
Chapter 4 Theory Development: Structuring Conceptual Relationships in Nursing
Dec 21, 2019
340 likes | 397 Views
Chapter 4 Theory Development: Structuring Conceptual Relationships in Nursing. Theory Development—Overview. Theories are systematic explanations of events in which: Concepts are identified. Relationships are proposed. Predictions are made. Theory Development—Overview—(cont.).

Share Presentation

Presentation Transcript
Theory Development—Overview • Theories are systematic explanations of events in which: • Concepts are identified. • Relationships are proposed. • Predictions are made.
Theory Development—Overview—(cont.) • Theories are invented to: • Describe or explain phenomena • Solve problems • Improve practice
Question Theory development in nursing seeks which of the following? A. Understand practice. B. Identify and express ideas. C. Organize existing knowledge. D. All of the above
Answer D. All of the above Rationale: Theory development helps nursing to understand practice, provides a method for identifying and expressing key ideas, helps organize existing knowledge, and makes new discoveries to advance the practice of nursing.
Theory Development—Overview—(cont.) • Theory development is the process used to create, modify, or refine a theory. • Theory development involves a number of stages. • Start with concept analysis. • Concepts are refined. • How concepts are related are proposed. • Propositions are tested.
Relationship among levels of theory. (From Walker, L. O., & Avant, K. C. [2011]. Strategies for theory construction in nursing [5th ed.]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Reprinted by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.)
Types of Theory • Descriptive—describe, observe, and name concepts • Explanatory—describe relationships between concepts • Predictive—describe causal or consequential relationships • Prescriptive—prescribe activities to reach goals
Components of a Theory • Purpose • Concepts and conceptual definitions • Theoretical statements • Structure and linkages • Assumptions • Models
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Purpose—why the theory was formulated; specifies the context or situation in which it should be applied
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Concepts and conceptual definitions • Theoretical definitions—description of the phenomenon • Operational definitions—identification of empirical referents
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Theoretical statements • Explain the relationship between concepts • Connect concepts • Several types • Propositions • Laws • Axioms • Hypotheses
Question Tell whether the following statement is true or false: Propositions and hypotheses are written to identify relationships between concepts.
Answer True Rationale: In theories, hypotheses and propositions are types of statements that describe or explain relationships between and among concepts.
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Theoretical statements—(cont.) • Existence statements—name a concept or make claims or clarify a concept (may be true or false) • Relational statements—assert that a relationship exists between two or more concepts • Correlational statements • Causal statements
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Structure and linkages • Logical arrangement of concepts and relational statements • Generally descriptive explanation (written) • Arrangement leads to hypotheses
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Assumptions • Statements that are taken to be true without proof • Can be argued philosophically
Components of a Theory—(cont.) • Models • Schematic representations of an aspect of reality • May be objects, diagrams, geometric formulas, or words
Relationship Among Theory, Research, and Practice • Theory and research • Research validates and modifies theory; theories identify research questions. • Theory and practice • Theory guides practice; practices shapes theory. • Research and practice • Research promotes effective practice; practice identifies problems for research.
Research–theory–practice cycle.
Approaches to Theory Development • Theory to practice to theory • An existing theory (borrowed or shared) is identified. • Components are analyzed for use in new context based on observation and experience. • Concepts, assumptions, and propositions are redefined, and a new “nursing” theory developed.
Approaches to Theory Development—(cont.) • Practice to theory • Theory is inductively derived from clinical situations. • Process uses grounded theory methodologies. • Researcher observes and analyzes phenomenon. • Researcher compares defining concepts and proposes relationships or linkages.
Approaches to Theory Development—(cont.) • Research to theory • Theory is a product of findings from repeated research. • Theories evolve from confirmed research findings. • Patterns are identified from research.
Approaches to Theory Development—(cont.) • Theory to research to theory • Theory drives the research questions, and results modify the theory. • Objective is theory testing.
Process of Theory Development • Concept development • Statement development • Theory construction • Theory testing • Theory application
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Concept development • Concepts are the building blocks of the theory. • In theory development, must create conceptual meaning • Involves defining and clarifying the concepts
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Statement development—Statements are the “skeletons” of the theory. • Statement development • Empirical referent identification
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Theory construction—developing the formal theoretical structure • Structure and contextualize the theory’s components. • Identify and define the concepts and assumptions. • Clarify the context in which the theory is placed. • Design relationship statements.
Question Which of the following would NOT be a component of the process of theory construction? Identify and define the concepts. Specify linkages between/among the concepts. Contextualize the theory. Review the theoretical literature.
Answer D. Review the theoretical literature. Rationale: This step should have been done prior to beginning the process of theory development.
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Theory testing—process of testing theoretical relationships • Name and define empirical indicators. • Validate relationships through research.
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Theory application—assess how theory is applied in practice • Select a setting for application. • Determine outcome variables or practice goals for application of the theory. • Implement a method to examine the theoretical relationships.
- More by User

Chapter 9: Communication & Collaboration in Nursing
Chapter 9: Communication & Collaboration in Nursing. Bonnie M. Wivell, MS, RN, CNS. Therapeutic Use of Self. Hildegard Peplau was first to focus on nurse-patient relationships, Interpersonal Relations in Nursing (1952)
1.66k views • 49 slides

The role of industrialization in economic development: theory and evidence
The role of industrialization in economic development: theory and evidence. Bineswaree Aruna Bolaky Africa Section Division for Africa, LDCs and special programmes United Nations Conference on Trade and Development UNCTAD. Outline of presentation. A – Conceptual definitions
1.38k views • 52 slides

Chapter 7: Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
Chapter 7: Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development. Module 7.1 General Principles of Piaget’s Theory Module 7.2 Piaget’s Four Stages of Cognitive Development Module 7.3 Evaluating Piaget’s Theory Module 7.4 Beyond Piaget’s Theory. Children and Their Development, 3/e by Robert Kail.
1.12k views • 25 slides

Nursing Theories
Nursing Theories. Dr. Belal M. Hijji, RN, PhD 19.09.2010. Learning Outcomes. At the end of this lecture, students will be able to: Define the working terms and theory Recognise the four metaparadigms for nursing Discuss some of the selected nursing theories. 2.
7.61k views • 27 slides

Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory
Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory. Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory (SCDNT). Original Source Impetus was to define content for practical nursing curricula for Department of Health, Education, and Welfare
1.95k views • 11 slides

International Tax Structuring
International Tax Structuring. Tax Structuring. Tax Structuring is defined as a form into which business or financial activities may be organized to minimize taxation.
390 views • 19 slides

Chapter 14: Love and Relationships
Chapter 14: Love and Relationships. For use with Human Sexuality Today (4 th Ed.) Bruce King Slides prepared by: Traci Craig. Chapter Overview. Theories of Love Attachment Theory Sternberg's Triangle Colors of Love Jealousy Relationship Maintenance. Romantic Love Friendship
748 views • 30 slides

CHAPTER 14 ATTACHMENT AND SOCIAL RELATIONSHIPS
CHAPTER 14 ATTACHMENT AND SOCIAL RELATIONSHIPS. Learning Objectives. How do relationships with others contribute to development? How did Bowlby explain the development of attachment? In Bowlby’s model, how do nature and nurture contribute to the development of attachment?
1.72k views • 113 slides

Assessment, Clinical Judgment and Nursing Diagnoses
Assessment, Clinical Judgment and Nursing Diagnoses . Chapter Two. Assessment, Clinical Judgment and Nursing Diagnoses. Contributor Margaret Lunney. Nursing Process. Conceptual Description of What Nurses Do Broadly Accepted Worldwide Five Phases, Cyclical: Assessment Diagnosis Planning
522 views • 23 slides

Social Development
Social Development. The changing nature of relationships with others over the life span. What Are the Issues ?. Individuals develop socially. How do social relationships develop? What factors drive social development? biological cultural cognitive. Erikson’s Theory.
413 views • 22 slides

Nursing Theory
Nursing Theory. Disciplinary Influences. Logical Empiricism. Manifested as: tests, experiments Measurements Scientific Hypotheses Control, Quantitative Diagnoses Positivist Science of Nursing = Reductionist Approach. Historicism. Manifested as: Interpretative Qualitative
548 views • 13 slides

Developing the theoretical and conceptual framework
Developing the theoretical and conceptual framework. J199 lecture, R.E.Khan. Theory. Theories are constructed in order to explain, predict and master phenomena (e.g. relationships, events, or the behavior). In many instances we are constructing models of reality.
328 views • 9 slides

Chapter 2 Cognitive Development
Chapter 2 Cognitive Development. Kyle McSherry, Kayley Robertson, Shamia Watts, Tiffany Renee BonneCarre. Erikson’s Cognitive Development Theory. Erikson based his theory of personality development on the epigenetic principle.
399 views • 15 slides

Chapter 1. Communication and Nursing: Historical Roots and Related Theory. Early Nursing Education. 1983 National League for Nursing Education 1917 first standard curriculum 1918 Goldmark Report 1928 Nurses Patients and Pocketbooks 1934 Nursing Schools Today and Tomorrow
285 views • 9 slides

Nursing Theorist Group Presentations
Nursing Theorist Group Presentations. By: Tara Braun, Nathan Buchinger , Leah Mueller, Elisabeth Vander Zwaagas. Ida J. rlando. Ida J. Orlando’s Nursing Process Theory. Theory of the Deliberative Nursing Process
1.1k views • 27 slides

Chapter 13: Nursing Theory: The Basis for Professional Nursing
Chapter 13: Nursing Theory: The Basis for Professional Nursing. Bonnie M. Wivell, MS, RN, CNS. Nursing Theory. Latin “a viewing”; Greek “contemplating” A body of knowledge shaped by how nurses see the world
1.12k views • 44 slides

Deal Structuring Process
Chapter 11 M&A Deal Structuring Process: Payment & Legal Considerations (Closely linked to Chapters 12 and 13). Deal Structuring Process. Deal structuring involves identifying The primary goals of the parties involved in the transaction ( Strategic versus financial ?);
977 views • 20 slides

Structuring Our Network San Francisco
Structuring Our Network San Francisco. Nature of our network. Existing legal relationships among our network partners (contractor/subcontractor, partnership, memorandum of understanding, … ) Subcontractors to Department of Aging and Adult Services MoUs between ILRC and others
208 views • 12 slides

Family-Provider Relationships in Early Care and Education
Family-Provider Relationships in Early Care and Education. Overview of Content. Brief Overview of Family-Provider Relationship Quality Project Development of a Conceptual Model of Family-Provider Relationships Review of Conceptual Literature Review of Empirical Literature
453 views • 29 slides

Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Nursing
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Nursing. Growth and Development Nurs. 321 Second lecture. Ali Hassan Abu Ryala 2010-2011. Biophysical Development Theory Arnold Gesell (1880-1961). Arnold Gesell Theory. Arnold Gesell was psychologist
566 views • 28 slides

The Theory of Goal Attainment Imogene M. King
The Theory of Goal Attainment Imogene M. King. Prepared By Prof.Dr Nefissa A. kader Vice Dean of Education and Student Affairs Faculty of Nursing – Cairo university. Outlines. Historical background. Origin of the Conceptual Model Model of transaction King's theory Assumptions.
3.7k views • 59 slides

NUR 513 Nerd Tutorials/nur513nerddotcom
NUR 513 Week 1 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 1 DQ 2 NUR 513 Week 2 Historical Development of Nursing Timeline NUR 513 Week 2 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 2 DQ 2 NUR 513 Week 3 Assignment Concept Comparison and Analysis Across Theories NUR 513 Week 3 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 3 DQ 2 NUR 513 Week 4 Assignment Literature Presentation NUR 513 Week 4 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 4 DQ 2 NUR 513 Week 5 Assignment Analysis of a Nursing Conceptual Model NUR 513 Week 5 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 5 DQ 2 NUR 513 Week 6 Assignment Nursing Theory Plan of Care PART 1 NUR 513 Week 6 Assignment Nursing Theory Plan of Care PART 2 NUR 513 Week 6 DQ 1 NUR 513 Week 6 DQ 2
275 views • 12 slides
- Preferences

The Application of Theory to Practice - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

The Application of Theory to Practice
... described birthday and christmas, flower giving on st. valentine's day, ... how by means of ceremony and gifts baptism or other birth ceremonies change a ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Theory is the formulation of thought about a specific discipline or subject
- Social theory is the formulation of thought in the social sciences
- Theory is made up of hypotheses or theses about specific aspects of a discipline
- Hypotheses (sing. hypothesis) or theses (sing. thesis) are the theoretical basis of research and teaching
- Emile Durkheim
- Alexandrov Vasilevich Chayanov
- de Haan et al. 2000
- Sociology is the study of society
- (Latin societas (society) Greek logos (study or word)
- Anthropology is the study of man
- (Greek anthropos (man) Greek logos
- In the social scienes we talk about these and other disciplines
- Psychology the study of the mind
- (Greek Psyche (mind) Greek logos
- Demography the study of populations
- (Greek Demos (people) and graphos (writing or study)
- Sociology is mainly the study of post-industrial society
- Sociologists study both rural and urban society
- They use both quantitative and qualitative research methods
- either systems and sub-systems of a particular society, or
- systems, such as farm households, which are common in all societies
- Anthropology is divided into
- physical anthropology, including forensic anthropology
- Social anthropology
- Cultural anthropology.
- In this course we are mainly concerned with social anthropology (the study of social man)
- In the social sciences anthropology has as its subject matter either
- simple or tribal societies in which the whole of society can be studied at the level of a village or
- a sub-system of such a society, such as kinship and marriage or the rural household
- or a sub-systems of an industrial society which can similarly be studied as a whole, for example a hospital or a factory, urban households or social networks.
- Anthropologists use mainly qualitative research but may also use quantitative methods such as socio-economic survey, household income and expenditure survey or labour use survey
- Methods are the tools or instruments, such as socio-economic survey, which a social scientist uses in research
- A methodology is the combination of a hypothesis or thesis with a statement of the researchers methods and approach
- In explaining a methodology the researcher may refer to his or her assumptions or underlying assumptions
- Corporate bodies are social institutions which
- have a membership with known rights and obligations
- have authority which can be inherited unchanged when their membership changes
- maintain specific relationships with individuals or other corporate bodies
- Examples of corporate bodies are households, clans or tribal groups, cities and bureaucracies.
- households are a form of corporate body based on kinship and economics
- the members of the household share a common set of resources including shelter (a house) and a source of livelihood such as a farm or a job or jobs
- they are under the authority of a household head who is usually the husband and father
- About one third of households in Cambodia are female headed households
- In ordinary speech we speak about my family as having the same meaning as my household
- In sociology we say that a family is not a corporate group that it is a system or a network but that the family may provide the basis of a household
- Most often a household is a nuclear family, consisting of father mother and children
- A compound family is one with more than two generations, including grandparents, or including the spouse and children of a sibling or of affines, people related by marriage
- Plato The Republic
- Metropolitanism
- Citizenship majorities and minorities
- Status is a bundle of rights and obligations which society confers on and recognises in an individual
- Examples of status are
- father, mother, son, daughter
- bank manager
- student, teacher, professor
- A role is the position occupied by a person or institution for specific purposes which may not be permanent.
- For example, we can say that
- when someone is buying a car he or she is performing the role of customer
- when someone is suffering from opression or persecution he or she is in the role of victim.
- However, role and status are often used interchangeably in sociology
- A patron client role relationship is one in which the dominant role is played by a patron who has power and resources to provide benefits and security to groups and individuals who attach themselves to him
- the client, such as a villager or a party member, is in a subordinate role, supports the patron and in turn receives protection and benefits from him.
- Auguste Comte (1789-1857), who we think of as the founder of sociology, was concerned in his writing with statics (order) and dynamics in society. He studied the foundations of social stability. He thought of society as being like an organism in biology such as the human body.
- Comte stated that the statical study of sociology consists in the investigation of the laws of action and reaction of different parts of the social system. A lack of harmony between the whole and the parts of the social system was pathological.
- Herbert Spencer (1820-1903) wrote that the social system had evolved by differentiation. By differentiation Spencer meant the mutual dependence of unlike parts of the system, which he thought was brought about inevitably by an increase in the size of society. He taught that this evolution in the structure of society was brought about by psychological forces through the individuals search for happiness.
- Emile Durkheim (1858-1917) is the most important forerunner of modern sociology and of functionalism. This is because of his major contribution not only to social theory but also to sociological research method. He taught that society should be studied comme une chose as social facts. He was concerned with the integration of people in society in what he called social solidarity, as the way in which social equilibrium is maintained.
- Durkheim said that social facts include laws, morals, customs, fashions, religious beliefs and practices and trends. Certain of these social facts are institutons, by which he meant beliefs and modes of behaviour instituted by the collectivity.
- Durkheim defined sociology as the science of institutions, their genesis and their functioning
- In The Rules of the Sociological Method Durkheim describes functions as general needs of the social organism. He says that social facts have to be explained by social rather than non-social causes.
- He used this approach in his great work Suicide, in which he made use of social statistics, on the suicide rates of catholics and non-catholics in Switzerland, to explain the causes of suicide that is basing his conclusions on social facts rather than on individual causes of suicide
- Durkheims The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life analyses religion in tribal societies as acting to integrate people into society through its institution of common values and identification of membership of society and social groups with a god or gods or religious spirits.
- Durkheim relates religious beliefs and practice with an explanation of widely shared conceptions of the good or beliefs that legitimize the existence and importance of specific social structures and the kinds of behaviour that transpire in social structure. This is now thought of as a functionalist explanation, followed in the work of social anthropologists such as Malinowksi and Radcliffe-Brown and to sociologists such as Talcott Parsons and Merton.
- Karl Marx is regarded as the founder of a theoretical approach to social organisation referred to a conflict theory and which assumes a conflict between an upper ruling capitalist class or elite and a lower class of workers and peasants. He is also the author of a theory of dialectical process (an unavoidable conflict between opposed social forces) which will be enacted in the course of the industrialisation of nations, in which this struggle will inevitably lead to the victory of the workers and the fading away of the State. He and other conflict theorists are also noted for their ideological commitment to the class struggle, the struggle of the masses against capitalism, and for their belief that their sociology is a weapon which should be used in this struggle. Marx was, in keeping with this belief, also the author with Engels of the Communist Manifesto, which was the basis of the failed German revolution of 1848 and more lastingly of the Soviet Communist Revolution of 1917. Both his theoretical and his poltical influence continue to be importance throughout the world.
- Max Weber shared with Marx a theoretical position founded on the belief that there is an economic or material foundation for social differentiation and social structure. However, he argued, especially in The Spirit of Capitalism and the Protestant Ethic that religious and other social and historical influences are equally if not more powerful in shaping social systems. He also conducted wide ranging and continuous research into social structures, including far-reaching research on bureaucracies and on authority systems, which still influence sociology into the 21st Century. His analysis of the function of legitimacy in the structure and conduct of bureaucracies, and on charismatic, traditional and routinised sources of authority continues to be relevant to the work of sociologist in every society, including current research in Cambodia.
- Chayanov is known not as a sociologist or anthropologist but as an agricultural scientist, but his Peasant Farm Organisation (1925, in Thorner ed. 1962) is a work of great importance in linking macro-economic theories of agricultural production with peasant farm economics and with the social determinants of Russian peasant farm production and household organisation. In it he demonstrated on the basis of socio-economic surveys conducted in a number of provinces of the Soviet Union that sustainability of livelihoods in the non-capitalised peasant farm household and the sustainability of the household itself were vital factors in their production systems. His work showed that in village surveys households could be seen to be at every stage of a developmental cycle in which the household was continuously renewed through social and economic systems in the community, regardless of profitability. He also showed that the productivity of the peasant household was based on its understanding and management of widely differing environmental, social and market conditions. His analysis of the developmental cycle in domestic groups predates that of UK anthropologists by thirty years.
- Malinowskis great contribution to the social sciences, and particularly to social anthropology, was his dedication to ethnography as an anthropological method. The depth and quality of his ethnographic material is such that anyone can read it and reach differing conclusion as to analyses of the social system and institutions which he describes. Malinowski first used the term functional for this kind of analysis of social institutions, which he borrowed from Durkheim.
- Malinowski described ritual exchanges of rare sea shells and other rare objects of the Trobriand Islanders which they undertook through long sea voyages to each others islands, visiting each neighbouring society over hundreds of miles. During these vists they exchanged these objects in what he described as the Kula Ring. He distinguished between ritual exchange, kula, and economic exchange, gimwali. The boats which they used were war canoes. Anthropologists describe this kind of ritual exchange as prestations, and see them as having a social function. The Kula Ring has been interpreted as a surrogate for war, as a way of social communication and exchange between otherwise distant peoples, and thus as a way of keeping the peace and avoiding war raids.
- Marcel Mauss made an important contribution to social theory mainly through his book The Gift (Essai sur le Don 1950), which describes ritual exchanges, or prestation, in a number of societies, establishing the wide occurence of such exchanges as social institutions in societies all over the world. He analysed Malinowskis descripton of the Kula Ring among the Trobriand Islanders, but also the Potlach among American Indians, in which canoes, blankets and other valuable objects are given to or burnt in front of neighbouring chiefs, or as part of marriage or initiation ceremonies. Modern sociologists have similarly described birthday and Christmas, flower giving on St. Valentines Day, or other gift exchange events and ceremonies in modern industrial society as having a similar function.
- Van Gennep is similarly mainly known for one major work, The Rites of Passage, in which he described and analysed ritual and ceremonial processes which universally mark changes of status in different societies. He describes how by means of ceremony and gifts baptism or other birth ceremonies change a newly born infant into becoming a socially acknowledged human being and member of the family how initiation changes a pubescent child into an adult how marriage changes a single man and woman into a married couple and unites their families and how a funeral changes a corpse into an ancestor. Van Genneps and Mausss work use ethnographic material from different societies to illustrate Durkheims functional analysis of religion as a universal process by which societies achieve cohesion and integration.
- Meyer Fortes and Jack Goody are Cambridge based social anthropologists whose contribution to social theory rests mainly on their analysis (in The Developmental Cycle in Domestic Groups 1957), independently of Chayanovs work thirty years earlier, of the cyclical dimension in peasant or tribal agricultural households. This work was founded on Meyer Fortes analysis of Ashanti family systems in an article called Time and Social Structure, in which he showed that social time, the cyclical recreating of the kin-based social group through marriages, initiation ceremonies and funerals (establishing the dead as ancestral members of the group) should be understood as a basic principle on which the society maintains its continuity. In related work other anthropologists have shown how such a cycle is important in relating the economic and social continuity of the social group to the ways in which it maintains and protects its environment.
- World Bank 2006 Justice for Peace study of Collective Grievances over Land and Local Governance in Cambodia, Annex F, section 1.2
- Diverse disciplines address the J4P teams underlying assumptions....this paper will draw on multiple bodies of literature. Anthropological texts, particularly field-based ethnographic research, have been used to achieve a level of depth and an understanding of village dynamics over time.....
- Sociological research has been used to examine disparities across geography and within various Cambodian regions. Political analyses, which themselves draw heavily from journalistic sources and key informant interviews, have been used to gauge the distribution of power over time and to better understand the post-Khmer Rouge era patronage system.
- Because this paper takes as its starting point the J4P teams initial analysis, it is restricted to an examination of primarily social phenomena macroeconomic issues and geopolitics, although they have undoubtedly played a role in Cambodias development process, are outside the scope of the study.
- Economic analysis, including the Banks own policy reports, have been used to contextualise findings evaluative reports by various development actors, including the Banks own monitoring and evaluation work, have been used to determine the effect of development assistance on social dynamics within the country. Finally historical sources have been used to illuminate changes in Cambodian society over time, with particular reference to power structures.
- Social Structure
- Societies are structured through
- Institutions and institutional relationships
- Personal statuses and inter-personal role relationships
- Corporate structures and corporate relationships
- Social institutions include
- Political institutions
- Legal institutions
- Ritual or religious institutions
- Economic institutions
- Kinship and marriage institutions
- Educational institutions
- Structural Functional theory states that institutions, corporate structures and statuses have functions in social systems
- the State is a corporate structure which functions to maintain government and citizenship
- marriage is an institution which functions to provide legitimacy to conjugal unions, children and nuclear families
- the status of father functions to confer authority over children.
- Social relationships are said to be reciprocal, that is to have a two-way function.
- For example
- the role of father is reciprocated by the behaviour, rights and obligations of a son or daughter
- the role of husband is reciprocated by the behaviour, rights and obligations of a wife
- the role of salesman is reciprocated by the behaviour, rights and obligations of a customer
- Durkheim Suicide
- Max Weber The Protestant Ethic
- Marcel Mauss The Gift
- Van Gennep Rites of Passage
- Durkheim Elementary forms of the religious life
- Levi-Strausse Myth
- Bronislaw Malinowski The Kula Ring
- Fredrik Barth Spheres of Economic Exchange in Southern Dafur
- Raymond Firth Economic Anthropology
- A.V. Chayanov
- Meyer Fortes
- J.R. Goody (ed)
- Fredrik Barth
- Applied Sociology and Applied Anthropology
- Applied sociology and anthropology deal with problems rather than theoretical issues
- Because problems, e.g. in rural development or health care, are often outside the box and inter-disciplinary, they may challenge existing method and theory
- In doing so they may advance the science
- Defining poverty internationally and in Cambodia
- Defining social exclusion
- Poverty reduction
- Means of escape from poverty
- One form of corporate body which has an important function in modern industrial society is a bureaucracy
- Bureaucracies as described by Max Weber are
- directed by explicit rules impersonally applied, staffed by full-time, life-time, professionals, who do not own the means of administration, or their jobs, or the sources of their funds, and live off a salary, not from income derived directly from the performance of their job (Kilcullen 1996)
- Bureaucracies, such as banks and civil service departments or the police force, matter because they function, fairly and impartially, to administer legally created systems on which a modern social system and a modern economy depend
- A recent study of disputes over land acquisition in Cambodia has argued that the senior government officials concerned and thus the departments they represented do not conform to the model of a modern bureaucracy as defined by Max Weber
- they are part-time officials on very small salaries, dependent for their income on other sources, which affects the way they conduct their jobs, they operate as if owning the means of administration, and do so in a way which is not explicit or impersonally applied
- as a result they do not administer land disputes in accordance with the land law
- (World Bank and Centre for Advanced Study October 2006)
- Policies should be sensitive to informal institutions that structure migration processes, because they may provide an opportunity for policies that aim to support livelihoods. For example, by providing information about migration opportunities, facilitating remittances, and enhancing their productive impact.
- Often-large spatial dimensions underly many livelihoods, though usually less so for poorer households.
- 1 summarised in Arjan de Haan et al. 2000
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Muhamet Yildiz
Departments
As taught in.
- Game Theory
Learning Resource Types
Economic applications of game theory, lecture slides.
The lecture notes are organized into chapters. You can see all of the chapters and topics in the Table of Contents of Topics (PDF) .

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
The application of the Mayer multimedia learning theory to medical PowerPoint slide show presentations
Affiliation.
- 1 a Paediatric Department , Mater Dei Hospital , Malta.
- PMID: 29381105
- DOI: 10.1080/17453054.2017.1408400
PowerPoint™ and other slideware have the potential to be overused and abused. Presentations should be tailored using scientifically derived principles in order to maximise teaching potential. This paper applies the Mayer Multimedia Learning Theory (with its twelve evidence-based principles of multimedia design) to medical slide show presentations. The best way to avoid audience boredom or mortification is to adhere to these precepts. Presentations stand or fall on the quality, relevance, and integrity of the content. Slide shows should supplement a presentation, and not substitute for it. The key principles are brevity, cogency and clarity.
Keywords: Access to information; attention; health education; *multimedia; science/*education; *teaching; information dissemination/*methods; peer review; publishing; research.
- Health Education / methods*
- Multimedia*
- Government Exam Articles
An Introduction To MS PowerPoint
MS PowerPoint is a program that is included in the Microsoft Office suite. It is used to make presentations for personal and professional purposes.
In this article, we shall discuss in detail the functions and features of a PowerPoint presentation, followed by some sample questions based on this topic for the upcoming competitive exams.
To learn more about the different programs under Microsoft Office , visit the linked article.
Given below are a few important things that one must know about the development and introduction of Microsoft PowerPoint:
- The program was created in a software company named Forethought, Inc. by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin.
- It was released on April 20, 1987, and after 3 months of its creation, it was acquired by Microsoft.
- The first version of this program, when introduced by Microsoft was MS PowerPoint 2.0 (1990).
- It is a presentation-based program that uses graphics, videos, etc. to make a presentation more interactive and interesting.
- The file extension of a saved Powerpoint presentation is “.ppt”.
- A PowerPoint presentation comprising slides and other features is also known as PPT.
Gradually, with each version, the program was more creative and more interactive. Various other features were added in PowerPoint which massively increased the requirement and use of this MS Office program.
From the examination point of view, MS PowerPoint happens to be a very important topic. Candidates who are preparing for the various Government exams can visit the Computer Knowledge page and get a list of topics included in the syllabus and prepare themselves accordingly.
Basics of MS PowerPoint
Discussed below are a few questions that one must be aware of while discussing the basics of MS PowerPoint. Once this is understood, using the program and analysing how to use it more creatively shall become easier.
Question: What is MS PowerPoint?
Answer: PowerPoint (PPT) is a powerful, easy-to-use presentation graphics software program that allows you to create professional-looking electronic slide shows.
The image given below shows the main page of MS PowerPoint, where a person lands when the program is opened on a computer system:
Question: How to open MS PowerPoint on a personal computer?
Answer: Follow the steps below to open MS PowerPoint on a personal computer:
- Click on the start button
- Then choose “All Programs”
- Next step is to select “MS Office”
- Under MS Office, click on the “MS PowerPoint”
A blank presentation is open on the screen. According to the requirement, a person can modify the template for a presentation and start using the program.
Question: What is a PowerPoint presentation or PPT?
Answer: A combination of various slides depicting a graphical and visual interpretation of data, to present information in a more creative and interactive manner is called a PowerPoint presentation or PPT.
Question: What is a slide show in a PowerPoint presentation?
Answer: When all the slides of a PowerPoint presentation are set in series and then presented to a group of people, where each slide appears one after the other, is a set pattern, this is known as a PowerPoint slide show.
Question: What all elements can be added to a slide?
Answer: The following elements can be added to a Powerpoint slide:
- Photographs
- Media Clips
All these elements are mainly used to enhance presentation skills and make the slide more interactive.
To learn more about the Fundamentals of Computer , visit the linked article.
For a better understanding of the Microsoft PowerPoint and its operations, functions and usage, refer to the video given below:

Features of MS PowerPoint
There are multiple features that are available in MS PowerPoint which can customise and optimise a presentation. The same have been discussed below.
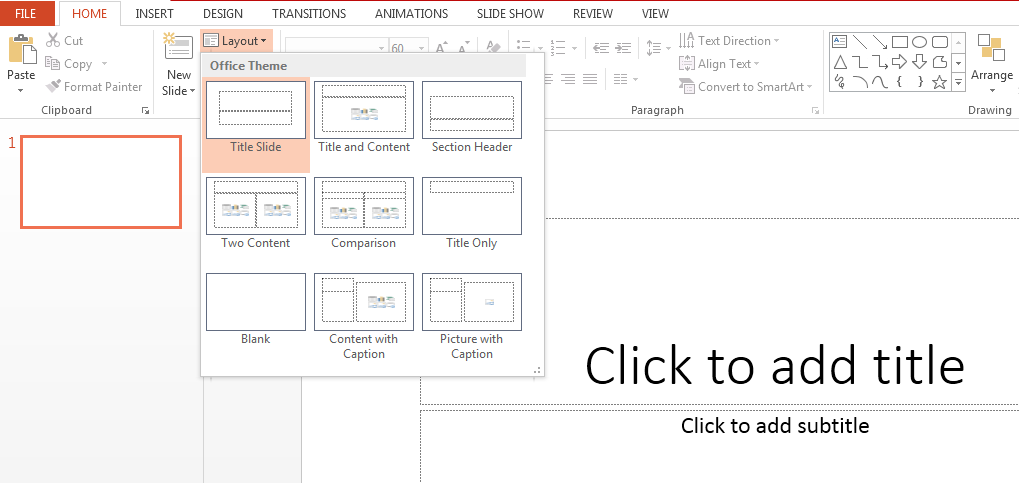
- Slide Layout
Multiple options and layouts are available based on which a presentation can be created. This option is available under the “Home” section and one can select from the multiple layout options provided.
The image below shows the different slide layout options which are available for use:
- Insert – Clipart, Video, Audio, etc.
Under the “Insert” category, multiple options are available where one can choose what feature they want to insert in their presentation. This may include images, audio, video, header, footer, symbols, shapes, etc.
The image below shows the features which can be inserted:

- Slide Design
MS PowerPoint has various themes using which background colour and designs or textures can be added to a slide. This makes the presentation more colourful and attracts the attention of the people looking at it.
This feature can be added using the “Design” category mentioned on the homepage of MS PowerPoint. Although there are existing design templates available, in case someone wants to add some new texture or colour, the option to customise the design is also available. Apart from this, slide designs can also be downloaded online.
Refer to the below for slide design:

During the slide show, the slides appear on the screen one after the other. In case, one wants to add some animations to the way in which a slide presents itself, they can refer to the “Animations” category.
The different animation styles available on PowerPoint are:

Apart from all these options; font size, font style, font colour, word art, date and time, etc. can also be added to a PPT.

Also, there are various other subjects that are included in the exam syllabus for various competitive exams. Candidates can check the detailed section-wise syllabus in the links given below:
Uses of PowerPoint Presentation
PowerPoint presentations are useful for both personal and professional usage. Given below are a few of the major fields where PPT is extremely useful:
- Education – With e-learning and smart classes being chosen as a common mode of education today, PowerPoint presentations can help in making education more interactive and attract students towards the modified version of studying
- Marketing – In the field of marketing, PowerPoint presentations can be extremely important. Using graphs and charts, numbers can be shown more evidently and clearly which may be ignored by the viewer if being read
- Business – To invite investors or to show the increase or decrease in profits, MS PowerPoint can be used
- Creating Resumes – Digital resumes can be formed using MS PowerPoint. Different patterns, photograph, etc. can be added to the resume
- Depicting Growth – Since both graphics and text can be added in a presentation, depicting the growth of a company, business, student’s marks, etc. is easier using PPT
Government exam aspirants can upgrade their preparation with the help of the links given below:
Sample MS PowerPoint Questions and Answers
As discussed earlier in this article, Computer Awareness is included in the syllabus for many competitive exams. Thus, to understand the program from the examination point of view is also a must.
Given below are a few sample questions based on MS PowerPoint.
Q 1. How many maximum slides can be added to a PowerPoint presentation?
- No fixed number
Answer: (3) No fixed number
Q 2. Slide Sorter view can be selected under which of the following categories?
Answer: (4) View
Q 3. The combination of which keyboard keys can be used as a shortcut to add a new slide in MS PowerPoint?
Answer: (3) ctrl+M
Q 4. Header and Footer option is available under which of the following categories?
Answer: (1) Insert
Q 5. Which of the following is not included in the “Insert” category in MS PowerPoint?
Answer: (4) Animation
Similar types of MS PowerPoint Questions may be asked based on the features or usage of the program. Thus, one must carefully go through the elements and aspects of PPT.
For any further assistance related to the upcoming Government exams, candidates can check the Preparation Strategy for Competitive Exams page.
Get the latest exam information, study material and other information related to the major Government exams conducted in the country, at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Connect with us for Free Preparation
Get access to free crash courses & video lectures for all government exams..
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

teacher appreciation
11 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates

46 templates

pediatrician
27 templates

spring season
34 templates

23 templates
Analyzing Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity Thesis Defense
Analyzing albert einstein's theory of relativity thesis defense presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Download the Analyzing Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity Thesis Defense presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase your research in the best way possible and impress your advisors. That's where this amazing template comes in. With it, you can be sure that your presentation will be top-notch and you'll be well on your way to success. Create a perfect presentation for your next thesis defense by using this template now!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
View Week 7 Application of Theory PowerPoint Presentation (1).pptx from NR 501 at Chamberlain College of Nursing. Week 7: Application of Theory: PowerPoint Presentation (The Health Belief
1. Application of theory to Nursing Practice Presented by ARUN.M. 2. • A casual visitor to a hospital or other health care setting might think that little has changed for nurses over the past decade. The majority of nurses still wear a traditional and recognizable uniform, and are to be found in areas where care is provided or advice offered ...
3. Theoretical formulations supported byTheoretical formulations supported by research findings may potentiallyresearch findings may potentially become the foundations of theory-become the foundations of theory- based practice in nursing. Theoreticalbased practice in nursing. Theoretical knowledge derived from either aknowledge derived from either a qualitative or a qualitative source ...
4. MAJOR CONCEPTS : Kings theory of goal attainment focuses on the interpersonal system and the interaction that takes place between individuals - specifically in the nurse client association, the dyadic phase. Each member of the dyad perceives the other and make judgments, action results and together these activities culminant in reaction. When nurse perceive about patient and patient ...
Application: Use Microsoft PowerPoint to create the PowerPoint presentation. Length: The PowerPoint presentation should be 7 total slides (excluding title and reference slides). Speaker notes are used and include in-text citations when applicable. A minimum of three (3) scholarly literature sources must be used. Submission: Submit your files.
lms.courselearn.net
Process of Theory Development—(cont.) • Theory application—assess how theory is applied in practice • Select a setting for application. • Determine outcome variables or practice goals for application of the theory. • Implement a method to examine the theoretical relationships.
Problems Addresse d by the Theory The theory addresses the following problems: • Resistance to Change: One of the most difficult aspects of any change process is dealing with resistance from people who will be affected by the change. • Lack of Direction in Change: Without a clear plan, change efforts can become chaotic and ineffective. The theory provides a clear, three-step process ...
This resource contains information regarding applications of consumer theory. Resource Type: Lecture Notes. pdf. 853 kB Applications of Consumer Theory - Lecture Slides Download File DOWNLOAD. Course Info Instructors Prof. Alexander Wolitzky; Alan Olivi; Departments Economics; As Taught In ...
Application: Use Microsoft PowerPoint to create the presentation. Submit as a .ppt or .pptx file. Length: The PowerPoint presentation must be 6-8 total slides (excluding title and reference slides). Speaker notes should be used and include in-text citations when applicable. Use the Notes Page view feature in PowerPoint to include speaker notes ...
Transcript and Presenter's Notes. Title: The Application of Theory to Practice. 1. The Application of Theory to Practice. Theory is the formulation of thought about a. specific discipline or subject. Social theory is the formulation of thought in. the social sciences. Theory is made up of hypotheses or theses about.
Four Major Concepts of Orem's Theory • Person • Health • Environment • Nursing. 35. Person • Person is defined by Orem as the patient (a recipient of nursing care)- a being who functions biologically, symbolically, and socially and who has the potential for learning and development.
CHAPTER 18 application theory in nursing practice.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Lecture slides (PDF - 1.2MB) 17-19. Static Applications with Incomplete Information. Lecture slides (PDF - 3.5MB) 20-23. Dynamic Games with Incomplete Information. Lecture slides (PDF - 3.9MB) This section provides the schedule of lecture topics along with the lectures slides used during the course.
PowerPoint Presentation. Applications of Number Theory. CS 202. Epp section 10.4. Aaron Bloomfield. About this lecture set I want to introduce RSA The most commonly used cryptographic algorithm today Much of the underlying theory we will not be able to get to It's beyond the scope of this course Much of why this all works won't be taught It ...
[5] The application of Mayer's theory to PowerPoint results in effective presentation and it has been noted that the appropriate usage of Multimedia Learning Theory results in significant ...
PowerPoint™ and other slideware have the potential to be overused and abused. Presentations should be tailored using scientifically derived principles in order to maximise teaching potential. This paper applies the Mayer Multimedia Learning Theory (with its twelve evidence-based principles of multimedia design) to medical slide show ...
2. APPLICATIONS OF GRAPH THEORY: The ideas and concepts of Graph theory are widely used in various branches of science. In general, without knowing the concepts of graph we also use these in our day to day life. For example when we have to go to a place which is connecting with our starting point by different ways then we use the shortest road to arrive the destination soon. Here if we observe ...
MS PowerPoint is a program that is included in the Microsoft Office suite. It is used to make presentations for personal and professional purposes. In this article, we shall discuss in detail the functions and features of a PowerPoint presentation, followed by some sample questions based on this topic for the upcoming competitive exams.
Download the Analyzing Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity Thesis Defense presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase your research in the best way possible and ...
The report discusses applications of graph theory. It provides an overview of graph theory concepts such as definitions of graphs, terminology used in graph theory, different types of graphs, trees and forests, graph isomorphism and operations, walks and paths in graphs, representations of graphs using matrices, applications of graphs in areas ...
Betty Neuman Theory.pptx. Apr 12, 2019 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 48 likes • 33,524 views. Prof Vijayraddi. Betty Neuman Theory.pptx. Healthcare. 1 of 28. Download now. Betty Neuman Theory.pptx - Download as a PDF or view online for free.