
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
The Five Generations of Computers
Published by Leona Melton Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "The Five Generations of Computers"— Presentation transcript:

Professor: Nabil Elmjati IB100 Introduction to computer Sciences Professor: Nabil Elmjati.

Generations of the Computer

5 Generations of Computers Ms. Ceejay Jader. FIRST GENERATION : Vacuum Tubes a glass tube surrounding a vacuum (an area from which all gases.

HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT By: Pratama Wahyu Purnama ( ) Maulida Yulianti ( )

1 Maninder Kaur

Online Counseling Resource YCMOU ELearning Drive… School of Architecture, Science and Technology Yashwantrao Chavan Maharashtra Open University, Nashik.

I NTRODUCTION TO C OMPUTERS AND P ROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Mr. Mohammed Rahmath.

Chapter Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe.

Chapter 1 An Overview of Personal Computers

CS 104 Introduction to Computer Science and Graphics Problems History of Computer 09/05/2008 Yang Song (Prepared by Yang Song and Suresh Solaimuthu)

SUBJECT NAME: BASIC COMPUTER SKILLS. What is computer ? A device that computes, especially a programmable electronic machine that performs high-speed.

A Brief History of Computers

Prepared by: Jasper Francisco. The Early Years 1 In the early years, before the computer was invented, there were several inventions of counting machine.

History of computers By Anne Perera.

COMPUTER SYSTEM.

Chapter 01 Nell Dale & John Lewis.

What is a computer? What is its definition? A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic.
SECOND GENERATION COMPUTERS (ERA OF TRANSISTORS)

CS 1410 Intro to Computer Tecnology Computers and History1.

Computer Programming History of Computers
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 7. Evolution of computers
Topic A: Computer generations
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Basic Terms

Vacuum tube – an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.

Transistor – an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
Integrated circuit (IC) – a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes , resistors, etc.).

Microprocessor – an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.

CPU (central processing unit) – It is often referred to as the brain or engine of a computer where most of the processing and operations take place (CPU is part of a microprocessor).

Magnetic drum – a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
Magnetic core – uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.

Machine language – a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
Assembly language is like the machine language that a computer can understand, except that assembly language uses abbreviated words (e.g. ADD, SUB, DIV…) in place of numbers (0s and 1s).

Artificial intelligence (AI) – an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
First Generation of Computers
Classification of generations of computers.
The evolution of computer technology is often divided into five generations.
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)

- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language

- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s).
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk

- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s).
- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk

- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).

- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present).

- VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).
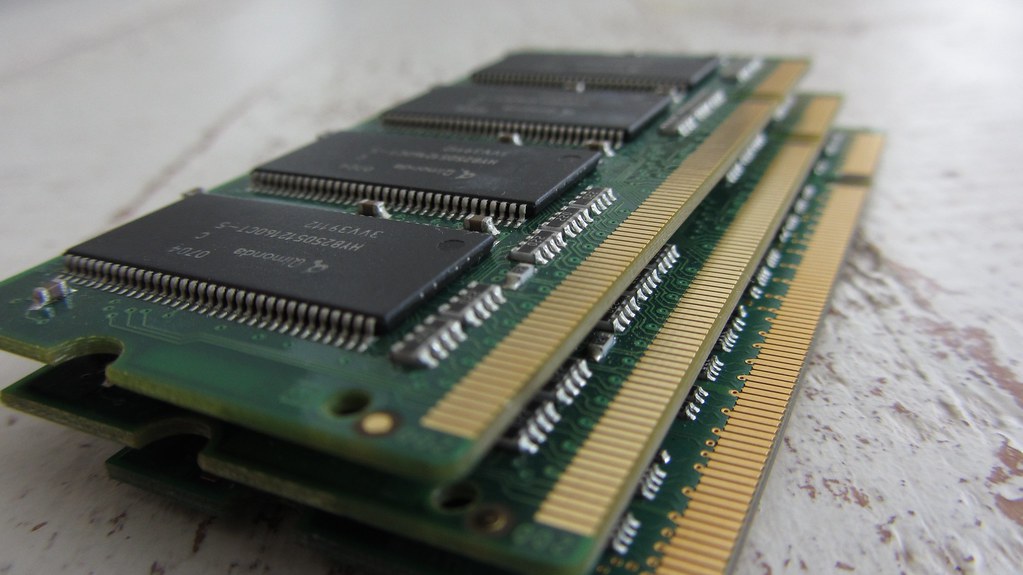

- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).

- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.

Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future).

- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.

- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

The computer – this amazing technology went from a government/business-only technology to being everywhere from people’s homes, work places, to people’s pockets in less than 100 years.

an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.
an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes, resistors, etc.).
an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer's central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.
The brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.
a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
a physical device that is used to store data, information, and programs in a computer.
an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
Key Concepts of Computer Studies Copyright © 2020 by Meizhong Wang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Generations of Computers - Computer Fundamentals
- Fourth Generation of Computers
- First Generation Of Computer
- Fifth Generation of Computers
- Second Generation of Computers
- Third Generation of Computers
- Basics of Computer and its Operations
- Performance of Computer in Computer Organization
- Elements of Computer Network
- Computer Fundamental Tutorial
- 10 Interesting Facts About Computers
- Why integer size varies from computer to computer?
- Computer Organization | Von Neumann architecture
- Computer Organization | Micro-Operation
- Importance of Computer Networking
- Human - Computer interaction through the ages
- Memory Organisation in Computer Architecture
- Computer Architecture | Flynn's taxonomy
- Full Form of Computer
- Computer Organization | Different Instruction Cycles
- Computer Networks - GATE CSE Previous Year Questions
- Ethernet Evolution in Computer Networks
- Memory Stack Organization in Computer Architecture
- Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
- Differences between Computer Architecture and Computer Organization
- Evolution and Features of Computerised Accounting
- Introduction to Computer Graphics
- Rethinking binary with Quantum computers
- Introduction of Quantum Computers
Generations of Computers – Computer Fundamentals
Generations of Computer : The modern computer took its shape with the arrival of your time. It had been around the 16th century when the evolution of the computer started. The initial computer faced many changes, obviously for the betterment. It continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the fashionable day computer.
Basic Terms Related to Computers
The basic terms related to generations of computers are listed below.
- Vacuum Tube: Vacuum tubes have the functionality of controlling the flow of electronics in a vacuum. Generally, it is used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc.
- Transistor: A transistor helps in controlling the flow of electricity in devices, it works as an amplifier or a switch.
- Integrated Circuit (IC): Integrated circuits are silicon chips that contain their circuit elements like transistors, resistors, etc.
- Microprocessors: Microprocessors are the components that contain the CPU and its circuits and are present in the Integrated Circuit.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is called the brain of the computer. CPU performs processing and operations work.
- Magnetic Drum: Magnetic Drum is like a cylinder that stores data and cylinder.
- Magnetic Core: Magnetic cores are used to store information. These are arrays of small rings.
- Machine Language: Machine Language is the language that a computer accepts (in the form of binary digits). It is also called low-level programming language.
- Memory: Memory is used to store data, information, and program in a computer.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence deals with creating intelligent machines and behaviors.
Phases of Computer Generations
This long period is often conveniently divided into the subsequent phases called computer generations.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
Before the generation of computers, we used calculators, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems, mathematicians and inventors searched for solutions to ease the burden of calculation.
Below are the 8 Mechanical Calculators before modern computers were invented.
- Abacus (ca. 2700 BC)
- Pascal’s Calculator (1652)
- Stepped Reckoner (1694)
- Arithmometer (1820)
- Comptometer (1887) and Comptograph (1889)
- The Difference Engine (1822)
- Analytical Engine (1834)
- The Millionaire (1893)
First Generation Computers
The technology behind the primary generation computers was a fragile glass device, which was called a vacuum tube. These computers were very heavy and really large. These weren’t very reliable and programming on them was a tedious task as they used low-level programming language and used no OS. First-generation computers were used for calculation, storage, and control purpose. They were too bulky and large that they needed a full room and consume a lot of electricity. Punch cards were used for improving the information for external storage. Magnetic card used . Machine and assembly language is developed.
Examples of some main first-generation computers are mentioned below.
- ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly was a general-purpose computer. It had been cumbersome, and large, and contained 18,000 vacuum tubes.
- EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer was designed by von Neumann. It could store data also as instruction and thus the speed was enhanced.
- UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer was developed in 1952 by Eckert and Mauchly.
.webp)
Vacuum Tube
Characteristics of First-Generation Computers
Second generation computers.
Second-generation computers used the technology of transistors rather than bulky vacuum tubes. Another feature was the core storage. A transistor may be a device composed of semiconductor material that amplifies a sign or opens or closes a circuit.
Transistors were invented in Bell Labs. The use of transistors made it possible to perform powerfully and with due speed. It reduced the dimensions and price and thankfully the warmth too, which was generated by vacuum tubes. Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, programming language, and input, and output units also came into the force within the second generation.
The programming language was shifted from high level to programming language and made programming comparatively a simple task for programmers. Languages used for programming during this era were FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
.webp)
Characteristics of Second-Generation Computers
Third generation computers.
During the third generation, technology envisaged a shift from huge transistors to integrated circuits, also referred to as IC. Here a variety of transistors were placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors. The most feature of this era’s computer was speed and reliability. IC was made from silicon and also called silicon chips.
The computer programs was designed to make the machine work. Operating system was a program designed to handle a machine completely. Because of the operating system machine could execute multiple jobs simultaneously. Integrated circuits were used to replace many transistors used in the second generation.
A single IC has many transistors, registers, and capacitors built on one thin slice of silicon. The value size was reduced and memory space and dealing efficiency were increased during this generation. Programming was now wiped out Higher level languages like BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code). Minicomputers find their shape during this era.
.webp)
Integrated Circuit
Characteristics of Third-Generation Computers
Fourth generation computers.
In 1971 First microprocessors were used, the large-scale of integration LSI circuits built on one chip called microprocessors. The advantage of this technology is that one microprocessor can contain all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on one chip. LSI placed thousands of transistors onto a single chip.
The computers using microchips were called microcomputers. This generation provided even smaller size of computers, with larger capacities. That’s not enough, then Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits replaced LSI circuits. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the pc from the central processing unit and memory to input/ output controls on one chip and allowed the dimensions to reduce drastically. VLSI placed several hundred thousand transistors on a single silicon chip. This silicon chip is known as the micro processor.
Technologies like multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time-sharing, operating speed, and virtual memory made it a more user-friendly and customary device. The concept of private computers and computer networks came into being within the fourth generation.

Microprocessor
Characteristics of Fourth-Generation Computers
Fifth generation computers.
The technology behind the fifth generation of computers is AI. It allows computers to behave like humans. It is often seen in programs like voice recognition, area of medicine, and entertainment. Within the field of game playing also it’s shown remarkable performance where computers are capable of beating human competitors.
The speed is the highest, size is the smallest and area of use has remarkably increased within the fifth generation computers. Though not a hundred percent AI has been achieved to date but keeping in sight the present developments, it is often said that this dream also will become a reality very soon.
To summarize the features of varied generations of computers, it is often said that a big improvement has been seen so far because of the speed and accuracy of functioning care, but if we mention the dimensions, it’s been small over the years. The value is additionally diminishing and reliability is increasing.

AI-Based Computers
Characteristics of Fifth-Generation Computers
Faqs on generations of computer, 1. what are the 5 types of generation of computer.
The five generations of computers are: 1. First Generation (1940s-1950s): Characterized by vacuum tubes and punched cards. Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC. 2. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, allowing smaller and more efficient computers. Introduction of high-level programming languages. Examples: IBM 1401, IBM 7094. 3. Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated circuits (ICs) replaced transistors, leading to smaller and faster computers. Introduction of operating systems. Examples: IBM System/360, DEC PDP-11. 4. Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): Microprocessors brought computing power to individual users. Introduction of personal computers. Examples: IBM PC, Apple Macintosh. 5. Fifth Generation (1980s-Present): Focus on parallel processing, artificial intelligence (AI), and natural language processing. Development of supercomputers and expert systems. Ongoing advancements in AI and machine learning. Examples: IBM Watson, Google’s DeepMind.
2. What is Gen Z technology?
Gen Z technology encompasses the digital tools and platforms that define the experiences of individuals born roughly between the mid-1990s and early 2010s. This generation is characterized by its seamless integration of smartphones, social media, online collaboration, and video content into daily life, shaping their communication, learning, and entertainment habits.
3. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It involves programming computers to think, learn, and perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, such as problem-solving and decision-making. AI encompasses subfields like machine learning and natural language processing, with applications ranging from virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles.

4. What was the First Computer?
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1945, is widely regarded as the first electronic general-purpose computer.
5. Who is Known as the Father of Computers?
Charles Babbage is known as the Father of Computers for his pioneering work on the concept of a programmable mechanical computer in the 19th century.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Preferences

The Five Generations of Computers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

The Five Generations of Computers
First generation computers second generation computers (1956-1963) ... the intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the computer. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.
- They were often enormous and taking up entire room.
- First generation computers relied on machine language.
- . They were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions.
- The UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are examples of first-generation computing devices.
- Transistors replaced vacuum tubes and ushered in the second generation of computers.
- Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic.
- High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN.
- These were also the first computers that stored their instructions in their memory.
- The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
- Transistors were miniaturized and placed on siliconchips, called semiconductors.
- Instead of punched cards and printouts, users interacted with third generation computers through keyboards and monitors and interfaced with an operating system.
- Allowed the device to run many different applicati ons at one time.
- The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip.
- The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the computer.
- From the central processing unit and memory to input/output controlson a single chip.
- . Fourth generation computers also saw the development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
- Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence.
- Are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition.
- The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
- The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
What the New Overtime Rule Means for Workers

One of the basic principles of the American workplace is that a hard day’s work deserves a fair day’s pay. Simply put, every worker’s time has value. A cornerstone of that promise is the Fair Labor Standards Act ’s (FLSA) requirement that when most workers work more than 40 hours in a week, they get paid more. The Department of Labor ’s new overtime regulation is restoring and extending this promise for millions more lower-paid salaried workers in the U.S.
Overtime protections have been a critical part of the FLSA since 1938 and were established to protect workers from exploitation and to benefit workers, their families and our communities. Strong overtime protections help build America’s middle class and ensure that workers are not overworked and underpaid.
Some workers are specifically exempt from the FLSA’s minimum wage and overtime protections, including bona fide executive, administrative or professional employees. This exemption, typically referred to as the “EAP” exemption, applies when:
1. An employee is paid a salary,
2. The salary is not less than a minimum salary threshold amount, and
3. The employee primarily performs executive, administrative or professional duties.
While the department increased the minimum salary required for the EAP exemption from overtime pay every 5 to 9 years between 1938 and 1975, long periods between increases to the salary requirement after 1975 have caused an erosion of the real value of the salary threshold, lessening its effectiveness in helping to identify exempt EAP employees.
The department’s new overtime rule was developed based on almost 30 listening sessions across the country and the final rule was issued after reviewing over 33,000 written comments. We heard from a wide variety of members of the public who shared valuable insights to help us develop this Administration’s overtime rule, including from workers who told us: “I would love the opportunity to...be compensated for time worked beyond 40 hours, or alternately be given a raise,” and “I make around $40,000 a year and most week[s] work well over 40 hours (likely in the 45-50 range). This rule change would benefit me greatly and ensure that my time is paid for!” and “Please, I would love to be paid for the extra hours I work!”
The department’s final rule, which will go into effect on July 1, 2024, will increase the standard salary level that helps define and delimit which salaried workers are entitled to overtime pay protections under the FLSA.
Starting July 1, most salaried workers who earn less than $844 per week will become eligible for overtime pay under the final rule. And on Jan. 1, 2025, most salaried workers who make less than $1,128 per week will become eligible for overtime pay. As these changes occur, job duties will continue to determine overtime exemption status for most salaried employees.

The rule will also increase the total annual compensation requirement for highly compensated employees (who are not entitled to overtime pay under the FLSA if certain requirements are met) from $107,432 per year to $132,964 per year on July 1, 2024, and then set it equal to $151,164 per year on Jan. 1, 2025.
Starting July 1, 2027, these earnings thresholds will be updated every three years so they keep pace with changes in worker salaries, ensuring that employers can adapt more easily because they’ll know when salary updates will happen and how they’ll be calculated.
The final rule will restore and extend the right to overtime pay to many salaried workers, including workers who historically were entitled to overtime pay under the FLSA because of their lower pay or the type of work they performed.
We urge workers and employers to visit our website to learn more about the final rule.
Jessica Looman is the administrator for the U.S. Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division. Follow the Wage and Hour Division on Twitter at @WHD_DOL and LinkedIn . Editor's note: This blog was edited to correct a typo (changing "administrator" to "administrative.")
- Wage and Hour Division (WHD)
- Fair Labor Standards Act
- overtime rule
SHARE THIS:

Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: improving diversity of commonsense generation by large language models via in-context learning.
Abstract: Generative Commonsense Reasoning (GCR) requires a model to reason about a situation using commonsense knowledge, while generating coherent sentences. Although the quality of the generated sentences is crucial, the diversity of the generation is equally important because it reflects the model's ability to use a range of commonsense knowledge facts. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown proficiency in enhancing the generation quality across various tasks through in-context learning (ICL) using given examples without the need for any fine-tuning. However, the diversity aspect in LLM outputs has not been systematically studied before. To address this, we propose a simple method that diversifies the LLM generations, while preserving their quality. Experimental results on three benchmark GCR datasets show that our method achieves an ideal balance between the quality and diversity. Moreover, the sentences generated by our proposed method can be used as training data to improve diversity in existing commonsense generators.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Create an email message
- Suggested recipients
- Use @mentions
- Create a signature
- Add attachments
- Check spelling
- Add a reaction
- Out of office replies
- Delay or schedule
- Recall a message
- Automatic forwarding
- Read receipt
- Save a file or draft
- Change display name
- Create a folder
- Use inbox rules
- Conditional formatting
- Use Favorites
- Custom views
- Message font size
- Message list view
- Focused Inbox
- View as conversations
- Filter and sort messages
- Number of messages
- Chat with recipients
- Share an email
- Status in Outlook
- Phishing and suspicious behavior
- Blocked senders
- Protected messages
- Open a protected message
- More to explore

Create and add an email signature in Outlook
In Outlook, you can create one or more personalized signatures for your email messages. Your signature can include text, links, pictures, and images (such as your handwritten signature or a logo).
Note: If the steps under this New Outlook tab don't work, you may not be using new Outlook for Windows yet. Select Classic Outlook and follow those steps instead.
Create and add an email signature
On the View tab, select View Settings .
Select Accounts > Signatures .
Select New signature , then give it a distinct name.
In the editing box below the new name, type your signature, then format it with the font, color, and styles to get the appearance you want.
Select Save when you're done.
With your new signature selected from the list above the editing box, go to Select default signatures and choose whether to apply the signature to new messages and to replies and forwards.
Select Save again.
Note: If you have a Microsoft account, and you use Outlook and Outlook on the web or Outlook on the web for business, you need to create a signature in both products.
Create your signature and choose when Outlook adds a signature to your messages
If you want to watch how it's done, you can go directly to the video below .
Open a new email message.

Under Select signature to edit , choose New , and in the New Signature dialog box, type a name for the signature.
Under Edit signature , compose your signature. You can change fonts, font colors, and sizes, as well as text alignment. If you want to create a more robust signature with bullets, tables, or borders, use Word to create and format your signature text, then copy and paste it into the Edit signature box. You can also use a pre-designed template to create your signature. Download the templates in Word, customize with your personal information, and then copy and paste into the Edit signature box.
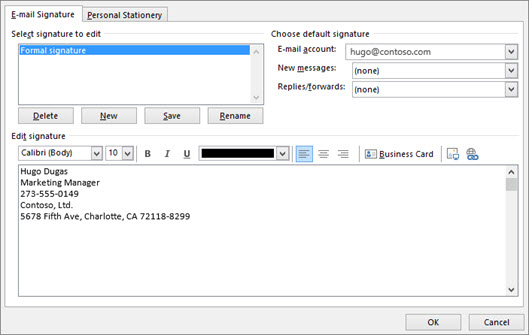
You can add links and images to your email signature, change fonts and colors, and justify the text using the mini formatting bar under Edit signature .
You can also add social media icons and links in your signature or customize one of our pre-designed temlates. For more information, see Create a signature from a template .
To add images to your signature, see Add a logo or image to your signature .
Under Choose default signature , set the following options.
In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account.
You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a signature to new messages, choose (none). This option does not add a signature to any messages you reply to or forward.
You can select to have your signature automatically appear in reply and forward messages. In the Replies/forwards drop-down, select one of your signatures. Otherwise, accept the default option of (none).
Choose OK to save your new signature and return to your message. Outlook doesn't add your new signature to the message you opened in Step 1, even if you chose to apply the signature to all new messages. You'll have to add the signature manually to this one message. All future messages will have the signature added automatically. To add the signature manually, select Signature from the Message menu and then pick the signature you just created.
Add a logo or image to your signature
If you have a company logo or an image to add to your signature, use the following steps.
Open a new message and then select Signature > Signatures .
In the Select signature to edit box, choose the signature you want to add a logo or image to.

To resize your image, right-click the image, then choose Picture . Select the Size tab and use the options to resize your image. To keep the image proportions, make sure to keep the Lock aspect ratio checkbox checked.
When you're done, select OK , then select OK again to save the changes to your signature.
Insert a signature manually
If you don't choose to insert a signature for all new messages or replies and forwards, you can still insert a signature manually.
In your email message, on the Message tab, select Signature .
Choose your signature from the fly-out menu that appears. If you have more than one signature, you can select any of the signatures you've created.
See how it's done

Top of page
Note: Outlook on the web is the web version of Outlook for business users with a work or school account.
Automatically add a signature to a message
You can create an email signature that you can add automatically to all outgoing messages or add manually to specific ones.
Select Settings at the top of the page.
Select Mail > Compose and reply .
Under Email signature , type your signature and use the available formatting options to change its appearance.
Select the default signature for new messages and replies.
Manually add your signature to a new message
If you've created a signature but didn't choose to automatically add it to all outgoing messages, you can add it later when you write an email message.
In a new message or reply, type your message.

If you created multiple signatures, choose the signature you want to use for your new message or reply.
When your email message is ready, choose Send .
Note: Outlook.com is the web version of Outlook for users signing in with a personal Microsoft account such as an Outlook.com or Hotmail.com account.
Related articles
Create and add an email signature in Outlook for Mac
Create an email signature from a template

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fifth Generation Computers. (present and beyond) Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence. Are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
THIS IS A PPT ON GENERATIONS OF COMPUTEER AND HOW THE COMPUTER WORLD TRANSITTED. 1. Generation of Computers Based on the characteristics of various computers developed from time to time, they are categorized as generation of computers. Generation of Computers First Second Third Fourth Fifth Generation Generation Generation Generation Generation.
INTRODUCTION The. First Generation -. Second Generation -. Third Generation -. Fourth Generation -. Fifth Generation -. REFERENCE www.library.thinkquest.org. THANK YOU. The five generations of computers presentation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
PDF | On Oct 21, 2019, Ishaq Zakari and others published History of computer and its generations. | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the first generation in 1946 to the present fifth generation. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, heat-producing machines. The second generation introduced transistors, reducing size and heat. The third generation used integrated circuits which further reduced size.
The Second Generation • Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words. • Second-generation computers still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output. • These were also the first computers that stored their
computer, which gets its power by variable programs, with the ability to calculate rapidly, hold lots of information and even learn. We mark computer generations by the logic technology they're built from. We're currently in the fourth generation, called large scale integrated circuit technology. The first generation began
The Third Generation, 1964-1979. The third generation officially began in April 1964 with IBM's announcement of its System/360 family of computers. Hardware technology began to use integrated circuits (ICs) which yielded significant advantages in both speed and economy. Operating System development continued with the introduction and ...
generation computer. Even the later first generation computers could run the first three generations of computer languages (the first high level language, FORTRAN, was released in 1957). There are hundreds of high-level programming languages. Most of these are procedural, emphasizing the algorithmic side of programming (the procedures showing
The 5 Generations of Computers - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. All about the 5 generations of computers
Download ppt "The Five Generations of Computers". Generations of Computer The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer. Each generation of computer is designed based on a new ...
Fifth generation computers are in developmental stage which is based on the artificial intelligence. The goal of the fifth generation is to develop the device which could respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will be used in this technology.
SECOND GENERATION - 1956-1963: TRANSISTORS Transistors replaced vacuum tubes allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient and more reliable than their first-generation predecessors. Still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output. Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s) Main electronic component - vacuum tube. Main memory - magnetic drums and magnetic tapes. Programming language - machine language. Power - consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat. Speed and size - very slow and very large in size (often taking up ...
Generations of Computers Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. Nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system.
Third Generation Computers (1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond) Generations of Computer. Time-Period. Evolving Hardware. First Generation. 1940s - 1950s. Vacuum Tube Based.
From the central processing unit and memory to input/output controls—on a single chip. . Fourth generation computers also saw the development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices. Fourth generation computers AMD' so. generation compu ers (present and beyond) Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence.
In comparison to first generation computers, the second generation computer had the following favorable features. 1. Smaller in size as compared to first generation computers 2. More reliable 3. Less heat generated 4. Faster computational speed Disadvantages: Some unfavorable features can also be seen in this generation. 1. Air conditioning ...
Title: The Five Generations of Computers 1 The Five Generations of Computers 2 First generation computers (1940-1956) The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. They were often enormous and taking up entire room. First generation computers relied on machine language. . They were very expensive to operate ...
Generations of computers. Sep 27, 2021 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 4 likes • 5,842 views. A. AajuSunariya. This ppt is about generations of computers. Technology. Download now. Generations of computers - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Computer Concepts INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 3 Fig. 1.1.1: Different Computer Operations Input: A computer accepts data that is provided by means of an input device, such as a keyboard. Processing: A computer performs operations on the data to transform it in some way. Output: A computer produces output on a device, such as a printer or a monitor, that shows
Generation of Computers - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
The Department of Labor's new overtime regulation is restoring and extending this promise for millions more lower-paid salaried workers in the U.S.
View PDF Abstract: Generative Commonsense Reasoning (GCR) requires a model to reason about a situation using commonsense knowledge, while generating coherent sentences. Although the quality of the generated sentences is crucial, the diversity of the generation is equally important because it reflects the model's ability to use a range of commonsense knowledge facts.
Presentation on computer generation. Mar 24, 2017 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 63 likes • 58,770 views. Pritam Das. Generation of computer,Computer Types. Devices & Hardware. Download now. Presentation on computer generation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Under Choose default signature, set the following options.. In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account. You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a ...