Home Essay Examples Science Hindi

Hindi: Types Of Verbs
- Category Science
- Subcategory Language and Linguistics
- Topic Hindi

If you explored the tenses in Hindi, you learned that in basic Hindi, verbs can be regular or irregular, intransitive or transitive, and that these concepts influence the conjugation or inflection of a verb when used in a sentence. However, as you have probably noticed, Hindi is a nuanced language! So there are also other basic Hindi verb types that can modify the inflection or the very meaning of a verb! Identifying and distinguishing between these verb types is a cornerstone of mastering basic Hindi. Ready for the challenge? चिंता मत करो! (Don’t worry!) In this section, we will define these verb types in greater detail and provide examples of each through basic Hindi sentences.
Intransitive And Transitive Verbs
As discussed previously, in basic Hindi we have both intransitive and transitive verbs. Verb transitivity is a classic and age old linguistic concept, but it is also a simple concept to understand.
Our writers can write you a new plagiarism-free essay on any topic
An intransitive verb has no direct object. In other words, there is no person or thing in the sentence that is the recipient of the action of the verb.
I exist. / Main astitva hoon. / अस्तित्व होना.
Because one cannot exist a person or exist a thing, the above verb ‘astitva honaa’ is an intransitive verb.
In contrast, a transitive verb has one or more direct objects. So, there is a person or thing in the sentence that receives the action of the verb.
He eats vegetables. / Voh sabziyaan khaataa hai. / वह सब्ज़ियाँ खाता है.
Because one can eat a thing, (hopefully one cannot eat a person!), and in this case the thing eaten is vegetables, the above verb ‘khaanaa’ is a transitive verb. Understanding transitivity is pivotal to basic Hindi, so it is helpful to practice identifying the transitivity of other Hindi verbs.
Notice that the verb ‘khaataa’ and the auxiliary verb ‘hai’ come at the end of the sentence, after the verb’s direct object. Why is this? Standard Hindi sentence structure differs from that of English! While in English the verb follows the subject and precedes its direct object, in Hindi, verbs are placed at the end of the sentence and auxiliary verbs are placed very last in the sentence.
Compound Verbs
A compound verb is, as you may have expected, a multi-word compound. This compound consists of a primary verb and an auxiliary (helping) verb that work together as a single verb. The compound verb has a subtle, altered meaning from its constituent verbs. The auxiliary verb typically adds specificity to the verb by describing the manner in which the primary verb is performed, to add depth and flair to basic Hindi sentences.
I sat down. / Main baith gayaa. / मैं बैठ गया.
The standard Hindi verb for ‘to sit’ is बैठना ‘baithnaa’. However, when we use the compound verb बैठ जाना ‘baith jaanaa,’ combining the root ‘baith’ of the primary verb baithnaa with the auxiliary verb jaanaa (to go), the compound verb meaning is ‘to sit down.’ Notice that when conjugating the compound verb, only the auxiliary verb is inflected, while the primary verb remains in its root form.
Conjunct Verbs
Similar to compound verbs, conjunct verbs also operate by combining two basic Hindi words. A conjunct verb is formed by joining either a noun or an adjective with a verb. When it is a noun joining with the verb, this is known as a nominal conjunct. When it is an adjective joining with the verb, this is known as an adjectival conjunct. As with compound verbs, conjunct verbs function as a single verb.
She cleans. / Voh saaf kartee hai. / वह साफ़ करती है.
The standard Hindi adjective for ‘clean’ is साफ़ ‘saaf.’ However, when we use the conjunct verb साफ़ करना ‘saaf karnaa,’ combining the adjective ‘saaf’ with the verb karnaa (to do), the conjunct verb meaning is ‘to clean.’
Imperative Verbs
Imperative verbs typically command, instruct, or request a person or thing to do or not to do something. You can think of imperative verbs as the bossy verbs! For this reason, it is wise to use discretion when employing imperative verbs in basic Hindi conversations, particularly when with strangers, so as not to give the impression of haughtiness or anger in our speaking tone. One can also use imperative verbs simply to offer permission or to extend an invitation.
Speak Hindi. / Hindee Bolo. / हिन्दी बोलो.
The standard Hindi verb for ‘to speak’ is बोलना ‘bolnaa.’ However, in the common ‘tum’ form of the imperative construction, ओ is appended to the verb root. Imperative verb conjugation depends upon which form of ‘you’ is used in the sentence. When the formal (aap) is used, we append इए to the verb root. When the informal (tum) is used as in the above example, we append ओ to the verb root. Finally, when the very informal (too) is used, we simply use the verb root on its own. Notice that the subject ‘You’ is implied but not literally stated in the sentence. This is typical in imperative constructions. Similarly, the word ‘Please’ is implied by the ‘aap’ form, but there is no need to literally state it.
Causal Verbs
Causal or causative verbs represent actions that are indirectly caused by the subject. In basic Hindi causal verb constructions, the subject causes, makes, or otherwise enables another person or thing to do something. Causal verbs are classified as transitive verbs.
I had him explain. / Mainne usse samajhvaayaa. / मैंने उससे समझवाया.
The standard Hindi verb for ‘to explain’ is समझाना ‘samjhaanaa.’ However, when we use the causal verb समझवाना ‘samajhvaanaa,’ by appending वा to the verb root as typically done to form a causal verb, the conjunct verb meaning is ‘to cause to explain.’ Notice that because causal verbs are transitive verbs and this sentence is in the past tense, the postposition ने is appended to the subject per the tenses in Hindi. The subject should also be put into the oblique case when used with the postposition ने, however ‘I’ is an exception pronoun so instead of using the traditional oblique form of ‘I,’ we simply use मैंने. Moreover, in causal verb constructions the postposition ‘से’ must be appended to the agent directly performing the action if the agent is named in the sentence as in the example, so उस became उससे.
Polysemantic Verbs
This concept goes beyond basic Hindi but I know you smart cookies are up for the challenge! What in the world is a polysemantic verb, you may be asking! Let’s break it down. ‘Poly’ means many, and ‘semantic’ relates to word meaning. Therefore, a polysemantic verb is one which can have multiple meanings. These secondary meanings typically add a more figurative aspect to the verb’s literal meaning.
I feel hungry. / Mujhe bhukh lagee hai. / मुझे भूख लगी है.
The standard Hindi verb for ‘to attach’ is लगना ‘lagaanaa.’ However, this polysemantic verb has more than one meaning. It can also be used to express feelings, such as hunger. In the example above, the feeling of hunger is conveyed through the literal attachment of hunger भूख ‘bhukh’ to the subject. Language works in funny ways, doesn’t it! In Hindi proverbs and Hindi idioms, you will see more complex examples of literal expressions with underlying figurative meanings.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
क्रिया – परिभाषा, भेद, और उदाहरण : हिन्दी, Verb / Kriya in Hindi
क्रिया – परिभाषा, भेद, और उदाहरण : हिन्दी, Verb/Kriya in Hindi हिंदी व्याकरण में कई सारे ऐसे मुख्य भेद होते हैं जिनके बारे में हम सही तरीके से जानकारी प्राप्त नहीं कर पाते और कहीं ना कहीं हम अपने वाक्य को भी गलत तरीके से लिख लेते हैं।
ऐसे में हमें भी निश्चित रूप से इन बातों का ध्यान रखना होगा ताकि हम आगे कोई भी गलती ना कर सके। आज हम आपको क्रिया के बारे में संपूर्ण जानकारी देंगे जिसे आप भी सही तरीके से वाक्यों का उपयोग कर सकें।
क्रिया – परिभाषा, भेद, और उदाहरण : हिन्दी, Verb/Kriya in Hindi
क्रिया मुख्य रूप से एक ऐसा शब्द है या शब्दों का समूह होता है, जो हमें किसी भी कार्य के होने का बोध कराता है। उदाहरण के तौर पर
- मेरी बहन हंस रही है।
- दुर्गा कॉलेज जाने वाली है।
- हंसा गाना गा रही है।
इन सभी उदाहरणों में जो भी कार्य किया जा रहा है उन्हें क्रिया के रूप में माना जाता है। ऐसे में हम दिन में कई बार वर्ब का उपयोग करते हैं।
क्रिया के मुख्य भेद
वर्ब के अंतर्गत कुछ मुख्य भेदों को देखा जाता है, जो रचना की दृष्टि से निम्न प्रकार के होते हैं।
- अकर्मकक्रिया
- सकर्मकक्रिया
- द्विकर्मकक्रिया
अकर्मकक्रिया— ऐसी क्रिया जिनका मुख्य असर करता पर होता है और जिस से वाक्य का अर्थ कुछ हद तक बदल जाता है। ऐसे क्रियाओं को अकर्मक वर्ब कहते हैं।
अगर आप दूसरी तरफ से देखते हैं, तो महसूस होगा कि अकर्मक क्रियाओं को कर्म करने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है वह अपना कार्य स्वता ही करते हैं।
अकर्मक क्रियाओं के मुख्य उदाहरण
- राकेश हमेशा हंसता है।
- छिपकली रेंग कर बढ़ती है|
- ट्रेन चलती रहती है|
कुछ मुख्य अकर्मकक्रिया—
खेलना, बैठना, चलना, ठहरना, चमकना, डोलना, कूदना, उछलना, मरना, जीना, जागना, उगना, सोना, होना, खोना, जीतना, हंसते रहना|
सकर्मकक्रिया— यह ऐसी क्रियाओं के रूप में होती हैं जिनका असर कर्म पर पड़ता है। इनका किसी भी तरह से करता पर असर नहीं होता है। ऐसी मुख्य वर्ब को सकर्मक वर्ब के नाम से जाना जाता है। जिनमें कर्म का होना मुख्य होता है।
सकर्मक क्रिया का उदाहरण
- मैं कहानी लिखती हूं|
- निधि नमकीन नहीं खाती है|
- मीरा को फूल पसंद है|
- उसे ऑरेंज जूस पसंद है|
द्विकर्मकक्रिया— इसे अन्य क्रियाओं के रूप में देखा जाता है जहां पर प्रत्येक क्रियाओं के दो कर्म होते हैं। सामान्य रूप से हम द्विकर्मक वर्ब का उपयोग कई बार करते हैं|
आज हम आपको कुछ उदाहरण के माध्यम से इसकी जानकारी देंगे| इन में प्रयुक्त होने वाले दोनों कर्म में से मुख्य कर्म किसी पदार्थ के रूप में मुख्य रूप से शामिल होता है।
द्विकर्मकक्रिया के उदाहरण —
- नेहा ने सुरेश को पेन दी थी।
- मैंने तुम्हें उस दिन अपनी ड्रेस दी थी।
- वीरु ने जय को ₹50 दिए।
- राजा ने ब्राह्मण को दान दिया|
रचना की दृष्टि से क्रिया के विभिन्न भेद
रचना की दृष्टि से क्रिया के दो प्रकार के भेद होते हैं जिनके बारे में भी हम विस्तार से जानकारी देंगे—
- रूढ़क्रिया— ऐसी क्रिया जिसकी रचना हम किसी धातु के माध्यम से करते हैं उसे रुढ़ क्रिया कहते हैं। उदाहरण के रूप में खाना-पीना, लिखना, जाना, आना आदि।
- योगिकक्रिया— ऐसी क्रिया जिनकी रचना एक से अधिक तत्वों से होती है उन्हें यौगिक क्रिया के नाम से जाना जाता है। कई बार हिंदी व्याकरण में इनका बहुलता से उपयोग भी होता है। उदाहरण के रूप में बताना, लिखवाना, कहीं जाना, बड़बड़ करते रहना, पढ़वाना आदि।
योगिक क्रिया के प्रमुख भेद—
- संयुक्तक्रिया
- नामधातुक्रिया
- प्रेरणार्थकक्रिया
- अनुकरण आत्मकक्रिया
प्रयोग तथा संरचना के आधार पर विभिन्न क्रिया के भेद
- सामान्यक्रिया
- सहायकक्रिया
- पूर्वकालिकक्रिया
- सजातीयक्रिया
सामान्यक्रिया— यह क्रिया का सामान्य रूप का वह प्रतिबिंब होता है जिसमें एक कार्य एवं एक ही क्रियापद शामिल होता है।
ऐसे वाक्य जिसमे मुख्य रुप से एक ही क्रियापद होते हैं उन्हें सामान्य क्रिया के रूप में देखा जाता है जिन्हें आसानी से ही पढ़ कर समझा जा सकता है।
उदाहरण—
1) राधाबाई आती है।
2) श्याम इमली खाता है।
3) प्रवीण खिलौना खेलता है।
4) मम्मी खाना देकर जाती है।
सहायकक्रिया– जिस प्रकार नाम से ही जाहिर होता है कि जब किसी वाक्य में मुख्य क्रिया की सहायता की जाती है और मुख्य रूप से ऐसा वाक्य जो किसी भी वाक्य को पूरा करने का दमखम रखता है उसे सहायक क्रिया कहा जाएगा।
- कविता पुस्तक पढ़ती है।
- मुझे खाना खाना पसंद है।
- मैंने पढ़ाई पूरी कर ली है।
यहां पर हम देख सकते हैं कि मुख्य क्रिया साथ-साथ सहायता करने वाला पद शामिल है, जहां पर किसी भी वाक्य को पूरा पढ़ाया जाता है।
संयुक्तक्रिया— संयुक्तक्रिया किसी भी क्रिया का वह भाग होता है, जो दो अलग-अलग क्रियाओं के माध्यम से पूरी होती है और दो अलग-अलग क्रियाओं को जोड़ने का भी कार्य करती है। ऐसी क्रियाओं को संयुक्तक्रिया कहा जाता है।
उदाहरण
1) श्याम ने पानी पी लिया है।
2) सुरेश ने अच्छा गाना गाया है।
3) राधा ने अपना खाना बना लिया है।
इस प्रकार से हमने देखा कि पहले वाक्य में “पानी” और “पी” मिलकर एक क्रिया बना रहे हैं जिसमें संयुक्त क्रिया हो रही है। इसी प्रकार से हम दूसरे और तीसरे वाक्य में भी देखते हैं जहां पर क्रिया मिलकर संयुक्त क्रिया बनाती है।
प्रेरणार्थकक्रिया— यह एक ऐसी क्रिया होती है जिसमें करता खुद की बजाय दूसरे क्रिया के लिए प्रेरित होता है और प्रेरणा देने का कार्य करता है।
इसीलिए इस क्रिया को प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया कहा जाता है। जब भी क्रिया बनती है तो सकर्मक होती है, जो मुख्य रूप से हम उदाहरण से दर्शा सकते हैं।
- नेहा ने निधि से होमवर्क करवाया है।
- संतोषी ने विमला से पूजा करने को कहा है।
- डॉक्टर ने नर्स से जरूरी सामान मंगवाया है।
- रवि अपनी पत्नी से कपड़े धुलवाता है।
इन सभी उदाहरणों में प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया बताई गई है जिसमें आसानी से ही हम इस वर्ब को समझ सकते हैं।
पूर्वकालिकक्रिया— यह प्रिया उस समय इस्तेमाल की जाएगी जब किसी भी वाक्य में वर्ब पहले से ही संपन्न हुई हो और दूसरी बाद में आई हो। ऐसे में पहले संपन्न हुई क्रिया को पूर्वकालिकक्रिया कहा जाएगा।
- वह पढ़ कर चला गया।
- समीक्षा नहा कर खाना बनाएगी।
- श्याम खेलकर पढ़ने जाएगा।
- विकास पढ़कर खाना खाता है।
- रानी खेल कर सो जाती है।
यहां पर दो प्रकार की क्रियाओं का प्रयोग किया गया है जिसमें पूर्वकालिक क्रिया बनती है। ऐसे में उदाहरण के माध्यम से ही ऐसी क्रियाओं को आसानी से समझा जा सकता है।
सजातीयक्रिया— मुख्य रूप से यह क्रिया का वह रूप होता है जिसमें कर्म और क्रिया एक ही धातु से बने होते हैं और एक साथ प्रयुक्त हो जाते हैं उन्हें सजातीय क्रिया में शामिल किया जाता है।
उदाहरण
- भारत ने लड़ाई लड़ी।
- तुमने खाना खाया।
नामधातुक्रिया— यह वर्ब का वह रूप होता है जिसमें किसी भी क्रिया की रचना संज्ञा, सर्वनाम या विशेषण के माध्यम से होती है। इस क्रिया में किसी भी धातु का उपयोग नहीं होता है और इसीलिए इसे नामधातु वर्ब कहा जाता है।
- अपना + ना = अपनाना
- चमक + ना = चमकना
- पटक + ना = पटकना
काल के आधार पर वर्ब के भेद
काल के आधार पर क्रिया के मुख्य भेद होते हैं–
- भूत कालिकक्रिया— इसमें वे क्रियाएं शामिल होती हैं जिनमें भूतकाल में किए गए कार्यों का बोध होता है और ऐसे क्रियाओं को भूतकालिक क्रिया कहा जाता है।
उदाहरण—
- उसने खाना खा लिया था।
- मैंने खिलौना मंगवाया था।
- कविता ने पुस्तक पढ़ ली थी।
भूत कालिक क्रिया के मुख्य भेद
- सामान्य भूतकालक्रिया
- आसन्न भूतकालक्रिया
- पूर्ण भूतकालक्रिया
- संदिग्ध भूतकालक्रिया
- अपूर्ण भूतकालक्रिया
- हेतु हेतु मद भूतकालक्रिया
2) वर्तमान कालिकक्रिया— यह क्रियाएं इस प्रकार से होती हैं जिनमें वर्तमान में संपन्न होने वाले कार्यों का बोध किया जाता है और उन्हें अपने वाक्यों में स्थान दिया जाता है।
वर्तमान कालिकक्रिया के मुख्य भेद
1) सामान्य वर्तमान कालिक क्रिया— इस वर्ब के माध्यम से कार्य का सामान्य समय में होने का बोध होता है। जिसके अंतर्गत ती है, ते हैं आते हैं।
2) अपूर्ण वर्तमान कालिकक्रिया— इस वर्ब के अंतर्गत कार्य का वर्तमान समय में जारी रखने का बोध होता है। जिसमें वाक्य के अंत में रहा है, रही है, रहे हैं शामिल होते हैं।
3) संदिग्ध वर्तमान कालिकक्रिया— इस वर्ब के अंतर्गत कार्य के वर्तमान समय में होने पर संशय का बोध होता है। जिस से वाक्य के अंत में रहा होगा, रही होगी, रहे होंगे आता है।
4) आज्ञाथक वर्तमानकालिकक्रिया— यह वर्ब का वह रूप है जिसमें आज्ञा या आदेश का बोध होता है।
5) संभाव्य वर्तमान कालिक क्रिया— इस वर्ब में वर्तमान समय में अपूर्ण क्रिया की संभावना या संशय होने का बोध किया जाता है। जिससे किसी वाक्य के अंत में रहा होगा, रही होगी, रहे होंगे शामिल होते हैं।
3) भविष्य कालिकक्रिया— वे क्रियाएं जिनके द्वारा भविष्य में होने वाले काम का बोध किया जाता है उन्हें भविष्य कालिक क्रिया कहा जाता है।
- हम कल जबलपुर जाएंगे।
- अगले सप्ताह सभी लोग अपने घर जाने वाले हैं।
- तुम लोग कब वापस आओगे?
भविष्य कालीक्रिया के भेद
- सामान्य भविष्य कालिक – इनमें मुख्य रूप से आने वाले समय का बोध होता है।
- आज्ञाथक भविष्य कालिक— इनमें आज्ञा या आदेश होने का बोध शामिल होता है।
- संभाव्य भविष्य कालिक— इसके माध्यम से भविष्य काल में होने वाले संभावना को व्यक्त किया जाता है।
- काल किसे कहते हैं परिभाषा, भेद और उदाहरण
- वचन किसे कहते हैं। परिभाषा, भेद और उदाहरण
- लिंग – परिभाषा, भेद और उदाहरण
इस प्रकार से हमने देखा कि जिस वर्ब का उपयोग हम हिंदी व्याकरण में प्रमुखता से करते हैं उसके अंदर कई प्रकार के भेद और आधार होते हैं जिसके माध्यम से हम अलग अलग तरीके से वाक्य को वर्गीकृत कर सकते हैं और सही तरीके से उनका आकलन भी किया जा सकता है।
आज हमने आपको क्रिया – परिभाषा, भेद, और उदाहरण हिन्दी, Verb Kriya in Hindi के बारे में संपूर्ण जानकारी दी है,
जो निश्चित रूप से आपके लिए कामगर होगी और उम्मीद करते हैं आपको हमारा यह हिंदी व्याकरण संबंधित लेख पसंद आएगा।
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Verb in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples
Verb in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples, Verbs in Hindi, Types/Kinds of Verbs in Hindi with definition and examples. What is a verb in Hindi? वर्ब इन हिंदी। क्रिया की परिभाषा, प्रकार, उदाहरण तथा नियम हिंदी में।
English Grammar में Verb का विशेष महत्व है। बिना क्रिया के किसी भी प्रकार के वाक्यों की संरचना संभव नहीं है अर्थात हम बिना क्रिया के वाक्य को नहीं बना सकते हैं। यदि आप हिंदी से अंग्रेजी में वाक्यों को बनाना सीखना चाहते हैं तो आपको क्रियाओं (Verbs) का ज्ञान होना अति आवश्यक होता है। क्रिया को अंग्रेजी में Verb कहते हैं।
इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से आप Verb in Hindi नियम उदाहरण तथा सहित पढ़ेंगे। इस पोस्ट में Verb Definition in Hindi में उदाहरण सहित विस्तार से समझायी गई है। तथा क्रिया के प्रकारों (Kinds of Verbs) का विस्तार से वर्णन किया गया है।

Page Contents
Verb in Hindi (Definition)
Definition of Verb in Hindi : जो शब्द कार्य का करना या होना प्रकट करें अवस्था किसी व्यक्ति वस्तु या स्थान के विषय में कुछ बताएं उसे Verb कहते हैं। जैसे ; जाना (go), आना (come), हंसना (laugh), रोना (weep), गाना (sing), पढ़ना (read), दौड़ना (run), खेलना (play), काम करना (work) आदि।
Definition of Verb in English : A word which denotes an action or a state of being of a person place or thing is called verb. For example : go, come, laugh, cry, sing, read, run, play, work, etc.
Examples of Verbs in Hindi
1. I cannot go to market. मैं बाजार नहीं जा सकता हूं।
2. वह अंग्रेजी पढ़ाता है। He teaches English.
3. You should come here daily. आपको यहां प्रतिदिन आना चाहिए।
4. She does not laugh . वह नहीं हंसती है।
5. Your child will cry . आपका बच्चा रोएगा।
6. The singer will sing a song in the party. गायक पार्टी में गाना गाएगा।
7. The students do not read it properly. विद्यार्थी यह सही तरीके से नहीं पढ़ते हैं।
8. We must not run on the road. हमें सड़क पर नहीं तोड़ना चाहिए।
9. You should play a game in the evening. आपको शाम को एक खेल खेलना चाहिए।
10. The boys work hard to get success. लड़के सफल होने के लिए मेहनत करते हैं।
Note : ऊपर दिए गए वाक्यों में गहरे काले रंग में लिखे शब्द के उदाहरण हैं। इनका प्रयोग वाक्यों के टेंस के अनुसार हुआ है। क्रियाओं के बिना वाक्यों की रचना संभव नहीं होती है।
- Noun in Hindi
- Pronoun in Hindi
- Adjective in Hindi
- Adverb in Hindi
What is the use of a verb in the sentence?
आप जानते हैं कि क्रिया के बिना हम किसी भी प्रकार के सेंटेंस को नहीं बना सकते हैं। वाक्यों में क्रियाओं का प्रयोग निम्नलिखित बातों को व्यक्त करने के लिए करते हैं;
1. किसी Verb से हमें किसी वस्तु या व्यक्ति के द्वारा किए गए कार्य का बोध होता है। जैसे;
- I teach you.
- She prepares tea.
- I did not think so.
2. Verb हमें ज्ञात होता है कि किसी वस्तु या व्यक्ति के साथ क्या होता है, क्या हुआ है या क्या हो रहा है। जैसे;
- The fruits are eaten.
- Students are taught English.
- The food is cooked.
3. Verb से हमें किसी वस्तु या व्यक्ति की दशा, अवस्था, व्यवसाय, नाम आदि के बारे में पता चलता है। जैसे;
- I am a teacher.
- She is ill now.
- My mother is a singer.
- His name is Priyanka.
4. Verb से हमें किसी वस्तु या व्यक्ति पर अधिकार (Possession) का पता चलता है। जैसे;
- He has a red ball.
- I have an old laptop.
- This chair has three legs.
- Use of It in Hindi
- Use of There in Hindi
- Sentence in Hindi
- Modal Auxiliary Verbs in Hindi
Kinds of Verbs in Hindi (क्रिया के प्रकार हिंदी में)
Verbs चार प्रकार की होती हैं;
Transitive verb : (सकर्मक क्रिया)
- Intransitive verb : (अकर्मक क्रिया)
- Linking verb : (संयोजक किया)
- Auxiliary Verbs (सहायक क्रिया)
Definition of Transitive Verb : A verb that requires an object to complete its meaning and sense is called a transitive verb. Definition of Transitive Verb in Hindi : वह क्रिया जिसे अपना अर्थ स्पष्ट करने के लिए किसी कर्म की आवश्यकता पड़ती है, उसे Transitive Verb (सकर्मक क्रिया) कहते हैं । जैसे;
- वह आपको कहानी सुना रहा है। He is telling you a story.
- मैं आम नहीं खाता हूं। I do not eat mangoes.
- वह सुबह से अंग्रेजी पढ़ रहा है। He has been reading a story since morning.
- क्या तुमने यह दरवाजा खोला? Did you open this door?
- क्या पिताजी कल फल खरीदेंगे? Will father buy the fruits tomorrow
- वह फुटबॉल खेलता है। He plays football.
- वह एक पत्र लिखती है । She writes a letter.
- उसने कल एक पेड़ काटा। He cut a tree yesterday.
- वह खाना पकाती है। She cooks the food.
- वे किताब पढ़ते हैं। They read a book.
- वह अपनी कहानी लिख चुका है। He has written his story.
Note : उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में गहरे काली रंग में लिखे हुए शब्द Intransitive Verbs हैं क्योंकि इनके बाद कर्म (object) आया है।
- Use of Is, Am and Are in Hindi
- Use of Was and Were in Hindi
- Use of Has and Have in Hindi
- Use of Had in Hindi
- Use of Has to and Have to in Hindi
Intransitive Verb: (अकर्मक क्रिया)
Definition : A verb that does not require an object to complete its meaning and sense but has a complete meaning in itself is called an intransitive verb.
Definition of Intransitive Verb in Hindi वह क्रिया जिसे अपना अर्थ स्पष्ट करने के लिए किसी कर्म की आवश्यकता नहीं पड़ती है, उसे अकर्मक क्रिया कहते हैं। जैसे;
ये लड़के हंसते हैं । These boys laugh .
सूरज उगता है । The sun shines .
कुत्ता भौंकता है। The dog barks .
पक्षी आसमान में उड़ते हैं। The bird fly in the sky.
तुम क्यों मुस्कुरा रहे हो? Why are you smiling ?
आप कहां जा रहे हैं? Where are you going ?
Note : ऊपर दिए गए हिंदी से अंग्रेजी में वाक्य के Examples में गहरे गहरे काले रंग में लिखे हुए शब्द Intransitive Verbs के उदाहरण हैं क्योंकि इनके बाद किसी कोई object नहीं आया है।
- Use of Can in Hindi
- Use of Could in Hindi
Linking Verb (संयोजक क्रिया)
Definition : The verb that connects the subjects with its complement is called linking verb.
Definition of Linking Verbs in Hindi : वे क्रियाएं हैं जिन्हें अपना अर्थ पूरा करने के लिए किसी पूरक की आवश्यकता होती है। जैसे;
यह ठंडा है। It is cold.
खाना स्वादिष्ट लगता है। The food taste delicious.
रश्मि खूबसूरत है। Rashmi is beautiful .
वह फलदाई रहता है । He remains fruitful .
वह खतरों को लेकर परेशान दिखाई देता है। He appears upset about the news.
वह एक डॉक्टर है। He is a doctor.
वह मेरे चाचा जी हैं। He is my uncle.
मेरा नाम रोहित शर्मा है। My name is Rohit Sharma.
वह बहुत प्रसन्न था। He was very busy.
किसान अपने खेतों पर थे। The farmers were on their field.
- Verb in Hindi
- This and That in Hindi
- Simple Sentences in Hindi
- Affirmative Sentences in Hindi
- Negative Sentences in Hindi
- Tense Exercises in Hindi
Auxiliary Verbs (सहायक क्रियाएं)
Definition of Auxiliary Verbs in Hindi : वे क्रियाएं जो मुख्य क्रिया के साथ मिलकर काल बनाने में मदद करती हैं वे Auxiliary Verbs कहलाती हैं। इन्हें Helping Verbs भी कहते हैं। जैसे: is, am, are, was, were, has, have, do, does, shall, will, can, could, may, might, should, must etc.
Types of Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary Verbs दो प्रकार की होती हैं;
- Primary Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Primary Auxiliary Verbs (प्राथमिक सहायक क्रियाएं)
प्राथमिक सहायक क्रियाएं तीन प्रकार की होती हैं।
वाक्यों में Primary Auxiliary Verbs की Forms का प्रयोग करते हैं।
- To be की Forms Is, am, are, was तथा were होती हैं।
- To have की Forms Has, Have तथा Had होती हैं।
- To Do की Forms Do, Does तथा Did होती हैं।
वह आप से नाराज नहीं है। He is not angry with you.
तुम खुश क्यों हो? Why are you happy?
आपके देश का क्या नाम है? What is the name of your country?
मैं अभी कहां हूं? Where am I now?
अशोक एक महान सम्राट था। Ashoka was a great emperor.
आपका शहर बहुत घनी आबादी वाला था। Your city was very densely populated.
मेरे पास समय नहीं है। I have no time.
उसके पास एक कार थी। He had a car.
क्या राजू के पास एक गाय है? Does Raju have a cow?
क्या तुम यहां आना चाहते हो? Do you want to come here?
क्या वह आपको पहचानता है? Does he recognise you?
रोहन ने यह पुस्तक कब खरीदी? When did Raju buy this book?
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में गहरे काले रंग में छपे हुए अक्षर प्राथमिक सहायक क्रियाओं के उदाहरण हैं।
Modal Auxiliary Verbs (रूपात्मक सहायक क्रिया)
Modal Auxiliary Verbs का प्रयोग वाक्यों में करता के बाद मुख्य क्रिया के साथ किया जाता है। यह निम्न प्रकार की होती हैं;
इनके अतिरिक्त कुछ और सहायक क्रियाएं होती हैं जिनका प्रयोग वाक्यों में होता है। इन सहायक क्रियाओं के बाद अधिकतर to लगा होता है।
- Will have to
- Shall have to
1. वह अपनी कार चला सकता है। He can drive his car.
2. तुम पतंग उड़ा सकते थे। You could fly a kite.
3. क्या हम अब बाहर जा सकते हैं? May we go out now?
4. कल शाम को बारिश हो सकती है। It might rain in the evening.
5. आपको हॉस्पिटल में धूम्रपान नहीं करना चाहिए। You must not smoke in the hospital.
6. बच्चों को बड़ों का आदर करना चाहिए। Children should respect the elders.
7. क्या आप चाय लेना पसंद करेंगे? Would you like to take tea?
8. मेरा मित्र झूठ बोला करता था। My friend used to tell a lie.
9. अब तुम कहां जाओगे? Where will you go now?
10. हम कल विद्यालय नहीं जाएंगे। We shall not go to school tomorrow.
11. पिताजी प्रतिदिन अखबार पढ़ा करते थे। Father used to read the newspaper daily.
12. हमें सड़क के नियमों का पालन करना चाहिए। We ought to follow the rules of the road.
13. उसे अब यहां नौकरी करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है। He need not work here anymore.
14. वह आपसे इस तरह बात करने की हिम्मत कैसे करता है? How dare he talk to you like that?
- Tense in Hindi (टेंस हिंदी में)
- Present Indefinite Tense in Hindi
- Present Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Present Perfect Tense in Hindi
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Past Indefinite Tense in Hindi
- Past Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Past Perfect Tense in Hindi
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Future Indefinite Tense in Hindi
- Future Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Future Perfect Tense in Hindi
Main Verb (मुख्य क्रिया)
Definition of Main Verb in Hindi: वह किया जो किसी वाक्य में मुख्य अर्थ को प्रकट करती है उसे मुख्य क्रिया कहते हैं। जैसे; खाना, पीना, हंसना, रोना, देखना, धोना, सफाई, करना, पढ़ना, लिखना, बजाना, गाना आदि।
1. वह खाना खा रहा है। He is eating the food.
2. बच्चा पानी पीता है। The child is drinking water.
3. वह क्यों रो रहा है? Why is he weeping ?
4. तुम क्या देखना चाहते हो? What do you want to see?
5. उसने मुझे एक पुस्तक दी। He gave me a book.
Types of Main Verb (मुख्य क्रिया के प्रकार)
Main Verbs दो भागों में बांटा गया –
- Finite Verbs
- Infinite Verbs
Finite Verb
Definition of Finite Verb : वह क्रिया जो अपने Subject, Tense तथा Person के अनुसार अपना रूप बदलती है, उसे Finite Verb कहते हैं।
1. वह एक पुस्तक पढ़ता है। He reads a book.
2. तुम एक पुस्तक पढ़ते हो। You read a book.
3. वह एक पुस्तक पढ़ रहा है। He is reading a book.
4. तुमने एक पुस्तक पढ़ी है। You have read a book.
5. वह 2 घंटे से पुस्तक पढ़ रहा है। He has been reading a book for 2 hours.
6. मैं एक पुस्तक पढ़ चुका हूं। I have read a book.
Non – Finite Verb
Definition of Non – Finite Verb: वे क्रियाएं जो अपने Tense, Subject तथा Person के अनुसार अपना रूप नहीं बदलते हैं, Non – Finite Verbs कहलाती हैं।
टहलना स्वास्थ्य के लिए लाभदायक है। Walking is good for health.
व्यायाम करना स्वास्थ्य के लिए लाभदायक है। Exercising is beneficial for health.
धूम्रपान करना स्वास्थ्य के लिए हानिकारक है। Smoking is injurious to health.
पेड़ पर चढ़ना मुश्किल है। It is difficult to climb a tree.
यह पढ़ना आसान नहीं है। It’s not easy to read .
मैंने कल एक घायल व्यक्ति देखा। I saw an injured person yesterday.
उसने एक टूटी हुई कुर्सी खरीदी। He bought a broken chair.
शेर देखकर वह डर गया। He got scared seeing the lion.
इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से आपने Verb in Hindi – Definition, Types and Examples विस्तार से पढ़ा है। इंग्लिश ग्रामर में किसी भी पार्ट्स ऑफ स्पीच को पढ़ने से पहले उसके पहले वाले भाग को अवश्य पढ़ना चाहिए। Verb की बारे में विस्तार से अध्ययन करने से पहले आपको Pronoun in Hindi के बारे में तुम करना चाहिए। इस तरीके से आप इंग्लिश ग्रामर के सभी इंपोर्टेंट टॉपिक्स को अच्छी तरह सीखते चले जाएंगे और आपको कोई परेशानी नहीं होगी।
Thanks for visiting 'www.grammarinhindi.in'. Our website provides quality lessons on English Grammar in Hindi. The website is helpful for them who want to learn English Grammar through Hindi.
Similar Posts
Adverb in hindi – definition, types and examples (क्रिया विशेषण).
Adverb in Hindi – Definition, Types and Examples. Adverb definition in Hindi. (क्रिया विशेषण की परिभाषा हिंदी में) Types of Adverbs in Hindi. (क्रिया विशेषण के प्रकार हिंदी में) Adverb of Examples of Hindi. (क्रिया विशेषण के उदाहरण हिंदी में।) Adverbs के बारे में पढ़ने से इन वाक्यों को देखें – She ran quickly. He…

Adjective in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples
Adjective in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples. Adjective Definition in Hindi. Types of Adjectives in Hindi. Examples of Adjective in Hindi. Adjective Exercises and Sentences in Hindi. एडजेक्टिव इन हिंदी। एडजेक्टिव की परिभाषा, प्रकार तथा उदाहरण हिंदी में। Parts of Speech का तीसरा Part ‘Adjective’ होता है। Adjective को हिंदी में विशेषण कहते…
Adverb in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples
Adverb in Hindi – Definition, Types, Rules and Examples. Definition of Adverb in Hindi. Types of Adverbs in Hindi. Examples of Adverbs in Hindi. Adverb rules in Hindi. एडवर्ब इन हिंदी डेफिनेशन टाइप्स एंड एग्जांपल्स। क्रिया विशेषण की परिभाषा प्रकार नियम तथा उदाहरण हिंदी में। Adverb को हिंदी में क्रिया विशेषण कहते हैं। English Grammar…
Noun in Hindi – Definition, Meaning, Examples and Types of Nouns
Noun in Hindi – Definition, Meaning, Examples and Types of Nouns in Hindi. Noun Definition in Hindi. Types of Noun in Hindi. Examples of Noun in Hindi. नाउन डेफिनेशन इन हिंदी। टाइप्स ऑफ़ नाउन इन हिंदी। संज्ञा की परिभाषा हिंदी में। संज्ञा के प्रकार हिंदी में। संज्ञा के उदाहरण। English Grammar में Noun का विशेष…
Prounoun in Hindi – Definition, Types, Examples and Meaning
Prounoun in Hindi – Definition, Types, Examples and Meaning in Hindi. Definition of Pronoun in Hindi. Types/Kinds of Pronoun in Hindi. Examples of Pronoun in Hindi with Meaning. प्रोनाउन इन हिंदी। सर्वनाम की परिभाषा नियम उदाहरण तथा प्रकार सहित। अंग्रेजी ग्रामर में सर्वनाम का विशेष महत्व है। Parts of Speech में Pronoun दूसरे स्थान पर…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

EnthuZiastic
Beginner’s Guide to Hindi Verbs – क्रिया क्या होते है?

I was ———— Book.
He ———— to Seattle.
Did any of these make sense to you? No, right?
While you may assume some action is being done, you can’t be sure unless someone specifies. This isn’t just the case in English Grammar, it is an integral part of Hindi grammar as well.
And it is not just about the assumption of action, you can’t even structure a sentence in Hindi without Hindi verbs. So let us take a look at this integral part of Hindi grammar.
Are you thinking about joining Rosetta Stone Hindi Classes?
Read An Honest Review to find out.
क्रिया क्या होते है? What is a Verb?
Just as in the English language, a verb is a word used to express some action(कार्य), feeling(भाव), or existence(अस्तित्व). It tells us something about the subject.
Every action either happens or is done by someone.
कर्ता (Karta)
The one who does the work is called कर्ता ( karta – doer)
धातु ( Dhatu)
The root form of a verb is called धातु (dhatu)
Example: भागता, भागा , भागना.
In all these, भाग is the dhatu or root form of the verb.
क्रिया के भेद. Types of Hindi Verbs
In Hindi, verbs can be divided into two different categories.
- प्रयोग के आधार पर (on the basis of use)
- रचना के आधार पर (on the basis of composition)
1. प्रयोग के आधार (on the basis of usage)
on the basis of usage, there are two different types
- सकर्मक क्रिया (Transitive verb)
- अकर्मक क्रिया (Intransitive verb)
सकर्मक क्रिया (Transitive Verbs)
सकर्मक (transitive) means with or with action.
The verb which has an effect on the action rather than on the doer is called सकर्मक क्रिया transitive verb. Examples:
- मै ख़ुशी से हॅसता हूँ।
- बच्चे जोरों से रो रहे हैं।
- एलेक्स खाना खा रही है।
सकर्मक क्रिया के भेद (Types of transitive verbs)
There are two types of transitive verbs in Hindi
- A verb that has only one action is called एककर्मक क्रिया।
- A verb in which there are two actions is called दवीकर्मक क्रिया।
अकर्मक क्रिया (Intransitive Verbs)
अकर्मक क्रिया (Intransitive verb) means without action or without action.
Actions which do not require action and the result of actions falls on the doer, are called अकर्मक क्रिया (intransitive verbs).
In other words, the verbs whose fruit and business are received by the doer are called अकर्मक क्रिया intransitive verbs.
- वे हसते है।
- बच्ची रो रही है।
- एलेक्स खा रही है।
2. रचना के आधार पर (on the basis of composition)
There are 10 distinctions of verbs on the basis of the composition.
- मुख्य क्रिया ( Main verbs)
- प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया (Insprational verbs)
- संयुक्त क्रिया (Compund Verbs)
नामधातु क्रिया
- पूर्वकारक क्रिया (Anterior Verbs)
अनुकरणात्मक क्रिया (Imitative Verbs)
सहायक क्रिया (auxillary verb), रंजक क्रिया, सरल क्रिया (simple verb).
- नामिक क्रिया (mixed kriya)
Let’s take a look at each of them.
मुख्य क्रिया (Main verbs)
A part of the main verb which gives the main meaning is called the main verb or the verb expressing the main actions of the subject or action is called the ‘main verb’.
- जॉन दूध लाया।
- मेगन ने दूकान खोली।
प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया (Inspirational verbs)
The verbs from which it is known that the doer, by not doing the work themselves, inspires others to do the work or get someone else, then the verb is called प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया (Inspirational verbs).
There are two subjects in an inspirational verb
- प्रेरक कर्ता (inspirational doer) – the one who inspires
- प्रेरित कर्ता (the inspired doer) – the one who is inspired, or the one who is being inspired.
There are two types of प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया (Inspirational verbs).
- प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया ( First inspirational verb)
- द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया (Second inspirational verb)
- पिता ने बेटे से अख़बार मँगवाया।
- मालकिन नौकर से सफाई करवाती है।
संयुक्त क्रिया (Compound Verbs)
In Hindi, the verb is sometimes manifested by one word and sometimes by more than one word. Therefore, we can say that when two or more verbs join together to form a complete verb, then they are called संयुक्त क्रिया (compound verbs.)
- में टेक्सास गया था।
- एमी पढ़ रही है।
In the first sentence, there are two verbs = गया + था
in the second sentence there are three verbs = पढ़ + रही + है
The verb that is formed by adding suffixes at the end of Namdhatu verb nouns, pronouns and adjectives, is called नामधातु क्रिया Namdhatu verb.
with संज्ञा :
- फिल्म + आना = फिल्माना
- दुःख + न = दुखना
with विशेषण :
- साठ + इयाना = सठियाना
- गरम + आना = गरमाना
with सर्वनाम
- अपना + आना = अपनाना
पूर्वकालिक क्रिया (Preterite verbs)
The verb whose completion is found before the second verb is called the pre-tense verb, that is, the action which takes place before the main verb is called the pre-verb.
Check out EnthuZiastic Hindi Classes for fun, interactive learning experience.
The preceding verb is formed by adding ‘kar’ with the root.
- लारा ने एक बार सुनकर कविता लिखी |
in the sentence, लिखी se pehle सुनकर verb is used.
Words which are formed on imitation of sounds or on imitation of the preceding sound. Such verbs are called अनुकरणात्मक क्रिया imitative verbs.
- थप – थप = थपथपाना
- झन – झन = झनझनाना
Verbs which do not give the main meaning in the verb phrase and is helpful to it, that is, whatever part remains apart from the main verb, it is called सहायक क्रिया (auxiliary verb).
- पिताजी अखबार पढ़ चुके हैं।
- माता जी खाना बनाने लगी।
When a verb joins with the main verb to make the main verb more effective, then it is called रंजक क्रिया. Not every reflexive verb can be used with every main verb.
ब्रॉडी को रोना आ गया।
रोया = मुख्या क्रिया
गया = सहायक क्रिया
आना = रंजक क्रिया
वह अधिकतर घुमा है।
घुमा = मुख्या क्रिया
है = सहायक क्रिया
करना = रंजक क्रिया
A verb that is prevalent in the language like customary words. We also call this verb the root verb.
This verb is neither derived from any other verb nor is it formed from the addition of more than one verb form, that’s why we call it a root verb.
Example: आना , जाना , लिखना , पढ़ना
नामिक क्रिया (Mixed kriya)
Under mixed verb, the first part is of a noun, adjective, or adverb and the second part is of a verb.
with संज्ञा
- याद + आना = याद याना
- भूक + लगाना = भूक लगाना
with विशेषण
- बुरा + लगना = बुरा लगना
- सुन्दर + दिखना = सुन्दर दिखना
with क्रियाविशेषण
- बाहर + करना = बाहर करना
- भीतर + करना = भीतर करना
Hindi Verbs Exercise
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ती उचित क्रियाओं से कीजिये। (Fill in the blanks)
- डॉक्टर ने रोगी को इंजेक्शन ___________ । (लगा / लगया )
- अडम ने किताब मे __________ । ( लिखना है / लिखा )
- शोन की दुकान मे _________ । ( मिलेगी / मिलूँगी )
- रोनी फूटबाल _______ रहा है। ( खेलेगा / खेल )
- मैरी ________ रही है। ( पढाई कर / पड़ेगी )
नीचे लिखे वाक्यों में क्रिया पहचान कर लिखिए।
- एनी बालक को सुलाती है। _______
- बॉनी है रही है। _______
- माँ बच्चे को नहलाती है। _______
- पिता जी बाज़ार से सब्जियां और फल ले आए। _______
- वे रोज शाम को बेसबॉल खेलने जाते है। _______
- हम सब ने एक फिल्म देखि। _______
- एलेक्स ने सुन्दर चित्र बनाया। _______
- माता भोजन पका रही है। _______
- घोडा घास खा रहा है। _______
- बारिश गिर रही है। _______

Learn Hindi from Native Speakers
Take Hindi Classes from our Hindi Speakers. Improve spoken and written Hindi in no time. Start Now!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- Search Your Topic

Hindi Verb (क्रिया)
Present tense, future tense, types of verb in hindi (क्रिया के प्रकार), effects of verb (क्रिया का प्रभाव), effects of verb in vachan (वचन में क्रिया का प्रभाव), forms of verbs:.
V1: Present Form
V2: Past Form
V3: Past Participle Form
V4: 'ing' Form.
Latest Release
How to write a Letter to the Principal (प्रधानाचार्य को पत्र कैसे लिखें)
Official Letter Writing in Hindi (हिन्दी मे आधिकारिक पत्र लेखन)
Identification of Grammatical Gender (व्याकरणिक लिंग की पहचान)
Hindi Story Writing (कहानी लेखन)
Common Verbs (सामान्य क्रियायें)
Verb in Hindi with Definition, Types, Examples & Meaning in Hindi
Verb Meaning in Hindi – Verb (क्रिया), Parts of Speech का चौथा प्रकार हैं जिसके बारे में हम इस आर्टिकल में पढ़ेंगे।
पार्ट्स ऑफ़ स्पीच के पहले ( Noun ), दूसरे ( Pronoun ) और तीसरे ( Adjectives ) के बारे में हम अपने पिछले आर्टिकल्स में पढ़ चुके हैं।
अंग्रेजी सिखने के लिए हमें Verb के बारे में भी जानना बहुत जरूरी हैं क्युकी इसका प्रयोग इंग्लिश के हर एक वाक्यों में जरूर किया जाता हैं।
हमें टेंस (Tense) को सिखने में भी इसकी जरूरत पड़ती ही हैं, आज हम इस पोस्ट में Verb (क्रिया) क्या हैं। ( What is Verb in Hindi ) इसके कितने प्रकार होते हैं।
और उनका परिभाषा (Definition), Examples इत्यादि इसके पूरी जानकारी हिंदी में लेंगे। अगर आप Verb को अच्छी तरह से सीखना चाहते हैं तो इस पोस्ट को ध्यानपूर्वक पढ़िए।
What is Verb in Hindi | Verb Definition, Types & Meaning in Hindi
Verb Definition in English – That word which refers to the doing or, happening of an action or, event is called the Verb.
Verb Definition in Hindi – वह शब्द जिससे कुछ करने या होने का बोध होता है उसे Verb कहते हैं।
Types of Verb in Hindi or Kinds of Verb in Hindi –
Verb (क्रिया) के मुख्यः दो प्रकार होते हैं –
1 . Main Verb / Principal Verb (मुख्य क्रिया)
2 . Helping Verb / Auxiliary Verb (सहायक क्रिया)
****************
1 . Main Verb (मुख्य क्रिया) –
Definition in English – That verb which expresses the central meaning of sentence is called the Main Verb.
Definition in Hindi – वह क्रिया जो वाक्य में मुख्य अर्थ को व्यक्त करता है, उसे Main Verb कहते हैं।
Examples – eat (खाना), go (जाना), come (आना), drink (पीना), die (मरना), live (रहना), play (खेलना) e.t.c.
2 . Helping Verb (सहायक क्रिया) –
Definition in English – That verb which is helpful to express the complete meaning of the main verb is called the Helping Verb.
Definition in Hindi – वह क्रिया जो मुख्य क्रिया के अर्थ को स्पष्ट करने में सहायक होता है, उसे Helping Verb कहते हैं।
Examples – is, am, are, was, were, has, have, had, do, does, did, can, could, would, may, might, must, dare, need, used to, ought to.
Verb Examples in Hindi –
1 . वह स्कूल जा रहा हैं। – He is going to school.
- वह (He) – subject
- स्कूल (school) – object
- जाना (go) – main verb
- हैं (is) – helping verb
2 . राम आम नहीं खाता हैं। – Ram does not eat mango.
- राम (Ram) – subject
- आम (mango) – object
- खाता (eat) – main verb
- हैं (does) – helping verb
अब हम Main Verb या Principal Verb (मुख्य क्रिया) के प्रकार (Types) के बारे में पढ़ते हैं।
*********************
Types of Main Verb Hindi –
जैसे की Verb (क्रिया) के दो प्रकार main verb और helping verb होते हैं उसी तरह Main Verb (सहायक क्रिया) के भी दो प्रकार होते है –
1 . Transitive Verb (सकर्मक क्रिया)
2 . intransitive verb (अकर्मक क्रिया).
Definition in English – That main verb which takes one or, more objects is called the Transitive Verb.
Definition in Hindi – वह मुख्य क्रिया जो अपने अर्थ को पूरा करने के लिए एक या एक से अधिक object लेती है, उसे Transitive Verb कहते हैं।
Examples –
1 . वह दुकान चलाता हैं। – He runs the shop.
- दुकान (shop) – object
- चलाता – transitive verb (Main Verb)
- हैं – helping verb
2 . मैं आपलोगों को एक कलम देता हूँ। – I give you a pen.
- मैं (I) – subject
- आपलोगों को (you) – object
- कलम – object
- देता – transitive verb (Main Verb)
- हूँ – helping verb
Definition in English – That main verb which does not have an object is called the Intransitive Verb.
Definition in Hindi – वह मुख्य क्रिया जो अपने अर्थ को पूरा करने के लिए object नहीं लेती है, उसे Intransitive Verb कहते हैं।
Examples –
1 . मैं हँसता हूँ। – I laugh.
- हँसना (laugh) – intransitive verb (Main Verb)
2 . तुम जाते हो। – You go.
- तुम (you) – subject
- जाना (go) – intransitive verb (Main Verb)
- हो – helping verb
Final Thoughts –
तो दोस्तों, आज के इस आर्टिकल मे आपने Verb के बारे में पूरी जानकारी पढ़ी। जिसे आप पढ़ कर Verb (क्रिया) को बहुत ही आसानी से समझ सकते हैं।
इस पोस्ट में आपने Verb की परिभाषा ( Verb Definition in Hindi ) और इसके दोनों प्रकार (Types of Verb in Hindi) और साथ ही वर्ब के Examples के बारे में जाना।
दोस्तों, आज का यह आर्टिकल Verb Meaning in Hindi आपको जरूर अच्छा लगा होगा। आप इस आर्टिकल Verb से जुड़ी अपनी कोई सुझाव देना चाहते हैं तो आप नीचे कमेंट कर सकते हैं।
Also Read –
- Noun Definition in Hindi and English with Types & Examples
- What is Pronoun in Hindi with Definition, Types & Examples
- Adjectives in Hindi with Definition, Types and Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- English ( English )

Verbs In Hindi: Forms And Types With Examples

Verb! Is word ko to aapne English mai kayi baar suna hoga. Lekin kya aap jante hai ki Verbs kya hai ya Verb kya hota hai? Is article mai hum aapko detail me batayenge ke Verb kya hota hai? Yani ke Verb meaning in Hindi kya hai? Aur types of Verbs konse hai aur ye English bolne me ya likhne mai aur aapki English Grammar improve karne mai aapki kis tarah help karke aapke sentences ko meaningful banate hai. Toh chaliye shuru karte hai.
Josh Skills App par Sikhe Fluent English Bolna
Verb Word Kaise Banaya Gaya?
Verb banaya gaya hai ek Latin word “Verbum” se, jiska English mai meaning hai “word” aur Hindi me ise kaha jata hai “Shabd”. Verb ko Hindi mai kaha jata hai “Kriya”.
Verb Kya Hota Hai? Verb Kise Kehte Hai?
Verb ek aise word ya combination of words ko kaha jata hai jo kisi action, event ya state ya condition ko darshata hai.Verb sentence ka wo part hai jo hume batata hai ki sentence mai jo subject hai uska action kya ka, aap ki understanding ke liye kaha jaye to sentence me hum jis kisi ke baare mai baat kar rahe hai wo kya kar raha hai.
Verb English Grammar ka ek important part hai, ya ise heart of the sentence bhi kaha ja sakta hai. Aaiye Verbs in Hindi ke kuch examples dekhte hai.
- Ye Verbs physical action ko darshate hai aur inhe Normal Verbs ya Action Verbs bhi kaha jata hai, aaiye dekhte hai iske examples. To swim – Tairna, To write – Likhna, To climb – Chadhna.
Physical actions ke kuch examples
- She sells books and bags – Wo books aur bags bech rahi hai. Is sentence mai “sells” yani “bech rahi” ek Verb hai. “ Sells” jo ke ek physical activity hai wo darsha raha hai.
- The doctor wrote the prescription – Doctor ne prescription likha hai. Is sentence mai word “wrote” ek Verb hai jo “Likhne” ki physical activity ko darsha raha hai.
- Ruby bought a ticket – Ruby ne ticket khareedi . Is sentence me “bought” yani ke “khareedi” ek Verb hai khareedne ki physical activity ko darsha raha hai.
- Ye mental action ko darshane wale Verbs hote hai, ye wo Verbs hote hai jo aise kaam ko batate hai jo hum kisi ko physically karte hue nahi dekh sakte. Inhe “Non – Continious Verbs” bhi kaha jata hai. jaise ke:To think – Sonchna, To guess – Guess karna, To consider – Consider karna
Aaiye inke kuch examples sentences mai dekhte hai:

Mental actions ke kuch examples
- She considers the job done – Us ne consider kiya ke job pura ho chuka hai. Is sentence mai “considers” Verb hai. Ye word consider karne ki mental activity ko darshata hai
- Peter guessed the number right.- Peter ne number sahi guess kiya hai. Is sentence me “guessed” ek Verb hai aur ye guess karne ki activity ko darsha raha hai
- I thought the same thing. – Maine yahi socha tha. Is sentence me “thought” ek Verb hai aur ye sochne ki activity ko darshata hai.
Verbs state of being ya condition ko batate hai, inhe Linking Verbs bhi kaha jata hai, jaise ke: To be – Hona, To exist – Exist karna, To appear – Appear hona
Ye group of words bahut hi chote hote hai lekin ye bahut important bhi hote hai. Ye words kisi bhi activity ko express nahi karte. Is group me sab se important Verb hai “to be”. State of being Verbs ko “Linking Verbs” bhi kaha jata hai.
Aaiye is ke kuch examples dekhte hai Hindi mai.
- Edwina is the largest elephant in this area – Edwina is area ka sab se bada hathi hai. Is sentence mai “is” ek Verb hai jo ki “to be” form of Verb se bana hai.
- It was a joke – Wo joke tha. Is sentence me “wo” ek Verb hai. Jo ki “to be” form of Verb se bana hai
- I am – Mai. Ye word “I am” ek Verb hai jo ki “to be” form of Verb se banta hai.
(Point of Interest: “I am” English ka sab se chota sentence hai.)
Action Verbs aur Linking Verbs strong hote hai aur wo sentence mai directly use kiye ja sakte hai. Inko “Main Verbs” bhi kaha jata hai. Jaise ke:
Action Verbs
- I love cheese – Mujhe cheese pasand hai
Linking Verbs
- I am a teacher – Mai teacher hu
Verbs mai ek aur category hoti hai jise “Helping Verbs” kaha jaata hai. Ye Verbs stand alone nahi karte sentence mai action aur linking Verbs ki tarah. Isi liye ye zyada notice nahi kiye jate. Jaise ke: is, are, be, have etc.
Janiye Forms Of Verbs In Hindi
Aap ne dekh liya aur samajh bhi liya hoga ke Verbs with examples kya hai. Ab aage badhte hai aur aapko batate hai forms of Verbs in Hindi.
Verbs ke six basic forms hote hai
a) Base form
Base form of Verb ko Root form of Verb bhi kaha jata hai. Inme suffixes aur Prefixes nahi hote. Jaise ke: See, be, were, go etc.
Base form of Verbs jab conjugate hote hai to inse dusre Verbs banaye ja sakte hai.
Example:
- I am going to school. – Mai school ja raha hu. (Base form hai “go” yani ke ja raha)
- Children play in the field – Bacche khet me khelte hai ( Base form hai “khelte”)
- What did you do yesterday? – Kal tumne kya kiya? (Base form hai “do” yani ke “karna”)
b) Infinitive Form
Infinitive form of Verbs un Verbs ko kaha jata hai jin ke aage “to” lagta hai.
- Tell them not to play – un se keh do ke wo na khele
- I like to dance – Mujhe dance karna pasand hai
- I like to write stories – Mujhe stories likhna pasand hai
c) Past Tense Verb Form
Ye wo words hote jo past me hue kaam ko batate hai. Jaise ke
- They played football yesterday – Un logon ne kal football khela tha
- They visited the doctor that day – Un logon ne us din doctor ke paas visit kiya tha
- She drank milk – Usne doodh piya
d) Past Participle Verb Form
Past participle form of Verb three types se banta hai. Aaiye dekhte hai past participle meaning in Hindi kya hai.
- Jo word kisi Verb se banta hai
- Yeh words Verb, Tense ya Adjectives ke liye use hote hai
- Ye words usually ed, d, t, en or n, se end hote hai
- I have forgotten my lines – Mai apne lines bhool gaya
- She had whispered him the answer – Use ne answer whisper kardiya
- She has taken the medicine – Usne medicine le li hai
e) Present Participle form of Verb
Jaante hai Present Participle meaning in Hindi. Present Participle un words ko kaha jata hai jo base word ke saath “ing” use karte hai. Usually ye Adjectives ka function perform karte hai, ye Verb jaise bhi kaam karte hai aur subject in construction jaise bhi kaam karte hai.
- I am watching Television – Mai television dekh raha hu
- She is eating food – Wo khana kha rahi hai
- Ruby is playing – Ruby khel rahi hai
f) Gerund
Dekhte hai Gerund meaning in Hindi. Gerund un words ko kaha jata hai jo bante to Verbs se hai lekin Noun jaisa kaam karte hai. Ye bahut aasani se pehchane jate hai. Simple words mai agar kaha jaye to har Gerund wo Verb hota hai jis ke peeche “ing” laga hota hai.
Yahan ye dhyan rakhna hota hai ki Present Participle form of Verbs bhi “ing” se end hote hai.
Ab aap ye soch rahe honge ke kaise pehchana jaye ke kon sa word Gerund hai aur kon sa Present Participle form of Verb hai. Chaliye hum aapko batate hai.
Gerund And Present Participle Mai Difference Janiye
Agar aap Verb ki defination par focus kare to aap dekhenge ki hum ne padha tha ke Gerunds bante to Verbs se hai lekin wo Noun jaisa kaam karte hai. Lekin Present Participle Noun jaisa kaam nahi karte balke wo modifiers ya complete progressive Verbs jaisa kaam karte hai.
Sentence me Gerund ko pehchanne ke liye dekhiye ”Verb” +”ing” jo Noun jaise kaam kar raha hai.
- Gerund As Subjects – Gerund Subjects Ke Roop Mai
- Reading is relaxing – Reading relaxing hoti hai
- Writing is an exchange of ideas – Writing exchange of ideas hota hai
Gerund Phrases As Subject – Gerund Phrases Ke Roop Mai
- Swimming laps is the most relaxing activity in the world – Swimming laps sab se relaxing activity hai duniya me.
- Filing papers can give you a paper cut – Papers filing aap ko papercut de sakte hai
- Gerund As Direct Objects – Gerund Direct Objects Ke Roop Mai
- I love reading – Mujhe padhna pasand hai (Verb = Love, Love what? = Reading)
- Patrick likes photographing nature – Patrick ko nature ki photographing karna pasand hai (Verb = Likes, Likes what? = Photographing)
Gerund Phrases As Direct Objects – Gerund Phrases Direct Objects Ke Roop Mai
- I enjoy shopping with friends – Mujhe friends ke saath shopping jana pasand hai
(Verb = Enjoy, Enjoy what? = Shopping with friends)
- My friends anticipated our trying on new shoes – Mere friends ne anticipate kiya hamare naye shoes try karne pe
- Gerund As Indirect Objects – Gerund Indirect Objects Ke Roop Mai
- I never gave reading enough of a chance – Maine reading ko kabhi zyada chance nahi diya (Verb = Gave, Gave what? = Reading)
- Last week, I made studying my priority – Last week mai ne padhai ko apni priority banayi hai (Verb = Made, Made what? = Studying)
Gerund Phrases As Indirect Objects – Gerund Phrases Indirect Objects Ke Roop Mai
- As part of her writing process, she began recording every detail . – Uske writing process ke part ke according, us ne har detail ko record karna shuru kar diya.
(Verb = Began, Began What? = Recording every detail)
- Once Tom gave the order, he started collecting all the evidence – Ek baar Tom ne order de diya, usne saare evidence collect karna shuru kardiya.
Ab aap samajh gaye honge Gerund meaning in Hindi aur ise kis tarah se sentence mai use karte hai.
Ab aage badhte hai aur dekhte types of Verbs in Hindi.
Verbs Kitne Prakar Ke Hote Hai – Types Of Verbs In Hindi And English
Verbs in Hindi twelve prakar ke hote hai. Inko kaha jata hai “Mixed Verbs”. Dekhte hai wo kya hai.
- Transitive Verbs – Sakarmak Kriya
- Intransitive Verbs – Akarmak Kriya
- Dynamic / Event Verbs – Gaatyatmak Kriya
- Stative Verbs – Sthithi Suchak Kriya
- Perception / Sensation Verbs – Bhavana Dharana Kriya
- Linking / Copular / Predicating Verbs – Videh Kriya
- Phrasal / Prepositional Verbs – Sanbandha Bodhak Kriya
- Modal Auxiliary Verbs – Rupatmak Kriya
- Helping Verbs / Auxiliary Verbs – Sahayak Kriya
- Hypothesis Verbs – Parikalpanatmak Kriya
- Causative Verbs – Kaaran Vachak Kriya
- Regular and Irregular Verbs – Niyamit aur Aniyamit Kriya
1. Transitive Verbs in Hindi – Sakarmak Kriya
Transitive Verbs, action Verbs hote hai jinka ek object hota hai, action ya ek complete thought receive karne ke liye. Ye Verbs ke baad Noun ya Noun phrase aata hai.
Aaiye is ke example dekhte hai.
- She drinks water – Wo pani pi rah i hai. Is sentence mai pani direct object hai aur drinks Transitive Verb hai.
- He drove the car – Usne car chalayi. Is sentence mai car direct object hai aur drove Transitive Verb hai
- I saw the dog – Maine dog dekha . Is sentence mai dog direct object hai aur saw Transitive Verb hai
- Lee ate the pie. Lee ne pie khayi. Is sentence mai Pie direct object hai aur ate Transitive Verb hai
- The postman will give Sarah “the letter”. Is sentence mai letter direct object hai aur will give transitive Verb hai.
Transitive Verbs ko pehchanne ke liye aap ko Verb ko find out karna padega aur question karna padega ke “kya?” for example “ kya dekha?”, “kya kiya?”, “kya bola?”.
2. Intransitive Verbs In Hindi – Akarmak Kriya
Intransitive Verbs ka koi direct object nahi hota agar dusre words me bola jaye to ye kisi cheez par act nahi karte jaise ke Transitive Verbs karte hai. Ye Verb sirf subject ko involve karta hai. Ye Transitive Verb ka opposite hota hai.
Ab aap soch rahe honge ke direct object se kya matlab hai. Aaiye dekhte hai.
“Taking A Direct Object” Ka Matlab Kya Hai?
Intransitive Verb direct object nahi leta. Aaiye is ko examples ke through samajhte hai.
- He laughed – Wo hasa . Laughed ek Intransitive Verb hai. Is ka koi direct object nahi hai. Yahan kis par hasa ja raha hai ye nahi bataya ja raha hai balki sirf itna bataya ja raha hai ke wo hasa.
- He disappeared after the party – Woh party ke baad gayab ho gaya . Is sentence mai “disappeared” ka koi direct object nahi hai aur ghayab ek Intransitive Verb hai.
- She is crying – Wo ro rahi hai.
- The sun shines – Suraj chamak raha hai
Note karne wali baat ye hai ke kuch Verbs jaise ke: cheer, sing, visit, trip, Transitive Verb aur Intransitive Verb dono ho sakte hai, inka usage sentence pe depend karta hai, ke wo sentence me kis tarah use kiye ja rahe hai.
Aaiye iske kuch examples dekhte hai.
- He sang – Wo gaaya. Yahan par ye nahi bataya ja raha hai ke wo kya gaaya ya kiske liye gaaya, bas itna bataya ja raha hai ke wo gaaya. Is ka koi direct object nahi hai isi liye ye Intransitive Verb kehlayega.
- He sang a song – Wo geet gaaya. Is sentence me hame ye bataya ja raha hai ke us ne “geet” gaaya. Yahan object hai “geet”. Isi liye ye Transitive Verb kehlaya jayega.
Chaliye aage badhte hai Dynamic / Event Verbs – Gaatyatmak Kriya ki oar.
3. Dynamic / Event Verbs in Hindi – Gaatyatmak Kriya
Dynamic / Event Verbs wo hote hai jin me body movements involve hote hai.Ye Verbs apne subject par continued or progressive action batate hai. Jaise ke: act, build, complete, design, draw, gather, help, interview, justify, listen, negotiate, outline, perform, record, save, show, travel, uncover, value, write, zoom etc.
Aaiye Dynamic / Event Verbs in Hindi ke kuch examples dekhte hai.
- She was writing a letter – Wo letter likh rahi thi
- They are playing in the playground – Wo log playground me khel rahe hai
- They are interviewing that girl – Wo log us ladki ka interview le rahe hai
- Ramu is helping his mother in cooking – Ramu apni maa ki help kar raha ha i cooking mai
- Ruby is drawing a picture – Ruby picture draw kar rahi hai
Ab aap samajh gaye honge ke Dynamic yani ke Event Verb kya hai aur wo kaise sentence mai use hote hai. Aaiye ab aage badhte hai aur jaante hai Stative Verbs in Hindi kya hai.
4. Stative Verbs In Hindi – Sthithi Suchak Kriya
Stative Verbs in Hindi wo Verbs hote hai jo action se zyada state ko express karte hai. Ye Verb usually mental feelings, emotions, state of a person, place, relationships, sense and measurements ko darshata hai.
Stative Verbs ke kuch important key takeaways:
- Stative Verbs, Action ya Dynamic Verbs nahi hote.
- Stative Verbs describe karte hai ke koi cheez kaisi hai, ya to yeh Verbs mental process batate hai
Stative Verbs ko “being Verbs” bhi kaha jata hai. Especially wo case mai jahan be, am, is, are, was and were use hota hai.
Stative Verbs four types ke hote hai. Jo hai Senses, Being, Possession aur Emotion. Ye words multiple categories me fit hote hai aur ye depend karta hai unke usage par. Inko four types me group kiya gaya hai. Aaiye dekhte hai wo kya hai.
- Perception and Sensation (Example – See, hear, smell, hurt, taste etc.)
- Cognition, Emotion, Attitude (Example – sochna, feel karna, bhool jana, remember etc)
- Having and Being (Example: be, have, have to, cost, require etc)
- Stance (Example Sit, stand, lie, live, face etc)
Aaiye dekhte hai ye four types ke Stative Verbs aur inke examples.
- Sensing Verbs
Jo data hamare five senses mai aata hai hum use Sensing Verbs kahenge. Jaise ke:
- See – Dekhna
- Hear – Sunna
- Smell – Soonghna
- Taste – Taste Karna
- Sound – Awaz
- Look – Dekhna
- Emotion and Thought Verbs
Emotion and Thought Verbs hamare emotions aur soch ko darshata hai. Jaise ke:
- Love – Chahna
- Hate – Nafrat Karna
- Adore – Bahut zyada pasand karna
- Forget – Bhool jana
- Believe – Bharosa karna
- Think – Sochna
- Possession Verbs
Possession Verbs wo hote hai jo possess karne ki quality ko darshata hai. Jaise ke:
- Have – Hai
- Belong – Jis kisi ka
- Include – Add karna
- Need – Zarurat
- Want – chahiye
- Own – Khud ka
- Being / Qualities Verbs
Ye un Verbs ko kaha jata hai jo state of being ya qualities ko batate hai. Jaise ke:
- Be / Are / Is
- Contain
Aaiye sentences mai is ke kuch examples dekhte hai.
- I believe in God – Mai God me Vishwas rakhti hu
- It sounds like a great idea – Ye idea bahut accha lag raha hai
- I feel your sadness – Mai tumhara sadness feel kar sakta hu
Ab aap samajh gaye honge ke Stative Verbs kya hai aur inhe sentence mai kaise use kiya jata hai. Chaliye aage badhte hai Perception / Sensation Verbs ki taraf.
5. Perception / Sensation Verbs In Hindi – Bhavana Dharana Kriya
Perception Verbs jinhe Sensation Verbs bhi kaha jata hai wo hamare five senses ko darshata hai. Jo hai , See, Smell, Taste, Touch, Hear. Aaiye is ke kuch examples dekhte hai.
- I smell the flowers – Maine phoolon ko soongha
- He is listening to the radio – Wo radio sun raha hai
- He is tasting the cake – Wo cake ko taste kar raha hai
- He is looking at me – Wo mujhe dekh raha hai
- He touched the roof – Usne roof ko touch kiya
6. Linking / Copular / Predicating Verbs – Videh Kriya
Linking Verbs action ko express nahi karte, balki wo Verb ke subject ko, subject ke related additional information se connect karte hai. In Verbs ke baad usually Adjectives ya Nouns aate hai.
Dekhte hai true Linking Verbs in Hindi ke kuch examples.
- Verb “be” ka koi bhi form jaise ke:am, is, are, was, were, has been, are being, might have been etc.
Ab dekhte hai wo Linking Verbs jin ki multiple personalities hoti hai. Ye sentence ke according kabhi Action Verb ki tarah kabhi Linking Verb ki tarah kaam karte hai.
- Appear
- Remain
- Sound
Chaliye dekhte hai in Linking Verbs in Hindi ke kuch examples sentences mai.
- He had many talents but he could not utilize them – Uske paas kayi talents they lekin wo use utilize nahi kar paya.
- The cake smells really good – Cake ki bahut acchi khusboo aa rahi hai
- He grew up in his village – Woh village me bada hua hai
- It appears to be a broken piece of glass – Aisa lag raha hai ke ye glass ka tuta hua piece hai.
7. Phrasal / Prepositional Verbs – Sanbandha Bodhak Kriya
Phrasal ya Prepositional Verbs, preposition aur adverbial particle ke combination se bante hai. Har preposition ka ek object hota hai isiliye saare prepostional verbs ke direct objects hote hai.
Ab aap soch rahe honge ke Adverbial particle kya hai?
Small adverbs jaise ke: above, about, in, out, up, down, before, across, off, on, below, behind etc ye Adverbial particle kehlaye jate hai.
Aaiye Phrasal / Prepositional Verbs ke kuch examples dekhte hai.
- I believe in God – Mai God me believe karta hu
- He is looking after the dog – Usne dog ki dekh bhaal ki
- They are talking about the issue – Wo log is issue ke baare me baat kar rahe hai
- The car ran over the pipe – Car pipe ke upar se chale gayi
- I got off the bus at school – Mai school ke paas bus se utar gayi.
8. Modal Auxiliary Verbs In Hindi – Rupatmak Kriya
Modal Auxiliary Verbs un Verbs ko kaha jata hai jo dusre Verbs se mil kar ideas ko expess karte hai. Jaise ke: possibility, prediction, speculation, deduction, and necessity. Modal Verbs speaker ke different moods aur attitudes ko darshata hai.
Jante hai rules for using Modal Verbs in a sentence
Shuru karne se pehle hum aapko Auxiliary ka meaning bata dete hai. Auxiliary ka meaning hai additional help and support provide karna.
- Modal Verbs hamesha follow hote hai “infinitive without to” se.
I can swim – Mai tair sakta hu (Correct)
I can to swim (Incorrect)
She could swimming well (Incorrect)
- Modal Verbs sab pronouns ke liye same hote hai aur singular subjective pronouns mai “s” ya “es” nahi lagaya jata.
She can swim – Wo tair sakti hai (Correct)
She cans swim (Incorrect)
They can swim (Correct)
- Modal Verbs ko auxiliaries ki zarurat nahi hoti. Ye directly negative aur question form lete hai.
Can you do this? – Kya tum ye kar sakte ho? (Correct)
Do you can do this? (Incorrect)
He may not like it. Us ko shayad ye pasand nahi aayega (Correct)
He does not may like it. (Incorrect)
Aaiye Modal Verbs aur in ke kuch examples dekhte hai:
- Ability: Ali can swim – Ali tair sakta hai
- Permission: Can I come with you? – Kya mai tumhare saath aa sakta hu. Is sentence me “can” ki jagah “May” bhi use kiya ja sakta hai.
- Offers: Can I help you? – kya mai tumhari help kar sakta hu?
- General Possibility: You can speak fluent English. Tum fluent English mai baat kar sakte ho.
- Possibility: I could do it, if you like – Mai ye kar sakta hu, agar tumhe pasand ho toh
Past ability: I could swim when I was three – Mai tair sakta tha jab mai teen saal ka tha.
- Permission: Could I use your phone please? – Kya mai tumhara phone use kar sakta hu?
- Requests: Could you babysit for us on Friday? – Kya tum hamare liye babysit karoge Friday ko?
- To Suggest: We could write a letter to the director – Hum director ko letter likh sakte hai
- Possibility: The director may come to our class – Director kal hamari class ko aa sakta hai
- Permission – May I use your dictionary? – Kya mai aapki dictionary use kar sakta hu?
Yahan par dhyan me rakhne wali baat ye hai ki may aur might, past, present aur future mai hone wali possibility batate hai. Jab “may” use hota hai to is mai 50% sureity hoti hai.
“Might” agar use kar rahe hai to might 30% doubt express karta hai.
- Slight Possibility: He said he might come tomorrow – Wo bol raha hai ke wo kal aa sakta hai
- Past form of “may” in reported speech: The President said he might come – President ne kaha tha ke wo aa sakta hai
- Polite Suggestion: You might try calling the help desk – Aap help desk ko call try kar sakte hai.
- Shall
Shall, will ka ek form hai, jo first person “I and we” ke saath use hota hai. Ye word question karte waqt use hota hai
- Offers: Shall I order a coffee? – Kya mai coffee order karu?
- Suggestion: Shall we go to the party tonight? – Ya aaj raat hum party par chale?
- Future Tense Auxiliary: I will buy a computer tomorrow. – Mai kal ek computer kharidunga
- Invitations: Will you join us for dinner? – Kya tum hume dinner par join karoge?
- Offers: Won’t you accept the appointment? – Kya tum ye appointment accept nahi karoge?
- Certainty: They must be the winners – Hosakta hai ke wo winners ho
- Necessity: Students must pass an entrance examination to study at this school – Is school me padhne ke liye students ko entrance examination pass karna hoga.
- Strong recommendation: They must come in time for the appointment. – Un ko time par aana hoga appointment ke liye
- Prohibition: Rahul, you must not play in the street! – Rahul, tumhe gali me nahi khelna chahiye.
- You should have studied more often (Past) – Tum ko zyada padhna chahiye tha
- You should brush your teeth every day (Present) – Tum ko chahiye ke tum roz brush karo
- They should take admission tomorrow (Future) – In ko kal admission le lena chahiye
“Ought to” word ka meaning bilkul “should” word jaisa hota hai, lekin “should” word thoda sa aur strong hota hai kyon ke wo negative consequence ke liye imply hota hai. In dono me aur ek difference ye bhi hai ke “Ought to” word question ke saath use nahi hota lekin “should” word question ke liye use hota hai.
- I ought to see a doctor
- Advice: If I were you, I would return the book – Agar mai tumhari jagah hoti to mai ye book return kar deti
- Past form of will: I thought I would be late. So I would have to take the train. – Maine socha tha ke mai late ho jaunga. Is liye mai na train le li.
- Hypothesis: It would be very expensive to stay in a hotel – Hotel mai stay karna bahut mehnga padega.
Aap ko ye note karna hai ke Have to, Has to, Will have to Modal Verbs nahi hote lekin wo unke equivalent hote jo express karte hai. Jaise ke: Express, Certainty, Necessity and Obligation.
9. Helping Verbs / Auxiliary Verbs in Hindi – Sahayak Kriya
Auxiliary or Helping Verbs use hote hai Main Verbs ke saath. Ye use hota hai Verb ka tense batane ke liye ya ek negative sentence form karne ke liye ya question form karne ke liye. Most common auxiliary Verbs hai: have, has, had, do, does, did aur to be Verbs.
- Have they completed the assignment? – Kya unhone assignment complete karliya?
- Ali is writing an email to a client. – Ali client ko email likh raha hai
- Samuel was playing with a ball – Samuel ball se khel raha tha
10. Hypothesis Verbs In Hindi – Parikalpanatmak Kriya
Hypothesis Verbs wo Verbs hote hai jo follow kiye jate hai subjunctives se, yani ke related words se. Hypothesis Verbs un Verbs ko kaha jata hai jo kisi idea ya suggestion jo ke known fact par based ho, aur ye reasoning par based ho ya further investigation ke liye kaam aaye.
“Wish” ko Hypothesis Verb kaha jata hai jab wo past tense ke saath use hota hai
Is se pehle ke hum aage badhe hum aapko batate hai ke Infinitive Form kya hota hai
Jab kisi Verb ke aage “to” lagta hai use Infinitive Form kehte hai. Jaise ke: to speak, to smoke etc.
Aaiye dekhte hai Hypothesis Verbs in Hindi “Wish” word ko different situations me kaise use karta hai
- Wish + Infinitive
Hum Wish + Infinitive formal situation me kisi se kuch puchne ke liye use karte hai
- I wish to see the manager, please – Mai manager is milna chahti hu, please
- If you wish to reserve a table, please call after two hours – Agar aap table reserve karna chahte hai to please aap do ghante baad call kijiye.
Wish + Object + Full Infinitive
- We don’t wish our name to appear in the report – Hum nahi chahte ke hamara naam report me aaye
- I wish him to be here right now – Mai chahti hu ke woh abhi isi samay yahan par aaye
Note: “Wish” ek non progressive Verb hai aur ye progressive forms ke saath use nahi kiya jasakta
- Wish + Object For Fixed Expression
Wish two objects ke saath kuch good wishes ke fixed expressions ko batane ke liye use hota hai
- We wish you a happy birthday – Hum aap ko janam din ki badhai dete hai
- I wish you good luck in your final exam – Mai aap ko final exam ke liye good luck wish karti hu
- Wish + Past indefinite tense for Present and Future Unreal
Hum “Wish” use karte hai “that” clause (Past Indefinite) ke saath jise hum informal style me likh sakte hai. Is case mai, “Wish” ka meaning “Want” nahi hota. Ye refer karta hai present and future situations jo unreal, impossible ya unlikely hai.
- I wish (that) I had a big car – Mai wish kar raha hun ke mere paas ek badi car hoti
- I wish (that) I could speak French – Mai wish kar raha hun ke mai French bol saku
- Don’t you wish (that) you could fly? – Kya tum wish nahi karte ke tum fly karo?
- Wish + Past Continuous Tense
Hum “Wish + Past Continuous Tense” use karte hai wo expression batane ke liye ke – hum chahte hai ke koi different action kare present mai ya future mai.
- I wish it was raining, But it is not. (Present Continuous Tense) – Mai wish kar rahi thi ke barish ho, lekin nahi ho rahi.
- I wish you weren’t leaving tomorrow. (Future Tense). Mai ye wish karti hun ke tum kal nahi ja rahe
Note: Is structure mai hum “were” ko use kar sakte hai “was” ki place par, especially formal style ke sentences mai.
- I wish (that) I was a doctor. (Informal)
- I wish (that) I were a doctor. (Formal)
- Wish + Past Perfect Tense for Past Unreal:
“Wish + Past Perfect Tenses” past ke wishes ke liye use hote hai ya agar hum chahte hai ke past ka situation kuch different hota.
- I wish you hadn’t said that. (It would be nice if you hadn’t said that)
- Now she wishes she had gone to college.
- Hope + First form of the verb for the Future Possibility:
Wish + Past tenses generally un wishes ke liye use hote hai jo future me possible ho. Is sense mai usually hum “hope” word ka use karte hai.
- I hope you pass your exams.
- I hope you feel better tomorrow.
- Wish + Would:
Hum “Wish + would + Bare infinitive” ka use isliye karte hai ke hum present action ke saath hone wale impatience, annoyance aur dissatisfaction ko express kar sake ya sentence with wish + would express karta hai regret or annoyance, un kaam ke liye ya situation ke liye jo nahi hone wale hai
- I wish you would stop smoking. (You are smoking at the moment and it is annoying me.)
- I wish it would stop raining. (I’m impatient because it is raining and I want to go outside.)
Note 1: Sentence with wish … un cheezon ko refer nahi karta jo hote hai ya future me ho sakte hai
- I wish you wouldn’t keep making that stupid noise. (You will keep making ….)
Note 2: Wish + Wouldn’t ek order ya request ho sakte hai
- I wish you wouldn’t drive so fast. (Similar to please don’t drive so fast)
- I wish you wouldn’t work on Sundays. (Why don’t you stop?)
Ab aap acche se samajh gaye honge ke Hyothesis Verbs kya hai. Chaliye aage badhte hai Causative Verbs in Hindi ki oar.
11. Causative Verbs In Hindi – Kaaran Vachak Kriya
Causative Verbs mai hum direct action perform nahi karte balki hum wo action kisi aur se perform karwate hai yani ke hum ye action kisi second person se karwate hai. Is ka formula change ho jayega second person ke absence aur presence ke according.
English Language me teen true Causative Verbs hai: Let, Have aur Make. Lekin is mai dusre Verbs bhi hai jaise ke cause, allow, help, enable, keep, force, require and persuade, jo ke Causative Verbs toh nahi hai lekin in ko Causative Verbs ki tarah hi use kiya jata hai
Chaliye ab is ke examples dekhte hai:
Causative Verbs: Let, Have, Make
Let: kisi ko kuch karne ke liye allow karna.
Form: [let + person + verb]
- The teacher let the students leave the class.
- I won’t let her lend him money.
- Will your parents let you go to the party tonight?
Have: Kisi ko kuch karne ki responsibility dena
Form: [have + person + verb]
- We’re having a mechanic repair our car.
- You’ve had your hair cut.
- Please have your secretary fax me the information.
Get vs Have
Kabhi “get someone to do something” interchange ho sakta hai “have someone do something” se. Lekin note karne wali baat ye hai ke ye expressions exactly same baat nahi bata rahe hai.
Is ko aur detail mai samajhne ke liye aaiye dekhte hai is ke kuch examples.
- I got the mechanic to check my brakes – Maine mechanic se brakes check karwaye..
At first the mechanic didn’t think it was necessary, but I convinced him to check the brakes.
Is sentence me ye bataya ja raha hai ki pehle to mechanic ne brakes check karna important nahi samjha lekin mai ne usey brakes check karne ke liye convince kar liya.
- I had the mechanic check my brakes.- Mai ne mechanic se brakes check karne ko kaha. (I asked the mechanic to check the brakes.).
Note: Get someone to do something ka matlab hai kisi ko convince karna koi kaam karne ke liye. Is mai Infinitive Verb use hota hai na ki Base Verb
Make: Kisi ko koi kaam karne ke liye force karna
Form: [make + person + verb]
- The teacher made him apologize for what he had said – Usne jo bola uske liye teacher ne usse apologize karaya.
- Nothing will make me change my mind. – Koi bhi cheez mera mind change nahi kar sakti
- She made her children do their homework. – Usne apne bachon se homework karwaya.
Structures Of Causative Verbs in Hindi
Causative Verbs ke structures two types ke hote hai
- Active Form
- Passive Form
Examples ke through jaaniye in dono forms me difference.
- Ali had his sister write the letter. (Active form) (Ali ne letter nahi likha. Uski sister ne letter likha hai. In a sense, Ali ne apni sister se letter likhne ko kaha aur uski sister ne accept karliya)
- Ahmed had the house painted. (Passive form) (Ahmed ne ghar paint nahi kiya. Kisi aur ne ghar paint kiya lekin is sentence me hume ye to pata chal raha hai ke Ahmed ka ghar paint hua hai lekin kis ne paint kiya ye pata nahi chal raha hai.
Ab aapko clear ho gaya hoga ke Causative Verbs in Hindi kya hai aur ye kaise use kiye jate hai setence formation mai. Ab aage badhte hai hamare last form of Verbs in Hindi ki taraf.
12. Regular and Irregular Verbs – Niyamit aur Aniyamit Kriya
Regular Verbs in Hindi
Regular Verbs bahut hi easy hote hai. Agar Verb already “e” se end ho raha hai to hum us Verb me “ed” – “d” add kar dete hai taake hum usey base form se past simple ya past participle form me change kar sake.. Agar Verb “y” se end ho raha ho to hum uska last letter jo ke “y” hoga usey “i” mai change karenge aur phir us ke baad “ed” add kardenge.
- Marry – Married
- Copy – Copied
Agar hun Gerund use karte hai to hum “ing” add karenge aur isko badalne ke liye hum “to” bhi add karenge.
Aaiye is ka ek example batate hai
Verb “call” uske base form mai “call” hi rahe ga aur “called” ban jayega dono past simple aur participle mai. Isi tarah se ye apply hoga “arrive”, “wait” jaise words ke liye.
Jaaniye Rules of Regular Verbs in Hindi
Rule – 1
Regular Verbs jo silent “e” mai end hote hai wo “d” ko add karte hai apne simple past aur past participle form mai.
- Share (Base Form) – Shared (Simple Past) – Shared (Past Participle)
- Scare (Base Form) – Scared (Simple Past) – Scared (Past Participle)
Rule – 2
Regular Verbs jo vowel me end hote hai uske baad “-e” aata hai wo “-d” ko add karte hai apne simple past aur past participle form mai.
Ski (Base Form)- Skied (Simple Past) – Skied (Past Participle)
Echo (Base Form)- Echoed (Simple Past) – Echoed (Past Participle)
Rule – 3
Regular Verbs jo “vowel + y” se end hote hai wo add karte hai “ed” apne simple past and past participle form mai.
Play (Base Form) – Played (Simple Past) – Played (Past Participle)
Survey (Base Form) – Surveyed (Simple Past) – Surveyed (Past Participle)
Rule – 4
Regular Verbs jo end hote hai “Consonant + y” mai, wo change karte hai “y” ko “i” mai aur add karte hai “ed” apne simple past aur past participle form mai.
Cry (Base Form) – Cried (Simple Past) – Cried (Past Participle)
Try (Base Form) – Tried (Simple Past) – Tried (Past Participle)
Rule – 5
Regular Verbs jo ek stressed vowel ke baad consonant mai end hote hai wo “ed” ko add karne se pehle consonant ko double kardete hai.
Stop (Base Form) – Stopped (Simple Past) – Stopped (Past Participle)
Ban (Base Form) – Banned (Simple Past) – Banned (Past Participle)
Ab aap samajh gaye honge ke Regular Verbs in Hindi kya hai. Ab aage badhte hai Irregular Verbs in Hindi ki Oar.
Irregular Verbs In Hindi
Irregular Verbs utne easy nahi hote jitne ke Regular Verbs hote hai, overall 200 se zyada Irregular Verbs hai aur aap inko sentence me asaani se set nahi kar sakte jaise ke aap Regular Verbs karte hai.
Irregular Verbs ka koi pattern nahi hota.
Iske liye hum aapko ek easy tarika batayenge Irregular Verbs ko samajhne ka aur inko apne sentences me use karne ka, toh chaliye dekhte hai wo kya hai.
Hum Irregular Verbs ko jaan sakte hai neeche diye gaye 4 groups ki help se.
Irregular Verbs ko four groups me divide kiya gaya hai.
- Group 1 – The Consonant Group
- Group 2 – The Common Past
- Group 3 – The Simple Different
- Group 4 – The Full Mix
The Consonant Group
Consonant Group me wo Verbs aayenge jahan base, past simple aur past participle mai same form hi use hoga. Chaliye example mai “Hurt” word ke bare me dekhte hai.
Base Form – I have just hurt my leg.
Past Simple – Yesterday, I hurt my leg.
Past Participle (Passive tense use hoga) – My leg was hurt. (adjective ka use) My hurt leg was painful.
Dusre Verbs jo is Consonant group me fit hote hai wo hai: Let, Cost, Put etc.

The Common Past
Is group mai jaise ke iska naam bata raha hai, Verbs jo past forms (past simple and past participle) mai use kiye jate hai wo same hi rahenge lekin un ka base form alag hoga.
Example me “Find” word ke baare me dekhte hai
Base Form – Can you help me find my glasses?
Past Simple – I found my glasses.
Past Participle – My glasses were found.
Ye Irregular Verbs ka bahut bada group hai. Iske kuch aur examples hai:
- Buy or Bought
- Feel or Felt
- Hear or Heard
- Keep or Kept
- Say or Said
- Sell or Sold etc.
Simply Different
Is group mai wo Verbs aate hai jahan simple past tense form of word differ karta hai base form and past participle se. Dekhte hai iska example “Run” word ke saath.
Base Form – I love to run (Yahan hum Infinitive version use kar rahe hai)
Past Simple – He ran to the finish line
Past Participle – His race was run.
Is group mai jo dusre Verbs include honge wo hai:
- Become or Became
- Come or Came
The Full Mix
Ye group sab se easiest group hai. Is ka simple side ye hai ke is ka har form alag hoga. Isse hume confusion nahi hoga base form, past simple aur past participle ke beech mai. Is ka usage depend karega ke hum Verb ka konsa version use kar rahe hai, isse hume pata chal jayega ke ye sentence mai use kis tarah se kiya ja raha hai. Example mai hum “Write” Verb lenge
Base Form – I write with pleasure
Past Simple – I wrote the letter
Past Participle – The written word is a joy to read.
Dusre Verbs jo is group me aate hai wo ye hai:
- Be, Was – Were, been
- Choose, Chose, Chosen
- Eat, Ate, Eaten
- Wake, Woke, Woken
- Speak, Spoke, Spoken
Ab aap samajh gaye honge ke Irregular Verbs in Hindi kya hai aur ise sentence me kis tarah use kiya jata hai.
Aaiye Irregular Verb ke aur kuch examples dekhte hai
Ab aap jaan gaye honge ke Verbs in Hindi kya hai aur Verbs in Hindi ke forms konse hai aur Verbs types in Hindi konse hai aur kitne hai. Hum ne aapke liye kayi saare examples bhi present kare hai jis se aap Verbs in Hindi me perfect ho sake. Aapko perfect banne ke liye bahut saari practice karni hogi.Toh practice kariye aur Verb me perfect baniye.
Join Josh Skills Spoken English Course
Judiye 20,000+ logo ko jo Josh ke saath English bolna aur padhna seekh rahe hai. Iss Spoken English Course ko aise design kiya gaya hai, ki koi bhi basic learner iss course se apne theoretical and practical grammar ko improve kar sakta hai. Everyday situations mei english ko kaise most effectively use kiya jaa sakta hai – iss par bhi extra dhyaan diya jaata hai.

Toh aaj hi shuru kare apni learning journey Josh Skills ke courses ke sath.
RELATED ARTICLES

Sikhe Punctuation Marks In Hindi

Strangers se baat kaise kare: 6 Important Tips

Future Continuous Tense In Hindi
Aap ne kamal ka kaam ki hai…Behut useful script hai aap ke
Excellent work by Sabiha Content suitable to , elementary, upper primary and Higher secondary students.. Easy to understand and simple.
Wow! This is so detailed and clear. Thank you so much for sharing your knowledge:)
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sikhe Nayi Skills aur Paye Apni Dream Job. Download Josh Skills App

Home / English / English Grammar / Verb in Hindi – Easy-to-understand definition, types with examples
Verb in Hindi – Easy-to-understand definition, types with examples
- Last updated on January 3, 2024
- Posted by Aniket Kumar
- Click here to join our Telegram
Table of Contents
नमस्कार साथियों, English Grammar के इस अध्याय मे आप Verb in Hindi के बारे मे सीखेंगे। Verb बहुत महत्वपूर्ण topic है, क्योंकि दुनिया का कोई भी अंग्रेजी के वाक्य बिना Verb के नहीं बनाया जा सकता है। इसके अलावा verb के उपयोग से ही किसी वाक्य का काल निर्धारित होता है। इस अध्याय के महत्वपूर्ण टॉपिक है- Verb definition in Hindi, Verb example sentences, Types of verb etc.

Verb in Hindi
“Verb” शब्द लैटिन शब्द “verbum” से उत्पन्न हुआ है और इसका मतलब है “क्रिया” या “action”. अतः वह शब्द जो कार्य, कार्य-व्यापर, सम्बन्ध या अधिकार या अवस्था को दर्शाता है वह शब्द Verb कहलाता है।
Verb Examples
20 Example of verb
- She runs every morning.
- They eat lunch at noon.
- I write in my journal every night.
- He studies for exams diligently.
- The children dance at the party.
- She sings beautifully.
- The artist creates stunning paintings.
- We play soccer on weekends.
- I often think about the future.
- They sleep soundly at night.
- She talks to her friends on the phone.
- We love to travel to new places.
- He reads a book every week.
- The kids swim in the pool.
- They work hard to achieve their goals.
- She listens to music while studying.
- Can you help me with this task?
- The construction workers build houses.
- The teacher teaches math.
- We complete the project before the deadline.
Types of Verb
वाक्य में प्रयोग के आधार पर verb दो प्रकार के होते है–
- Transitive Verb
- Intransitive Verb
- Primary Auxiliaries या Principal Auxiliaries
- Modal Auxiliaries या Modal Verbs
- Semi modal Auxiliaries या Marginal Auxiliaries
इनके अलावा Verb अन्य प्रकार के भी होते है-
Linking Verbs
Stative verbs.
- Regular verbs
- Irregular Verbs
- Finite Verbs
- Non-Finite Verbs
- Phrasal Verbs
Form of Verbs
Principal verb in hindi.
वह verb जो sentence के subject के साथ मिलकर sentence को पूरा करने में मदद करता है और उसका प्रमुख भूमिका निभाता है, उसे “Principal Verb” या “Main Verb” कहा जाता है। इसे वाक्य की मुख्य क्रिया भी कहते हैं।
Principal Verb Examples
पहले उदाहरण में, “read” main verb है जो “He” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करती है।
दूसरे उदाहरण में, “play” main verb है जो “I” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करती है।
तीसरे उदाहरण मे, “go” main verb है जो “We” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करती है।
Types of Main Verb
Main verb दो प्रकार के होते है-
Transitive verb in Hindi
वह verb जो किसी sentence में अपना object निश्चित रूप से लेता है, उसे “Transitive Verb” कहा जाता है। इसका मतलब है कि इस क्रिया को पूरा करने के लिए एक object की आवश्यकता होती है। उदाहरण से समझें-
She reads a book .
इस वाक्य में, “reads” transitive verb है जो “a book” को अपना object बनाता है।
Transitive verb Examples
- She reads a novel every week.
- The professor teaches mathematics .
- We ate pizza .
इन sentences में, object के सहारे transitive verbs को पूरा किया जा रहा है और इस प्रकार ये क्रियाएं sentence को सम्पूर्णता की भावना प्रदान करती हैं।
Types of Transitive Verb
Transitive verb दो प्रकार के होते है-
- Mono-transitive verb
- Dis-transitive verb
“Mono-transitive verb” वह verb है जो किसी sentence में अपने साथ एक object लेता है, जबकि “Di-transitive verb” वह verb है जो किसी sentence में अपने साथ दो object लेता है। यहां दिए गए उदाहरणों के साथ यह अधिक स्पष्ट हो सकता है:
Mono-transitive verb:
“I eat a mango.” – “eat” एक mono-transitive verb है, जो “a mango” को अपना object लेता है।
“She loves him.” – “loves” भी mono-transitive verb है, जो “him” को अपना object बनाता है।
Di-transitive verb:
- “He takes his wife to London.” – “takes” एक di-transitive verb है, जो “his wife” और “to London” दोनों को अपने objects बनाता है।
Intransitive verb in Hindi
“Intransitive verb” वह verb है जो किसी sentence में अपने बाद कोई भी object नहीं लेता है। इसे समझने के लिए यहां उदाहरण दिए गए हैं:
“She smiles.” – “smiles” एक intransitive verb है जो किसी भी object को नहीं लेता है।
“We laugh.” – “laugh” भी intransitive verb है जो किसी object को नहीं लेता है।
“They walk in the morning daily.” – “walk” यहां एक intransitive verb है, क्योंकि इसके बाद कोई भी object नहीं है।
- The baby sleeps peacefully.
- The sun sets in the west.
- He runs every morning.
- The bird flies in the sky.
- They arrived late.
Transitive verb and Intransitive verb
Helping verbs in hindi.
Helping verb, वह verb होता है जो किसी अन्य मुख्य verb के साथ मिलकर sentence को पूरा करने में मदद करता है और इसे विस्तारित बनाता है। इन verbs का अपना कोई स्वतंत्र अर्थ नहीं होता है, लेकिन वे sentence को सूचना प्रदान करने में मदद करते हैं। इसे Auxiliary verb या Supporting verb भी कहते है।
Helping Verb Examples
- “She is reading.” – “Is” यहां helping verb है जो मुख्य verb “reading” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करता है।
- “We were playing cricket.” – “Were” यहां helping verb है जो मुख्य verb “playing” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करता है।
- “She will teach them.” – “Will” यहां helping verb है जो मुख्य verb “teach” के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को पूरा करता है।
Types of Helping Verb
Helping verb तीन प्रकार के होते है–
1) Primary Auxiliary Verb in Hindi
जो किसी sentence में main verb के साथ मिलकर कार्य करता है, उसे Primary auxiliary verb या Principal auxiliaries कहते है।
Note – जब यह verb किसी sentence में अकेले रहता है तब यह main verb होता है तथा जब यह main verb के आता है तब यह helping verb बन जाता है।
For Examples-
- She did well in exam.
- She did not do well in exam.
- Milk is white.
Primary Auxiliary Verb तीन types के होते है–
- be (to be)– is, am, are, was, were
- have (to have)– has, have, had
- do (to do)– do, does, did
2) Modal Verbs or Modal Auxiliary
ये verbs अवस्था, भावना, क्षमता, योजना, संभावना, आवश्यकता, इच्छा, सक्षमता आदि को व्यक्त करने में मदद करते हैं। इनका प्रयोग sentence में हमेशा helping verb की तरह किया जाता है।
Modal Auxiliary की संख्या मात्र 13 है-
Modal Verb Examples
- I can do it.
- I shall go to Mumbai tomorrow.
- You may pass this year.
- I can not solve this puzzle.
Semi modal Auxiliaries or Marginal Auxiliary Verb
वैसे Modal Auxiliary verb जो main verb एवं helping verb दोनों रूप में कार्य करता है, तो उसे Semi modal Auxiliaries कहते है| Example–
- Need he come here daily?
- He need come here daily.
Linking verbs” वे क्रियाएँ हैं जो वाक्य के subject को उसके complement से जोड़ती हैं और इस प्रकार subject को और भी स्पष्टता मिलती है।
इनका प्रमुख उदाहरण “to be” की various forms (is, am, are, was, were) हैं, जो वाक्य में संबंध बनाने में मदद करते हैं।
इनका प्रयोग अक्सर व्यक्ति या वस्तु की स्थिति, भाव, या गुण को दिखाने में होता है।
Linking Verb Examples
- She is a teacher.
- The flowers are beautiful.
- They were my friends.
- I was happy.
Stative Verbs किसी व्यक्ति या चीज की वर्तमान या स्थायी स्थिति को बताती हैं। ये गतिविधि या कार्रवाई नहीं दिखाती, बल्कि किसी चीज के गुण, राय, या अवस्था का वर्णन करती हैं।
- I don’t know it.
- This house looks big.
- They seem happy.
- The coffee smells wonderful.
- He appears confident.
List of Stative Verbs
- be (am, is, are, was, were)
याद रखें कि कुछ verbs वाक्य में का उपयोग के आधार पर stative और dynamic दोनों verbs के रूप में कार्य कर सकते हैं।
Finite verb and Non-Finite verb
Finite Verb
“Finite Verb” वह verb है, जो अपने subject, number (singular/plural), और tense (काल) के अनुसार अपना रूप बदलते है।
Finite Verb Examples
- I write a letter.
- She writes a letter.
पहले एवं दूसरे वाक्य को देखे, इससे आपको पता लगेगा की किस प्रकार verb का रूप subject के अनुसार बदल गया है।
Non-Finite Verb
“Finite Verb” वह verb है, जो अपने subject, number (singular/plural), और tense (काल) के अनुसार अपना रूप नहीं बदलते है।
Non-Finite Verb Examples
- To eat is a basic human need.
- She wants to travel around the world.
- Reading helps me relax.
- The boy playing in the park is my nephew.
Types of Non-Finite Verbs
Non-Finite Verb तीन प्रकार के होते है।
- Participial
Infinitive – यह Verb का base form होता है। Example –
- To swim in the ocean is my dream.
- I need your help to complete the project.
- The decision to resign was unexpected.
Gerund – Verb के अंत मे ing लगा होता है और यह वाक्य मे noun की तरह कार्य करता है। Example-
- Swimming is good exercise.
- I enjoy reading novels.
- She apologized for interrupting the meeting.
Participle – इसके अंत मे अक्सर ed तथा ing लगा होता है तथा वाक्य मे इसका प्रयोग adjective की तरह किया जाता है। Example –
- The broken window needs to be repaired.
- The movie was boring, so I left in the middle of the boring scene.
- The man holding the umbrella is my brother. (छाता पकड़े हुए आदमी मेरा भाई है।)
Regular Verb and Irregular Verb
Regular verb वे होते है जिनके second form (v2) एवं third form (v3) के अंत मे अक्सर ed लगा होता है। जबकि Irregular verb का second form (v2) एवं third form (v3) अलग-अलग होता है।
Regular Verb Examples
Irregular Verb Examples
किसी verb के पाँच प्रमुख रूप (form) होते हैं – V1, V2, V3, V4, और V5। ये रूप क्रिया के प्रति व्यक्ति, संख्या, वचन, और काल को दर्शाते हैं।
- V1 (Base Form / Infinitive – सीधा रूप): V1 क्रिया की सामान्य रूप होती है जो आमतौर पर ‘to’ के साथ जुड़कर वाक्य में प्रयुक्त होती है। Example- to write, to eat, to read etc.
- V2 (Past Simple – पूर्वकालीन रूप): V2 क्रिया का Past रूप होता है जो किसी क्रिया का पूर्वकाल को दर्शाता है। Example- wrote, ate, read etc.
- V3 (Past Participle – पूर्व पर्याय): V3 क्रिया का पूर्व पर्याय रूप होता है जो पूर्वकाल की क्रिया के साथ रूपांतरण का कारण बनता है। Example- written, eaten, read etc.
- V4 (Gerund – क्रियावाचक): V4 क्रिया का वह रूप होता है जो किसी क्रिया की निरन्तरता को दर्शाने में मदद करता है। Example- writing, eating, reading etc.
- V5 (S Form – विशेष रूप): V5 क्रिया का विशेष रूप होता है जो किसी क्रिया की विशेष अवस्था या कौशल को दर्शाता है। Examples- writes, eats, reads etc.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
Share This Post
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You may also like

Join Our Social Media

600+ Essential Verb Forms with Hindi Meaning
Copyright © 2024 Taiyari UPSC

Hindi Grammar
This page will give you an overview of some of Hindi’s basic grammatical features including verbal forms, counting, and postpositions. Click through the tabs below to explore the content.
3 tenses: past, present, future 4 aspects: simple, habitual, continuous, perfect 4 moods: indicative, imperative, subjunctive, presumptive
Verbs combine with nouns, adjectives or other verbs to make complex verbs. If the verb combines with a noun or an adjective, it becomes a conjunct verb whereas if it combines with another verb, it becomes a compound verb. We will focus first on the former: the conjunct verb. In this case, the second element of the conjunct verb will show the grammatical agreement. Since there is no rule for which combination of noun, adjective and verbs must be used, the best way to understand the possible combinations and their meanings is to observe examples:
मैं उस गाड़ी के रंग से नफ़रत करता हूँ । I hate the color of that car.
उस आदमी का नाम पता करो । Find out that man’s name.
अपना कमरा साफ़ करो निखिल । Clean your room, Nikhil.
क्या आप कल तक मेरी गाड़ी को ठीक कर सकेंगे ? Will you be able to fix my car by tomorrow?
इस कमीज़ को छोटी कर दीजिए । Please shorten this shirt.
अपनी माँ से पार्क जाने की आज्ञा लो । Get permission from your mother to go to the park.
क्या मैं आप से कुछ पैसा उधार ले सकता हूँ ? Can I borrow some money from you?
मनु ने कमला से शादी करने की दुआ ली । Manu received blessings to marry Kamala.
मैंने उससे कल सात बजे तक पहुँचने का वचन लिया । S/he promised me that s/he will arrive tomorrow by seven o’clock.
मेरा मन परीक्षा के नतीजे पर लगा था । My mind was fixed on the results of the exam.
क्या तुमको ठंड लग रही है ? Are you feeling cold?
मुझे भूल लग रही है, सुबह से कुछ नहीं खाया । I’m feeling hungry, I haven’t eaten anything since morning.
मुझे अभी माँ यहाँ आने का पता लगा । I just now found out about mom coming here.
कल बहुत ज़बरदस्त तूफ़ान आया । A very powerful storm came yesterday
ज़रा-सा पानी दे दो, मुझे चक्कर आ रहा है । Give me some water, I’m dizzy.
मुझे अचानक याद आया कि कल परीक्षा देनी है । I suddenly remembered that I have to take an exam tomorrow.
Some sentences using conjunct verbs are given below. Note how, in general, the verb agrees with the subject of the sentence. However, if the subject is in its oblique form (i.e., it is followed by a postposition), then the verb will agree with the adjective or noun before it.
In negative sentences, the negative particle occurs between the noun/adjective and the verb:
Compound verbs are formed by using a combination of verbs, the first verb gives the meaning to the sentence and the second one adds nuance and shows the agreement. लेना, देना, and जाना are the most common compound verbs, though there are others used less frequently including बठैना, डालना, उठना, रखना, आना, and पड़ना. In many sentences—though not always—लेना shows that the action is towards the subject (e.g., किताब ले लो, नोट्स लिख लो). देना often—but not always—shows that the action is away from the subject (e.g., किताब पढ़ दो, जूते दे दो). Finally, जाना typically—but, again, not always—indicates that the action indicated by the main verb has been completed (e.g., काम हो गया, मैं सो गई थी, खुद समझ जाओ, इधर आ जाओ). Below are some common examples of compound verbs:
बड़ा अफ़सोस हुआ । मेरी बिल्ली बीमार होके मर गयी । Something really sad happened. My cat got sick and died.
बच्चे को चोट कैसे लगी ? क्या वह गिर गया ? How did the child get hurt? Did he fall down?
काम करने के बाद वह घर आते ही सो गयी । She fell asleep as soon as she got home after work.
कल आप मुझे बहुत दूर से दिख गये । I saw you from afar yesterday. (lit. You appeared to me from far away yesterday)
ऐसे मत खेलो, खिलौना टूट जाएगा । Don’t play like that, the toy will break.
मैं तो सारा खाना खा गया । I ate up all the food.
मौसम अचानक से बदल गया । तेज़ बारिश होने वाली है । The weather changed all of a sudden. It’s about to rain really hard.
The typical word order for sentences depicting a sense of compulsion is as follows:
Subject + को + Object + Infinitive verb + चाहिए / होना / पड़गा
तुम + को + किताब + ख़रीदना + चाहिए ।
You should buy a book.
The words चाहिए, होना, and पड़गा all have different meanings conveying a different degree of compulsion.
चाहिए (should / ought to)
For the present tense, simply add चाहिए after the infinitive form of the main verb:
For past tense, you’ll have to add a past tense form of होना (usually just था) after चाहिए:
होना (a mild sense of compulsion: “is/was to” )
Constructions with होना require you to add a past, present, or future form (depending on the tense of the statement) of होना after the infinitive form of the main verb:
पड़ना (an unwelcome sense of compulsion: “have to/had to/must)
Like होना, constructions with पड़ना require you to add a past, present, or future form (depending on the tense of the statement) of पड़ना after the infinitive form of the main verb:
चाहना is like other transitive verbs. It shows fondness or desire. It can be in any tense or aspect but habitual aspect (past or present) and future tense are the most common.
Perfective often conveys that what the subject had wanted didn’t actually happen.
चाहना sentence structure in habitual aspect:
Subject + Object + को + चाहना (habitual) + होना
चाहना sentence structure with infinitives when the doer of चाहना and doer of infinitive verb are the same:
Subject + Object + Verb (infinitive)+ चाहना (future/habitual)
पूरी दुनिया हिन्दी सीखना चाहती है । The whole world wants to learn Hindi.
“मैं उड़ना चाहता हूँ, दौड़ना चाहता हूँ, गिरना भी चाहता हूँ, बस रुकना नहीं चाहता” … “I want to fly, I want to run, I even want to fall, I just don’t want to stop”… From the movie यह जवानी है दीवानी, 2013:
चाहना sentence structure when the doer of चाहना is different from the doer of the other verb:
Subject (1) + चाहना (habitual/future)+ होना + कि + Subject (2) + Object + Verb (subjunctive)
शिक्षक / शिक्षिका चाहती है कि छात्र हिन्दी पढ़ें । The teacher wants the students to read.
चाहिये is one of the various indirect verbs, which means that the subject is followed by को. This means that चाहिए agrees with the object. It can be used with both nouns and verbs, giving slightly different meanings.
With nouns:
If the object is marked by the post-position को, then it is in the default form of masculine, singular. It is used to express polite demand (want), request, or need. होना form in present tense is dropped after चाहिए.
Subject + को + Noun/Object + चाहिए (+ होना in past & future tenses)
मिनाक्षी को डुपट्टा चाहिए । Minakshi wants a scarf. सौरभ को तुम्हारी किताब चाहिए थी । Saurabh wanted your book. मुझे कल आपकी गाड़ी चाहिए होगी । I will want/need your car tomorrow.
The plural form of चाहिए is चाहियें or चाहिएँ, but most people use the singular form in place of plural form too.
With verbs:
When used with verbs, takes on the meaning of “should” or “ought to”. It is used to give strong suggestions or recommendations.
Subject + को + Object (if applicable) + Verb (infinitive) चाहिए (+ होना in past & future tenses)
आनंद को सच बताना चाहिए । Anand should tell the truth. मुन्ना को मिनाक्षी से झूठ नहीं बोलना चाहिए था । Munna should not have lied to Minakshi.
Exception: If the infinitive verb is intransitive (eg. रहना, होना), then the subject appears without को postposition and the infinitive verb agrees with the subject. For example:
मिनाक्षी खुश रहनी चाहिए । Minakshi should stay happy. डुपट्टा बाहर होना चाहिए । The scarf should be on the outside.
For the use of चाहिए to state obligations, use the following form:
Subject 1 + को + चाहिए कि + Subject 2 + Object + Verb (in subjunctive/imperative)
हमें चाहिए कि हम खूब पढ़ें । We need to read a lot. आनंद को चाहिए कि वो मिनाक्षी से झूठ न बोले । Anand needs to not lie to Minakshi.
Since चाहिए makes such heavy use of the को postposition, here is a quick reminder of different “pronoun-को” forms:
ज़रूरत is a feminine noun. ज़रूरत होना and ज़रूरत पड़ना are compound verbs built on that feminine noun. The subject in these sentences is followed by को and the object is marked with the postposition की. It is used to express necessity or need.
Unlike जरूरत, which is a noun, ज़रूरी is an adjective. As such, it is typically used with the verb होना to express a need for something—e.g., “X is necessary”. That X can be a verb in the infinitive or a noun.
You can also use ज़रूरी to express what is necessary in order to accomplish something else. In such cases, the following form is used:
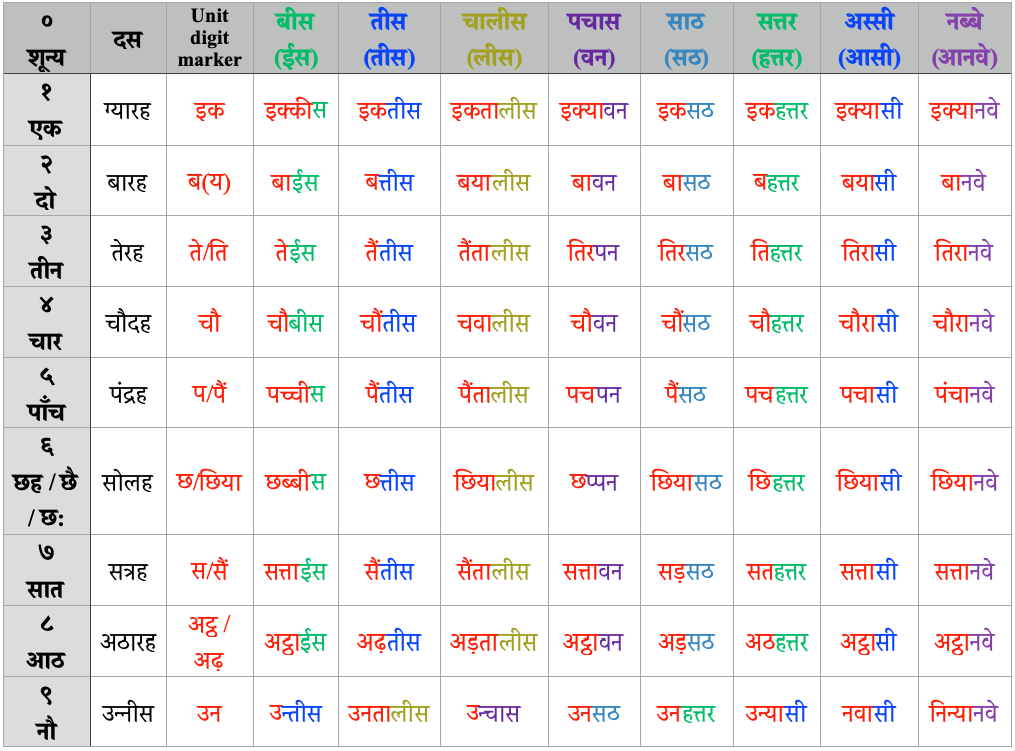
After twenty, we see that every number takes the unit digit marker and then adds the tens marker to it. For example, twenty – four is written as चौ बीस : चौ , four digit marker, attached to the twenty marker ईस . The nines are an exception to this because they take the marker for the following tens. For example, fifty – nine is उन सठ , with the उन coming from the unit digit nine and the सठ coming from the following tens digit sixty (not the expected tens digit fifty). However, eighty-nine and ninety-nine are not exceptions; they take their tens digit from the expected tens of eighty and ninety.
Notice how there is a comma after each two digits starting with one lakh rather than after every three in English numbering—e.g., १,००,००० in Hindi vs. 100,000 in English. What is one million (1,000,000) in English is actually ten lakhs (१०,००,०००) in Hindi; the comma placement simply reflects that parlance.
Colors often function as adjectives and can be divided into two grammatical types: those that show agreement with the nouns they modify and those that do not show agreement with the nouns they modify. Both are given in the tables below:
Colors that show grammatical agreement with the noun:
Colors that do not show grammatical agreement with the noun:, simple postpositions, compound postpositions with के, compound postpositions with की, compound postpositions with से.
Postpositions are also used with infinitive form of the verbs (आना, खाना, नाचना); verbs in these constructions are behaving grammatically like nouns.
को / से are mostly used with the animate object of transitive verbs and they must be used with the indirect object in cases where verbs take both direct and indirect objects. For example:
आप ने मुझसे किताब क्यों ली ? Why did you take the book from me?
The से marks the indirect object (me) rather than the direct object (the book).
को and से are used with transitive verbs in two cases:
- both are usually used if the direct object is animate:
- को (not से ) is added to give definiteness to an inanimate object:
In sentences like “ मैंने कल बच्चा देखा ”, the object बच्चा has been objectified like a table, rock, mat, etc., as opposed to in the sentence “ मैंने कल बच्चे को देखा ”.
को and से are used with ditransitive verbs with an indirect object (which is almost always animate):
Note: The correct order of sentence should be:
मैं तुमको किताब दूँगा । I will give you the book.
Emphasis can be added to the indirect object by using the following sentence order:
मैं किताब तुमको दूँगा । I will give you the book.
Using से as preposition from, by, since:
To mark instrumental case:
Making adverbs from nouns:
To make comparisons:
With interactive verbs:
Interactive verbs are verbs that convey some type of interaction between two actors. Examples include: बात करना, बोलना, कहना, पूछना, मिलना, नफ़रत करना, नाराज़ होना, डरना, इनकार करना, प्यार करना, नफ़रत / घृणा करना, लड़ना, शादी करना, माँगना, शिकायत करना
Using से in place of को with these verbs can convey a sense that the person on the receiving end of the interactive verb is more involved in the action itself:
The songs bahut pyār karte haiṃ tumko sanam and sāthiyā tūne kyā kiyā have a good contrast of these two phrasings:
The possessive pronouns (मेरा, तेरा, इसके , उसकी, हमारा, etc.) are replaced by the possessive pronoun अपना / अपने / अपनी if the possession is possessed by the subject of the same clause. Consider this sentence, which is grammatically improper:
To correct the above example, use the possessive pronoun अपने in place of the “राधा के” since the object (जूते) belongs to the subject (राधा):
Similarly, अपना will be used in the following examples too:
When both अपना and a possessive pronoun are used, it lays emphasis on the ownership:
Below are conditions where अपना cannot be used:
- अपना will not be used if the possessed does not belong to the subject
Correct: उन्होंने तेरे फ़ोन को फेंक दिया । They threw your phone away.
Incorrect: उन्होंने अपने फ़ोन को फेंक दिया ; this would mean “They threw their own phone away.”
- अपना will not be used if the possessed also functions as the subject of the sentence
Correct: मेरी किताब खो गयी । My book got lost.
Incorrect: अपनी किताब खो गयी ।
- अपना will not be used in cases where there are joint subjects
Correct: मैं और मेरा भाई मलयालम सीख रहे हैं । My brother and I are learning Malayalam.
Incorrect: मैं और अपना भाई मलयालम सीख रहे हैं ।
"Hindi Grammar" created by Mansi Bajaj

All resources on this site are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Funded by a grant (P017A200040) from the U.S. Department of Education’s International and Research Studies program, with additional support from the South Asia Institute , University of Texas at Austin.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Past Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण
- Updated on
- जुलाई 21, 2023

टेंस को इंग्लिश ग्रामर का सबसे बेसिक और महत्वपूर्ण टॉपिक माना जाता है क्योंकि इंग्लिश भाषा को सीखने या बोलने के लिए टेंस को समझना बहुत जरूरी होता है। इस के जरिये हम कोई भी सेंटेंस बना सकते हैं और समझ भी सकते हैं। इस ब्लॉग में हम Past Tense in Hindi के बारे में विस्तार से जानेंगे।
This Blog Includes:
टेंस किसे कहते हैं, past tense क्या है, past tense के उदाहरण, past tense के प्रकार, past indefinite tense के उदाहरण, past indefinite tense in hindi में क्रिया (verb), past continuous tense के उदाहरण, past continuous tense in hindi में क्रिया (verb), past perfect tense के उदाहरण, past perfect tense में क्रिया (verb), past perfect continuous tense के उदाहरण, past perfect continuous tense में क्रिया (verb), संबंधित आर्टिकल.
टेंस के माध्यम से हमें किसी कार्य के घटित होने का सही समय पता चलता है यानी कि वह घटना वर्तमान में घटित हुई है, बीते हुए समय में घटित हुई है या आने वाले समय में घटित होगी।
टेंस तीन प्रकार के होते हैं- Present Tense , Past Tense, Future Tense , जिन्हें चार-चार भाग में बांटा गया है। टेंस को विस्तार से समझने के लिए हमे उसके हर भाग को बारीकी से समझना होगा। आज के इस ब्लॉग में हम आपको Past Tense in Hindi के बारे में सम्पूर्ण जानकरी देंगे। इस टेंस को विस्तार से समझने के लिए यह ब्लॉग अंत तक पढ़ें।

वह क्रिया या घटना जो भूतकाल में पूरी हो चुकी है, उसे पास्ट टेंस कहा जाता है। हम पास्ट टेंस का यूज़ बीते समय में होने वाले कार्यो के लिए करते हैं। इस लेख में, आप Past Tense के उदाहरण, संरचना और उपयोग के नियम सीखेंगे।
Past Tense के उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:-
- वह कल राहुल के साथ खेल रहा था।
- मैं कल स्कूल नहीं गयी थी।
- वह मेरी किताब थी।
- मैं रोज शाम को खेलता था।
- वह पहले मेरे साथ रहता था।
Past Tense को मुख्यतः चार भागों में विभाजित किया गया है जो की निम्नलिखित हैं-
- Past Indefinite Tense (सामान्य भूतकाल)
- Past Continuous Tense (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
- Past Perfect Tense (पूर्ण भूतकाल)
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense (पूर्ण तत्कालिक भूतकाल)

Past Indefinite Tense क्या हैं?
पास्ट में होने वाली किसी घटना का बोध कराने के लिए Past Indefinite Tense का प्रयोग किया जाता है। Past Indefinite Tense के वाक्यों के अंत में था, थी, थे जैसे शब्दों आते हैं।
Past indefinite Tense के उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:
- I went to the market.
- I asked him.
- I ate food.
Past Indefinite Tense में वर्ब (Verb) की सेकंड फॉर्म और वर्ब की फर्स्ट फॉर्म का प्रयोग किया जाता है, जैसे: went, ate, asked, bought, आदि और इसमें Did (helping verb) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Past Continuous Tense क्या हैं?
Past continuous Tense में किसी काम का जारी रहना भूतकाल में पाया जाता है। इस टेंस के वाक्य का अन्त ‘रहा था’ ‘रही थी’ ‘रहे थे’ जैसे-शब्दों से होता है।
Past Continuous Tense के उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:
- I was writing.
- We were eating.
- I was playing.
Past Continuous Tense में वर्ब (Verb) की फर्स्ट फोर्थ फॉर्म के साथ ing का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे: going, eating, singing आदि। इसमें was/were (helping verb) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
- Was का प्रयोग सिंगुलर नंबर और (He, She, It) के साथ किया जाता है जबकि Were का प्रयोग प्लुरल नंबर और We, You, They के साथ किया जाता है।
Past Perfect Tense क्या हैं?
जो घटना या कार्य Past में शुरू होकर ख़त्म हो चूका होता है उसके लिए Past Perfect Tense का प्रयोग किया जाता है। Past Perfect Tense के वाक्यों का अंत चूका था, चुकी थी, चुके थे जैसे शब्दों से होता हैं।
Past Perfect Tense के उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:
- I had fever.
- My sister had cooked food.
- I had done homework before bedtime.
Past Perfect Tense in Hindi में वर्ब (Verb) की थर्ड फॉर्म (V3 ) का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे: gone, taught, cooked, आदि। इसमें Had (helping verb) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Past Perfect Continuous Tense क्या हैं?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense में किसी कार्य के भूतकाल में जारी रहने का बोध होता है। इस टेंस के वाक्यों अंत रहा था, रही थी, रहे थे आदि शब्द होता है।
Past Perfect Continuous Tense के उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:
- I had been living there for 10 years .
- Baby had been weeping bitterly for an hour.
- They had been deceiving others.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense में वर्ब (Verb) की फर्स्ट फॉर्म के साथ ing का प्रयोग किया जाता है, जैसे: going, eating, singing आदि। इसमें Had been (helping verb) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
निश्चित समय के लिए ‘since’ और अनिश्चित समय के लिए ‘for’ का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
- Past Perfect Continuous tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण
- 50+ Present Indefinite Tense Examples in Hindi जो करेंगे आपकी इंग्लिश सिखने में मदद
- Past Continuous Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण
- Past Indefinite Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण, एक्सरसाइज
- Present Indefinite Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण, एक्सरसाइज
- Present Continuous Tense in Hindi: परिभाषा, नियम, उदाहरण, एक्सरसाइज
उम्मीद है कि इस ब्लॉग में आपको Past Tense in Hindi के बारे में रोचक जानकारी मिल गयी होगी। ऐसे ही अन्य रोचक और महत्वपूर्ण ब्लॉग पढ़ने के लिए Leverage Edu के साथ बने रहिए।
Nupur Chatterjee is a passionate content writer working with the Hindi content team. She writes blogs in a comprehensive manner that engages with the readers. She has a strong command over both Hindi and English language, which helps her build a strong hold over multiple niches. In her leisure, you can find her doodling with crayons or binge-watching Netflix.
प्रातिक्रिया दे जवाब रद्द करें
अगली बार जब मैं टिप्पणी करूँ, तो इस ब्राउज़र में मेरा नाम, ईमेल और वेबसाइट सहेजें।
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

Learn About Adverbs in Hindi with 100+ Examples

Do you like to read daily or occasionally? Sit quietly or sing loudly! Oh! Did we just use an adverb of frequency in the first sentence?
Okay, enough dancing around the trees. You guessed it right! Today, we’ll be introducing you to the concept and meaning of the adverb in Hindi .
In the English language, adjectives are known to specify the quality of nouns and pronouns , while adverbs may describe the quality of a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
But there’s a slight difference for adverbs in Hindi. While adjectives tell us the quality of nouns and pronouns, an adverb in Hindi grammar modifies only the verb regardless of its placement in the sentence.
Before we continue, we recommend that you check out our amazing article on “ Hindi Adjectives .” Not only will this polish your vocabulary, but it will also empower you with a greater understanding of grammatical concepts and many practical example sentences .
Coming back to our current topic, spotting an adverb is easy. More often than not, in Hindi grammar, adverbs come right before the verb . That means the adverb is immediately followed by the related verb. However, this doesn’t hold true in all cases.To be honest, there’s no specific pattern for forming adverbs in Hindi, such as adding a prefix or suffix. Each adverb in Hindi is completely different from each other adverb. So, basically, you’ll have to learn and memorize them. And what could give you a better head start than our rich and versatile vocabulary list ?
- What are Adverbs in Hindi?
- Types of Adverbs in Hindi
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Degree
- Interrogative Adverbs
- What are Adverb Clauses?
- Placement of Adverbs in a Sentence
1. What are Adverbs in Hindi?
So, the first thing we’ll look at is what an adverb is in Hindi. In literal terms, the meaning of “adverb” in Hindi is क्रिया विशेषण ( kriyaa visesan ).
क्रिया ( kriyaa ) refers to a verb. Hence, a word which tell us the quality of verbs is known as क्रिया विशेषण ( kriyaa visesan ), or “adverb.”
Mind you that Indians are really expressive folks and love to paint their conversations with all sorts of adverbs. Being fluent in your use of the adverb in Hindi will give you a native feel and bring you closer to the local people. Thus, with this article, we’ll give you 100+ adverb examples in Hindi.

2. Types of Adverbs in Hindi
Now that you know the meaning of adverbs and the basic difference between adjectives and adverbs in Hindi, let’s look at the main types of adverb in Hindi.
These are the most fundamental types of adverb in Hindi, and we’ll be discussing each of them in the respective sub-headings below.
3. Adverbs of Time
To begin our Hindi adverbs list, let’s look at the adverb of time in Hindi. As the name indicates, these adverb words in Hindi tell us about when an action happened or happens. In the chart below, we’ve covered some of the most popular adverbs of time in Hindi and will show you how to use them in sentences.

4. Adverbs of Frequency
After time adverbs, another significant type is the adverb of frequency in Hindi. The term is self-explanatory. These adverbs tell us the frequency with which an action takes place, whether that be daily, weekly, or never.
5. Adverbs of Place
You know, it’s not just enough to know the difference between adjectives and adverbs in Hindi. When it comes to adverbs of place, it’s natural to get confused between adverbs and prepositions, too!
So, what’s the mantra ? Well, it all boils down to this. A preposition will always need an object to count on, whereas this is not the case with adverbs of place. The adverbs do not depend on an object to form a complete sentence.
Let’s check out the most useful adverbs of place and learn their usage in a sentence.

6. Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner are the words which show us how an action happened. Whether you touched the flower gently or entered the house haphazardly! Such types of clarity are brought to us by the adverb of manner in Hindi. So, are you ready to dive in? Let’s get going, because this is yet another very useful type of adverb in Hindi.

7. Adverbs of Degree
Earlier in this article, we covered the adverb of frequency in Hindi. A bit similar to that is another category: adverbs of degree in Hindi. So what’s the difference between the two?
Well, the adverb of degree specifies the extent or amount of the action which is being talked about. The best way to understand this is with the help of our simple and useful Hindi adverbs examples below.
8. Interrogative Adverbs
The human mind is full of reasoning and curiosity. After all, this is what gives rise to the multitude of questions that surround us. When something happens, we naturally want to know why, how, where, and when it happened. Interrogative adverbs are those words which give us the power to pose questions and ask these things about an action.
9. What are Adverb Clauses?

Another important term that you may have heard is “adverb clause” in Hindi. In order to become more familiar with it, let’s observe the concept more closely.
Adverb clauses are actually a group of words which specify the answers of interrogative adverbs. In short, this could be an adverb clause of condition in Hindi, an adverb clause of manner in Hindi, and so on.
But how do you recognize an adverb clause in Hindi? Here are some quick tips!
- An adverb clause will never be without a subject and verb.
- Adverb clauses alone can’t give complete meaning to the sentence.
- An adverb clause will always provide a potential answer to an interrogative adverb.
Yeah, this concept sounds a bit tiresome and confusing. But once we go through a few examples, you’ll be amazed at how easy it actually is.
- बारिश रुकने के बाद घर जाना। ( baaris rukaNe ke baaD ghar jaaNaa.) “Go home when the rain stops .”
- जब तुम्हें भूख लगे, तो मुझे बता देना। ( jab Tumhen bhuukh Lage, To mujhe baTaa DeNaa.) “Let me know whenever you feel hungry .”
- मैं तभी सोऊंगी जब ये फ़िल्म ख़त्म हो जाएगी। ( main Tabhii Souungii jab ye fiLm khaTm ho jaayegii.) “I will sleep only when this movie is finished .”
- ख़ूब मेहनत करो ताकि तुम ज़िंदगी में आगे बढ़ सको । (khuub mehaNaT karo Taaki Tum zinDagii men aage badh Sako. ) “Work hard so that you can progress in life .”
- मैं ये कार ख़रीद लूंगी अगर तुम मुझे कुछ पैसे दे दो तो । (main ye kaar khariiD Luungii agar Tum mujhe kuch paiSe De Do To. ) “I will buy this car if you can lend me some money .”
Wasn’t that simple! Now, let’s move on to another crucial aspect of adverbs in Hindi grammar: the placement of adverbs in a sentence.
10. Placement of Adverbs in a Sentence
In Hindi sentences , adverbs come between the subject and verb . Usually, the adverb comes before the verb; however, sometimes, an object may be put between the adverb and verb.

We would also like to bring to your attention that, similar to the English language, an adverb clause in Hindi may also come at the beginning or end of a sentence.
Below are a few example sentences to show the different placements of adverbs in Hindi sentences.
1 – Adverb Before Verb
- तुमने मुझे एक बार में पहचान लिया। (Tum Ne mujhe ek baar men pahacaaN Liyaa.) “You recognized me at once.”
Here, the adverb is “at once,” or एक बार में (ek baar men) , which comes just before the verb “recognized,” or पहचान लिया (pah caaN Liyaa) .
2 – Adverb -> Object -> Verb
- मुझे जल्दी घर पहुंचना है। (mujhe jaLDii ghar pahuncNaa hai.) “I have to reach home early.”
Here, the sequence is:
1. The adverb “early,” or जल्दी (jaLDii)
2. The object “home,” or घर (ghar)
3. The verb “have to reach,” or पहुंचना है (pahuncNaa hai)
3 – Adverb at the Beginning
- आख़िरकार, हमें वो बिल्ली मिल ही गयी। ( aakhirakaar, hamen vo biLLii miL hii gayii.) “We finally found the cat.”
Here, the adverb is “finally,” or आख़िरकार (aakhirkaar) , which is the first word in the Hindi sentence.
11. Conclusion
Whoa! We must say that Hindi adverbs are nothing less than a wonderful rollercoaster ride. Don’t you feel the same? Well, from learning what adverbs are to covering all the main types of adverbs , we thoroughly enjoyed sharing each and every concept with you.
So, which one was your favorite? Did you like adverbs of manner better, or did the adverbs of frequency interest you more? We’d love to hear you out in the comment box below. You can also let us know if there’s still an adverb in Hindi you want to learn!
We want you to learn without limits, and that’s why our free online Hindi-English dictionary is sure to steal your heart! Having you with us on this Hindi learning journey is the best thing that could happen. Show your love by signing up on HindiPod101.com . You can always reach out to us at our help center if there’s a glitch or issue.
Happy Hindi learning!
Or sign up using Facebook
Got an account? Sign in here

How To Say ‘Thank you’ in Hindi

Popular Words in Hindi for Hello and How to Say Hello in Hindi

How to Say I Love You in Hindi – Romantic Word List

How to Start a Conversation in Hindi: A Beginner’s Guide

40+ Advanced Hindi Phrases for You to Master!

30+ Intermediate Hindi Phrases to Help You Sound Like a Pro!
How to celebrate april fools’ day in hindi.
- General Announcements
- Hindi Language
- Hindi Translation
- Indian Holidays
- Advanced Hindi
- Hindi Alphabet
- Hindi Grammar
- Hindi Lessons
- Hindi Online
- Hindi Phrases
- Hindi Podcasts
- Hindi Words
- Tips & Techniques
- Feature Spotlight
- Speak Hindi
- Success Stories
- Teaching Hindi
- Team HindiPod101
- Word of the Day
Copyright © 2024 Innovative Language Learning. All rights reserved. HindiPod101.com Privacy Policy | Terms of Use . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
90 Irregular Verbs with Hindi
Table of Contents
In this post, I am sharing with you 90 Irregular Verbs with Hindi, which are frequently used in Daily Life. If you want to speak English, you must learn these verbs with Hindi. These are very common verbs with Hindi meaning. These are very common verbs which you can use in your everyday speaking.
Join Our Telegram Group
- 1000 Verb Forms with Hindi Meaning A to Z
Top 90 Irregular Verbs
1. Arise – उठना (uthna) 2. Awake – जागना (jagna) 3. Become – बन जाना (ban jana) 4. Begin – शुरू करना (shuru karna) 5. Bend – मोड़ना (modna) 6. Bet – दांव लगाना (daav lagana) 7. Bite – काटना (kaatna) 8. Blow – फूंकना (phookna) 9. Break – तोड़ना (todna) 10. Bring – लाना (laana) 11. Build – बनाना (banaana) 12. Burn – जलाना (jalana) 13. Buy – खरीदना (khareedna) 14. Catch – पकड़ना (pakadna) 15. Choose – चुनना (chunna) 16. Come – आना (aana) 17. Cost – कीमत होना (keemat hona) 18. Cut – काटना (kaatna) 19. Do – करना (karna) 20. Draw – खींचना (kheenchana)
Irregular Verbs
21. Drink – पीना (peena) 22. Drive – चलाना (chalaana) 23. Eat – खाना (khaana) 24. Fall – गिरना (girna) 25. Feel – महसूस करना (mahsoos karna) 26. Fight – लड़ना (ladna) 27. Find – ढूंढना (dhoondhna) 28. Fly – उड़ना (udna) 29. Forget – भूल जाना (bhool jaana) 30. Forgive – माफ़ करना (maaf karna) 31. Get – प्राप्त करना (praapt karna) 32. Give – देना (dena) 33. Go – जाना (jana) 34. Grow – बढ़ना (badhna) 35. Hang – लटकना (latkana) 36. Have – होना (hona) 37. Hear – सुनना (sunna) 38. Hide – छिपाना (chhipana) 39. Hit – मारना (maarna) 40. Hold – पकड़ना (pakadna)
- Top 25 One Word Substitution with Hindi
Irregular Verbs List
41. Hurt – चोट पहुँचाना (chot pahunchana) 42. Keep – रखना (rakhna) 43. Know – जानना (jaanna) 44. Leave – छोड़ना (chhodna) 45. Lend – उधार देना (udhaar dena) 46. Let – देना (dena) 47. Lose – खो द 48. Make – बनाना (banaana) 49. Mean – मतलब होना (matlab hona) 50. Meet – मिलना (milna) 51. Read – पढ़ना (padhna) 52. Ride – सवारी करना (sawaari karna) 53. Ring – घंटी बजाना (ghanti bajana) 54. Rise – उठना (uthna) 55. Run – दौड़ना (daudna) 56. Say – कहना (kahna) 57. See – देखना (dekhaana) 58. Seek – खोजना (khojna) 59. Sell – बेचना (bechna) 60. Send – भेजना (bhejna)
- Top 100 Commonly Misspelled Words with Hindi
List of Irregular Verbs
61. Set – सेट करना (set karna) 62. Shake – हिलाना (hilana) 63. Shine – चमकना (chamakna) 64. Shoot – गोली मारना (goli maarna) 65. Show – दिखाना (dikhana) 66. Shrink – सूखना (sookhna) 67. Shut – बंद करना (band karna) 68. Sing – गाना गाना (gaana gaana) 69. Sink – डूबना (doobna) 70. Sit – बैठना (baithna) 71. Sleep – सोना (sona) 72. Slide – स्लाइड करना (slide karna) 73. Speak – बोलना (bolna) 74. Spend – खर्च करना (kharch karna) 75. Stand – खड़े होना (khade hona) 76. Steal – चुराना (churaana) 77. Stick – चिपकना (chipakna) 78. Swim – तैरना (tairna) 79. Take – लेना (lena) 80. Teach – सिखाना (sikhaana)
- How to Describe Food – Adjectives with Hindi
Irregular Verbs Pdf
81. Tear – फाड़ना (faadna) 82. Tell – बताना (batana) 83. Think – सोचना (sochna) 84. Throw – फेंकना (phenkna) 85. Understand – समझना (samajhna)
86. Wake – जागना (jagna) 87. Wear – पहनना (pahanna) 88. Win – जीतना (jeetna) 89. Write – लिखना (likhna) 90. Wring – निचोडना (nichodna)
Some More Verbs List
100 Verbs in English with Hindi
200 Most Common Verbs in English with Hindi
1000 Verb Forms with Hindi Part-2
Common Irregular Verbs List with Hindi
Verbs Forms with Hindi Meaning Part-1
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
As you found this post useful...
Follow us on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Similar Posts:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Adverb (क्रिया विशेषण): Definition, and Examples – Adverb in Hindi
सामान्यतः इंग्लिश ग्रामर में एडवर्ब वह शब्द है जो Noun और Pronoun को छोड़कर अन्य सभी शब्दों की विशेषता व्यक्त करता है. इसके अलावा जो शब्द Noun और Pronoun की विशेषता व्यक्त करता है उसे Adjectives के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है. विद्यार्थियों के बिच Adverb और Adjective के बिच हमेशा मतभेद रहता है. क्योंकि, वे इसे सरलता से पहचान नही पाते है.
इस confusion को दूर करने के लिए Adverb in Hindi के सभी आवश्यक पहलुओं जैसे; adverb kya hai, adverb ki paribhasha, adverb definition in hindi, adverb examples in hindi आदि को दर्शाया गया है. इन सभी तथ्यों का अध्ययन करने के बाद एडवर्ब से सम्बन्धीत कोई भी संदेह आपके मन में नही होगा.
अंग्रेजी बोलने में सबसे आवश्यक टॉपिक एडवर्ब है. क्योंकि, यह नाउन और प्रोनाउन के अलावा सभी शब्दों की विशेषता व्यक्त करता है. इसलिए, इसे Modifier Word भी कहा जाता है. इसे पार्ट्स ऑफ़ स्पीच का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण भाग के रूप माना जाता है. इसलिए, इसके सम्बन्ध में सभी जानकारी प्राप्त करना आवश्यक है.
Table of Contents
Adverb Definition in Hindi
एडवर्ब किसे कहते है: जो शब्द किसी Verb, Adjective, दुसरे Adverb या पुरे वाक्य की विशेषता प्रकट करता हो, तो उसे Adverb कहते है.
Definition of Adverb in Hindi: The word which modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb or a full sentence is called Adverb.
Or What is Adverb in Hindi
An adverb is a word which qualifies an adjective, a verb or another Adverb.
Adverb Definition in Hindi: क्रिया विशेषण एक ऐसा शब्द है जिसका प्रयोग Verb, Adjective या किसी अन्य Adverb के साथ अपने अर्थ में कुछ जोड़ने के लिए किया जाता है.
दूसरे शब्दों में,
क्रिया विशेषण एक ऐसा शब्द है जो संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, Interjection को छोड़कर पार्ट्स ऑफ़ स्पीच के किसी भी भाग को संशोधित करता है.
Example:-
- She speaks English fluently .
- She sings sweetly .
- Mohan came quickly .
- He reads slowly .
- The elections are coming soon .
- They only shopped locally .
- They are happily married.
- The roads are very steep.
- He stopped by briefly to say hello.
- My daughter calls me regularly .
Note:- दिए गए उदहारण में English, Sing, Came and Reads के विशेषता को Adverb ( Fluently, Sweetly, Quickly और slowly) प्रकट कर रहा है. इसलिए ये सभी Adverb है.
Adverb की बनावट
अंग्रेजी वाक्य में Adverb की बनावट कुछ इस प्रकार होते है.
1. Verb + Adverb
- He is walking slowly .
- The cute dog runs quickly .
- My patient mother walks slowly .
- The quiet boy plays happily
उदहारण में Slowly, Quickly, happily वर्ब walking, runs, walks, plays आदि की विशेषता व्यक्त कर रहा है.
2. Helping Verb + Adverb + Main Verb
- he is not Reading.
- My roommate is so annoying.
- This car is incredibly expensive.
- You are quite right.
3. Adverb + Adjective + Noun
- you are a very good boy.
4. Adverb + A Sentence
- Fortunately no one was injured in the car accident.
- Unfortunately , we were too late.
Note:- हिंदी वाक्य में Adverb उसी वाक्य के पहले होता है जिसे वह Modify करता है.
Adverb Meaning in Hindi
क्रिया विशेषण संज्ञा, Adjective और verb के साथ Parts of Speech के मुख्य भागों में से एक है. Adverb की परिभाषा इसे समझने में मदद करता है कि इसका प्रयोग noun, pronoun को के अलावे शेष सभी शब्दों को मॉडिफाई करने के लिए होता है. लेकिन Adverb Meaning in Hindi इसके प्रभाव को समझने में मदद करता है कि कैसे यह वाक्य में Adjective और verb को व्यक्त करता है.
- एडवर्ब की हिंदी मीनिंग – क्रिया विशेषण
एडवर्ब निम्न प्रकार के होते है: fast, slow, very, slowly, loudly, silently, badly, fluently, twice, yesterday, आदि.
इसे भी पढ़े,
- Infinitive in Hindi
- Participle in Hindi
- Gerund in Hindi
- Not-Finite Verb in Hindi
- Modal Auxiliaries Verb in Hindi
Classification Of Adverb ( क्रिया विशेषण का प्रकार)
Adverb को 9 प्रमुख वर्गों में विभाजित किया गया है.
- Adverb of Time (काल वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Frequency (बारम्बारता वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Place (स्थान वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Manner (रिती वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Degree (परिणाम वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Sentence ( वाक्य वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
- Adverb of Affirmation and Negation
- Interrogative Adverbs(प्रश्नवाचक क्रियाविशेषण)
- Relative adverbs(सम्बन्धवाचक क्रियाविशेषण)
1. Adverb of Time (काल वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of time tell the time of an action.
जिस Adverb से समय का बोध हो, तो वह Adverb of Time कहलाता है.
दुसरें शब्दों में,
वे एडवर्ब जो समय को व्यक्त करता है, वह Adverb of Time कहलाता है.
Yesterday, today, tomorrow, then, now, ago, before, just, just now, late, early, soon, shortly, recently, immediately, instantly, after tomorrow, next year, already, इत्यादि इसके उदाहरण है.
- I shall be back tomorrow .
- They went yesterday .
- Do it now .
- Why do you always come late ?
- He saw me yesterday .
- I have seen her before .
- Mukesh will soon return.
- Ajay arrived late .
दिए गए उदहारण में एडवर्ब समय का बोध करा रहा है. जैसे Do it now. (अभी इसे करे). यह वाक्य समय को संबोधित कर रहा है जिसमे now, Adverb of time है.
Note:-
Adverb of time सवाल का जवाब देता है. “When”
अर्ताथ, Adverb of time का पता लगने के लिए वाक्य में “कब” लगाकर प्रश्न किया जाता है.
जैसे; She comes late . वह देर से आती है.
- प्रश्न: वह कब आती है.
- उत्तर: देर से
दिए गए वाक्य में “कब” लगाकर प्रश्न करने पर Adverb of time का पता चलता है.
- शब्द-भेद (Parts of Speech)
- Noun एवं भेद
- Pronoun के प्रकार एवं परिभाषा
- Adjective क्या है एवं भेद
- Verb एवं प्रकार
2. Adverb of Frequency (बारम्बारता वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of frequency tell how frequent an action is done.
परिभाषा: Adverb of Frequency से यह बोध होता है कि कोई कार्य कब / कैसे और कितनी बार होता है.
Once, twice, firstly, secondly, again, never, seldom, sometimes, often, always, secondly, thirdly, hardly, इत्यादि Adverb of Frequency के उदाहरण है.
जैसे:-
- I go to her frequently .
- I seldom visit any public place.
- We really find such a talent.
- I never visit movies.
- He has not seen her once .
- The postman called again .
- She seldom dances.
- Every person often makes mistakes.
किसी भी वाक्य से Adverb of frequency ज्ञात करने के लिए “कितनी बार” लगाकर प्रश्न करे. जैसे;
She seldom dances (वह शायद ही कभी नाचती है.)
- प्रश्न: वह कितनी बार नाचती है.
- उत्तर: शायद ही कभी
Note:- Adverb of frequency निम्न प्रश्न का उत्तर देता है. जैसे:- How often, How many
3. Adverb of Place (स्थान वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of place tell where or in what direction an action is done.
Adverb of place से स्थान का बोध होता है और यह पता चलता है कि कार्य कहा हुआ, कहा हो रहा है और कहा होगा.
Here, there, inside, down, up, in, out, near, away, indoors, outdoors, outside, far, hither, within, everywhere, without, somewhere, nowhere, anywhere इत्यादि Adverb of Place के उदाहरण है.
- Come here .
- The doctor is out .
- My father is out of station.
- She looked up .
- There is air everywhere .
- He was sitting there .
किसी भी वाक्य से Adverb of Place ज्ञात करने के लिए “कहाँ” लगाकर प्रश्न करे. जैसे
There is air everywhere . हवा प्रत्येक जगह है.
- प्रश्न: वह कहाँ है.
- उत्तर: प्रत्येक जगह
Note:- Adverb of Place निम्न प्रश्न का उत्तर देता है जैसे:- Where or in what direction.
4. Adverb of Manner (रिती वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of manner tell in what manner an action is done.
Adverb of Manner से किसी के ढंग या रिती का बोध होता है और पता चलता है कि कार्य कैसे हुआ.
वैसे Adverbs जिससे किसी कार्य के होने के तरीका का होने का अभिव्यक्ति होती है, तो वह Adverb of Manner कहलाता है.
Beautifully, clearly, badly, sweetly, loudly, carefully, timidly, any how, bravely, foolishly, wisely, certainly, well, doubtfully, इत्यादि Adverb of Manner के उदाहरण है.
- she gave me money reluctantly . (उसने मुझे अनिच्छा से पैसे दिए.)
- She walks beautifully .
- They study carefully .
- He speaks loudly .
- The horse runs fast .
- He worked hard .
- This book is well written.
दिए गए वाक्यों में reluctantly, beautifully, carefully, loudly, fast, hard, well, का प्रयोग वर्ब की विशेषता व्यक्त करने के लिए किया गया है. इसलिए, ये सभी Adverb of Manner है.
Adjective of quality में + ly जोड़कर Adverb of Manner बनाया जाता है.
- Preposition एवं उदाहरण
- Conjunction के प्रकार एवं उदाहरण
- Interjection in Hindi
5. Adverb of Degree (परिणाम वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of Degree tell the degree of action, quantity of an action and extent of an action.
डिग्री के क्रियाविशेषण एक क्रिया की मात्रा और क्रिया की सीमा को बताते हैं.
Adverb of Degree से कितना, किस हद तक जैसे प्रश्नों का उत्तर मिलता है.
Almost, very, quite, too, fully, enough, pretty, partly, rather, so, well, whole, nearly इत्यादि Adverb of Degree के उदाहरण है.
- She is extremely beautiful.
- You are quite handsome.
- You are right to a great extent.
- You are partly right.
Adverb of Degree निम्न प्रश्न का उत्तर देता है जैसे:- How much.
इसे भी पढ़े,
- Use of Am, Is, Are in Hindi
- Was and Were in Hindi
- Have and Has in Hindi
- Use of Had in Hindi
- Do, Does in Hindi
- Use of Did in Hindi
6. Adverb of Sentence ( वाक्य वाचक क्रिया विशेषण)
Adverbs of Sentence tell the reason for action.
वाक्य के विशेषण क्रिया के कारण बताते है उसे Adverb of Sentence कहते है.
जो Adverb पुरे वाक्य को modify करता है, उसे Adverb of Sentence कहते है.
Generally, personally, finally, luckily, fortunately इत्यादि Adverb of Sentence के उदाहरण है.
- Generally , two and two is four.
- Personally , you can solve this.
- Luckly , you won the lottery.
- Finally , your brother passed the examination.
7. Adverb of Affirmation and Negation
The Adverbs which express positive or negative answers are called Adverbs of Affirmation or Negation.
जो Adverbs सकारात्मक या नकारात्मक उत्तर व्यक्त करते हैं, उन्हें Adverbs of Affirmation या Negation कहा जाता है.
Not, surely, certainly, indeed, by, no, means, not at all, yes-no probably इत्यादि Adverb of Affirmation and Negation के उदाहरण है.
- She did not come after all .
- Surely he is right.
- Yes , I will come in time.
- Probably , it may rain today.
- She is certainly alive.
- I do not know her.
दिए गए वाक्यों में not, surely, certainly, probably, का प्रयोग एडवर्ब के रूप में come, right, alive आदि के विशेषता बताने के लिए किया गया है.
Yes तथा No का प्रयोग Affirmation and Negation sentence के substitute के रूप में होता है. जैसे;
- प्रश्न: Have you learnt the lesson.
- उत्तर: Yes, ( यहाँ yes का अर्थ, you learnt the lesson है.)
अवश्य पढ़े,
- Tense in Hindi
- Active Passive Voice in Hindi
8. Interrogative Adverb
वे adverbs जो प्रश्न पूछने के लिए प्रयुक्त होते है, वह Interrogative Adverb कहलाता है.
Types of adverb used to ask questions are called Interrogative adverbs.
When, how long, where, whence, whiter, howoften, howmany times, howmuch, howfar, in whatdegree, how, in what way, why, werefor, etc. Interrogative Adverb के उदहारण है.
- When will you return?
- How long will she stay there?
- Where do you live?
- How did you visit here?
- Why you are late?
- How much did the child weep?
9. Relative adverbs (सम्बन्धवाचक क्रियाविशेषण)
परिभाषा: जब दो Interrogative adverbs का प्रयोग दो सेंटेंसेस को जोड़ने के लिए होता है, वे Relative adverbs कहलाते है.
Adverbs used to join two sentences together are called relative adverbs.
why, where, when आदि Relative adverbs के उदहारण है.
- This is the house where he lived.
- Do you know when he will come?
- This the place where the king lived.
- I know the time when he came.
- This is the college where my friend had studied.
दिए गए उदहारण में Where और when Relative adverbs है जो house, know, place, time और college को Relate कर रहे है.
Adverb in Hindi को प्रतियोगिता परीक्षा एवं जानकारी के माध्यम से विस्तार से समझाया किया है जो अपने आप में एक महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है. Adverb की जानकारी अंग्रेजी में मजबूत पकड़ बनाने के लिए पर्याप्त है. इसलिए इसका अध्ययन ध्यानपूर्वक करे और याद रखे. आज की पोस्ट में adverb in hindi, adverb kise kahate hain, adverb meaning in hindi, adverb examples in hindi ज्यदा focus किया गया है ताकि आप इसे सरलता से समझ सके.
ग्रामर से सम्बंधित पोस्ट
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Hindi Essay (Hindi Nibandh) | 100 विषयों पर हिंदी निबंध लेखन – Essays in Hindi on 100 Topics
हिंदी निबंध: हिंदी हमारी राष्ट्रीय भाषा है। हमारे हिंदी भाषा कौशल को सीखना और सुधारना भारत के अधिकांश स्थानों में सेवा करने के लिए बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है। स्कूली दिनों से ही हम हिंदी भाषा सीखते थे। कुछ स्कूल और कॉलेज हिंदी के अतिरिक्त बोर्ड और निबंध बोर्ड में निबंध लेखन का आयोजन करते हैं, छात्रों को बोर्ड परीक्षा में हिंदी निबंध लिखने की आवश्यकता होती है।
निबंध – Nibandh In Hindi – Hindi Essay Topics
- सच्चा धर्म पर निबंध – (True Religion Essay)
- राष्ट्र निर्माण में युवाओं का योगदान निबंध – (Role Of Youth In Nation Building Essay)
- अतिवृष्टि पर निबंध – (Flood Essay)
- राष्ट्र निर्माण में शिक्षक की भूमिका पर निबंध – (Role Of Teacher In Nation Building Essay)
- नक्सलवाद पर निबंध – (Naxalism In India Essay)
- साहित्य समाज का दर्पण है हिंदी निबंध – (Literature And Society Essay)
- नशे की दुष्प्रवृत्ति निबंध – (Drug Abuse Essay)
- मन के हारे हार है मन के जीते जीत पर निबंध – (It is the Mind which Wins and Defeats Essay)
- एक राष्ट्र एक कर : जी०एस०टी० ”जी० एस०टी० निबंध – (Gst One Nation One Tax Essay)
- युवा पर निबंध – (Youth Essay)
- अक्षय ऊर्जा : सम्भावनाएँ और नीतियाँ निबंध – (Renewable Sources Of Energy Essay)
- मूल्य-वृदधि की समस्या निबंध – (Price Rise Essay)
- परहित सरिस धर्म नहिं भाई निबंध – (Philanthropy Essay)
- पर्वतीय यात्रा पर निबंध – (Parvatiya Yatra Essay)
- असंतुलित लिंगानुपात निबंध – (Sex Ratio Essay)
- मनोरंजन के आधुनिक साधन पर निबंध – (Means Of Entertainment Essay)
- मेट्रो रेल पर निबंध – (Metro Rail Essay)
- दूरदर्शन पर निबंध – (Importance Of Doordarshan Essay)
- दूरदर्शन और युवावर्ग पर निबंध – (Doordarshan Essay)
- बस्ते का बढ़ता बोझ पर निबंध – (Baste Ka Badhta Bojh Essay)
- महानगरीय जीवन पर निबंध – (Metropolitan Life Essay)
- दहेज नारी शक्ति का अपमान है पे निबंध – (Dowry Problem Essay)
- सुरीला राजस्थान निबंध – (Folklore Of Rajasthan Essay)
- राजस्थान में जल संकट पर निबंध – (Water Scarcity In Rajasthan Essay)
- खुला शौच मुक्त गाँव पर निबंध – (Khule Me Soch Mukt Gaon Par Essay)
- रंगीला राजस्थान पर निबंध – (Rangila Rajasthan Essay)
- राजस्थान के लोकगीत पर निबंध – (Competition Of Rajasthani Folk Essay)
- मानसिक सुख और सन्तोष निबंध – (Happiness Essay)
- मेरे जीवन का लक्ष्य पर निबंध नंबर – (My Aim In Life Essay)
- राजस्थान में पर्यटन पर निबंध – (Tourist Places Of Rajasthan Essay)
- नर हो न निराश करो मन को पर निबंध – (Nar Ho Na Nirash Karo Man Ko Essay)
- राजस्थान के प्रमुख लोक देवता पर निबंध – (The Major Folk Deities Of Rajasthan Essay)
- देशप्रेम पर निबंध – (Patriotism Essay)
- पढ़ें बेटियाँ, बढ़ें बेटियाँ योजना यूपी में लागू निबंध – (Read Daughters, Grow Daughters Essay)
- सत्संगति का महत्व पर निबंध – (Satsangati Ka Mahatva Nibandh)
- सिनेमा और समाज पर निबंध – (Cinema And Society Essay)
- विपत्ति कसौटी जे कसे ते ही साँचे मीत पर निबंध – (Vipatti Kasauti Je Kase Soi Sache Meet Essay)
- लड़का लड़की एक समान पर निबंध – (Ladka Ladki Ek Saman Essay)
- विज्ञापन के प्रभाव – (Paragraph Speech On Vigyapan Ke Prabhav Essay)
- रेलवे प्लेटफार्म का दृश्य पर निबंध – (Railway Platform Ka Drishya Essay)
- समाचार-पत्र का महत्त्व पर निबंध – (Importance Of Newspaper Essay)
- समाचार-पत्रों से लाभ पर निबंध – (Samachar Patr Ke Labh Essay)
- समाचार पत्र पर निबंध (Newspaper Essay in Hindi)
- व्यायाम का महत्व निबंध – (Importance Of Exercise Essay)
- विद्यार्थी जीवन पर निबंध – (Student Life Essay)
- विद्यार्थी और राजनीति पर निबंध – (Students And Politics Essay)
- विद्यार्थी और अनुशासन पर निबंध – (Vidyarthi Aur Anushasan Essay)
- मेरा प्रिय त्यौहार निबंध – (My Favorite Festival Essay)
- मेरा प्रिय पुस्तक पर निबंध – (My Favourite Book Essay)
- पुस्तक मेला पर निबंध – (Book Fair Essay)
- मेरा प्रिय खिलाड़ी निबंध हिंदी में – (My Favorite Player Essay)
- सर्वधर्म समभाव निबंध – (All Religions Are Equal Essay)
- शिक्षा में खेलकूद का स्थान निबंध – (Shiksha Mein Khel Ka Mahatva Essay)a
- खेल का महत्व पर निबंध – (Importance Of Sports Essay)
- क्रिकेट पर निबंध – (Cricket Essay)
- ट्वेन्टी-20 क्रिकेट पर निबंध – (T20 Cricket Essay)
- मेरा प्रिय खेल-क्रिकेट पर निबंध – (My Favorite Game Cricket Essay)
- पुस्तकालय पर निबंध – (Library Essay)
- सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी और मानव कल्याण निबंध – (Information Technology Essay)
- कंप्यूटर और टी.वी. का प्रभाव निबंध – (Computer Aur Tv Essay)
- कंप्यूटर की उपयोगिता पर निबंध – (Computer Ki Upyogita Essay)
- कंप्यूटर शिक्षा पर निबंध – (Computer Education Essay)
- कंप्यूटर के लाभ पर निबंध – (Computer Ke Labh Essay)
- इंटरनेट पर निबंध – (Internet Essay)
- विज्ञान: वरदान या अभिशाप पर निबंध – (Science Essay)
- शिक्षा का गिरता स्तर पर निबंध – (Falling Price Level Of Education Essay)
- विज्ञान के गुण और दोष पर निबंध – (Advantages And Disadvantages Of Science Essay)
- विद्यालय में स्वास्थ्य शिक्षा निबंध – (Health Education Essay)
- विद्यालय का वार्षिकोत्सव पर निबंध – (Anniversary Of The School Essay)
- विज्ञान के वरदान पर निबंध – (The Gift Of Science Essays)
- विज्ञान के चमत्कार पर निबंध (Wonder Of Science Essay in Hindi)
- विकास पथ पर भारत निबंध – (Development Of India Essay)
- कम्प्यूटर : आधुनिक यन्त्र–पुरुष – (Computer Essay)
- मोबाइल फोन पर निबंध (Mobile Phone Essay)
- मेरी अविस्मरणीय यात्रा पर निबंध – (My Unforgettable Trip Essay)
- मंगल मिशन (मॉम) पर निबंध – (Mars Mission Essay)
- विज्ञान की अद्भुत खोज कंप्यूटर पर निबंध – (Vigyan Ki Khoj Kampyootar Essay)
- भारत का उज्जवल भविष्य पर निबंध – (Freedom Is Our Birthright Essay)
- सारे जहाँ से अच्छा हिंदुस्तान हमारा निबंध इन हिंदी – (Sare Jahan Se Achha Hindustan Hamara Essay)
- डिजिटल इंडिया पर निबंध (Essay on Digital India)
- भारतीय संस्कृति पर निबंध – (India Culture Essay)
- राष्ट्रभाषा हिन्दी निबंध – (National Language Hindi Essay)
- भारत में जल संकट निबंध – (Water Crisis In India Essay)
- कौशल विकास योजना पर निबंध – (Skill India Essay)
- हमारा प्यारा भारत वर्ष पर निबंध – (Mera Pyara Bharat Varsh Essay)
- अनेकता में एकता : भारत की विशेषता – (Unity In Diversity Essay)
- महंगाई की समस्या पर निबन्ध – (Problem Of Inflation Essay)
- महंगाई पर निबंध – (Mehangai Par Nibandh)
- आरक्षण : देश के लिए वरदान या अभिशाप निबंध – (Reservation System Essay)
- मेक इन इंडिया पर निबंध (Make In India Essay In Hindi)
- ग्रामीण समाज की समस्याएं पर निबंध – (Problems Of Rural Society Essay)
- मेरे सपनों का भारत पर निबंध – (India Of My Dreams Essay)
- भारतीय राजनीति में जातिवाद पर निबंध – (Caste And Politics In India Essay)
- भारतीय नारी पर निबंध – (Indian Woman Essay)
- आधुनिक नारी पर निबंध – (Modern Women Essay)
- भारतीय समाज में नारी का स्थान निबंध – (Women’s Role In Modern Society Essay)
- चुनाव पर निबंध – (Election Essay)
- चुनाव स्थल के दृश्य का वर्णन निबन्ध – (An Election Booth Essay)
- पराधीन सपनेहुँ सुख नाहीं पर निबंध – (Dependence Essay)
- परमाणु शक्ति और भारत हिंदी निंबध – (Nuclear Energy Essay)
- यदि मैं प्रधानमंत्री होता तो हिंदी निबंध – (If I were the Prime Minister Essay)
- आजादी के 70 साल निबंध – (India ofter 70 Years Of Independence Essay)
- भारतीय कृषि पर निबंध – (Indian Farmer Essay)
- संचार के साधन पर निबंध – (Means Of Communication Essay)
- भारत में दूरसंचार क्रांति हिंदी में निबंध – (Telecom Revolution In India Essay)
- दूरसंचार में क्रांति निबंध – (Revolution In Telecommunication Essay)
- राष्ट्रीय एकता का महत्व पर निबंध (Importance Of National Integration)
- भारत की ऋतुएँ पर निबंध – (Seasons In India Essay)
- भारत में खेलों का भविष्य पर निबंध – (Future Of Sports Essay)
- किसी खेल (मैच) का आँखों देखा वर्णन पर निबंध – (Kisi Match Ka Aankhon Dekha Varnan Essay)
- राजनीति में अपराधीकरण पर निबंध – (Criminalization Of Indian Politics Essay)
- प्रधानमंत्री नरेन्द्र मोदी पर हिन्दी निबंध – (Narendra Modi Essay)
- बाल मजदूरी पर निबंध – (Child Labour Essay)
- भ्रष्टाचार पर निबंध (Corruption Essay in Hindi)
- महिला सशक्तिकरण पर निबंध – (Women Empowerment Essay)
- बेटी बचाओ बेटी पढ़ाओ पर निबंध (Beti Bachao Beti Padhao)
- गरीबी पर निबंध (Poverty Essay in Hindi)
- स्वच्छ भारत अभियान पर निबंध (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan Essay)
- बाल विवाह एक अभिशाप पर निबंध – (Child Marriage Essay)
- राष्ट्रीय एकीकरण पर निबंध – (Importance of National Integration Essay)
- आतंकवाद पर निबंध (Terrorism Essay in hindi)
- सड़क सुरक्षा पर निबंध (Road Safety Essay in Hindi)
- बढ़ती भौतिकता घटते मानवीय मूल्य पर निबंध – (Increasing Materialism Reducing Human Values Essay)
- गंगा की सफाई देश की भलाई पर निबंध – (The Good Of The Country: Cleaning The Ganges Essay)
- सत्संगति पर निबंध – (Satsangati Essay)
- महिलाओं की समाज में भूमिका पर निबंध – (Women’s Role In Society Today Essay)
- यातायात के नियम पर निबंध – (Traffic Safety Essay)
- बेटी बचाओ पर निबंध – (Beti Bachao Essay)
- सिनेमा या चलचित्र पर निबंध – (Cinema Essay In Hindi)
- परहित सरिस धरम नहिं भाई पर निबंध – (Parhit Saris Dharam Nahi Bhai Essay)
- पेड़-पौधे का महत्व निबंध – (The Importance Of Trees Essay)
- वर्तमान शिक्षा प्रणाली – (Modern Education System Essay)
- महिला शिक्षा पर निबंध (Women Education Essay In Hindi)
- महिलाओं की समाज में भूमिका पर निबंध (Women’s Role In Society Essay In Hindi)
- यदि मैं प्रधानाचार्य होता पर निबंध – (If I Was The Principal Essay)
- बेरोजगारी पर निबंध (Unemployment Essay)
- शिक्षित बेरोजगारी की समस्या निबंध – (Problem Of Educated Unemployment Essay)
- बेरोजगारी समस्या और समाधान पर निबंध – (Unemployment Problem And Solution Essay)
- दहेज़ प्रथा पर निबंध (Dowry System Essay in Hindi)
- जनसँख्या पर निबंध – (Population Essay)
- श्रम का महत्त्व निबंध – (Importance Of Labour Essay)
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि के दुष्परिणाम पर निबंध – (Problem Of Increasing Population Essay)
- भ्रष्टाचार : समस्या और निवारण निबंध – (Corruption Problem And Solution Essay)
- मीडिया और सामाजिक उत्तरदायित्व निबंध – (Social Responsibility Of Media Essay)
- हमारे जीवन में मोबाइल फोन का महत्व पर निबंध – (Importance Of Mobile Phones Essay In Our Life)
- विश्व में अत्याधिक जनसंख्या पर निबंध – (Overpopulation in World Essay)
- भारत में बेरोजगारी की समस्या पर निबंध – (Problem Of Unemployment In India Essay)
- गणतंत्र दिवस पर निबंध – (Republic Day Essay)
- भारत के गाँव पर निबंध – (Indian Village Essay)
- गणतंत्र दिवस परेड पर निबंध – (Republic Day of India Essay)
- गणतंत्र दिवस के महत्व पर निबंध – (2020 – Republic Day Essay)
- महात्मा गांधी पर निबंध (Mahatma Gandhi Essay)
- ए.पी.जे. अब्दुल कलाम पर निबंध – (Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Essay)
- परिवार नियोजन पर निबंध – (Family Planning In India Essay)
- मेरा सच्चा मित्र पर निबंध – (My Best Friend Essay)
- अनुशासन पर निबंध (Discipline Essay)
- देश के प्रति मेरे कर्त्तव्य पर निबंध – (My Duty Towards My Country Essay)
- समय का सदुपयोग पर निबंध – (Samay Ka Sadupyog Essay)
- नागरिकों के अधिकारों और कर्तव्यों पर निबंध (Rights And Responsibilities Of Citizens Essay In Hindi)
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग पर निबंध – (Global Warming Essay)
- जल जीवन का आधार निबंध – (Jal Jeevan Ka Aadhar Essay)
- जल ही जीवन है निबंध – (Water Is Life Essay)
- प्रदूषण की समस्या और समाधान पर लघु निबंध – (Pollution Problem And Solution Essay)
- प्रकृति संरक्षण पर निबंध (Conservation of Nature Essay In Hindi)
- वन जीवन का आधार निबंध – (Forest Essay)
- पर्यावरण बचाओ पर निबंध (Environment Essay)
- पर्यावरण प्रदूषण पर निबंध (Environmental Pollution Essay in Hindi)
- पर्यावरण सुरक्षा पर निबंध (Environment Protection Essay In Hindi)
- बढ़ते वाहन घटता जीवन पर निबंध – (Vehicle Pollution Essay)
- योग पर निबंध (Yoga Essay)
- मिलावटी खाद्य पदार्थ और स्वास्थ्य पर निबंध – (Adulterated Foods And Health Essay)
- प्रकृति निबंध – (Nature Essay In Hindi)
- वर्षा ऋतु पर निबंध – (Rainy Season Essay)
- वसंत ऋतु पर निबंध – (Spring Season Essay)
- बरसात का एक दिन पर निबंध – (Barsat Ka Din Essay)
- अभ्यास का महत्व पर निबंध – (Importance Of Practice Essay)
- स्वास्थ्य ही धन है पर निबंध – (Health Is Wealth Essay)
- महाकवि तुलसीदास का जीवन परिचय निबंध – (Tulsidas Essay)
- मेरा प्रिय कवि निबंध – (My Favourite Poet Essay)
- मेरी प्रिय पुस्तक पर निबंध – (My Favorite Book Essay)
- कबीरदास पर निबन्ध – (Kabirdas Essay)
इसलिए, यह जानना और समझना बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है कि विषय के बारे में संक्षिप्त और कुरकुरा लाइनों के साथ एक आदर्श हिंदी निबन्ध कैसे लिखें। साथ ही, कक्षा 1 से 10 तक के छात्र उदाहरणों के साथ इस पृष्ठ से विभिन्न हिंदी निबंध विषय पा सकते हैं। तो, छात्र आसानी से स्कूल और प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं के लिए हिंदी में निबन्ध कैसे लिखें, इसकी तैयारी कर सकते हैं। इसके अलावा, आप हिंदी निबंध लेखन की संरचना, हिंदी में एक प्रभावी निबंध लिखने के लिए टिप्स आदि के बारे में कुछ विस्तृत जानकारी भी प्राप्त कर सकते हैं। ठीक है, आइए हिंदी निबन्ध के विवरण में गोता लगाएँ।
हिंदी निबंध लेखन – स्कूल और प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं के लिए हिंदी में निबन्ध कैसे लिखें?
प्रभावी निबंध लिखने के लिए उस विषय के बारे में बहुत अभ्यास और गहन ज्ञान की आवश्यकता होती है जिसे आपने निबंध लेखन प्रतियोगिता या बोर्ड परीक्षा के लिए चुना है। छात्रों को वर्तमान में हो रही स्थितियों और हिंदी में निबंध लिखने से पहले विषय के बारे में कुछ महत्वपूर्ण बिंदुओं के बारे में जानना चाहिए। हिंदी में पावरफुल निबन्ध लिखने के लिए सभी को कुछ प्रमुख नियमों और युक्तियों का पालन करना होगा।
हिंदी निबन्ध लिखने के लिए आप सभी को जो प्राथमिक कदम उठाने चाहिए उनमें से एक सही विषय का चयन करना है। इस स्थिति में आपकी सहायता करने के लिए, हमने सभी प्रकार के हिंदी निबंध विषयों पर शोध किया है और नीचे सूचीबद्ध किया है। एक बार जब हम सही विषय चुन लेते हैं तो विषय के बारे में सभी सामान्य और तथ्यों को एकत्र करते हैं और अपने पाठकों को संलग्न करने के लिए उन्हें अपने निबंध में लिखते हैं।
तथ्य आपके पाठकों को अंत तक आपके निबंध से चिपके रहेंगे। इसलिए, हिंदी में एक निबंध लिखते समय मुख्य बिंदुओं पर ध्यान केंद्रित करें और किसी प्रतियोगिता या बोर्ड या प्रतिस्पर्धी जैसी परीक्षाओं में अच्छा स्कोर करें। ये हिंदी निबंध विषय पहली कक्षा से 10 वीं कक्षा तक के सभी कक्षा के छात्रों के लिए उपयोगी हैं। तो, उनका सही ढंग से उपयोग करें और हिंदी भाषा में एक परिपूर्ण निबंध बनाएं।
हिंदी भाषा में दीर्घ और लघु निबंध विषयों की सूची
हिंदी निबन्ध विषयों और उदाहरणों की निम्न सूची को विभिन्न श्रेणियों में विभाजित किया गया है जैसे कि प्रौद्योगिकी, पर्यावरण, सामान्य चीजें, अवसर, खेल, खेल, स्कूली शिक्षा, और बहुत कुछ। बस अपने पसंदीदा हिंदी निबंध विषयों पर क्लिक करें और विषय पर निबंध के लघु और लंबे रूपों के साथ विषय के बारे में पूरी जानकारी आसानी से प्राप्त करें।
विषय के बारे में समग्र जानकारी एकत्रित करने के बाद, अपनी लाइनें लागू करने का समय और हिंदी में एक प्रभावी निबन्ध लिखने के लिए। यहाँ प्रचलित सभी विषयों की जाँच करें और किसी भी प्रकार की प्रतियोगिताओं या परीक्षाओं का प्रयास करने से पहले जितना संभव हो उतना अभ्यास करें।
हिंदी निबंधों की संरचना

उपरोक्त छवि आपको हिंदी निबन्ध की संरचना के बारे में प्रदर्शित करती है और आपको निबन्ध को हिन्दी में प्रभावी ढंग से रचने के बारे में कुछ विचार देती है। यदि आप स्कूल या कॉलेजों में निबंध लेखन प्रतियोगिता में किसी भी विषय को लिखते समय निबंध के इन हिस्सों का पालन करते हैं तो आप निश्चित रूप से इसमें पुरस्कार जीतेंगे।
इस संरचना को बनाए रखने से निबंध विषयों का अभ्यास करने से छात्रों को विषय पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने और विषय के बारे में छोटी और कुरकुरी लाइनें लिखने में मदद मिलती है। इसलिए, यहां संकलित सूची में से अपने पसंदीदा या दिलचस्प निबंध विषय को हिंदी में चुनें और निबंध की इस मूल संरचना का अनुसरण करके एक निबंध लिखें।
हिंदी में एक सही निबंध लिखने के लिए याद रखने वाले मुख्य बिंदु
अपने पाठकों को अपने हिंदी निबंधों के साथ संलग्न करने के लिए, आपको हिंदी में एक प्रभावी निबंध लिखते समय कुछ सामान्य नियमों का पालन करना चाहिए। कुछ युक्तियाँ और नियम इस प्रकार हैं:
- अपना हिंदी निबंध विषय / विषय दिए गए विकल्पों में से समझदारी से चुनें।
- अब उन सभी बिंदुओं को याद करें, जो निबंध लिखने शुरू करने से पहले विषय के बारे में एक विचार रखते हैं।
- पहला भाग: परिचय
- दूसरा भाग: विषय का शारीरिक / विस्तार विवरण
- तीसरा भाग: निष्कर्ष / अंतिम शब्द
- एक निबंध लिखते समय सुनिश्चित करें कि आप एक सरल भाषा और शब्दों का उपयोग करते हैं जो विषय के अनुकूल हैं और एक बात याद रखें, वाक्यों को जटिल न बनाएं,
- जानकारी के हर नए टुकड़े के लिए निबंध लेखन के दौरान एक नए पैराग्राफ के साथ इसे शुरू करें।
- अपने पाठकों को आकर्षित करने या उत्साहित करने के लिए जहाँ कहीं भी संभव हो, कुछ मुहावरे या कविताएँ जोड़ें और अपने हिंदी निबंध के साथ संलग्न रहें।
- विषय या विषय को बीच में या निबंध में जारी रखने से न चूकें।
- यदि आप संक्षेप में हिंदी निबंध लिख रहे हैं तो इसे 200-250 शब्दों में समाप्त किया जाना चाहिए। यदि यह लंबा है, तो इसे 400-500 शब्दों में समाप्त करें।
- महत्वपूर्ण हिंदी निबंध विषयों का अभ्यास करते समय इन सभी युक्तियों और बिंदुओं को ध्यान में रखते हुए, आप निश्चित रूप से किसी भी प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं में कुरकुरा और सही निबंध लिख सकते हैं या फिर सीबीएसई, आईसीएसई जैसी बोर्ड परीक्षाओं में।
हिंदी निबंध लेखन पर अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
1. मैं अपने हिंदी निबंध लेखन कौशल में सुधार कैसे कर सकता हूं? अपने हिंदी निबंध लेखन कौशल में सुधार करने के सर्वोत्तम तरीकों में से एक किताबों और समाचार पत्रों को पढ़ना और हिंदी में कुछ जानकारीपूर्ण श्रृंखलाओं को देखना है। ये चीजें आपकी हिंदी शब्दावली में वृद्धि करेंगी और आपको हिंदी में एक प्रेरक निबंध लिखने में मदद करेंगी।
2. CBSE, ICSE बोर्ड परीक्षा के लिए हिंदी निबंध लिखने में कितना समय देना चाहिए? हिंदी बोर्ड परीक्षा में एक प्रभावी निबंध लिखने पर 20-30 का खर्च पर्याप्त है। क्योंकि परीक्षा हॉल में हर मिनट बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है। इसलिए, सभी वर्गों के लिए समय बनाए रखना महत्वपूर्ण है। परीक्षा से पहले सभी हिंदी निबन्ध विषयों से पहले अभ्यास करें और परीक्षा में निबंध लेखन पर खर्च करने का समय निर्धारित करें।
3. हिंदी में निबंध के लिए 200-250 शब्द पर्याप्त हैं? 200-250 शब्दों वाले हिंदी निबंध किसी भी स्थिति के लिए बहुत अधिक हैं। इसके अलावा, पाठक केवल आसानी से पढ़ने और उनसे जुड़ने के लिए लघु निबंधों में अधिक रुचि दिखाते हैं।
4. मुझे छात्रों के लिए सर्वश्रेष्ठ औपचारिक और अनौपचारिक हिंदी निबंध विषय कहां मिल सकते हैं? आप हमारे पेज से कक्षा 1 से 10 तक के छात्रों के लिए हिंदी में विभिन्न सामान्य और विशिष्ट प्रकार के निबंध विषय प्राप्त कर सकते हैं। आप स्कूलों और कॉलेजों में प्रतियोगिताओं, परीक्षाओं और भाषणों के लिए हिंदी में इन छोटे और लंबे निबंधों का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
5. हिंदी परीक्षाओं में प्रभावशाली निबंध लिखने के कुछ तरीके क्या हैं? हिंदी में प्रभावी और प्रभावशाली निबंध लिखने के लिए, किसी को इसमें शानदार तरीके से काम करना चाहिए। उसके लिए, आपको इन बिंदुओं का पालन करना चाहिए और सभी प्रकार की परीक्षाओं में एक परिपूर्ण हिंदी निबंध की रचना करनी चाहिए:
- एक पंच-लाइन की शुरुआत।
- बहुत सारे विशेषणों का उपयोग करें।
- रचनात्मक सोचें।
- कठिन शब्दों के प्रयोग से बचें।
- आंकड़े, वास्तविक समय के उदाहरण, प्रलेखित जानकारी दें।
- सिफारिशों के साथ निष्कर्ष निकालें।
- निष्कर्ष के साथ पंचलाइन को जोड़ना।
निष्कर्ष हमने एक टीम के रूप में हिंदी निबन्ध विषय पर पूरी तरह से शोध किया और इस पृष्ठ पर कुछ मुख्य महत्वपूर्ण विषयों को सूचीबद्ध किया। हमने इन हिंदी निबंध लेखन विषयों को उन छात्रों के लिए एकत्र किया है जो निबंध प्रतियोगिता या प्रतियोगी या बोर्ड परीक्षाओं में भाग ले रहे हैं। तो, हम आशा करते हैं कि आपको यहाँ पर सूची से हिंदी में अपना आवश्यक निबंध विषय मिल गया होगा।
यदि आपको हिंदी भाषा पर निबंध के बारे में अधिक जानकारी की आवश्यकता है, तो संरचना, हिंदी में निबन्ध लेखन के लिए टिप्स, हमारी साइट LearnCram.com पर जाएँ। इसके अलावा, आप हमारी वेबसाइट से अंग्रेजी में एक प्रभावी निबंध लेखन विषय प्राप्त कर सकते हैं, इसलिए इसे अंग्रेजी और हिंदी निबंध विषयों पर अपडेट प्राप्त करने के लिए बुकमार्क करें।

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. पढ़ना ( padhaNaa) riimaa kiTaab padh rahii hai. "Reema is reading a book.". Here, रीमा ( riimaa) = Subject, किताब ( kiTaab) = Object, and पढ़ रही है ( padh rahii hai) = Verb. Now that we've looked at the ways verbs work in Hindi, it's time to study the different types of verbs in Hindi.
The auxiliary verb typically adds specificity to the verb by describing the manner in which the primary verb is performed, to add depth and flair to basic Hindi sentences. Example: I sat down. / Main baith gayaa. / मैं बैठ गया. The standard Hindi verb for 'to sit' is बैठना 'baithnaa'.
Verbs Definition in Hindi: Verb की परिभाषा. What is Verb in Hindi: The Verb is a word used to express some action, feeling or existance. It tells us something about the subject in a sentence. क्रिया की परिभाषा: Verb एक शब्द है जिसका प्रयोग कुछ कार्य, भावना या ...
क्रिया - परिभाषा, भेद, और उदाहरण : हिन्दी, Verb/Kriya in Hindi हिंदी व्याकरण में कई सारे ऐसे मुख्य भेद होते हैं जिनके बारे में हम सही तरीके से
Definition of Main Verb in Hindi: वह किया जो किसी वाक्य में मुख्य अर्थ को प्रकट करती है उसे मुख्य क्रिया कहते हैं। जैसे; खाना, पीना, हंसना, रोना, देखना, धोना ...
सरल क्रिया (simple verb) A verb that is prevalent in the language like customary words. We also call this verb the root verb. This verb is neither derived from any other verb nor is it formed from the addition of more than one verb form, that's why we call it a root verb. Example: आना , जाना , लिखना ...
Types of Verb in Hindi (क्रिया के प्रकार) Verb is divided into two parts: 1) Transitive verb: Transitive verb are those verb which normally have a direct object: (सकर्मक क्रिया: सकर्मक क्रिया मे कर्ता (काम करने वाला ...
Definition of Verb in Hindi - क्रिया की परिभाषा. जिस शब्द से किसी काम का करना या होना समझा जाय, उसे क्रिया कहते है।. जैसे- पढ़ना, खाना, पीना, जाना इत्यादि ...
Verb stem + ना ( Naa) So every verb stem would have ना ( Naa) as a suffix. Here are a few examples to help you grasp this conjugation in Hindi: Verb Stem + Infinitive Suffix. Infinitive Verb Form. English Meaning. बोल ( boL) + ना ( Naa) बोल ना ( boLaNaa) "To speak".
In this lesson, we will explore the different tenses of Hindi verbs, including the present, past, and future, and learn how to conjugate them. Verbs are an essential part of any language, and mastering their conjugation is crucial for effective communication. By the end of this lesson, you will be able to confidently use verbs in a variety of ...
इस आर्टिकल में आप Verb के बारे में सम्पूर्ण जानकारी पढ़ सकते हैं जैसे की Verb in Hindi : Definition, Types, Examples and Meaning in Hindi | वर्ब मीनिंग इन हिंदी
They. Were / been. Are / being. Will be. Aaiye is ke kuch examples dekhte hai Hindi mai. Edwina is the largest elephant in this area - Edwina is area ka sab se bada hathi hai. Is sentence mai "is" ek Verb hai jo ki "to be" form of Verb se bana hai. It was a joke - Wo joke tha. Is sentence me "wo" ek Verb hai.
नमस्कार साथियों, English Grammar के इस अध्याय मे आप Verb in Hindi के बारे मे सीखेंगे। Verb बहुत महत्वपूर्ण topic है, क्योंकि दुनिया का कोई भी अंग्रेजी के वाक्य बिना Verb के नहीं ...
A free version of "Hindi and Urdu Since 1800: A Common Reader" by Christopher Shackle and Rupert Snell. The Hindi-Urdu Verb: A Guided Tour. A guide to the main verb tenses and constructions of Hindi. Interviews. A wide range of Hindi interviews with famous singers, writers, and personalities. Textbooks
Definition of Verb . a word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence, and forming the main part of the predicate of a sentence is called a verb. In other words, Verbs are words that show an action (sing), occurrence (develop), or state of being (exist). 100 verbs in English with Hindi meaning
The correct verb form is "करते हो" (b) as it matches the second person singular subject "तुम" (you). 3. The correct verb form is "आता हैं" (c) as it matches the third person singular subject "वह" (he/she/it). 4. The correct verb form is "जाते हैं" (a) as it matches the first person plural subject ...
हमे उमीद है इस आर्टिकल में Verb के बारे में दी गई जानकारी से Verb In Hindi को समझने में आपको काफी मदद मिली होगी। यदि आपके मन में कोई सवाल हो तो आप हमे नीचे कमेंट में ...
Past Perfect Tense में क्रिया (Verb) Past Perfect Tense in Hindi में वर्ब (Verb) की थर्ड फॉर्म (V3 ) का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे: gone, taught, cooked, आदि। इसमें Had (helping verb) का प्रयोग किया ...
In the chart below, we've covered some of the most popular adverbs of time in Hindi and will show you how to use them in sentences. 1. आज. (aaj) "Today". कुनाल आज वापस जा रहा है।. kuNaaL aaj vaapaS jaa rahaa hai. "Kunal is going back today.". 2.
In this Post, I am sharing 100 Irregular Verbs List Pdf, with their Hindi Meaning. Irregular Verbs are always very confusing for students specially for new learners. Join Our Telegram Group. Let's learn 100 Irregular Verbs with Hindi Meaning. IELTS Vocabulary Pdf Download.
90 Irregular Verbs with Hindi. April 29, 2023 by Ranjan Sir. Spread the love. 5. ( 1) Total Views 562.
Adverb Definition in Hindi. एडवर्ब किसे कहते है: जो शब्द किसी Verb, Adjective, दुसरे Adverb या पुरे वाक्य की विशेषता प्रकट करता हो, तो उसे Adverb कहते है. Definition of Adverb in Hindi: The word which modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb or ...
आतंकवाद पर निबंध (Terrorism Essay in hindi) सड़क सुरक्षा पर निबंध (Road Safety Essay in Hindi) बढ़ती भौतिकता घटते मानवीय मूल्य पर निबंध - (Increasing Materialism Reducing Human Values Essay)