mail, print advertising in local publications, sponsorship of a local radio or TV show, your own YouTube content or some other method entirely? List all of the methods you will use.
Make sure readers know exactly what the path to a sale will be and why that approach will resonate with customers in your ideal target markets as well as existing customer segments. If you have already begun using the methods you’ve outlined, include data on the results so readers know whether they have been effective.
8. Financials
In a new business, you may not have any past financial data or financial statements to include, but that doesn’t mean you have nothing to share. Preparing a budget and financial plan will help show investors or bankers that you have developed a clear understanding of the financial aspects of running your business. (The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has prepared a guide you can use; SCORE , a nonprofit organization that partners with the SBA, offers a financial projections template to help you look ahead.) For an existing business, you will want to include income statements, profit and loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets, ideally going back three years.
Make a list of the specific steps you plan to take to achieve the financial results you have outlined. The steps are generally the most detailed for the first year, given that you may need to revise your plan later as you gather feedback from the marketplace.
Include interactive spreadsheets that contain a detailed financial analysis showing how much it costs your business to produce the goods and services you provide, the profits you will generate, any planned investments and the taxes you will pay. See our startup costs calculator to get started.
9. Financial projections
Creating a detailed sales forecast can help you get outside backers excited about supporting you. A sales forecast is typically a table or simple line graph that shows the projected sales of the company over time with monthly or quarterly details for the next 12 months and a broader projection as much as five years into the future. If you haven’t yet launched the company, turn to your market research to develop estimates. For more information, see “ How to create a sales forecast for your small business. ”
10. Funding request
If you are seeking outside financing such as a loan or equity investment, your potential backers will want to know how much money you need and how you will spend it. Describe the amount you are trying to raise, how you arrived at that number and what type of funding you are seeking (such as debt, equity or a combination of both). If you are contributing some of your own funds, it is worth noting this, as it shows that you have skin in the game.
11. Appendix
This should include any information and supporting documents that will help investors and bankers gain a greater understanding of the potential of your business. Depending on your industry, you might include local permits, licenses, deeds and other legal documents; professional certifications and licenses; media clips; information on patents and other intellectual property; key customer contracts and purchase orders; and other relevant documents.
Some business owners find it helpful to develop a list of key concepts, such as the names of the company’s products and industry terms. This can be helpful if you do business in an industry that may not be familiar to the readers of the business plan.
Tips for creating an effective business plan
Use clear, simple language. It’ll be easier to win people over if your plan is easy to read. Steer clear of industry jargon, and if you must use any phrases the average adult won’t know, be sure to define them.
Emphasize what makes your business unique. Investors and bankers want to know how you will solve a problem or gap in the marketplace differently from anyone else. Make sure you’re conveying your differentiating factors.
Nail the details. An ideal business plan will be detailed and accurate. Make sure that any financial projections you make are realistic and grounded in solid market research. (If you need help in making your calculations, you can get free advice at SCORE.) Seasoned bankers and investors will quickly spot numbers that are overly optimistic.
Take time to polish it. Your final version of the plan should be neat and professional with an attractive layout and copy that has been carefully proofread.
Include professional photos. High-quality shots of your product or place of business can help make it clear why your business stands out.
Updating an existing business plan
Some business owners in rapidly growing businesses update their business plan quarterly. Others do so every six months or every year. When you update your plan make sure you consider these three things:
- Are your goals still current? As you’ve tested your concept, your goals may have changed. The plan should reflect this.
- Have you revised any strategies in response to feedback from the marketplace? You may have found that your offerings resonated with a different customer segment than you expected or that your advertising plan didn’t work and you need to try a different approach. Given that investors will want to see a marketing and advertising plan that works, keeping this section current will ensure you are always ready to meet with one who shows interest.
- Have your staffing needs changed? If you set ambitious goals, you may need help from team members or outside consultants you did not anticipate when you first started the business. Take stock now so you can plan accordingly.
Final thoughts
Most business owners don’t follow their business plans exactly. But writing one will get you off to a much better start than simply opening your doors and hoping for the best, and it will be easier to analyze any aspects of your business that aren’t working later so you can course-correct. Ultimately, it may be one of the best investments you can make in the future of your business.
Business plan FAQs
What are common mistakes when writing a business plan.
The biggest mistake you can make when writing a business plan is creating one before the idea has been properly researched and tested. Not every idea is meant to become a business. Other common mistakes include:
- Not describing your management team in a way that is appealing to investors. Simply cutting and pasting someone’s professional bio into the management section won’t do the trick. You’ll want to highlight the credentials of each team member in a way that is relevant to this business.
- Failing to include financial projections — or including overly optimistic ones. Investors look at a lot of business plans and can tell quickly whether your numbers are accurate or pie in the sky. Have a good small business accountant review your numbers to make sure they are realistic.
- Lack of a clear exit strategy for investors. Investors may want the option to cash out eventually and would want to know how they can go about doing that.
- Slapdash presentation. Make sure to fact-check any industry statistics you cite and that any charts, graphs or images are carefully prepared and easy to read.
What are the different types of business plans?
There are a variety of styles of business plans. Here are three major types:
Traditional business plan. This is a formal document for pitching to investors based on the outline in this article. If your business is a complicated one, the plan may exceed the typical length and stretch to as many as 50 pages.
One-page business plan. This is a simplified version of a formal business plan designed to fit on one page. Typically, each section will be described in bullet points or in a chart format rather than in the narrative style of an executive summary. It can be helpful as a summary document to give to investors — or for internal use. Another variation on the one-page theme is the business model canvas .
Lean plan. This methodology for creating a business plan is ideal for a business that is evolving quickly. It is designed in a way that makes it easy to update on a regular basis. Lean business plans are usually about one page long. The SBA has provided an example of what this type of plan includes on its website.
Is the business plan for a nonprofit different from the plan for other business types?
Many elements of a business plan for a nonprofit are similar to those of a for-profit business. However, because the goal of a nonprofit is achieving its mission — rather than turning a profit — the business plan should emphasize its specific goals on that front and how it will achieve them. Many nonprofits set key performance indicators (KPIs) — numbers that they track to show they are moving the needle on their goals.
Nonprofits will generally emphasize their fundraising strategies in their business plans rather than sales strategies. The funds they raise are the lifeblood of the programs they run.
What is the difference between a business plan, a strategic plan and a marketing plan?
A strategic plan is different from the type of business plan you’ve read about here in that it emphasizes the long-term goals of the business and how your business will achieve them over the long run. A strong business plan can function as both a business plan and a strategic plan.
A marketing plan is different from a business plan in that it is focused on four main areas of the business: product (what you are selling and how you will differentiate it), price (how much your products or services will cost and why), promotion (how you will get your ideal customer to notice and buy what you are selling) and place (where you will sell your products). A thorough business plan may cover these topics, doing double duty as both a business plan and a marketing plan.
Explore more
Editable business plan workbook
Starting a new business
1 . Francis J. Green and Christian Hopp. “Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed.” HBR. July 14, 2017. Available online at https://hbr.org/2017/07/research-writing-a-business-plan-makes-your-startup-more-likely-to-succeed.
2 . CorpNet, “The Startup Business Plan: Why It’s Important and How You Can Create One,” June 29, 2022.
Important Disclosures and Information
Bank of America, Merrill, their affiliates and advisors do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. Consult your own legal and/or tax advisors before making any financial decisions. Any informational materials provided are for your discussion or review purposes only. The content on the Center for Business Empowerment (including, without limitations, third party and any Bank of America content) is provided “as is” and carries no express or implied warranties, or promise or guaranty of success. Bank of America does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, completeness, usefulness, non-infringement of intellectual property rights, or quality of any content, regardless of who originates that content, and disclaims the same to the extent allowable by law. All third party trademarks, service marks, trade names and logos referenced in this material are the property of their respective owners. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of any third party.
Not all materials on the Center for Business Empowerment will be available in Spanish.
Certain links may direct you away from Bank of America to unaffiliated sites. Bank of America has not been involved in the preparation of the content supplied at unaffiliated sites and does not guarantee or assume any responsibility for their content. When you visit these sites, you are agreeing to all of their terms of use, including their privacy and security policies.
Credit cards, credit lines and loans are subject to credit approval and creditworthiness. Some restrictions may apply.
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated (also referred to as “MLPF&S" or “Merrill") makes available certain investment products sponsored, managed, distributed or provided by companies that are affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“BofA Corp."). MLPF&S is a registered broker-dealer, registered investment adviser, Member SIPC , and a wholly owned subsidiary of BofA Corp.
Banking products are provided by Bank of America, N.A., and affiliated banks, Members FDIC, and wholly owned subsidiaries of BofA Corp.
“Bank of America” and “BofA Securities” are the marketing names used by the Global Banking and Global Markets division of Bank of America Corporation. Lending, derivatives, other commercial banking activities, and trading in certain financial instruments are performed globally by banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation, including Bank of America, N.A., Member FDIC. Trading in securities and financial instruments, and strategic advisory, and other investment banking activities, are performed globally by investment banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“Investment Banking Affiliates”), including, in the United States, BofA Securities, Inc., which is a registered broker-dealer and Member of SIPC , and, in other jurisdictions, by locally registered entities. BofA Securities, Inc. is a registered futures commission merchant with the CFTC and a member of the NFA.
Investment products:
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
How to write a business case: the formula for getting project approval from stakeholders.
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
April 29, 2024
Do you feel you’ve found a solution to one of your company’s most pressing problems? Do you want to go straight to your seniors and tell them about your idea, basking in the glory of your eureka moment? 💡
Before you do that, take a deep breath and consider if your solution requires a significant financial commitment or a shift into critical business functions . If it does, you should learn how to write a business case to properly present your idea to the higher-ups.
Never done that before? No worries. In this article, we’ll explore:
- The concept of a business case
- The difference between a business case and a business plan
- The process of building a compelling business case
- Some real-life examples to understand how business cases help win project approval
Importance of a business case in project management
What is the difference between a business case and a business plan, 1. executive summary, 2. project definition, 3. financial appraisal, 4. project goals and success criteria , 5. project scope and schedule, 6. risks and mitigation strategies, step 1: problem identification, step 2: stakeholder identification, step 3: drafting background information and project definition, step 4: cost-benefit analysis and financial appraisal, step 5: evaluation of alternatives, step 6: describing the project scope and implementation approach, step 7: drafting the executive summary, step 8: putting it all together, lean startup example, venture capital funding example, outsourcing example, supply chain example, 1. drafting it alone, 2. not taking stakeholder feedback, 3. not reviewing or proofreading, create a compelling business case with clickup.
What Is a Business Case?
A business case explains how the rewards of investing in a business idea or initiative outweigh the risks and costs .
It’s one of the many project management documents (like a project charter or a project plan ) you may have to create when seeking the green light to proceed with a project. A well-crafted business case can be crucial for obtaining approval from your client, management, or other stakeholders in the early stages of your project’s lifecycle . 🟢
The key role of a business case is to justify an investment . It plays other important roles that make project management more efficient . Some of them include:
- Providing clarity: Drafting a business case requires careful planning and research, which brings clarity of thought and improves your understanding of the initiative or project you’re going to propose
- Resource optimization: A business case helps ensure that the company’s resources are being used productively and contributing to its long-term strategic objectives
- Removing doubt: By comparing different solutions, the document eliminates any doubt that an alternative way to fix a business problem is better than what you’re proposing
Preparing a business case can take a lot of time and effort, so it only makes sense when a project or an initiative requires a significant financial commitment. For all other approvals, you can use the project charter. Some scenarios in which a business case can make sense include:
- A new project
- New product line
- Introduction of a new customer persona to your marketing strategy
- Major changes to the supply chain, like introducing new suppliers or distributors
While a business case may seem like a synonym for a business plan , based on its definition, content, and name, there are major differences between them. The most notable ones are:
- Use case: A business plan is made for an entirely new business, while a business case is created when asking for a substantial financial commitment within an existing business
- Purpose: A business plan aims to hammer out the complete business strategy, while a business case tries to explain the advantages of a specific initiative
- A company’s mission and vision
- Financial projections
- SWOT Analysis
- Market analysis
- Go-to-market strategy
- Team profile
A business case, on the other hand, includes only financial projections, risks, and costs of a project
- Level of detail: Given the scope of information they need to cover, business plans tend to be much more detailed than business cases
Key Elements of a Business Case
While the exact structure of a business case will vary based on a specific situation, here are some of the essential components:
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the critical details covered in your business case.
Given that managers and executives are usually strapped for time, the executive summary will often be the only part of the document they actually read. That’s why it’s crucial to get this part of the document right and leave a powerful first impression.
The project definition sets the context for your business case by explaining the problem you aim to solve. It highlights an unfulfilled business requirement, outlines why it’s not being met, and finally presents your solution for addressing the mentioned shortcomings.
This is the crux of the matter—the financial appraisal part outlines the ROI your proposed initiative or project will likely generate for the business. It also covers the expected cost of executing your project or implementing your solution.
This part of the business case defines all the objectives and key results (OKRs) you want to achieve through the proposed project or solution. It also explains how those goals align with the company’s short-term and long-term goals. Lastly, it establishes success criteria for your project in the form of KPIs and key metrics .
The project scope sets limits and boundaries for your project by allocating resources and budgets and developing a schedule for completion.
A business case has to list all the risks associated with implementing the proposed solution and the mitigation strategies for dealing with them. It also weighs in on alternative approaches and their respective risks to explain why your initiative should be the preferred option.
How to Write a Business Case in 8 Steps
Writing a business case is an elaborate task that requires extensive research and numerous analyses, from SWOT and cost-benefit analysis to stakeholder analysis. It’s no walk in the park, but it becomes much easier with an exceptional project management platform like ClickUp .
ClickUp equips project managers and business professionals with all the tools they need to craft a business case that will win the hearts and minds of their superiors—from ready-made templates to AI-powered document management features. Let’s find out how to write a business case in eight steps with the help of ClickUp.
Many business ventures fail because they create solutions to non-existing problems. To prevent this scenario, make sure you consider the following:
- Objective(s) your company wants to achieve. Examples include achieving a revenue target , meeting an unaddressed customer need, or achieving a competitive advantage
- Problem(s) holding your company from achieving its desired objectives. Examples include a lack of operational efficiency , incorrect customer targeting, and supply chain issues
- The solution you want to propose to solve the problem and meet the objectives
- Evidence and case studies to prove that your proposed solution can indeed solve the problem
A structured way to identify your business problems is to use the ClickUp Root Cause Analysis Template . Classify everything going wrong with your business into multiple “Why” columns and then add their root causes in the relevant color-coded blocks. Once you analyze the root causes, you can tailor your solution to target and fix them.
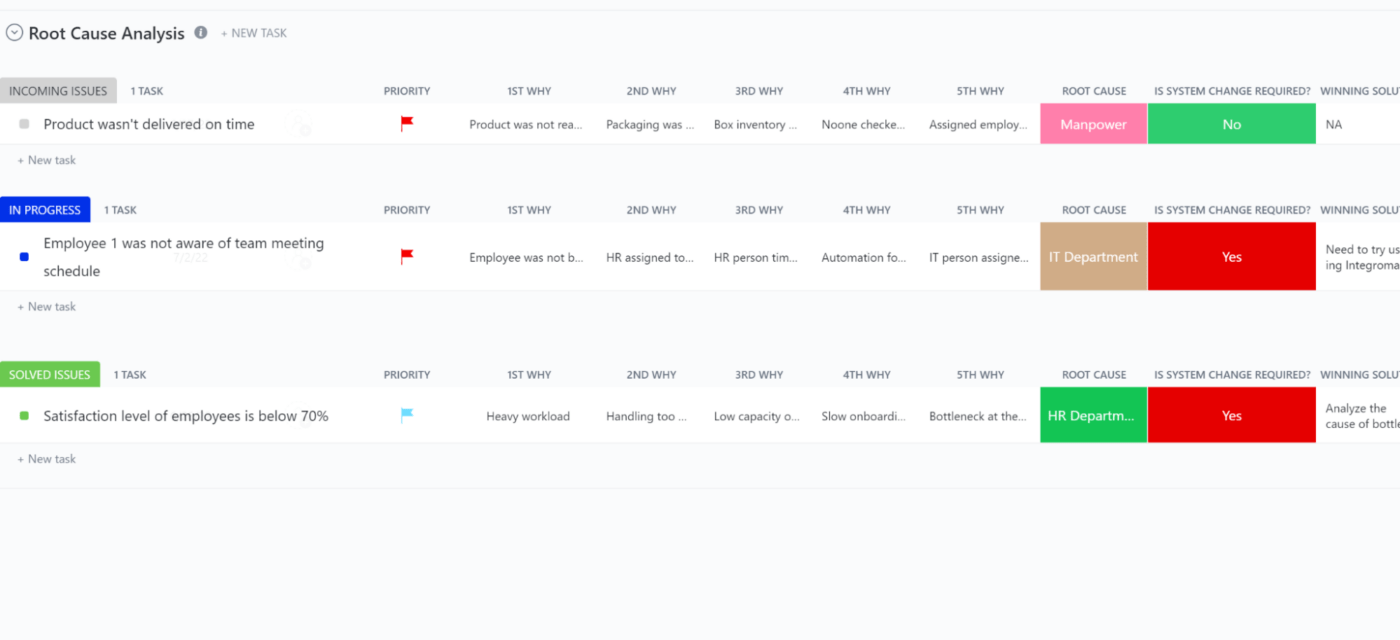
After pinpointing the problem, the next step is identifying the stakeholders to whom you’ll pitch your business case. A stakeholder is anyone who has a say in approving your business case . Depending on the scope and complexity of your business case, one or all of the following stakeholders may play a role in its approval:
- The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the company
- The head of the finance department
- The head of business operations
- The head of the marketing and sales department
- The representative of a client
Discuss your initiative with the stakeholders to see whether they’re interested in it or not. It can also help you understand their perspective on the problem you’re aiming to solve. After all, you don’t want to put your efforts into a full business case only for the stakeholders to reject it. 🙅♂️
The easiest way to identify key stakeholders is to leverage the ClickUp Stakeholder Analysis Template . This framework can help you gauge the influence and support level of all stakeholders who will play a role in approving your business case. This information can also come in handy when you want to collect feedback from a stakeholder.
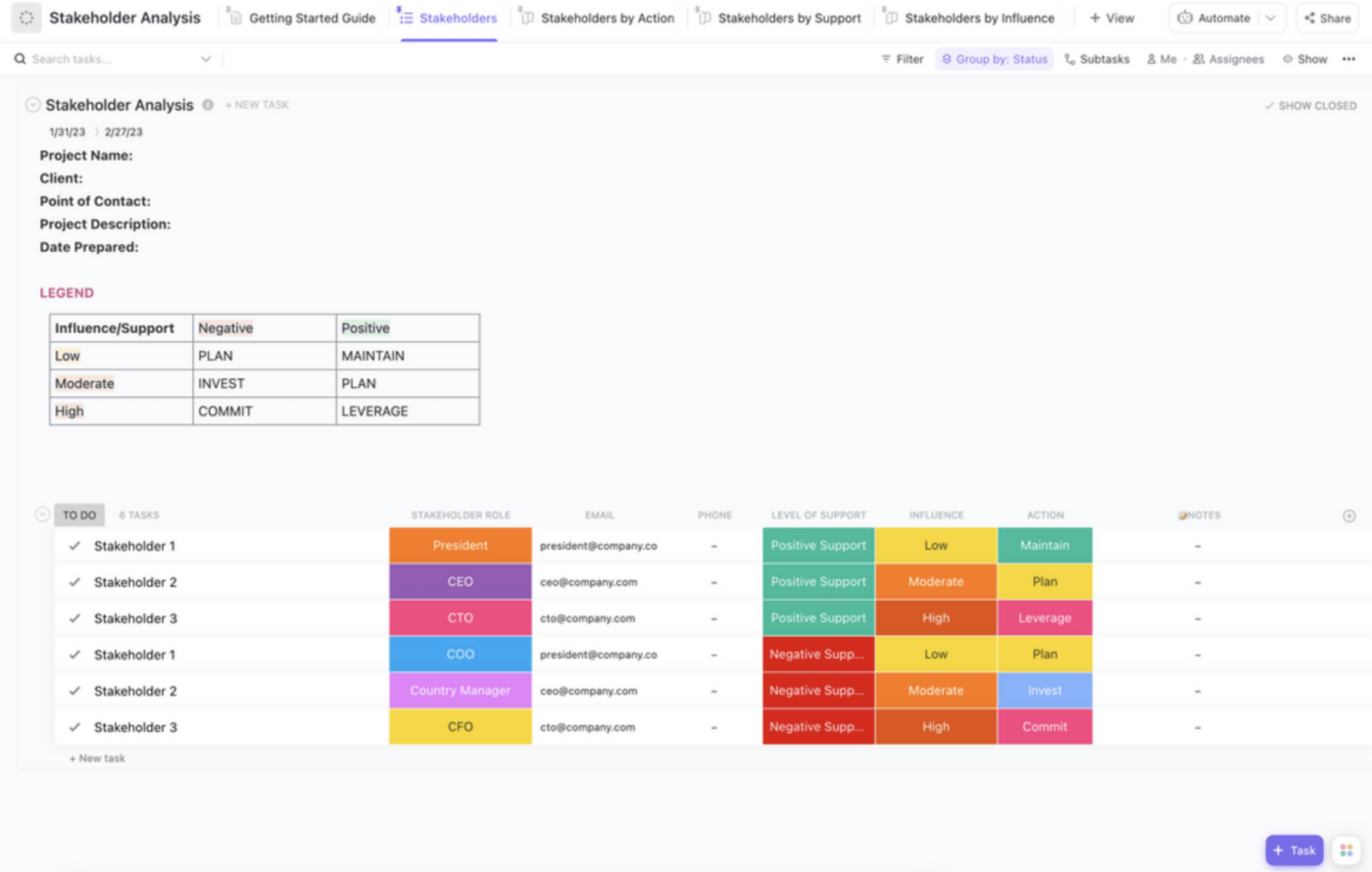
Once you’ve identified your problem and the involved stakeholders, it’s time to start drafting your business case.
The first part is the project definition section, which sets the background for presenting your case before stakeholders . It covers the problem your business case proposes to solve and explains why solving the problem is important. The section should cover the following:
- The problem you identified and its impact on business functions
- How your project or solution can fix it
- The goals your project or initiative wants to achieve
- How project goals align with the company’s near-term objectives
- The success criteria for your project or initiative
- How its success will move the company towards its long-term strategic goals
The best tool for drafting this part of the document is ClickUp Docs —ClickUp’s built-in text editor and documentation management platform.
With ClickUp Docs’ collaborative editing possibilities, you and your stakeholders can work on the business case document in real time, ensuring its speedy and accurate completion. Stakeholders can also comment on areas for improvement . Finally, you can add a cover image to make your business case look more appealing or use slash commands to quickly add compelling blocks of formatted text.
After setting the background, the next step is the financial appraisal part. This section will be examined carefully during your pitch and serves to capture the stakeholders’ interest in your business case. For maximum accuracy, consult with a colleague from the finance department while drafting this part of the document.
Some of the information you may want to cover here includes:
- Projections about financial gains
- Costs to be incurred by the project
- Cash flow forecast
- Cost-benefit analysis and return on investment (ROI)
- Sensitivity analysis to explain the margin of error in your numbers
Besides the financial aspects, this section also deals with risk analysis . Information on all potential risk factors identified through SWOT analysis, Monte Carlo analysis, and other risk identification strategies are outlined along with their respective mitigation strategies . It’ll be best to discuss the project risks with stakeholders identified in the first step—they can often share hidden insights and perspectives.
ClickUp provides a number of tools to help you conduct each of these analyses. For instance, you can use the ClickUp Cost Benefit Analysis Template to complete your cost-benefit analysis.
Similarly, the ClickUp SWOT Analysis Template can save you from jotting down rows of data to identify your initiative’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is a visually rich template that lets you easily identify high-impact activities and functions.

In this section, you should evaluate the alternatives to your proposed solution in the business case. Highlight the pros and cons of each option so the stakeholders can have a complete overview of every possible solution. Make sure to include your proposed solution in the comparison as well to explain why it’s better than all the alternatives.
If you need help examining and comparing the alternatives, fall back on the ClickUp Comparison Matrix Template . Use it to record all the information about each possible alternative in different fields and then compare them on a Kanban board. Its visual format makes decision making easier, while its fully customizable fields allow you to record as many comparison parameters as you wish.
After you detail all the financial aspects of your project and compare it to alternatives, define a project scope in your business case. This section sets boundaries for the pending work and limitations on resources needed to complete it. Crucial information covered in it includes:
- Budget and resource allocation: Financial and other resources, like team members, workspace, equipment, etc., that should be allocated to the project
- Deadlines: Time required to complete each part of the project
- Dependencies and relationships : Details of current business functions that may be affected by the project
- Deliverables: What you plan to deliver by the end of your project
- Exclusions: What’s not a part of your project
Once you define the project scope, outline the exact steps for implementing it. The easiest way to do this is to use the ClickUp Scope of Work Template . It allows you to record every aspect of the project scope in a well-organized manner to share with your stakeholders and get their opinions.
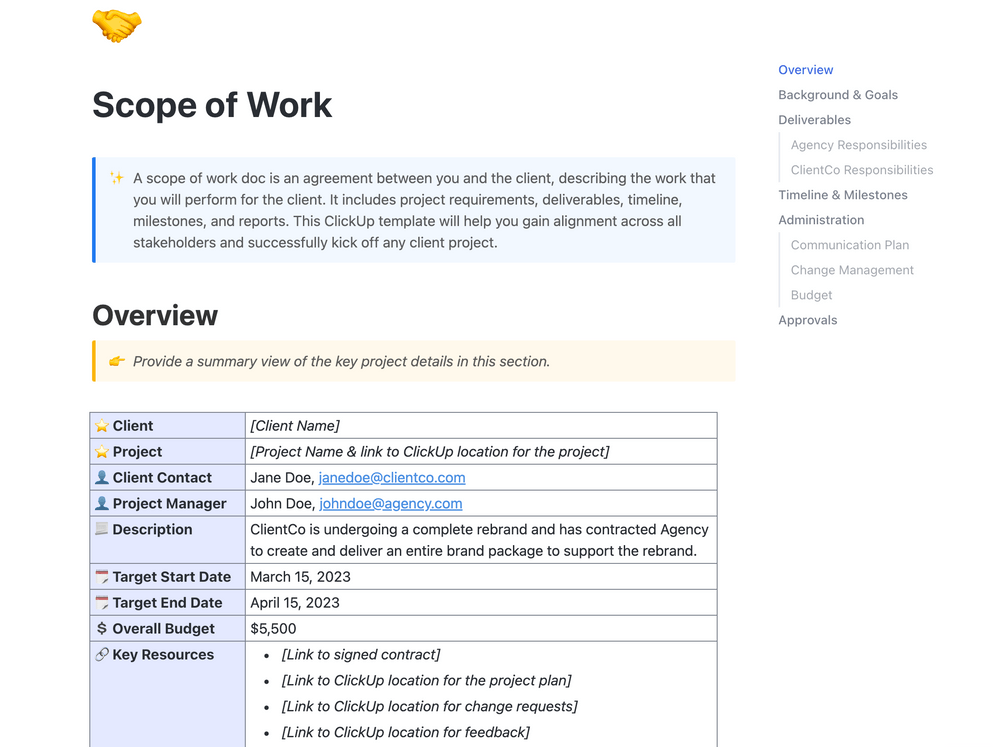
Once all major sections of your business case have been completed, you need to draft an executive summary to digest the crucial details from each section. This summary should be concise, ideally no longer than two pages. It will appear as the first item in your business case, providing stakeholders with a quick overview of your proposed project.
If you need help drafting your executive summary, team up with ClickUp Brain , a neural network and AI writing assistant built into ClickUp Docs. In mere seconds, it can generate a pitch-perfect summary of any business case document prepared until now.
Once you have your executive summary draft, use the ClickUp Executive Summary Template to format and organize it in a structured and presentable manner.

Now, it’s time to put together and structure all the sections drafted to this point to finalize your business case. That’s where the ClickUp Business Case Analysis Template can be a lifesaver.
The template includes dedicated sections to record each part of the business case. All sections are arranged in a structured manner to ensure that when you pitch your case, it makes a lasting impact on your stakeholders.

Real-Life Examples of Business Cases
Now that you know how to write a business case, let’s check out some real-life examples of how business cases allow companies to approve major projects and make strategic decisions:
A lean startup operating in the healthcare space is facing workforce issues, which are preventing it from launching its product on time. The head of the product development team wants to hire three more engineers to speed up the product development process .
However, since it’s a lean startup with budget constraints , the team head needs approval from the startup founders before making the decision. So, the product team compiles a business case for hiring additional employees , and here are the main elements of their proposal:
- A brief overview of how insufficient staffing is delaying product development and pushing the product launch beyond the planned deadline
- Elaboration of how three new engineers can bring product development back on track
- Cost-benefit analysis of the move
- Exploration of the involved risks
- Presentation of alternatives and their associated risks
- Scope of the change, like the nature of work the new engineers will perform
A venture capital-funded fintech startup decides to launch a new product line of credit cards . It will allow the startup to onboard a slew of new customers but will also require significant financial investment for marketing and lending purposes. So the company prepares a business case for this new product line in an effort to obtain funding for it. Here’s what they detail in their business case:
- The need for this new product line and how it complements the company’s other offerings
- The market opportunity with revenue projections and cost-benefit analysis
- Risks involved in the project, like competition, mass default, and regulatory scrutiny
- Alternatives available, like launching prepaid debit cards, which probably wouldn’t be as useful for customer acquisition
- Scope of the project, like team members working on it, the budget allocated, launch schedule, and timeline
A SaaS software vendor based out of Silicon Valley wants to reduce customer service spending without compromising service quality . The product manager of one of their leading products comes up with the idea of outsourcing customer service . So, they decide to prepare a business case before proposing the solution to the management. The business case outlines:
- The problem, which is a significant share of revenue going into customer service operations and how outsourcing can help bring it down
- Risks associated with outsourced customer service and mitigation strategies for them, like having an escalation mechanism for unresolved support tickets
- Alternatives and their risks, like using AI chatbots to automate customer service , which can be frustrating for customers who need human guidance
- Cost-benefit analysis of making the change
- Scope of change, like how many of the customer support employees will be laid off
A construction company in Virginia is facing raw material supply issues . The cement supplier they work with repeatedly fails to meet the demand, so the project supervisor decides to add some redundancy by onboarding a new vendor.
This change can greatly influence the project, so the supervisor prepares a business case to propose the initiative to the management. The case addresses the following:
- How the new cement supplier can keep the project from being delayed
- The supplier’s reliability, as demonstrated by the years of industry presence, major companies for which they have supplied cement, etc.
- Alternative suppliers, their capacity, and reliability information
- Cost-benefit analysis of making the change, since the rates of this supplier are slightly higher than those of the existing vendor
- Scope of change, including how much of the supplies will be delivered by the new supplier, for how long, and at what price
Potential Business Case Challenges and How to Overcome Them
There are a number of mistakes project managers make when drafting a business case, which can jeopardize the approval of the entire project or initiative. Now that we’ve covered the complete process of writing a compelling business case, let’s look at the most common pitfalls and explore ways to avoid them.
The details of a business case require extensive research and knowledge of different business functions. No project manager can do it all alone without making mistakes or errors of judgment, so look for help from different departments in your company, whether it’s finance, marketing, or operations. 💁
Another crucial mistake when building a business case is presenting the document to stakeholders out of the blue. When you don’t involve relevant stakeholders at any stage in your business case development process, you increase the risk of it being rejected. That happens because:
- You don’t know their expectations
- They didn’t have any role in your business case, which keeps them detached from your work
To avoid this scenario, involve stakeholders at different stages of your business case drafting process and get your progress reviewed regularly.
The last thing you want when pitching your business case is a typo or a misrepresentation of facts. That can leave a bad impression on the stakeholders listening to your pitch. They may not take you seriously and ultimately reject your project proposal .
To ensure a bulletproof document, you should always review and proofread your entire business case before submitting it . Pay special attention to numbers and facts and double-check that they’re correct. Then, go ahead with your pitch.
A solid business case is the first step to getting project approval from your stakeholders. However, building it requires careful planning and the right tools to streamline the entire process. Fortunately, ClickUp equips you with everything you need at each step of building your business case—from ready-made templates and documentation tools to AI-powered writing assistance.
Sign up for ClickUp today and write a business case that will earn support and trust for your project or initiative.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
- Best Web Design Companies
Best Web Design Companies Of 2024

Published: Apr 29, 2024, 5:00pm
Having a quality website is imperative. Statistics show that 71% of businesses had a website in 2023 —and a further 43% of small businesses plan to invest in their website performance. Whether you’re looking to improve your website or build a new one from scratch, consider a web design company to help.
A web design agency has the tools and experience necessary to craft responsive, compelling websites that will provide a great experience for users. To help you find the right agency for you, we’ve compiled this list of the best web design companies of 2024.
- Best Website Builders
- Best Blogging Platforms
- Best Web Design Software
- Best Domain Registrars
- Best Portfolio Website Builder
- Cheap Website Builders
Featured Partners
$17 per month

On Wix’s Website
$1.95 per month
Customizable templates, Easy drag-and-drop technology, SSL certificate

On Web.com’s Website
Squarespace
$16 per month

On Squarespace’s Website
The Best Web Design Companies of 2024
Forbes advisor ratings, what is a web design company, benefits of using a web design company, how to choose the best web design company, cost of using a web design company, should i choose a web design company or build a site on my own, methodology, frequently asked questions (faqs).
- DD.NYC : Best Overall
- The Free Website Guys : Best for a Free Website
- SmartSites : Best for Local Businesses
- Intero Digital : Best for Digital Marketing
- Digital Silk : Best for E-Commerce
- Clay : Best for Large Businesses
- DIGITECH : Best for User-Centric Designs
Best Overall

Average project pricing
$10,000 to $50,000
Walmart, Lowe's, Groupon
Websites designed
If you’re looking for a top-tier web design experience, DD.NYC is a great option. It offers a four-step design process that starts by discovering your needs. Then, its team of web designers collaborates with your brand to start building your site. The development stage is where backend designers get into the nitty-gritty of the work, while the final support stage helps you maintain and monitor yourself after it’s built.
DD.NYC offers WordPress-specific designs, mobile-responsive websites, corporate websites, brochure websites and custom designs for when none of those work for your needs. Throughout its eight years, it has successfully designed over 250 websites for big-name clients including L’Oréal, Walmart and Forbes.
In particular, DD.NYC focuses on the real estate, medical, finance/tech and industrial industries. In addition to basic web design, it can also offer branding, packaging design and graphic design services, making it an all-in-one option for launching a new brand.
Who should use it:
If your company is looking for a beautifully designed, responsive website, DD.NYC should be your choice. The team has successfully handled several high-profile clients, which should give you confidence that it can also handle your site.
- Support and maintenance services included
- Branding, packaging, app and graphic design also available
- Received numerous design awards
- A bit pricey
- Only four industry specializations
Best for a Free Website
The free website guys.

Tarandip, Optimate, Freckles 'n' Frowns
10,000-plus
If your website budget leaves a lot to be desired, The Free Website Guys should be a top consideration. The company designs websites for free qualified applicants. The company accepts every two in five applicants, so you have a good chance of scoring a great deal. Even if you don’t qualify, the design service offers custom websites for the low price of $3,000.
Once you’re selected, The Free Website Guys builds the back end of your site on WordPress, including plugin installation. Next, you’ll choose a theme, and the company will tailor it to your liking. It gives you complete instructions on how to edit and update your site on your own moving forward. All sites are mobile optimized, search engine optimization (SEO) ready and load quickly to reduce abandonment rates. If you need ongoing maintenance and support, you can add that on for a fee. Other add-ons include lead magnet setup, app development and SEO reporting and optimization.
As with all free things in life, there are a few stipulations. First, your website has to be relatively simple—The Free Website Guys doesn’t create advanced functionalities for free. You’ll also need to host your site on WordPress and use one of the company’s preferred web hosting companies. The reason is that it makes money from affiliate commissions. Still, these are pretty small sacrifices to make for a free custom-designed site.
For companies that don’t want to invest a ton in their website at first, The Free Website Guys is an excellent starting point. If you outgrow your theme in the future, The Free Website Guys also offers paid design services with more thorough customization.
- Completely free custom website
- Includes Google Analytics and Google Search Console installs
- Maintenance training provided
- Websites can’t be complicated or have advanced functionality
- Need to sign up for a preferred web hosting company to get offer
- No long-term support
Best for Local Businesses

Under $10,000
Airtech, Bluesource, Harvard University
SmartSites specializes in home service, medical, B2B, B2C, industrial, e-commerce and local business websites. It can also design websites for content management systems (CMS) including WordPress, Adobe Commerce (formerly Magento), Shopify and more. And if you’re on the fence, SmartSites offers a huge portfolio of its previous work organized by industry, helping you to see what it’s capable of.
But why we really like SmartSites is its local focus. It specializes in redesigning old and tired small business websites to help make them modern and mobile-optimized. Other standout features include on-site SEO implementation, advanced website security, fast loading times and Google Analytics integrations.
SmartSites doesn’t offer ongoing support in its initial design packages, but it is a service you can add on after the fact if you need help. And if you need more assistance, SmartSites also offers logo and graphic design, content writing services and SEO marketing, all of which can help rocket your site to the top of search engine results pages (SERPs).
Local businesses that want a professional-looking site with modern features will appreciate the affordability and breadth of services offered by SmartSites.
- Can choose from a number of CMS platforms
- Huge website portfolio
- Guaranteed fast load times
- Ongoing support not included
- Some designs are just templates
Best for Digital Marketing
Intero digital.

EASE Logistics, Updox, Covail
Intero Digital made our list of the best SEO services , so it’s not a huge surprise to see it also excel at web design. Intero Digital’s web design services are heavily SEO-focused, meaning your new site should be well-positioned in SERPs. It does this by making lead generation a highlight of every page so you can push your viewers toward a sale. Also, it can design pages that will focus on top-of-funnel leads, hone measurable engagement and support the buyer’s journey.
Along with these digital marketing features, Intero Digital can integrate and migrate your site from an old CMS, optimize the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) and integrate e-commerce features to allow you to sell products directly. It can even work on brand positioning and messaging so you come across as professional, fun, serious—whatever your preferred tone is.
After choosing your CMS, Intero Digital creates a workable sitemap and wireframe. Then, once your site is almost ready, Intero Digital performs a cyclic process to test, analyze and measure your site to make sure it’s running smoothly.
Because Intero Digital is so focused on marketing and offers robust SEO and paid media services, we think it’s a good choice for businesses that can use the service to optimize immediate conversions.
- Excellent SEO and paid media services
- UX- and UI-friendly designs
- Brand positioning assistance
- Not a good designer for businesses that aren’t focused on immediate conversions
- Does not mention ongoing support
Best for E-Commerce
Digital silk.

Starts at $7,500
IBM, Sony, Northwestern University
Digital Silk specializes in B2C, B2B and e-commerce solutions. In particular, it creates websites that are optimized for conversion, engagement and traffic. It gives you the choice of creating a custom e-commerce design or using platforms such as Shopify , WooCommerce, Adobe Commerce or BigCommerce. You can also go the WordPress route if that’s what you’re used to.
The process begins with a strategy meeting to find the positioning for your brand, select your target audience and define measurable key performance indicators. From there, Digital Silk plans your site’s structure, begins to design the color and custom elements and adds in responsive elements.
The second to last step is a quality assurance test to make sure your site functions correctly without any bugs. Finally, Digital Silk sets up your server on your behalf, configures the DNS and adds in Cloudflare security protection. If you need other services after your website launches, Digital Silk also offers digital marketing and mobile app development.
Businesses looking to launch a new e-commerce store (or redesign an old one) will love the flexibility of Digital Silk.
- B2B and B2C designs
- Strong redesign services
- Comprehensive design process
- Can take up to four months to complete custom website
- Custom websites start at $18,000
Best for Large Businesses

Starts at $75,000
Meta, Slack, Stripe
500-plus projects
If you’re looking to spare no expense, then Clay is the web design agency for you. It’s expensive, but for a reason—it’s trusted by some of the top names in the business, including UPS, Cisco, Uber and more. Unsurprisingly, it also covers a wide range of industries, including fintech, B2B, technology, crypto, e-commerce and more.
When you choose to have Clay build your website, you’re not just getting a stagnant landing page. It offers everything from content strategy and production to interactive experiences. The design team will be led by the co-founders and senior-level teams to ensure your project goes off without a hitch. Clay prides itself on its communication and transparency at every step of the process.
It also boasts that its work is “future-proof,” as many of the websites in its portfolio haven’t been updated for five years. Considering the average website life span is just two years and seven months, that’s some impressive longevity. Naturally, you can also opt for several other services from Clay, including branding, content and development.
Businesses that want to partner with a well-known web design agency can’t go wrong with Clay. Because of the price point, it might be best for businesses with larger pockets.
- Designed for many big-name clients
- Responsive and interactive websites
- Both front-end and back-end development
- Doesn’t disclose what CMS it works with
Best for User-Centric Designs

Starts at $10,000
Universal Music Group, Marlinz Pharma, Citizens, Inc.
128 projects
As soon as you visit the DIGITECH site, you can tell the designers are masters of their craft. The interactive, space-style website delivers a heavy dose of originality that showcases what you can expect with your web design. DIGITECH’s main focus is UX and SEO—both are considered from the very start to help keep coding clean.
It also boasts a content-first approach, meaning that once you nail down your messaging, it will create a visual design focused on your brand. After nailing down the basics, DIGITECH creates a wireframe of your site using FlowMapp, a collaborative tool that allows every team member to contribute. If necessary, it can also use full-stack development to create web applications that take your site to the next level.
Along with many of the other web design agencies on this list, DIGITECH also offers a few other services, including SEO, branding and identity and paid marketing. One thing it doesn’t mention is what happens after your site is complete, so we’re not sure if it includes ongoing support or not.
DIGITECH creates beautiful websites for brands that want to stand out from the crowd. It’s a great pick for businesses that want a marketing website to attract and engage readers.
- Beautiful, visually striking designs
- SEO- and UX-focused
- Excels at marketing websites
- Not e-commerce focused
A web design company is a company that can help you build a website for your business. A web design agency may employ web designers, web developers, graphic designers and UX/UI designers who all contribute their various skills to the production of a website. With their expertise, web design companies can build a site from scratch that’s completely customized for your needs, whether you want a responsive design, e-commerce gateways or interactive features.
Benefits of enlisting a web design company include professional expertise, advanced customization and more.
- Professional and industry expertise: The staff at web design agencies are pros. They build websites for a living, so they’ll know how to get the best results every time.
- Customization beyond what you could do yourself: Even if you dabble in programming languages, chances are you don’t have the skill set to completely customize a website on your own . For a web design company, customization is easy, because it’s what they do.
- Saves time and energy: Yes, it’s possible to create a passable website with one of the best website builders , but this still takes hours or days of work. With a web design agency, you won’t have to deal with any of the hassle.
- Future support and maintenance: Many of the best web design companies offer long-term support for your site. This can be crucial if a page suddenly crashes or you need to update a plugin but don’t know how.
- Search engine optimized design: SEO is a vital tool for boosting your website’s appearance in search engine results. Web design companies know about SEO best practices and can design your site with these optimizations in mind.
There’s a lot to consider before choosing a web design company. Here are some of the top factors to think about when you’re narrowing down your options.
Essential Features
- Ongoing support and maintenance: A web design company should continue to look after your site even once it finishes building it.
- Knowledge of SEO and UX : Any modern website must be designed with SEO and UX in mind—otherwise, you may not appear in search engines or provide users with a good browsing experience.
- Responsive design capability: Responsive design is what users have come to know and expect from a website. It also means your site will display properly whether it’s viewed on a phone or desktop.
- Security protocols: For starters, you need a site that’s secured with encrypted data through SSL certificates.
- Clear design process: A web design company should be able to tell you how the process will go from start to finish so there are no surprises.
- Works with preferred CMS: Your web design team should be able to build your site on the platform of your choice, whether you prefer WordPress, Cosmic or something in-between.
- Training and documentation: A good web design company will provide you with documentation so you know how to make updates and add content on your own.
- Ability to integrate with apps and third-party services: For example, if you want to integrate your site with Mailchimp or Google Analytics, a web design agency should be able to do that for you.
- Legal and accessibility compliance: A good web design agency should make sure your site complies with both the General Data Protection Regulation and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
- Ability to scale in the future: Let’s say you want to expand your site in three years. Your web design company should be able to create a site that’s easy to build onto so you don’t need a complete redesign.
Portfolio or Past Examples
Always check a web design company’s portfolio. Many agencies feature a collection of previous websites they’ve designed to showcase their skills. Browse these sites carefully to make sure you like the design and features. If something feels off or you think the design looks amateurish, consider another designer.
This is a given, but you have to make sure a web design company is within your budget. The best way to do this is to reach out for an estimate. After you provide details about your needs, a company can provide a personalized quote to build your site. Collect at least three to five quotes to see which companies are more affordable.
Production Timeline
We estimate that it takes about 10 to 14 weeks on average to build a website. The agency you choose should offer a timeline similar to that if they’re competitive. If the agency is in high demand, it may take longer. Other agencies without a lot of clients may take less time. In any case, just make sure the production timeline matches your needs.
Positive Customer Reviews
Always consider what past customers of the company are saying. Read through reviews on sites, such as Capterra, DesignRush, Clutch and G2, to get an idea of the pros and cons of the service. These reviews can often be far more enlightening than reading a company’s website copy and give tales of real-life experiences.
On Wix's Website
On Web.com's Website
On Squarespace's Website
Web design companies aren’t typically very transparent about their pricing. They’re not intentionally gatekeeping, but rather, they withhold pricing because web design is such a customized experience. What it costs to build a simple one-page website is far different than what it costs for a multi-page e-commerce store.
Listing a standard set of web design prices could be misleading and inaccurate. Even the price ranges we’ve quoted in this article are averages curated from various customer experiences, so they may not reflect what you’d pay for a project. With all of this in mind, a good range for web design services is anywhere from $2,000 up to $150,000.
Typically, most companies are happy to provide a quote if you give them details about what you’re looking for. Companies typically charge by the project, but some do charge by the hour.
For most businesses that want a reputable web presence, hiring a web design company is the right choice. There is web design software available that can guide you in creating a site that will look mostly professional. But if you want advanced features, such as payment gateways, mobile-friendly designs and live chat integration, then having a professional build your site for you is a much better option.
To start, we took a look at ratings for each design service on four review sites: Capterra, DesignRush, Clutch and G2. We automatically disqualified any service that had a cumulative rating of less than 4.5 stars. Some services weren’t rated on every site, but we made sure they had high ratings on at least three of the sites to keep things fair.
After curating the highest-rated services, we then took a look at key offerings. Each service needed to have a thorough design process from start to finish. They also needed to include some industry-specific offerings as well as modern design principles focused on user experience, user interface and search engine optimization.
Other important considerations were whether or not the web design company has worked with any big-name clients. This isn’t a deal-breaker, as many designers purposely focus on local businesses instead of major corporations, and we included some of those picks on our list. However, the bigger the client, the more likely a company will do top-tier work.
Pricing and fees also played a consideration. Most companies did not offer transparent pricing systems since web design is such a complicated and personalized service. However, we were able to ascertain ranges by comparing customer reviews. We tried to find picks that offered good value for the money.
How much do companies charge to design a website?
How much companies charge to design a website varies greatly depending on the industry, size of the website and design experience of the company. In our review of the top web design companies, we found companies designing websites for free up to companies charging over $100,000 for a site. The more you pay, the higher quality your site should be.
How do I choose a web development company?
We recommend taking a look at reviews to see what customers are saying about a company. It’s also vital to look at a web design agency’s portfolio to take a look at their past work. Finally, get a quote from each company you’re considering to see which fits into your budget.
How many hours does it take to design a website?
It can take anywhere from 150 to 500 hours to design a website from scratch. It all depends on the complexity and size of the website. A simple website built from a WordPress theme will take far fewer hours to complete than an interactive website completely built and coded from scratch.
Next Up In Web Design
- Weebly Vs. Wix
- Best Wix Alternatives
- Best Squarespace Alternatives
- Best Shopify Competitors & Alternatives
- Best Free Website Builders

Kristy Snyder is a freelance writer and editor with 12 years of experience, currently contributing to the Forbes Advisor Small Business vertical. She uses her experience managing her own successful small business to write articles about software, small business tools, loans, credit cards and online banking. Kristy's work also appears in Newsweek and Fortune, focusing on personal finance.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc order bans former pioneer ceo from exxon board seat in exxon-pioneer deal.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
Fact Sheet on FTC’s Proposed Final Noncompete Rule
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC’s proposed final rule :
- Specifically, the final rule provides that it is an unfair method of competition—and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act—for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers after the effective date.
- Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule.
- Specifically, the final rule defines the term “senior executive” to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a “policy-making position.”
- Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade.
- New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year.
- This reflects an estimated increase of about 3,000 to 5,000 new patents in the first year noncompetes are banned, rising to about 30,000-53,000 in the tenth year.
- This represents an estimated increase of 11-19% annually over a ten-year period.
- The average worker’s earnings will rise an estimated extra $524 per year.
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contact.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs 415-848-5121
TechRepublic
Account information.

Share with Your Friends
How to Use TODAY() to Highlight Fast-Approaching Dates in an Excel Sheet
Your email has been sent

Many applications track dates for lots of different reasons. You might track due dates, delivery dates, appointments and so on. Depending how you use these dates, you might want to highlight specific dates as they approach the current date in Microsoft Excel. Similarly, you might want to highlight future dates.
Using the TODAY() function and a few conditional highlighting rules, you’ll never get caught unaware.
Highlight today in Microsoft Excel
While you probably won’t want to wait until a due date to start a project, highlighting the current date can help alert you when timing is essential. Fortunately, Excel’s TODAY() function always equals the current date, so you don’t have to update the rule or even include an input value.
SEE: Explore these 87 Excel tips every user should master .
Let’s add a conditional format that always highlights the current date:
- Select the cells or rows you want to highlight. In this case, select B3:E12 — the data range.
- Click the Home tab, and then, click Conditional Formatting in the Styles group and choose Highlight Cells Rules.
- Choose A Date Occurring.
- In the resulting dialog, choose Today from the first dropdown, and then, choose Light Red Fill from the second ( Figure A ). As you can see, the current date is December 6.
This method is the easiest way to quickly apply a conditional format to highlight the current date, but it is a bit limited. First, you have only a few format combinations available. Second, it doesn’t highlight the entire row — only the cell containing the date. This rule is able to detect dates in the selected range and apply the format only to those cells. So, it doesn’t matter where the date column is in relation to the selected range.
SEE: Check out these ways to suppress 0 in Excel .
Highlight yesterday in Microsoft Excel
There are built-in rules for yesterday and tomorrow, but let’s enter a rule instead, so you’ll know how to do so when there isn’t an adequate built-in rule. Let’s start with yesterday:
- Select the data range B3:E12.
- Click the Home tab. Then, click Conditional Formatting in the Styles group, and choose New Rule.
- In the resulting dialog, select the Use a Formula to Determine Which Cells To Format option in the top pane.
- In the bottom pane, enter the expression =$B3=TODAY()-1. The simple expression TODAY()-1 subtracts one from the current date. That’s the same thing as yesterday.
- Click Format.
- Click the Fill tab, choose red and click OK. Figure B shows the rule and the format.
- Click OK to apply the format.
As you can see in Figure B , the rule highlights the entire record when the date in column B is yesterday. Notice that the rule has an absolute column reference ($B). If you omit the dollar sign, Excel applies the highlight to the cell instead of the entire row. The reference to row 3 isn’t absolute, so the rule can evaluate all of the rows in the selected range.
SEE: Here’s how to parse data in Microsoft Excel .
Highlight tomorrow in Microsoft Excel
To highlight tomorrow, repeat the above steps, but enter the rule =$B3=TODAY()+1, as shown in Figure C . Click Format, and choose any color, but I chose medium blue. Click OK (twice) to apply the format, which highlights the entire row when the date in column B is tomorrow. Again, the absolute and relative referencing is important.
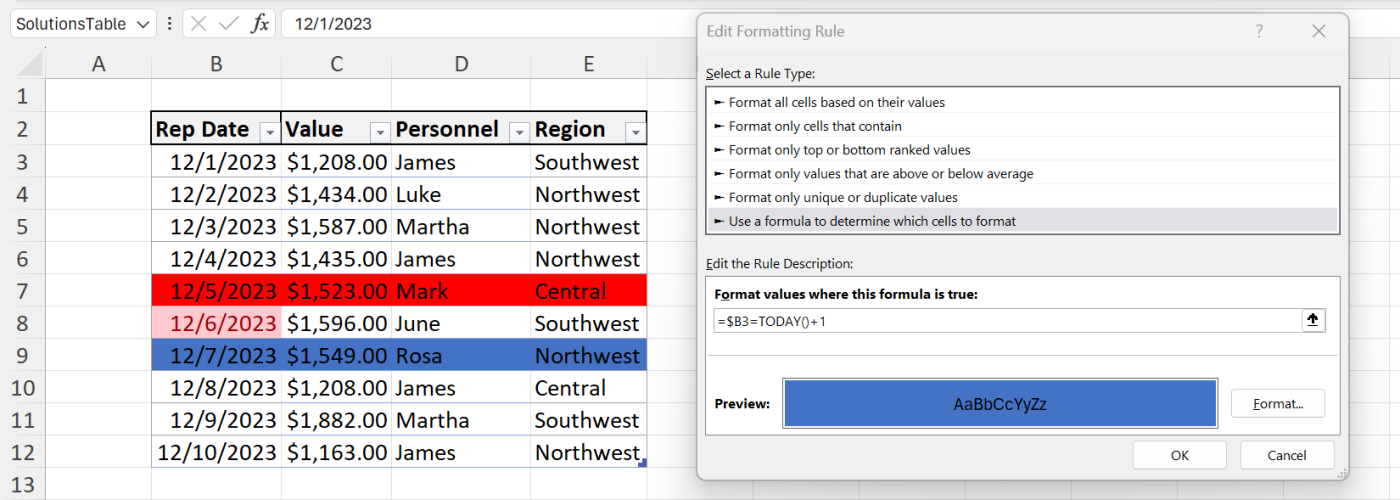
All three rules are simple to implement, but they are limited to today, yesterday and tomorrow. What if you want to highlight other daily increments beyond these three?
Highlight past dates in Microsoft Excel
There may come a time when you’ll want a bit more flexibility when highlighting important dates. For instance, you might want to highlight dates that are a week ahead or a week past. When this is the case, I recommend using an input cell where you can specify the number of days. By referencing the input cell in the formula, the highlight will update automatically depending on your needs at the time.
Using Figure D as a guide, format two input cells: days in the past and days into the future. Accordingly, we’ll reference C1 in the past rule and C2 in the future.
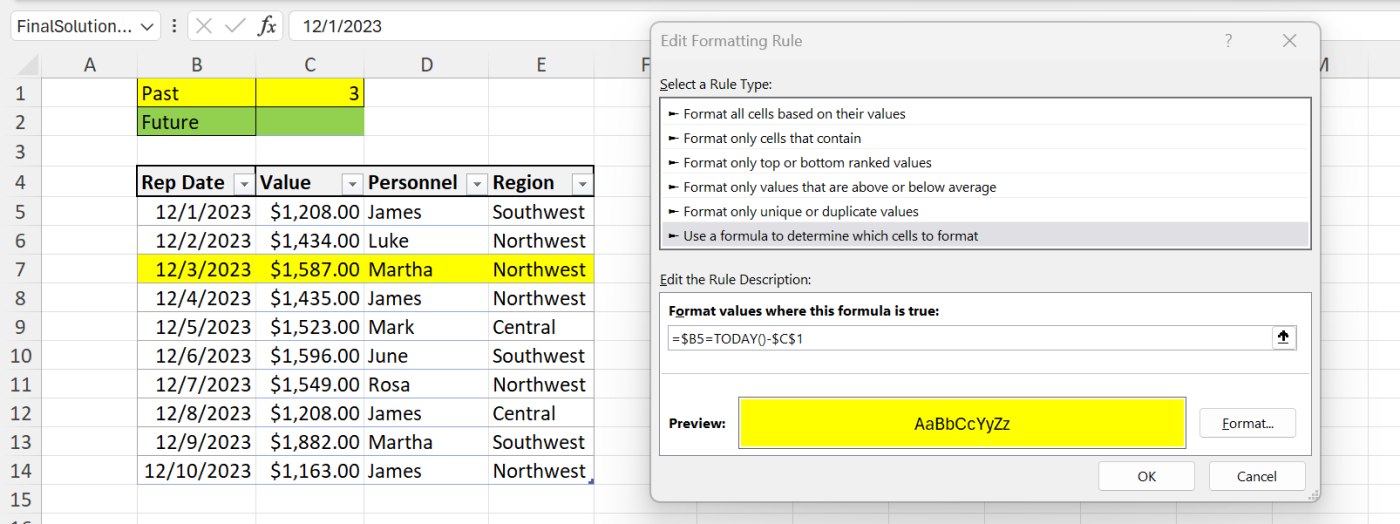
First, let’s enter the rule for the past:
- Select the data range B5:E14. Notice that I’ve updated the range rows because I inserted rows for the input cells.
- In the bottom pane, enter the expression =$B5=TODAY()-$C$1.
- Click the Fill tab, choose yellow and click OK. Figure E shows the rule and the format.
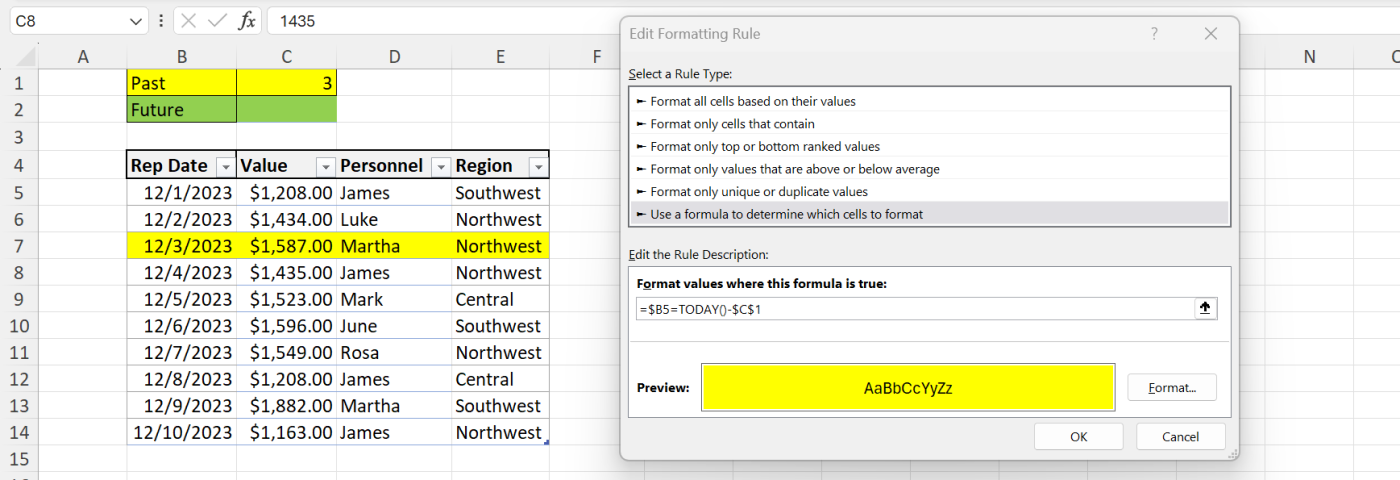
Figure E shows the result of entering 3 in C. Once again, the absolute address, $C$1 is important. If you leave this relative, the highlight won’t work as expected. When C1 is empty or contains 0, this rule highlights the current day.
SEE: Discover how to adjust text to fit in Excel cells .
Highlight future dates in Microsoft Excel
Repeat the steps above to apply a highlight for the future. Except in step 4, enter the expression =$B5=TODAY()+$C$2, and choose green. Figure F shows the resulting sheet after entering the value 3 into C2.
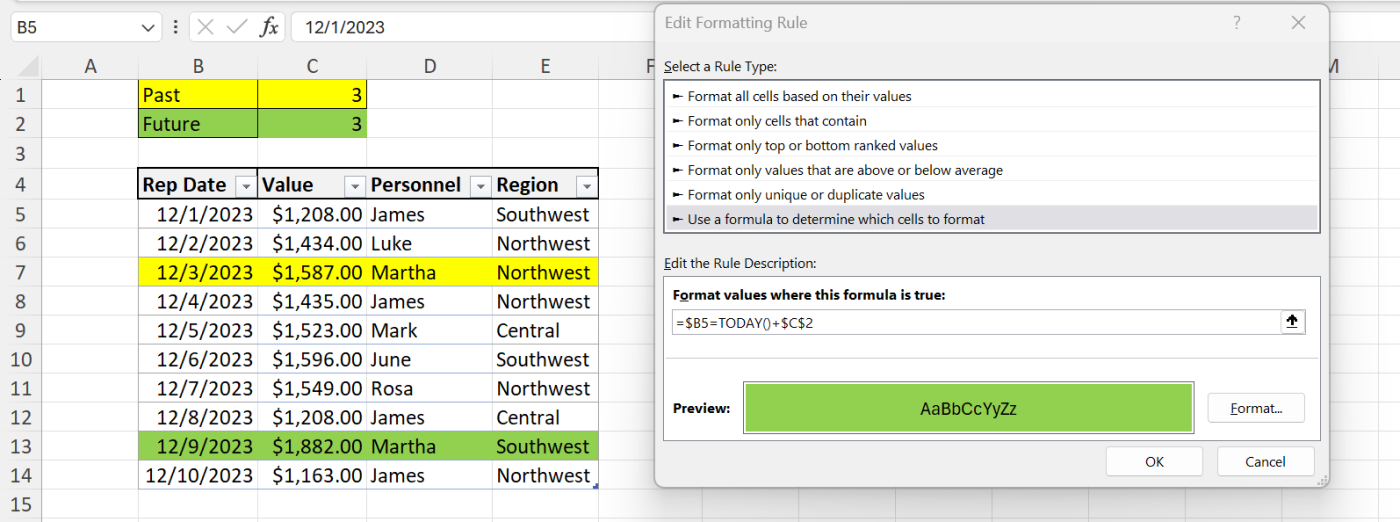
With the input cells and rules in place, feel free to change the values in C1 and C2. If the value is too far into the past or into the future for the existing dates, Excel won’t apply the highlight. Go ahead now and change those dates to see how both rules work.
Helpful hints
When applying conditional formats, the position of the rule is important. The last rules you enter will take precedence because they’re the first Excel evaluates. When several rules are in play, Excel might not apply them in the order you expect.
To change this, open the rules using Manage Rules on the Conditional Formatting dropdown and move the rules accordingly. One more thing that you might consider. Use the fill color of C1 and C2 to match the highlight fill color in the rule, as shown in Figures E and F . Doing so will offer a visual clue for the users, so they don’t have to remember what those two colors mean.
Subscribe to the Microsoft Weekly Newsletter
Be your company's Microsoft insider by reading these Windows and Office tips, tricks, and cheat sheets. Delivered Mondays and Wednesdays
- How to Extract Delimited Data Using Excel Power Query
- Support for these Microsoft enterprise products ends in 2023
- How to Create a Local Account in Windows 11 Pro
- Excel power user guide
- Best software for businesses and end users

Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
Download Free Business Plan Examples
Download a free business plan in pdf or word doc format to make writing a plan fast and easy, find your sample plan.
Discover the sample plan that best fits your business. Search our gallery of over 550 sample business plans and find the one that's right for you.
View the Gallery

What You'll Get:
A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours.
A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that’s proven to raise money from lenders and investors.
Instructions and help at every step Get help with clear, simple instructions for each section of the business plan. No business experience necessary.
A Word doc you can edit We don’t just have PDF documents that make editing a challenge. Each plan is available in Word format so you can start editing your business plan example right away.
Key Sections Included in our Example Business Plans:
Executive Summary : A quick overview of your plan and entices investors to read more of your plan.
Company : Describes the ownership and history of your business.
Products and Services : Reviews what you sell and what you’re offering your customers.
Market Analysis : Describes your customers and the size of your target market.
Strategy and Implementation : Provides the details of how you plan on building the business.
Management Team : An overview of the people behind the business and why they’re the right team to make the business a success.
Financial Plan : A complete set of forecasts including a Profit and Loss Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet.
Looking for a sample business plan PDF? You can download a few PDF examples below:
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Sample Business Plan PDF
- Agriculture Farm Sample Business Plan PDF
- Cleaning Service Sample Business Plan PDF

Need a faster way to write your business plan? LivePlan is the #1 planning tool for over 1 million businesses.

Your download should begin immediately
If your download doesn't begin after 5 seconds, please click here .
View our entire gallery of free downloads
Tweet about it
I just downloaded a free business plan from Bplans.com!#smb #startup
Recommended Articles

Recommended Download

You might also enjoy:

The Small Business Toolkit
Access a free list of must–have resources for new and growing businesses in any industry.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start off your new real estate business on the right foot by using a real estate business plan template to ensure your goals, visions, and finances are sorted. Trucking Business Plan Template Empower your journey to success with our trucking business plan template, designed as a valuable tool to organize the essentials of your trucking business.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A faster way to plan. LivePlan is the #1 planning tool for over 1 million businesses. Create your business plan. Download a free business plan template in Google Doc, Microsoft Word, and PDF formats. Includes expert guidance to help fill out each section.
With this business plan template, you'll be able to: Write a company description that sells your story. Plan for the future: lay out goals and metrics for success. Describe your product line in detail and plan for how to stand out from competitors. Consider any legal formalities that require attention when starting your business.
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format: 1. Executive summary. This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business ...
Using Asana's free business plan template is simple. Start by creating a new project with our free template. From there, add relevant information for your specific business plan in the sections provided in our template. If there's more information you want to include in your business plan, you're free to add sections, custom fields, or ...
Business Glossary. Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know. Bplans offers free business plan samples and templates, business planning resources, how-to articles, financial calculators, industry reports and entrepreneurship webinars.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
In times of uncertainty, being prepared is your best strategy. This template helps your business not just survive but thrive in challenging situations, keeping your customers, employees, and investors satisfied. 🤝. Download This Template. 6. ClickUp Lean Business Plan Template. ClickUp Lean Business Plan Template.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
8. Panda Doc's Free Business Plan Template. PandaDoc's free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
706 templates. Create a blank Business Plan. Beige Aesthetic Modern Business Plan A4 Document. Document by Rise & Roar Design. Green Professional Strategic Business Plan Executive Summary. Document by Antler. Startup Business Plan. Document by Maea Studio. Blue White Corporate Business Plan Cover Document.
Powerful business plan templates. Plan for the future, no matter what your business plans are or the size of your business with these designs and templates. Whether it's just one big project or an entire organization's worth of dreams, these templates will keep you and your company on track from ideation to completion. Category.
Once you've got your audience in mind, you can start your business plan, which should include: 1. Executive summary. Even though it appears first in the official plan, write this section last so you can condense essential ideas from the other nine sections. For now, leave it as a placeholder.
The Bplans Weekly. Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business. A business plan is the backbone of a successful business. Learn to write, use, and improve your business plan with exclusive guides, templates, and examples.
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan. Business plan templates. Download a free business plan template on The Prince's Trust website.
Traditional business plan. This is a formal document for pitching to investors based on the outline in this article. If your business is a complicated one, the plan may exceed the typical length and stretch to as many as 50 pages. One-page business plan. This is a simplified version of a formal business plan designed to fit on one page.
Use case: A business plan is made for an entirely new business, while a business case is created when asking for a substantial financial commitment within an existing business; Purpose: A business plan aims to hammer out the complete business strategy, while a business case tries to explain the advantages of a specific initiative
Having a quality website is imperative. Statistics show that 71% of businesses had a website in 2023—and a further 43% of small businesses plan to invest in their website performance. Whether ...
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year. Rise in innovation: an average of 17,000-29,000 more patents each year for the next ten years.
Click Format, and choose any color, but I chose medium blue. Click OK (twice) to apply the format, which highlights the entire row when the date in column B is tomorrow. Again, the absolute and ...
A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that ...
Walmart's plan to renovate 13 stores across the state includes locations in Waukesha and West Milwaukee. Walmart's remodeling plans for 650 stores nationwide in 2024 will affect 13 locations in ...