CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Development
Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should practise these solved case studies to get more marks in examinations.
Chapter 1 Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science
1. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Once it is realised that even though the level of income is important, yet it is an inadequate measure of the level of development, we begin to think of other criterion. There could be a long list of such criterion but then it would not be so useful. What we need is a small number of the most important things. Health and education indicators, such as the ones we used in comparison of Kerala and Haryana, are among them. Over the past decade or so, health and education indicators have come to be widely used along with income as a measure of development. For instance, Human Development Report published by UNDP compares countries based on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capita income. It would be interesting to look at certain relevant data regarding India and its neighbours from Human Development Report 2019.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) The Human Development Report compares countries on the basis of: (a) The educational levels of the people (b) Health status of the people (c) Per capita income of the people (d) All the above factors
(ii) Which one of the following criteria is the basis to measure the development of a country according to UNDP? (a) Per capita income (b) Educational levels of the people (c) Health status of the people (d) All the above
(iii) HDI stands for: (a) Heavy Developed Industry (b) Human Development Index (c) Heavy Developed Infrastructure (d) Heavy Industries Development
(iv) Which organisation publishes the Human Development Report: (a) WHO (b) UNDP (c) WTO (d) IMF
2. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of a country? Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country. However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such an useful measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
(i) What is the most important attribute while comparing countries? (a) Their population (b) Their political status (c) Their income (d) None of the above
(ii) Per capita income is : (a) Income per person (b) Income per family (c) Income per earning person (d) Income per month
(iii) The average income is also called: (a) Per capita profit (b) Per capita income (c) Limited income (d) None of the above
(iv) In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, which criterion is used in Classifying countries? (a) Total income (b) Gross income (c) per capita income (d) Net income
Data analysis questions:
1. Read the given data and find out which country has most equitable distribution of income.
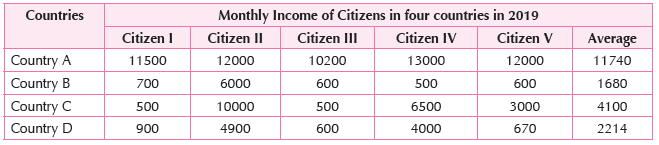
(a) Country A (b) Country B (c) Country C (d) Country D
2. Read the given data and find out which country has most equitable distribution of income.
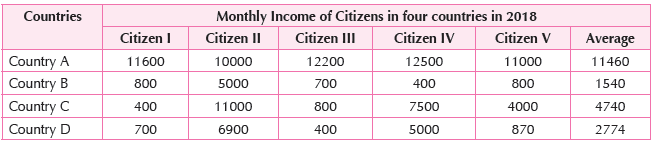
3. Read the given data and find out which country has most equitable distribution of income.
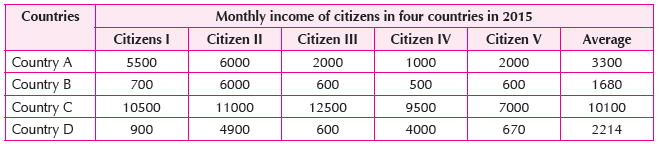
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Study the picture and answer the question that follows:

What could be the development goal for the shown area? Ans. The developmental goal for the people living in a slum will be provision of sturdy but affordable houses and other living conditions including food, water and health facilities.
Question. What may be a developmental goal of farmers who depend only on rain for growing crops ? Ans . The development goal of a farmer who is only dependent on rain for growing crop, would be a good and suffcient monsoon season so that his crops get the required irrigation and he can benefit from the good produce.
Question. Study the table and answer the questions given below : Some comparative data on Haryana, Kerala and Bihar
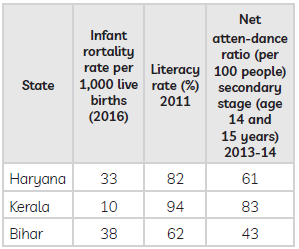
Sources : Economic Survey, 2017-18 Vol. 2, Government of India; National Sample Survey Organisation Question : In comparison to Kerala, which state has the highest infant mortality rate ? Ans. Bihar
Question. Study the statistics in the table and Answer the question that follows:
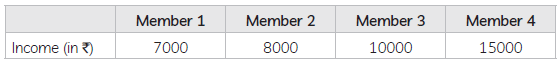
Ans . 10,000
Question. Define the term ‘per capita income’. Ans. Per capita income is calculated as the average income of a citizen of a country. Per capita Income = total income of a country/ total population
Question. Who wrote ‘Small is Beautiful’? Ans. Schumacher wrote ‘Small is Beautiful’.
Question. Define the term ‘literacy rate’. Ans. Literacy rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7-and-above age group in a country. The higher the literacy rate, the more the development in the country.
Question. How can two people have different developmental goals ? Ans . Different people have different developmental goals because people come from different backgrounds and have different dreams and aspirations.
Question. What may be a developmental goal of the urban unemployed youth? Ans. The development goal of an urban unemployed youth would be to find a good job and earn a decent wage with that work. He/she will aspire to maintain a good standard of living.
Question. Define IMR. Ans. The number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year, is called infant mortality rate or IMR.
Question. Study the table and answer the question given below:
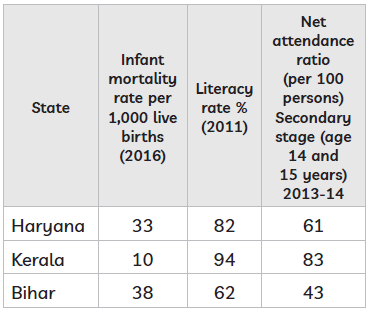
Question: Which State has the lowest net attendance ratio at the secondary stage? Ans. Bihar
Question. Mention the formula to calculate the BMI (Body Mass Index). Ans. BMI- (BODY MASS INDEX) Weight of person in kg and height in metres is taken. Divide the weight by the square of the height.
Question. The total number of children of age group 14 and 15 years attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group is referred as …………………… . Ans. Net Attendance Ratio.
Question. What may be one of the developmental goals of a girl who belongs to a rich urban family? Ans. The developmental goals of a girl who belongs to a rich urban family may be getting the same freedom as her brother, pursue higher studies and a high standard of living.
Question. Based on the data given in the following table, calculate the average income for both countries: Which country has more equitable distribution of income?
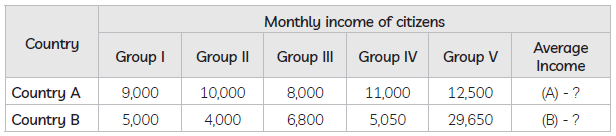
Ans. (A) 10,100 (B) 10,100 Even though, average income of both countries is equal, Country A possesses a more equitable distribution of income and less economic disparities accordingly.
Question. What criteria does UNDP compare to measure the human development index? Ans. UNDP compares countries based on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capita income.
Question. Study the picture given above. Identify an appropriate developmental goal for the characters.
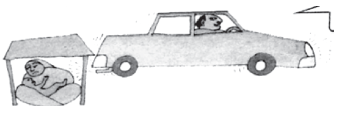
Ans. An appropriate developmental goal for the poor lady would be to have a stable job and affordable house for her small family. For the rich man, his developmental goal can be more opportunities for profit and investment from foreign countries, more luxurious life or even a bigger car.
Question. What may be one of the developmental goals of a rich farmer? Ans. The developmental goals of a rich farmer might be gaining high profits on the produce or availability of cheap labour to work in the farm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. “Money in your pocket cannot buy all the goods and services that you may need to live well.” Justify the statement with example. Ans. It is true because income by itself is not a completely adequate indicator of material goods and services that citizens are able to use. For example, money cannot buy us a pollution-free environment or ensure that we would get unadulterated medicines. Money may also not be able to protect us from infectious diseases, unless the whole of our society takes preventive steps. 46. Explain the three components of Human Development Index. Ans. Components of HDI (1) Life expectancy (2) Literacy rate (3). Per capita income These three to be explained.
Question. Suggest any three ways to improve public facilities in India. Ans. Public facilities are the base for any kind of development. Three ways to improve public facilities in India are: (1) One of the most essential facility is education. Easily accessible and affordable education must be provided to all the children of the country, irrespective of their caste, class or gender. More government and public schools should be opened, tuition fee should be reduced and education must be made free up to elementary level. (2) Public Distribution System should be reformed to include people from the remotest of areas. Corruption should be checked and the food grains provided should be rigorously monitored for quality. (3) Health facilities should be made free to children below 10 years of age and senior citizens, disadvantaged classes etc. (4) Transport facility must be available to everyone, easily, even in the remotest of areas. The availability of transport facility makes commute affordable and hence brings down the cost of accessing regular commodities.
Question. How do different people have different developmental goals? Explain with examples. OR “What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.” Analyse the statement. Ans. Different people have different developmental goals because: (1) People come from different economic and social backgrounds and their priorities and aspirations vary. (2) People set their goals according to the changing circumstances and the prevailing situation. For example, a rich family would always want to earn more luxuries, but if they suddenly suffer a huge loss, their developmental goals will change to first securing a stable source of income, ensuring education for their children, etc.
Question. What is Per Capita Income? Can Per-Capita Income be considered real income of a citizen? Ans. To calculate income of every citizen in a country is difficult therefore an average income is calculated by dividing the total income of the country by its total population. This average income is also known as per capita income or average income of every citizen in a country. Per capita income however is not the real income of a citizen but an estimate.Per capita income doesn’t prove to be a reliable unit to measure whether or not a citizen is developing in a country.
Question. Beside income, what can be the other attributes to compare development? Ans. Income is not only the criterion but it is one of the important indicators of economic develop-ment. Some of the others attributes can be: Infant Morality Rate: It is an indicator of the availability of doctors and medical facilities for pre, post and natal care in the region. Low infant mortality rate indicates good medical facilities and all round development in the society. Literacy Rate: This indicates the availablity and accessibility of educational institutions in rhe region to all age groups and genders. It indicates the mentality of the people, whether there’re socially developed and updated or not. Low literacy rate shows less development. Life expectancy: This indicates the availability of health facilities throughout one’s life, whether the region has sanitized, safe surroundings to sustain. Low life expectancy means that the region lacks items for a healthy living.
Question. Suggest and explain any three ways to reduce the use of petrol. Ans. To save petrol, the following steps can be taken: (1) Using public transports: People should avoid using personal vehicles unless the distance is a lot and public transport is not available. Using public transport can save a lot of petrol. (2) Use of alternative clean energy sources: Cleaner and easily available sources of energy like natural gas can also help save petrol. (3) Car pooling: Walking short distances for groceries and other work instead of pulling a two/four-wheeler everywhere should be encouraged. If the destination is the same, carpooling can be used to save fuel. (4) Electric vehicles: People should consider switching to electric vehicles to save fuels. Electric vehicles are safe and cause almost no pollution. They can be charged at charging points which can be conveniently installed for the purpose
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What should India do or achieve to become a developed country? Explain. Ans. India should focus on the following points to become a developed country: (1) It should reduce the gap between rich and the poor. (2) It should make provision for accommodating all its existing able people in jobs to get a suitable job. (3) Primary health and education must access to all even in the remote parts of the country. (4) Government should make provisions for making the country self-reliant by providing skill education to all. (5) Government should encourage smallscale and cottage industries by giving cheaper credits and training to those who are willing to be the entrepreneurs.
Question. What is human development? Explan its indicators. Ans. Human development can be seen as a ‘human-centred’ approach towards development which focuses on measurement of values like satisfaction, literacy, harmony, peace, freedom and happiness of people. It is concerned with the people and their wellbeing and fulfillment of their needs, choice and aspirations. Human development is measured by various indicators: (1) Per Capita Income – World Bank measures human development by measuring Pthe per capita income or average income per citizen of a country. High per capita vouches for better capacity of citizens to avail facilities. Low per capita signals poverty and less development. (2) Literacy rate – UNDP measures literacy rate to calculate whether a country is developed or not. Higher literacy rate means easy availability of educational facilities which signals better development. (3) Infant mortality rate – Less infants dying due to abundance of medicinal and natal and post-natal facilities available easily to all citizens signal that the government of the country has provided adequate health facilities which translate to development. (4) Net attendance ratio – This is also an important indicator. More attendance at school means greater literacy and better development.
Question. What is national development? What are the aspects covered under the National development? Ans. National development refers to the improvement of the life standards of a country’s citizens through actualization of their different developmental goals: provision of a healthy, free, safe and dignified life to every citizen without any discrimination. (1) Under national development, the government decides what would be a fair and just for all citizens. (2) Under National development,only those programmes and policies are implemented which (3) would benefit maximum number of people.. (4) Under national development, national interests are prioritised over self interests. (5) National development also entails inclusivity of citizens in decision making, provision of compulsory health and educational facilities, affordable housing and food for every citizen. (6) National development also entails invoking feelings of belongingness, national unity among all communities.
Question. ‘Per capita income is not considered a true measure of development.’ Comment. Ans . When the total income of a country is divided by its total population, it is called per capita income or average income. It is not considered a true measure of development because of the following reasons: (1) It does not tell us how this income is distributed as population is a variable component. (2) Life expectancy and infant mortality rate can be used as other criteria for measuring development. (3) Literacy rate and health status of people in the country can be the other criteria for measuring development. (4) Corruption free society, gender equality, pollution free environment, investment in the health and education sector etc. can be the other indicators of measuring development.
Question. Suggest some of the developmental goals for your locality or place you are residing? Ans. The developmental goals for my locality can be as follows: (1) There should be a primary health centre in the locality. (2) There should be a school catering quality education up to higher secondary level for the children living nearby. (3) Government should construct pucca houses for people to be given them on subsidized cost. (4) All weather roads in the locality must be constructed and well maintained by the authority responsible for it. (5) There should be a provision of potable drinking water in each house in the locality.

Related Posts

Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Database management system class 10 information technology important questions.

How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science Important Questions

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Social Science Economics Development. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Development.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
Case Study 1:
Development and growth are often used interchangeably, however, they represent distinct facets of progress. Growth primarily pertains to quantitative expansion, such as an augmentation in GDP, population, or production. It is quantifiable and readily observable. Conversely, development encompasses a broader range of factors. It encompasses enhancements in living standards, education, healthcare, and overall well-being. Development places emphasis on the quality of growth rather than mere quantity. It is possible for a nation to experience growth without truly developing, resulting in disparities and inequalities. Consequently, the pursuit of sustainable development is paramount, ensuring not only economic growth but also social progress, equity, and environmental sustainability. Striking a balance between growth and development is the ultimate challenge for societies striving for comprehensive advancement.
Q1) Is development only calculated in monetary terms? Mark 2
Answer Quality of life also depends on non materialistic thing like quality of air, peaceful society , healthy environment and law and order condition which cannot be majorly buy by money. Development is majorly a subjective term and hence precise by different people differently.
Q2) Give an example where a situation is development for one but not for other? Mark 1
Answer An industrialist seek construction of dam for more electricity and more production however people who will required to migrate due to dam may not seek it as a development process in their life.
Q3) What are the two fundamental principle of development? Mark 1
Answer First different persons can have different developmental goals and second, what may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
Case Study 2:
A developed country is a highly industrial growth oriented country where quality of life is high, presence of developed economy and advanced technology. While the developing countries are those that are in either pre industrialization or in industrialization process. These economies are mostly relies in agrarian form of economy and there per capita income is generally less than the others. Another aspect of the developed countries are their highly dominating tertiary and Quaternary Sector. While tertiary sector provides services such as entertainment, finance and retailers quaternary sector comprises of knowledge based activities like of Information technology , research and development as well as areas of consulting services etc. There is no all-agreed definition of a developed country.
Agencies such as the United Nations, the World Bank, the World Trade Organization, and the World Economic Forum use their indicators to club developed and developing countries. For example, the UN classifies countries into low, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high-income countries.
This classification is based on an individual country’s gross national income (GNI) per capita. Low –Income Economy: GNI per capita of up to $1,085 Lower Middle-income: GNI per capita up to $4,255 Upper-Middle-income: GNI per capita $13,205 High-Income economy: GNI per capita above $13,205.
Q1) What do you understand by the term per capita income? Mark 1
Answer Average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income
Q2) What is the most important attribute to compare development of the countries? Mark 1
Answer Income is considered as the most important attribute while comparing development of the country.
Q3) Differentiate between development and growth? Mark 2
Answer Development refers to a broader, multidimensional improvement in living standards, education, healthcare, and overall well-being. Growth is primarily quantitative and relates to an increase in factors like GDP, population, or production. While growth is measurable, development encompasses qualitative aspects and focuses on the quality of life.
Case Study 3:
The Human Development Report (HDR) by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a vital tool for assessing a nation’s progress beyond mere economic growth. In the context of India, the HDR provides a nuanced perspective. While India has made significant economic strides, socio-economic disparities persist. The report highlights challenges in health, education, and income inequality, reflecting the complexity of India’s development journey. It underscores the importance of inclusive policies to ensure that the nation’s remarkable growth benefits all citizens. As India continues its development path, the HDR serves as a crucial benchmark, guiding efforts towards a more equitable and prosperous future. A student’s BMI could be within the normal range or less than that (underweight) or more (obesity). For example, if a girl student is 14 years and 8 month old and the BMI is 15.2, then she is undernourished. Similarly, if the BMI of a boy aged 15 years and 6 months is 28, then he is overweight.
Q1) What do you understand by Body mass index? Mark 1
Answer BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a numerical measure that assesses a person’s body weight in relation to their height. It is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. BMI provides a rough estimate of whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese, serving as a basic indicator of overall body composition and health.
Q2) What is ranking of India in human development index? Mark 1
Answer As of last knowledge update in September 2021, India’s ranking on the Human Development Index (HDI) was 131 out of 189 countries.
Q3) On what factors human development report based on. Mark 2
The Human Development Report (HDR) is based on several key factors and indicators that collectively assess the overall well-being and development of a country or region. These factors include:
Life Expectancy at Birth
Educational Attainment:
Per Capita Income
Case Study 4:
The Public Distribution System (PDS) in India is an essential social welfare program with the primary objective of guaranteeing food security for a significant number of vulnerable citizens. Since its establishment in 1947, the PDS has undergone significant developments and now plays a pivotal role in the distribution of vital commodities such as rice, wheat, and sugar to those in dire need. This extensive network of fair price shops operates in both rural and urban areas, effectively bridging the gap between surplus production and food scarcity.
Despite the numerous challenges it faces, the PDS has proven to be a lifeline for low-income households, particularly during times of crisis. It serves to stabilize food prices and ensures that essential items are accessible to the needy at affordable rates. However, there are concerns regarding leakages and inefficiencies within the system that necessitate immediate attention. Continuous efforts to enhance the effectiveness of the PDS and reduce corruption are of utmost importance for its success in combating hunger and malnutrition in India.
Q1) Why Kerala has low infant mortality rate? Mark 1
Answer Kerala has a low Infant Mortality Rate because it has adequate provision of basic health and educational facilities. Similarly, in some states, the Public Distribution System (PDS) functions well. Health and nutritional status of people of such states is certainly likely to be better.
Q2) Money in your pocket cannot buy all the goods and services that you may need to live well. Explain this statement Mark 2
Answer Normally, money cannot buy us a pollution-free environment or ensure that you get unadulterated medicines, unless you can afford to shift to a community that already has all these things. Money may also not be able to protect us from infectious diseases, unless the whole of your community takes preventive steps
Q3) What do you understand by infant mortality rate? Mark 1
Answer Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) is a crucial demographic indicator that measures the number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births in a given population and time period
Case Study 5:
Despite being the first state in India to report COVID cases, Kerala was well-prepared due to its past experience in effectively managing the Nipah outbreak and Kerala floods. The state was able to initiate the necessary measures for containment because of its prior experience in mobilizing community-based groups, involving local self-government in decentralized planning, and participating in containment and relief measures, as well as having a well-equipped health system and infrastructure. The measures taken to “flatten the curve” in Kerala, which were unique to the state, and the factors that contributed to their success are described in detail using the framework developed after the Nipah outbreak containment experience. These insights are being shared with the hope that other regions can use them to replicate successful components.
Kerala’s remarkable success in managing the COVID-19 pandemic is a testament to its well-established infrastructure for social and human development. This foundation includes an efficient public healthcare delivery system that positions the state far ahead of the rest of India in numerous vital indicators.
Q1) Explain the term infant mortality rate , literacy rate and net attendance ratio? Mark 2
Answer Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR) indicates the number of children that die before the age of one yearas a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year.
Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7-and-above age group.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 14 and 15 years attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group
Q2) Why kerala health infrastructure stand strong in times of covid? Mark 2
Answer Kerala’s resilient health infrastructure during COVID-19 is a result of long-term investments, a high doctor-to-patient ratio, well-equipped healthcare facilities, and a robust public healthcare system. Effective governance, a focus on education, community engagement, and transparent data reporting further bolstered its ability to respond effectively to the pandemic.
Also See : Gender, Religion and Caste Chapter Case Study Questions
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
My view to make exams stress free essay in 400 words, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 1 jib jogot, 700 word essay on a nation can develop only if all are educated, dav class 6 sst solution chapter 2 representation of the earth.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development
Development Class 10 Questions and Answers Provided helps you to answer complex Questions too easily. You can use them while preparing for board exams and all of them are given by subject experts. Reading NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development familiarizes you with the kind of questions appearing in the board exams. Students are advised to read these solutions on a regular basis to score well.
Development Class 10 Questions and Answers Economics Chapter 1
Make your learning experience enjoyable by preparing from the quick links available on this page. Use the Class 10 SST Economics Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions and get to know different concepts involved. All the Solutions are covered as per the latest syllabus guidelines. Knowing the NCERT Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Questions and Answers helps students to attempt the exam with confidence.
Development NCERT Intext Questions and Answers
Let’s Work These Out (NCERT Textbook page 6)
Question 1. Why do different persons have different notions of development? Which of the following explanations is more important and why? (a) Because people are different. (b) Because life situations of persons are different. Answer: Explanation (b) is more important than explanation (a) because life situations affect the way an individual thinks about development. What may be development for one person may not be development for the other. It all depends on the situations in which he lives.
Question 2. Do the following two statements mean the same? Justify your answer. (a) People have different developmental goals. (b) People have conflicting developmental goals. Answer: No, the above two statements do not mean the same. (a) When we say that people have different developmental goals it means they seek different things. They seek things that are most important for them, i.e. that which can fulfil their aspirations or desires.
(b) At times, two persons may seek things which are conflicting. For example, a girl expects as much freedom and opportunity as her brother, and that he also shares in the household work. Her brother may not like this.
Percentage Off Calculator … give accurate answers, this discount calculator and percentage off calculator is sure to save you a lot of trouble and time.
Question 3. Give some examples where factors other than income are important aspects of our lives. Answer:
- Sense of security
- Equal treatment
- Respect of others
- Good working atmosphere
- Protection from infectious diseases.
If one gets a job in a far off place, before accepting it one would try to consider many factors, apart from income such as facilities for one’s family, working atmosphere or opportunity to learn, etc.
Question 4. Explain some of the important ideas of the above section in your own words. Answer: For self-attempt.
Let’s Work These Out (NCERT Textbook page 7)
Discuss the following situations:
Question 1. Look at the picture on the right given on Textbook Page 7. What should be the developmental goals for such an area? Answer: From the picture, it seems that it is in the outskirt of the town. There must be the connectivity of roads, availability of water, electricity, schools, market places and a police check post for the safety of public.
Question 2. Read this newspaper report and answer the question that follow: A vessel dumped 500 tonnes of liquid toxic wastes into open-air dumps in a city and in the surrounding sea. This happened in a city called Abidjan in Ivory Coast, a country in Africa. The fumes from the highly toxic waste caused nausea, skin rashes, fainting, diarrhoea, etc. After a month seven, persons were dead, twenty in hospital and twenty six thousand treated for symptoms of poisoning. A multinational company dealing in petroleum and metals had contracted a local company of the Ivory Coast to dispose the toxic waste from its ship. (i) Who are the people who benefitted and who did not? (ii) What should be the developmental goal for this country? Answer: (i) Those who were in position to avail good facilities got benefitted and the people of lower income group did not get much benefit. (ii) The developmental goal for this country should be health facilities, good environment, establish¬ment of factories for generating employment and the facilities of home for the homeless.
Question 3. What can be some of the developmental goals for your village, town or locality? Answer: The developmental goals for village, town or locality should be:
- Road and rail connectivity
- Good transportation system
- Sanitation facilities
- Pure and safe drinking water
- Hospitals, etc.
Let’s Work These Out (NCERT Textbook page 9)
Question 1. Give three examples where an average is used for comparing situations. Answer: An average is used for comparing
- income of people of a country
- health of the students of a class
- talent of the students of a class.
Question 2. Why do you think average income is an important criterion for development? Explain. Answer: Income i.e. money enables us to buy things of our needs including the basic necessities of life. We can fulfil our desires and be able to do what we wish for only with the help of our income. More income means more of all things that we need. Whatever we like and should have, we will be able to get with greater income. If the average income of a country is on a higher side, it will definitely stand ahead on development index. Hence, average income can be an important criterion for development.
Question 3. Besides size of per capita income, what other property of income is important in comparing two or more societies? Answer: Besides size of per capita income, other important property of income is equality in people’s purchasing power. Purchasing power parity shows the ability of people to purchase items of their requirement which are taken for comparison.
Question 4. Suppose records show that the average income in a country has been increasing over a period of time. From this, can we conclude that all sections of the economy have become better? Illustrate your answer with an example. Answer: Increase in the average income in a country cannot be a guarantee of overall progress of the economy. The data of Maharashtra and Kerala show that there are other factors which also need to be analysed before arriving at a conclusion. These factors include infant mortality rate, literacy rate, proper health facilities, etc.
Question 5. From the text, find out the per capita income level of low-income countries as per World Development Reports. Answer:
- Sri Lanka – $ 4390
- India – $ 3139
- Pakistan – $ 2225
Question 6. Write a paragraph on your notion of what should India do, or achieve, to become a developed country. Answer: India is a vast country with a large population. Although it has been doing well since its Independence, it needs much more to achieve to become a developed country. The country still lags behind on several parameters of human development such as life expectancy, infant mortality, and literacy rate. The absolute number of infants who die before completing one year is very high. This shows that there is no proper facilities for healthcare, drinking water, sanitation and nutrition in our country. A great number of our children are victims of malnutrition. In rural India, the situation is worse. Hence, India needs to develop facilities to improve on these parameters, to become a developed country.
Let’s Work These Out (NCERT Textbook page 12)
Question 1. Look at data in Table 1.3 and 1.4 on Textbook Page 10. Is Maharashtra ahead of Bihar in literacy rate, etc. as it is in terms of per capita income? Answer: Yes; Maharashtra is far ahead of Bihar in both these parameters. Literacy rate in Maharashtra is 82% while it is only 62% in Bihar as per the census of 2011. In terms of per capita income, Maharashtra is again far ahead of Bihar. It is ₹ 1,07,670 in Maharashtra while ₹ 28, 772 in Bihar.
Question 2. Think of other examples where collective provision of goods and services is cheaper than individual provision. Answer: In factories/industries, in manufacturing, in agriculture etc. we find collective provision of goods and services cheaper than individual provision.
Question 3. Does availability of good health and educational facilities depend only on amount of money spent by the government on these facilities? What other factors could be relevant? Answer: No. It does not depend only on amount of money spent. Although it is a major factor, other factors also play an important role in it. These factors include availability of required number of doctors and quality of medicines in case of health facilities. In education, a good number of qualified and dedicated teachers, well-constructed school buildings, etc. are important.
Question 4. In Tamil Nadu, 75 percent of the people living in rural areas use a ration shop, whereas in Jharkhand only 8 percent of rural people do so. Where would people be better off and why? Answer: People would be better off in Tamil Nadu because in this state the Public Distribution System (PDS) functions well which enables more and more people to use ration shops to get things like foodgrains, sugar, kerosene oil etc. at reasonable rate. Needless to say that these things are basic necessities of human beings. Their easy availability ensures better health and nutritional status of people in that state (Tamil Nadu).
Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1. Development of a country can generally be determined by (i) its per capita income (ii) its average literacy level (iii) health status of its people (iv) all the above. Answer: (iv) all the above
Question 2. Which of the following neighbouring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India? (i) Bangladesh (ii) Sri Lanka (iii) Nepal (iv) Pakistan Answer: (ii) Sri Lanka
Question 3. Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is ₹ 5000. If the income of three families is ₹ 4000, ₹ 7000 and ₹ 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family? (i) ₹ 7500 (ii) ₹ 3000 (iii) ₹ 2000 (iv) ₹ 6000 Answer: (iv) ₹ 6000
Question 4. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What . are the limitations of this criterion, if any? Answer: Per capita income is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries. But there are limitations of this criterion-
- It covers only the economic aspect and thus ignores many other factors which affect the development such as literacy rate, life expectancy, healthcare facilities, environment, etc.
- It does not tell us about how this average income is distributed among the people in the individual countries.
Question 5. In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank? Answer: The World Bank uses per capita income as the most important criterion for development. If we go into the depth, we will find that the level of income is not an adequate measure of the level of development. UNDP compares countries based on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capita income. Thus, UNDP gives much importance to those factors which help in improving the quality of life and in making the citizens more capable and productive.
Question 6. Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate with your own examples related to development. Answer: Whenever we need to analyse a big sample size, we find it difficult to analyse individual data. Averages are used in such cases. But averages have some limitations
- Averages do not give the true picture. For example, the per capita income does not show the distribution of income among people.
- Averages do not show the percentage of the poor in the population. They also hide disparities.
Question 7. Kerala, with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss. Answer: Although the per capita income of Maharashtra is more than that of Kerala, the state (Maharashtra) shows a very high child mortality rate compared to Kerala. Literacy rate and the net attendance ratio of children in age group 14-15 are higher in Kerala, as compared to Maharashtra. Bihar is at the bottom which reveals its poor record on Human Development Index.
Question 8. Find out the present sources of energy that are used by the people in India. What could be the other possibilities fifty years from now? Answer: The present sources of energy that are used by the people in India are firewood, coal, crude oil, dung cake, etc. Solar power could be the other possibilities fifty years from now. It can reduce our dependency on the fossil fuel and can give us security against energy crisis in the future. India, being a tropical country has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy and therefore it should be encouraged.
Question 9. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development? Answer: Development i.e. progress does not only mean securing a better present, but it also means securing a better future for the coming generations. Sustainable development means development should take place without undue draining of resources, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations. Thus, the issue of sustainability is important for development because if natural resources are not sustained, then development will be hindered and will stop after some time. This also compels us to think that we should minimise our needs as far as possible so that future generations may not face crisis of anything.
Question 10. “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person”. How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss. Answer: This famous quote from Mahatma Gandhi shows his concern about resource conservation. What he meant to say is that our earth has no dearth of resources but they should be used judiciously and not exploited over a few years. Our greedy attitude would push our future generations into perils. So, we need to think about and stop overusing resources. We should control our greed and take as little from the nature as is really essential for us. Such an attitude will not only save us from dangers but also the generations to come.
Question 11. List a few examples of environmental degradation that you may have observed around you. Answer: We find lack of greenery around us. The air quality is also degrading very fast. It seems as if we are living in gas chambers. Going outside in such an environment is just like inviting several health problems. Children and old people are the worst affected. The condition of the river that flows through the city is not better than a filthy drain. It has become a dumping ground for the city people. These are a few examples of environmental degradation. It is a matter of serious concern for all of us. We must think collectively and take some measures to curb this situation.
Question 12. For each of the items given in Table 1.6 (Textbook Page 13), find out which country is at the top and which is at the bottom. Answer: Following are the top and bottom-ranked countries on various parameters
Question 13. The following table shows the proportion of undernourished adults in India. It is based on a survey of various states for the year 2001. Look at the table and answer the following questions.
(i) Compare the nutritional level of people in Kerala and Madhya Pradesh. (ii) Can you guess why around 40 percent of people in the country are undernourished even though it is argued that there is enough food in the country? Describe in your own words. Answer: (i) People of Kerala get better nutrition than the people of Madhya Pradesh. (ii) It is unfortunate that around 40 percent of people in our country do not get proper nutrition. Several reasons can be held responsible for this
- The Public Distribution System is not functioning well.
- Foodgrain production is not evenly distributed.
- Supply chain is also erratic and unsystematic.
Additional Project/Activity Invite three different speakers to talk to you about the development of your region. Ask them all the questions that come to your mind. Discuss these ideas in groups. Each group should prepare a wall chart, giving reasons about ideas that you agree or do not agree with. Answer: For self-attempt.
Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 NCERT Intext Activity Questions and Answers
Study Table 1.5 of Textbook Page 12 carefully and fill in the blanks in the following paragraphs. For this, you may need to make calculations based on the table. Table: Educational Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar Pradesh
(a) The literacy rate for all age groups, including young and old, is for rural males and ………….. for rural females. However, it is not just that these many adults could not attend school but that there are …………….. who are currently not in school.
(b) It is clear from the table that ……………… % of rural girls and …………. % of rural boys are not attending school. Therefore, literacy among children in the age group 10-14 is as high as ………………. % for rural females and % for rural males.
(c) This high level of illiteracy among …………. age group, even after more than 60 years of our independence, is most disturbing. In many other states also we are nowhere near realisation of the constitutional goal of free and compulsory education for all children up to the age of 14, which was expected to be achieved by 1960. Answer: (a) 52%, 19%, 36% males and 69% females (b) 69%, 36%, 61%, 32% (c) 10-14.
Hope the data shared above regarding the NCERT Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development PDF has aided in your exam preparation. If you ever need any assistance you can always reach us and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development - Free PDF Download
Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development is a crucial part of this subject that comprises five chapters covering the different aspects of the Indian economy, global rights and consumer rights. To complete your preparation for these chapters, download the Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Solutions as a perfect guide and find the accurate answers to the exercise questions.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development is a brilliant section of your Social Science syllabus. This section is entirely based on economics and the terms related to the economic development of a country. In this subject, you will find several notions related to the economic development of a country and how it is calculated. To understand the technical terms of this subject, you will need the assistance of Understanding Economic Development Class 10 Solutions. This solution is prepared by top experts of Vedantu so that every student can understand the new concepts of the subjects well. It is an important subject that delivers excellent information related to the average income of our country, national income, per capita income and economic growth.
To study the subjects well, you will need accurate answers from the experts. For this, you must download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics (Understanding Economic Development). Subjects like Science, Maths, English, Hindi and Social Science will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science , Maths solutions and solutions of other subjects. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Detailed Overview of Class 10 Social Science - Understanding Economic Development NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science - Chapter-wise List
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science . The experts provide these solutions at Vedantu in a detailed manner. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
NCERT Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Solutions:
NCERT Class 10 Understanding Economic Development
The subject focuses on the terminology and the basic concepts of Economics. Class 10 students will find these new concepts not easy to understand unless they have good support from the proper study material. The best way to study this subject is to follow the solution prepared for Class 10 Understanding Economic Development. This subject will concentrate on the basic concepts of economics and the economic development of different countries.
This guide will give you the best support to understand what per capita income, human development index, national income, etc stand for. This is a crucial subject and you can score better by answering the questions correctly. Hence, it is better to use the Class 10th Economics Solution for easy preparation and manage your study schedule efficiently.
You will study how a country’s economic condition is calculated and compared with that of the other countries in Class 10 Economics. In fact, the value obtained from the calculation also determines whether a country can be called a developed or an underdeveloped nation. You will have to pay attention to the classroom sessions to understand what these terms state. If you are done with the study, test your knowledge proceeding to the exercise.
Class 10 Social Science Chapter Wise NCERT Solutions
Overview of class 10 social science economics chapters for cbse term i and term ii 2024-25, chapter 1 - development.
In this chapter, you will learn about different people's incomes and goals, national development, etc. You will learn how to find the average income and compare different countries and states. Practice the formula and solve exercise questions. Learn about the sustainability of development, where you will learn about the overuse of groundwater and the exhaustion of natural resources. To learn the chapter, you can use the NCERT solutions as the proper explanation of the topics can be availed. You can find all the exercise questions answers in the NCERT solutions, thus, it is better that you follow them while preparing each chapter. The solutions are designed by experts and you can download the development class 10 solutions PDF for free.
Important Topics Covered under Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 - Development
What development promises - Different people different goals
Income and other goals
National development
How to compare different countries or states?
Income and other criteria
Public facilities
Sustainability of development
Chapter 2 - Sectors of the Indian Economy
This is the second chapter and it is one of the most important chapters in the syllabus. First, you will learn about sectors of economic activities, in this, you will learn about primary sectors, secondary sectors, and tertiary sectors. Thoroughly learn about all three sectors and go through the examples. Next, you have to compare the three sectors, where you will also get to know about GDP and how to calculate it. You will even understand how to create employment, division of sectors as organized and unorganized differences. Learn the difference between public sectors and private sectors. In the last exercise, you will learn about the responsibilities of the government, learn all the steps and processes. Practice the exercise questions from the NCERT solutions and be thorough while learning. The NCERT solutions provide all the solutions for the NCERT economics class 10.
Important Topics Covered under Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 - Sectors of the Indian Economy
Sectors of economic activities
Comparing the three sectors
Primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors in India
Division of sectors as organised and unorganised
Sectors in terms of ownership: Public and private sectors
Chapter 3 - Money and Credit
In this chapter, you have to learn about money and its uses. Money as a medium of exchange is the first topic. In this, you will learn how money helps to make an exchange for goods and other things. Get to know about the modern form of money such as currency and deposits in the bank. Use the NCERT solutions for a better understanding of all the concepts involved in this chapter. Also, you should solve the exercise questions using the solutions. You will also learn about the loan activities of banks. Be very thorough and learn the process carefully. In the next topic, you will learn about terms of credit, you will also learn about formal sector loans and informal sector loans. You will also get to know about formal and informal credit. In the last topic, you will learn about the self-help groups for the poor. Practice all the exercise questions from the NCERT solutions to get more acquainted with the chapter and to answer the questions in a timely manner.
Important Topics Covered under Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 - Money and Credit
Money as a medium of exchange
Modern forms of money
Loan activities of banks
Two different credit situations
Terms of credit
Formal sector credit in India
Self Help Groups for the Poor
Chapter 4 - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
The first topic in this chapter is production across countries. In this topic, you will learn about MNCs and their role. Next, you will learn about interlinking production across countries. You should try to learn all the steps and methods. Learn about globalization, the factors affecting it, and the impact that it can have on a country. Also, learn about the struggle for fair globalization. Practice the exercise questions and use the NCERT solutions for the CBSE Class 10 economics.
Important Topics Covered under Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Production across countries
Interlinking production across countries
Foreign trade and integration of markets
What is globalisation?
Factors that have enabled globalisation
World Trade Organisation
Impact of globalisation on India
The struggle for a fair globalisation
Chapter 5 - Consumer Rights
This is the last chapter in the economics syllabus. This chapter is important and you have to learn and prepare it properly. The solutions provide an easy explanation for all the topics and chapters. You can use the solutions for the exercise questions. In this chapter, you will learn about the consumers in the marketplace, consumer movement, etc. In the next topic, you will get to know about information about goods and services. Another important topic is ‘where should consumers go to get justice’. You will also understand how to become a well-informed consumer and how to take the consumer movement further. Practice the exercise questions from the solutions and you can also use the solutions for revision purposes.
Important Topics Covered under Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 - Consumer Rights
The consumer in the marketplace
Consumer movement
Consumer Rights
Learning to become well-informed consumers
Taking the consumer movement forward
Class 10 Social Science Syllabus Term 1
Class 10 social science syllabus term 2, internal assessment class 10 social science, ncert solutions class 10 social science for cbse 2024-25 term i and term ii.
The links to the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Free PDFs (Geography, Political Science/Civics and Economics) are given below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India II
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Democratic Politics II
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science India and the Contemporary World-II
Class 10 NCERT Solutions for All Subjects for CBSE Term I and Term II 2024-25
Get the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 all subjects (Maths, Science, English, Social Science and Hindi) PDFs on Vedantu. Download these NCERT Solutions PDFs for free by clicking on the links below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
Why Should You Prefer Using NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics?
The reason why Class 10 students prefer using NCERT Economics Class 10 PDF solution is convenience. What if you can study the subject at your convenience? You will not have to wait for the teachers to present the best answers as you have the solution file with you. Download the file on your computer and use it at your convenience to study CBSE Class 10 Economics to stay ahead of the class.
Standard answers are what you will find in these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economic Development. The experts are highly experienced teachers of Vedantu who have designed the solutions following the CBSE format. This format tells us to follow a simple language to answer and to stick to the word count for every answer. It will become a lot easier when you practise answering questions related to this subject following the solution. You will get accustomed to the quality of answers and the format used by the experts.
Vedantu is the prime choice for Class 10 students to discover the best NCERT Solution for Class 10 Economics. This solution will save you time to prepare other subjects. You can use your time more efficiently and prepare the syllabus before any exam.
Importance of Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Solutions
This is a fundamental subject in the CBSE Class 10 syllabus that students study to develop their concepts. In this subject, an important section is the Understanding Economic Development part of the syllabus.Following are the Importance of Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Solutions.
This part of the NCERT Class 10 Social Science syllabus contains five vivid chapters that enable students to understand what economics stands for in the modern era.
These chapters deliver knowledge related to the development of a country, different sectors of the Indian Economy, credit and money, the impact of globalisation on the Indian Economy, and the consumer rights that have developed in due course of time.
To make these chapters easier to comprehend and assess your preparation level, the chapters have provided vivid exercises with conceptual questions. Answering these questions will help you find out where you need to focus more. This is where the Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapters solutions come into the picture.
You can study the answers given in the solutions and develop your answering skills accordingly. Cover the entire syllabus and find the exact answers to fundamental questions such as What is Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development.
Benefits of Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapters Solutions
Following are the benefits of Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapters Solutions:
The solutions to the exercise questions of a chapter have been consolidated to form a downloadable file. You can easily find the files when you know the Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development all Chapter Name. It will help you organise your study material and proceed with the preparation of the subject.
Use the solutions as a Social Science Understanding Economic Development Guide for Class 10 and complete preparing one chapter after the other.
Develop your concepts by using these solutions as an assessment tool. Find out which part of the chapters you need to focus on more and fortify your preparation.
Learn how to attempt such questions by following the answering formats compiled by the experts. Escalate your answering skills to the next level.
Download Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter Wise PDF
Get the free PDF version of the exercise solutions for all the chapters and boost your preparation for this subject. Resolve doubts faster and make your study sessions more productive by referring to the solutions. Follow the answers given by the subject experts to score more in the exams.
Important Related Links for NCERT Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
NCERT Books for Class 10
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
CBSE Class 10 Maths Formulas

FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development
Q1. What is the Best Way to Study Class 10 Understanding Economic Development?
Focus on the class lectures. Read the subject repeatedly to understand the definitions and concepts well. Follow Understanding Economic Development Class 10 PDF solution file for framing the best answers to the exercise questions and make your knowledge more fortified.
Q2. How can you Find the Right Answers to Economics Class 10 Questions?
If you follow how the experienced teachers of Vedantu have framed the right answers to the exercise questions and practice, you will be able to do the same. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics PDF for your convenience.
Q3. How can you Develop Knowledge Related to Economics in Class 10?
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development should be studied with proper attention. You will need good study material and a proper solution to the exercise questions to develop your knowledge.
Q4. Is it important to study Economics in Class 10?
The syllabus of Economics is relatively short when compared to other subjects under Social Science. Hence, this makes it even more important. You must make notes and go through all the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics to score the maximum marks. You must also keep in mind the important terms and definitions as they are very essential while framing an answer.
Q5. Which is the most important Chapter in Class 10 Economics?
All the chapters are equally important and you must prepare all of them. You must also practice all the Ncert questions from the page NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics on Vedantu’s website (vedantu.com) and revise all the key concepts. The definitions and key features are extremely important as they give weightage to your answers. All the resources are also available on the Vedantu app free of cost.
Q6. Do I need to practice all the questions provided in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics?
All the questions are extremely important as they are from NCERT and they have a higher rate of coming in the board examinations. Also, the solutions are written in such a way that they are best suited to the exam pattern and if one studies carefully and thoroughly, they will surely get full marks. The answers cover all the important points and the keywords that are used now and then. The answers can either be seen or downloaded from the page NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics free of cost.
Q7. How can I understand Economics Class 10?
The best way to understand Economics is to start with NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics. A thorough read followed by noting down all the important concepts is the ideal approach to tackle down Economics. Once you are through with the syllabus, you must then attempt the NCERT questions and then check them using the NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu. This will not only improve your answers but will also help you figure out where you went wrong so that you don't repeat those mistakes.
NCERT SOLUTIONS FOR CLASS 10
Cbse class 10 study materials, home tuitions in india.

CBSE Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development Lesson Plan

Written By Avinash Sharan
Class 10 | lesson plan 10, 0 comment(s), 26th june 2023, class x economics chapter 1 development lesson plan.
CBSE Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development is a crucial module that introduces students to the fundamental concepts and principles of economic development. This lesson plan aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing development, such as resources, technology, and human capital. Through this chapter, students will delve into the diverse aspects of development, including its measurement, indicators, and different approaches. By studying Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development, students will gain insights into the significance of sustainable development and the role of various sectors in promoting economic growth. This lesson plan emphasizes active engagement through discussions, case studies, and real-world examples to foster critical thinking and analytical skills in students. Get ready to explore the fascinating world of development and its impact on societies as we embark on this exciting journey with Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development.
“Building a Strong Foundation Through Class IX Economics Lesson Plan”
Pointwise Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development
Lesson Plan: Chapter 1 – Development
Class: X (Economics)
- Define the concept of development and understand its various dimensions.
- Identify the indicators used to measure development.
- Understand the different factors that affect development.
- Analyze the relationship between economic development and human development.
- Appreciate the importance of sustainable development.
Teaching Aids:
- Whiteboard and markers.
- Projector or computer with slides.
- Handouts or worksheets.
- Examples and case studies.
- Visuals such as charts, graphs, and images.
Teaching Points:
- Introduction to development and its meaning.
- Dimensions of development: economic, social, political, cultural, and environmental.
- Indicators of development: GDP per capita, literacy rate, life expectancy, HDI, etc.
- Factors affecting development: historical, geographical, economic, social, and political factors.
- Economic development and human development: understanding the relationship.
- Sustainable development: concept, goals, and importance.
Methodology:
The teaching methodology to be adopted by the teacher while teaching Class X Chapter 1 Development will involve an interactive method, where students
will be actively engaged in the learning process.
Teacher also uses gamification in creating interest in the subject.
Warm-up activity:
The warm-up activity will be initiated by the teacher to introduce the concept of development and stimulate student interest.
Presentation:
Visual aids, slides, and examples will be used by the teacher to explain the concept of development and its various dimensions.
The teacher engage students in discussions and encourage them to ask questions.
Class Discussions:
Discussions and questions will be encouraged by the teacher to involve students in the learning process and promote critical thinking.
Group Activity:
Small groups will be formed by the teacher, and case studies or examples of different countries or regions will be provided to facilitate group discussions.
At first, Findings from group discussions will be presented by each group.
Then, whole-class discussion will be facilitated by the teacher to encourage active participation.
Further, The concept of sustainable development will be introduced by the teacher.
Thereafter, students will be asked to create concept maps illustrating its goals and components.
Finally, the teacher will summarize the key points covered in the lesson and address any remaining questions or doubts from the students.
Lastly, Reflective writing tasks or research assignments related to the lesson’s topic will be assigned as homework by the teacher to reinforce learning.
11 Point Project On Consumer Awareness
Classroom Activities:
Firstly, the teacher will divide the class into pairs or small groups.
Secondly, provide them with a set of development indicators such as GDP per capita, life expectancy, literacy rate, etc.
Thirdly, ask them to rank these indicators based on their importance in measuring development and
Finally, each group can present their rankings and explain their reasoning.
Here, the teacher assign roles to different students, such as a representative from a developed country, a representative from a developing country, and a
representative from an underdeveloped country.
Conduct a role-play activity where students have to negotiate and discuss the challenges and strategies for development.
Class work:
The teacher asks the students to discuss and find out the answers in pair.
Students can refer the text book.
- What is meant by the term “development” in the context of economics?
- Why is economic development important for a country?
- What are the main indicators used to measure the level of development in a country?
- Explain the difference between developed and developing countries.
- What is the role of human capital in the development process?
- How does technology contribute to economic development?
- Discuss the importance of infrastructure development for a country’s economic growth.
- What are the major challenges faced by developing countries in achieving sustainable development?
- Explain the concept of income inequality and its impact on development.
- How can a country promote inclusive development?
- Discuss the role of education in promoting economic development. Provide examples to support your answer.
- Compare and contrast the economic development strategies of two countries, one developed and one developing. Analyze the factors that have contributed to their respective levels of development.
- Find out why the Middle East countries are not considered as developed countries?
- Solve the given source based questions important for Board exams.
Assessment Criteria:
- Participation in class discussions and activities.
- Accuracy and depth of responses during the group activity.
- Completion and quality of the homework assignment.
- Understanding and application of the key concepts and indicators of development.
Learning Outcome:
By the end of this lesson, students will:
Firstly, Understand the concept of development and its various dimensions.
Secondly, Identify and explain the indicators used to measure development.
Thirdly, Recognize the factors that affect development.
Fourthly, Analyze the relationship between economic development and human development and
Finally, appreciate the significance of sustainable development.

Remedial Measures:
Firstly, the teacher will provide additional reading materials or resources for students who require extra support in understanding the concepts.
Secondly, he / she will conduct one-on-one or small group discussions with struggling students to address their specific concerns and provide additional
explanations.
Thirdly, will also encourage peer learning and collaboration by pairing students with different learning abilities.
Fourthly, allow them to support each other during activities and assignments.
Lastly, provide additional practice exercises or worksheets to reinforce understanding and application of the concepts covered in the lesson.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Economics lesson plan on Chapter 1 Development has proven to be an exceptional resource that effectively educates and engages students in the complex topic of economic development. The lesson plan’s structure and content have demonstrated the expertise and thoughtfulness of its creators.
One of the notable strengths of the lesson plan is its ability to connect theoretical concepts with real-world examples. By integrating case studies and illustrations, the plan has successfully bridged the gap between theory and practice, making the subject matter more relatable and engaging for students.
Furthermore, the lesson plan’s emphasis on critical thinking and analysis has encouraged students to delve deeper into the subject matter. The inclusion of thought-provoking questions and discussion prompts has stimulated meaningful class discussions, allowing students to develop their analytical skills and form well-rounded perspectives on the challenges and opportunities associated with development.
Overall, the Economics lesson plan on Chapter 1 Development has proven to be an exemplary educational resource that effectively imparts knowledge, fosters critical thinking, and engages students in a meaningful exploration of economic development.
Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development Source-Based Questions
Online Fraud And Prevention – A Consumer Awareness Project
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

Class 10 Economics Project on Social Issue “Effect Of Corruption On India’s Economy”
Apr 25, 2024
Class X Economics Project On "Effect Of Corruption on India's Economy" As class X students it is crucial to...

Honour Killings in West Asian Domestic Violence: Causes, Patterns, Impact & The Role Of Education
Apr 16, 2024
Honor Killings in West Asian Domestic Violence Did you know that Honour Killings in West Asian Domestic Violence often...

Empowering Women: Legal and Political challenges for women in West Asian countries
Apr 15, 2024
A Project On Legal and Political challenges for women in West Asia In this project we will explore the latest insights...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment
- School Guide
- Class 10 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 10
- Science Notes Class 10
- History Notes Class 10
- Geography Notes Class 10
- Political Science Notes Class 10
- NCERT Soln. Class 10 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 10
- Math Formulas Class 10
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
Class 10: History Notes
- CBSE Class 10 History Notes
- The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Class 10 History Notes Chapter 1
- Nationalism in India - CBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 2
- The Making of Global World Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3
- The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History Notes Chapter 4
- Print Culture and the Modern World Class 10 Notes History Chapter 5
Class 10: Geography Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Notes
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1- Resources and Development
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 2- Forest and Wildlife Resources
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Notes Chapter 3 : Water Resources
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 - Agriculture
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 5: Minerals and Energy Resources
- Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Geography Notes Chapter 6
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 7- Lifelines of National Economy
Class 10: Polity Notes
- Class 10 Political Science Notes
- Power Sharing Class 10 Civics Notes Chapter 1
- Federalism Class 10 Notes Civics Chapter 2
- Gender, Religion and Caste: Class-10 Chapter-3 Civics Notes
- Political Parties: Chapter-4, Class-10 Civics Notes
- Outcomes of Democracy: CBSE Notes Class-10 Chapter-5; Political Science (Civics)
Class 10: Economics Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes
CBSE Class 10 Notes Economics Chapter 1: Development
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 : Sectors of the Indian Economy
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 3: Money and Credit
- Globalisation and the Indian Economy : CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes Chapter 4
- Consumer Rights Class 10 Notes
In the CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 1, you will learn about the concept of development, what it means, & how it is measured. The chapter begins with a discussion of the different ways in which people define development, & the various indicators that are used to measure it, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Human Development Index (HDI), Average Income, Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), etc. The chapter also covers the different dimensions of development, such as economic, social, & political.
The chapter also examines the concept of sustainable development & the need to balance economic growth with environmental conservation. It concludes by highlighting the importance of inclusive & sustainable development in creating a better future for all. Overall, the chapter provides a broad introduction to the concept of development.

Development class 10 notes
- Introduction to Development
Development refers to a positive change or improvement or progress in people’s life or well-being, which can be economic, social, or political. It enshrines economic, social, political, cultural, and environmental dimensions, thus, causing a significant & positive effect on one’s life. Development helps people to grow & make a mark in society.
Read More: Introduction to Development Economics
What Development Promises – Different People Have Different Goals
Different people have different goals for development, which may include higher income, better health, education, equality, freedom, & environmental sustainability. Thus, development has many aspects & they vary from person to person.
People tend to seek things that are most important to them. Example: For a girl, having freedom & will to decide what she wants, as her brother have, would be her notion of development.
At times, the idea of development can be contrasting. In simpler terms- Different persons can have different developmental goals & what may be developed for one may not be developed for the other. It may even be destructive for the other. Example: In order to reserve land for forestation, those residing in the nearby area would need to relocate from the area.
Income And Other Goals
Income is widely associated with the notion of development as it can be a good & common parameter for measuring development. Besides income, people also expect- security, equal treatment & freedom. At times, they become more important than income & materialistic goods. For development, people look at a mix of goals.
Example: An inclusive, safe & sound workplace would pave the way for greater participation & engagement of women in jobs.
National Development
National development refers to the improvement of the economic, social, and political conditions of a country over time. National development can be compared across countries or states using different indicators, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Human Development Index (HDI), etc. These indicators provide a comprehensive picture of the different dimensions of development, including income, education, health, and standard of living.
Read More: National Development
How to Compare Different Countries or States?
For comparing the countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes, and countries which have higher income are more developed as compared to the other countries which have less income. As different countries usually have different populations, comparing the total income will not let us know what the average person earns. So, we compare the average income of the countries.
Average Income refers to the total income of the country which is divided among its total population and is known as per capita income.
Average Income or Per Capita Income: Total income of the country/Total population of the country
Country A has a total income of 50,000/- INR & has a population of 10 citizens.
So, in this case, to calculate the average income we would simply do a simple calculation which is as follows:
50000/10 = 5000/- INR would be the average income of country A
In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, this criterion is used in classifying countries:
- Countries with a per capita income of US$ 49,300 per annum and above in 2019, are called high-income or rich countries and those with a per capita income of US$ 2500 or less are called low-income countries.
- India comes in the category of low-middle-income countries because its per capita income in 2019 was just US$ 6700 per annum. The rich countries, excluding countries of the Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Income and Other Criteria
When thinking about a country or region, apart from average income, public facilities also play an important role.
- Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR) indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year.
- The literacy Rate measures the proportion of the literate population in the 7-and-above age group.
- Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 14 and 15 years attending school as a percentage of the total number of children in the same age group.
- Public Facilities
Public facilities are essential components of development, as they provide basic services to people, such as health care, education, transportation, and communication. Government via- Public welfare schemes, boosting infrastructure in the health & education sector, can pave the way for the effective & comprehensive delivery of development & progress to the citizens.
Public facilities can be a mode to create an inclusive & open society as they provide equal access to services & resources for everyone irrespective of background.
Read More: Public Facilities
- Sustainability of Development
Sustainable Development is the kind of development that meets the needs and demands of the present generation without compromising the availability of resources for future generations. Sustainable development requires a balance between economic growth, social well-being, and environmental protection. The pursuit of economic growth should not come at the expense of environmental degradation, as this can have negative consequences for people’s health, livelihoods, and future opportunities.
Scientists have been warning that present use and methods are not sustainable. Some examples are as follows:
- Overuse of groundwater
- Exhaustion of natural resources
Read More: Sustainability of Development
FAQs on CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes Chapter 1: Development
Q1. how would you define development.
Development refers to a positive change or improvement or progress in people’s life or well-being, which can be economic, social, or political.
Q2: What is per capita income? How it is calculated?
Per Capita Income is defined as the average income a person earns in a year. It is calculated as follows: Per Capita Income = Total income of the country/Total population of the country
Q3. What is Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)?
Answer-
IMR indicates the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children born in that particular year.
Q4. What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable Development is the kind of development that meets the needs and demands of the present generation without compromising the availability of resources for future generations.
Related Links
- National Development and How to Compare Different Countries or States?
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Economics-Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class-10
- School Economics
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
SMART STUDY POINT
Notes, Assignment, important Question Answer.
- Privacy Policy
- CBSE CLASS 10 (19)
- CBSE CLASS 8 (4)
- CBSE CLASS 9 (9)
- Competitive Exam (10)
Development Class 10 Economic Important Questions (2021-22) / Development class 10 Economic ncert solutions

(i) its per capita income
(ii) its average literacy level
(iii) health status of its people
(iv) all the above
Answer: (iv) all the above
2. Which of the following neighbouring countries has better performance in terms of human development than India?
(i) Bangladesh
(ii) Sri Lanka
(iii) Nepal
(iv) Pakistan
Answer: (ii) Sri Lanka
3. Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is Rs 5000. If the income of three families is Rs 4000, Rs 7000 and Rs 3000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth family?
(i) Rs 7500
(ii) Rs 3000
(iii) Rs 2000
(iv) Rs 6000
Answer: (iv) Rs 6000
Explanation:
Total income of four families = 5,000 × 4 = ₹20,000
Total income of three families
= 4,000+7, 000+3, 000 = 14,000
Income of the fourth Family is
20,000 - 14,000 = 6000
4. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries? What are the limitations of this criterion, if any?
Answer:
i) The main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different countries is - the pet capita income ( the average income of a person in the country) .
ii) It is calculated by dividing the total income of the country by the population of the country.
iii) As per 2017, the countries with per capita income of US $12,056 or more are declared rich countries and the countries with per capita income of US $ 955 or less are called low-income countries.
The limitations of the criterion are as follow:-
- i) It does not give any information about the distribution of the average income among the people in a country.
- ii) It ignores important factors like literacy rate, infant mortality rate, healthcare, etc.
5. In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring development different from the one used by the World Bank?
Answer: The criterion used by UNDP is different from the one used by the World Bank because
i) World bank only uses per capita income for measuring the development of a country .
ii) UNDP besides considering per capita incomes, compares countries on the basis of the educational level of the people, healthcare facilities and infant mortality rate which are important in improving the quality of life and making the citizens more productive.
6. Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate with your own examples related to development.
i) We use averages for a better understanding.
ii) While taking total income as comparison, it is the total population that makes variations and big countries have always higher value than smaller countries.
iii) So, average income shows per capita income of the citizens. It gives an edge over counting total income.
Yes it also has some Limitations like There may not be equal distribution of income.
A small number of people may be extremely rich and the masses may be poor.
7. Kerala, with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Haryana. Hence, per capita income is not a useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
No, I do not agree that income or per capita income should not be used to compare states.
However other factors like Infant Mortality Rate, Literacy Rate and Net Attendance Ratio are also very crucial for overall human development. With keeping these factors in mind alongwith per capita, Kerala is better than Haryana.
8. Find out the present sources of energy that are used by the people in India. What could be the other possibilities fifty years from now?
i) The present sources of energy used by people in India are firewood, coal, petroleum, crude oil and natural gas.
ii) The other possibilities fifty years from now could be using solar energy, wind energy, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, hydrogen energy, tidal energy, wave energy, hydroelectric energy, biomass energy, etc.
9. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development?
Sustainable development refers to , development should take place without damaging the environment. The issue of sustainability is important for development because it should not compromise on the needs of future generations.
The unchecked exploitation of non-renewable natural resources like Petroleum, oil and minerals are increasing, as these natural resources are limited, so development should not take place at the cost of these scarce natural resources.
10. “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person”. How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss.
According to the statement the statement, “The Earth has enough resources to meet the needs of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person” is completely relevant in terms of the development of a country because
The Earth provides enough resources to meet the needs of all living beings still today's generation has become so greedy for their own betterment and development they do activities like - Deforestation, indiscriminate use of Agro-chemicals, extraction of ground water in excess of recharge capacity etc.
As both resources and development are important, we should use the resources in a judicious way to meet our needs not to satisfy our greed.
11. List a few examples of environmental degradation that you may have observed around you.
Answer: The few examples of environmental degradation that we can observe around us are:
- i. Water pollution by use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
- iv. Deforestation
- v. Burning of coal and mineral oil.
Jyotirmayee
Report Abuse
Copyright (c) 2023| https://www.cbsesocialsciencenotes.in/ smart study point
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development
Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development Chapter 1 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Resources and Development Assignments Class 10 Social Science
ONE MARK QUESTIONS
Question. Give examples of biotic resources. Ans : Human beings, flora, fauna, fisheries, livestock, etc.
Question. In which states laterite soil is found? Ans : Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
Question. Which relief features of India has 30 percent of the total surface area of country? Ans : Mountain.
Question. In which states is black soil found? Ans : Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Question. Which soil is ideal for growing cotton? Ans : Regur soil.
Question. In which states overgrazing is responsible for land degradation? Ans : Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Question. Which state has the largest area under black soil? Ans : Maharashtra.
Question. What are resources which are found in a region but have not been utilised called? Ans : Potential resources.
Question. In which states has mining caused severe land degradation? Ans : Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha.
Question. What is the percentage share of plains in the total land area? Ans : 43%.
Question. Which resources are surveyed and determined on the basis of their quantity and quality for utilisation? Ans : Developed resources.
THREE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Describe any five distinct characteristics of ‘Arid soils’. Ans : a. Arid soils range from red to brown in colour. b. Sandy in texture and saline in nature. c. Evaporation is faster, soil lacks humus and moisture. d. Soil occupied by Kankar. e. Kankar restricts the infiltration of water.
Question. Mention any three features of arid soils. Ans : Features of arid soils : 1. Arid soils range from red to brown in colour. 2. They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. 3. Due to dry climate, high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture. 4. The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by Kankar because of the increasing calcium content downwards.
Question. Differentiate between stock and reserve stating two points of difference. Ans : a. Stock: Materials, which have the potential to satisfy human beings but human do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are termed as stock. We do not have the required technical ‘know-how’ to use them for a specific purpose, e.g., water which is a compound of two inflammable gases hydrogen and oxygen and can be a rich source of energy. We do not know how to use them. b. Reserves: These are subset of the stock. They can be put into use with existing know-how but their use has not been started. For e.g., river water is used as a source of hydroelectricity but to a limited extent. Thus, the water in the dams, forests, etc., are reserves which can be used in the future.
Question. ‘Land is a natural resource of utmost importance’. Justify the statement with appropriate arguments. Ans : a. We live on land, we perform our economic activities on land and we use it in different ways. b. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems. c. It is an asset of a finite magnitude.
Question. What is meant by the term “resource”? List the types of resources classified on the basis of its ownership. Ans : a. Resource: Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable is known as a resource. b. Types of resources on the basis of ownership are: Individual, community, national and international.
Question. Distinguish between the renewable and nonrenewable resources. Ans : a. Renewable resources: Resources which can be renewed or reproduced by mechanical, physical or chemical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources, e.g., solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. b. Non-renewable resources : These occur over very long geological times. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some of them such as fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
39. Distinguish between stock and potential resource. Give one example of each. Ans :
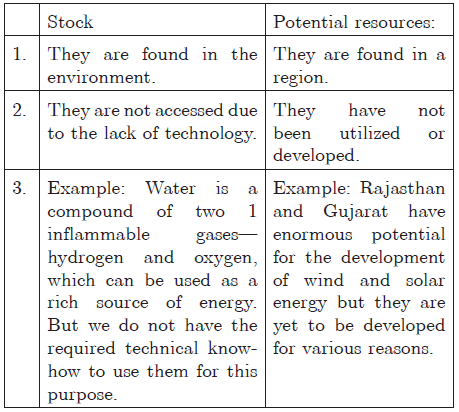
Question. What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give four main features of this type of soil. Ans : Alluvial soil is found in the entire northern plain It is the most widely spread soil of India. Main features of alluvial soil: a. It is formed by the deposition of materials brought down by the Himalayan rivers. b. It is highly fertile. c. It consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. d. It is rich in potash, phosphoric acid and lime but deficient in organic matter.
Question. Distinguish between Khadar and Bangar soil. or How are alluvial soils formed? How is Bangar different from Khadar? Ans : Alluvial soil: It is soil formed by the sediments deposited by river water.

Question. Explain any three factors responsible for soil formation. Ans : a. The parent rock is the first factor which provides the basic material for the formation of soil. b. Climate breaks the parent rock into small pieces. c. Vegetation: Plant and animal organisms help in the weathering of the rocks slowly but continuously d. Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc., contribute to the formation of soil. e. Chemical and organic changes take place in the soil.
Question. Which geographical factors are responsible for the evolution of black soil? Why is it considered the most suitable for growing cotton? Ans : a. Climatic conditions along with present rock material are important factors for making of black soil. The parent rock is volcanic rock. b. It is ideal for growing cotton because of the following reasons: c. It has capacity to hold moisture. d. It is rich in soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate and potash. e. Deep cracks in the soil help in aeration.
Question. Explain any three human activities responsible for land degradation in India. or How are human activities responsible for the degradation of land? Ans : a. Mining: Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars in states such as Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha. Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation. b. Over irrigation: Over irrigation in the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, has caused water logging and increase in salinity of soil. c. Overgrazing: Overgrazing in states such as Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra is a huge cause due to cattle population d. Industries: Mineral processing industry like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust. This retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil. e. Industrial waste: Industrial effluents also have become a major source of land degradation.
Question. Mention any two human activities which are responsible for the process of soil erosion. Explain the two types of soil erosion mostly observed in India? Ans : Two human activities which are responsible for the process of soil erosion are deforestation and overgrazing, mining, construction, etc. Types of Soil Erosion : a. Gullies: The running water cuts through the clayey soil and makes deep channels/gullies. The unfit land caused by gullies is called bad land or ravines. b. Sheet erosion: water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. The top soil is washed away .This process is known as sheet erosion.
Question. Explain the types of resources on the basis of exhaustibility with the help of examples. Ans : a. Renewable resources: Resources which can be renewed or reproduced by mechanical, physical or chemical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources, e.g., solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. b. Non-renewable resources: These occur over very long geological times. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some of them such as fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
FIVE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. What is meant by ‘Land Resource’ ? Ans : We live on land and it satisfies our needs in all the possible ways. Land resource, thus is, of much importance for us which includes forests, mountains, plains, plateaus and islands. These support natural vegetation, wild life, economic activities, and transport and communication systems. Therefore, it is necessary for us to use these resources in a wise manner and with careful planning, we should develop holistic and ecological approach towards economic development without compromising the ability of resources to future generations to meet their needs. Though we have the right to meet our present needs by consuming natural resources, we should not deprive the future generations from it.
Question. Explain land use pattern in India and why the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61. Ans : Land in India has been divided into different categories with reference to usage. Different categories of land are: a. Farming land which is used for farming. b. Forest land which comes under forest area c. Land meant for grazing d. Non-farming land which is used for industrialization e. Waste lands, such as rocky areas and deserts
The irrational use of forest land has degraded the available land area, and has made conservation of forests difficult. Human actions such as deforestation, mining and quarrying have contributed to the slow growth rate of forests. Thus, land under forest has increased by only about 4% since 1960-61. a. The use of natural resources has been increased with the development of the technology in the country. b. Over utilisation of soil due to development in technology. c. Growth in the quality of production and better services to the people. d. Improvement in the process of mining. e. Demand for more resources due to urbanisation.
Question. What do you understand by the term ‘land degradation’ ? Which human activities lead to land degradation ? What are the measures to solve the problems of land degradation ? Ans : Land resource is fixed and cannot be increased. Land resource has been used since the ancient time. This continuous usage of land over a long period of time, without taking necessary steps to conserve and manage it has resulted in land degradation. As a matter of fact, the quality of the land has become inferior due to regular loss of fertility and irregular usage. Human activities have also contributed towards land degradation. There are : a. Deforestation i.e., cutting down of forests. b. Over grazing. c. Mining i.e., extraction of valuable minerals from the soil. d. Mineral processing like grinding of limestone. e. Faulty methods of cultivation and over-irrigation.
These damages can be prevented with the help of these measures : a. Afforestation and proper management of grazing. b. Plantation of shelter and stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes in windy and arid areas like the deserts of Rajasthan. c. Proper management of wasteland and control of mining activities. d. Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and waste after treatment in industrial and suburban areas.
Question. What is the purpose of ‘Land Utilisation’ ? Ans : Land resources are used for the following purposes : a. Forests. b. Land not available for cultivation : (1) Barren and waste land. (2) Land put to non-agricultural uses, e.g., buildings, roads, factories, etc.
c. Other uncultivated land : (1) Permanent pastures and grazing land. (2) Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves. (3) Cultural waste land’left uncultivated for more than 5 years.
d. Fallow lands: (1) Current fallow land left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year. (2) Other than current fallow land, left uncultivated for the past one to five years.
e. Net sown area, sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Question. What are the main types of soil found in India ? Which type of soil is the most widespread and important soil of India ? Describe in detail about this soil type. Ans : The main types soil found in various parts of India are as follows : a. Alluvial soil b. Black soil c. Red and yellow soil d. Laterite soil e. Arid or Desert soil f. Forest and Mountainous soil.
Alluvial Soil : Alluvial soil is the most fertile and extensively found soil in India. This type of soil is found near the river banks and is deposited by the rivers of India. The Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra are the three main rivers which are responsible for its deposition and have created the entire northern plains. These soils also extend in Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor. Alluvial soil is also found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers. Alluvial soil is more common in pediment plains such as Duars, Chos and Terai. Alluvial soil is very fertile because it contains potash, phosphoric acid and lime in adequate amount. This is why the areas where alluvial soil is found are densely populated, for example, the northern plains and the eastern coastal plain are densely populated and the most productive regions of India. The mineral content of the alluvial soil makes it ideal for the growth of paddy, wheat, other cereals and pulses and sugarcane. The alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. They are coarse in the upper reaches of the river valley especially near the break of slope and in pediment plains like Duars, Chos and Terai. Every year during annual floods alluvial soils are renewed. The Alluvial soil is of two types-Khadar and Bangar.
Question. Explain resource planning. What are the steps involved in resource planning? or Why is resource planning essential in India? or What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential? Explain it with three reasons. Ans : Resource planning is a procedure of proper utilisation of resources. Resource planning is important because : a. Resources in India are not evenly distributed. Some parts of the county are rich in one resource but deficient in other important resources which are essential. For example, Rajasthan is rich in solar and wind energy but lacks water resource. Jharkhand is rich in minerals and coal deposits but lack in industrialisation. This is the reason why resource planning is essential. An effective resource planning will help in effective use of the resources available in the environment. b. Secondly, most of the resources present in our environment are limited. Therefore, if these resources are not preserved or not used rationally we will be in great trouble. For example : Petrol is a limited resource and it cannot be renewed. Exhaustion of petrol will create huge chaos in the country as we are extensively dependent on the petrol. c. Thirdly, resource planning is important because it minimises the wastage or over utilisation of resources. The very first step of resource planning is to make a list of resources available in the environment. This helps us to assess which resources should be used and how much it should be used to prevent over utilisation and minimise wastage.
Related Posts

Assignments For Class 10 Mathematics Circles
Case study chapter 5 arithmetic progression mathematics.

Assignment on Experiments in Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 Geography
- Chapter 1 Resources And Development
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Geography Social Science Chapter 1 : Resources and Development
Ncert book solutions for class 10 geography contemporary india – ii chapter 1 resources and development – cbse free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources and Development are important resources for students to prepare for CBSE exams. By going through these solutions, students will get to know the answer writing style, which will help them in fetching more marks in the exam. They will also understand how to write their answers by covering all the important details. These NCERT Class 10 Solutions are created by subject experts and help students to prepare effectively for their Social Science exam.
- Chapter 1 Resources and Development
- Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Water Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
- Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
- Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Students can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography PDF below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography (Contemporary India II) Chapter 1 – Resources and Development

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources and Development
The solutions for Chapter 1 – Resources and Development are given below. Students should also check NCERT Solutions for Class 10 for other subjects.
Exercise Page No 12
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following types of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(d) Non-renewable
Non-renewable
(ii) Under which of the following type of resources can tidal energy not be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic
(d) Non-recyclable
Replenishable
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Over-irrigation
(d) Overgrazing
Over-irrigation
(iv) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised?
(b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(c) Haryana
(d) Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand
(v) In which of the following states is black soil predominantly found?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jharkhand
- Maharashtra
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words .
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
3 states are
- Madhya Pradesh
The crop grown is cotton.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
The type of soil found in river deltas is Alluvial Soil.
- It is very fertile and, therefore, good for the cultivation of crops
- It consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay
- Alluvial soil has a good quantity of potash, lime and phosphoric acid, which is good for the growth of paddy and sugarcane.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in hilly areas?
The main techniques that can be used are given below.
- Contour ploughing
- Terrace farming
- Strips of grass are allowed to grow between the crops. This method is known as strip cropping.
(iv) What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Biotic resource:
- These are resources that are obtained from the biosphere
- These resources have life
- Examples are plants, animals, fish, human beings, livestock etc.
Abiotic resource:
- These resources are composed of non-living things
- Examples are water, minerals, metals, wind, solar energy etc.
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Explain the land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61.
The use of land is determined both by physical factors, such as topography, climate, and soil types, as well as by human factors, such as population density, technological capability, culture, traditions etc. The pattern of the net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman Nicobar Islands. Forest area in the country is far lower than the desired 33 per cent of the geographical area, as it was outlined in the National Forest Policy (1952). It was considered essential for the maintenance of the ecological balance. A part of the land is termed a wasteland, and it is put to other non-agricultural uses like settlements, roads, railways, industry etc. It includes rocky, arid and desert areas. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it has resulted in land degradation.
(ii) How has technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
There are various reasons for this.
- Large-scale production led to over utilisation of resources.
- Technological advancement led to greater exploitation of resources.
- Improved medical and health resources led to huge consumption of resources.
Resources and Development Summary
The students will get to know about the following topics:
- On the basis of origin – Biotic and Abiotic resources;
- On the basis of exhaustibility – Renewable resources and non-renewable resources
- On the basis of ownership – Individual, community, national and international resources
- On the basis of status development – Potential resources and Developed Resources
- Development of Resources
- Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit
- Resource Planning
- Conservation of Resources
- Land Utilisation
- Land use pattern in India
- Classification of soils
- Soil erosion and conservation
‘Contemporary India-II’ is an important book for Class 10 Social Science subject. Apart from this chapter, the full set of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science is given in the linked article.
Disclaimer –
Dropped Topics – Types of Resources, Box information
Also, explore –
NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
What are the main topics that students will learn in chapter 1 of ncert solutions for class 10 geography, how can i download the ncert solutions for class 10 geography chapter 1 pdf online, why should students opt the byju’s ncert solutions for class 10 geography chapter 1 for reference.
It’s very useful I always see the solutions from this website only coz I believe that here is what I can the correct and valueable answer
Thanks a lot
Tq it has helped me lot
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


- THE WEEK TV
- ENTERTAINMENT
- WEB STORIES
- JOBS & CAREER
- Home Home -->
- News News -->
- India India -->
Karnataka horror: Kodagu man decapitates Class X girl after engagement called off, flees with victim's head
Govt intervention forced the families to call off the union until the girl was 18

In a horrific development in Karnataka's Kodagu, a 16-year-old girl was beheaded by a man after the two families mutually decided to postpone their marriage until she turned major. The 32-year-old accused, who fled with the victim's decapitated head, is yet to be traced by the police.
According to news reports, the 16-year-old Meena, the youngest among the family's six kids, was to get engaged to the accused, identified as Prakash on May 9, Thursday. She had passed class 10 in the recently declared results.
However, the decision to get the minor girl married off was leaked to the officials by some informers via the Child Helpline number. Soon, authorities reached Kodagu's Surlabbi village and met with the two families at Meena's house. They were told about the implications of getting a minor girl married off. If they went ahead with the marriage, it would attract provisions of the POCSO Act and Child Marriage Act, they pointed out.
Thus, the two families mutually decided to suspend the alliance until Meena turned 18, news agency PTI said in a report.
However, things took an ugly turn on Thursday evening, only hours after Prakash's family left the bride's residence after counselling with the government staff.
Barging into the house armed with a sharp-edged weapon, Prakash kicked and assaulted Meena's father until he became incapable of defending the family. He then attacked the girl's mother with a tool used to cut trees. The couple are undergoing treatment at a hospital for the injuries suffered during the home invasion.
Prakash then dragged Meena out of the house for about 100 metres before murdering her with the weapon, PTI said. Kodagu Superintendent of Police Ramarajan K told the news agency that he took the minor girl's head with her while fleeing the crime scene.
A case has been registered against the accused under Sections 307 (attempt to murder) and 302 (murder) of the Indian Penal Code and relevant sections of the Protection of Children against Sexual Offences Act, police said.
Join our WhatsApp Channel to get the latest news, exclusives and videos on WhatsApp

UNRWA shuts down its East Jerusalem headquarters after Israeli extremists attack

IPL 2024: Virat Kohli, Rajat Patidar power RCB to 241/7 against Punjab Kings

Netflix confirms 'Wednesday Season 2': What we know so far

SIP flows into mutual funds top Rs 20,000 crore in April

Should we fight climate change by re-engineering life itself?
Editor's pick.

Pawar and Thackeray should introspect about why people left them: Devendra Fadnavis

Are unique names a boon or bane? Isenhower, Loosamma and others open up

Mandeep meets Mandeep: How a techie's act of kindness saved an acute leukaemia patient

Evolving luxury
*Articles appearing as INFOCUS/THE WEEK FOCUS are marketing initiatives

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The students will also be able to develop an idea of how the questions are set in the examination. Share this with your friends. Download PDF. Download Development CBSE Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 notes PDF for free. Secure good marks by referring NCERT Class 10 Development revision notes prepared by Vedantu experts.
In this chapter, students will understand the various aspects of development that a country needs. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 - Development contain the answers to the exercises given at the end of the book of Chapter 1. These solutions will help students to write their answers in an effective way during the CBSE exams.
Chapter 1 Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science. 1. Read the source given below and answer the following questions: Once it is realised that even though the level of income is important, yet it is an inadequate measure of the level of development, we begin to think of other criterion. There could be a long list of such ...
Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Development. Contents. Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development Case Study 1: Case Study 2: Case Study 3: Case Study 4: Case Study 5: At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph.
Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers. Question 1. Development of a country can generally be determined by. (i) its per capita income. (ii) its average literacy level. (iii) health status of its people. (iv) all the above. Answer: (iv) all the above.
CBSE Class 10 Economics MIQs, Subjective Questions & More. Important Questions Multiple Choice Questions Fill In The Blanks Subjective Questions CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics CBSE Chapter 1: Get free access to Development Class 10 Solutions which includes all the exercises with solved solutions.
Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics - Understanding of Economic Development. Chapter 1: Development. Chapter 2: Sectors of the Indian economy. Chapter 3: Money and credit. Chapter 4: Globalization and the Indian economy.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics: Understanding Economic Development - II. Chapter 1 Understanding Economic Development. Chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy. Chapter 3 Money and Credit. Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy. Chapter 5 Consumer Rights.
CBSE Class X Economics Chapter 1 Development is a crucial module that introduces students to the fundamental concepts and principles of economic development. This lesson plan aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing development, such as resources, technology, and human capital. Through this chapter, students will ...
2015. Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] Question 5. Give any two common developmental goals of the people. Answer: Social equality, freedom, peace, pollution-free environment, improved health and literacy levels, awareness and control on population are common development goals of the people. Question 6.
In the CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 1, you will learn about the concept of development, what it means, & how it is measured. The chapter begins with a discussion of the different ways in which people define development, & the various indicators that are used to measure it, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Human Development Index (HDI), Average Income, Infant Mortality Rate (IMR ...
Development Class 10 Economic Important Questions (2021-22) / Development class 10 Economic ncert solutions CBSE CLASS 10 ... Important Assignment Questions Of Class 10 Economic Chapter 1 Development Very Short type Questions. Q. 1. What is Infant mortality rate? Ans. It is the number of deaths of infants under one year per 1000 live births in ...
1. Secure and proper lifestyle for future generations 2. Reduces various kinds of pollution on Earth 3. Economic growth and development. Know the different aspects of development by going through the CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 on Development. Download these notes in pdf for quick revision.
Class 10 Social Science MCQs Chapter 1 Development. 1. What will be the top priority in the developmental goal of a landless labourer? (a) Expansion of rural banking. (b) More days of work and better wages. (c) Metal roads for transportation. (d) Establishment of a high school. Answer. 2.
Resources can be classified in the following ways: (a) On the basis of origin - biotic and abiotic. (b) On the basis of exhaustibility - renewable and non-renewable. (c) On the basis of ownership - individual, community, national and international. (d) On the basis of the status of development - potential, developed stock and reserves.
Resource and Development Class 10 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1. 'Resource': Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, is called a resource. It should be technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable. Only then, it can be termed as a 'Resource'.
We have provided Class 10 Social Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class ...
NCERT Book Solutions For Class 10 Geography Contemporary India - II Chapter 1 Resources and Development - CBSE Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development are important resources for students to prepare for CBSE exams. By going through these solutions, students will get to know the answer writing style, which will help them in fetching more ...
In a horrific development in Karnataka's Kodagu, a 16-year-old girl was beheaded by a man after the two families mutually decided to postpone their marriage until she turned major. The 32-year-old accused, who fled with the victim's decapitated head, is yet to be traced by the police. ... Karnataka horror: Kodagu man decapitates Class X girl ...
Module 1 • 2 hours to complete. This module provides you with an overview to the field of software engineering. In the first lesson of this module, you will be introduced to the field of software engineering, and learn about the software development lifecycle (SDLC), elements of building high-quality software, and writing requirements.
Join us at 6 PM (WAT) this Thursday May 9, 2024, as our distinguish guest will be discussing the topic: GEN-Z ACCOUNTANTS: Redefining Traditional...