An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.21(3); Fall 2022

Literature Reviews, Theoretical Frameworks, and Conceptual Frameworks: An Introduction for New Biology Education Researchers
Julie a. luft.
† Department of Mathematics, Social Studies, and Science Education, Mary Frances Early College of Education, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-7124
Sophia Jeong
‡ Department of Teaching & Learning, College of Education & Human Ecology, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210
Robert Idsardi
§ Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA 99004
Grant Gardner
∥ Department of Biology, Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, TN 37132
Associated Data
To frame their work, biology education researchers need to consider the role of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks as critical elements of the research and writing process. However, these elements can be confusing for scholars new to education research. This Research Methods article is designed to provide an overview of each of these elements and delineate the purpose of each in the educational research process. We describe what biology education researchers should consider as they conduct literature reviews, identify theoretical frameworks, and construct conceptual frameworks. Clarifying these different components of educational research studies can be helpful to new biology education researchers and the biology education research community at large in situating their work in the broader scholarly literature.
INTRODUCTION
Discipline-based education research (DBER) involves the purposeful and situated study of teaching and learning in specific disciplinary areas ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Studies in DBER are guided by research questions that reflect disciplines’ priorities and worldviews. Researchers can use quantitative data, qualitative data, or both to answer these research questions through a variety of methodological traditions. Across all methodologies, there are different methods associated with planning and conducting educational research studies that include the use of surveys, interviews, observations, artifacts, or instruments. Ensuring the coherence of these elements to the discipline’s perspective also involves situating the work in the broader scholarly literature. The tools for doing this include literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks. However, the purpose and function of each of these elements is often confusing to new education researchers. The goal of this article is to introduce new biology education researchers to these three important elements important in DBER scholarship and the broader educational literature.
The first element we discuss is a review of research (literature reviews), which highlights the need for a specific research question, study problem, or topic of investigation. Literature reviews situate the relevance of the study within a topic and a field. The process may seem familiar to science researchers entering DBER fields, but new researchers may still struggle in conducting the review. Booth et al. (2016b) highlight some of the challenges novice education researchers face when conducting a review of literature. They point out that novice researchers struggle in deciding how to focus the review, determining the scope of articles needed in the review, and knowing how to be critical of the articles in the review. Overcoming these challenges (and others) can help novice researchers construct a sound literature review that can inform the design of the study and help ensure the work makes a contribution to the field.
The second and third highlighted elements are theoretical and conceptual frameworks. These guide biology education research (BER) studies, and may be less familiar to science researchers. These elements are important in shaping the construction of new knowledge. Theoretical frameworks offer a way to explain and interpret the studied phenomenon, while conceptual frameworks clarify assumptions about the studied phenomenon. Despite the importance of these constructs in educational research, biology educational researchers have noted the limited use of theoretical or conceptual frameworks in published work ( DeHaan, 2011 ; Dirks, 2011 ; Lo et al. , 2019 ). In reviewing articles published in CBE—Life Sciences Education ( LSE ) between 2015 and 2019, we found that fewer than 25% of the research articles had a theoretical or conceptual framework (see the Supplemental Information), and at times there was an inconsistent use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Clearly, these frameworks are challenging for published biology education researchers, which suggests the importance of providing some initial guidance to new biology education researchers.
Fortunately, educational researchers have increased their explicit use of these frameworks over time, and this is influencing educational research in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. For instance, a quick search for theoretical or conceptual frameworks in the abstracts of articles in Educational Research Complete (a common database for educational research) in STEM fields demonstrates a dramatic change over the last 20 years: from only 778 articles published between 2000 and 2010 to 5703 articles published between 2010 and 2020, a more than sevenfold increase. Greater recognition of the importance of these frameworks is contributing to DBER authors being more explicit about such frameworks in their studies.
Collectively, literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks work to guide methodological decisions and the elucidation of important findings. Each offers a different perspective on the problem of study and is an essential element in all forms of educational research. As new researchers seek to learn about these elements, they will find different resources, a variety of perspectives, and many suggestions about the construction and use of these elements. The wide range of available information can overwhelm the new researcher who just wants to learn the distinction between these elements or how to craft them adequately.
Our goal in writing this paper is not to offer specific advice about how to write these sections in scholarly work. Instead, we wanted to introduce these elements to those who are new to BER and who are interested in better distinguishing one from the other. In this paper, we share the purpose of each element in BER scholarship, along with important points on its construction. We also provide references for additional resources that may be beneficial to better understanding each element. Table 1 summarizes the key distinctions among these elements.
Comparison of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual reviews
This article is written for the new biology education researcher who is just learning about these different elements or for scientists looking to become more involved in BER. It is a result of our own work as science education and biology education researchers, whether as graduate students and postdoctoral scholars or newly hired and established faculty members. This is the article we wish had been available as we started to learn about these elements or discussed them with new educational researchers in biology.
LITERATURE REVIEWS
Purpose of a literature review.
A literature review is foundational to any research study in education or science. In education, a well-conceptualized and well-executed review provides a summary of the research that has already been done on a specific topic and identifies questions that remain to be answered, thus illustrating the current research project’s potential contribution to the field and the reasoning behind the methodological approach selected for the study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). BER is an evolving disciplinary area that is redefining areas of conceptual emphasis as well as orientations toward teaching and learning (e.g., Labov et al. , 2010 ; American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ; Nehm, 2019 ). As a result, building comprehensive, critical, purposeful, and concise literature reviews can be a challenge for new biology education researchers.
Building Literature Reviews
There are different ways to approach and construct a literature review. Booth et al. (2016a) provide an overview that includes, for example, scoping reviews, which are focused only on notable studies and use a basic method of analysis, and integrative reviews, which are the result of exhaustive literature searches across different genres. Underlying each of these different review processes are attention to the s earch process, a ppraisa l of articles, s ynthesis of the literature, and a nalysis: SALSA ( Booth et al. , 2016a ). This useful acronym can help the researcher focus on the process while building a specific type of review.
However, new educational researchers often have questions about literature reviews that are foundational to SALSA or other approaches. Common questions concern determining which literature pertains to the topic of study or the role of the literature review in the design of the study. This section addresses such questions broadly while providing general guidance for writing a narrative literature review that evaluates the most pertinent studies.
The literature review process should begin before the research is conducted. As Boote and Beile (2005 , p. 3) suggested, researchers should be “scholars before researchers.” They point out that having a good working knowledge of the proposed topic helps illuminate avenues of study. Some subject areas have a deep body of work to read and reflect upon, providing a strong foundation for developing the research question(s). For instance, the teaching and learning of evolution is an area of long-standing interest in the BER community, generating many studies (e.g., Perry et al. , 2008 ; Barnes and Brownell, 2016 ) and reviews of research (e.g., Sickel and Friedrichsen, 2013 ; Ziadie and Andrews, 2018 ). Emerging areas of BER include the affective domain, issues of transfer, and metacognition ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Many studies in these areas are transdisciplinary and not always specific to biology education (e.g., Rodrigo-Peiris et al. , 2018 ; Kolpikova et al. , 2019 ). These newer areas may require reading outside BER; fortunately, summaries of some of these topics can be found in the Current Insights section of the LSE website.
In focusing on a specific problem within a broader research strand, a new researcher will likely need to examine research outside BER. Depending upon the area of study, the expanded reading list might involve a mix of BER, DBER, and educational research studies. Determining the scope of the reading is not always straightforward. A simple way to focus one’s reading is to create a “summary phrase” or “research nugget,” which is a very brief descriptive statement about the study. It should focus on the essence of the study, for example, “first-year nonmajor students’ understanding of evolution,” “metacognitive prompts to enhance learning during biochemistry,” or “instructors’ inquiry-based instructional practices after professional development programming.” This type of phrase should help a new researcher identify two or more areas to review that pertain to the study. Focusing on recent research in the last 5 years is a good first step. Additional studies can be identified by reading relevant works referenced in those articles. It is also important to read seminal studies that are more than 5 years old. Reading a range of studies should give the researcher the necessary command of the subject in order to suggest a research question.
Given that the research question(s) arise from the literature review, the review should also substantiate the selected methodological approach. The review and research question(s) guide the researcher in determining how to collect and analyze data. Often the methodological approach used in a study is selected to contribute knowledge that expands upon what has been published previously about the topic (see Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation, 2013 ). An emerging topic of study may need an exploratory approach that allows for a description of the phenomenon and development of a potential theory. This could, but not necessarily, require a methodological approach that uses interviews, observations, surveys, or other instruments. An extensively studied topic may call for the additional understanding of specific factors or variables; this type of study would be well suited to a verification or a causal research design. These could entail a methodological approach that uses valid and reliable instruments, observations, or interviews to determine an effect in the studied event. In either of these examples, the researcher(s) may use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods methodological approach.
Even with a good research question, there is still more reading to be done. The complexity and focus of the research question dictates the depth and breadth of the literature to be examined. Questions that connect multiple topics can require broad literature reviews. For instance, a study that explores the impact of a biology faculty learning community on the inquiry instruction of faculty could have the following review areas: learning communities among biology faculty, inquiry instruction among biology faculty, and inquiry instruction among biology faculty as a result of professional learning. Biology education researchers need to consider whether their literature review requires studies from different disciplines within or outside DBER. For the example given, it would be fruitful to look at research focused on learning communities with faculty in STEM fields or in general education fields that result in instructional change. It is important not to be too narrow or too broad when reading. When the conclusions of articles start to sound similar or no new insights are gained, the researcher likely has a good foundation for a literature review. This level of reading should allow the researcher to demonstrate a mastery in understanding the researched topic, explain the suitability of the proposed research approach, and point to the need for the refined research question(s).
The literature review should include the researcher’s evaluation and critique of the selected studies. A researcher may have a large collection of studies, but not all of the studies will follow standards important in the reporting of empirical work in the social sciences. The American Educational Research Association ( Duran et al. , 2006 ), for example, offers a general discussion about standards for such work: an adequate review of research informing the study, the existence of sound and appropriate data collection and analysis methods, and appropriate conclusions that do not overstep or underexplore the analyzed data. The Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation (2013) also offer Common Guidelines for Education Research and Development that can be used to evaluate collected studies.
Because not all journals adhere to such standards, it is important that a researcher review each study to determine the quality of published research, per the guidelines suggested earlier. In some instances, the research may be fatally flawed. Examples of such flaws include data that do not pertain to the question, a lack of discussion about the data collection, poorly constructed instruments, or an inadequate analysis. These types of errors result in studies that are incomplete, error-laden, or inaccurate and should be excluded from the review. Most studies have limitations, and the author(s) often make them explicit. For instance, there may be an instructor effect, recognized bias in the analysis, or issues with the sample population. Limitations are usually addressed by the research team in some way to ensure a sound and acceptable research process. Occasionally, the limitations associated with the study can be significant and not addressed adequately, which leaves a consequential decision in the hands of the researcher. Providing critiques of studies in the literature review process gives the reader confidence that the researcher has carefully examined relevant work in preparation for the study and, ultimately, the manuscript.
A solid literature review clearly anchors the proposed study in the field and connects the research question(s), the methodological approach, and the discussion. Reviewing extant research leads to research questions that will contribute to what is known in the field. By summarizing what is known, the literature review points to what needs to be known, which in turn guides decisions about methodology. Finally, notable findings of the new study are discussed in reference to those described in the literature review.
Within published BER studies, literature reviews can be placed in different locations in an article. When included in the introductory section of the study, the first few paragraphs of the manuscript set the stage, with the literature review following the opening paragraphs. Cooper et al. (2019) illustrate this approach in their study of course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs). An introduction discussing the potential of CURES is followed by an analysis of the existing literature relevant to the design of CUREs that allows for novel student discoveries. Within this review, the authors point out contradictory findings among research on novel student discoveries. This clarifies the need for their study, which is described and highlighted through specific research aims.
A literature reviews can also make up a separate section in a paper. For example, the introduction to Todd et al. (2019) illustrates the need for their research topic by highlighting the potential of learning progressions (LPs) and suggesting that LPs may help mitigate learning loss in genetics. At the end of the introduction, the authors state their specific research questions. The review of literature following this opening section comprises two subsections. One focuses on learning loss in general and examines a variety of studies and meta-analyses from the disciplines of medical education, mathematics, and reading. The second section focuses specifically on LPs in genetics and highlights student learning in the midst of LPs. These separate reviews provide insights into the stated research question.
Suggestions and Advice
A well-conceptualized, comprehensive, and critical literature review reveals the understanding of the topic that the researcher brings to the study. Literature reviews should not be so big that there is no clear area of focus; nor should they be so narrow that no real research question arises. The task for a researcher is to craft an efficient literature review that offers a critical analysis of published work, articulates the need for the study, guides the methodological approach to the topic of study, and provides an adequate foundation for the discussion of the findings.
In our own writing of literature reviews, there are often many drafts. An early draft may seem well suited to the study because the need for and approach to the study are well described. However, as the results of the study are analyzed and findings begin to emerge, the existing literature review may be inadequate and need revision. The need for an expanded discussion about the research area can result in the inclusion of new studies that support the explanation of a potential finding. The literature review may also prove to be too broad. Refocusing on a specific area allows for more contemplation of a finding.
It should be noted that there are different types of literature reviews, and many books and articles have been written about the different ways to embark on these types of reviews. Among these different resources, the following may be helpful in considering how to refine the review process for scholarly journals:
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., & Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book addresses different types of literature reviews and offers important suggestions pertaining to defining the scope of the literature review and assessing extant studies.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., & Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. This book can help the novice consider how to make the case for an area of study. While this book is not specifically about literature reviews, it offers suggestions about making the case for your study.
- Galvan, J. L., & Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). Routledge. This book offers guidance on writing different types of literature reviews. For the novice researcher, there are useful suggestions for creating coherent literature reviews.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of theoretical frameworks.
As new education researchers may be less familiar with theoretical frameworks than with literature reviews, this discussion begins with an analogy. Envision a biologist, chemist, and physicist examining together the dramatic effect of a fog tsunami over the ocean. A biologist gazing at this phenomenon may be concerned with the effect of fog on various species. A chemist may be interested in the chemical composition of the fog as water vapor condenses around bits of salt. A physicist may be focused on the refraction of light to make fog appear to be “sitting” above the ocean. While observing the same “objective event,” the scientists are operating under different theoretical frameworks that provide a particular perspective or “lens” for the interpretation of the phenomenon. Each of these scientists brings specialized knowledge, experiences, and values to this phenomenon, and these influence the interpretation of the phenomenon. The scientists’ theoretical frameworks influence how they design and carry out their studies and interpret their data.
Within an educational study, a theoretical framework helps to explain a phenomenon through a particular lens and challenges and extends existing knowledge within the limitations of that lens. Theoretical frameworks are explicitly stated by an educational researcher in the paper’s framework, theory, or relevant literature section. The framework shapes the types of questions asked, guides the method by which data are collected and analyzed, and informs the discussion of the results of the study. It also reveals the researcher’s subjectivities, for example, values, social experience, and viewpoint ( Allen, 2017 ). It is essential that a novice researcher learn to explicitly state a theoretical framework, because all research questions are being asked from the researcher’s implicit or explicit assumptions of a phenomenon of interest ( Schwandt, 2000 ).
Selecting Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks are one of the most contemplated elements in our work in educational research. In this section, we share three important considerations for new scholars selecting a theoretical framework.
The first step in identifying a theoretical framework involves reflecting on the phenomenon within the study and the assumptions aligned with the phenomenon. The phenomenon involves the studied event. There are many possibilities, for example, student learning, instructional approach, or group organization. A researcher holds assumptions about how the phenomenon will be effected, influenced, changed, or portrayed. It is ultimately the researcher’s assumption(s) about the phenomenon that aligns with a theoretical framework. An example can help illustrate how a researcher’s reflection on the phenomenon and acknowledgment of assumptions can result in the identification of a theoretical framework.
In our example, a biology education researcher may be interested in exploring how students’ learning of difficult biological concepts can be supported by the interactions of group members. The phenomenon of interest is the interactions among the peers, and the researcher assumes that more knowledgeable students are important in supporting the learning of the group. As a result, the researcher may draw on Vygotsky’s (1978) sociocultural theory of learning and development that is focused on the phenomenon of student learning in a social setting. This theory posits the critical nature of interactions among students and between students and teachers in the process of building knowledge. A researcher drawing upon this framework holds the assumption that learning is a dynamic social process involving questions and explanations among students in the classroom and that more knowledgeable peers play an important part in the process of building conceptual knowledge.
It is important to state at this point that there are many different theoretical frameworks. Some frameworks focus on learning and knowing, while other theoretical frameworks focus on equity, empowerment, or discourse. Some frameworks are well articulated, and others are still being refined. For a new researcher, it can be challenging to find a theoretical framework. Two of the best ways to look for theoretical frameworks is through published works that highlight different frameworks.
When a theoretical framework is selected, it should clearly connect to all parts of the study. The framework should augment the study by adding a perspective that provides greater insights into the phenomenon. It should clearly align with the studies described in the literature review. For instance, a framework focused on learning would correspond to research that reported different learning outcomes for similar studies. The methods for data collection and analysis should also correspond to the framework. For instance, a study about instructional interventions could use a theoretical framework concerned with learning and could collect data about the effect of the intervention on what is learned. When the data are analyzed, the theoretical framework should provide added meaning to the findings, and the findings should align with the theoretical framework.
A study by Jensen and Lawson (2011) provides an example of how a theoretical framework connects different parts of the study. They compared undergraduate biology students in heterogeneous and homogeneous groups over the course of a semester. Jensen and Lawson (2011) assumed that learning involved collaboration and more knowledgeable peers, which made Vygotsky’s (1978) theory a good fit for their study. They predicted that students in heterogeneous groups would experience greater improvement in their reasoning abilities and science achievements with much of the learning guided by the more knowledgeable peers.
In the enactment of the study, they collected data about the instruction in traditional and inquiry-oriented classes, while the students worked in homogeneous or heterogeneous groups. To determine the effect of working in groups, the authors also measured students’ reasoning abilities and achievement. Each data-collection and analysis decision connected to understanding the influence of collaborative work.
Their findings highlighted aspects of Vygotsky’s (1978) theory of learning. One finding, for instance, posited that inquiry instruction, as a whole, resulted in reasoning and achievement gains. This links to Vygotsky (1978) , because inquiry instruction involves interactions among group members. A more nuanced finding was that group composition had a conditional effect. Heterogeneous groups performed better with more traditional and didactic instruction, regardless of the reasoning ability of the group members. Homogeneous groups worked better during interaction-rich activities for students with low reasoning ability. The authors attributed the variation to the different types of helping behaviors of students. High-performing students provided the answers, while students with low reasoning ability had to work collectively through the material. In terms of Vygotsky (1978) , this finding provided new insights into the learning context in which productive interactions can occur for students.
Another consideration in the selection and use of a theoretical framework pertains to its orientation to the study. This can result in the theoretical framework prioritizing individuals, institutions, and/or policies ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Frameworks that connect to individuals, for instance, could contribute to understanding their actions, learning, or knowledge. Institutional frameworks, on the other hand, offer insights into how institutions, organizations, or groups can influence individuals or materials. Policy theories provide ways to understand how national or local policies can dictate an emphasis on outcomes or instructional design. These different types of frameworks highlight different aspects in an educational setting, which influences the design of the study and the collection of data. In addition, these different frameworks offer a way to make sense of the data. Aligning the data collection and analysis with the framework ensures that a study is coherent and can contribute to the field.
New understandings emerge when different theoretical frameworks are used. For instance, Ebert-May et al. (2015) prioritized the individual level within conceptual change theory (see Posner et al. , 1982 ). In this theory, an individual’s knowledge changes when it no longer fits the phenomenon. Ebert-May et al. (2015) designed a professional development program challenging biology postdoctoral scholars’ existing conceptions of teaching. The authors reported that the biology postdoctoral scholars’ teaching practices became more student-centered as they were challenged to explain their instructional decision making. According to the theory, the biology postdoctoral scholars’ dissatisfaction in their descriptions of teaching and learning initiated change in their knowledge and instruction. These results reveal how conceptual change theory can explain the learning of participants and guide the design of professional development programming.
The communities of practice (CoP) theoretical framework ( Lave, 1988 ; Wenger, 1998 ) prioritizes the institutional level , suggesting that learning occurs when individuals learn from and contribute to the communities in which they reside. Grounded in the assumption of community learning, the literature on CoP suggests that, as individuals interact regularly with the other members of their group, they learn about the rules, roles, and goals of the community ( Allee, 2000 ). A study conducted by Gehrke and Kezar (2017) used the CoP framework to understand organizational change by examining the involvement of individual faculty engaged in a cross-institutional CoP focused on changing the instructional practice of faculty at each institution. In the CoP, faculty members were involved in enhancing instructional materials within their department, which aligned with an overarching goal of instituting instruction that embraced active learning. Not surprisingly, Gehrke and Kezar (2017) revealed that faculty who perceived the community culture as important in their work cultivated institutional change. Furthermore, they found that institutional change was sustained when key leaders served as mentors and provided support for faculty, and as faculty themselves developed into leaders. This study reveals the complexity of individual roles in a COP in order to support institutional instructional change.
It is important to explicitly state the theoretical framework used in a study, but elucidating a theoretical framework can be challenging for a new educational researcher. The literature review can help to identify an applicable theoretical framework. Focal areas of the review or central terms often connect to assumptions and assertions associated with the framework that pertain to the phenomenon of interest. Another way to identify a theoretical framework is self-reflection by the researcher on personal beliefs and understandings about the nature of knowledge the researcher brings to the study ( Lysaght, 2011 ). In stating one’s beliefs and understandings related to the study (e.g., students construct their knowledge, instructional materials support learning), an orientation becomes evident that will suggest a particular theoretical framework. Theoretical frameworks are not arbitrary , but purposefully selected.
With experience, a researcher may find expanded roles for theoretical frameworks. Researchers may revise an existing framework that has limited explanatory power, or they may decide there is a need to develop a new theoretical framework. These frameworks can emerge from a current study or the need to explain a phenomenon in a new way. Researchers may also find that multiple theoretical frameworks are necessary to frame and explore a problem, as different frameworks can provide different insights into a problem.
Finally, it is important to recognize that choosing “x” theoretical framework does not necessarily mean a researcher chooses “y” methodology and so on, nor is there a clear-cut, linear process in selecting a theoretical framework for one’s study. In part, the nonlinear process of identifying a theoretical framework is what makes understanding and using theoretical frameworks challenging. For the novice scholar, contemplating and understanding theoretical frameworks is essential. Fortunately, there are articles and books that can help:
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book provides an overview of theoretical frameworks in general educational research.
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research. Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 (2), 020101-1–020101-13. This paper illustrates how a DBER field can use theoretical frameworks.
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 . This paper articulates the need for studies in BER to explicitly state theoretical frameworks and provides examples of potential studies.
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage. This book also provides an overview of theoretical frameworks, but for both research and evaluation.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of a conceptual framework.
A conceptual framework is a description of the way a researcher understands the factors and/or variables that are involved in the study and their relationships to one another. The purpose of a conceptual framework is to articulate the concepts under study using relevant literature ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ) and to clarify the presumed relationships among those concepts ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Conceptual frameworks are different from theoretical frameworks in both their breadth and grounding in established findings. Whereas a theoretical framework articulates the lens through which a researcher views the work, the conceptual framework is often more mechanistic and malleable.
Conceptual frameworks are broader, encompassing both established theories (i.e., theoretical frameworks) and the researchers’ own emergent ideas. Emergent ideas, for example, may be rooted in informal and/or unpublished observations from experience. These emergent ideas would not be considered a “theory” if they are not yet tested, supported by systematically collected evidence, and peer reviewed. However, they do still play an important role in the way researchers approach their studies. The conceptual framework allows authors to clearly describe their emergent ideas so that connections among ideas in the study and the significance of the study are apparent to readers.
Constructing Conceptual Frameworks
Including a conceptual framework in a research study is important, but researchers often opt to include either a conceptual or a theoretical framework. Either may be adequate, but both provide greater insight into the research approach. For instance, a research team plans to test a novel component of an existing theory. In their study, they describe the existing theoretical framework that informs their work and then present their own conceptual framework. Within this conceptual framework, specific topics portray emergent ideas that are related to the theory. Describing both frameworks allows readers to better understand the researchers’ assumptions, orientations, and understanding of concepts being investigated. For example, Connolly et al. (2018) included a conceptual framework that described how they applied a theoretical framework of social cognitive career theory (SCCT) to their study on teaching programs for doctoral students. In their conceptual framework, the authors described SCCT, explained how it applied to the investigation, and drew upon results from previous studies to justify the proposed connections between the theory and their emergent ideas.
In some cases, authors may be able to sufficiently describe their conceptualization of the phenomenon under study in an introduction alone, without a separate conceptual framework section. However, incomplete descriptions of how the researchers conceptualize the components of the study may limit the significance of the study by making the research less intelligible to readers. This is especially problematic when studying topics in which researchers use the same terms for different constructs or different terms for similar and overlapping constructs (e.g., inquiry, teacher beliefs, pedagogical content knowledge, or active learning). Authors must describe their conceptualization of a construct if the research is to be understandable and useful.
There are some key areas to consider regarding the inclusion of a conceptual framework in a study. To begin with, it is important to recognize that conceptual frameworks are constructed by the researchers conducting the study ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Maxwell, 2012 ). This is different from theoretical frameworks that are often taken from established literature. Researchers should bring together ideas from the literature, but they may be influenced by their own experiences as a student and/or instructor, the shared experiences of others, or thought experiments as they construct a description, model, or representation of their understanding of the phenomenon under study. This is an exercise in intellectual organization and clarity that often considers what is learned, known, and experienced. The conceptual framework makes these constructs explicitly visible to readers, who may have different understandings of the phenomenon based on their prior knowledge and experience. There is no single method to go about this intellectual work.
Reeves et al. (2016) is an example of an article that proposed a conceptual framework about graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research. The authors used existing literature to create a novel framework that filled a gap in current research and practice related to the training of graduate teaching assistants. This conceptual framework can guide the systematic collection of data by other researchers because the framework describes the relationships among various factors that influence teaching and learning. The Reeves et al. (2016) conceptual framework may be modified as additional data are collected and analyzed by other researchers. This is not uncommon, as conceptual frameworks can serve as catalysts for concerted research efforts that systematically explore a phenomenon (e.g., Reynolds et al. , 2012 ; Brownell and Kloser, 2015 ).
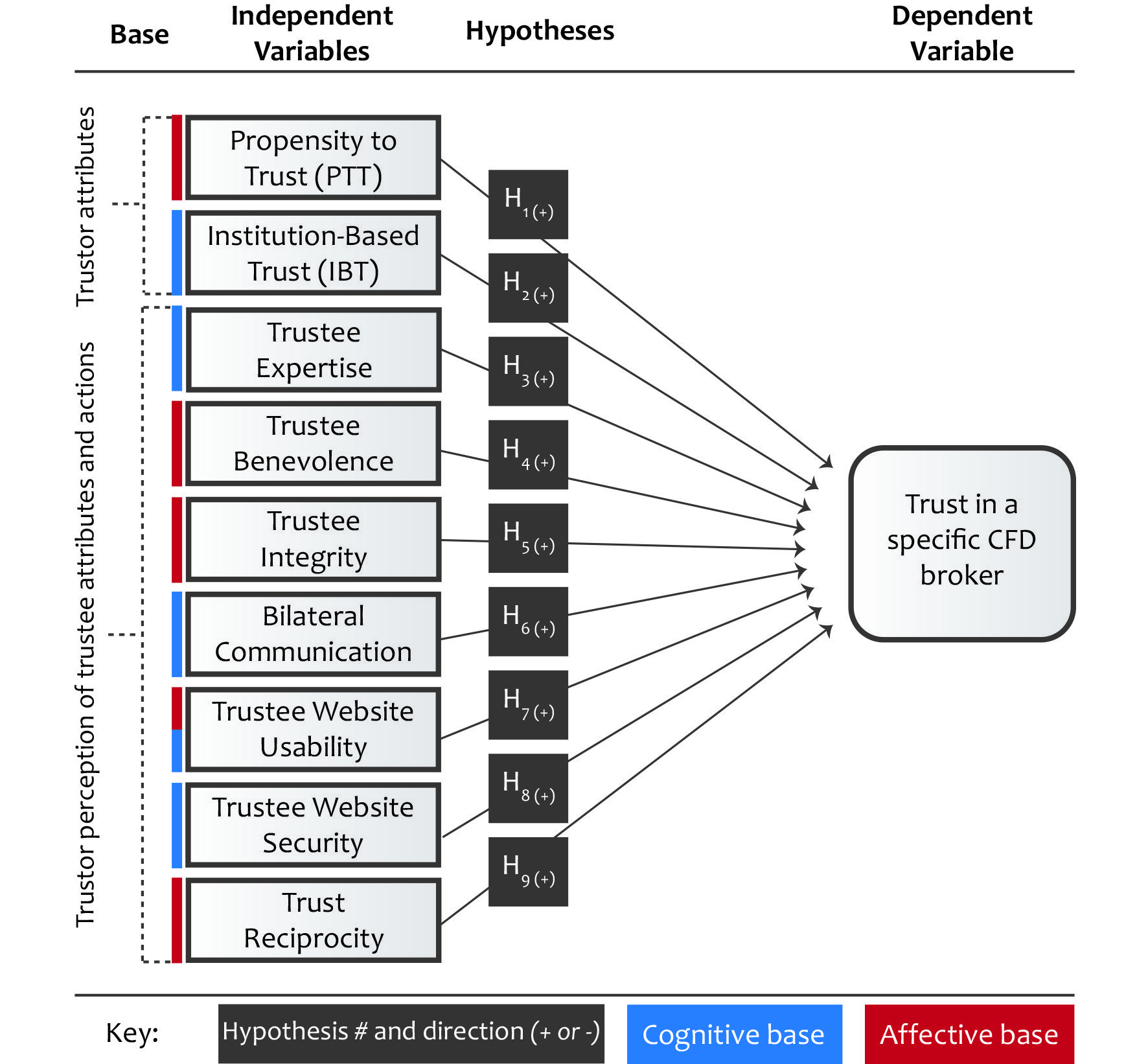
Sabel et al. (2017) used a conceptual framework in their exploration of how scaffolds, an external factor, interact with internal factors to support student learning. Their conceptual framework integrated principles from two theoretical frameworks, self-regulated learning and metacognition, to illustrate how the research team conceptualized students’ use of scaffolds in their learning ( Figure 1 ). Sabel et al. (2017) created this model using their interpretations of these two frameworks in the context of their teaching.

Conceptual framework from Sabel et al. (2017) .
A conceptual framework should describe the relationship among components of the investigation ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). These relationships should guide the researcher’s methods of approaching the study ( Miles et al. , 2014 ) and inform both the data to be collected and how those data should be analyzed. Explicitly describing the connections among the ideas allows the researcher to justify the importance of the study and the rigor of the research design. Just as importantly, these frameworks help readers understand why certain components of a system were not explored in the study. This is a challenge in education research, which is rooted in complex environments with many variables that are difficult to control.
For example, Sabel et al. (2017) stated: “Scaffolds, such as enhanced answer keys and reflection questions, can help students and instructors bridge the external and internal factors and support learning” (p. 3). They connected the scaffolds in the study to the three dimensions of metacognition and the eventual transformation of existing ideas into new or revised ideas. Their framework provides a rationale for focusing on how students use two different scaffolds, and not on other factors that may influence a student’s success (self-efficacy, use of active learning, exam format, etc.).
In constructing conceptual frameworks, researchers should address needed areas of study and/or contradictions discovered in literature reviews. By attending to these areas, researchers can strengthen their arguments for the importance of a study. For instance, conceptual frameworks can address how the current study will fill gaps in the research, resolve contradictions in existing literature, or suggest a new area of study. While a literature review describes what is known and not known about the phenomenon, the conceptual framework leverages these gaps in describing the current study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). In the example of Sabel et al. (2017) , the authors indicated there was a gap in the literature regarding how scaffolds engage students in metacognition to promote learning in large classes. Their study helps fill that gap by describing how scaffolds can support students in the three dimensions of metacognition: intelligibility, plausibility, and wide applicability. In another example, Lane (2016) integrated research from science identity, the ethic of care, the sense of belonging, and an expertise model of student success to form a conceptual framework that addressed the critiques of other frameworks. In a more recent example, Sbeglia et al. (2021) illustrated how a conceptual framework influences the methodological choices and inferences in studies by educational researchers.
Sometimes researchers draw upon the conceptual frameworks of other researchers. When a researcher’s conceptual framework closely aligns with an existing framework, the discussion may be brief. For example, Ghee et al. (2016) referred to portions of SCCT as their conceptual framework to explain the significance of their work on students’ self-efficacy and career interests. Because the authors’ conceptualization of this phenomenon aligned with a previously described framework, they briefly mentioned the conceptual framework and provided additional citations that provided more detail for the readers.
Within both the BER and the broader DBER communities, conceptual frameworks have been used to describe different constructs. For example, some researchers have used the term “conceptual framework” to describe students’ conceptual understandings of a biological phenomenon. This is distinct from a researcher’s conceptual framework of the educational phenomenon under investigation, which may also need to be explicitly described in the article. Other studies have presented a research logic model or flowchart of the research design as a conceptual framework. These constructions can be quite valuable in helping readers understand the data-collection and analysis process. However, a model depicting the study design does not serve the same role as a conceptual framework. Researchers need to avoid conflating these constructs by differentiating the researchers’ conceptual framework that guides the study from the research design, when applicable.
Explicitly describing conceptual frameworks is essential in depicting the focus of the study. We have found that being explicit in a conceptual framework means using accepted terminology, referencing prior work, and clearly noting connections between terms. This description can also highlight gaps in the literature or suggest potential contributions to the field of study. A well-elucidated conceptual framework can suggest additional studies that may be warranted. This can also spur other researchers to consider how they would approach the examination of a phenomenon and could result in a revised conceptual framework.
It can be challenging to create conceptual frameworks, but they are important. Below are two resources that could be helpful in constructing and presenting conceptual frameworks in educational research:
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. Chapter 3 in this book describes how to construct conceptual frameworks.
- Ravitch, S. M., & Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book explains how conceptual frameworks guide the research questions, data collection, data analyses, and interpretation of results.
CONCLUDING THOUGHTS
Literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are all important in DBER and BER. Robust literature reviews reinforce the importance of a study. Theoretical frameworks connect the study to the base of knowledge in educational theory and specify the researcher’s assumptions. Conceptual frameworks allow researchers to explicitly describe their conceptualization of the relationships among the components of the phenomenon under study. Table 1 provides a general overview of these components in order to assist biology education researchers in thinking about these elements.
It is important to emphasize that these different elements are intertwined. When these elements are aligned and complement one another, the study is coherent, and the study findings contribute to knowledge in the field. When literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are disconnected from one another, the study suffers. The point of the study is lost, suggested findings are unsupported, or important conclusions are invisible to the researcher. In addition, this misalignment may be costly in terms of time and money.
Conducting a literature review, selecting a theoretical framework, and building a conceptual framework are some of the most difficult elements of a research study. It takes time to understand the relevant research, identify a theoretical framework that provides important insights into the study, and formulate a conceptual framework that organizes the finding. In the research process, there is often a constant back and forth among these elements as the study evolves. With an ongoing refinement of the review of literature, clarification of the theoretical framework, and articulation of a conceptual framework, a sound study can emerge that makes a contribution to the field. This is the goal of BER and education research.
Supplementary Material
- Allee, V. (2000). Knowledge networks and communities of learning . OD Practitioner , 32 ( 4 ), 4–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen, M. (2017). The Sage encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1–4 ). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. 10.4135/9781483381411 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2011). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: A call to action . Washington, DC. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (2014). Setting the stage . In Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (eds.), Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research (pp. 1–22). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnes, M. E., Brownell, S. E. (2016). Practices and perspectives of college instructors on addressing religious beliefs when teaching evolution . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), ar18. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-11-0243 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boote, D. N., Beile, P. (2005). Scholars before researchers: On the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation . Educational Researcher , 34 ( 6 ), 3–15. 10.3102/0013189x034006003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownell, S. E., Kloser, M. J. (2015). Toward a conceptual framework for measuring the effectiveness of course-based undergraduate research experiences in undergraduate biology . Studies in Higher Education , 40 ( 3 ), 525–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1004234 [ Google Scholar ]
- Connolly, M. R., Lee, Y. G., Savoy, J. N. (2018). The effects of doctoral teaching development on early-career STEM scholars’ college teaching self-efficacy . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar14. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-02-0039 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, K. M., Blattman, J. N., Hendrix, T., Brownell, S. E. (2019). The impact of broadly relevant novel discoveries on student project ownership in a traditional lab course turned CURE . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar57. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-06-0113 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeHaan, R. L. (2011). Education research in the biological sciences: A nine decade review (Paper commissioned by the NAS/NRC Committee on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline Based Education Research) . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www7.nationalacademies.org/bose/DBER_Mee ting2_commissioned_papers_page.html [ Google Scholar ]
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research . Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 ( 2 ), 020101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dirks, C. (2011). The current status and future direction of biology education research . Paper presented at: Second Committee Meeting on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline-Based Education Research, 18–19 October (Washington, DC). Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://sites.nationalacademies.org/DBASSE/BOSE/DBASSE_071087 [ Google Scholar ]
- Duran, R. P., Eisenhart, M. A., Erickson, F. D., Grant, C. A., Green, J. L., Hedges, L. V., Schneider, B. L. (2006). Standards for reporting on empirical social science research in AERA publications: American Educational Research Association . Educational Researcher , 35 ( 6 ), 33–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebert-May, D., Derting, T. L., Henkel, T. P., Middlemis Maher, J., Momsen, J. L., Arnold, B., Passmore, H. A. (2015). Breaking the cycle: Future faculty begin teaching with learner-centered strategies after professional development . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 14 ( 2 ), ar22. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.14-12-0222 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvan, J. L., Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315229386 [ Google Scholar ]
- Gehrke, S., Kezar, A. (2017). The roles of STEM faculty communities of practice in institutional and departmental reform in higher education . American Educational Research Journal , 54 ( 5 ), 803–833. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217706736 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghee, M., Keels, M., Collins, D., Neal-Spence, C., Baker, E. (2016). Fine-tuning summer research programs to promote underrepresented students’ persistence in the STEM pathway . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar28. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0046 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Education Sciences & National Science Foundation. (2013). Common guidelines for education research and development . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www.nsf.gov/pubs/2013/nsf13126/nsf13126.pdf
- Jensen, J. L., Lawson, A. (2011). Effects of collaborative group composition and inquiry instruction on reasoning gains and achievement in undergraduate biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 10 ( 1 ), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kolpikova, E. P., Chen, D. C., Doherty, J. H. (2019). Does the format of preclass reading quizzes matter? An evaluation of traditional and gamified, adaptive preclass reading quizzes . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar52. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Labov, J. B., Reid, A. H., Yamamoto, K. R. (2010). Integrated biology and undergraduate science education: A new biology education for the twenty-first century? CBE—Life Sciences Education , 9 ( 1 ), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.09-12-0092 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lane, T. B. (2016). Beyond academic and social integration: Understanding the impact of a STEM enrichment program on the retention and degree attainment of underrepresented students . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0070 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lave, J. (1988). Cognition in practice: Mind, mathematics and culture in everyday life . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lo, S. M., Gardner, G. E., Reid, J., Napoleon-Fanis, V., Carroll, P., Smith, E., Sato, B. K. (2019). Prevailing questions and methodologies in biology education research: A longitudinal analysis of research in CBE — Life Sciences Education and at the Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 1 ), ar9. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.18-08-0164 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lysaght, Z. (2011). Epistemological and paradigmatic ecumenism in “Pasteur’s quadrant:” Tales from doctoral research . In Official Conference Proceedings of the Third Asian Conference on Education in Osaka, Japan . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://iafor.org/ace2011_offprint/ACE2011_offprint_0254.pdf
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems . Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perry, J., Meir, E., Herron, J. C., Maruca, S., Stal, D. (2008). Evaluating two approaches to helping college students understand evolutionary trees through diagramming tasks . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 7 ( 2 ), 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.07-01-0007 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Posner, G. J., Strike, K. A., Hewson, P. W., Gertzog, W. A. (1982). Accommodation of a scientific conception: Toward a theory of conceptual change . Science Education , 66 ( 2 ), 211–227. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ravitch, S. M., Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reeves, T. D., Marbach-Ad, G., Miller, K. R., Ridgway, J., Gardner, G. E., Schussler, E. E., Wischusen, E. W. (2016). A conceptual framework for graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), es2. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-10-0225 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds, J. A., Thaiss, C., Katkin, W., Thompson, R. J. Jr. (2012). Writing-to-learn in undergraduate science education: A community-based, conceptually driven approach . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 11 ( 1 ), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.11-08-0064 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rocco, T. S., Plakhotnik, M. S. (2009). Literature reviews, conceptual frameworks, and theoretical frameworks: Terms, functions, and distinctions . Human Resource Development Review , 8 ( 1 ), 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484309332617 [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodrigo-Peiris, T., Xiang, L., Cassone, V. M. (2018). A low-intensity, hybrid design between a “traditional” and a “course-based” research experience yields positive outcomes for science undergraduate freshmen and shows potential for large-scale application . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 4 ), ar53. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-11-0248 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabel, J. L., Dauer, J. T., Forbes, C. T. (2017). Introductory biology students’ use of enhanced answer keys and reflection questions to engage in metacognition and enhance understanding . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 16 ( 3 ), ar40. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-10-0298 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sbeglia, G. C., Goodridge, J. A., Gordon, L. H., Nehm, R. H. (2021). Are faculty changing? How reform frameworks, sampling intensities, and instrument measures impact inferences about student-centered teaching practices . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 20 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.20-11-0259 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwandt, T. A. (2000). Three epistemological stances for qualitative inquiry: Interpretivism, hermeneutics, and social constructionism . In Denzin, N. K., Lincoln, Y. S. (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 189–213). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sickel, A. J., Friedrichsen, P. (2013). Examining the evolution education literature with a focus on teachers: Major findings, goals for teacher preparation, and directions for future research . Evolution: Education and Outreach , 6 ( 1 ), 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1936-6434-6-23 [ Google Scholar ]
- Singer, S. R., Nielsen, N. R., Schweingruber, H. A. (2012). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Todd, A., Romine, W. L., Correa-Menendez, J. (2019). Modeling the transition from a phenotypic to genotypic conceptualization of genetics in a university-level introductory biology context . Research in Science Education , 49 ( 2 ), 569–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-017-9626-2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning as a social system . Systems Thinker , 9 ( 5 ), 2–3. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ziadie, M. A., Andrews, T. C. (2018). Moving evolution education forward: A systematic analysis of literature to identify gaps in collective knowledge for teaching . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar11. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-08-0190 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Theoretical vs Conceptual Framework
What they are & how they’re different (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, sooner or later you’re bound to run into the terms theoretical framework and conceptual framework . These are closely related but distinctly different things (despite some people using them interchangeably) and it’s important to understand what each means. In this post, we’ll unpack both theoretical and conceptual frameworks in plain language along with practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Theoretical vs Conceptual
What is a theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, what is a conceptual framework, example of a conceptual framework.
- Theoretical vs conceptual: which one should I use?
A theoretical framework (also sometimes referred to as a foundation of theory) is essentially a set of concepts, definitions, and propositions that together form a structured, comprehensive view of a specific phenomenon.
In other words, a theoretical framework is a collection of existing theories, models and frameworks that provides a foundation of core knowledge – a “lay of the land”, so to speak, from which you can build a research study. For this reason, it’s usually presented fairly early within the literature review section of a dissertation, thesis or research paper .

Let’s look at an example to make the theoretical framework a little more tangible.
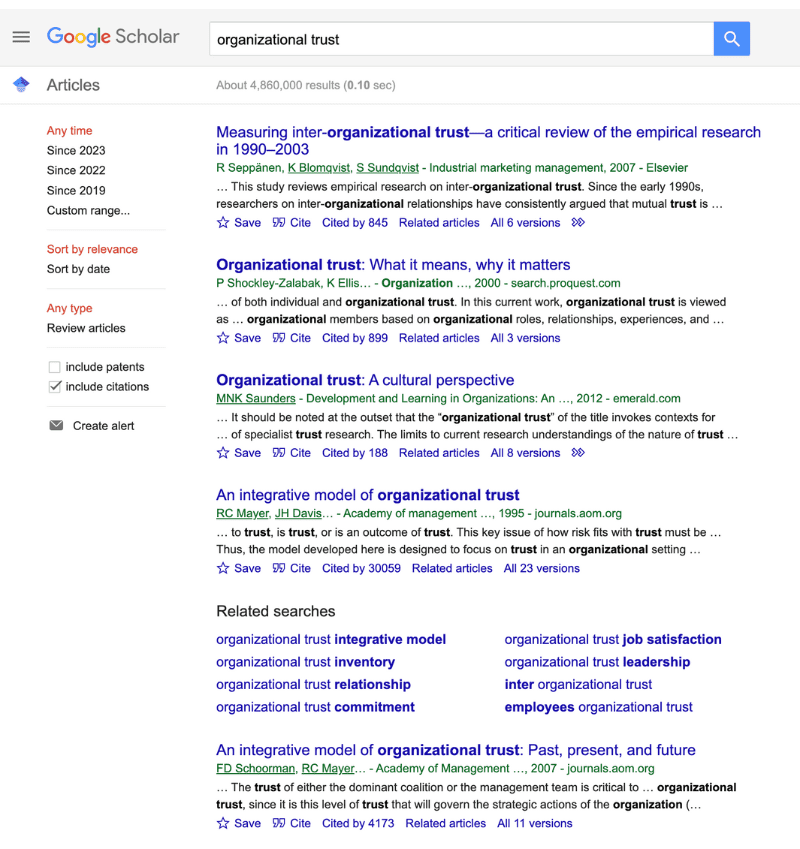
If your research aims involve understanding what factors contributed toward people trusting investment brokers, you’d need to first lay down some theory so that it’s crystal clear what exactly you mean by this. For example, you would need to define what you mean by “trust”, as there are many potential definitions of this concept. The same would be true for any other constructs or variables of interest.
You’d also need to identify what existing theories have to say in relation to your research aim. In this case, you could discuss some of the key literature in relation to organisational trust. A quick search on Google Scholar using some well-considered keywords generally provides a good starting point.
Typically, you’ll present your theoretical framework in written form , although sometimes it will make sense to utilise some visuals to show how different theories relate to each other. Your theoretical framework may revolve around just one major theory , or it could comprise a collection of different interrelated theories and models. In some cases, there will be a lot to cover and in some cases, not. Regardless of size, the theoretical framework is a critical ingredient in any study.
Simply put, the theoretical framework is the core foundation of theory that you’ll build your research upon. As we’ve mentioned many times on the blog, good research is developed by standing on the shoulders of giants . It’s extremely unlikely that your research topic will be completely novel and that there’ll be absolutely no existing theory that relates to it. If that’s the case, the most likely explanation is that you just haven’t reviewed enough literature yet! So, make sure that you take the time to review and digest the seminal sources.
Need a helping hand?
A conceptual framework is typically a visual representation (although it can also be written out) of the expected relationships and connections between various concepts, constructs or variables. In other words, a conceptual framework visualises how the researcher views and organises the various concepts and variables within their study. This is typically based on aspects drawn from the theoretical framework, so there is a relationship between the two.
Quite commonly, conceptual frameworks are used to visualise the potential causal relationships and pathways that the researcher expects to find, based on their understanding of both the theoretical literature and the existing empirical research . Therefore, the conceptual framework is often used to develop research questions and hypotheses .
Let’s look at an example of a conceptual framework to make it a little more tangible. You’ll notice that in this specific conceptual framework, the hypotheses are integrated into the visual, helping to connect the rest of the document to the framework.
As you can see, conceptual frameworks often make use of different shapes , lines and arrows to visualise the connections and relationships between different components and/or variables. Ultimately, the conceptual framework provides an opportunity for you to make explicit your understanding of how everything is connected . So, be sure to make use of all the visual aids you can – clean design, well-considered colours and concise text are your friends.
Theoretical framework vs conceptual framework
As you can see, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are closely related concepts, but they differ in terms of focus and purpose. The theoretical framework is used to lay down a foundation of theory on which your study will be built, whereas the conceptual framework visualises what you anticipate the relationships between concepts, constructs and variables may be, based on your understanding of the existing literature and the specific context and focus of your research. In other words, they’re different tools for different jobs , but they’re neighbours in the toolbox.
Naturally, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are not mutually exclusive . In fact, it’s quite likely that you’ll include both in your dissertation or thesis, especially if your research aims involve investigating relationships between variables. Of course, every research project is different and universities differ in terms of their expectations for dissertations and theses, so it’s always a good idea to have a look at past projects to get a feel for what the norms and expectations are at your specific institution.
Want to learn more about research terminology, methods and techniques? Be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach blog . Alternatively, if you’re looking for hands-on help, have a look at our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process, step by step.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
19 Comments
Thank you for giving a valuable lesson
good thanks!
VERY INSIGHTFUL
thanks for given very interested understand about both theoritical and conceptual framework
I am researching teacher beliefs about inclusive education but not using a theoretical framework just conceptual frame using teacher beliefs, inclusive education and inclusive practices as my concepts
good, fantastic
great! thanks for the clarification. I am planning to use both for my implementation evaluation of EmONC service at primary health care facility level. its theoretical foundation rooted from the principles of implementation science.
This is a good one…now have a better understanding of Theoretical and Conceptual frameworks. Highly grateful
Very educating and fantastic,good to be part of you guys,I appreciate your enlightened concern.
Thanks for shedding light on these two t opics. Much clearer in my head now.
Simple and clear!
The differences between the two topics was well explained, thank you very much!
Thank you great insight
Superb. Thank you so much.
Hello Gradcoach! I’m excited with your fantastic educational videos which mainly focused on all over research process. I’m a student, I kindly ask and need your support. So, if it’s possible please send me the PDF format of all topic provided here, I put my email below, thank you!
I am really grateful I found this website. This is very helpful for an MPA student like myself.
I’m clear with these two terminologies now. Useful information. I appreciate it. Thank you
I’m well inform about these two concepts in research. Thanks
I found this really helpful. It is well explained. Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work.
Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research, showing that your work is grounded in established ideas.
In other words, your theoretical framework justifies and contextualises your later research, and it’s a crucial first step for your research paper , thesis, or dissertation . A well-rounded theoretical framework sets you up for success later on in your research and writing process.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why do you need a theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework, structuring your theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, frequently asked questions about theoretical frameworks.
Before you start your own research, it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with the theories and models that other researchers have already developed. Your theoretical framework is your opportunity to present and explain what you’ve learned, situated within your future research topic.
There’s a good chance that many different theories about your topic already exist, especially if the topic is broad. In your theoretical framework, you will evaluate, compare, and select the most relevant ones.
By “framing” your research within a clearly defined field, you make the reader aware of the assumptions that inform your approach, showing the rationale behind your choices for later sections, like methodology and discussion . This part of your dissertation lays the foundations that will support your analysis, helping you interpret your results and make broader generalisations .
- In literature , a scholar using postmodernist literary theory would analyse The Great Gatsby differently than a scholar using Marxist literary theory.
- In psychology , a behaviourist approach to depression would involve different research methods and assumptions than a psychoanalytic approach.
- In economics , wealth inequality would be explained and interpreted differently based on a classical economics approach than based on a Keynesian economics one.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
To create your own theoretical framework, you can follow these three steps:
- Identifying your key concepts
- Evaluating and explaining relevant theories
- Showing how your research fits into existing research
1. Identify your key concepts
The first step is to pick out the key terms from your problem statement and research questions . Concepts often have multiple definitions, so your theoretical framework should also clearly define what you mean by each term.
To investigate this problem, you have identified and plan to focus on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
Research question : How can the satisfaction of company X’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
2. Evaluate and explain relevant theories
By conducting a thorough literature review , you can determine how other researchers have defined these key concepts and drawn connections between them. As you write your theoretical framework, your aim is to compare and critically evaluate the approaches that different authors have taken.
After discussing different models and theories, you can establish the definitions that best fit your research and justify why. You can even combine theories from different fields to build your own unique framework if this better suits your topic.
Make sure to at least briefly mention each of the most important theories related to your key concepts. If there is a well-established theory that you don’t want to apply to your own research, explain why it isn’t suitable for your purposes.
3. Show how your research fits into existing research
Apart from summarising and discussing existing theories, your theoretical framework should show how your project will make use of these ideas and take them a step further.
You might aim to do one or more of the following:
- Test whether a theory holds in a specific, previously unexamined context
- Use an existing theory as a basis for interpreting your results
- Critique or challenge a theory
- Combine different theories in a new or unique way
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation. As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
There are no fixed rules for structuring your theoretical framework, but it’s best to double-check with your department or institution to make sure they don’t have any formatting guidelines. The most important thing is to create a clear, logical structure. There are a few ways to do this:
- Draw on your research questions, structuring each section around a question or key concept
- Organise by theory cluster
- Organise by date
As in all other parts of your research paper , thesis, or dissertation , make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
To get a sense of what this part of your thesis or dissertation might look like, take a look at our full example .
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/the-theoretical-framework/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Theoretical Framework
Definition:
Theoretical framework refers to a set of concepts, theories, ideas , and assumptions that serve as a foundation for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It provides a conceptual framework that helps researchers to design and conduct their research, as well as to analyze and interpret their findings.
In research, a theoretical framework explains the relationship between various variables, identifies gaps in existing knowledge, and guides the development of research questions, hypotheses, and methodologies. It also helps to contextualize the research within a broader theoretical perspective, and can be used to guide the interpretation of results and the formulation of recommendations.
Types of Theoretical Framework
Types of Types of Theoretical Framework are as follows:
Conceptual Framework
This type of framework defines the key concepts and relationships between them. It helps to provide a theoretical foundation for a study or research project .
Deductive Framework
This type of framework starts with a general theory or hypothesis and then uses data to test and refine it. It is often used in quantitative research .
Inductive Framework
This type of framework starts with data and then develops a theory or hypothesis based on the patterns and themes that emerge from the data. It is often used in qualitative research .
Empirical Framework
This type of framework focuses on the collection and analysis of empirical data, such as surveys or experiments. It is often used in scientific research .
Normative Framework
This type of framework defines a set of norms or values that guide behavior or decision-making. It is often used in ethics and social sciences.
Explanatory Framework
This type of framework seeks to explain the underlying mechanisms or causes of a particular phenomenon or behavior. It is often used in psychology and social sciences.
Components of Theoretical Framework
The components of a theoretical framework include:
- Concepts : The basic building blocks of a theoretical framework. Concepts are abstract ideas or generalizations that represent objects, events, or phenomena.
- Variables : These are measurable and observable aspects of a concept. In a research context, variables can be manipulated or measured to test hypotheses.
- Assumptions : These are beliefs or statements that are taken for granted and are not tested in a study. They provide a starting point for developing hypotheses.
- Propositions : These are statements that explain the relationships between concepts and variables in a theoretical framework.
- Hypotheses : These are testable predictions that are derived from the theoretical framework. Hypotheses are used to guide data collection and analysis.
- Constructs : These are abstract concepts that cannot be directly measured but are inferred from observable variables. Constructs provide a way to understand complex phenomena.
- Models : These are simplified representations of reality that are used to explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
How to Write Theoretical Framework
A theoretical framework is an essential part of any research study or paper, as it helps to provide a theoretical basis for the research and guide the analysis and interpretation of the data. Here are some steps to help you write a theoretical framework:
- Identify the key concepts and variables : Start by identifying the main concepts and variables that your research is exploring. These could include things like motivation, behavior, attitudes, or any other relevant concepts.
- Review relevant literature: Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in your field to identify key theories and ideas that relate to your research. This will help you to understand the existing knowledge and theories that are relevant to your research and provide a basis for your theoretical framework.
- Develop a conceptual framework : Based on your literature review, develop a conceptual framework that outlines the key concepts and their relationships. This framework should provide a clear and concise overview of the theoretical perspective that underpins your research.
- Identify hypotheses and research questions: Based on your conceptual framework, identify the hypotheses and research questions that you want to test or explore in your research.
- Test your theoretical framework: Once you have developed your theoretical framework, test it by applying it to your research data. This will help you to identify any gaps or weaknesses in your framework and refine it as necessary.
- Write up your theoretical framework: Finally, write up your theoretical framework in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate terminology and referencing the relevant literature to support your arguments.
Theoretical Framework Examples
Here are some examples of theoretical frameworks:
- Social Learning Theory : This framework, developed by Albert Bandura, suggests that people learn from their environment, including the behaviors of others, and that behavior is influenced by both external and internal factors.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs : Abraham Maslow proposed that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom, followed by safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization at the top. This framework has been used in various fields, including psychology and education.
- Ecological Systems Theory : This framework, developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, suggests that a person’s development is influenced by the interaction between the individual and the various environments in which they live, such as family, school, and community.
- Feminist Theory: This framework examines how gender and power intersect to influence social, cultural, and political issues. It emphasizes the importance of understanding and challenging systems of oppression.
- Cognitive Behavioral Theory: This framework suggests that our thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes influence our behavior, and that changing our thought patterns can lead to changes in behavior and emotional responses.
- Attachment Theory: This framework examines the ways in which early relationships with caregivers shape our later relationships and attachment styles.
- Critical Race Theory : This framework examines how race intersects with other forms of social stratification and oppression to perpetuate inequality and discrimination.
When to Have A Theoretical Framework
Following are some situations When to Have A Theoretical Framework:
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research in any discipline, as it provides a foundation for understanding the research problem and guiding the research process.
- A theoretical framework is essential when conducting research on complex phenomena, as it helps to organize and structure the research questions, hypotheses, and findings.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when the research problem requires a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts and principles that govern the phenomenon being studied.
- A theoretical framework is particularly important when conducting research in social sciences, as it helps to explain the relationships between variables and provides a framework for testing hypotheses.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research in applied fields, such as engineering or medicine, as it helps to provide a theoretical basis for the development of new technologies or treatments.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to address a specific gap in knowledge, as it helps to define the problem and identify potential solutions.
- A theoretical framework is also important when conducting research that involves the analysis of existing theories or concepts, as it helps to provide a framework for comparing and contrasting different theories and concepts.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to make predictions or develop generalizations about a particular phenomenon, as it helps to provide a basis for evaluating the accuracy of these predictions or generalizations.
- Finally, a theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to make a contribution to the field, as it helps to situate the research within the broader context of the discipline and identify its significance.
Purpose of Theoretical Framework
The purposes of a theoretical framework include:
- Providing a conceptual framework for the study: A theoretical framework helps researchers to define and clarify the concepts and variables of interest in their research. It enables researchers to develop a clear and concise definition of the problem, which in turn helps to guide the research process.
- Guiding the research design: A theoretical framework can guide the selection of research methods, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures. By outlining the key concepts and assumptions underlying the research questions, the theoretical framework can help researchers to identify the most appropriate research design for their study.
- Supporting the interpretation of research findings: A theoretical framework provides a framework for interpreting the research findings by helping researchers to make connections between their findings and existing theory. It enables researchers to identify the implications of their findings for theory development and to assess the generalizability of their findings.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research: A well-developed theoretical framework can enhance the credibility of the research by providing a strong theoretical foundation for the study. It demonstrates that the research is based on a solid understanding of the relevant theory and that the research questions are grounded in a clear conceptual framework.
- Facilitating communication and collaboration: A theoretical framework provides a common language and conceptual framework for researchers, enabling them to communicate and collaborate more effectively. It helps to ensure that everyone involved in the research is working towards the same goals and is using the same concepts and definitions.
Characteristics of Theoretical Framework
Some of the characteristics of a theoretical framework include:
- Conceptual clarity: The concepts used in the theoretical framework should be clearly defined and understood by all stakeholders.
- Logical coherence : The framework should be internally consistent, with each concept and assumption logically connected to the others.
- Empirical relevance: The framework should be based on empirical evidence and research findings.
- Parsimony : The framework should be as simple as possible, without sacrificing its ability to explain the phenomenon in question.
- Flexibility : The framework should be adaptable to new findings and insights.
- Testability : The framework should be testable through research, with clear hypotheses that can be falsified or supported by data.
- Applicability : The framework should be useful for practical applications, such as designing interventions or policies.
Advantages of Theoretical Framework
Here are some of the advantages of having a theoretical framework:
- Provides a clear direction : A theoretical framework helps researchers to identify the key concepts and variables they need to study and the relationships between them. This provides a clear direction for the research and helps researchers to focus their efforts and resources.
- Increases the validity of the research: A theoretical framework helps to ensure that the research is based on sound theoretical principles and concepts. This increases the validity of the research by ensuring that it is grounded in established knowledge and is not based on arbitrary assumptions.
- Enables comparisons between studies : A theoretical framework provides a common language and set of concepts that researchers can use to compare and contrast their findings. This helps to build a cumulative body of knowledge and allows researchers to identify patterns and trends across different studies.
- Helps to generate hypotheses: A theoretical framework provides a basis for generating hypotheses about the relationships between different concepts and variables. This can help to guide the research process and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Facilitates communication: A theoretical framework provides a common language and set of concepts that researchers can use to communicate their findings to other researchers and to the wider community. This makes it easier for others to understand the research and its implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George.
Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review .
A strong theoretical framework gives your research direction. It allows you to convincingly interpret, explain, and generalize from your findings and show the relevance of your thesis or dissertation topic in your field.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Sample problem statement and research questions, sample theoretical framework, your theoretical framework, other interesting articles.
Your theoretical framework is based on:
- Your problem statement
- Your research questions
- Your literature review
A new boutique downtown is struggling with the fact that many of their online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases. This is a big issue for the otherwise fast-growing store.Management wants to increase customer loyalty. They believe that improved customer satisfaction will play a major role in achieving their goal of increased return customers.
To investigate this problem, you have zeroed in on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
- Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
- Research question : How can the satisfaction of the boutique’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
The concepts of “customer loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” are clearly central to this study, along with their relationship to the likelihood that a customer will return. Your theoretical framework should define these concepts and discuss theories about the relationship between these variables.
Some sub-questions could include:
- What is the relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction?
- How satisfied and loyal are the boutique’s online customers currently?
- What factors affect the satisfaction and loyalty of the boutique’s online customers?
As the concepts of “loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” play a major role in the investigation and will later be measured, they are essential concepts to define within your theoretical framework .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Below is a simplified example showing how you can describe and compare theories in your thesis or dissertation . In this example, we focus on the concept of customer satisfaction introduced above.
Customer satisfaction
Thomassen (2003, p. 69) defines customer satisfaction as “the perception of the customer as a result of consciously or unconsciously comparing their experiences with their expectations.” Kotler & Keller (2008, p. 80) build on this definition, stating that customer satisfaction is determined by “the degree to which someone is happy or disappointed with the observed performance of a product in relation to his or her expectations.”
Performance that is below expectations leads to a dissatisfied customer, while performance that satisfies expectations produces satisfied customers (Kotler & Keller, 2003, p. 80).
The definition of Zeithaml and Bitner (2003, p. 86) is slightly different from that of Thomassen. They posit that “satisfaction is the consumer fulfillment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product of service itself, provides a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfillment.” Zeithaml and Bitner’s emphasis is thus on obtaining a certain satisfaction in relation to purchasing.
Thomassen’s definition is the most relevant to the aims of this study, given the emphasis it places on unconscious perception. Although Zeithaml and Bitner, like Thomassen, say that customer satisfaction is a reaction to the experience gained, there is no distinction between conscious and unconscious comparisons in their definition.
The boutique claims in its mission statement that it wants to sell not only a product, but also a feeling. As a result, unconscious comparison will play an important role in the satisfaction of its customers. Thomassen’s definition is therefore more relevant.
Thomassen’s Customer Satisfaction Model
According to Thomassen, both the so-called “value proposition” and other influences have an impact on final customer satisfaction. In his satisfaction model (Fig. 1), Thomassen shows that word-of-mouth, personal needs, past experiences, and marketing and public relations determine customers’ needs and expectations.
These factors are compared to their experiences, with the interplay between expectations and experiences determining a customer’s satisfaction level. Thomassen’s model is important for this study as it allows us to determine both the extent to which the boutique’s customers are satisfied, as well as where improvements can be made.
Figure 1 Customer satisfaction creation
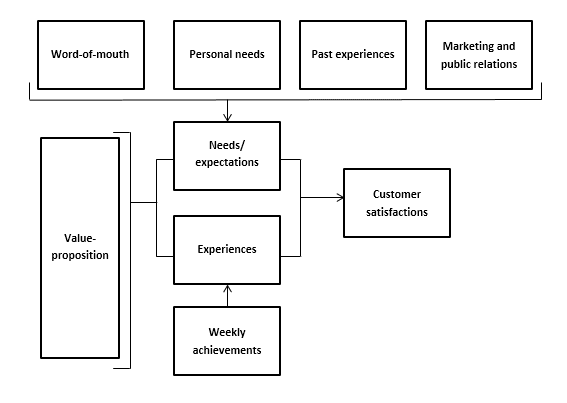
Of course, you could analyze the concepts more thoroughly and compare additional definitions to each other. You could also discuss the theories and ideas of key authors in greater detail and provide several models to illustrate different concepts.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Vinz, S. (2023, July 18). Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Scribbr. Retrieved April 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework-example/
Is this article helpful?
Sarah's academic background includes a Master of Arts in English, a Master of International Affairs degree, and a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science. She loves the challenge of finding the perfect formulation or wording and derives much satisfaction from helping students take their academic writing up a notch.
Other students also liked
What is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Table of Contents
A literature review and a theoretical framework are both important components of academic research. However, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. In this article, we will examine the concepts of literature review and theoretical framework, explore their significance, and highlight the key differences between the two.
Defining the Concepts: Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
Before we dive into the details, let's clarify what a literature review and a theoretical framework actually mean.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research and scholarly articles on a specific topic. It involves reviewing and summarizing the current knowledge and understanding of the subject matter. By examining previous studies, the scholar can identify knowledge gaps, assess the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, and present a comprehensive overview of the topic.
When conducting a literature review, the scholar delves into a vast array of sources, including academic journals, books, conference proceedings, and reputable online databases. This extensive exploration allows them to gather relevant information, theories, and methodologies related to their research topic.
Furthermore, a literature review provides a solid foundation for the research by establishing the context and significance of the study. It helps researchers identify the key concepts, theories, and variables that are relevant to their research objectives. By critically analyzing the existing literature, scholars can identify research gaps and propose new avenues for scientific investigation.
Moreover, a literature review is not merely a summary of previous studies. It requires a critical evaluation of the methodologies used, the quality of the data collected, and the validity of the conclusions drawn.
Researchers must assess the credibility and reliability of the sources they include in their review to ensure the accuracy and robustness of their analysis.
What is a Theoretical Framework?
A theoretical framework provides a conceptual explanation for the research problem or question being investigated. It serves as a foundation that guides the formulation of hypotheses and research objectives. A theoretical framework helps researchers to analyze and interpret their findings by establishing a set of assumptions, concepts, and relationships that underpin their study. It provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting research outcomes.
When developing a theoretical framework, researchers draw upon existing theories and concepts from relevant disciplines to create a conceptual framework that aligns with their research objectives. This framework helps researchers to define the variables they will study, establish the relationships between these variables, and propose hypotheses that can be tested through empirical research.
Furthermore, a theoretical framework provides a roadmap for researchers to navigate through the complexities of their study. It helps them to identify the key constructs and variables that need to be measured and analyzed. By providing a clear structure, the theoretical framework ensures that researchers stay focused on their research objectives and avoid getting lost in a sea of information.
Moreover, a theoretical framework allows researchers to make connections between their study and existing theories or models. By building upon established knowledge, researchers can contribute to the advancement of their field and provide new insights and perspectives. The theoretical framework also helps researchers interpret their findings in a meaningful way and draw conclusions that have theoretical and practical implications.
In summary, both a literature review and a theoretical framework play crucial roles in the research process. While a literature review provides a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge and identifies research gaps, a theoretical framework establishes the conceptual foundation for the study and guides the formulation of research objectives and hypotheses. Together, these two elements contribute to the development of a robust and well-grounded research study.
The Purpose and Importance of Literature Reviews
Now that we have a clear understanding of what a literature review is, let's explore its purpose and significance.
A literature review plays a crucial role in academic research. It serves several purposes, including:
- Providing a comprehensive understanding of the existing literature in a particular field.
- Identifying the gaps, controversies, or inconsistencies in the current knowledge.
- Helping researchers to refine their research questions and objectives.
- Ensuring that the research being conducted is novel and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
The Benefits of Conducting a Literature Review
There are numerous benefits to conducting a literature review, such as:
- Enhancing the researcher's knowledge and understanding of the subject area.
- Providing a framework for developing research hypotheses and objectives.
- Identifying potential research methodologies and approaches.
- Informing the selection of appropriate data collection and analysis methods.
- Guiding the interpretation and discussion of research findings.
The Purpose and Importance of Theoretical Frameworks
Moving on to theoretical frameworks, let us discuss their purpose and importance.
When conducting research, theoretical frameworks play a crucial role in providing a solid foundation for the study. They serve as a guiding tool for researchers, helping them navigate through the complexities of their research and providing a framework for understanding and interpreting their findings.
The Function of Theoretical Frameworks in Research
Theoretical frameworks serve multiple functions in research:
- Providing a conceptual framework enables researchers to clearly define the scope and direction of their study.
- Acting as a roadmap, guiding researchers in formulating their research objectives and hypotheses. It helps them identify the key variables and relationships they want to explore, providing a solid foundation for their research.
- Helping researchers identify and select appropriate research methods and techniques. When it comes to selecting research methods and techniques, theoretical frameworks are invaluable. They provide researchers with a lens through which they can evaluate different methods and techniques, ensuring that they choose the most appropriate ones for their study. By aligning their methods with the theoretical framework, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their research.
- Supporting the interpretation and explanation of research findings. Once the data has been collected, theoretical frameworks help researchers make sense of their findings. They provide a framework for interpreting and explaining the results, allowing researchers to draw meaningful conclusions. By grounding their analysis in a theoretical framework, researchers can provide a solid foundation for their findings and contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
- Facilitating the integration of new knowledge with existing theories and concepts. Theoretical frameworks also play a crucial role in the advancement of knowledge. By integrating new findings with existing theories and concepts, researchers can contribute to the development of their field.
The Advantages of Developing a Theoretical Framework
Developing a theoretical framework offers several advantages:
- Enhancing the researcher's understanding of the research problem. By developing a theoretical framework, researchers gain a deeper understanding of the research problem they are investigating. This enhanced understanding allows researchers to approach their study with clarity and purpose.
- Facilitating the selection of an appropriate research design. Choosing the right research design is crucial for the success of a study. A well-developed theoretical framework helps researchers select the most appropriate research design by providing a clear direction and focus. It ensures that the research design aligns with the research objectives and hypotheses, maximizing the chances of obtaining valid and reliable results.
- Helping researchers organize their thoughts and ideas systematically. This organization helps researchers stay focused and ensures that all aspects of the research problem are considered. By structuring their thoughts, researchers can effectively communicate their ideas and findings to others.
- Guiding the analysis and interpretation of research findings. When it comes to analyzing and interpreting research findings, a theoretical framework provides researchers with a framework to guide their process. It helps researchers identify patterns, relationships, and themes within the data, allowing for a more comprehensive analysis.
Developing a theoretical framework is essential for ensuring the validity and reliability of a study. By aligning the research with established theories and concepts, researchers can enhance the credibility of their study. A well-developed theoretical framework provides a solid foundation for the research, increasing the chances of obtaining accurate and meaningful results.
Differences Between Literature Reviews and Theoretical Frameworks
Now, let's explore the key differences between literature reviews and theoretical frameworks.
Key Differences:
- Focus: A literature review focuses on summarizing existing research, while a theoretical framework focuses on providing a conceptual foundation for the study.
- Scope: A literature review covers a broad range of related research, while a theoretical framework is more specific to the research problem at hand.
- Timing: A literature review is typically conducted early in the research process, while a theoretical framework is often developed alongside the research design.
- Purpose: A literature review aims to inform the research and establish its context, while a theoretical framework aims to guide the interpretation and analysis of findings.
In conclusion
Understanding the distinction between a literature review and a theoretical framework is crucial for conducting effective and meaningful academic research. While a literature review provides an overview of existing research, a theoretical framework guides the formulation, analysis, and interpretation of research. Both components are essential for building a strong foundation of knowledge in any field. By comprehending their purpose, significance, and key differences, researchers can enhance the quality and rigor of their research endeavors.
Love using SciSpace tools? Enjoy discounts! Use SR40 (40% off yearly) and SR20 (20% off monthly). Claim yours here 👉 SciSpace Premium
Learn more about Literature Review
5 literature review tools to ace your reseach (+2 bonus tools)
Role of AI in Systematic Literature Review
Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
A complete guide on how to write a literature review
How to Use AI Tools for Conducting a Literature Review
You might also like

AI for Meta-Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Literature reviews, conceptual frameworks, and theoretical frameworks: Terms, functions, and distinctions

Abstract This essay starts with a discussion of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. This discussion includes similarities and distinctions among these components and their relation to other sections of a manuscript such as the problem statement, discussion, and implications. The essay concludes with an overview of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as separate types of manuscripts.
Related Papers
Ernest Kwakye
Human Resource Development Review
Maria Plakhotnik
Tonette S Rocco
Abstract Making the transition to management is one of the most difficult challenges first-time managers face. Organizations pay for the failure of first-time managers and benefit from their success. The purpose of this article is to challenge Hill's (1992) argument that the transition to management involves two processes:“a process of learning from experience” and “a transformation of professional identity”(p. 121) and suggest a third process—building leadership potential.
Monica Lee , Thomas Garavan
Abstract One aspect of personality, perceptions of internal versus external control of reinforcement, shifts under conditions of change. This review of the literature examines the relationship between planned organizational change and locus of control. The review includes literature from the disciplines of clinical and social psychology, adult development, education and learning theory, business and management, and human resource development (HRD).
Tonette Rocco
Carlos Albornoz
Judith Bernier , Maria Plakhotnik
ED492742 - An Examination of Qualitative Empirical Studies at the AHRD from 1999-2003: Research Purpose, Research Questions, and Inquiry Literature Cited.
RELATED PAPERS
Chaundra L. Whitehead
Drea Zigarmi
Ciaran McFadden , Tonette S Rocco
New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development
Diane Chapman , Nancy C. Hunt-Fire , Tonette S Rocco , Nancy Fire
Tonette S Rocco , Maria Plakhotnik
Sunyoung Park
Usman Ghani
Drea Zigarmi , Brad Shuck
Human Resource Development …
Robin S. Grenier
Research on Humanities and Social Sciences
Nana Oppong
Ian Baptiste
Brad Shuck , A. Herd
Ronan Carbery
Tonette S Rocco , Linda Bliss
zakia ghani
Tonette S Rocco , Judith Bernier
ΡΙΤΑ ΠΟΥΠΑΚΗ
farouk iddrisu
Human Resource Development Quarterly
Khalil Dirani
HTTP://EDUCATION. FIU. EDU/ …
Sanghamitra Chaudhuri
mahdi kateb
Vicky Zygouris-Coe
Jamie Callahan
Rajendran Raju
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Political Alternation in the Azores, Madeira and the Canary Islands pp 15–34 Cite as
Theoretical Framework and Literature Review
- Teresa Ruel 6
- First Online: 01 October 2020
129 Accesses
Part of the book series: Palgrave Studies in Sub-National Governance ((PSSNG))
This chapter advances the theoretical framework and the major contributions of political science that are critical to frame my argument. It defines the concepts and a body of studies that will help to address my research puzzle. This chapter is structured as follow: first it looks at democracy literature and party competition; secondly it discusses the key-concept of this book—political alternation—and the scholarly contributions that have been developed on this topic, connecting the perspectives. Finally, it addresses through the regional politics literature the major research advances to the topic.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Contested concepts are “concepts the proper use of which inevitably evolves endless disputes about their proper uses on the part of their users” (Gallie, 1956 , p. 167).
Schumpeter adds other conditions: (1) appropriate leadership; (2) the effective range of policy decision should not be extended too far; (3) the existence of a well-trained bureaucracy of good standing and tradition, endowed with a strong sense of duty and a no less strong esprit de corps; (4) political leaders should practice a good amount of democratic self-control and mutual respect; (5) a large measure of tolerance for difference of opinion, and (6) all the interests that matter must be nearly unanimous not only in their allegiance to the country but also to the structural principles of the existing society (Schumpeter, 1942 /2003, pp. 289–296).
Sartori considers the length of incumbency (three consecutive legislatures at least) and the threshold of 50% of seats ( 1976 , p. 196).
Pempel established four dimensions of party dominance: (1) a party must be dominant in numbers, it must hold more legislative seats than its opponents; (2) a party must enjoy a dominant bargaining position over other parties; (3) a party must be dominant in terms of time in power and (4) a party must be dominant in the public office ( 1990 , pp. 3–4).
Alesina, A., & Rosenthal, H. (1989). Partisan cycles in congressional elections and the macroeconomy. American Political Science Review, 83 (2), 373–398. https://doi.org/10.2307/1962396
Alesina, A., & Rosenthal, H. (1995). Partisan politics, divided government, and the economy . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Anderson, C. D. (2006). Economic voting and multilevel governance: A comparative individual-level analysis. American Journal of Political Science, 50 , 449–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5907.2006.00194.x
Article Google Scholar
Andrews, J., & Jackman, R. (2008). If winning isn’t everything, why do they keep score? Consequences of electoral performance for party leaders. British Journal of Political Science, 38 (4), 657–675. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000712340800032X
Aron, R. (1982). Alternation in government in the industrialized countries. Government and Opposition, 17 (1), 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1477-7053.1982.tb00675.x
Bäck, H., Debus, M., Müller, J., & Bäck, H. (2013). Regional government formation in varying multi-level contexts: A comparison of eight European countries. Regional Studies, 47 (3), 368–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2012.733072
Beetham, D., Bracking, S., Kearton, I., & Weir, S. (2002). The IDEA handbook on democracy assessment . The Hague: IDEA/Kluwer Law International.
Google Scholar
Blondel, J. (1968). Party systems and patterns of government in western democracies. Canadian Journal of Political Science, 1 (2), 180–203. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0008423900036507
Bobbio, N. (1987). The future of democracy: A defense of rules of the game . Polity Press.
Bogaards, M., & Boucek, F. (2010). Dominant political parties and democracy: Concepts, measures, cases and comparisons . London and New York: Routledge/ECPR Studies in European Political Science.
Bratton, M., & van de Walle, N. (1997). Democratic experiments in Africa: Regime transitions in comparative perspective . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Bueno de Mesquita, B., Smith, A., Siverson, R., & Morrow, J. (2005). The logic of political survival . Cambridge: MIT Press.
Collier, D., & Lewinsky, S. (1997). Democracy with adjectives: Conceptual innovation in comparative research. World Politics, 49 (3), 430–451.
Cox, G. (1997). Making votes count . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Curini, L., & Zucchini, F. (2012). Government alternation and legislative party unity: The case of Italy 1988–2008. West European Politics, 35 (1), 826–846.
Dahl, R. (1966). Political opposition in western democracies . New-Haven: Yale University Press.
Dahl, R. (1971). Polyarchy: Participation and opposition . New Haven: Yale University Press.
Dahl, R. (1989). Democracy and its critics . New-Haven: Yale University Press.
Dandoy, R., & Schakel, A. (Eds.). (2013). Regional and national elections in Western Europe: Territoriality of the vote in thirteen countries . Basingstoke: Palgrave.
Däubler, T., & Debus, M. (2009). Government formation and policy formulation in the German states. Regional and Federal Studies, 19 (1), 73–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/13597560802692322
De Winter, L., & Tursan, T. (Eds.). (1998). Regionalist parties in Western Europe . London: Routledge.
Debus, M. (2008). Party competition and government formation in multi-level settings: Evidence from Germany. Government and Opposition, 43 , 505–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1477-7053.2008.00267.x
Deschouwer, K. (2009). The rise and fall of the Belgian regionalist parties. Regional & Federal Studies, 19 (4–5), 559–577. https://doi.org/10.1080/13597560903310279
Di Palma, G. (1990). Craft democracies: An essay on democratic transitions . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Diamond, L. (1999). Developing democracy: Toward consolidation . Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Diamond, L., & Morlino, L. (Eds.). (2005). Assessing the quality of democracy . Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Downs, A. (1957). An economic theory of democracy . New York: Harper and Brothers.
Duverger, M. (1954). Political parties: Their organization and activity in the modern state . New York: Wiley.
Duverger, M. (1959). Political parties: Their organization and activity in the modern state . New York: Wiley.
Falcó-Gimeno, A., & Verge, T. (2013). Coalition trading in Spain: Explaining state-wide parties’ government formation strategies at the regional level. Regional & Federal Studies, 23 (4), 387–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/13597566.2012.758115
Gallie, W. B. (1956). Essentially contested concepts. Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society, 56 (1), 167–198. https://doi.org/10.1093/aristotelian/56.1.167
Gerring, J. (2001). Social science methodology: A criterial framework . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gibson, E. (2005). Boundary control: Subnational authoritarianism in democratic countries. World Politics, 58 (1), 101–132. https://doi.org/10.1353/wp.2006.0018
Goertz, G. (2006). Concept intension and extension. In Social science concepts: A user’s guide . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Greene, K. (2007). Creating competition: Patronage politics and the PRI’ demise . Working Paper #345, Kellogg Institute.
Hansen, M. H. (1991). The Athenian democracy in the age of Demosthenes . Oxford: Blackwell.
Horowitz, S., Hoff, K., & Milanovic, B. (2009). Government turnover: Concepts, measures and applications. European Journal of Political Research, 48 , 107–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6765.2008.00827.x
Hough, D., & Jeffery, C. (Eds.). (2006). Devolution and electoral politics . Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Ieraci, G. (2012). Government alternation and patterns of competition in Europe: Comparative data in search of explanations. West European Politics, 35 (3), 530–550. https://doi.org/10.1080/01402382.2012.665739
Jeffery, C., & Hough, D. (2003). Regional elections in multilevel systems. European Urban and Regional Studies, 10 (3), 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1177/09697764030103002
Kaiser, A., Lenhet, B., Miller & Sieberer, U. (2002). The democratic quality of institutional regimes: A conceptual framework. Political Studies, 50 (2), 313–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9248.t01-1-00372 .
Kelsen, H. (1988/1929). La Démocratie. Sa Nature—Sa Valeur. Paris: Economica.
Key, V. O. (1953). Politics, parties and pressure groups . Tomas Y. Crowell Company.
King, G., Burns, J., & Laver, M. (1990). A unified model of cabinet dissolution in parliamentary democracies. American Journal of Political Science, 34 (3), 846–871.
Laver, M. (2003). Government termination. Annual Review of Political Science, 6 (1), 23–40. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.polisci.6.121901.085530
León, S. (2012). How citizens attribute responsibility in multilevel states? Learning biases and asymmetric federalism: Evidences from Spain. Electoral Studies, 31 , 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electstud.2011.09.003
Levintsky, S., & Way, L. (2010). Competitive authoritarianism: Hybrid regimes after the Cold War . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lijphart, A. (1994). Electoral systems and party systems: A study of twenty-seven Democracies, 1945–1990 . New York: Oxford University Press.
Lipset, S. M. (1963). Political man—The social bases of politics . Doubleday Anchor Books.
Mair, P. (1996). Party systems and structures of competition. In L. Niemi LeDuc & P. Norris (Eds.), Comparing democracies—Elections and voting in global perspective . London: Sage Publications.
Mair, P. (1997). Party system change—Approaches and interpretations . Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Mair, P. (2007). Party systems and alternation in government, 1950–2000: Innovation and institutionalization. In S. Gloppen & L. Rakner (Eds.), Globalisation and democratisation: Challenges for political parties . Fagbokforlaget: Bergen.
Mair, P. (2008). Concepts and concept formation. In D. Della Porta & M. Keating (Eds.), Approaches and methodologies in the social sciences—A pluralist perspective . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Manin, B. (1997). The principles of representative government . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Cambridge.
Morlino, L. (1998). Democracy between consolidation and crisis: Parties, groups and citizens in Southern Europe . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
O’Donnell, G. (2004). Democracy, human rights and human development. In G. O’Donnell, J. V. Cullell, & O. M. Iazzetta (Eds.), The quality of democracy: Theory and applications . Indiana: Notre Dame University Press.
Online Oxford English Dictionary. n.d.
Pallarés, F., & Keating, M. (2003). Multi-level electoral competition: Regional elections and party systems in Spain. European Urban and Regional Studies, 10 (3), 239–255. https://doi.org/10.1177/09697764030103005
Pasquino, G. (2011). Teorizzare l’alternanza, la sua pratica e la sua mancanza. In G. Pasquino & M. Valbruzzi (Eds.), Il potere dell'alternanza: teorie e ricerche sui cambi di governo . Bologna: Bologna University Press.
Pempel, T. J. (1990). Uncommon democracies: The one-party dominance regime . Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
Powell, B. G. (1984). Party systems and election outcomes. In Contemporary democracies—Participation, stability and violence . President and Fellows of Harvard College, Congress Cataloguing in Publication Data.
Przeworski, A. (1991). Democracy and the market—Political and economic reforms in Eastern Europe and Latin America . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Przeworski, A. (1999). Minimalist conception of democracy: A defense. In I. Shapiro & C. Hacker-Cordón (Eds.), Democracy’s value . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Przeworski, A. (2005). Democracy as an equilibrium. Public Choice, 123 , 253–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11127-005-7163-4
Przeworski, A. (2009). Self-government in our times. Annual Review of Political Studies, 12 , 71–92. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.polisci.062408.120543
Przeworski, A. (2010). Democracy and the limits of self-government . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Przeworski, A., Alvarez, M., Cheibub, A., & Limongi, F. (2000). Democracies and dictatorships. In Democracy and development: Political institutions and well-being in the world 1950–1990 . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Riker, W. (1965/1982). Liberalism against populism: A confrontation between the theory of democracy and the theory of social choice . San Francisco: W.H. Freeman.
Riker, W. (1976). The number of political parties: A reexamination of Duverger’s law. Comparative Politics, 9 (1), 93–106. https://doi.org/10.2307/421293
Riker, W. (1981). A confrontation between the theory of social choice and the theory of democracy. In R. L. Braham (Ed.), Social justice . Dordrecht: Springer.
Rokkan, S. (1968). The comparative study of nation-building. International Social Science Council, 7 (3), 51–52.
Rokkan, S., & Urwin, D. (1983). Economy, territory, identity: Politics of West European peripheries . London: Sage.
Samuels, D. (2004). Presidentialism and accountability for the economy in comparative perspective. American Political Science Review, 98 (3), 425–436. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000305540400125X
Sartori, G. (1970). Concept misformation in comparative politics. The American Political Science Review, 64 (4), 1033–1053. https://doi.org/10.2307/1958356
Sartori, G. (1976). Parties and party systems—A framework of analysis . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Schakel, A. (ed.). (2017). Regional and national elections in Eastern Europe. Territoriality of the vote in ten countries . Houndmills: Palgrave Macmillan. https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-51787-6
Schakel, A., & Massetti, E. (2018). A world of difference: The sources of regional government composition and alternation. West European Politics, 41 (3), 703–727. https://doi.org/10.1080/01402382.2017.1400237
Schlesinger, J. (1984). On the theory of party organization. The Journal of Politics, 46 (2), 369–400.
Schmitter, P., & Karl, T. (1991). What democracy is …. and is not. Journal of Democracy, 2 (3), 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1353/jod.1991.0033
Schumpeter, J. (1942/2003). Capitalism, socialism and democracy . New York: Routledge.
Snyder, R. (2001). Scaling down: The subnational comparative method. Studies in Comparative International Development, 36 (1), 93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02687586
Ştefuriuc, I. (2009). Government formation in multi-level settings: Spanish regional coalitions and the quest for vertical congruence. Party Politics, 15 (1), 93–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354068808097895
Thorlakson, L. (2007). An institutional explanation of party system congruence: Evidence from six federations. European Journal of Political Research, 46 , 69–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6765.2006.00647.x
Vampa, D. (2018). Developing new measures of party dominance: Definition, operationalization and application to 54 European regions. Government and Opposition, 55 (1), 88–113. https://doi.org/10.1017/gov.2018.12
Ware, A. (1996). Political parties and party system . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Warwick, P. V. (1994). Government survival in parliamentary democracies . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Whithead, L. (2002). Democratization: Theory and experience . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal
Teresa Ruel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Ruel, T. (2021). Theoretical Framework and Literature Review. In: Political Alternation in the Azores, Madeira and the Canary Islands. Palgrave Studies in Sub-National Governance. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53840-8_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53840-8_2
Published : 01 October 2020
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-53839-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-53840-8
eBook Packages : Political Science and International Studies Political Science and International Studies (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
What is the Difference Between Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
The main difference between literature review and theoretical framework is their function. The literature review explores what has already been written about the topic under study in order to highlight a gap, whereas the theoretical framework is the conceptual and analytical approach the researcher is going to take to fill that gap.
Literature review and theoretical framework are two indispensable components of research . Both are equally important for the foundation of a research study.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is Literature Review – Definition, Features 2. What is Theoretical Framework – Definition, Features 3. Difference Between Literature Review and Theoretical Framework – Comparison of Key Differences

What is a Literature Review
A literature review is a vital component of a research study. A literature review is a discussion on the already existing material in the subject area. Thus, this will require a collection of published (in print or online) work concerning the selected research area. In other words, a literature review is a review of the literature in the related subject area. A literature review makes a case for the research study. It analyzes the existing literature in order to identify and highlight a gap in the literature.

Moreover, a good literature review is a critical discussion, displaying the writer’s knowledge of relevant theories and approaches and awareness of contrasting arguments. A literature review should have the following features (Caulley, 1992)
- Compare and contrast different researchers’ views
- Identify areas in which researchers are in disagreement
- Group researchers who have similar conclusions
- Criticize the methodology
- Highlight exemplary studies
- Highlight gaps in research
- Indicate the connection between your study and previous studies
- Indicate how your study will contribute to the literature in general
- Conclude by summarizing what the literature indicates
Furthermore, the structure of a literature review is similar to that of an article or essay . Overall, literature reviews help researchers to evaluate the existing literature, identify a gap in the research area, place their study in the existing research and identify future research.
What is a Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework is the research component that introduces and describes the theory that explains why the research problem under study exists. It is also the conceptual and analytical approach the researcher is going to take to fill the research gap identified by the literature review. Moreover, it is the structure that holds the structure of the research theory.
The researcher may not easily find the theoretical framework within the literature. Therefore, he or she may have to go through many research studies and course readings for theories and models relevant to the research problem under investigation. In addition, the theory must be selected based on its relevance, ease of application, and explanatory power.
Difference Between Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
A literature review is a critical evaluation of the existing published work in a selected research area, while a theoretical framework is a component in research that introduces and describes the theory behind the research problem.
Moreover, the literature review explores what has already been written about the topic under investigation in order to highlight a gap, whereas the theoretical framework is the conceptual and analytical approach the researcher is going to take to fill that gap. Therefore, a literature review is backwards-looking while theory framework is forward-looking.
In conclusion, the main difference between literature review and theoretical framework is their function. The literature review explores what has already been written about the topic under study in order to highlight a gap, whereas the theoretical framework is the conceptual and analytical approach the researcher is going to take to fill that gap.
1. Caulley, D. N. “Writing a critical review of the literature.” La Trobe University: Bundoora (1992). 2. “ Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Theoretical Framework .” Research Guide.
Image Courtesy:
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
- Systematic review
- Open access
- Published: 16 April 2024
Identifying barriers and facilitators to primary care practitioners implementing health assessments for people with intellectual disability: a Theoretical Domains Framework-informed scoping review
- Paul Caltabiano 1 , 2 ,
- Jodie Bailie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4393-5773 3 , 4 ,
- Alison Laycock ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7756-4398 3 ,
- Bradley Shea 2 , 3 ,
- Sally Hall Dykgraaf ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8532-1086 5 ,
- Nicholas Lennox ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3201-3186 6 ,
- Kanchana Ekanayake ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4324-311X 7 &
- Ross Bailie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5966-3368 8
Implementation Science Communications volume 5 , Article number: 39 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Introduction
People with intellectual disability experience poorer health outcomes compared with the general population, partly due to the difficulties of accessing preventive care in primary care settings. There is good evidence that structured annual health assessments can enhance quality of care for people with intellectual disability, and their use has become recommended policy in several high-income countries. However, uptake remains low. The Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF) offers a conceptual structure for understanding barriers to implementation and has been usefully applied to inform implementation of health assessments for other high-need groups, but not for people with intellectual disability. We conducted a scoping review of the literature, using the TDF, to identify barriers and facilitators influencing primary care practitioners’ implementation of annual health assessments for people with intellectual disability as part of routine primary care practice.
This study was conducted according to the JBI methodological approach for scoping reviews. Searches were conducted in Medline (OVID-SP), Embase (OVID-SP), PsycINFO (OVID-SP), CINHAL (EBSCO), Scopus (Elsevier) and Web of Science (Clarivate) for relevant peer-reviewed publications up to May 2023. Screening, full-text review and data extraction were completed by two independent reviewers. Data were extracted and mapped to the TDF to identify relevant barriers and facilitators.
The search yielded 1057 publications, with 21 meeting the inclusion criteria. Mapping data to the TDF, the most frequently identified domains were (a) environmental context and resources, (b) skills, (c) knowledge and (d) emotion. Predominant factors impacting on implementation included practitioners’ lack of awareness about health assessments and their identified benefits; inadequate training and experience by practitioners in the delivery of health assessments for people with intellectual disability; insufficient time to provide health assessments; and practitioner burnout.
Using a theory-informed behavioural framework, our review aids understanding of the barriers and facilitators to improving the implementation of health assessments as part of routine care for people with intellectual disability. However, there is a clear need for further qualitative research to examine the perceptions of primary care practitioners regarding implementation barriers and facilitators to health assessments in general, including views from practitioners who are not currently undertaking health assessments.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to the literature
Using a theory-informed behavioural framework, this scoping review systematically identifies and categorises barriers and facilitators affecting primary care practitioners’ implementation of structured annual health assessments for people with intellectual disability.
Barriers and facilitators to implementation were most frequently mapped to the following framework domains: (a) environmental context and resources, (b) skills, (c) knowledge and (d) emotion.
There is a need for further qualitative research to examine the perceptions of primary care practitioners regarding implementation barriers and facilitators to health assessments in general, and to ensure that the views of primary care practitioners not currently providing health assessments are investigated.
People with intellectual disability experience higher rates of mortality [ 1 ] and morbidity [ 2 ] compared with the general population. These additional health burdens are present across the life-course and are often ineffectively managed or under-recognised [ 3 ]. Inadequate access to preventive care is thought to contribute to inequitable health outcomes for people with intellectual disability [ 4 ].
To address these health disparities, structured comprehensive annual health assessments for people with intellectual disability, delivered in primary care settings, have become a feature of health policies in some high-income countries [ 5 , 6 ]. These assessments are best viewed as a vehicle for improving the delivery of evidence-based preventive care and have been used to target priority population groups, such as people with intellectual disability, the elderly, children and, in Australia, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
Multiple publications, including a systematic review that synthesised evidence from 80 studies in the UK [ 7 ], have found that health assessments for people with intellectual disability identify new health needs [ 8 , 9 ], improve the management of existing health needs [ 10 , 11 ] and enable the provision of health promotion [ 8 , 12 , 13 ]. Crucially, patients with intellectual disability who receive regular health assessments have a lower mortality rate than those who do not [ 14 ]. Despite this evidence, uptake of annual health assessments in primary care has been low [ 9 , 15 ].
The Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF) was initially developed and validated by behavioural scientists to identify behavioural barriers and facilitators related to the implementation of evidence-based recommendations among health professionals [ 16 , 17 ]. The TDF, which has 14 theoretical domains and 84 constructs derived through a systematic expert consensus process, provides a basis for understanding the broad set of factors that may influence behaviours (Table 1 ). It has also been used as a framework for synthesising behavioural influences in reviews reporting perceived barriers and facilitators, including: the adoption of prescribing guidelines [ 18 ], the de-implementation of low-value care [ 19 ], and the treatment and transfer of acute stroke patients in emergency care settings [ 20 ].
In addition, the TDF has been used to examine the uptake of health assessments for targeted population groups, such as for people with autism [ 21 ], children [ 22 ] and adults with cardiovascular disease [ 23 ]. However, to date it has not been used to understand determinants of effective implementation of health assessments for people with intellectual disability.
By assessing the published literature against the TDF, we aimed to identify and categorise barriers and facilitators that influence the implementation of structured health assessments for people with intellectual disability as part of routine practice in primary care. We anticipate that our review findings will contribute to a greater understanding of implementation barriers and facilitators and how they operate to influence practitioner behaviour.
Scoping review methodology was selected because our purpose was to systematically identify and characterise the breadth of research that exists around implementation factors, and distinguish the barriers and facilitators to implementation of preventive health assessments [ 24 , 25 ]. This review drew on methodological guidance for scoping reviews from JBI [ 26 ], and was conducted in accordance with a published a priori protocol [ 27 ]. Reporting was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist [ 28 ]. Critical appraisal and risk of bias assessment were not conducted, consistent with JBI methodology for scoping reviews.
Stage 1: research question
The research question was: ‘What are the barriers and facilitators to primary care practitioners implementing comprehensive health assessments as part of routine practice in primary care for people with intellectual disability?’
Stage 2: relevant literature identification
An initial search of Medline (OVID-SP) and Google Scholar was conducted to identify key publications on the topic and develop a list of search terms. A full search strategy for MEDLINE (OVID-SP) was subsequently developed in consultation with an academic librarian (KE) and research experts in the fields of preventive health assessments, primary care and disability (SHD, NL, RB, JB, BS, AL). The search was then systematically repeated in Medline (OVID-SP), Embase (OVID-SP), PsycINFO (OVID-SP), CINHAL (EBSCO), Scopus (Elsevier) and Web of Science (Clarivate). Database searches were conducted on 1 May 2023. The final search strategy can be found in Additional file 1 . Grey literature and theses were not searched.
Stage 3: study selection
All identified citations were uploaded into COVIDENCE [ 29 ], a web-based review platform, and duplicates removed. Following a pilot review, we undertook title and abstract screening and then full-text review using predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria (Table 2 ). Two reviewers (PC and JB) independently conducted all stages, with disagreements resolved through discussion.
Stage 4: data extraction
A data extraction template, developed within COVIDENCE and based on the scoping review template by JBI, was utilised. The template considered the methodological and design characteristics of each publication, study setting, and factors influencing uptake or implementation of health assessments. The data extraction tool underwent a pilot phase using two randomly selected publications. Following refinement through discussion, the tool was updated before application to the remaining publications (Additional file 2 ). Data extraction was carried out independently by JB and PC.
Stage 5: data analysis and presentation
As data were extracted, JB and PC independently deductively coded according to the single most relevant TDF domain. To do this, JB and PC read the whole publication, and then line-by-line considered the relevance to the definitions of each domain, attributing the data to the most relevant domain. To guide the data extraction and coding we developed a code book a priori . This code book was updated iteratively throughout the data extraction and analysis process by PC and JB. To facilitate consensus for coding extracted data to the most relevant TDF domain, JB and PC articulated their understanding of the coded text (i.e. key meaning) and justified their rationale for selecting the TDF domain by writing notes. JB and PC meet regularly, and resolved through discussion any differences in understanding of the most relevant domain the data should be coded to. Examples of data coded and categorised is provided in Table 3 .
Data coded to TDF domains were analysed in a recursive process that followed the steps of content analysis outlined by Elo and Kyngas [ 35 ]. Specifically:
PC and JB independently immersed themselves in the extracted data, reading and re-reading publications to get a sense of the whole, primarily to gain a general understanding of the data that had been deductively coded to TDF domains.
Within each TDF domain, PC and JB coded data as barriers or facilitators, writing notes and headings describing the content. ‘Barriers’ were defined as behaviours that impeded the implementation of health assessments, and ‘facilitators’ those that promoted health assessments. Examples of coded data categorised as a barrier or facilitator are detailed in Table 3 .
Building on the initial categorisation of barriers and facilitators, PC and JB developed higher level ‘factors’ that described the barrier/and or facilitator.
Through a process of comparison, rereading and revisiting source publications to review context, PC and JB refined the barriers, facilitators, and factors within each TDF domain.
During analysis it became apparent that study participants within some publications perceived the same factor differently. Consequently, a TDF domain could be mapped as both a barrier and a facilitator for the same publication. For example, some practitioners within a publication had known of or were already implementing health assessments for people with intellectual disability, whereas others within the same publications were unaware. Throughout this process, PC and JB conferred to resolve any differences in categorisation or perceptions of relevance. This included reflection sessions between PC and JB, and collaboration with authors RB and AL. To ensure consistency, all authors, drawing on their experience, checked the results against their understanding of how targeted preventive health interventions were implemented in primary care, any access barriers to primary care for people with intellectual disability and the TDF itself.
Search results and publication selection
The search yielded 1057 publications. After duplicate removal, title and abstract screening, and full-text review, 21 publications were included as depicted in Fig. 1 .

PRISMA-ScR flow diagram
Characteristics of included studies
The characteristics of the 21 included publications, derived from 20 studies, are presented in Table 4 . The majority were qualitative study designs ( n =12). All included publications were undertaken in one of four high-income countries, presented here in descending order by frequency: United Kingdom ( n =14) [ 33 , 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], Australia ( n =3) [ 30 , 31 , 44 ], Canada ( n =3) [ 12 , 42 , 47 ], and the Netherlands ( n =1) [ 32 ]. Most were published between 2011 and 2023 ( n =15), with the remaining ( n =6) published between 1996 and 2002. The majority did not specify the rurality of the study setting, but five did include regional or rural perspectives [ 31 , 45 , 48 , 49 , 50 ]. Some publications had the primary care practice as the unit of analysis ( n =8), whereas others included perspectives solely from individual general medical practitioners (GPs) ( n =7), both GPs and practice nurses ( n =5), or practice nurses alone ( n =1). Most publications ( n =13) were set in primary care practices that were already implementing health assessments. Two publications from one study included people with intellectual disability as part of the research team [ 48 , 49 ].
Barriers and facilitators to implementation
In our review of the barriers and facilitators influencing practitioners’ behaviour regarding the implementation of health assessments, data were most frequently coded to the following TDF domains: a) environmental context and resources, b) skills, c) knowledge, and d) emotion. The frequency of each TDF domain is presented in Table 5 .
Domain 1: Knowledge
Factors identified within 13 publications corresponded to the knowledge domain. In the context of this review, this domain encompasses the awareness, or lack thereof, of vital information regarding people with intellectual disability and health assessments. Some practitioners expressed a lack of awareness regarding the adverse health outcomes experienced by people with intellectual disability [ 12 , 32 , 48 ], a lack of understanding about the assessments themselves [ 12 , 31 , 36 ] and unfamiliarity with their proven health benefits [ 30 , 31 , 33 , 45 , 46 , 50 ]. Although some GPs questioned the need for any screening at all in this patient group [ 45 ], others were aware of [ 12 , 30 , 43 , 44 ], and acknowledged the existence [ 31 , 45 ] and benefits of, health assessments [ 30 , 34 ]. More specific barriers included a lack of knowledge regarding precise codes in clinical information systems to identify patients with intellectual disability [ 32 , 50 ], and of evidence-based preventive care guidelines [ 31 ].
Domain 2: Skills
Sixteen publications identified factors corresponding to the skills domain, which in the context of this review refers to practitioners’ perspectives about possessing the training and skills required to perform the health assessments. Communication difficulties as a primary obstacle in conducting the health assessments were identified in six publications [ 30 , 32 , 34 , 41 , 48 ]. For example, practitioners may rely on support workers to communicate with the patient, which has the potential for diminishing the patient’s autonomy and ability to communicate effectively [ 40 ]. Conversely, this same publication suggested that interacting directly with the patient establishes both respect for, and empowerment of, the patient. One practice attempted to overcome barriers to communication by assigning all contact with patients to the member of their staff who had the most skills in, and comfort with, communicating with people with intellectual disability [ 42 ].
Other barriers mapped included both inadequate exposure to people with intellectual disability, and not enough relevant curriculum content throughout medical school as well as a lack of advanced training in this area [ 12 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 45 , 47 , 48 ]. Practitioners also recommended further education on the delivery of care to people with intellectual disability [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 38 , 44 , 47 , 50 ], and on how to conduct their health assessments [ 33 , 34 , 36 ]. There were a number of GPs who expressed the belief that all patients should be treated the same, which simply highlights the lack of training about the need for reasonable adjustments for people with intellectual disability and targeted interventions to ensure access to care [ 12 , 48 , 50 ].
Domain 3: Social/professional role and identity
Factors identified within 10 publications corresponded to the social/professional role and identity domain, which in the context of this review covers the recognition that it is the practitioners’ responsibility to conduct health assessments. While most GPs acknowledged their responsibility to provide medical care to people with intellectual disability, some did not feel that it was their responsibility to undertake a yearly health assessment [ 37 , 43 , 45 ]. Others sought further clarity about the role before committing, as they felt out of their depth [ 30 , 34 ]. Conversely, several practitioners acknowledged that since people with intellectual disability live in the community, the initiation and management of medical care falls within the remit of general practice [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 37 , 45 , 47 , 50 ]. There were contradictory views regarding whose role it was to follow up any abnormal findings or referrals required as part of the health assessment. Some practitioners felt themselves to be responsible in ensuring that these plans are followed up and monitored [ 50 ], whereas others were confused as to whose role this was [ 47 ].
Domain 4: Beliefs about capabilities
Factors identified within seven publications corresponded to the beliefs about capabilities domain, which in the context of this review encompasses practitioners’ level of confidence in their ability to conduct health assessments. Practitioners at times felt unprepared, incompetent and/or lacked confidence in their ability to perform all aspects of the health assessments, thereby creating a barrier to their implementation [ 12 , 32 , 39 , 46 ]. However, as identified in four publications, some practitioners felt comfortable with caring for people with intellectual disability [ 34 ] and believed themselves to be capable of providing adequate care without having a special interest in the patient population [ 12 , 31 , 47 ].
Domain 5: Optimism
Factors identified within nine publications corresponded to the optimism domain, which in the context of this review refers to the general belief that health assessments are worthwhile, without specifying any expected outcomes. Barriers to implementing the health assessments were identified in six publications, specifically practitioners’ scepticism about the value of screening [ 31 , 34 , 45 , 46 , 48 ] and their inability to perceive any associated benefits from providing the assessments [ 30 ]. Conversely, a sense of optimism among practitioners that assessments were beneficial for patients was identified in seven publications [ 12 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 47 , 48 ].
Domain 6: Beliefs about consequences
Factors identified within 10 publications corresponded to the beliefs about consequences domain, which in the context of this review relates to understanding the potential outcomes of providing health assessments. The majority of publications identified the provision of health assessments as a facilitating factor both for practitioners [ 12 , 32 , 47 ] and for support workers [ 30 ] to gain further knowledge on how best to care for patients with intellectual disability. The assessments were also seen as a means of building collaboration between the parties involved [ 44 , 47 ], and of further developing the practitioner–patient relationship through enhanced continuity of care [ 32 , 47 , 48 ]. Furthermore, there was a common belief among practitioners that assessments specifically lead to an improvement in health outcomes for those patients who utilise them [ 30 , 32 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 48 , 50 ]. However, a perception that more evidence on the benefits of health assessments was required to support their implementation was identified in three publications [ 31 , 32 , 43 ].
Domain 7: Reinforcement
Factors identified within seven publications corresponded to the reinforcement domain, which in the context of this review looks at the incentives needed to influence the implementation of health assessments. Five publications indicated that practitioners believed there is insufficient financial compensation for the extra time required to prepare for and provide these assessments [ 12 , 32 , 38 , 47 , 48 ]. However, in two other publications, these sentiments were contradicted, with participants claiming that there was adequate compensation both to implement health assessments [ 31 ] and to attend the necessary training [ 42 ].
Domain 8: Intentions
Factors identified within nine publications corresponded to the intentions domain, which in the context of this review relates to how inclined practitioners are to provide health assessments to people with intellectual disability. Barriers to this included a perceived lack of willingness to do so [ 47 ], an explicit admission that the provision of health assessments was not a priority [ 42 ] and a general lack of interest in providing care for people with intellectual disability at all [ 30 ]. Additionally, some practices had practitioners attempting to conduct the assessment within a 15-min consultation, thereby demonstrating a lack of intent to provide a comprehensive service [ 36 , 48 ]. Practitioners who were facilitating the implementation of health assessments were driven either by a personal interest [ 33 , 45 , 50 ] or a practice-wide focus [ 42 ]. Practices that intended to implement reasonable adjustments—including the offer of home visits [ 48 ], weekend clinics [ 36 ], greater choice in appointment times, reduced wait times [ 50 ] and the provision of Easy Read heath information [ 39 ]—were identified in four publications.
Domain 9: Goals
A factor identified within one publication corresponded to the goals domain, which indicated that a practice had set a specific goal of providing health assessments to 75% of its patients with intellectual disability within an 18-month period [ 42 ]. This facilitating factor demonstrated a commitment to the goal of promoting the delivery of health assessments and to improving the quality of care to people with intellectual disability.

Domain 10: Memory, attention and decision processes
Factors identified within seven publications corresponded to the memory, attention and decision processes domain. In the context of this review, this domain relates to the ability to remember, or to pay attention to, the relevant information needed to make informed decisions relating to health assessments. Barriers identified in seven publications were associated with actually identifying people with intellectual disability due to the lack of a sufficient pre-existing registry or list of eligible patients on clinical information systems [ 32 , 33 , 36 , 42 , 43 , 48 , 50 ]. One of the publications described a practice that utilised an alert system to inform practitioners about upcoming health assessments. Timely reminders such as this are an excellent mechanism to enhance memory and attention [ 42 ].
Domain 11: Environmental context and resources
Factors identified within 18 publications corresponded to the environmental context and resources domain. In the context of this review, this domain refers to the availability of the resources needed to encourage or discourage the implementation of health assessments. Concerns were raised about the ability of support workers and advocates to contribute effectively to the assessment process due to a lack of clarity about their roles [ 30 ], their unfamiliarity with the patients [ 31 ] and even that their involvement could result in disempowering the patients [ 40 ] or practitioner [ 41 ]. However, the important role that support workers play, both in making patients feel comfortable and in encouraging their acceptance of recommended health interventions, was also recognised [ 31 , 33 , 40 , 41 , 45 , 48 , 50 ]. Some practitioners reported that a lack of support workers [ 30 , 38 ], allied health staff or specialist service providers [ 31 , 32 , 37 , 48 ] posed a barrier to conducting health assessments. These professionals were valued for their ability to enhance the process and reduce the time required to perform health assessments [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 37 , 43 , 45 ]. There was a suggestion from several GPs that physicians who specialise in treating patients with intellectual disability could aid in the identification of patients requiring assessment [ 32 ].
A general lack of resources and inadequate time to support the implementation of health assessments were other barriers indicated by practitioners, as assessments not only take longer than standard consultations but also require additional preparation and training [ 12 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 38 , 41 , 42 , 47 , 48 ]. Patient-related barriers identified as acting as a deterrent included the perceived lack of demand for health assessments from people with intellectual disability [ 46 ], their limited access to general practice [ 30 ], practitioners’ difficulties in contacting patients [ 48 ] and the need for longer appointments [ 42 ]. Easy access to patient histories [ 31 , 34 ] and to health assessment template scripts [ 30 , 44 , 47 , 48 ], along with electronic compatibility of these templates with existing information systems, were identified as facilitators [ 42 , 47 ].
Domain 12: Social influence
Factors identified within five publications corresponded to the social influence domain, all of which were mapped as facilitators. In the context of this review, this domain relates to interpersonal processes and relationships that influence the implementation of health assessments, such as the encouragement received from colleagues who shared good practices and provided positive reinforcement [ 50 ]. Additional support for practices to conduct the health assessments came from stakeholder groups [ 37 , 47 ] and communities [ 31 , 44 ] and was also mapped as a motivating factor in their implementation.
Domain 13: Emotion
Factors identified within 12 publications corresponded to the emotion domain, which in the context of this review encompasses the complex feelings and attitudes of practitioners regarding the provision of health assessments. Emotions coded as barriers were identified in nine of these publications with burn-out, the most commonly mentioned, appearing in six [ 34 , 37 , 38 , 43 , 45 , 46 ]. Practitioners with an already high workload expressed concerns about feeling overwhelmed by the additional work required to provide health assessments. Conversely, within six publications facilitating factors were identified with the most frequently mentioned being eagerness to perform assessments [ 32 , 47 , 48 , 50 ] and satisfaction with the care that practitioners were able to provide [ 33 , 34 , 47 ]. Other less commonly identified barriers included anxiety about performing health assessments [ 33 ] and an aversion to completing the checklists [ 32 ], along with the fear of stigmatising patients, particularly if they had not yet received a formal diagnosis of intellectual disability [ 32 , 42 ].
Domain 14: Behavioural regulation
Factors identified within five publications corresponded to the behavioural regulation domain, which in the context of this review refers to the self-monitoring and management of implementation strategies that will continuously improve the health assessment process. Barriers relating to organisational factors were identified in two publications. One highlighted the coordination issues that arise from the regular scheduling of these periodic assessments [ 30 ], while the other described a practice’s difficulties in scheduling patients due to the limitations of its clinical information system [ 50 ]. Facilitating factors identified in two publications included the recruitment of a coordinator to a practice to handle the organisation and uptake of health assessments [ 36 , 50 ] and a proposal by another practice to automate its computer system to prompt staff when a patient was due for their next assessment [ 42 ]. Other facilitating factors mapped related to whether practices actively sought [ 33 , 42 ] or responded to feedback from patients and their families. Feedback that was thought to improve the implementation of health assessments was identified in three publications [ 50 ].
This scoping review identified a range of barriers and facilitators that influence the implementation of health assessments in primary care for people with intellectual disability. These were mapped to each of the 14 TDF domains. Potential barriers and facilitators were identified within each domain. The most commonly identified barriers were a lack of awareness regarding the availability and advantages of health assessments specifically targeting individuals with intellectual disability, and concerns about a perceived deficiency in the training and experience of the health care professionals conducting these assessments. Time constraints, lack of availability of staff to support health assessment processes, and practitioner burnout given already high workloads also emerged as barriers. A further barrier to implementation was the inability of many practices to identify the records of patients with intellectual disability in primary care clinical information systems.
Conversely, several facilitators were identified and mapped. Primary care professionals recognised their role in providing health assessments to people with intellectual disability and an eagerness to provide preventive health care. Also identified was a belief in the overall effectiveness of assessments in improving health outcomes, and the potential for these health assessments to facilitate care coordination among practitioners, support personnel and others. Access to resources such as health assessment template scripts, complemented by the electronic compatibility of these templates with existing information systems, was highlighted as pivotal in supporting successful implementation.
The most frequently mapped TDF domains were as follows: (a) environmental context and resources, (b) skills, (c) knowledge and (d) emotion. The predominance of the environmental context and resources domain identified in this review is consistent with other studies that have utilised the TDF to assess barriers and facilitators to accessing preventive health care [ 22 , 23 , 51 ]. It is also in line with contemporary evidence about the importance of taking a systems perspective when implementing interventions [ 52 ]. Under-reported in our review were the domains of (a) goals, (b) behavioural regulation and (c) social influences. Similarly, Atkins and colleagues [ 23 ] undertook a systematic review using the TDF to examine the uptake of health assessments for people aged 40–74 years in the UK and found a paucity of reporting of the TDF domains related to goals and behavioural regulation. Interestingly, our study differed with Atkins and colleagues [ 23 ] in that we found a deficit in the reporting of barriers and facilitators related to social influences whereas they did not. There is a need for further inquiry into these three TDF domains to ensure that primary care practices have a nuanced understanding of the barriers and facilitators to implementation of health assessments for people with an intellectual disability.
Consistent with our review, common findings across studies that have used the TDF to examine uptake of health assessments for other targeted population groups have included the perception that practitioners are inadequately trained in the delivery of comprehensive health assessments [ 22 , 23 ] the belief that screening and preventive care should be performed by specialists in the respective patient population’s field [ 22 , 23 ] and a perceived lack of knowledge about relevant health information relating to the patient group [ 21 , 22 ].
A key finding in our review was that many practitioners identified a lack of skills, knowledge and confidence in providing preventive health care to people with intellectual disability. This is unsurprising given that audits of medical and nursing curricula in Australia revealed that, on average, less than 6 h of teaching time was devoted to intellectual disability throughout any of the degree programmes, with the majority of nursing schools providing none [ 53 , 54 ]. The Royal Commission into Violence, Abuse, Neglect and Exploitation of People with Disability, established in 2019, found that Australian health professionals often do not have the knowledge, skills and attitudes needed for addressing the health needs of people with intellectual disability [ 55 , 56 ]. However, research indicates that those health professionals who have received training in disability-related knowledge and communication skills feel more positive and confident in delivering care to those with disability [ 57 ].
Although this review included international literature with no date limits applied, there were only 21 publications, derived from 20 studies that met the eligibility criteria. This limited amount of literature also only comes from four high-income countries—the UK, Australia, Canada and the Netherlands. This is likely to be because these countries have policy settings related to the implementation of structured annual health assessments for people with intellectual disability as part of routine practice in primary care, as well as the resources to investigate their impact. For example, in the UK and Australia, there are specific policy directives to strengthen the uptake of health assessments, such as Australia’s National Roadmap to Improve Health Outcomes for People with Intellectual Disability [ 5 ] and the UK’s Direct Enhanced Service [ 6 ].
The need to improve health outcomes for people with intellectual disability is gaining increasing attention. However, even though interventions or actions designed to address known barriers to quality care are more likely to produce change, there have been few interventions based on a systematic assessment of barriers [ 58 , 59 ]. As such, this review provides a foundation for future primary research regarding relevant behavioural change interventions [ 60 ]. In addition, there is a need for more qualitative research that examines the perceptions of primary care practitioners regarding the implementation barriers and facilitators to health assessments in general and that includes the views of primary care practitioners who are not currently undertaking health assessments.
Strengths and limitations
The strengths of our review are as follows: 1) a published a priori protocol; and 2) the rigour of having two reviewers independently conducting screening, full text review and data extraction. Review limitations include: 1) the risk of language bias as only publications in English were included; 2) potentially missing relevant evidence as we excluded grey literature and theses; 3) possible selection bias as more than half of the publications involved practitioners who were already implementing health assessments and so would potentially be more motivated to conduct them; 4) all publications were from high-income countries—potentially reflecting where the policy initiatives have driven related investigation.
The comprehensiveness of our review is contingent upon the scope of the incorporated studies, and these have not all taken a comprehensive approach to investigating barriers and facilitators that hinder or support the implementation of health assessments. Consequently, the insights only present a partial picture of influences on behaviours. To clarify, when a TDF domain is indicated as irrelevant to a certain behaviour, it could stem from the fact that no investigation into the barriers and facilitators related to that domain was conducted in the study, rather than from concrete evidence suggesting its irrelevance. A further limitation is that our coding of the barriers and enablers to the most predominant domain does not account for potential relevance of barriers and enablers across domains.
Conclusions
Using a well-established theory-based framework, this scoping review provides a synthesis of the current literature describing barriers and enablers that impact on the implementation of comprehensive health assessments for people with intellectual disability in the primary care setting. Further inquiry into the TDF domains of (a) goals, (b) behavioural regulations and (c) social influences may be warranted to ensure a comprehensive understanding of what drives and constrains the implementation of health assessments for people with intellectual disability in primary care. These insights provide a foundation for future research to improve the delivery and accessibility of preventive care for people with intellectual disability.
Availability of data and materials
Available on request, by contacting the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews
Theoretical Domains Framework
Trollor J, Srasuebkul P, Xu H, Howlett S. Cause of death and potentially avoidable deaths in Australian adults with intellectual disability using retrospective linked data. BMJ Open. 2017;7(2):e013489. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013489 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cooper SA, McLean G, Guthrie B, McConnachie A, Mercer S, Sullivan F, et al. Multiple physical and mental health comorbidity in adults with intellectual disabilities: population-based cross-sectional analysis. BMC Fam Pract. 2015;16:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-015-0329-3 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lennox N, Bain C, Rey-Conde T, Purdie D, Bush R, Pandeya N. Effects of a comprehensive health assessment programme for Australian adults with intellectual disability: a cluster randomized trial. Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36(1):139–46. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyl254 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Weise J, Pollack AJ, Britt H, Trollor JN. Who provides primary health care for people with an intellectual disability: General practitioner and general practice characteristics from the BEACH dataset. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2017;42(4):416–21. https://doi.org/10.3109/13668250.2016.1250252 .
Article Google Scholar
Australian Goverment Department of Health and Aged Care. National Roadmap for Improving the Health of People with Intellectual Disability. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia; 2021. https://www.health.gov.au/our-work/national-roadmap-for-improving-the-health-of-people-with-intellectual-disability . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Google Scholar
National Health Service. Primary Medical Services (Directed Enhanced Services) Directions. NHS England; 2023. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/primary-medical-services-directed-enhanced-services-directions . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Cantrell A, Croot E, Johnson M, Wong R, Chambers D, Baxter SK, et al. Access to primary and community health-care services for people 16 years and over with intellectual disabilities: a mapping and targeted systematic review. Health Serv Deliv Res. 2020; https://doi.org/10.3310/hsdr08050 .
Cooper SA, Morrison J, Allan LM, McConnachie A, Greenlaw N, Melville CA, et al. Practice nurse health checks for adults with intellectual disabilities: a cluster-design, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(7):511–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(14)00078-9 .
Bakker-van Gijssel E, Lucassen P, Hartman TO, Van Son L, Assendelft W, van Schrojenstein Lantman-de Valk H. Health assessment instruments for people with intellectual disabilities—A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2017;64:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2017.03.002 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Byrne JH, Lennox NG, Ware RS. Systematic review and meta-analysis of primary healthcare interventions on health actions in people with intellectual disability. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2016;41(1):66–74. https://doi.org/10.3109/13668250.2015.1105939 .
Carey IM, Shah SM, Hosking FJ, DeWilde S, Harris T, Beighton C, et al. Health characteristics and consultation patterns of people with intellectual disability: a cross-sectional database study in English general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 2016;66(645):e264-ee70. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp16X684301 .
Durbin J, Selick A, Casson I, Green L, Perry A, Chacra MA, et al. Improving the quality of primary care for adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: Value of the periodic health examination. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65(Suppl 1):S66-s72.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Byrne JH, Ware RS, Lennox NG. Health actions prompted by health assessments for people with intellectual disability exceed actions recorded in general practitioners’ records. Aust J Prim Health. 2015;21(3):317–20. https://doi.org/10.1071/py14007 .
Kennedy N, Brophy S, Kennedy J, Kerr M. Mortality in adults with learning disabilities with and without a health check: A cohort study. Lancet. 2019;394:S27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32824-7 .
Koritsas S, Iacono T, Davis R. Australian general practitioner uptake of a remunerated Medicare health assessment for people with intellectual disability. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2012;37(2):151–4. https://doi.org/10.3109/13668250.2012.676636 .
Cane J, O’Connor D, Michie S. Validation of the theoretical domains framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research. Implement Sci. 2012;7:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-7-37 .
Atkins L, Francis J, Islam R, O’Connor D, Patey A, Ivers N, et al. A guide to using the Theoretical Domains Framework of behaviour change to investigate implementation problems. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):77.
Paksaite P, Crosskey J, Sula E, West C, Watson M. A systematic review using the Theoretical Domains Framework to identify barriers and facilitators to the adoption of prescribing guidelines. Int J Pharm Pract. 2021;29(1):3–11.
Gangathimmaiah V, Evans R, Moodley N, Sen Gupta T, Drever N, Cardona M, et al. Identification of barriers, enablers and interventions to inform deimplementation of low-value care in emergency medicine practice: A protocol for a mixed methods scoping review informed by the Theoretical Domains Framework. BMJ Open. 2022;12(11):e062755.
Craig LE, McInnes E, Taylor N, Grimley R, Cadilhac DA, Considine J, et al. Identifying the barriers and enablers for a triage, treatment, and transfer clinical intervention to manage acute stroke patients in the emergency department: a systematic review using the theoretical domains framework. Implement Sci. 2016;11(1):157.
Davies J, Remington A, Buckley C, et al. “It seems like a luxury to be able to offer that”: Factors influencing the implementation of annual health checks for autistic people in England. Autism. 2023;2023:13623613231182012. https://doi.org/10.1177/13623613231182011 .
Alexander KE, Brijnath B, Mazza D. Barriers and enablers to delivery of the Healthy Kids Check: an analysis informed by the Theoretical Domains Framework and COM-B model. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-9-60 .
Atkins L, Stefanidou C, Chadborn T, Thompson K, Michie S, Lorencatto F. Influences on NHS Health Check behaviours: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1359. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09365-2 .
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Munn Z, Pollock D, Khalil H, Alexander L, McLnerney P, Godfrey CM, et al. What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid Synth. 2022;20(4).
Aromataris E, Munn Z. JBI manual for Evidence Synthesis. 2020. https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Caltabiano P, Bailie J, Laycock A, Shea B, Lennox N, Ekanayake K, et al. Applying the Theoretical Domains Framework to identify barriers and facilitators to implementation of comprehensive health assessments for people with an intellectual disability in primary care: a scoping review protocol. OSF; 2023. https://osf.io/7zbwm/ . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Covidence systematic review software. Melbourne: Veritas Health Innovation; 2020. Available from www.covidence.org . Accessed 14 Apr 2024.
Lennox NG, Brolan CE, Dean J, Ware RS, Boyle FM, Taylor Gomez M, et al. General practitioners’ views on perceived and actual gains, benefits and barriers associated with the implementation of an Australian health assessment for people with intellectual disability. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2013;57(10):913–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.2012.01586.x .
Burton H, Walters L. Access to Medicare-funded annual comprehensive health assessments for rural people with intellectual disability. Rural Remote Health. 2013;13(3):2278. https://doi.org/10.22605/RRH2278z .
Bakker-van Gijssel EJ, Olde Hartman TC, Lucassen PL, van den Driessen MF, Dees MK, Assendelft WJ, et al. GPs’ opinions of health assessment instruments for people with intellectual disabilities: a qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2017;67(654):e41-ee8. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp16X688585 .
Bollard M. Improving primary health care for people with learning disabilities. Br J Nurs. 1999;8(18):1216. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.1999.8.18.6484 .
Macdonald S, Morrison J, Melville CA, Baltzer M, MacArthur L, Cooper SA. Embedding routine health checks for adults with intellectual disabilities in primary care: practice nurse perceptions. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2018;62(4):349–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/jir.12475 .
Elo S, Kyngäs H. The qualitative content analysis process. J Adv Nurs. 2008;62(1):107–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x .
Anderson K, Jones J. Improving annual health checks for service users. Learn Disabil Pract. 2015;18(9):18. https://doi.org/10.7748/ldp.18.9.18.s24 .
Bond L, Kerr M, Dunstan F, Thapar A. Attitudes of general practitioners towards health care for people with intellectual disability and the factors underlying these attitudes. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1997;41(Pt 5):391–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.1997.tb00726.x .
Chambers R, Milsom G, Evans N, Lucking A, Campbell I. The primary care workload and prescribing costs associated with patients with learning disability discharged from long-stay care to the community. Br J Learn Disabil. 1998;26(1):9–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3156.1998.tb00039.x .
Chinn D. An empirical examination of the use of Easy Read health information in health consultations involving patients with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2020;33(2):232–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/jar.12657 .
Chinn D, Rudall D. Who is Asked and Who Gets to Answer the Health-Care Practitioner’s Questions When Patients with Intellectual Disabilities Attend UK General Practice Health Checks with Their Companions? Health Commun. 2021;36(4):487–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2019.1700440 .
Chinn D. “I Have to Explain to him”: How Companions Broker Mutual Understanding Between Patients with Intellectual Disabilities and Health Care Practitioners in Primary Care. Qual Health Res. 2022;32(8–9):1215–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/10497323221089875 .
Durbin J, Selick A, Casson I, Green L, Spassiani N, Perry A, et al. Evaluating the Implementation of Health Checks for Adults With Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities in Primary Care: The Importance of Organizational Context. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2016;54(2):136–50. https://doi.org/10.1352/1934-9556-54.2.136 .
Kerr M, Dunstan F, Thapar A. Attitudes of general practitioners to caring for people with learning disability. Br J Gen Pract. 1996;46(403):92–4.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lennox NG, Green M, Diggens J, Ugoni A. Audit and comprehensive health assessment programme in the primary healthcare of adults with intellectual disability: a pilot study. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2001;45(Pt 3):226–32. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2788.2001.00303.x .
McConkey R, Moore G, Marshall D. Changes in the Attitudes of GPs to the Health Screening of Patients with Learning Disabilities. J Learn Disabil. 2002;6(4):373–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/146900470200600404 .
McConkey R, Taggart L, Kane M. Optimizing the uptake of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil. 2015;19(3):205–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744629514568437 .
Shooshtari S, Temple B, Waldman C, Abraham S, Ouellette-Kuntz H, Lennox N. Stakeholders’ Perspectives towards the Use of the Comprehensive Health Assessment Program (CHAP) for Adults with Intellectual Disabilities in Manitoba. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2017;30(4):672–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/jar.12261 .
Walmsley J. An investigation into the implementation of annual health checks for people with intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil. 2011;15(3):157–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744629511423722 .
Michell B. Checking Up On Des: My Life My Choice's research into annual health checks for people with learning disabilities in Oxfordshire. Br J Learn Disabil. 2012;40 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3156.2012.00742.x .
Wigham S, Bourne J, McKenzie K, Rowlands G, Petersen K, Hackett S. Improving access to primary care and annual health checks for people who have a learning disability: a multistakeholder qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(12):e065945. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065945 .
Sethu S, Lawrenson JG, Kekunnaya R, Ali R, Borah RR, Suttle C. Barriers and enablers to access childhood cataract services across India. A qualitative study using the Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF) of behaviour change. PLoS One. 2021;16(12):e0261308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261308 .
Whelan J, Fraser P, Bolton KA, Love P, Strugnell C, Boelsen-Robinson T, et al. Combining systems thinking approaches and implementation science constructs within community-based prevention: a systematic review. Health Res Policy Syst. 2023;21(1):85.
Trollor JN, Ruffell B, Tracy J, Torr JJ, Durvasula S, Iacono T, et al. Intellectual disability health content within medical curriculum: an audit of what our future doctors are taught. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0625-1 .
Trollor JN, Eagleson C, Turner B, Salomon C, Cashin A, Iacono T, et al. Intellectual disability health content within nursing curriculum: An audit of what our future nurses are taught. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;45:72–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2016.06.011 .
Royal Commission into Violence Abuse, Neglect and Exploitation of People with Disability. Public hearing report: public hearing 10 education and training of health professionals in relation to people with cognitive disability. 2022. https://disability.royalcommission.gov.au/public-hearings/public-hearing-10 . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Royal Commission into Violence Abuse, Neglect and Exploitation of People with Disability. Final report of the royal commission into violence, abuse, neglect and exploitation of people with disability. 2023. https://disability.royalcommission.gov.au/publications/final-report . Accessed 17 Feb 2024 .
Smith SE, McCann HP, Dykens EM, Hodapp RM. Chapter six - The disability-training needs of healthcare professionals: Scoping review and new initiatives. Int Rev Res Dev Disabil. 2020;58:219–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irrdd.2020.07.003 .
Baker R, Camosso-Stefinovic J, Gillies C, Shaw EJ, Cheater F, Flottorp S, et al. Tailored interventions to address determinants of practice. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;4 https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005470.pub3 .
Gagliardi AR, Alhabib S. Trends in guideline implementation: a scoping systematic review. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0247-8 .
Michie S, Atkins L, West R. The behaviour change wheel. In: A guide to designing interventions. 1st ed. Great Britain: Silverback Publishing; 2014. p. 1003–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-6-42 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Jane Yule for editing and proof-reading support and thank Professor Megan Passey for her comments on an early draft of the manuscript.
This project was completed as a course requirement for the Doctor of Medicine at The University of Sydney’s Faculty of Medicine and Health. JB is supported by the NHMRC Centre for Research Excellence in Disability Health, grant #1116385 and NHMRC Synergy Grant ‘Developing interventions for better life-time mental health for young Australians (aged 15 to 24 years) with disability’, grant #2010290.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Rural Health, The University of Sydney, Dubbo, Australia
Paul Caltabiano
Sydney Medical School, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia
Paul Caltabiano & Bradley Shea
University Centre for Rural Health, The University of Sydney, Lismore, Australia
Jodie Bailie, Alison Laycock & Bradley Shea
Centre for Disability Research and Policy, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia
Jodie Bailie
Rural Clinical School, Australian National University, ACT, Canberra, Australia
Sally Hall Dykgraaf
Queensland Centre for Intellectual and Developmental Disability, Mater Research Institute, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Nicholas Lennox
University of Sydney Library, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia
Kanchana Ekanayake
School of Public Health, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia
Ross Bailie
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JB conceived of the study; PC and JB designed the study; JB, PC, KE and RB developed the search terms and database searches with input from NL, SHD and BS. PC and JB independently screened the papers and undertook data extraction, with conflicts resolved through discussion between PC and JB; PC led the analysis and writing of the manuscript. AL provided expert advice regarding the TDF. PC, JB, AL, BS, SHD, NL, KE and RB critically reviewed draft versions of the manuscript, revisions were made in response to their input. PC, JB, AL, BS, SHD, NL, KE and RB gave final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jodie Bailie .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
No ethics approval was required and consent to participate is not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The University of Queensland owns one particular targeted preventive health assessment for people with intellectual disability, which is generically mentioned in this manuscript. The university receives licensing fees from organisations using this health assessment. One third of these fees are paid to Professor Nicholas Lennox.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Caltabiano, P., Bailie, J., Laycock, A. et al. Identifying barriers and facilitators to primary care practitioners implementing health assessments for people with intellectual disability: a Theoretical Domains Framework-informed scoping review. Implement Sci Commun 5 , 39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43058-024-00579-8
Download citation
Received : 29 September 2023
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 16 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43058-024-00579-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health assessments
- Intellectual disability
- Primary care
- Implementation
- Theoretical domains framework
- Scoping review
Implementation Science Communications
ISSN: 2662-2211
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 26 April 2022
Definition and conceptualization of the patient-centered care pathway, a proposed integrative framework for consensus: a Concept analysis and systematic review
- Jean-Baptiste Gartner 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ,
- Kassim Said Abasse 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 ,
- Frédéric Bergeron 6 ,
- Paolo Landa 3 , 7 ,
- Célia Lemaire 8 &
- André Côté 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5
BMC Health Services Research volume 22 , Article number: 558 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
7182 Accesses
18 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Confusion exists over the definition of the care pathway concept and existing conceptual frameworks contain various inadequacies which have led to implementation difficulties. In the current global context of rapidly changing health care systems, there is great need for a standardized definition and integrative framework that can guide implementation. This study aims to propose an accurate and up-to-date definition of care pathway and an integrative conceptual framework.
An innovative hybrid method combining systematic review, concept analysis and bibliometric analysis was undertaken to summarize qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method studies. Databases searched were PubMed, Embase and ABI/Inform. Methodological quality of included studies was then assessed.
Forty-four studies met the inclusion criteria. Using concept analysis, we developed a fine-grained understanding, an integrative conceptual framework, and an up-to-date definition of patient-centered care pathway by proposing 28 subcategories grouped into seven attributes. This conceptual framework considers both operational and social realities and supports the improvement and sustainable transformation of clinical, administrative, and organizational practices for the benefit of patients and caregivers, while considering professional experience, organizational constraints, and social dynamics. The proposed attributes of a fluid and effective pathway are (i) the centricity of patients and caregivers, (ii) the positioning of professional actors involved in the care pathway, (iii) the operation management through the care delivery process, (iv) the particularities of coordination structures, (v) the structural context of the system and organizations, (vi) the role of the information system and data management and (vii) the advent of the learning system. Antecedents are presented as key success factors of pathway implementation. By using the consequences and empirical referents, such as outcomes and evidence of care pathway interventions, we went beyond the single theoretical aim, proposing the application of the conceptual framework to healthcare management.
Conclusions
This study has developed an up-to-date definition of patient-centered care pathway and an integrative conceptual framework. Our framework encompasses 28 subcategories grouped into seven attributes that should be considered in complex care pathway intervention. The formulation of these attributes, antecedents as success factors and consequences as potential outcomes, allows the operationalization of this model for any pathway in any context.
Peer Review reports
While having a performant healthcare system is a crucial issue for every country, the health sector operates in silos that need to be challenged. Indeed, many authors have pointed to fragmented care processes as a cause of breakdowns in the continuity of healthcare services [ 1 ], unnecessary waiting times [ 2 , 3 ], flaws in the flow of information between the different episodes [ 4 ] and the realization of exams that may be superfluous [ 5 ]. This fragmentation results in a sub-optimal use of material and financial resources and unsatisfactory team management [ 4 ]. Based on this observation, several repeated calls to improve the quality and performance of healthcare services have been made since 2001 by national and international institutions such as the Institute of Medicine of America (IOM) in 2001 [ 6 ] and 2013 [ 7 ], the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, Medicine in 2018 [ 8 ] and the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2016 [ 9 ] and 2020 [ 10 ]. These calls have progressively shifted from an injunction to improve quality based on criteria to provide safe, effective, efficient, timely, equitable and patient-centered care [ 6 ], to the development of models for the organization of health care and services that meet the current challenges of effectiveness and efficiency in healthcare systems. The WHO urges member countries to base their quality improvement policies on the entire continuum of care, taking into account at least the criteria of effectiveness, safety, equity, efficiency, integrated care and timeliness [ 11 ]. These calls also emphasize the need to improve care pathways by focusing on outcomes that matter to the patient from a clinical, quality of life and health system experience perspective [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ], rather than on the needs of the production units. This change of perspective leads to the study of the redesign of performance evaluation models by focusing on the needs and expectations of the patient [ 16 , 17 ]. The problem is that there is confusion about the definition and characterization of a care and health service pathway. Indeed, Bergin et al. [ 2 ] identified 37 different definitions of the term care pathway based on a review of the literature. Definitions and characteristics vary across countries and include multiple phases ranging from prevention or screening to cure or palliative care. This confusion has led to wide variability in the outcomes of these interventions, resulting in underutilization of care pathway improvement programs [ 2 ]. Furthermore, such confusion leads to great variability in the analysis and modeling of care pathways. For example, in their scoping review, Khan et al. [ 18 ] showed the great variability that exists among studies of oncology care pathways in both the phases of care represented, and their characteristics. The lack of a common definition and clearly defined criteria leads to a lack of standardization, resulting in an inability to conduct reliable comparative studies of care pathway programs internationally [ 19 ].
The Oxford Concise Medical Dictionary 10th ed. [ 20 ] and the Oxford Dictionary of Nursing 8th ed. [ 21 ] define, in a concise way, care pathway as “a multidisciplinary plan for delivering health and social care to patients with a specific condition or set of symptoms. Such plans are often used for the management of common conditions and are intended to improve patient care by reducing unnecessary deviation from best practice”. The concept of a care pathway is one originally used in the field of Health Operations Management, whose definition was proposed by Vissers and Beech [ 22 ]. However, these definitions seem to be too imprecise and address neither the aim nor the social reality of implementing such pathways. The European Pathway Association (EPA) adopts the more precise definition from the 2007 thesis of Vanhaecht [ 23 ]. However this has not yet led to an international consensus, as confusion over the concepts remains high. Moreover, this definition does not clearly define the antecedents or factors favoring the success of such interventions, the means by which to implement them or the best practices through which to support them; nor does it sufficiently take into account the importance of the patient-centered care and patient-centered services approach. Similarly, the proposed implementation models largely neglected the social reality and the social dynamic of organizations [ 24 ], resulting in major implementation difficulties, as care pathways still being considered as complex interventions [ 25 , 26 ].
However, care pathway programs have recently demonstrated encouraging results in terms of reduced variation in care, improved accessibility, quality, sustainability, and cost effectiveness of care [ 2 ]. The definition we aim to develop through this research is significant and timely, in that it has the potential to guide the ongoing development, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of care pathway programs within the rapidly changing service and system contexts that we are experiencing. For example, the following initial barriers to the systemic and holistic implementation of care pathways have recently been removed. Firstly, limited access to valid and reliable data from multiple organizations [ 27 ] has been offset by a massive investment in Electronic Medical Records [ 28 ]. Secondly, the main difficulties in highlighting the complexity of the referral trajectory [ 29 ], frequently resulting from the clinicians’ perspective, have been overcome by proposing new approaches such as data mining or qualitative methods, focusing on the real care trajectory and the qualitative part of the patients’ experience [ 16 , 17 , 30 ]. Therefore, the evolution of knowledge and information technology and the investment of health systems in data-sharing infrastructure, as well as a definition of the levers of patient engagement and the advent of patient-centered-care and patient-centered services, make it possible to define a powerful model for improving them by placing the patient’s needs and expectations at the center of the care pathway. It is therefore the right time to define a recognized definition and an integrative conceptual framework that meets the demand for sharing knowledge internationally regarding the development, implementation, and evaluation of care pathways.
The concept of patient-centered care is defined as “care provision that is consistent with the values, needs, and desires of patients and is achieved when clinicians involve patients in healthcare discussions and decisions” [ 31 ]. This approach is known to provide benefits by improving health outcomes, patient satisfaction, but also to reducing health costs [ 32 ].
A preliminary search for existing reviews was conducted in Cochrane Database, JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports and PROSPERO. Care pathways have been the subject of few reviews, but these were limited to a single pathology such as cancer in general [ 33 ], blunt thoracic injury [ 34 ], cardiovascular disease [ 35 ], adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [ 36 ] or for particular pathway phases [ 37 ]. In the end, focusing on a single condition is not entirely consistent with a patient-centered approach to care insofar as patients often have comorbidities. The only review that did not focus on one specific pathology was made in 2006 [ 38 ] and was interested in the concept of clinical pathway. Authors reviewed literature published within 3 years using only one bibliographic database. Therefore, the aim of this article is to propose an accurate and up-to-date definition of care pathway and to develop an integrative conceptual framework for the patient-centered care pathway concept in a holistic operational approach of the concept.
Combining systematic review, concept analysis and bibliometric analysis
To achieve a fine-grained understanding of the concept, we have chosen a hybrid method combining the systematic review, the concept analysis and the bibliometric analysis methodologies. We followed the latest PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement for conducting and reporting a systematic review [ 39 ]. However, the systematic review methodology presents some limitations on the qualitative analysis of literature, hence derives our interest to use Concept analysis. Concept analysis [ 40 ] aims specifically to clarify a specific concept including a semantic field linked to a specific theoretical framework. This approach is based on eight steps allowing to: (1) select the concept, (2) determine the aims or purposes of the analysis, (3) identify all uses of the concept, (4) determine the defining attributes, (5) identify a model case, (6) identify additional cases, (7) identify antecedents and consequences and (8) define empirical referents. However, this method does not provide a systematic and rigorous procedure for identifying and selecting relevant literature. Therefore, we decided to combine the strengths of both methods to overcome the limitations of each. In order to make our analysis more robust and to base our inferences, specifically in the comparative analysis of the related concepts, we performed a bibliometric analysis allowing us to link the attributes of each of the concepts to make a comparison.
Information sources and search strategy
We developed a search strategy, in collaboration with a Health Sciences Librarian who specializes in systematic literature review in healthcare, to identify relevant peer-reviewed studies. An initial limited search of MEDLINE and CINAHL was conducted, followed by analysis of the text words containing title and abstract and index terms used to describe the article. This informed the development of a search strategy that was tailored toward each information source. The search strategy was applied to the following databases: PubMed, Embase and ABI/Inform. The complete search strategy is provided in Additional file 1 .
Eligibility criteria
This review considers studies that focus on quantitative and/or qualitative data, with no limitation in terms of methodology. Our search focused on peer-reviewed scientific articles. Therefore, books, doctoral or master’s theses were excluded due to time and resource limitations. In order to guide the selection, we chose the Population, Context, Concept (PCC) mnemonic criteria [ 41 ]. The population considers all types of patients managed by healthcare delivery systems. The context studied is composed of healthcare providers in any geographic area, including all providers of primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary care. For the concept, this review focuses on theoretical and empirical studies that contribute to the definition and conceptualization of the different related concepts of care processes at the organizational or system level, such as care pathway, clinical pathway, patient journey and care processes. Quantitative, qualitative and mixed method studies involving a single episode of care limited in time (a one-time treatment) or space (a single hospital service/department) were excluded to the extent that care pathway involves multiple points of interaction over time [ 13 , 42 ] and multiple organizational structures or intra-organizational entities along the care continuum [ 43 ]. In addition, studies with no theoretical or conceptual input were excluded. Finally, there was no language or geographic restrictions applied to the search, and the study period was limited from 1995 to 2020.
These studies were imported into the Covidence® software (version 2020). The team developed screening questions and forms for levels 1 (abstract) and 2 (full text) screening based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Two reviewers independently screened the titles and abstracts. In case of disagreement, two senior reviewers decided after analysis and discussion. Review author pairs then screened the full-text articles against inclusion and exclusion criteria. In case of disagreement, the same process as for the title and abstract selection was implemented. Reasons for excluding studies were recorded.
Assessment of methodological quality
Because of the heterogeneity of the methods used in the selected articles, we decided to use a separate appraisal tool for each study type. The following appraisal tools were selected for their clarity, relevance, and because their items covered the most common assessment criteria comparing to other tools:
For qualitative studies: the JBI Qualitative Assessment Research Instrument (QARI) [ 41 ]
For surveys: the Center for Evidence Based Management (CEBMa) Appraisal Questions for a Survey [ 44 ]
For descriptive cross-sectional studies: the Institute for Public Health Sciences 11 questions to help you make sense of descriptive/cross-sectional studies [ 45 ]
For mixed-method: the scoring system for appraising mixed methods research [ 46 ]
No articles were excluded from this systematic review due to the weaknesses of their methodological quality, so as not to exclude valuable information [ 47 ].
Data extraction and analysis
Descriptive numerical summary analysis followed the systematic review guidelines, and the following items were systematically extracted: Reference, Title, First Author country, Case country, Year of publication, Type of publication, Target patient population, Phases of the pathway included, People involved in the modeling process, Study parameters and level of analysis.
Qualitative data were extracted using MaxQDA® software (version 2020) by two independent analysts. The data extraction followed the concept analysis guideline [ 40 ] and the following items were systematically extracted: Variant concept studied, Concept uses, Concept definition, Concept attributes, Antecedents, Consequences and empirical referents. In order to develop a detailed analysis and arrive at a robust theoretical framework, we relied on general inductive analysis [ 48 ], consisting of coding, categorization, linking, integration and modeling. Each step has been validated by at least two senior authors.
A bibliometric analysis was performed with the complete texts of the 44 selected studies using Vosviewer® software (version 2020).
The systematic review was reported following the latest PRISMA statement for conducting and reporting a systematic review [ 39 ] and mobilized the PRISMA 2020 checklist (see Additional file 2 ).
The interrogation of the three databases resulted in 15,281 articles. Figure 1 details the selection process following the PRISMA 2020 statement [ 39 ]. After deleting the duplicates, 15,072 records were reviewed but only 44 publications ultimately met the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram of the systematic review process
Description and methodological quality appraisal of studies
A summary table containing a brief description of selected studies and their evaluation results for methodological quality is presented in Table 1 . Quality appraisal of selected studies is presented in Additional file 3 .
Published articles, describing care pathways as multiple points, in time and space, of patient interaction appeared in the early 2000s. However, most of this work has been published since 2010, with a progressive and growing interest, whatever the theoretical position, to reach 22 articles in the last 3 years (see Fig. 2 ).
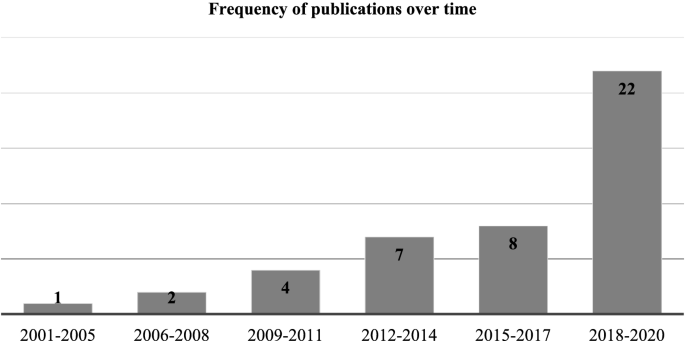
Frequency of selected publications over time
The countries of the first authors interested in this concept are predominantly anglophone such as the United Kingdom (k = 9), Australia (k = 5), the United States (k = 4), and Canada (k = 3). Researchers from other countries are less represented.
Three types of publications were found; 34 were original research studies, eight were literature reviews and two were perspective studies. In the original research studies, 23 used a qualitative approach to study either the implementation of a care pathway program or patient experience of a care pathway, four used a descriptive cross-sectional approach, four used a mix-method approach and three used a survey.
Since the definition of the concept is still unclear and terminology is important, the studies meeting the selection criteria reported several terminologies. The most frequently used terms in the selected studies were the patient journey (k = 14) and the care pathway (k = 13) with their some country-specific modifications namely integrated care pathway mainly in the United Kingdom [ 73 , 74 ], optimal care pathway in Australia [ 2 ] and standardized care pathway in Sweden [ 15 ]. The other terms used were clinical pathway (k = 8), patient-centered care (k = 4), care process (k = 3), disease pathway management (k = 1) and value-based integrated care (k = 1).
Studies focused mainly on the care of chronic conditions (k = 24), followed by acute diseases (k = 11). Of those with a chronic care focus, cancer was by far the most studied disease (k = 10), followed by stroke, hearing impairment and mental disease. Acute care studies covered, articular pathologies of the hip and knee, and pregnancy.
Concerning the level of the study, most addressed the systemic (k = 31) rather than the organizational (k = 13) level. Most authors, in their approach to the concept, largely focused on the treatment phase (k = 39), but some included, more or less, pretreatment and subsequent phases. Only seven articles took a global approach starting from the prevention phase and screening to survivorship or palliative care phase.
Concept analysis results
The conceptual analysis followed an automatic data extraction method in the proposed main categories and then, after several iterations, resulted in a coding of subcategories grouped into main themes. The detailed results of the coding are presented in Additional file 4 .
Concept uses
Uses of the concepts of care pathway have evolved in the literature over time with a strong tendency to focus on the care pathway at the systemic level. Main objectives have been improving quality and safety (k = 26), improving efficiency in the delivery of care (k = 24), optimizing the delivery process through an operation management point of view (k = 22) and integrating best practices through guidelines and evidence-based medicine (k = 17). These objectives were widely shared and present throughout the period. However, interest emerged in 2009 and quickly grew, in improving the patient experience through the analysis of the patient journey (k = 17). To a lesser extent, the goals of developing patient-centered care (k = 13), improving patient outcomes (k = 13), improving coordination of service delivery (k = 13), and standardizing care delivery (k = 12) were also present. Beyond standardization, reduced variation in care practices (k = 9) was not well addressed, nor was continuous performance assessment (k = 8). The aim of meeting the patient’s needs (k = 6) has been addressed more frequently in recent years, since its first appearance in 2011 [ 71 ], and is considered of crucial importance by some authors. Other concept uses were proposed, such as to improve interprofessional collaboration (k = 5), support changes (k = 5), support clinical decision making (k = 4), improve communication (k = 3), consider needs of healthcare workers, improve referral system, define shared purposes and meaningful objectives (k = 2), monitor staff compliance, support the knowledge management, improve patient and family member access to information, adopt a system approach and understanding power dynamics and relational factors (k = 1). As described previously, these concept uses came mainly from the chronic disease care context, although acute care was also represented.
Defining attributes
Definitional attributes are features commonly encountered in definitions of the concept or frequently used to describe it [ 40 ]. Twenty-eight attributes were inductively extracted and categorized into seven main themes, ordered by level of empirical importance: (1) The centricity of patients and caregivers; (2) the positioning of professional actors involved in the care pathway; (3) the operation management through the care delivery process; (4) the particularities of coordination structures; (5) the structural context of the system and organizations; (6) the special role of the information system and data management; and (7) the advent of the learning system (k = 3).
Attribute theme 1: The centricity of patients and caregivers
Firstly, there has been a growing interest in the patient experience (k = 15), mainly through the concept of the patient journey [ 5 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 24 , 30 , 42 , 51 , 52 , 58 ], which has progressively emerged as the third pillar of quality in healthcare with clinical effectiveness and patient quality and safety [ 30 ]. It is formed by all the interactions at the meeting point, or point of contact, between health services and patient [ 14 , 30 , 42 , 51 ]. However, taking the patient experience into account is complex insofar as it requires a detailed understanding of what influences it. Therefore, some authors have defined the dimensions that can influence the patient experience as the temporal dimension, meaning that accessibility and short waiting times are valued [ 13 , 15 , 30 , 42 , 51 ], the spatial dimension [ 30 ], and the geographical position of the services [ 42 ], the emotional dimension [ 13 , 30 , 42 ] and the social and cognitive dimensions [ 13 , 42 ]. All these dimensions can be the source of both positive outcomes [ 13 , 30 ] and negative outcomes [ 15 ] or for socio-political authors, a feeling of considerable disempowerment [ 53 ]. Although authors are increasingly interested in it, the patient experience is still sometimes overlooked [ 14 ].
Patient information and education (k = 15) were addressed in numerous studies. Patient information contributes to the quality of the patient experience [ 3 , 15 , 36 , 42 , 53 , 64 , 71 , 75 ]. Beyond the simple satisfaction, the provision of information, at an appropriate health literacy level, increases patient awareness [ 36 , 51 ] and thus increases patient education. This results in a better detection of the symptoms at an early stage by the patient [ 3 , 36 ], the development of the “expert patient” [ 51 , 57 , 58 , 71 ], which aids adherence to treatment, supports shared decision-making [ 57 ] and improves self-management [ 51 , 58 ]. However, many empirical studies showed there to be a lack of patient information throughout patient journeys [ 5 , 14 , 15 , 42 , 51 , 53 , 64 ].
Patient engagement (k = 15) was an important attribute of this theme in the more recent literature. The management by the patient of his or her care treatment plan has become increasingly important [ 24 , 50 , 51 , 53 , 67 ]. This translates into shared decision-making on care and treatment [ 3 , 14 , 24 , 35 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 54 , 55 , 58 , 64 , 65 ]. According to Devi et al. [ 51 ], this process can only be viable if supported by good information about treatment possibilities and possible outcomes. However, socio-political authors see this as a major issue of patient empowerment, which is “seen as a solution to many of the most pressing problems facing modern healthcare” [ 53 ].
Proposed only since 2014, and strongly present in the last 3 years, relationship as the basic need (k = 9) is also a subject of interest. Part of the patient experience, the relational quality reflects how patients perceive their interactions [ 13 , 42 ]. Some empirical studies have shown that a poor relationship can negatively affect other processes and tasks [ 3 , 5 ]. Therefore, quality of the relationship seems a fundamental prerequisite [ 14 , 64 ]. For this reason, some authors have placed the notion of trust as essential to the quality of interactions and to the patient’s follow-up through the care pathway [ 3 , 12 , 58 ].
Patient and Public Involvement (k = 9) is part of these new topics. Its importance in the design and improvement of the care pathway is supported by some international organizations [ 9 ]. The objective is to improve the quality of care provided by assessing patients’ perceptions [ 12 , 13 ]. In this way, the design of care delivery can be based on the real needs and expectations of patients [ 12 , 13 , 51 , 56 , 62 ]. However, some models have been criticized as tokenistic rather than being viable solution for balancing power between patients and health care providers [ 53 ].
Although the stated goal of care pathways incorporates an approach aimed at standardizing care practices, several authors have raised the need for individualized care (k = 8). Joosten et al. [ 74 ] saw a potential conflict between standardization and the demand for a personalized approach to healthcare. However, several authors have subsequently agreed that there is still room for individualization of care beyond the standardization [ 55 ], in particular through the definition of personalized treatment goals [ 51 ], or even maintaining flexibility in the interaction to better adapt to the patient’s specific needs [ 64 , 65 ].
Developed only since 2016, the importance of psychosocial support (k = 8) has increased rapidly. Although the need has been clearly identified and documented [ 5 , 15 , 42 , 58 ] and many international guidelines have integrated it, it seems that its translation within the care pathway is still complex [ 62 ] and no obvious answer was provided.
The inclusion of family and caregiver (k = 8) is also a new topic of the last 5 years which highlights the potential of family or caregivers involvement in decision-making [ 50 , 51 , 57 , 65 ]; notably by supporting both the integration of information and personal decision-making [ 14 , 15 ].
Attribute theme 2: The positioning of professional actors involved in the care pathway
Firstly, most authors consider the care pathway as a tool to develop patient-centered care (k = 18). The patient-centered care approach has a disease-specific orientation [ 25 ] and considers the patient as a real partner [ 51 , 25 ]. In doing so, this approach recognizes an individual’s specific health needs and preferences as the driving force in all healthcare decisions [ 13 , 51 , 65 , 67 ]. Thus, professional actors emphasize their accessibility and their attitudes and behaviors towards patients [ 13 ]. In addition, this approach considers the importance of integrating family and caregivers and is recognized as a necessary attribute of healthcare quality [ 65 ]. Finally, its implementation seems to improve patient satisfaction by moving toward an individualized therapy approach and personalized treatment goals [ 51 ].
Not surprisingly, multidisciplinary team-working (k = 17), and attribute which is consistent with previous definitions, is supported by several authors. The enrollment of all professional categories involved directly or indirectly in the care pathway at all steps is valued [ 2 , 50 , 75 ]. The multidisciplinary teamwork allows tackling the complexity of patient care across the pathway and developing a shared understanding supported by knowledge sharing among professionals [ 53 , 72 ]. In addition, it allows outlining the optimal sequence and timing of interventions [ 38 , 59 ] and to focus only on patient needs and engagement rather than on problems of a particular profession [ 56 ]. From an operational view, multidisciplinary care teams make it possible to share formal screening between disciplines [ 62 ]. Recently, multidisciplinary engagement was identified as a mandatory prerequisite for successful care pathway programs [ 24 , 50 ].
Staff skills (k = 10) could be considered equally important for care pathways. However, they were not addressed in this literature before 2014. Authors gave little attention to technical skills, except to point out possible deficiencies, particularly in diagnosis [ 3 , 13 ], but also in training [ 3 ]. Rather, authors focused almost exclusively on interpersonal skills [ 3 , 12 , 13 , 15 , 51 , 64 ], which were considered critical, both in the relations between professionals [ 12 , 15 , 51 , 56 , 64 ] as well as those with patients and their caregivers [ 15 , 51 , 64 ]. Interpersonal skills could be seen as facilitators or barriers to the patient experience [ 64 ]. Some authors have recently suggested that peer cooperation was critical [ 5 , 50 , 56 ] and that creating a culture of mutual respect among both medical and administrative colleagues can ultimately improve the fluidity of care [ 3 , 5 ].
Few authors have highlighted that the implementation of a care pathway leads professionals to examine their roles and responsibilities (k = 6). The need to define each step in the care process requires professionals to describe precisely the tasks and roles of professional actors [ 25 ]. In doing so, it creates a rare opportunity to step back from daily tasks and reassess competences, roles and responsibilities [ 12 , 51 , 73 ].
Finally, very recently, authors have been interested in the experience of staff (k = 2) in care pathway programs. These authors have demonstrated the link between staff experiences and their individual performance [ 24 , 53 ]. They therefore support the idea that staff well-being is directly related to engagement and performance and, thus, a negative staff experience can influence patient, clinician, and organizational outcomes.
Attribute theme 3: The operation management through the care delivery process
This analysis has shown, unsurprisingly, that the process approach to care delivery (k = 23) was the core of the care pathway approach across the literature to date. From an engineering perspective, as define by the International Organization for Standardization, a process is “a set of interrelated or interacting activities that transforms inputs into outputs” (ISO 9000:2000 clause 3.4.1). Through this approach, the care process can be defined as an arrangement of tasks or actions sequenced in time resulting in a time matrix [ 24 , 30 , 38 , 52 , 60 , 68 , 25 , 73 ]. What distinguishes the different process approaches to care delivery are the tasks and actions included with them. Some authors tend to focus on operational planning by treating tasks, actions and their timing through business processes [ 43 , 49 , 54 , 60 , 69 ], while other authors consider both the context of action through the physical and organizational environment [ 24 , 30 ] and social dynamic through the experience of actors [ 24 , 52 , 53 ]. Through this approach to care processes, some authors focus on patients and caregivers [ 52 ] and other authors focus on human actors, both patients and caregivers and the professional actors involved in the care pathway [ 24 ]. In 2018, Ponsignon et al. [ 13 ] proposed to differentiate the direct, indirect and independent interactions (those disconnected from the delivery system), in care processes. Direct interactions constitute the points of contact between patients and the system, and so are responsible, along with indirect interactions, for the patient version of the pathway that some authors call the patient journey [ 5 , 13 , 30 , 51 , 53 ]. More recently, the complexity of the care process has led some authors to consider that the care pathway should involve pathway rules which control the process [ 70 ]. Thus, decision-making becomes a central element in the smooth running of the care pathway [ 60 ]. In addition, many authors consider that healthcare decisions and care pathways are intertwined so that it becomes imperative to co-design both care pathways and the decision-making activities [ 60 ].
The issue of process management for the delivery of care naturally raises the question of process modeling methods (k = 18). In the empirical articles, the use of the Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) developed by the Object Management Group seems to be progressively imposed, sometimes improved by decision modeling [ 4 , 43 , 54 , 60 , 68 , 69 ]. The use of process mapping or flowcharts with sometimes less formal rules seems to be favored for global approaches to processes, especially for the patient journey, although some authors such as Combi et al. [ 60 ], have demonstrated that BPMN modeling was quite compatible with the systemic approach.
For healthcare service designers, the methods for building care pathways are important considerations. Several methods exist, but all involve the discovery of a different path, thus change is inevitable and change management a necessity. The initial method came mainly from the expertise of professionals through interviews, focus groups or Delphi methods [ 49 , 59 ]. The advantage of collaboration with staff and experts is that more information can be gathered about certain decisions and possible variances from the pathway [ 49 ]. However, this method did not consider the real trajectory or the ideal pathway but rather the one integrating the constraints of the professionals. Since these early efforts, data driven approaches has developed considerably [ 43 , 49 ]. Their advantage is that they inform pathway development from data derived factually and objectively from actual occurrences of the pathway [ 49 ]. Moreover, data on the perspectives of patients through experience mapping, interviews, focus groups or observations [ 5 , 13 , 30 ], and patient shadowing [ 53 ] can be integrated to better reflect the real trajectory and to define the ideal pathway according to the needs and expectations of patients and caregivers. However, this approach does not allow for the integration of context and organizational constraints. Finally, few authors adopt an approach that consists of comparing the experience of professionals and patients, making it possible to define the lived experience, the patient’s journey, and its confrontation with operational realities and constraints through the experience of professionals [ 1 , 3 , 4 , 15 , 65 , 71 ].
Regarding the process of care delivery, the management of operations aims to integrate the organization of the delivery process with its ongoing improvement (k = 11) by focusing as much on analyzing the variations as on eliminating the wastes [ 74 ]. Process improvement tools serve as much to redesign the processes as define a workflow management system to monitor the care pathway [ 4 ]. The information generated [ 60 , 61 , 63 ] can be used for process re-engineering, objective reassessment or supporting non-clinical decision-making [ 60 ], such as the identification of bottlenecks [ 61 , 67 ] or highlighting interfacing problems between organizations [ 61 ]. The output generated by the analysis of the process-related data allows defining standardized expedited diagnostic processes [ 4 , 60 ]. Finally, the data obtained allows the use of simulation and optimization models. On this subject, Aspland et al.’s literature review [ 49 ] provides an exhaustive review of available methods.
Attribute theme 4: The particularities of coordination structures
In line with most of the definitions, the integration of the clinical practice guidelines, based on evidenced-based medicine, into the care pathway (k = 24) has been accepted since the beginning of such programs. The clinical decisions directly affect the flow of the care delivery process and thus the process performance and the quality of outcomes [ 60 ]. Therefore, the adherence to clinical practice guidelines must support decision-making [ 70 , 73 ] and aid diagnosis and treatment in order to improve patient outcomes [ 50 , 51 , 58 ]. In 2010, Vanhaecht et al. [ 25 ] expressed concern about a lack of evidence-based key interventions within care pathways. The care pathway can be an effective method to integrate and guarantee the appropriate use of evidence-based interventions and clinical practice guidelines [ 55 ] and may help to overcome two limitations of clinical practice guideline use, which are emerging as key issues [ 60 , 66 ]. Firstly, that they should not be followed blindly as they represent only explicit medical knowledge [ 67 ], but rather require integration of the contextual knowledge of healthcare professionals for appropriate use [ 72 ]. Secondly, it has been shown that physicians can be unaware of updates and changes to clinical guidelines [ 3 ], and so, integrating them into care pathway maps may improve guideline use and adherence. Finally, collectively integrating and discussing clinical practice guidelines appears to improve interprofessional collaboration and clarify roles [ 36 ], but also could benefit the involvement of patients in the co-design of the care pathway [ 35 ].
Some authors consider information continuity (k = 13) as a key factor. Not only because sharing information must support decision-making [ 60 , 75 ] and facilitate communication [ 2 , 12 , 38 ], but more broadly because the disruption of the information flow can lead to coordination problems and easily avoidable costs linked to the repetition of examinations [ 5 , 56 , 59 ]. Therefore, the continuity of information must be supported to ensure sustainable health improvements [ 51 , 70 ]. Some authors insist on the importance of defining an information medium throughout the pathway which is as accessible to care professionals as it is to patients and caregivers [ 65 ].
Recently, some authors have dealt with the subject of leadership of the care pathway (k = 9). The importance of defining a leader for each step of the care pathway was noted [ 25 ]. The lack of coordination without a responsible actor has been shown, especially when the care pathway includes actors in several contexts such as primary care [ 3 ]. Thus, new roles have been defined, such as case managers, joint program or nurse coordinators [ 4 , 15 , 42 , 65 ], roles that enhance coordination among providers through the improvement of the continuity and quality of the information as well as communication [ 15 ].
More recently, the integration of services (k = 9) has been addressed. Because the care pathway approach can involve multiple partnerships between organizations and primary care, it is essential to integrate all stakeholders. The integration needs to be both organizational, at the macro and meso-level through shared purpose and priorities [ 4 , 57 , 25 ] and shared governance mechanisms [ 4 , 12 , 14 , 59 ], and functional at the micro level through communication mechanisms and tools [ 4 , 12 , 14 ]. The unifying element is discussed between the shared interest for the patient [ 56 , 57 ] or the outcomes [ 12 ] to align strategic goals. For Louis et al. [ 56 ], achieving shared purpose is part of the structural context.
Finally, the care pathway is seen as a means of health knowledge management (k = 7) that optimizes quality, efficiency, and organization [ 68 , 70 , 72 ]. But this topic, although strongly addressed between 2011 and 2012, did not seem to be unanimously agreed upon because it was not very well addressed afterwards. However, particular attention can be paid to the elicitation and integration of the contextual knowledge of the various actors involved throughout the care pathway into daily healthcare routine [ 3 , 70 , 72 ].
Attribute theme 5: The structural context of the system and organizations
Firstly, the local physical context (k = 10), topical in the recent literature, includes both the number of units and their positions [ 12 , 67 ], but also the variety of services offered [ 13 ], and can be either an asset in terms of choice and accessibility or a constraint becoming a source of delay [ 14 ]. These barriers are important as the pathway crosses several formal healthcare organizations or informal care settings [ 24 ]. Therefore, the challenge of service integration has become essential [ 51 ].
Secondly, the availability of resources (k = 10) (human, material and financial) has a direct impact on the care pathway and the ability to meet the needs of the population [ 2 , 62 , 25 ]. A lack of adequate resources is an obvious obstacle to care pathways [ 50 ]. A lack of material and human resources, such as the availability of time at each service point [ 52 , 53 ], or the lack of an electronic medical record [ 5 ], meant the unnecessary repetition of history taking, examinations and full investigations. From a financial point of view, the financial and personal resources that people have, are also key to determinants of the care pathways followed by patients [ 51 ].
Thirdly, the social context (k = 7) is less addressed in the current literature but has shown rapid growth in recent years. Social structure includes material and social resources including roles, rules, norms, and values [ 3 , 24 , 53 , 68 ]. Some authors consider the social context as regularities of perception, behavior, belief and value that are expressed as customs, habits, patterns of behavior and other cultural artifacts [ 68 ]. Other authors consider that social structures shape people’s actions and that through people’s interactions they can then reproduce or change these social structures [ 53 ]. While others consider, for their part, that social and physical contexts can be at the origin of boundaries that mitigate against collaboration, adding to the complexity of shared clinical practices in this field [ 3 , 24 ].
Attribute theme 6: The special role of the information system and data management
Data management (k = 14) plays an increasingly important role in the analysis and improvement of care pathways. The implementation of a care flow management system aligned to clinical workflows [ 67 , 69 ], allows real-world data to be used [ 51 ], and visualized through performance dashboards to generate timely corrective action [ 4 ]. It also enables the analysis and monitoring of the variance in time and space within care pathways [ 43 ]. It is considered responsible for the rise of accountability [ 12 , 75 ].
The Electronic Health Record system is a support tool (k = 13) in several aspects. Numerous authors consider that it supports the patient-centered approach [ 51 , 67 ]. In particular, it has the capacity to support communication between health professionals, and between them and the patient [ 5 , 12 , 65 , 67 , 73 , 75 ], but also to support healthcare knowledge learning [ 67 , 73 ], and integrate clinical decision support into IT applications and clinical workflows [ 70 ]. This support throughout the care pathway can improve the quality of care and health outcomes by reducing medication errors and unnecessary investigations [ 5 ]. As stated by Fung-Kee-Fung et al. [ 4 ], the information system provides the fundamental connectivity across silos and professional groups to support the creation of care pathways and sustainable change at the system level.
The issue of digitalization (k = 5) has been treated very recently. It raises the issue of system integration throughout the care pathway. Despite the technological advances and the support of international organizations such as the guidelines on evidence-based digital health interventions for health system strengthening released by the WHO [ 76 ], there are still inefficiencies associated with trying to integrate EHRs across organizations [ 56 ]. These are frequently due to the use of different technological solutions by different stakeholders [ 30 ]. The challenge is therefore to propose a model for integrating information systems throughout the care pathway that are accessible to all stakeholders including patients themselves [ 4 , 50 , 51 , 65 ].
Attribute theme 7: The advent of the learning system
Although it was not frequently addressed, some authors have developed, very recently, the importance of setting up a learning system (k = 3) to support the care pathway. Resulting from the work of Quinn [ 77 ] and Senge [ 78 ], it consists of the development of a system to learn from itself and its past experience and improve the effectiveness, efficiency, safety, and patient and family/caregiver experiences [ 65 ] through a feedback loop [ 24 ]. Data on outcomes can be used as feedback to identify improvement opportunities at various stages of the process or at specific interfaces between stakeholders. The learning system promotes “individual competence, systems thinking, cohesive vision, team learning, and integrating different perspectives” [ 4 ].
Related concepts
The related concepts are confusingly close or even integrated with the main concept studied [ 40 ]. Given the complexity of the use of concepts, we have relied, in addition to definitions found on an analysis of a bibliometric network by integrating all 44 articles, excluding abstracts and bibliographies, into the Vosviewer® software (version 2020). The results help us to refine our understanding of the concepts which define the links between the different keywords. The care pathway bibliometric links are provided as a comparator (see Fig. 3 ).
Care pathway bibliometric links
Clinical pathway (Fig. 4 ) was initially defined by De Bleser et al. [ 38 ]. It is a multidisciplinary intervention that aims to integrate the guidelines into daily routine and manage medical activities in order to improve the quality of service and optimize the use of resources [ 70 ]. It integrates a process of care approach [ 72 ] and aims at standardize care on a procedure or an episode of care [ 38 , 49 , 68 ], integrating decision-making supported by knowledge. What differentiates it from the care pathway is that it is restrained in time and is anchored in an organization [ 25 ], or even a service, and does not deal with the patient experience in any way. Clinical pathways are thus integrated in care pathways at the local level and focus on a single phase of care.
Clinical pathway bibliometric links
Patient journey (Fig. 5 ) consisted of sequential steps in the clinical process of the patient through their experience. It can be defined as “the spatiotemporal distribution of patients’ interactions with multiple care settings over time” [ 24 ]. By analyzing and mapping the patient experience from their perspective [ 5 , 14 , 57 , 58 , 71 ], the objective is to improve the quality of the service provided [ 14 , 52 ]. In this approach, the patient journey is an integral part, and an essential component, of the care pathway. Although it also integrates the process approach, it is not linked to decision-making or knowledge management and does not consider structural constraints or the perception of the providers.
Patient journey bibliometric links
Finally, the care process (Fig. 6 ) is involved across the care continuum to standardize and streamline end-to-end care using management tools [ 4 ]. It is directly linked to the care pathway, the clinical pathway and the patient journey. However, although it supports coordination through decision-making and knowledge management, it does not consider the patient experience, the social relationships and the social dynamics. So, the care process is an integral part of the care pathway but does not consider all the characteristics of the latter.
Care process bibliometric links
Antecedents of the concept
Antecedents are events occurring or in place before the concept can emerge [ 40 ]. Our analysis has highlighted several prerequisites for care pathway implementation (see Additional file 4 ).
Firstly, several authors have stressed the importance of the availability of managerial skills (k = 10). They recommend the creation of a change management team [ 49 , 55 ] consisting of a multidisciplinary team integrating not only knowledge about care pathways [ 60 , 70 ], but also knowledge about operations research, information systems and industrial engineering [ 49 , 55 ]. In addition, some authors advocate the presence of key change leaders in the group included clinicians, administrators, IT leaders, process experts, data analysts, nurses, and patient and family members [ 4 , 24 ]. The project leaders must be available on a long-term basis [ 50 , 75 ], have the ability to understand system interdependencies [ 24 ] and have the ability to create a safe learning environment in which openness is encouraged and everyone’s opinion is valued [ 3 , 50 ]. This could be achieved by using consensus-driven approaches that could address institutional process barriers, resistance to change, and conflicting targets and priorities [ 4 ].
Secondly, care pathway projects should have a priori the adequate resources (k = 4), but their availability must be verified [ 62 , 75 ]. The presence of an EHR is necessary to have access to reliable data at the pre-analysis phase and during the implementation phase to identify the relationships between the context, the mechanisms and the results obtained [ 2 , 73 ].
Finally, other key success factors emerged from the literature (k = 10). Some authors noted that rules of co-involvement and a bottom-up strategy was needed [ 55 ]. Other authors emphasized that the selection of areas where there were clearly established deficiencies was essential given the cost of such projects, but also that the identification of any subgroups for whom its use may not be appropriate, was also required [ 73 ]. They highlighted the importance of following guidelines to achieve professional adherence [ 2 , 50 , 62 , 72 , 73 ], while maintaining flexibility in the approach to implementing a care pathway improvement program [ 62 ]. They also pointed to the importance of communicating on the progress of the project [ 50 ] and of monitoring the applicability of daily work tasks [ 73 ]. Finally, they consider it essential to embed the pathway into policy and strategy [ 2 , 50 , 72 , 75 ]. While others, for their part, highlighted the importance of defining an iterative feedback loop for individuals and aggregated operational and clinical data [ 4 , 24 ].
Consequences (outcomes) and identification of empirical referents
Consequences are events that are the results of the mobilization of the concept [ 40 ] and empirical referents, for their part, consist of observable phenomena by which defining attributes are recognized [ 40 ] (see Additional file 4 ). In a larger sense, this could be the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) by which one can recognize the defining attributes and their outcomes.
Although the terms of quality and safety, efficiency and process improvement were the first themes in terms of aims, the most frequently occurring theme in the findings pertained to effects on the patient experience (k = 16). These were measured in different ways, including the impact of waiting times (k = 10), patient satisfaction (k = 7) and the patient quality of life (QALYs) (k = 4). There were also attempts to analyze the patient experience more broadly (k = 5), and to integrate patient needs into the redesign of the care pathway [ 5 , 13 , 56 ].
Efficiency of care (k = 15) was strongly supported by some authors as a desired outcome in care pathways. This outcome was first seen, as an objective, through the costs and cost effectiveness of programs [ 49 , 55 , 61 , 70 ], however, more recently it has been considered a consequence of process improvements, rather than a program objective. It has been clearly defined as the reduction of costs through the reduction of the use of healthcare services [ 57 ]. Moreover, reduction in time spent in care, such as the length of stay or cycle time [ 2 , 55 ], is commonly the consequence of process improvements.
Quality of care (k = 11) was addressed but much less frequently than expected. In the global approach, time to diagnostic is a good empirical referent to analyze the capacity of the first steps of the care pathway [ 4 , 69 ]. Other referents such as reduction of unnecessary investigations and medication errors are also addressed but the number and types of complaints were addressed only by socio-political authors [ 53 ].
Health outcomes (k = 11) were also proposed but only since 2009 [ 73 ]. Clinical outcomes and mortality rates are empirical referents that are unanimously accepted. Recovery time and readmission rates were less frequently considered. Single disease index evaluation was proposed by very few authors [ 49 , 70 ].
Process metrics and patient flow (k = 11) was addressed but only the execution time was unanimously accepted as an empirical referent. Apart from the process variance which is shared, only few authors have developed other KPIs such as the percentage of pathway completion [ 70 ], and evaluation for the reasons of pathway failure [ 70 ].
The variance of practices (k = 9) was not frequently addressed as an empirical referent; however, this is one of the objectives of the care pathway addressed in the literature. The introduction of guidelines [ 2 ] aims to decrease the variation within or between practices (k = 3).
Continuity of care (k = 6) was poorly addressed, even though we might assume that this is one of the primary objectives of the care pathway. This may be due to the difficulty of providing tangible results given the duration of such interventions.
Some authors noted an improvement in documentation and data collection (k = 5), measured by rate of documentation [ 54 ], the ability to better understand resource adequacy (k = 3) and a better comprehension of the links between decision outcomes and process performance (k = 2).
Not defined as an outcome, the Human Resources metrics are proposed by some authors and notably diagnostic quality and referral appropriateness, professional competences and staffing levels. Only Carayon et al. [ 24 ] proposed to integrate the quality of working life as an indicator, based on the principle that well-being at work has a direct impact on individual performance and on the results of the care pathway.
Moreover, not present in the empirical references, the measure of the team relationship and coordination (k = 4) has been proposed by some authors, however, the type of indicator has not been clearly explained.
An integrative definition and conceptual framework of patient-centered care pathways
Given the results of our systematic review and concept analysis and our main objective of defining an integrative framework, we suggest the following definition:
“A patient-centered care pathway is a long-term and complex managerial intervention adopting a systemic approach, for a well-defined group of patients who journey across the entire continuum of care, from prevention and screening to recovery or palliative care. This intervention:
prioritizes the centricity of patients and caregivers by analyzing the patient experience through their needs and expectations, taking into account the need for information, education, engagement and involvement and integrates the patient relationships as a fundamental need.
supports the roles of professional actors involved in the care pathway by developing adherence to the patient-centered care approach; working on interdisciplinarity through the development of skills, both technical and above all relational; the clarification of roles and responsibilities; and by taking into account the experience of professionals both in understanding the organizational constraints and their well-being at work.
integrates a process of care approach through the modeling and improvement of the care pathway by continuously integrating the latest knowledge and information to support clinical decision-making and by defining feedback loops to continuously improve clinical and non-clinical process supported by operation management contained within process improvement methodology approaches;
embeds coordination structures through: the implementation of best practices and the translation of guidelines into daily practice; the support of informational continuity through the integration of services at the systemic level; the implementation of knowledge management along the care continuum; and the identification of leaders at each step of the care pathway;
adapts to the contexts of both the physical and social structures by integrating the human, material, economic and financial resource constraints, as well as the social dynamics of power and trust relationships;
is supported by information systems and data management, enabled by digitalization, which ensure the flow of information within the right context at the right time and place, and allows the continuous integration of the latest knowledge into the care flow and the management of accessible data in real time to monitor and evaluate variances in practices and outcomes;
promotes the development of a learning health system to support the care pathway.
The aim and shared goal of a care pathway is to meet the needs and expectations of patients through continuous improvement of patient experience, patient outcomes, quality and safety while taking into account operational and social realities of the system.”
We know that this definition is important but feel that there is a great need for clarification of this concept and how these interventions can be successful given the costs involved. Furthermore, we consider that the proper sequencing of the care pathway should be defined according to the following eight phases: (1) Prevention and screening; (2) Signs and symptoms; (3) Early detection; (4) Diagnostic; (5) Referral systems; (6) Treatment; (7) Follow-ups; (8) Reeducation or Palliative care. In this way, the development of recognized KPIs enabling international comparisons of care pathways should finally make it possible to share knowledge and improve care pathways.
According to this definition and based on the literature review, we propose the following integrative conceptual framework illustrated in Fig. 7 .
Integrative conceptual framework of care pathway
Using systematic review, concept analysis and bibliometric analysis, it was possible to develop a detailed understanding of the care pathway concept enabling us to propose an integrative conceptual framework and definition to try to meet the need for an international consensus and thus enabling international comparisons and improvement of care pathways.
The results of our work have highlighted the evolution and advances of the various uses of care pathways. Initially focused more on an organizational approach, there is growing support in the literature for a holistic approach that addresses the entire care across the continuum at the system level [ 4 , 24 , 42 , 60 ]. Thus, patient centeredness has become the primary focus as more and more authors focus on the patient experience as the unit of quality analysis. In doing so, they have given greater importance to social relationships and especially to the relationship as a basic need and highlighted the need to design the service line structures mirroring patients’ needs [ 56 ]. They therefore approach the patient, not only as the individual who follows the pathway, but as a social being who has needs and expectations to fulfill, making meeting the needs and expectations of the patient and caregivers the core of the care pathway [ 24 , 50 , 51 , 57 ]. However, the evaluation of the quality of healthcare services by the patient still raises several methodological questions to finally go beyond the simple consideration of satisfaction. Finally, patient and public involvement and patient engagement are also important issues to the point that some authors see a real power struggle between patients and clinicians [ 53 ] that can lead to tokenistic involvement.
The professional actors involved in the care pathway are naturally essential players, both because of their professional competencies and their ability to orient themselves towards the needs of the patient. However, they are also often part of a neglected factor. Some authors have shown one of the key criteria for the potential failure of care pathways is a failure to take into account the prevailing social dynamics and the importance of the buy-in of all stakeholders [ 65 ]. Moreover, some authors insist on the importance of the actors involved in the pathway to both integrate the social dynamics and confront the patient’s needs with operational realities and organizational constraints [ 24 ].
The operation management of process approach to care delivery also raises many challenges. Thus, some authors have developed tools for modeling and improving care processes by applying them in a systemic approach to incorporate clinical decision support into the modeling method [ 60 ]. This issue of continuous integration of updated guidelines into care pathways is indeed a major challenge given the rapid evolution of knowledge and the limited capacity of professionals to continuously integrate new knowledge. In addition, data simulation and data analysis methods coupled with process improvement methods are undeniable contributions to improve the issue of fluidity of processes and therefore the overall performance [ 49 ]. However, one of the pitfalls of staying focused on the process would be a failure to consider the social dimension, particularly the prevailing social dynamics.
Coordination structures are one of the points of improvement in the systemic approach. Ensuring the continuity of information along the care pathway, as well as having a formal leader for each portion of the pathway, would solve many of the problems of path breaks or unnecessary repetition of exams that cause unnecessary costs [ 5 , 56 , 59 ]. This begins with the implementation of a single information system and the integration of IT infrastructures across the entire care pathway at the system level and accessible to care professionals as well as patients and caregivers [ 4 , 50 , 51 , 65 ].
The structural context of the system and organizations cannot be neglected because it directly impacts the results of the implementation of the care pathway. Firstly, because some physical constraints such as distances between several organizational entities [ 12 , 14 ] can only be solved by major transformations in the infrastructures or in the initial process. Secondly, because failing to consider the dominant social dynamics could immediately call into question the entire care pathway intervention [ 3 , 24 ] by implementing only cosmetic changes and not transforming clinical, administrative and organizational practices in a sustainable manner.
The information system plays a special role in care pathway, not only because it is the support of the informational continuity, but also because it enables real-time data analysis to support decision-making within the care pathway in the form of feedback loops [ 4 , 24 , 51 ].
Finally, it seems clear that care pathway programs at the systemic level are one potential intervention which could benefit from the implementation of a learning system [ 4 ]. Care pathway outcome data can be used as feedback to identify improvement opportunities at various stages of the process or at specific interfaces between stakeholders. This approach makes it possible to support the continuous improvement of the care process.
Given the richness of the contributions of the last 20 years, we advocate an integrated approach resulting in a fine-grained and comprehensive understanding of care pathway. Our proposal is compatible with the definition of Vanhaecht et al. [ 25 ] currently used by the EPA, but in our opinion, enriches it. It allows users to specify the operational realities to which stakeholders should pay attention. Moreover, it insists on adaptation to the social realities and the changes that inevitably accompany it and directly impact the success or failure. However, we were surprised that the approach to managing organizational change and transformation of practices were little addressed. Only Van Citters et al. [ 65 ] had noted that change management approaches were critical for successful care transformation and that they had been largely neglected in care pathways. We share this point of view and believe that care pathway intervention leaders must develop communicative action skills to support practices transformation. Not mentioned in the selected literature, we propose to enrich our conceptual framework of communicative action proposed by Habermas [ 79 ]. From our point of view, this dimension could explain the failures of such interventions or at least the difficulty in developing sustainable transformations in practices.
In general, the concept analysis approach has raised several questions about the depth of concept analysis and its place in knowledge advancement [ 80 ]. However, we believe that the combination of systematic review rigor and concept analysis richness, was necessary to meet the aims of this study and produced an integrated conceptual framework which is ready for use. However, this research has some limitations. Although interest is growing, few studies offer comprehensive empirical results on the deployment of a care pathway and its outcomes in a global systemic approach over the entire continuum of care. Moreover, there are a few examples of in-depth analysis of car pathways over a long period of time. Together, this means that the literature still offers little insight into potential outcomes of care pathways. Lastly, our analysis was limited to peer-reviewed articles; including other contributions such as theses and dissertations as well as grey literature could have brought out other categories or themes.
This study has resulted in a fine-grained understanding of care pathways and in a clear definition relying on a powerful conceptual framework. It responds to a strong need for conceptual precision, as previous reviews have not addressed the care pathway on a systemic scale and in a holistic manner. In addition, our framework offers a holistic view of the pathway without being specific to a particular condition or context. Our framework encompasses 28 subcategories grouped into seven care pathway attributes that should be considered in complex care pathway intervention. It considers both operational and social realities and supporting the improvement and sustainable transformation of clinical, administrative, and organizational practices for the benefit of patients and caregivers, while taking into account professional experience, organizational constraints, and social dynamics. The formulation of these attributes, antecedents as success factors and consequences as potential outcomes, linked to their KPIs, allows the operationalization of this model for any pathway in any context. We believe that these results are of particular interest to policymakers, decision makers, managers and researchers alike, and that they could lead to an international consensus that would finally allow comparison of care pathway improvement programs. However, we consider that the development of a framework for analyzing the performance of such an intervention has yet to be developed in a more in-depth manner, such as by focusing on certain particularities of each phase so that managers and decision makers can rely on validated dashboards and KPIs. More empirical work needs to be done on the comprehensive approach, as defined in our proposed definition, to provide reliable results on the ability of these interventions to result in an overall improvement. In addition, the question of the understanding of social evaluation of the quality of care by the patient remains an open question, as the patient experience does not yet have conclusive KPIs as it is too often limited to patient satisfaction or QALYs.
Availability of data and materials
This systematic review is based on an analysis of 44 published papers which are all referenced within this manuscript. Data supporting our findings are included in the form of additional files.
Abbreviations
European Pathway Association
Institute of Medicine of America
Key Performance Indicator
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses
Quality Adjusted Life Year
World Health Organization
Kelly J, Dwyer J, Mackean T, O’Donnell K, Willis E. Coproducing Aboriginal patient journey mapping tools for improved quality and coordination of care. Aust J Prim Health. 2018;23(6):536–42. https://doi.org/10.1071/PY16069 .
Article Google Scholar
Bergin RJ, Whitfield K, White V, et al. Optimal care pathways: a national policy to improve quality of cancer care and address inequalities in cancer outcomes. J Cancer Policy. 2020;25:100245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpo.2020.100245 .
Hutchinson K, Herkes G, Shih P, et al. Identification and referral of patients with refractory epilepsy from the primary to the tertiary care interface in New South Wales, Australia. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;111:107232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107232 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fung-Kee-Fung M, Maziak D, Pantarotto J, et al. Regional process redesign of lung cancer care: a learning health system pilot project. Curr Oncol. 2018;25(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.25.3719 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alkandari M, Ryan K, Hollywood A. The experiences of people living with peripheral neuropathy in Kuwait-a process map of the patient journey. Pharmacy (Basel, Switzerland). 2019;7(3):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7030127 .
Institute of Medicine of America. Committee on quality of health Care in a. crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press; 2001. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.323.7322.1192 .
Book Google Scholar
Institute of Medicine of America. Committee on improving the quality of cancer care: addressing the challenges of an aging population, board on healthcare services, Institute of Medicine, delivering high-quality Cancer care: charting a new course for a system in crisis. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press; 2013. https://doi.org/10.17226/18359 .
National Academies of sciences, engineering, medicine. Committee on improving the quality of health care globally. Crossing the global quality chasm: improving healthcare worldwide. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2018. https://doi.org/10.17226/25152 .
World Health Organization. Framework on integrated, people-centered health services: report by the secretariat. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2016. https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA69/A69_39-en.pdf . Accessed June 16, 2020
Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Report on Cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing Care for all. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330745 . Accessed June 20, 2020
World Health Organization. Guide to developing a national quality policy and strategy: a practical approach to formulating a policy and strategy for quality of care improvement. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565561 . Accessed June 21, 2020
Valentijn PP, Biermann C, Bruijnzeels MA. Value-based integrated (renal) care: setting a development agenda for research and implementation strategies. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1586-0 .
Ponsignon F, Smart A, Phillips L. A customer journey perspective on service delivery system design: insights from healthcare. Int J Qual Relia Manag. 2018;35(10):2328–47. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJQRM-03-2018-0073 .
Gualandi R, Masella C, Viglione D, Tartaglini D. Exploring the hospital patient journey: what does the patient experience? PLoS One. 2019;14(12):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224899 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Schildmeijer K, Frykholm O, Kneck Å, Ekstedt M. Not a straight line-Patients' experiences of prostate Cancer and their journey through the healthcare system. Cancer Nurs. 2019;42(1):E36–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/NCC.0000000000000559 .
Burns K. ISQUA18-2613Patients measuring their experiences with their healthcare system: targeting improvement in access, quality, safety and patient and family Centred care outcomes. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018;30((suppl_2):22–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzy167.29 .
Nuti S, De Rosis S, Bonciani M, Murante AM. Rethinking healthcare performance evaluation systems towards the people-Centredness approach: their pathways, their experience, their evaluation. Healthc Pap. 2018;17(2):56–64. https://doi.org/10.12927/hcpap.2017.25408 .
Khan AI, Arthurs E, Gradin S, MacKinnon M, Sussman J, Kukreti V. Integrated care planning for cancer patients: a scoping review. Int J Integr Care. 2017;17(6):5. https://doi.org/10.5334/ijic.2543 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ran T, Cheng C-Y, Misselwitz B, Brenner H, Ubels J, Schlander M. Cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening strategies—a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(10):1969–1981. e1915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.014 .
Oxford Dictionaries. Concise medical dictionary: Main edition (10th edition). Oxford University Press. 2020. https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780198836612.001.0001/acref-9780198836612 . Accessed June 18, 2020.
Oxford Dictionaries. A dictionary of nursing (8th edition). Oxford University Press 2021. https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780198864646.001.0001/acref-9780198864646 . Accessed June 18, 2020.
Visser J, Beech R. Health operations management: patient flow logistics in health care. Psychol Press. 2005. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203356791 .
Vanhaecht K. The impact of clinical pathways on the organisation of care processes. [PhD Thesis, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven]. 2007; https://lirias.kuleuven.be/1718750?limo=0 . Accessed January 18, 2020.
Carayon P, Wooldridge A, Hoonakker P, Hundt AS, Kelly MM. SEIPS 3.0: human-centered design of the patient journey for patient safety. Appl Ergon. 2020;84:103033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2019.103033 .
Vanhaecht K, Panella M, van Zelm R, Sermeus W. An overview on the history and concept of care pathways as complex interventions. Int J Care Coord. 2010;14(3):117–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2019.103033 .
Seys D, Panella M, VanZelm R, et al. Care pathways are complex interventions in complex systems: new European pathway association framework. Int J Care Coord. 2019;22(1):5–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053434519839195 .
Solomon R, Damba C, Bryant S. Measuring quality at a system level: an impossible task? The Toronto central LHIN experience. Healthc Q. 2013;16(4):36–42.
Rayner J, Khan T, Chan C, Wu C. Illustrating the patient journey through the care continuum: leveraging structured primary care electronic medical record (EMR) data in Ontario, Canada using chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as a case study. Int J Med Inform. 2020;140:104159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104159 .
Galvin M, Madden C, Maguire S, et al. Patient journey to a specialist amyotrophic lateral sclerosis multidisciplinary clinic: an exploratory study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-015-1229-x .
McCarthy S, O'Raghallaigh P, Woodworth S, Lim YL, Kenny LC, Adam F. An integrated patient journey mapping tool for embedding quality in healthcare service reform. J Decis Syst. 2016;25:354–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2016.1187394 .
Mead N, Bower P. Patient-centredness: a conceptual framework and review of the empirical literature. Soc Sci Med. 2000;51(7):1087–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(00)00098-8 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Stewart M, Brown JB, Weston W, McWhinney IR, McWilliam CL, Freeman T. Patient-centered medicine: transforming the clinical method. Abingdon: Radcliffe Medical Press; 2003.
Van Hoeve JC, Vernooij RW, Fiander M, Nieboer P, Siesling S, Rotter T. Effects of oncological care pathways in primary and secondary care on patient, professional and health systems outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0693-x .
Baker E, Woolley A, Xyrichis A, Norton C, Hopkins P, Lee G. How does the implementation of a patient pathway-based intervention in the acute care of blunt thoracic injury impact on patient outcomes? A systematic review of the literature. Injury. 2020;51(8):1733–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2020.06.002 .
Seguin ML, Rangnekar A, Renedo A, Palafox B, McKee M, Balabanova D. Systematic review of frameworks used to conceptualise health pathways of individuals diagnosed with cardiovascular diseases. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(9):e002464. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002464 .
Beausejour M, Goulet L, Debbie Ehrmann F, et al. Pathways of healthcare utilisation in patients with suspected adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:500. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-015-1152-1 .
Chan RJ, Webster J, Bowers A. End-of-life care pathways for improving outcomes in caring for the dying. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2(2):CD008006. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008006.pub4 .
De Bleser L, Depreitere R, Waele KD, Vanhaecht K, Vlayen J, Sermeus W. Defining pathways. J Nurs Manag. 2006;14(7):553–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2934.2006.00702.x .
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021:372. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 .
Walker L, Avant K, Concept analysis. Strategies for theory construction in nursing (pp. 157–179). Upper Saddle River: Pearson; 2011.
Aromataris E, Munn Z (Editors). Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual (pp. 1-487). The Joanna Briggs Institute; 2017. Available from: https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org/ .
Cherif E, Martin-Verdier E, Rochette C. Investigating the healthcare pathway through patients’ experience and profiles: implications for breast cancer healthcare providers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05569-9 .
Kempa-Liehr AW, Lin CY-C, Britten R, et al. Healthcare pathway discovery and probabilistic machine learning. Int J Med Inform. 2020;137:104087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104087 .
Center for Evidence-Based Management. Critical appraisal of a survey [Available from: https://www.cebma.org/wp-content/uploads/Critical-Appraisal-Questions-for-a-Survey.pdf ]. Accessed September 27, 2020.
Institute for Public Health Sciences. 11 questions to help you make sense of descriptive/cross-sectional studies. Yeshiva University New York; 2002. [Available from: https://reache.files.wordpress.com/2010/03/cross-sectional-appraisal-tool.pdf ]. Accessed October 03, 2020.
Pluye P, Gagnon M-P, Griffiths F, Johnson-Lafleur J. A scoring system for appraising mixed methods research, and concomitantly appraising qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods primary studies in mixed studies reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009;46(4):529–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.01.009 .
Hannes K, Booth A, Harris J, et al. Celebrating methodological challenges and changes: reflecting on the emergence and importance of the role of qualitative evidence in Cochrane reviews. Syst Rev. 2013;2:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-2-84 .
Thomas DR. A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data. Am J Eval. 2006;27(2):237–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098214005283748 .
Aspland E, Gartner D, Harper P. Clinical pathway modelling: a literature review. Health Syst. 2020;10(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/20476965.2019.1652547 .
Busari JO, Yaldiz H, Gans RO, Duits AJ. Clinical leadership as an agent for change: a health system improvement intervention in Curaçao. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:787–98. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S262415 .
Devi R, Kanitkar K, Narendhar R, Sehmi K, Subramaniam K. A narrative review of the patient journey through the Lens of non-communicable diseases in low- and middle-income countries. Adv Ther. 2020;37(12):4808–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01519-3 .
Elkhuizen SG, Vissers JM, Mahdavi M, Van De Klundert JJ. Modeling patient journeys for demand segments in chronic care, with an illustration to type 2 diabetes. Front. Public Health. 2020;8:428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00428 eCollection 2020.
Ocloo J, Goodrich J, Tanaka H, Birchall-Searle J, Dawson D, Farr M. The importance of power, context and agency in improving patient experience through a patient and family centred care approach. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020;18(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-019-0487-1 .
Ayachi FL, Rahmouni HB, Ammar MB, Mahjoubi H. A reverse-engineering methodology for medical enhancement processes. Proc Comput Sci. 2019;164:714–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.12.240 .
De Belvis AG, Lohmeyer FM, Barbara A, et al. Ischemic stroke: clinical pathway impact. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2019;32(3):588–98. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHCQA-05-2018-0111 .
Louis CJ, Clark JR, Gray B, Brannon D, Parker V. Service line structure and decision-maker attention in three health systems: implications for patient-centered care. Health Care Manag Rev. 2019;44(1):41–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/HMR.0000000000000172 .
Meyer MA. Mapping the patient journey across the continuum: lessons learned from one Patient's experience. J Patient Exp. 2019;6(2):103–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/2374373518783763 .
Mohr P, Galderisi S, Boyer P, et al. Value of schizophrenia treatment I: The patient journey. Eur Psychiatry. 2018;53:107–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2018.06.007 .
Aziz AFA, Nordin NAM, Ali MF, Abd Aziz NA, Sulong S, Aljunid SM. The integrated care pathway for post stroke patients (iCaPPS): a shared care approach between stakeholders in areas with limited access to specialist stroke care services. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1963-8 .
Combi C, Oliboni B, Zardini A, Zerbato F. Ieee Seamless Design of Decision-Intensive Care Pathways. 2016:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICHI.2016.9 .
Gillespie J, McClean S, Garg L, Barton M, Scotney B, Fullerton K. A multi-phase DES modelling framework for patient-centred care. J Oper Res Soc. 2016;67(10):1239–49. https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2015.114 .
Shaw JM, Price MA, Clayton JM, et al. Developing a clinical pathway for the identification and management of anxiety and depression in adult cancer patients: an online Delphi consensus process. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2742-5 .
Walker C, O’Sullivan M, Ziedins I, Furian N. Faster Cancer treatment: using timestamp data to improve patient journeys. Healthc. 2016;4:252–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjdsi.2016.04.012 .
Grenness C, Hickson L, Laplante-Lévesque A, Davidson B. Patient-centred audiological rehabilitation: perspectives of older adults who own hearing aids. Int J Audiol. 2014;53(sup1):S68–75. https://doi.org/10.3109/14992027.2013.866280 .
Van Citters AD, Fahlman C, Goldmann DA, et al. Developing a pathway for high-value, patient-centered Total joint Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1619–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3398-4 .
Evans WK, Ung YC, Assouad N, Chyjek A, Sawka C. Improving the quality of lung cancer care in Ontario: the lung cancer disease pathway initiative. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(7):876–82. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e31828cb548 .
Huang B, Zhu P, Wu C. Customer-centered careflow modeling based on guidelines. J Med Syst. 2012;36(5):3307–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9823-5 .
Tehrani J, Liu K, Michel V. Ontology modeling for generation of clinical pathways. J Ind Eng Manag. 2012;5(2):442–56. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.586 .
Vandborg MP, Edwards K, Kragstrup J, Vedsted P, Hansen DG, Mogensen O. A new method for analyzing diagnostic delay in gynecological cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22(5):712–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0b013e31824c6d0e .
Yang H, Li W, Liu K, Zhang J. Knowledge-based clinical pathway for medical quality improvement. Inf Syst Front. 2012;14(1):105–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-011-9307-z .
Manchaiah VK, Stephens D, Meredith R. The patient journey of adults with hearing impairment: the patients’ views. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011;36(3):227–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-4486.2011.02320.x .
Yamazaki T, Ikeda M, Umemoto K. Enhancement of healthcare quality using clinical-pathways activities. Vine. 2011;41(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1108/03055721111115557 .
Allen D, Gillen E, Rixson L. Systematic review of the effectiveness of integrated care pathways: what works, for whom, in which circumstances? Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2009;7(2):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-1609.2009.00127.x .
Joosten TC, Bongers IM, Meijboom IBR. Care programmes and integrated care pathways. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2008;21(5):472–86. https://doi.org/10.1108/09526860810890440 .
Bond S, Balogh R, McKeever M. Care pathways: integrated clinical record or management information tool? J Integr Care Pathways. 2001;5(2):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/147322970100500204 .
World Health Organization. WHO guideline: recommendations on digital interventions for health system strengthening. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
Quinn JB. Intelligent Enterprise: a knowledge and service based paradigm for Industr: Simon and Schuster; 1992.
Senge PM. The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization (pp. 1-464). Currency; 2006[1990].
Habermas J. The theory of communicative action: Reason and the rationalization of society. Vol 1: Beacon press; 1984.
Lam Wai Shun P, Swaine B, Bottari C. Combining scoping review and concept analysis methodologies to clarify the meaning of rehabilitation potential after acquired brain injury. Disabil Rehabil. 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2020.1779825 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
No funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Département de management, Faculté des sciences de l’administration, Université Laval, 2325 rue de la Terrasse, Québec, QC, G1V 0A6, Canada
Jean-Baptiste Gartner, Kassim Said Abasse & André Côté
Centre de recherche en gestion des services de santé, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada
Centre de recherche du CHU de Québec, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada
Jean-Baptiste Gartner, Kassim Said Abasse, Paolo Landa & André Côté
Centre de recherche du CISSS de Chaudière-Appalaches, Québec, QC, Canada
Jean-Baptiste Gartner & André Côté
VITAM, Centre de recherche en santé durable, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada
Bibliothèque-Direction des services-conseils, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada
Frédéric Bergeron
Département d’opérations et systèmes de décision, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada
Paolo Landa
Université de Strasbourg, EM Strasbourg-Business School, HuManiS, Strasbourg, France
Célia Lemaire
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JBG study selection, appraisal and analysis, review design, manuscript writing, KSA study selection, study appraisal, review design, content discussion and manuscript review, FB review design, content discussion, critical input and manuscript review, PL study analysis, content discussion, critical input and manuscript review, CL study analysis, content discussion, critical input and manuscript review, and AC study analysis, review design, content discussion and manuscript review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
JBG: MSc, PhD candidate in the Department of Management, Laval University; KSA: PhD, Post-doctoral researcher in the Department of Management, Laval University; Frédéric Bergeron: Health Sciences Librarian, Laval University; PL: PhD, Assistant Professor in the Department of Operations and Decision Systems, Laval University; CL: PhD, Associate Professor at the EM Strasbourg Business School, Strasbourg University and AC: PhD, Full Professor & Director of the Centre for Health Services Management Research, Laval University.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jean-Baptiste Gartner .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Search strategy.
Additional file 2.
PRISMA 2020 checklist.
Additional file 3.
Quality appraisal of studies.
Additional file 4.
Concept analysis coding.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gartner, JB., Abasse, K.S., Bergeron, F. et al. Definition and conceptualization of the patient-centered care pathway, a proposed integrative framework for consensus: a Concept analysis and systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res 22 , 558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07960-0
Download citation
Received : 06 February 2022
Accepted : 13 April 2022
Published : 26 April 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07960-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Care pathway
- Patient journey
- Care process
- Patient-centered
- Healthcare management
- Sustainable transformation
- Learning health system
- Concept analysis
- Systematic review
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Short report
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024
A modified action framework to develop and evaluate academic-policy engagement interventions
- Petra Mäkelä ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0938-1175 1 ,
- Annette Boaz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0557-1294 2 &
- Kathryn Oliver ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4326-5258 1
Implementation Science volume 19 , Article number: 31 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
594 Accesses
19 Altmetric
Metrics details
There has been a proliferation of frameworks with a common goal of bridging the gap between evidence, policy, and practice, but few aim to specifically guide evaluations of academic-policy engagement. We present the modification of an action framework for the purpose of selecting, developing and evaluating interventions for academic-policy engagement.
We build on the conceptual work of an existing framework known as SPIRIT (Supporting Policy In Health with Research: an Intervention Trial), developed for the evaluation of strategies intended to increase the use of research in health policy. Our aim was to modify SPIRIT, (i) to be applicable beyond health policy contexts, for example encompassing social, environmental, and economic policy impacts and (ii) to address broader dynamics of academic-policy engagement. We used an iterative approach through literature reviews and consultation with multiple stakeholders from Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and policy professionals working at different levels of government and across geographical contexts in England, alongside our evaluation activities in the Capabilities in Academic Policy Engagement (CAPE) programme.
Our modifications expand upon Redman et al.’s original framework, for example adding a domain of ‘Impacts and Sustainability’ to capture continued activities required in the achievement of desirable outcomes. The modified framework fulfils the criteria for a useful action framework, having a clear purpose, being informed by existing understandings, being capable of guiding targeted interventions, and providing a structure to build further knowledge.
The modified SPIRIT framework is designed to be meaningful and accessible for people working across varied contexts in the evidence-policy ecosystem. It has potential applications in how academic-policy engagement interventions might be developed, evaluated, facilitated and improved, to ultimately support the use of evidence in decision-making.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to the literature
There has been a proliferation of theories, models and frameworks relating to translation of research into practice. Few specifically relate to engagement between academia and policy.
Challenges of evidence-informed policy-making are receiving increasing attention globally. There is a growing number of academic-policy engagement interventions but a lack of published evaluations.
This article contributes a modified action framework that can be used to guide how academic-policy engagement interventions might be developed, evaluated, facilitated, and improved, to support the use of evidence in policy decision-making.
Our contribution demonstrates the potential for modification of existing, useful frameworks instead of creating brand-new frameworks. It provides an exemplar for others who are considering when and how to modify existing frameworks to address new or expanded purposes while respecting the conceptual underpinnings of the original work.
Academic-policy engagement refers to ways that Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and their staff engage with institutions responsible for policy at national, regional, county or local levels. Academic-policy engagement is intended to support the use of evidence in decision-making and in turn, improve its effectiveness, and inform the identification of barriers and facilitators in policy implementation [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Challenges of evidence-informed policy-making are receiving increasing attention globally, including the implications of differences in cultural norms and mechanisms across national contexts [ 4 , 5 ]. Although challenges faced by researchers and policy-makers have been well documented [ 6 , 7 ], there has been less focus on actions at the engagement interface. Pragmatic guidance for the development, evaluation or comparison of structured responses to the challenges of academic-policy engagement is currently lacking [ 8 , 9 ].
Academic-policy engagement exists along a continuum of approaches from linear (pushing evidence out from academia or pulling evidence into policy), relational (promoting mutual understandings and partnerships), and systems approaches (addressing identified barriers and facilitators) [ 4 ]. Each approach is underpinned by sets of beliefs, assumptions and expectations, and each raises questions for implementation and evaluation. Little is known about which academic-policy engagement interventions work in which settings, with scarce empirical evidence to inform decisions about which interventions to use, when, with whom, or why, and how organisational contexts can affect motivation and capabilities for such engagement [ 10 ]. A deeper understanding through the evaluation of engagement interventions will help to identify inhibitory and facilitatory factors, which may or may not transfer across contexts [ 11 ].
The intellectual technologies [ 12 ] of implementation science have proliferated in recent decades, including models, frameworks and theories that address research translation and acknowledge difficulties in closing the gap between research, policy and practice [ 13 ]. Frameworks may serve overlapping purposes of describing or guiding processes of translating knowledge into practice (e.g. the Quality Implementation Framework [ 14 ]); or helping to explain influences on implementation outcomes (e.g. the Theoretical Domains Framework [ 15 ]); or guiding evaluation (e.g. the RE-AIM framework [ 16 , 17 ]. Frameworks can offer an efficient way to look across diverse settings and to identify implementation differences [ 18 , 19 ]. However, the abundance of options raises its own challenges when seeking a framework for a particular purpose, and the use of a framework may mean that more weight is placed on certain aspects, leading to a partial understanding [ 13 , 17 ].
‘Action frameworks’ are predictive models that intend to organise existing knowledge and enable a logical approach for the selection, implementation and evaluation of intervention strategies, thereby facilitating the expansion of that knowledge [ 20 ]. They can guide change by informing and clarifying practical steps to follow. As flexible entities, they can be adapted to accommodate new purposes. Framework modification may include the addition of constructs or changes in language to expand applicability to a broader range of settings [ 21 ].
We sought to identify one organising framework for evaluation activities in the Capabilities in Academic-Policy Engagement (CAPE) programme (2021–2023), funded by Research England. The CAPE programme aimed to understand how best to support effective and sustained engagement between academics and policy professionals across the higher education sector in England [ 22 ]. We first searched the literature and identified an action framework that was originally developed between 2011 and 2013, to underpin a trial known as SPIRIT (Supporting Policy In health with Research: an Intervention Trial) [ 20 , 23 ]. This trial evaluated strategies intended to increase the use of research in health policy and to identify modifiable points for intervention.
We selected the SPIRIT framework due to its potential suitability as an initial ‘road map’ for our evaluation of academic-policy interventions in the CAPE programme. The key elements of the original framework are catalysts, organisational capacity, engagement actions, and research use. We wished to build on the framework’s embedded conceptual work, derived from literature reviews and semi-structured interviews, to identify policymakers’ views on factors that assist policy agencies’ use of research [ 20 ]. The SPIRIT framework developers defined its “locus for change” as the policy organisation ( [ 20 ], p. 151). They proposed that it could offer the beginning of a process to identify and test pathways in policy agencies’ use of evidence.
Our goal was to modify SPIRIT to accommodate a different locus for change: the engagement interface between academia and policy. Instead of imagining a linear process in which knowledge comes from researchers and is transmitted to policy professionals, we intended to extend the framework to multidirectional relational and system interfaces. We wished to include processes and influences at individual, organisational and system levels, to be relevant for HEIs and their staff, policy bodies and professionals, funders of engagement activities, and facilitatory bodies. Ultimately, we seek to address a gap in understanding how engagement strategies work, for whom, how they are facilitated, and to improve the evaluation of academic-policy engagement.
We aimed to produce a conceptually guided action framework to enable systematic evaluation of interventions intending to support academic-policy engagement.
We used a pragmatic combination of processes for framework modification during our evaluation activities in the CAPE programme [ 22 ]. The CAPE programme included a range of interventions: seed funding for academic and policy professional collaboration in policy-focused projects, fellowships for academic placements in policy settings, or for policy professionals with HEI staff, training for policy professionals, and a range of knowledge exchange events for HEI staff and policy professionals. We modified the SPIRIT framework through iterative processes shown in Table 1 , including reviews of literature; consultations with HEI staff and policy professionals across a range of policy contexts and geographic settings in England, through the CAPE programme; and piloting, refining and seeking feedback from stakeholders in academic-policy engagement.
A number of characteristics of the original SPIRIT framework could be applied to academic-policy engagement. While keeping the core domains, we modified the framework to capture dynamics of engagement at multiple academic and policy levels (individuals, organisations and system), extending beyond the original unidirectional focus on policy agencies’ use of research. Components of the original framework, the need for modifications, and their corresponding action-oriented implications are shown in Table 2 . We added a new domain, ‘Impacts and Sustainability’, to consider transforming and enduring aspects at the engagement interface. The modified action framework is shown in Fig. 1 .
SPIRIT Action Framework Modified for Academic-Policy Engagement Interventions (SPIRIT-ME), adapted with permission from the Sax Institute. Legend: The framework acknowledges that elements in each domain may influence other elements through mechanisms of action and that these do not necessarily flow through the framework in a ‘pipeline’ sequence. Mechanisms of action are processes through which engagement strategies operate to achieve desired outcomes. They might rely on influencing factors, catalysts, an aspect of an intervention action, or a combination of elements
Identifying relevant theories or models for missing elements
Catalysts and capacity.
Within our evaluation of academic-policy interventions, we identified a need to develop the original domain of catalysts beyond ‘policy/programme need for research’ and ‘new research with potential policy relevance’. Redman et al. characterised a catalyst as “a need for information to answer a particular problem in policy or program design, or to assist in supporting a case for funding” in the original framework (p. 149). We expanded this “need for information” to a perceived need for engagement, by either HEI staff or policy professionals, linking to the potential value they perceived in engaging. Specifically, there was a need to consider catalysts at the level of individual engagement, for example HEI staff wanting research to have real-world impact, or policy professionals’ desires to improve decision-making in policy, where productive interactions between academic and policy stakeholders are “necessary interim steps in the process that lead to societal impact” ( [ 24 ], p. 214). The catalyst domain expands the original emphasis on a need for research, to take account of challenges to be overcome by both the academic and policy communities in knowing how, and with whom, to engage and collaborate with [ 25 ].
We used a model proposing that there are three components for any behaviour: capability, opportunity and motivation, which is known as the COM-B model [ 26 ]. Informed by CAPE evaluation activities and our discussions with stakeholders, we mapped the opportunity and motivation constructs into the ‘catalysts’ domain of the original framework. Opportunity is an attribute of the system that can facilitate engagement. It may be a tangible factor such as the availability of seed funding, or a perceived social opportunity such as institutional support for engagement activities. Opportunity can act at the macro level of systems and organisational structures. Motivation acts at the micro level, deriving from an individual’s mental processes that stimulate and direct their behaviours; in this case, taking part in academic-policy engagement actions. The COM-B model distinguishes between reflective motivation through conscious planning and automatic motivation that may be instinctive or affective [ 26 ].
We presented an early application of the COM-B model to catalysts for engagement at an academic conference, enabling an informal exploration of attendees’ subjective views on the clarity and appropriateness, when developing the framework. This application introduces possibilities for intervention development and support by highlighting ‘opportunities’ and ‘motivations’ as key catalysts in the modified framework.
Within the ‘capacity’ domain, we retained the original levels of individuals, organisations and systems. We introduced individual capability as a construct from the COM-B model, describing knowledge, skills and abilities to generate behaviour change as a precursor of academic-policy engagement. This reframing extends the applicability to HEI staff as well as policy professionals. It brings attention to different starting conditions for individuals, such as capabilities developed through previous experience, which can link with social opportunity (for example, through training or support) as a catalyst.
Engagement actions
We identified a need to modify the original domain ‘engagement actions’ to extend the focus beyond the use of research. We added three categories of engagement actions described by Best and Holmes [ 27 ]: linear, relational, and systems. These categories were further specified through a systematic mapping of international organisations’ academic-policy engagement activities [ 5 ]. This framework modification expands the domain to encompass: (i) linear ‘push’ of evidence from academia or ‘pull’ of evidence into policy agencies; (ii) relational approaches focused on academic-policy-maker collaboration; and (iii) systems’ strategies to facilitate engagement for example through strategic leadership, rewards or incentives [ 5 ].
We retained the elements in the original framework’s ‘outcomes’ domain (instrumental, tactical, conceptual and imposed), which we found could apply to outcomes of engagement as well as research use. For example, discussions between a policy professional and a range of academics could lead to a conceptual outcome by considering an issue through different disciplinary lenses. We expanded these elements by drawing on literature on engagement outcomes [ 28 ] and through sense-checking with stakeholders in CAPE. We added capacity-building (changes to skills and expertise), connectivity (changes to the number and quality of relationships), and changes in organisational culture or attitude change towards engagement.
Impacts and sustainability
The original framework contained endpoints described as: ‘Better health system and health outcomes’ and ‘Research-informed health policy and policy documents’. For modification beyond health contexts and to encompass broader intentions of academic-policy engagement, we replaced these elements with a new domain of ‘Impacts and sustainability’. This domain captures the continued activities required in achievement of desirable outcomes [ 29 ]. The modification allows consideration of sustainability in relation to previous stages of engagement interventions, through the identification of beneficial effects that are sustained (or not), in which ways, and for whom. Following Borst [ 30 ], we propose a shift from the expectation that ‘sustainability’ will be a fixed endpoint. Instead, we emphasise the maintenance work needed over time, to sustain productive engagement.
Influences and facilitators
We modified the overarching ‘Policy influences’ (such as public opinion and media) in the original framework, to align with factors influencing academic-policy engagement beyond policy agencies’ use of research. We included influences at the level of the individual (for example, individual moral discretion [ 31 ]), the organisation (for example, managerial practices [ 31 ]) and the system (for example, career incentives [ 32 ]). Each of these processes takes place in the broader context of social, policy and financial environments (that is, potential sources of funding for engagement actions) [ 29 ].
We modified the domain ‘Reservoir of relevant and reliable research’ underpinning the original framework, replacing it with ‘Reservoir of people skills’, to emphasise intangible facilitatory work at the engagement interface, in place of concrete research outputs. We used the ‘Promoting Action on Research Implementation in Health Services’ (PARiHS) framework [ 33 , 34 ], which gives explicit consideration to facilitation mechanisms for researchers and policy-makers [ 13 ] . Here, facilitation expertise includes mechanisms that focus on particular goals (task-oriented facilitation) or enable changes in ways of working (holistic-oriented facilitation). Task-orientated facilitation skills might include, for example, the provision of contacts, practical help or project management skills, while holistic-oriented facilitation involves building and sustaining partnerships or support skills’ development across a range of capabilities. These conceptualisations aligned with our consultations with facilitators of engagement in CAPE. We further extended these to include aspects identified in our evaluation activities: strategic planning, contextual awareness and entrepreneurial orientation.
Piloting and refining the modified framework through stakeholder engagement
We piloted an early version of the modified framework to develop a survey for all CAPE programme participants. During this pilot stage, we sought feedback from the CAPE delivery team members across HEI and policy contexts in England. CAPE delivery team members are based at five collaborating universities with partners in the Parliamentary Office for Science and Technology (POST) and Government Office for Science (GO-Science), and Nesta (a British foundation that supports innovation). The HEI members include academics and professional services knowledge mobilisation staff, responsible for leading and coordinating CAPE activities. The delivery team comprised approximately 15–20 individuals (with some fluctuations according to individual availabilities).
We assessed appropriateness and utility, refined terminology, added domain elements and explored nuances. For example, stakeholders considered the multi-layered possibilities within the domain ‘capacity’, where some HEI or policy departments may demonstrate a belief that it is important to use research in policy, but this might not be the perception of the organisation as a whole. We also sought stakeholders’ views on the utility of the new domains, for example, the identification of facilitator expertise such as acting as a knowledge broker or intermediary; providing training, advice or guidance; facilitating engagement opportunities; creating engagement programmes; and sustainability of engagement that could be conceptualised at multiple levels: personally, in processes or through systems.
Testing against criteria for useful action framework
The modified framework fulfils the properties of a useful action framework [ 20 ]:
It has a clearly articulated purpose: development and evaluation of academic-policy engagement interventions through linear, relational and/or system approaches. It has identified loci for change, at the level of the individual, the organisation or system.
It has been informed by existing understandings, including conceptual work of the original SPIRIT framework, conceptual models identified from the literature, published empirical findings, understandings from consultation with stakeholders, and evaluation activities in CAPE.
It can be applied to the development, implementation and evaluation of targeted academic-policy engagement actions, the selection of points for intervention and identification of potential outcomes, including the work of sustaining them and unanticipated consequences.
It provides a structure to build knowledge by guiding the generation of hypotheses about mechanisms of action in academic-policy engagement interventions, or by adapting the framework further through application in practice.
The proliferation of frameworks to articulate processes of research translation reveals a need for their adaptation when applied in specific contexts. The majority of models in implementation science relate to translation of research into practice. By contrast, our focus was on engagement between academia and policy. There are a growing number of academic-policy engagement interventions but a lack of published evaluations [ 10 ].
Our framework modification provides an exemplar for others who are considering how to adapt existing conceptual frameworks to address new or expanded purposes. Field et al. identified the multiple, idiosyncratic ways that the Knowledge to Action Framework has been applied in practice, demonstrating its ‘informal’ adaptability to different healthcare settings and topics [ 35 ]. Others have reported on specific processes for framework refinement or extension. Wiltsey Stirman et al. adopted a framework that characterised forms of intervention modification, using a “pragmatic, multifaceted approach” ( [ 36 ], p.2). The authors later used the modified version as a foundation to build a further framework to encompass implementation strategies in a range of settings [ 21 ]. Oiumet et al. used the approach of borrowing from a different disciplinary field for framework adaptation, by using a model of absorptive capacity from management science to develop a conceptual framework for civil servants’ absorption of research knowledge [ 37 ].
We also took the approach of “adapting the tools we think with” ( [ 38 ], p.305) during our evaluation activities on the CAPE programme. Our conceptual modifications align with the literature on motivation and entrepreneurial orientation in determining policy-makers’ and researchers’ intentions to carry out engagement in addition to ‘usual’ roles [ 39 , 40 ]. Our framework offers an enabler for academic-policy engagement endeavours, by providing a structure for approaches beyond the linear transfer of information, emphasising the role of multidirectional relational activities, and the importance of their facilitation and maintenance. The framework emphasises the relationship between individuals’ and groups’ actions, and the social contexts in which these are embedded. It offers additional value by capturing the organisational and systems level factors that influence evidence-informed policymaking, incorporating the dynamic features of contexts shaping engagement and research use.
Conclusions
Our modifications extend the original SPIRIT framework’s focus on policy agencies’ use of research, to encompass dynamic academic-policy engagement at the levels of individuals, organisations and systems. Informed by the knowledge and experiences of policy professionals, HEI staff and knowledge mobilisers, it is designed to be meaningful and accessible for people working across varied contexts and functions in the evidence-policy ecosystem. It has potential applications in how academic-policy engagement interventions might be developed, evaluated, facilitated and improved, and it fulfils Redman et al.’s criteria as a useful action framework [ 20 ].
We are testing the ‘SPIRIT-Modified for Engagement’ framework (SPIRIT-ME) through our ongoing evaluation of academic-policy engagement activities. Further empirical research is needed to explore how the framework may capture ‘additionality’, that is, to identify what is achieved through engagement actions in addition to what would have happened anyway, including long-term changes in strategic behaviours or capabilities [ 41 , 42 , 43 ]. Application of the modified framework in practice will highlight its strengths and limitations, to inform further iterative development and adaptation.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Stewart R, Dayal H, Langer L, van Rooyen C. Transforming evidence for policy: do we have the evidence generation house in order? Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2022;9(1):1–5.
Article Google Scholar
Sanderson I. Complexity, ‘practical rationality’ and evidence-based policy making. Policy Polit. 2006;34(1):115–32.
Lewin S, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Carlsen B, Colvin CJ, Gülmezoglu M, et al. Using Qualitative Evidence in Decision Making for Health and Social Interventions: An Approach to Assess Confidence in Findings from Qualitative Evidence Syntheses (GRADE-CERQual). PLOS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001895.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bonell C, Meiksin R, Mays N, Petticrew M, McKee M. Defending evidence informed policy making from ideological attack. BMJ. 2018;10(362):k3827.
Hopkins A, Oliver K, Boaz A, Guillot-Wright S, Cairney P. Are research-policy engagement activities informed by policy theory and evidence? 7 challenges to the UK impact agenda. Policy Des Pract. 2021;4(3):341–56.
Google Scholar
Head BW. Toward More “Evidence-Informed” Policy Making? Public Adm Rev. 2016;76(3):472–84.
Walker LA, Lawrence NS, Chambers CD, Wood M, Barnett J, Durrant H, et al. Supporting evidence-informed policy and scrutiny: A consultation of UK research professionals. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(3):e0214136.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Graham ID, Tetroe J, Group the KT. Planned action theories. In: Knowledge Translation in Health Care. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd; 2013. p. 277–87. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118413555.ch26 Cited 2023 Nov 1
Davies HT, Powell AE, Nutley SM. Mobilising knowledge to improve UK health care: learning from other countries and other sectors – a multimethod mapping study. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015. (Health Services and Delivery Research). Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK299400/ Cited 2023 Nov 1
Oliver K, Hopkins A, Boaz A, Guillot-Wright S, Cairney P. What works to promote research-policy engagement? Evid Policy. 2022;18(4):691–713.
Nelson JP, Lindsay S, Bozeman B. The last 20 years of empirical research on government utilization of academic social science research: a state-of-the-art literature review. Adm Soc. 2023;28:00953997231172923.
Bell D. Technology, nature and society: the vicissitudes of three world views and the confusion of realms. Am Sch. 1973;42:385–404.
Milat AJ, Li B. Narrative review of frameworks for translating research evidence into policy and practice. Public Health Res Pract. 2017; Available from: https://apo.org.au/sites/default/files/resource-files/2017-02/apo-nid74420.pdf Cited 2023 Nov 1
Meyers DC, Durlak JA, Wandersman A. The quality implementation framework: a synthesis of critical steps in the implementation process. Am J Community Psychol. 2012;50(3–4):462–80.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cane J, O’Connor D, Michie S. Validation of the theoretical domains framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):37.
Glasgow RE, Battaglia C, McCreight M, Ayele RA, Rabin BA. Making implementation science more rapid: use of the RE-AIM framework for mid-course adaptations across five health services research projects in the veterans health administration. Front Public Health. 2020;8. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00194 Cited 2023 Jun 13
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci IS. 2015 Apr 21 10. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4406164/ Cited 2020 May 4
Sheth A, Sinfield JV. An analytical framework to compare innovation strategies and identify simple rules. Technovation. 2022;1(115):102534.
Birken SA, Powell BJ, Shea CM, Haines ER, Alexis Kirk M, Leeman J, et al. Criteria for selecting implementation science theories and frameworks: results from an international survey. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):124.
Redman S, Turner T, Davies H, Williamson A, Haynes A, Brennan S, et al. The SPIRIT Action Framework: A structured approach to selecting and testing strategies to increase the use of research in policy. Soc Sci Med. 2015;136:147–55.
Miller CJ, Barnett ML, Baumann AA, Gutner CA, Wiltsey-Stirman S. The FRAME-IS: a framework for documenting modifications to implementation strategies in healthcare. Implement Sci. 2021;16(1):36.
CAPE. CAPE. 2021. CAPE Capabilities in Academic Policy Engagement. Available from: https://www.cape.ac.uk/ Cited 2021 Aug 3
CIPHER Investigators. Supporting policy in health with research: an intervention trial (SPIRIT)—protocol for a stepped wedge trial. BMJ Open. 2014;4(7):e005293.
Spaapen J, Van Drooge L. Introducing ‘productive interactions’ in social impact assessment. Res Eval. 2011;20(3):211–8.
Williams C, Pettman T, Goodwin-Smith I, Tefera YM, Hanifie S, Baldock K. Experiences of research-policy engagement in policymaking processes. Public Health Res Pract. 2023. Online early publication. https://doi.org/10.17061/phrp33232308 .
Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci. 2011;6(1):42.
Best A, Holmes B. Systems thinking, knowledge and action: towards better models and methods. Evid Policy J Res Debate Pract. 2010;6(2):145–59.
Edwards DM, Meagher LR. A framework to evaluate the impacts of research on policy and practice: A forestry pilot study. For Policy Econ. 2020;1(114):101975.
Scheirer MA, Dearing JW. An agenda for research on the sustainability of public health programs. Am J Public Health. 2011;101(11):2059–67.
Borst RAJ, Wehrens R, Bal R, Kok MO. From sustainability to sustaining work: What do actors do to sustain knowledge translation platforms? Soc Sci Med. 2022;1(296):114735.
Zacka B. When the state meets the street: public service and moral agency. Harvard university press; 2017. Available from: https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=3KdFDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=zacka+when+the+street&ots=x93YEHPKhl&sig=9yXKlQiFZ0XblHrbYKzvAMwNWT4 Cited 2023 Nov 28
Torrance H. The research excellence framework in the United Kingdom: processes, consequences, and incentives to engage. Qual Inq. 2020;26(7):771–9.
Rycroft-Malone J. The PARIHS framework—a framework for guiding the implementation of evidence-based practice. J Nurs Care Qual. 2004;19(4):297–304.
Stetler CB, Damschroder LJ, Helfrich CD, Hagedorn HJ. A guide for applying a revised version of the PARIHS framework for implementation. Implement Sci. 2011;6(1):99.
Field B, Booth A, Ilott I, Gerrish K. Using the knowledge to action framework in practice: a citation analysis and systematic review. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):172.
Wiltsey Stirman S, Baumann AA, Miller CJ. The FRAME: an expanded framework for reporting adaptations and modifications to evidence-based interventions. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):58.
Ouimet M, Landry R, Ziam S, Bédard PO. The absorption of research knowledge by public civil servants. Evid Policy. 2009;5(4):331–50.
Martin D, Spink MJ, Pereira PPG. Multiple bodies, political ontologies and the logic of care: an interview with Annemarie Mol. Interface - Comun Saúde Educ. 2018;22:295–305.
Sajadi HS, Majdzadeh R, Ehsani-Chimeh E, Yazdizadeh B, Nikooee S, Pourabbasi A, et al. Policy options to increase motivation for improving evidence-informed health policy-making in Iran. Health Res Policy Syst. 2021;19(1):91.
Athreye S, Sengupta A, Odetunde OJ. Academic entrepreneurial engagement with weak institutional support: roles of motivation, intention and perceptions. Stud High Educ. 2023;48(5):683–94.
Bamford D, Reid I, Forrester P, Dehe B, Bamford J, Papalexi M. An empirical investigation into UK university–industry collaboration: the development of an impact framework. J Technol Transf. 2023 Nov 13; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-023-10043-9 Cited 2023 Dec 20
McPherson AH, McDonald SM. Measuring the outcomes and impacts of innovation interventions assessing the role of additionality. Int J Technol Policy Manag. 2010;10(1–2):137–56.
Hind J. Additionality: a useful way to construct the counterfactual qualitatively? Eval J Australas. 2010;10(1):28–35.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the CAPE Programme Delivery Group members, for many discussions throughout this work. Our thanks also go to the Sax Institute, Australia (where the original SPIRIT framework was developed), for reviewing and providing helpful feedback on the article. We also thank our reviewers who made very constructive suggestions, which have strengthened and clarified our article.
The evaluation of the CAPE programme, referred to in this report, was funded by Research England. The funding body had no role in the design of the study, analysis, interpretation or writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health Services Research and Policy, Faculty of Public Health and Policy, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, 15-17 Tavistock Place, Kings Cross, London, WC1H 9SH, UK
Petra Mäkelä & Kathryn Oliver
Health and Social Care Workforce Research Unit, The Policy Institute, Virginia Woolf Building, Kings College London, 22 Kingsway, London, WC2B 6LE, UK
Annette Boaz
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PM conceptualised the modification of the framework reported in this work. All authors made substantial contributions to the design of the work. PM drafted the initial manuscript. AB and KO contributed to revisions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Petra Mäkelä .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approval was granted for the overarching CAPE evaluation by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Research Ethics Committee (reference 26347).
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mäkelä, P., Boaz, A. & Oliver, K. A modified action framework to develop and evaluate academic-policy engagement interventions. Implementation Sci 19 , 31 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01359-7
Download citation
Received : 09 January 2024
Accepted : 20 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-024-01359-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence-informed policy
- Academic-policy engagement
- Framework modification
Implementation Science
ISSN: 1748-5908
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Literature Review 4:2
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 16 April 2024
Designing a framework for entrepreneurship education in Chinese higher education: a theoretical exploration and empirical case study
- Luning Shao 1 ,
- Yuxin Miao 2 ,
- Shengce Ren 3 ,
- Sanfa Cai 4 &
- Fei Fan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8756-5140 5 , 6
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 519 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Business and management
Entrepreneurship education (EE) has rapidly evolved within higher education and has emerged as a pivotal mechanism for cultivating innovative and entrepreneurial talent. In China, while EE has made positive strides, it still faces a series of practical challenges. These issues cannot be effectively addressed solely through the efforts of universities. Based on the triple helix (TH) theory, this study delves into the unified objectives and practical content of EE in Chinese higher education. Through a comprehensive literature review on EE, coupled with educational objectives, planned behavior, and entrepreneurship process theories, this study introduces the 4H objective model of EE. 4H stands for Head (mindset), Hand (skill), Heart (attitude), and Help (support). Additionally, the research extends to a corresponding content model that encompasses entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup services, and the entrepreneurial climate as tools for achieving the objectives. Based on a single-case approach, this study empirically explores the application of the content model at T-University. Furthermore, this paper elucidates how the university plays a role through the comprehensive development of entrepreneurial learning, practices, services, and climate in nurturing numerous entrepreneurs and facilitating the flourishing of the regional entrepreneurial ecosystem. This paper provides important contributions in its application of TH theory to develop EE within the Chinese context, and it provides clear guidance by elucidating the core objectives and practical content of EE. The proposed conceptual framework serves not only as a guiding tool but also as a crucial conduit for fostering the collaborative development of the EE ecosystem. To enhance the robustness of the framework, this study advocates strengthening empirical research on TH theory through multiple and comparative case studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Extra-curricular support for entrepreneurship among engineering students: development of entrepreneurial self-efficacy and intentions
Deepa Subhadrammal, Martin Bliemel, … Helene de Burgh-Woodman
The mediating effects of entrepreneurial self-efficacy in the relationship between entrepreneurship education and start-up readiness
Adeshina Olushola Adeniyi
Individual entrepreneurial orientation for entrepreneurial readiness
Adeshina Olushola Adeniyi, Vangeli Gamede & Evelyn Derera
Introduction
In the era of the knowledge economy, entrepreneurship has emerged as a fundamental driver of social and economic development. As early as 1911, Schumpeter proposed the well-known theory of economic development, wherein he first introduced the concepts of entrepreneurship and creative destruction as driving forces behind socioeconomic development. Numerous endogenous growth theories, such as the entrepreneurial ecosystem mechanism of Acs et al. ( 2018 ), which also underscores the pivotal role of entrepreneurship in economic development, are rooted in Schumpeter’s model. Recognized as a key means of cultivating entrepreneurs and enhancing their capabilities (Jin et al., 2023 ), entrepreneurship education (EE) has received widespread attention over the past few decades, especially in the context of higher education (Wong & Chan, 2022 ).
Driven by international trends and economic demands, China places significant emphasis on nurturing innovative talent and incorporating EE into the essential components of its national education system. The State Council’s “Implementation Opinions on Deepening the Reform of Innovation and Entrepreneurship Education in Higher Education” (hereafter referred to as the report) underscores the urgent necessity for advancing reforms in innovation and EE in higher education institutions. This initiative aligns with the national strategy of promoting innovation-driven development and enhancing economic quality and efficiency. Furthermore, institutions at various levels are actively and eagerly engaging in EE.
Despite the positive strides made in EE in China, its development still faces a series of formidable practical challenges. As elucidated in the report, higher education institutions face challenges such as a delay in the conceptualization of EE, inadequate integration with specialized education, and a disconnect from practical applications. Furthermore, educators exhibit a deficiency in awareness and capabilities, which manifests in a singular and less effective teaching methodology. The shortage of practical platforms, guidance, and support emphasizes the pressing need for comprehensive innovation and EE systems. These issues necessitate collaborative efforts from universities, industry, and policymakers.
Internationally established solutions for the current challenges have substantially matured, providing invaluable insights and guidance for the development of EE in the Chinese context. In the late 20th century, the concept of the entrepreneurial university gained prominence (Etzkowitz et al., 2000 ). Then, entrepreneurial universities expanded their role from traditional research and teaching to embrace a “third mission” centered on economic development. This transformation entailed fostering student engagement in entrepreneurial initiatives by offering resources and guidance to facilitate the transition of ideas into viable entrepreneurial ventures. Additionally, these entrepreneurial universities played a pivotal role in advancing the triple helix (TH) model (Henry, 2009 ). The TH model establishes innovation systems that facilitate knowledge conversion into economic endeavors by coordinating the functions of universities, government entities, and industry. The robustness of this perspective has been substantiated through comprehensive theoretical and empirical investigations (Mandrup & Jensen, 2017 ).
Therefore, this study aims to explore how EE in Chinese universities can adapt to new societal trends and demands through the guidance of TH theory. This research involves two major themes: educational objectives and content. Educational objectives play a pivotal role in regulating the entire process of educational activities, ensuring alignment with the principles and norms of education (Whitehead, 1967 ), while content provides a practical pathway to achieving these objectives. Specifically, the study has three pivotal research questions:
RQ1: What is the present landscape of EE research?
RQ2: What unified macroscopic goals should be formulated to guide EE in Chinese higher education?
RQ3: What specific EE system should be implemented to realize the identified goals in Chinese higher education?
The structure of this paper is as follows: First, we conduct a comprehensive literature review on EE to answer RQ1 , thereby establishing a robust theoretical foundation. Second, we outline our research methodology, encompassing both framework construction and case studies and providing a clear and explicit approach to our research process. Third, we derive the objectives and content model of EE guided by educational objectives, entrepreneurial motivations, and entrepreneurial process theories. Fourth, focusing on a typical university in China as our research subject, we conduct a case study to demonstrate the practical application of our research framework. Finally, we end the paper with the findings for RQ2 and RQ3 , discussions on the framework, and conclusions.
Literature review
The notion of TH first appeared in the early 1980s, coinciding with the global transition from an industrial to a knowledge-based economy (Cai & Etzkowitz, 2020 ). At that time, the dramatic increase in productivity led to overproduction, and knowledge became a valuable mechanism for driving innovation and economic growth (Mandrup & Jensen, 2017 ). Recognizing the potential of incorporating cutting-edge university technologies into industry and facilitating technology transfer and innovation, the US government took proactive steps to enhance the international competitiveness of American industries. This initiative culminated in the enactment of relevant legislation in 1980, which triggered a surge in technology transfer, patent licensing, and the establishment of new enterprises within the United States. Subsequently, European and Asian nations adopted similar measures, promoting the transformation of universities’ identity (Grimaldi et al., 2011 ). Universities assumed a central role in technology transfer, the formation of businesses, and regional revitalization within the knowledge society rather than occupying a secondary position within the industrial community. The conventional one-to-one relationships between universities, companies, and the government evolved into a dynamic TH model (Cai & Etzkowitz, 2020 ). Beyond their traditional roles in knowledge creation, wealth production, and policy coordination, these sectors began to engage in multifaceted interactions, effectively “playing the role of others” (Ranga & Etzkowitz, 2013 ).
The TH model encompasses three fundamental elements: 1) In a knowledge-based society, universities assume a more prominent role in innovation than in industry; 2) The three entities engage in collaborative relationships, with innovation policies emerging as a result of their mutual interactions rather than being solely dictated by the government; and 3) Each entity, while fulfilling its traditional functions, also takes on the roles of the other two parties (Henry, 2009 ). This model is closely aligned with EE.
On the one hand, EE can enhance the effectiveness of TH theory by strengthening the links between universities, industry, and government. The TH concept was developed based on entrepreneurial universities. The emerging entrepreneurial university model integrates economic development as an additional function. Etzkowitz’s research on the entrepreneurial university identified a TH model of academia-industry-government relations implemented by universities in an increasingly knowledge-based society (Galvao et al., 2019 ). Alexander and Evgeniy ( 2012 ) articulated that entrepreneurial universities are crucial to the implementation of triple-helix arrangements and that by integrating EE into their curricula, universities have the potential to strengthen triple-helix partnerships and boost the effectiveness of the triple-helix model.
On the other hand, TH theory also drives EE to achieve high-quality development. Previously, universities were primarily seen as sources of knowledge and human resources. However, they are now also regarded as reservoirs of technology. Within EE and incubation programs, universities are expanding their educational capabilities beyond individual education to shaping organizations (Henry, 2009 ). Surpassing their role as sources of new ideas for existing companies, universities blend their research and teaching processes in a novel way, emerging as pivotal sources for the formation of new companies, particularly in high-tech domains. Furthermore, innovation within one field of the TH influences others (Piqué et al., 2020 ). An empirical study by Alexander and Evgeniy ( 2012 ) outlined how the government introduced a series of initiatives to develop entrepreneurial universities, construct innovation infrastructure, and foster EE growth.
Overview of EE
EE occupies a crucial position in driving economic advancement, and this domain has been the focal point of extensive research. Fellnhofer ( 2019 ) examined 1773 publications from 1975 to 2014, introducing a more closely aligned taxonomy of EE research. This taxonomy encompasses eight major clusters: social and policy-driven EE, human capital studies related to self-employment, organizational EE and TH, (Re)design and evaluation of EE initiatives, entrepreneurial learning, EE impact studies, and the EE opportunity-related environment at the organizational level. Furthermore, Mohamed and Sheikh Ali ( 2021 ) conducted a systematic literature review of 90 EE articles published from 2009 to 2019. The majority of these studies focused on the development of EE (32%), followed by its benefits (18%) and contributions (12%). The selected research also addressed themes such as the relationship between EE and entrepreneurial intent, the effectiveness of EE, and its assessment (each comprising 9% of the sample).
Spanning from 1975 to 2019, these two reviews offer a comprehensive landscape of EE research. The perspective on EE has evolved, extending into multiple dimensions (Zaring et al., 2021 ). However, EE does not always achieve the expected outcomes, as challenges such as limited student interest and engagement as well as persistent negative attitudes are often faced (Mohamed & Sheikh Ali, 2021 ). In fact, the challenges faced by EE in most countries may be similar. However, the solutions may vary due to contextual differences (Fred Awaah et al., 2023 ). Furthermore, due to this evolution, there is a need for a more comprehensive grasp of pedagogical concepts and the foundational elements of modern EE (Hägg & Gabrielsson, 2020 ). Based on the objectives of this study, four specific themes were chosen for an in-depth literature review: the objectives, contents and methods, outcomes, and experiences of EE.
Objectives of EE
The objectives of EE may provide significant guidance for its implementation and the assessment of its effectiveness, and EE has evolved to form a diversified spectrum. Mwasalwiba ( 2010 ) presented a multifaceted phenomenon in which EE objectives are closely linked to entrepreneurial outcomes. These goals encompass nurturing entrepreneurial attitudes (34%), promoting new ventures (27%), contributing to local community development (24%), and imparting entrepreneurial skills (15%). Some current studies still emphasize particular dimensions of these goals, such as fostering new ventures or value creation (Jones et al., 2018 ; Ratten & Usmanij, 2021 ). These authors further stress the significance of incorporating practical considerations related to the business environment, which prompts learners to contemplate issues such as funding and resource procurement. This goal inherently underscores the importance of entrepreneurial thinking and encourages learners to transition from merely being students to developing entrepreneurial mindsets.
Additionally, Kuratko and Morris ( 2018 ) posit that the goal of EE should not be to produce entrepreneurs but to cultivate entrepreneurial mindsets in students, equipping them with methods for thinking and acting entrepreneurially and enabling them to perceive opportunities rapidly in uncertain conditions and harness resources as entrepreneurs would. While the objectives of EE may vary based on the context of the teaching institution, the fundamental goal is increasingly focused on conveying and nurturing an entrepreneurial mindset among diverse stakeholders. Hao’s ( 2017 ) research contends that EE forms a comprehensive system in which multidimensional educational objectives are established. These objectives primarily encompass cultivating students’ foundational qualities and innovative entrepreneurial personalities, equipping them with essential awareness of entrepreneurship, psychological qualities conducive to entrepreneurship, and a knowledge structure for entrepreneurship. Such a framework guides students towards independent entrepreneurship based on real entrepreneurial scenarios.
Various studies and practices also contain many statements about entrepreneurial goals. The Entrepreneurship Competence Framework, which was issued by the EU in 2016, delineates three competency domains: ideas and opportunities, resources and action. Additionally, the framework outlines 15 specific entrepreneurship competencies (Jun, 2017 ). Similarly, the National Content Standards for EE published by the US Consortium encompass three overarching strategies for articulating desired competencies for aspiring entrepreneurs: entrepreneurial skills, ready skills, and business functions (Canziani & Welsh, 2021 ). First, entrepreneurial skills are unique characteristics, behaviors, and experiences that distinguish entrepreneurs from ordinary employees or managers. Second, ready skills, which include business and entrepreneurial knowledge and skills, are prerequisites and auxiliary conditions for EE. Third, business functions help entrepreneurs create and operate business processes in business activities. These standards explain in the broadest terms what students need to be self-employed or to develop and grow a new venture. Although entrepreneurial skills may be addressed in particular courses offered by entrepreneurship faculties, it is evident that business readiness and functional skills significantly contribute to entrepreneurial success (Canziani & Welsh, 2021 ).
Contents and methods of EE
The content and methods employed in EE are pivotal factors for ensuring the delivery of high-quality entrepreneurial instruction, and they have significant practical implications for achieving educational objectives. The conventional model of EE, which is rooted in the classroom setting, typically features an instructor at the front of the room delivering concepts and theories through lectures and readings (Mwasalwiba, 2010 ). However, due to limited opportunities for student engagement in the learning process, lecture-based teaching methods prove less effective at capturing students’ attention and conveying new concepts (Rahman, 2020 ). In response, Okebukola ( 2020 ) introduced the Culturo-Techno-Contextual Approach (CTCA), which offers a hybrid teaching and learning method that integrates cultural, technological, and geographical contexts. Through a controlled experiment involving 400 entrepreneurship development students from Ghana, CTCA has been demonstrated to be a model for enhancing students’ comprehension of complex concepts (Awaah, 2023 ). Furthermore, learners heavily draw upon their cultural influences to shape their understanding of EE, emphasizing the need for educators to approach the curriculum from a cultural perspective to guide students in comprehending entrepreneurship effectively.
In addition to traditional classroom approaches, research has highlighted innovative methods for instilling entrepreneurial spirit among students. For instance, students may learn from specific university experiences or even engage in creating and running a company (Kolb & Kolb, 2011 ). Some scholars have developed an educational portfolio that encompasses various activities, such as simulations, games, and real company creation, to foster reflective practice (Neck & Greene, 2011 ). However, some studies have indicated that EE, when excessively focused on applied and practical content, yields less favorable outcomes for students aspiring to engage in successful entrepreneurship (Martin et al., 2013 ). In contrast, students involved in more academically oriented courses tend to demonstrate improved intellectual skills and often achieve greater success as entrepreneurs (Zaring et al., 2021 ). As previously discussed, due to the lack of a coherent theoretical framework in EE, there is a lack of uniformity and consistency in course content and methods (Ribeiro et al., 2018 ).
Outcomes of EE
Research on the outcomes of EE is a broad and continually evolving field, with most related research focusing on immediate or short-term impact factors. For example, Anosike ( 2019 ) demonstrated the positive effect of EE on human capital, and Chen et al. ( 2022 ) proposed that EE significantly moderates the impact of self-efficacy on entrepreneurial competencies in higher education students through an innovative learning environment. In particular, in the comprehensive review by Kim et al. ( 2020 ), six key EE outcomes were identified: entrepreneurial creation, entrepreneurial intent, opportunity recognition, entrepreneurial self-efficacy and orientation, need for achievement and locus of control, and other entrepreneurial knowledge. One of the more popular directions is the examination of the impact of EE on entrepreneurial intentions. Bae et al. ( 2014 ) conducted a meta-analysis of 73 studies to examine the relationship between EE and entrepreneurial intention and revealed little correlation. However, a meta-analysis of 389 studies from 2010 to 2020 by Zhang et al. ( 2022 ) revealed a positive association between the two variables.
Nabi et al. ( 2017 ) conducted a systematic review to determine the impact of EE in higher education. Their findings highlight that studies exploring the outcomes of EE have primarily concentrated on short-term and subjective assessments, with insufficient consideration of longer-term effects spanning five or even ten years. These longer-term impacts encompass factors such as the nature and quantity of startups, startup survival rates, and contributions to society and the economy. As noted in the Eurydice report, a significant impediment to advancing EE is the lack of comprehensive delineation concerning education outcomes (Bourgeois et al., 2016 ).
Experiences in the EE system
With the deepening exploration of EE, researchers have turned to studying university-centered entrepreneurship ecosystems (Allahar and Sookram, 2019 ). Such ecosystems are adopted to fill gaps in “educational and economic development resources”, such as entrepreneurship curricula. A growing number of universities have evolved an increasingly complex innovation system that extends from technology transfer offices, incubators, and technology parks to translational research and the promotion of EE across campuses (Cai & Etzkowitz, 2020 ). In the university context, the entrepreneurial ecosystem aligns with TH theory, in which academia, government, and industry create a trilateral network and hybrid organization (Ranga & Etzkowitz, 2013 ).
The EE system is also a popular topic in China. Several researchers have summarized the Chinese experience in EE, including case studies and overall experience, such as the summary of the progress and system development of EE in Chinese universities over the last decade by Weiming et al. ( 2013 ) and the summary of the Chinese experience in innovation and EE by Maoxin ( 2017 ). Other researchers take an in-depth look at the international knowledge of EE, such as discussions on the EE system of Denmark by Yuanyuan ( 2015 ), analyzes of the ecological system of EE at the Technical University of Munich by Yubing and Ziyan ( 2015 ), and comparisons of international innovation and EE by Ke ( 2017 ).
In general, although there has been considerable discussion on EE, the existing body of work has not properly addressed the practical challenges faced by EE in China. On the one hand, the literature is fragmented and has not yet formed a unified and mature theoretical framework. Regarding what should be taught and how it can be taught and assessed, the answers in related research are ambiguous (Hoppe, 2016 ; Wong & Chan, 2022 ). On the other hand, current research lacks empirical evidence in the context of China, and guidance on how to put the concept of EE into practice is relatively limited. These dual deficiencies impede the effective and in-depth development of EE in China. Consequently, it is imperative to comprehensively redefine the objectives and contents of EE to provide clear developmental guidance for Chinese higher education institutions.
Research methodology
To answer the research questions, this study employed a comprehensive approach by integrating both literature-based and empirical research methods. The initial phase focused on systematically reviewing the literature related to entrepreneurial education, aiming to construct a clear set of frameworks for the objectives and content of EE in higher education institutions. The second phase involved conducting a case study at T-University, in which the theoretical frameworks were applied to a real-world context. This case not only contributed to validating the theoretical constructs established through the literature review but also provided valuable insights into the practical operational dynamics of entrepreneurial education within the specific university setting.
Conceptual framework stage
This paper aims to conceptualize the objective and content frameworks for EE. The methodology sequence is as follows: First, we examine the relevant EE literature to gain insights into existing research themes. Subsequently, we identify specific research articles based on these themes, such as “entrepreneurial intention”, “entrepreneurial self-efficacy”, and “entrepreneurial approach”, among others. Third, we synthesize the shared objectives of EE across diverse research perspectives through an analysis of the selected literature. Fourth, we construct an objective model for EE within higher education by integrating Bloom’s educational objectives ( 1956 ) and Gagne’s five learning outcomes ( 1984 ), complemented by entrepreneurship motivation and process considerations. Finally, we discuss the corresponding content framework.
Case study stage
To further elucidate the conceptual framework, this paper delves into the methods for the optimization of EE in China through a case analysis. Specifically, this paper employs a single-case approach. While a single case study may have limited external validity (Onjewu et al., 2021 ), if a case study informs current theory and conceptualizes the explored issues, it can still provide valuable insights from its internal findings (Buchanan, 1999 ).
T-University, which is a comprehensive university in China, is chosen as the subject of the case study for the following reasons. First, T-University is located in Shanghai, which is a Chinese international technological innovation center approved by the State Council. Shanghai’s “14th Five-Year Plan” proposes the establishment of a multichannel international innovation collaboration platform and a global innovation cooperation network. Second, T-University has initiated curriculum reforms and established a regional knowledge economy ecosystem by utilizing EE as a guiding principle, which aligns with the characteristics of its geographical location, history, culture, and disciplinary settings. This case study will showcase T-University’s experiences in entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup services, and the entrepreneurial climate, elucidating the positive outcomes of this triangular interaction and offering practical insights for EE in other contexts.
The data collection process of this study was divided into two main stages: field research and archival research. The obtained data included interview transcripts, field notes, photos, internal documents, websites, reports, promotional materials, and published articles. In the initial stage, we conducted a 7-day field trip, including visits to the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Institute, the Career Development Centre, the Academic Affairs Office, and the Graduate School. Moreover, we conducted semistructured interviews with several faculty members and students involved in entrepreneurship education at the university to understand the overall state of implementation of entrepreneurship education at the university. In the second stage, we contacted the Academic Affairs Office and the Student Affairs Office at the university and obtained internal materials related to entrepreneurship education. Additionally, we conducted a comprehensive collection and created a summary of publicly available documents, official school websites, public accounts, and other electronic files. To verify the validity of the multisource data, we conducted triangulation and ultimately used consistent information as the basis for the data analysis.
For the purpose of our study, thematic analysis was employed to delve deeply into the TH factors, the objective and content frameworks, and their interrelationships. Thematic analysis is a method for identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns within data. This approach emphasizes a comprehensive interpretation of the data, as it extracts information from multiple perspectives and derives valuable conclusions through summary and induction (Onjewu et al., 2021 ). Therefore, thematic analysis likely serves as the foundation for most other qualitative data analysis methods (Willig, 2013 ). In this study, three researchers individually conducted rigorous analyses and comprehensive reviews to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data. Subsequently, they engaged in collaborative discussions to explore their differences and ultimately reach a consensus.
Framework construction
Theoretical basis of ee in universities.
The study is grounded in the theories of educational objectives, planned behavior, and the entrepreneurial process. Planned behavior theory can serve to elucidate the emergence of entrepreneurial activity, while entrepreneurial process theory can be used to delineate the essential elements of successful entrepreneurship.
Theory of educational objectives. The primary goal of education is to assist students in shaping their future. Furthermore, education should directly influence students and facilitate their future development. Education can significantly enhance students’ prospects by imparting specific skills and fundamental principles and cultivating the correct attitudes and mindsets (Bruner, 2009 ). According to “The Aims of Education” by Whitehead, the objective of education is to stimulate creativity and vitality. Gagne identifies five learning outcomes that enable teachers to design optimal learning conditions based on the presentation of these outcomes, encompassing “attitude,” “motor skills,” “verbal information,” “intellectual skills,” and “cognitive strategies”. Bloom et al. ( 1956 ) argue that education has three aims, which concern the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. Gedeon ( 2017 ) posits that EE involves critical input and output elements. The key objectives encompass mindset (Head), skill (hand), attitude (heart), and support (help). The input objectives include EE teachers, resources, facilities, courses, and teaching methods. The output objectives encompass the impacts of the input factors, such as the number of students, the number of awards, and the establishment of new companies. The primary aims of Gedeon ( 2017 ) correspond to those of Bloom et al. ( 1956 ).
Theory of planned behavior. The theory of planned behavior argues that human behavior is the outcome of well-thought-out planning (Ajzen, 1991 ). Human behavior depends on behavioral intentions, which are affected by three main factors. The first is derived from the individual’s “attitude” towards taking a particular action; the second is derived from the influence of “subjective norms” from society; and the third is derived from “perceived behavioral control” (Ajzen, 1991 ). Researchers have adopted this theory to study entrepreneurial behavior and EE.
Theory of the entrepreneurship process. Researchers have proposed several entrepreneurial models, most of which are processes (Baoshan & Baobao, 2008 ). The theory of the entrepreneurship process focuses on the critical determinants of entrepreneurial success. The essential variables of the entrepreneurial process model significantly impact entrepreneurial performance. Timmons et al. ( 2004 ) argue that successful entrepreneurial activities require an appropriate match among opportunities, entrepreneurial teams, resources, and a dynamic balance as the business develops. Their model emphasizes flexibility and equilibrium, and it is believed that entrepreneurial activities change with time and space. As a result, opportunities, teams, and resources will be unbalanced and need timely adjustment.
4H objective model of EE
Guided by TH theory, the objectives of EE should consider universities’ transformational identity in the knowledge era and promote collaboration among students, faculty, researchers, and external players (Mandrup & Jensen, 2017 ). Furthermore, through a comprehensive analysis of the literature and pertinent theoretical underpinnings, the article introduces the 4H model for the EE objectives, as depicted in Fig. 1 .
The 4H objective model of entrepreneurship education.
The model comprises two levels. The first level pertains to outcomes at the entrepreneurial behavior level, encompassing entrepreneurial intention and entrepreneurial performance. These two factors support universities’ endeavors to nurture individuals with an entrepreneurial mindset and potential and contribute to the region’s growth of innovation and entrepreneurship. The second level pertains to fundamentals, which form the foundation of the first level. The article defines these as the 4H model, representing mindset (Head), skill (Hand), attitude (Heart), and support (Help). This model integrates key theories, including educational objectives, the entrepreneurship process, and planned behavior.
First, according to the theory of educational objectives, the cognitive, emotional, and skill objectives proposed by Bloom et al. ( 1956 ) correspond to the key goals of education offered by Gedeon ( 2017 ), namely, Head, Hand, and Heart; thus, going forward, in this study, these three objectives are adopted. Second, according to the theory of planned behavior, for the promotion of entrepreneurial intention, reflection on the control of beliefs, social norms, and perceptual behaviors must be included. EE’s impact on the Head, Hand, and Heart will promote the power of entrepreneurs’ thoughts and perceptual actions. Therefore, this approach is beneficial for enhancing entrepreneurial intentions. Third, according to entrepreneurship process theory, entrepreneurial performance is affected by various factors, including entrepreneurial opportunities, teams, and resources. Consideration of the concepts of Head, Hand, and Heart can enhance entrepreneurial opportunity recognition and entrepreneurial team capabilities. However, as the primary means of obtaining external resources, social networks play an essential role in improving the performance of innovation and entrepreneurship companies (Gao et al., 2023 ). Therefore, an effective EE program should tell students how to take action, connect them with those who can help them succeed (Ronstadt, 1985 ), and help them access the necessary resources. If EE institutions can provide relevant help, they will consolidate entrepreneurial intentions and improve entrepreneurial performance, enabling the EE’s objective to better support the Head, Hand, and Heart.
Content model of EE
EE necessitates establishing a systematic implementation framework to achieve the 4H objectives. Current research on EE predominantly focuses on two facets: one focuses on EE methods to improve students’ skills, and the other focuses on EE outcome measurements, which consider the impact of EE on different stakeholders. Based on this, to foster innovation in EE approaches and enable long-term sustainable EE outcomes, the 4H Model of EE objectives mandates that pertinent institutions provide entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup services, and a suitable entrepreneurial climate. These components constitute the four integral facets of the content model for EE, as depicted in Fig. 2 .
The content model of entrepreneurship education.
Entrepreneurial learning
Entrepreneurial learning mainly refers to the learning of innovative entrepreneurial knowledge and theory. This factor represents the core of EE and can contribute significantly to the Head component. It can also improve the entrepreneurial thinking ability of academic subjects through classroom teaching, lectures, information reading and analysis, discussion, debates, etc. Additionally, it can positively affect the Hand and Heart elements of EE.
Entrepreneurial practice
Entrepreneurial practice mainly refers to academic subjects comprehensively enhancing their cognition and ability by participating in entrepreneurial activities. This element is also a key component of EE and plays a significant role in the cultivation of the Hand element. Entrepreneurial practice is characterized by participation in planning and implementing entrepreneurial programs, competitions, and simulation activities. Furthermore, it positively impacts EE’s Head, Heart, and Help factors.
Startup services
Startup services mainly refer to entrepreneurial-related support services provided by EE institutions, which include investment and financing, project declaration, financial and legal support, human resources, marketing, and intermediary services. These services can improve the success of entrepreneurship projects. Therefore, they can reinforce the expectations of entrepreneurs’ success and positively impact the Heart, Hand, and Head objectives of EE.
Entrepreneurial climate
The entrepreneurial climate refers to the entrepreneurial environment created by EE institutions and their community and is embodied mainly in the educational institutions’ external and internal entrepreneurial culture and ecology. The environment can impact the entrepreneurial attitude of educated individuals and the Heart objective of EE. Additionally, it is beneficial for realizing EE’s Head, Hand, and Help goals.
Case study: EE practice of T-University
Overview of ee at t-university.
T-University is one of the first in China to promote innovation and EE. Since the 1990s, a series of policies have been introduced, and different platforms have been set up. After more than 20 years of teaching, research, and practice, an innovation and entrepreneurship education system with unique characteristics has gradually evolved. The overall goal of this system is to ensure that 100% of students receive such education, with 10% of students completing the program and 1% achieving entrepreneurship with a high-quality standard. The overall employment rate of 2020 graduates reached 97.49%. In recent years, the proportion of those pursuing entrepreneurship has been more than 1% almost every year. The T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle, an industrial cluster formed around knowledge spillover from T-University’s dominant disciplines, employs more than 400 T-University graduates annually.
In 2016, T-University established the School of Innovation & Entrepreneurship, with the president serving as its dean. This school focuses on talent development and is pivotal in advancing innovation-driven development strategies. It coordinates efforts across various departments and colleges to ensure comprehensive coverage of innovation and EE, the integration of diverse academic disciplines, and the transformation of interdisciplinary scientific and technological advancements (see Fig. 3 ).
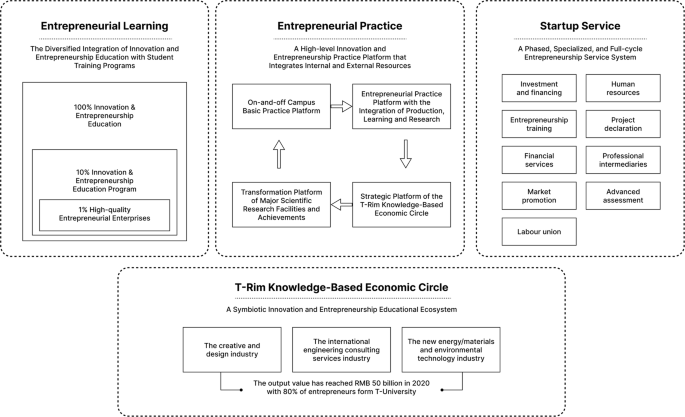
T-University innovation and entrepreneurship education map.
T-University is dedicated to integrating innovation and EE into every stage of talent development. As the guiding framework for EE, the university has established the Innovation and EE sequence featuring “three-dimensional, linked, and cross-university cooperation” with seven educational elements. These elements include the core curriculum system of innovation and entrepreneurship, the “one top-notch and three excellences” and experimental zones of innovation and entrepreneurship talent cultivation model, the four-level “China-Shanghai-University-School” training programs for innovation and entrepreneurship, four-level “International-National-Municipal-University” science and technology competitions, four-level “National-Municipal-University-School” innovation and entrepreneurship practice bases, three-level “Venture Valley-Entrepreneurship Fund-Industry Incubation” startup services and a high-level teaching team with both full-time and part-time personnel.
T-University has implemented several initiatives. First, the university has implemented 100% student innovation and EE through reforming the credit setting and curriculum system. Through the Venture Valley class, mobile class, and “joint summer school”, more than 10% of the students completed the Innovation and EE program. Moreover, through the professional reform pilot and eight professional incubation platforms in the National Science and Technology Park of T-University and other measures, 1% of the students established high-quality entrepreneurial enterprises. Second, the university is committed to promoting the integration of innovation and entrepreneurship and training programs, exploring and practising a variety of innovative talent cultivation models, and adding undergraduate innovation ability development as a mandatory component of the training program. In addition, pilot reforms have been conducted in engineering, medicine, and law majors, focusing on integrating research and education.
T-University has constructed a high-level integrated innovation and entrepreneurship practice platform by combining internal and external resources. This platform serves as the central component in Fig. 3 , forming a sequence of innovation and entrepreneurship practice opportunities, including 1) the On-and-off Campus Basic Practice Platform, 2) the Entrepreneurship Practice Platform with the Integration of Production, Learning, and Research, 3) the Transformation Platform of Major Scientific Research Facilities and Achievements, and 4) the Strategic Platform of the T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle. All these platforms are accessible to students based on their specific tasks and objectives.
Moreover, the university has reinforced its support for entrepreneurship and collaborated with local governments in Sichuan, Dalian, and Shenzhen to establish off-campus bases jointly. In 2016, in partnership with other top universities in China, the university launched the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance of Universities in the Yangtze River Delta. This alliance effectively brings together government bodies, businesses, social communities, universities, and funding resources in the Yangtze River Delta, harnessing the synergistic advantages of these institutions. In 2018, the university assumed the director role for the Ministry of Education’s Steering Committee for Innovation and Entrepreneurship. Through collaborations with relevant government agencies and enterprises, T-University has continued its efforts to reform and advance innovation and EE, establishing multiple joint laboratories to put theory into practice.
Startup service
In terms of entrepreneurial services, T-University has focused on the employment guidance center and the science and technology Park, working closely with the local industrial and commercial bureaus in the campus area to provide centralized entrepreneurial services. Through entities such as the Shanghai Municipal College Entrepreneurship Guidance Station, entrepreneurship seedling gardens, the science and technology park, and off-campus bases such as the entrepreneurship valley, the university has established a full-cycle service system that is tailored to students’ innovative and entrepreneurial activities, providing continuous professional guidance and support from the early startup stage to maturity.
Notably, the T-University Science and Technology Park has set up nine professional incubation service platforms that cover investment and financing, human resources, entrepreneurship training, project declaration, financial services, professional intermediaries, market promotion, advanced assessment, and the labor union. Moreover, the Technology Park has established a corporate service mechanism for liaison officers, counselors, and entrepreneurship mentors to ensure that enterprises receive comprehensive support and guidance. Through these services, T-University has successfully cultivated numerous high-tech backbone enterprises, such as New Vision Healthcare, Zhong Hui Ecology, Tongjie Technology, Tonglei Civil Engineering, and Tongchen Environmental Protection, which indicates the positive effect of these entrepreneurial services.
T-University places significant emphasis on fostering the entrepreneurial climate, which is effectively nurtured through the T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle and on-campus entrepreneurship activities. Moreover, T-University is dedicated to establishing and cultivating a dynamic T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle in strategic alignment with the district government and key agencies. This innovative ecosystem strategically centers around three prominent industrial clusters: the creative and design industry, the international engineering consulting services industry, and the new energy/materials and environmental technology industry. These industrial clusters provide fertile ground for graduates’ employment and entrepreneurial pursuits and have yielded remarkable economic outputs. In 2020, the combined value of these clusters surged to a staggering RMB 50 billion, with 80% of entrepreneurs being teachers, students, or alumni from T-University.
This commitment has led to the establishment of an intricate design industry chain featuring architectural design and urban planning design; it also supports services in automobile design, landscape design, software design, environmental engineering design, art media design, and associated services such as graphic production, architectural modeling, and engineering consulting.
The EE system at T-University
T-University has undertaken a comprehensive series of initiatives to promote EE, focusing on four key aspects: entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup service, and the entrepreneurial climate. As of the end of 2021, the National Technology Park at T-University has cumulatively supported more than 3000 enterprises. Notably, the park has played a pivotal role in assisting more than 300 enterprises established by college students.
In its commitment to EE, the university maintains an open approach to engaging with society. Simultaneously, it integrates innovative elements such as technology, information, and talent to facilitate students’ entrepreneurial endeavors. Through the synergy between the university, government entities, and the market, EE cultivates a cadre of entrepreneurial talent. The convergence of these talents culminates in the formation of an innovative and creative industry cluster within the region, representing the tangible outcome of the university’s “disciplinary chain—technology chain—industry chain” approach to EE. This approach has gradually evolved into the innovative ecosystem of the T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle.
Findings and discussion
Unified macroscopic objectives of ee.
To date, a widespread consensus on defining EE in practical terms has yet to be achieved (Mwasalwiba, 2010 ; Nabi et al., 2017 ). Entrepreneurial education should strive towards a common direction, which is reflected in the agreement on educational objectives and recommended teaching methods(Aparicio et al., 2019 ). Mason and Arshed ( 2013 ) criticized that entrepreneurial education should teach about entrepreneurship rather than for entrepreneurship. Therefore, EE should not only focus on singular outcome-oriented aspects but also emphasize the cultivation of fundamental aspects such as cognition, abilities, attitudes, and skills.
This study embarks on a synthesis of the EE-related literature, integrating educational objective theory, planned behavior theory, and entrepreneurial process theory. The 4H model of EE objectives, which consists of basic and outcome levels, is proposed. This model aims to comprehensively capture the core elements of EE, addressing both students’ performance in entrepreneurial outcomes and their development of various aspects of foundational cognitive attributes and skills.
The basic level of the EE objective model includes the 4Hs, namely Head (mindset), Hand (skill), Heart (attitude), and Help (support). First, Head has stood out as a prominent learning outcome within EE over the past decade (Fretschner & Lampe, 2019 ). Attention given to the “Head” aspect not only highlights the development of individuals recognized as “entrepreneurs” (Mitra, 2017 ) but also underscores its role in complementing the acquisition of skills and practical knowledge necessary for initiating new ventures and leading more productive lives (Neck & Corbett, 2018 ).
Second, the Hand aspect also constitutes a significant developmental goal and learning outcome of EE. The trajectory of EE is evolving towards a focus on entrepreneurial aspects, and the learning outcomes equip students with skills relevant to entrepreneurship (Wong & Chan, 2022 ). Higher education institutions should go beyond fundamental principles associated with knowledge and actively cultivate students’ entrepreneurial skills and spirit.
Third, Heart represents EE objectives that are related to students’ psychological aspects, as students’ emotions, attitudes, and other affective factors impact their perception of entrepreneurship (Cao, 2021 ). Moreover, the ultimate goal of EE is to instill an entrepreneurial attitude and pave the way for future success as entrepreneurs in establishing new businesses and fostering job creation (Kusumojanto et al., 2021 ). Thus, the cultivation of this mindset is not only linked to the understanding of entrepreneurship but also intricately tied to the aspiration for personal fulfillment (Yang, 2013 ).
Fourth, entrepreneurship support (Help) embodies the goal of providing essential resource support to students to establish a robust foundation for their entrepreneurial endeavors. The establishment of a comprehensive support system is paramount for EE in universities. This establishment encompasses the meticulous design of the curriculum, the development of training bases, and the cultivation of teacher resources (Xu, 2017 ). A well-structured support system is crucial for equipping students with the necessary knowledge and skills to successfully navigate the complexities of entrepreneurship (Greene & Saridakis, 2008 ).
The outcome level of the EE objective model encompasses entrepreneurial intention and entrepreneurial performance, topics that have been extensively discussed in the previous literature. Entrepreneurial intention refers to individuals’ subjective willingness and plans for entrepreneurial behavior (Wong & Chan, 2022 ) and represents the starting point of the entrepreneurial process. Entrepreneurial performance refers to individuals’ actual behaviors and achievements in entrepreneurial activities (Wang et al., 2021 ) and represents the ultimate manifestation of entrepreneurial goals. In summary, the proposed 4H model of the EE objectives covers fundamental attitudes, cognition, skills, support, and ultimate outcomes, thus answering the question of what EE should teach.
Specific implementable system of EE
To facilitate the realization of EE goals, this study developed a corresponding content model as an implementable system and conducted empirical research through a case university. Guided by the 4H objectives, the content model also encompasses four dimensions: entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup service, and entrepreneurial climate. Through a detailed exposition of the practical methods at T-university, this study provides support for addressing the question of how to teach EE.
In the traditional EE paradigm, there is often an overreliance on the transmission of theoretical knowledge, which leads to a deficiency in students’ practical experience and capabilities (Kremel and Wetter-Edman, 2019 ). Moreover, due to the rapidly changing and dynamic nature of the environment, traditional educational methods frequently become disconnected from real-world demands. In response to these issues, the approach of “learning by doing” has emerged as a complementary and improved alternative to traditional methods (Colombelli et al., 2022 ).
The proposed content model applies the “learning by doing” approach to the construction of the EE system. For entrepreneurial learning, the university has constructed a comprehensive innovation and EE chain that encompasses courses, experimental areas, projects, competitions, practice bases, and teaching teams. For entrepreneurial practice, the university has built a high-level, integrated innovation and entrepreneurship practice platform that provides students with the opportunity to turn their ideas into actual projects. For startup services, the university has established close collaborative relationships with local governments and enterprises and has set up nine professional incubation service platforms. For the entrepreneurial climate, the university cultivated a symbiotic innovation and EE ecosystem by promoting the construction of the T-Rim Knowledge-Based Economic Circle. Through the joint efforts of multiple parties, the entrepreneurial activities of teachers, students, and alumni have become vibrant and have formed a complete design industry chain and an enterprise ecosystem that coexists with numerous SMEs.
Development of a framework based on the TH theory
Through the exploration of the interactive relationships among universities, governments, and industries, TH theory points out a development direction for solving the dilemma of EE. Through the lens of TH theory, this study developed a comprehensive framework delineating the macroscopic objectives and practical methods of EE, as depicted in Fig. 4 . In this context, EE has become a common undertaking for multiple participants. Therefore, universities can effectively leverage the featured external and internal resources, facilitating the organic integration of entrepreneurial learning, practice, services, and climate. This, in turn, will lead to better achievement of the unified goals of EE.
Practical contents and objectives based on the triple helix theory.
Numerous scholars have explored the correlation between EE and the TH theory. Zhou and Peng ( 2008 ) articulated the concept of an entrepreneurial university as “the university that strongly influences the regional development of industries as well as economic growth through high-tech entrepreneurship based on strong research, technology transfer, and entrepreneurship capability.” Moreover, Tianhao et al. ( 2020 ) emphasized the significance of fostering collaboration among industry, academia, and research as the optimal approach to enhancing the efficacy of EE. Additionally, Ribeiro et al. ( 2018 ) underscored the pivotal role of MIT’s entrepreneurial ecosystem in facilitating startup launches. They called upon educators, university administrators, and policymakers to allocate increased attention to how university ecosystems can cultivate students’ knowledge, skills, and entrepreneurial mindsets. Rather than viewing EE within the confines of universities in isolation, we advocate for establishing an integrated system that encompasses universities, government bodies, and businesses. Such a system would streamline their respective roles and ultimately bolster regional innovation and entrepreneurship efforts.
Jones et al. ( 2021 ) reported that with the widespread embrace of EE by numerous countries, the boundaries between universities and external ecosystems are becoming increasingly blurred. This convergence not only fosters a stronger entrepreneurial culture within universities but also encourages students to actively establish startups. However, these startups often face challenges related to limited value and long-term sustainability. From the perspective of TH theory, each university can cultivate an ecosystem conducive to specialized entrepreneurial activities based on its unique resources and advantages. To do so, universities should actively collaborate with local governments and industries, leveraging shared resources and support to create a more open, inclusive, and innovation-supporting ecosystem that promotes lasting reform and sustainability.
There are two main ways in which this paper contributes to the literature. First, this study applies TH theory to both theoretical and empirical research on EE in China, presenting a novel framework for the operation of EE. Previous research has applied TH theory in contexts such as India, Finland, and Russia, showcasing the unique contributions of TH in driving social innovation. This paper introduces the TH model to the Chinese context, illustrating collaborative efforts and support for EE from universities, industries, and governments through the construction of EE objectives and content models. Therefore, this paper not only extends the applicability of the TH theory globally but also provides valuable insights for EE in the Chinese context.
Second, the proposed conceptual framework clarifies the core goals and practical content of EE. By emphasizing the comprehensive cultivation of knowledge, skills, attitudes, and resources, this framework provides a concrete reference for designing EE courses, activities, and support services. Moreover, the framework underscores the importance of collaborative efforts among stakeholders, facilitating resource integration to enhance the quality and impact of EE. Overall, the conceptual framework presented in this paper serves not only as a guiding tool but also as a crucial bridge for fostering the collaborative development of the EE ecosystem.
While EE has widespread global recognition, many regions still face similar developmental challenges, such as a lack of organized objectives and content delivery methods. This article, grounded in the context of EE in Chinese higher education institutions, seeks to address the current challenges guided by TH theory. By aligning EE with socioeconomic demands and leveraging TH theory, this study offers insights into the overall goals and practical content of EE.
This study presents a 4H objective model of EE comprising two levels. The first level focuses on outcomes related to entrepreneurial behavior, including entrepreneurial intentions and performance, which highlight the practical effects of EE. The second level is built as the foundation of the outcomes and encompasses the four elements of mindset, skill, attitude, and support. This multilayered structure provides a more systematic and multidimensional consideration for the cultivation of entrepreneurial talent. The framework offers robust support for practical instructional design and goal setting. Additionally, the research extends to the corresponding content model, incorporating four elements: entrepreneurial learning, entrepreneurial practice, startup services, and the entrepreneurial climate. This content model serves as a practical instructional means to achieve EE goals, enhancing the feasibility of implementing these objectives in practice.
Moreover, this study focused on a representative Chinese university, T-University, to showcase the successful implementation of the 4H and content models. Through this case, we may observe how the university, through comprehensive development in entrepreneurial learning, practice, services, and climate, nurtured many entrepreneurs and facilitated the formation of the innovation and entrepreneurship industry cluster. This approach not only contributes to the university’s reputation and regional economic growth but also offers valuable insights for other regions seeking to advance EE.
This study has several limitations that need to be acknowledged. First, the framework proposed is still preliminary. While its application has been validated through a case study, further exploration is required to determine the detailed classification and elaboration of its constituent elements to deepen the understanding of the EE system. Second, the context of this study is specific to China, and the findings may not be directly generalizable to other regions. Future research should investigate the adaptability of the framework in various cultural and educational contexts from a broader international perspective. Finally, the use of a single-case approach limits the generalizability of the research conclusions. Subsequent studies can enhance comprehensiveness by employing a comparative or multiple-case approach to assess the framework’s reliability and robustness.
In conclusion, this study emphasizes the need to strengthen the application of TH theory in EE and advocates for the enhancement of framework robustness through multiple and comparative case studies. An increase in the quantity of evidence will not only generate greater public interest but also deepen the dynamic interactions among universities, industries, and the nation. This, in turn, may expedite the development of EE in China and foster the optimization of the national economy and the overall employment environment.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available. Making the full data set publicly available could potentially breach the privacy that was promised to participants when they agreed to take part, in particular for the individual informants who come from a small, specific population, and may breach the ethics approval for the study. The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acs ZJ, Estrin S, Mickiewicz T et al. (2018) Entrepreneurship, institutional economics, and economic growth: an ecosystem perspective. Small Bus Econ 51(2):501–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0013-9
Article Google Scholar
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 50(2):179–211
Alexander U, Evgeniy P (2012) The entrepreneurial university in Russia: from idea to reality. Paper presented at the 10TH triple helix conference 2012
Allahar H, Sookram R (2019) Emergence of university-centred entrepreneurial ecosystems in the Caribbean. Ind Higher Educ 33(4):246–259. https://doi.org/10.1177/0950422219838220
Anosike P (2019) Entrepreneurship education as human capital: Implications for youth self-employment and conflict mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Ind Higher Educ 33(1):42–54. https://doi.org/10.1177/0950422218812631
Aparicio G, Iturralde T, Maseda A (2019) Conceptual structure and perspectives on entrepreneurship education research: A bibliometric review. Eur res on manage and bus econ 25(3):105–113
Awaah F, Okebukola P, Shabani J et al. (2023) Students’ career interests and entrepreneurship education in a developing country. High Educ Skills Work-Based Learn 13(1):148–160
Awaah F (2023) In the classroom I enhance students understanding of entrepreneurship development—the culturo–techno-contextual approach. J Res Innov Teach Learn https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIT-08-2022-0047
Bae TJ, Qian S, Miao C et al. (2014) The relationship between entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurial intentions: a meta–analytic review. Entrep Theory Pract 38(2):217–254
Baoshan G, Baobao D (2008) 创业模型比较研究 [A comparative retrospective study of classic entrepreneurial models]. Foreign Econ Manag. 3:19–28
Google Scholar
Bloom BS, Engelhart MD, Furst EJ, Hill WH, Krathwohl DR (1956) Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals. Handbook 1: Cognitive domain. David McKay, New York
Bourgeois A, Balcon M-P & Riiheläinen JM (2016) Entrepreneurship education at school in Europe. Eurydice Report. Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency, European Commission
Bruner JS (2009) The process of education. Harvard University Press
Buchanan DA (1999) The Logic of Political Action: an experiment with the epistemology of the particular. Br J Manag 10(s1):73–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.10.s1.7
Cai Y, Etzkowitz H (2020) Theorizing the triple helix model: past, present, and future. Triple Helix J 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1163/21971927-bja10003
Canziani BF, Welsh DHB (2021) How entrepreneurship influences other disciplines: an examination of learning goals. Int J Manag Educ 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.01.003
Cao Q (2021) Entrepreneurial psychological quality and quality cultivation of college students in the higher education and moral education perspectives. Front Psychol 12:700334
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chen H, Tang Y, Han J (2022) Building students’ entrepreneurial competencies in Chinese universities: diverse learning environment, knowledge transfer, and entrepreneurship education. Sustainability 14(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159105
Colombelli A, Panelli A, Serraino F (2022) A learning-by-doing approach to entrepreneurship education: evidence from a short intensive online international program. Admin Sci 12(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12010016
Etzkowitz H, Webster A, Gebhardt C et al. (2000) The future of the university and the university of the future: evolution of ivory tower to entrepreneurial paradigm. Res Policy 29(2):313–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-7333(99)00069-4
Fellnhofer K (2019) Toward a taxonomy of entrepreneurship education research literature: a bibliometric mapping and visualization. Educ Res Rev 27:28–55
Fretschner M, Lampe HW (2019) Detecting hidden sorting and alignment effects of entrepreneurship education. J Small Bus Manage 57(4):1712–1737
Gagne RM (1984) Learning outcomes and their effects: useful categories of human performance. Am Psychol 39(4):377
Galvao A, Mascarenhas C, Marques C et al. (2019) Triple helix and its evolution: a systematic literature review. J Sci Technol Policy Manag 10(3):812–833. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSTPM-10-2018-0103
Gao J, Cheng Y, He H et al. (2023) The mechanism of entrepreneurs’ Social Networks on Innovative Startups’ innovation performance considering the moderating effect of the entrepreneurial competence and motivation. Entrep Res J 13(1):31–69. https://doi.org/10.1515/erj-2020-0541
Gedeon SA (2017) Measuring student transformation in entrepreneurship education programs. Educ Res Int 2017:8475460. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8475460
Greene FJ, Saridakis G (2008) The role of higher education skills and support in graduate self-employment. Stud High Educ 33(6):653–672. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070802457082
Grimaldi R, Kenney M, Siegel DS et al. (2011) 30 years after Bayh–Dole: reassessing academic entrepreneurship. Res Policy 40(8):1045–1057
Hägg G, Gabrielsson J (2020) A systematic literature review of the evolution of pedagogy in EE research. Int J Entrep Behav Res 26(5):829–861
Hao Y (2017) Research on building curriculum system of entrepreneurship education for college students in China. In: Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 7th international conference on education, management, computer and medicine (EMCM 2016)
Henry E (2009) The entrepreneurial university and the triple helix model of innovation. Stud Sci Sci 27(4):481–488
Hoppe M (2016) Policy and entrepreneurship education. Small Bus Econ. 46(1):13–29
Jin D, Liu X, Zhang F et al. (2023) Entrepreneurial role models and college students’ entrepreneurial calling: a moderated mediation model. Front Psychol 14:1129495
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jones C, Penaluna K, Penaluna A et al. (2018) The changing nature of enterprise: addressing the challenge of Vesper and Gartner. Ind High Educ 32(6):430–437
Jones P, Maas G, Kraus S et al. (2021) An exploration of the role and contribution of entrepreneurship centres in UK higher education institutions. J Small Bus Enterp Dev 28(2):205–228. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-08-2018-0244
Jun C (2017) 欧盟创业能力框架: 创业教育行动新指南 [EU’s entrepreneurship competence framework: a new guide to entrepreneurship education]. Int Comp Educ 1:45–51
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Ke L (2017) 创新创业教育的国际比较与借鉴 [International comparison and reference of innovation and entrepreneurship education]. Stud Dialect Nat 9:73–78
Kim G, Kim D, Lee WJ, et al (2020) The effect of youth entrepreneurship education programs: two large-scale experimental studies. Sage Open 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020956976
Kolb A, Kolb D (2011) Experiential learning theory: a dynamic, holistic approach to management learning, education and development. In Armstrong SJ, Fukami C (Eds) Handbook of management learning, education and development. https://doi.org/10.4135/9780857021038.n3
Kremel A, Wetter-Edman K (2019) Implementing design thinking as didactic method in entrepreneurship education, the importance of through. Des J 22:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/14606925.2019.1595855
Kuratko DF, Morris MH (2018) Examining the future trajectory of entrepreneurship. J Small Bus Manag 56(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsbm.12364
Kusumojanto DD, Wibowo A, Kustiandi J, et al (2021) Do entrepreneurship education and environment promote students’ entrepreneurial intention? The role of entrepreneurial attitude. Cogent Educ 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2021.1948660
Mandrup M, Jensen TL (2017) Educational Action Research and Triple Helix principles in entrepreneurship education: introducing the EARTH design to explore individuals in Triple Helix collaboration. Triple Helix 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40604-017-0048-y
Maoxin Y (2017) 创业教育的中国经验 [“China’s experiences” of entrepreneurship education]. Educ Res 38(9):70–75
Martin BC, McNally JJ, Kay MJ (2013) Examining the formation of human capital in entrepreneurship: a meta-analysis of entrepreneurship education outcomes. J Bus Ventur 28(2):211–224
Mason C, Arshed N (2013) Teaching entrepreneurship to university students through experiential Learning: a case study. Ind High Educ 27(6):449–463
Mitra J (2017) Holistic experimentation for emergence: a creative approach to postgraduate entrepreneurship education and training. Ind High Educ 31(1):34–50
Mohamed NA, Sheikh Ali AY (2021) Entrepreneurship education: systematic literature review and future research directions. World J Entrep Manag Sustain Dev 17(4):644–661
Mwasalwiba ES (2010) Entrepreneurship education: a review of its objectives, teaching methods, and impact indicators. Educ+ Train 52(1):20–47
Nabi G, Liñán F, Fayolle A et al. (2017) The impact of entrepreneurship education in higher education: a systematic review and research agenda. Acad Manag Learn Educ 16(2):277–299. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2015.0026
Neck HM, Greene PG (2011) Entrepreneurship education: known worlds and new frontiers. J Small Bus Manag 49(1):55–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-627X.2010.00314.x
Neck HM, Corbett AC (2018) The scholarship of teaching and learning entrepreneurship. Entrep Educ Pedagog 1(1):8–41
Okebukola P (2020) Breaking barriers to learning: the culture techno-contextual approach (CTCA). Sterling Publishers, Slough
Onjewu AKE, Sukumar A, Prakash KVD et al (2021) The triple helix: a case study of Centurion University of Technology and Management. In Jones P, Apostolopoulos N, Kakouris A, Moon C, Ratten V & Walmsley A (Eds), Universities and entrepreneurship: meeting the educational and social challenges (Vol 11, pp 199–218)
Piqué JM, Berbegal-Mirabent J, Etzkowitz H (2020) The role of universities in shaping the evolution of Silicon Valley’s ecosystem of innovation. Triple Helix J 1–45. https://doi.org/10.1163/21971927-bja10009
Rahman S (2020) Improving the power of lecture method in higher education. In Teaching learning and new technologies in higher education (pp 135–147)
Ranga M, Etzkowitz H (2013) Triple helix systems: an analytical framework for innovation policy and practice in the knowledge society. Ind. High Educ. 27(4):237–262. https://doi.org/10.5367/ihe.2013.0165
Ratten V, Usmanij P (2021) Entrepreneurship education: time for a change in research direction? Int J Manag Educ 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2020.100367
Ribeiro ATVB, Uechi JN, Plonski GA (2018) Building builders: entrepreneurship education from an ecosystem perspective at MIT. Triple Helix 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40604-018-0051-y
Ronstadt R (1985) The educated entrepreneurs: a new era of EE is beginning. Am J Small Bus 10(1):7–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/104225878501000102
Tianhao L, Beiwei L, Yang L (2020) 国外创新创业教育发展述评与启示 [The development of innovation and entrepreneurship education in foreign countries: review and enlightenment]. Manag Innov Entrep 1:23–36
Timmons JA, Spinelli S, Tan Y (2004) New venture creation: entrepreneurship for the 21st century (Vol 6). McGraw-Hill/Irwin, New York
Wang SY, Wu XL, Xu M et al. (2021) The evaluation of synergy between university entrepreneurship education ecosystem and university students’ entrepreneurship performance. Math Probl Eng, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3878378
Weiming L, Chunyan L, Xiaohua D (2013) 我国高校创业教育十年: 演进, 问题与体系建设 [Research on ten-year entrepreneurship education in Chinese universities: evolution, problems and system construction]. Educ Res 6:42–51
Whitehead AN (1967) Aims of education: Simon and Schuster
Willig C (2013) EBOOK: introducing qualitative research in psychology. McGraw-Hill Education, UK
Wong HY, Chan CK (2022) A systematic review on the learning outcomes in entrepreneurship education within higher education settings. Assess Eval High Educ 47(8):1213–1230
Xu Y (2017) Research on the Construction of Support System of University Students’ Entrepreneurship Education under the Background of the New Normal [Proceedings Paper]. 2017 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON FRONTIERS IN EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGIES AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES (FETMS 2017)
Yang J (2013) The theory of planned behavior and prediction of entrepreneurial intention among Chinese undergraduates. Soc Behav Personal Int J 41(3):367–376
Yuanyuan C (2015) 从 ABC 到 PhD: 丹麦创业教育体系的框架设计与特点 [From ABC to PhD: the guiding ideas and development framework of Danish EE (Entrepreneurship Education) system]. Int Comp Educ 8:7–13
Yubing H, Ziyan G (2015) 慕尼黑工业大学创业教育生态系统建设及启示 [The EE ecosystem of TUM and some recommendations to China]. Sci Sci Manag 10:41–49
Zaring O, Gifford E, McKelvey M (2021) Strategic choices in the design of entrepreneurship education: an explorative study of Swedish higher education institutions. Stud High Educ 46(2):343–358
Zhang W, Li Y, Zeng Q, et al. (2022) Relationship between entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurial intention among college students: a meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 19(19) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912158
Zhou C, Peng X-M (2008) The entrepreneurial university in China: nonlinear paths. Sci Public Policy 35(9):637–646
Download references
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere gratitude to all individuals who contributed to the data collection process. Furthermore, we extend our appreciation to Linlin Yang and Jinxiao Chen from Tongji University for their invaluable suggestions on the initial draft. Special thanks are also due to Prof. Yuzhuo Cai from Tampere University for his insightful contributions to this paper. Funding for this study was provided by the Chinese National Social Science Funds [BIA190205] and the Shanghai Educational Science Research General Project [C2023033].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Luning Shao
Shanghai International College of Design & Innovation, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Shanghai International College of Intellectual Property, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Shengce Ren
Institute of Higher Education, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
College of Design and Innovation, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Shanghai Industrial Innovation Ecosystem Research Center, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Luning Shao, Yuxin Miao, Sanfa Cai and Fei Fan. The first Chinese outline and draft were written by Luning Shao, Yuxin Miao, and Shengce Ren. The English draft of the manuscript was prepared by Fei Fan. All the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Fei Fan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This research was approved by the Tongji University Ethics Committee for Human Research (No. tjdxsr079). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shao, L., Miao, Y., Ren, S. et al. Designing a framework for entrepreneurship education in Chinese higher education: a theoretical exploration and empirical case study. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 519 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03024-2
Download citation
Received : 22 May 2023
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 16 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03024-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A literature review may reach beyond BER and include other education research fields. A theoretical framework does not rationalize the need for the study, and a theoretical framework can come from different fields. A conceptual framework articulates the phenomenon under study through written descriptions and/or visual representations.
This essay starts with a discussion of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. This discussion includes similarities and distinctions ...
The theoretical framework is used to lay down a foundation of theory on which your study will be built, whereas the conceptual framework visualises what you anticipate the relationships between concepts, constructs and variables may be, based on your understanding of the existing literature and the specific context and focus of your research.
This essay starts with a discussion of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. This discussion includes similarities and distinctions among these components and their relation to other sections of a manuscript such as the problem statement, discussion, and implications.
Fourthly, the paper explains how a theoretical framework for a research project is developed. Finally, I provide an example of the development of a real theoretical framework and explain how it could be applied in data analysis. 2. Systematic Literature Review Methodology: What Is a Theory? A systematic review of pertinent literature provides ...
first section will discuss literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. The second section will discuss literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as types of manuscripts. The first area to be discussed is that these terms are used interchangeably.
reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks as critical elements of the research and writing process. However, these elements can be confusing for scholars new ... A literature review is foundational to any research study in edu - cation or science. In education, a well-conceptualized and ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
Abstract. While 'conceptual framework' means a researcher's own perceptions about the scope and structure of a problem, the literature review provides others' ideas and work in areas close to that under study. With such a philosophy in mind, this chapter first constructs the author's own thinking as to how the problem in question has ...
This essay starts with a discussion of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. This discussion includes similarities and distinctions among these components and their relation to other sections of a manuscript such as the problem statement, discussion, and implications. The essay concludes with an overview of the literature review ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
work. I have also inferred, like many have done, that the basic components of literature review consist of introduction, review of theoretical and empirical literature, implication of the review, and theoretical and/or conceptual framework/s. Its implication is that any research work needs to pave its pathways distinctly for its successful ...
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You'll likely need both in your dissertation.
conceptual and theoretical frameworks. As conceptual defines the key co ncepts, variables, and. relationships in a research study as a roadmap that outlines the researcher's understanding of how ...
Theoretical Framework. Definition: Theoretical framework refers to a set of concepts, theories, ideas, and assumptions that serve as a foundation for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It provides a conceptual framework that helps researchers to design and conduct their research, as well as to analyze and interpret their findings.
The author bicker that whereas a deductive approach to literature review typically makes use of theories and theoretical frameworks, the inductive approach tends to lead to the development of a ...
Your theoretical framework is based on: Your problem statement. Your research questions. Your literature review. Example: Problem statement and research questions. A new boutique downtown is struggling with the fact that many of their online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases. This is a big issue for the otherwise fast-growing ...
Now, let's explore the key differences between literature reviews and theoretical frameworks. Key Differences: Focus: A literature review focuses on summarizing existing research, while a theoretical framework focuses on providing a conceptual foundation for the study. Scope: A literature review covers a broad range of related research, while a ...
The second area is that the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework serve similar functions within a manuscript reporting the results of an empirical study. The third area presents the distinctions among literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as a component of an empirical manuscript.
Abstract. This chapter advances the theoretical framework and the major contributions of political science that are critical to frame my argument. It defines the concepts and a body of studies that will help to address my research puzzle. This chapter is structured as follow: first it looks at democracy literature and party competition ...
The main difference between literature review and theoretical framework is their function. The literature review explores what has already been written about the topic under study in order to highlight a gap, whereas the theoretical framework is the conceptual and analytical approach the researcher is going to take to fill that gap.
Step 2: Build a Literature Review and Identify a Theoretical or Conceptual Framework Written and Compiled by Amanda J. Rockinson-Szapkiw & Anita Knight Introduction Foundations are important. There is a Biblical parable about two builders. One builder builds his house on a solid foundation. When storms come, the house remains standing.
Scoping review methodology was selected because our purpose was to systematically identify and characterise the breadth of research that exists around implementation factors, and distinguish the barriers and facilitators to implementation of preventive health assessments [24, 25].This review drew on methodological guidance for scoping reviews from JBI [], and was conducted in accordance with a ...
Background Confusion exists over the definition of the care pathway concept and existing conceptual frameworks contain various inadequacies which have led to implementation difficulties. In the current global context of rapidly changing health care systems, there is great need for a standardized definition and integrative framework that can guide implementation. This study aims to propose an ...
The key elements of the original framework are catalysts, organisational capacity, engagement actions, and research use. We wished to build on the framework's embedded conceptual work, derived from literature reviews and semi-structured interviews, to identify policymakers' views on factors that assist policy agencies' use of research .
Comments on the article by Sauter, et al. (see record 2023-72906-001). Sauter et al. (2023) provide a comprehensive and much-needed review of the literature, guiding the development of their mild intellectual disabilities or borderline intellectual functioning (AAIDD)-Informed Framework for cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) case formulations and treatment for young people with mild intellectual ...
This study aims to review recent writing on the dynamic capabilities view practices of business firms to examine the concepts and create a more thorough theoretical description from a conceptual standpoint. A thorough review of the literature on dynamic capabilities view practice was conducted.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK Literature Review: Theory Identification Essay Assignment Lev Vygotsky's (2013) theory of sociocultural describes how an individual mental functioning is related to cultural, institutional, and historical context, the roles that participate in social interactions, and culturally organized activities (Scott, p. 1). Vygotsky broke the theory into two parts; individual ...
The structure of this paper is as follows: First, we conduct a comprehensive literature review on EE to answer RQ1, thereby establishing a robust theoretical foundation. Second, we outline our ...