
Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research

How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
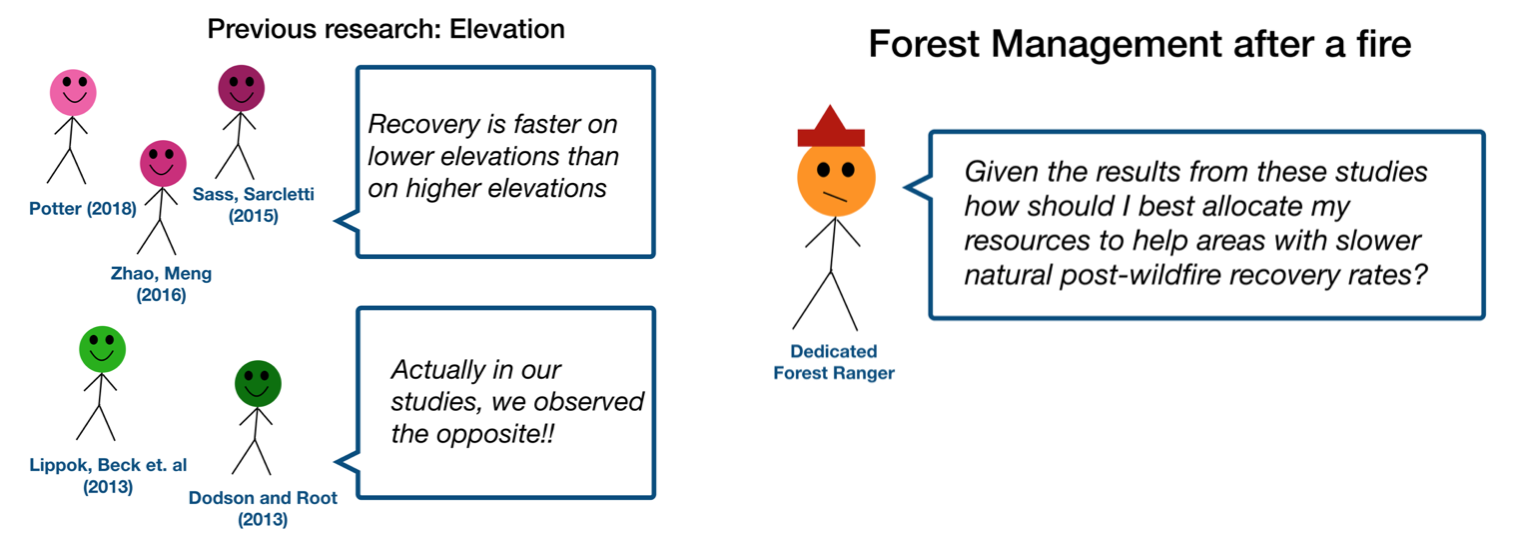
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation
How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation

Every research endeavor ends up with the communication of its findings. Graduate-level research culminates in a thesis defense , while many academic and scientific disciplines are published in peer-reviewed journals. In a business context, PowerPoint research presentation is the default format for reporting the findings to stakeholders.
Condensing months of work into a few slides can prove to be challenging. It requires particular skills to create and deliver a research presentation that promotes informed decisions and drives long-term projects forward.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Presentation
Key slides for creating a research presentation, tips when delivering a research presentation, how to present sources in a research presentation, recommended templates to create a research presentation.
A research presentation is the communication of research findings, typically delivered to an audience of peers, colleagues, students, or professionals. In the academe, it is meant to showcase the importance of the research paper , state the findings and the analysis of those findings, and seek feedback that could further the research.
The presentation of research becomes even more critical in the business world as the insights derived from it are the basis of strategic decisions of organizations. Information from this type of report can aid companies in maximizing the sales and profit of their business. Major projects such as research and development (R&D) in a new field, the launch of a new product or service, or even corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives will require the presentation of research findings to prove their feasibility.
Market research and technical research are examples of business-type research presentations you will commonly encounter.
In this article, we’ve compiled all the essential tips, including some examples and templates, to get you started with creating and delivering a stellar research presentation tailored specifically for the business context.
Various research suggests that the average attention span of adults during presentations is around 20 minutes, with a notable drop in an engagement at the 10-minute mark . Beyond that, you might see your audience doing other things.
How can you avoid such a mistake? The answer lies in the adage “keep it simple, stupid” or KISS. We don’t mean dumbing down your content but rather presenting it in a way that is easily digestible and accessible to your audience. One way you can do this is by organizing your research presentation using a clear structure.
Here are the slides you should prioritize when creating your research presentation PowerPoint.
1. Title Page
The title page is the first thing your audience will see during your presentation, so put extra effort into it to make an impression. Of course, writing presentation titles and title pages will vary depending on the type of presentation you are to deliver. In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include:
- The full title of the report
- The date of the report
- The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report
- The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended
When writing the title of your research presentation, it should reflect the topic and objective of the report. Focus only on the subject and avoid adding redundant phrases like “A research on” or “A study on.” However, you may use phrases like “Market Analysis” or “Feasibility Study” because they help identify the purpose of the presentation. Doing so also serves a long-term purpose for the filing and later retrieving of the document.
Here’s a sample title page for a hypothetical market research presentation from Gillette .

2. Executive Summary Slide
The executive summary marks the beginning of the body of the presentation, briefly summarizing the key discussion points of the research. Specifically, the summary may state the following:
- The purpose of the investigation and its significance within the organization’s goals
- The methods used for the investigation
- The major findings of the investigation
- The conclusions and recommendations after the investigation
Although the executive summary encompasses the entry of the research presentation, it should not dive into all the details of the work on which the findings, conclusions, and recommendations were based. Creating the executive summary requires a focus on clarity and brevity, especially when translating it to a PowerPoint document where space is limited.
Each point should be presented in a clear and visually engaging manner to capture the audience’s attention and set the stage for the rest of the presentation. Use visuals, bullet points, and minimal text to convey information efficiently.

3. Introduction/ Project Description Slides
In this section, your goal is to provide your audience with the information that will help them understand the details of the presentation. Provide a detailed description of the project, including its goals, objectives, scope, and methods for gathering and analyzing data.
You want to answer these fundamental questions:
- What specific questions are you trying to answer, problems you aim to solve, or opportunities you seek to explore?
- Why is this project important, and what prompted it?
- What are the boundaries of your research or initiative?
- How were the data gathered?
Important: The introduction should exclude specific findings, conclusions, and recommendations.

4. Data Presentation and Analyses Slides
This is the longest section of a research presentation, as you’ll present the data you’ve gathered and provide a thorough analysis of that data to draw meaningful conclusions. The format and components of this section can vary widely, tailored to the specific nature of your research.
For example, if you are doing market research, you may include the market potential estimate, competitor analysis, and pricing analysis. These elements will help your organization determine the actual viability of a market opportunity.
Visual aids like charts, graphs, tables, and diagrams are potent tools to convey your key findings effectively. These materials may be numbered and sequenced (Figure 1, Figure 2, and so forth), accompanied by text to make sense of the insights.

5. Conclusions
The conclusion of a research presentation is where you pull together the ideas derived from your data presentation and analyses in light of the purpose of the research. For example, if the objective is to assess the market of a new product, the conclusion should determine the requirements of the market in question and tell whether there is a product-market fit.
Designing your conclusion slide should be straightforward and focused on conveying the key takeaways from your research. Keep the text concise and to the point. Present it in bullet points or numbered lists to make the content easily scannable.

6. Recommendations
The findings of your research might reveal elements that may not align with your initial vision or expectations. These deviations are addressed in the recommendations section of your presentation, which outlines the best course of action based on the result of the research.
What emerging markets should we target next? Do we need to rethink our pricing strategies? Which professionals should we hire for this special project? — these are some of the questions that may arise when coming up with this part of the research.
Recommendations may be combined with the conclusion, but presenting them separately to reinforce their urgency. In the end, the decision-makers in the organization or your clients will make the final call on whether to accept or decline the recommendations.

7. Questions Slide
Members of your audience are not involved in carrying out your research activity, which means there’s a lot they don’t know about its details. By offering an opportunity for questions, you can invite them to bridge that gap, seek clarification, and engage in a dialogue that enhances their understanding.
If your research is more business-oriented, facilitating a question and answer after your presentation becomes imperative as it’s your final appeal to encourage buy-in for your recommendations.
A simple “Ask us anything” slide can indicate that you are ready to accept questions.
1. Focus on the Most Important Findings
The truth about presenting research findings is that your audience doesn’t need to know everything. Instead, they should receive a distilled, clear, and meaningful overview that focuses on the most critical aspects.
You will likely have to squeeze in the oral presentation of your research into a 10 to 20-minute presentation, so you have to make the most out of the time given to you. In the presentation, don’t soak in the less important elements like historical backgrounds. Decision-makers might even ask you to skip these portions and focus on sharing the findings.
2. Do Not Read Word-per-word
Reading word-for-word from your presentation slides intensifies the danger of losing your audience’s interest. Its effect can be detrimental, especially if the purpose of your research presentation is to gain approval from the audience. So, how can you avoid this mistake?
- Make a conscious design decision to keep the text on your slides minimal. Your slides should serve as visual cues to guide your presentation.
- Structure your presentation as a narrative or story. Stories are more engaging and memorable than dry, factual information.
- Prepare speaker notes with the key points of your research. Glance at it when needed.
- Engage with the audience by maintaining eye contact and asking rhetorical questions.
3. Don’t Go Without Handouts
Handouts are paper copies of your presentation slides that you distribute to your audience. They typically contain the summary of your key points, but they may also provide supplementary information supporting data presented through tables and graphs.
The purpose of distributing presentation handouts is to easily retain the key points you presented as they become good references in the future. Distributing handouts in advance allows your audience to review the material and come prepared with questions or points for discussion during the presentation.
4. Actively Listen
An equally important skill that a presenter must possess aside from speaking is the ability to listen. We are not just talking about listening to what the audience is saying but also considering their reactions and nonverbal cues. If you sense disinterest or confusion, you can adapt your approach on the fly to re-engage them.
For example, if some members of your audience are exchanging glances, they may be skeptical of the research findings you are presenting. This is the best time to reassure them of the validity of your data and provide a concise overview of how it came to be. You may also encourage them to seek clarification.
5. Be Confident
Anxiety can strike before a presentation – it’s a common reaction whenever someone has to speak in front of others. If you can’t eliminate your stress, try to manage it.
People hate public speaking not because they simply hate it. Most of the time, it arises from one’s belief in themselves. You don’t have to take our word for it. Take Maslow’s theory that says a threat to one’s self-esteem is a source of distress among an individual.
Now, how can you master this feeling? You’ve spent a lot of time on your research, so there is no question about your topic knowledge. Perhaps you just need to rehearse your research presentation. If you know what you will say and how to say it, you will gain confidence in presenting your work.
All sources you use in creating your research presentation should be given proper credit. The APA Style is the most widely used citation style in formal research.
In-text citation
Add references within the text of your presentation slide by giving the author’s last name, year of publication, and page number (if applicable) in parentheses after direct quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
The alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (Smith, 2020, p. 27).
If the author’s name and year of publication are mentioned in the text, add only the page number in parentheses after the quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
According to Smith (2020), the alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (p. 27).
Image citation
All images from the web, including photos, graphs, and tables, used in your slides should be credited using the format below.
Creator’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Image.” Website Name, Day Mo. Year, URL. Accessed Day Mo. Year.
Work cited page
A work cited page or reference list should follow after the last slide of your presentation. The list should be alphabetized by the author’s last name and initials followed by the year of publication, the title of the book or article, the place of publication, and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. New York, NY: ABC Publications.
When citing a document from a website, add the source URL after the title of the book or article instead of the place of publication and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. Retrieved from https://www.smith.com/climate-change-and-biodiversity.
1. Research Project Presentation PowerPoint Template

A slide deck containing 18 different slides intended to take off the weight of how to make a research presentation. With tons of visual aids, presenters can reference existing research on similar projects to this one – or link another research presentation example – provide an accurate data analysis, disclose the methodology used, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Research Presentation Scientific Method Diagram PowerPoint Template

Whenever you intend to raise questions, expose the methodology you used for your research, or even suggest a scientific method approach for future analysis, this circular wheel diagram is a perfect fit for any presentation study.
Customize all of its elements to suit the demands of your presentation in just minutes.
3. Thesis Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

If your research presentation project belongs to academia, then this is the slide deck to pair that presentation. With a formal aesthetic and minimalistic style, this research presentation template focuses only on exposing your information as clearly as possible.
Use its included bar charts and graphs to introduce data, change the background of each slide to suit the topic of your presentation, and customize each of its elements to meet the requirements of your project with ease.
4. Animated Research Cards PowerPoint Template

Visualize ideas and their connection points with the help of this research card template for PowerPoint. This slide deck, for example, can help speakers talk about alternative concepts to what they are currently managing and its possible outcomes, among different other usages this versatile PPT template has. Zoom Animation effects make a smooth transition between cards (or ideas).
5. Research Presentation Slide Deck for PowerPoint

With a distinctive professional style, this research presentation PPT template helps business professionals and academics alike to introduce the findings of their work to team members or investors.
By accessing this template, you get the following slides:
- Introduction
- Problem Statement
- Research Questions
- Conceptual Research Framework (Concepts, Theories, Actors, & Constructs)
- Study design and methods
- Population & Sampling
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
Check it out today and craft a powerful research presentation out of it!
A successful research presentation in business is not just about presenting data; it’s about persuasion to take meaningful action. It’s the bridge that connects your research efforts to the strategic initiatives of your organization. To embark on this journey successfully, planning your presentation thoroughly is paramount, from designing your PowerPoint to the delivery.
Take a look and get inspiration from the sample research presentation slides above, put our tips to heart, and transform your research findings into a compelling call to action.

Like this article? Please share
Academics, Presentation Approaches, Research & Development Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Leave a Reply
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to make a scientific presentation

Scientific presentation outlines
Questions to ask yourself before you write your talk, 1. how much time do you have, 2. who will you speak to, 3. what do you want the audience to learn from your talk, step 1: outline your presentation, step 2: plan your presentation slides, step 3: make the presentation slides, slide design, text elements, animations and transitions, step 4: practice your presentation, final thoughts, frequently asked questions about preparing scientific presentations, related articles.
A good scientific presentation achieves three things: you communicate the science clearly, your research leaves a lasting impression on your audience, and you enhance your reputation as a scientist.
But, what is the best way to prepare for a scientific presentation? How do you start writing a talk? What details do you include, and what do you leave out?
It’s tempting to launch into making lots of slides. But, starting with the slides can mean you neglect the narrative of your presentation, resulting in an overly detailed, boring talk.
The key to making an engaging scientific presentation is to prepare the narrative of your talk before beginning to construct your presentation slides. Planning your talk will ensure that you tell a clear, compelling scientific story that will engage the audience.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to make a good oral scientific presentation, including:
- The different types of oral scientific presentations and how they are delivered;
- How to outline a scientific presentation;
- How to make slides for a scientific presentation.
Our advice results from delving into the literature on writing scientific talks and from our own experiences as scientists in giving and listening to presentations. We provide tips and best practices for giving scientific talks in a separate post.
There are two main types of scientific talks:
- Your talk focuses on a single study . Typically, you tell the story of a single scientific paper. This format is common for short talks at contributed sessions in conferences.
- Your talk describes multiple studies. You tell the story of multiple scientific papers. It is crucial to have a theme that unites the studies, for example, an overarching question or problem statement, with each study representing specific but different variations of the same theme. Typically, PhD defenses, invited seminars, lectures, or talks for a prospective employer (i.e., “job talks”) fall into this category.
➡️ Learn how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The length of time you are allotted for your talk will determine whether you will discuss a single study or multiple studies, and which details to include in your story.
The background and interests of your audience will determine the narrative direction of your talk, and what devices you will use to get their attention. Will you be speaking to people specializing in your field, or will the audience also contain people from disciplines other than your own? To reach non-specialists, you will need to discuss the broader implications of your study outside your field.
The needs of the audience will also determine what technical details you will include, and the language you will use. For example, an undergraduate audience will have different needs than an audience of seasoned academics. Students will require a more comprehensive overview of background information and explanations of jargon but will need less technical methodological details.
Your goal is to speak to the majority. But, make your talk accessible to the least knowledgeable person in the room.
This is called the thesis statement, or simply the “take-home message”. Having listened to your talk, what message do you want the audience to take away from your presentation? Describe the main idea in one or two sentences. You want this theme to be present throughout your presentation. Again, the thesis statement will depend on the audience and the type of talk you are giving.
Your thesis statement will drive the narrative for your talk. By deciding the take-home message you want to convince the audience of as a result of listening to your talk, you decide how the story of your talk will flow and how you will navigate its twists and turns. The thesis statement tells you the results you need to show, which subsequently tells you the methods or studies you need to describe, which decides the angle you take in your introduction.
➡️ Learn how to write a thesis statement
The goal of your talk is that the audience leaves afterward with a clear understanding of the key take-away message of your research. To achieve that goal, you need to tell a coherent, logical story that conveys your thesis statement throughout the presentation. You can tell your story through careful preparation of your talk.
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient.
Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
- Outline your presentation
- Plan your presentation slides
- Make the presentation slides
- Practice your presentation

Writing an outline helps you consider the key pieces of your talk and how they fit together from the beginning, preventing you from forgetting any important details. It also means you avoid changing the order of your slides multiple times, saving you time.
Plan your talk as discrete sections. In the table below, we describe the sections for a single study talk vs. a talk discussing multiple studies:
The following tips apply when writing the outline of a single study talk. You can easily adapt this framework if you are writing a talk discussing multiple studies.
Introduction: Writing the introduction can be the hardest part of writing a talk. And when giving it, it’s the point where you might be at your most nervous. But preparing a good, concise introduction will settle your nerves.
The introduction tells the audience the story of why you studied your topic. A good introduction succinctly achieves four things, in the following order.
- It gives a broad perspective on the problem or topic for people in the audience who may be outside your discipline (i.e., it explains the big-picture problem motivating your study).
- It describes why you did the study, and why the audience should care.
- It gives a brief indication of how your study addressed the problem and provides the necessary background information that the audience needs to understand your work.
- It indicates what the audience will learn from the talk, and prepares them for what will come next.
A good introduction not only gives the big picture and motivations behind your study but also concisely sets the stage for what the audience will learn from the talk (e.g., the questions your work answers, and/or the hypotheses that your work tests). The end of the introduction will lead to a natural transition to the methods.
Give a broad perspective on the problem. The easiest way to start with the big picture is to think of a hook for the first slide of your presentation. A hook is an opening that gets the audience’s attention and gets them interested in your story. In science, this might take the form of a why, or a how question, or it could be a statement about a major problem or open question in your field. Other examples of hooks include quotes, short anecdotes, or interesting statistics.
Why should the audience care? Next, decide on the angle you are going to take on your hook that links to the thesis of your talk. In other words, you need to set the context, i.e., explain why the audience should care. For example, you may introduce an observation from nature, a pattern in experimental data, or a theory that you want to test. The audience must understand your motivations for the study.
Supplementary details. Once you have established the hook and angle, you need to include supplementary details to support them. For example, you might state your hypothesis. Then go into previous work and the current state of knowledge. Include citations of these studies. If you need to introduce some technical methodological details, theory, or jargon, do it here.
Conclude your introduction. The motivation for the work and background information should set the stage for the conclusion of the introduction, where you describe the goals of your study, and any hypotheses or predictions. Let the audience know what they are going to learn.
Methods: The audience will use your description of the methods to assess the approach you took in your study and to decide whether your findings are credible. Tell the story of your methods in chronological order. Use visuals to describe your methods as much as possible. If you have equations, make sure to take the time to explain them. Decide what methods to include and how you will show them. You need enough detail so that your audience will understand what you did and therefore can evaluate your approach, but avoid including superfluous details that do not support your main idea. You want to avoid the common mistake of including too much data, as the audience can read the paper(s) later.
Results: This is the evidence you present for your thesis. The audience will use the results to evaluate the support for your main idea. Choose the most important and interesting results—those that support your thesis. You don’t need to present all the results from your study (indeed, you most likely won’t have time to present them all). Break down complex results into digestible pieces, e.g., comparisons over multiple slides (more tips in the next section).
Summary: Summarize your main findings. Displaying your main findings through visuals can be effective. Emphasize the new contributions to scientific knowledge that your work makes.
Conclusion: Complete the circle by relating your conclusions to the big picture topic in your introduction—and your hook, if possible. It’s important to describe any alternative explanations for your findings. You might also speculate on future directions arising from your research. The slides that comprise your conclusion do not need to state “conclusion”. Rather, the concluding slide title should be a declarative sentence linking back to the big picture problem and your main idea.
It’s important to end well by planning a strong closure to your talk, after which you will thank the audience. Your closing statement should relate to your thesis, perhaps by stating it differently or memorably. Avoid ending awkwardly by memorizing your closing sentence.
By now, you have an outline of the story of your talk, which you can use to plan your slides. Your slides should complement and enhance what you will say. Use the following steps to prepare your slides.
- Write the slide titles to match your talk outline. These should be clear and informative declarative sentences that succinctly give the main idea of the slide (e.g., don’t use “Methods” as a slide title). Have one major idea per slide. In a YouTube talk on designing effective slides , researcher Michael Alley shows examples of instructive slide titles.
- Decide how you will convey the main idea of the slide (e.g., what figures, photographs, equations, statistics, references, or other elements you will need). The body of the slide should support the slide’s main idea.
- Under each slide title, outline what you want to say, in bullet points.
In sum, for each slide, prepare a title that summarizes its major idea, a list of visual elements, and a summary of the points you will make. Ensure each slide connects to your thesis. If it doesn’t, then you don’t need the slide.
Slides for scientific presentations have three major components: text (including labels and legends), graphics, and equations. Here, we give tips on how to present each of these components.
- Have an informative title slide. Include the names of all coauthors and their affiliations. Include an attractive image relating to your study.
- Make the foreground content of your slides “pop” by using an appropriate background. Slides that have white backgrounds with black text work well for small rooms, whereas slides with black backgrounds and white text are suitable for large rooms.
- The layout of your slides should be simple. Pay attention to how and where you lay the visual and text elements on each slide. It’s tempting to cram information, but you need lots of empty space. Retain space at the sides and bottom of your slides.
- Use sans serif fonts with a font size of at least 20 for text, and up to 40 for slide titles. Citations can be in 14 font and should be included at the bottom of the slide.
- Use bold or italics to emphasize words, not underlines or caps. Keep these effects to a minimum.
- Use concise text . You don’t need full sentences. Convey the essence of your message in as few words as possible. Write down what you’d like to say, and then shorten it for the slide. Remove unnecessary filler words.
- Text blocks should be limited to two lines. This will prevent you from crowding too much information on the slide.
- Include names of technical terms in your talk slides, especially if they are not familiar to everyone in the audience.
- Proofread your slides. Typos and grammatical errors are distracting for your audience.
- Include citations for the hypotheses or observations of other scientists.
- Good figures and graphics are essential to sustain audience interest. Use graphics and photographs to show the experiment or study system in action and to explain abstract concepts.
- Don’t use figures straight from your paper as they may be too detailed for your talk, and details like axes may be too small. Make new versions if necessary. Make them large enough to be visible from the back of the room.
- Use graphs to show your results, not tables. Tables are difficult for your audience to digest! If you must present a table, keep it simple.
- Label the axes of graphs and indicate the units. Label important components of graphics and photographs and include captions. Include sources for graphics that are not your own.
- Explain all the elements of a graph. This includes the axes, what the colors and markers mean, and patterns in the data.
- Use colors in figures and text in a meaningful, not random, way. For example, contrasting colors can be effective for pointing out comparisons and/or differences. Don’t use neon colors or pastels.
- Use thick lines in figures, and use color to create contrasts in the figures you present. Don’t use red/green or red/blue combinations, as color-blind audience members can’t distinguish between them.
- Arrows or circles can be effective for drawing attention to key details in graphs and equations. Add some text annotations along with them.
- Write your summary and conclusion slides using graphics, rather than showing a slide with a list of bullet points. Showing some of your results again can be helpful to remind the audience of your message.
- If your talk has equations, take time to explain them. Include text boxes to explain variables and mathematical terms, and put them under each term in the equation.
- Combine equations with a graphic that shows the scientific principle, or include a diagram of the mathematical model.
- Use animations judiciously. They are helpful to reveal complex ideas gradually, for example, if you need to make a comparison or contrast or to build a complicated argument or figure. For lists, reveal one bullet point at a time. New ideas appearing sequentially will help your audience follow your logic.
- Slide transitions should be simple. Silly ones distract from your message.
- Decide how you will make the transition as you move from one section of your talk to the next. For example, if you spend time talking through details, provide a summary afterward, especially in a long talk. Another common tactic is to have a “home slide” that you return to multiple times during the talk that reinforces your main idea or message. In her YouTube talk on designing effective scientific presentations , Stanford biologist Susan McConnell suggests using the approach of home slides to build a cohesive narrative.
To deliver a polished presentation, it is essential to practice it. Here are some tips.
- For your first run-through, practice alone. Pay attention to your narrative. Does your story flow naturally? Do you know how you will start and end? Are there any awkward transitions? Do animations help you tell your story? Do your slides help to convey what you are saying or are they missing components?
- Next, practice in front of your advisor, and/or your peers (e.g., your lab group). Ask someone to time your talk. Take note of their feedback and the questions that they ask you (you might be asked similar questions during your real talk).
- Edit your talk, taking into account the feedback you’ve received. Eliminate superfluous slides that don’t contribute to your takeaway message.
- Practice as many times as needed to memorize the order of your slides and the key transition points of your talk. However, don’t try to learn your talk word for word. Instead, memorize opening and closing statements, and sentences at key junctures in the presentation. Your presentation should resemble a serious but spontaneous conversation with the audience.
- Practicing multiple times also helps you hone the delivery of your talk. While rehearsing, pay attention to your vocal intonations and speed. Make sure to take pauses while you speak, and make eye contact with your imaginary audience.
- Make sure your talk finishes within the allotted time, and remember to leave time for questions. Conferences are particularly strict on run time.
- Anticipate questions and challenges from the audience, and clarify ambiguities within your slides and/or speech in response.
- If you anticipate that you could be asked questions about details but you don’t have time to include them, or they detract from the main message of your talk, you can prepare slides that address these questions and place them after the final slide of your talk.
➡️ More tips for giving scientific presentations
An organized presentation with a clear narrative will help you communicate your ideas effectively, which is essential for engaging your audience and conveying the importance of your work. Taking time to plan and outline your scientific presentation before writing the slides will help you manage your nerves and feel more confident during the presentation, which will improve your overall performance.
A good scientific presentation has an engaging scientific narrative with a memorable take-home message. It has clear, informative slides that enhance what the speaker says. You need to practice your talk many times to ensure you deliver a polished presentation.
First, consider who will attend your presentation, and what you want the audience to learn about your research. Tailor your content to their level of knowledge and interests. Second, create an outline for your presentation, including the key points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support those points. Finally, practice your presentation several times to ensure that it flows smoothly and that you are comfortable with the material.
Prepare an opening that immediately gets the audience’s attention. A common device is a why or a how question, or a statement of a major open problem in your field, but you could also start with a quote, interesting statistic, or case study from your field.
Scientific presentations typically either focus on a single study (e.g., a 15-minute conference presentation) or tell the story of multiple studies (e.g., a PhD defense or 50-minute conference keynote talk). For a single study talk, the structure follows the scientific paper format: Introduction, Methods, Results, Summary, and Conclusion, whereas the format of a talk discussing multiple studies is more complex, but a theme unifies the studies.
Ensure you have one major idea per slide, and convey that idea clearly (through images, equations, statistics, citations, video, etc.). The slide should include a title that summarizes the major point of the slide, should not contain too much text or too many graphics, and color should be used meaningfully.


- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper
- 4 minute read
- 119.7K views
Table of Contents
A research paper presentation is often used at conferences and in other settings where you have an opportunity to share your research, and get feedback from your colleagues. Although it may seem as simple as summarizing your research and sharing your knowledge, successful research paper PowerPoint presentation examples show us that there’s a little bit more than that involved.
In this article, we’ll highlight how to make a PowerPoint presentation from a research paper, and what to include (as well as what NOT to include). We’ll also touch on how to present a research paper at a conference.
Purpose of a Research Paper Presentation
The purpose of presenting your paper at a conference or forum is different from the purpose of conducting your research and writing up your paper. In this setting, you want to highlight your work instead of including every detail of your research. Likewise, a presentation is an excellent opportunity to get direct feedback from your colleagues in the field. But, perhaps the main reason for presenting your research is to spark interest in your work, and entice the audience to read your research paper.
So, yes, your presentation should summarize your work, but it needs to do so in a way that encourages your audience to seek out your work, and share their interest in your work with others. It’s not enough just to present your research dryly, to get information out there. More important is to encourage engagement with you, your research, and your work.
Tips for Creating Your Research Paper Presentation
In addition to basic PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, think about the following when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Know your audience : First and foremost, who are you presenting to? Students? Experts in your field? Potential funders? Non-experts? The truth is that your audience will probably have a bit of a mix of all of the above. So, make sure you keep that in mind as you prepare your presentation.
Know more about: Discover the Target Audience .
- Your audience is human : In other words, they may be tired, they might be wondering why they’re there, and they will, at some point, be tuning out. So, take steps to help them stay interested in your presentation. You can do that by utilizing effective visuals, summarize your conclusions early, and keep your research easy to understand.
- Running outline : It’s not IF your audience will drift off, or get lost…it’s WHEN. Keep a running outline, either within the presentation or via a handout. Use visual and verbal clues to highlight where you are in the presentation.
- Where does your research fit in? You should know of work related to your research, but you don’t have to cite every example. In addition, keep references in your presentation to the end, or in the handout. Your audience is there to hear about your work.
- Plan B : Anticipate possible questions for your presentation, and prepare slides that answer those specific questions in more detail, but have them at the END of your presentation. You can then jump to them, IF needed.
What Makes a PowerPoint Presentation Effective?
You’ve probably attended a presentation where the presenter reads off of their PowerPoint outline, word for word. Or where the presentation is busy, disorganized, or includes too much information. Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation.
- Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon.
- Clean and professional : Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font changes, animations, and too many words. Instead of whole paragraphs, bullet points with just a few words to summarize and highlight are best.
- Know your real-estate : Each slide has a limited amount of space. Use it wisely. Typically one, no more than two points per slide. Balance each slide visually. Utilize illustrations when needed; not extraneously.
- Keep things visual : Remember, a PowerPoint presentation is a powerful tool to present things visually. Use visual graphs over tables and scientific illustrations over long text. Keep your visuals clean and professional, just like any text you include in your presentation.
Know more about our Scientific Illustrations Services .
Another key to an effective presentation is to practice, practice, and then practice some more. When you’re done with your PowerPoint, go through it with friends and colleagues to see if you need to add (or delete excessive) information. Double and triple check for typos and errors. Know the presentation inside and out, so when you’re in front of your audience, you’ll feel confident and comfortable.
How to Present a Research Paper
If your PowerPoint presentation is solid, and you’ve practiced your presentation, that’s half the battle. Follow the basic advice to keep your audience engaged and interested by making eye contact, encouraging questions, and presenting your information with enthusiasm.
We encourage you to read our articles on how to present a scientific journal article and tips on giving good scientific presentations .
Language Editing Plus
Improve the flow and writing of your research paper with Language Editing Plus. This service includes unlimited editing, manuscript formatting for the journal of your choice, reference check and even a customized cover letter. Learn more here , and get started today!

- Manuscript Preparation
Know How to Structure Your PhD Thesis

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?
You may also like.

What is a Good H-index?

What is a Corresponding Author?

How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Submit Manuscript
Easy Online Form
Get Newsletter
Sign Up Today
11 Tips to Make an Effective Research Presentation
Home » Presenting Your Research » 11 Tips to Make an Effective Research Presentation

The purpose of a presentation is to tell your audience a story. To achieve this goal, the person giving the presentation must place themselves in the shoes of their listeners and determine what they need to know to understand the story. Telling a great story is more important than any embellishments or technology you use to do it. Below are 11 tips for giving an effective research presentation.
1. Decide what your most important messages are, tailored to your specific audience.
Research can be messy, and so can the results of research. Your audience does not usually need to know every tiny detail about your work or results. Try to narrow down your findings to two or three of the most important takeaways that would resonate with the people in attendance. These takeaways are the messages of your presentation.
2. Start at the beginning and keep it simple.
Now that you have your messages, think about how you got to that point. What question did you ask that led you to do this research, and why did you ask it? Tell your audience this information, just enough of it for them to understand why the story is important and why you’re telling it. Use language that is tailored to the level of understanding of your audience.
3. Tell them how you addressed your question.
This part of any presentation usually involves the greatest risk of being dull. Tell your audience how you address your question, but don’t overwhelm them with detail they don’t need. Tell them what they need to know to get a basic idea of how you got your results.
4. Tell them your most important findings.
Again, do not overwhelm your listeners with noisy data or too much information. Give them a streamlined version of your results, using as your guide what you might include in an abstract of the work.
5. Give them the payoff—your main messages.
Link your results to the main or most important conclusions from your work. Make sure that the results you talk about directly connect with these final messages.
6. Hint at where you’re going next.
If appropriate, you can also tell your audience the new questions that your findings open up, leaving them a little intrigued about where things will go next.
7. Do not go over your time.
No one wants to listen to anyone talk longer than they are supposed to talk. If you’ve been given a 10-minute limit for your presentation, do not take more than 10 minutes. Your best bet is to practice it beforehand, timing yourself, to make sure that you have the right pace to stay within limits. Don’t make it too short, either, although that is almost never a problem.
8. Think about questions people might ask.
If a question-and-answer session is to follow your presentation, go through your talk and put yourself again in your audience’s shoes. What questions would you have if you were listening to this research presentation? Try to anticipate what people might ask and how you’ll answer. If you have friends or family you can use for practice, encourage them to ask questions so you can gain experience answering them.
9. Do not overwhelm with too much text, busy images, tables, or charts.
Having too much text on a slide or busy, illegible images is a major fault of many academic research presentations. Consider the people in your audience and what they’ll be able to see from where they sit. Keep text limited and plain and figures simple and clear. Explain each image that you show, including axis labels and their meaning, and don’t just assume your audience will understand with a quick glance. Also, you do not need to use the tricks that some digital software allows for slides to fade in or out or advance automatically. In fact, you should avoid the latter entirely.
10. Do not read text word for word.
If you are using some form of presentation that involves slides or words on a screen, do not read these words verbatim. Your best approach is to use short phrases in the slides and then add your own expansion as you talk. That way, your audience sees an important, brief phrase and hears you add context around it. Listening to someone read a slide packed with text while reading along with them is mind numbing.
11. Engage with your audience.
If you are comfortable, you can always present your research in a way that invites audience engagement, asking questions as you go that anticipate a slide you are about to show, a result you are about to introduce, or a conclusion you will present.
San Francisco Edit specializes in scientific editing in the United States and we work with scientists from all over the world.
Sign up for our newsletter, latest from the blog.

Strategies for Avoiding Plagiarism: Ensuring Originality in Academic Writing

Achieving Clarity and Impact: Guidelines for Writing Medical Case Reports

Abstract Versus Introduction: Enhancing Your Academic Writing Skills

Figure Legends: How to Align Your Visuals with Your Narrative
- Knowledge Center
- English Grammar
- Getting Published
- Journal Submission
- Marketing Your Paper and Yourself
- Peer Reviewing a Scientific Paper
- Presenting Your Research
- Thesis vs Dissertation
- What is Scientific Editing
- Why Edit and Types of Editing
- Writing the Manuscript
- Scientific Editing
- Business Editing
- Language Editing
- Newsletters
- Testimonials
- Areas of Expertise
San Francisco Edit 1755 Jackson Street Suite 610 San Francisco, CA 94109 Email: [email protected]
Copyright © 2003-2022 San Francisco Edit. All Rights Reserved.
Join 90,000+ Scientist Who Get Useful Tips For Writing Better Manuscripts
Don't miss out on future newsletters. sign up now..

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
12 Proven Tips to Make an Effective Research Presentation as an Invited Speaker

Tips to Make an Effective Research Presentation
Research presentation tip #1: start confidently, research presentation tip #2: eye to eye contact with the audience, research presentation tip #3: welcome your audience, research presentation tip #4: adjust your voice.
- Research Presentation Tip #5: Memorize your Opening Line
- Research Presentation Tip #6: Use the words “ 'Think for while', 'Imagine', 'Think of', 'Close Your Eyes' ”
Research Presentation Tip #7: Story Telling
Research presentation tip #8: facts and statistics.
- Research Presentation Tip #9: Power of "Pause"
Research Presentation Tip #10: Quote a Great Researcher
Research presentation tip #11: begin with a video, research presentation tip #12: avoid using filler words, side benefits of giving great research presentations, how should i dress for my invited talk at a research conference, can i share my conference presentation slides after my talk with the audience, shall i entertain questions in between my presentation as an invited speaker to a research conference, can you give some tips for a successful q&a session:.
- How to handle questions where I don't know the answers in my presentation?
Introduction
As an invited speaker, delivering an effective research presentation is essential to engage and inform your audience. A well-crafted presentation can help you communicate your research findings, ideas, and insights in a clear, concise, and engaging manner.
However, many presenters face challenges when it comes to delivering a successful presentation. Some of these challenges include nervousness, lack of confidence, and difficulty connecting with the audience.
In this article, we will discuss tips to help you make an effective research presentation as an invited speaker. We will cover strategies to prepare for your presentation, ways to deliver your presentation with confidence and impact, and common mistakes to avoid. By following these tips, you can improve your presentation skills and create a compelling and engaging talk that resonates with your audience.
- Tip 1: Start confidently
- Tip 2: Eye To Eye Contact With the Audience
- Tip 3: Welcome Your Audience
- Tip 4: Adjust your Voice
- Tip 5: Memorize your Opening Line
- Tip 6: Use the words “ ‘Think for while’, ‘Imagine’, ‘Think of’, ‘Close Your Eyes’ ”
- Tip 7: Story Telling
- Tip 8: Facts and Statistics
- Tip 9: Power of “Pause”
- Tip 10: Quote a Great Researcher
- Tip 11: Begin with a Video
- Tip 12: Avoid using Filler Words
Starting your presentation confidently is essential as it sets the tone for the rest of your presentation. It will help you grab your audience’s attention and make them more receptive to your message. Here are a few ways you can start confidently.
- Begin with a self-introduction: Introduce yourself to the audience and establish your credibility. Briefly mention your educational background, your professional experience, and any relevant achievements that make you an authority on the topic. For example, “Good morning everyone, my name is John and I’m a researcher at XYZ University. I have a Ph.D. in molecular biology, and my research has been published in several reputable journals.”
- Introduce the topic: Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and provide a brief overview of what you’ll be discussing. This helps the audience understand the context of your research and what they can expect from your presentation. For example, “Today, I’ll be presenting my research on the role of DNA repair mechanisms in cancer development. I’ll be discussing the current state of knowledge in this field, the methods we used to conduct our research and the novel insights we’ve gained from our findings.”
- Start with a strong opening statement: Once you’ve introduced yourself and the topic, start your presentation confidently with a statement that captures the audience’s attention and makes them curious to hear more. As mentioned earlier, you could use a strong opening statement, a powerful visual aid, or show enthusiasm for your research. For example:
- “Have you ever wondered how artificial intelligence can be used to predict user behaviour? Today, I’ll be sharing my research on the latest AI algorithms and their potential applications in the field of e-commerce.”
- “Imagine a world where cybersecurity threats no longer exist. My research is focused on developing advanced security measures that can protect your data from even the most sophisticated attacks.”
- “Think for a moment about the amount of data we generate every day. My research focuses on how we can use machine learning algorithms to extract meaningful insights from this vast amount of data, and ultimately drive innovation in industries ranging from healthcare to finance.”
By following these steps, you’ll be able to start your research presentation confidently, establish your credibility and expertise, and create interest in your topic.
Speaking confidently as an invited speaker can be a daunting task, but there are ways to prepare and feel more confident. One such way is through practising yoga. Yoga is a great tool for reducing stress and anxiety, which can be major barriers to confident public speaking.
By practising yoga, you can learn to control your breathing, calm your mind, and increase your focus and concentration. All of these skills can help you feel more centred and confident when it’s time to give your presentation.
If you’re interested in learning more about the benefits of yoga, check out our blog post on the subject YOGA: The Ultimate Productivity Hack for Ph.D. Research Scholars and Researchers .
If you’re ready to dive deeper and start your own yoga practice, be sure to download my e-book on :
Unlock Your Research Potential Through Yoga: A Research Scholar’s Companion
A large number of audiences in the presentation hall make you feel jittery and lose your confidence in no time. This happens because you are seeing many of the audience for the first time and you don’t know their background and their knowledge of the subject in which you are presenting.
The best way to overcome this fear is to go and attack the fear itself. That is come at least 10-15 minutes early to the conference room and start interacting with the people over there. This short span of connectivity with a few of the audience will release your tension.
When you occupy the stage for presenting, the first thing you need to do is gaze around the room, establish one-to-one eye contact, and give a confident smile to your audience whom you had just met before the start of the presentation.
Just gazing around the presentation hall will make you feel connected to everyone in the hall. Internally within your mind choose one of the audience and turn towards him/her make eye contact and deliver a few sentences, then proceed to the next audience and repeat the same set of steps.
This will make everyone in the room feel that you are talking directly to them. Make the audience feel that you are engaging with them personally for this topic, which makes them invest fully in your topic.
The third tip for making an effective research presentation is to welcome your audience. This means taking a few minutes to greet your audience, introduce yourself, and set the tone for your presentation. Here are a few ways you can welcome your audience:
- Greet your audience: Start by greeting your audience with a smile and a warm welcome. This will help you establish a connection with your audience and put them at ease.
- Introduce yourself: Introduce yourself to the audience and give a brief background on your expertise and how it relates to your presentation. This will help your audience understand your qualifications and why you’re the right person to be delivering the presentation.
- Explain the purpose of your presentation: Explain to your audience why you’re presenting your research and what they can expect to learn from your presentation. This will help your audience understand the context of your research and what they can expect from your presentation.
- Set the tone: Set the tone for your presentation by giving a brief overview of your presentation structure and what your audience can expect throughout your presentation. This will help your audience understand what to expect and keep them engaged.
Here are a few examples of how you can welcome your audience:
- If you’re presenting to a group of industry professionals, welcome them by acknowledging their expertise and experience. This will show that you value their knowledge and experience.
- If you’re presenting to a group of students or academics, welcome them by acknowledging their interest in your research area. This will help you establish a connection with your audience and show that you’re excited to share your research with them.
- If you’re presenting to a mixed audience, welcome them by acknowledging their diversity and the different perspectives they bring to the presentation. This will help you set an inclusive tone and show that you’re open to different viewpoints.
Overall, welcoming your audience is an important aspect of delivering an effective research presentation. It helps you establish a connection with your audience, set the tone for your presentation, and keep your audience engaged throughout your presentation.
In my earlier days of presentations, I just used to go on stage and start my presentations without greeting anyone. Later I learned stage etiquette with the help of my fellow research scholars and underwent professional etiquette courses .
The fourth tip for making an effective research presentation is to adjust your voice. This means using your voice effectively to convey your message and engage your audience. Here are a few ways you can adjust your voice during your research presentation:
- Speak clearly: Speak clearly and enunciate your words so that your audience can understand what you’re saying. Avoid speaking too fast or mumbling, which can make it difficult for your audience to follow your presentation.
- Use a varied pace: Use a varied pace to keep your audience engaged. Speak slowly and clearly when you’re making important points, and speed up when you’re discussing less important points. This will help you maintain your audience’s attention throughout your presentation.
- Use a varied pitch: Use a varied pitch to convey emotion and emphasize important points. Lower your pitch when you’re discussing serious or important topics, and raise your pitch when you’re excited or enthusiastic.
- Use pauses: Use pauses to emphasize important points and give your audience time to reflect on what you’re saying. Pausing also helps to break up your presentation and make it easier for your audience to follow.
Here are a few examples of how you can adjust your voice during your research presentation:
- If you’re discussing a complex or technical topic, speak slowly and clearly so that your audience can understand what you’re saying. Use pauses to emphasize important points and give your audience time to reflect on what you’re saying.
- If you’re discussing an exciting or enthusiastic topic, raise your pitch and use a varied pace to convey your excitement to your audience. This will help you engage your audience and keep them interested in your presentation.
- If you’re discussing a serious or emotional topic, lower your pitch and use a slower pace to convey the gravity of the situation. Use pauses to emphasize important points and give your audience time to process what you’re saying.
Overall, adjusting your voice is an important aspect of delivering an effective research presentation. It helps you convey your message clearly, engage your audience, and keep their attention throughout your presentation.
Many researchers are less talkative and speak with a very low voice and this makes their concepts unheard by other researchers. To overcome this drawback, they go for vocal coaching to improve their voice modulation.
Research Presentation Tip #5: Memorize your Opening Line
The fifth tip for making an effective research presentation is to memorize your opening line. This means having a powerful and memorable opening line that will grab your audience’s attention and set the tone for your presentation. Here are a few ways you can create a memorable opening line:
- Use a quote or statistic: Start your presentation with a powerful quote or statistic that relates to your research. This will grab your audience’s attention and show them why your research is important.
- Use a story or anecdote: Use a personal story or anecdote to illustrate the importance of your research. This will help you connect with your audience on an emotional level and show them why your research is relevant to their lives.
- Ask a question: Ask your audience a thought-provoking question that relates to your research. This will help you engage your audience and get them thinking about your topic.
Once you’ve created a memorable opening line, it’s important to memorize it so that you can deliver it confidently and without hesitation. Here are a few examples of powerful opening lines:
- “In the United States, someone dies of a drug overdose every seven minutes. Today, I want to talk to you about the opioid epidemic and what we can do to prevent it.”
- “When I was a child, my grandmother was diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease. Today, I want to share with you the latest research on Alzheimer’s and what we can do to slow its progression.”
- “Have you ever wondered why some people are more resilient than others? Today, I want to talk to you about the science of resilience and how we can use it to overcome adversity.”
Overall, memorizing your opening line is an important aspect of delivering an effective research presentation. It helps you grab your audience’s attention, set the tone for your presentation, and establish your credibility as a speaker.
Remembering the concepts at the right time and in the right sequence is critical for every researcher. Few of my research scholars face the problem of forgetting everything once they reach the stage for presentation. To overcome this difficulty I gift them with one of my favourite books on improving memory power: “Limitless by Jim Quick” . This book has changed many lives. You can also try.
Research Presentation Tip #6: Use the words “ ‘Think for while’, ‘Imagine’, ‘Think of’, ‘Close Your Eyes’ ”
The sixth tip for making an effective research presentation is to use specific phrases that encourage your audience to think, imagine, and engage with your presentation. Here are a few examples of phrases you can use to encourage your audience to engage with your presentation:
- “Think for a moment about…” This phrase encourages your audience to reflect on a particular point or idea that you’ve just discussed. For example, “Think for a moment about the impact that climate change is having on our planet.”
- “Imagine that…” This phrase encourages your audience to visualize a particular scenario or idea. For example, “Imagine that you’re living in a world without access to clean water. How would your daily life be affected?”
- “Think of a time when…” This phrase encourages your audience to reflect on their own experiences and relate them to your presentation. For example, “Think of a time when you felt overwhelmed at work. How did you manage that stress?”
- “Close your eyes and picture…” This phrase encourages your audience to use their imagination to visualize a particular scenario or idea. For example, “Close your eyes and picture a world without poverty. What would that look like?”
By using these phrases, you can encourage your audience to actively engage with your presentation and think more deeply about your research. Here are a few examples of how you might incorporate these phrases into your presentation:
- “Think for a moment about the impact that our use of plastics is having on our environment. Each year, millions of tons of plastic end up in our oceans, harming marine life and polluting our planet.”
- “Imagine that you’re a scientist working to develop a cure for a deadly disease. What kind of research would you conduct, and what challenges might you face?”
- “Think of a time when you had to overcome a significant challenge. How did you persevere, and what lessons did you learn from that experience?”
- “Close your eyes and picture a world where renewable energy is our primary source of power. What benefits would this have for our planet, and how can we work together to make this a reality?”
Overall, using phrases that encourage your audience to think and engage with your presentation is an effective way to make your research presentation more impactful and memorable.
The seventh tip for making an effective research presentation is to incorporate storytelling into your presentation. Storytelling is a powerful way to connect with your audience, illustrate your points, and make your research more engaging and memorable.
People love stories, but your story has to be relevant to your research. You can craft a story about an experience you had and tell how you could able to define your research problem based on the experience you had. This makes your presentation both interesting and incorporates information about the work you are carrying out.
Storytelling or sharing your own experience is the best way to connect with your audience. Many researchers use this technique and it remains one of the most critical pieces to becoming an effective presenter.
Here are a few examples of how you can incorporate storytelling into your presentation:
- Personal stories: Use a personal story to illustrate the importance of your research. For example, if you’re researching a new cancer treatment, you might share a story about a friend or family member who has been affected by cancer. This personal connection can help your audience relate to your research on a more emotional level.
- Case studies: Use a case study to illustrate how your research has been applied in the real world. For example, if you’re researching the impact of a new educational program, you might share a case study about a school that has implemented the program and seen positive results.
- Historical examples: Use a historical example to illustrate the significance of your research. For example, if you’re researching the impact of climate change, you might share a story about the Dust Bowl of the 1930s to illustrate the devastating effects of drought and soil erosion.
- Analogies: Use an analogy to explain complex concepts or ideas. For example, if you’re researching the workings of the brain, you might use the analogy of a computer to help your audience understand how neurons communicate with each other.
By incorporating storytelling into your presentation, you can help your audience connect with your research on a more personal level and make your presentation more memorable. Here are a few examples of how you might incorporate storytelling into your presentation:
- “When my mother was diagnosed with cancer, I felt helpless and afraid. But thanks to the groundbreaking research that is being done in this field, we now have more treatment options than ever before. Today, I want to share with you the latest research on cancer treatments and what we can do to support those who are fighting this disease.”
- “Imagine for a moment that you’re a small business owner trying to grow your online presence. You’ve heard that search engine optimization (SEO) is important for driving traffic to your website, but you’re not sure where to start. That’s where my research comes in. By analyzing millions of search queries, I’ve identified the key factors that search engines use to rank websites. Using this information, I’ve developed a new algorithm that can help businesses like yours optimize their websites for better search engine rankings. Imagine being able to reach more customers and grow your business, all thanks to this new algorithm. That’s the power of my research.”
In these examples, the speaker is using storytelling to help the audience understand the real-world impact of their research in a relatable way. By framing the research in terms of a relatable scenario, the speaker is able to engage the audience and make the research feel more relevant to their lives. Additionally, by highlighting the practical applications of the research, the speaker is able to demonstrate the value of the research in a tangible way.
Here I recommend without any second thought “ Storytelling with Data: A Data Visualization Guide for Business Professionals ” by Cole Nussbaumer Knaflic. This is one of the powerful techniques to showcase data in the form of graphs and charts.
The eighth tip for making an effective research presentation is to incorporate facts and statistics into your presentation. Facts and statistics can help you communicate the significance of your research and make it more compelling to your audience.
Make your audience curious about your topic with a fact they didn’t know. Explaining the importance of your topic to your audience is essential. Showcasing data and statistics to prove a point remains a critical strategy not just at the beginning but also throughout. Statistics can be mind-numbing but if there is some compelling information that can help further the conversation.
Here are a few examples of how you might use facts and statistics in your research presentation:
- Contextualize your research: Use statistics to provide context for your research. For example, if you’re presenting on the prevalence of a particular disease, you might start by sharing statistics on how many people are affected by the disease worldwide.
- Highlight key findings: Use facts and statistics to highlight the key findings of your research. For example, if you’re presenting on new drug therapy, you might share statistics on the success rate of the therapy and how it compares to existing treatments.
- Support your arguments: Use facts and statistics to support your arguments. For example, if you’re arguing that a particular policy change is needed, you might use statistics to show how the current policy is failing and why a change is necessary.
- Visualize your data: Use graphs, charts, and other visual aids to help illustrate your data. This can make it easier for your audience to understand the significance of your research. For example, if you’re presenting on the impact of climate change, you might use a graph to show the rise in global temperatures over time.
Here’s an example of how you might use facts and statistics in a research presentation:
“Did you know that over 80% of internet users own a smartphone? That’s a staggering number when you think about it. And with the rise of mobile devices, it’s more important than ever for businesses to have a mobile-friendly website. That’s where my research comes in.
By analyzing user behaviour and website performance data, I’ve identified the key factors that make a website mobile-friendly. And the results are clear: mobile-friendly websites perform better in search engine rankings, have lower bounce rates, and are more likely to convert visitors into customers. By implementing the recommendations from my research, businesses can improve their online presence and reach more customers than ever before.”
In this example, the speaker is using statistics to provide context for their research (the high prevalence of smartphone ownership) and to support their argument (that businesses need to have mobile-friendly websites).
By emphasizing the benefits of mobile-friendly websites (better search engine rankings, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates), the speaker is able to make the research more compelling to their audience. Finally, by using concrete examples (implementing the recommendations from the research), the speaker is able to make the research feel actionable and relevant to the audience.
In my blog posts on the benefits of using graphs and tables in research presentations, I have presented different ways that these tools can enhance the impact and effectiveness of your research presentation. By incorporating graphs and tables, you can help your audience to engage more deeply with your research and better grasp the significance of your findings. To learn more about the benefits of using graphs and tables in research presentations, check out my blog posts listed below, on the subject.
- Maximizing the Impact of Your Research Paper with Graphs and Charts
- Best Practices for Designing and Formatting Tables in Research Papers
You can also refer the book “Information Visualization: An Introduction” for getting more clarity on the representation of facts and statistics.
Research Presentation Tip #9: Power of “Pause”
The ninth tip for making an effective research presentation is to use the power of “pause.” Pausing at key moments in your presentation can help you emphasize important points, allow your audience to process information, and create a sense of anticipation.
We are all uncomfortable when there is a pause. Yet incorporating pause into your presentation can be a valuable tool causing the audience to be attentive to what you are going to say next.
A pause is an effective way to grab attention. There are two ways you might use this technique. After you are introduced, walk on stage and say nothing. Simply pause for three to five seconds and wait for the full attention of the audience. It’s a powerful opening. Depending on the audience, you might need to pause for longer than five seconds.
At another point in your presentation, you might be discussing the results or you are about to provide important information, that’s when you pause to grab attention. You’ll probably feel uncomfortable when you first try this technique, but it’s worth mastering.
Here are a few examples of how you might use the power of the pause in your research presentation:
- Emphasize key points: Pause briefly after making an important point to allow your audience to absorb the information. For example, if you’re presenting on the benefits of a new product, you might pause after stating the most compelling benefits to give your audience time to reflect on the information.
- Create anticipation: Pause before revealing a key piece of information or making a surprising statement. This can create a sense of anticipation in your audience and keep them engaged. For example, if you’re presenting on the results of a study, you might pause before revealing the most surprising or unexpected finding.
- Allow time for reflection: Pause after asking a thought-provoking question to give your audience time to reflect on their answer. This can help create a more interactive and engaging presentation. For example, if you’re presenting on the impact of social media on mental health, you might pause after asking the audience to reflect on their own social media use.
- Control the pace: Use pauses to control the pace of your presentation. Pausing briefly before transitioning to a new topic can help you signal to your audience that you’re about to move on. This can help prevent confusion and make your presentation more organized.
Here’s an example of how you might use the power of the pause in a research presentation:
“Imagine being able to reduce the risk of heart disease by 50%. That’s the potential impact of my research. By analyzing the diets and lifestyles of over 10,000 participants, I’ve identified the key factors that contribute to heart disease. And the results are clear: by making a few simple changes to your diet and exercise routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease. So, what are these changes? Pause for effect. It turns out that the most important factors are a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, and limited alcohol consumption.”
In this example, the speaker is using the pause to create anticipation before revealing the most important findings of their research. By pausing before revealing the key factors that contribute to heart disease, the speaker is able to create a sense of anticipation and emphasize the importance of the information. By using the power of the pause in this way, the speaker is able to make their research presentation more engaging and memorable for the audience.
The tenth tip for making an effective research presentation is to quote a great researcher. By including quotes from respected researchers or experts in your field, you can add credibility to your presentation and demonstrate that your research is supported by other respected professionals.
Quoting someone who is a well-known researcher in your field is a great way to start any presentation. Just be sure to make it relevant to the purpose of your speech and presentation. If you are using slides, adding a picture of the person you are quoting will add more value to your presentation.
Here are a few examples of how you might use quotes in your research presentation:
- Begin with a quote: Starting your presentation with a quote from a respected researcher can help set the tone and establish your credibility. For example, if you’re presenting on the benefits of exercise for mental health, you might begin with a quote from a well-known psychologist or psychiatrist who has researched the topic.
- Use quotes to support your argument: Including quotes from experts who support your argument can help reinforce your ideas and add credibility to your presentation. For example, if you’re presenting on the importance of early childhood education, you might include a quote from a respected educational psychologist who has studied the topic.
- Challenge conventional wisdom: Including quotes from experts who challenge conventional wisdom can help you make a more compelling argument and stand out from other presenters. For example, if you’re presenting on the effects of technology on social interaction, you might include a quote from a respected sociologist who argues that technology can actually improve social connections.
- Add a personal touch: Including quotes from researchers who have inspired you personally can help you connect with your audience and add a more personal touch to your presentation. For example, if you’re presenting on the importance of diversity in the workplace, you might include a quote from a researcher who has inspired you to pursue your own research on the topic.
Here’s an example of how you might use a quote in a research presentation:
“As the great psychologist Abraham Maslow once said, ‘What a man can be, he must be.’ This quote perfectly captures the essence of my research on human potential. By analyzing the lives of highly successful individuals, I’ve identified the key factors that contribute to success. And the results are clear: by cultivating a growth mindset, setting ambitious goals, and surrounding yourself with supportive people, you can unlock your full potential and achieve greatness.”
In this example, the speaker is using a quote from a respected psychologist to support their argument about human potential. By including the quote, the speaker is able to add credibility to their presentation and demonstrate that their research is supported by other respected professionals in the field. By using quotes in this way, the speaker is able to make their research presentation more engaging and persuasive for the audience.
The eleventh tip for making an effective research presentation is to begin with a video. Using a video at the beginning of your presentation can capture the audience’s attention and help establish the theme of your talk
Video remains a powerful mechanism to begin a presentation. Limit your videos to 2–3 minutes. People like video, and it can capture their attention, but they can also tire of it easily. It gives the presenter and the attendees a break from each other. Sometimes, you just look for visible reactions from the audience that might provide a transition from video back to speaking. Conversely, for the attendees, the video provides a break from the speaker.
Here are a few examples of how you might use a video in your research presentation:
- Introduce a new technology: Use a video to introduce a new technology or innovation that is related to your research. For example, if you’re presenting on the potential of artificial intelligence in healthcare, you might use a video that shows how AI is being used to detect cancer early.
- Demonstrate a problem: Use a video to demonstrate a problem or challenge that your research is trying to solve. For example, if you’re presenting on the importance of cybersecurity in the finance industry, you might use a video that shows how easily hackers can gain access to sensitive financial information.
- Showcase your research: Use a video to showcase your own research and the methods you used to conduct it. For example, if you’re presenting on a new algorithm for image recognition, you might use a video that shows how the algorithm works in action.
- Add a personal touch: Use a video to share a personal story or experience that relates to your research. For example, if you’re presenting on the impact of technology on society, you might use a video that shows how technology has changed your own life.
Here’s an example of how you might use a video at the beginning of a research presentation in computer science:
“Before I dive into my research on the potential of blockchain technology in supply chain management, I want to show you a video that demonstrates the challenges that the industry currently faces. As you’ll see, there are numerous pain points that blockchain could help to address, from tracking the provenance of goods to reducing fraud and counterfeiting. By leveraging the power of blockchain, we can create a more transparent, efficient, and secure supply chain for everyone involved.”
In this example, the speaker is using a video to demonstrate a problem or challenge that their research is trying to solve. By showing the audience the current pain points in supply chain management, the speaker is able to establish the need for blockchain technology and capture the audience’s attention. By using a video in this way, the speaker is able to make their research presentation more engaging and impactful for the audience.
One sincere piece of advice while preparing the video is not to install the full video and start searching for the clip to be displayed to the audience. If you show this side or that side of the video content not relevant to the context, the audience may lose patience and drift away from the presentation. This shows your unpreparedness for the presentation. I suggest you go ahead with professional video editing software to edit your video before showing it to your audience.
When giving a research presentation, it’s important to sound confident and knowledgeable. However, using too many filler words such as “ok”, “so”, and “umms” can make you sound unsure of yourself and can distract from the content of your presentation.
Here are a few tips to help you avoid using too many filler words:
- Practice your presentation: One of the best ways to reduce the use of filler words is to practice your presentation. By rehearsing what you want to say, you’ll become more comfortable with the content and won’t need to rely on filler words as much.
- Use a script: If you’re prone to using filler words, consider writing out a script for your presentation. This will help you stay on track and avoid unnecessary pauses or verbal crutches.
- Record yourself: Another helpful strategy is to record yourself giving your presentation. By listening back to the recording, you can identify any filler words or other verbal tics and work on eliminating them in future presentations.
- Take pauses: Instead of relying on filler words to fill pauses in your presentation, try taking intentional pauses. This will help you gather your thoughts and emphasize important points.
Here’s an example of how to avoid using too many filler words in a research presentation:
“Today, I want to talk to you about the impact of machine learning on cybersecurity. Ok, so, umm, as you all know, cybersecurity is a critical issue for businesses and organizations. But did you know that machine learning can help to identify and mitigate cyber threats before they become a major problem? By using algorithms to analyze data, we can create more effective security protocols and protect sensitive information from being compromised. So, in conclusion, machine learning has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach cybersecurity.”
In this example, the speaker is using several filler words throughout the presentation, which can detract from the content and make them sound less confident. By practising their presentation and focusing on eliminating filler words, the speaker can deliver a more polished and engaging presentation that highlights the important points.
Many presenters, though have good content fail to impress the audience by using too many “ok” “so” and “umms” which shows a lack of good communication skills. This can be due to stage fear/poor preparation/happen unconsciously.
Such filler words can ruin your credibility despite how innocent they look. One tip for avoiding this annoying habit is to practice your speech or presentation multiple times beforehand in front of your supervisor/research scholars / yourself in front of the mirror. If you are hesitant then the best option is to record your speech on your mobile and check for the mistakes unconsciously you make.
Giving a good research presentation as a keynote speaker is an excellent opportunity to showcase your expertise and knowledge in your research domain. As a keynote speaker, you can communicate your research findings, methodologies, and the impact of your research to a wider audience.
A well-delivered presentation can also demonstrate your ability to engage with diverse stakeholders and effectively communicate complex ideas. This can be an advantage when looking for research consultancy work, as potential clients or employers can assess your ability to deliver quality work, understand their needs, and provide innovative solutions to their problems.
If you are interested in exploring research consultancy jobs, check out the link Research Consultancy: An Alternate Career for Researchers to discover some exciting opportunities in your research domain.
Delivering a successful research presentation requires careful planning, practice, and attention to detail. By starting confidently, making eye contact with your audience, and using effective communication techniques like storytelling and statistics, you can engage your audience and communicate your research findings in a compelling way.
Remember to adjust your voice, avoid filler words, and take intentional pauses to keep your audience engaged and focused. By following these tips and incorporating your own unique style and perspective, you can deliver a powerful and memorable research presentation that showcases your expertise and leaves a lasting impression.
Frequently Asked Questions
As a speaker at a research conference, it’s important to dress professionally and appropriately to make a positive impression on the audience and fellow researchers. Here are some general guidelines for what to wear: Business Formal Attire : Most research conferences have a business formal dress code. This typically means wearing a suit or dress pants/skirt with a collared shirt/blouse. For men, a suit with a tie is appropriate, and for women, a pantsuit or a skirt/dress with a blazer is a good choice. Neutral and Classic Colors : Stick to neutral and classic colours like black, navy, grey, or beige for a polished and sophisticated look. Avoid loud or overly bright colors and patterns that may distract from your presentation. Comfortable and Well-Fitted Clothing : Ensure that your clothing fits well and is comfortable to wear for an extended period. This will help you feel more at ease during your presentation. Appropriate Footwear : Wear closed-toe shoes that are comfortable and complement your outfit. For men, dress shoes are ideal, and for women, low-heeled pumps or flats are a good choice. Minimal Accessories : Keep your accessories simple and minimal. A wristwatch, small earrings, and a modest necklace can add a touch of elegance without being distracting. Grooming and Hygiene : Pay attention to personal grooming and hygiene. Make sure your hair is well-groomed, and avoid heavy cologne or perfume, as some attendees may be sensitive to strong scents. Bring Layers : Conference venues can sometimes be chilly due to air conditioning, so consider bringing a light sweater or jacket that complements your outfit. Check the Conference Theme : Occasionally, research conferences may have specific themes or cultural considerations. In such cases, you can subtly incorporate elements related to the theme or culture into your outfit if appropriate. You can visit my blog post on ” How to dress for academic / research conferences ” for further details.
Absolutely! Sharing your conference presentation slides with the audience after your talk can be a great way to provide additional value to those who attended your presentation and those who couldn’t make it to the event.
As an invited speaker at a research conference, it is generally expected and encouraged to entertain questions from the audience during or after your presentation. Q&A sessions are a valuable part of academic conferences as they allow attendees to engage with the speaker, seek clarifications, and gain further insights into the research being presented. However, a few speakers as well as the audience may get distracted by the questions asked during the presentation. Check your preparedness and the mood of the audience and then decide.
Tips for a Successful Q&A Session: Be Prepared : Anticipate potential questions that may arise from your presentation and be prepared to answer them. This will boost your confidence during the Q&A. Encourage Questions : After your presentation, let the audience know that you welcome their questions. Creating a supportive and inclusive environment will encourage more participation. Active Listening : Listen carefully to each question and ensure you understand it before responding. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification to provide the best possible answer. Be Respectful and Professional : Even if you receive challenging or critical questions, respond in a respectful and professional manner. Avoid becoming defensive and maintain a positive tone. Manage Time : If there’s a specific time allocated for the Q&A session, manage it effectively so that you can address as many questions as possible without exceeding the allocated time.
How to handle questions where I don’t know the answers in my presentation?
Handling a question during your presentation when you don’t know the answer is a common scenario, and it’s essential to respond gracefully and professionally. Here’s how to handle such situations: Stay Calm and Composed : Take a deep breath and remain calm. It’s okay not to know the answer to every question, and the audience understands that. Acknowledge the Question : Show appreciation for the question and the person who asked it. You can say something like, “Thank you for the question; that’s an interesting point to consider.” Be Honest : It’s best to be honest if you don’t know the answer. Avoid making up information or guessing as it can harm your credibility. Admit You Don’t Know : You can respond with a polite acknowledgement that you don’t have the information at hand. For example, say, “I’m afraid I don’t have the answer to that question right now.” Offer to Follow Up : Express your willingness to find the answer later. You can say, “I’ll make sure to look into this further and get back to you with an answer.” Redirect the Question : If appropriate, you can redirect the question to the audience or to someone who might have more expertise on the topic. Stay Positive : Maintain a positive tone throughout your response. Avoid apologizing excessively or sounding defensive. Bridge to Related Topics : If you can’t answer the specific question, try to bridge it to related topics you are familiar with. This way, you can still contribute to the discussion. Use It as a Learning Opportunity : If the question raises a valid point you haven’t considered before, acknowledge it as a learning opportunity. You can say, “That’s an excellent question, and it gives me something to think about.” Learn for the Future : After the presentation, take note of the questions you couldn’t answer and use them as a basis for further research or study. This will help you better prepare for similar situations in the future.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- PhD or Industry Job? A Comprehensive Career Guide
- Post Doc Positions in India
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- How to Request for Journal Publishing Charge (APC) Discount or Waiver?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

Get in touch
555-555-5555

Limited time offer: 20% off all templates ➞

Scientific Presentation Guide: How to Create an Engaging Research Talk
Creating an effective scientific presentation requires developing clear talking points and slide designs that highlight your most important research results..
Scientific presentations are detailed talks that showcase a research project or analysis results. This comprehensive guide reviews everything you need to know to give an engaging presentation for scientific conferences, lab meetings, and PhD thesis talks. From creating your presentation outline to designing effective slides, the tips in this article will give you the tools you need to impress your scientific peers and superiors.

Step 1. Create a Presentation Outline
The first step to giving a good scientific talk is to create a presentation outline that engages the audience at the start of the talk, highlights only 3-5 main points of your research, and then ends with a clear take-home message. Creating an outline ensures that the overall talk storyline is clear and will save you time when you start to design your slides.
Engage Your Audience
The first part of your presentation outline should contain slide ideas that will gain your audience's attention. Below are a few recommendations for slides that engage your audience at the start of the talk:
- Create a slide that makes connects your data or presentation information to a shared purpose, such as relevance to solving a medical problem or fundamental question in your field of research
- Create slides that ask and invite questions
- Use humor or entertainment

Identify Clear Main Points
After writing down your engagement ideas, the next step is to list the main points that will become the outline slide for your presentation. A great way to accomplish this is to set a timer for five minutes and write down all of the main points and results or your research that you want to discuss in the talk. When the time is up, review the points and select no more than three to five main points that create your talk outline. Limiting the amount of information you share goes a long way in maintaining audience engagement and understanding.

Create a Take-Home Message
And finally, you should brainstorm a single take-home message that makes the most important main point stand out. This is the one idea that you want people to remember or to take action on after your talk. This can be your core research discovery or the next steps that will move the project forward.
Step 2. Choose a Professional Slide Theme
After you have a good presentation outline, the next step is to choose your slide colors and create a theme. Good slide themes use between two to four main colors that are accessible to people with color vision deficiencies. Read this article to learn more about choosing the best scientific color palettes .
You can also choose templates that already have an accessible color scheme. However, be aware that many PowerPoint templates that are available online are too cheesy for a scientific audience. Below options to download professional scientific slide templates that are designed specifically for academic conferences, research talks, and graduate thesis defenses.
Step 3. Design Your Slides
Designing good slides is essential to maintaining audience interest during your scientific talk. Follow these four best practices for designing your slides:
- Keep it simple: limit the amount of information you show on each slide
- Use images and illustrations that clearly show the main points with very little text.
- Read this article to see research slide example designs for inspiration
- When you are using text, try to reduce the scientific jargon that is unnecessary. Text on research talk slides needs to be much more simple than the text used in scientific publications (see example below).
- Use appear/disappear animations to break up the details into smaller digestible bites
- Sign up for the free presentation design course to learn PowerPoint animation tricks
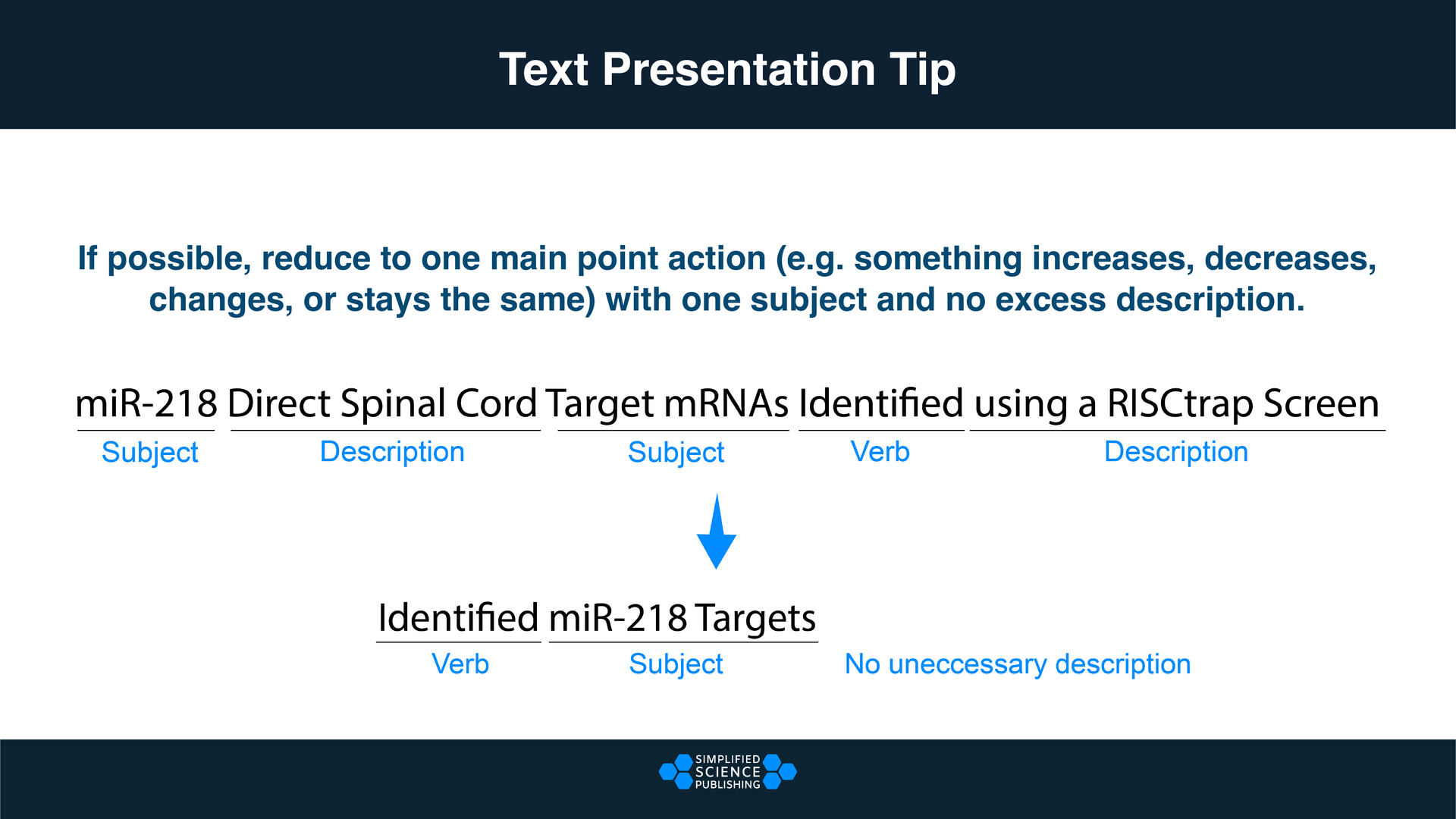
Scientific Presentation Design Summary
All of the examples and tips described in this article will help you create impressive scientific presentations. Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community.
Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home message.
Step 2. Choose Slide Theme. Use a slide template or theme that looks professional, best represents your data, and matches your audience's expectations. Do not use slides that are too plain or too cheesy.
Step 3. Design Engaging Slides. Effective presentation slide designs use clear data visualizations and limits the amount of information that is added to each slide.
And a final tip is to practice your presentation so that you can refine your talking points. This way you will also know how long it will take you to cover the most essential information on your slides. Thank you for choosing Simplified Science Publishing as your science communication resource and good luck with your presentations!
Interested in free design templates and training?
Explore scientific illustration templates and courses by creating a Simplified Science Publishing Log In. Whether you are new to data visualization design or have some experience, these resources will improve your ability to use both basic and advanced design tools.
Interested in reading more articles on scientific design? Learn more below:

Data Storytelling Techniques: How to Tell a Great Data Story in 4 Steps

Best Science PowerPoint Templates and Slide Design Examples

Free Research Poster Templates and Tutorials
Content is protected by Copyright license. Website visitors are welcome to share images and articles, however they must include the Simplified Science Publishing URL source link when shared. Thank you!
Online Courses
Stay up-to-date for new simplified science courses, subscribe to our newsletter.
Thank you for signing up!
You have been added to the emailing list and will only recieve updates when there are new courses or templates added to the website.
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience and we do not sell data. By using this website, you are giving your consent for us to set cookies: View Privacy Policy
Simplified Science Publishing, LLC
How to create a powerful research presentation

I used to write research reports, which then essentially turned into weighty research presentations. My trick was to copy and paste the information from my report into slides. There was little design or consideration of the flow of my research presentations. Instead, my audience would be facing walls of text while I spoke about the critical information that I couldn’t squeeze into the ever-so-small slides.
It was about four years into my career when I hit a breakthrough with this. I had always been envious of people who could put together beautiful and concise presentations that seemed to flow out of them. I figured, since I was a researcher (with a background in academia), my presentations would have to be ugly and filled with information. However, for this meeting, I had to do a good job. I was presenting research to executives and was hoping for a promotion.
I went through my slides and got to the halfway point when one of the audience members put their hand up. I froze, and my internal dialogue consisted of a cornucopia of swear words and considerations of running out of the room. It was as bad as I thought. The person said they were lost—agreeing nods circled the room—and asked me to “fix-up” the presentation. We would reschedule the meeting for when the slides were more concise and easier to follow.
I had a week to change the way I reported and presented user research. In that week, I overhauled my entire structure and flow into a three-step approach I still follow today:
Before creating the presentation
Creating the presentation
During and after the presentation.
Each step has its preparation that leads to a more thoughtful and deliberate presentation.
.css-1nrevy2{position:relative;display:inline-block;} Before creating the presentation
I no longer start with creating a presentation as my first step. I found that starting with the design and creation of slides was detrimental. Instead, I focused on beginning with ideas that could help me better create the presentation:
Know your audience. Always consider your audience beforehand and the level of information your audience needs (or likely wants). Executive levels don’t want the nitty-gritty details of the study. Instead, they are interested in the overall themes you found and, most importantly, what the implications are for these findings. If you do what I did and present all the research details, you may see eyes glazing over. However, the team directly impacted by the study will want to know more detailed information. One tip: create the same presentation for everyone, but skip specific slides you know won’t be relevant to particular audiences.
Outline the key insights. Before designing your slides, you should feel comfortable with the research and how it all fits together. I determine the critical insights by the information that came up the most frequently from users—usually focused on pain points. I only let myself choose up to five key insights to report.
Think about your teams. Ask yourself: “what is the most important information my team needs to know to make immediate decisions?” The answer to this question will likely mean you have to leave some information out of your report. That’s okay! You can always resurface those findings later when the timing is better, and the team can work on them. Instead, think about what your team needs to know now to make better decisions on their current work.
Keep it short. As mentioned, only consider up to five key insights! If you have many more than that, you might need to break down the presentations into different phases. When you present too much information at once, you lose your audience. I like to have my presentations be around 30-45 minutes, with 15 minutes after for questions.
State your expected outcomes. If you feel comfortable, you can email your expected outcomes to your audience beforehand. For example, I would email the contents/plan of what I want to cover during the presentation and ask if I am missing anything. Doing this before helps to align your presentation with the audience’s expectations.
Now, let’s get started on the actual presentation.
I was missing flow and had an overabundance of information. By prepping with the model above, I was able to cut down on the amount of data. However, I still struggled quite a lot because I like to write things, not show them, but that was an area I was losing my audience. With the feedback I received, I redid the structure of my report. This flow and design are what I use now in almost all of my reports:
First portion
Agenda/contents. This section includes what you will cover during the presentation. By making it clear upfront, your audience will understand what to expect and be better able to follow the presentation flow.
Expected outcomes (reiterated). Hopefully, you were able to share these beforehand. Regardless, I like to repeat or share my expected results of the presentation. For example, at the end of the presentation, the teams can make X or Y decisions by the end or understand A and B implications and what to do next.
About the study. These slides give context to the background of the project, methodology, recruitment, and approach you took to the study. It grounds the audience in understanding why the study happened as it did.
Executive summary (three to five significant insights). Arguably one of the most important slides of the presentation. Remember the three or five insights you outlined above? Those insights should go into this slide with a brief overview, and they will be the driving force for the rest of the presentation.
Second portion (repeat with each insight)
Insight one recap. This slide gives a summary of the first major insight you will tackle.
Findings within the insight. Usually, findings make up insights. These findings are supporting evidence to the overarching insight. I include up to three findings that support each insight.
Deep dive into finding one, two, three. Each deep-dive is a different slide where you explain the finding and include media such as quotes, videos, or photos. It is super key to have this type of evidence (especially videos) because that is how people connect with users outside of research sessions.
Opportunity area for each finding. For each finding, you can highlight an opportunity area. For this, you can include a recommendation or a How Might We statement.
Third portion
Recap of the insights. After going through all the insights and findings, give a general synopsis of your audience’s insights. This slide can mirror the executive study slide.
Overview of the opportunity areas. If you have too many opportunity areas, you can pick the top three to five opportunity areas the teams should focus on in the next quarter or half-year. Think back to the essential information for your teams, and use it to pick the opportunity areas.
Impact/implications. In this slide, write down the implications or impact the research may have. For example, you might have to write that the team is focused on the wrong area or pain point and needs to pivot or that a new innovative product/feature might be a high priority.
Recommendations. If you have pointed recommendations based on pain points, this is the slide to include them! I report on recommendations in a table that consists of the finding, the recommendation based on the finding, and evidence supporting this. For example, I find people cannot fill out a form, so I include that finding, my recommendation, and proof (quote, video, photo).
Links to all raw data. For those who want to dive deeper, include all the other information, such as notes, research summaries, recordings, and any other raw data.
One final tip: try to stay away from fractions when explaining how many participants encountered a particular problem or stated an insight. It is a lot more powerful to say 80% of participants felt X or struggled with Y than it is to say 4/7 participants. You disclose the number of participants at the beginning of the presentation, so there is no need to continue bringing that up.
After putting in this information, I will start playing around with colors, fonts, alignments, and other design elements—first, the content, then the tweaking.
Ask questions, engage people. I always stop at each section to see if there are any questions. You can also use polls or software (such as Mentimeter) to ask questions and engage with your audience.
Request feedback. After each presentation, ask your audience for feedback on what went well and what you could do better. With this information, you can continuously develop and hone your presentations.
Since implementing this process, I have had a lot more engagement and success with my presentations. People pay attention, have an easier time following the information, and then feel more compelled to take action. Having others get excited by, understand, and act on research is such a fulfilling feeling and one of the top outcomes we strive for. Try out this process and see what happens!
Get started for free

Keep reading

Log in or sign up
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Office of Undergraduate Research
Creating a research presentation, by divya ganugapati, our peer research ambassador.
If you are ready to embark upon the exciting and rewarding journey of presenting your research – congrats! Whether complete or in-progress, take a moment to acknowledge all of the hard work you have put in to make it this far in your undergraduate research career. Now is time for the fun and creative part – displaying your research.
There are a number of important questions to consider before beginning your research presentation:
1. Where am I presenting? Students present research in many different environments. While some may travel to other countries to take part in conferences and symposiums, others may choose to stay local and present at UConn’s own Frontiers in Undergraduate Research Poster Exhibition. With this comes the question of travel; are you able to take a 3 x 4 ft research poster with you or is something more transportable like printed power point slides mounted on cardstock a better option? Also, make sure you read the guidelines sent by the conference organizers. There may be specific limitations or criteria to keep in mind, such as size restrictions, poster orientation requirements, or that you have your poster mounted on foam board.
2. Who is my audience? When speaking in public, it is always important to identify your audience. If you are presenting mostly to students your own age, you might choose to format your presentation in an approachable and relatable manner – focus on visuals and refrain from masses of text. However, if your audience primarily consists of distinguished professionals who are masters of your research field, it may be worthwhile to put a spotlight on specificities such as important vocabulary, references to relevant literature, and statistical measures.
3. In what modality am I presenting? At some conferences, presenters are asked to speak about their research in more of a lecture format, in this case you want to make sure you are able to address a large and diverse audience. If given tech equipment, creating a unique Powerpoint or Prezi could be in your best interest. However, if presenters are placed in corridors, auditoriums, or hallways, a poster may be best to attract any passersby. Be sure to understand the format of the event you are presenting at beforehand!
4. What type of project am I presenting? Don’t forget that research is a broad term that encompasses a variety of subjects and projects. Some research projects are confined to the lens of a microscope while others may investigate trans-continental movements. Not all research projects are best displayed and celebrated on a 3 x 4 ft research poster. If you are looking for other options, consider if setting up models, displaying artwork, or creating a video or film would better feature your work.
Once you’ve found the best way to display your research in a professional yet understandable manner, you are ready to start creating! Here are some tips that I have found useful when creating my own presentations:
- Make sure your title is catchy – you want to draw people to your presentation
- Use a font size that is big enough for viewers to read important material from 7-10 feet away
- Avoid colors that make it hard to read words (white text on yellow is not a good idea!)
- Include graphs, tables, or images – as a viewer, having visuals will draw my attention right away and show data in a way I can understand
- Acknowledge important contributors, institutions, and grants
- Keep the text to a minimum (please!!) – use bullets when appropriate and avoid paragraphs
- Re-read, have your co-presenters re-read, have your roommate re-read, have anyone re-read – opening your project on the day of the presentation to find a spelling error can be very disheartening but easily avoidable (been there before, so trust me I know!)
Condensing months to even years of work to around 500 words can be very frustrating and difficult, especially your first time! Luckily, you’re not alone – use your mentors or co-presenters as resources. UConn also has numerous resources for presenters which I highly recommend using if you need some help:
- UConn Office for Undergraduate Research : tips on what to include and how to prepare yourself for presenting ( https://ugradresearch.uconn.edu/poster-presentations/ )
- UConn Brand Standard Templates : use UConn headers and branding that has been pre-approved and available to all! ( https://brand.uconn.edu/downloads/print-templates/uconn-templates )
- UConn Design and Document Production Center: have graphic designers check your work and print right on campus! ( https://ddpc.uconn.edu/ )
Divya is a senior majoring in Cognitive Science and minoring in Chemistry. Click here to learn more about Divya.
- 2018/03/18/Making-a-presentation-from-your-research-proposal
Making a presentation from your research proposal
In theory, it couldn’t be easier to take your written research proposal and turn it into a presentation. Many people find presenting ideas easier than writing about them as writing is inherently difficult. On the other hand, standing up in front of a room of strangers, or worse those you know, is also a bewildering task. Essentially, you have a story to tell, but does not mean you are story telling. It means that your presentation will require you to talk continuously for your alloted period of time, and that the sentences must follow on from each other in a logical narative; i.e. a story.
So where do you start?
Here are some simple rules to help guide you to build your presentation:
- One slide per minute: However many minutes you have to present, that’s your total number of slides. Don’t be tempted to slip in more.
- Keep the format clear: There are lots of templates available to use, but you’d do best to keep your presentation very clean and simple.
- Be careful with animations: You can build your slide with animations (by adding images, words or graphics). But do not flash, bounce, rotate or roll. No animated little clipart characters. No goofy cartoons – they’ll be too small for the audience to read. No sounds (unless you are talking about sounds). Your audience has seen it all before, and that’s not what they’ve come for. They have come to hear about your research proposal.
- Don’t be a comedian: Everyone appreciates that occasional light-hearted comment, but it is not stand-up. If you feel that you must make a joke, make only one and be ready to push on when no-one reacts. Sarcasm simply won’t be understood by the majority of your audience, so don’t bother: unless you’re a witless Brit who can’t string three or more sentences together without.
Keep to your written proposal formula
- You need a title slide (with your name, that of your advisor & institution)
- that put your study into the big picture
- explain variables in the context of existing literature
- explain the relevance of your study organisms
- give the context of your own study
- Your aims & hypotheses
- Images of apparatus or diagrams of how apparatus are supposed to work. If you can’t find anything, draw it simply yourself.
- Your methods can be abbreviated. For example, you can tell the audience that you will measure your organism, but you don’t need to provide a slide of the callipers or balance (unless these are the major measurements you need).
- Analyses are important. Make sure that you understand how they work, otherwise you won’t be able to present them to others. Importantly, explain where each of the variables that you introduced, and explained how to measure, fit into the analyses. There shouldn’t be anything new or unexpected that pops up here.
- I like to see what the results might look like, even if you have to draw graphs with your own lines on it. Use arrows to show predictions under different assumptions.
Slide layout
- Your aim is to have your audience listen to you, and only look at the slides when you indicate their relevance.
- You’d be better off having a presentation without words, then your audience will listen instead of trying to read. As long as they are reading, they aren't listening. Really try to limit the words you have on any single slide (<30). Don’t have full sentences, but write just enough to remind you of what to say and so that your audience can follow when you are moving from point to point.
- Use bullet pointed lists if you have several points to make (Font 28 pt)
- If you only have words on a slide, then add a picture that will help illustrate your point. This is especially useful to illustrate your organism. At the same time, don’t have anything on a slide that has no meaning or relevance. Make sure that any illustration is large enough for your audience to see and understand what it is that you are trying to show.
- Everything on your slide must be mentioned in your presentation, so remove anything that becomes irrelevant to your story when you practice.
- Tables: you are unlikely to have large complex tables in a presentation, but presenting raw data or small words in a table is a way to lose your audience. Make your point in another way.
- Use citations (these can go in smaller font 20 pt). I like to cut out the title & authors of the paper from the pdf and show it on the slide.
- If you can, have some banner that states where you are in your presentation (e.g. Methods, or 5 of 13). It helps members of the audience who might have been daydreaming.
Practice, practice, practice
- It can’t be said enough that you must practice your presentation. Do it in front of a mirror in your bathroom. In front of your friends. It's the best way of making sure you'll do a good job.
- If you can't remember what you need to say, write flash cards with prompts. Include the text on your slide and expand. When you learn what’s on the cards, relate it to what’s on the slide so that you can look at the slides and get enough hints on what to say. Don’t bring flashcards with you to your talk. Instead be confident enough that you know them front to back and back to front.
- Practice with a pointer and slide advancer (or whatever you will use in the presentation). You should be pointing out to your audience what you have on your slides; use the pointer to do this.
- Avoid taking anything with you that you might fiddle with.
Maybe I've got it all wrong?
There are some things that I still need to learn about presentations. Have a look at the following video and see what you think. There are some really good points made here, and I think I should update my example slides to reflect these ideas. I especially like the use of contrast to focus attention.


Making a short presentation based on your research: 11 tips
Markus goldstein, david evans.
Over the past few weeks, we’ve both spent a fair amount of time at conferences. Given that many conferences ask researchers to summarize their work in 15 to 20 minutes, we thought we’d reflect on some ideas for how to do this, and – more importantly – how to do it well.
- You have 15 minutes. That’s not enough time to use the slides you used for that recent 90-minute academic seminar. One recent presentation one of us saw had 52 slides for 15 minutes. No amount of speed talking will get you through this in anything resembling coherence. (And quit speed talking, anyway. This isn’t a FedEx commercial !) There is no magic number of slides since the content you’ll have and how you talk will vary. But if you have more than 15 slides, then #2 is doubly important.
- Practice. This is the great thing about a 15-minute talk: You can actually afford to run through it, out loud. Running through it once in advance can reveal to you – wow! – that it’s actually a 25-minute talk and you need to cut a bunch. Of course, the first time through the presentation it may take a bit longer than you will when you present, but if you have any doubts, practice again (bringing your prep time to a whopping 30 minutes plus a little bit).
- You need a (short) narrative. What is the main story you are trying to tell with this paper? Fifteen minutes works better for communicating a narrative then for taking an audience through every twist and turn of your econometric grandeur. Deciding on your narrative will help with the discipline in the points that follow.
- A model or results? Even if your audience is all academics, you don’t have academic seminar time. So the first thing to do is to figure out which is more important to get across – your model or your empirical results. Then trim the other one down to one slide, max. If the results are your focus (usually the case for us), give the audience a sense of how the model is set up, and what the main implications are as they pertain to the results you will show. Conversely, if it’s the model that’s more important, the empirical results will come later and you can just give the very brief highlights that bolster the key points.
- The literature. Really, really minimal. If you do it at all, choose only the papers that you are either going to build on in a major way or contradict. For some types of discussants, it may help to include them, even if they don’t meet the other criteria. Marc Bellemare takes an even stronger stance: “Never, ever have a literature review in your slides. If literature reviews are boring to read in papers, they are insanely boring to listen to during presentations.”
- Program details. Here it’s a bit of a balance. The audience needs a flavor for the program, they need to understand what it did and how it’s different from other things (particularly other things with some kinds of evidence). But only in exceptional cases (as in, it’s a really different program for theoretical reasons, or you don’t have more than process results yet) do you want this to eat up a lot of your time.
- You don’t have time to go through the nitty gritty of the data. We get that every detail about the survey was fascinating (we spend a lot of our lives thinking about this). But if it’s not key to the story, save it for a longer presentation (or another paper). And if you’re doing a primarily theoretical paper, this is a bullet on one slide.
- Balance and summary stats. Key summary stats that tell the audience who the people are might make the cut, but 3 slides of every variable that you’ll use are going to be slides you either rip through (telling the audience nothing) or waste most of your time on. Summarize the summary stats. On balance tests: you are either balanced or not. If you are, this gets a bullet at most (you can also just say that). If you’re not, tell us what’s up and why we should or should not worry.
- Pre-analysis plan. If you had it, mention it (quickly). If not, don’t. It’s not critical here.
- A picture may be worth 1,000 numbers. Sometimes, taking that really packed table which is currently in 12 point font and turning it into a graph is going to help you with self-control and help your audience with comprehension. Put the significant results in a bar chart, and use asterisks to tell folks which are significant.
- A special warning about presenting your job market paper. When I (Markus) submitted my job market paper to a journal, the referee report came back noting that this was surely a job market paper since it had 40(!) tables. Key example of how everything matters when you just spent four years of your life collecting each observation. Discipline. You have (or will have) an elevator pitch from the job market – use this to trim your presentation.
- Marc Bellemare has a great series of “22 tips for conference and seminar presentations,” many of which apply to short presentations: “Always provide a preview of your results. This isn’t a murder mystery: it’s only when people know where you’re taking them that they can enjoy the scenery along the way.”
- Jeff Leek has a great guide to giving presentations of different lengths, and what your goal should be: “As a scientist, it is hard to accept that the primary purpose of a talk is advertising, not science.” This is doubly true for a 15-minute talk.
- The AEA Committee on the Status of Women in the Economics Profession has a top 10 list. “Never cut and paste a table from your paper onto a slide. These tables are never easy to read and only irritate your audience. Instead, choose a few results that you want to highlight and present them on a slide in no smaller than 28 font.” We’ve pretty much all done this. It’s bad practice. (“I’m sorry you can’t read this table.” “Oh really, then why did you cut and paste that giant table from your paper into the presentation?!”)
- I (Dave) go back and re-read Jesse Shapiro’s guide on “ How to Give an Applied Micro Talk ” from time to time. It’s more geared toward a full-length seminar, but the advice is so good I can’t resist plugging it here.

Lead Economist, Africa Gender Innovation Lab and Chief Economists Office

Senior Fellow, Center for Global Development
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added

How to Make an Effective Research Presentation
Presentation software programs have advanced to the point where you no longer need to be an experienced designer to put together a compelling piece of collateral that conveys your findings about academic research in exactly the right way. With the right materials, the right presentation software, and a little bit of time, you can visualize any data that you have in the form of a terrific presentation that sells your research better than numbers alone ever could. However, this does not mean that you shouldn’t keep in mind a few things. As both a marketing tool and a means to convey information, presentations are helpful because they are malleable—the format can essentially be anything you need it to be at any given time. The other side of this, however, is that there are certain traps that are all too easy for even experts to fall into that will harm your ultimate message, not help it. If you wish to learn how to make a professional research presentation as an author, or a researcher, then you should avoid some mistakes at all costs.
Mistakes to Avoid
As a researcher or a student, your number one goal isn’t just to provide insight into a topic—it’s to do so in a compelling way. It is important to communicate ideas in a way that is both easy to understand for people who haven’t completed the work you have and to do so in a compelling and engaging way. In many ways, it’s a lot like telling a story—albeit one that is heavily research-oriented. Every story has a beginning, middle, and end and you need to ensure that the content in the presentation has a proper narrative flow.
In many ways, your presentation will operate exactly along the same lines. To that end, always remember to make sure that the information is presented not only in the right manner but also in the right order to complement intent and maximize impact. If you have three subtopics within a presentation, all of which are related but are still different ideas, don’t mix and match the content. Don’t jump from one topic to the other and back again—you’re only going to lose focus and eventually, the attention of your reader.
If you start preparing your presentation and realize that you’re actually kind of covering two distinct and different topics, don’t be afraid to break one presentation into two. You’ll be able to devote more attention to promoting each idea and you’ll walk away with two great pieces of research presentations instead of one “okay” one.
Length of Your Presentation
Another element of your presentation that you need to pay extremely close attention to is the length. This goes back to another one of the old rules of storytelling: “Whatever you do, don’t overstay your welcome.” While it is true that presentations are naturally designed to be a longer form than something like an Infographic, it’s important to recognize when you’re asking too much of your reader/viewer. A presentation isn’t just a visualized form of something like a white paper. It’s a unique medium all unto itself.
When you start preparing your presentation for the first time, feel free to include as many slides or as much information as you want. Also, don’t forget that there are three versions of your presentation that will exist—the initial outline, the “first draft” of the presentation and the final edited version that you release. Make an effort to only include information that A) is needed to understand your research topic, and B) is necessary to contextualize your findings or the points you’re trying to make. Go through your presentation from start to finish and really try to experience it with fresh eyes—the same way your audience will.
Does it feel like the end of your presentation is getting a little sluggish? You feel that it should be over but there are ten slides to go still. Be precise in your editing process —rest assured that you’ll thank yourself when the end result is much more powerful than it would be if it had remained bloated.
The Power of Presentations
In many ways, presentations provide a unified experience where you can have text, images, video, and more. Remember that human beings are visual learners— visuals are processed up to 60,000 times faster than text and people have a much easier time understanding complex information when it is paired with relevant images as opposed to just text. As an author, researcher, or student, your job is to take complicated ideas and present them in a way that is appealing to a larger audience. Presentations are one of the most essential ways for you to do exactly that. The central message you are trying to convey—the thesis, if you will—needs to be strong enough to justify the creation of a presentation in the first place.
It needs to be a big enough topic to warrant a lengthy experience and a compelling enough story that demands to be told in this particular format above all others. If you start from that simple foundation and build outward, you’ll be left with the best type of marketing tool—one that promotes your research for you and one that people can’t wait to share with their friends and colleagues.
About the Author
Payman Taei is the founder of Visme , an easy-to-use online tool to create engaging presentations, infographics, and other forms of visual content. He is also the founder of HindSite Interactive , an award-winning Maryland based digital agency specializing in website design, user experience, and web app development.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Beyond the Podium: Understanding the differences in conference and academic presentations
Conferences can be captivating as it where knowledge meets presentation skills. They serve as dynamic…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
How to Ace Your Next Virtual Academic Conference
Identifying the right conference Designing video presentations Handling Q&A professionally Tips for virtual networking

- Global Korea Webinars
국제회의를 위한 연구발표 준비하는 방법
올바른 컨퍼런스 식별하기 프레젠테이션 설계 전략 질의응답 확인 및 관리 네트워킹에 대한 효과적인 팁

- Career Corner
- PhDs & Postdocs
Tips to Present Your Scientific Poster Effectively
This article focuses on the prerequisites and tips on developing a poster/e-poster. Traditionally, scientific posters…

A Researcher’s Guide to Making the Most of Academic Conferences
Academics know the importance of attending conferences as part of their career. Conferences provide valuable…
6 Simple Ways to Handle a Q&A Session at a Conference
4 Quick Tips to Effectively Engage the Audience in Your Research Presentation

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Presenting Your Research
A WORD Studio guide to presenting your research.
I. The Research Proposal Presentation
The overall purpose of a research proposal presentation is inquiry: you’re sharing what you’ve learned so far and how you hope to develop it so that you might hear from others what questions they have, where they felt confused, and new directions they think you might pursue.
WHAT TO SAY
- Remember that the proposal presentation is about your work in progress. You don’t have to have firm conclusions yet. Offer some possible ends you see reaching, and find out from your audience whether they think those are achievable.
- Don’t worry at this point about having every statistic lined up to support yourself or every quotation at hand. However, do be able to speak confidently about what the major scholars you’ve read have argued.
- Discuss your methodology, both what you have already done and what else you hope to do. A classmate may have run into a source that would work well for you and can bring this up during this time.
HOW TO SAY IT
- Although you are on the spot for a somewhat formal presentation, think of the proposal presentation as a conversation. Be open to interruptions or questions as you go, and stop and ask questions yourself if some occur to you.
VISUAL AIDS
You might not use many visual aids during a proposal feedback session; a full PowerPoint show, for example, might not be feasible if you haven’t yet collected all the information you’d want to share in this visual medium. A handout, however, might be helpful. Consider a handout of the working outline of your final paper; don’t read the outline at your audience but call their attention to each section as it comes up in your presentation. And since it’s a working outline, you can solicit advice from your listeners on how you might improve the organization or the development of ideas.
Active Listening and Peer Feedback
- Remember that the feedback you provide here will have a direct impact on the way your classmate shapes his or her final research project.
- Take notes (on an outline, if provided) with questions you have or terms you want better explained. Also note any parts of the proposal that sounded particularly interesting or fruitful. However, don’t let note-taking keep you from giving attention and eye contact to the speaker.
- Try to make a sketch of the speaker’s organizational scheme—even if the speaker has provided you with an outline, you may find as a listener that the speaker skips around or needs to bring related points closer together.
- When it comes time to offer feedback, make comments that are constructive and specific rather than general. For example, instead of saying, “I was confused by your organization,” say, “The section on the economic implications of the Beijing Olympics needs to go earlier.”
- Ask the presenter what visual aids they might plan to use in the final presentation. Make specific suggestions about what the audience might find helpful: “I’d like to see images of Beijing clean-up” or “You’ll probably want to offer a graph that shows how the population changed over time.”
II. The Final Research Presentation
Once you have completed your research project, you’ll want to share your findings and conclusions with others, helping each other add to the knowledge base you will all draw on as you continue your conversation with others in the field.
- Begin by making a sentence outline of your entire paper—this entails summarizing each paragraph in a single sentence and organizing those sentences into smaller paragraphs of related points.
- Then, keeping in mind the time allotted for your presentation, cut out any of these sentences that are interesting but not vital for an audience’s understanding.
- Using your pared-down sentence outline, find one or two specific pieces of evidence from your research to support each; then work on smooth transitions between all the sections. Depending on the context of your presentation, you might add introductory remarks about your methodology.
- Although one or two well-placed quotations can help add some power and authority to your presentation, don’t overwhelm your audience by reading many long quotations from other sources, no matter how interesting or well-written they may be—listeners might get confused about where the quote begins or ends, or whether it’s a quotation at all.
- Similarly, decide which statistics, facts, figures, or dates are essential for you to discuss aloud. If you must show a progression over time or make a comparison of statistics, use a visual aid of some sort to display the information rather than trying to make listeners strain to keep it all straight.
- Prepare ahead of time for questions: rehearse your presentation in front of a friend or WORD Studio tutor and ask them to lob the questions they might imagine your listeners having.
- If possible and permissible within the context of your presentation, add an interactive element, something that asks the audience to respond to you or to each other. This can be as simple as taking a show of hands on a few questions to see how much your audience knows, or asking them to describe to you what they see on a visual aid (for example, telling you what a graph seems to be showing).
VISUAL AIDS:
Handouts can be useful for showing data that you want everyone to look at several times (rather than having them squint at a PowerPoint slide); handouts can also be a place to gather some of the important quotations that you don’t read aloud during your presentation. Avoid the temptation to simply read a handout straight through to your audience; even consider not giving the handout out until near the end of the presentation.
PowerPoint might be preferable to handouts if you have many different data sets you need to go through, or if you want to display visual images (photographs, maps, etc.) to complement your discussion. Using PowerPoint well is an art; consult with good online guides or a WORD Studio tutor for more advice.
- Since you’ve heard your classmates’ proposals, you already have an idea of what the presentation will cover. Before a classmate begins speaking, therefore, identify at least one question you have and listen to see how (or if) they answer it.
- Use handouts actively: take notes, underline key points, jot down questions in the margin.
- If the speaker gives a PowerPoint presentation, consider it a visual outline of the overall presentation. Don’t attempt to write down everything on a slide; instead, write down one key point from each to remind yourself of questions and observations later.
- If this is a final research product, offering structural feedback might not be that helpful. Instead, aim for questions about content that might engender further thought in the speaker and the rest of the audience—even if the speaker never revises this particular research project further, he or she will have been exposed to new venues of exploration through your questions.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center

[Guide] How to Present Qualitative Research Findings in PowerPoint?
By: Author Shrot Katewa
![how to make a research project presentation [Guide] How to Present Qualitative Research Findings in PowerPoint?](https://artofpresentations.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Featured-Image-Present-qualitative-findings-using-Powerpoint.jpg)
As a researcher, it is quite pointless to do the research if we are unable to share the findings with our audience appropriately! Using PowerPoint is one of the best ways to present research outcomes. But, how does one present qualitative research findings using PowerPoint?
In order to present the qualitative research findings using PowerPoint, you need to create a robust structure for your presentation, make it engaging and visually appealing, present the patterns with explanations for it and highlight the conclusion of your research findings.
In this article, we will help you understand the structure of your presentation. Plus, we’ll share some handy tips that will make your qualitative research presentation really effective!
How to Create a Structure for your Qualitative Research Presentation?
Creating the right structure for your presentation is key to ensuring that it is correctly understood by your audience.
The structure of your Research Presentation not only makes it easier for you to create the document, it also makes it simple for the audience to understand what all will be covered in the presentation at the time of presenting it to your audience.
Furthermore, having a robust structure is a great way to ensure that you don’t miss out on any of the points while working on creating the presentation.
But, what structure should one follow?
Creating a good structure can be tricky for some. Thus, I’m sharing what has worked well for me during my previous research projects.
NOTE – It is important to note that although the following structure is highly effective for most research findings presentation, it has been generalized in order to serve a wide range of research projects. You may want to take a look at points that are very specific to the nature of your research project and include them at your discretion.
Here’s my recommended structure to create your Research Findings presentation –
1. Objective of the Research
A great way to start your presentation is to highlight the objective of your research project.
It is important to remember that merely sharing the objective may sometimes not be enough. A short backstory along with the purpose of your research project can pack a powerful punch ! It not only validates the reasoning for your project but also subtly establishes trust with your audience.
However, do make sure that you’re not reading the backstory from the slide. Let it flow naturally when you are delivering the presentation. Keep the presentation as minimalistic as possible.
2. Key Parameters Considered for Measurement
Once you’ve established the objective, the next thing that you may want to do is perhaps share the key parameters considered for the success of your project.
Every research project, including qualitative research, needs to have a few key parameters to measure against the objective of the research.
For example – If the goal of your project is to gather the sentiments of a certain group of people for a particular product, you may need to measure their feelings. Are they happy or unhappy using the product? How do they perceive the branding of the product? Is it affordable?
Make sure that you list down all such key parameters that were considered while conducting the qualitative research.
In general, laying these out before sharing the outcome can help your audience think from your perspective and look at the findings from the correct lens.
3. Research Methodology Adopted
The next thing that you may want to include in your presentation is the methodology that you adopted for conducting the research.
By knowing your approach, the audience can be better prepared for the outcome of your project. Ensure that you provide sound reasoning for the chosen methodology.
This section of your presentation can also showcase some pictures of the research being conducted. If you have captured a video, include that. Doing this provides further validation of your project.
4. Research Outcomes (Presenting Descriptive Analysis)

This is the section that will constitute the bulk of the your presentation.
Use the slides in this section to describe the observations, and the resulting outcomes on each of the key parameters that were considered for the research project.
It is usually a good idea to dedicate at least 1 or more slides for each parameter . Make sure that you present data wherever possible. However, ensure that the data presented can be easily comprehended.
Provide key learnings from the data, highlight any outliers, and possible reasoning for it. Try not to go too in-depth with the stats as this can overwhelm the audience. Remember, a presentation is most helpful when it is used to provide key highlights of the research !
Apart from using the data, make sure that you also include a few quotes from the participants.
5. Summary and Learnings from the Research
Once you’ve taken the audience through the core part of your research findings, it is a good practice to summarize the key learnings from each of the section of your project.
Make sure your touch upon some of the key learnings covered in the research outcome of your presentation.
Furthermore, include any additional observations and key points that you may have had which were previously not covered.
The summary slide also often acts as “Key Takeaways” from the research for your audience. Thus, make sure that you maintain brevity and highlight only the points that you want your audience to remember even after the presentation.
6. Inclusions and Exclusions (if any)
While this can be an optional section for some of the researchers.
However, dedicating a section on inclusions and exclusions in your presentation can be a great value add! This section helps your audience understand the key factors that were excluded (or included) on purpose!
Moreover, it creates a sense of thoroughness in the minds of your audience.
7. Conclusion of the Research
The purpose of the conclusion slide of your research findings presentation is to revisit the objective, and present a conclusion.
A conclusion may simply validate or nullify the objective. It may sometimes do neither. Nevertheless, having a conclusion slide makes your presentation come a full circle. It creates this sense of completion in the minds of your audience.
8. Questions
Finally, since your audience did not spend as much time as you did on the research project, people are bound to have a few questions.
Thus, the last part of your presentation structure should be dedicated to allowing your audience to ask questions.
Tips for Effectively Presenting Qualitative Research Findings using PowerPoint
For a presentation to be effective, it is important that the presentation is not only well structured but also that it is well created and nicely delivered!
While we have already covered the structure, let me share with you some tips that you can help you create and deliver the presentation effectively.
Tip 1 – Use Visuals

Using visuals in your presentation is a great way to keep the presentations engaging!
Visual aids not only help make the presentation less boring, but it also helps your audience in retaining the information better!
So, use images and videos of the actual research wherever possible. If these do not suffice or do not give a professional feel, there are a number of resources online from where you can source royalty-free images.
My recommendation for high-quality royalty-free images would be either Unsplash or Pexels . Both are really good. The only downside is that they often do not provide the perfect image that can be used. That said, it can get the job done for at least half the time.
If you are unable to find the perfect free image, I recommend checking out Dreamstime . They have a huge library of images and are much cheaper than most of the other image banks. I personally use Dreamstime for my presentation projects!
Tip 2 – Tell a Story (Don’t Show Just Data!)
I cannot stress enough on how important it is to give your presentation a human touch. Delivering a presentation in the form of a story does just that! Furthermore, storytelling is also a great tool for visualization .
Data can be hard-hitting, whereas a touching story can tickle the emotions of your audience on various levels!
One of the best ways to present a story with your research project is to start with the backstory of the objective. We’ve already talked about this in the earlier part of this article.
Start with why is this research project is so important. Follow a story arc that provides an exciting experience of the beginning, the middle, and a progression towards a climax; much like a plot of a soap opera.
Tip 3 – Include Quotes of the Participants
Including quotes of the participants in your research findings presentation not only provides evidence but also demonstrates authenticity!
Quotes function as a platform to include the voice of the target group and provide a peek into the mindset of the target audience.
When using quotes, keep these things in mind –
1. Use Quotes in their Unedited Form
When using quotes in your presentation, make sure that you use them in their raw unedited form.
The need to edit quotes should be only restricted to aid comprehension and sometimes coherence.
Furthermore, when editing the quotes, make sure that you use brackets to insert clarifying words. The standard format for using the brackets is to use square brackets for clarifying words and normal brackets for adding a missing explanation.
2. How to Decide which Quotes to Consider?
It is important to know which quotes to include in your presentation. I use the following 3 criteria when selecting the quote –
- Relevance – Consider the quotes that are relevant, and trying to convey the point that you want to establish.
- Length – an ideal quote should be not more than 1-2 sentences long.
- Choose quotes that are well-expressed and striking in nature.
3. Preserve Identity of the Participant
It is important to preserve and protect the identity of the participant. This can be done by maintaining confidentiality and anonymity.
Thus, refrain from using the name of the participant. An alternative could be using codes, using pseudonyms (made up names) or simply using other general non-identifiable parameters.
Do note, when using pseudonyms, remember to highlight it in the presentation.
If, however, you do need to use the name of the respondent, make sure that the participant is okay with it and you have adequate permissions to use their name.
Tip 4 – Make your Presentation Visually Appealing and Engaging
It is quite obvious for most of us that we need to create a visually appealing presentation. But, making it pleasing to the eye can be a bit challenging.
Fortunately, we wrote a detailed blog post with tips on how to make your presentation attractive. It provides you with easy and effective tips that you can use even as a beginner! Make sure you check that article.
7 EASY tips that ALWAYS make your PPT presentation attractive (even for beginners)
In addition to the tips mentioned in the article, let me share a few things that you can do which are specific to research outcome presentations.
4.1 Use a Simple Color Scheme
Using the right colors are key to make a presentation look good.
One of the most common mistakes that people make is use too many colors in their presentation!
My recommendation would be to go with a monochromatic color scheme in PowerPoint .
4.2 Make the Data Tables Simple and Visually Appealing
When making a presentation on research outcomes, you are bound to present some data.
But, when data is not presented in a proper manner, it can easily and quickly make your presentation look displeasing! The video below can be a good starting point.
Using neat looking tables can simply transform the way your presentation looks. So don’t just dump the data from excel on your PowerPoint presentation. Spend a few minutes on fixing it!
4.3 Use Graphs and Charts (wherever necessary)
When presenting data, my recommendation would be that graphs and charts should be your first preference.
Using graphs or charts make it easier to read the data, takes less time for the audience to comprehend, and it also helps to identify a trend.
However, make sure that the correct chart type is used when representing the data. The last thing that you want is to poorly represent a key piece of information.
4.4 Use Icons instead of Bullet Points
Consider the following example –
This slide could have been created just as easily using bullet points. However, using icons and representing the information in a different format makes the slide pleasing on the eye.
Thus, always try to use icons wherever possible instead of bullet points.
Tip 5 – Include the Outliers
Many times, as a research project manager, we tend to focus on the trends extracted from a data set.
While it is important to identify patterns in the data and provide an adequate explanation for the pattern, it is equally important sometimes to highlight the outliers prominently.
It is easy to forget that there may be hidden learnings even in the outliers. At times, the data trend may be re-iterating the common wisdom. However, upon analyzing the outlier data points, you may get insight into how a few participants are doing things successfully despite not following the common knowledge.
That said, not every outlier will reveal hidden information. So, do verify what to include and what to exclude.
Tip 6 – Take Inspiration from other Presentations
I admit, making any presentation can be a tough ask let alone making a presentation for showcasing qualitative research findings. This is especially hard when we don’t have the necessary skills for creating a presentation.
One quick way to overcome this challenge could be take inspiration from other similar presentations that we may have liked.
There is no shame in being inspired from others. If you don’t have any handy references, you can surely Google it to find a few examples.
One trick that almost always works for me is using Pinterest .
But, don’t just directly search for a research presentation. You will have little to no success with it. The key is to look for specific examples for inspiration. For eg. search for Title Slide examples, or Image Layout Examples in Presentation.
Tip 7 – Ask Others to Critic your Presentation
The last tip that I would want to provide is to make sure that you share the presentation with supportive colleagues or mentors to attain feedback.
This step can be critical to iron out the chinks in the armor. As research project manager, it is common for you to get a bit too involved with the project. This can lead to possibilities wherein you miss out on things.
A good way to overcome this challenge is to get a fresh perspective on your project and the presentation once it has been prepared.
Taking critical feedback before your final presentation can also prepare you to handle tough questions in an adept manner.
Final Thoughts
It is quite important to ensure that we get it right when working on a presentation that showcases the findings of our research project. After all, we don’t want to be in a situation wherein we put in all the hard-work in the project, but we fail to deliver the outcome appropriately.
I hope you will find the aforementioned tips and structure useful, and if you do, make sure that you bookmark this page and spread the word. Wishing you all the very best for your project!
30+ Best Research Presentation Templates for PowerPoint (PPT)
Finding the right PowerPoint template plays an important part in getting your message across to the audience during a presentation. And it’s especially true for research presentations.
Using the right colors, graphs, infographics, and illustrations in your slides is the key to delivering information more effectively and making your presentation a success.
Today, we handpicked a great collection of research presentation PowerPoint templates for you to make the perfect slideshows for various types of research papers and studies.
Whether you’re preparing for a presentation at a school, event, or conference, there are templates in this list for all purposes. Let’s dive in.
How Does Unlimited PowerPoint Templates Sound?
Download thousands of PowerPoint templates, and many other design elements, with a monthly Envato Elements membership. It starts at $16 per month, and gives you unlimited access to a growing library of over 2,000,000 presentation templates, fonts, photos, graphics, and more.

Business PPT Templates
Corporate & pro.

Modern PPT Templates
New & innovative.

Explore PowerPoint Templates
Science & Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is a perfect choice for preparing a research presentation to share your scientific findings and reports.
The template has 30 unique slides with unlimited color options. There are a few infographics included in the slideshow as well.
Why This Is A Top Pick
The presentation has a very modern and creative design where you can showcase your data and information in an attractive way. You won’t be making boring research presentations ever again.
Labvire – Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Labvire is another modern PowerPoint template you can use for various types of research presentations. It’s also ideal for laboratory-related research presentations. The template has fully customizable slide layouts with editable charts, graphs, and more. You can choose from more than 40 unique slide designs as well.
Novalabs – Science Research PowerPoint Template

Novalabs PowerPoint template features a highly visual and attractive design. The template includes 36 different slides that feature large image placeholders for adding a more visual look to your presentations. There are lots of editable graphics, shapes, and tables included in the template too. Feel free to customize them however you like.
Research & Development PowerPoint Template

The minimal and clean design of this PowerPoint template makes it a great choice for delivering more effective research presentations. With fewer distractions in each slide, you’ll be able to convey your message more easily. The template comes with 30 unique slides. You can change the colors, fonts, and shapes to your preference as well.
Marketing Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

When talking about research presentations, we can’t forget about marketing research. Most sales and marketing meetings usually include a sophisticated marketing research presentation. This PowerPoint template will help you design those research presentations without effort. It includes a total of 150 slides, featuring 30 unique slides in 5 different color schemes.
Free Business Market Research Presentation Template

This is a free PowerPoint template designed for making business market research presentations. It gives you 27 different and fully customizable slides to create professional slideshows for your business meetings.
Free Business Data Analysis & Research Presentation

With this PowerPoint template, you can create colorful and creative business research and data analysis presentation without any design skills. It includes 35 unique slides with lots of infographics and editable shapes. The template is free to use as well.
Lernen – Research Thesis PowerPoint Presentation

Larnen is the ideal PowerPoint template for making research slideshows for your thesis presentations. It includes 30 unique slides that are available in light and dark color themes. It also has editable charts and graphs.
Aristo – Research Academic PowerPoint Presentation
This PowerPoint template is also made with academic research presentations in mind. The template has a professional design with clean layouts and light colors. It comes with more than 30 different slides.
Biosearch – Science Research PowerPoint Template

You can use this PowerPoint template to make professional presentations to present research data and results. It lets you choose from 40 different slides and 90 color themes. The slides are available in both light and dark color themes as well.
Neolabs – Laboratory & Science Research PPT

Neolabs is another science research presentation made with laboratory research teams in mind. You can use it to make effective slideshows to present your research findings. There are 30 unique slides in this template.
Free Business Cost Analysis PowerPoint Template

This is a free PowerPoint and Google Slides template that comes with 35 unique slides. It’s ideal for making research presentations related to business financials.
Research & Case Study PowerPoint Template

Create the perfect case study presentation using your research data with this PowerPoint template. It includes a modern slide design with infographics and charts for effectively presenting your data.
Liron Labs – Laboratory Research PowerPoint Template

Another PowerPoint template for laboratory research presentations. This template includes 15 useful slide layouts with editable graphics, free fonts, and image placeholders. You can edit and customize the colors and text as well.
Research Thesis PowerPoint Template

Make an attractive and creative research thesis presentation using this PowerPoint template. There are over 30 unique slides in this template. You can either use dark or light color themes to create your presentations.
Colorful Thesis Research PowerPoint Template

If you want to make your research presentations look more colorful and creative, this PowerPoint template is for you. It has 15 different slides with fully customizable layouts. It has editable shapes, free fonts, and image placeholders too.
Free Data Analysis Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is also free to download. You can also customize it using PowerPoint or Google Slides. This template is ideal for marketing agencies and teams for presenting research and data analysis.
Laboratory & Science Research PowerPoint Template

You can make more convincing and unique lab research presentations using this PowerPoint template. It features a creative design that will easily attract the attention of your audience. You can use it to make various other science and research presentations too. The template includes 30 unique slides.
The Biologist – Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Just as the name suggests, this PowerPoint template is designed with biology and science-related presentations in mind. It includes many useful slide layouts that can be used to make various types of research presentations. There are 30 different slide designs included in this template with editable shapes and colors.
Modern Science & Research PowerPoint Template

If you’re looking for a PowerPoint template to create a modern-looking research presentation, this template is perfect for you. It features a collection of modern and attractive slides with lots of space for including images, icons, and graphs. There are 30 unique slides in the template with light and dark color themes to choose from.
Marketing Report & Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template doubles as both a research and report slideshow. You can use it to create various marketing reports as well as marketing research presentations. It comes with 30 slides that feature minimal and clean designs. It includes lots of editable charts, infographics, and tables as well.
Market Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Another modern PowerPoint template for making market research presentations. This template includes 25 unique slides with master slides, image placeholders, and editable colors. The template is ideal for marketing agencies and corporate businesses.
Free Academic Research Thesis PowerPoint Template

This free PowerPoint template is designed for defending your academic research thesis dissertation. Needless to say, it’s a useful template for academics as well as teachers. The template features 23 unique slide layouts with customizable designs.
Free Economics Research Thesis Presentation Template

You can use this free template to create thesis and research presentations related to economics. It’s useful for academic students and gives you the freedom to choose from 21 slide layouts to make your own presentations.
Labia – Research Presentation Powerpoint Template

Labia is a research presentation template made for professionals. It comes with a set of modern slides with multipurpose designs. That means you can customize them to make many different types of research presentations. There are 30 unique slides included in this template that come in 5 different color themes.
Medical Research Infographics & Powerpoint Slides
You’ll be using lots of charts, graphs, and infographics in your presentations to showcase data in visual form. Not to mention that visuals always work well for attracting the audience’s attention. You can use the infographic slides in this template to create better research presentations. Each slide features a unique infographic with animated designs.
Foreka – Biology Education & Research Presentation PPT

Foreka is a PowerPoint template made for educational presentations, especially for covering topics related to biology. But it can also be customized to present your research presentations. The slides have very useful layouts that are most suitable for making research slide designs. There are 30 slides included with light and dark color themes.
Maua – Aesthetic Business Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is suitable for making elegant and stylish business reports and business research presentations. It’s especially great for making background research and competitor research slideshows. The template comes with 30 slides featuring master slides, image placeholders, and more.
World Data Scientist Powerpoint Presentation Template

You can use this PowerPoint template to create research presentations for many different types of topics, industries, and projects. The template includes lots of data-centric slides where you can easily showcase your data in visual form. There are 30 unique slides included with the template as well.
Free SWOT Analysis Infographics PowerPoint Template
SWOT analysis is a commonly used methodology in business research presentations. With this free PowerPoint template, you can create stylish SWOT analysis infographics for your presentations. It includes SWOT infographics in 30 different styles.
Free Market Research Presentation Infographics PPT
This is a collection of free PowerPoint slides that feature various styles of infographics you can use in your business and market research presentations. There are 30 different infographic slides included in this template. You can edit, change colors, and customize them however you like.
Sinara – Science & Research Powerpoint Template

Sinara is a brilliant PowerPoint template you can use to craft a professional presentation for science-related research and reports. It’s available in 3 different color schemes as well as the option to customize the colors to your preference. The template comes in light and dark themes too.
Political Science and Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template will be quite useful to political science and international relations students. It features a total of 150 slides you can use to create attractive presentations for your research and methodologies. There are slides in 5 different color schemes.
How to Make a Research Poster in PowerPoint
We bet you didn’t know that you could actually design posters in PowerPoint. Well, you can and it’s very easy to do so.
The easiest way to make a poster in PowerPoint is to use a pre-made template like the one above.
You can easily copy one of the slides from a template, and resize the slide dimensions to create a vertical poster. Then add a title with a few lines of text and you’ll have yourself a poster.
Or, if you want to craft a poster from scratch, you can read our complete guide on how to create posters in PowerPoint with step-by-step instructions.
For more useful presentation templates, be sure to check out our best educational PowerPoint templates collection.
How to Create a Research Poster
- Poster Basics
- Design Tips
- Logos & Images
What is a Research Poster?
Posters are widely used in the academic community, and most conferences include poster presentations in their program. Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion.
The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view the presentation and interact with the author.
What Makes a Good Poster?
- Important information should be readable from about 10 feet away
- Title is short and draws interest
- Word count of about 300 to 800 words
- Text is clear and to the point
- Use of bullets, numbering, and headlines make it easy to read
- Effective use of graphics, color and fonts
- Consistent and clean layout
- Includes acknowledgments, your name and institutional affiliation
A Sample of a Well Designed Poster
View this poster example in a web browser .

Image credit: Poster Session Tips by [email protected], via Penn State
Where do I begin?
Answer these three questions:.
- What is the most important/interesting/astounding finding from my research project?
- How can I visually share my research with conference attendees? Should I use charts, graphs, photos, images?
- What kind of information can I convey during my talk that will complement my poster?
What software can I use to make a poster?
A popular, easy-to-use option. It is part of Microsoft Office package and is available on the library computers in rooms LC337 and LC336. ( Advice for creating a poster with PowerPoint ).
Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign
Feature-rich professional software that is good for posters including lots of high-resolution images, but they are more complex and expensive. NYU Faculty, Staff, and Students can access and download the Adobe Creative Suite .
Open Source Alternatives
- OpenOffice is the free alternative to MS Office (Impress is its PowerPoint alternative).
- Inkscape and Gimp are alternatives to Adobe products.
- For charts and diagrams try Gliffy or Lovely Charts .
- A complete list of free graphics software .
A Sample of a Poorly Designed Poster
View this bad poster example in a browser.
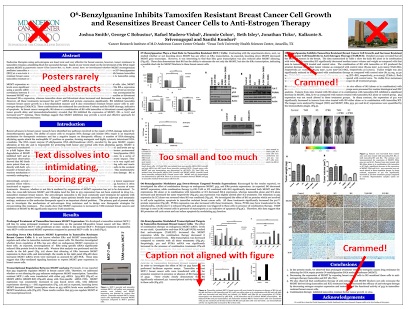
Image Credit: Critique by Better Posters
- Next: Design Tips >>
- Last Updated: Jul 11, 2023 5:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/posters
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
A Dear Colleague Letter (DCL) is an informal correspondence which is written by a Requesting Office and distributed to communities within a specific program area, to attract individuals eligible under a Visiting Scientist, Engineer, and Educator (VSEE) appointment, an Intergovernmental Personnel Act (IPA) assignment and/or a Federal Temporary appointment. These letters may be circulated in paper form through internal mail, distributed electronically using listservs or accessed through NSF.gov’s Career Page.
Acting Senior Advisor for Facilities
Application timeline, position summary.
The Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (MPS) is offering a detail opportunity to serve as the Senior Advisor for Facilities, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (MPS), Office of the Assistant Director (OAD). This detail is open to all qualified permanent NSF employees. The initial appointment will be 120-days, with the possibility to extend up to one year. For purposes of pay and benefits, the selectee will continue to encumber the position from which detailed. Further, the individual selected will be required to file an “Executive Branch Personnel Public Financial Disclosure Report” (OGE-278) in accordance with the Ethics in Government Act of 1978 at the beginning and completion of the detail assignment.
MPS coordinates the investment of $1.6 billion annually for research and education projects in the mathematical and physical sciences and related areas. Through a staff of approximately 180 in five divisions and the Office of Strategic Initiatives, it provides program support in astronomical sciences, chemistry, materials science, mathematical sciences, and physics. MPS also oversees the management of the largest number of Major Research Equipment and Facilities Construction (MREFC) scale projects and major multi-user facilities, through their full life cycle.
The Senior Advisor for Facilities (SAF) serves to advise the MPS Assistant Director (AD) on all aspects of MREFC-scale facilities design and development, construction, and operations and maintenance, as well as coordination of mid-scale activities. In doing so, the SAF is a resource for general institutional knowledge concerning NSF policy, procedures, practice, and culture. He/she will work closely with the Office of the Chief Officer for Research Facilities, Research Infrastructure Office, and other science directorates. The SAF also serves as a member of the MPS senior staff, providing advice to the AD and Deputy Assistant Director (DAD) on other related issues.
Position Description
The SAF serves as a member of the directorate leadership team and, as such, assists the Assistant Director and Deputy Assistant Director by providing scientific and strategic analysis and program planning for all MPS scientific facilities. The SAF must possess a Ph.D. and have a strong, fundamental understanding of a broad range of scientific research, including astronomy, physics, and materials research conducted by the MPS facilities. Major duties include:
• Works closely with all directorate senior leaders and agency officials to plan, facilitate, evaluate, and oversee broad and complex directorate-wide activities related to MPS scientific facilities.
• Engages in strategic planning and oversees budget preparation and evaluation for the entire PS facilities portfolio including midscale activities.
• Provides guidance to the Assistant Director on strategic assessment of projects, including readiness for Director's Review Board (DRB) and National Science Board (NSB) actions, need for advisory structures, coordination with other agencies; working with MPS OAD, and the Office of the Director (OD) in developing process for assessing priorities of large projects across MPS disciplines.
• Coordinates and oversees the facilities-related interface between MPS and other offices and functions within NSF such as the Office of the Chief Officer for Research Facilities (OCORF), Research Infrastructure Office (RIO), Director's Review Board (DRB), National Science Board Office (NSBO), Office of General Counsel (OGC), Division of Acquisition and Cooperative Support (DACS), and Office of Legislative and Public Affairs (OLPA).
• Provides assistance in all planning and preparation of the MPS facilities and MREFC project sections of the NSF budget, as well as material requested by the RIO, OD, and the NSB and its various committees including the Committee on Awards and Facilities.
• Mentors and coaches MPS senior leadership and staff on complex facilities-related issues and events that occur over the full life cycle of major research facilities.
• Maintaining awareness, through strong communication with the managing units, of plans for all major projects and NSF-conducted facility reviews. Through the SAF, the MPS OAD is consulted on the charge and review committee membership for such reviews.
• Provides critical analyses and assists in the development of NSB packages and NSB presentations as needed: providing guidance to ensure that the strategic view of projects within the overall NSF science portfolio is presented, that management plans of the projects and NSF are effective and robust, that appropriate responses are planned in case of difficulties developing in the project. In addition, will provide guidance on the response to critiques from DRB and NSB.
• Working with MPS facilities and projects, facilities in other directorates, and the Office of Advanced Cyberinfrastructure to assess common needs and to make recommendations on how to best leverage the emerging national cyberinfrastructure, strengthening the projects while facilitating collaborative, compute- and data-driven science activities enabled by large facilities.
• Oversees the MPS master schedule for all NSB approvals and information items associated with MPS MREFC projects and MREFC-scale facilities, including allowance of time for adequate MPS OAD review; DRB submissions and subsequent revision, presentation dry runs, etc.
Qualifications
The position requires an individual with a strong work ethic and initiative; and excellent interpersonal, communication, analytical, and project management skills. Additional requirements include:
Ph.D. in a field of science or engineering or equivalent professional experience in a field related to the NSF mission or in a field relevant to the duties required.
QUALITY RANKING FACTORS: Final ranking is based on an evaluation of experience, education, and training as they relate to the knowledge, skills and abilities specified in the following factors:
- Experience working with facilities-related projects, events, and relevant stakeholders.
- Significant involvement in policy, budgeting, planning, and project management related to scientific research facilities.
- Superior skill in applying analytic reasoning to complex issues and problems, identifying the key priorities, solutions, and options, and making recommendations.
- Demonstrated ability to conceptualize and express complex issues and ideas in a clear and concise manner, both orally and in writing.
- Demonstrated ability to work effectively with high-level staff and those in other stakeholder organizations.
- Broad knowledge and understanding of NSF's mission, goals, policies, procedures, and processes.
How to apply
Interested applicants must submit a resume and a narrative statement addressing their background in terms of the qualification requirements. Applications must be received by 11:59 P.M. on the closing date. Applications may be submitted electronically to:
Krystal Mendenhall
Email: [email protected]
Phone: (703) 292-4345

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include: The full title of the report. The date of the report. The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report. The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended.
Related Articles. This guide provides a 4-step process for making a good scientific presentation: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slide outlines, constructing slides, and practicing the talk. We give advice on how to make effective slides, including tips for text, graphics, and equations, and how to use rehearsals of your talk to ...
Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation. Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon. Clean and professional: Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font ...
Below are 11 tips for giving an effective research presentation. 1. Decide what your most important messages are, tailored to your specific audience. Research can be messy, and so can the results of research. Your audience does not usually need to know every tiny detail about your work or results.
🔥Join me for my Certification Course on 'A-Z of Research Writing & Presentation' 😃: https://wiseupcommunications.com/course/research-writing/In this video,...
Visualize Data Instead of Writing Them. When adding facts and figures to your research presentation, harness the power of data visualization. Add interactive charts and graphs to take out most of the text. Text with visuals causes a faster and stronger reaction than words alone, making your presentation more memorable.
Tips to Make an Effective Research Presentation. Tip 1: Start confidently. Tip 2: Eye To Eye Contact With the Audience. Tip 3: Welcome Your Audience. Tip 4: Adjust your Voice. Tip 5: Memorize your Opening Line. Tip 6: Use the words " 'Think for while', 'Imagine', 'Think of', 'Close Your Eyes' ". Tip 7: Story Telling.
Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community. Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home ...
Outline the key insights. Before designing your slides, you should feel comfortable with the research and how it all fits together. I determine the critical insights by the information that came up the most frequently from users—usually focused on pain points. I only let myself choose up to five key insights to report.
Identify a few "nodders" in the audience and speak to them. Handling Questions. Different types of questions/comments - handle accordingly: Need clarification Suggest something helpful Want to engage in research dialog Show that he/she knows more than you. Anticipate questions as you prepare.
Not all research projects are best displayed and celebrated on a 3 x 4 ft research poster. If you are looking for other options, consider if setting up models, displaying artwork, or creating a video or film would better feature your work. The first time I set out to make a research presentation, I decided to go with a tradition research poster.
they will look around, exchange glances, and make you feel foolish. Find a trusted friend in the audience and direct the question to him or her. (D) Make use of visual aids (e.g., a drawing of your 2 x 2 design). A picture is worth well over a thousand words. Supplement your speech with pictures. But --remember that a complicated picture is useless
Keep to your written proposal formula. You need a title slide (with your name, that of your advisor & institution) Several slides of introduction. that put your study into the big picture. explain variables in the context of existing literature. explain the relevance of your study organisms. give the context of your own study.
Discipline. You have (or will have) an elevator pitch from the job market - use this to trim your presentation. A few bonus resources from others Marc Bellemare has a great series of "22 tips for conference and seminar presentations," many of which apply to short presentations: "Always provide a preview of your results. This isn't a ...
Presentation software programs have advanced to the point where you no longer need to be an experienced designer to put together a compelling piece of collateral that conveys your findings about academic research in exactly the right way. With the right materials, the right presentation software, and a little bit of time, you can visualize any data that you have in the form of a terrific ...
A WORD Studio guide to presenting your research. I. The Research Proposal Presentation. The overall purpose of a research proposal presentation is inquiry: you're sharing what you've learned so far and how you hope to develop it so that you might hear from others what questions they have, where they felt confused, and new directions they ...
Delivering a research presentation is a great way to showcase your research to the world. In this video you will learn the benefits of presenting your resear...
Writing a Research Report: Presentation. Tables, Diagrams, Photos, and Maps. - Use when relevant and refer to them in the text. - Redraw diagrams rather than copying them directly. - Place at appropriate points in the text. - Select the most appropriate device. - List in contents at beginning of the report.
A step-by-step explanation on making the slideshow of your research thesis presentation. This video mainly discusses about the content, structure and flow of...
When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences. As an ...
Make sure that you list down all such key parameters that were considered while conducting the qualitative research. In general, laying these out before sharing the outcome can help your audience think from your perspective and look at the findings from the correct lens. 3. Research Methodology Adopted.
Science & Research Presentation PowerPoint Template. This PowerPoint template is a perfect choice for preparing a research presentation to share your scientific findings and reports. The template has 30 unique slides with unlimited color options. There are a few infographics included in the slideshow as well.
Research posters summarize information or research concisely and attractively to help publicize it and generate discussion. The poster is usually a mixture of a brief text mixed with tables, graphs, pictures, and other presentation formats. At a conference, the researcher stands by the poster display while other participants can come and view ...
The SAF serves as a member of the directorate leadership team and, as such, assists the Assistant Director and Deputy Assistant Director by providing scientific and strategic analysis and program planning for all MPS scientific facilities. The SAF must possess a Ph.D. and have a strong, fundamental understanding of a broad range of scientific research, including astronomy, physics, and ...