CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration . These Assignments for Grade 8 Mathematics Mensuration cover all important topics which can come in your standard 8 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 8 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Mensuration Class 8. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration class 8 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Mensuration assignments in Pdf for grade 8th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 8 important questions and answers for Mathematics Mensuration as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 will be really helpful for standard 8th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 8th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Download in Pdf
Advantages of Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics Mensuration assignments for Grade 8, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics Mensuration textbooks for Class 8 .
- All Mathematics Mensuration assignments for Class 8 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 8 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Mensuration chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 8 Mathematics Mensuration chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Mensuration in Grade 8, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Mensuration Grade 8 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 8 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 8 Mathematics Exponents and Powers Assignments

Class 8 Tamil Assignments

Class 8 Mathematics Introduction to Graphs Assignments
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 9: Mensuration
Mensuration 9.1.
- Area of trapezoids (Opens a modal)
- Area of composite shapes (Opens a modal)
- Mensuration 9.1 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
Mensuration 9.2
- Surface area of a box (cuboid) (Opens a modal)
- Cylinder volume & surface area (Opens a modal)
- Mensuration 9.2 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
Mensuration 9.3
- Volume of a rectangular prism (Opens a modal)
- Mensuration 9.3 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Mensuration
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Mensuration and Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Try These Solutions in Hindi and English Medium prepared for CBSE Board session 2023-24. According to new rationalised syllabus and latest NCERT books for CBSE 2023-24, there are only three exercises in chapter 9 of 8th ncert solutions of mathematics.
8th Maths Chapter 9 Solutions in English Medium
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Try These Solutions
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 in English
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.2 in English
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.3 in English
8th Maths Chapter 9 Solutions in Hindi Medium
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.1 in Hindi
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.2 in Hindi
- Class 8 Maths Exercise 9.3 in Hindi
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 NCERT Book
- Class 8 Maths Solutions Page
- Class 8 all Subjects Solutions
Class VIII Mathematics Exercise 9.1, Exercise 9.2 and Exercise 9.3 in English Medium and Hindi Medium updated for new academic session following new syllabus. Download Prashnavali 9.1, Prashnavali 9.2 and Prashnavali 9.3 in Hindi Medium to study online or free PDF download. All NCERT Solutions 2023-24 are updated as per the latest CBSE Syllabus for the academic session 2023-24. Students can download NCERT Books in the PDF file format to use it offline.
Free App for Grade 8 Solutions

Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Mensuration all exercises in English Medium as well as Hindi Medium are given below to study online or download in PDF format. Download NCERT Solutions offline apps , which work without internet, once downloaded. All the solutions given in apps are updated for academic session 2023-24.
Important Terms about Class 8 Maths Chapter 9
A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is 24 cm and the corresponding height is 10 cm. how many such tiles are required to cover a floor of area 1080 m^2 [if required you can split the tiles in whatever way you want to fill up the corners].
Base of flooring tile = 24 cm = 0.24 m Corresponding height of a flooring tile = 10 cm = 0.10 m Now Area of flooring tile = Base x Altitude = 0.24 x 0.10 = 0.024 m^2
Number of tiles required to cover the floor = Area of Floor/Area of one tile = 1080/0.024 = 45000 tiles Hence 45000 tiles are required to cover the floor.
Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6 cm and whose altitude is 4 cm. If one of the diagonals is 8 cm long, find the length of the other diagonal.
Since rhombus is also a kind of parallelogram. Area of rhombus = Base x Altitude = 6 x 4 = 24 cm^2 Also, Area of rhombus = 1/2 x d1 x d2 According to question, 24 = 1/2 x 8 x d2 So, 4d2 = 24 and d2 = 6 cm Hence, the length of the other diagonal is 6 cm.
In 8th Maths NCERT Chapter 9 Mensuration, we have to find the Areas, Perimeter, missing dimensions of the geometrical figures. Area of triangle, square, parallelogram, trapezium on the basis of given information and applying simple formula. Area of various specific quadrilateral like parallelogram, rhombus, rectangle, square and general quadrilateral in which we divide the quadrilateral into two triangles and then find the area of triangles and add them. Similarly we can find the area of polygon by dividing it into triangles and adding the areas of all triangles. Surface area and volumes of solid figures like Cube, Cuboids, Cylinders, Cones, etc. are given to find one the basis of application of formulae.
The methods used in this chapter have to be used in high school as well. Therefore, this lesson is also important from the point of view of the coming classes. Students should carefully understand all the facts used in this lesson so that there is no problem in the successive classes.
« Chapter 8: Algebraic Expressions and Identities
Chapter 10: exponents and powers ».
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - Mensuration
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration - Free PDF Download
Class 8 students have a lot on their plate in terms of academics. A subject like Maths requires them to spend enough time in solving assignments and preparing for exams. Vedantu’s team of scholars understand the needs and understanding level of Class 8 students and have designed NCERT Solution for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 keeping all of this in mind. NCERT Solution Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration Solution is entirely based on the latest CBSE curriculum. It will be able to clarify all the doubts that you might have in the Mensuration chapter. The problems in the Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 are well explained with diagrams and step-by-step explanations to make it simple for you to follow the solution.
You can also download Class 8 Science to help you to revise complete syllabus ans score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 – Mensuration
Exercise 11.1
Q1. A square and a rectangular field with measurements as given in the figure have the same perimeter. Which field has a larger area?
Ans: Let Side of a Square be ‘ \[{\text{a}}\] ’.
Length and Breadth of Rectangle are ‘ \[{\text{l}}\] ’ and ‘ \[{\text{b}}\] ’ respectively.
Perimeter of Square = $4$ (side of square) = $4$ ( \[{\text{a}}\] )
= $4$ ( $60$${\text{m}}$ ) = $240{\text{m}}$
Perimeter of Rectangle = $2$ (Length+Breadth) = $2$ ( \[{\text{l + b}}\] )
= $2$ ( $80{\text{m}}$ + \[{\text{b}}\] )
Now, It is given that the perimeter of the square and the perimeter of the rectangle are equal.
So, $240{\text{m}}$ = $2$ ( $80{\text{m}}$ + \[{\text{b}}\] )
$240{\text{m}}$ = $160{\text{m}}$ + $2$\[{\text{b}}\]
$80{\text{m}}$ = 2 \[{\text{b}}\]
$40{\text{m}}$ = \[{\text{b}}\]
Area of square = $\mathop {{\text{(side)}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $ = $\mathop {{\text{(60m)}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $ = $\mathop {{\text{3600m}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $
Area of Rectangle = Length x Breadth = $(80 x 40)$$\mathop {\text{m}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $ = $3200$${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Thus, the area of the square field is larger than the area of the rectangular field.
Q2. Mrs. Kaushik has a square plot with the measurement as shown in the following figure. She wants to construct a house in the middle of the plot. A garden is developed around the house. Find the total cost of developing a garden around the house at the rate of ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{55}}\;{\text{per}}\;{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$?
Ans: Area of the Square Plot = ${{\text{(side)}}^{\text{2}}}$ = \[{{\text{(25m)}}^{\text{2}}}\] = ${\text{625}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Area of the House = Length x Breadth = ${\text{15m x 20m}}$ = ${\text{300}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Now, Area of the remaining portion = Area of the square plot – Area of the house
= ${\text{625}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ - ${\text{300}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{325}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
The cost of developing the garden around the house is ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{55}}\;{\text{per}}\;{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
Therefore, total cost of developing the area ${\text{325}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ is ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{(55 x 325)}}$ = ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{17875}}$ .
Q3. The shape of a garden is rectangular in the middle and semi circular at the ends as shown in the diagram. Find the area and the perimeter of the garden (Length of rectangle is ${\text{20 - (3}}{\text{.5 + 3}}{\text{.5)m}}$)?
Ans: As we have given that length of rectangle = ${\text{[20 - (3}}{\text{.5 + 3}}{\text{.5)]m}}$
= ${\text{[20 - 7]m}}$ = ${\text{13m}}$
Breadth = \[{\text{7m}}\] .
Now, we have to find the circumference of both semi circles.
As, Diameter = ${\text{7m}}$ , so, Radius(r) = $\dfrac{7}{{\text{2}}}{\text{m}}$ = ${\text{3}}{\text{.5m}}$
Circumference of one semicircle = ${\text{$\pi$ r}}$ = $\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{(3}}{\text{.5)m}}$ = ${\text{11m}}$
Circumference of both circles = ${\text{2 x 11m}}$ = ${\text{22m}}$
Now, Perimeter of the garden = AB + CD + Length of both semi-circular regions AD & BC
= ${\text{(13 + 13 + 22)m}}$
= ${\text{48m}}$
Area of the garden = Area of the rectangle + $2 x $ Area of two semi-circular regions
= (Length x Breadth) + ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{[(13 x 7) + 2 x (}}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 3}}{\text{.5 x 3}}{\text{.5)]}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{(91 + 38}}{\text{.5)}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= \[{\text{129}}{\text{.5}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Q4. A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is ${\text{24cm}}$and the corresponding height is ${\text{10cm}}$.How many such tiles are required to cover a floor of area ${\text{1080}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$? (If required you can split the tiles in whatever way you want to fill up the corners).
Ans: Given that the Base of a parallelogram is ${\text{24cm}}$ and Height of a parallelogram is ${\text{10cm}}$ .
Therefore, Area of Parallelogram = Base x Height
= ${\text{(24 x 10)c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
= ${\text{240c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ .
Therefore, Area of parallelogram = Area of one tile.
Now, we have to find the number of tiles.
Given that Area of floor = ${\text{1080}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
So, Number of tiles = $\dfrac{{{\text{Area}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{floor}}}}{{{\text{Area}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{one}}\;{\text{tile}}}}$
= $\dfrac{{{\text{1080}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}}}{{{\text{240c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ = $\dfrac{{{\text{1080 x 10000}}}}{{{\text{240}}}}{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ \[(\because \;1{\text{m}} = 100{\text{cm}})\]
= $45000$ tiles.
Hence, $45000$ tiles are required to cover a floor of area ${\text{1080}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q5. An ant is moving around a few food pieces of different shapes scattered on the floor. For which food − piece would the ant have to take a longer round? Remember,
circumference of a circle can be obtained by using the expression c =${\text{2$\pi$ r}}$, where r is
the radius of the circle.
Ans: (a) Diameter( \[{\text{d}}\] ) = ${\text{2}}{\text{.8cm}}$ , so radius( \[{\text{r}}\] ) = $\dfrac{{{\text{2}}{\text{.8}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm}}$ = ${\text{1}}{\text{.4cm}}$
Therefore, Perimeter = ${\text{d + $\pi$ r}}$
= ${\text{2}}{\text{.8cm + }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{(1}}{\text{.4cm)}}$
= ${\text{[2}}{\text{.8 + (0}}{\text{.2 x 22)]cm}}$
= ${\text{(2}}{\text{.8 + 4}}{\text{.4)cm}}$
= ${\text{7}}{\text{.2cm}}$
(b) Diameter( \[{\text{d}}\] ) = ${\text{2}}{\text{.8cm}}$ , so radius( \[{\text{r}}\] ) = $\dfrac{{{\text{2}}{\text{.8}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm}}$ = ${\text{1}}{\text{.4cm}}$
Therefore, Perimeter = ${\text{1}}{\text{.5cm + 2}}{\text{.8cm + 1}}{\text{.5cm + $\pi$ (1}}{\text{.4cm)}}$
= ${\text{5}}{\text{.8cm + }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{(1}}{\text{.4cm)}}$
= ${\text{5}}{\text{.8cm + 4}}{\text{.4cm}}$
= ${\text{10}}{\text{.2cm}}$ .
(c) Radius( \[{\text{r}}\] ) = $\dfrac{{{\text{2}}{\text{.8}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm}}$ = ${\text{1}}{\text{.4cm}}$
Perimeter = ${\text{2cm + $\pi$ r + 2cm}}$
= ${\text{4cm + }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{(1}}{\text{.4cm)}}$
= ${\text{4cm + 4}}{\text{.4cm}}$
= ${\text{8}}{\text{.4cm}}$ .
Thus, the ant will have to take a longer round for the food piece (b) because its perimeter is ${\text{10}}{\text{.2cm}}$ which is the greatest among all.
Exercise 11.2
Q1. The shape of the top surface of a table is a trapezium. Find its area if its parallel sides are ${\text{1m}}$and ${\text{1}}{\text{.2m}}$and perpendicular distance between them is${\text{0}}{\text{.8m}}$.
Ans: Area of Trapezium = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ ( Sum of parallel sides) x (Distances between parallel sides) }}$
= $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{[(1m + 1}}{\text{.2m) x 0}}{\text{.8m]}}$
= $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(1}}{\text{.76}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}$ = ${\text{0}}{\text{.88}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q2. The area of a trapezium is ${\text{34c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$and the length of one of the parallel sides is ${\text{10cm}}$and its height is ${\text{4cm}}$. Find the length of the other parallel side.
Ans: It is given that Area of Trapezium = ${\text{34c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
Length of one parallel side = ${\text{10cm}}$
Height = ${\text{4cm}}$
Now, let length of other parallel side = ‘ \[{\text{a}}\] ’ cm
Therefore, Area of Trapezium = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ ( Sum of parallel sides) x (Distances between parallel sides) }}$
${\text{34c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{[(10 + a) x 4]cm}}$
${\text{34c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = ${\text{(20 + 2a)cm}}$
$\dfrac{{{\text{14}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm}}$ = \[{\text{a}}\] cm
Thus, Length of the other parallel side ( \[{\text{a}}\] ) = ${\text{7cm}}$ .
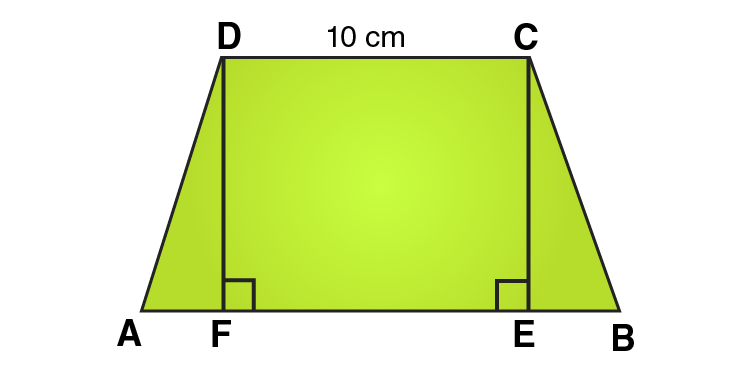
Q3. Length of the fence of a trapezium shaped field ABCD is ${\text{120m}}$. If BC = ${\text{48m}}$, CD =${\text{17m}}$ and AD =${\text{40m}}$, find the area of this field. Side AB is perpendicular to the parallel sides AD and BC.
Ans: Length of the fence of Trapezium ABCD = AB+BC+CD+DA
${\text{120m}}$ =${\text{(AB + 48 + 17 + 40)m}}$
${\text{120m}}$ = ${\text{AB + 105m}}$
Therefore, AB = ${\text{15m}}$
Area of the field ABCD = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(AD + BC) x AB}}$
=$\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(40 + 48) x 15}}$
=$\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(88) x 15}}$
= ${\text{660}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q4. The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24m and the perpendiculars dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 8m and 13m. Find the area of the field.
Ans: It is given that Length of diagonal = ${\text{24m}}$
Length of the perpendiculars ${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}$ from the opposite vertices to the diagonal are
${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}$ = ${\text{8m}}$ and ${{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}$ = ${\text{13m}}$
Area of Quadrilateral = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{d}}\left( {{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$
= $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(24m) x (13m + 8cm)}}$
= $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(24m)(21m)}}$
= ${\text{252}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Thus, Area of field = ${\text{252}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q5. The diagonals of a rhombus are ${\text{7}}{\text{.5cm}}$and ${\text{12cm}}$. Find its area.
Ans: Area of Rhombus = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ (Product of its diagonals) }}$
= $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 7}}{\text{.5cm x 12cm}}$
= ${\text{45c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q6. Find the area of a rhombus whose side is ${\text{6cm}}$and whose altitude is ${\text{4cm}}$. If one of its diagonals is ${\text{8cm}}$long, find the length of the other diagonal.
Ans: Let the length of other diagonal of Rhombus be ‘ \[{\text{X}}\] ’
A Rhombus is a special case of Parallelogram
The area of Parallelogram is given by its base and height
Thus, Area of Rhombus = Base x Height
= ${\text{6cm x 4cm}}$ = ${\text{24c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
So,
Area of Rhombus = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ (Product of its diagonals) }}$
${\text{24c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(8cm x X)}}$
${\text{X = }}\;{\text{6cm}}$
Therefore, Length of other diagonal of Rhombus = ${\text{6cm}}$
Q7. The floor of a building consists of $3000$tiles which are rhombus shaped and each of its diagonals are ${\text{45cm}}$and ${\text{30cm}}$in length. Find the total cost of polishing the floor, if the cost per ${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$is Rs$4$.
Ans: Given that each diagonals of Rhombus are ${\text{45cm}}$ and ${\text{30cm}}$
= $\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 45 x 30}}} \right){\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{675c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
So, Area of $3000$ tiles = $(675 x 3000){\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} = 2025000\;{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} = 202.5\;{{\text{m}}^2}$
Now, it is given that cost of polishing is ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{4}}\;{\text{per}}\;{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
So, Cost of Polishing ${\text{202}}{\text{.5}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ area = ${\text{Rs(4 x 202}}{\text{.5) = Rs 810}}$
Hence, Cost of polishing the floor is ${\text{Rs}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{810}}$
Q8. Mohan wants to buy a trapezium shaped field. Its side along the river is parallel to and twice the side along the road. It the area of this field is ${\text{10500}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$and the perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides is ${\text{100m}}$, find the length of the side along the river.
Ans: Let the length of the side along the road = ‘ \[{\text{l}}\] ’
And Let the length of the side along the river = ‘ ${\text{2l}}$ ’
It is given that distance between two parallel sides = ${\text{100m}}$
and Area of Trapezium = ${\text{10500}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Area of Trapezium = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ (Sum of parallel sides) (Distance between the parallel sides) }}$
${\text{10500}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(l + 2l) x (100m)}}$
${\text{3l = }}\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{2 x 10500}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}} \right){\text{m = 210m}}$
${\text{l = }}\;\dfrac{{{\text{210}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{m}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{70m}}$
Therefore, Length of the side along the river ‘ ${\text{2l}}$ ’ = ${\text{140m}}$
Q9. Top surface of a raised platform is in the shape of a regular octagon as shown in the figure. Find the area of the octagonal surface.
It is given in the figure that side of octagon = ${\text{5cm}}$
Area of Trapezium ABCH = Area of Trapezium DEFG
Area of Trapezium = $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ (Sum of parallel sides) (Distance between the parallel sides) }}$
= $\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(4)(11 + 5)}}} \right]{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= $\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 4 x 16}}} \right){{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 32}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
In rectangle HCDG, Length( \[{\text{l}}\] ) = ${\text{11m}}$ and Breadth( \[{\text{b}}\] ) = ${\text{5m}}$
So, Area of rectangle = ${\text{(11 x 5)}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = ${\text{55}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Therefore, Area of octagon = Area of Trapezium ABCH + Area of Trapezium DEFG +
Area of Rectangle
= ${\text{(32 + 32 + 55)}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{119}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q10. There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in the figure. For finding its area Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways. Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some other way of finding its area?
Ans: From Jyoti’s Way of finding area ,
Area of Pentagon = $2$ (Area of Trapezium ABCF)
= $2$ [ $\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ (Sum of parallel sides) (Distance between the parallel sides) }}$ ]
= $\left[ {{\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{(15 + 30)}}\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{15}}}}{{\text{2}}}} \right)} \right]{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{337}}{\text{.5}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
From Kavita’s Way of finding area ,
Area of Pentagon = Area of Triangle ABE + Area of Square BCDE
= [ $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (basexheight)] + (sidexside)
= $\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 15 x (30 - 15) + (15}}{{\text{)}}^{\text{2}}}} \right]{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= $\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 15 x 15 + 225}}} \right){{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{(112}}{\text{.5 + 225)}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{337}}{\text{.5}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q11. Diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions = ${\text{24cm}}$× ${\text{28cm}}$and inner dimensions ${\text{16cm}}$× ${\text{20cm}}$ Find the area of each section of the frame, if the width of each section is same.
Given that, the width of each section is the same.
IB = BJ = CK = CL = DM = DN = AO = AP
IL = IB + BC + CL
\[28\ =\ \text{IB}\ +\ 20\ +\ \text{CL}\]
$\begin{align} & 28-20\ \text{=}\ \text{IB+}\ \text{CL} \\ & 8\ \text{=}\ \text{IB+}\ \text{CL} \\ \end{align}$
IB = CL = \[{\text{4cm}}\]
Hence, IB = BJ = CK = CL = DM = DN = AO = AP = $\text{4}\,\text{cm}$
Area of section BEFC = Area of section DGHA = Area of Trapezium
$\left[ \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{(bas}{{\text{e}}_{1}}\text{ + bas}{{\text{e}}_{2}}\text{)(h)} \right]=\left[ \frac{1}{2}(20\text{ }+\text{ }28)(4) \right]\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}96\ \text{c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Therefore, Area of section ABEH = Area of section CDGF.
Hence area of each section of frame is $96\ \text{c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Exercise 11.3
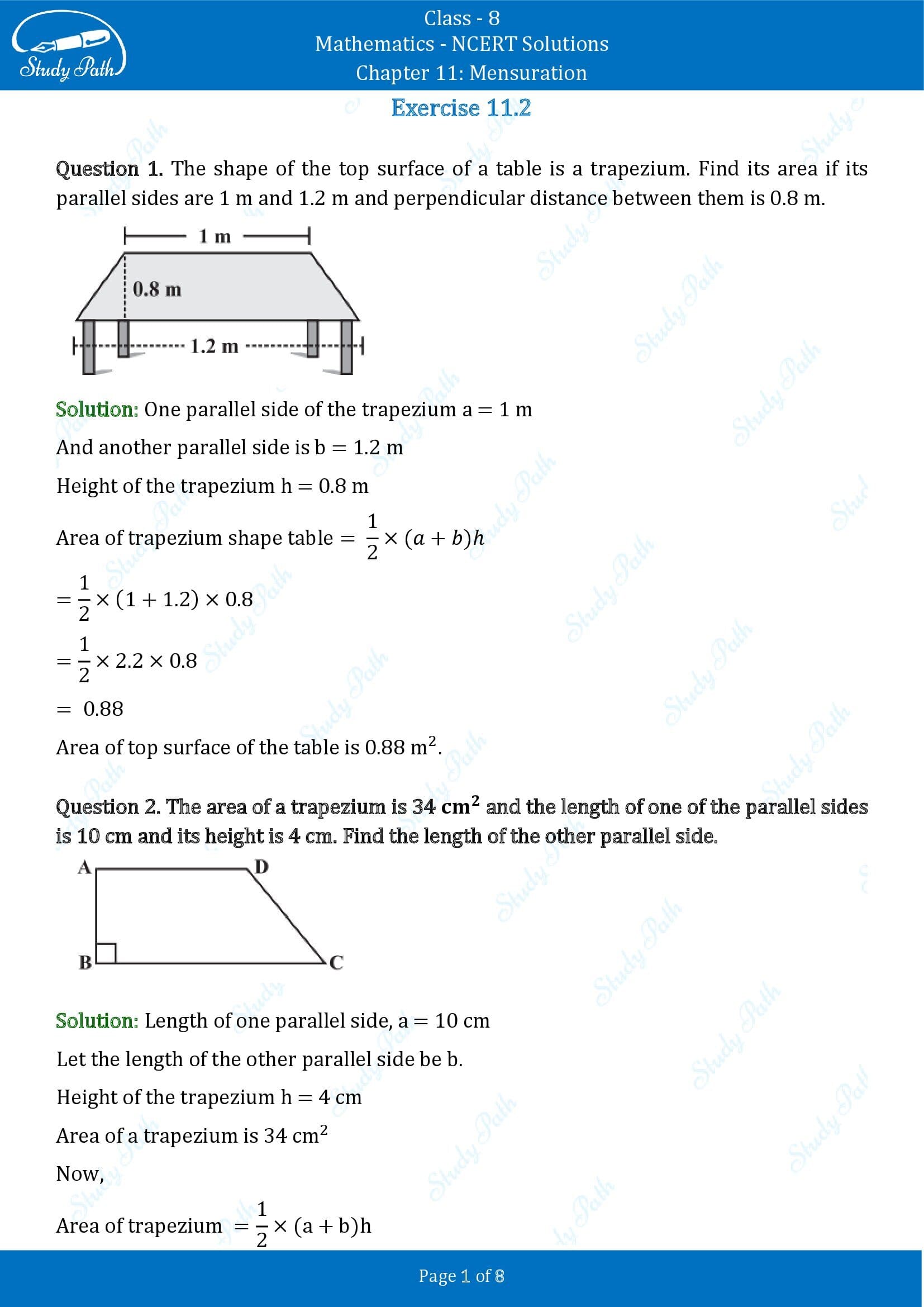
Q1. There are two cuboidal boxes as shown in the adjoining figure. Which box requires the lesser amount of material to make?
Ans: From the given figure; Length( \[{\text{l}}\] ), Breadth( \[{\text{b}}\] ) and Height( \[{\text{h}}\] ) of the Cuboid is
\[{\text{60cm}}\] , ${\text{40cm}}$ , ${\text{50cm}}$ respectively.
And, Side of Cube is ${\text{50cm}}$ .
Now, Total Surface area of Cuboid(a) = $2$ ( \[{\text{l}}\] \[{\text{h}}\] + \[{\text{b}}\] \[{\text{h}}\] + \[{\text{l}}\] \[{\text{b}}\] )
= \[{\text{[2\{ (60)(40) + (40)(50) + (50)(60)\} ]c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
= ${\text{[2(2400 + 2000 + 3000)]c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{(2 x 7400)c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{14800c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Total Surface area of Cube(b) = \[{\text{6}}{{\text{l}}^{\text{2}}}\]
= $6{(50\;{\text{cm}})^2} = 15000\;{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Therefore, Cuboidal box(a) requires a lesser amount of material for making.
Q2. A suitcase with measure ${\text{80cm x 48cm x 24cm}}$is to be covered with a tarpaulin cloth. How many metres of tarpaulin of width ${\text{96cm}}$is required to cover $100$ such suitcases?
Ans: Given that length( \[{\text{l}}\] ),breadth( \[{\text{b}}\] ),height( \[{\text{h}}\] ) of suitcase is \[{\text{(80,48,24)cm}}\] respectively.
Total surface area of suitcase = $2$ ( \[{\text{l}}\] \[{\text{h}}\] + \[{\text{b}}\] \[{\text{h}}\] + \[{\text{l}}\] \[{\text{b}}\] )
= ${\text{2[(80)(48) + (48)(24) + (24)(80)]}}$
= \[{\text{2[3840 + 1152 + 1920]}}\]
= ${\text{13824}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Total surface area of $100$ suitcases = ${\text{100 x 13824c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{1382400c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= required Tarpaulin
We have given that breadth of Tarpaulin is ${\text{96cm}}$ and we have to find Length
of tarpaulin.
Required Tarpaulin = (Length x Breadth) of Tarpaulin
${\text{1382400c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = Length x ${\text{96cm}}$
Length = $\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{1382400}}}}{{{\text{96}}}}} \right){\text{cm = 14400cm}}$
Therefore, Length = \[{\text{144m}}\;\;\;\;\;(\because \;{\text{1m = 100cm)}}\]
Thus, ${\text{144m}}$ of tarpaulin is required to cover $100$ suitcases.
Q3. Find the side of a cube whose surface area is ${\text{600c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
Ans: It is given that the surface area of the cube is ${\text{600c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ .
We have to find the side of the cube ( \[{\text{a}}\] ).
Surface area of cube = ${\text{6}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}$
${\text{600c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = ${\text{6}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}$
$\therefore \;{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 100c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
\[{\text{a}}\] = ${\text{10cm}}$
Thus, the side of the cube is ${\text{10cm}}$ .
Q4. Rukhsar painted the outside of the cabinet of measure${\text{1m x 2m x 1}}{\text{.5m}}$. How much surface area did she cover if she painted all except the bottom of the cabinet?
Ans: It is given that length ( \[{\text{l}}\] ), breadth( \[{\text{b}}\] ), height( \[{\text{h}}\] ) of the cabinet is
${\text{2m,1m,1}}{\text{.5m}}$ respectively.
Area of the surface = ${\text{2h(1 + b) + lb}}$
= ${\text{[2 x 1}}{\text{.5 x (2 + 1) + (2)(1)]}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{[3(3) + 2]}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{11}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Q5. Daniel is painting the walls and ceiling of a cuboidal hall with length, breadth and height of ${\text{15m,10m and 7m}}$respectively. From each can of paint ${\text{100}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ of area is painted. How many cans of paint will she need to paint the room?
Ans: Given that length ( \[{\text{l}}\] ), breadth( \[{\text{b}}\] ), height( \[{\text{h}}\] ) of Cuboid is
${\text{15m,10m and 7m}}$ respectively.
Area of the hall to be painted = Area of the wall + Area of ceiling
= $2$ \[{\text{h}}\] ( \[{\text{l}}\] + \[{\text{b}}\] ) + \[{\text{l}}\]\[{\text{b}}\]
= ${\text{[2 x 7(15 + 10) + (15 x 10)]}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{[(2 x 175) + 150]}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{500}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
It is given that ${\text{100}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ area is to be painted from each can.
Therefore, Number of cans required to paint an area of ${\text{500}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= $\dfrac{{500}}{{100}}{\kern 1pt} \; = \;5$
Hence, $5$ cans of paint are required to paint the room.
Q6. Describe how the two figures at the right are alike and how they are different. Which box has a larger lateral surface area?
Ans: The above given two figures alike for same height( \[{\text{h}}\] )= ${\text{7cm}}$
And the difference between in these two figures is that one is cylinder and the other
One is a cube.
Now, we have to find the lateral surface area for both of the given figures.
Given that Side of cube( \[{\text{l}}\] )= ${\text{7cm}}$
Height and Diameter of cylinder = ${\text{7cm}}$ each
Radius of cylinder = $\dfrac{{{\text{Diameter}}}}{{\text{2}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm = }}\;{\text{3}}{\text{.5cm}}$
First, Lateral surface area of Cube = ${\text{4}}{{\text{l}}^{\text{2}}}$ = ${\text{4(}}{{\text{7}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{4 x 49c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{196c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Second, Lateral surface area of cylinder = ${\text{2$\pi$ rh}}$
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 3}}{\text{.5cm x 7cm}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{154c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Therefore, the Cube has a larger lateral surface area.
Q7. A closed cylindrical tank of radius ${\text{7m}}$ and height ${\text{3m}}$ is made from a sheet of metal. How much sheet of metal is required?
Ans: Given that the radius and height of Cylinder is ${\text{7m}}$ and ${\text{3m}}$ respectively.
Therefore, Total surface area of Cylinder = ${\text{2$\pi$ }}$\[{\text{r}}\] ( \[{\text{r}}\] + \[{\text{h}}\] )
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 7m(7m + 3m)}}$
= ${\text{440}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Thus, ${\text{440}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ of metal sheet is required.
Q8. The lateral surface area of a hollow cylinder is ${\text{4224c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$. It is cut along its height and formed a rectangular sheet of width ${\text{33cm}}$. Find the perimeter of the rectangular?
Ans: It is given that Hollow cylinder is cut along its height and formed a
Rectangular sheet.
Area of cylinder = ${\text{4224c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
And, Breadth of rectangular sheet = ${\text{33cm}}$
So, Area of Cylinder = Area of Rectangular Sheet
${\text{4224c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = Length x Breadth
${\text{4224c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ = Length x ${\text{33cm}}$
Length = \[\dfrac{{{\text{4224}}}}{{{\text{33}}}}{\text{cm}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{128cm}}\]
Now, Perimeter of Rectangle = $2$ (length + breadth)
= ${\text{2(128 + 33)cm}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{2(161cm)}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{322cm}}$
Q9. A road roller takes ${\text{750}}$complete revolutions to move once over to level a road. Find the area of the road if the diameter of a road roller is ${\text{84cm}}$ and length is ${\text{1m}}$.
Ans: In one revolution, the roller will cover an area equal to its lateral surface area.
Here, Radius = $\dfrac{{{\text{diameter}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{84}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm = 42cm = }}\dfrac{{{\text{42}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{\text{m}}\;\;\;\;\;\;(\because {\text{1m = 100cm}})$
Height = ${\text{1m}}$
Thus, In One Revolution,
Area of the road covered = ${\text{2$\pi$ }}$ rh
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{{\text{42}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{\text{ x 1}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= $\dfrac{{{\text{264}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
In ${\text{750}}$ revolutions, area of road covered = ${\text{750 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{264}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= \[{\text{1980}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Q10. A company packages its milk powder in a cylindrical container whose base has a diameter of ${\text{14cm}}$and height ${\text{20cm}}$. Company places a label around the surface of the container (as shown in the figure). If the label is placed ${\text{2cm}}$from top and bottom, what is the area of the label?
Ans: It is given that Radius = $\dfrac{{{\text{diameter}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{14}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm = 7cm}}$
Height of label = ${\text{(20 - 2 - 2)cm}}\;\;\;\;\;\;(\because {\text{2cm}}\;{\text{deducted}}\;{\text{from}}\,{\text{top}}\;{\text{bottom}}\;{\text{each)}}$
= ${\text{16cm}}$
As shown in the figure, the label is in the shape of a cylinder.
So, Area of label(cylinder)= ${\text{2$\pi$ }}$ rh
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 7cm x 16cm}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{44 x 16c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= ${\text{704c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Exercise 11.4
Q1. Given a cylindrical tank, in which situation will you find surface area and in which situation volume.
(a) To find how much it can hold
(b) Number of cement bags required to plaster it
(c) To find the number of smaller tanks that can be filled with water from it.
Ans: (a) In this situation, we will find the volume.
(b) Number of cement bags required to plaster cylindrical bags so for that
situation, we will find the surface area.
(c) Number of smaller tanks that can be filled with so for that situation, we will
find the volume.
Q2. Diameter of cylinder A is ${\text{7cm}}$, and the height is ${\text{14cm}}$. Diameter of cylinder B is ${\text{14cm}}$ and height is ${\text{7cm}}$. Without doing any calculations can you suggest whose volume is greater? Verify it by finding the volume of both the cylinders. Check whether the cylinder with greater volume also has greater surface area?
Ans: The heights and diameters of these cylinders A and B are interchanged.
We know that,
Volume of cylinder = ${\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}$
If measures of radius(r) and height(h) are same, then the cylinder with greater
radius will have greater area.
Here, Radius of cylinder A = $\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm}}$
Radius of cylinder B = $\dfrac{{{\text{14}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm = 7cm}}$
As the radius of cylinder B is greater, therefore, the volume of cylinder B will
be greater.
Let us verify it by calculating the volume of both the cylinders.
Volume of Cylinder A = ${\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}$
= $\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x 14c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{11 x 49c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\;{\text{ = 539c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
Volume of Cylinder B = ${\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}$
= $\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 7 x 7 x 7c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{22 x 49c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\;{\text{ = 1078c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
Therefore, the volume of cylinder B is greater.
Now, Surface area of cylinder A = ${\text{2$\pi$ r(r + h)}}$
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ x (}}\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 14)c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= \[{\text{22 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{35}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\;{\text{385c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Surface area of cylinder B = ${\text{2$\pi$ r(r + h)}}$
= ${\text{2 x }}\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 7 x (7 + 7)c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
= \[{\text{44 x 14c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\;{\text{616c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Q3. Find the height of a cuboid whose base area is ${\text{180c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ and volume is ${\text{900c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$?
Ans. Here, we have given that Base Area of Cuboid = Length x Breadth
= ${\text{180c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$
Volume of Cuboid = Length x Breadth x Height
${\text{900c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ = ${\text{180c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ x Height
Height = $\dfrac{{{\text{900}}}}{{{\text{180}}}}{\text{cm = 5cm}}$
Q4. A cuboid is of dimensions ${\text{60cm x 54cm x 30cm}}$. How many small cubes with side${\text{6cm}}$can be placed in the given cuboid?
Ans. From given condition,
Volume of Cuboid = ${\text{60cm x 54cm x 30cm}}$
= ${\text{97200c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
Given that side of cube = ${\text{6cm}}$
So, Volume of cube = ${\text{(6 x 6 x 6)c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{216c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
Required number of cubes = \[\dfrac{{{\text{volume}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{cuboid}}}}{{{\text{volume}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{cube}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{97200}}}}{{{\text{216}}}}{\text{ = 450}}\]
Therefore, ${\text{450}}$ cubes can be placed in the given Cuboid.
Q5. Find the height of the cylinder whose volume is ${\text{1}}{\text{.54}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$and diameter of the base is ${\text{140cm}}$?
Ans. It is given that Radius of Cylinder = $\dfrac{{{\text{140}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{cm = 70cm}}$
Volume of Cylinder = ${\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}$
${\text{1}}{\text{.54}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ = $\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x }}\dfrac{{{\text{70}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{\text{m x }}\dfrac{{{\text{70}}}}{{{\text{100}}}}{\text{m x h}}$
Height = $\dfrac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.54 x 100}}}}{{{\text{22 x 7}}}}{\text{m = 1m}}$
Hence, the height of cylinder = ${\text{1m}}$
Q6. A milk tank is in the form of cylinder whose radius is ${\text{1}}{\text{.5m}}$and length is ${\text{7m}}$. Find the quantity of milk in litres that can be stored in the tank?
Ans. It is given that Radius and height of the cylinder is ${\text{1}}{\text{.5m}}$ and ${\text{7m}}$ respectively .
Therefore, Volume of Cylinder = ${\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}$
= $\dfrac{{{\text{22}}}}{{\text{7}}}{\text{ x 1}}{\text{.5m x 1}}{\text{.5m x 7m}}$
= ${\text{22 x 2}}{\text{.25}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
= ${\text{49}}{\text{.5}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$
As, ${\text{1}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ = 1000}}\;{\text{litre}}$
So, Required Quantity = ${\text{49}}{\text{.5 x 1000}}\;{\text{litre}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{49500}}\;{\text{litre}}$
Therefore, ${\text{49500}}\;{\text{litre}}$ can be stored in the tank.
Q7. If each edge of a cube is doubled,
(i) how many times will its surface area increase?
(ii) how many times will its volume increase?
Ans. (i) Let the edge of the cube be ‘ \[{\text{a}}\] ’.
Surface area of cube = ${\text{6}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}$
If each edge of the cube is doubled, then it becomes ${\text{2a}}$
Therefore, New surface area = ${\text{6(2a}}{{\text{)}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 24}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 4(6}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}$
Clearly, the surface area will be increased by ${\text{4}}$ times.
(ii) Let Volume of the cube = ${{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}$
When each edge of the cube is doubled, it becomes ${\text{2a}}$ .
New volume = \[{{\text{(2a)}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ = 8}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ = 8 x }}{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\]
Clearly, the volume of the cube will be increased by ${\text{8}}$ times.
Q8. Water is pouring into a cubiodal reservoir at the rate of $60$litres per minute. If the volume of reservoir is ${\text{108}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$, find the number of hours it will take to fill the reservoir.
Ans. Volume of cuboidal reservoir = ${\text{108}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ = $(108 x 1000)$ \[{\text{L}}\] = $108000$ \[{\text{L}}\]
It is given that water is being poured at the rate of $60$ L per minute.
That is, $(60 x 60)$ \[{\text{L}}\] = $3600$ \[{\text{L}}\] per hour
Required number of hours = $30$ hours
Thus, it will take $30$ hours to fill the reservoir.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration - PDF Download
It is not compulsory to be connected to the internet to access our solutions as Vedantu has made NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Mensuration available in the PDF format on its official website. Now download the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 PDF on your devices or get a printout and access it from anywhere, anytime. This mode of revision is quick and easy and can be done at your pace during a crucial exam period.
All Topics of NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - Mensuration
The topics covered under chapter 11 Mensuration are given below.
Table of Important Formulas
Below given are the list of important formulas that you must remember to solve the exercise of chapter 11 NCERT Maths Class 8 th .
You should also remember some of the basic conversion parameters. For your ease, the most important parameters are given below.
1 m 3 = 1000000 cm 3 = 1000 L
1 cm 3 = 1 mL
1 L = 1000 cm 3
List of Exercises in class 8 Maths Chapter 11:
Chapter 11 – mensuration.
Introduction
Mensuration is the process applied to different 2-D and 3-D solids of various shapes and figures to measure their lengths, volumes, area, heights, perimeters and several other dimensions. In this section of Ch 11 Maths Class 8, you will recall the areas of plane figures like triangles, circles, rectangles, etc., that you learned in the previous chapter. In NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Ch 11, you would learn how to calculate perimeter and areas of other closed figures like Quadrilaterals.
Let us Recall
In this section of Mensuration Class 8 NCERT, students would recall the formula for calculating the perimeter and area of a park, flower bed, and amount of cement required to cover a given area. All the problems are based on areas of the following shape:
Rectangle - The area of a rectangle is x*y where x is the length and y is the breadth of the rectangle.
Square - The area of a square is x 2 where x is the length of one side of a square.
Triangle - The area of a triangle is ½ *b*h where b is the length of the base and h is the height of the triable
Circle - The area of a circle is πr 2 where r is the radius of the circle.
Area of a Trapezium
A trapezium is a quadrilateral where two of the sides are parallel to each other. In this portion of Mensuration Class 8 NCERT Solutions, students will learn how to derive the area of a trapezium which is given by:
Area of a trapezium = h * (x + y)/2, where h is the height of the trapezium, x and y are the lengths of its two sides.
Area of a general Quadrilateral
A simple definition of a general quadrilateral is a closed 2-D shape having 4 straight sides. If we break the word Quadrilateral, Quad means 4, and lateral means sides. The area of a quadrilateral in Class 8th Maths Chapter 11 is calculated by splitting it into two triangles and then calculating and adding the areas of the two triangles.
(Image to be added soon)
So if PQRS is a quadrilateral, then its area = (area of triangle PQR) + (area of triangle PRS) = ½ * d * (h 1 + h 2 ), where d is the length of the diagonal from P to R and h 1 and h 2 are heights of perpendiculars dropped from Q and Pr and S or PR respectively.
11.8 Volume of Cube, Cuboid, and Cylinder
The amount of space that a 3-D object occupies gives the volume of that object. To take examples from real life, the volume of a cupboard in a room is less than the volume of the room where it is placed.
11.8.1 - Volume of a Cuboid - A 3-D structure with 6 rectangular faces is a cuboid. Its volume is given by “l * h* b”, here l = length, b = breadth, and h= height.
11.8.2 - Volume of a Cube - A cube is a special type of cuboid where its length, breadth, and height are the same. Hence the volume of a cube = length 3 .
11.8.3 - Volume of a Cylinder - A cylinder has two circular bases that are parallel to each other and separated by a distance. To measure the volume of a cylinder we use the formula πr 2 * h. Here r is the radius of the circular base and h is the distance between the bases.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11
You will find the NCERT Solutions of Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 by Vedantu extremely beneficial for your exams. The key features are:
Comprehensive explanations for each exercise and questions, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject.
Clear and structured presentation for easy comprehension.
Accurate answers aligned with the curriculum, boosting students' confidence in their knowledge.
Visual aids like diagrams and illustrations to simplify complex concepts.
Additional tips and insights to enhance students' performance.
Chapter summaries for quick revision.
Online accessibility and downloadable resources for flexible study and revision.
NCERT Solutions play a crucial role in Class 8 exam prep. Start by thoroughly reading the textbook chapter. After that, solve the NCERT questions for Class 8 Chapter 11. You can find detailed solutions on Vedantu, aligning with CBSE guidelines. Download the free NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 11 to guide your exam preparation with expert-reviewed answers.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - Mensuration
1. What are some of the applications of mensuration in our everyday lives?
In real life, mensuration is applied in many fields like:
Measuring floor and site areas required for purchasing or selling land.
Measuring agricultural fields.
Measuring surface areas of a house required for estimating painting cost.
To know the volume of the level of water in rivers and tanks.
To find out the amount of carpet required for covering a specific room.
The volume of soil that is needed to fill a ditch.
2. What are solid shapes and what is the method of measuring the surface area of a solid shape?
Any 3-D shapes occupying some space are called solid shapes like cube, sphere, cylinder, etc. To measure the surface area of a solid shape, we need to draw the net of that solid shape. From the net, we can see all the faces of the solid clearly. Then, we calculate the areas of each of the faces and add them up to get the total surface area of the solid shape. Surface area is measured in a square unit.
3. What are the concepts covered under Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths?
The ideas or topics that are included in Chapter 11 “Mensuration” of Class 8 Maths are given below:
Let Us Recall
Area of Trapezium
Area of a General Quadrilateral
Area of Special Quadrilaterals
Area of a Polygon
Solid Shapes
Surface Area of Cylinder, Cube and Cuboid
Cuboid Cube Cylinders
Volume of Cuboid, Cube and Cylinder
Cuboid Cube Cylinder
Volume and Capacity
What Have We Discussed?
4. The base area of the cuboid is 25cm sq. Its volume is 275 cubic cm. What will be the height of the cuboid?
In the question, we are given the base area of the cuboid which is equal to 25cm sq.
The volume of the cuboid is 275 cubic cm.
We know that according to the formula,
The volume of a cuboid = Height × Base Area
Therefore, the height of the cuboid will be = Volume of cuboid/ Base Area
Height = 275/25 = 11cm
Thus, 11cm is the height of the cuboid.
5. The distance between two parallel sides is 15m and the length of one parallel side is 20m. 480m sq. Is the area of the trapezium-shaped field. What is the length of the other parallel side?
Let one parallel side be a = 20m and the other parallel side is ‘b’.
The height of the field is 15m.
Given, the area of the trapezium is 480m sq.
The formula of trapezium is,
Area of trapezium = ½ (a + b) * h
480 = ½ (20 + b) * 15
20 + b = 480 × 2/ 15
64 = 20 + b
Thus, the length of the other parallel side is 44m.
6. What are the perks of NCERT Solutions of Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths?
The perks of the NCERT Solutions of Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths are given below:
The NCERT Solutions of Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths offers comprehensive learning.
It enables students to develop their reasoning and logical skills.
These solutions assist students in understanding the difficult concepts.
By practising these, students will have a strong grip over the chapter.
You will get a hint of how to answer the questions in the proper format.
It helps in scoring good marks in Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths.
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths are available free of cost on the Vedantu website and on the Vedantu app.
7. How can I make the best study plan for Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths?
Keep the following points in mind while making an effective study plan for Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths:
Have a timetable or schedule to manage your time.
Centralize the NCERT book to read Chapter 11 of Class 8 Maths.
Practice the NCERT Solutions to comprehend the Chapter.
Give yourself a break.
Do meditation and exercise to keep your body and mind fit.
Attend all your school lectures.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 8.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration are provided below. Our solutions covered each questions of the chapter and explains every concept with a clarified explanation. To score good marks in Class 8 Mathematics examination, it is advised to solve questions provided at the end of each chapter in the NCERT book.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration are prepared based on Class 8 NCERT syllabus, taking the types of questions asked in the NCERT textbook into consideration. Further, all the CBSE Class 8 Solutions Maths Chapter 11 are in accordance with the latest CBSE guidelines and marking schemes.
Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Exercise 11.1 Solutions

Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Exercise 11.2 Solutions
Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Exercise 11.3 Solutions

Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Exercise 11.4 Solutions

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Books and Solutions for all classes
Assignments Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration PDF Download
Students can refer to Assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration available for download in Pdf. We have given below links to subject-wise free printable Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 which you can download easily. All assignments have a collection of questions and answers designed for all topics given in your latest NCERT Books for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration for the current academic session. All Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Grade 8 have been designed by expert faculty members and have been designed based on the type of questions asked in standard 8 class tests and exams. All Free printable Assignments for NCERT CBSE Class 8, practice worksheets, and question banks have been designed to help you understand all concepts properly. Practicing questions given in CBSE NCERT printable assignments for Class 8 with solutions and answers will help you to further improve your understanding. Our faculty have used the latest syllabus for Class 8. You can click on the links below to download all Pdf assignments for class 8 for free. You can get the best collection of Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration assignments and questions workbooks below.
Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments Pdf Download
CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Class 8 have been provided below covering all chapters given in your CBSE NCERT books. We have provided below a good collection of assignments in Pdf for Mathematics Mensuration standard 8th covering Class 8 questions and answers for Mathematics Mensuration. These practice test papers and workbooks with question banks for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Pdf Download and free CBSE Assignments for Class 8 are really beneficial for you and will support in preparing for class tests and exams. Standard 8th students can download in Pdf by clicking on the links below.
Subjectwise Assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration
Benefits of Solving Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments
- The best collection of Grade 8 assignments for Mathematics Mensuration have been provided below which will help you in getting better marks in class tests and exams.
- The solved question for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration will help you to gain more confidence to attempt all types of problems in exams
- Latest NCERT Books for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration have been referred to for designing these assignments
- We have provided step by step solutions for all questions in the Class 8 assignments so that you can understand the solutions in detail.
- We have provided single click download links to all chapterwise worksheets and assignments in Pdf.
- Class 8 practice question banks will support to enhance subject knowledge and therefore help to get better marks in exam
FAQs by Mathematics Mensuration Students in Class 8
At https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com is the best website that has the biggest collection of free printable assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration.
We provide here Standard 8 subject-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free. Our teachers have provided these Grade 8 Mathematics Mensuration test sheets for Mathematics Mensuration given in your books.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Mensuration in Grade 8, all chapters and topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here subject-wise Grade 8 Mathematics Mensuration question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material. You can download it all without any charge by clicking on the links provided above.
We have provided the best quality question bank for Class 8 for Mathematics Mensuration available for Pdf Download. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts:

Related Posts

Assignments Class 8 Hindi PDF Download

Assignments Class 8 Social Science Geography PDF Download

Assignments Class 8 Mathematics Rational Numbers PDF Download
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Chapter 20 Area Of Trapezium And Polygon
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Mensuration - I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
In this chapter, students shall study methods of finding the area of a trapezium and also problems on finding areas of some polygons by using the formulae for the area of a triangle and that of a trapezium. Our subject experts have solved the problems using shortcut methods to help students in solving the problems effortlessly. RD Sharma Class 8 is the best study material, provided in accordance with the latest CBSE syllabus. One can use this to prepare well for the final exam. Students can refer to and download the PDF easily from the links provided below.
Chapter 20 – Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon) contains three exercises, and the RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions present in this page provide solutions to the questions given in each exercise. Now, let us have a look at the concepts discussed in this chapter.
- Area of a trapezium
- Area of a polygon
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Powers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Cubes and Cube Roots
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Playing with Numbers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions and Identities
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Factorization
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 8 Division of Algebraic Expressions
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variations
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Time and Work
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Percentage
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Profit, Loss, Discount and Value Added Tax (VAT)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Compound Interest
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Understanding Shapes – I (Polygons)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 16 Understanding Shapes – II (Quadrilaterals)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 17 Understanding Shapes – II (Special Types of Quadrilaterals)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 18 Practical Geometry (Constructions)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 19 Visualising Shapes
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 21 Mensuration – II (Volumes and Surface Areas of a Cuboid and a Cube)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 22 Mensuration – III (Surface Area and Volume of a Right Circular Cylinder)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 23 Data Handling – I (Classification and Tabulation of Data)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 24 Data Handling – II (Graphical Representation of Data as Histograms)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 25 Data Handling – III (Pictorial Representation of Data as Pie Charts)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 26 Data Handling – IV (Probability)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 27 Introduction to Graphs
- Exercise 20.1 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
- Exercise 20.2 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
- Exercise 20.3 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
EXERCISE 20.1 PAGE NO: 20.13
1. A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is 24 cm, and the corresponding height is 10 cm. How many such tiles are required to cover a floor of area 1080 m 2 ?
Given that,
Base of parallelogram = 24cm
Height of parallelogram = 10cm
Area of floor = 1080m 2
We know that,
Area of parallelogram = Base × Height
Area of 1 tile = 24 × 10 = 240cm 2
We know that, 1m = 100cm
So for 1080m 2 = 1080 × 100 × 100 cm 2
To calculate the Number of tiles required = Area of floor/Area of 1 tile
i.e., Number of tiles required = (1080 × 100 × 100) / (24 × 10) = 45000
∴ Number of tiles required = 45000
2. A plot is in the form of a rectangle ABCD having semi-circle on BC, as shown in Fig. 20.23. If AB = 60 m and BC = 28 m, Find the area of the plot.
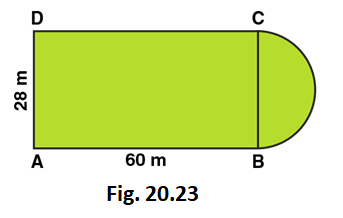
Area of the plot = Area of the rectangle + Area of semi-circle
Radius of semi-circle = BC/2 = 28/2 = 14m
Area of the Rectangular plot = Length × Breadth = 60 × 28 = 1680 m 2
Area of the Semi-circular portion = πr 2 /2
= 1/2 × 22/7 × 14 × 14
= 308 m 2
∴ The total area of the plot = 1680 + 308 = 1988 m 2
3. A playground has the shape of a rectangle, with two semi-circles on its smaller sides as diameters, added to its outside. If the sides of the rectangle are 36 m and 24.5 m, find the area of the playground. (Take π= 22/7.)
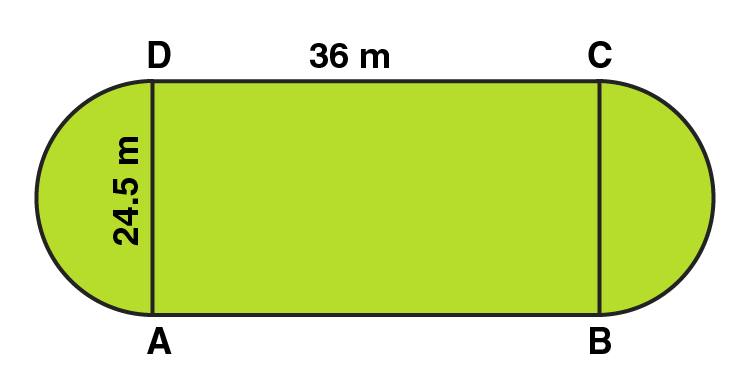
Area of the plot = Area of the Rectangle + 2 × area of one semi-circle
Radius of semi-circle = BC/2 = 24.5/2 = 12.25m
Area of the Rectangular plot = Length × Breadth = 36 × 24.5 = 882 m 2
Area of the Semi-circular portions = 2 × πr 2 /2
= 2 × 1/2 × 22/7 × 12.25 × 12.25 = 471.625 m 2
Area of the plot = 882 + 471.625 = 1353.625 m 2
4. A rectangular piece is 20 m long and 15 m wide. From its four corners, quadrants of radii 3.5 m have been cut. Find the area of the remaining part.
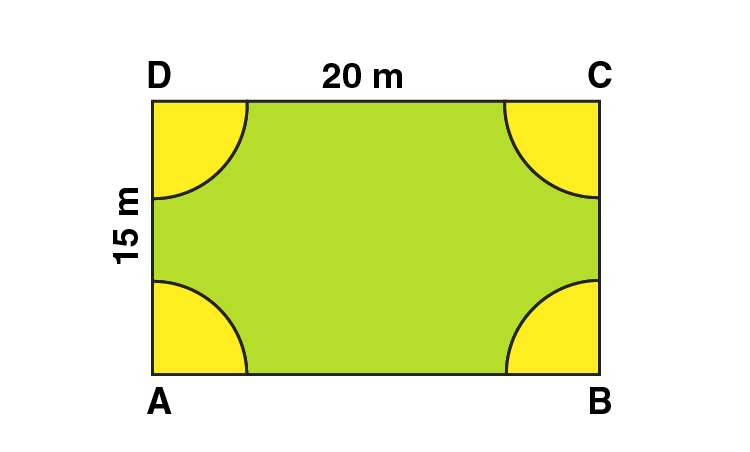
Area of the plot = Area of the rectangle – 4 × area of one quadrant
Radius of semi-circle = 3.5 m
Area of four quadrants = area of one circle
Area of the plot = Length × Breadth – πr 2
Area of the plot = 20 × 15 – (22/7 × 3.5 × 3.5)
Area of the plot = 300 – 38.5 = 261.5 m 2
5. The inside perimeter of a running track (shown in Fig. 20.24) is 400 m. The length of each of the straight portion is 90 m and the ends are semi-circles. If track is everywhere 14 m wide, find the area of the track. Also, find the length of the outer running track.
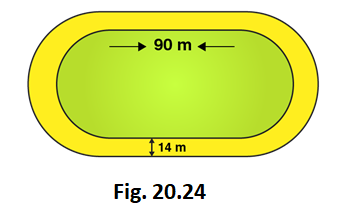
Perimeter of the inner track = 2 × Length of rectangle + perimeter of two semi-circular ends
Perimeter of the inner track = Length + Length + 2πr
400 = 90 + 90 + (2 × 22/7 × r)
(2 × 22/7 × r) = 400 – 180
(2 × 22/7 × r) = 220
44r = 220 × 7
r = 1540/44 = 35
So, the radius of inner circle = 35 m
Now, let’s calculate the radius of outer track
Radius of outer track = Radius of inner track + width of the track
Radius of outer track = 35 + 14 = 49m
Length of outer track = 2× Length of rectangle + perimeter of two outer semi-circular ends
Length of outer track = 2× 90 + 2πr
Length of outer track = 2× 90 + (2 × 22/7 × 49)
Length of outer track = 180 + 308 = 488
So, Length of outer track = 488m
Area of inner track = Area of inner rectangle + Area of two inner semi-circles
Area of inner track = Length × Breadth + πr 2
Area of inner track = 90 × 70 + (22/7 × 35 × 35)
Area of inner track = 6300 + 3850
So, Area of inner track = 10150 m 2
Area of outer track = Area of outer rectangle + Area of two outer semi-circles
Breadth of outer track = 35 + 35 +14 + 14 = 98 m
Area of outer track = length× breadth + πr 2
Area of outer track = 90 × 98 + (22/7 × 49 × 49)
Area of outer track = 8820 + 7546
So, Area of outer track = 16366 m 2
Now, let’s calculate area of path
Area of path = Area of outer track – Area of inner track
Area of path = 16366 – 10150 = 6216
So, Area of path = 6216 m 2
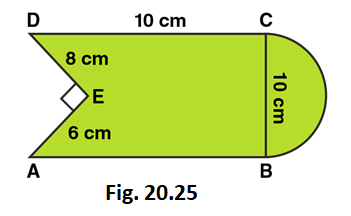
Area of the Figure = Area of square + Area of semi-circle – Area of right angled triangle
Area of the Figure = side × side + πr 2 /2 – (1/2 × base × height)
Area of the Figure = 10 × 10 + (1/2 × 22/7 × 5 × 5) – (1/2 × 8 × 6)
Area of the Figure = 100 + 39.28 – 24
Area of the Figure = 115.3
So, Area of the Figure = 115.3 cm 2
7. The diameter of a wheel of a bus is 90 cm which makes 315 revolutions per minute. Determine its speed in kilometres per hour. (Take π=22/7)
Given that, Diameter of a wheel = 90 cm
We know that, Perimeter of wheel = πd
Perimeter of wheel = 22/7 × 90 = 282.857
So, Perimeter of a wheel = 282.857 cm
Distance covered in 315 revolutions = 282.857× 315 = 89099.955 cm
One km = 100000 cm
Therefore, Distance covered = 89099.955/100000 = 0.89 km
Speed in km per hour = 0.89 × 60 = 53.4 km per hour
8. The area of a rhombus is 240 cm 2 and one of the diagonal is 16 cm. Find another diagonal.
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d 1 × d 2
240 = 1/2 × 16 × d 2
240 = 8 × d 2
d 2 = 240/8 = 30
So, the other diagonal is 30 cm
9. The diagonals of a rhombus are 7.5 cm and 12 cm. Find its area.
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 7.5 × 12
Area of rhombus = 6 × 7.5 = 45
So, Area of rhombus = 45 cm 2
10. The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24 m and the perpendiculars dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 8 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.
Area of quadrilateral = 1/2 × d 1 × (p 1 + p 2 )
Area of quadrilateral = 1/2 × 24 × (8 + 13)
Area of quadrilateral = 12 × 21 = 252
So, Area of quadrilateral is 252 cm 2
11. Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6 cm and whose altitude is 4 cm. If one of its diagonals is 8 cm long, find the length of the other diagonal.
Side of rhombus = 6 cm
Altitude of rhombus = 4 cm
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore area of parallelogram = base × altitude
i.e., Area of parallelogram = 6 × 4 = 24 cm 2
Area of parallelogram = Area of rhombus
24 = 1/2 × 8 × d 2
24 = 4 × d 2
d 2 = 24/4 = 6
So, length of other diagonal of rhombus is 6 cm
12. The floor of a building consists of 3000 tiles which are rhombus shaped and each of its diagonals are 45 cm and 30 cm in length. Find the total cost of polishing the floor, if the cost per m 2 is Rs. 4.
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 45 × 30
Area of rhombus = 1350/2 = 675
So, Area of rhombus = 675 cm 2
∴ Area of one tile = 675 cm 2
Now, Area of 3000 tiles = 675× 3000 = 2025000 cm 2
Area of tiles in m 2 = 2025000/10000 = 202.5 m 2
Total cost for polishing the floor = 202.5× 4 = Rs 810
13. A rectangular grassy plot is 112 m long and 78 m broad. It has gravel path 2.5 m wide all around it on the side. Find the area of the path and the cost of constructing it at Rs. 4.50 per square metre.
Outer area of rectangle = length × breadth
Outer area of rectangle = 112 × 78 = 8736 m 2
Width of path = 2.5 m
Length of inner rectangle = 112 – (2.5 + 2.5) = 107 m
Breadth of inner rectangle = 78 – (2.5 + 2.5) = 73 m
Inner area of rectangle = length × breadth
Inner area of rectangle = 107 × 73 = 7811 m 2
Now let’s calculate Area of path,
Area of path = Outer area of rectangle – Inner area of rectangle
Area of path = 8736 – 7811 = 925 m 2
Also given that,
Cost of construction for 1 m 2 = Rs 4.50
∴ Cost of construction for 925 m 2 = 925 × 4.50 = Rs 4162.5
14. Find the area of a rhombus, each side of which measures 20 cm and one of whose diagonals is 24 cm.

Length of side of rhombus = 20 cm
Length of one diagonal = 24 cm
In ΔAOB,
Using Pythagoras theorem:
AB 2 = OA 2 + OB 2
20 2 = 12 2 + OB 2
OB 2 = 20 2 – 12 2
OB 2 = 400 – 144
OB 2 = 256
So, length of the other diameter = 16 × 2 = 32 cm
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 24 × 32
Area of rhombus = 384 cm 2
15. The length of a side of a square field is 4 m. What will be the altitude of the rhombus, if the area of the rhombus is equal to the square field and one of its diagonal is 2 m?
Length of a side of a square = 4 m
Area of square = side 2
Area of square = 4 × 4 = 16 m 2
Area of square = Area of rhombus
So, Area of rhombus = 16 m 2
16 = 1/2 × 2 × d 2
16 = d 2
∴ the diagonal of rhombus = 16 m

AB 2 = 8 2 + 1 2
AB 2 = 65
AB = √65
Area of parallelogram = AB × DE
16 = √65 × DE
DE = 16/√65
i.e., Altitude of Rhombus = 16/√65 cm
16. Find the area of the field in the form of a rhombus, if the length of each side be 14 cm and the altitude be 16 cm.
Side of rhombus = 14 cm
Altitude of rhombus = 16 cm
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore
Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
Area of parallelogram = 14 × 16 = 224 cm 2
17. The cost of fencing a square field at 60 paise per metre is Rs. 1200. Find the cost of reaping the field at the rate of 50 paise per 100 sq. metres.
Perimeter of square field = Cost of fencing / rate of fencing
Perimeter of square field = 1200/0.6 = 2000
So, Perimeter of square field = 2000 m
Perimeter of square = 4 × side
Side of square = Perimeter / 4 = 2000/4 = 500
So, Side of square = 500 m
We know that, Area of square = side 2
Area of square = 500 × 500 = 250000 m 2
Cost of reaping = (250000 × 0.5) / 100 = 1250
∴ Cost of reaping the field is Rs 1250
18. In exchange of a square plot one of whose sides is 84 m, a man wants to buy a rectangular plot 144 m long and of the same area as of the square plot. Find the width of the rectangular plot.
Area of square = 84 × 84 = 7056
Since, Area of square = Area of rectangle
7056 = 144 × width
Width = 7056/144 = 49
∴ Width of rectangle = 49 m
19. The area of a rhombus is 84 m 2 . If its perimeter is 40 m, then find its altitude.
Area of rhombus = 84 m 2
Perimeter = 40 m
Perimeter of rhombus = 4 × side
∴ Side of rhombus = Perimeter / 4 = 40/4 = 10
So, Side of rhombus = 10 m
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
84 = 10 × altitude
Altitude = 84/10 = 8.4
So, Altitude of rhombus = 8.4 m
20. A garden is in the form of a rhombus whose side is 30 metres and the corresponding altitude is 16 m. Find the cost of levelling the garden at the rate of Rs. 2 per m 2 .
Side of rhombus = 30 m
Altitude of rhombus = 16 m
Area of parallelogram = 30 × 16 = 480 m 2
Cost of levelling the garden = area × rate
Cost of levelling the garden = 480 × 2 = 960
So, Cost of levelling the garden is Rs 960
21. A field in the form of a rhombus has each side of length 64 m and altitude 16 m. What is the side of a square field which has the same area as that of a rhombus?
Side of rhombus = 64 m
Area of parallelogram = 64 × 16 = 1024 m 2
Since Area of rhombus = Area of square
Therefore, Area of square = side 2
Or side 2 = Area of square
Side of a square = √square
Side of square = √1024 = 32
∴ Side of square = 32 m
22. The area of a rhombus is equal to the area of a triangle whose base and the corresponding altitude are 24.8 cm and 16.5 cm respectively. If one of the diagonals of the rhombus is 22 cm, find the length of the other diagonal.
Length of base of triangle = 24.8 cm
Length of altitude of triangle= 16.5 cm
∴ Area of triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of triangle = 1/2 × 24.8 × 16.5 = 204.6
So, Area of triangle = 204.6 cm
Since, Area of triangle = Area of rhombus
∴ Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d 1 × d 2
204.6 = 1/2 × 22 × d 2
204.6 = 11 × d 2
d 2 = 204.6/11 = 18.6
∴ The length of other diagonal is 18.6 cm
EXERCISE 20.2 PAGE NO: 20.22
1. Find the area, in square metres, of the trapezium whose bases and altitudes are as under: (i) bases = 12 dm and 20 dm, altitude = 10 dm (ii) bases = 28 cm and 3 dm, altitude = 25 cm (iii) bases = 8 m and 60 dm, altitude = 40 dm (iv) bases = 150 cm and 30 dm, altitude = 9 dm
(i) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 12 dm and 20 dm
Length of altitude = 10 dm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.2 m and 2 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 1 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.2 + 2.0) × 1
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 3.2 = 1.6
So, Area of trapezium = 1.6m 2
(ii) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 28 cm and 3 dm
Length of altitude = 25 cm
∴ Length of bases in m = 0.28 m and 0.3 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 0.25 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (0.28 + 0.3) × 0.25
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 0.58× 0.25 = 0.0725
So, Area of trapezium = 0.0725m 2
(iii) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 8 m and 60 dm
Length of altitude = 40 dm
∴ Length of bases in m = 8 m and 6 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 4 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (8 + 6) × 4
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 56 = 28
So, Area of trapezium = 28m 2
(iv) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 150 cm and 30 dm
Length of altitude = 9 dm
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.5 m and 3 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 0.9 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.5 + 3) × 0.9
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 4.5 × 0.9 = 2.025
So, Area of trapezium = 2.025m 2
2. Find the area of trapezium with base 15 cm and height 8 cm, if the side parallel to the given base is 9 cm long.
Length of bases of trapezium = 15 cm and 9 cm
Length of altitude = 8 cm
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (15 + 9) × 8
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 192 = 96
So, Area of trapezium = 96m 2
3. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides are of length 16 dm and 22 dm and whose height is 12 dm.
Length of bases of trapezium = 16 dm and 22 dm
Length of altitude = 12 dm
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.6 m and 2.2 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 1.2 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.6 + 2.2) × 1.2
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 3.8 × 1.2 = 2.28
So, Area of trapezium = 2.28m 2
4. Find the height of a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of whose bases (parallel sides) is 60 cm and whose area is 600 cm 2 .
Length of bases of trapezium = 60 cm
Area = 600 cm 2
600 = 1/2 (60) × altitude
600 = 30 × altitude
Which implies, altitude = 600/30 = 20
∴ Length of altitude is 20 cm
5. Find the altitude of a trapezium whose area is 65 cm 2 and whose base are 13 cm and 26 cm.
Length of bases of trapezium = 13 cm and 26 cm
Area = 65 cm 2
65 = 1/2 (13 + 26) × altitude
65 = 39/2 × altitude
Which implies, altitude = (65×2) /39 = 130/39 = 10/3
∴ Length of altitude = 10/3 cm
6. Find the sum of the lengths of the bases of a trapezium whose area is 4.2 m 2 and whose height is 280 cm.
Height of trapezium = 280 cm = 2.8m
Area = 4.2 m 2
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude To calculate the length of parallel sides we can rewrite the above equation as,
Sum of lengths of parallel sides = (2 × Area) / altitude
Sum of lengths of parallel sides = (2 × 4.2) / 2.8 = 8.4/2.8 = 3
∴ Sum of lengths of parallel sides = 3 m
7. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides of lengths 10 cm and 15 cm are at a distance of 6 cm from each other. Calculate this area as, (i) the sum of the areas of two triangles and one rectangle. (ii) the difference of the area of a rectangle and the sum of the areas of two triangles.
We know that, Area of a trapezium ABCD
= area (∆DFA) + area (rectangle DFEC) + area (∆CEB)
= (1/2 × AF × DF) + (FE × DF) + (1/2 × EB × CE)
= (1/2 × AF × h) + (FE × h) + (1/2 × EB × h)
= 1/2 × h × (AF + 2FE + EB)
= 1/2 × h × (AF + FE + EB + FE)
= 1/2 × h × (AB + FE)
= 1/2 × h × (AB + CD) [Opposite sides of rectangle are equal]
= 1/2 × 6 × (15 + 10)
= 1/2 × 6 × 25 = 75
∴ Area of trapezium = 75 cm 2
8. The area of a trapezium is 960 cm 2 . If the parallel sides are 34 cm and 46 cm, find the distance between them.
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
To calculate the distance between parallel sides we can rewrite the above equation as,
Distance between parallel sides = (2 × Area) / Sum of sides
= (2 × 960) / (34 + 46)
= (2 × 960) / 80 = 1920/80 = 24
∴ Distance between parallel sides = 24 cm
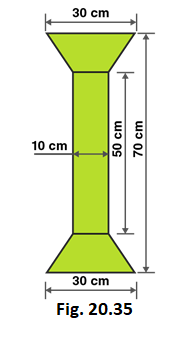
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of two trapeziums + Area of rectangle
Length of rectangle = 50 cm
Breadth of rectangle = 10 cm
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 30 cm and 10 cm
Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = (70–50)/2 = 20/2 = 10
So, Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = 10 cm
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 (30+10) × 10 + 50 × 10
Area of figure = 40 × 10 + 50 × 10
Area of figure = 400 + 500 = 900
∴ Area of figure = 900 cm 2
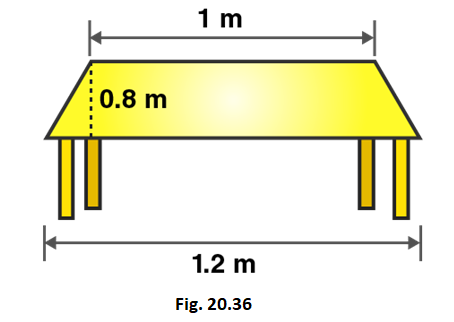
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 1.2m and 1m
Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = 0.8m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.2 + 1) × 0.8
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 2.2 × 0.8 = 0.88
So, Area of trapezium = 0.88m 2
11. The cross-section of a canal is a trapezium in shape. If the canal is 10 m wide at the top 6 m wide at the bottom and the area of cross-section is 72 m 2 determine its depth.
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 10m and 6m
Area = 72 m 2
Let the distance between parallel sides of trapezium = x meter
72 = 1/2 (10 + 6) × x
72 = 8 × x
x = 72/8 = 9
∴ The depth is 9m.
12. The area of a trapezium is 91 cm 2 and its height is 7 cm. If one of the parallel sides is longer than the other by 8 cm, find the two parallel sides.
Let the length of one parallel side of trapezium = x meter
Length of other parallel side of trapezium = (x+8) meter
Area of trapezium = 91 cm 2
Height = 7 cm
91 = 1/2 (x+x+8) × 7
91 = 1/2(2x+8) × 7
91 = (x+4) × 7
(x+4) = 91/7
x = 13 – 4
∴ Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 9 cm
And, Length of other parallel side of trapezium = x+8 = 9+8 = 17 cm
13. The area of a trapezium is 384 cm 2 . Its parallel sides are in the ratio 3:5 and the perpendicular distance between them is 12 cm. Find the length of each one of the parallel sides.
Let the length of one parallel side of trapezium = 3x meter
Length of other parallel side of trapezium = 5x meter
Area of trapezium = 384 cm 2
Distance between parallel sides = 12 cm
384 = 1/2 (3x + 5x) × 12
384 = 1/2 (8x) × 12
4x = 384/12
∴ Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 3x = 3× 8 = 24 cm
And, Length of other parallel side of trapezium = 5x = 5× 8 = 40 cm
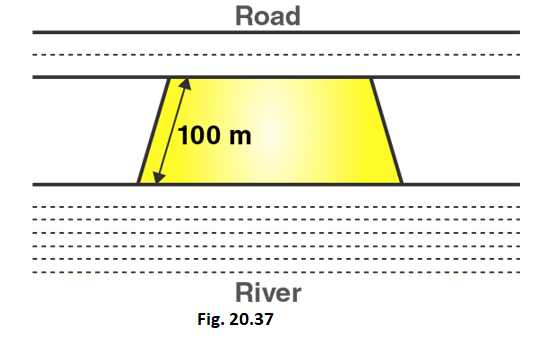
Let the length of side of trapezium shaped field along road = x meter
Length of other side of trapezium shaped field along road = 2x meter
Area of trapezium = 10500 cm 2
Distance between parallel sides = 100 m
10500 = 1/2 (x + 2x) × 100
10500 = 1/2 (3x) × 100
3x = 10500/50
x = 210/3 = 70
∴ Length of side of trapezium shaped field along road = 70 m
And, Length of other side of trapezium shaped field along road = 2x = 70× 2 = 140 m
15. The area of a trapezium is 1586 cm 2 and the distance between the parallel sides is 26 cm. If one of the parallel sides is 38 cm, find the other.
Let the length of other parallel side of trapezium = x cm
Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 38 cm
Area of trapezium = 1586 cm 2
Distance between parallel sides = 26 cm
1586 = 1/2 (x + 38) × 26
1586 = (x + 38) × 13
(x + 38) = 1586/13
x = 122 – 38
∴ Length of the other parallel side of trapezium = 84 cm
16. The parallel sides of a trapezium are 25 cm and 13 cm; its nonparallel sides are equal, each being 10 cm, find the area of the trapezium.
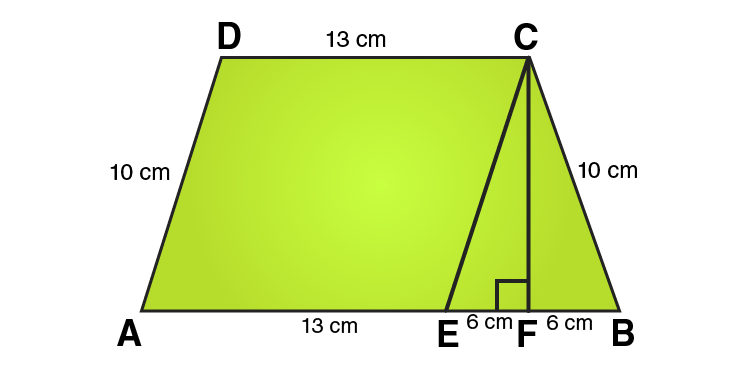
In ΔCEF,
CE = 10 cm and EF = 6cm
CE 2 = CF 2 + EF 2
CF 2 = CE 2 – EF 2
CF 2 = 10 2 – 6 2
CF 2 = 100-36
CF 2 = 64
Area of trapezium = Area of parallelogram AECD + Area of area of triangle CEF
Area of trapezium = base × height + 1/2 (base × height)
Area of trapezium = 13 × 8 + 1/2 (12 × 8)
Area of trapezium = 104 + 48 = 152
∴ Area of trapezium = 152 cm 2
17. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 cm, 13 cm and the other sides are 15 cm each.
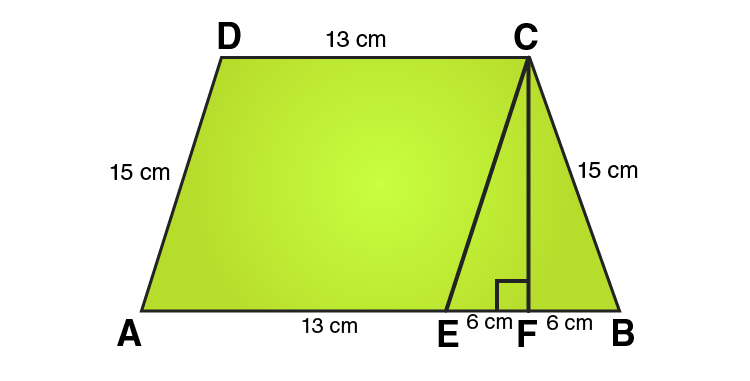
CF 2 = 15 2 – 6 2
CF 2 = 225-36
CF 2 = 189
CF = √189
= √ (9×21)
= 3√21 cm
Area of trapezium = height + 1/2 (sum of parallel sides)
Area of trapezium = 3√21 × 1/2 (25 + 13)
Area of trapezium = 3√21 × 19 = 57√21
∴ Area of trapezium = 57√21 cm 2
18. If the area of a trapezium is 28 cm 2 and one of its parallel sides is 6 cm, find the other parallel side if its altitude is 4 cm.
Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 6 cm
Area of trapezium = 28 cm 2
Length of altitude of trapezium = 4 cm
28 = 1/2 (6 + x) × 4
28 = (6 + x) × 2
(6 + x) = 28/2
(6 + x) = 14
x = 14 – 6
∴ Length of the other parallel side of trapezium = 8 cm
Area of parallelogram = 80 cm 2
Area of trapezium = 10 × 8 + 1/2 (12 × 8)
Area of trapezium = 80 + 48 = 128
∴ Area of trapezium = 128 cm 2
Area of given figure = Area of square ABCD + Area of rectangle DEFG + Area of rectangle GHIJ + Area of triangle FHI
i.e., Area of given figure = side × side + length × breadth + length × breadth + 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of given figure = 4×4 + 8×4 + 3×4 + 1/2×5×5
Area of given figure = 16 + 32 + 12 + 10 = 70
∴ Area of given figure = 70 cm 2
EXERCISE 20.3 PAGE NO: 20.28
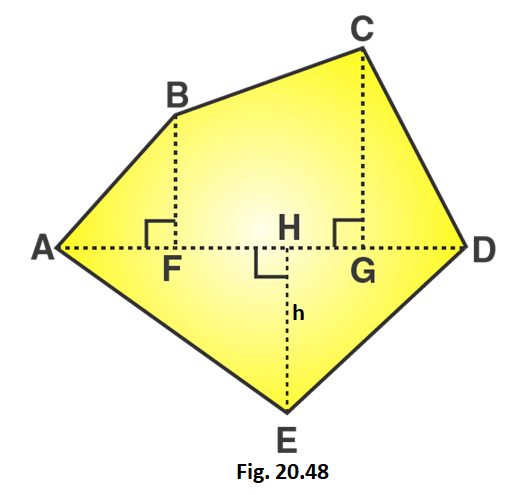
GH = AG – AH = 8 – 6 = 2 cm
HF = AH – AF = 6 – 5 = 1 cm
GD = AD – AG = 10 – 8 = 2 cm
Area of given figure = Area of triangle AFB + Area of trapezium BCGF + Area of triangle CGD + Area of triangle AHE + Area of triangle EGD
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × AF × BF + 1/2 (CG + BF) × FG + 1/2 × GD × CG + 1/2 × AH × EH + 1/2 × HD × EH
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × 5 × 5 + 1/2 (7 + 5) × 3 + 1/2 × 2 × 7 + 1/2 × 6 × 3 + 1/2 × 4 × 3
Area of given pentagon = 12.5 + 18 + 7 + 9 + 6 = 52.5
∴ Area of given pentagon = 52.5 cm 2
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of figure = 1/2 (18 + 7) × 8 + 18 × 18
Area of figure = 1/2 (25) × 8 + 18 × 18
∴ Area of figure is 424 cm 2
Figure (ii)
Area of given figure = 1/2 (15 + 6) × 8 + 15 × 20
Area of given figure = 84 + 300 = 384
∴ Area of figure is 384 cm 2
Figure (iii)
Using Pythagoras theorem in the right angled triangle,
5 2 = 4 2 + x 2
x 2 = 25 – 16
x 2 = 9
Area of given figure = 1/2 (14 + 6) × 3 + 4 × 6
Area of given figure = 30 + 24 = 54
∴ Area of figure is 54 cm 2
3. There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in Fig. 20.50. Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways. Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some another way of finding its area?
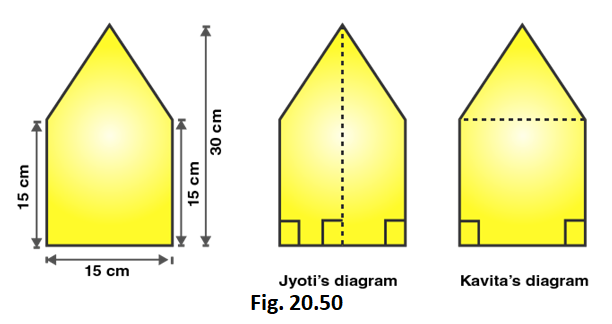
Area of Jyoti’s diagram = 2 × 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 × (15 + 30) × 7.5
Area of figure = 45 × 7.5 = 337.5
Therefore, Area of figure = 337.5 cm 2
We also know that,
Area of Pentagon = Area of triangle + area of rectangle
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × Base × Altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × 15 × 15 + 15 × 15
Area of Pentagon = 112.5 + 225 = 337.5
∴ Area of pentagon is 337.5 m 2
4. Find the area of the following polygon, if AL = 10 cm, AM = 20 cm, AN = 50 cm. AO = 60 cm and AD = 90 cm.
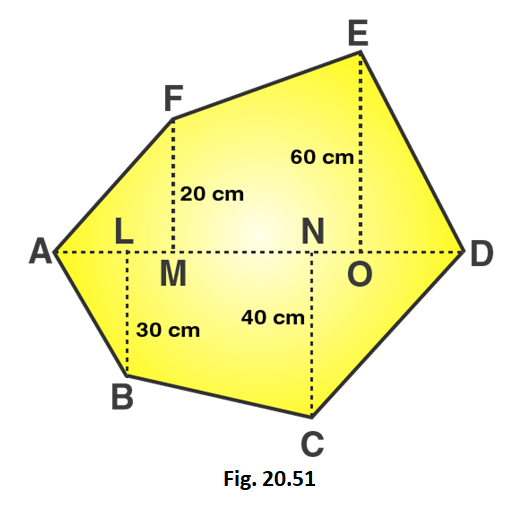
AL = 10 cm; AM = 20 cm; AN = 50 cm; AO = 60 cm; AD = 90 cm
LM = AM – AL = 20 – 10 = 10 cm
MN = AN – AM = 50 – 20 = 30 cm
OD = AD – AO = 90 – 60 = 30 cm
ON = AO – AN = 60 – 50 = 10 cm
DN = OD + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
OM = MN + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
LN = LM + MN = 10 + 30 = 40 cm
Area of figure = Area of triangle AMF + Area of trapezium FMNE + Area of triangle END + Area of triangle ALB + Area of trapezium LBCN + Area of triangle DNC
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × AM × FM + 1/2 (MF + OE) × OM + 1/2 × OD × OE + 1/2 × AL × BL + 1/2 × (BL + CN) × LN + 1/2 × DN × CN
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × 20 × 20 + 1/2 (20 + 60) × 40 + 1/2 × 30 × 60 + 1/2 × 10 × 30 + 1/2 × (30 + 40) × 40 + 1/2 × 40 × 40
Area of given hexagon = 200 + 1600 + 900 + 150 + 1400 + 800 = 5050
∴ Area of given hexagon is 5050 cm 2
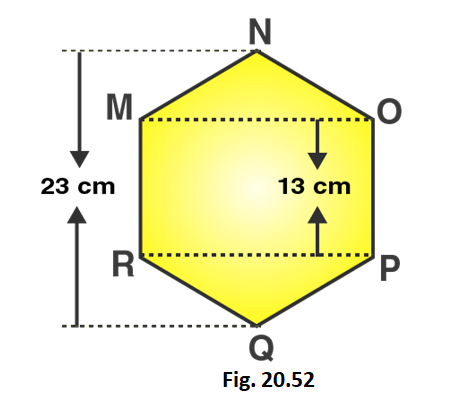
NA = BQ = 10/2 = 5 cm
MR = OP = 13 cm
In the right triangle BPQ
PQ 2 = BQ 2 + BP 2
Substituting the values
(13) 2 = (5) 2 + BP 2
169 = 25 + BP 2
BP 2 = 169 – 25 = 144
PR = MO = 2 × 12 = 24 cm
Area of rectangle RPOM = RP × PO = 24 × 13 = 321 cm 2
Area of triangle PRQ = 1/2 × PR × BQ
= 1/2 × 24 × 5
Area of triangle MON = 60 cm 2
Area of hexagon = 312 + 60 + 60 = 432 cm 2
∴ Area of given hexagon is 432 cm 2
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Make Studies fun with over 9000+ Animated Videos
- Make Homework stress free with Guaranteed Homework Help
- Ace your exams with our Accurate Sample Papers
Select Board & Class
Assignments
Class Test Divisibility of a Number - II Chapter: Playing with Numbers Take test
Class Test Divisibility of a Number - I Chapter: Playing with Numbers Take test
Class Test General Form and Properties of Numbers Chapter: Playing with Numbers Take test
Class Test Applications of Line Graphs Chapter: Introduction to Graphs Take test
Class Test Position of a Point on a Graph Chapter: Introduction to Graphs Take test
Class Test Line Graph Chapter: Introduction to Graphs Take test
Class Test Probability - II Chapter: Data Handling Take test
Class Test Probability - I Chapter: Data Handling Take test
Class Test Circle Graphs Chapter: Data Handling Take test
Class Test Histograms Chapter: Data Handling Take test
Class Test Frequency Distribution Chapter: Data Handling Take test
Class Test Division of Polynomials - II Chapter: Factorisation Take test
Class Test Division of Polynomials - I Chapter: Factorisation Take test
Class Test Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions - II Chapter: Factorisation Take test
Class Test Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions - I Chapter: Factorisation Take test
Class Test Visualising Solid Shapes - II Chapter: Visualising Solid Shapes Take test
Class Test Visualising Solid Shapes - I Chapter: Visualising Solid Shapes Take test
Class Test Direct and Inverse Proportions Chapter: Direct and Inverse Proportions Take test
Class Test Applications of Compound Interest Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Simple Interest and Compound Interest - II Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Simple Interest and Compound Interest - I Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Concept of Discount Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Concept of Profit Percent and Loss Percent Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Sales Tax and GST Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Percentage Chapter: Comparing Quantities Take test
Class Test Algebraic Expressions and Identities - II Chapter: Algebraic Expressions and Identities Take test
Class Test Algebraic Expressions and Identities - I Chapter: Algebraic Expressions and Identities Take test
Class Test Multiplication of Monomials and Polynomials Chapter: Algebraic Expressions and Identities Take test
Class Test Exponents and Powers - II Chapter: Exponents and Powers Take test
Class Test Exponents and Powers - I Chapter: Exponents and Powers Take test
Class Test Volume of Cubes, Cuboids and Right Circular Cylinders Chapter: Mensuration Take test
Class Test Surface Area of Cubes, Cuboids and Right Circular Cylinders Chapter: Mensuration Take test
Class Test Area of Rhombus and Polygons Chapter: Mensuration Take test
Class Test Area of Trapezium and General Quadrilateral Chapter: Mensuration Take test
Class Test Method of Finding Cube Roots Chapter: Cubes and Cube Roots Take test
Class Test Cubes of Numbers Chapter: Cubes and Cube Roots Take test
Class Test Square Root of Numbers - II Chapter: Squares and Square Roots Take test
Class Test Square Root of Numbers - I Chapter: Squares and Square Roots Take test
Class Test Squares of Numbers - II Chapter: Squares and Square Roots Take test
Class Test Squares of Numbers - I Chapter: Squares and Square Roots Take test
Class Test Perfect Squares Chapter: Squares and Square Roots Take test
Class Test Properties of Rhombus, Rectangle and Square Chapter: Understanding Quadrilaterals Take test
Class Test Properties of Parallelogram Chapter: Understanding Quadrilaterals Take test
Class Test Polygons and Their Properties - II Chapter: Understanding Quadrilaterals Take test
Class Test Polygons and Their Properties - I Chapter: Understanding Quadrilaterals Take test
Class Test Solution of Linear Equations in One Variable Chapter: Linear Equations in One Variable Take test
Class Test Linear Equation in One Variable Chapter: Linear Equations in One Variable Take test
Class Test Representation of Rational Numbers on the Number Line Chapter: Rational Numbers Take test
Class Test Properties of Rational Numbers: Identities and Inverses Chapter: Rational Numbers Take test
Class Test Properties of Rational Numbers: Closure, Commutative and Associative properties Chapter: Rational Numbers Take test
- Terms & Conditions
- Our Results
Copyright © 2024 Aakash EduTech Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
E.g: 9876543210, 01112345678
We will give you a call shortly, Thank You
Office hours: 9:00 am to 9:00 pm IST (7 days a week)
Search This Blog
Cbse mathematics.
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12. A complete resource centre of mathematics for students and teachers
Featured Posts
Maths assignment class viii | quadrilateral, lesson plan math class 8 | mensuration ch-14, e- lesson plan subject mathematics class- 8, ch-14.

E-LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS CLASS-VIII CHAPTER - 14 MENSURATION
BASIC GEOMETRY:
Students should have a good understanding of basic geometric shapes like rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles. PERIMETER AND AREA CONCEPTS:
Prior knowledge of the concepts of perimeter and area is essential. Students should understand that the perimeter is the total distance around a shape, while area represents the space enclosed by the shape. MEASUREMENT UNITS:
Familiarity with measurement units like centimeters, meters, and square units (e.g., square centimeters, square meters) is necessary. This will enable them to work with measurements in real-world scenarios. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS:
A strong grasp of basic arithmetic operations, including addition, multiplication, and division, is important since these operations will be used in calculating perimeters and areas.
Whiteboard and markers, Geometric shapes (e.g., cutouts or drawings), Worksheets with exercises.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this lesson, students should: Understand the concepts of perimeter and area of plane figureslike Quadrilateral, Trapezium, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus and square. Be able to calculate the perimeter and area of basic geometric shapes as mensioned above.
Be able to understand the surface area and volume of geometrical solid figures like: cube, cuboid, and cylinder.
Apply these concepts to solve practical problems in real-life situations.
Curved Surface area of cube = 4(side) 2
Total surface area of cube = (side) 2
Volume of Cube = (side) 3
Diagonal of Cube = √3(side) 2
Number of faces = 6
Number of vertices = 8
Number of Edges = 12
Each face of a cube is a square

Curved Surface Area of cuboid = 2(l + b) ✖ h Total Surface Area of cuboid = 2(lb + bh + hl) Volume of cuboid = Length ✖ Breadth ✖ Height
Number of faces = 6
Each face of a cube is a rectangle
Curved Surface Area of cylinder = 2πrh
Total Surface Area of cylinder = 2πr(r + h)
Volume of cylinder = πr 2 h
Number of faces = 3 (One curved surface and two plane surface)
Number of vertices = 0
Number of edges = 2
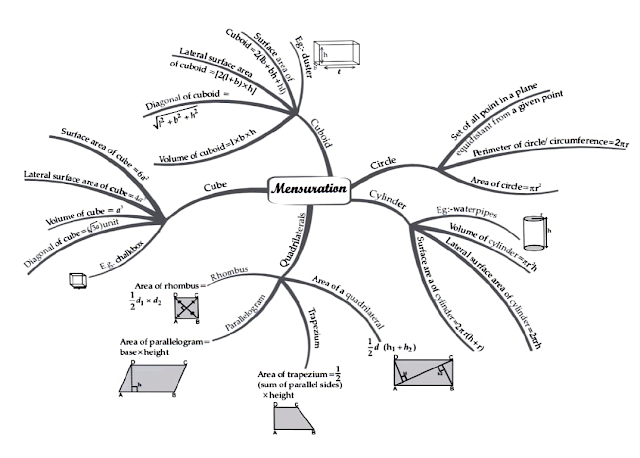
THANKS FOR YOUR VISIT
PLEASE COMMENT BELOW
Post a Comment
Breaking news, popular post on this blog, lesson plan maths class 10 | for mathematics teacher.

Lesson Plan Math Class 10 (Ch-1) | Real Numbers

Lesson Plan Maths Class XII | For Maths Teacher

- Assignment 10 15
- Assignment 11 12
- Assignment 12 14
- Assignment 8 8
- Assignment 9 5
- Lesson plan 10 15
- Lesson Plan 12 13
- Lesson Plan 8 10
- Maths 10 20
- Maths 11 21
- Maths 12 17
SUBSCRIBE FOR NEW POSTS
Get new posts by email:.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet Class PDF with Answers
These Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF can be helpful for both teachers and students. Teachers can track their student’s performance in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8. Students can easily identify their strong points and weak points by solving questions from the worksheet. Accordingly, students can work on both weak points and strong points.
All students studying in CBSE class 8th, need to practise a lot of questions for the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8. Students can easily practise questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet PDF. By practising a lot of questions, students can improve their confidence level. With the help of confidence level, students can easily cover all the concepts included in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheets with Solutions
Solutions is the written reply for all questions included in the worksheet. With the help of Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheets with solutions, students can solve all doubts regarding questions. Students can have deep learning in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8 by solving all their doubts. By solving doubts, students can also score well in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF
Worksheet is a sheet which includes many questions to solve for class 8th students. The Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF provides an opportunity for students to enhance their learning skills. Through these skills, students can easily score well in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8. Students can solve the portable document format (PDF) of the worksheet from their own comfort zone.
How to Download the Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF?
To solve questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF, students can easily go through the given steps. Those steps are-
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar.
- Drop down menu will appear, select KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheet.
- A new page will appear, select class 8th from the given list of classes.
- Select Mathematics from the given list of subjects. Now click the chapter’s name that is Mensuration Assignment 8.
Features of the Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF
Before starting to solve questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet PDF, students need to know everything about the worksheet. Those features are-
- Variety of questions are included: The Mensuration Assignment 8 Maths Worksheet for Class 8 includes varieties of questions. Those varieties of questions are- one mark questions, two mark questions, three mark questions, etc.
- Solutions are provided: Doubts regarding each question can be easily solved through the solutions given. Through solving questions, a student's comprehensive skill can be increased.
- All concepts are covered: By solving questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet, students can easily cover all the concepts included in the chapter.
- Created by Expert: These worksheets are personally created by the subject experts. These Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet pdf are created with proper research.
- Provides plenty of questions: The Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet provides plenty of questions to practise. Through good practice, students can get engaged in the learning process.
Benefits of the Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF
With the help of Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet PDF, students can easily track their performance. This is the most crucial benefit, other than this there are more benefits. Those benefits are-
- Builds a strong foundation: Regular solving questions from the worksheet can help students to build a strong foundation. Through the strong foundation, students can score well in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
- Improves speed and accuracy: While solving questions from the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8, students need to maintain the speed and accuracy. Speed and accuracy can be easily maintained and improved by solving questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF.
- Acts as a guide: Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheets with solutions acts as guide for both the teachers and students. Through the worksheet, teachers can guide their students according to the answers given by them. Students can also analyse themselves with the help of answers and can improve accordingly.
- Enhances the learning process: Regular solving of questions from the worksheet can help students enhance their learning process. According to the learning skills, students can easily understand all topics and concepts included in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
- Improvisation of grades: Regular solving of questions from the worksheet can help students to improve their marks and grades. With the help of good marks and good grades, students can select their desired field further.
Tips to Score Good Marks in Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet
Students are requested to follow some tips to score good marks in the Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet. Those tips are-
- Complete all the concepts: First and the most crucial step is to understand all the concepts included in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
- Practise questions: Next step is to practise questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet. Through this students can identify all types of questions: easy, moderate, difficult, etc.
- Note down the mistakes: After practising questions, students need to note down the wrong sums that have been done earlier.
- Rectify the mistakes: After noting down the mistakes, students need to rectify all the mistakes made.
- Maintain a positive attitude: Students are requested to maintain a positive attitude while solving worksheets. By maintaining a positive attitude, students can improve speed and accuracy while solving the worksheets.
- Remain focused: Students need to remain focused while solving questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 problems worksheet pdf. As it helps students to solve the questions as fast as possible.
When should a student start solving the Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF?
Students studying in class 8 should start solving worksheets after covering each and every concept included in the chapter. Regular solving questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF, can help students to have a better understanding of the chapter. Better understanding of the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8 can help students to score well in the class 8th board exam.
Regular solving questions from the Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF can help students to build a strong foundation for the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8. Strong foundation of the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8 can help students to understand further chapters.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Mensuration
Class 8 IMO Mensuration
Student assignments, create unlimited student assignments., online practice, online tests, printable worksheets and tests.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 8 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Mensuration chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf. Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration is a very important resource for CBSE students. It helps them get a fair idea of the chapter, specifically, the sort of questions that are possibly asked in the exam and the method of answering them.
Assignments for Class 8 Mathematics Mensuration have been developed for Standard 8 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 8 Mathematics Mensuration from our website as we have provided all topic wise ...
Mensuration Class 8 Chapter 11 notes, important questions and formulas are mentioned here. Class 8 Chapter 11 Mensuration materials are provided here as per CBSE syllabus (2022-2023) and latest exam pattern. Get through the formulas and practise the concept of mensuration with the help of given examples. Mensuration chapter has been further ...
Class 8; Unit 9: Mensuration. 300 possible mastery points. Mastered. Proficient. Familiar. Attempted. Not started. Quiz. Unit test. Mensuration 9.1; Mensuration 9.2; Mensuration 9.3; Mensuration: Unit test; Mensuration 9.1. Learn. Area of trapezoids (Opens a modal) Area of composite shapes (Opens a modal) Practice. Mensuration 9.1 Get 7 of 10 ...
Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Solutions. Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Mensuration all exercises in English Medium as well as Hindi Medium are given below to study online or download in PDF format. Download NCERT Solutions offline apps, which work without internet, once downloaded. All the solutions given in apps are updated for academic session 2023-24.
NCERT Solution Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration Solution is entirely based on the latest CBSE curriculum. It will be able to clarify all the doubts that you might have in the Mensuration chapter. The problems in the Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 are well explained with diagrams and step-by-step explanations to make it simple for you to follow ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Mensuration are provided below. Our solutions covered each questions of the chapter and explains every concept with a clarified explanation. To score good marks in Class 8 Mathematics examination, it is advised to solve questions provided at the end of each chapter in the NCERT book. ...
All Assignments for Mathematics Mensuration Grade 8 have been designed by expert faculty members and have been designed based on the type of questions asked in standard 8 class tests and exams. All Free printable Assignments for NCERT CBSE Class 8, practice worksheets, and question banks have been designed to help you understand all concepts ...
Access answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 20 Mensuration - I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon) EXERCISE 20.1 PAGE NO: 20.13. 1. A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is 24 cm, and the corresponding height is 10 cm.
Mensuration Assignment - 2 Worksheet PDF. Worksheet is a sheet which includes many questions to solve for class 8th students. The Mensuration Assignment - 2 worksheet PDF provides an opportunity for students to enhance their learning skills. Through these skills, students can easily score well in the chapter Mensuration Assignment - 2.
Class 8 - Mensuration problems, online practice, tests, worksheets, quizzes, and teacher assignments.
Filed Under: CBSE, Class 8 Maths Tagged With: CBSE assignments for Class Mensuration CBSE Assignments CBSE assignments Mensuration Mensuration pdf CBSE assignments, CBSE maths Worksheets, CBSE Worksheets for Class Mensuration CBSE printable Worksheets, CBSE worksheets Mensuration, Mensuration CBSE Class 8 Maths Assignment 1, Mensuration pdf ...
Class 8; Mensuration; Class 8. 1. Rational Numbers 2. Linear Equations in One Variable. 3. Understanding Shapes. 4. Practical Geometry. 5. Data Handling ... Student Assignments . Create unlimited student assignments. Create New Student Assignment. Online Practice . Start New Online Practice Session. Online Tests .
Assignments for the Mensuration, CBSE Class 8 MATHS, Math.
Lesson Plan for CBSE mathematics class 8 Mensuration, Step by step teaching strategy for mathematics teachers. Perfect lesson plan ... definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and ...
Mensuration Assignment 8 Worksheet PDF. Worksheet is a sheet which includes many questions to solve for class 8th students. The Mensuration Assignment 8 worksheet PDF provides an opportunity for students to enhance their learning skills. Through these skills, students can easily score well in the chapter Mensuration Assignment 8.
Mensuration problems, practice, tests, worksheets, questions, quizzes, teacher assignments | Class 8 | IMO