Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
School Stress Takes A Toll On Health, Teens And Parents Say
Patti Neighmond

Colleen Frainey, 16, of Tualatin, Ore., cut back on advanced placement classes in her junior year because the stress was making her physically ill. Toni Greaves for NPR hide caption
Colleen Frainey, 16, of Tualatin, Ore., cut back on advanced placement classes in her junior year because the stress was making her physically ill.
When high school junior Nora Huynh got her report card, she was devastated to see that she didn't get a perfect 4.0.
Nora "had a total meltdown, cried for hours," her mother, Jennie Huynh of Alameda, Calif., says. "I couldn't believe her reaction."
Nora is doing college-level work, her mother says, but many of her friends are taking enough advanced classes to boost their grade-point averages above 4.0. "It breaks my heart to see her upset when she's doing so awesome and going above and beyond."
And the pressure is taking a physical toll, too. At age 16, Nora is tired, is increasingly irritated with her siblings and often suffers headaches, her mother says.
Teens Talk Stress
When NPR asked on Facebook if stress is an issue for teenagers, they spoke loud and clear:
- "Academic stress has been a part of my life ever since I can remember," wrote Bretta McCall, 16, of Seattle. "This year I spend about 12 hours a day on schoolwork. I'm home right now because I was feeling so sick from stress I couldn't be at school. So as you can tell, it's a big part of my life!"
- "At the time of writing this, my weekend assignments include two papers, a PowerPoint to go with a 10-minute presentation, studying for a test and two quizzes, and an entire chapter (approximately 40 pages) of notes in a college textbook," wrote Connor West of New Jersey.
- "It's a problem that's basically brushed off by most people," wrote Kelly Farrell in Delaware. "There's this mentality of, 'You're doing well, so why are you complaining?' " She says she started experiencing symptoms of stress in middle school, and was diagnosed with panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder in high school.
- "Parents are the worst about all of this," writes Colin Hughes of Illinois. "All I hear is, 'Work harder, you're a smart kid, I know you have it in you, and if you want to go to college you need to work harder.' It's a pain."
Parents are right to be worried about stress and their children's health, says Mary Alvord , a clinical psychologist in Maryland and public education coordinator for the American Psychological Association.
"A little stress is a good thing," Alvord says. "It can motivate students to be organized. But too much stress can backfire."
Almost 40 percent of parents say their high-schooler is experiencing a lot of stress from school, according to a new NPR poll conducted with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the Harvard School of Public Health. In most cases, that stress is from academics, not social issues or bullying, the poll found. (See the full results here .)
Homework was a leading cause of stress, with 24 percent of parents saying it's an issue.
Teenagers say they're suffering, too. A survey by the American Psychological Association found that nearly half of all teens — 45 percent — said they were stressed by school pressures.
Chronic stress can cause a sense of panic and paralysis, Alvord says. The child feels stuck, which only adds to the feeling of stress.
Parents can help put the child's distress in perspective, particularly when they get into what Alvord calls catastrophic "what if" thinking: "What if I get a bad grade, then what if that means I fail the course, then I'll never get into college."
Then move beyond talking and do something about it.

Colleen pets her horse, Bishop. They had been missing out on rides together because of homework. Toni Greaves for NPR hide caption
Colleen pets her horse, Bishop. They had been missing out on rides together because of homework.
That's what 16-year-old Colleen Frainey of Tualatin, Ore., did. As a sophomore last year, she was taking all advanced courses. The pressure was making her sick. "I didn't feel good, and when I didn't feel good I felt like I couldn't do my work, which would stress me out more," she says.
Mom Abigail Frainey says, "It was more than we could handle as a family."
With encouragement from her parents, Colleen dropped one of her advanced courses. The family's decision generated disbelief from other parents. "Why would I let her take the easy way out?" Abigail Frainey heard.
But she says dialing down on academics was absolutely the right decision for her child. Colleen no longer suffers headaches or stomachaches. She's still in honors courses, but the workload this year is manageable.
Even better, Colleen now has time to do things she never would have considered last year, like going out to dinner with the family on a weeknight, or going to the barn to ride her horse, Bishop.
Psychologist Alvord says a balanced life should be the goal for all families. If a child is having trouble getting things done, parents can help plan the week, deciding what's important and what's optional. "Just basic time management — that will help reduce the stress."
- Children's Health
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Improving lives through learning
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
The Truth About Homework Stress: What Parents & Students Need to Know
- Fact Checked
Written by:
published on:
- December 21, 2023
Updated on:
- January 9, 2024
Looking for a therapist?
Homework is generally given out to ensure that students take time to review and remember the days lessons. It can help improve on a student’s general performance and enhance traits like self-discipline and independent problem solving.
Parents are able to see what their children are doing in school, while also helping teachers determine how well the lesson material is being learned. Homework is quite beneficial when used the right way and can improve student performance.
This well intentioned practice can turn sour if it’s not handled the right way. Studies show that if a student is inundated with too much homework, not only do they get lower scores, but they are more likely to get stressed.
The age at which homework stress is affecting students is getting lower, some even as low as kindergarten. Makes you wonder what could a five year old possibly need to review as homework?
One of the speculated reasons for this stress is that the complexity of what a student is expected to learn is increasing, while the breaks for working out excess energy are reduced. Students are getting significantly more homework than recommended by the education leaders, some even nearly three times more.
To make matters worse, teachers may give homework that is both time consuming and will keep students busy while being totally non-productive.
Remedial work like telling students to copy notes word for word from their text books will do nothing to improve their grades or help them progress. It just adds unnecessary stress.
Explore emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in affordable online therapy. With 30,000+ licensed therapists and plans starting from only $65 per week, BetterHelp makes self-care accessible to all. Complete the questionnaire to match with the right therapist.
Effects of homework stress at home
Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.
Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students.
Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and time spent doing homework, a child can get headaches, sleep deprivation or even ulcers.
And homework stress doesn’t just impact grade schoolers. College students are also affected, and the stress is affecting their academic performance.
Even the parent’s confidence in their abilities to help their children with homework suffers due increasing stress levels in the household.
Fights and conflict over homework are more likely in families where parents do not have at least a college degree. When the child needs assistance, they have to turn to their older siblings who might already be bombarded with their own homework.
Parents who have a college degree feel more confident in approaching the school and discussing the appropriate amount of school work.
“It seems that homework being assigned discriminates against parents who don’t have college degree, parents who have English as their second language and against parents who are poor.” Said Stephanie Donaldson Pressman, the contributing editor of the study and clinical director of the New England Center for Pediatric Psychology.
With all the stress associated with homework, it’s not surprising that some parents have opted not to let their children do homework. Parents that have instituted a no-homework policy have stated that it has taken a lot of the stress out of their evenings.
The recommended amount homework
The standard endorsed by the National Education Association is called the “10 minute rule”; 10 minutes per grade level per night. This recommendation was made after a number of studies were done on the effects of too much homework on families.
The 10 minute rule basically means 10 minutes of homework in the first grade, 20 minute for the second grade all the way up to 120 minutes for senior year in high school. Note that no homework is endorsed in classes under the first grade.
Parents reported first graders were spending around half an hour on homework each night, and kindergarteners spent 25 minutes a night on assignments according to a study carried out by Brown University.
Making a five year old sit still for half an hour is very difficult as they are at the age where they just want to move around and play.
A child who is exposed to 4-5 hours of homework after school is less likely to find the time to go out and play with their friends, which leads to accumulation of stress energy in the body.
Their social life also suffers because between the time spent at school and doing homework, a child will hardly have the time to pursue hobbies. They may also develop a negative attitude towards learning.
The research highlighted that 56% of students consider homework a primary source of stress.
And if you’re curious how the U.S stacks up against other countries in regards to how much time children spend on homework, it’s pretty high on the list .
Signs to look out for on a student that has homework stress
Since not every student is affected by homework stress in the same way, it’s important to be aware of some of the signs your child might be mentally drained from too much homework.
Here are some common signs of homework stress:
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent stomachaches and headaches
- Decreased appetite or changed eating habits
- New or recurring fears
- Not able to relax
- Regressing to behavior they had when younger
- Bursts of anger crying or whining
- Becoming withdrawn while others may become clingy
- Drastic changes in academic performance
- Having trouble concentrating or completing homework
- Constantly complains about their ability to do homework
If you’re a parent and notice any of these signs in your child, step in to find out what’s going on and if homework is the source of their stress.
If you’re a student, pay attention if you start experiencing any of these symptoms as a result of your homework load. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or parents for help if the stress of homework becomes too much for you.
What parents do wrong when it comes to homework stress
Most parents push their children to do more and be more, without considering the damage being done by this kind of pressure.
Some think that homework brought home is always something the children can deal with on their own. If the child cannot handle their homework then these parents get angry and make the child feel stupid.
This may lead to more arguing and increased dislike of homework in the household. Ultimately the child develops an even worse attitude towards homework.
Another common mistake parents make is never questioning the amount of homework their children get, or how much time they spend on it. It’s easy to just assume whatever the teacher assigned is adequate, but as we mentioned earlier, that’s not always the case.
Be proactive and involved with your child’s homework. If you notice they’re spending hours every night on homework, ask them about it. Just because they don’t complain doesn’t mean there isn’t a problem.
How can parents help?
- While every parent wants their child to become successful and achieve the very best, it’s important to pull back on the mounting pressure and remember that they’re still just kids. They need time out to release their stress and connect with other children.
- Many children may be afraid to admit that they’re overwhelmed by homework because they might be misconstrued as failures. The best thing a parent can do is make home a safe place for children to express themselves freely. You can do this by lending a listening ear and not judging your kids.
- Parents can also take the initiative to let the school know that they’re unhappy with the amount of homework being given. Even if you don’t feel comfortable complaining, you can approach the school through the parent-teacher association available and request your representative to plead your case.
- It may not be all the subjects that are causing your child to get stressed. Parents should find out if there is a specific subject of homework that is causing stress. You could also consult with other parents to see what they can do to fix the situation. It may be the amount or the content that causes stress, so the first step is identifying the problem.
- Work with your child to create a schedule for getting homework done on time. You can set a specific period of time for homework, and schedule time for other activities too. Strike a balance between work and play.
- Understanding that your child is stressed about homework doesn’t mean you have to allow them not to try. Let them sit down and work on it as much as they’re able to, and recruit help from the older siblings or a neighbor if possible.
- Check out these resources to help your child with their homework .
The main idea here is to not abolish homework completely, but to review the amount and quality of homework being given out. Stress, depression and lower grades are the last things parents want for their children.
The schools and parents need to work together to find a solution to this obvious problem.
Take the stress test!
Join the Find-a-therapist community and get access to our free stress assessment!
Additional Resources
Online therapy.
Discover a path to emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in convenient and affordable online therapy. With a vast network of 30,000+ licensed therapists, they’re committed to helping you find the one to support your needs. Take advantage of their Free Online Assessment, and connect with a therapist who truly understands you. Begin your journey today.
Relationship Counceling
Whether you’re facing communication challenges, trust issues, or simply seeking to strengthen your connection, ReGain’ s experienced therapists are here to guide you and your partner toward a healthier, happier connection from the comfort of your own space. Get started.
Therapist Directory
Discover the perfect therapist who aligns with your goals and preferences, allowing you to take charge of your mental health. Whether you’re searching for a specialist based on your unique needs, experience level, insurance coverage, budget, or location, our user-friendly platform has you covered. Search here.
About the author
You might also be interested in
6 Little Known Things Mindful People Do Differently
Structural Family Therapy: 5 Techniques and Applications
What Does the Ensō Circle Mean?
Disclaimers
Online Therapy, Your Way
Follow us on social media
We may receive a commission if you click on and become a paying customer of a therapy service that we mention.
The information contained in Find A Therapist is general in nature and is not medical advice. Please seek immediate in-person help if you are in a crisis situation.
Therapy Categories
More information
If you are in a life threatening situation – don’t use this site. Call +1 (800) 273-8255 or check these resources to get immediate help.

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Top 10 Stress Management Techniques for Students
Elizabeth Scott, PhD is an author, workshop leader, educator, and award-winning blogger on stress management, positive psychology, relationships, and emotional wellbeing.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Elizabeth-Scott-MS-660-695e2294b1844efda01d7a29da7b64c7.jpg)
Akeem Marsh, MD, is a board-certified child, adolescent, and adult psychiatrist who has dedicated his career to working with medically underserved communities.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/akeemmarsh_1000-d247c981705a46aba45acff9939ff8b0.jpg)
Most students experience significant amounts of stress. This can significantly affect their health, happiness, relationships, and grades. Learning stress management techniques can help these students avoid negative effects in these areas.
Why Stress Management Is Important for Students
A study by the American Psychological Association (APA) found that teens report stress levels similar to adults. This means teens are experiencing significant levels of chronic stress and feel their stress levels generally exceed their ability to cope effectively .
Roughly 30% of the teens reported feeling overwhelmed, depressed, or sad because of their stress.
Stress can also affect health-related behaviors. Stressed students are more likely to have problems with disrupted sleep, poor diet, and lack of exercise. This is understandable given that nearly half of APA survey respondents reported completing three hours of homework per night in addition to their full day of school work and extracurriculars.
Common Causes of Student Stress
Another study found that much of high school students' stress originates from school and activities, and that this chronic stress can persist into college years and lead to academic disengagement and mental health problems.
Top Student Stressors
Common sources of student stress include:
- Extracurricular activities
- Social challenges
- Transitions (e.g., graduating, moving out , living independently)
- Relationships
- Pressure to succeed
High school students face the intense competitiveness of taking challenging courses, amassing impressive extracurriculars, studying and acing college placement tests, and deciding on important and life-changing plans for their future. At the same time, they have to navigate the social challenges inherent to the high school experience.
This stress continues if students decide to attend college. Stress is an unavoidable part of life, but research has found that increased daily stressors put college-aged young adults at a higher risk for stress than other age groups.
Making new friends, handling a more challenging workload, feeling pressured to succeed, being without parental support, and navigating the stresses of more independent living are all added challenges that make this transition more difficult. Romantic relationships always add an extra layer of potential stress.
Students often recognize that they need to relieve stress . However, all the activities and responsibilities that fill a student’s schedule sometimes make it difficult to find the time to try new stress relievers to help dissipate that stress.
10 Stress Management Techniques for Students
Here you will learn 10 stress management techniques for students. These options are relatively easy, quick, and relevant to a student’s life and types of stress .
Get Enough Sleep
Blend Images - Hill Street Studios / Brand X Pictures / Getty Images
Students, with their packed schedules, are notorious for missing sleep. Unfortunately, operating in a sleep-deprived state puts you at a distinct disadvantage. You’re less productive, may find it more difficult to learn, and may even be a hazard behind the wheel.
Research suggests that sleep deprivation and daytime sleepiness are also linked to impaired mood, higher risk for car accidents, lower grade point averages, worse learning, and a higher risk of academic failure.
Don't neglect your sleep schedule. Aim to get at least 8 hours a night and take power naps when needed.
Use Guided Imagery
David Malan / Getty Images
Guided imagery can also be a useful and effective tool to help stressed students cope with academic, social, and other stressors. Visualizations can help you calm down, detach from what’s stressing you, and reduce your body’s stress response.
You can use guided imagery to relax your body by sitting in a quiet, comfortable place, closing your eyes, and imagining a peaceful scene. Spend several minutes relaxing as you enjoy mentally basking in your restful image.
Consider trying a guided imagery app if you need extra help visualizing a scene and inducting a relaxation response. Research suggests that such tools might be an affordable and convenient way to reduce stress.
Exercise Regularly
One of the healthiest ways to blow off steam is to get regular exercise . Research has found that students who participate in regular physical activity report lower levels of perceived stress. While these students still grapple with the same social, academic, and life pressures as their less-active peers, these challenges feel less stressful and are easier to manage.
Finding time for exercise might be a challenge, but there are strategies that you can use to add more physical activity to your day. Some ideas that you might try include:
- Doing yoga in the morning
- Walking or biking to class
- Reviewing for tests with a friend while walking on a treadmill at the gym
- Taking an elective gym class focused on leisure sports or exercise
- Joining an intramural sport
Exercise can help buffer against the negative effects of student stress. Starting now and keeping a regular exercise practice throughout your lifetime can help you live longer and enjoy your life more.
Take Calming Breaths
When your body is experiencing a stress response, you’re often not thinking as clearly as you could be. You are also likely not breathing properly. You might be taking short, shallow breaths. When you breathe improperly, it upsets the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your body.
Studies suggest this imbalance can contribute to various physical symptoms, including increased anxiety, fatigue, stress, emotional problems, and panic attacks.
A quick way to calm down is to practice breathing exercises . These can be done virtually anywhere to relieve stress in minutes.
Because they are fast-acting, breathing exercises are a great way to cope with moments of acute stress , such as right before an exam or presentation. But they can also help manage longer-lasting stress such as dealing with relationships, work, or financial problems.
Practice Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
Another great stress management technique for students that can be used during tests, before bed, or at other times when stress has you physically wound up is progressive muscle relaxation ( PMR ).
This technique involves tensing and relaxing all muscles until the body is completely relaxed. With practice, you can learn to release stress from your body in seconds. This can be particularly helpful for students because it can be adapted to help relaxation efforts before sleep for a deeper sleep.
Once a person learns how to use PMR effectively, it can be a quick and handy way to induce relaxation in any stressful situation, such as bouts of momentary panic before a speech or exam, dealing with a disagreement with your roommate, or preparing to discuss a problem with your academic advisor.
Listen to Music
A convenient stress reliever that has also shown many cognitive benefits, music can help relieve stress and calm yourself down or stimulate your mind depending on what you need in the moment.
Research has found that playing upbeat music can improve processing speed and memory. Stressed students may find that listening to relaxing music can help calm the body and mind. One study found that students who listened to the sounds of relaxing music were able to recover more quickly after a stressful situation.
Students can harness the benefits of music by playing classical music while studying, playing upbeat music to "wake up" mentally, or relaxing with the help of their favorite slow melodies.
Build Your Support Network
Halfpoint Images / Getty Images
Having emotional support can help create a protective buffer against stress. Unfortunately, interpersonal relationships can also sometimes be a source of anxiety for students. Changes in friendships, romantic breakups, and life transitions such as moving away for college can create significant upheaval and stress for students.
One way to combat feelings of loneliness and make sure that you have people to lean on in times of need is to expand your support network and nurture your relationships.
Look for opportunities to meet new people, whether it involves joining study groups or participating in other academic, social, and leisure activities.
Remember that different types of relationships offer differing types of support . Your relationships with teachers, counselors, and mentors can be a great source of information and resources that may help you academically. Relationships with friends can provide emotional and practical support.
Widening your social circle can combat student stress on various fronts and ensure you have what you need to succeed.
Eat a Healthy Diet
Niedring/Drentwett / Getty Images
You may not realize it, but your diet can either boost your brainpower or sap you of mental energy. It can also make you more reactive to the stress in your life. As a result, you might find yourself turning to high-sugar, high-fat snacks to provide a temporary sense of relief.
A healthy diet can help combat stress in several ways. Improving your diet can keep you from experiencing diet-related mood swings, light-headedness, and more.
Unfortunately, students are often prone to poor dietary habits. Feelings of stress can make it harder to stick to a consistently healthy diet, but other concerns such as finances, access to cooking facilities, and time to prepare healthy meals can make it more challenging for students.
Some tactics that can help students make healthy choices include:
- Eating regularly
- Carrying a water bottle to class
- Keeping healthy snacks such as fruits and nuts handy
- Limiting caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol intake
Find Ways to Minimize Stress
One way to improve your ability to manage student stress is to look for ways you cut stress out of your life altogether. Evaluate the things that are bringing stress or anxiety into your life. Are they necessary? Are they providing more benefits than the toll they take on your mental health? If the answer is no, sometimes the best option is just to ditch them altogether.
This might mean cutting some extracurricular activities out of your schedule. It might mean limiting your use of social media. Or it might mean learning to say no to requests for your time, energy, and resources.
While it might be challenging at first, learning how to prioritize yourself and your mental well-being is an important step toward reducing your stress.
Try Mindfulness
When you find yourself dealing with stress—whether it's due to academics, relationships, financial pressures, or social challenges—becoming more aware of how you feel in the moment may help you respond more effectively.
Mindfulness involves becoming more aware of the present moment. Rather than judging, reacting, or avoiding problems, the goal is to focus on the present, become more aware of how you are feeling, observe your reactions, and accept these feelings without passing judgment on them.
Research suggests that mindfulness-based stress management practices can be a useful tool for reducing student stress. Such strategies may also help reduce feelings of anxiety and depression.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that stress isn't the same for everyone. Figuring out what works for you may take some trial and error. A good start is to ensure that you are taking care of yourself physically and emotionally and to experiment with different stress relief strategies to figure out what works best to help you feel less stressed.
If stress and anxiety are causing distress or making it difficult to function in your daily life, it is important to seek help. Many schools offer resources that can help, including face-to-face and online mental health services. You might start by talking to your school counselor or student advisor about the stress you are coping with. You can also talk to a parent, another trusted adult, or your doctor.
If you or a loved one are struggling with anxiety, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
American Psychological Association. Stress in America: Are Teens Adopting Adults' Stress Habits?
Leonard NR, Gwadz MV, Ritchie A, et al. A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools . Front Psychol. 2015;6:1028. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01028
Acharya L, Jin L, Collins W. College life is stressful today - Emerging stressors and depressive symptoms in college students . J Am Coll Health . 2018;66(7):655-664. doi:10.1080/07448481.2018.1451869
Beiter R, Nash R, McCrady M, Rhoades D, Linscomb M, Clarahan M, Sammut S. The prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and stress in a sample of college students . J Affect Disord . 2015;173:90-6. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2014.10.054
Hershner SD, Chervin RD. Causes and consequences of sleepiness among college students . Nat Sci Sleep . 2014;6:73-84. doi:10.2147/NSS.S62907
Gordon JS, Sbarra D, Armin J, Pace TWW, Gniady C, Barraza Y. Use of a guided imagery mobile app (See Me Serene) to reduce COVID-19-related stress: Pilot feasibility study . JMIR Form Res . 2021;5(10):e32353. doi:10.2196/32353
Cowley J, Kiely J, Collins D. Is there a link between self-perceived stress and physical activity levels in Scottish adolescents ? Int J Adolesc Med Health . 2017;31(1). doi:10.1515/ijamh-2016-0104
Paulus MP. The breathing conundrum-interoceptive sensitivity and anxiety . Depress Anxiety . 2013;30(4):315–320. doi:10.1002/da.22076
Toussaint L, Nguyen QA, Roettger C, Dixon K, Offenbächer M, Kohls N, Hirsch J, Sirois F. Effectiveness of progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery in promoting psychological and physiological states of relaxation . Evid Based Complement Alternat Med . 2021;2021:5924040. doi:10.1155/2021/5924040.
Gold BP, Frank MJ, Bogert B, Brattico E. Pleasurable music affects reinforcement learning according to the listener . Front Psychol . 2013;4:541. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00541
Thoma MV, La Marca R, Brönnimann R, Finkel L, Ehlert U, Nater UM. The effect of music on the human stress response . PLoS ONE . 2013;8(8):e70156. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070156
American Psychological Association. Manage stress: Strengthen your support network .
Nguyen-rodriguez ST, Unger JB, Spruijt-metz D. Psychological determinants of emotional eating in adolescence. Eat Disord . 2009;17(3):211-24. doi:10.1080/10640260902848543
Parsons D, Gardner P, Parry S, Smart S. Mindfulness-based approaches for managing stress, anxiety and depression for health students in tertiary education: A scoping review . Mindfulness (N Y) . 2022;13(1):1-16. doi:10.1007/s12671-021-01740-3
By Elizabeth Scott, PhD Elizabeth Scott, PhD is an author, workshop leader, educator, and award-winning blogger on stress management, positive psychology, relationships, and emotional wellbeing.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Using a cellphone compass to measure tiny concentrations of compounds important for human health
50 minutes ago

Stingray sand 'sculpture' in South Africa may be oldest example of humans creating an image of another creature
Researchers observe anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence phenomenon

Acids enable adhesive electrodes for thin, flexible supercapacitors
Researchers reveal evidence of transition from ergodic toward ergodic breaking dynamics
2 hours ago

Ancient Adélie penguin DNA reveals that small repeats persist for hundreds of millions of years

Machine learning provides a new picture of the great gray owl
3 hours ago
New single-cell analysis tech incorporates advanced fiber optics directly into microfluidic chips
The role of interfacial amino acids in shaping bio-electronic communication between proteins

Supercomputer simulations decode the mass puzzle of the first stars
Relevant physicsforums posts, how is physics taught without calculus.
Mar 29, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
The New California Math Framework: Another Step Backwards?
Mar 14, 2024
Rant about working in the tutoring lab: How should I deal with this?
Feb 25, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you
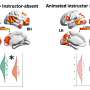
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024


Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published, study finds
Mar 23, 2024

Using Twitter/X to promote research findings found to have little impact on number of citations
Mar 22, 2024

Gender and racial discrimination uncovered in leadership positions at Australia's leading universities
Mar 15, 2024
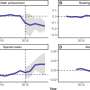
Study finds children in Flint experienced educational declines even if they did not have lead pipes

Could iPhones replace microscopes in early STEM education?
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.
#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.
#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
The New York Times
Motherlode | when homework stresses parents as well as students, when homework stresses parents as well as students.

Educators and parents have long been concerned about students stressed by homework loads , but a small research study asked questions recently about homework and anxiety of a different group: parents. The results were unsurprising. While we may have already learned long division and let the Magna Carta fade into memory, parents report that their children’s homework causes family stress and tension — particularly when additional factors surrounding the homework come into play.
The researchers, from Brown University, found that stress and tension for families (as reported by the parents) increased most when parents perceived themselves as unable to help with the homework, when the child disliked doing the homework and when the homework caused arguments, either between the child and adults or among the adults in the household.
The number of parents involved in the research (1,173 parents, both English and Spanish-speaking, who visited one of 27 pediatric practices in the greater Providence area of Rhode Island) makes it more of a guide for further study than a basis for conclusions, but the idea that homework can cause significant family stress is hard to seriously debate. Families across income and education levels may struggle with homework for different reasons and in different ways, but “it’s an equal opportunity problem,” says Stephanie Donaldson-Pressman , a contributing editor to the research study and co-author of “ The Learning Habit .”
“Parents may find it hard to evaluate the homework,” she says. “They think, if this is coming home, my child should be able to do it. If the child can’t, and especially if they feel like they can’t help, they may get angry with the child, and the child feels stupid.” That’s a scenario that is likely to lead to more arguments, and an increased dislike of the work on the part of the child.
The researchers also found that parents of students in kindergarten and first grade reported that the children spent significantly more time on homework than recommended. Many schools and organizations, including the National Education Association and the Great Schools blog , will suggest following the “10-minute rule” for how long children should spend on school work outside of school hours: 10 minutes per grade starting in first grade, and most likely more in high school. Instead, parents described their first graders and kindergartners working, on average, for 25 to 30 minutes a night. That is consistent with other research , which has shown an increase in the amount of time spent on homework in lower grades from 1981 to 2003.
“This study highlights the real discrepancy between intent and what’s actually happening,” Ms. Donaldson-Pressman said, speaking of both the time spent and the family tensions parents describe. “When people talk about the homework, they’re too often talking about the work itself. They should be talking about the load — how long it takes. You can have three problems on one page that look easy, but aren’t.”
The homework a child is struggling with may not be developmentally appropriate for every child in a grade, she suggests, noting that academic expectations for young children have increased in recent years . Less-educated or Spanish-speaking parents may find it harder to evaluate or challenge the homework itself, or to say they think it is simply too much. “When the load is too much, it has a tremendous impact on family stress and the general tenor of the evening. It ruins your family time and kids view homework as a punishment,” she said.
At our house, homework has just begun; we are in the opposite of the honeymoon period, when both skills and tolerance are rusty and complaints and stress are high. If the two hours my fifth-grade math student spent on homework last night turn out the be the norm once he is used to the work and the teacher has had a chance to hear from the students, we’ll speak up.
We should, Ms. Donaldson-Pressman says. “Middle-class parents can solve the problem for their own kids,” she says. “They can make sure their child is going to all the right tutors, or get help, but most people can’t.” Instead of accepting that at home we become teachers and homework monitors (or even taking classes in how to help your child with his math ), parents should let the school know that they’re unhappy with the situation, both to encourage others to speak up and to speak on behalf of parents who don’t feel comfortable complaining.
“Home should be a safe place for students,” she says. “A child goes to school all day and they’re under stress. If they come home and it’s more of the same, that’s not good for anyone.”
Read more about homework on Motherlode: Homework and Consequences ; The Mechanics of Homework ; That’s Your Child’s Homework Project, Not Yours and Homework’s Emotional Toll on Students and Families.
What's Next
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Is Homework a Waste of Students' Time? Study Finds It's the Biggest Cause of Teen Stress
As the debate over the need for homework continues, a new study found that it's the biggest cause of teen stress, leading to sleepless nights and poor academic performance
Julie Mazziotta is the Sports Editor at PEOPLE, covering everything from the NFL to tennis to Simone Biles and Tom Brady. She was previously an Associate Editor for the Health vertical for six years, and prior to joining PEOPLE worked at Health Magazine. When not covering professional athletes, Julie spends her time as a (very) amateur athlete, training for marathons, long bike trips and hikes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/J.Mazziotta2334-e3daa71fe1a745929e739c08e585253f.jpg)
It’s the bane of every teen’s existence. After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to get started on mountains of homework. And educators are mixed on its effectiveness . Some say the practice reinforces what students learned during the day, while others argue that it put unnecessary stress on kids and parents , who are often stuck nagging or helping.
According to a new study, conducted by the Better Sleep Council , that homework stress is the biggest source of frustration for teens, with 74 percent of those surveyed ranking it the highest, above self-esteem (51 percent) parental expectations (45 percent) and bullying (15 percent).
Homework is taking up a large chunk of their time , too — around 15-plus hours a week, with about one-third of teens reporting that it’s closer to 20-plus hours.
The stress and excessive homework adds up to lost sleep, the BSC says. According to the survey, 57 percent of teenagers said that they don’t get enough sleep, with 67 reporting that they get just five to seven hours a night — a far cry from the recommended eight to ten hours. The BSC says that their research shows that when teens feel more stressed, their sleep suffers. They go to sleep later, wake up earlier and have more trouble falling and staying asleep than less-stressed teens.
“We’re finding that teenagers are experiencing this cycle where they sacrifice their sleep to spend extra time on homework, which gives them more stress — but they don’t get better grades,” said Mary Helen Rogers, the vice president of marketing and communications for the BSC.
RELATED VIDEO: To Help Or Not To Help: Moms Talk About Whether Or Not They Help Their Children With Homework
Another interesting finding from this study: students who go to bed earlier and wake up earlier do better academically than those who stay up late, even if those night owls are spending that time doing homework.
To end this cycle of sleep deprivation and stress, the BSC recommends that students try setting a consistent time to go to sleep each night, regardless of leftover homework. And their other sleep tips are good for anyone, regardless of age — keep the temperature between 65 and 67 degrees, turn off the electronic devices before bed, make sure the mattress is comfy and reduce noise with earplugs or sound machines.
Related Articles

How to Reduce Homework Stress
If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.

Author Katie Wickliff
Published March 2024

If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.
- Key takeaways
- Homework stress can be a significant problem for children and their families
- An appropriate amount of quality homework can be beneficial for students
- Parents can help reduce homework stress in several key ways
Table of contents
- Homework stress effects
- How to reduce homework stress
As a parent who has felt the frustration of watching my child be reduced to tears because of her homework each night, I’ve often wondered: do these math worksheets and reading trackers really make a difference to a child’s academic success? Or does homework cause stress without having a positive impact on learning?
If your child experiences a significant amount of homework stress, you may feel at a loss to help. However, there are several things you can do at home to minimize the negative effects of this stress on your child–and you! We’ve put together a list of research-based practices that can help your child better handle their homework load.
The Effects of Homework Stress on Students
Does homework cause stress? Short answer: Yes. It’s been well documented that too much homework can cause stress and anxiety for students–and their parents. However, do the benefits of homework outweigh the costs? Is homework “worth” the frustration and exhaustion that our children experience?
Findings on the benefits of homework at the elementary school level are mixed, with studies showing that homework appears to have more positive effects under certain conditions for certain groups of students.
After examining decades of studies on the relationship between homework and academic achievement, leading homework researcher Harris M. Cooper has proposed the “10-minute rule,” suggesting that homework be limited to 10 minutes per grade level. For example, children in 3rd grade should do no more than 30 minutes of homework daily, while a 1st grader should do no more than 10 minutes of homework. The National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association both endorse this guideline as a general rule of thumb.
Because of these research findings, Doodle believes that an appropriate amount of quality homework can help students feel more positive about learning and can provide parents with a critical connection to their child’s school experience . But to keep learning positive, we need to reduce the amount of stress both students and parents feel about homework.
1. Routine, Routine, Routine
Creating an after-school routine and sticking to it helps children feel organized, but with sports, tutoring, or music lessons, many children have varying weekday schedules. As a former classroom teacher and private tutor, I suggest that families post a weekly schedule somewhere visible and communicate that schedule with their child.
At our house, we have a dry-erase calendar posted on the wall. Every Sunday evening, I write both of my children’s schedules for the following week–including homework time. We go through the calendar together, and they reference it often throughout the week. I can tell both my son and daughter feel better when they know when they’ll get their homework done.
2. Create a Homework Space
Ideally, your child should have a dedicated homework space. It doesn’t matter if that space is a desk, a dining room table, or a kitchen countertop. What does matter is that the homework area is tidy, because an unorganized homework area is very distracting.
3. Start Homework Early
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress.
4. Encourage Breaks
If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their homework, encourage them to take a breather and come back to it later. As a teacher and tutor, I called this a “brain break” and believe these breaks are essential. Taking a short break will give your child a chance to step away from a frustrating problem or assignment.
5. It’s Okay to Ask for Help
Sometimes, homework can become just too stressful and overwhelming. In that case, it really is okay to stop. Children can learn to advocate for themselves by making a list of questions for their teacher and asking for help the next day. Depending on their age, you might need to help role-play how to approach their teacher with their frustrations.
Additionally, parents should never feel afraid to contact their child’s teacher to talk about homework issues. When I was teaching elementary school, I always wanted parents to feel comfortable reaching out about any issues, including homework stress.
6. Get Plenty of Rest
Sleep is critical to a child’s overall wellbeing , which includes their academic performance. Tired kids can’t concentrate as well, which can lead to feeling more overwhelmed about homework assignments. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, kids aged 6-12 should get at least 9 hours of sleep each night.
7. Consider a Homework Group
Organizing a homework group a few times a week is another way for your child to view homework more positively. Working as a group encourages collaboration, while discussions can solidify concepts learned in class.
8. Encourage Positivity
No matter what your school experience was like, it’s important to model a growth mindset for your child. A growth mindset is the belief that your abilities can develop and improve over time. So if your child says something like “ I can’t do this! ” first acknowledge their frustration. Then, encourage them to say, “ I may not understand this yet, but I will figure it out. ” Speaking positively about tough experiences takes practice, but it will go a long way in reducing homework stress for your child.
9. Develop Skills With Fun Games
Feeling stressed about homework is no fun. Completing worksheets and memorizing facts is necessary, but playing games is a great way to inject some excitement into learning. Doodle’s interactive math app is filled with interactive exercises, engaging math games, and unique rewards that help kids develop their skills while having fun.
Lower Math Anxiety with DoodleMath
Does your child struggle with math anxiety? DoodleMath is an award-winning math app f illed with fun, interactive math questions aligned to state standards. Doodle creates a unique work program tailored to each child’s skill level to boost confidence and reduce math anxiety. Try it free today!

FAQs About Homework Stress
Many studies have shown that homework and stress often go hand-in-hand, often because many children feel pressure to perform perfectly or they have trouble managing their emotions–they get overwhelmed or flooded easily.
You can help your child reduce homework stress in several ways, including by establishing a routine, creating a homework space, encouraging breaks, and making homework fun with online games or math apps.

Lesson credits

Katie Wickliff
Katie holds a master’s degree in Education from the University of Colorado and a bachelor’s degree in both Journalism and English from The University of Iowa. She has over 15 years of education experience as a K-12 classroom teacher and Orton-Gillingham certified tutor. Most importantly, Katie is the mother of two elementary students, ages 8 and 11. She is passionate about math education and firmly believes that the right tools and support will help every student reach their full potential.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
March 7 Movie review: “Don’t Worry Darling”
February 8 What has iSchool been listening this fall and winter?
January 19 Ronaldo vs. Messi – Differences and Similarities
January 19 What iSchoolers are wearing: Updated version!
January 19 The true cost of fast fashion
January 16 What motivates you to work?
January 11 New teachers at the iSchool
January 4 Holiday traditions around the globe
December 18 Holidays in New York City
December 14 Sports recap: Ohtani, World Cup, & more

The iNews Network

Student stress: How homework really affects education

Sydney Wargo , Reporter January 10, 2019
For centuries, children have been going to school in order to receive an education and learn valuable, basic skills. In the United States, the average student starts going to school when they are 5 years old, and continues on until they are 18. Beyond that, many people seek higher education through colleges, universities, and graduate schools.
Along with school comes homework.The amount of homework a student receives depends on the class, the teacher, and the school.
Many New York City public high schools given 2 to 4 hours of homework a night. These students tend to feel more pressured and anxious about school. However, the iSchool gives much less homework compared to other schools. As a result, the students are much less stressed.
Homework is a main source of stress for students, and it does not improve students’ grades. Schools that give less homework, such as the iSchool, have overall better performing, more mentally stable, less stressed students.
“Too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress,” an article from the American Psychological Association says.
According to a survey sent out to the iSchool community, the majority of 30 respondents reported that they spent 2-4 hours on homework every night. When asked if homework was a major source of stress, 96% of respondents said yes.
Stanford University conducted a study concerning the relationship between homework and stress. Over 4,000 students were asked questions related to how homework affects their stress levels. The results showed that “56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress… Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor… Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.”
Dela Sluymer, a freshman at Brooklyn Millennium High School, said that she usually has 2 hours of homework per night.
“I’m usually working on essays and projects that I’m not given time to complete in class, and also other worksheets and more small work like that,” Dela says. She admits homework is often stressful for her, and it takes up a lot of her time outside of school.
Typically, students are in school 5 days a week for 6-8 hours a day, not including extracurricular activities. This gives most kids a fairly small amount of time to participate in activities outside of school, such as spending time with friends and family, taking part in hobbies, and more. Unfortunately, homework takes up a lot of this time, further limiting students from their freedom.
At the iSchool, with less homework, students are able to participate in clubs and other extracurricular activities, as well as spend valuable time with loved ones.
Slava Hasuler-Lew, a freshman at the iSchool, explains how less homework has improved her school life. “At this school, I almost never have over an hour of homework a night. Whenever I talk to my friends, they always say they have several hours of homework, and how they’re so stressed out about [it].”
“Having a light homework load has gotten rid of a lot of the negative feelings I used to have surrounding school,” Slava explains. “The less stressed out I am, the better I do in my classes, and homework used to be my main source of stress in middle school.”
Washington Post analyzed a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education. This study surveyed several thousand students on the negative impact of too much homework. The survey revealed that “Many (63%) reported that the amount of work they received oft or always made it challenging to spend time with family and friends, and a similar percent (61%) indicated that they had been forced to drop an activity they enjoyed because of their school workload.”
Noah Mcguane is a freshman at Edward R. Murrow High School. Noah describes his homework load and its affect on him.
“I get a lot of homework on a daily basis. I usually have assigned reading, DeltaMath, worksheets, essays, pretty much any type of assignment you could imagine. I’d say I usually have 2 hours of homework a night, but it varies.”
“Homework can be really stressful and time consuming for me,” Noah says. “It is really important to me that I get good grades and do well, but that mindset sometimes makes me feel even more pressured, making the stress even worse.”
Stress includes a large number of negative side effects that can greatly impact a person’s daily life. Insomnia, exhaustion, acne, headaches, nausea, vulnerability to sickness, mood swings, and short-temperedness are only some of the effects stress can have on people. Extreme stress can have even worse consequences, such as hair loss, depression, and anxiety.
The previously mentioned study conducted by Stanford University shows that many students suffer from similar symptoms when given too much homework. Some students reported that in order to make time for their homework, they deprive themselves of sleep; sleep deprivation on its own comes with many negative side effects.
Having such high stress will inevitably lead to lower performance in school. Stressed students often have trouble focusing in class, making school work harder for them. It is a common misconception that homework leads to better grades; the result is actually the opposite.
When adding up stress, sleep deprivation, and lack of focus, it is impossible for the average adolescent to handle everything and still manage to perform to the best of their ability, leaving many students feeling hopeless.
Compared to the NYC iSchool, students here suffer from less of these problems. Laura Hickson, iSchool freshman, gives her insight on homework: “I have trouble sleeping as it is, and staying up doing homework really doesn’t help with that. Now that I go to the iSchool, I get better sleep, and I feel better when coming to school.”
Huffington Post further alludes this same point in an article discussing the impact large amounts of homework has on students test scores:
“Data shows that in countries where more time is spent on homework, students score lower on a standardized test called the Program for International Student Assessment… The same correlation is also seen when comparing homework time and test performance at schools within countries.”
Homework can be beneficial; it is important to practice in order to fully understand the topics students learn about in school. However, when the amount of homework assigned starts to become excessive, it can negatively impact how a student performs in school.
At the iSchool, the student body’s happiness is one of the main priorities. The lives students have outside of school are taken into consideration when assigning work outside of the classroom. Additionally, many students have Independent Work periods, where they can fully complete homework in school, leaving them stress free for the night.
Rather than making school a stressful environment, school should be a place where students can perform the best they possibly can and truly thrive, focus, and be educated. Education is a privilege, and we shouldn’t mistreat it.
Sydney Wargo is a junior at the NYC iSchool and a reporter for iNews. She enjoys reading and creative writing in and hopes to pursue a career as a journalist.
- Polls Archive

How to become an academic weapon

Why is America so unhealthy?

Traveling’s transformation: Discovering benefits

How does your cat in heat affect others? What can you do to prevent it?
The second avenue subway: A 100 year old aspiration

How do you live your life?

The unspoken half of mental health

The romance and reality of the 90s and early 2000s: Nostalgia, nostalgia everywhere

Luxury vs. drugstore makeup

Now that the college process is over, here’s what some iSchool seniors have learned
The Student News Site of NYC iSchool
Shop NewBeauty Reader’s Choice Awards winners — from $13
- TODAY Plaza
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Music Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
Is homework robbing your family of joy? You're not alone
Children are not the only ones who dread their homework these days. In a 2019 survey of 1,049 parents with children in elementary, middle, or high school, Office Depot found that parents spend an average of 21 minutes a day helping their children with their homework. Those 21 minutes are often apparently very unpleasant.
Parents reported their children struggle to complete homework. One in five believed their children "always or often feel overwhelmed by homework," and half of them reported their children had cried over homework stress.
Parents are struggling to help. Four out of five parents reported that they have had difficulty understanding their children's homework.
This probably comes as no surprise to any parent who has come up against a third grade math homework sheet with the word "array" printed on it. If you have not yet had the pleasure, for the purposes of Common Core math, an array is defined as a set of objects arranged in rows and columns and used to help kids learn about multiplication. For their parents, though, it's defined as a "What? Come again? Huh?"
It's just as hard on the students. "My high school junior says homework is the most stressful part of high school...maybe that’s why he never does any," said Mandy Burkhart, of Lake Mary, Florida, who is a mother of five children ranging in age from college to preschool.
In fact, Florida high school teacher and mother of three Katie Tomlinson no longer assigns homework in her classroom. "Being a parent absolutely changed the way I assign homework to my students," she told TODAY Parents .
"Excessive homework can quickly change a student’s mind about a subject they previously enjoyed," she noted. "While I agree a check and balance is necessary for students to understand their own ability prior to a test, I believe it can be done in 10 questions versus 30."
But homework is a necessary evil for most students, so what is a parent to do to ensure everyone in the house survives? Parents and professionals weigh in on the essentials:
Understand the true purpose of homework
"Unless otherwise specified, homework is designed to be done by the child independently, and it's most often being used as a form of formative assessment by the teacher to gauge how the kids are applying — independently — what they are learning in class," said Oona Hanson , a Los Angeles-area educator and parent coach.
"If an adult at home is doing the heavy lifting, then the teacher never knows that the child isn't ready to do this work alone, and the cycle continues because the teacher charges ahead thinking they did a great job the day before!" Hanson said. "It's essential that teachers know when their students are struggling for whatever reason."
Hanson noted the anxiety both parents and children have about academic achievement, and she understands the parental impulse to jump in and help, but she suggested resisting that urge. "We can help our kids more in the long run if we can let them know it's OK to struggle a little bit and that they can be honest with their teacher about what they don't understand," she said.
Never miss a parenting story with the TODAY Parenting newsletter! Sign up here.
Help kids develop time management skills
Some children like to finish their homework the minute they get home. Others need time to eat a snack and decompress. Either is a valid approach, but no matter when students decide to tackle their homework, they might need some guidance from parents about how to manage their time .
One tip: "Set the oven timer for age appropriate intervals of work, and then let them take a break for a few minutes," Maura Olvey, an elementary school math specialist in Central Florida, told TODAY Parents. "The oven timer is visible to them — they know when a break is coming — and they are visible to you, so you can encourage focus and perseverance." The stopwatch function on a smartphone would work for this method as well.
But one size does not fit all when it comes to managing homework, said Cleveland, Ohio, clinical psychologist Dr. Sarah Cain Spannagel . "If their child has accommodations as a learner, parents know they need them at home as well as at school: quiet space, extended time, audio books, etcetera," she said. "Think through long assignments, and put those in planners in advance so the kid knows it is expected to take some time."
Know when to walk away
"I always want my parents to know when to call it a night," said Amanda Feroglia, a central Florida elementary teacher and mother of two. "The children's day at school is so rigorous; some nights it’s not going to all get done, and that’s OK! It’s not worth the meltdown or the fight if they are tired or you are frustrated...or both!"
Parents also need to accept their own limits. Don't be afraid to find support from YouTube videos, websites like Khan Academy, or even tutors. And in the end, said Spannagel, "If you find yourself yelling or frustrated, just walk away!" It's fine just to let a teacher know your child attempted but did not understand the homework and leave it at that.
Ideally, teachers will understand when parents don't know how to help with Common Core math, and they will assign an appropriate amount of homework that will not leave both children and their parents at wits' ends. If worst comes to worst, a few parents offered an alternative tip for their fellow homework warriors.
"If Brittany leaves Boston for New York at 3:00 pm traveling by train at 80 MPH, and Taylor leaves Boston for New York at 1:00 pm traveling by car at 65 MPH, and Brittany makes two half hour stops, and Taylor makes one that is ten minutes longer, how many glasses of wine does mommy need?" quipped one mom of two.
Also recommended: "Chocolate, in copious amounts."
Allison Slater Tate is a freelance writer and editor in Florida specializing in parenting and college admissions. She is a proud Gen Xer, ENFP, Leo, Diet Coke enthusiast, and champion of the Oxford Comma. She mortifies her four children by knowing all the trending songs on TikTok. Follow her on Twitter and Instagram .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
Homework was a leading cause of stress, with 24 percent of parents saying it's an issue. Teenagers say they're suffering, too. A survey by the American Psychological Association found that nearly ...
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
As homework load increased, so did family stress, the researchers found (American Journal of Family Therapy, 2015). Many high school students also seem to be exceeding the recommended amounts of homework. Pope and Galloway recently surveyed more than 4,300 students from 10 high-achieving high schools.
Effects of homework stress at home. Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.. Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students. Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and ...
Here are 10 tips to help your child learn how to make homework less stressful. 1. Stick to a Schedule. Help your child plan out his or her time, scheduling time for homework, chores, activities, and sleep. Keep this schedule handy so your child knows what he or she should be working on, and when. 2.
March 10, 2014 Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework. A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress ...
Stress can also affect health-related behaviors. Stressed students are more likely to have problems with disrupted sleep, poor diet, and lack of exercise. This is understandable given that nearly half of APA survey respondents reported completing three hours of homework per night in addition to their full day of school work and extracurriculars.
Homework's value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn't time to digest ...
These 5 tips can help kids cope with school stress and homework pressure -- and ease school anxiety for kids of all ages. Medically Reviewed by John M Goldenring, MD, MPH, JD on June 01, 2007.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
Stress is the body's emotional, physical, or behavioral response to environmental change. Stress can be a short-term reaction in response to an upcoming event, such as homework deadlines, an upcoming exam, or speaking in front of the class. Stress can also result from traumatic or ongoing experiences, such as coping with parents' divorce ...
You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you've got SAT studying to do. It's just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you're reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time. 5.
Keywords: homework, stress, mental health The outcomes of adolescent mental health is a threat to students' health and wellbeing, more so than it ever has been in the modern era. As of 2019, the CDC reported a nearly 40. percent increase in feelings of sadness or hopelessness over the last ten years, and similar.
A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were "often or always stressed by schoolwork." High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach ...
Educators and parents have long been concerned about students stressed by homework loads, but a small research study asked questions recently about homework and anxiety of a different group: parents. The results were unsurprising. While we may have already learned long division and let the Magna Carta fade into memory, parents report that their children's homework causes family stress and ...
The stress and excessive homework adds up to lost sleep, the BSC says. According to the survey, 57 percent of teenagers said that they don't get enough sleep, with 67 reporting that they get ...
Effective strategies to reduce homework stress in elementary students from a private tutor & mom of two. ... Creating an after-school routine and sticking to it helps children feel organized, but with sports, tutoring, or music lessons, many children have varying weekday schedules. As a former classroom teacher and private tutor, I suggest that ...
A heavy workload. Whether it's advanced-level classes or the amount of studying required, a heavy workload can be a major source of stress for students. This is especially common for older high school students as they start making their post-secondary plans. Lack of organization. Students with poor organizational skills tend to experience ...
Stressed students often have trouble focusing in class, making school work harder for them. It is a common misconception that homework leads to better grades; the result is actually the opposite. When adding up stress, sleep deprivation, and lack of focus, it is impossible for the average adolescent to handle everything and still manage to ...
Children are not the only ones who dread their homework these days. In a 2019 survey of 1,049 parents with children in elementary, middle, or high school, Office Depot found that parents spend an ...
The time students spend on so-called enrichment activities—tutoring, sports, school clubs and even homework—is creating too much stress while underdelivering on academic benefits. ... At the same time, even as educators point out the role homework plays in stress, not to mention the questionable academic value, many parents may still be ...
Here are ten tips to help kids and parents reduce the stress of homework time. 1. Have a Set Homework Space. This first tip is probably one of the most important recommendations you'll get. Children need a set space to work that is away from the usual distractions of the house.