- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1, the scientific method.
- Controlled experiments
- The scientific method and experimental design
Introduction
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation..
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
2. Ask a question.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?
3. Propose a hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
4. Make predictions.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
5. Test the predictions.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- Iteration time!
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


- Peterborough

Understanding Hypotheses and Predictions
Hypotheses and predictions are different components of the scientific method. The scientific method is a systematic process that helps minimize bias in research and begins by developing good research questions.
Research Questions
Descriptive research questions are based on observations made in previous research or in passing. This type of research question often quantifies these observations. For example, while out bird watching, you notice that a certain species of sparrow made all its nests with the same material: grasses. A descriptive research question would be “On average, how much grass is used to build sparrow nests?”
Descriptive research questions lead to causal questions. This type of research question seeks to understand why we observe certain trends or patterns. If we return to our observation about sparrow nests, a causal question would be “Why are the nests of sparrows made with grasses rather than twigs?”
In simple terms, a hypothesis is the answer to your causal question. A hypothesis should be based on a strong rationale that is usually supported by background research. From the question about sparrow nests, you might hypothesize, “Sparrows use grasses in their nests rather than twigs because grasses are the more abundant material in their habitat.” This abundance hypothesis might be supported by your prior knowledge about the availability of nest building materials (i.e. grasses are more abundant than twigs).
On the other hand, a prediction is the outcome you would observe if your hypothesis were correct. Predictions are often written in the form of “if, and, then” statements, as in, “if my hypothesis is true, and I were to do this test, then this is what I will observe.” Following our sparrow example, you could predict that, “If sparrows use grass because it is more abundant, and I compare areas that have more twigs than grasses available, then, in those areas, nests should be made out of twigs.” A more refined prediction might alter the wording so as not to repeat the hypothesis verbatim: “If sparrows choose nesting materials based on their abundance, then when twigs are more abundant, sparrows will use those in their nests.”
As you can see, the terms hypothesis and prediction are different and distinct even though, sometimes, they are incorrectly used interchangeably.
Let us take a look at another example:
Causal Question: Why are there fewer asparagus beetles when asparagus is grown next to marigolds?
Hypothesis: Marigolds deter asparagus beetles.
Prediction: If marigolds deter asparagus beetles, and we grow asparagus next to marigolds, then we should find fewer asparagus beetles when asparagus plants are planted with marigolds.
A final note
It is exciting when the outcome of your study or experiment supports your hypothesis. However, it can be equally exciting if this does not happen. There are many reasons why you can have an unexpected result, and you need to think why this occurred. Maybe you had a potential problem with your methods, but on the flip side, maybe you have just discovered a new line of evidence that can be used to develop another experiment or study.
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction

Due to insufficient knowledge, many misconstrue hypothesis for prediction, which is wrong, as these two are entirely different. Prediction is forecasting of future events, which is sometimes based on evidence or sometimes, on a person’s instinct or gut feeling. So take a glance at the article presented below, which elaborates the difference between hypothesis and prediction.
Content: Hypothesis Vs Prediction
Comparison chart, definition of hypothesis.
In simple terms, hypothesis means a sheer assumption which can be approved or disapproved. For the purpose of research, the hypothesis is defined as a predictive statement, which can be tested and verified using the scientific method. By testing the hypothesis, the researcher can make probability statements on the population parameter. The objective of the hypothesis is to find the solution to a given problem.
A hypothesis is a mere proposition which is put to the test to ascertain its validity. It states the relationship between an independent variable to some dependent variable. The characteristics of the hypothesis are described as under:
- It should be clear and precise.
- It should be stated simply.
- It must be specific.
- It should correlate variables.
- It should be consistent with most known facts.
- It should be capable of being tested.
- It must explain, what it claims to explain.
Definition of Prediction
A prediction is described as a statement which forecasts a future event, which may or may not be based on knowledge and experience, i.e. it can be a pure guess based on the instinct of a person. It is termed as an informed guess, when the prediction comes out from a person having ample subject knowledge and uses accurate data and logical reasoning, to make it.
Regression analysis is one of the statistical technique, which is used for making the prediction.
In many multinational corporations, futurists (predictors) are paid a good amount for making prediction relating to the possible events, opportunities, threats or risks. And to do so, the futurists, study all past and current events, to forecast future occurrences. Further, it has a great role to play in statistics also, to draw inferences about a population parameter.
Key Differences Between Hypothesis and Prediction
The difference between hypothesis and prediction can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- A propounded explanation for an observable occurrence, established on the basis of established facts, as an introduction to the further study, is known as the hypothesis. A statement, which tells or estimates something that will occur in future is known as the prediction.
- The hypothesis is nothing but a tentative supposition which can be tested by scientific methods. On the contrary, the prediction is a sort of declaration made in advance on what is expected to happen next, in the sequence of events.
- While the hypothesis is an intelligent guess, the prediction is a wild guess.
- A hypothesis is always supported by facts and evidence. As against this, predictions are based on knowledge and experience of the person making it, but that too not always.
- Hypothesis always have an explanation or reason, whereas prediction does not have any explanation.
- Hypothesis formulation takes a long time. Conversely, making predictions about a future happening does not take much time.
- Hypothesis defines a phenomenon, which may be a future or a past event. Unlike, prediction, which always anticipates about happening or non-happening of a certain event in future.
- The hypothesis states the relationship between independent variable and the dependent variable. On the other hand, prediction does not state any relationship between variables.
To sum up, the prediction is merely a conjecture to discern future, while a hypothesis is a proposition put forward for the explanation. The former, can be made by any person, no matter he/she has knowledge in the particular field. On the flip side, the hypothesis is made by the researcher to discover the answer to a certain question. Further, the hypothesis has to pass to various test, to become a theory.
You Might Also Like:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Hypothesis vs. Prediction
What's the difference.
Hypothesis and prediction are both important components of the scientific method, but they serve different purposes. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation or statement that can be tested through experimentation or observation. It is based on prior knowledge, observations, or theories and is used to guide scientific research. On the other hand, a prediction is a specific statement about what will happen in a particular situation or experiment. It is often derived from a hypothesis and serves as a testable outcome that can be confirmed or refuted through data analysis. While a hypothesis provides a broader framework for scientific inquiry, a prediction is a more specific and measurable expectation of the results.
Further Detail
Introduction.
When it comes to scientific research and inquiry, two important concepts that often come into play are hypothesis and prediction. Both of these terms are used to make educated guesses or assumptions about the outcome of an experiment or study. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of hypothesis and prediction, highlighting their differences and similarities.
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation or statement that can be tested through experimentation or observation. It is typically formulated based on existing knowledge, observations, or theories. A hypothesis is often used as a starting point for scientific research, as it provides a framework for investigation and helps guide the research process.
One of the key attributes of a hypothesis is that it is testable. This means that it can be subjected to empirical evidence and observations to determine its validity. A hypothesis should be specific and measurable, allowing researchers to design experiments or gather data to either support or refute the hypothesis.
Another important aspect of a hypothesis is that it is falsifiable. This means that it is possible to prove the hypothesis wrong through experimentation or observation. Falsifiability is crucial in scientific research, as it ensures that hypotheses can be objectively tested and evaluated.
Hypotheses can be classified into two main types: null hypotheses and alternative hypotheses. A null hypothesis states that there is no significant relationship or difference between variables, while an alternative hypothesis proposes the existence of a relationship or difference. These two types of hypotheses are often used in statistical analysis to draw conclusions from data.
In summary, a hypothesis is a testable and falsifiable statement that serves as a starting point for scientific research. It is specific, measurable, and can be either a null or alternative hypothesis.
While a hypothesis is a proposed explanation or statement, a prediction is a specific outcome or result that is anticipated based on existing knowledge or theories. Predictions are often made before conducting an experiment or study and serve as a way to anticipate the expected outcome.
Unlike a hypothesis, a prediction is not necessarily testable or falsifiable on its own. Instead, it is used to guide the research process and provide a basis for comparison with the actual results obtained from the experiment or study. Predictions can be based on previous research, theoretical models, or logical reasoning.
One of the key attributes of a prediction is that it is specific and precise. It should clearly state the expected outcome or result, leaving little room for ambiguity. This allows researchers to compare the prediction with the actual results and evaluate the accuracy of their anticipated outcome.
Predictions can also be used to generate hypotheses. By making a prediction and comparing it with the actual results, researchers can identify discrepancies or unexpected findings. These observations can then be used to formulate new hypotheses and guide further research.
In summary, a prediction is a specific anticipated outcome or result that is not necessarily testable or falsifiable on its own. It serves as a basis for comparison with the actual results obtained from an experiment or study and can be used to generate new hypotheses.
Similarities
While hypotheses and predictions have distinct attributes, they also share some similarities in the context of scientific research. Both hypotheses and predictions are based on existing knowledge, observations, or theories. They are both used to make educated guesses or assumptions about the outcome of an experiment or study.
Furthermore, both hypotheses and predictions play a crucial role in the scientific method. They provide a framework for research, guiding the design of experiments, data collection, and analysis. Both hypotheses and predictions are subject to evaluation and revision based on empirical evidence and observations.
Additionally, both hypotheses and predictions can be used to generate new knowledge and advance scientific understanding. By testing hypotheses and comparing predictions with actual results, researchers can gain insights into the relationships between variables, uncover new phenomena, or challenge existing theories.
Overall, while hypotheses and predictions have their own unique attributes, they are both integral components of scientific research and inquiry.
In conclusion, hypotheses and predictions are important concepts in scientific research. While a hypothesis is a testable and falsifiable statement that serves as a starting point for investigation, a prediction is a specific anticipated outcome or result that guides the research process. Hypotheses are specific, measurable, and can be either null or alternative, while predictions are precise and serve as a basis for comparison with actual results.
Despite their differences, hypotheses and predictions share similarities in terms of their reliance on existing knowledge, their role in the scientific method, and their potential to generate new knowledge. Both hypotheses and predictions contribute to the advancement of scientific understanding and play a crucial role in the research process.
By understanding the attributes of hypotheses and predictions, researchers can effectively formulate research questions, design experiments, and analyze data. These concepts are fundamental to the scientific method and are essential for the progress of scientific research and inquiry.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
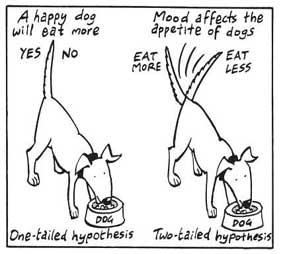
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.

Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
If...,Then...
Angela Lumsden/Getty Images
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject.
In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
In the study of logic, a hypothesis is an if-then proposition, typically written in the form, "If X , then Y ."
In common usage, a hypothesis is simply a proposed explanation or prediction, which may or may not be tested.
Writing a Hypothesis
Most scientific hypotheses are proposed in the if-then format because it's easy to design an experiment to see whether or not a cause and effect relationship exists between the independent variable and the dependent variable . The hypothesis is written as a prediction of the outcome of the experiment.
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Statistically, it's easier to show there is no relationship between two variables than to support their connection. So, scientists often propose the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis assumes changing the independent variable will have no effect on the dependent variable.
In contrast, the alternative hypothesis suggests changing the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable. Designing an experiment to test this hypothesis can be trickier because there are many ways to state an alternative hypothesis.
For example, consider a possible relationship between getting a good night's sleep and getting good grades. The null hypothesis might be stated: "The number of hours of sleep students get is unrelated to their grades" or "There is no correlation between hours of sleep and grades."
An experiment to test this hypothesis might involve collecting data, recording average hours of sleep for each student and grades. If a student who gets eight hours of sleep generally does better than students who get four hours of sleep or 10 hours of sleep, the hypothesis might be rejected.
But the alternative hypothesis is harder to propose and test. The most general statement would be: "The amount of sleep students get affects their grades." The hypothesis might also be stated as "If you get more sleep, your grades will improve" or "Students who get nine hours of sleep have better grades than those who get more or less sleep."
In an experiment, you can collect the same data, but the statistical analysis is less likely to give you a high confidence limit.
Usually, a scientist starts out with the null hypothesis. From there, it may be possible to propose and test an alternative hypothesis, to narrow down the relationship between the variables.
Example of a Hypothesis
Examples of a hypothesis include:
- If you drop a rock and a feather, (then) they will fall at the same rate.
- Plants need sunlight in order to live. (if sunlight, then life)
- Eating sugar gives you energy. (if sugar, then energy)
- White, Jay D. Research in Public Administration . Conn., 1998.
- Schick, Theodore, and Lewis Vaughn. How to Think about Weird Things: Critical Thinking for a New Age . McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2002.
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- Independent Variable Definition and Examples
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- Hypothesis Test for the Difference of Two Population Proportions
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Science Struck
What’s the Real Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction
Both hypothesis and prediction fall in the realm of guesswork, but with different assumptions. This Buzzle write-up below will elaborate on the differences between hypothesis and prediction.
Like it? Share it!

“There is no justifiable prediction about how the hypothesis will hold up in the future; its degree of corroboration simply is a historical statement describing how severely the hypothesis has been tested in the past.” ― Robert Nozick, American author, professor, and philosopher
A lot of people tend to think that a hypothesis is the same as prediction, but this is not true. They are entirely different terms, though they can be manifested within the same example. They are both entities that stem from statistics, and are used in a variety of applications like finance, mathematics, science (widely), sports, psychology, etc. A hypothesis may be a prediction, but the reverse may not be true.
Also, a prediction may or may not agree with the hypothesis. Confused? Don’t worry, read the hypothesis vs. prediction comparison, provided below with examples, to clear your doubts regarding both these entities.
- A hypothesis is a kind of guess or proposition regarding a situation.
- It can be called a kind of intelligent guess or prediction, and it needs to be proved using different methods.
- Formulating a hypothesis is an important step in experimental design, for it helps to predict things that might take place in the course of research.
- The strength of the statement is based on how effectively it is proved while conducting experiments.
- It is usually written in the ‘If-then-because’ format.
- For example, ‘ If Susan’s mood depends on the weather, then she will be happy today, because it is bright and sunny outside. ‘. Here, Susan’s mood is the dependent variable, and the weather is the independent variable. Thus, a hypothesis helps establish a relationship.
- A prediction is also a type of guess, in fact, it is a guesswork in the true sense of the word.
- It is not an educated guess, like a hypothesis, i.e., it is based on established facts.
- While making a prediction for various applications, you have to take into account all the current observations.
- It can be testable, but just once. This goes to prove that the strength of the statement is based on whether the predicted event occurs or not.
- It is harder to define, and it contains many variations, which is why, probably, it is confused to be a fictional guess or forecast.
- For example, He is studying very hard, he might score an A . Here, we are predicting that since the student is working hard, he might score good marks. It is based on an observation and does not establish any relationship.
Factors of Differentiation
♦ Consider a statement, ‘If I add some chili powder, the pasta may become spicy’. This is a hypothesis, and a testable statement. You can carry on adding 1 pinch of chili powder, or a spoon, or two spoons, and so on. The dish may become spicier or pungent, or there may be no reaction at all. The sum and substance is that, the amount of chili powder is the independent variable here, and the pasta dish is the dependent variable, which is expected to change with the addition of chili powder. This statement thus establishes and analyzes the relationship between both variables, and you will get a variety of results when the test is performed multiple times. Your hypothesis may even be opposed tomorrow.
♦ Consider the statement, ‘Robert has longer legs, he may run faster’. This is just a prediction. You may have read somewhere that people with long legs tend to run faster. It may or may not be true. What is important here is ‘Robert’. You are talking only of Robert’s legs, so you will test if he runs faster. If he does, your prediction is true, if he doesn’t, your prediction is false. No more testing.
♦ Consider a statement, ‘If you eat chocolates, you may get acne’. This is a simple hypothesis, based on facts, yet necessary to be proven. It can be tested on a number of people. It may be true, it may be false. The fact is, it defines a relationship between chocolates and acne. The relationship can be analyzed and the results can be recorded. Tomorrow, someone might come up with an alternative hypothesis that chocolate does not cause acne. This will need to be tested again, and so on. A hypothesis is thus, something that you think happens due to a reason.
♦ Consider a statement, ‘The sky is overcast, it may rain today’. A simple guess, based on the fact that it generally rains if the sky is overcast. It may not even be testable, i.e., the sky can be overcast now and clear the next minute. If it does rain, you have predicted correctly. If it does not, you are wrong. No further analysis or questions.
Both hypothesis and prediction need to be effectively structured so that further analysis of the problem statement is easier. Remember that, the key difference between the two is the procedure of proving the statements. Also, you cannot state one is better than the other, this depends entirely on the application in hand.
Get Updates Right to Your Inbox
Privacy overview.
What is a scientific hypothesis?
It's the initial building block in the scientific method.

Hypothesis basics
What makes a hypothesis testable.
- Types of hypotheses
- Hypothesis versus theory
Additional resources
Bibliography.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method . Many describe it as an "educated guess" based on prior knowledge and observation. While this is true, a hypothesis is more informed than a guess. While an "educated guess" suggests a random prediction based on a person's expertise, developing a hypothesis requires active observation and background research.
The basic idea of a hypothesis is that there is no predetermined outcome. For a solution to be termed a scientific hypothesis, it has to be an idea that can be supported or refuted through carefully crafted experimentation or observation. This concept, called falsifiability and testability, was advanced in the mid-20th century by Austrian-British philosopher Karl Popper in his famous book "The Logic of Scientific Discovery" (Routledge, 1959).
A key function of a hypothesis is to derive predictions about the results of future experiments and then perform those experiments to see whether they support the predictions.
A hypothesis is usually written in the form of an if-then statement, which gives a possibility (if) and explains what may happen because of the possibility (then). The statement could also include "may," according to California State University, Bakersfield .
Here are some examples of hypothesis statements:
- If garlic repels fleas, then a dog that is given garlic every day will not get fleas.
- If sugar causes cavities, then people who eat a lot of candy may be more prone to cavities.
- If ultraviolet light can damage the eyes, then maybe this light can cause blindness.
A useful hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable. That means that it should be possible to prove it wrong. A theory that can't be proved wrong is nonscientific, according to Karl Popper's 1963 book " Conjectures and Refutations ."
An example of an untestable statement is, "Dogs are better than cats." That's because the definition of "better" is vague and subjective. However, an untestable statement can be reworded to make it testable. For example, the previous statement could be changed to this: "Owning a dog is associated with higher levels of physical fitness than owning a cat." With this statement, the researcher can take measures of physical fitness from dog and cat owners and compare the two.
Types of scientific hypotheses

In an experiment, researchers generally state their hypotheses in two ways. The null hypothesis predicts that there will be no relationship between the variables tested, or no difference between the experimental groups. The alternative hypothesis predicts the opposite: that there will be a difference between the experimental groups. This is usually the hypothesis scientists are most interested in, according to the University of Miami .
For example, a null hypothesis might state, "There will be no difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't." The alternative hypothesis would state, "There will be a difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't."
If the results of the experiment show a relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis has been rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, according to the book " Research Methods in Psychology " (BCcampus, 2015).
There are other ways to describe an alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis above does not specify a direction of the effect, only that there will be a difference between the two groups. That type of prediction is called a two-tailed hypothesis. If a hypothesis specifies a certain direction — for example, that people who take a protein supplement will gain more muscle than people who don't — it is called a one-tailed hypothesis, according to William M. K. Trochim , a professor of Policy Analysis and Management at Cornell University.
Sometimes, errors take place during an experiment. These errors can happen in one of two ways. A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. This is also known as a false positive. A type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false. This is also known as a false negative, according to the University of California, Berkeley .
A hypothesis can be rejected or modified, but it can never be proved correct 100% of the time. For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red. During research, the scientist then finds that each tomato of this type is red. Though the findings confirm the hypothesis, there may be a tomato of that type somewhere in the world that isn't red. Thus, the hypothesis is true, but it may not be true 100% of the time.
Scientific theory vs. scientific hypothesis
The best hypotheses are simple. They deal with a relatively narrow set of phenomena. But theories are broader; they generally combine multiple hypotheses into a general explanation for a wide range of phenomena, according to the University of California, Berkeley . For example, a hypothesis might state, "If animals adapt to suit their environments, then birds that live on islands with lots of seeds to eat will have differently shaped beaks than birds that live on islands with lots of insects to eat." After testing many hypotheses like these, Charles Darwin formulated an overarching theory: the theory of evolution by natural selection.
"Theories are the ways that we make sense of what we observe in the natural world," Tanner said. "Theories are structures of ideas that explain and interpret facts."
- Read more about writing a hypothesis, from the American Medical Writers Association.
- Find out why a hypothesis isn't always necessary in science, from The American Biology Teacher.
- Learn about null and alternative hypotheses, from Prof. Essa on YouTube .
Encyclopedia Britannica. Scientific Hypothesis. Jan. 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-hypothesis
Karl Popper, "The Logic of Scientific Discovery," Routledge, 1959.
California State University, Bakersfield, "Formatting a testable hypothesis." https://www.csub.edu/~ddodenhoff/Bio100/Bio100sp04/formattingahypothesis.htm
Karl Popper, "Conjectures and Refutations," Routledge, 1963.
Price, P., Jhangiani, R., & Chiang, I., "Research Methods of Psychology — 2nd Canadian Edition," BCcampus, 2015.
University of Miami, "The Scientific Method" http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/161/evolution/161app1_scimethod.pdf
William M.K. Trochim, "Research Methods Knowledge Base," https://conjointly.com/kb/hypotheses-explained/
University of California, Berkeley, "Multiple Hypothesis Testing and False Discovery Rate" https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~hhuang/STAT141/Lecture-FDR.pdf
University of California, Berkeley, "Science at multiple levels" https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/0_0_0/howscienceworks_19
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Siberia's 'gateway to the underworld' is growing a staggering amount each year
Earth from space: Mysterious wave ripples across 'galaxy' of icebergs in Arctic fjord
Iron Age necropolis that predates Rome unearthed near Naples
Most Popular
- 2 'It would be within its natural right to harm us to protect itself': How humans could be mistreating AI right now without even knowing it
- 3 Key events in the Bible, such as the settlement and destruction of Jerusalem, confirmed using radiocarbon dating
- 4 Asteroid that exploded over Berlin was fastest-spinning space rock ever recorded
- 5 Cave of Crystals: The deadly cavern in Mexico dubbed 'the Sistine Chapel of crystals'
- 2 Cave of Crystals: The deadly cavern in Mexico dubbed 'the Sistine Chapel of crystals'
- 3 Why do dogs sniff each other's butts?
- 4 Antarctic ice hole the size of Switzerland keeps cracking open. Now scientists finally know why.
- 5 'It would be within its natural right to harm us to protect itself': How humans could be mistreating AI right now without even knowing it

Hypotheses Versus Predictions
Hypotheses and predictions are not the same thing..
Posted January 12, 2018

Blogs are not typically places where professors post views about arcane matters. But blogs have the advantage of providing places to convey quick messages that may be of interest to selected parties. I've written this blog to point students and others to a spot where a useful distinction is made that, as far as I know, hasn't been made before. The distinction concerns two words that are used interchangeably though they shouldn't be. The words are hypothesis (or hypotheses) and prediction (or predictions).
It's not uncommon to see these words swapped for each other willy-nilly, as in, "We sought to test the hypothesis that the two groups in our study would remember the same number of words," or "We sought to test the prediction that the two groups in our study would remember the same number of words." Indifference to the contrast in meaning between "hypothesis" and "prediction" is unfortunate, in my view, because "hypothesis" and "prediction" (or "hypotheses" and "predictions") mean very different things. A student proposing an experiment, or an already-graduated researcher doing the same, will have more gravitas if s/he states a hypothesis from which a prediction follows than if s/he proclaims a prediction from thin air.
Consider the prediction that the time for two balls to drop from the Tower Pisa will be the same if the two balls have different mass. This is the famous prediction tested (or allegedly tested) by Galileo. This experiment — one of the first in the history of science — was designed to test two contrasting predictions. One was that the time for the two balls to drop would be the same. The other was that the time for the heavier ball to drop would be shorter. (The third possibility, that the lighter ball would drop more quickly, was logically possible but not taken seriously.) The importance of the predictions came from the hypotheses on which they were based. Those hypotheses couldn't have been more different. One stemmed from Aristotle and had an entire system of assumptions about the world's basic elements, including the idea that motion requires a driving force, with the force being greater for a heavier object than a lighter one, in which case the heavier object would land first. The other hypothesis came from an entirely different conception which made no such assumptions, as crystallized (later) by Newton. It led to the prediction of equivalent drop times. Dropping two balls and seeing which, if either, landed first was a more important experiment if it was motivated by different hypotheses than if it was motivated by two different off-the-cuff predictions. Predictions can be ticked off by a monkey at a typewriter, so to speak. Anyone can list possible outcomes. That's not good (interesting) science.
Let me say this, then, to students or colleagues reading this (some of whom might be people to whom I give the URL for this blog): Be cognizant of the distinction between "hypotheses" and "predictions." Hypotheses are claims or educated guesses about the world or the part of it you are studying. Predictions are derived from hypotheses and define opportunities for seeing whether expected consequences of hypotheses are observed. Critically, if a prediction is confirmed — if the data agree with the prediction — you can say that the data are consistent with the prediction and, from that point onward you can also say that the data are consistent with the hypothesis that spawned the prediction. You can't say that the data prove the hypothesis, however. The reason is that any of an infinite number of other hypotheses might have caused the outcome you obtained. If you say that a given data pattern proves that such-and-such hypothesis is correct, you will be shot down, and rightly so, for any given data pattern can be explained by an infinite number of possible hypotheses. It's fine to say that the data you have are consistent with a hypothesis, and it's fine for you to say that a hypothesis is (or appears to be) wrong because the data you got are inconsistent with it. The latter outcome is the culmination of the hypothetico-deductive method, where you can say that a hypothesis is, or seems to be, incorrect if you have data that violates it, but you can never say that a hypothesis is right because you have data consistent with it; some other hypothesis might actually correspond to the true explanation of what you found. By creating hypotheses that lead to different predictions, you can see which prediction is not supported, and insofar as you can make progress by rejecting hypotheses, you can depersonalize your science by developing hypotheses that are worth disproving. The worth of a hypothesis will be judged by how resistant it is to attempts at disconfirmation over many years by many investigators using many methods.
Some final comments.... First, hypotheses don't predict; people do. You can say that a prediction arose from a hypothesis, but you can't say, or shouldn't say, that a hypothesis predicts something.
Second, beware of the admonition that hypotheses are weak if they predict no differences. Newtonian mechanics predicts no difference in the landing times of heavy and light objects dropped from the same height at the same time. The fact that Newtonian mechanics predicts no difference hardly means that Newtonian mechanics is lightweight. Instead, the prediction of no difference in landing times demands creation of extremely sensitive experiments. Anyone can get no difference with sloppy experiments. By contrast, getting no difference when a sophisticated hypothesis predicts none and when one has gone to great lengths to detect even the tiniest possible difference ... now that's good science.
Third and finally, according to the hypothesis that a blog about hypotheses versus predictions will prove informative, the prediction that follows is that those who read and heed this blog will exhibit less confusion about which term to use when. More important, they will exhibit greater gravitas and deeper thoughtfulness as they generate their hypotheses and subsequent predictions. I hope this blog will prove useful. Its utility will be judged by how long it takes to disconfirm the prediction I have just advanced.

David A. Rosenbaum, Ph.D. , is a cognitive psychologist and a Distinguished Professor of Psychology at the University of California, Riverside.
- Find Counselling
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United Kingdom
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Home » Language » English Language » Words and Meanings » What is the Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction
What is the Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction
The main difference between hypothesis and prediction is that the hypothesis proposes an explanation to something which has already happened whereas the prediction proposes something that might happen in the future.
Hypothesis and prediction are two significant concepts that give possible explanations to several occurrences or phenomena. As a result, one may be able to draw conclusions that assist in formulating new theories , which can affect the future advancements in the human civilizations. Thus, both these terms are common in the field of science, research and logic. In addition, to make a prediction, one should need evidence or observation whereas one can formulate a hypothesis based on limited evidence .
Key Areas Covered
1. What is a Hypothesis – Definition, Features 2. What is a Prediction – Definition, Features 3. What is the Relationship Between Hypothesis and Prediction – Outline of Common Features 4. What is the Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction – Comparison of Key Differences
Hypothesis, Logic, Prediction, Theories, Science

What is a Hypothesis
By definition, a hypothesis refers to a supposition or a proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation. In brief, a hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. Nevertheless, this is based on limited evidence, facts or information one has based on the underlying causes of the problem. However, it can be further tested by experimentation. Therefore, this is yet to be proven as correct.
This term hypothesis is, thus, used often in the field of science and research than in general usage. In science, it is termed as a scientific hypothesis. However, a scientific hypothesis has to be tested by a scientific method. Moreover, scientists usually base scientific hypotheses on previous observations which cannot be explained by the existing scientific theories.

Figure 01: A Hypothesis on Colonial Flagellate
In research studies, a hypothesis is based on independent and dependent variables. This is known as a ‘working hypothesis’, and it is provisionally accepted as a basis for further research, and often serves as a conceptual framework in qualitative research. As a result, based on the gathered facts in research, the hypothesis tends to create links or connections between the different variables. Thus, it will work as a source for a more concrete scientific explanation.
Hence, one can formulate a theory based on the hypothesis to lead on the investigation to the problem. A strong hypothesis can create effective predictions based on reasoning. As a result, a hypothesis can predict the outcome of an experiment in a laboratory or the observation of a natural phenomenon. Hence, a hypothesis is known as an ‘educated guess’.
What is a Prediction
A prediction can be defined as a thing predicted or a forecast. Hence, a prediction is a statement about something that might happen in the future. Thus, one can guess as to what might happen based on the existing evidence or observations.
In the general context, although it is difficult to predict the uncertain future, one can draw conclusions as to what might happen in the future based on the observations of the present. This will assist in avoiding negative consequences in the future when there are dangerous occurrences in the present.
Moreover, there is a link between hypothesis and prediction. A strong hypothesis will enable possible predictions. This link between a hypothesis and a prediction can be clearly observed in the field of science.
Figure 2: Weather Predictions
Hence, in scientific and research studies, a prediction is a specific design that can be used to test one’s hypothesis. Thus, the prediction is the outcome one can observe if their hypothesis were supported with experiment. Moreover, predictions are often written in the form of “if, then” statements; for example, “if my hypothesis is true, then this is what I will observe.”
Relationship Between Hypothesis and Prediction
- Based on a hypothesis, one can create a prediction
- Also, a hypothesis will enable predictions through the act of deductive reasoning.
- Furthermore, the prediction is the outcome that can be observed if the hypothesis were supported proven by the experiment.
Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction
Hypothesis refers to the supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence, as a starting point for further investigation. On the other hand, prediction refers to a thing that is predicted or a forecast of something. Thus, this explains the main difference between hypothesis and prediction.
Interpretation
Hypothesis will lead to explaining why something happened while prediction will lead to interpreting what might happen according to the present observations. This is a major difference between hypothesis and prediction.
Another difference between hypothesis and prediction is that hypothesis will result in providing answers or conclusions to a phenomenon, leading to theory, while prediction will result in providing assumptions for the future or a forecast.
While a hypothesis is directly related to statistics, a prediction, though it may invoke statistics, will only bring forth probabilities.
Moreover, hypothesis goes back to the beginning or causes of the occurrence while prediction goes forth to the future occurrence.
The ability to be tested is another difference between hypothesis and prediction. A hypothesis can be tested, or it is testable whereas a prediction cannot be tested until it really happens.
Hypothesis and prediction are integral components in scientific and research studies. However, they are also used in the general context. Hence, hypothesis and prediction are two distinct concepts although they are related to each other as well. The main difference between hypothesis and prediction is that hypothesis proposes an explanation to something which has already happened whereas prediction proposes something that might happen in the future.
1. “Prediction.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Sept. 2018, Available here . 2. “Hypothesis.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 20 Sept. 2018, Available here . 3. Bradford, Alina. “What Is a Scientific Hypothesis? | Definition of Hypothesis.” LiveScience, Purch, 26 July 2017, Available here . 4. “Understanding Hypotheses and Predictions.” The Academic Skills Centre Trent University, Available here .
Image Courtesy:
1. “Colonial Flagellate Hypothesis” By Katelynp1 – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia 2. “USA weather forecast 2006-11-07” By NOAA – (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
About the Author: Upen
Upen, BA (Honours) in Languages and Linguistics, has academic experiences and knowledge on international relations and politics. Her academic interests are English language, European and Oriental Languages, Internal Affairs and International Politics, and Psychology.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
What to Know A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
As anyone who has worked in a laboratory or out in the field can tell you, science is about process: that of observing, making inferences about those observations, and then performing tests to see if the truth value of those inferences holds up. The scientific method is designed to be a rigorous procedure for acquiring knowledge about the world around us.

In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven. And that's where we see the difference between a hypothesis and a theory .
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
When a character which has been lost in a breed, reappears after a great number of generations, the most probable hypothesis is, not that the offspring suddenly takes after an ancestor some hundred generations distant, but that in each successive generation there has been a tendency to reproduce the character in question, which at last, under unknown favourable conditions, gains an ascendancy. Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species , 1859 According to one widely reported hypothesis , cell-phone transmissions were disrupting the bees' navigational abilities. (Few experts took the cell-phone conjecture seriously; as one scientist said to me, "If that were the case, Dave Hackenberg's hives would have been dead a long time ago.") Elizabeth Kolbert, The New Yorker , 6 Aug. 2007
What is a Theory?
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
It is evident, on our theory , that coasts merely fringed by reefs cannot have subsided to any perceptible amount; and therefore they must, since the growth of their corals, either have remained stationary or have been upheaved. Now, it is remarkable how generally it can be shown, by the presence of upraised organic remains, that the fringed islands have been elevated: and so far, this is indirect evidence in favour of our theory . Charles Darwin, The Voyage of the Beagle , 1839 An example of a fundamental principle in physics, first proposed by Galileo in 1632 and extended by Einstein in 1905, is the following: All observers traveling at constant velocity relative to one another, should witness identical laws of nature. From this principle, Einstein derived his theory of special relativity. Alan Lightman, Harper's , December 2011
Non-Scientific Use
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theory is more common in this regard):
The theory of the teacher with all these immigrant kids was that if you spoke English loudly enough they would eventually understand. E. L. Doctorow, Loon Lake , 1979 Chicago is famous for asking questions for which there can be no boilerplate answers. Example: given the probability that the federal tax code, nondairy creamer, Dennis Rodman and the art of mime all came from outer space, name something else that has extraterrestrial origins and defend your hypothesis . John McCormick, Newsweek , 5 Apr. 1999 In his mind's eye, Miller saw his case suddenly taking form: Richard Bailey had Helen Brach killed because she was threatening to sue him over the horses she had purchased. It was, he realized, only a theory , but it was one he felt certain he could, in time, prove. Full of urgency, a man with a mission now that he had a hypothesis to guide him, he issued new orders to his troops: Find out everything you can about Richard Bailey and his crowd. Howard Blum, Vanity Fair , January 1995
And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde , was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis , the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club , 2001 Researchers use this information to support the gateway drug theory — the hypothesis that using one intoxicating substance leads to future use of another. Jordy Byrd, The Pacific Northwest Inlander , 6 May 2015 Fox, the business and economics columnist for Time magazine, tells the story of the professors who enabled those abuses under the banner of the financial theory known as the efficient market hypothesis . Paul Krugman, The New York Times Book Review , 9 Aug. 2009
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general use to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
More Differences Explained
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Diagnosis vs. Prognosis
- Treatment vs. Cure
Word of the Day
Extemporize.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Commonly Confused
'canceled' or 'cancelled', 'virus' vs. 'bacteria', your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, is it 'jail' or 'prison', 'deduction' vs. 'induction' vs. 'abduction', grammar & usage, primary and caucus: what is the difference, words commonly mispronounced, merriam-webster’s great big list of words you love to hate, more commonly misspelled words, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, 12 words for signs of spring, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 13 unusually long english words, 12 star wars words, the words of the week - may 3.

COMMENTS
The difference between hypothesis and prediction is explained through explanations & examples. Use our simple table for hypothesis vs prediction reference.
They make the following hypothesis and prediction: Hypothesis: Eating greasy, high-fat foods causes acne. Prediction: If I eat healthier food, then my skin will produce less oil. In this scenario, the independent variable is the person's diet, and the dependent variable is their skin. To test their hypothesis, the teenager can change the ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
Prediction. On the other hand, a prediction is the outcome you would observe if your hypothesis were correct. Predictions are often written in the form of "if, and, then" statements, as in, "if my hypothesis is true, and I were to do this test, then this is what I will observe.". Following our sparrow example, you could predict that ...
Hypothesis always have an explanation or reason, whereas prediction does not have any explanation. Hypothesis formulation takes a long time. Conversely, making predictions about a future happening does not take much time. Hypothesis defines a phenomenon, which may be a future or a past event. Unlike, prediction, which always anticipates about ...
A hypothesis is an idea about how something works that can be tested using experiments. A prediction says what will happen in an experiment if the hypothesis is correct. Presenter 1: We are going ...
Conclusion. In conclusion, hypotheses and predictions are important concepts in scientific research. While a hypothesis is a testable and falsifiable statement that serves as a starting point for investigation, a prediction is a specific anticipated outcome or result that guides the research process. Hypotheses are specific, measurable, and can ...
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Definitions. A (causal) hypothesis is a proposed explanation. A prediction is the expected result of a test that is derived, by deduction, from a hypothesis or theory. A law (or rule or principle) is a statement that summarises an observed regularity or pattern in nature.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy. Types of Hypothesis
scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world.The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ability to be supported or refuted through observation and experimentation.
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
The alternate hypothesis is usually your initial hypothesis that predicts a relationship between variables. The null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in. Hypothesis testing example. You want to test whether there is a relationship between gender and height. Based on your knowledge of human ...
Prediction. A prediction is also a type of guess, in fact, it is a guesswork in the true sense of the word. It is not an educated guess, like a hypothesis, i.e., it is based on established facts. While making a prediction for various applications, you have to take into account all the current observations.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method. Many describe it as an "educated guess ...
First, hypotheses don't predict; people do. You can say that a prediction arose from a hypothesis, but you can't say, or shouldn't say, that a hypothesis predicts something. Second, beware of the ...
This is the famous prediction tested (or allegedly tested) by Galileo. This experiment — one of the first in the history of science — was designed to test two contrasting predictions. One was ...
Relationship Between Hypothesis and Prediction. Based on a hypothesis, one can create a prediction; Also, a hypothesis will enable predictions through the act of deductive reasoning. Furthermore, the prediction is the outcome that can be observed if the hypothesis were supported proven by the experiment. Difference Between Hypothesis and Prediction
A hypothesis is an explanation for something. It is a provisional idea, an educated guess that requires some evaluation. A good hypothesis is testable; it can be either true or false. In science, a hypothesis must be falsifiable, meaning that there exists a test whose outcome could mean that the hypothesis is not true.
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.