Movie Reviews
Tv/streaming, collections, great movies, chaz's journal, contributors, the book of life.

Now streaming on:
“The Book of Life” bedazzles your eyes and buoys your spirits as it treads upon themes most commonly associated with the macabre universe of Tim Burton . But instead of being gaga for ghoulishness, this Mexican fiesta of animated splendor is packed with visual delights far more sunny than sinister as they burst forth as if flung from an over-packed piñata.
A collaboration between fledgling Reel FX Creative Studios and 20th Century Fox, “The Book of Life” is a rare cartoon feature that doesn’t just deserve to be seen in 3-D, but practically demands it. Complementing the eye candy is a quirkily eclectic soundtrack, including catchy new songs by award-winning score writer Gustavo Santaolalla and Paul Williams of “The Rainbow Connection” fame, and a wide-ranging voice cast. If you always wanted to hear opera great Placido Domingo sing “Cielto Lindo” and its “ay-yai-yai-yai” refrain as if it were Verdi, here is your chance.
That said, the basics of this fantastical fable, whose ingenious puppet-like character designs draw upon the familiar wooden folk-art figures associated with the annual celebration of The Day of the Dead, are somewhat overly familiar despite all the rich cultural references that spice up the proceedings.
There is the ever-popular love triangle in the form of three childhood amigos. Our main hero, the tender-hearted Manola ( Diego Luna , whose boyish vocals are a constant source of plaintive pleasure), comes from a long line of legendary bullfighters and is skilled in the ring himself. But his true calling is that of a guitar-strumming troubadour. The boastful Joaquin ( Channing Tatum , who taps into his abundant reserve of amusing swagger) is a man of action, a mucho-macho mustachioed bandit-rustler with a broad chest crammed with medals.
They both pursue Maria, the smart and headstrong daughter of the general who runs their village of San Angel. She has all the usual attributes of the typical empowered animated female lead – a bookworm with martial-arts fighting skills and all that -- but is lucky enough to be blessed with the vivacious vocal spark of Avatar’s Zoe Saladana.
The Book of Life’s multi-tiered plot also involves dueling married deities who reign over separate domains in the afterlife and decide to make a wager. La Muerte (well-known telenovela star Kate del Castillo ), who oversees the cheery Land of the Remembered and believes in the decency of mortals, bets that sensitive soul Manolo will win Maria’s hand. Xiabalba ( Ron Perlman , a pet actor of the film’s producer, Guillermo del Toro), a devious sort who rules the dour Land of the Forgotten, backs the vain Joaquin.
Xiabalba fools Manolo into entering The Land of the Remembered to seek Maria, when it turns out she has only fallen into a “Sleeping Beauty”-style slumber. In order to return to The Land of the Living himself, Manolo must undergo a series of challenges involving his colorful ancestors. Meanwhile, San Angel is being threatened by the fearsome bandit Chakal (whose metallic monster form feels like a del Toro invention) and his gang of nasty thieves.
A three-way romance, multiple worlds, numerous feats, combative gods, a monstrous foe – all these layers make for a rather dense confection. But first-time feature director and co-writer Jorge R. Gutierrez (co-creator of Nickelodeon’s “El Tigre: The Adventures of Manny Rivera”) smartly tames his somewhat unwieldy story by cleverly having a modern-day museum guide ( Christina Applegate ) transfix a group of rowdy school kids by relating the tale we are watching as if it were a fable of old.
Where this device comes in handiest is when the subject of death is broached and the children think Maria has really passed away. As one dismayed boy exclaims, “Maria died? What kind of story is this? We’re just kids.” Gutierrez thoughtfully deflects any parental concern about dealing with a potentially morbid subject with a refreshing directness that goes beyond such iconic animated tragedies as the deaths of Bambi’s mother and Simba’s father in “ The Lion King .”
There is genius to be mined in the smaller details, something that Gutierrez excels at as he playfully mixes mythology both real and invented with pop-art touchstones. From a chorus of angelic singing nuns and hirsute town elders whose protruding snouts recall the hippie era’s Fabulous Furry Freak Brothers to pigs-gone-wild mayhem and a tipsy mariachi trio who slur their way through Rod Stewart’s “Do Ya Think I’m Sexy” and Biz Markie’s “I’m Just a Friend,” “The Book of Life” isn’t afraid to catch us off guard. When a forlorn Manolo, abandoned by the townsfolk after refusing to kill a bull in the ring, starts to wail Radiohead’s “Creep,” you could hear teen girls at my screening yelp in joyful recognition.
But Guiterrez even goes a step beyond, as “The Book of Life” personifies the philosophy that drives The Day of the Dead and encourages a healthy way to celebrate those who are gone. As he puts it, “As long as you remember those who came before you, and as long as you tell their stories, cook their dishes, and sing their songs … they’re with you. They live inside your heart.”
And this filmmaker’s heart definitely beats inside this impressive debut.


Susan Wloszczyna
Susan Wloszczyna spent much of her nearly thirty years at USA TODAY as a senior entertainment reporter. Now unchained from the grind of daily journalism, she is ready to view the world of movies with fresh eyes.
Now playing

The Listener
Matt zoller seitz.

Glenn Kenny

Megamind vs the Doom Syndicate

Remembering Gene Wilder

Carol Doda Topless at the Condor
Marya e. gates.

The Greatest Hits
Film credits.

The Book of Life (2014)
Rated PG mild action, rude humor, some thematic elements and brief scary images
Diego Luna as Manolo (voice)
Channing Tatum as Joaquin (voice)
Zoe Saldana as Maria (voice)
Christina Applegate as Mary Beth (voice)
Eugenio Derbez
Cheech Marin as Pancho Rodriguez (voice)
Gabriel Iglesias as Pepe Rodriguez (voice)
Ron Perlman as Xibalba (voice)
- Guillermo Del Toro
- Jorge R. Gutierrez
Latest blog posts

The Scene That Clint Eastwood Cut to Make Unforgiven a Classic

Ape Shall Not Kill Ape: A Look at the Entire Apes Franchise

Criterion Celebrates the Films That Forever Shifted Our Perception of Kristen Stewart

The Estate of George Carlin Destroys AI George Carlin in Victory for Copyright Protection (and Basic Decency)
What Is the Book of Life?
The Bible Speaks of the Lamb's Book of Life in Revelation
- Christianity Origins
- The New Testament
- The Old Testament
- Practical Tools for Christians
- Christian Life For Teens
- Christian Prayers
- Inspirational Bible Devotions
- Denominations of Christianity
- Christian Holidays
- Christian Entertainment
- Key Terms in Christianity
- Catholicism
- Latter Day Saints
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Jack-Zavada-578397205f9b5831b5977026.jpeg)
- M.A., English Composition, Illinois State University
- B.S., English Literature, Illinois State University
The Book of Life is a record written by God before the creation of the world, listing people who will live forever in the kingdom of heaven . The term appears in both the Old Testament and New Testament.
Is Your Name Written in the Book of Life?
The Bible says believers' names are written in the Book of Life. In Judaism today, it plays a role in the feast known as Yom Kippur , or Day of Atonement . The ten days between Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur are days of repentance , when Jews express remorse for their sins through prayer and fasting . Jewish tradition tells how God opens the Book of Life and studies the words, actions, and thoughts of every person whose name he has written there. If a person's good deeds outweigh or outnumber their sinful acts, his or her name will remain inscribed in the book for another year.
On the most holy day of the Jewish calendar—Yom Kippur, the final day of judgment—each person's fate is sealed by God for the upcoming year.
References in the Bible
In the Psalms, those who are obedient to God among the living are considered worthy to have their names written in the Book of Life. In other occurrences in the Old Testament , "opening of the books" typically refers to the Final Judgment. The prophet Daniel mentions a heavenly court ( Daniel 7:10 ).
Jesus Christ alludes to the Book of Life in Luke 10:20 , when he tells the 70 disciples to rejoice because "your names are written in heaven."
Paul says the names of his fellow missionary workers "are in the Book of Life." (Philippians 4:3, NIV )
The Lamb's Book of Life in Revelation
At the Last Judgment, believers in Christ are assured that their names are recorded in the Lamb's Book of Life and that they have nothing to fear:
"The one who conquers will be clothed thus in white garments, and I will never blot his name out of the book of life. I will confess his name before my Father and before his angels." (Revelation 3:5, ESV)
The Lamb, of course, is Jesus Christ ( John 1:29 ), who was sacrificed for the sins of the world. Unbelievers, however, will be judged on their own works, and no matter how good those works were, they cannot earn that person salvation:
"And anyone not found written in the Book of Life was cast into the lake of fire." (Revelation 20:15, NIV)
Christians who believe a person can lose their salvation point to the term "blotted out" in connection with the Book of Life. They cite Revelation 22:19 , which refers to people who take away or add to the book of Revelation . It seems logical, however, that true believers would not try to take away or add to the Bible. Two requests for blotting out come from men: Moses in Exodus 32:32 and the psalmist in Psalm 69:28 . God denied Moses's request that his name be removed from the Book. The request of the psalmist to blot out the names of the wicked asks God to remove his ongoing sustenance from the living.
Believers who hold to eternal security say Revelation 3:5 shows that God never blots out a name from the Book of Life. Revelation 13:8 refers to these names being "written before the foundation of the world" in the Book of Life. They further argue that God, who knows the future, would never list a name in the Book of Life in the first place if it would have to be blotted out later.
The Book of Life assures that God knows his true followers, keeps and protects them during their earthly journey, and brings them home to him in heaven when they die.
Also Known As
The Lamb's Book of Life
Sources: gotquestions.org ; Holman Illustrated Bible Dictionary , Expository Dictionary of Bible Words , and Totally Saved , by Tony Evans.
- Why Is Rosh Hashanah Called the Feast of Trumpets in the Bible?
- The Names and Titles of Jesus Christ
- What Is the Firmament in the Bible?
- 35 Bible Verses About Life
- The Book of Revelation, a Prophecy of Warning and Hope
- Christian Symbols Illustrated Glossary
- What Is the Bible?
- Moses in the Bible, Giver of the Law
- Are Crystals in the Bible?
- What Does Hallelujah Mean in the Bible?
- The Role of Anointing Oil in the Bible
- The 66 Books of the Bible
- An Overview of Genesis in the Bible
- Learn What the Bible Says About Righteousness
- Heroes of Faith in the Book of Hebrews
- What Does the Bible Say About Angels?
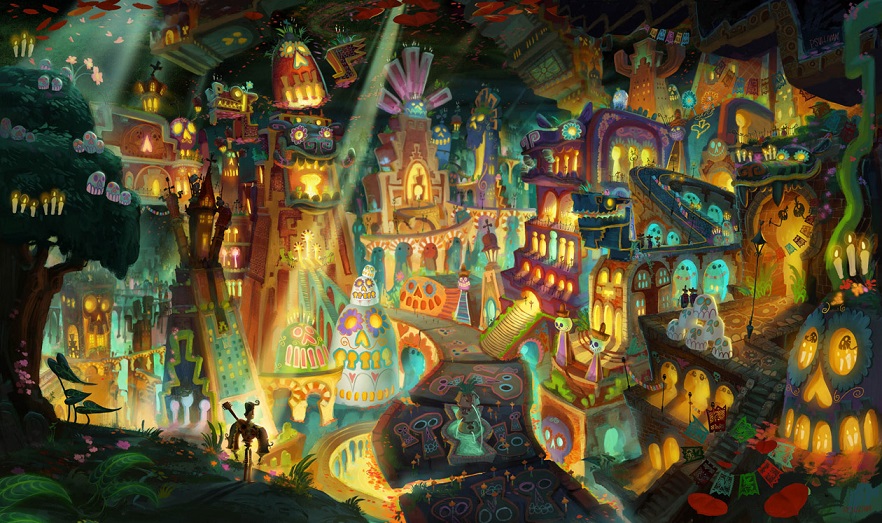

The Book of Life | Jorge R. Gutiérrez
Jorge R. Gutierrez wants to teach people about his heritage. He also wants to make colorful, energetic animated films to dazzle a wide audience. With The Book of Life , Gutierrez manages to scratch both itches at once. It’s his first credit as a director and his sixth as an animator; his comfort with the medium shows in each frame, but not nearly as much as his passion for the customs of Día de los Muertos, Mexico’s holiday of remembrance.
Gutierrez hasn’t simply made a movie that’s based around the Day of the Dead’s macabre, misunderstood iconography; rather, he’s made a movie that embraces its rituals and meanings, expounding on the lessons of the three-day festival while seizing every available opportunity to entertain young and old viewers alike. In a best-case scenario, you will walk away from the film in a state of informed delight, smarter than you were before you went in and all the happier for it. Now that’s a cultural experience.
Gutierrez structures The Book of Life as a story within a story. The film begins on a museum field trip, with a handful of delinquent students on a tour of the gallery’s hidden Mexico exhibit, and from there turns into a moral tale of love and loss. The principal narrative focuses on the dynamic trio of Joaquín (Channing Tatum), Manolo (Diego Luna), and Maria (Zoe Saldana), starting from the days of their youth and following them through to their adulthoods. It’s a love triangle complicated first by the boys’ friendship, and second by the machinations of La Muerta (Kate del Castillo) and Xibalba (Ron Perlman). She is the glowing embodiment of death, ruler of the Land of the Remembered, while he presides over the underworld, a dark place where the souls of the forgotten crumble away like so much ash.
In spite of its excesses, Gutierrez miraculously manages to wrap up all its various odds and ends neatly enough by the end.
They’re gods, and as gods will do, they place a wager on whether Maria will fall for Manolo or Joaquín. Trailers suggest that The Book of Life ’s plot kicks off when that “friendly” bet goes awry and sends Manolo to the realm of La Muerta. In truth, the film reserves its traipses through the afterlife for its final act, and spends the bulk of its time dealing with the travails of the living. Competition over Maria’s heart drives much of the proceedings, as well as constant threat of attack from roving bandits. While trying to balance all these moving parts, Gutierrez keeps the proceedings briskly zany with hyperactive humor.
If anything, it’s perhaps a bit too hyperactive, not to mention overstuffed. Even at 95 minutes, The Book of Life bursts with thematic through-lines: self-discovery, heroism, romance, challenging gender roles, living in the shadows of one’s ancestors, growing up, and so on and so forth. None of Gutierrez’s ideas are bad, per se; they’re just too many of them, with some threads inevitably less well-developed than others. Would the picture lose anything by dropping Manolo’s struggle with his family’s bullfighting dynasty? Does the movie change drastically if its male leads aren’t bosom buddies? Frankly, it all becomes exhausting after a while.
In spite of its excesses, Gutierrez miraculously manages to wrap up all its various odds and ends neatly enough by the end. Besides, you’ll be too enthralled by the film’s infectious sense of adventure to care about overflow in the first place. Gutierrez’s enchantingly spooky wood-carved aesthetic transcends the messy plot, and that’s true even before he guides us from this life to the next. Once we arrive in the Land of the Remembered, we are treated to an exhilaratingly realized place of perpetual celebration — but as the film makes clear, it’s only one leg of a broader, more personal journey. Just as Día de los Muertos gives its characters a chance to learn about themselves, their pasts, and one another, so too does Gutierrez’s film offer us the opportunity to engage with a tradition that’s not our own. Sure, The Book of Life could have been tighter and more coherent, but there’s no way it could be any more sincere.
- Blockbuster Beat
- by Andy Crump
You Might Also Like...

La Belle Èpoque | Nicolas Bedos

The Witches | Robert Zemeckis

El Gran Movimiento — Kiro Russo
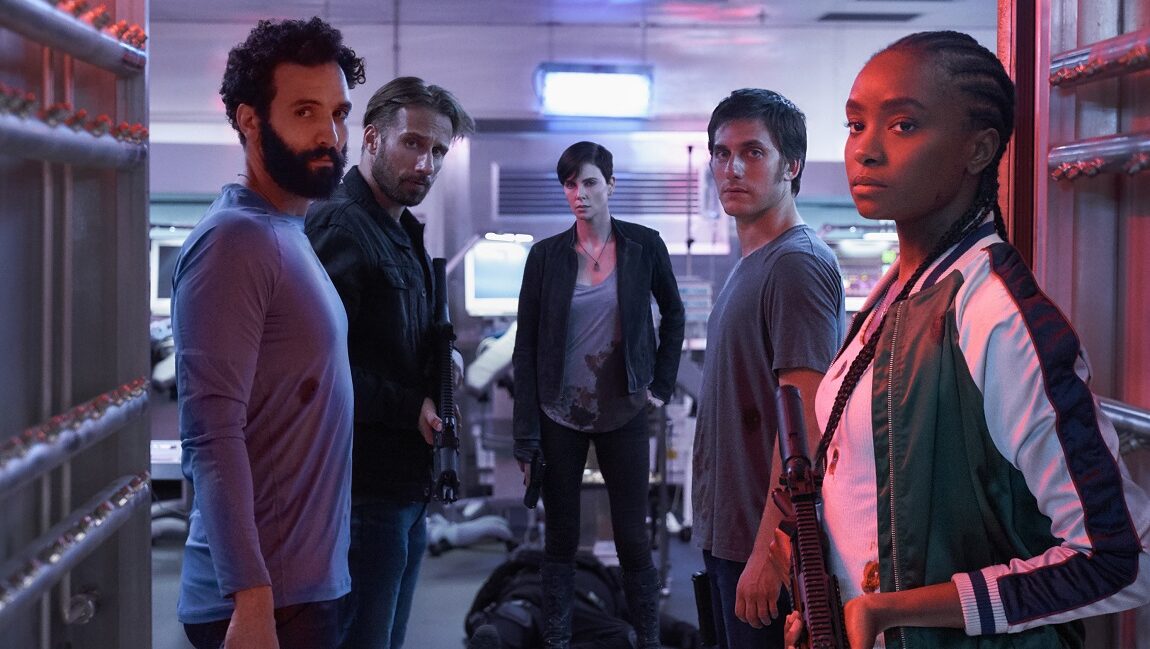

The Old Guard | Gina Prince-Bythewood
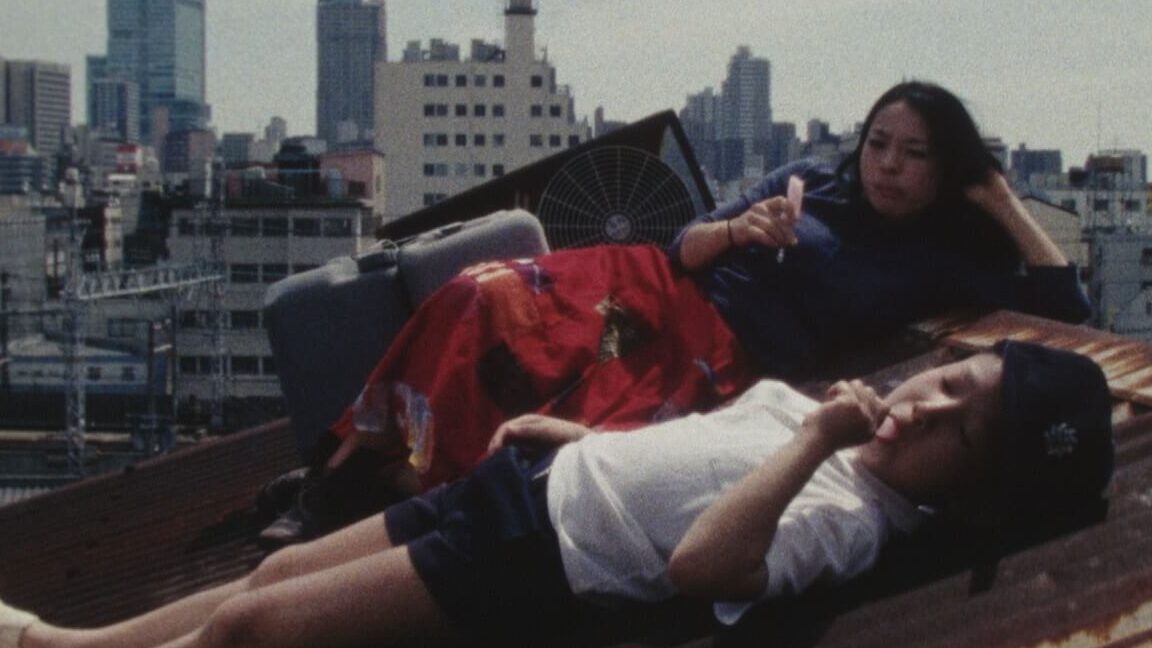

The Kamagasaki Cauldron War | Leo Sato
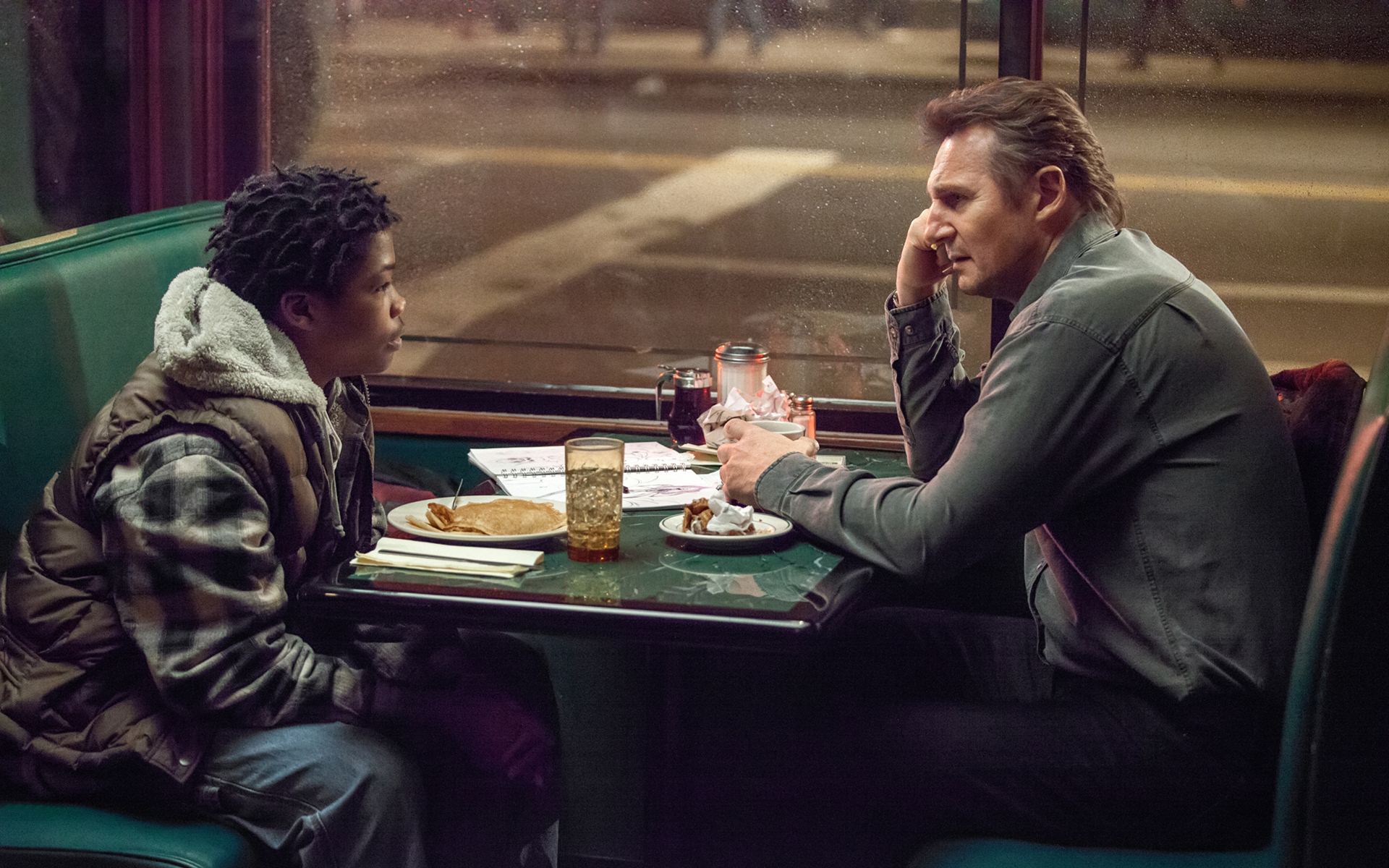

A Walk Among the Tombstones | Scott Frank
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
(C) Copyright 2019 - Solo Pine Designs. All Rights Reserved. Designed & Developed by Solo Pine . | Privacy Policy
Privacy Overview
Common Sense Media
Movie & TV reviews for parents
- For Parents
- For Educators
- Our Work and Impact
Or browse by category:
- Get the app
- Movie Reviews
- Best Movie Lists
- Best Movies on Netflix, Disney+, and More
Common Sense Selections for Movies

50 Modern Movies All Kids Should Watch Before They're 12

- Best TV Lists
- Best TV Shows on Netflix, Disney+, and More
- Common Sense Selections for TV
- Video Reviews of TV Shows

Best Kids' Shows on Disney+

Best Kids' TV Shows on Netflix
- Book Reviews
- Best Book Lists
- Common Sense Selections for Books

8 Tips for Getting Kids Hooked on Books

50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12
- Game Reviews
- Best Game Lists
Common Sense Selections for Games
- Video Reviews of Games

Nintendo Switch Games for Family Fun

- Podcast Reviews
- Best Podcast Lists
Common Sense Selections for Podcasts

Parents' Guide to Podcasts

- App Reviews
- Best App Lists

Social Networking for Teens

Gun-Free Action Game Apps

Reviews for AI Apps and Tools
- YouTube Channel Reviews
- YouTube Kids Channels by Topic

Parents' Ultimate Guide to YouTube Kids

YouTube Kids Channels for Gamers
- Preschoolers (2-4)
- Little Kids (5-7)
- Big Kids (8-9)
- Pre-Teens (10-12)
- Teens (13+)
- Screen Time
- Social Media
- Online Safety
- Identity and Community

Explaining the News to Our Kids
- Family Tech Planners
- Digital Skills
- All Articles
- Latino Culture
- Black Voices
- Asian Stories
- Native Narratives
- LGBTQ+ Pride
- Best of Diverse Representation List

Celebrating Black History Month

Movies and TV Shows with Arab Leads

Celebrate Hip-Hop's 50th Anniversary
The book of life, common sense media reviewers.

Beautifully animated film has some scary imagery.

A Lot or a Little?
What you will—and won't—find in this movie.
Kids will learn the cultural traditions of the Day
There's an ongoing message that doing what'
Manolo is pressured to be as great a bullfighter a
Potentially scary imagery/pervasive death referenc
Manolo and Joaquin are both in love with Maria. Th
Words like "kick his butt" and insults l
There's no consumerism in the film, which is s
There's drinking, but it's not clear what&
Parents need to know that The Book of Life is a refreshingly original animated film that takes viewers to the underworld and back. Smaller children might find the scenes in the Land of the Remembered scary, especially those featuring the king of the underworld, Xibalba (who's named after the Mayan name…
Educational Value
Kids will learn the cultural traditions of the Day of the Dead and what it was like to live in an old Mexican town without technology.
Positive Messages
There's an ongoing message that doing what's right is more important than other people's expectations of you. When Manolo goes to the underworld, he learns that he's part of a bigger world. On the Day of the Dead, family members that have died are honored and remembered in a big celebration.
Positive Role Models
Manolo is pressured to be as great a bullfighter as his father and other ancestors were, but he defies them by not killing the bull in the ring because it’s wrong. His kindness and integrity end up saving him in the end. Maria is strong and self-sufficient; at first, she won't be pressured into marrying Joaquin just because her father wants her to and everyone in town admires him. Joaquin is egotistical and keeps a great secret about how he came to be the town's invincible hero. Xibalba is a classic villain who will stop at nothing to trade places with La Muerte.

Violence & Scariness
Potentially scary imagery/pervasive death references (skeletons, beheaded figures, etc.) throughout the movie. Manolo fights real-life bulls, and, near the end, he also fights a scary demon bull the size of a building. Xiabalba, the king of the underworld, is scary and makes loud frightening movements that could scare some children. Manolo dies and becomes a skeleton figure and reunites with his dead ancestors, including his mother. His grandfather has his head chopped off, and Manolo's mother carries it around. Maria and Manolo are bitten by a snake that transforms from a cane. There's a battle scene at the end with punching and sword fighting. Joaquin, the town hero, fights throughout the movie. Manolo and Joaquin get in a slap fight over Maria. Throughout the movie, there are little scares where characters jump out or react loudly. At the beginning of the movie, children visiting a museum are taken through a magical door to a secret room.
Did you know you can flag iffy content? Adjust limits for Violence & Scariness in your kid's entertainment guide.
Sex, Romance & Nudity
Manolo and Joaquin are both in love with Maria. They try to kiss her several times, and Manolo eventually does. Manolo's mariachi friends sing "If You Think I'm Sexy" and "Just a Friend" to help Manolo court Maria.
Did you know you can flag iffy content? Adjust limits for Sex, Romance & Nudity in your kid's entertainment guide.
Words like "kick his butt" and insults like "lazy bum." Some kids are called "detention kids."
Did you know you can flag iffy content? Adjust limits for Language in your kid's entertainment guide.
Products & Purchases
There's no consumerism in the film, which is set in the past, but there are tie-in marketing deals for clothing, jewelry, toys, etc.
Drinking, Drugs & Smoking
There's drinking, but it's not clear what's being consumed.
Did you know you can flag iffy content? Adjust limits for Drinking, Drugs & Smoking in your kid's entertainment guide.
Parents Need to Know
Parents need to know that The Book of Life is a refreshingly original animated film that takes viewers to the underworld and back. Smaller children might find the scenes in the Land of the Remembered scary, especially those featuring the king of the underworld, Xibalba (who's named after the Mayan name for the realm of the dead). The characters in the Land of the Remembered are traditional Day of the Dead figures, which are skeletons in brightly colored clothing. One dead character's head is separate from his body. There are some bullfighting scenes and battle sequences that are a little violent, and things get somewhat darker when the action shifts to the underworld (there's a demonic bull surrounded by fire). Expect a little bit of kissing and a few insults ("kick his butt," "lazy bum"), too. But the fun definitely outweighs the scary/iffy parts, and ultimately this is a vibrant, colorful movie about doing the right thing and the importance of family -- messages that can be appreciated by both kids and parents. It's also an invitation to explore and learn more about Mexican culture, from the details of the Day of the Dead celebrations to legendary creatures like Chupacabras. To stay in the loop on more movies like this, you can sign up for weekly Family Movie Night emails .
Where to Watch
Videos and photos.

Community Reviews
- Parents say (29)
- Kids say (41)
Based on 29 parent reviews
Violence, sexism, just junk
Enthralling story that highlights mexican culture, what's the story.
In THE BOOK OF LIFE, Manolo (voiced by Diego Luna ) and Joaquin ( Channing Tatum ) have loved Maria ( Zoe Saldana ) all their lives. What they don't know is that the kind La Muerte ( Kate del Castillo ) and the evil Xibalba ( Ron Perlman ) -- the rulers of the underworld -- made a bet over which boy Maria would marry. She's sent away to school and comes back more confident and more beautiful. Meanwhile, Manolo grows up into a sensitive guitar player whose family wants him to be a ruthless bullfighter, while Joaquin becomes the town hero -- with a big secret and huge ego. Xibalba will go to any lengths to win the bet, so he sets his snake on Manolo. So Manolo must travel through the underworld on the Day of the Dead, the biggest party of the year, to return to his true love.
Is It Any Good?
This is a beautifully animated film about Dia de los Muertos that combines essential Mexican folklore, ancient mythology, and pop culture. Luna is charming as Manolo, the guitar playing bullfighter who's too kind to kill the bull. Tatum has just the right amount of bravado to play Joaquin, who shouts his own name as he rushes into battle, and Saldana is sassy and adorable as the smart, independent Maria.
Most impressive is the visually stunning underworld that director Jorge Gutierrez has created. The Book of Life immerses viewers into the environment, traditions, colors, and sounds of Day of the Dead celebration; La Muerte is the most gorgeous animated queen since Maleficent in the original Sleeping Beauty , and Xibalba is perfect as her scary king. The characters and the music (excellent reworkings of classic and alternative pop songs) are absorbing and memorable, and you'll be thinking about the world full of color and fun that Gutierrez has created long after you've seen the movie.
Talk to Your Kids About ...
Families can talk about the pressure to live up to expectations. Can you relate to Manolo and Joaquin's feeling that they can't fill the shoes of the family that came before them in The Book of Life ? What's the best way to handle that type of situation? Manolo, Maria, and Joaquin all ultimately realize that they must follow their own paths. Kids: Is it ever OK to defy your parents' wishes?
How scary is The Book of Life ? Is it ever fun to be scared? Why or why not?
How do the characters in The Book of Life demonstrate integrity ? Why is this an important character strength ?
Are you familiar with Day of the Dead? Does your culture celebrate loved ones after they've died? How could you learn more about this holiday? What other Latino traditions and values does the movie include?
Especially considering the movie's time setting (likely the early 1900s), Maria is a very progressive young woman, with a strong, determined personality. How does that make her a role model? How are her goals and dreams out of the ordinary for the world she's part of?
Movie Details
- In theaters : October 17, 2014
- On DVD or streaming : January 27, 2015
- Cast : Diego Luna , Zoe Saldana , Channing Tatum
- Director : Jorge R. Gutierrez
- Inclusion Information : Latino actors, Female actors, Black actors
- Studio : Twentieth Century Fox Film Corporation
- Genre : Family and Kids
- Topics : Magic and Fantasy , Adventures , Fairy Tales , Great Boy Role Models , Great Girl Role Models
- Character Strengths : Integrity
- Run time : 95 minutes
- MPAA rating : PG
- MPAA explanation : mild action, rude humor, some thematic elements and brief scary images
- Award : Common Sense Selection
- Last updated : January 20, 2024
Did we miss something on diversity?
Research shows a connection between kids' healthy self-esteem and positive portrayals in media. That's why we've added a new "Diverse Representations" section to our reviews that will be rolling out on an ongoing basis. You can help us help kids by suggesting a diversity update.
Suggest an Update
Our editors recommend.

The Nightmare Before Christmas

Fantastic Mr. Fox

Tim Burton's Corpse Bride
Offbeat animated movies, animation apps, games, and websites, related topics.
- Magic and Fantasy
- Fairy Tales
- Great Boy Role Models
- Great Girl Role Models
Want suggestions based on your streaming services? Get personalized recommendations
Common Sense Media's unbiased ratings are created by expert reviewers and aren't influenced by the product's creators or by any of our funders, affiliates, or partners.
- Cast & crew
- User reviews

The Book of Life
- Manolo, a young man who is torn between fulfilling the expectations of his family and following his heart, embarks on an adventure that spans three fantastic worlds where he must face his greatest fears.
- From producer Guillermo del Toro and director Jorge Gutierrez comes an animated comedy with a unique visual style. THE BOOK OF LIFE is the journey of Manolo, a young man who is torn between fulfilling the expectations of his family and following his heart. Before choosing which path to follow, he embarks on an incredible adventure that spans three fantastical worlds where he must face his greatest fears. Rich with a fresh take on pop music favorites, THE BOOK OF LIFE encourages us to celebrate the past while looking forward to the future. — 20th Century Fox
- Mary Beth, a museum tour guide, takes a group of school detention students on a secret museum tour, telling them, with wooden figures, the story of a Mexican town called San Angel from the Book of Life, holding every story in the world. On the Day of the Dead, La Muerte, ruler of the Land of the Remembered, and Xibalba, ruler of the Land of the Forgotten, see Manolo Sánchez and Joaquín Mondragon competing over María Posada. They strike a wager: if María marries Manolo, Xibalba will no longer interfere in mortal affairs, but if she marries Joaquín, La Muerte and Xibalba will swap realms. However, Xibalba cheats by giving Joaquín his Medal of Everlasting Life, which grants the wearer invincibility.
- While visiting a museum, a group of five troubled youth, on detention, are won over by their tour guide, Mary Beth. Part of what wins them over is the story she tells from the Book of Life, which contains all the stories of the world, both true and made-up. The story she tells centers on the Day of the Dead in San Angel, Mexico - the center of the universe - of three childhood best friends, strong-willed María Posada, Joaquín Mondragon Jr., who likes to show he's a man by sporting a fake mustache without truly knowing what it means to be a man, and guitar-playing Manolo Sánchez, the offspring of the town's general, a deceased military hero and a bullfighter respectively. Even at this age, both Joaquín and Manolo are in love with María, each knowing he would like eventually to marry her. They are separated when María's father sends her to Europe for school to learn to be a lady. By the time María returns to San Angel as a young woman, Joaquín has become a military hero like his father, and Manolo has become a bullfighter like all his Sánchez ancestors, male and female. While Manolo showed his aptitude for bullfighting at a young age, his heart still remains music, singing and playing his guitar, and not with bullfighting. Each still pines for María as his wife. What they are unaware of is that two leaders of the afterlife, estranged wife and husband, La Muerte, ruler of the Land of the Remembered, and Xibalba, ruler of the Land of the Forgotten, long ago made a wager on which of the two will marry María, the outcome which will have a profound effect not only on María, Joaquín and Manolo's joint lives, but the course of San Angel, which is constantly under threat by evil Chakal, and the world. What La Muerte is further unaware of is that Xibalba is taking underhanded measures to win, which also affects María, Joaquín and Manolo's live and possible deaths. — Huggo
- A bus full of children arrives at a museum. They're a rowdy bunch that frighten the guards. A young woman named Mary Beth (voice of Christina Applegate) comes out and gets the kids to follow her as she tells them about the famous legends and myths of Mexican folklore. She leads them to the Book of Life, which holds the story of how the ways of their world were shaped. She opens a box of dolls that represent the characters of the story. As the story begins, Mary Beth says there were two gods - La Muerte (voice of Kate Del Castillo), ruler of the Land of the Remembered, where the spirits live on with their memories kept by their loved ones; and Xibalba (voice of Ron Perlman), ruler of the Land of the Forgotten, where the forgotten souls decay into oblivion. The two spirits watch over the town of San Angel and see three young children playing - Manolo (voice of Emil-Bastien Bouffard), Maria (voice of Genesis Ochoa), and Joaquin (voice of Elias Garza). Both boys are in love with Maria, but she does not wish to be claimed by anyone. Manolo comes from a family of bullfighters, but his real passion lies in music. Joaquin is more adventurous, hoping to avenge his father after he was killed by the sinister bandit Chakal (voice of Dan Navarro). Disguised as peasants, La Muerte and Xibalba go down to San Angel during a celebration of the Day of the Dead. Manolo and his father, Carlos Sanchez (voice of Hector Elizondo), remember his mother Carmen. La Muerte, as an old woman, asks Manolo for a piece of bread. He gladly gives her a whole loaf. Xibalba, as an old man, asks Joaquin for some, but he is more hesitant. Xibalba gives Joaquin a pin that is called the Pin of Everlasting Life, which is something Chakal is after as it can protect him from death. Xibalba then bets La Muerte that Maria will end up marrying Joaquin, while La Muerte bets on Manolo. The winner will be allowed to rule over the Land of the Remembered. The wager is set. Maria, a free and rebellious spirit, sets free a group of animals into the town after seeing a cute baby pig and fearing that he would be killed by the butcher, to the chagrin of her father General Posada (voice of Carlos Alazraqui). A wild boar comes into town and nearly gets Posada, but Manolo manages to lure the boar like a bullfighter with the red cape. He gets the boar to crash into a wall, but Posada, who was unable to see anything, thinks it was Joaquin that saved him, ignoring Manolo in favor of him. As punishment for her actions, Posada orders Maria to be sent to a private boarding school. She sadly leaves her two friends behind. Manolo gives her the baby pig that she wanted to save, which Manolo names Chuy. Maria gives him a guitar after his old one is broken. On it is an engraving that says "Always play from your heart." Over the years, Carlos mentors Manolo (now played by Diego Luna) into becoming a skilled bullfighter, while Joaquin (now voiced by Channing Tatum), with the help of the pin, manages to conquer many enemies and become the town hero. The day comes for Maria (now voiced by Zoe Saldana) to return home. A big celebration is held in town. Manolo and Joaquin see her and are captivated by her beauty. Manolo is set to fight a bull, but he has qualms over killing it. Although he is able to make it crash into the wall, he is told by Carlos to kill it, but he refuses. Everybody boos him, but Maria applauds him for his compassion. Somebody throws Manolo a guitar to his head, knocking him out. When he comes to, his father expresses his disappointment, saying he is not a real Sanchez. General Posada holds a party for Maria, where Joaquin suggests that Maria ought to be with him so that he can make her happy. This does not go over well with Maria, who tells him off and leaves. Meanwhile, Manolo gets his Mariachi band friends, the Rodriguez brothers (voices of Gabriel Iglesias, Cheech Marin, and Ricardo Sanchez), to help serenade her. The brothers play some tunes (like Biz Markie's "Just A Friend"), none of which impress Maria. Manolo serenades her with a song from his heart, which even moves all the townspeople. The brothers form a ladder to bring Manolo up to Maria's balcony so they may kiss, but she tells him it's not gonna be that easy. Joaquin proposes to Maria. Their marriage would keep San Angel safe from Chakal and his bandits. Manolo arrives and fights with Joaquin over Maria, which she thinks is foolish. Manolo later tells Maria to meet him at dawn. Fearing he will lose the wager, Xibalba turns his staff into a snake and sends it after Manolo. Maria follows a trail of candles to a tree where Manolo is. He professes his love to her, which she reciprocates. Then, the snake slithers into the area. Maria pushes Manolo out of the way, getting bitten by the snake. She dies instantly. Manolo screams in rage. He carries Maria's body back to San Angel, where both Joaquin and General Posada blame him for Maria's death. Manolo returns to the tree, mourning his love. Xibalba appears before him, and Manolo states that he will do anything to be with Maria again. Xibalba uses his staff to form a two-headed snake, which bites Manolo and kills him. Manolo's spirit goes down to the Land of the Remembered, looking like a skeleton. It is a remarkably wonderful looking place where the remembered spirits roam around. The captain of the land comes by and learns he is part of the Sanchez family. He escorts Manolo to meet them. He meets his famous ancestors, including Carmelo (Jorge R. Gutierrez), who never used capes to fight; Jorge (Placido Domingo), who fought with one arm and leg, and is a skilled singer; and Luis (Danny Trejo), Manolo's grandfather who is upset with Manolo for dying so soon. Manolo is taken to meet his mother Carmen (Ana de la Reguera). She is happy to see her son, but not happy that he is there so soon. With the help of his family, Manolo goes to La Muerte's castle, which is now run by Xibalba. He explains that the snake bite only put Maria to sleep, and Joaquin revived her with the pin. She is awake and learns that Manolo is dead. Angry over being cheated, Manolo vows to tell La Muerte what Xibalba did and to return to the human world. Manolo, Carmen, and Luis are told to travel to the Cave of Souls to make it to the Land of the Forgotten and meet with La Muerte. There, Manolo is thrown into a labyrinth where three large boulders roll around trying to crush him. Manolo evades all of them, to the surprise of the spirit guardian. The guardian takes a gigantic form and swings down a huge sword onto Manolo, which shatter upon hitting him. Realizing he is pure of heart, the guardian allows Manolo to pass on through The Sanchez's meet the Candle Maker (voice of Ice Cube), who oversees the lives of everybody in the living world. Manolo convinces him to take him through to the Land of the Forgotten to meet La Muerte. The Candle Maker agrees after seeing that Manolo's story has yet to be written, because he is writing it himself. In The Land of the Forgotten, Manolo, Carmen, and Luis see the lonely spirits decaying and withering away. They make it to Xibalba's castle to find La Muerte. Manolo tells her that Xibalba cheated, sending her into a rage. She summons him and angrily chastises him for betraying her again. Manolo then offers a wager himself. If he wins, Xibalba must let him return to the human world, and La Muerte adds that he may never interfere with the affairs of the living ever again. Otherwise, Xibalba may rule over both realms. The wager is set. Manolo is forced to face off against every bull that his family has ever fought. In the living world, Chakal and his bandits are making their way to San Angel, just as Maria and Joaquin are about to marry. Carlos charges toward Chakal, only to be killed. His spirit joins his family to watch Manolo fight. The bulls come together to form one giant bull. Instead of fighting it, Manolo sings it a song, apologizing for all the wrongs his family has brought to the bulls. Even as the giant bull nearly kills him, he keeps singing, bringing the bulls to peace, and surprising his family. La Muerte and Xibalba, impressed by Manolo's will, grant him his life back and send him to the living world just in time to fight back The three spirits decide, since it is the Day of the Dead, to have some fun by summoning all of Manolo's family to fight back against Chakal. Maria rounds up the whole town to fight back as well. Manolo and Joaquin make amends and decide to fight against Chakal together. Chakal grabs Maria and climbs the top of a tower. With the help of his forefathers, including a now proud Carlos, Manolo is sent up to the tower to face off Chakal. With Maria, they fight the bandit and knock him off the tower, also sending them falling as well, but they land safely. Chakal then lights up the bombs on his belt to take the whole town down with him. Manolo and Joaquin push Chakal beneath a bell and tie him up. Manolo knocks over a column to bring the bell down on him and Chakal. He tells Maria not to forget him. The bell traps them both as the bombs go off, killing Chakal, and supposedly Manolo. However, Manolo emerges safely, after Joaquin gave him the pin to stay alive. Joaquin now realizes that a true hero is selfless General Posada gives Manolo his blessing to marry Maria. The two are wed, with Manolo's family proud of their boy. Manolo and Maria then sing a song and dance with everybody. Xibalba apologizes to La Muerte for betraying her, telling her he loves her. They kiss. Back at the museum, Mary Beth ends the story as the children must leave. They leave excited after hearing the story. As the bus is set to depart, the kids wave goodbye to Mary Beth, who takes the form of La Muerte, to the joy of the kids. The security guard appears as Xibalba. They kiss again. The story ends, and the Candle Maker closes the Book of Life, reminding us all to write our own stories.
Contribute to this page

- See more gaps
- Learn more about contributing
More from this title
More to explore.

Recently viewed
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission
I Reluctantly Love This Website About How to Live and Be

I came across The Book of Life by way of a newsletter started by a man who once wrote an article about sugar that I enjoyed (I’m not sure if I still like the sugar article, but I guess that’s how life goes).
In his newsletter, the man ( Ian Leslie ) linked to a short, elegant essay about teasing and why we like it — “We sense the teaser trying to give us a useful little shove in a good (and secretly welcome) direction and therefore know that, at its affectionate best, teasing is at once sweet and constructive” — and I was like, huh, yes, that’s exactly true, more please. And there was more: There were hundreds of essays about love, relationships, breakups, work, friendship, ambition, and perseverance — all the big topics that I keep trying to throw myself at and understand. (The site is broken into six categories: Relationships, Work, Self-Knowledge, Sociability, Calm, and Leisure.)
The essays in each category are all presented without bylines, in the same gentle, restrained, no-nonsense but vaguely poetic and mysterious British voice. What IS this site? I thought. Who is profiting? Hmm. After about the fifth essay on how to find love , or cultivate it, or recognize when it’s going wrong (“You are, to a far greater extent than you perhaps realise, already alone”), I initiated the full “Oh, I like this” protocol, which included signing up for the newsletter and following it on Twitter . The content felt loony enough, though — is this a scam? Is this secretly conservative propaganda? (I’m always falling for that; I think I’m more conservative than I like to admit) — that I was relieved to see a number of people I admire already followed the site on Twitter. The Book of Life is an offshoot of the London-based School of Life , an organization started in 2008 by the philosopher Alain de Botton and the artist Sophie Howarth , aimed at helping people “develop self-knowledge.”
And now I’ve been getting the newsletter, and I love it. That’s all. I recommend the site. Its layout is also quietly welcoming — taken all together, it feels like an earth-tone quilt, made up of modest but carefully pieced together squares. Reading it, I feel wrapped up and comforted. Also inspired, heartened, and forgiven, or at least hopeful. The site also sells cheesy stuff like aprons and tote bags , which I also found strangely relieving, like “Aha, they’re just trying to make money like the rest of us.” (There remains a sense of being lured in and potentially tricked … like I’m leaving a trail of breadcrumbs directly to my soul.)
There was a moment I did not like, however, when the newsletter sent me something about “the gift of a long lasting marriage,” right when that was the last thing I wanted to hear about. But then what they were really suggesting was that people buy their books to give as wedding gifts. I had sort of thought the website was “on my wavelength,” and so this seeming betrayal ( this is not the content I want to hear about right now ) was unexpectedly jarring. But then it was just about giving someone a present. It’s not that I, personally, need to be married now. Okay. Carry on.
I also really like the essay about the importance of making a home (“We need to get home to remember who we are”). That’s what I’m talking about.
- relationships
- the internet
- the book of life
- the school of life
- science of us
- the cut opinion pages
The Cut Shop
Most viewed stories.
- Get Ready for the Solar Eclipse in Aries to Change You
- Madame Clairevoyant: Horoscopes for the Week of April 7–13
- The Case for Marrying an Older Man
- This Mercury Retrograde in Aries Will Be Peak Chaos
- Behold, the Ballet Sneaker
- ‘Our Relationship Ended Because He Was Too Close With His Ex’
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
What is your email.
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
The Meaning of Life
Many major historical figures in philosophy have provided an answer to the question of what, if anything, makes life meaningful, although they typically have not put it in these terms (with such talk having arisen only in the past 250 years or so, on which see Landau 1997). Consider, for instance, Aristotle on the human function, Aquinas on the beatific vision, and Kant on the highest good. Relatedly, think about Koheleth, the presumed author of the Biblical book Ecclesiastes, describing life as “futility” and akin to “the pursuit of wind,” Nietzsche on nihilism, as well as Schopenhauer when he remarks that whenever we reach a goal we have longed for we discover “how vain and empty it is.” While these concepts have some bearing on happiness and virtue (and their opposites), they are straightforwardly construed (roughly) as accounts of which highly ranked purposes a person ought to realize that would make her life significant (if any would).
Despite the venerable pedigree, it is only since the 1980s or so that a distinct field of the meaning of life has been established in Anglo-American-Australasian philosophy, on which this survey focuses, and it is only in the past 20 years that debate with real depth and intricacy has appeared. Two decades ago analytic reflection on life’s meaning was described as a “backwater” compared to that on well-being or good character, and it was possible to cite nearly all the literature in a given critical discussion of the field (Metz 2002). Neither is true any longer. Anglo-American-Australasian philosophy of life’s meaning has become vibrant, such that there is now way too much literature to be able to cite comprehensively in this survey. To obtain focus, it tends to discuss books, influential essays, and more recent works, and it leaves aside contributions from other philosophical traditions (such as the Continental or African) and from non-philosophical fields (e.g., psychology or literature). This survey’s central aim is to acquaint the reader with current analytic approaches to life’s meaning, sketching major debates and pointing out neglected topics that merit further consideration.
When the topic of the meaning of life comes up, people tend to pose one of three questions: “What are you talking about?”, “What is the meaning of life?”, and “Is life in fact meaningful?”. The literature on life's meaning composed by those working in the analytic tradition (on which this entry focuses) can be usefully organized according to which question it seeks to answer. This survey starts off with recent work that addresses the first, abstract (or “meta”) question regarding the sense of talk of “life’s meaning,” i.e., that aims to clarify what we have in mind when inquiring into the meaning of life (section 1). Afterward, it considers texts that provide answers to the more substantive question about the nature of meaningfulness (sections 2–3). There is in the making a sub-field of applied meaning that parallels applied ethics, in which meaningfulness is considered in the context of particular cases or specific themes. Examples include downshifting (Levy 2005), implementing genetic enhancements (Agar 2013), making achievements (Bradford 2015), getting an education (Schinkel et al. 2015), interacting with research participants (Olson 2016), automating labor (Danaher 2017), and creating children (Ferracioli 2018). In contrast, this survey focuses nearly exclusively on contemporary normative-theoretical approaches to life’s meanining, that is, attempts to capture in a single, general principle all the variegated conditions that could confer meaning on life. Finally, this survey examines fresh arguments for the nihilist view that the conditions necessary for a meaningful life do not obtain for any of us, i.e., that all our lives are meaningless (section 4).
1. The Meaning of “Meaning”
2.1. god-centered views, 2.2. soul-centered views, 3.1. subjectivism, 3.2. objectivism, 3.3. rejecting god and a soul, 4. nihilism, works cited, classic works, collections, books for the general reader, other internet resources, related entries.
One of the field's aims consists of the systematic attempt to identify what people (essentially or characteristically) have in mind when they think about the topic of life’s meaning. For many in the field, terms such as “importance” and “significance” are synonyms of “meaningfulness” and so are insufficiently revealing, but there are those who draw a distinction between meaningfulness and significance (Singer 1996, 112–18; Belliotti 2019, 145–50, 186). There is also debate about how the concept of a meaningless life relates to the ideas of a life that is absurd (Nagel 1970, 1986, 214–23; Feinberg 1980; Belliotti 2019), futile (Trisel 2002), and not worth living (Landau 2017, 12–15; Matheson 2017).
A useful way to begin to get clear about what thinking about life’s meaning involves is to specify the bearer. Which life does the inquirer have in mind? A standard distinction to draw is between the meaning “in” life, where a human person is what can exhibit meaning, and the meaning “of” life in a narrow sense, where the human species as a whole is what can be meaningful or not. There has also been a bit of recent consideration of whether animals or human infants can have meaning in their lives, with most rejecting that possibility (e.g., Wong 2008, 131, 147; Fischer 2019, 1–24), but a handful of others beginning to make a case for it (Purves and Delon 2018; Thomas 2018). Also under-explored is the issue of whether groups, such as a people or an organization, can be bearers of meaning, and, if so, under what conditions.
Most analytic philosophers have been interested in meaning in life, that is, in the meaningfulness that a person’s life could exhibit, with comparatively few these days addressing the meaning of life in the narrow sense. Even those who believe that God is or would be central to life’s meaning have lately addressed how an individual’s life might be meaningful in virtue of God more often than how the human race might be. Although some have argued that the meaningfulness of human life as such merits inquiry to no less a degree (if not more) than the meaning in a life (Seachris 2013; Tartaglia 2015; cf. Trisel 2016), a large majority of the field has instead been interested in whether their lives as individual persons (and the lives of those they care about) are meaningful and how they could become more so.
Focusing on meaning in life, it is quite common to maintain that it is conceptually something good for its own sake or, relatedly, something that provides a basic reason for action (on which see Visak 2017). There are a few who have recently suggested otherwise, maintaining that there can be neutral or even undesirable kinds of meaning in a person’s life (e.g., Mawson 2016, 90, 193; Thomas 2018, 291, 294). However, these are outliers, with most analytic philosophers, and presumably laypeople, instead wanting to know when an individual’s life exhibits a certain kind of final value (or non-instrumental reason for action).
Another claim about which there is substantial consensus is that meaningfulness is not all or nothing and instead comes in degrees, such that some periods of life are more meaningful than others and that some lives as a whole are more meaningful than others. Note that one can coherently hold the view that some people’s lives are less meaningful (or even in a certain sense less “important”) than others, or are even meaningless (unimportant), and still maintain that people have an equal standing from a moral point of view. Consider a consequentialist moral principle according to which each individual counts for one in virtue of having a capacity for a meaningful life, or a Kantian approach according to which all people have a dignity in virtue of their capacity for autonomous decision-making, where meaning is a function of the exercise of this capacity. For both moral outlooks, we could be required to help people with relatively meaningless lives.
Yet another relatively uncontroversial element of the concept of meaningfulness in respect of individual persons is that it is logically distinct from happiness or rightness (emphasized in Wolf 2010, 2016). First, to ask whether someone’s life is meaningful is not one and the same as asking whether her life is pleasant or she is subjectively well off. A life in an experience machine or virtual reality device would surely be a happy one, but very few take it to be a prima facie candidate for meaningfulness (Nozick 1974: 42–45). Indeed, a number would say that one’s life logically could become meaningful precisely by sacrificing one’s well-being, e.g., by helping others at the expense of one’s self-interest. Second, asking whether a person’s existence over time is meaningful is not identical to considering whether she has been morally upright; there are intuitively ways to enhance meaning that have nothing to do with right action or moral virtue, such as making a scientific discovery or becoming an excellent dancer. Now, one might argue that a life would be meaningless if, or even because, it were unhappy or immoral, but that would be to posit a synthetic, substantive relationship between the concepts, far from indicating that speaking of “meaningfulness” is analytically a matter of connoting ideas regarding happiness or rightness. The question of what (if anything) makes a person’s life meaningful is conceptually distinct from the questions of what makes a life happy or moral, although it could turn out that the best answer to the former question appeals to an answer to one of the latter questions.
Supposing, then, that talk of “meaning in life” connotes something good for its own sake that can come in degrees and that is not analytically equivalent to happiness or rightness, what else does it involve? What more can we say about this final value, by definition? Most contemporary analytic philosophers would say that the relevant value is absent from spending time in an experience machine (but see Goetz 2012 for a different view) or living akin to Sisyphus, the mythic figure doomed by the Greek gods to roll a stone up a hill for eternity (famously discussed by Albert Camus and Taylor 1970). In addition, many would say that the relevant value is typified by the classic triad of “the good, the true, and the beautiful” (or would be under certain conditions). These terms are not to be taken literally, but instead are rough catchwords for beneficent relationships (love, collegiality, morality), intellectual reflection (wisdom, education, discoveries), and creativity (particularly the arts, but also potentially things like humor or gardening).
Pressing further, is there something that the values of the good, the true, the beautiful, and any other logically possible sources of meaning involve? There is as yet no consensus in the field. One salient view is that the concept of meaning in life is a cluster or amalgam of overlapping ideas, such as fulfilling higher-order purposes, meriting substantial esteem or admiration, having a noteworthy impact, transcending one’s animal nature, making sense, or exhibiting a compelling life-story (Markus 2003; Thomson 2003; Metz 2013, 24–35; Seachris 2013, 3–4; Mawson 2016). However, there are philosophers who maintain that something much more monistic is true of the concept, so that (nearly) all thought about meaningfulness in a person’s life is essentially about a single property. Suggestions include being devoted to or in awe of qualitatively superior goods (Taylor 1989, 3–24), transcending one’s limits (Levy 2005), or making a contribution (Martela 2016).
Recently there has been something of an “interpretive turn” in the field, one instance of which is the strong view that meaning-talk is logically about whether and how a life is intelligible within a wider frame of reference (Goldman 2018, 116–29; Seachris 2019; Thomas 2019; cf. Repp 2018). According to this approach, inquiring into life’s meaning is nothing other than seeking out sense-making information, perhaps a narrative about life or an explanation of its source and destiny. This analysis has the advantage of promising to unify a wide array of uses of the term “meaning.” However, it has the disadvantages of being unable to capture the intuitions that meaning in life is essentially good for its own sake (Landau 2017, 12–15), that it is not logically contradictory to maintain that an ineffable condition is what confers meaning on life (as per Cooper 2003, 126–42; Bennett-Hunter 2014; Waghorn 2014), and that often human actions themselves (as distinct from an interpretation of them), such as rescuing a child from a burning building, are what bear meaning.
Some thinkers have suggested that a complete analysis of the concept of life’s meaning should include what has been called “anti-matter” (Metz 2002, 805–07, 2013, 63–65, 71–73) or “anti-meaning” (Campbell and Nyholm 2015; Egerstrom 2015), conditions that reduce the meaningfulness of a life. The thought is that meaning is well represented by a bipolar scale, where there is a dimension of not merely positive conditions, but also negative ones. Gratuitous cruelty or destructiveness are prima facie candidates for actions that not merely fail to add meaning, but also subtract from any meaning one’s life might have had.
Despite the ongoing debates about how to analyze the concept of life’s meaning (or articulate the definition of the phrase “meaning in life”), the field remains in a good position to make progress on the other key questions posed above, viz., of what would make a life meaningful and whether any lives are in fact meaningful. A certain amount of common ground is provided by the point that meaningfulness at least involves a gradient final value in a person’s life that is conceptually distinct from happiness and rightness, with exemplars of it potentially being the good, the true, and the beautiful. The rest of this discussion addresses philosophical attempts to capture the nature of this value theoretically and to ascertain whether it exists in at least some of our lives.
2. Supernaturalism
Most analytic philosophers writing on meaning in life have been trying to develop and evaluate theories, i.e., fundamental and general principles, that are meant to capture all the particular ways that a life could obtain meaning. As in moral philosophy, there are recognizable “anti-theorists,” i.e., those who maintain that there is too much pluralism among meaning conditions to be able to unify them in the form of a principle (e.g., Kekes 2000; Hosseini 2015). Arguably, though, the systematic search for unity is too nascent to be able to draw a firm conclusion about whether it is available.
The theories are standardly divided on a metaphysical basis, that is, in terms of which kinds of properties are held to constitute the meaning. Supernaturalist theories are views according to which a spiritual realm is central to meaning in life. Most Western philosophers have conceived of the spiritual in terms of God or a soul as commonly understood in the Abrahamic faiths (but see Mulgan 2015 for discussion of meaning in the context of a God uninterested in us). In contrast, naturalist theories are views that the physical world as known particularly well by the scientific method is central to life’s meaning.
There is logical space for a non-naturalist theory, according to which central to meaning is an abstract property that is neither spiritual nor physical. However, only scant attention has been paid to this possibility in the recent Anglo-American-Australasian literature (Audi 2005).
It is important to note that supernaturalism, a claim that God (or a soul) would confer meaning on a life, is logically distinct from theism, the claim that God (or a soul) exists. Although most who hold supernaturalism also hold theism, one could accept the former without the latter (as Camus more or less did), committing one to the view that life is meaningless or at least lacks substantial meaning. Similarly, while most naturalists are atheists, it is not contradictory to maintain that God exists but has nothing to do with meaning in life or perhaps even detracts from it. Although these combinations of positions are logically possible, some of them might be substantively implausible. The field could benefit from discussion of the comparative attractiveness of various combinations of evaluative claims about what would make life meaningful and metaphysical claims about whether spiritual conditions exist.
Over the past 15 years or so, two different types of supernaturalism have become distinguished on a regular basis (Metz 2019). That is true not only in the literature on life’s meaning, but also in that on the related pro-theism/anti-theism debate, about whether it would be desirable for God or a soul to exist (e.g., Kahane 2011; Kraay 2018; Lougheed 2020). On the one hand, there is extreme supernaturalism, according to which spiritual conditions are necessary for any meaning in life. If neither God nor a soul exists, then, by this view, everyone’s life is meaningless. On the other hand, there is moderate supernaturalism, according to which spiritual conditions are necessary for a great or ultimate meaning in life, although not meaning in life as such. If neither God nor a soul exists, then, by this view, everyone’s life could have some meaning, or even be meaningful, but no one’s life could exhibit the most desirable meaning. For a moderate supernaturalist, God or a soul would substantially enhance meaningfulness or be a major contributory condition for it.
There are a variety of ways that great or ultimate meaning has been described, sometimes quantitatively as “infinite” (Mawson 2016), qualitatively as “deeper” (Swinburne 2016), relationally as “unlimited” (Nozick 1981, 618–19; cf. Waghorn 2014), temporally as “eternal” (Cottingham 2016), and perspectivally as “from the point of view of the universe” (Benatar 2017). There has been no reflection as yet on the crucial question of how these distinctions might bear on each another, for instance, on whether some are more basic than others or some are more valuable than others.
Cross-cutting the extreme/moderate distinction is one between God-centered theories and soul-centered ones. According to the former, some kind of connection with God (understood to be a spiritual person who is all-knowing, all-good, and all-powerful and who is the ground of the physical universe) constitutes meaning in life, even if one lacks a soul (construed as an immortal, spiritual substance that contains one’s identity). In contrast, by the latter, having a soul and putting it into a certain state is what makes life meaningful, even if God does not exist. Many supernaturalists of course believe that God and a soul are jointly necessary for a (greatly) meaningful existence. However, the simpler view, that only one of them is necessary, is common, and sometimes arguments proffered for the complex view fail to support it any more than the simpler one.
The most influential God-based account of meaning in life has been the extreme view that one’s existence is significant if and only if one fulfills a purpose God has assigned. The familiar idea is that God has a plan for the universe and that one’s life is meaningful just to the degree that one helps God realize this plan, perhaps in a particular way that God wants one to do so. If a person failed to do what God intends her to do with her life (or if God does not even exist), then, on the current view, her life would be meaningless.
Thinkers differ over what it is about God’s purpose that might make it uniquely able to confer meaning on human lives, but the most influential argument has been that only God’s purpose could be the source of invariant moral rules (Davis 1987, 296, 304–05; Moreland 1987, 124–29; Craig 1994/2013, 161–67) or of objective values more generally (Cottingham 2005, 37–57), where a lack of such would render our lives nonsensical. According to this argument, lower goods such as animal pleasure or desire satisfaction could exist without God, but higher ones pertaining to meaning in life, particularly moral virtue, could not. However, critics point to many non-moral sources of meaning in life (e.g., Kekes 2000; Wolf 2010), with one arguing that a universal moral code is not necessary for meaning in life, even if, say, beneficent actions are (Ellin 1995, 327). In addition, there are a variety of naturalist and non-naturalist accounts of objective morality––and of value more generally––on offer these days, so that it is not clear that it must have a supernatural source in God’s will.
One recurrent objection to the idea that God’s purpose could make life meaningful is that if God had created us with a purpose in mind, then God would have degraded us and thereby undercut the possibility of us obtaining meaning from fulfilling the purpose. The objection harks back to Jean-Paul Sartre, but in the analytic literature it appears that Kurt Baier was the first to articulate it (1957/2000, 118–20; see also Murphy 1982, 14–15; Singer 1996, 29; Kahane 2011; Lougheed 2020, 121–41). Sometimes the concern is the threat of punishment God would make so that we do God’s bidding, while other times it is that the source of meaning would be constrictive and not up to us, and still other times it is that our dignity would be maligned simply by having been created with a certain end in mind (for some replies to such concerns, see Hanfling 1987, 45–46; Cottingham 2005, 37–57; Lougheed 2020, 111–21).
There is a different argument for an extreme God-based view that focuses less on God as purposive and more on God as infinite, unlimited, or ineffable, which Robert Nozick first articulated with care (Nozick 1981, 594–618; see also Bennett-Hunter 2014; Waghorn 2014). The core idea is that for a finite condition to be meaningful, it must obtain its meaning from another condition that has meaning. So, if one’s life is meaningful, it might be so in virtue of being married to a person, who is important. Being finite, the spouse must obtain his or her importance from elsewhere, perhaps from the sort of work he or she does. This work also must obtain its meaning by being related to something else that is meaningful, and so on. A regress on meaningful conditions is present, and the suggestion is that the regress can terminate only in something so all-encompassing that it need not (indeed, cannot) go beyond itself to obtain meaning from anything else. And that is God. The standard objection to this relational rationale is that a finite condition could be meaningful without obtaining its meaning from another meaningful condition. Perhaps it could be meaningful in itself, without being connected to something beyond it, or maybe it could obtain its meaning by being related to something else that is beautiful or otherwise valuable for its own sake but not meaningful (Nozick 1989, 167–68; Thomson 2003, 25–26, 48).
A serious concern for any extreme God-based view is the existence of apparent counterexamples. If we think of the stereotypical lives of Albert Einstein, Mother Teresa, and Pablo Picasso, they seem meaningful even if we suppose there is no all-knowing, all-powerful, and all-good spiritual person who is the ground of the physical world (e.g., Wielenberg 2005, 31–37, 49–50; Landau 2017). Even religiously inclined philosophers have found this hard to deny these days (Quinn 2000, 58; Audi 2005; Mawson 2016, 5; Williams 2020, 132–34).
Largely for that reason, contemporary supernaturalists have tended to opt for moderation, that is, to maintain that God would greatly enhance the meaning in our lives, even if some meaning would be possible in a world without God. One approach is to invoke the relational argument to show that God is necessary, not for any meaning whatsoever, but rather for an ultimate meaning. “Limited transcendence, the transcending of our limits so as to connect with a wider context of value which itself is limited, does give our lives meaning––but a limited one. We may thirst for more” (Nozick 1981, 618). Another angle is to appeal to playing a role in God’s plan, again to claim, not that it is essential for meaning as such, but rather for “a cosmic significance....intead of a significance very limited in time and space” (Swinburne 2016, 154; see also Quinn 2000; Cottingham 2016, 131). Another rationale is that by fulfilling God’s purpose, we would meaningfully please God, a perfect person, as well as be remembered favorably by God forever (Cottingham 2016, 135; Williams 2020, 21–22, 29, 101, 108). Still another argument is that only with God could the deepest desires of human nature be satisfied (e.g., Goetz 2012; Seachris 2013, 20; Cottingham 2016, 127, 136), even if more surface desires could be satisfied without God.
In reply to such rationales for a moderate supernaturalism, there has been the suggestion that it is precisely by virtue of being alone in the universe that our lives would be particularly significant; otherwise, God’s greatness would overshadow us (Kahane 2014). There has also been the response that, with the opportunity for greater meaning from God would also come that for greater anti-meaning, so that it is not clear that a world with God would offer a net gain in respect of meaning (Metz 2019, 34–35). For example, if pleasing God would greatly enhance meaning in our lives, then presumably displeasing God would greatly reduce it and to a comparable degree. In addition, there are arguments for extreme naturalism (or its “anti-theist” cousin) mentioned below (sub-section 3.3).
Notice that none of the above arguments for supernaturalism appeals to the prospect of eternal life (at least not explicitly). Arguments that do make such an appeal are soul-centered, holding that meaning in life mainly comes from having an immortal, spiritual substance that is contiguous with one’s body when it is alive and that will forever outlive its death. Some think of the afterlife in terms of one’s soul entering a transcendent, spiritual realm (Heaven), while others conceive of one’s soul getting reincarnated into another body on Earth. According to the extreme version, if one has a soul but fails to put it in the right state (or if one lacks a soul altogether), then one’s life is meaningless.
There are three prominent arguments for an extreme soul-based perspective. One argument, made famous by Leo Tolstoy, is the suggestion that for life to be meaningful something must be worth doing, that something is worth doing only if it will make a permanent difference to the world, and that making a permanent difference requires being immortal (see also Hanfling 1987, 22–24; Morris 1992, 26; Craig 1994). Critics most often appeal to counterexamples, suggesting for instance that it is surely worth your time and effort to help prevent people from suffering, even if you and they are mortal. Indeed, some have gone on the offensive and argued that helping people is worth the sacrifice only if and because they are mortal, for otherwise they could invariably be compensated in an afterlife (e.g., Wielenberg 2005, 91–94). Another recent and interesting criticism is that the major motivations for the claim that nothing matters now if one day it will end are incoherent (Greene 2021).
A second argument for the view that life would be meaningless without a soul is that it is necessary for justice to be done, which, in turn, is necessary for a meaningful life. Life seems nonsensical when the wicked flourish and the righteous suffer, at least supposing there is no other world in which these injustices will be rectified, whether by God or a Karmic force. Something like this argument can be found in Ecclesiastes, and it continues to be defended (e.g., Davis 1987; Craig 1994). However, even granting that an afterlife is required for perfectly just outcomes, it is far from obvious that an eternal afterlife is necessary for them, and, then, there is the suggestion that some lives, such as Mandela’s, have been meaningful precisely in virtue of encountering injustice and fighting it.
A third argument for thinking that having a soul is essential for any meaning is that it is required to have the sort of free will without which our lives would be meaningless. Immanuel Kant is known for having maintained that if we were merely physical beings, subjected to the laws of nature like everything else in the material world, then we could not act for moral reasons and hence would be unimportant. More recently, one theologian has eloquently put the point in religious terms: “The moral spirit finds the meaning of life in choice. It finds it in that which proceeds from man and remains with him as his inner essence rather than in the accidents of circumstances turns of external fortune....(W)henever a human being rubs the lamp of his moral conscience, a Spirit does appear. This Spirit is God....It is in the ‘Thou must’ of God and man’s ‘I can’ that the divine image of God in human life is contained” (Swenson 1949/2000, 27–28). Notice that, even if moral norms did not spring from God’s commands, the logic of the argument entails that one’s life could be meaningful, so long as one had the inherent ability to make the morally correct choice in any situation. That, in turn, arguably requires something non-physical about one’s self, so as to be able to overcome whichever physical laws and forces one might confront. The standard objection to this reasoning is to advance a compatibilism about having a determined physical nature and being able to act for moral reasons (e.g., Arpaly 2006; Fischer 2009, 145–77). It is also worth wondering whether, if one had to have a spiritual essence in order to make free choices, it would have to be one that never perished.
Like God-centered theorists, many soul-centered theorists these days advance a moderate view, accepting that some meaning in life would be possible without immortality, but arguing that a much greater meaning would be possible with it. Granting that Einstein, Mandela, and Picasso had somewhat meaningful lives despite not having survived the deaths of their bodies (as per, e.g., Trisel 2004; Wolf 2015, 89–140; Landau 2017), there remains a powerful thought: more is better. If a finite life with the good, the true, and the beautiful has meaning in it to some degree, then surely it would have all the more meaning if it exhibited such higher values––including a relationship with God––for an eternity (Cottingham 2016, 132–35; Mawson 2016, 2019, 52–53; Williams 2020, 112–34; cf. Benatar 2017, 35–63). One objection to this reasoning is that the infinity of meaning that would be possible with a soul would be “too big,” rendering it difficult for the moderate supernaturalist to make sense of the intution that a finite life such as Einstein’s can indeed count as meaningful by comparison (Metz 2019, 30–31; cf. Mawson 2019, 53–54). More common, though, is the objection that an eternal life would include anti-meaning of various kinds, such as boredom and repetition, discussed below in the context of extreme naturalism (sub-section 3.3).
3. Naturalism
Recall that naturalism is the view that a physical life is central to life’s meaning, that even if there is no spiritual realm, a substantially meaningful life is possible. Like supernaturalism, contemporary naturalism admits of two distinguishable variants, moderate and extreme (Metz 2019). The moderate version is that, while a genuinely meaningful life could be had in a purely physical universe as known well by science, a somewhat more meaningful life would be possible if a spiritual realm also existed. God or a soul could enhance meaning in life, although they would not be major contributors. The extreme version of naturalism is the view that it would be better in respect of life’s meaning if there were no spiritual realm. From this perspective, God or a soul would be anti-matter, i.e., would detract from the meaning available to us, making a purely physical world (even if not this particular one) preferable.
Cross-cutting the moderate/extreme distinction is that between subjectivism and objectivism, which are theoretical accounts of the nature of meaningfulness insofar as it is physical. They differ in terms of the extent to which the human mind constitutes meaning and whether there are conditions of meaning that are invariant among human beings. Subjectivists believe that there are no invariant standards of meaning because meaning is relative to the subject, i.e., depends on an individual’s pro-attitudes such as her particular desires or ends, which are not shared by everyone. Roughly, something is meaningful for a person if she strongly wants it or intends to seek it out and she gets it. Objectivists maintain, in contrast, that there are some invariant standards for meaning because meaning is at least partly mind-independent, i.e., obtains not merely in virtue of being the object of anyone’s mental states. Here, something is meaningful (partially) because of its intrinsic nature, in the sense of being independent of whether it is wanted or intended; meaning is instead (to some extent) the sort of thing that merits these reactions.
There is logical space for an orthogonal view, according to which there are invariant standards of meaningfulness constituted by what all human beings would converge on from a certain standpoint. However, it has not been much of a player in the field (Darwall 1983, 164–66).
According to this version of naturalism, meaning in life varies from person to person, depending on each one’s variable pro-attitudes. Common instances are views that one’s life is more meaningful, the more one gets what one happens to want strongly, achieves one’s highly ranked goals, or does what one believes to be really important (Trisel 2002; Hooker 2008). One influential subjectivist has recently maintained that the relevant mental state is caring or loving, so that life is meaningful just to the extent that one cares about or loves something (Frankfurt 1988, 80–94, 2004). Another recent proposal is that meaningfulness consists of “an active engagement and affirmation that vivifies the person who has freely created or accepted and now promotes and nurtures the projects of her highest concern” (Belliotti 2019, 183).
Subjectivism was dominant in the middle of the twentieth century, when positivism, noncognitivism, existentialism, and Humeanism were influential (Ayer 1947; Hare 1957; Barnes 1967; Taylor 1970; Williams 1976). However, in the last quarter of the twentieth century, inference to the best explanation and reflective equilibrium became accepted forms of normative argumentation and were frequently used to defend claims about the existence and nature of objective value (or of “external reasons,” ones obtaining independently of one’s extant attitudes). As a result, subjectivism about meaning lost its dominance. Those who continue to hold subjectivism often remain suspicious of attempts to justify beliefs about objective value (e.g., Trisel 2002, 73, 79, 2004, 378–79; Frankfurt 2004, 47–48, 55–57; Wong 2008, 138–39; Evers 2017, 32, 36; Svensson 2017, 54). Theorists are moved to accept subjectivism typically because the alternatives are unpalatable; they are reasonably sure that meaning in life obtains for some people, but do not see how it could be grounded on something independent of the mind, whether it be the natural or the supernatural (or the non-natural). In contrast to these possibilities, it appears straightforward to account for what is meaningful in terms of what people find meaningful or what people want out of their lives. Wide-ranging meta-ethical debates in epistemology, metaphysics, and the philosophy of language are necessary to address this rationale for subjectivism.
There is a cluster of other, more circumscribed arguments for subjectivism, according to which this theory best explains certain intuitive features of meaning in life. For one, subjectivism seems plausible since it is reasonable to think that a meaningful life is an authentic one (Frankfurt 1988, 80–94). If a person’s life is significant insofar as she is true to herself or her deepest nature, then we have some reason to believe that meaning simply is a function of those matters for which the person cares. For another, it is uncontroversial that often meaning comes from losing oneself, i.e., in becoming absorbed in an activity or experience, as opposed to being bored by it or finding it frustrating (Frankfurt 1988, 80–94; Belliotti 2019, 162–70). Work that concentrates the mind and relationships that are engrossing seem central to meaning and to be so because of the subjective elements involved. For a third, meaning is often taken to be something that makes life worth continuing for a specific person, i.e., that gives her a reason to get out of bed in the morning, which subjectivism is thought to account for best (Williams 1976; Svensson 2017; Calhoun 2018).
Critics maintain that these arguments are vulnerable to a common objection: they neglect the role of objective value (or an external reason) in realizing oneself, losing oneself, and having a reason to live (Taylor 1989, 1992; Wolf 2010, 2015, 89–140). One is not really being true to oneself, losing oneself in a meaningful way, or having a genuine reason to live insofar as one, say, successfully maintains 3,732 hairs on one’s head (Taylor 1992, 36), cultivates one’s prowess at long-distance spitting (Wolf 2010, 104), collects a big ball of string (Wolf 2010, 104), or, well, eats one’s own excrement (Wielenberg 2005, 22). The counterexamples suggest that subjective conditions are insufficient to ground meaning in life; there seem to be certain actions, relationships, and states that are objectively valuable (but see Evers 2017, 30–32) and toward which one’s pro-attitudes ought to be oriented, if meaning is to accrue.
So say objectivists, but subjectivists feel the pull of the point and usually seek to avoid the counterexamples, lest they have to bite the bullet by accepting the meaningfulness of maintaining 3,732 hairs on one’s head and all the rest (for some who do, see Svensson 2017, 54–55; Belliotti 2019, 181–83). One important strategy is to suggest that subjectivists can avoid the counterexamples by appealing to the right sort of pro-attitude. Instead of whatever an individual happens to want, perhaps the relevant mental state is an emotional-perceptual one of seeing-as (Alexis 2011; cf. Hosseini 2015, 47–66), a “categorical” desire, that is, an intrinsic desire constitutive of one’s identity that one takes to make life worth continuing (Svensson 2017), or a judgment that one has a good reason to value something highly for its own sake (Calhoun 2018). Even here, though, objectivists will argue that it might “appear that whatever the will chooses to treat as a good reason to engage itself is, for the will, a good reason. But the will itself....craves objective reasons; and often it could not go forward unless it thought it had them” (Wiggins 1988, 136). And without any appeal to objectivity, it is perhaps likely that counterexamples would resurface.
Another subjectivist strategy by which to deal with the counterexamples is the attempt to ground meaningfulness, not on the pro-attitudes of an individual valuer, but on those of a group (Darwall 1983, 164–66; Brogaard and Smith 2005; Wong 2008). Does such an intersubjective move avoid (more of) the counterexamples? If so, does it do so more plausibly than an objective theory?
Objective naturalists believe that meaning in life is constituted at least in part by something physical beyond merely the fact that it is the object of a pro-attitude. Obtaining the object of some emotion, desire, or judgment is not sufficient for meaningfulness, on this view. Instead, there are certain conditions of the material world that could confer meaning on anyone’s life, not merely because they are viewed as meaningful, wanted for their own sake, or believed to be choiceworthy, but instead (at least partially) because they are inherently worthwhile or valuable in themselves.
Morality (the good), enquiry (the true), and creativity (the beautiful) are widely held instances of activities that confer meaning on life, while trimming toenails and eating snow––along with the counterexamples to subjectivism above––are not. Objectivism is widely thought to be a powerful general explanation of these particular judgments: the former are meaningful not merely because some agent (whether it is an individual, her society, or even God) cares about them or judges them to be worth doing, while the latter simply lack significance and cannot obtain it even if some agent does care about them or judge them to be worth doing. From an objective perspective, it is possible for an individual to care about the wrong thing or to be mistaken that something is worthwhile, and not merely because of something she cares about all the more or judges to be still more choiceworthy. Of course, meta-ethical debates about the existence and nature of value are again relevant to appraising this rationale.
Some objectivists think that being the object of a person’s mental states plays no constitutive role in making that person’s life meaningful, although they of course contend that it often plays an instrumental role––liking a certain activity, after all, is likely to motivate one to do it. Relatively few objectivists are “pure” in that way, although consequentialists do stand out as clear instances (e.g., Singer 1995; Smuts 2018, 75–99). Most objectivists instead try to account for the above intuitions driving subjectivism by holding that a life is more meaningful, not merely because of objective factors, but also in part because of propositional attitudes such as cognition, conation, and emotion. Particularly influential has been Susan Wolf’s hybrid view, captured by this pithy slogan: “Meaning arises when subjective attraction meets objective attractiveness” (Wolf 2015, 112; see also Kekes 1986, 2000; Wiggins 1988; Raz 2001, 10–40; Mintoff 2008; Wolf 2010, 2016; Fischer 2019, 9–23; Belshaw 2021, 160–81). This theory implies that no meaning accrues to one’s life if one believes in, is satisfied by, or cares about a project that is not truly worthwhile, or if one takes up a truly worthwhile project but fails to judge it important, be satisfied by it, or care about it. A related approach is that, while subjective attraction is not necessary for meaning, it could enhance it (e.g., Audi 2005, 344; Metz 2013, 183–84, 196–98, 220–25). For instance, a stereotypical Mother Teresa who is bored by and alienated from her substantial charity work might have a somewhat significant existence because of it, even if she would have an even more significant existence if she felt pride in it or identified with it.
There have been several attempts to capture theoretically what all objectively attractive, inherently worthwhile, or finally valuable conditions have in common insofar as they bear on meaning in a person’s life. Over the past few decades, one encounters the proposals that objectively meaningful conditions are just those that involve: positively connecting with organic unity beyond oneself (Nozick 1981, 594–619); being creative (Taylor 1987; Matheson 2018); living an emotional life (Solomon 1993; cf. Williams 2020, 56–78); promoting good consequences, such as improving the quality of life of oneself and others (Singer 1995; Audi 2005; Smuts 2018, 75–99); exercising or fostering rational nature in exceptional ways (Smith 1997, 179–221; Gewirth 1998, 177–82; Metz 2013, 222–36); progressing toward ends that can never be fully realized because one’s knowledge of them changes as one approaches them (Levy 2005); realizing goals that are transcendent for being long-lasting in duration and broad in scope (Mintoff 2008); living virtuously (May 2015, 61–138; McPherson 2020); and loving what is worth loving (Wolf 2016). There is as yet no convergence in the field on one, or even a small cluster, of these accounts.
One feature of a large majority of the above naturalist theories is that they are aggregative or additive, objectionably treating a life as a mere “container” of bits of life that are meaningful considered in isolation from other bits (Brännmark 2003, 330). It has become increasingly common for philosophers of life’s meaning, especially objectivists, to hold that life as a whole, or at least long stretches of it, can substantially affect its meaningfulness beyond the amount of meaning (if any) in its parts.
For instance, a life that has lots of beneficence and otherwise intuitively meaning-conferring conditions but that is also extremely repetitive (à la the movie Groundhog Day ) is less than maximally meaningful (Taylor 1987; Blumenfeld 2009). Furthermore, a life that not only avoids repetition but also ends with a substantial amount of meaningful (or otherwise desirable) parts seems to have more meaning overall than one that has the same amount of meaningful (desirable) parts but ends with few or none of them (Kamm 2013, 18–22; Dorsey 2015). Still more, a life in which its meaningless (or otherwise undesirable parts) cause its meaningful (desirable) parts to come about through a process of personal growth seems meaningful in virtue of this redemptive pattern, “good life-story,” or narrative self-expression (Taylor 1989, 48–51; Wong 2008; Fischer 2009, 145–77; Kauppinen 2012; May 2015, 61–138; Velleman 2015, 141–73). These three cases suggest that meaning can inhere in life as a whole, that is, in the relationships between its parts, and not merely in the parts considered in isolation. However, some would maintain that it is, strictly speaking, the story that is or could be told of a life that matters, not so much the life-story qua relations between events themselves (de Bres 2018).
There are pure or extreme versions of holism present in the literature, according to which the only possible bearer of meaning in life is a person’s life as a whole, and not any isolated activities, relationships, or states (Taylor 1989, 48–51; Tabensky 2003; Levinson 2004). A salient argument for this position is that judgments of the meaningfulness of a part of someone’s life are merely provisional, open to revision upon considering how they fit into a wider perspective. So, for example, it would initially appear that taking an ax away from a madman and thereby protecting innocent parties confers some meaning on one’s life, but one might well revise that judgment upon learning that the intention behind it was merely to steal an ax, not to save lives, or that the madman then took out a machine gun, causing much more harm than his ax would have. It is worth considering how far this sort of case is generalizable, and, if it can be to a substantial extent, whether that provides strong evidence that only life as a whole can exhibit meaningfulness.
Perhaps most objectivists would, at least upon reflection, accept that both the parts of a life and the whole-life relationships among the parts can exhibit meaning. Supposing there are two bearers of meaning in a life, important questions arise. One is whether a certain narrative can be meaningful even if its parts are not, while a second is whether the meaningfulness of a part increases if it is an aspect of a meaningful whole (on which see Brännmark 2003), and a third is whether there is anything revealing to say about how to make tradeoffs between the parts and whole in cases where one must choose between them (Blumenfeld 2009 appears to assign lexical priority to the whole).
Naturalists until recently had been largely concerned to show that meaning in life is possible without God or a soul; they have not spent much time considering how such spiritual conditions might enhance meaning, but have, in moderate fashion, tended to leave that possibility open (an exception is Hooker 2008). Lately, however, an extreme form of naturalism has arisen, according to which our lives would probably, if not unavoidably, have less meaning in a world with God or a soul than in one without. Although such an approach was voiced early on by Baier (1957), it is really in the past decade or so that this “anti-theist” position has become widely and intricately discussed.
One rationale, mentioned above as an objection to the view that God’s purpose constitutes meaning in life, has also been deployed to argue that the existence of God as such would necessarily reduce meaning, that is, would consist of anti-matter. It is the idea that master/servant and parent/child analogies so prominent in the monotheist religious traditions reveal something about our status in a world where there is a qualitatively higher being who has created us with certain ends in mind: our independence or dignity as adult persons would be violated (e.g., Baier 1957/2000, 118–20; Kahane 2011, 681–85; Lougheed 2020, 121–41). One interesting objection to this reasoning has been to accept that God’s existence is necessarily incompatible with the sort of meaning that would come (roughly stated) from being one’s own boss, but to argue that God would also make greater sorts of meaning available, offering a net gain to us (Mawson 2016, 110–58).
Another salient argument for thinking that God would detract from meaning in life appeals to the value of privacy (Kahane 2011, 681–85; Lougheed 2020, 55–110). God’s omniscience would unavoidably make it impossible for us to control another person’s access to the most intimate details about ourselves, which, for some, amounts to a less meaningful life than one with such control. Beyond questioning the value of our privacy in relation to God, one thought-provoking criticism has been to suggest that, if a lack of privacy really would substantially reduce meaning in our lives, then God, qua morally perfect person, would simply avoid knowing everything about us (Tooley 2018). Lacking complete knowledge of our mental states would be compatible with describing God as “omniscient,” so the criticism goes, insofar as that is plausibly understood as having as much knowledge as is morally permissible.
Turn, now, to major arguments for thinking that having a soul would reduce life’s meaning, so that if one wants a maximally meaningful life, one should prefer a purely physical world, or at least one in which people are mortal. First and foremost, there has been the argument that an immortal life could not avoid becoming boring (Williams 1973), rendering life pointless according to many subjective and objective theories. The literature on this topic has become enormous, with the central reply being that immortality need not get boring (for more recent discussions, see Fischer 2009, 79–101, 2019, 117–42; Mawson 2019, 51–52; Williams 2020, 30–41, 123–29; Belshaw 2021, 182–97). However, it might also be worth questioning whether boredom is sufficient for meaninglessness. Suppose, for instance, that one volunteers to be bored so that many others will not be bored; perhaps this would be a meaningful sacrifice to make. Being bored for an eternity would not be blissful or even satisfying, to be sure, but if it served the function of preventing others from being bored for an eternity, would it be meaningful (at least to some degree)? If, as is commonly held, sacrificing one’s life could be meaningful, why not also sacrificing one’s liveliness?
Another reason given to reject eternal life is that it would become repetitive, which would substantially drain it of meaning (Scarre 2007, 54–55; May 2009, 46–47, 64–65, 71; Smuts 2011, 142–44; cf. Blumenfeld 2009). If, as it appears, there are only a finite number of actions one could perform, relationships one could have, and states one could be in during an eternity, one would have to end up doing the same things again. Even though one’s activities might be more valuable than rolling a stone up a hill forever à la Sisyphus, the prospect of doing them over and over again forever is disheartening for many. To be sure, one might not remember having done them before and hence could avoid boredom, but for some philosophers that would make it all the worse, akin to having dementia and forgetting that one has told the same stories. Others, however, still find meaning in such a life (e.g., Belshaw 2021, 197, 205n41).
A third meaning-based argument against immortality invokes considerations of narrative. If the pattern of one’s life as a whole substantially matters, and if a proper pattern would include a beginning, a middle, and an end, it appears that a life that never ends would lack the relevant narrative structure. “Because it would drag on endlessly, it would, sooner or later, just be a string of events lacking all form....With immortality, the novel never ends....How meaningful can such a novel be?” (May 2009, 68, 72; see also Scarre 2007, 58–60). Notice that this objection is distinct from considerations of boredom and repetition (which concern novelty ); even if one were stimulated and active, and even if one found a way not to repeat one’s life in the course of eternity, an immortal life would appear to lack shape. In reply, some reject the idea that a meaningful life must be akin to a novel, and intead opt for narrativity in the form of something like a string of short stories that build on each other (Fischer 2009, 145–77, 2019, 101–16). Others, though, have sought to show that eternity could still be novel-like, deeming the sort of ending that matters to be a function of what the content is and how it relates to the content that came before (e.g., Seachris 2011; Williams 2020, 112–19).
There have been additional objections to immortality as undercutting meaningfulness, but they are prima facie less powerful than the previous three in that, if sound, they arguably show that an eternal life would have a cost, but probably not one that would utterly occlude the prospect of meaning in it. For example, there have been the suggestions that eternal lives would lack a sense of preciousness and urgency (Nussbaum 1989, 339; Kass 2002, 266–67), could not exemplify virtues such as courageously risking one’s life for others (Kass 2002, 267–68; Wielenberg 2005, 91–94), and could not obtain meaning from sustaining or saving others’ lives (Nussbaum 1989, 338; Wielenberg 2005, 91–94). Note that at least the first two rationales turn substantially on the belief in immortality, not quite immortality itself: if one were immortal but forgot that one is or did not know that at all, then one could appreciate life and obtain much of the virtue of courage (and, conversely, if one were not immortal, but thought that one is, then, by the logic of these arguments, one would fail to appreciate limits and be unable to exemplify courage).
The previous two sections addressed theoretical accounts of what would confer meaning on a human person’s life. Although these theories do not imply that some people’s lives are in fact meaningful, that has been the presumption of a very large majority of those who have advanced them. Much of the procedure has been to suppose that many lives have had meaning in them and then to consider in virtue of what they have or otherwise could. However, there are nihilist (or pessimist) perspectives that question this supposition. According to nihilism (pessimism), what would make a life meaningful in principle cannot obtain for any of us.
One straightforward rationale for nihilism is the combination of extreme supernaturalism about what makes life meaningful and atheism about whether a spiritual realm exists. If you believe that God or a soul is necessary for meaning in life, and if you believe that neither is real, then you are committed to nihilism, to the denial that life can have any meaning. Athough this rationale for nihilism was prominent in the modern era (and was more or less Camus’ position), it has been on the wane in analytic philosophical circles, as extreme supernaturalism has been eclipsed by the moderate variety.
The most common rationales for nihilism these days do not appeal to supernaturalism, or at least not explicitly. One cluster of ideas appeals to what meta-ethicists call “error theory,” the view that evaluative claims (in this case about meaning in life, or about morality qua necessary for meaning) characteristically posit objectively real or universally justified values, but that such values do not exist. According to one version, value judgments often analytically include a claim to objectivity but there is no reason to think that objective values exist, as they “would be entities or qualities or relations of a very strange sort, utterly different from anything else in the universe” (Mackie 1977/1990, 38). According to a second version, life would be meaningless if there were no set of moral standards that could be fully justified to all rational enquirers, but it so happens that such standards cannot exist for persons who can always reasonably question a given claim (Murphy 1982, 12–17). According to a third, we hold certain beliefs about the objectivity and universality of morality and related values such as meaning because they were evolutionarily advantageous to our ancestors, not because they are true. Humans have been “deceived by their genes into thinking that there is a distinterested, objective morality binding upon them, which all should obey” (Ruse and Wilson 1986, 179; cf. Street 2015). One must draw on the intricate work in meta-ethics that has been underway for the past several decades in order to appraise these arguments.
In contrast to error-theoretic arguments for nihilism, there are rationales for it accepting that objective values exist but denying that our lives can ever exhibit or promote them so as to obtain meaning. One version of this approach maintains that, for our lives to matter, we must be in a position to add objective value to the world, which we are not since the objective value of the world is already infinite (Smith 2003). The key premises for this view are that every bit of space-time (or at least the stars in the physical universe) have some positive value, that these values can be added up, and that space is infinite. If the physical world at present contains an infinite degree of value, nothing we do can make a difference in terms of meaning, for infinity plus any amount of value remains infinity. One way to question this argument, beyond doubting the value of space-time or stars, is to suggest that, even if one cannot add to the value of the universe, meaning plausibly comes from being the source of certain values.
A second rationale for nihilism that accepts the existence of objective value is David Benatar’s (2006, 18–59) intriguing “asymmetry argument” for anti-natalism, the view that it is immoral to bring new people into existence because doing so would always be on balance bad for them. For Benatar, the bads of existing (e.g., pains) are real disadvantages relative to not existing, while the goods of existing (pleasures) are not real advantages relative to not existing, since there is in the latter state no one to be deprived of them. If indeed the state of not existing is no worse than that of experiencing the benefits of existence, then, since existing invariably brings harm in its wake, it follows that existing is always worse compared to not existing. Although this argument is illustrated with experiential goods and bads, it seems generalizable to non-experiential ones, including meaning in life and anti-matter. The literature on this argument has become large (for a recent collection, see Hauskeller and Hallich 2022).
Benatar (2006, 60–92, 2017, 35–63) has advanced an additional argument for nihilism, one that appeals to Thomas Nagel’s (1986, 208–32) widely discussed analysis of the extremely external standpoint that human persons can take on their lives. There exists, to use Henry Sidgwick’s influential phrase, the “point of view of the universe,” that is, the standpoint that considers a human being’s life in relation to all times and all places. When one takes up this most external standpoint and views one’s puny impact on the world, little of one’s life appears to matter. What one does in a certain society on Earth over 75 years or so just does not amount to much, when considering the billions of temporal years and billions of light-years that make up space-time. Although this reasoning grants limited kinds of meaning to human beings, from a personal, social, or human perspective, Benatar both denies that the greatest sort of meaning––a cosmic one––is available to them and contends that this makes their lives bad, hence the “nihilist” tag. Some have objected that our lives could in fact have a cosmic significance, say, if they played a role in God’s plan (Quinn 2000, 65–66; Swinburne 2016, 154), were the sole ones with a dignity in the universe (Kahane 2014), or engaged in valuable activities that could be appreciated by anyone anywhere anytime (Wolf 2016, 261–62). Others naturally maintain that cosmic significance is irrelevant to appraising a human life, with some denying that it would be a genuine source of meaning (Landau 2017, 93–99), and others accepting that it would be but maintaining that the absence of this good would not count as a bad or merit regret (discussed in Benatar 2017, 56–62; Williams 2020, 108–11).
Finally, a distinguishable source of nihilism concerns the ontological, as distinct from axiological, preconditions for meaning in life. Perhaps most radically, there are those who deny that we have selves. Do we indeed lack selves, and, if we do, is a meaningful life impossible for us (see essays in Caruso and Flanagan 2018; Le Bihan 2019)? Somewhat less radically, there are those who grant that we have selves, but deny that they are in charge in the relevant way. That is, some have argued that we lack self-governance or free will of the sort that is essential for meaning in life, at least if determinism is true (Pisciotta 2013; essays in Caruso and Flanagan 2018). Non-quantum events, including human decisions, appear to be necessited by a prior state of the world, such that none could have been otherwise, and many of our decisions are a product of unconscious neurological mechanisms (while quantum events are of course utterly beyond our control). If none of our conscious choices could have been avoided and all were ultimately necessited by something external to them, perhaps they are insufficient to merit pride or admiration or to constitute narrative authorship of a life. In reply, some maintain that a compatibilism between determinism and moral responsibility applies with comparable force to meaning in life (e.g., Arpaly 2006; Fischer 2009, 145–77), while others contend that incompatibilism is true of moral responsibility but not of meaning (Pereboom 2014).
- Agar, N., 2013, Humanity’s End: Why We Should Reject Radical Enhancement , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Alexis., A., 2011, The Meaning of Life: A Modern Secular Answer to the Age-Old Fundamental Question , CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
- Arpaly, N., 2006, Merit, Meaning, and Human Bondage , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Audi, R., 2005, “Intrinsic Value and Meaningful Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 331–55.
- Ayer, A. J., 1947, “The Claims of Philosophy”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 219–32.
- Baier, K., 1957, “The Meaning of Life”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 101–32.
- Barnes, H., 1967, An Existentialist Ethics , New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Belliotti, R., 2019, Is Human Life Absurd? A Philosophical Inquiry into Finitude, Value, and Meaning . Leiden: Brill.
- Belshaw, C., 2021, The Value and Meaning of Life , London: Routledge.
- Benatar, D., 2006, Better Never to Have Been: The Harm of Coming into Existence , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2017, The Human Predicament , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Bennett-Hunter, G., 2014, Ineffability and Religious Experience , Oxford: Routledge.
- Blumenfeld, D., 2009, “Living Life over Again”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 79: 357–86.
- Bradford, G., 2015, Achievement , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Brännmark, J., 2003, “Leading Lives”, Philosophical Papers , 32: 321–43.
- Brogaard, B. and Smith, B., 2005, “On Luck, Responsibility, and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 443–58.
- Calhoun, C., 2018, Doing Valuable Time: The Present, the Future, and Meaningful Living , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Campbell, S., and Nyholm, S., 2015, “Anti-Meaning and Why It Matters”, Journal of the American Philosophical Association , 1: 694–711.
- Caruso, G. and Flanagan, O. (eds.), 2018, Neuroexistentialism: Meaning, Morals, and Purpose in an Age of Neuroscience , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Cooper, D., 2003, Meaning . Durham: Acumen Publishing.
- Cottingham, J., 2005, The Spiritual Dimension: Religion, Philosophy and Human Value , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2016, “Meaningfulness, Eternity, and Theism”, in God and Meaning , J. Seachris and S. Goetz (eds.), New York: Bloomsbury Academic: 123–36.
- Craig, W., 1994, “The Absurdity of Life Without God”, repr. in Exploring the Meaning of Life: An Anthology and Guide , J. Seachris (ed.), Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013: 153–72.
- Danaher, J., 2017, “Will Life Be Worth Living in a World Without Work? Technological Unemployment and the Meaning of Life”, Science and Engineering Ethics , 23: 41–64.
- Darwall, S., 1983, Impartial Reason , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Davis, W., 1987, “The Meaning of Life”, Metaphilosophy , 18: 288–305.
- de Bres, H., 2018, “Narrative and Meaning in Life”, Journal of Moral Philosophy , 15: 545–71.
- Dorsey, D., 2015, “The Significance of a Life’s Shape”, Ethics , 125: 303–30.
- Egerstrom, K., 2015, “ Practical Identity and Meaninglessness ”, PhD Dissertation, Syracuse University.
- Ellin, J., 1995, Morality and the Meaning of Life , Ft. Worth, TX: Harcourt Brace.
- Evers, D., 2017, “Meaning in Life and the Metaphysics of Value”, De Ethica , 4: 27–44.
- Feinberg, J., 1980, “Absurd Self-Fulfillment,” repr. in Freedom and Fulfillment: Philosophical Essays , Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1992: 297–330.
- Ferracioli, L., 2018, “Procreative-parenting, Love’s Reasons, and the Demands of Morality”, The Philosophical Quarterly , 68: 77–97.
- Fischer, J. M., 2009, Our Stories: Essays on Life, Death, and Free Will , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2019, Death, Immortality, and Meaning in Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Frankfurt, H., 1988, The Importance of What We Care About , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2004, The Reasons of Love , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Gewirth, A., 1998, Self-Fulfillment , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Goetz, S., 2012, The Purpose of Life: A Theistic Perspective , New York: Continuum.
- Goldman, A., 2018, Life’s Values: Pleasure, Happiness, Well-Being, and Meaning , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Greene, P., 2021, “It Doesn’t Matter Because One Day It Will End”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 24: 165–82.
- Hanfling, O., 1987, The Quest for Meaning , New York: Basil Blackwell Inc.
- Hare, R. M., 1957, “Nothing Matters”, repr. in Applications of Moral Philosophy , London: Macmillan, 1972: 32–47.
- Hauskeller, M. and Hallich, O. (eds.), 2022, “Would It Be Better if We Had Never Existed? David Benatar's Anti-Natalism”, special issue of The Journal of Value Inquiry , 56: 1–151.
- Hooker, B., 2008, “The Meaning of Life: Subjectivism, Objectivism, and Divine Support”, in The Moral Life: Essays in Honour of John Cottingham , N. Athanassoulis and S. Vice (eds.), New York: Palgrave Macmillan: 184–200.
- Hosseini, R., 2015, Wittgenstein and Meaning in Life: In Search of the Human Voice , New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Kahane, G., 2011, “Should We Want God to Exist?”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 82: 674–96.
- –––, 2014, “Our Cosmic Insignificance”, Noûs , 48: 745–72.
- Kamm, F. M., 2013, Bioethical Prescriptions: To Create, End, Choose, and Improve Lives , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kass, L., 2002, Life, Liberty, and the Defense of Dignity: The Challenge for Bioethics , San Francisco: Encounter Books.
- Kauppinen, A., 2012, “Meaningfulness and Time”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 82: 345–77.
- Kekes, J., 1986, “The Informed Will and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 47: 75–90.
- –––, 2000, “The Meaning of Life”, in Midwest Studies in Philosophy, Volume 24; Life and Death: Metaphysics and Ethics , P. French and H. Wettstein (eds.), Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers: 17–34.
- Kraay, K. (ed.), 2018, Does God Matter? Essays on the Axiological Consequences of Theism , New York: Routledge.
- Landau, I., 1997, “Why Has the Question of the Meaning of Life Arisen in the Last Two and a Half Centuries?”, Philosophy Today , 41: 263–70.
- –––, 2017, Finding Meaning in an Imperfect World , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Le Bihan, B., 2019, “The No-Self View and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophy East and West , 69: 419–38.
- Levinson, J., 2004, “Intrinsic Value and the Notion of a Life”, The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 62: 319–29.
- Levy, N., 2005, “Downshifting and Meaning in Life”, Ratio , 18: 176–89.
- Lougheed, K., 2020, The Axiological Status of Theism and Other Worldviews , New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Mackie, J. L., 1977, Ethics: Inventing Right and Wrong , repr. London: Penguin Books, 1990.
- Markus, A., 2003, “Assessing Views of Life, A Subjective Affair?”, Religious Studies , 39: 125–43.
- Martela, F., 2017, “Meaningfulness as Contribution”, Southern Journal of Philosophy , 55: 232–56.
- Matheson, D., 2017, “The Worthwhileness of Meaningful Lives”, Philosophia , 48: 313–24.
- –––, 2018, “Creativity and Meaning in Life”, Ratio , 31: 73–87.
- Mawson, T., 2016, God and the Meanings of Life , London: Bloomsbury Publishing.
- –––, 2019, Monotheism and the Meaning of Life , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- May, T., 2009, Death , Stocksfield: Acumen.
- –––, 2015, A Significant Life: Human Meaning in a Silent Universe , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- McPherson, D., 2020, Virtue and Meaning: A Neo-Aristotelian Perspective , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Metz, T., 2002, “Recent Work on the Meaning of Life”, Ethics , 112: 781–814.
- –––, 2013, Meaning in Life: An Analytic Study , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2019, God, Soul and the Meaning of Life , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mintoff, J., 2008, “Transcending Absurdity”, Ratio , 21: 64–84.
- Moreland, J. P., 1987, Scaling the Secular City: A Defense of Christianity , Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Book House.
- Morris, T., 1992, Making Sense of It All: Pascal and the Meaning of Life , Grand Rapids, MI: Willliam B. Eerdmans Publishing Company.
- Mulgan, T., 2015, Purpose in the Universe: The Moral and Metaphysical Case for Ananthropocentric Purposivism , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Murphy, J., 1982, Evolution, Morality, and the Meaning of Life , Totowa, NJ: Rowman and Littlefield.
- Nagel, T., 1970, “The Absurd”, Journal of Philosophy , 68: 716–27.
- –––, 1986, The View from Nowhere , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Nozick, R., 1974, Anarchy, State and Utopia , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 1981, Philosophical Explanations , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1989, The Examined Life , New York: Simon and Schuster.
- Nussbaum, M., 1989, “Mortal Immortals: Lucretius on Death and the Voice of Nature”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 50: 303–51.
- Olson, N., 2016, “Medical Researchers’ Ancillary Care Obligations”, Bioethics , 30: 317–24.
- Pereboom, D., 2014, Free Will, Agency, and Meaning in Life , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Pisciotta, T., 2013, “ Determinism and Meaningfulness in Lives ”, PhD Dissertation, University of Melbourne.
- Purves, D. and Delon, N., 2018, “Meaning in the Lives of Humans and Other Animals”, Philosophical Studies , 175: 317–38.
- Quinn, P., 2000, “How Christianity Secures Life’s Meanings”, in The Meaning of Life in the World Religions , J. Runzo and N. Martin (eds.), Oxford: Oneworld Publications: 53–68.
- Raz, J., 2001, Value, Respect, and Attachment , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Repp, C., 2018, “Life Meaning and Sign Meaning”, Philosophical Papers , 47: 403–27.
- Ruse, M. and Wilson, E., 1986, “Moral Philosophy as Applied Science”, Philosophy , 61: 173–92.
- Scarre, G., 2007, Death . Stocksfield: Acumen.
- Schinkel, A., De Ruyter, D., and Aviram, A., 2015, “Education and Life’s Meaning”, Journal of Philosophy of Education , 50: 398–418.
- Seachris, J., 2011, “Death, Futility, and the Proleptic Power of Narrative Ending”, Religious Studies , 47: 141–63.
- –––, 2013, “General Introduction”, in Exploring the Meaning of Life: An Anthology and Guide , J. Seachris (ed.), Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell: 1–20.
- –––, 2016, “From the Meaning Triad to Meaning Holism: Unifying Life’s Meaning”, Human Affairs , 29: 363–78.
- Singer, I., 1996, Meaning in Life, Volume 1: The Creation of Value , Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Singer, P., 1995, How Are We to Live? Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
- Smith, Q., 1997, Ethical and Religious Thought in Analytic Philosophy of Language , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- –––, 2003, “Moral Realism and Infinite Spacetime Imply Moral Nihilism”, in Time and Ethics: Essays at the Intersection , H. Dyke (ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers: 43–54.
- Smuts, A., 2011, “Immortality and Significance”, Philosophy and Literature , 35: 134–49.
- –––, 2018, Welfare, Meaning, and Worth , New York: Routledge
- Solomon, R., 1993, The Passions: Emotions and the Meaning of Life , Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing Company.
- Street, S., 2015, “Does Anything Really Matter or Did We Just Evolve to Think So?”, in The Norton Introduction to Philosophy , G. Rosen et al. (eds.), New York: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc.: 685–95.
- Svensson, F., 2017, “A Subjectivist Account of Meaning in Life”, De Ethica , 4: 45–66.
- Swenson, D., 1949, “The Dignity of Human Life”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 21–30.
- Swinburne, R., 2016, “How God Makes Life a Lot More Meaningful”, in God and Meaning , J. Seachris and S. Goetz (eds.), New York: Bloomsbury Academic: 151–63.
- Tabensky, P., 2003, “Parallels Between Living and Painting”, The Journal of Value Inquiry , 37: 59–68.
- Tartaglia, J., 2015, Philosophy in a Meaningless Life , London: Bloomsbury.
- Taylor, C., 1989, Sources of the Self , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1992, The Ethics of Authenticity , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Taylor, R., 1970, “The Meaning of Life”, in Good and Evil , repr. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Boooks, 2000: 319–34.
- –––, 1987, “Time and Life’s Meaning”, The Review of Metaphysics , 40: 675–86.
- Thomas, J., 2018, “Can Only Human Lives Be Meaningful?”, Philosophical Papers , 47: 265–97.
- –––, 2019, “Meaningfulness as Sensefulness”, Philosophia , 47: 1555–77.
- Thomson, G., 2003, On the Meaning of Life , South Melbourne: Wadsworth.
- Tooley, M., 2018, “Axiology: Theism Versus Widely Accepted Monotheisms”, in Does God Matter? Essays on the Axiological Consequences of Theism , K. Kraay, (ed.), New York: Routledge: 46–69.
- Trisel, B. A., 2002, “Futility and the Meaning of Life Debate”, Sorites , 14: 70–84.
- –––, 2004, “Human Extinction and the Value of Our Efforts”, The Philosophical Forum , 35: 371–91.
- –––, 2016, “Human Extinction, Narrative Ending, and Meaning of Life”, Journal of Philosophy of Life , 6: 1–22.
- Velleman, J. D., 2015, Beyond Price: Essays on Birth and Death , Cambridge: Open Book Publishers.
- Visak, T., 2017, “Understanding ‘Meaning of Life’ in Terms of Reasons for Action”, The Journal of Value Inquiry , 51: 507–30.
- Waghorn, N., 2014, Nothingness and the Meaning of Life: Philosophical Approaches to Ultimate Meaning through Nothing and Reflexivity , London: Bloomsbury.
- Wielenberg, E., 2005, Value and Virtue in a Godless Universe , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wiggins, D., 1988, “Truth, Invention, and the Meaning of Life”, rev. edn. in Essays on Moral Realism , G. Sayre-McCord (ed.), Ithaca: Cornell University Press: 127–65.
- Williams, B., 1973, “The Makropulos Case: Reflections on the Tedium of Immortality”, in Problems of the Self , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 82–100.
- –––, 1976, “Persons, Character and Morality”, in The Identities of Persons , A. O. Rorty (ed.), Berkeley: University of California Press: 197–216.
- Williams, C., 2020, Religion and the Meaning of Life: An Existential Approach , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wolf, S., 2010, Meaning in Life and Why It Matters , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2015, The Variety of Values: Essays on Morality, Meaning, and Love , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2016, “Meaningfulness: A Third Dimension of the Good Life”, Foundations of Science , 21: 253–69.
- Wong, W., 2008, “Meaningfulness and Identities”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 11: 123–48.
- Buber, M., 1923, I and Thou , W. Kaufmann (tr.), New York: Simon & Schuster Inc., 1970.
- Camus, A., 1942, The Myth of Sisyphus , J. O’Brian (tr.), London: H. Hamilton, 1955.
- James, W., 1899, “What Makes a Life Significant?”, in On Some of Life’s Ideals , New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1900.
- Jaspers, K., 1931, Man in the Modern Age , E. Paul and C. Paul (tr.), New York: Routledge, 2010.
- Kant, I., 1791, Critique of the Power of Judgment , P. Guyer and E. Mathews (tr.), New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
- Kierkegaard, S., 1849, The Sickness unto Death , H. V. Hong and E. H. Hong (tr.), Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1980.
- Marx, K., 1844, Economic and Philosophical Manuscripts , in Karl Marx Selected Writings, 2 nd Ed. , D. McLellan (ed., tr.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000.
- Nietzsche, F., 1885, Thus Spoke Zarathustra , in The Portable Nietzsche , W. Kaufmann (ed., tr.), New York: Viking Press, 1954.
- Sartre, J.-P., 1946, Existentialism Is a Humanism , P. Mairet (tr.), London: Methuen & Co, 1948.
- Schlick, M., 1927, “ On the Meaning of Life ”, P. Heath (tr.).
- Schopenhauer, A., 1851, Parerga and Paralipomena: Short Philosophical Essays, Volume 2 , E. F. J. Payne (tr.), New York: Oxford University Press, 1974.
- Tolstoy, L., 1884, A Confession , L. Maude and A. Maude (tr.).
- Wittgenstein, L., 1929, Lecture on Ethics , E. Zamuner et al. (eds.), Malden, MA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014.
- Benatar, D. (ed.), 2016, Life, Death & Meaning, 3 rd Ed. , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
- Cottingham, J. (ed.), 2007, Western Philosophy: An Anthology, 2 nd Ed. , Oxford: Blackwell: pt. 12.
- Garcia, R. and King, N. (eds.), 2009, Is Goodness Without God Good Enough? Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
- Klemke, E. D. and Cahn, S. M. (eds.), 2018, The Meaning of Life: A Reader, 4 th Ed. , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kolodny, N. (ed.), 2013, Death and the Afterlife , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Leach, S. and Tartaglia, J. (eds.), 2018, The Meaning of Life and the Great Philosophers , London: Routledge.
- Morioka, M. (ed.), 2015, Reconsidering Meaning in Life , Saitama: Waseda University.
- ––– (ed.), 2017, Nihilism and the Meaning of Life , Saitama: Waseda University.
- Seachris, J. (ed.), 2013, Exploring the Meaning of Life: An Anthology and Guide , Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Seachris, J. and Goetz, S. (eds.), 2016, God and Meaning: New Essays , New York: Bloombsury Academic.
- Baggini, J., 2004, What’s It All About?: Philosophy and the Meaning of Life , London: Granta Books.
- Belliotti, R., 2001, What Is the Meaning of Life? , Amsterdam: Rodopi.
- Belshaw, C., 2005, 10 Good Questions About Life and Death , Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Cottingham, J., 2003, On the Meaning of Life , London: Routledge.
- Eagleton, T., 2007, The Meaning of Life: A Very Short Introduction , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Fischer, J. M., 2019, Death, Immortality, and Meaning in Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Ford, D., 2007, The Search for Meaning: A Short History , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Hauskeller, M., 2020, The Meaning of Life and Death: Ten Classic Thinkers on the Ultimate Question , London: Bloomsbury Academic.
- Martin, M., 2002, Atheism, Morality, and Meaning , Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
- Messerly, J., 2012, The Meaning of Life: Religious, Philosophical, Transhumanist, and Scientific Approaches , Seattle: Darwin and Hume Publishers.
- Ruse, M., 2019, A Meaning to Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Young, J., 2003, The Death of God and the Meaning of Life , New York: Routledge.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Delon, N., 2021, “ The Meaning of Life ”, a bibliography on PhilPapers.
- Metz, T., 2021, “ Life, Meaning of ”, in Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy , E. Mason (ed.).
- O’Brien, W., 2021, “ The Meaning of Life: Early Continental and Analytic Perspectives ”, in Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy , J. Fieser and B. Dowden (eds.).
- Seachris, J., 2021, “ Meaning of Life: The Analytic Perspective ”, in Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy , J. Fieser and B. Dowden (eds.).
afterlife | death | ethics: ancient | existentialism | friendship | love | perfectionism, in moral and political philosophy | value: intrinsic vs. extrinsic | well-being
Copyright © 2021 by Thaddeus Metz < th . metz @ up . ac . za >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Essays About Life: Top 5 Examples Plus 7 Prompts
Life envelops various meanings; if you are writing essays about life, discover our comprehensive guide with examples and prompts to help you with your essay.
What is life? You can ask anyone; I assure you, no two people will have the same answer. How we define life relies on our beliefs and priorities. One can say that life is the capacity for growth or the time between birth and death. Others can share that life is the constant pursuit of purpose and fulfillment. Life is a broad topic that inspires scholars, poets, and many others. It stimulates discussions that encourage diverse perspectives and interpretations.
5 Essay Examples
1. essay on life by anonymous on toppr.com, 2. the theme of life, existence and consciousness by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. compassion can save life by anonymous on papersowl.com, 4. a life of consumption vs. a life of self-realization by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 5. you only live once: a motto for life by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 1. what is the true meaning of life, 2. my life purpose, 3. what makes life special, 4. how to appreciate life, 5. books about life, 6. how to live a healthy life, 7. my idea of a perfect life.
“…quality of Life carries huge importance. Above all, the ultimate purpose should be to live a meaningful life. A meaningful life is one which allows us to connect with our deeper self.”
The author defines life as something that differentiates man from inorganic matter. It’s an aspect that processes and examines a person’s actions that develop through growth. For some, life is a pain because of failures and struggles, but it’s temporary. For the writer, life’s challenges help us move forward, be strong, and live to the fullest. You can also check out these essays about utopia .
“… Kafka defines the dangers of depending on art for life. The hunger artist expresses his dissatisfaction with the world by using himself and not an external canvas to create his artwork, forcing a lack of separation between the artist and his art. Therefore, instead of the art depending on the audience, the artist depends on the audience, meaning when the audience’s appreciation for work dwindles, their appreciation for the artist diminishes as well, leading to the hunger artist’s death.”
The essay talks about “ A Hunger Artist ” by Franz Kafka, who describes his views on life through art. The author analyzes Kafka’s fictional main character and his anxieties and frustrations about life and the world. This perception shows how much he suffered as an artist and how unhappy he was. Through the essay, the writer effectively explains Kafka’s conclusion that artists’ survival should not depend on their art.
“Compassion is that feeling that we’ve all experienced at some point in our lives. When we know that there is someone that really cares for us. Compassion comes from that moment when we can see the world through another person’s eyes.”
The author is a nurse who believes that to be professional, they need to be compassionate and treat their patients with respect, empathy, and dignity. One can show compassion through small actions such as talking and listening to patients’ grievances. In conclusion, compassion can save a person’s life by accepting everyone regardless of race, gender, etc.
“… A life of self-realization is more preferable and beneficial in comparison with a life on consumption. At the same time, this statement may be objected as person’s consumption leads to his or her happiness.”
The author examines Jon Elster’s theory to find out what makes a person happy and what people should think and feel about their material belongings. The essay mentions a list of common activities that make us feel happy and satisfied, such as buying new things. The writer explains that Elster’s statement about the prevalence of self-realization in consumption will always trigger intense debate.
“Appreciate the moment you’ve been given and appreciate the people you’ve been given to spend it with, because no matter how beautiful or tragic a moment is, it always ends. So hold on a little tighter, smile a little bigger, cry a little harder, laugh a little louder, forgive a little quicker, and love a whole lot deeper because these are the moments you will remember when you’re old and wishing you could rewind time.”
This essay explains that some things and events only happen once in a person’s life. The author encourages teenagers to enjoy the little things in their life and do what they love as much as they can. When they turn into adults, they will no longer have the luxury to do whatever they want.
The author suggests doing something meaningful as a stress reliever, trusting people, refusing to give up on the things that make you happy, and dying with beautiful memories. For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
7 Prompts for Essays About Life

Life encompasses many values and depends on one’s perception. For most, life is about reaching achievements to make themselves feel alive. Use this prompt to compile different meanings of life and provide a background on why a person defines life as they do.
Take Joseph Campbell’s, “Life has no meaning. Each of us has meaning, and we bring it to life. It is a waste to be asking the question when you are the answer,” for example. This quote pertains to his belief that an individual is responsible for giving life meaning.
For this prompt, share with your readers your current purpose in life. It can be as simple as helping your siblings graduate or something grand, such as changing a national law to make a better world. You can ask others about their life purpose to include in your essay and give your opinion on why your answers are different or similar.
Life is a fascinating subject, as each person has a unique concept. How someone lives depends on many factors, such as opportunities, upbringing, and philosophies. All of these elements affect what we consider “special.”
Share what you think makes life special. For instance, talk about your relationships, such as your close-knit family or best friends. Write about the times when you thought life was worth living. You might also be interested in these essays about yourself .
Life in itself is a gift. However, most of us follow a routine of “wake up, work (or study), sleep, repeat.” Our constant need to survive makes us take things for granted. When we endlessly repeat a routine, life becomes mundane. For this prompt, offer tips on how to avoid a monotonous life, such as keeping a gratitude journal or traveling.
Many literary pieces use life as their subject. If you have a favorite book about life, recommend it to your readers by summarizing the content and sharing how the book influenced your outlook on life. You can suggest more than one book and explain why everyone should read them.
For example, Paulo Coelho’s “The Alchemist” reminds its readers to live in the moment and never fear failure.

To be healthy doesn’t only pertain to our physical condition. It also refers to our mental, spiritual, and emotional well-being. To live a happy and full life, individuals must strive to be healthy in all areas. For this prompt, list ways to achieve a healthy life. Section your essay and present activities to improve health, such as eating healthy foods, talking with friends, etc.
No one has a perfect life, but describe what it’ll be like if you do. Start with the material things, such as your house, clothes, etc. Then, move to how you connect with others. In your conclusion, answer whether you’re willing to exchange your current life for the “perfect life” you described and why. See our essay writing tips to learn more!

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
The War at Stanford
I didn’t know that college would be a factory of unreason.

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
This article was featured in the One Story to Read Today newsletter. Sign up for it here .
ne of the section leaders for my computer-science class, Hamza El Boudali, believes that President Joe Biden should be killed. “I’m not calling for a civilian to do it, but I think a military should,” the 23-year-old Stanford University student told a small group of protesters last month. “I’d be happy if Biden was dead.” He thinks that Stanford is complicit in what he calls the genocide of Palestinians, and that Biden is not only complicit but responsible for it. “I’m not calling for a vigilante to do it,” he later clarified, “but I’m saying he is guilty of mass murder and should be treated in the same way that a terrorist with darker skin would be (and we all know terrorists with dark skin are typically bombed and drone striked by American planes).” El Boudali has also said that he believes that Hamas’s October 7 attack was a justifiable act of resistance, and that he would actually prefer Hamas rule America in place of its current government (though he clarified later that he “doesn’t mean Hamas is perfect”). When you ask him what his cause is, he answers: “Peace.”
I switched to a different computer-science section.
Israel is 7,500 miles away from Stanford’s campus, where I am a sophomore. But the Hamas invasion and the Israeli counterinvasion have fractured my university, a place typically less focused on geopolitics than on venture-capital funding for the latest dorm-based tech start-up. Few students would call for Biden’s head—I think—but many of the same young people who say they want peace in Gaza don’t seem to realize that they are in fact advocating for violence. Extremism has swept through classrooms and dorms, and it is becoming normal for students to be harassed and intimidated for their faith, heritage, or appearance—they have been called perpetrators of genocide for wearing kippahs, and accused of supporting terrorism for wearing keffiyehs. The extremism and anti-Semitism at Ivy League universities on the East Coast have attracted so much media and congressional attention that two Ivy presidents have lost their jobs. But few people seem to have noticed the culture war that has taken over our California campus.
For four months, two rival groups of protesters, separated by a narrow bike path, faced off on Stanford’s palm-covered grounds. The “Sit-In to Stop Genocide” encampment was erected by students in mid-October, even before Israeli troops had crossed into Gaza, to demand that the university divest from Israel and condemn its behavior. Posters were hung equating Hamas with Ukraine and Nelson Mandela. Across from the sit-in, a rival group of pro-Israel students eventually set up the “Blue and White Tent” to provide, as one activist put it, a “safe space” to “be a proud Jew on campus.” Soon it became the center of its own cluster of tents, with photos of Hamas’s victims sitting opposite the rubble-ridden images of Gaza and a long (and incomplete) list of the names of slain Palestinians displayed by the students at the sit-in.
Some days the dueling encampments would host only a few people each, but on a sunny weekday afternoon, there could be dozens. Most of the time, the groups tolerated each other. But not always. Students on both sides were reportedly spit on and yelled at, and had their belongings destroyed. (The perpetrators in many cases seemed to be adults who weren’t affiliated with Stanford, a security guard told me.) The university put in place round-the-clock security, but when something actually happened, no one quite knew what to do.
Conor Friedersdorf: How October 7 changed America’s free speech culture
Stanford has a policy barring overnight camping, but for months didn’t enforce it, “out of a desire to support the peaceful expression of free speech in the ways that students choose to exercise that expression”—and, the administration told alumni, because the university feared that confronting the students would only make the conflict worse. When the school finally said the tents had to go last month, enormous protests against the university administration, and against Israel, followed.
“We don’t want no two states! We want all of ’48!” students chanted, a slogan advocating that Israel be dismantled and replaced by a single Arab nation. Palestinian flags flew alongside bright “Welcome!” banners left over from new-student orientation. A young woman gave a speech that seemed to capture the sense of urgency and power that so many students here feel. “We are Stanford University!” she shouted. “We control things!”
“W e’ve had protests in the past,” Richard Saller, the university’s interim president, told me in November—about the environment, and apartheid, and Vietnam. But they didn’t pit “students against each other” the way that this conflict has.
I’ve spoken with Saller, a scholar of Roman history, a few times over the past six months in my capacity as a student journalist. We first met in September, a few weeks into his tenure. His predecessor, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, had resigned as president after my reporting for The Stanford Daily exposed misconduct in his academic research. (Tessier-Lavigne had failed to retract papers with faked data over the course of 20 years. In his resignation statement , he denied allegations of fraud and misconduct; a Stanford investigation determined that he had not personally manipulated data or ordered any manipulation but that he had repeatedly “failed to decisively and forthrightly correct mistakes” from his lab.)
In that first conversation, Saller told me that everyone was “eager to move on” from the Tessier-Lavigne scandal. He was cheerful and upbeat. He knew he wasn’t staying in the job long; he hadn’t even bothered to move into the recently vacated presidential manor. In any case, campus, at that time, was serene. Then, a week later, came October 7.
The attack was as clear a litmus test as one could imagine for the Middle East conflict. Hamas insurgents raided homes and a music festival with the goal of slaughtering as many civilians as possible. Some victims were raped and mutilated, several independent investigations found. Hundreds of hostages were taken into Gaza and many have been tortured.
This, of course, was bad. Saying this was bad does not negate or marginalize the abuses and suffering Palestinians have experienced in Gaza and elsewhere. Everyone, of every ideology, should be able to say that this was bad. But much of this campus failed that simple test.
Two days after the deadliest massacre of Jews since the Holocaust, Stanford released milquetoast statements marking the “moment of intense emotion” and declaring “deep concern” over “the crisis in Israel and Palestine.” The official statements did not use the words Hamas or violence .
The absence of a clear institutional response led some teachers to take matters into their own hands. During a mandatory freshman seminar on October 10, a lecturer named Ameer Loggins tossed out his lesson plan to tell students that the actions of the Palestinian “military force” had been justified, that Israelis were colonizers, and that the Holocaust had been overemphasized, according to interviews I conducted with students in the class. Loggins then asked the Jewish students to identify themselves. He instructed one of them to “stand up, face the window, and he kind of kicked away his chair,” a witness told me. Loggins described this as an effort to demonstrate Israel’s treatment of Palestinians. (Loggins did not reply to a request for comment; a spokesperson for Stanford said that there were “different recollections of the details regarding what happened” in the class.)
“We’re only in our third week of college, and we’re afraid to be here,” three students in the class wrote in an email that night to administrators. “This isn’t what Stanford was supposed to be.” The class Loggins taught is called COLLEGE, short for “Civic, Liberal, and Global Education,” and it is billed as an effort to develop “the skills that empower and enable us to live together.”
Loggins was suspended from teaching duties and an investigation was opened; this angered pro-Palestine activists, who organized a petition that garnered more than 1,700 signatures contesting the suspension. A pamphlet from the petitioners argued that Loggins’s behavior had not been out of bounds.
The day after the class, Stanford put out a statement written by Saller and Jenny Martinez, the university provost, more forcefully condemning the Hamas attack. Immediately, this new statement generated backlash.
Pro-Palestine activists complained about it during an event held the same day, the first of several “teach-ins” about the conflict. Students gathered in one of Stanford’s dorms to “bear witness to the struggles of decolonization.” The grievances and pain shared by Palestinian students were real. They told of discrimination and violence, of frightened family members subjected to harsh conditions. But the most raucous reaction from the crowd was in response to a young woman who said, “You ask us, do we condemn Hamas? Fuck you!” She added that she was “so proud of my resistance.”
David Palumbo-Liu, a professor of comparative literature with a focus on postcolonial studies, also spoke at the teach-in, explaining to the crowd that “European settlers” had come to “replace” Palestine’s “native population.”
Palumbo-Liu is known as an intelligent and supportive professor, and is popular among students, who call him by his initials, DPL. I wanted to ask him about his involvement in the teach-in, so we met one day in a café a few hundred feet away from the tents. I asked if he could elaborate on what he’d said at the event about Palestine’s native population. He was happy to expand: This was “one of those discussions that could go on forever. Like, who is actually native? At what point does nativism lapse, right? Well, you haven’t been native for X number of years, so …” In the end, he said, “you have two people who both feel they have a claim to the land,” and “they have to live together. Both sides have to cede something.”
The struggle at Stanford, he told me, “is to find a way in which open discussions can be had that allow people to disagree.” It’s true that Stanford has utterly failed in its efforts to encourage productive dialogue. But I still found it hard to reconcile DPL’s words with his public statements on Israel, which he’d recently said on Facebook should be “the most hated nation in the world.” He also wrote: “When Zionists say they don’t feel ‘safe’ on campus, I’ve come to see that as they no longer feel immune to criticism of Israel.” He continued: “Well as the saying goes, get used to it.”
Z ionists, and indeed Jewish students of all political beliefs, have been given good reason to fear for their safety. They’ve been followed, harassed, and called derogatory racial epithets. At least one was told he was a “dirty Jew.” At least twice, mezuzahs have been ripped from students’ doors, and swastikas have been drawn in dorms. Arab and Muslim students also face alarming threats. The computer-science section leader, El Boudali, a pro-Palestine activist, told me he felt “safe personally,” but knew others who did not: “Some people have reported feeling like they’re followed, especially women who wear the hijab.”
In a remarkably short period of time, aggression and abuse have become commonplace, an accepted part of campus activism. In January, Jewish students organized an event dedicated to ameliorating anti-Semitism. It marked one of Saller’s first public appearances in the new year. Its topic seemed uncontroversial, and I thought it would generate little backlash.
Protests began before the panel discussion even started, with activists lining the stairs leading to the auditorium. During the event they drowned out the panelists, one of whom was Israel’s special envoy for combatting anti-Semitism, by demanding a cease-fire. After participants began cycling out into the dark, things got ugly.
Activists, their faces covered by keffiyehs or medical masks, confronted attendees. “Go back to Brooklyn!” a young woman shouted at Jewish students. One protester, who emerged as the leader of the group, said that she and her compatriots would “take all of your places and ensure Israel falls.” She told attendees to get “off our fucking campus” and launched into conspiracy theories about Jews being involved in “child trafficking.” As a rabbi tried to leave the event, protesters pursued him, chanting, “There is only one solution! Intifada revolution!”
At one point, some members of the group turned on a few Stanford employees, including another rabbi, an imam, and a chaplain, telling them, “We know your names and we know where you work.” The ringleader added: “And we’ll soon find out where you live.” The religious leaders formed a protective barrier in front of the Jewish students. The rabbi and the imam appeared to be crying.

S aller avoided the protest by leaving through another door. Early that morning, his private residence had been vandalized. Protesters frequently tell him he “can’t hide” and shout him down. “We charge you with genocide!” they chant, demanding that Stanford divest from Israel. (When asked whether Stanford actually invested in Israel, a spokesperson replied that, beyond small exposures from passive funds that track indexes such as the S&P 500, the university’s endowment “has no direct holdings in Israeli companies, or direct holdings in defense contractors.”)
When the university finally said the protest tents had to be removed, students responded by accusing Saller of suppressing their right to free speech. This is probably the last charge he expected to face. Saller once served as provost at the University of Chicago, which is known for holding itself to a position of strict institutional neutrality so that its students can freely explore ideas for themselves. Saller has a lifelong belief in First Amendment rights. But that conviction in impartial college governance does not align with Stanford’s behavior in recent years. Despite the fact that many students seemed largely uninterested in the headlines before this year, Stanford’s administrative leadership has often taken positions on political issues and events, such as the Paris climate conference and the murder of George Floyd. After Russia invaded Ukraine, Stanford’s Hoover Tower was lit up in blue and yellow, and the school released a statement in solidarity.
Thomas Chatterton Williams: Let the activists have their loathsome rallies
When we first met, a week before October 7, I asked Saller about this. Did Stanford have a moral duty to denounce the war in Ukraine, for example, or the ethnic cleansing of Uyghur Muslims in China? “On international political issues, no,” he said. “That’s not a responsibility for the university as a whole, as an institution.”
But when Saller tried to apply his convictions on neutrality for the first time as president, dozens of faculty members condemned the response, many pro-Israel alumni were outraged, donors had private discussions about pulling funding, and an Israeli university sent an open letter to Saller and Martinez saying, “Stanford’s administration has failed us.” The initial statement had tried to make clear that the school’s policy was not Israel-specific: It noted that the university would not take a position on the turmoil in Nagorno-Karabakh (where Armenians are undergoing ethnic cleansing) either. But the message didn’t get through.
Saller had to beat an awkward retreat or risk the exact sort of public humiliation that he, as caretaker president, had presumably been hired to avoid. He came up with a compromise that landed somewhere in the middle: an unequivocal condemnation of Hamas’s “intolerable atrocities” paired with a statement making clear that Stanford would commit to institutional neutrality going forward.
“The events in Israel and Gaza this week have affected and engaged large numbers of students on our campus in ways that many other events have not,” the statement read. “This is why we feel compelled to both address the impact of these events on our campus and to explain why our general policy of not issuing statements about news events not directly connected to campus has limited the breadth of our comments thus far, and why you should not expect frequent commentary from us in the future.”
I asked Saller why he had changed tack on Israel and not on Nagorno-Karabakh. “We don’t feel as if we should be making statements on every war crime and atrocity,” he told me. This felt like a statement in and of itself.
In making such decisions, Saller works closely with Martinez, Stanford’s provost. I happened to interview her, too, a few days before October 7, not long after she’d been appointed. When I asked about her hopes for the job, she said that a “priority is ensuring an environment in which free speech and academic freedom are preserved.”
We talked about the so-called Leonard Law—a provision unique to California that requires private universities to be governed by the same First Amendment protections as public ones. This restricts what Stanford can do in terms of penalizing speech, putting it in a stricter bind than Harvard, the University of Pennsylvania, or any of the other elite private institutions that have more latitude to set the standards for their campus (whether or not they have done so).
So I was surprised when, in December, the university announced that abstract calls for genocide “clearly violate Stanford’s Fundamental Standard, the code of conduct for all students at the university.” The statement was a response to the outrage following the congressional testimony of three university presidents—outrage that eventually led to the resignation of two of them, Harvard’s Claudine Gay and Penn’s Liz Magill. Gay and Magill, who had both previously held positions at Stanford, did not commit to punishing calls for the genocide of Jews.
Experts told me that Stanford’s policy is impossible to enforce—and Saller himself acknowledged as much in our March interview.
“Liz Magill is a good friend,” Saller told me, adding, “Having watched what happened at Harvard and Penn, it seemed prudent” to publicly state that Stanford rejected calls for genocide. But saying that those calls violate the code of conduct “is not the same thing as to say that we could actually punish it.”
Stanford’s leaders seem to be trying their best while adapting to the situation in real time. But the muddled messaging has created a policy of neutrality that does not feel neutral at all.
When we met back in November, I tried to get Saller to open up about his experience running an institution in turmoil. What’s it like to know that so many students seem to believe that he—a mild-mannered 71-year-old classicist who swing-dances with his anthropologist wife—is a warmonger? Saller was more candid than I expected—perhaps more candid than any prominent university president has been yet. We sat in the same conference room as we had in September. The weather hadn’t really changed. Yet I felt like I was sitting in front of a different person. He was hunched over and looked exhausted, and his voice broke when he talked about the loss of life in Gaza and Israel and “the fact that we’re caught up in it.” A capable administrator with decades of experience, Saller seemed almost at a loss. “It’s been a kind of roller coaster, to be honest.”
He said he hadn’t anticipated the deluge of the emails “blaming me for lack of moral courage.” Anything the university says seems bound to be wrong: “If I say that our position is that we grieve over the loss of innocent lives, that in itself will draw some hostile reactions.”
“I find that really difficult to navigate,” he said with a sigh.
By March, it seemed that his views had solidified. He said he knew he was “a target,” but he was not going to be pushed into issuing any more statements. The continuing crisis seems to have granted him new insight. “I am certain that whatever I say will not have any material effect on the war in Gaza.” It’s hard to argue with that.
P eople tend to blame the campus wars on two villains: dithering administrators and radical student activists. But colleges have always had dithering administrators and radical student activists. To my mind, it’s the average students who have changed.
Elite universities attract a certain kind of student: the overachieving striver who has won all the right accolades for all the right activities. Is it such a surprise that the kids who are trained in the constant pursuit of perfect scores think they have to look at the world like a series of multiple-choice questions, with clearly right or wrong answers? Or that they think they can gamify a political cause in the same way they ace a standardized test?
Everyone knows that the only reliable way to get into a school like Stanford is to be really good at looking really good. Now that they’re here, students know that one easy way to keep looking good is to side with the majority of protesters, and condemn Israel.
It’s not that there isn’t real anger and anxiety over what is happening in Gaza—there is, and justifiably so. I know that among the protesters are many people who are deeply connected to this issue. But they are not the majority. What really activates the crowds now seems less a principled devotion to Palestine or to pacifism than a desire for collective action, to fit in by embracing the fashionable cause of the moment—as if a centuries-old conflict in which both sides have stolen and killed could ever be a simple matter of right and wrong. In their haste to exhibit moral righteousness, many of the least informed protesters end up being the loudest and most uncompromising.
Today’s students grew up in the Trump era, in which violent rhetoric has become a normal part of political discourse and activism is as easy as reposting an infographic. Many young people have come to feel that being angry is enough to foment change. Furious at the world’s injustices and desperate for a simple way to express that fury, they don’t seem interested in any form of engagement more nuanced than backing a pure protagonist and denouncing an evil enemy. They don’t, always, seem that concerned with the truth.
At the protest last month to prevent the removal of the sit-in, an activist in a pink Women’s March “pussy hat” shouted that no rape was committed by Hamas on October 7. “There hasn’t been proof of these rape accusations,” a student told me in a separate conversation, criticizing the Blue and White Tent for spreading what he considered to be misinformation about sexual violence. (In March, a United Nations report found “reasonable grounds to believe that conflict-related sexual violence,” including “rape and gang rape,” occurred in multiple locations on October 7, as well as “clear and convincing information” on the “rape and sexualized torture” of hostages.) “The level of propaganda” surrounding Hamas, he told me, “is just unbelievable.”
The real story at Stanford is not about the malicious actors who endorse sexual assault and murder as forms of resistance, but about those who passively enable them because they believe their side can do no wrong. You don’t have to understand what you’re arguing for in order to argue for it. You don’t have to be able to name the river or the sea under discussion to chant “From the river to the sea.” This kind of obliviousness explains how one of my friends, a gay activist, can justify Hamas’s actions, even though it would have the two of us—an outspoken queer person and a Jewish reporter—killed in a heartbeat. A similar mentality can exist on the other side: I have heard students insist on the absolute righteousness of Israel yet seem uninterested in learning anything about what life is like in Gaza.
I’m familiar with the pull of achievement culture—after all, I’m a product of the same system. I fell in love with Stanford as a 7-year-old, lying on the floor of an East Coast library and picturing all the cool technology those West Coast geniuses were dreaming up. I cried when I was accepted; I spent the next few months scrolling through the course catalog, giddy with anticipation. I wanted to learn everything.
I learned more than I expected. Within my first week here, someone asked me: “Why are all Jews so rich?” In 2016, when Stanford’s undergraduate senate had debated a resolution against anti-Semitism, one of its members argued that the idea of “Jews controlling the media, economy, government, and other societal institutions” represented “a very valid discussion.” (He apologized, and the resolution passed.) In my dorm last year, a student discussed being Jewish and awoke the next day to swastikas and a portrait of Hitler affixed to his door.
David Frum: There is no right to bully and harass
I grew up secularly, with no strong affiliation to Jewish culture. When I found out as a teenager that some of my ancestors had hidden their identity from their children and that dozens of my relatives had died in the Holocaust (something no living member of my family had known), I felt the barest tremor of identity. After I saw so many people I know cheering after October 7, I felt something stronger stir. I know others have experienced something similar. Even a professor texted me to say that she felt Jewish in a way she never had before.
But my frustration with the conflict on campus has little to do with my own identity. Across the many conversations and hours of formal interviews I conducted for this article, I’ve encountered a persistent anti-intellectual streak. I’ve watched many of my classmates treat death so cavalierly that they can protest as a pregame to a party. Indeed, two parties at Stanford were reported to the university this fall for allegedly making people say “Fuck Israel” or “Free Palestine” to get in the door. A spokesperson for the university said it was “unable to confirm the facts of what occurred,” but that it had “met with students involved in both parties to make clear that Stanford’s nondiscrimination policy applies to parties.” As a friend emailed me not long ago: “A place that was supposed to be a sanctuary from such unreason has become a factory for it.”
Readers may be tempted to discount the conduct displayed at Stanford. After all, the thinking goes, these are privileged kids doing what they always do: embracing faux-radicalism in college before taking jobs in fintech or consulting. These students, some might say, aren’t representative of America.
And yet they are representative of something: of the conduct many of the most accomplished students in my generation have accepted as tolerable, and what that means for the future of our country. I admire activism. We need people willing to protest what they see as wrong and take on entrenched systems of repression. But we also need to read, learn, discuss, accept the existence of nuance, embrace diversity of thought, and hold our own allies to high standards. More than ever, we need universities to teach young people how to do all of this.
F or so long , Stanford’s physical standoff seemed intractable. Then, in early February, a storm swept in, and the natural world dictated its own conclusion.
Heavy rains flooded campus. For hours, the students battled to save their tents. The sit-in activists used sandbags and anything else they could find to hold back the water—at one point, David Palumbo-Liu, the professor, told me he stood in the lashing downpour to anchor one of the sit-in’s tents with his own body. When the storm hit, many of the Jewish activists had been attending a discussion on anti-Semitism. They raced back and struggled to salvage the Blue and White Tent, but it was too late—the wind had ripped it out of the ground.
The next day, the weary Jewish protesters returned to discover that their space had been taken.
A new collection of tents had been set up by El Boudali, the pro-Palestine activist, and a dozen friends. He said they were there to protest Islamophobia and to teach about Islam and jihad, and that they were a separate entity from the Sit-In to Stop Genocide, though I observed students cycling between the tents. Palestinian flags now flew from the bookstore to the quad.
Administrators told me they’d quickly informed El Boudali and his allies that the space had been reserved by the Jewish advocates, and offered to help move them to a different location. But the protesters told me they had no intention of going. (El Boudali later said that they did not take over the entire space, and would have been “happy to exist side by side, but they wanted to kick us off entirely from that lawn.”)
When it was clear that the area where they’d set up their tents would not be ceded back to the pro-Israel group willingly, Stanford changed course and decided to clear everyone out in one fell swoop. On February 8, school officials ordered all students to vacate the plaza overnight. The university was finally going to enforce its rule prohibiting people from sleeping outside on campus and requiring the removal of belongings from the plaza between 8 p.m. and 8 a.m. The order cited the danger posed by the storm as a justification for changing course and, probably hoping to avoid allegations of bias, described the decision as “viewpoint-neutral.”
That didn’t work.
About a week of protests, led by the sit-in organizers, followed. Chants were chanted. More demands for a “river to the sea” solution to the Israel problem were made. A friend boasted to me about her willingness to be arrested. Stanford sent a handful of staff members, who stood near balloons left over from an event earlier in the day. They were there, one of them told me, to “make students feel supported and safe.”
In the end, Saller and Martinez agreed to talk with the leaders of the sit-in about their demands to divest the university and condemn Israel, under the proviso that the activists comply with Stanford’s anti-camping guidelines “regardless of the outcome of discussions.” Eight days after they were first instructed to leave, 120 days after setting up camp, the sit-in protesters slept in their own beds. In defiance of the university’s instructions, they left behind their tents. But sometime in the very early hours of the morning, law-enforcement officers confiscated the structures. The area was cordoned off without any violence and the plaza filled once more with electric skateboards and farmers’ markets.
The conflict continues in its own way. Saller was just shouted down by protesters chanting “No peace on stolen land” at a Family Weekend event, and protesters later displayed an effigy of him covered in blood. Students still feel tense; Saller still seems worried. He told me that the university is planning to change all manner of things—residential-assistant training, new-student orientation, even the acceptance letters that students receive—in hopes of fostering a culture of greater tolerance. But no campus edict or panel discussion can address a problem that is so much bigger than our university.
At one rally last fall, a speaker expressed disillusionment about the power of “peaceful resistance” on college campuses. “What is there left to do but to take up arms?” The crowd cheered as he said Israel must be destroyed. But what would happen to its citizens? I’d prefer to believe that most protesters chanting “Palestine is Arab” and shouting that we must “smash the Zionist settler state” don’t actually think Jews should be killed en masse. But can one truly be so ignorant as to advocate widespread violence in the name of peace?
When the world is rendered in black-and-white—portrayed as a simple fight between colonizer and colonized—the answer is yes. Solutions, by this logic, are absolute: Israel or Palestine, nothing in between. Either you support liberation of the oppressed or you support genocide. Either Stanford is all good or all bad; all in favor of free speech or all authoritarian; all anti-Semitic or all Islamophobic.
At January’s anti-anti-Semitism event, I watched an exchange between a Jewish attendee and a protester from a few feet away. “Are you pro-Palestine?” the protester asked.
“Yes,” the attendee responded, and he went on to describe his disgust with the human-rights abuses Palestinians have faced for years.
“But are you a Zionist?”
“Then we are enemies.”
The Book of Life
72 pages • 2 hours read
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Chapters 1-5
Chapters 6-10
Chapters 11-16
Chapters 17-21
Chapters 22-26
Chapters 27-31
Chapters 32-36
Chapters 37-41
Character Analysis
Symbols & Motifs
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
“Ghosts didn’t have much substance. All they were composed of was memories and heart.”
The opening quote from The Book of Life serves as a stark reminder to the reader of the immense stakes faced by Diana and Matthew. Several pivotal characters have already met their demise in pursuit of the Book of Life, and the threat of becoming ghosts looms as a tangible possibility for Diana, Matthew, and their offspring. This quote also underscores the recurring theme of family as both comfort and grief , as the departed spirits continue to harbor concerns and affection for their family, even though they cannot engage with them directly.
“‘What will happen now, Philippe?’ Emily asked […]
‘Endings. Beginnings,’ Philippe said with deliberate vagueness. ‘Change.’
Get access to this full Study Guide and much more!
- 7,400+ In-Depth Study Guides
- 4,950+ Quick-Read Plot Summaries
- Downloadable PDFs
‘Diana has never liked change,’ Emily said.
‘That is because Diana is afraid of what she must become,’ Philippe replied.”
This quote is an ominous foreshadowing of several pivotal events in the narrative . Firstly, it suggests that Diana’s trepidation is the primary obstacle preventing her from unleashing the full extent of her powers—a fear she must ultimately overcome to acquire Ashmole 782. Secondly, it alludes to the profound transformations the characters are poised to undergo throughout the story, accompanied by the arduous challenges these metamorphoses will inevitably entail.
“Long experience had taught him that whatever the mess, Gallowglass had made it with good intentions and a complete disregard for possible disaster.”

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Related Titles
By Deborah Harkness
A Discovery of Witches
Deborah Harkness
Shadow of Night
Featured Collections
Books on Justice & Injustice
View Collection
Good & Evil
New York Times Best Sellers
Popular Study Guides
Valentine's Day Reads: The Theme of Love
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
The physical sensations of watching a total solar eclipse

Regina G. Barber

Science writer David Baron witnesses his first total solar eclipse in Aruba, 1998. He says seeing one is "like you've left the solar system and are looking back from some other world." Paul Myers hide caption
Science writer David Baron witnesses his first total solar eclipse in Aruba, 1998. He says seeing one is "like you've left the solar system and are looking back from some other world."
David Baron can pinpoint the first time he got addicted to chasing total solar eclipses, when the moon completely covers up the sun. It was 1998 and he was on the Caribbean island of Aruba. "It changed my life. It was the most spectacular thing I'd ever seen," he says.
Baron, author of the 2017 book American Eclipse: A Nation's Epic Race to Catch the Shadow of the Moon and Win the Glory of the World , wants others to witness its majesty too. On April 8, millions of people across North America will get that chance — a total solar eclipse will appear in the sky. Baron promises it will be a surreal, otherworldly experience. "It's like you've left the solar system and are looking back from some other world."
Baron, who is a former NPR science reporter, talks to Life Kit about what to expect when viewing a total solar eclipse, including the sensations you may feel and the strange lighting effects in the sky. This interview has been edited for length and clarity.

Baron views the beginning of a solar eclipse with friends in Western Australia in 2023. Baron says getting to see the solar corona during a total eclipse is "the most dazzling sight in the heavens." Photographs by David Baron; Bronson Arcuri, Kara Frame, CJ Riculan/NPR; Collage by Becky Harlan/NPR hide caption
Baron views the beginning of a solar eclipse with friends in Western Australia in 2023. Baron says getting to see the solar corona during a total eclipse is "the most dazzling sight in the heavens."
What does it feel like to experience a total solar eclipse — those few precious minutes when the moon completely covers up the sun?
It is beautiful and absolutely magnificent. It comes on all of a sudden. As soon as the moon blocks the last rays of the sun, you're plunged into this weird twilight in the middle of the day. You look up and the blue sky has been torn away. On any given day, the blue sky overhead acts as a screen that keeps us from seeing what's in space. And suddenly that's gone. So you can look into the middle of the solar system and see the sun and the planets together.
Can you tell me about the sounds and the emotions you're feeling?
A total solar eclipse is so much more than something you just see with your eyes. It's something you experience with your whole body. [With the drop in sunlight], birds will be going crazy. Crickets may be chirping. If you're around other people, they're going to be screaming and crying [with all their emotions from seeing the eclipse]. The air temperature drops because the sunlight suddenly turns off. And you're immersed in the moon's shadow. It doesn't feel real.

Everything you need to know about solar eclipse glasses before April 8
In your 2017 Ted Talk , you said you felt like your eyesight was failing in the moments before totality. Can you go into that a little more?
The lighting effects are very weird. Before you get to the total eclipse, you have a progressive partial eclipse as the moon slowly covers the sun. So over the course of an hour [or so], the sunlight will be very slowly dimming. It's as if you're in a room in a house and someone is very slowly turning down the dimmer switch. For most of that time your eyes are adjusting and you don't notice it. But then there's a point at which the light's getting so dim that your eyes can't adjust, and weird things happen. Your eyes are less able to see color. It's as if the landscape is losing its color. Also there's an effect where the shadows get very strange.

Crescent-shaped shadows cast by the solar eclipse before it reaches totality appear on a board at an eclipse-viewing event in Antelope, Ore., 2017. Kara Frame and CJ Riculan/NPR hide caption
You see these crescents on the ground.
There are two things that happen. One is if you look under a tree, the spaces between leaves or branches will act as pinhole projectors. So you'll see tiny little crescents everywhere. But there's another effect. As the sun goes from this big orb in the sky to something much smaller, shadows grow sharper. As you're nearing the total eclipse, if you have the sun behind you and you look at your shadow on the ground, you might see individual hairs on your head. It's just very odd.
Some people might say that seeing the partial eclipse is just as good. They don't need to go to the path of totality.
A partial solar eclipse is a very interesting experience. If you're in an area where you see a deep partial eclipse, the sun will become a crescent like the moon. You can only look at it with eye protection. Don't look at it with the naked eye . The light can get eerie. It's fun, but it is not a thousandth as good as a total eclipse.
A total eclipse is a fundamentally different experience, because it's only when the moon completely blocks the sun that you can actually take off the eclipse glasses and look with the naked eye at the sun.
And you will see a sun you've never seen before. That bright surface is gone. What you're actually looking at is the sun's outer atmosphere, the solar corona. It's the most dazzling sight in the heavens. It's this beautiful textured thing. It looks sort of like a wreath or a crown made out of tinsel or strands of silk. It shimmers in space. The shape is constantly changing. And you will only see that if you're in the path of the total eclipse.

Shots - Health News
Watching a solar eclipse without the right filters can cause eye damage. here's why.
So looking at a partial eclipse is not the same?
It is not at all the same. Drive those few miles. Get into the path of totality.
This is really your chance to see a total eclipse. The next one isn't happening across the U.S. for another 20 years.
The next significant total solar eclipse in the United States won't be until 2045. That one will go from California to Florida and will cross my home state of Colorado. I've got it on my calendar.
The digital story was written by Malaka Gharib and edited by Sylvie Douglis and Meghan Keane. The visual editor is Beck Harlan. We'd love to hear from you. Leave us a voicemail at 202-216-9823, or email us at [email protected].
Listen to Life Kit on Apple Podcasts and Spotify , and sign up for our newsletter .
NPR will be sharing highlights here from across the NPR Network throughout the day Monday if you're unable to get out and see it in real time.
Correction April 3, 2024
In a previous audio version of this story, we made reference to an upcoming 2025 total solar eclipse. The solar eclipse in question will take place in 2045.
- Life Kit: Life Skills
- total eclipse
- solar eclipse
Serial Season 4

“Serial” returns with a history of Guantánamo told by people who lived through key moments in Guantánamo’s evolution, who know things the rest of us don’t about what it’s like to be caught inside an improvised justice system.
Published March 21, 2024
Listen to and follow Serial Season 4
- Apple Podcasts

Listen to the trailer for Serial Season 4: Guantánamo.
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio. Try listening here.

“So, it felt very like college-like… Without it being… Obviously the next day wasn’t classes, it was Gitmo… ”
Poor baby raul, episode 1 — poor baby raul.

“I wanted to create a persona, a thing that was not human.”
The special project, episode 2 — the special project.

“Am I one of them? I mean, is he innocent? I don’t know!”
Ahmad the iguana feeder, episode 3 — ahmad the iguana feeder.
- Episode 4 arrives April 11
About Serial Season 4
Right after Sept. 11, the United States created a brand-new criminal justice system at Guantánamo Bay. It was a prison and a court designed to deal with the people we had captured whom we suspected of being members of the Taliban or al Qaeda.
But to do what we wanted to do at Guantánamo — to interrogate detainees the way we wanted, to hold them indefinitely without charging them with a crime — we had to push aside the old, time-tested rules for detaining prisoners of war. And the consequences of that fell on ordinary people: thousands of military personnel, hundreds of prisoners, everybody scrambling through the same experiment.
There has been great journalism about the legal maneuvering to justify Guantánamo, and about the detainee abuse and the politics and policy. But “Serial” reporters Sarah Koenig and Dana Chivvis were after the inside stories, a picture of Guantánamo you could get only from the people who went through it. For years, though, all the best stories they heard about Guantánamo were off the record. But they stuck with it, figuring maybe once enough people were back in civilian life they’d be willing to tell those stories on the record. A couple of years ago, the “Serial” team started contacting people again: guards, interrogators, commanders, lawyers, chaplains, translators and former prisoners. More than a hundred people. And a remarkable number of them said: Okay, I’m ready. Here’s what happened.
“Serial” Season 4 is a history of Guantánamo told by people who lived through key moments in its evolution, who know things the rest of us don’t about what it’s like to be caught inside an improvised justice system.

- Sofia degli Alessandri is an Italian composer based in London. Her music combines field recordings, synths, chamber instruments and electronic beats. She composes for film, television, dance and other media.
- Hosts Sarah Koenig and Dana Chivvis Producer Jessica Weisberg Editor Julie Snyder Additional Reporting Cora Currier Fact Checking and Research Ben Phelan Additional Fact Checking Jessica Suriano Music supervision, sound design, and mixing Phoebe Wang Original score Sofia degli Alessandri Additional Editing David Kestenbaum, Jen Guerra, Alvin Melathe, Ellen Weiss and Ira Glass Contributing Editors Rozina Ali and Carol Rosenberg Assistant Producer Emma Grillo Translators and Interpreters Muhammad Raza Sayibzada, Nael Hijjo, Atiq Rahin, Dana El-Issa, Bachar Alhalabi, and Omama Othman Art Direction Pablo Delcan Art Max Guther Standards Editors Susan Wessling and Aisha Khan Legal Review Al-Amyn Sumar and Maya Gandhi Reporting and Research Amir Khafagy and Sami Yousafazai Additional Production Daniel Guillemette and Katie Mingle Executive Assistant Mack Miller Supervising Producer Ndeye Thioubou Deputy Managing Editor Sam Dolnick
- At the New York Times, thanks to Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Nina Lassam, Susan Beachy, Kitty Bennett, Alain Delaquérière, Sheelagh McNeill, Kirsten Noyes, Jack Begg, Jeffrey Miranda, Colleen Wormsley, Peter Rentz, John-Michael Murphy, Jordan Cohen, Zoe Murphy, Pierre-Antoine Louis, Mahima Chablani, Kelly Doe, Anisha Muni, Kimmy Tsai, Victoria Kim, Ashka Gami, Brad Fisher, Maddy Masiello, Daniel Powell, Marion Lozano, and Tug Wilson
- Special thanks Katie Mingle, Jenelle Pifer, Alissa Shipp, Nadia Reiman, Anita Badejo, Katie Fuchs, Alison Beckman at the Center for Victims of Torture, Clive Stafford Smith, Alisa Dogramadzieva, Shuaib Almosawa, Mohamed Elfaki, Freshta Taeb, Edgar August, Esther Whitfield, Lauren Myerscough-Mueller, Mark Fallon, Pardiss Kebriaei, Steve Vladeck, Charlie Savage, Michelle Shephard, Bastian Berbner, John Goetz, Sarah Mirk and everyone involved in “Guantánamo Voices,” Peter Jan Honigsberg, Tim Golden, John Ryan, Stuart Couch, Shayana Kadidal, Ray Rivera, Steven Kleinman, Steve Wood, Lee Riffaterre, Manny Supervielle, Mansoor Adayfi, Daniel May, and Mark Denbeaux, and Mariam Ghani

Serial is a podcast from the creators of This American Life, hosted by Sarah Koenig. Serial tells one story — a true story — over the course of a season.
A high-school senior named Hae Min Lee disappeared one day after school in 1999, in Baltimore County, Maryland. A month later, her body was found in a city park. She'd been strangled. Her 17-year-old ex-boyfriend, Adnan Syed, was arrested for the crime, and within a year, he was sentenced to life in prison.
In May 2014, a U.S. Special Operations team in a Black Hawk helicopter landed in the hills of Afghanistan. Waiting for them were more than a dozen Taliban fighters and a tall American, who looked pale and out of sorts: Bowe Bergdahl. Bergdahl, a U.S. soldier, had been a prisoner of the Taliban for nearly five years, and now he was going home. Listen here
“Serial” is heading back to court. This time, in Cleveland. Not for one extraordinary case; instead, Serial wanted to tackle the whole criminal justice system. To do that we figured we’d need to look at something different: ordinary cases. So we did. Inside these ordinary cases we found the troubling machinery of the criminal justice system on full display. Listen here

Serial Productions makes narrative podcasts that have transformed the medium. From the powerful forces shaping our public schools to a mystery at the heart of a scandal that rocked Britain, Serial expands the boundaries of audio investigative storytelling. Learn more
Further Reading From The Times
The guantánamo docket, a closer look at what the u.s. lets you see of its war court at guantánamo bay, conditions at guantánamo are cruel and inhuman, u.n. investigation finds.
- Share full article
Podcasts From The New York Times
The Daily: The biggest stories, five days a week, including the indictment of Donald Trump , the implosion of Silicon Valley Bank and the threat to abortion pills .
The Run-Up: Astead W. Herndon grapples with the big ideas already animating the 2024 election by reporting from inside the political establishment .
Hard Fork: Kevin Roose and Casey Newton make sense of the world of tech, including Google's Place in the A.I. Arms Race and the arrival of GPT-4 .
Modern Love: Anna Martin unpacks the complicated love lives of real people, exploring topics like getting ghosted and how to stop searching for the perfect partner .
Popcast: A weekly conversation from Jon Caramanica and The Times’s music team, with roundtables on artists like Ice Spice , Taylor Swift and SZA .
From Opinion
The Ezra Klein Show: Real conversations on the forces shaping the world, such as the increasing pace of A.I. development and China's global influence .
First Person: Lulu Garcia-Navarro explores intimate conversations about big ideas, like the experiences of a war reporter and treating obesity as a disease.
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Book of Life's multi-tiered plot also involves dueling married deities who reign over separate domains in the afterlife and decide to make a wager. La Muerte (well-known telenovela star Kate del Castillo ), who oversees the cheery Land of the Remembered and believes in the decency of mortals, bets that sensitive soul Manolo will win Maria ...
By Mekado Murphy. Oct. 15, 2014. From Mexican folk art to Sergio Leone to Radiohead, the director Jorge R. Gutierrez reached far and wide for inspiration in making "The Book of Life," his ...
After taking on lots of dangerous tasks, Manolo's pure heart allows him and his family to enter the Cave. They meet the Candle Maker who oversees the lives of everybody in the living world. Every ones life is symbolised by a burning candle. Manolo convinces him to take him through to the Land of the Forgotten to meet The good god.
When Esteban was a young man and felt his life was out of control after his betrothed, Clara's sister, Rosa, died, he went to the small village he owned. When Esteban first moves to Tres Marías, living on his family's country estate, he violently rapes a young peasant girl named Pancha García.
The film The Book Of Life is a film about a character named Manolo who tries to rescue the girl he loves and protect his family and city. Characters La Muerte and Xibalba go to the town of San Angel during the day of the dead. The Characters are seen with traditional sugar skulls as faces throughout the film. Some major themes in this movie are ...
Is Your Name Written in the Book of Life? The Bible says believers' names are written in the Book of Life. In Judaism today, it plays a role in the feast known as Yom Kippur, or Day of Atonement.The ten days between Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur are days of repentance, when Jews express remorse for their sins through prayer and fasting.Jewish tradition tells how God opens the Book of Life and ...
826 Words4 Pages. The Book of Life directed by Jorge R. Gutierrez follows the love story of three childhood friends, Manolo, Maria, and Joaquin, in a little town in Mexico. Their story involves many twists and turns, eye catching design, and even a little death. Following a story line that seems to come from the mind of Tim Burton, The Book of ...
October 17, 2014. Jorge R. Gutierrez wants to teach people about his heritage. He also wants to make colorful, energetic animated films to dazzle a wide audience. With The Book of Life, Gutierrez manages to scratch both itches at once. It's his first credit as a director and his sixth as an animator; his comfort with the medium shows in each ...
March 20, 2021. age 12+. Violence, sexism, just junk. The Book of Life So much hate. Non-stop insults, tons and tons of unnecessary violence. Put sexist ideas into my kids' minds that weren't there before. Flow was awful- just non-stop heavy action. I can't believe this movie had an editor.
THE BOOK OF LIFE is the journey of Manolo, a young man who is torn between fulfilling the expectations of his family and following his heart. Before choosing which path to follow, he embarks on an incredible adventure that spans three fantastical worlds where he must face his greatest fears. Rich with a fresh take on pop music favorites, THE ...
4,950+ Quick-Read Plot Summaries. Downloadable PDFs. Subscribe for $3 a Month. The Bishop-Mather family, consisting of Emily, Sarah, and Diana, offers a poignant illustration of this dichotomy within a traditional family structure. Emily's demise, a heartbreaking loss for the family, sends Sarah and Diana into profound grief.
Diana and Matthew initially encountered Jack during their timewalk in Shadow of Night.In The Book of Life, Jack transforms into a vampire when Andrew Hubbard, the vampire king of London, turns the dying 20-year-old before he succumbs to the plague.Jack's character significantly illustrates Diana and Matthew's parenting skills while offering an alternate example of how blood rage can manifest.
Thanks for exploring this SuperSummary Study Guide of "The Book of Life" by Deborah Harkness. A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides that feature detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, quotes, and essay topics.
The Book of Life uses an exemplary fusion of art and science to tell the story of life on earth. The text, under the editorship of Stephen Jay Gould, provides a thorough understanding of the latest research and is accompanied by paintings prepared especially for this book. ... Many of Gould's essays were reprinted in collected volumes, such as ...
An essay about The Book of Life, a website that delivers short, thoughtful, and affecting essays on love, relationships, work, self-knowledge, and sociability, among other topics. The site is an offshoot of the London-based "School of Life."
Yom Kippur is the 10th day of the seventh month and is often referred to as "the sabbath of sabbaths". Yom Kippur is a Jewish tradition that is observed by Jews, Samaritans, and some Christian groups . According to the Jewish tradition, God inscribes each person's fate for the coming year into a book. This book is called the Book of Life.
3. Naturalism. Recall that naturalism is the view that a physical life is central to life's meaning, that even if there is no spiritual realm, a substantially meaningful life is possible. Like supernaturalism, contemporary naturalism admits of two distinguishable variants, moderate and extreme (Metz 2019).
Each of us has meaning, and we bring it to life. It is a waste to be asking the question when you are the answer," for example. This quote pertains to his belief that an individual is responsible for giving life meaning. 2. My Life Purpose. For this prompt, share with your readers your current purpose in life.
This book and its question inspired a generation of biologists and scientists to focus on molecular biology and a few years later unravel the structure of the master molecule of life: DNA. This ...
The Book of Life is the 2014 concluding volume of Deborah Harkness's acclaimed All Souls Trilogy, a romantic fantasy series.Deborah Harkness, a professor, historian, and novelist, began her bestselling series with A Discovery of Witches (2011), followed by a Shadow of Night (2012). A prequel, Time's Convert (2019), delves into the backstory of the character Marcus Whitmore.
Affirmation of Life - essay about the book: The Denial of Death. Zoom. We all have the potential to pioneer this universe of wonders and discoveries, but we are like genies trapped in bottles. Not only that, the bottle is rusting away, and we have barely gotten to exercise our powers. Yet here we sit, instead of working on the situation, we ...
If a year of life lost is valued at five or fewer additional years spent in poverty, low-income countries suffered greater total well-being loss than high-income countries. For a wide range of valuations, the greatest well-being losses fell on upper-middle-income countries and countries in the Latin America region.
How to cite Book of Life essay. Check out this FREE essay on Book of Life ️ and use it to write your own unique paper. New York Essays - database with more than 65.000 college essays for A+ grades .
Two days after the deadliest massacre of Jews since the Holocaust, Stanford released milquetoast statements marking the "moment of intense emotion" and declaring "deep concern" over "the ...
Thanks for exploring this SuperSummary Study Guide of "The Book of Life" by Deborah Harkness. A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides that feature detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, quotes, and essay topics.
Baron, author of the 2017 book American Eclipse: A Nation's Epic Race to Catch the Shadow of the Moon and Win the Glory of the World, wants others to witness its majesty too. On April 8, millions ...
3/5: There is so much beauty in Rilke's thoughts. I love his poetry a little less than some of the wisdom he dispensed in letters and essays. i like to open the book blindly and put my finger down on a word and read the thought with it. Some are fairly bland, but when he gets it, he opens the sky and I am rocked. "There is only a single, urgent task: to attach oneself someplace to nature ...
"Serial" returns with a history of Guantánamo told by people who lived through key moments in Guantánamo's evolution, who know things the rest of us don't about what it's like to be ...