myCBSEguide
- Business Studies
- Class 11 Business Studies...

Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions are available on myCBSEguide App . You can also download them from our student dashboard .
For students appearing for grade 11 CBSE exams from the Commerce stream, Business Studies is a fundamental subject. Business Studies is considered to be quite interesting as well as an occupying subject as compared to all other core subjects of the CBSE class 11 commerce stream. To ace this CBSE exam, students are not only required to work hard but they ought to learn to do smart work too.
Among all the other core subjects of the Commerce stream i.e accountancy, economics and business studies, Business Studies is the one that is purely theoretical. It is termed to be comparatively easier and more scoring than the other mandatory subjects of the commerce stream. Many students who opt for the commerce stream after their 10-grade exams desire to learn in-depth about the business organizations and their work, for them the subject is of utmost importance. Business Studies is an essential component of the class 11 commerce stream curriculum.
In order to ace the subject the student needs to have conceptual clarity. CBSE has designed the syllabus for class 11 Business Studies so as to provide students with a basic understanding of the various principles prevalent in the Business organizations as well as their interaction with their corresponding environment.
Case Study Questions in class 11 (Business Studies)
Case-based questions have always been an integral part of the Business Studies question paper for many years in the past. The case studies have always been considered to be challenging for the students, for such questions demand the application of their knowledge of the fundamental business concepts and principles. Last year i.e- 2021 CBSE introduced a few changes in the Business Studies question paper pattern to enhance and develop analytical and reasoning skills among students.
It was decided that the questions would be based on real-life scenarios encountered by the students.CBSE not only changed the way case-based questions were formulated but also incremented their weightage in the Business Studies question paper. The sole purpose of increasing the weightage of case-based questions in the class 11 curriculum by CBSE was to drift from rote learning to competency and situation-based learning.
What is a case study question? (Business Studies)
In Business Studies, a case study is more like a real-world test of how the implementation works. It is majorly a report of an organization’s implementation of anything, such as a practice,a product, a system, or a service. The questions would be based on the NCERT textbook for class 11 Business Studies. Case-based questions will definitely carry a substantial weightage in the class 11 Business Studies question paper. questions.
A hypothetical text will be provided on the basis of which the student is expected to solve the given case-based question asked in the Business Studies class 11 exam. Initially, the newly introduced case-based questions appeared to be confusing for both the students and the teachers. Perhaps, they were reluctant to experiment with something new but now a lot more clarity is there that has made the question paper quite student-friendly.
Case study questions could be based on any chapter or concept present in the NCERT textbook. Thus, it is expected from the students to thoroughly revise and memorize the key business fundamentals.
Business Studies syllabus of class 11 CBSE
The entire Business Studies course is divided into 2 parts:
- Part A, Foundation of Business
- Part B, Finance and Trade
The class 11 Business Studies exam is for a total of 100 marks, 80 marks are for the theory and the remaining 20 for the project. Most of the questions are based on the exercises from the NCERT textbook. It is recommended to rigorously go through the contents of the book. A single textbook has been published by NCERT for Class 11 Business studies. There are a total of 10 chapters in this book divided into 2 parts.
CBSE Class – 11
Business Studies (Code No. 054)
Theory: 80 Marks Time: 3 Hours Project: 20 Marks
Case Study Passage (Business Studies class)
As part of these questions, the students would be provided with a hypothetical situation or text, based on which analytical questions will have to be answered by them. It is a must for the students to read the passage in depth before attempting the questions. In the coming examination cycle (2022-23), case-based questions have a weightage of around 30%. These questions can be based on each chapter in the NCERT book for Business Studies, grade 11.
Students must prepare well for the case-based questions before appearing for their Business Studies exam as these questions demand complete knowledge of the various concepts in their syllabus. CBSE plans to increase the weightage of such questions in the upcoming years.
Sample case-based Questions in Business Studies
Business Studies as a subject provides a way of perceiving and interacting with the business ecosystem. It is a core subject of the commerce stream that is purely theoretical and relevantly easier than the other compulsory subjects of the stream. Class 11 Business Studies syllabus is closely related to trade and commerce. The subject cannot be ignored as it is the foundation of many concepts and theories which are studied at an advanced level in class 12.
The case-based questions asked in the CBSE Business Studies question paper for class 11 are of two types:
As per the latest circular issued by CBSE on Assessment and Evaluation practices of the board for the session 2022-23, CBSE has clearly mentioned that competency-based questions including case studies will be different from subjective questions.
The questions can also be categorized on their difficulty level:
- Direct: such questions can be easily solved. Their answer is visible in the given passage itself.
- Indirect/ Analytical: such questions are confusing and tricky. These can be solved by the application of the theory or principle that is highlighted in the provided text.
How To Prepare For Case-based Questions? (Business Studies grade 11)
Students need to prepare well for the case-based questions before appearing for their class 11 Business Studies exam. Here are some tips which will help the student to solve the case-based questions at ease:
- Read the provided text carefully
- Try to comprehend the situation and focus on the question asked
- Analyze and carefully answer the question asked
- In general, the passage given would be lengthy in Business Studies case-based questions but their solutions are comparatively short and simple
- One can significantly save time if they follow a reversal pattern, that is going through the questions before reading the comprehensive case study passage.
- Answer in a concise manner
- One should concentrate on solidifying key fundamental principles/theories
- Go through the NCERT textbook in depth. The language used is crisp and simple.
- While providing solutions to the case-based question, pick the keyword/keyline based on which you are driving insights.
In order to excel in the Business Studies class 11 exam, one needs to ignore the shortcut techniques and get to read the NCERT textbook rigorously. Case studies can be easily solved if your key fundamentals are strong and clear. The best part of having these questions is that the asked question itself projects a hint of its answer. These simple points if kept in mind will definitely help the students to fetch good marks in case study questions, class 11 Business Studies.
Case study question examples in Business Studies
Here a re some given case study questions for CBSE class 11 Business Studies. If you wish to get more case study questions and other study material, download the myCBSEguide app now. You can also access it through our student dashboard.
Business Studies Case Study 1
Read the hypothetical text given and answer the following questions:
Manish, Rahul and Madhav live in the same locality. They used to meet and discuss their ideas. After discussing the recent fire breakout in their area, they decided to take fire insurance for their house or work area. Manish gets his house insured against fire for ₹1 lakh and during the policy period, his house gets damaged due to fire and the actual loss amounts to ₹2.5 lakh. The insurance company acquired the burning material and approved his claim. Rahul gets his godown insured against fire for ₹1 lakh but does not take enough precautions to minimize the chances of fire like installing fire extinguishers in the factory. During the policy, a fire takes place in his godown and he does not take any preventive steps like throwing water and calling the employees from the fire fighting department to control the fire. He suffered a loss of ₹1,20,000. Madhav took a fire insurance policy of ₹20 lakh for his factory at an annual payment of ₹24,000. In order to reduce the annual premium, he did not disclose that highly explosive chemicals are being manufactured in his factory. Due to a fire, his factory gets severely damaged. The insurance company refused to make payment for the claim as it became aware of the highly explosive chemicals.
How much can Manish claim from the insurance company?
- None of the above
How much compensation can Rahul get from the insurance company?
Which principle is violated in the case of Rahul?
- Insurable Interest
- Utmost Good Faith
How much amount is the insurance company liable to pay to Madhav if he files a case against it?
- Insufficient information
Which principle of Insurance is violated by Madhav?
- Insurable interest
- Subrogation
- Proximate Cause
The insurance company acquired the burnt material and approved his claim. Which principle of Insurance is highlighted in the given statement.
- (a) Mitigation
- (a) Utmost Good Faith
- (d) Subrogation
Business Studies Case Study 2
Sarthak Electronics Ltd. has a loss of Rs 15,00,000 to pay. They are short of funds so they are trying to find means to arrange funds. Their manager suggested a claim from the insurance company against stock lost due to fire in the warehouse. He actually meant that they can put their warehouse on fire and claim from insurance companies against stock insured. They will use the claim money to pay the loan.
- Will the company receive a claim if the surveyor from the insurance company comes to know the real cause of fire?
- Write any two Values which the company ignores while planning to arrange money from false claims.
- State any three elements of fire insurance
Business Studies Case Study 3
OLX and qickr are examples of well-known websites used to conduct business. Tarasha’s sofa set got spoiled in the rain. Her friend suggested that she should change the fabric so that it looks new and put it for sale on Olx. Tarasha followed her friend’s advice and got her sofa repaired so that it looked better and uploaded nicely clicked pictures on the website without disclosing the fact that it was damaged from the inside. She found a buyer and sold it for Rs 10,000. After five days the buyer found the real state of the sofa set and called Tarasha but she did not answer any of the calls.
- identify the type of business highlighted in the above case.
- Identify any two values which are overlooked by Tarasha.
- Explain any two benefits and limitations of e-business.
Advantages of case study questions in Business Studies
Class 11 Business Studies syllabus is not very vast but has to be focussed upon as it forms the base for your 12th grade Business Studies syllabus. Students are supposed to prepare themselves thoroughly from the NCERT textbook. The Case-based questions prominently focus on the real and current scenarios of the Business world. Approximately 30% of the question paper will comprise case study questions that demand high-order thinking and reasoning skills from the students. The students ought to practice class 11 Business Studies case-based questions from the various options available to them, so as to excel in the subject.
- Enhance the qualitative and quantitative analysis skills of students
- Provides an in-depth understanding of the key Business theories/concepts
- Inculcate intellectual capabilities in students
- Help students retain knowledge for a longer period of time
- The questions would help to discard the concept of rote learning
- Case studies promote and strengthen practical learning.
“Failure is success if you learn from it”
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 Important Questions and Answers
Home » CBSE » Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 Important Questions and Answers

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Business Studies is a subject taught in a Commerce student’s syllabus beginning in Class 11 and continuing through Class 12. Students will master an understanding of the area of management and other business disciplines if they study this subject. Forms of Business Organisation is the second chapter of the Class 11 syllabus, and it teaches about different forms of Business. This chapter covers concepts such as various forms of business organisation, features, merits, and demerits, and factors determining the appropriate form of business organisation. It carries significant weightage in the Business Studies syllabus. Students can easily access all this and more on the Extramarks website.
Quick Links
Students must read through all the chapters to score well in Business Studies. Extramarks understands the importance of solving questions. As a result, we’ve gathered them from various sources, such as the NCERT Textbook, NCERT Exemplar, other reference books, past exam papers, and so on. Our Business Studies experts have curated step-by-step solutions to help students better comprehend the topics. Students can register with Extramarks and access Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2.
Apart from Chapter 2 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions, there is so much that the Extramarks website has to offer. Students can easily find materials like NCERT Solutions, CBSE revision notes , past year question papers, NCERT books, and more on the Extramarks website.
Get Access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions 2022-23 with Solutions
Sign Up and get complete access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions for other chapters too:
A team of Extramarks specialists have developed an entire list of Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 Important Questions taking cues from numerous sources. The questions comprise a wide variety of topics, including the different forms of business organisation, features, merits, and demerits of business organisation, factors determining the appropriate form of business organisation, and so on. These questions and their solutions help students better comprehend Forms of Business Organisations.
Mentioned below are a few Important Questions from Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 and their solutions:
Q1. What are the important privileges available to a private company?
Answer: When a business is formed as a private corporation, it has several advantages and exemptions that are not accessible to public companies. Some of the main benefits that a private corporation has are as follows:
- A private business can be formed with as few as two members, but a public corporation requires seven.
- In private business the public is not asked to subscribe to company’s shares and hence a prospectus is unnecessary.
- Shares can be distributed without a minimum subscription requirement.
- A private company can start operating as soon as it receives its establishment certificate. On the other hand, the public company must wait until it gets the starting certificate before it may begin operations.
- A private company only needs two directors, but a public company requires at least three.
- A member index is not necessary for a private organisation but is required for a public corporation.
Q2. With a notable example, explain mutual agency in partnership.
Answer: Mutual agency refers to the legal connection between participants in a partnership who have authorization powers and the authority to engage the collaboration in business contracts. In another way, each partnership member has the authority to make business choices that commit or bind the entire partnership to a commercial contract with a third party or entity. For example, even if the partnership agreement prohibits it, a grocery store partner who acquires a delivery truck in the partnership’s name enters a legally enforceable transaction. On the other hand, such behaviour would be unlawful if a law firm partner purchased a snowmobile for the firm.
Q3. What is meant by “partner by estoppel”? Explain.
Answer: A person who shows others that they are a company partner via their actions, behaviour, or statements, is referred to as Partner by estoppel. Such a person is not a partner, and they are not responsible for providing any cash to the company, nor are they accountable for any portion of the company’s profit or loss. The same individual, however, may be held accountable for the firm’s debts. Hence, as a result, if the Business has adequate assets or finances, debt repayment can be obtained by selling off the partner’s private assets via estoppel.
Q4. What exactly is HUF?
Answer: Although the Income Tax Act does not define the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), it is recognised under Hindu law. Unmarried daughters are included in the HUF, as are all those who are lineally settled from the same ancestor. A person does not create HUF but by a family’s standing, i.e., it is created automatically in any Hindu household.
Q5. Why do some consider partnership a relatively unpopular form of business ownership? Explain the merits and limitations of partnership.
Answer: A partnership is viewed as a relatively unattractive sort of company ownership due to the inherent limitations that come with it. These limits include infinite responsibility, limited resources, the possibility of conflict, and a lack of consistency.
- Ease of closure and creation: A partnership business can be established rapidly by agreement amongst potential partners. A company doesn’t need to be registered.
- Balance decision-making: The partners might manage various responsibilities depending on their expertise. As a result, the decision-making process in a partnership business is more balanced than in any other kind of corporate ownership.
- A large amount of funds: Each partner in a partnership provides a certain amount of money. Consequently, compared to a single owner, it is feasible to collect a more considerable sum of cash and carry out additional activities as needed.
- Confidentiality: There is no legal requirement for a partnership business to publish its financial accounts or submit reports. As a result, it may maintain secrecy regarding its operations.
- Sharing the risk: The risks that come with running a partnership business are shared by all partners. As a result, individual partners experience less worry, tension, and stress.
Limitations of business partnership:
- Restricted Resources: Capital investment contributions are frequently insufficient to sustain large-scale commercial activity due to the limited number of partners. As a result, partnership firms struggle to expand beyond a particular scale.
- Conflicts of Interest: The decision-making authority in a partnership business is distributed among the partners. This is also dependent on their level of competence, foresight, and ability.
- Unlimited liability: Partners are accountable for repaying debts from their assets if the Business’s assets are insufficient to fulfil its obligations.
- Lack of continuity: When one of the partners dies, retires, becomes bankrupt, or becomes mad, the partnership comes to an end. On the other side, the surviving partners might enter into a new agreement and continue to run the business.
Q6. In what form of Business do individuals associate freely for profit, with capital dividends into transferable shares, and ownership of which is a requirement of membership? Explain in terms of characteristics.
Answer. A joint-stock company is a non-profit organisation formed by a group of people to do profitable economic activities. It has a legal status distinct from its members and a capital structure separated into transferable shares. A corporation is an independent legal entity with its legal identity, perpetual succession, and a common seal. In a corporation, the shareholders are the company’s owners, and the Board of Directors, which the shareholders elect, is the company’s central management body.
The company’s capital is divided into smaller components known as “shares,” which can be freely transferred from one shareholder to the next (except in a private company). A joint-stock firm has the following characteristics:
- A corporation is a made-up entity. It is a legal entity that exists without the participation of its members.
- The legal personality of a corporation is established. The law does not regard the Business and its owners as the same.
- Starting a business is a time-consuming, costly, and challenging endeavour. Therefore, incorporation is required for all enterprises.
- It will only be deactivated after completing a specialised operation known as winding up. Members may come and go, but the firm does not cease to exist.
- A company’s common seal may or may not exist.
- All shareholders share the risk of a company’s losses.
Q7. Even though there are limitations of size and resources, several people continue to prefer sole proprietorship compared to other forms of organisation? Why?
Answer: Due to the numerous sheer benefits, it provides despite the size and resource limits. The sole proprietorship is the company’s form of choice. The following are some of the advantages:
- A single proprietorship firm is simple to set up since there are few legal requirements. Similarly, closing a firm is a painless process.
- The sole owner controls the firm as the only decision-maker, allowing for swift choices.
- The sole proprietor enjoys all the Business’s gains while bearing all its misfortunes.
- Because the lone proprietor is the only person in charge of the business, it is highly flexible.
Q8. Which business model is best for the following businesses, and why?
- Coaching centre for the students of science subject
- A beauty salon
- A shopping centre
- Little repair shops
Answer. The suitable business model for the businesses as mentioned earlier would be:
- Coaching center for the students of science subject: Collaboration with a science coaching facility. It’s simple to set up and run, and it’s inexpensive. Partners report their share of profit or loss on their tax returns.
- A beauty salon: A salon can be run as a sole proprietorship. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
- A shopping center: shopping malls are JSCs (joint-stock corporations). Personal responsibility for commercial debts is restricted for business owners.
- Hotel: In the hotel industry, there are joint-stock companies. Small businesses are drawn to LLCs and corporations because they minimize their owners’ liability for corporate debts and court judgments against the company. Another factor to consider is income taxes: you may set up a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation to benefit from reduced tax rates. Furthermore, an LLC or company may be able to deduct the cost of a range of fringe benefits passed on to its employees (including the owners) as a business expense.
- A little repair shop: A sole proprietorship is appropriate for a small repair shop. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
- Restaurant: Ownership of a restaurant as a sole proprietor. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
Q9. How does a cooperative society exemplify democracy and secularism? Explain.
Answer: A cooperative society is run by persons chosen by all members through a democratic process. Each member has an equal right to vote, regardless of the amount of money they have invested. As a result, it functions as a democracy in which all members are treated equally and have similar rights. Members are not discriminated against because of their caste, religion, or gender. People of the management committee can select the members they believe best represent them. As a result, it denotes secularism.
Q10. What does it mean to have unlimited liability?
Answer: General partners and sole proprietors with unlimited liability are jointly and severally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. However, this obligation is not limited and can be paid off by seizing the owners’ assets, distinguishing it from limited liability partnerships.
Q11. Compare the status of a minor in a Hindu joint family business with that in a partnership firm.
Answer: A person under 18 is considered a minor in Indian law. By being born into a Joint Hindu household, a minor becomes a member of the family company. Like other family members, the minor has equal ownership and rights to the property and company. However, his obligation is limited to his part of the property.
As per the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, a minor cannot become a partner in a partnership business. However, if all partners agree, a minor can be initiated and partake in a firm’s profits. Still, a minor does not need to contribute capital or carry any obligation if the Business supports the firm. Therefore, minors aren’t regarded as partners. However, once they reach the age of 18, they have the option of continuing the relationship or terminating it.
Q12. Who has equal ownership rights to an ancestor’s property? Emphasise its most important aspects
Answer: A Joint Hindu Family is a form of business owned and operated by members of the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). The company’s membership is based on birth in a specific family, and three generations of the same family can be members. The family’s business is run by the eldest member of the family, known as Karta. Joint Hindu Family Business members with equal ownership rights over an ancestor’s property are known as coparceners.
A combined Hindu family company has the following characteristics:
- Because membership is by birth, there is no requirement for an agreement.
- Except for the Karta, all members are only responsible for their portion of the Business’s co-coparcenary property. The Karta’s responsibility is boundless.
- Karta oversees the family company, and his choices bind everyone.
- After Karta’s death, the business is carried on by the next eldest son, Karta.
Q13. Why is it important to choose an appropriate form of organisation? Discuss the factors that determine the choice of form of organisation.
Answer: Choosing an appropriate business organisation is necessary since it is one of the most important decisions to make when beginning a business or expanding an existing one. A business can be owned and run in several ways. It’s challenging to modify a company model after it’s been decided. As a result, the type of business company chosen should be done with care and consideration.
The following factors influence organisational structure selection:
- Control: With a sole proprietorship, you have complete control over your operations and decision-making authority. If the owners, on the other hand, want to share ownership to make better judgments, they can form a partnership or a corporation.
- Nature of Business: Businesses that involve direct personal connection with customers, such as beauty salons or grocery stores, are better suited to a single proprietorship. The corporate kind of structure benefits large manufacturing units. The partnership structure is significantly more served in the case of professional services.
- Management Skills: Being informed in all firm parts is difficult for a sole owner. Members split their labour in other organisations, such as partnerships and businesses, allowing management to specialise in specific areas and make better judgments.
- Capital Requirements: The corporation form is suitable for large-scale activity since it may generate a large amount of money by issuing shares. There are two options for medium and small firms: partnership or sole proprietorship. In the framework of a company, expansion capital requirements may be managed more easily.
- Continuity: The continuity of sole proprietorship and partnership enterprises can be disrupted by events such as the owners’ death, insolvency, or insanity. In organisations like joint Hindu family companies, cooperative societies, and corporations, such factors, on the other hand, have minimal influence on the business’s survival.
- Liability: The liability of the owners/partners of a sole proprietorship or partnership is unlimited. This might lead to the owners’ assets being used to repay the debt.
- Cost and Convenience of Starting a Company: A sole proprietorship is straightforward to start in terms of initial business costs and legal procedures, but because of its more minor activities, a partnership has the advantage of less legal formalities and lower prices. Registration is necessary in the case of cooperative societies and companies. The process of founding a company takes time and money.
Q14. What are the reasons for the formation of cooperative forms of organisation? Describe the different sorts of cooperative societies.
Answer. A cooperative society is a collection of individuals who get together voluntarily for the common welfare of its members. They are motivated by a desire to defend their economic interests from potential exploitation by intermediaries looking to increase their profits. The process of founding a cooperative organisation is simple, and all that is necessary is the agreement of at least ten adults. A society’s capital is raised by selling shares to its members. An organisation acquires a distinct legal character when it is registered.
One sort of cooperative society is the consumer cooperative society.
- It was designed to protect consumers’ interests.
- To improve operational savings, society strives to eliminate intermediaries. Instead, it purchases things in bulk from wholesalers and resells them to its members.
- Profits are dispersed depending on capital contributions to the organisation or purchases made by individual members.
Producer Cooperative Societies are a specific sort of producer cooperative society.
- It was established to protect the interests of small farmers.
- Members are producers looking for inputs to create commodities to fulfil customer demands.
- Profits are distributed according to their contributions to the society’s overall pool of products produced or sold.
Cooperative Societies Marketing-this organisation was established to help small manufacturers market their products.
- Producers that demand fair pricing for their commodities are among the group’s members.
- It combines individual members’ production and marketing activities such as shipping, storage, and packaging to sell the commodities for the best feasible price. Profits are dispersed according to the amount of money each member puts in.
Farmers’ Cooperative Societies were formed to protect farmers’ interests by providing high-quality inputs at a reasonable price.
- Members are farmers who want to collaborate on farming projects.
- The idea is to increase productivity while reaping the benefits of large-scale farming. Improving farmer output and returns while addressing challenges associated with farming on fragmented land holdings.
Cooperative Financing Societies were established to give members timely credit at reasonable rates.
- Members are individuals seeking financial assistance in the form of loans.
- The purpose of such groups is to protect members from being taken advantage of by lenders who demand high-interest rates on loans.
A cooperative housing organisation is a sort of Cooperative Housing Societies.
- It was established to assist low-income people in constructing homes at a reasonable cost.
- These societies are people looking for a cheaper location to reside in.
- The purpose is to alleviate members’ housing issues by constructing homes and allowing them to pay in instalments.
Q15. If registration is optional, why do partnership firms willingly go through this legal formality and register themselves? Explain.
Answer: Although partnership business registration is optional, many firms choose to do so. This is owing to the severe legal consequences of failing to register. Listed below are a few examples:
- The partners of a non-registered business cannot sue a third party, but the non-registration of a partnership firm does not prevent other firms from hiring it.
- The company is forbidden from filing a lawsuit against any of its partners. Similarly, a partner in a non-registered firm cannot sue their co-partners or the company.
- Claims against a third party by a non-registered partnership entity cannot be enforced in court. As a result, partnerships are established to overcome these disadvantages.
Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Important Questions – Key Topics Covered
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Important Questions covers the following key topics:
Forms of business organizations
There are several different types of business organizations from which to choose:
- Sole proprietorship
Joint Hindu family business
- Partnership
- Cooperative societies
Joint-stock company
Sole Proprietorship
It is a type of Business owned, managed, and controlled by a single person who carries all the risks and reaps all the rewards.
- It can be formed and disbanded without the need for any legal requirements.
- In this business organisation, the lone proprietor’s responsibility is unrestricted.
- As the single risk carrier and profit recipient, he bears all the risks and reaps all the rewards.
- There is no distinction between the owner and the Business in the eyes of the law.
- All choices must be made by the owner, which necessitates prompt decision-making.
- As a lone proprietor, it is simple to keep company secrets.
- Because there is no one to share gains with, the owner enjoys all the profits.
- There are no legal requirements for establishing and closing a business, making creating and completing one simple.
Limitations:
- The owner’s savings or money borrowed from friends and family might be used to support the Business.
- A business’s life expectancy is limited as it is dependent on the owner’s health and mental state.
- His assets are at stake if the firm fails to satisfy its debts.
- A single individual may not be able to oversee all of the functions.
It is a type of business that is owned and managed by members of an undivided Hindu family, with three generations of family members potentially participating.
- Hindu Undivided Families are created when at least two family members have ancestral property. The Hindu Succession Act of 1956 governs it.
- Except for the Karta, all family members have limited responsibility for their part of the company property.
- Karta oversees all actions inside the corporate organisation.
- It can be stopped if all members of the family agree to it.
- Organisation membership is based on birth.
- With ‘Karta,’ you have complete control over your firm and can make better decisions.
- If ‘Karta’ dies, the Business continues until all members desire to continue, and then control is given to the next eldest member.
- Family members are only liable for their share of the business party.
- Because family members feel connected and loyal, they work together to achieve a common goal of progress.
- Businesses might be supported primarily via inheritance, restricting financial resources.
- Karta’s personal property is at risk due to his unlimited liability.
- Differences of opinion among members and the ‘Karta’ might lead to conflict.
- Karta’s managerial abilities are limited, and he may not be familiar with all of the Business’s functions.
Partnership:
According to the Partnership Act of 1932, a partnership is a relationship between people who have agreed to share the earnings of a firm run by all or by one acting on behalf of all of them.
- The partnership Act of 1932 governs the establishment of the Business.
- The liability of all company partners is unlimited.
- All the partners share the risk in the Business.
- All decisions are made with the approval of all partners, and each partner bears responsibility for the company’s day-to-day operations.
- Because registration is optional, a business can be formed and ended with the approval of all partners.
- As partners take on tasks according to their competence, all choices are made by consensual partners.
- All partners contribute money, broadening the scope of large-scale company operations.
- There is no need to report financial results; therefore, maintaining corporate secrets is simple.
- Their complete responsibility covers each partner’s personal property.
- All parties may have differing viewpoints, which can lead to conflict.
- Any disagreement between partners or the death of a partner might put the company out of operation.
- Due to a lack of financial disclosures, an outsider can’t determine the actual economic situation.
Cooperative society
An organisation of volunteers working for a shared goal to protect members’ economic and social interests. The Cooperative Societies Act of 1912 requires it to be registered.
- Any individual with a shared interest, regardless of caste, gender, or religion, is free to join or leave a cooperative organisation at any time.
- A cooperative society has a different identity from its members, and the registration of such a group is required.
- The goal of forming a society is to provide mutual assistance to team members.
- Each member has the same right to vote and elect managing committee members.
- Cooperative societies maintain their existence in the face of death, bankruptcy, or insanity among their members.
- Members of society work willingly, which helps to save expenses.
- The only funding source is the member’s capital contribution, and the low dividend discourages members from contributing money to the organisation.
- Volunteer members may lack the requisite competence and skills, resulting in inefficient operations and management.
- It’s challenging to preserve secrets since members provide all information about the society’s operations at the meeting.
“A corporation is an artificial person with a separate legal existence, eternal succession, and a common seal,” according to the Companies Act of 2013.
- A corporation is a legal entity with legal standing but does not act as humans do. The board of directors conducts all corporate actions in the corporation’s name.
- Companies are founded following the legal requirements outlined in the Companies Act of 2013.
- A corporation is formed by law and may only be disbanded by legislation. Therefore, the company’s existence is unaffected by the status of its members.
- The responsibility of shareholders is limited to their investment in the firm. Therefore, there is no chance of personal assets being lost.
- The firm’s existence is unaffected by its stockholders’ status; it continues to exist.
- Companies can borrow vast sums of money from financial institutions or banks and solicit cash from the public.
- The formation of a corporation necessitates the completion of several documents and legal requirements, making the process lengthy and complicated.
- There is no confidentiality or secrecy because all financial information is given to the general public.
- Decision-making must adhere to a hierarchy, leading to delays in making judgments and implementing actions.
Choice of the Type of Business organisation
- Nature of Business
- Cost of setting up the organisation
- Capital consideration
- Degree of control
- Management ability
The briefly described topics in the above sections are covered in the Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2.
Benefits of Solving Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Important Questions
Business Studies is one subject that requires a lot of reading and revisions. This subject is introduced in Class 11, and it prepares the base for Class 12 board examinations. Therefore, students are advised to access Important Questions of Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 . Students will get a sense of confidence by solving essential questions from all the chapters and overlooking their solutions.
Mentioning below are some benefits of solving Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2:
- Students will benefit from practising questions similar to exam questions to do better in their examinations and earn high grades.
- The questions and answers follow CBSE criteria and are based on the most recent CBSE syllabus . As a result, students can rely on them.
- These important questions are prepared by following the exam writing pattern. Therefore, going through these will help students prepare for exams too.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. We have abundant resources available on our website, along with essential questions and answers. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE previous year’s question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 The North Coast Cooperative that was Established in 1973 was the large consumer cooperative that offered a full service grocery store and deli. Director started to deal with bulk purchasing and packaging issues. Many people in the college-campus area wanted a supply of natural food products, which didnt exist. They wanted a cheaper, more reliable supply if they purchased togetherin bulk.
From the start, the co-op tried to provide a market for local produce. Initially, the farmers provided a fairly limited variety, mostly tomatoes, sweet corn, zucchini and other common garden vegetables. The co-op uses purchasing contracts, which act as a type of insurance to motivate farmers to produce new and different varieties
Explain the type of cooperative society that is refered to here. Also give three points to support the formation of such a form of business enterprise.
Marks: 1 Ans
This is a consumer cooperative society. These are formed to protect the interests of consumers. Members are consumers who want to get good quality products at reasonable prices. The society aims at eliminating middlemen for economy in operations.
Society purchases goods in bulk directly from the wholesalers and sells goods to the members directly.
Profits are distributed on the basis of either their capital contributions to the society or purchases made by individual members.
Merits of cooperative form of organisation are:
(i) Equal voting status: There is a principle of ‘one man one vote’ i.e., irrespective of the capital contribution by a member, each member is entitled to equal voting rights.
(ii) Limited liability: As the liability of members of a cooperative society is limited to the extent of their capital contribution, their personal assets of the members are safe from being used to repay business debts.
(iii) Stability: Death, bankruptcy or insanity of the members do not affect continuity of a cooperative Society i.e., it remains unaffected by any change in the membership.
(iv) Economy in operations: Focus of society is on elimination of middlemen which helps in reducing costs.
(v) Government support: Cooperative society exemplifies the idea of democracy and hence Government supports in the form of low taxes, subsidies, and low interest rates on loans.
(vi) Ease of formation: It can be started with a minimum of ten members and registration procedure is simple with few legal formalities.
Q.2 A friends group of a hotel management institute wants to start their own catering house that will serve parties, weddings, church functions and business events. All 4 of them are very good cooks and have managed the university parties very well. They want to start and see that how this business works with contributing small small savings initially.
What form of business organisation shall they form with limited funds
Looking at their conditions and case, the friends shall form a partnership initially. Partnership offers the advantage of less legal formalities and lower cost because of limited scale of operations.
After being successful, this partnership can take form of any other form of business organisation based on the decisions of partners.
Q.3 Karan is the sole owner of a shoe manufacturing factory. He took loan of `30 lakhs from a bank so as to expand his business further. However, he incurred losses in the business, due to which Karan was not able to pay the loan on time and his assets were also not sufficient enough repay back the loan. As a result, the bank asked him for repayment of loan, but he refused to pay on the ground that the loan was taken in the name of business and not for personal use. The bank file a case against Karan and the court gave the decision in favor of Bank on the on the basis that Karan is the sole proprietor and his business doesnt have separate identity from his own. The Court further stated that Karan is liable to repay the loan even by selling his personal property.
State the demerits of the business organisation being highlighted in the above case.
Marks: 6 Ans
The form of business organisation being highlighted above is Sole proprietorship.
Demerits of Sole proprietorship
- Limited life: Death, insolvency or illness of proprietor affects the business and may even lead to its closure as he/she is the sole owner of the business.
- Unlimited liability: Owner has unlimited liability. In case of business failure, creditors can recover their dues not only from the business assets, but also from the personal assets of proprietor. It makes the sole proprietor less inclined towards taking risks in the form of innovation or expansion
- Limited resources: Resources are limited to his/her personal savings or borrowing from other parties. Banks and other financial institutions might hesitate in lending long term loan to the sole proprietor. Size of the business rarely grows much and generally remains small due to lack of resources.
- Limited Managerial Ability: The proprietor has to assume responsibility of varied managerial tasks. Since a business owner may not be a specialist in every field, there is a possibility of unbalanced decision making. Moreover, proprietor may not be able to employ and retain talented and ambitious employees, due to limited resources.
Q.4 A private company is superior to a public company. Discuss this statement in the light of privileges of a private company.
Privileges of a private limited company as against a public limited company:i. A private company can be formed only by two members, whereas seven persons are needed to form a public company. ii. There is no need to issue a prospectus as public is not invited to subscribe to the shares of a private company. iii. Allotment of shares can be done without receiving the minimum subscription. iv. A private company can start business as soon as it obtains the certificate of incorporation, whereas a public company can start its business only after receiving the certificate of commencement of the business. v. A private company needs to have only two directors as against the minimum of three directors in case of a public company. vi. A private company is not required to keep an index of members, while it is necessary in case of a public company.
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 11 business studies important questions, chapter 1 - business, trade and commerce.

Chapter 3 - Private, Public and Global Enterprises
Chapter 4 - business services, chapter 5 - emerging modes of business, chapter 6 - social responsibilities of business and business ethics, chapter 7 - formation of a company, chapter 8 - sources of business finance, chapter 9 - small business, chapter 10 - internal trade, chapter 11 - international business, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. how many business studies books are there for class 11.
For Class 11 Business Studies, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) only recommends one book. Therefore, the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has released this book, which is available in both English and Hindi. This book is broken into two sections and has ten chapters. Part A comprises six units that address business foundation information, while part B contains the remaining four units that discuss financial and trade knowledge.
2. What are the essential chapters in Business Studies in Class 11?
There are ten chapters in the Business Studies syllabus for Class 11. Chapter 7 – Sources of Business Finance, Chapter 8 – Small Business, Chapter 9 – Internal Trade, and Chapter 10 – International Business are the most significant. It is so because they have a greater weight than the rest of the syllabus. Students can refer to Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 for easier comprehension of these chapters.

3. What is so special about Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 that it makes Extramarks stand out from the rest?
These Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 are developed exclusively by the Extramarks subject experts. These solutions are 100 percent authentic and have been made after much research. They cover the concepts of the entire chapter and are written in simple and easy language.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Students can read the important questions given below for Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies. All Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Business Studies Question Bank Class 11 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Forms of Business Organisation Class 11
Short /Long Answer type Questions :
Question. ABC Ltd. filed an application for registration to registrar of companies. He submitted copy of name approval, memorandum of association, articles of association, address of registered office and paid the required registration fees. His application for registration was rejected on the ground of not submitted some others important documents. List the documents he needs to file so that he can get his company incorporated. Answer. (a) Statement of authorised capital. (b) Consent of proposed directiors. (c) Statutory declaration. (d) The agreement, if any, with proposed Managing Director or Whole time Director or Manager.
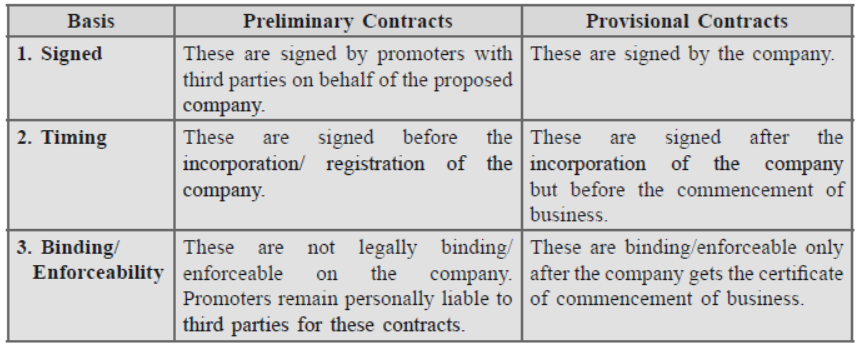
Question. Distinguish between preliminary contracts and provisional contracts. Answer.
Question. A group of 15 people decides to form a company and hence appointed Creators Pvt. Ltd. Creators Pvt. Ltd. were assigned the job of scanning the business environment and to identify various business opportunities. After thoroughly exploring the environment, Creators Pvt. Ltd. suggested them to start a ‘Cab Services’ in the posh areas of Delhi. Before converting the business opportunities into real project, Creators Pvt. Ltd., conducted feasibility studies and also suggested the name for the company. They have entered into contract on behalf of the company also. (a) Identify the stage in the formation of a particular form of business organisation. (b) Under what category is Creators Pvt. Ltd. is working. (c) Are the contracts which are entered into before incorporation, of above mentioned form of organisation, are binding after incorporation? Answer. (a) Promotion. (b) Creators Pvt. Ltd. is working as promoters. (c) Yes.
Question. Is it necessary for a public company to get its shares listed on a stock exchange? What happens if a public company going for a public issue fails to apply to a stock exchange for permission to deal in its securities or fails to get such permission. Answer. Yes, it is necessary for a public company to get its shares listed or quoted on a stock exchange. If a company going for a public issue fails to apply to a stock exchange for permission to deal in its securities or fails to gets such permission within 10 weeks from the date of closure of subscription list, then the allotment will become void Consequently, all money received from the applicants will have to be returned to them within 8 days.
Question. Name the following: (a) A company having at least 7 members. (b) An enterprise owned by a single person. (c) A company in which the number of members cannot exceed 200. (d) Its main aim is to provide services to the members. (e) This form of business organisation is owned, financed, managed and controlled by a single person. (f) A document containing terms and conditions of partnership. Answer. (a) Public company. (b) Sole proprietorship. (c) Private company. (d) Cooperative society. (e) Sole proprietorship. (f) Partnership deed.

Related Posts

Getting Started With Python Class 11 Computer Science Important Questions
Animal kingdom class 11 biology important questions, body fluids and circulation class 11 biology important questions.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Business Studies
- Forms Of Business Organisation
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
11th Class Business Studies Forms Of Business Organisation Question Bank
Done forms of business organisation (higher) total questions - 18.

question_answer 1) X is interested in the floatation of a company. Briefly discuss the steps he should take.
question_answer 2) Distinguish between Joint Hindu Family Business and Partnership.
question_answer 3) Explain the factors which affect the choice of form of business organization.
question_answer 5) Differentiate between a Joint Stock Company and a Cooperative Society.
question_answer 6) How is a partnership firm different from a sole proprietorship?
question_answer 7) What is the objective behind one person company concept?
question_answer 8) Explain the features of one Person Company.
question_answer 10) X, Y and z are partners in a firm. X makes use of firm's money to buy shares without disclosing it to Y and Z. Which value is being violated by X and what will the treatment of profit earned by X?
question_answer 11) A, B and C are partners. They are into a business of exports and imports. They earned a profit of Rs10,00,000 in year 2016-17. They decided to give 10% of the profits to a blind children orphanage home. They also decided to distribute defective clothes to poor people free of cost. Identify the values that are being followed by the firm.
Study Package

Forms Of Business Organisation (Higher)
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
Case Studies in Business, Management, and Organizations
Case studies - full text as part of library subscription.
- Sage Business Cases This link opens in a new window SAGE Business Cases is a digital collection of business cases tailored to library needs – providing faculty, students and researchers with unlimited access to more than 4,850 authoritative cases from over 120 countries. SAGE curates interdisciplinary cases on in-demand subjects such as entrepreneurship, accounting, healthcare management, leadership, social enterprise, and more. Publishing partners include Yale University, Kellogg School of Management, Society of Human Resource Management, and more. For Instructors: additional teaching note material is available; please contact the library for more information on how to access this content.
- HS Talks Business & Management Collection This link opens in a new window Specially commissioned talks from leading experts in industry, commerce, the professions and academia. The collection also includes 20 peer reviewed vocational journals.
Case Studies - summary collections available at low/no cost
- Business Source Premier --Abstracts for Harvard Business School Case Studies from 1942 to the present are available as part of Business Source Premier. Full text of the case is not available.
- Harvard Business School Case Studies The case method forms the basis of learning at Harvard Business School. It is a method designed to provide an "immersion" experience, challenging students by bringing them as close as possible to the business situations of the real world. Harvard Business School Publishing makes these cases and related materials available to improve and enhance business education around the world. They are available to purchase online for around $7.00.
- Case Depositories Page at GlobalEdge This section of the GlobalEdge database provides information about publishers or depositories of cases. Some sites list cases by that institution. Other sites act as clearinghouses and feature cases from a variety of sources.
- LearningEdge The case studies available on LearningEdge are teaching case studies, narratives that facilitate class discussion about a particular business or management issue.
- Darden Case Collection The Darden case collection provides numerous business and management case studies.
- European Case Clearing House The Clearing House distributes the European Collection from the Babson College Office including case collections of IMD, INSEAD, IESE, London Business School, Cranfield School of Management, Babson College and cases from independent authors. Cases cost about $3.50.
- Kellogg School of Management Case Study Abstracts The Kellogg School of Management is making available to academic practitioners and corporate trainers selected cases and teaching materials, developed by Kellogg faculty and taught in the Kellogg classroom. Information on how to order the case studies is included on the web site.
- Stanford Graduate School of Business Case Studies Abstracts This database contains abstracts and ordering information for case studies written and published by the Stanford Graduate School of Business. You may search by authors name, title, keyword, etc. Most cases in this collection are distributed by Harvard Business School Publishing and you will find a link to the HBSP site to place your order. Contact them for availability of other cases.
- Case Research Journal Available in Print: Case research journal. Published: [United States] : The North American Case Research Association (NACRA), 1980--present. Availability: TC Wilson Periodicals --Basement The Index to the cases in the print journal is available at the link shown above. This site from the North American Case Research Association also shows how to purchase the cases available in the journal.
- NASPAA Publicases Publicases is an online repository and marketplace developed by NASPAA (Network of Schools of Public Policy, Affairs, and Administration) as platform connecting students and faculty in public affairs schools around the world with simulations, case studies, data, and other experiential learning opportunities. Currently, case content is developed by the Evans School and the Humphrey School and is available without charge to member schools.
Writing Case Studies - teaching and research
Find Case Studies in Books by using MNCAT :
- Search for a subject term, such as marketing, and add the phrase: case studies. See below for examples:
- Books on the case method: Search our MNCAT catalog using the subject term: Case method.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Business Organisations: An Overview

Introduction to Business Organisation
A business organisation is an entity created with the intention of conducting a business. These organisations are operated on legal systems that control contracts, exchanges of goods and services, ownership rights, and incorporation.
Managing and planning various activities is a concern of the business organisation system. In order to generate goods and services, resources like labour, equipment, capital, and money must be accumulated and coordinated. The business organisation works to manage and regulate all of these production factors.
Forms of Business Organisations
Forms of Business Organisation
1. Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a form of business in which one individual is in charge of the entire business. The owner of a firm controls every aspect of how it is run and is responsible for all financial obligations and debts.
A sole proprietorship is the least expensive option and relatively simple to set up. It is not governed by a separate law and can easily be formed with only the proper licensing required to operate a business and the registration of the business name.
Merits of Sole Proprietorship
The benefits of being a sole proprietor are numerous. The following are a few of the significant ones:
A sole proprietor has a great deal of freedom in doing business. This results in quick and inexpensive decision-making.
A sole proprietorship can be easily formed or closed, as there are only a few legal requirements.
The capital requirement to set up a sole proprietorship is generally low and least among all forms of business.
Demerits of Sole Proprietorship
Despite its many benefits, the sole proprietorship business structure has limitations. The following are some significant demerits of a sole proprietorship business structure:
The resources of a sole proprietor are limited to his savings and the money he can borrow from others. The lack of resources is one of the key causes of the business's typically limited size and lack of significant growth.
A significant demerit of the sole proprietorship is the unlimited liability of the sole proprietor. In the event of business failure, the owner has to bear a heavy financial burden.
2. Partnership
A partnership is when two or more people work together to conduct a business. Each partner contributes their fair share of money, assets, labour, and experience and expects to earn money from the firm.
There are different types of partnership firms, including general partnership, limited partnership, LLP partnership, and limited liability partnership (LLP) firms.
This form of organisation is governed by the Partnership Act, of 1932. A partnership deed is drafted by the partners to establish a partnership firm. This deed contains information like the profit sharing ratio, capital contribution by each partner, the purpose of the partnership, etc. The number of people is limited to a maximum of 10 for banking businesses and 20 for other businesses.
Merits of Partnership
The following are some merits of partnership firms:
One of the major advantages of a partnership firm is increased resources. A prospective partner will bring not only more capital but also expertise and connection, which can help the business.
Compared to sole proprietorship, the decisions taken by the partners would be more balanced.
The legal obligations for forming a partnership are minimal, and the process of registration is relatively easy.
All of the partners in a partnership firm share the risks associated with running the business. As a result, each individual has less stress, anxiety, and pressure.
Demerits of Partnership
Some of the drawbacks of a partnership firm are:
Conflicts could arise because the partnership is operated by a group of people with shared decision-making authority. Disagreements between partners may result from different perspectives on some problems.
Another drawback of this form of business is the unlimited liability of partners. The liability of partners is joint and several, i.e., if one or more partners are unable to pay their part of the debt, the others are liable to repay the full amount.
3. Joint Stock Company
A company is an organisation of people created for the purpose of conducting business activities and has a legal existence separate from that of its members. The statute governing this form of organisation is the Companies Act, 2013.
A company is an artificial person with a separate legal entity and perpetual succession. The company is managed by a Board of Directors and management, whereas shareholders are the owner of the company.
Merits of Joint Stock Company
Some major advantages of a joint stock company are:
Unlike other different forms of ownership, the liability of owners (shareholders) is limited to the extent of shares held by them.
The perpetual existence of the company allows it to take on long-term projects and also serves as a strong incentive for creditors and investors to engage in the company.
The company's large operation would lead to the realisation of economies in purchasing, management, distribution, or selling. The consumer would receive things at a lower cost thanks to these economies.
A significant number of people belong to a company. The company's members share the business risk in different ways. Small investors are encouraged to invest as a result.
Demerits of Joint Stock Company
Some major disadvantages of a joint stock company are:
There are numerous legal formalities and processes necessary for the formation of a company which results in incurring huge costs and time.
In a company structure, salaried employees or executives who have no personal stake in the business are responsible for day-to-day operations. This could result in inefficiencies and lower employee motivation.
Statutory limitations on meetings, voting, audits, and other internal operations of the firm apply. Therefore, due to complex legal requirements, starting and maintaining a business would prove to be difficult and burdensome.
4. Joint Hindu Family Business
It is also known as the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) business. A business that is owned and managed by the Hindu undivided family is referred to as a Joint Hindu Family business. Birth in a particular family serves as the prerequisite for membership in the business.
The family head, known as Karta, is the oldest member and is in charge of the company. All members have an equal ownership interest in an ancestor's property and are known as co-parceners.
Merits of Joint Hindu Family Business
The following are some benefits of a joint Hindu family business:
Karta has ultimate control over all decisions. As no one can restrict his right to make a decision, this prevents disputes amongst members. Moreover, quick and flexible decision-making results from this.
The business won't be impacted by Karta's death because the next eldest member will step into the role. As a result, operations are not stopped, and business continuity is not in danger.
Demerits of Joint Hindu Family Business
The following are demerits of a joint Hindu family business:
Karta’s dominance may seem unreasonable to other members and may cause conflict among members.
Disputes over ancestral property are common in this form of organisation.
5. Cooperative Society
A cooperative society is a group of people who get together voluntarily for the benefit of their fellow members. They are motivated by the need to defend their financial interests against potential exploitation at the hands of intermediaries who are driven by the desire to make bigger profits.
A cooperative society should be registered under the Cooperative Societies Act
Merits of Cooperative Society
The following are some merits of a joint Hindu family business:
The cooperative society is governed by the 'one man, one vote' premise. Each member has an equal right to vote, regardless of how much capital they have contributed.
The cooperative society is often supported by the government through low taxes, subsidies, and loan interest rates.
In a cooperative society, each member's liability is limited to the amount of their capital contribution.
Demerits of Cooperative Society
The following are some demerits of a joint Hindu family business:
Due to their inability to afford to pay experienced managers high salaries, cooperative societies struggle to attract and retain them.
Cooperative societies are subject to a number of laws and regulations on the auditing of finances, the submission of accounts, etc. in exchange for the benefits provided by the government, which may negatively affect the operations.
Factors Affecting the Choice of Form of Business Organisation
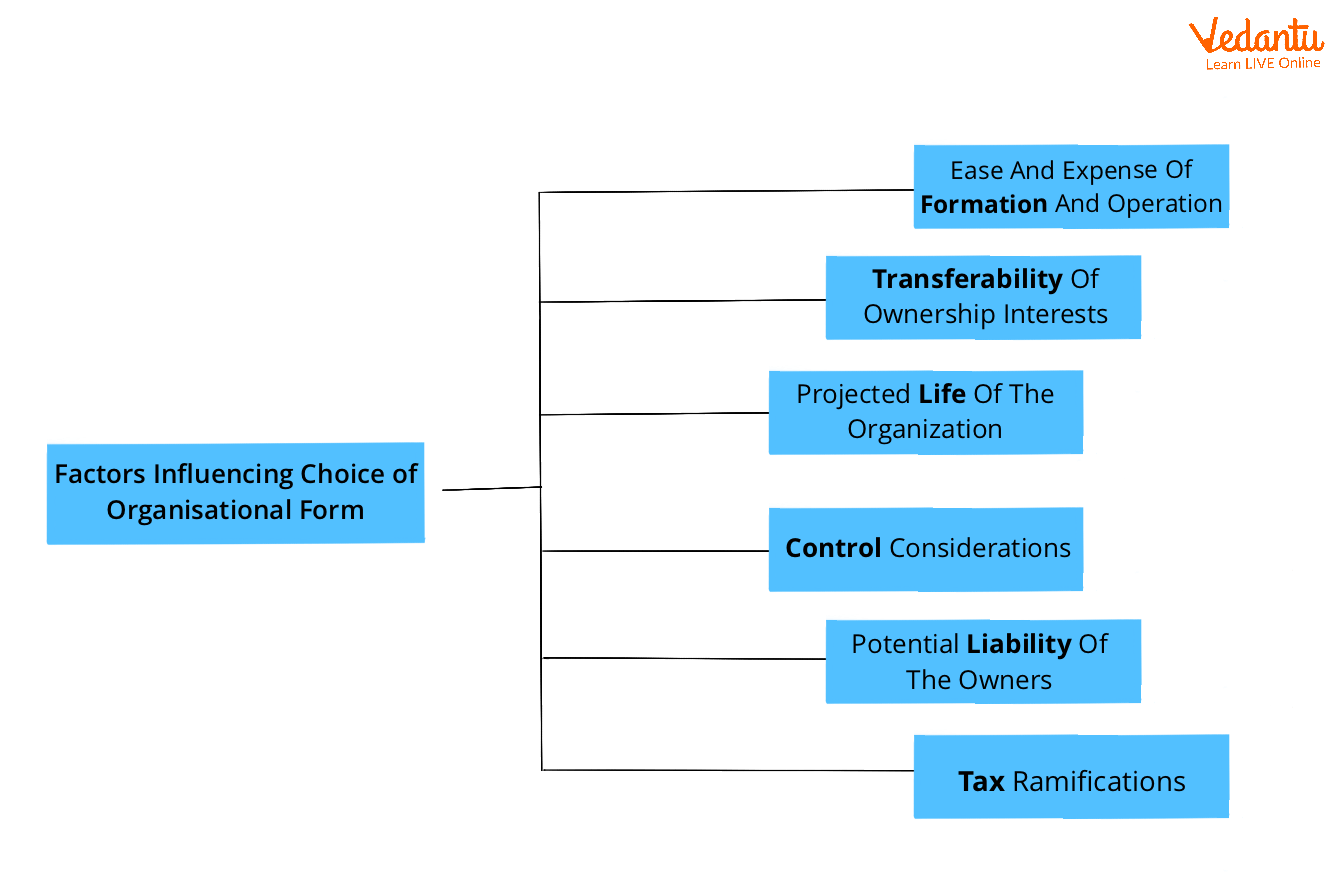
Factors Affecting the Choice of Form of Business
It is clear from analysing different forms of organisation that each kind has its own benefits and limitations. Therefore, it becomes crucial to keep a few fundamental factors in mind while selecting an acceptable form of organisation. Following are some factors that can help in deciding the form of organisation:
Size and Nature of the Business: Determining the nature and size are important factors. For instance, a manufacturing business producing large quantities of goods would be unsuitable for a sole proprietorship form.
Continuity of Business: How the life of the business is affected by its owner is another factor in determining the form of organisation. A sole proprietorship and partnership are affected by the death of its owners but that is not the case for other forms.
Statutory Obligations: A company has to deal with many statutory obligations, whereas other forms of organisation have relatively fewer statutory obligations.
Liability: Whether liability is a limited liability or unlimited, also affects the choice of form of business.
Capital Requirement: Forms of business such as a company have a relatively huge capital requirement, in comparison to other forms of organisation.
Dinesh Sarabhai runs a business producing food items, including sweets and namkeen. He lives in a joint family and has a massive proportion of inherited wealth. This business is run by all the 18 members of the family. His father, Akash is the eldest male family member, so he heads the business. Since Akash makes all of the major decisions, he is liable to all of its creditors. Dinesh’s son Ashok was born a few months ago and he is also a member of the business.
1. Identify the form of business Dinesh is working under and explain any two features of this form of business.
Ans : Dinesh Sarabhai is involved in a Hindu undivided family business. Following are the features of Hindu undivided family business:
Control and Management - Karta oversees and manages all the major operations of a Hindu undivided family business.
Membership by Birth - The way to become a member of the family business is through birth. A child is considered a member of the family business from the moment they are born. No agreement or consent is necessary for membership.
A business organisation is an entity created with the intention of conducting commercial transactions such as selling and buying. These operate in accordance with an established structure.
It seeks to establish positive working relationships between personnel, tasks, and other resources so that they can cooperate to accomplish shared objectives.
Forms of business organisation are different organisational structures that vary in terms of ownership and management.
Sole proprietorship, partnership, joint Hindu family business, cooperative society, and joint stock company are some major forms of business.

FAQs on Business Organisations: An Overview
1. Why do partnership firms voluntarily comply with this legal requirement if registration is optional?
The Indian Partnership Act, of 1932 governs partnerships in India, and according to this act, a partnership deed may be registered or unregistered. However, there are certain advantages to registering a partnership firm. Following are some of the benefits of registration of partnership firms:
A partner has the authority to file a lawsuit in court against the business or other partners. The partner of an unregistered firm is not granted this authority.
Partners get the authority to file a case in Court on behalf of the firm against third parties.
Registered firms also get the power to set off claims. An unregistered firm is not granted access to this authority.
2. In which type of partnership firm the liability of partners is limited?
All partners in a limited liability partnership (LLP) have limited liability. The liability of each partner in a limited liability partnership (LLP) is restricted to the amount they invested in the business. It means that in the event in which any partner is unable to repay, creditors cannot seize the personal assets or income of a partner. Unlike in a general partnership, changes in partners won't affect the LLP's ability to function. It has the legal authority to possess property in its own name and to enter into contracts.
3. What is the concept of mutual agency in a partnership?
A mutual agency is a contractual relationship between business partners that provides each partner power to act on the other's behalf. As a result of this agreement, each partner is now the company's agent and has the authority to take business decisions, such as concluding a legally binding contract with a third party.
Only partners engaging in the course of regular business operations and dealings can claim to have mutual agency. Each of the partners must be able to enter into business contracts and possess the necessary authority in order to establish this type of relationship.
Commerce Aspirant » Business Studies Class 11 MCQs » Forms of Business Organisation MCQ Class 11
Forms of Business Organisation MCQ Class 11
Forms of Business Organisation MCQ Class 11 Business Studies are covered in this Article. Forms of Business Organisation MCQs Test contains 74 questions. Answers to MCQs on Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies are available after clicking on the answer. These MCQ have been made for Class 11 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge.
Forms of Business Organisation MCQ Class 11 Business Studies
1.The most popular form of business organisation is: a) Sole proprietorship b) Company c) Partnership d) Joint Hindu Family business
Answer: A) Sole proprietorship
2. The form of business organisation which is specifically found in India is: a) Sole proprietorship b) NGO c) Cooperative society d) Joint Hindu Family business
Answer: D) Joint Hindu Family business
3. Cooperative Societies are compulsorily registered under which of the following Act: a) The Companies Act, 2013 b) The Cooperative Societies Act, 1922 c) The Indian Contract Act, 1872 d) The Cooperative Societies Act, 1912
Answer: D) The Cooperative Societies Act, 1912
4. How many types of Cooperative Societies are there: a) 5 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8
Answer: C) 6
5. Satish lost his job during the Covid-19 pandemic now he wants to start a business of his own in his hometown, Satish had limited finance available with him and he does not want many legal formalities to start a business, suggest Satish which forms of business organisation he should go for: a) Partnership b) Sole proprietorship c) Joint hindu family business d) Cooperative society
Answer: B) Sole proprietorship
6. Which of the following forms of business organisation has limited liability to his members: a) Partnership b) Company c) Sole proprietorship d) Joint Hindu Family business
Answer: B) Company
7. Minimum number of members required to form a public company is: a) 12 b) 1 c) 7 d) No limit
Answer: C) 7
8. As per The Companies Act, 2013, a public company is defined as: a) A company which is not a private company b) A company which has restrictions on the transferability of its shares c) A company which is prohibited from issuing shares to the public d) A company which has limited the number of its members upto 200
Answer: A) A company which is not a private company
9. Amit is performing a business activity in which he enjoys all the profits and bears all the risk alone, which type of organisation do you think Amit is running: a) Partnership b) Company c) Sole proprietorship d) Joint stock company
Answer: C) Sole proprietorship
10. A is running a retail shop of grocery items under the sole proprietorship form of business, A’s son wants him to expand the shop and deal in other types of goods as well but A does not agree with his son’s plan. Do you think that A’s son can execute his plan without A’s consent? a) Yes b) No c) Yes but after completing a few legal formalities d) None of these
Answer: B) No
11. Which of the following is a demerit of a partnership firm: a) Unfair distribution of profits b) Unlimited liability c) Limited managerial ability d) Dominance of one partner
Answer: B) Unlimited liability
12. Harish was a sole proprietor and was running a retail shop of gift items. Unfortunately, due to an accident Harish died, due to which his business also came to an end. Which feature of the sole proprietorship is applied here: a) No separate entity b) Lack of business continuity c) Sole risk bearer and profit recipient d) None of these
Answer: B) Lack of business continuity
13. Which type of organisation is not bound to show its accounts to anyone: a) Company b) Partnership c) Sole proprietorship d) Cooperative society
14. Sense of accomplishment is present in which of business organisation: a) Partnership b) Company c) Joint Hindu Family business d) Sole proprietorship
Answer: D) Sole proprietorship
15. Pooja is engaged in a business of clothes. She has to manage all the tasks related to the business alone and because of her weak marketing skills and knowledge her business is not making profits up to her expectations. Pooja’s business is a ________ form of business organisations: a) Joint Hindu Family Business b) Sole proprietorship c) Partnership d) Cooperative society
Answer: B) Sole Proprietorship
16. The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 defines Partnership as: a) The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all. b) The relation between persons who have agreed to carry on business activities together. c) The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all of them together. d) None of these
Answer: A) The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.
17. The partners of a partnership firm have unlimited liability, this means that: a) Partner’s personal assets cannot be used for repaying the firm’s debt b) Partner’s personal assets can be used to repay the firm’s debt/liability c) Partners will enjoy unlimited profits d) Profit is distributed according to the amount of their capital contribution.
Answer: B) Partners’s personal assets can be used to repay the firm’s debt/liability
18. A, B and C together made a donation of Rs.60,000 to an organization called Smart Healthcare Club. Can this contribution be called as partnership: a) Yes b) No c) Yes, if the amount contributed by A,B and C is equal d) None of these
19. Which of the following is not an advantage of a partnership firm: a) Secrecy b) Ease of Formation and Closure c) Limited liability of members d) More funds
Answer: C) Limited liability of members
20. Ram, Shyam and Kavi were in a partnership firm. Kavi wants his son to enter into the firm, Shyam agrees to this but Ram does not agree to Kavi’s intentions. Can Kavi bring his son to the partnership firm even if Ram does not agree a) Yes b) No c) Yes, but after completing certain legal formalities d) None of these
21. Possibility of conflicts is a limitation of which type of business organisation: a) Sole proprietorship b) Partnership c) Company d) Joint Hindu Family business
Answer: B) Partnership
22. How many types of partners are there: a) 5 b) 7 c) 6 d) 2
23. Partner who does not take part in the day to day activities of the business is a ________ partner: a) Active b) Dormant c) Secret d) None of these
Answer: B) Dormant
24. Partner who does not contribute to the capital neither takes part in the management of the firm but still he/she is liable to pay the firm’s debt because they are considered to be a partner of the firm in the eyes of a third party: a) Dormant b) Nominal c) Active d) Partner by estoppel
Answer: D) Partner by estoppel
25. On the basis of duration partnership are classified into: a) Partnership at will and particular partnership b) General partnership and limited partnership c) Long partnership and short partnership d) None of these
Answer: A) Partnership at will and particular partnership
26. In a limited partnership, the liability of at least one partner is _______ while of other partners is _______: a) Limited; unlimited b) Limited; general c) General; unlimited d) Unlimited; limited
Answer: D) Unlimited; limited
27. Document that is made during the formation of a partnership is: a) Partnership agreement b) Partnership deed c) Partnership registration d) Partnership document
Answer: B) Partnership deed
28. Which of the following is not mentioned in the partnership deed: a) Name of the firm b) Duration of business c) Method of solving disputes d) Amount of profit and losses
Answer: D) Amount of profit and losses
29. It is ________ for a partnership firm to get registered: a) Mandatory b) Optional c) Necessary d) None of these
Answer: B) Optional
30. Which of the following is a consequence of not registering the partnership firm a) A partner cannot file a suit against the partner or the firm b) A partner cannot file a suit against third parties c) Firm cannot file a suit against any of its partners d) All of these
Answer: D) All of these
31. A partnership firm can be registered under: a) The Partnership Act, 1932 b) The Indian Contract Act, 1872 c) The Partnership Act, 1994 d) The Partnership Act,1922
Answer: A) The Partnership Act, 1932
32. The Joint Hindu Family business is governed by which of the following laws: a) Hindu law, 2002 b) Hindu Undivided law, 1994 c) Hindu Family law, 1965 d) Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
Answer: D) Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
33. The person in the Joint Hindu Family business who carries on the business and is the head of the family is called the _______: a) Karta b) Director c) Sole proprietor d) Head of the business
Answer: A) Karta
34. All members who have equal ownership rights over the property of an ancestor are known as __________: a) Family members b) Coparceners c) Business Partners d) Heirs of the Business
Answer: B) Coparceners
35. The liability of the Karta is______, while that of the other members is _______: a) Limited; unlimited b) Unlimited; limited c) Limited; limited d) Unlimited; unlimited
Answer: B) Unlimited; limited
36. Can a minor be a member in a Joint Hindu Family business: a) Yes b) No c) Partially yes d) Yes, if all the members make an agreement of entering him/her
Answer: A) Yes
37. Which among these is a merit of a Joint Hindu Family business: a) Limited managerial skills b) Disputes among the members c) Effective control d) Limited resources
Answer: C) Effective Control
38. Which of these is a limitation of the Joint Hindu Family business: a) Unlimited liability of all the members b) Limited managerial skills c) Delay in decision making d) Lack of public confidence
Answer: B) Lack of managerial skills
39. Can a minor be entered into a partnership firm a) No b) Yes c) Yes, but by mutual consent of the partners and only to share profits d) None of these
Answer: C) Yes, but by mutual consent of the partners
40. ________ is an example of a cooperative society in India a) Amul b) Infosys c) Wipro d) All of these
Answer: A) Amul
41. Which of the organisation has a feature of separate legal entity from its members: a) Company b) Cooperative society c) Sole proprietorship d) Both A and B
Answer: D) Both A and B
42. The main motive of a cooperative society is: a) To earn profits b) To provide service to its members c) To inculcate a habit of savings among members d) To cooperate and work as a team with members
Answer: B) To provide service to its members
43. Why does the cooperative societies has a merit of government support: a) Because these societies exemplifies the idea of democracy b) Because these societies are formed for the welfare of the members c) Because these societies help in the development of the country d) Because government wants to increase the number of such societies
Answer: A) Because these societies exemplifies the idea of democracy
44. How does the Cooperative societies raise its capital: a) By issuing shares to its members b) By issuing shares to the public c) By getting donations d) None of these
Answer:A) By issuing shares to its members
45. Which of the following is a limitation of a Cooperative society: a) Unlimited resource b) Government Control c) Complexity in formation d) Delay in decision making
Answer:B) Government Control
46. ________is formed to protect the welfare of farmers: a) Producers cooperative society b) Consumers cooperative society c) Farmers cooperative society d) Marketing cooperative society
Answer: C) Farmers cooperative society
47. Gokuldham society is made by a group of people in which these members are able to construct/buy houses at reasonable cost. This is an example of: a) Cooperative credit society b) Marketing cooperative society c) Cooperative housing society d) Producer’s cooperative society
Answer: C) Cooperative housing society
48. The chief managing body of a company is: a) Board of Directors b) Shareholders c) Debenture holders d) All of these
Answer: A) Board of Directors
49. A private company is one which: a) Limits the number of members b) Restricts the transferability of shares c) Prohibits the public to subscribe to its securities d) All of these
50. Common seal of a company acts as its: a) Official signature of the company b) Signature of the Board of Directors c) Signature of the promoters d) Signature of the CEO
Answer: A) Official signature of the company
51. A company being an artificial person can: a) Enter into contracts b) Can sue the third party or its members c) Can be sued by its members or any other third party d) All of these
52. Which of these is a merit of a company: a) Quick decision making b) Lack of secrecy c) Professional management d) Ease of formation
Answer: C) Professional management
53. Priyansh formed a private company named ABC pvt ltd. After the death of Priyansh the company continued its operations because of its_______ feature: a) Common seal b) Limited liability c) Artificial person d) Perpetual succession
Answer: D) Perpetual succession
54. ________ are the real owners of a company: a) Shareholders b) Board of directors c) Promoters d) Employees
Answer: A) Shareholders
55. The process for forming a Joint Stock Company is: a) Complex b) Easy c) Easier than sole proprietorship d) Easier than Partnership
Answer: A) Complex
56. Reliance Industries is a _______ company: a) Private b) Public c) Subsidiary d) NGO
Answer: A) Private
57. A company named Tech pvt ltd wants to issue its shares to the general public. Can the company do so: a) Yes b) Yes, after taking permission from the government c) Yes but there will be a few restrictions d) No
Answer: D) No
58) The limit of maximum number of members in a public company is: a) 100 b) 200 c) 500 d) There is no limit of maximum number of members in a public company
Answer: D) There is no limit of maximum number of members in a public company
59) Minimum number of members required to form a private company is: a) 5 b) 3 c) 2 d) 4
Answer: C) 2
60) Aman wants to start a business which requires good managerial skills. Which type of business organisation do you think Aman should form: a) Sole proprietorship b) Company c) Joint Hindu Family business d) Cooperative society
61) Which of these types of partners does not participate in the management of the firm: a) Sleeping partner b) Partner by estoppel c) Partner by holding out d) All of these
62) A _________ partner contributes to the capital but does not participate in the management: a) Active b) Dormant c) Partner by estoppel d) Partner by holding out
63) Partners who do not share profit or losses: a) Nominal partner b) Partner by estoppel c) Partner by holding out d) All of these
64) _______ type of partner have unlimited liability: a) Active b) Sleeping c) Nominal d) All
Answer: D) All
65) Unlike sole proprietorship and partnership, a company has large financial resources and therefore there is a scope for________ of the company: a) Earning more profit b) Expansion c) More recruitment d) None of these
Answer: B) Expansion
66) The most inexpensive way of starting a business is: a) Sole proprietorship b) Partnership c) Company d) Cooperative societies
67) Ajay wants to start a business in which the initial cost required is the least. He should go for a: a) Company b) Cooperative society c) Sole Proprietorship d) Joint Hindu Family Business
68) Minimum number of directors required in a public company is____and in a private company is_____: a) 7; 2 b) 3; 2 c) 1; 1 d) 10; 5
Answer: B) 3; 2
69. Binod wants to start a business organisation but he is afraid that in case the assets of his business fall short of repaying the liabilities, his personal assets could also be used to repay the liabilities. Suggest Binod which form of business organisation he should start so that his fear comes to an end: a) Partnership b) Sole proprietorship c) Company d) Joint Hindu Family Business
Answer: C) Company
70) A company is created by ______ and only ______ can bring an end to its life: a) Law; law b) Promoters; law c) Shareholders; promoters d) Directors; promoters
Answer: A) Law; law
71) Is it compulsory for a private company to have index of members: a) Yes b) Partially yes c) Partially no d) No
72) The continuity of a company is stable because of: a) Separate legal entity b) Perpetual succession c) Common seal d) Artificial person
Answer: A) Separate legal entity
73) Minimum number of members required to form a cooperative society is: a) 5 b) 4 c) 10 d) 1
Answer: C) 10
74) In case of running a Joint Hindu Family business there must be at least _____ members in a family. a) 6 b) 4 c) 2 d) 8
Class 11 Business Studies MCQs
Business Studies MCQ – Term 1
Part A – Foundations of Business
- Evolution and Fundamentals of Business
- Forms of Business Organisations
- Public, Private and Global Enterprises
- Business Services
- Emerging Modes of Business
- Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics
Business Studies MCQ – Term 2
Part B – Finance and Trade
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship Development
- Internal Trade
- International Business
Useful Links
- CBSE Class 11 MCQs
- CBSE Class 11 Notes
- Economics Class 11 Notes
- Accountancy Class 11 Notes
- Economics Class 11 MCQs
Business Studies Class 11 MCQ
Unit Number 319, Vipul Trade Centre, Sohna Road, Gurgaon, Sector 49, Gurugram, Haryana-122028, India
- +91-9667714335
- [email protected]
Class 11 Notes
Class 11 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 11 MCQs
Class 12 Notes
- Economics Class 12 Notes
- Business Studies Class 12 Notes
- Accountancy Class 12 Notes
Class 12 MCQs
- Economics Class 12 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 12 MCQs
- Accountancy Class 12 MCQs
BUSINESS STUDIES FOR CLASS 11 CHAPTER 2 FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANISATIONS MCQS ALONG WITH ANSWERS
Free CBSE Business Studies Multiple Choice Questions for Class 11 along with answers, Chapter 2: Forms of Business Organisations. Business Studies MCQs for Class 11 chapter-wise with answers are prepared based on the current exam pattern. Students can tackle MCQs with answers to realise their spadework level.
1. The simplest form of business ownership is a _____.
(a) Proprietorship
(b) Partnership
(c) Corporation
(d) Cooperative
Answer: (a) Proprietorship
2. At least 10 adults, no maximum limit in case of ________.
(a) Cooperative Society
(b) Joint Hindu Family
(c) Partnership
(d) Company
Answer: (a) Cooperative Society
3. The main disadvantage of a general partnership is _____.
(a) The unlimited liability of the partners
(b) Disagreement amongst partners
(c) Shared management
(d) Difficulty of termination
Answer: (a) The unlimited liability of the partners
4. The major advantage of a franchise is _____.
(a) Training and management assistance
(b) Personal ownership
(c) Nationally recognised name
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
5. Profits do not have to be shared. This statement refers to _____.
(a) Company
(b) Sole proprietorship
(c) Joint Hindu family business
(d) Partnership
Answer: (b) Sole proprietorship
6. The form of business organisation that has the largest sales volume is the _____.
(a) Partnership
(b) Corporation
(c) Cooperative
(d) Multinational
Answer: (b) Corporation
7. Which of the following is probably the most important reason for incorporating?
(a) Limited liability of shareholders
(b) More money for investment
(c) Increased flexibility
(d) Shared management
Answer: (a) Limited liability of shareholders
8. The structure in which there is a separation of ownership and management as per law is called _____.
(b) All business organisations
(d) Sole proprietorship
Answer: (a) Company
9. Provision of residential accommodation to the members at reasonable rates is the objective of _____.
(a) Consumers cooperative
(b) Credit cooperative
(c) Housing cooperative
(d) Producers cooperative
Answer: (c) Housing cooperative
10. In a cooperative society, the principle followed is ______.
(a) One share, one vote
(b) One man, one vote
(c) No vote
(d) Multiple votes
Answer: (b) One man, one vote
11. Which of the following is an advantage of a sole proprietorship?
(a) Ease of starting a business
(b) Being your own boss
(c) Pride of ownership
12. In case of ___________, registration is compulsory.
(a) Sole Proprietorship
(c) Company
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Company
13. A partner whose association with the firm is unknown to the general public is called _____.
(a) Active partner
(b) Sleeping partner
(c) Nominal partner
(d) Secret partner
Answer: (d) Secret partner
14. The Karta in the Joint Hindu family business has _____.
(a) No liability for debts
(b) Unlimited liability
(c) Joint liability
(d) Limited liability
Answer: (b) Unlimited liability
15. A partner who is not actually involved in the partnership but lends his name for public relations purposes is a _____.
(a) Silent partner
(b) General partner
(d) Dominant partner
Answer: (c) Nominal partner
We trust that the offered Business Studies MCQs for Class 11 with respect to Chapter 2: Forms of Business Organisations will help you. Assuming you have any questions with respect to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies, Forms of Business Organisations MCQs, drop a remark underneath, and we will hit you up at the most punctual.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Studies Case Study 1. Read the hypothetical text given and answer the following questions: Manish, Rahul and Madhav live in the same locality. They used to meet and discuss their ideas. After discussing the recent fire breakout in their area, they decided to take fire insurance for their house or work area.
Case Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Business studies case study for forms of business organisation.
Forms of Business Organisation Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type. Question 1. Differentiate sole proprietorship and partnership form of business. l. Specific Act. It is governed by Partnership Act 1932. There is no specific Act. 2. Number of Member.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Organisation. Short Questions for NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 11 Chapter 2. 1. Compare the status of a minor in a Joint Hindu Family Business with that in a partnership firm. According to Indian Law, a person below 18 years of age is said to be a minor.
Business studies class 11 chapter 2Forms of Business organisationCase Study QuestionsCase Based questions Business studies class 11 chapter 2 Case Study Ques... CBSE Exam, class 10
Forms of Business Organisation is the second chapter of the Class 11 syllabus, and it teaches about different forms of Business. This chapter covers concepts such as various forms of business organisation, features, merits, and demerits, and factors determining the appropriate form of business organisation.
Students will be able to download the Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Notes in the PDF format absolutely free of cost. Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 - Topics Covered . Following are the topics that are covered in Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Organizations: Introduction. Sole proprietorship. Joint Hindu family ...
Question. Name the following: (a) A company having at least 7 members. (b) An enterprise owned by a single person. (c) A company in which the number of members cannot exceed 200. (d) Its main aim is to provide services to the members. (e) This form of business organisation is owned, financed, managed and controlled by a single person.
Free Question Bank for 11th Class Business Studies Forms Of Business Organisation Forms Of Business Organisation (Higher) Customer Care : 6267349244 ... done Forms Of Business Organisation (Higher) Total Questions - 18. question_answer1) ... Identify two limitations of partnership reflected in above case. (b) Identify two values that are ...
Providing a complete portal to the world of case study research, the Fifth Edition of Robert K. Yin′s bestselling text offers comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method as a valid research tool. The book offers a clear definition of the case study method as well as discussion of design and analysis techniques.
Question 2. Mention 2 necessary conditions that form a Joint Hindu Family business. Answer: At least 2 members in a family. Ancestral property to be inherited by him or her. Question 3. Which company has no restrictions on the transfer of shares? Answer: Public company has no restrictions on the transfer of shares.
Tick the appropriate answer. Question 1. The structure in which there is separation of ownership and management is called. (i) Sole proprietorship (ii) Partnership. (iii) Company (iv) All business organizations. Question 2. The Karta in Joint Hindu family business has: (i) Limited liability (ii) Unlimited liability.
identify different forms of business organisation; • explain features, merits and limitations of different forms of business organisations; • distinguish between various forms of organisations; and • discuss the factors determining choice of an appropriate form of business organisation. Chapter 2.indd 26 13-01-2021 09:40:59. Rationalised ...
Understand the concept of Case Studies & MCQs of Forms of Business Organization with CBSE Class 11 course curated by Bharat Anuragi on Unacademy. The Business Studies course is delivered in Hindi. ... Case Studies & MCQs of Forms of Business Organization. Aug 26, 2022. 54:26. EN ... Call us and we will answer all your questions about learning ...
It is considered the best reference study material for preparing the Business Studies chapter "Forms of Business Organisation" for exams. It highlights the important topics of the chapter that need to be studied well. Extra Questions for Practice. List different forms of business organisation. Write two merits and demerits of a business ...
Learn CBSE Business Studies Index Terms for Class 11, Chapter 2 Including Definitions and Meanings. 1. Sole Proprietorship - A sole proprietorship, otherwise called a sole tradership, individual business, or individual entrepreneurship or ownership, is a kind of a business enterprise owned and run by one individual and in which there is no ...
A business organisation is an entity created with the intention of conducting a business. These organisations are operated on legal systems that control contracts, exchanges of goods and services, ownership rights, and incorporation. Managing and planning various activities is a concern of the business organisation system.
These MCQ have been made for Class 11 students to help check the concept you have learnt from detailed classroom sessions and application of your knowledge. Forms of Business Organisation MCQ Class 11 Business Studies. 1.The most popular form of business organisation is: a) Sole proprietorship. b) Company.
In addition, the form of business organisation cannot be changed easily. Thus, due care should be taken to select the correct form of organisation. Factors determining the choice of form of organisation: Nature of business: The type of business one wants to do is the most important factor in determining the form of business. If one wants to ...
Free CBSE Business Studies Multiple Choice Questions for Class 11 along with answers, Chapter 2: Forms of Business Organisations. Business Studies MCQs for Class 11 chapter-wise with answers are prepared based on the current exam pattern. Students can tackle MCQs with answers to realise their spadework level. 1.
In this session educator girish agrawal will cover case studies on forms of business organisation. Understand the concept of Case Studies of Forms of Business Organisation with CBSE Class 11 course curated by Girish Agrawal on Unacademy. The Business Studies course is delivered in Hindi.
Girish Agrawal. In this course educator girish agrawal will cover case studies on forms of business organisation. Understand the concept of Case Studies on Forms of Business Organisation with CBSE Class 11 course curated by Girish Agrawal on Unacademy. The Business Studies course is delivered in Hindi.