Worksheet on Discounts
Math worksheet on discounts will help us to practice the questions on how to solve the problems related to marked price, selling price and discount in profit and loss. Students can recall the word problems on discount to practice this worksheet on discounts to get the exact answers given below.
1. The marked price of a water cooler is $ 4650. The shopkeeper offers an off-season discount of 18% on it. Find its selling price. 2. The price of a sweater was slashed from $ 960 to $ 816 by a shopkeeper in the winter season. Find the rate of discount given by him. 3. Find the rate of discount being given on a shirt whose selling price is $ 546 after deducting a discount of $ 104 on its marked price. Hint. MP = (SP) + (discount).
4. After allowing a discount of 8% on a toy, it is sold for $ 216.20. Find the marked price of the toy.
5. A tea set was bought for $ 528 after getting a discount of 12% on its marked price. Find the marked price of the tea set.
6. A dealer marks his goods at 35% above the cost price and allows a discount of 20% on the marked price. Find his gain or loss per cent.
7. A cell phone was marked at 40% above the cost price and a discount of 30% was given on its marked price. Find the gain or loss percent made by the shopkeeper. 8. A dealer purchased a fan for $ 1080. After allowing a discount of 25% on its marked price, he gains 25%. Find the marked price of the fan. 9. A dealer bought a refrigerator for $ 11515. After allowing a discount of 16% on its marked price, he gains 20%. Find the marked price of the refrigerator. 10. A carpenter allows a discount of 16% to his customers and still gains 20%. Find the marked price of a dining table which costs the carpenter $ 1190. 11. After allowing a discount of 10% on the marked price, a trader still makes a gain of 17%. By what percent is the marked price above the cost price? 12. How much per cent above the cost price should a shopkeeper mark his goods so that after allowing a discount of 10% on the marked price, he gains 8%? 13. The marked price of a television is $ 18500. A dealer allows two successive discounts of 20% and 5%. For how much is the television available? 14. Find the single discount which is equivalent to two successive discounts of 20% and 5%.
Answers for worksheet on discounts are given below to calculate the discounted price on the marked price.
6. Gain = 8%
7. Loss = 2%
13. $ 14060
● Profit, Loss and Discount
Calculating Profit Percent and Loss Percent
Word Problems on Profit and Loss
Examples on Calculating Profit or Loss
Practice Test on Profit and Loss
Practice Test on Profit Loss and Discount
● Profit, Loss and Discount - Worksheets
Worksheet to Find Profit and Loss
Worksheets on Profit and Loss Percentage
Worksheet on Gain and Loss Percentage
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice From Worksheet on Discounts to HOME PAGE

New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
Properties of Division | Division of Property Overview|Math Properties
Apr 04, 24 03:22 PM

Long Division | Method | Steps | Examples | Long Division Worksheets
Apr 04, 24 01:09 PM

Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers | Dividing Larger Numbers
Apr 04, 24 09:31 AM

Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Number | Long Division |Worksheet Answer
Apr 04, 24 09:30 AM

Months of the Year | List of 12 Months of the Year |Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr
Apr 02, 24 02:08 PM

© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
- → Resources
- → 7th Grade
Percents Applications Discount, Sale Price, and Tips Lesson Plan
Get the lesson materials.

Discount, Sale Price, Tips Guided Notes with Doodles | Percents Sketch Notes

Ever wondered how to teach percent applications involving discount, sale price, and tips in an engaging way to your seventh grade students?
In this lesson plan, students will learn about calculating discount, finding sale prices, and determining tips, all using percentages. Through artistic and interactive guided notes, check for understanding questions, a doodle and color by number activity, and a maze worksheet, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of percent applications.
The lesson culminates with a real-life example that explores how calculating discounts and finding sale prices is useful in everyday situations, such as shopping or dining out. This real-life application will help students see the relevance and importance of understanding and using percentages in their daily lives.
- Standard : CCSS 7.RP.A.3
- Topic : Percents
- Grade : 7th Grade
- Type : Lesson Plans
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students will be able to:
Calculate the discount amount and sale price of an item given the original price and the percent discount.
Solve problems involving finding the original price of an item given the sale price and the percent discount.
Determine the total cost including tips based on a percentage of the bill amount.
Apply the concepts of discount, sale price, and tips to real-life situations, such as shopping and dining out.
Prerequisites
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
How to convert between decimals and percents
Basic understanding of multiplication and division of integers and decimals
Colored pencils or markers
Discount, Sale Price, and Tips Guided Notes
Key Vocabulary
Introduction.

As a hook, ask students why it is important to calculate discounts, sale prices, and tips in real life situations. Refer to the last page of the guided notes as well as the FAQs below for ideas.
Use the first page of the guided notes to introduce the concept of discounts. Walk through how to calculate the discount amount and the sale price. Explain the difference between the discount and the sale price. Have students fill in the steps to calculating discount and sale price. Then, have students practice using the 3 problems in the "you try" section on the page. Students will have to calculate the sale prices of the different furniture shown.
Next, use the second page of the guided notes to introduce tip calculations. Discuss the purpose of tipping and how it is typically calculated as a percentage of the total bill. Show students how to calculate the tip amount and the total amount, including the tip. Emphasize the importance of good tipping etiquette and have students fill in some services like waitressing, salons, and food delivery that often accept tips.
Based on student responses, reteach concepts that students need extra help with. If your class has a wide range of proficiency levels, you can pull out students for reteaching, and have more advanced students begin work on the practice exercises.
After finishing the first two pages of the guided notes, have students practice finding discounts, sale prices, and tips using the maze activity (page 3). Walk around the classroom to answer any questions students may have.
Fast finishers can dive into the color by number activity (page 4) for extra practice. You can assign it as homework for the remainder of the class.
Real-Life Application
Bring the class back together, and introduce the concept of calculating tips and sale price in real-life situations. Explain that understanding how to find the tip when dining at a restaurant or calculating the sale price when shopping can be useful in everyday life. Use the last page of the guided notes where students will read about a detailed example of real life applications.
Provide examples and scenarios where calculating tips and sale prices are relevant. For example, you can discuss scenarios such as:
Dining at a restaurant: Explain that when dining out, it is customary to leave a tip for the server. Show the students how to calculate a specific percentage tip based on the total bill. Discuss common tipping percentages, such as 15%, 18%, and 20%, and emphasize the importance of considering the quality of service when determining the appropriate tip.
Shopping during a sale: Explain that when there is a sale at a store, the price of an item is often reduced by a certain percentage. Show the students how to calculate the sale price of an item by applying the discount percentage to the original price. Discuss the concept of finding the better deal between items with different sale prices and comparing the savings.
Discounts and coupons: Explain that discounts and coupons are often used to reduce the price of items. Show the students how to calculate the discounted price using a specific percentage discount or a fixed amount coupon. Discuss the importance of reading the fine print to understand the terms and conditions of the discounts or coupons.
Encourage students to share their own experiences or examples of situations where they have encountered the need to calculate tips or sale prices. This will help them see the relevance and practicality of the concept in their daily lives.
Refer to the FAQ section or provide additional examples and scenarios to reinforce the concept further, if needed.
Additional Print Practice
A fun, no-prep way to practice discount, sale price, and tips is Doodle Math — they’re a fresh take on color by number or color by code. It includes multiple levels of practice, perfect for a review day or sub plan.
Here is an activity to try:
Discount, Sale Price, and Tips Doodle Math Activity
What is a discount? Open
A discount is a reduction in price or cost. It is usually expressed as a percentage off the original price.
How do I calculate the sale price? Open
To calculate the sale price, you need to subtract the discount amount from the original price. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Convert the discount percentage to a decimal by dividing it by 100.
Step 2: Multiply the decimal by the original price to find the discount amount.
Step 3: Subtract the discount amount from the original price to get the sale price.
How do I calculate the amount of discount? Open
To calculate the amount of discount, you need to multiply the original price by the discount percentage. Here are the steps:
How can I find the tip for a bill? Open
To find the tip for a bill, you need to multiply the bill amount by the tip percentage. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Convert the tip percentage to a decimal by dividing it by 100.
Step 2: Multiply the decimal by the bill amount to find the tip.
Can you give an example of a discount problem? Open
Sure! Here's an example:
Original price: $100
Discount percentage: 20%
To find the sale price:
Step 1: Convert the discount percentage to a decimal: 20% = 0.2
Step 2: Multiply the decimal by the original price: 0.2 * $100 = $20
Step 3: Subtract the discount amount from the original price: $100 - $20 = $80
So, the discount amount is $20 and the sale price is $80.
How do I find the total amount after adding a tip? Open
To find the total amount after adding a tip, you need to add the tip amount to the original bill. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Find the tip amount by multiplying the bill amount by the tip percentage (converted to a decimal).
Step 2: Add the tip amount to the bill amount to get the total amount.
Can you explain the concept of sale price in real-life examples? Open
Certainly! Here are some real-life examples of sale price:
A store offers a 30% discount on a $50 shirt. The sale price would be $35.
A restaurant reduces the price of a meal by 15% during a special promotion. If the original price of the meal was $100, the sale price would be $85.
An online retailer offers a 20% discount on a $200 electronic gadget. The sale price would be $160.
How can I use percentages and discounts in everyday situations? Open
Percentages and discounts are commonly used in everyday situations. Here are some examples:
Calculating how much you will save during a sale or promotion.
Determining the amount of money to tip at a restaurant or for a service.
Understanding the discount applied to a coupon or promotional code when shopping online.
Comparing prices of products with different discounts to find the best deal.
Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.3: Discounts, Markups, and Sales Tax
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 129573

Learning Objectives
After completing this section, you should be able to:
- Calculate discounts.
- Solve application problems involving discounts.
- Calculate markups.
- Solve application problems involving markups.
- Compute sales tax.
- Solve application problems involving sales tax.
Many people first encounter percentages during a retail transaction such as a percent discount (SALE! 25% off!!), or through sales tax ("Wait, I thought this was $1.99?"), a report that something has increased by some percentage of the previous value (NOW! 20% more!!). These are examples of percent decreases and percent increases. In this section, we discuss decrease, increase, and then the case of sales tax.
Calculating Discounts
Retailers frequently hold sales to help move merchandise. The sale price is almost always expressed as some amount off the original price. These are discounts , a reduction in the price of something. The price after the discount is sometimes referred to as the reduced price or the sale price.
When a reduction is a percent discount, it is an application of percent, which was introduced in Understanding Percent. The formula used was part = percentage × total part = percentage × total . In a discount application, the discount plays the role of the part, the percent discount is the percentage, and the original price plays the role of the total.
The formula for a discount based on a percentage is discount = percent discount × original price discount = percent discount × original price , with the percent discount expressed as a decimal. The price of the item after the discount is sale price = original price - discount sale price = original price - discount .
These are often combined into the following formula
sale price = original price - percent discount × original price = original price × ( 1 - percent discount ) sale price = original price - percent discount × original price = original price × ( 1 - percent discount )
When the original price and the percent discount are known, the discount and the sale price can be directly computed.
Example 6.10
Calculating discount for a percent discount.
Calculate the discount for the given price and discount percentage. Then calculate the sale price.
- Original price = $75.80; percent discount is 25%
- Original price = $168.90; percent discount is 30%
The sale price of the item is then sale price = original price - discount = 75.80 - 18.95 = 56.85 sale price = original price - discount = 75.80 - 18.95 = 56.85 , or $56.85.
The sale price of the item is then sale price = original price - discount = 168.90 - 50.67 = 118.23 sale price = original price - discount = 168.90 - 50.67 = 118.23 , or $118.23.
Your Turn 6.10
Sometimes the original price and the sale price of an item is known. From this, the percent discount can be computed using the formula discount = percent discount × original price discount = percent discount × original price , by solving for the percent discount.
Example 6.11
Calculating the percent discount from the original and sale prices.
Determine the percent discount based on the given original and sale prices.
- Original price = $1,200.00; sale price = $900.00
- Original price = $36.70; sale price = $29.52
Step 2. Find the percent discount. Substituting the discount of $300.00 and the original price of $1,200.00, into the formula discount = percent discount × original price discount = percent discount × original price , we can find the percent discount.
300 .00 = percent discount × 1,200 .00 300 .00 1 , 200.00 = percent discount 0.25 = percent discount 300 .00 = percent discount × 1,200 .00 300 .00 1 , 200.00 = percent discount 0.25 = percent discount
Converting to percent form, the percent discount is 25%.
Step 2. Find the percent discount. Substituting the discount of $7.38 and the original price of $36.70, into the formula discount = percent discount × original price discount = percent discount × original price , we can find the percent discount.
29 .52 = percent discount × 36 .70 29 .52 36.70 = percent discount 0.2 = percent discount 29 .52 = percent discount × 36 .70 29 .52 36.70 = percent discount 0.2 = percent discount
Converting to percent form, the percent discount is 20%.
Your Turn 6.11
Sometimes the sale price and the percent discount of an item are known. From this, the original price can be found. To avoid multiple steps, though, the formula that we will use is sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) . The original price can be found by solving this equation for the original price.
Example 6.12
Calculating the original price from the percent discount and sale price.
Determine the original price based on the percent discount and sale price.
- Percent discount 10%; sale price = $450.00
- Percent discount 75%, sale price = $90.00
sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 450 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .10) 450 .00 = original price × (0 .90) 500 .00 = original price sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 450 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .10) 450 .00 = original price × (0 .90) 500 .00 = original price
sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 90 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .75) 90 .00 = original price × (0 .25) 360 .00 = original price sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 90 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .75) 90 .00 = original price × (0 .25) 360 .00 = original price
Your Turn 6.12
Solve application problems involving discounts.
In application problems, identify what is given and what is to be found, using the terms that have been learned, such as discount, original price, percent discount, and sale price. Once you have identified those, use the appropriate formula (or formulas) to find the solution(s).
Example 6.13
Determine discount and new price a sale rack item.
The sale rack at a clothing store is marked “All Items 30% off.” Ian finds a shirt that had an original price of $80.00. What is the discount on the shirt? What is the sale price of the shirt?
We are asked to find the discount, and the sale price. We know the percent discount is 30%, or 0.30 in decimal form. The original price was $80.
Substituting into the percent discount formula, we find that the discount is discount = percent discount × original price = 0 .30 × 80 = 24 discount = percent discount × original price = 0 .30 × 80 = 24 .
The discount is $24 on that shirt. The sale price is the original price minus the discount, so the sale price is $80 – $24 = $56.
Your Turn 6.13
Example 6.14, determine the percent discount of a bus pass.
An annual pass on the city bus is priced at $240. The student price, though, is $168. What is the percent discount for students for the bus pass?
We know the original price of the item, $240. We also know the sale price of the item, $168. From this we know the discount is $ 240 - $ 168 = $ 72 $ 240 - $ 168 = $ 72 . Substituting these values into the formula discount = percent discount × original price discount = percent discount × original price , we can find the percent discount.
discount = percent discount × original price 72 = percent discount × 240 72 240 = percent discount × 240 240 0.3 = percent discount discount = percent discount × original price 72 = percent discount × 240 72 240 = percent discount × 240 240 0.3 = percent discount
The student percent discount on the bus pass is 30%.
Your Turn 6.14
Example 6.15, finding the original price of a new pair of tires.
Kendra’s car developed a flat, and the tire store told her that two tires had to be replaced. She got a 10% discount on the pair of tires, and the sale price came to $189.00. What was the original price of the tires?
Using the percent discount and the sale price, we can find the original price with the formula sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) sale price = original price × (1 - percent discount) . Substituting and solving for the original price, we find
sales price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 189 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .10) 189 .00 = original price × (0 .90) 210 .00 = original price sales price = original price × (1 - percent discount) 189 .00 = original price × (1 - 0 .10) 189 .00 = original price × (0 .90) 210 .00 = original price
The original price of the two tires Kendra bought was $210.00.
Your Turn 6.15
Computing Price Based on a Percent Off Coupon
WORK IT OUT
There are cases where retailers allow multiple discounts to be applied. However, it is rare that the discount percentages are added together. For example, if you have a 15% coupon and qualify for a 20% price reduction, the retailer typically does not add those two percentages together to determine the new price. The retailer instead applies one discount, then applies the second discount to the price obtained after the first discount was deducted.
Research the original prices of two different laptops offered by one retail outlet. Assume you will receive a student discount of 12% and your outlet of choice is having a 15% off sale on all laptops.
For each laptop:
- List the original price and calculate the price after applying the student discount (12%) only.
- Then find the price after applying the sale discount (15% off) to the price found in Step 1.
- Determine the total saved on the laptop and what percent discount the total savings represents.
- Now, apply the discounts in reverse order (first the sale discount, then the student discount).
- Note anything interesting about your findings.
Calculate Markups
When retailers purchase goods to sell, they pay a certain price, called the cost . The retailer then charges more than that amount for the goods. This increase is called the markup . This selling price, or retail price , is what the retailer charges the consumer in order to pay their own costs and make a profit. Markup, then is very similar to discount, except we add the markup, while we subtract the discount.
The formula for a markup based on a percentage is markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost , with the percent markup expressed as a decimal. The price of the item after the markup is retail price = cost + markup retail price = cost + markup .
retail price = cost + percent markup × cost = cost × ( 1 + percent markup) retail price = cost + percent markup × cost = cost × ( 1 + percent markup)
It should be noted that the formulas used for a markup are very similar to those for a discount, with addition replacing the subtraction.
Example 6.16
Determining the retail price based on the cost and the percent markup.
Calculate the markup for the given cost and markup percentage. Then calculate the retail price.
- Cost = $62.00; percent markup is 15%
- Cost = $750.00; percent markup is 45%
- Substituting the values into the formula markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost , we find that the markup is markup = 0.15 × 62.00 = 9.30 markup = 0.15 × 62.00 = 9.30 . The markup is $9.30. The retail price of the item is then retail price = cost + markup retail price = cost + markup , or $62.00 + $9.30 = $71.30.
- Substituting the values into the formula markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost , we find that the markup is markup = 0.45 × 750.00 = 337.50 markup = 0.45 × 750.00 = 337.50 . The markup is $337.50. The retail price of the item is then retail price = cost + markup retail price = cost + markup , or $750.00 + $337.50 = $1,087.50.
Your Turn 6.16
Sometimes the cost and the retail price of an item are known. From this, the percent markup can be computed using the formula markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost , by solving for the percent markup.
Example 6.17
Calculating the percent markup from the cost and retail price.
Determine the percent markup based on the given cost and retail price. Round percentages to two decimal places.
- Cost = $90.00; retail price = $103.50
- Cost = $5.20; retail price = $9.90
13 .50 = percent markup × 90.00 13 .50 90.00 = percent markup 0.15 = percent markup 13 .50 = percent markup × 90.00 13 .50 90.00 = percent markup 0.15 = percent markup
4 .70 = percent markup × 5.20 4.70 5.20 = percent markup 0.9038 = percent markup 4 .70 = percent markup × 5.20 4.70 5.20 = percent markup 0.9038 = percent markup
Your Turn 6.17
Sometimes the retail price and the percent markup of an item are known. From this, the cost can be found. To avoid multiple steps, though, the formula that we will use is retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) . The cost can be found by solving this equation for the cost.
Example 6.18
Calculating the cost from the percent markup and retail price.
Determine the cost based on the percent markup and retail price.
- Percent markup 20%; retail price = $10.62
- Percent markup 125%; retail price = $26.55
retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 10 .62 = cost × ( 1 + 0.2 ) 10 .62 = cost × (1 .2) 8 .85 = cost retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 10 .62 = cost × ( 1 + 0.2 ) 10 .62 = cost × (1 .2) 8 .85 = cost
retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 26 .55 = cost × (1+2 .25) 26 .55 = cost × (3 .25) 11 .80 = cost retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 26 .55 = cost × (1+2 .25) 26 .55 = cost × (3 .25) 11 .80 = cost
Your Turn 6.18
Solve application problems involving markups.
As before when working with application problems, be sure to look for what is given and identify what you are to find. Once you have evaluated the problem, use the appropriate formula to find the solution(s). These application problems address markups.
Example 6.19
Determine retail price of a power bar.
Janice works at a convenience store near campus. It sells protein bars at a 60% markup. If a bar costs the store $1.30, how much is the retail price at the convenience store?
We are asked to find the retail price. We know the percent markup is 60%. The cost of the bar was $1.30. Substituting into the percent markup formula, we find that the markup is markup = percent markup × cost = 0.60 × 1.30 = 0.78 markup = percent markup × cost = 0.60 × 1.30 = 0.78 . The markup is $0.78 on that protein bar. The retail price is the cost plus the markup, so the retail price is retail price = cost + markup = 1.30 + 0.78 = 2.08 retail price = cost + markup = 1.30 + 0.78 = 2.08 . The retail price is $2.08.
Your Turn 6.19
Example 6.20, determine the percent markup of a phone.
Javi began working at a phone outlet. In a recent shipment, he noticed that the cost of the phone to the store was $480.00. The phone sells for $840.00 in the store. What is the percent markup on the phone?
We know the cost of the phone, $480. We also know the retail price of the phone, $840.00. From this we know the markup is $ 840.00 - $ 480.00 = $ 360.00 $ 840.00 - $ 480.00 = $ 360.00 . Substituting these values into the formula markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost , we can find the percent markup.
markup = percent markup × cost 360 = percent markup × 480 360 480 = percent markup × 480 480 0.75 = percent markup markup = percent markup × cost 360 = percent markup × 480 360 480 = percent markup × 480 480 0.75 = percent markup
The markup on the phone is 75%.
Your Turn 6.20
Example 6.21, finding the cost of a t-shirt.
Bob decided to order a t-shirt for his gaming friend online for $29.50. He knows the markup on such t-shirts is 18%. What was the t-shirt’s cost before the markup?
Using the percent markup and the retail price, $29.50, we can find the cost with the formula retail price = original price × (1 + percent markup) retail price = original price × (1 + percent markup) . Substituting and solving for cost we find
retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 29 .50 = cost × (1+0 .18) 29 .50 = cost × (1 .18) 25 .00 = cost retail price = cost × (1 + percent markup) 29 .50 = cost × (1+0 .18) 29 .50 = cost × (1 .18) 25 .00 = cost
The cost of the t-shirt was $25.00.
Your Turn 6.21
Compute sales tax.
Sales tax is applied to the sale or lease of some goods and services in the United States but is not determined by the federal government. It is most often set, collected, and spent by individual states, counties, parishes, and municipalities. None of these sales tax revenues go to the federal government.
For example, North Carolina has a state sales tax of 4.75% while New Mexico has a state sales tax of 5%. Additionally, many counties in North Carolina charge an additional 2% sales tax, bringing the total sales tax for most (72 of the 100) counties in North Carolinians to 6.75%. However, in Durham, the county sales tax is 2.25% plus an additional 0.5% tax used to fund public transportation, bringing Durham County’s sales tax to 7%. To find the sales tax in a particular place, then, add other locality sales taxes to the base state sales tax rate.
How much we pay in sales tax depends on where we are, and what we are buying.
To determine the amount of sales tax on taxable purchase, we need to find the product of the purchase price, or marked price, and the sales tax rate for that locality.
To calculate the amount of sales tax paid on the purchase price in a locality with sales tax given in decimal form, calculate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate The total price is then Total price = purchase price + purchase price × tax rate = purchase price × ( 1 + tax rate) Total price = purchase price + purchase price × tax rate = purchase price × ( 1 + tax rate)
When the sales tax calculation results in a fraction of a penny, then normal rounding rules apply, round up for half a penny or more, but round down for less than half a penny.
You should notice that this the same as markup, except using a different term. Sales tax plays the role of markup, the purchase price plays the role of cost, and the tax rate plays the role of percent markup. This means all the strategies developed for markups apply to this situation, with the changes indicated.

Example 6.22
Sales tax in kankakee illinois.
The sales tax in Kankakee, Illinois, is 8.25%. Find the sales tax and total price of items based on the purchase price listed.
- Purchase price = $428.99
- Purchase price = $34.88
- The sales tax is found using sales tax = purchase price × tax rate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate . The purchase price is $428.99 and the tax rate is 8.25%. Substituting and calculating, the sales tax is sales tax = $ 428.99 × 0.0825 = $ 35.391675 sales tax = $ 428.99 × 0.0825 = $ 35.391675 . The sales tax needs to be rounded off. Since the third decimal place (fraction of a penny) is 1, we round down and the sales tax is $35.39. The total price is the sales tax plus the purchase price, so is $ 428.99 + $ 35.88 = $ 464.87 $ 428.99 + $ 35.88 = $ 464.87 .
- The sales tax on the item is found using sales tax = purchase price × tax rate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate . The purchase price is $34.88 and the tax rate is 8.25%. Substituting and calculating, the sales tax is sales tax = $ 34.88 × 0.0825 = $ 2.8776 sales tax = $ 34.88 × 0.0825 = $ 2.8776 . The sales tax needs to be rounded off. Since the third decimal place (fraction of a penny) is 7, we round up and the sales tax is $2.88. The total price of the item is the sales tax plus the purchase price, so is $ 34.88 + $ 2.88 = $ 37.76 $ 34.88 + $ 2.88 = $ 37.76 .
Your Turn 6.22
As before, the information available might be different than only the purchase price and the sales tax rate. In these cases, use either sales tax = purchase price × tax rate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate or Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) and solve for the indicated tax, price, or rate. These problems mirror those for percent markup.
Be aware, almost all sales tax rates are structured as full percentages, or half percent, or one-quarter percent, or three-quarter percent. This means the decimal value of the sales tax rate, written as a percent, will be either 0, as in 5.0%, 5 as in 7.5%, 25 as in 3.25%, or 75 as in 4.75%. When rounding for the sales tax percentage, be sure to use this guideline.
Example 6.23
Calculating the sales tax from the purchase price and the total price.
Find the sales tax rate for the indicated purchase price and total price. Round using the guideline for sales tax percentages.
- Purchase price = $329.50; total price = $354.21
- Purchase Price = $13.77; total price = $14.39
Sales Tax = purchase price × tax rate $ 24.71 = $ 329.50 × tax rate $ 24.71 $ 329.50 = tax rate 0 .07499 = tax rate Sales Tax = purchase price × tax rate $ 24.71 = $ 329.50 × tax rate $ 24.71 $ 329.50 = tax rate 0 .07499 = tax rate
sales tax = purchase price × tax rate $ 0.62 = $ 13.77 × tax rate $ 0.62 $ 13.77 = tax rate 0 .04503 = tax rate sales tax = purchase price × tax rate $ 0.62 = $ 13.77 × tax rate $ 0.62 $ 13.77 = tax rate 0 .04503 = tax rate
Your Turn 6.23
Example 6.24, calculating the purchase price from the sales tax and total price.
Find the purchase price for the indicated sales tax rate and total price.
- Sales tax rate = 5.75%; total price = $36.56
- Sales tax rate = 4.25%; total price = $97.17
Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) $ 36.56 = purchase price × (1 + 0 .0575) $ 36.56 1.0575 = purchase price $ 34.57 = purchase price Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) $ 36.56 = purchase price × (1 + 0 .0575) $ 36.56 1.0575 = purchase price $ 34.57 = purchase price
Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) $ 97.17 = purchase price × (1 + 0 .0425) $ 97.17 1.0425 = purchase price $ 93.21 = purchase price Total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) $ 97.17 = purchase price × (1 + 0 .0425) $ 97.17 1.0425 = purchase price $ 93.21 = purchase price
Your Turn 6.24
Solve application problems involving sales tax.
Solving problems involving sales tax follows the same ideas and steps as solving problems for markups. But here we will use the following formula:
total price = purchase price + sales tax total price = purchase price + sales tax
We can also use the formula:
total price = purchase price × (1 + sales tax rate) total price = purchase price × (1 + sales tax rate) .
This can be seen in the following examples.
Example 6.25
Compute sales tax for denver, colorado.
The sales tax rate in Denver Colorado is 8.81%. Keven buys a TV in Denver, and the purchase price (before taxes) is $499.00. How much will Keven pay in sales tax and what will be the total amount he spends when he buys the TV?
The sales tax rate in Denver is 8.81%. To find the sales tax Keven will pay, find 8.81% of the purchase price. In decimal form, that sales tax rate is 0.0881. Using the formula and substituting 499.00 for purchase price, we find that Keven will pay purchase price × tax rate = $499 × 0.0881 = $ 43.96 purchase price × tax rate = $499 × 0.0881 = $ 43.96 in sales tax for the TV.
The total price that Keven will pay is the purchase price plus the sales tax, or $ 499.00 + $ 43.96 = $ 542.96 $ 499.00 + $ 43.96 = $ 542.96 .
Your Turn 6.25
Example 6.26, compute sales tax for austin, texas.
Jillian visits Austin, Texas, and purchases a new set of weights for her home. She spends, including sales tax, $467.64. The sales tax rate in Austin Texas is 8.25%. How much of the total price is sales tax?
The sales tax paid for this purchase is the difference in the total price and the purchase price. We know the total price is $467.64. We also know the sales tax rate, which is 8.25%. In decimal form, this is 0.0825. Using these values and the formula total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) total price = purchase price × (1 + tax rate) to find the purchase price.
Knowing both the total price and the now the purchase price, we can find the difference, which is the sales tax.
The total price was $467.64. The purchase price was $432. The difference of the total price and the purchase price, or the sales tax, is then $467.64 − $432.00, which is $35.64. Jillian pays $35.64 in sales tax.
Your Turn 6.26
Finding Sales Tax Percentage
West Virginia was the first state to impose a sales tax. This happened on May 3, 1921.
Look up your locality on this website that lists standard state-level sales tax rates and compare the sales tax structure in your state to two nearby states (for the lower 48) and for any two states (Alaska and Hawaii).
Check Your Understanding
Section 6.2 exercises.

Percent Problems involving Discount

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.


Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Financial Literacy >
Discount Worksheets
Happy discount day! Our pdf discount worksheets, awash with exercises involving discount, discount rate, marked price, and selling price, grandly open the discount store for students in grade 6, grade 7, and grade 8. Graduate into prolific discount scholars with our printable tools; do employ the correct formula and validate the answers using the answer key. Our free discount and discount percent worksheets are a great place to start if you are keen to explore the topic of discount soup to nuts!
Finding Discount Amount
Discounts are a relief in an otherwise fast-paced life! Find the discount amount by subtracting the selling price from the marked price, reiterating the life skill of knowing how to calculate a discount amount.
- Download the set
What Is Discount?
When things are outrageously expensive, only a generous discount can help! Here, the 6th grade and 7th grade students subtract the new price from the original price to obtain the price reduction.

Finding Selling Price or Marked Price
Ace the task of calculating the marked price and selling price when the discount amount is given. Selling Price = Marked Price − Discount, and Marked Price = Selling Price + Discount.

Finding Missing Amounts | Complete the Table
In this section of our printable discount worksheets, focus on finding the unknown price to complete the table. Find the discount amount, marked price, or sale price by using the appropriate formula.

Finding Discount Percent
How much discount is enough discount? To find discount rates in a jiffy, you must know the application of percentage in and out. Here's the formula: discount percent = discount amount ÷ marked price × 100.

Finding Selling Price or Marked Price Using Discount Percent
What is the marked price if the selling price is $86 after a discount of 6% is applied? Experience the ease of finding the sale price or marked price in this section of our calculating discount worksheets.
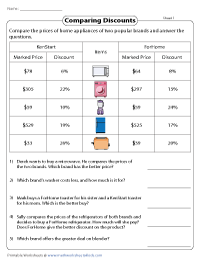
Comparing Discounts
Don't discount yourself, no matter where you're shopping! To solve these printable worksheets, work out the selling prices of items in 2 stores, compare the discount at each store, and find the best price.

Discount Themed Worksheets
It is about discounts! What's more, it is in pdf discount themed worksheets! The discount brokers in grade 6, grade 7, and grade 8 grab every discount around, while boosting their percent application skills.

Discount Word Problems
Students in 7th grade and 8th grade certainly know their money's worth. Calculate the discount amount/discount percent. Find, for example, the discount % when the marked price is $121 and the selling price is $110.

Finding Missing Price | Word Problems
Find the marked price or selling price, given the discount or discount rate. Our word problems gently trickle in one after another, each time presenting a fresh scenario, and you keep finding the missing prices.
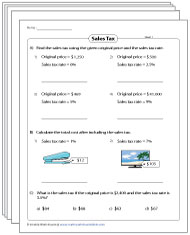
Sales Tax Worksheets
Don't let the students falter on their way to becoming financial geniuses! Utilize our specially curated printable worksheets and watch smart learners grow from novices into expert sales tax calculators by delving into a sea of fascinating exercises and word problems.
(15 Worksheets)
Related Worksheets
» Percent
» Profit and Loss
» Simple Interest
» Compound Interest
Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.2: Discount Problems
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 45782
Learning outcome
- Use mathematical notation to solve discount problems

Applications of discount are very common in retail settings. When you buy an item on sale, the original or list price of the item has been reduced by some dollar amount. The discount rate , usually given as a percent, is used to determine the amount of the discount. To determine the amount of discount , we multiply the discount rate by the original price. We summarize the discount model in the box below.
An amount of discount is subtracted from the original price.
The sale price should always be less than the original price.
[reveal-answer q=”967734″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”967734″]
[/hidden-answer]
[ohm_question]146772[/ohm_question]
In the first example, the amount of discount was a set or static amount. In the next example, the discount is given as a percent of the original price.
Solution ⓐ Before beginning, you may find it helpful to organize the information in a list.
Amount of discount = ?
Sale price = ?
[ohm_question]146775[/ohm_question]
There may be times when you buy something on sale and want to know the discount rate. The next example will show this case.
ⓑ Before beginning, you may find it helpful to organize the information in a list.
Discount rate = ?
[ohm_question]156971[/ohm_question]
In the following video we show another example of how to find the discount rate (also called the percent of change) given the original price and the marked-down price.

A YouTube element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: http://pb.libretexts.org/afm-2/?p=108
- Screenshot from Big W Square Bedroom Video. Authored by : Clay Fisher. Located at : https://vimeo.com/266614917 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- No category
pizzazz book e
Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Worksheet on Discounts | Calculating Prices using Discounts Worksheets
Students who are searching for different problems on Discounts can get them in one place. Get all the problems on discounts along with the answers here. Use the Worksheet on Discounts and kick start your preparation. Students can assess their strengths and weaknesses by solving all questions from Discounts Worksheet with Answers. Make use of these Discount Questions and understand different formulas and ways of solving problems related to all discount problems.
Different Questions are covered in the Discount Worksheets. Get the formulas and step-by-step process to solve each and every question. Here, we are offering a detailed solution along with an explanation for each and every problem for a better understanding of concepts.
- Practice Test on Profit and Loss
- Examples on Calculating Profit or Loss
- Word Problems on Profit and Loss
Discounts Problems with Solutions
1. The marked price of a washing machine is $ 3650. The shopkeeper offers an off-season discount of 18% on it. Find its selling price.
Given that the market price of a washing machine is $ 3650. The shopkeeper offers an off-season discount of 18% on it. The price of a washing machine is $ 3650. The discount percent on a washing machine is 18% Firstly, find out the discount on the washing machine. Discount on washing machine = (18 * $3650)/100 = $657 To find the selling price of the washing machine, subtract the discount on the washing machine from The price of a washing machine. Selling price = $ 3650 – $657 = $2993
Therefore, the selling price of a washing machine is $2993.
2. The price of a sweater was slashed from $ 860 to $ 716 by a shopkeeper in the winter season. Find the rate of discount given by him.
Given that the price of a sweater was slashed from $ 860 to $ 716 by a shopkeeper in the winter season. Cost Price = Price of the Sweater in the starting = ₹ 860 Selling Price = Price of the Sweater after slashing = ₹ 716 To Find the Rate of discount which is given by him, first, we have to find the amount that has been discounted. The discount on the sweater = Cost Price – Selling Price Substitute the Cost Price and Selling Price in the above equation. The discount on the sweater = 860 – 716 = ₹ 144 Now, We need to calculate the discount percentage. To find out the discount percentage we use the formula, Discount Percentage = Discounted Price / Cost Price x 100 Now, Substitute the Discounted Price and Cost Price in the above equation. Discount Percentage = ₹ 144/₹ 860 x 100 = 16.7% (approximately)
Therefore, the rate of discount that is given to him is 16.7%.
3. Find the rate of discount is given on a shirt whose selling price is $ 1092 after deducting a discount of $ 208 on its marked price.
Given that a shirt whose selling price is $ 1092 after deducting a discount of $ 208 on its marked price. Selling Price of the Shirt = $ 1092 Discounted Price = $ 208 To Find the Rate of discount on a shirt, first, we have to find the Marked Price of the Shirt. The formula for the Marked Price is Marked Price = Selling Price + Discount Price Substitute the Selling Price and Discount Price in the above equation. Marked Price = $ 1092 + $ 208 = $1300 Now, We need to calculate the rate of discount on the shirt. To find out the rate of discount on the shirt we use the formula, Rate of Discount = Discount Price / Marked Price x 100 Now, Substitute the Discount Price and Marked Price in the above equation. Rate of Discount = $ 208/$1300 x 100 = 16%
Therefore, the rate of discount on the trouser is 16 %.
4. After allowing a discount of 76% on a toy, it is sold for $ 582. Find the marked price of the toy.
Given that after allowing a discount of 76% on a toy, it is sold for $ 582. The discount on a toy = 76% The selling price of the toy = $ 582 Also, the Selling price of = 100 – 76% = 24% To find the cost price of the toy, Selling Price = 24% Selling Price = $ 582 24% = $ 582 1% = $ 582 ÷ 24 = $ 24.25 100% = $ 24.25 x 100 = $ 2425
Therefore, the marked price of the toy is $ 2425.
5. A tea set was bought for $ 344 after getting a discount of 14% on its marked price. Find the marked price of the tea set.
Given that a tea set was bought for $ 344 after getting a discount of 14% on its marked price. Let the marked price of tea set be Rs = X The selling price = $ 344 Also, the discount = 14% Marked Price – Discount on Marked Price = $ 344 X – 14X/100 = $ 344 100X – 14X = $ 344 * 100 86X = $34400 X = $34400/86 X = $400
Therefore, the marked price of the tea set is $ 400.
6. A dealer marks his goods at 45% above the cost price and allows a discount of 30% on the marked price. Find his gain or loss percent.
Given that a dealer marks his goods at 45% above the cost price and allows a discount of 30% on the marked price. Let the Cost Price of the goods be X The Marked price of the goods = X + (45/100 of x) = Rs 1.45 X Also, the discount = 30% Marked Price – Discount on Marked Price = Selling Price Substitute the values in the above equation. Discount = 30% of 1.45X = 1.45X × 0.3 = Rs 0.435X Selling Price = 1.45 X – 0.435X = 1.015X Selling Price = 1.015X As Selling Price is more than Cost Price, there is a profit. So, Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price = 1.015X – X = 0.015X Profit percentage = (Profit / Cost Price) x 100 = (0.015X / X) x 100 = 1.5%
Therefore, the Profit percentage is 1.5%.
7. A cell phone was marked at 50% above the cost price and a discount of 20% was given on its marked price. Find the gain or loss percent made by the shopkeeper.
Given that a cell phone was marked at 10% above the cost price and a discount of 20% was given on its marked price. Let the Cost Price of the cell phone is Rs. 100. The Marked price of the cell phone = (100 +10)% The Marked price of the cell phone = (110)% Also, the discount = 10% of 130 = 10/100 * 130 The Discount = 13 Selling Price = Marked price – Discount Substitute the values in the above equation. Selling Price = 110 – 13 = 97 Loss = 3 Loss % = (Loss × 100)/ CP Loss% = 3%
Therefore, the Loss percentage is 3%.
8. A dealer purchased a fan for $ 620. After allowing a discount of 35% on its marked price, he gains 35%. Find the marked price of the fan?
Given that a dealer purchased a fan for $ 620. After allowing a discount of 35% on its marked price, he gains 35%. Let the Cost Price of a fan is $ 620. The Discount on its marked price = 35% The Profit % = 35% Selling price = C.P + Profit% of C.P Substitute the values in the above equation. Selling price = 620 + 35% of 620 = 620 + 0.35 × 620 = 620 + 217 = 867 Selling Price = $867 Now, the next step is to find the marked price of the fan. M.P = (S.P × 100)/(100 – discount) = (867 × 100)/(100 – 35) = 86700/65 = 1333.84
Therefore, the marked price of the fan is 1333.84.
9. A dealer bought a refrigerator for $ 23030. After allowing a discount of 32% on its marked price, he gains 40%. Find the marked price of the refrigerator.
Given that a dealer bought a refrigerator for $ 23030. After allowing a discount of 32% on its marked price, he gains 40%. Let the Cost Price of a fan is $ 23030. The Discount on its marked price = 32% The Profit % = 40% Selling price = C.P + Profit% of C.P Substitute the values in the above equation. Selling price = 23030 + 40% of 23030 = 23030 + 0.4 × 23030 = 23030 + 9212 = 32242 Selling Price = $32242 Now, the next step is to find the marked price of the fan. M.P = (S.P × 100)/(100 – discount) = (32242 × 100)/(100 – 32) = 3224200/68 = 47414.70
Therefore, the marked price of the refrigerator is 47414.70.
10. A carpenter allows a discount of 32% to his customers and still gains 40%. Find the marked price of a dining table which costs the carpenter $ 2380.
Given that a carpenter allows a discount of 32% to his customers and still gains 40%. Let the Marked Price of a dining table is M. The Discount on its marked price = 32% Selling price = Marked Price – Discount on its marked price Substitute the values in the above equation. Selling price = M – 0.32M = 0.68M Cost = $ 2380 Gain 40% = 0.4 * 2380 = 952 Selling price = 2380 + 952 = 3332 Selling price = 0.68M = 3332 M = 3332/0.68 M = 4900
Therefore, the marked price of the dining table costs the carpenter $ 2380. is 4900.
11. After allowing a discount of 20% on the marked price, a trader still makes a gain of 34%. By what percent is the marked price above the cost price?
Given that after allowing a discount of 20% on the marked price, a trader still makes a gain of 34%. Let the cost price be 100 Rupees. There is a gain of 34%. So, the Selling price will be 100 + 34 Rupees. Selling price = 134 Rupees. Let marked price be M Then 80% of M = 134 0.8M = 134 M = 134/0.8 M = 167.5 Above cost price =167.5 – 100 = 67.5 So, the marked price is 67.5 rupees more than CP.
Therefore, the shopkeeper must mark his good’s price 67.5% more than the cost price.
12. How much percent above the cost price should a shopkeeper mark his goods so that after allowing a discount of 20% on the marked price, he gains 16%?
Given that after allowing a discount of 20% on the marked price, he gains 16%. Let the cost price be 100 Rupees and also the marked price be M. There is a gain of 16%. So, the selling price of the article = Cost Price + Gain Substitute the values in the above equation. The selling price will be 100 + 16 Rupees. Selling price = 116 Rupees. Discount % = 20% Discount = 20% of Marked Price = Rs.20/100 * M = Rs. 20M/100 = Rs. M/5 Marked Price – Discount = Selling price => M – M/5 = 116 => (5M – M)/5 = 116 => 4M/5 = 116 => M = 116 * 5/4 = Rs. 145 Marked Price = Rs. 145 The amount marked above the CP = MP – CP = Rs. (145 – 100) = Rs. 45 ∴ % amount marked above the CP = Amount increased/CP * 100 = 45/100 * 100 = 45%
Therefore, the shopkeeper must mark his good’s price 45% more than the cost price.
13. The marked price of a television is $ 37000. A dealer allows two successive discounts of 10% and 5%. For how much is the television available?
Given that the marked price of a television is $ 37000. A dealer allows two successive discounts of 10% and 5%. The Price after 10% discount. = $ 37000 – 10/100 * $ 37000 = $ 37000 – 0.05 * $ 37000 = $ 37000 – 3700 = 33300 The Price after 5% discount. = $ 37000 – 5/100 * $ 37000 = $ 37000 – 0.1 * $ 37000 = $ 37000 – 1850 = 35150
Therefore, tv is available at price = 35150
14. Find the single discount which is equivalent to two successive discounts of 30% and 10%.
Given that two successive discounts of 30% and 10%. The marked price = 100 1st discount = 30% of 100 = 30 since, 100 – 30 = 70 2nd discount = 10% of 70 = 7 Selling price = 70 – 7 = 63 Single Equivalent Discount = MP – SP = 100 -63= 37 Since the discount of 37 is on 100
Required single discount = 37%
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Module 2: Calculations and Solving Equations
Discount problems, learning outcome.
- Use mathematical notation to solve discount problems

Feminine Furnishings Bedding Sale
A store called Feminine Furnishings is having a sale on bedding. Their queen sheet sets have a list price of [latex]$126[/latex]. During the first two weeks of February, the store has a—Snuggle Up In Love Sale— where customers save [latex]14\%[/latex] on any white, pink, or red bedding set. Carly selects a bedding set with pink stripes and pays [latex]$108.36[/latex].
Applications of discount are very common in retail settings. When you buy an item on sale, the original or list price of the item has been reduced by some dollar amount. The discount rate , usually given as a percent, is used to determine the amount of the discount. To determine the amount of discount , we multiply the discount rate by the original price. We summarize the discount model in the box below.
An amount of discount is subtracted from the original price.
amount of discount = discount rate [latex]\cdot[/latex] original price
sale price = original price [latex]-[/latex] discount
The sale price should always be less than the original price.
In some cases, the amount of discount is a fixed dollar amount. Then we just find the sale price by subtracting the amount of discount from the original price. For example, as you walk into a store you may see a sign that says “Spend [latex]$100[/latex] or more, and receive a [latex]$20[/latex] discount!”
Jason bought a pair of sunglasses from a rack that was labeled [latex]\text{\$10}[/latex] off all Retrop brand glasses. The original price of the sunglasses was [latex]\text{\$39}[/latex]. What was the sale price of the sunglasses?
In the first example, the amount of discount was a set or static amount. In the next example, the discount is given as a percent of the original price.
Elise bought a dress that was discounted [latex]\text{35%}[/latex] off of the original price of [latex]\text{\$140}[/latex]. What was the amount of discount and the sale price of the dress?
Solution ⓐ Before beginning, you may find it helpful to organize the information in a list.
Original price = [latex]\text{\$140}[/latex]
Discount rate = [latex]35\text{%}[/latex]
Amount of discount = ?
Amount of discount = [latex]\text{\$49}[/latex]
Sale price = ?
There may be times when you buy something on sale and want to know the discount rate. The next example will show this case.
Jeannette bought a swimsuit at a sale price of [latex]\text{\$13.95}[/latex]. The original price of the swimsuit was [latex]\text{\$31}[/latex]. Find the ⓐ amount of discount and ⓑ discount rate.
Original price = [latex]\text{\$31}[/latex]
Sale price = [latex]\text{\$13.95}[/latex]
ⓑ Before beginning, you may find it helpful to organize the information in a list.
Original price = [latex]$31[/latex]
Amount of discount = [latex]$17.05[/latex]
Discount rate = ?
In the following video we show another example of how to find the discount rate (also called the percent of change) given the original price and the marked-down price.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Screenshot from Big W Square Bedroom Video. Authored by : Clay Fisher. Located at : https://vimeo.com/266614917 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]

discounts and markup word problem worksheets
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Discounts and markup word problem worksheets

Sales Tax, Tip, Discounts , and Mark-up Word Problem Practice Worksheet

Multi-step Money Word Problems Worksheet

- Easel Activity

Math Menu: Percent Applications - Tax, Tip, Discount , and Markup Word Problems

Tax, Tip, Discount and Mark Up Real World Practical Word Problems Maze Activity

- Google Drive™ folder

Proportions Word Problems Task Cards: 7.RP.3

Discount , Markup , & Percent w/ Proportions Mystery Activity + Digital

- Google Apps™

Discounts and Markups (Sale Price, Original Price, Markup and Discount Percent)

Percent Word Problems Digital Maze Activity for Distance Learning

- Google Slides™

Finding Percent Markup and Discount Activity (Increase and Decrease) 7th Grade

Discount and Markup Maze

Markup and Markdown Tiered Worksheets

Markups , Discounts , and Tax Riddle Sheet

Markup , Discount , Sales Tax, Tip, Commission, Simple Interest Coloring Worksheet

Percent Word Problems Maze Activity

7.RP.3 Calculate Markups and Markdowns Worksheets

Black Friday Math Sales Shopping Markups and Markdowns Percent Discounts

Markup , Discount , Tax, & Tip Practice Bundle | Coloring Page, BINGO, & Stations!

Markup , Discount , Tax, & Tip Coloring Activity

Multi-Step Consumer Math Worksheet 2 (7th grade)

- Word Document File

Percents - Markups , discounts , tax, and commission

Proportions, Markups , Discounts , Commission, and Interest

Discounts and Markups (Percent Proportion)

Black Friday Math Sales Shopping Markups and Markdowns Percent Discounts Metric

Tips, Discounts , and Markups : Working with Percentages Worksheet

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
TOPIC 2-j: Problem Solving: Discounts and Sale Prices . Why Can't an Elephant Ride a Bicycle? Do each exercise and find your answer in the corresponding set of answers. Write the ... TOPIC 2-0: Finding a Number When a Percent of It Is Known 11. Find the number. Use a decimal for the percent.
Welcome to How to Calculate a Discount and Sale Price with Mr. J! Need help with calculating discounts and sale prices? You're in the right place!Whether you...
Analysis: The phrase, "Get a 20% discount," refers to the rate. Solution: The rate is 20%. The discount is: 0.20 x $12.00 = $2.40. The sale price is calculated as follows: Answer: The discount is $2.40 and the sale price is $9.60. Example 3: In a candy store, a $5.00 jar of candy is labeled, "50% off."
Finding Discounts and sales prices The video covers a one-step and a two-step process for finding a sale price, given a percent of discount. It includes four examples. Example: Find the sale price (a) Original Price = $49.50, Discount = 30% (b) Original Price = $1,348.35, Discount = 25% (c) Original Price = $19.89, Discount = 15%
below, cross out the box containing each correct answer. When you finish, write the letters from the remaining boxes in the spaces at the bottom of the page. IMIDDLE SCHOOL MATH WITH PIZZAZZ! BOOK E O Creative Publications TOPIC 2-j: Problem Solving: Discounts and Sale Prices
Math worksheet on discounts will help us to practice the questions on how to solve the problems related to marked price, selling price and discount in profit and loss. ... Answers for worksheet on discounts are given below to calculate the discounted price on the marked price. Answers: 1. $ 3813. 2. 15% . 3. 16% . 4. $ 235. 5. $ 600 . 6. Gain = 8%
After this lesson, students will be able to: Calculate the discount amount and sale price of an item given the original price and the percent discount. Solve problems involving finding the original price of an item given the sale price and the percent discount. Determine the total cost including tips based on a percentage of the bill amount.
below, cross out the box containing each correct answer. When you finish, write the letters from the remaining boxes in the spaces at the bottom of the page. IMIDDLE SCHOOL MATH WITH PIZZAZZ! BOOK E O Creative Publications TOPIC 2-j: Problem Solving: Discounts and Sale Prices
Consumer Math is presented through Percent Applications in this unit. Lessons include percent and proportions, discount and sale price, simple interest, commission, sales tax and percent increase and decrease. Real-life money problems are used throughout this unit for consumers. Try our sample lessons below, or browse other units. Consumer Math.
Solve Discount Applications. Applications of discount are very common in retail settings Figure 6.8. When you buy an item on sale, the original price of the item has been reduced by some dollar amount. The discount rate, usually given as a percent, is used to determine the amount of the discount.To determine the amount of discount, we multiply the discount rate by the original price.
1. Cost = $1,800.00; percent markup is 22%. 2. Cost = $10.50; percent markup is 10%. Sometimes the cost and the retail price of an item are known. From this, the percent markup can be computed using the formula markup = percent markup × cost markup = percent markup × cost, by solving for the percent markup.
5. Multiply the decimal by the price. This is what you save. 6. Subtract your savings from the original price to find the current price. How to find the discount. Finding Discounts. The video covers a one-step and a two-step process for finding a sale price, given a percent of discount. It includes four examples.
Employ our pdf discount worksheets to find exercises involving discount amounts or rates and marked price and sale price and solve discount word problems. Main Menu Math ... the answers using the answer key. Our free discount and discount percent worksheets are a great place to start if you are keen to explore the topic of discount soup to nuts
The commission is $3,945.00. Discount: Suppose that the regular price of an item is $80, and the item is on sale at 25% off. Since 25% of 80 is $20, the sale price is $80 - $20, or $60. We call $80 the original , or marked price , 25% the rate of discount, $20 the discount, and $60 the sale price .
Let the sale price. Write a sentence that gives the information to find it. The sale price is the original price minus the discount. Translate into an equation. Simplify. Check if this answer is reasonable. Yes. The sale price, , is less than the original price, . Write a complete sentence that answers the question. The sale price of the ...
Problem solving - use acquired knowledge to solve sales price practice problems Interpreting information - verify that you can read information in word problems regarding original price and sales ...
What is the final price of an item discount at 45% off that normally sells for $65.00? ... answer a question about it Problem solving - use your understanding of the formula for finding percentage ...
In the rectangle below, cross out the box containing each correct answer. When you finish, write the letters from the remaining boxes in the spaces at the bottom of the page. IMIDDLE SCHOOL MATH WITH PIZZAZZ! BOOK E O Creative Publications TOPIC 2-j: Problem Solving: Discounts and Sale Prices What Is the Title?
Find his gain or loss percent. Solution: 7. A cell phone was marked at 50% above the cost price and a discount of 20% was given on its marked price. Find the gain or loss percent made by the shopkeeper. Solution: 8. A dealer purchased a fan for $ 620. After allowing a discount of 35% on its marked price, he gains 35%.
The sale price should always be less than the original price. In some cases, the amount of discount is a fixed dollar amount. Then we just find the sale price by subtracting the amount of discount from the original price. For example, as you walk into a store you may see a sign that says "Spend $100 $ 100 or more, and receive a $20 $ 20 ...
Solve each word problem using either method. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. ... Find the discount and the sales price if a customer buys an item that normally sells for $365. Jean Junction is selling jeans at 15% off the regular price. The regular price is $25.00 per pair.
Trade and Discount Problems with Answers. basic review for exams, quizzes, assignments or exercises. Course. ... Invoice price - Sales P 72, - Sales on Account, terms: 40, 1/10, n/ - P 72, ... , Cash P 117, Sales Discount P 2, Accounts Receivable P 120, Collection within the discount period d. Invoice Price P 96, Less: Cash Discount (P96,000 x ...
The worksheet has 8 problems which include tables to help students organize data and solve word problems related to percentages for tips, discounts, and markups. Several problems require students to explain their thinking in writing. . An answer key is provided for all 8 problems. Subjects: