The 8 Types of Presentation Styles: Which Category Do You Fall Into?
Updated: December 16, 2020
Published: September 24, 2018

Types of Presentations
- Visual Style
- Freeform Style
- Instructor Style
- Coach Style
- Storytelling Style
- Connector Style
- Lessig Style
- Takahashi Style
Everyone on the internet has an opinion on how to give the “perfect” presentation.

One group champions visual aids, another thinks visual aids are a threat to society as we know it. One expert preaches the benefits of speaking loudly, while another believes the softer you speak the more your audience pays attention. And don’t even try to find coordinating opinions on whether you should start your presentation with a story, quote, statistic, or question.
But what if there wasn’t just one “right” way to give a presentation? What if there were several? Below, I’ve outlined eight types of presentation styles. They’re used by famous speakers like Steve Jobs and Al Gore -- and none of them are wrong.
Check out each one and decide which will be most effective for you.
![presentation style analysis → Free Download: 10 PowerPoint Presentation Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/2d0b5298-2daa-4812-b2d4-fa65cd354a8e.png)
Types of Presentation Styles
1. visual style.
What it is: If you’re a firm believer slides simply exist to complement your talking points, this style is for you. With this speaking style, you might need to work a little harder to get your audience engaged, but the dividends can be huge for strong public speakers, visionaries, and storytellers.
When to use it: This style is helpful when speaking to a large audience with broad interests. It’s also great for when you need to throw together slides quickly.
Visual style presenter: Steve Jobs
2. Freeform Style
What it is: This impromptu style of presenting doesn’t require slides. Instead, the speaker relies on strong stories to illustrate each point. This style works best for those who have a short presentation time and are extremely familiar with their talking points.
When to use it: Elevator pitches, networking events, and impromptu meetings are all scenarios in which to use a freeform style of speaking. You’ll appear less rehearsed and more conversational than if you were to pause in the middle of a happy hour to pull up your presentation on a tablet.
Freeform style presenter: Sir Ken Robinson
3. Instructor Style
What it is: This presentation style allows you to deliver complex messages using figures of speech, metaphors, and lots of content -- just like your teachers and professors of old. Your decks should be built in logical order to aid your presentation, and you should use high-impact visuals to support your ideas and keep the audience engaged.
When to use it: If you’re not a comfortable presenter or are unfamiliar with your subject matter (i.e., your product was recently updated and you’re not familiar with the finer points), try instructor-style presenting.
Instructor style presenter: Al Gore
4. Coach Style
What it is: Energetic and charismatic speakers gravitate towards this style of presenting. It allows them to connect and engage with their audience using role play and listener interaction.
When to use it: Use this presentation style when you’re speaking at a conference or presenting to an audience who needs to be put at ease. For example, this style would work well if you were speaking to a group of executives who need to be sold on the idea of what your company does rather than the details of how you do it.
Coach style presenter: Linda Edgecombe
5. Storytelling Style
What it is: In this style, the speaker relies on anecdotes and examples to connect with their audience. Stories bring your learning points to life, and the TED’s Commandments never let you down: Let your emotions out and tell your story in an honest way.
When to use it: Avoid this style if you’re in the discovery phase of the sales process. You want to keep the conversation about your prospect instead of circling every point or question back to you or a similar client. This style is great for conference speaking, networking events, and sales presentations where you have adequate time to tell your stories without taking minutes away from questions.
Storytelling style presenter: Jill Bolte Taylor
6. Connector Style
What it is: In this style, presenters connect with their audience by showing how they’re similar to their listeners. Connectors usually enjoy freeform Q&A and use gestures when they speak. They also highly encourage audience reaction and feedback to what they’re saying.
When to use it: Use this style of presenting early in the sales process as you’re learning about your prospect’s pain points, challenges, and goals. This type of speaking sets your listener at ease, elicits feedback on how you’re doing in real time, and is more of a dialogue than a one-sided presentation
Connector style presenter: Connie Dieken
7. Lessig Style
What it is: The Lessig Style was created by Lawrence Lessig , a professor of law and leadership at Harvard Law School. This presentation style requires the presenter to pass through each slide within 15 seconds. When text is used in a slide, it’s typically synchronized with the presenter’s spoken words.
When to use it: This method of presentation is great for large crowds -- and it allows the speaker to use a balance of text and image to convey their message. The rapid pace and rhythm of the slide progression keeps audiences focused, engaged, and less likely to snooze.
Lessig style presenter: Lawrence Lessig
8. Takahashi Style
What it is: This method features large, bold text on minimal slides. It was devised by Masayoshi Takahashi , who found himself creating slides without access to a presentation design tool or PowerPoint. The main word is the focal point of the slide, and phrases, used sparingly, are short and concise.
When to use it: If you find yourself in Takahashi’s shoes -- without presentation design software -- this method is for you. This style works well for short presentations that pack a memorable punch.
Takahashi style presenter: Masayoshi Takahashi
Slides from one of Takahashi’s presentations:
Whether you’re speaking on a conference stage or giving a sales presentation , you can find a method that works best for you and your audience. With the right style, you’ll capture attention, engage listeners, and effectively share your message. You can even ask an AI presentation maker tool to create presentations for you in your preferred style
![presentation style analysis Blog - Beautiful PowerPoint Presentation Template [List-Based]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/013286c0-2cc2-45f8-a6db-c71dad0835b8.png)
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![presentation style analysis 10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales-deck.jpg)
10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]

15 Sales Presentation Techniques That Will Help You Close More Deals Today

9 Ways to End Your Sales Presentation With a Bang

7 Apps That Help Salespeople Become Even Better Speakers

7 Secrets of a Winning Capabilities Presentation

Insight Selling: The 8-Slide Framework for a Better Pitch

The Best Work-Appropriate GIFs to Use in Your Next Sales Slide Deck
![presentation style analysis How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-make-a-business-presentation.jpg)
How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]

How to Handle Difficult Sales Calls Like a Pro

Technology Give You the Middle Finger in a Demo? 7 Reactions to Avoid
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
PHILADELPHIA, MAY 9-10 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
Analytical Presentation Style
Analytical presentation style-great at technical presentations and scientific talks.

We will cover the other three styles, Energetic, Authoritative, and Empathetic, in a future session.

Strengths of the Analytical Presentation Style
DETAILS: As we mentioned on the last posting, the real strengths of this style are the details of the delivery. Natural Analytical styled presenters will be extremely thorough. As a result, the presentation will have a nice, orderly flow. It will also cover details and data that will explain the content in depth. In many cases, the Analytical presenter will feel a tremendous need to explain to the audience everything that he or she knows about the topic. So, it is always a good idea for the Analytical presenter to spend narrowing down the topic ahead of time.
CONTENT: Out of all of the presentation styles, the Analytical is most likely to have way more content to deliver than he or she could ever cover in the assigned time period. As a result, they will often have handouts, charts, and graphs to accompany their presentations.
HUMOR: Many of the most famous comedians are Analytical presenters. This style of presenter has a natural and dry sense of humor that can be very entertaining. Jerry Seinfeld, Bob Newhart, and Bob Hope were all Analytical presenters. Each of these comedians were so good at their craft, that they were popular among a number of different generations and popular for decades.
In fact, Bob Newhart described the analytical presenter well when he said, “Comedians are innately programmed to pick up oddities like mispronounced words, upside-down books on a shelf, and generally undetectable mistakes in everyday life.”
Weaknesses of the Analytical Presenter
BORING: The absolute biggest weakness of the Analytical presenter is that they are often described as boring. The natural delivery of this style of presenter tends to be slow and methodical. As a result, this will be perceived as a lack of enthusiasm. One of the most famous caricatures of this style was Ben Stein playing the economics teacher in the movie Ferris Bueller’s Day Off . Although, the character played is an exaggeration, Stein himself is an Analytical presenter. You can easily see the sense of humor that the Analytical presenter possesses in the clip.
OVERKILL: We sometimes jokingly say that this speaker thinks that a little data is good, a lot of data is better, and too much data is just right. Remember that audience members can really only focus on one thing at a time. So the more data that you deliver in a single sitting, the more overwhelmed the audience will become. Often, it is better to put your data into a handout that the more detail-oriented in the group can look over on their own. We sometimes feel that if we don’t explain everything that we know about the topic in our presentation, then we have failed as a speaker. However, that is an unrealistic expectation. Remember to only cover the most important items that your audience needs to know, right now. You will have a better presentation.
OVER-ACADEMIC: The Analytical presenter will sometimes forget that good communication is a combination of both good content and an entertaining delivery. They focus so much on the data and the details, that they forget to make the presentation interesting. Captivating stories along with using analogies to reinforce your points will help. My Business Law professor in college used this technique. He was an extremely detailed presenter, ad the content was really dry as well. So, he intermixed real stories from his experience as an attorney to make the classes more interesting. He was actually one of my top three teachers in college.
TOO MUCH MATERIAL: This one can really backfire on you if you are not careful. People who fall into the Overkill category above will likely prepare way more content than can actually be delivered in the time frame allotted. The speaker will likely look at the clock as the presentation goes on and begin to panic. In order to fix the challenge, the speaker will often begin to skip important material or breeze through complicated steps. As a result, the audience leaves the presentation dazed and confused.
Five Key Things that a Analytical Presenter Can Do to Deliver a Better Technical Presentation.
Make your topic more focused.
Remember that you can’t realistically tell your audience every, single, thing that you know about your topic in a single sitting. Instead, look at your presentation from the audience’s perspective. If you were sitting in the audience, what would be the most critical outcome or understanding from the presentation that would make the sitting through the presentation worth while? Once you determine that, make that main outcome your topic.
For instance, if you are giving a quarterly financial report to the board of directors, don’t make your presentation title “Quarterly Report.” Instead, ask yourself, “What is the most critical financial outcome from this quarter that the board would be most interested in?” Keep in mind that they will receive a written document with the entire report. Your presentation should just highlight the most important information. If they want to know more of the details, they will ask you questions. A better topic would be, “Shareholder Equity Increased 2.1% This Quarter.” Thousands of transactions occurred during the quarter. Trying to create a presentation that is a summary of ALL of those transactions would be impossible. However, if the board is most interested in shareholder equity, a presentation about the few transactions that occurred during the quarter that effected equity is a much easier presentation to both design and deliver.
Insert Stories and Examples
The Analytical Style often thinks that data is the most important item in a presentation. However, one good story or example will allow the audience to comprehend an enormous amount of data without overwhelming the audience. Compare these two examples.
- Since our last sales meeting, the average number of RFIs has decreased slightly by 1.2%. Our sales reps responded to 980 requests in the previous report and only 970 in this period. Of those 970 requests, 165 went to contract. We closed 166 of these contracts in the last report. However, even though total contracts were down slightly, total revenue increased significantly. In the last report, our average revenue from contract was was $6490, but in this period, that average increased significantly to $7235 per contract. If you look on the screen, I have a graph that addresses each of these data points so that you can see their relationship.
- Although the total number of requests for information and number of contracts were similar in the last two pay period, revenue increased dramatically. Our sales team has been focusing on increasing the average revenue per contract by up-selling additional services, and it is beginning to pay off. For example, one of our sales reps, Joe, closed a big contract with J. P. Morgan last week that was repeat business. Since we already had a relationship with the buyer, Joe promoted a couple of new service lines to the client. They upped their order in this period from $21,000 to $27,000. That was just one contract. We had a few up-sell orders just like this, so the total revenue went up over 11% in this period. We are going to continue this policy to see if we have similar numbers in the next period.
The first example gives lots of data, but doesn’t connect the data into a conclusion. It leaves the interpretation to the listener. The second example, however, is a much clearer way to deliver the data. The example give the listener the context of the data in a better way.
Use Your Humor to Entertain
Humor can be added in a lot of different ways. You can tell a self-deprecating story. Clever analogies can also work. I don’t suggest that you tell jokes, but funny anecdotes often work really well. In one of my classes years ago, a young lady was talking about how data wasn’t being shared between departments. She said that the data exchange was like when she and her boyfriend got their first checking account together. He was keeping track of his transactions. She was keeping track of her transactions. However, neither of them were keeping track of ALL of the transactions. Before long they had a mess. She said that the tow departments doing their own thing without communicating with the other group was causing a similar challenge. She had the whole class laughing.
Give Your Data in a Handout
If you have a lot of data, give the audience a handout. Don’t try to cover all of the data in a slideshow. I don’t care how good you are at delivering information, if you have too much data, your delivery will be boring.
Speed Up Your Delivery
One of the easiest ways to improve your delivery is to just speak a little faster. Typically, the Analytical presenter will often speak fairly slowly. Just speak and move a little faster than normal, and your audience will see that speed as energy and enthusiasm. One of my early presentation coaches used to tell me, “Present like your double-parked.” (Keep in mind, this is a tip for the Analytical speaker. If you are more of an Authoritative speaker or Energetic speaker, don’t speed up. You talk fast already.) I know this goes against conventional wisdom, but it is one of the most important things that the Analytical speaker can do to improve performance.
What If I Have a Different Style of Speaking, But I’m Delivering the Presentation to an Analytical Audience?
A couple of decades ago, I was asked to be a guest speaker at the Petroleum Accountants Association. I was introduced, and there was absolutely no applause. I began speaking, and I looked out at the audience, and the entire group was stoic. No smiles were seen anywhere. I was a little concerned, because I was used to interacting with my audiences. I was used to having my audiences laughing and having fun within minutes of my start. I took me the better part of 30 minutes to get the group loosened up. When I finished, I got a huge round of applause, and no less than a dozen of the participants rushed to me after the speech. Each of them was asking if I could come speak at their companies. I was so confused. This speech was, at best, mediocre compared to most of my keynotes. To them, though, I was a superstar.
I didn’t realize until later, but group loved my delivery, because I was giving them something that most other speakers to the association wouldn’t. The culture of the group was extremely analytical. They were used to presentations with 120 slides and 15 bullets on each slide. They were used to slow and methodical deliveries. So, when I stood up with just a single slide, just a few well designed bullets, lots of stories, and quite a bit of humor, they loved it.
The main take away here is that you don’t have to overturn their cart. You just have to be a little better than what they are used to, and they will love you. Deliver your presentation with just a little more energy than they are used to. Cover just a few fewer slides. Tell just a few more stories. If you do, the Analytical audience will love you!

Free Public Speaking Tips , Podcasts | presentation styles
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action
support your career
get the interview & get the job
- Career Development
12 Common Presentation Styles Used in the Workplace
- Visual Style.
- Freeform Style.
- Instructor Style.
- Coach Style.
- Storytelling Style.
- Connector Style.
- Lessig Style.
- Takahashi Style.
What are presentation styles?
The techniques a business professional employs when giving a speech are known as presentation styles. The best presentation style to use often depends on the topic you’re discussing, your audience, and the preferred method you use to explain the subject matter to your audience. In some cases, you might select one main style for the duration of the presentation or you might select a combination of styles to better explain your subject.
Common types of presentation styles in the workplace
There are many different presentational styles that people can use when giving speeches or presenting their topics. Common presentation styles most workplace professionals may deliver include:
Storyteller
When they have plenty of time to present on their topic, presenters frequently adopt this technique. It’s also frequently employed when a presentation doesn’t require a lot of numbers, data, or statistics to back it up. When telling a story, the presenter frequently uses anecdotes and appeals to the audience’s emotions.
Usually, it begins with a personal story that relates to the presentation’s main theme. If you are aware that your audience doesn’t respond as strongly to charts, data, or statistics, you should use this style instead.
When a speaker has in-depth knowledge of the subject they’re speaking about, they frequently use a freeform style to elaborate on it. Short stories about the author’s own experiences with the subject matter are used to tell personal stories in the freeform style. When presenting in this manner, speakers hardly ever employ slides or data. Instead, they emphasize each point they want to make through their personal stories. This usually makes the speech appear less overly prepared and more spontaneous, creative, and personal.
To support their topic and discussion points, this style makes extensive use of visual components. To help the audience better visualize and comprehend the subject, they use charts, pictures, graphs, and any other visual aids. It’s crucial for presenters using this method to have a solid balance of both text and visuals in order to complete their presentation. This is also a great approach to take if you want your audience to comprehend your complex or in-depth talking points more readily.
Presenters who employ the director style take pleasure in organizing their talking points, transitions, and slides to follow a logical and linear flow. Typically, they prepare and adhere to a precise script, with little to no improvisation during the speech. This is frequently used by speakers who have a limited amount of time and a lot of material to cover. To stay in control and stay on topic throughout the entire presentation, they typically plan to discuss a specific talking point at a specific time during the speech.
Data scientist
In this presentation style, talking points are explained and expanded upon using facts, data, analysis, and statistics. Presenters can better convince their audience by using a data scientist presentation style to support their arguments. This presentation style is excellent to use if you’re giving a presentation on a subject that requires additional facts and data to support it. Additionally, it is advantageous for business professional audiences who prefer facts and figures to stories or anecdotes when hearing about topics you are discussing.
Presenters who employ the closer style excel at persuading their audience to act They frequently have a strong understanding of their target audience and are adept at crafting talking points that will engage listeners and influence them to take action. The majority of presenters who employ this technique are aware of their ultimate objective and use their speech to effectively accomplish it.
As the speaker may only briefly cover their main points and conclude the presentation with an enticing offer to the audience, these presentations are frequently much shorter than most.
The speaker interacts and connects with the audience during connector presentations. This typically entails the speaker regularly soliciting questions from the audience and encouraging participation and feedback. Speakers frequently employ this technique to highlight their commonalities with the audience in order to more effectively engage them.
If you’re a salesperson giving a presentation at the beginning of the sales process, this is a great presentation style to use. It aids in understanding the objectives and difficulties of the target audience and instructs them on how to address these issues.
This type of presentation is popular among speakers who want to instruct their audience on a challenging or advanced subject. It entails using well-known expressions, rhetorical devices, metaphors, and illustrations to simplify a complex subject so that the audience can more readily understand it.
In order to support ideas and the overall presentation and keep the audience interested, the decks for this presentation style are typically organized logically. Presenters who are extremely knowledgeable about their subject matter perform best in this style.
Speaking in this manner is ideal for presenters who are passionate about their subject. They frequently enjoy imparting knowledge to their listeners, which increases their enthusiasm for interaction and connection Role-playing and audience participation are two techniques this kind of presenter frequently employs. Instead of focusing on the specifics of a particular topic, they typically try to sell the audience on an overall concept. This method is often used during motivational speeches.
When a speaker wants the audience to comprehend and concur with their viewpoint more fully, they use this technique. Its often used during a sales pitch. Some persuasive speeches employ feelings in order to better relate to and connect with the audience. If persuading or convincing your audience to do something is your primary objective for the presentation, this is frequently the best approach to take.
Interactive
In this manner of presentation, the speaker engages the audience by providing outlines or notes before the speech. To maintain the audience’s interest and ensure that they comprehend the speaker’s talking points, they may also use whiteboards or other visuals.
It also makes it easier for speakers to follow along and feel like a part of the presentation when the audience is kept interested and involved in certain talking points throughout. Additionally, printouts enable listeners to add notes or ask the speaker questions to further their understanding of the subject.
This presentation technique was developed by Harvard Law School professor and founder Lawrence Lessig, who spends just fifteen seconds on each slide. Any text on a slide should exactly reflect what a speaker says. In order to maintain the audience’s attention and engagement, it should keep the presentation positive and moving quickly.
If you have a lot of talking points to cover and little time to do so, this is a great style to use. Its often used by professionals with extensive experience giving presentations.
Different Presentation Styles
What are the 4 presentation styles?
- Communication Style: Action-Oriented.
- Communication Style: Process-Oriented.
- Communication Style: People-Oriented.
- Communication Style: Idea-Oriented.
What are the 6 types of presentation?
- 1) Providing Information. …
- 2) Teaching a Skill. …
- 3) Reporting Progress. …
- 4) Selling a Product or Service. …
- 5) Making a Decision. …
- 6) Solving a Problem.
What are the 3 different presentation types?
- Informative Presentations. …
- Instructive Presentations. …
- Persuasive Presentations. …
- Motivational Presentations. …
- Decision-making Presentations. …
- Progress Presentations. …
- Whichever Presentation Type You Choose, Create it With Beautiful.ai.
Related posts:
- 15 BPI Certifications (With Tips for Choosing One)
- Report Writing Skills: Definition and Examples
- How To Measure Training Effectiveness in 5 Steps
- What Is ABC Inventory? (With Benefits, Steps and an Example)
- FAQ: What Is an Oil and Gas Management Degree?
- 30 Inspirational Career Change Quotes (And How They Help)
- 10 of the Best Master’s Degrees for the Future (And Jobs To Consider)
- ECPM: Definition, Importance and How To Calculate
Related Posts
How to write a letter to the editor in 8 steps, how to learn embedded systems programming in 6 steps, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Home Blog Business Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
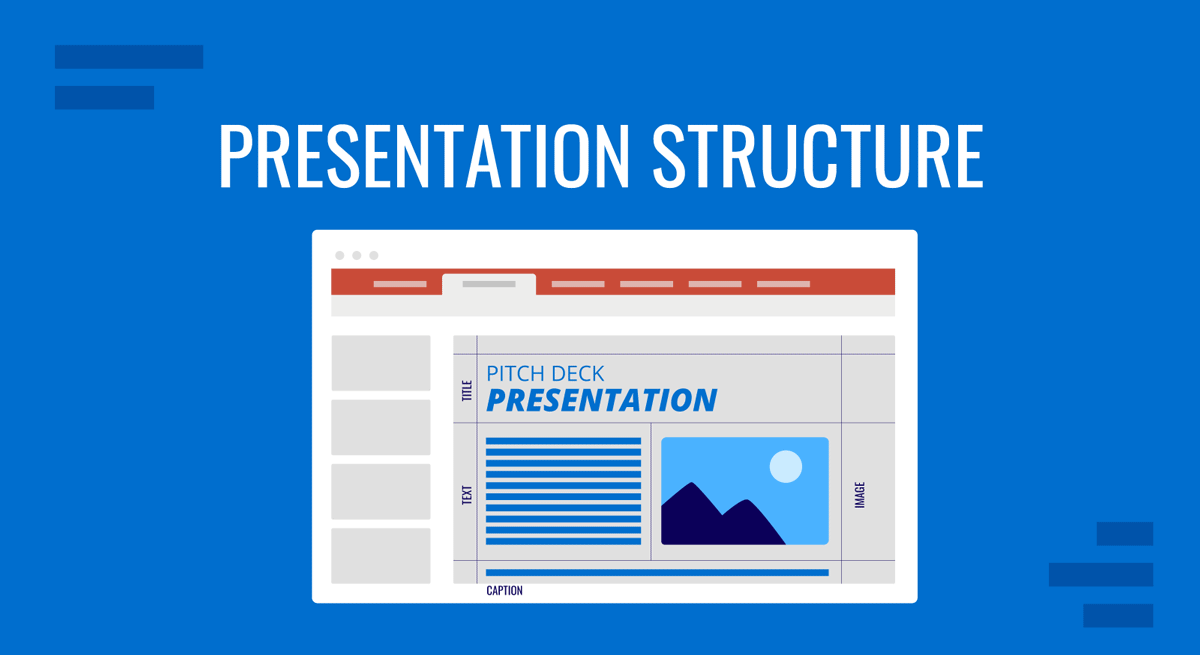
In the business world, a presentation is so much more than just a bunch of slides or points—it’s a golden opportunity. It can sway decisions, propel change, or bring people together. How you structure your presentation is absolutely critical in getting your ideas across clearly and compellingly.
When you’ve got a structured presentation just right, it’s like you’re taking your audience by the hand and guiding them through your thoughts, making sure they pick up all the important bits along the way. Moreover, it speaks of your degree of professionalism and how much knowledge you bear on the topic in question.
Therefore, nailing your presentation structure isn’t just helpful; it’s downright necessary to get the results you’re after. Whether you’re pitching a new concept to the investors, sharing the latest findings with your team, or taking the stage at a conference, how you lay out your content becomes the language you use to interact with your audience. Get to know all that’s required to create a powerful presentation structure that will guarantee success in business meetings, academic dissertations, or motivational talks .
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Structure
Introduction, techniques to structure your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when designing a presentation structure, final words.
Let’s compare a presentation structure to a business plan . Just as a business plan is essential for guiding a company’s strategy and ensuring all aspects of the business are aligned toward common goals, a presentation structure is crucial for organizing the content and delivery of your talk.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company’s mission , market analysis , and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and influencing your target audience.
Key Elements of a Presentation Structure
The easiest way to study a presentation structure is to subdivide it into sections. Basically, every presentation has a structure that follows this formula: Introduction > Body > Conclusion.
The introduction is the first section of the presentation and sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. It should be attention-grabbing and make the audience want to listen to the rest of the presentation.
When defining how to start a presentation , these are the best tips we recommend you implement.
Start with a Hook
Kick off your introduction with a strong hook that grabs your audience’s attention. This could be an intriguing fact, a thought-provoking question, or a compelling story related to your topic. A captivating opening will make your audience want to listen and engage with your presentation.
Clearly State Your Topic
Be clear and concise when stating your topic. Your audience should immediately understand what your presentation is about and what they can expect to learn. A clear statement of your topic sets the stage and provides a roadmap for the rest of your presentation.
Establish Credibility
Take a moment to establish your credibility by briefly sharing your qualifications or experience related to the topic. This helps to build trust and rapport with your audience, and it shows that you are knowledgeable and well-prepared.
Engage Your Audience
Make your audience part of the presentation by engaging them from the start. Ask a question, encourage participation, or invite them to think about how the topic relates to their own experiences. Engagement helps to create a connection between you and your audience. Using a surprise factor is an alternative if you feel the topic you’re about to present may not fully resonate with the target audience.
Preview Main Points
End your introduction by briefly previewing the main points you will cover in your presentation. This provides a clear structure for your audience to follow and helps them understand what to expect in the body of your presentation. An agenda slide is the perfect tool for this purpose.
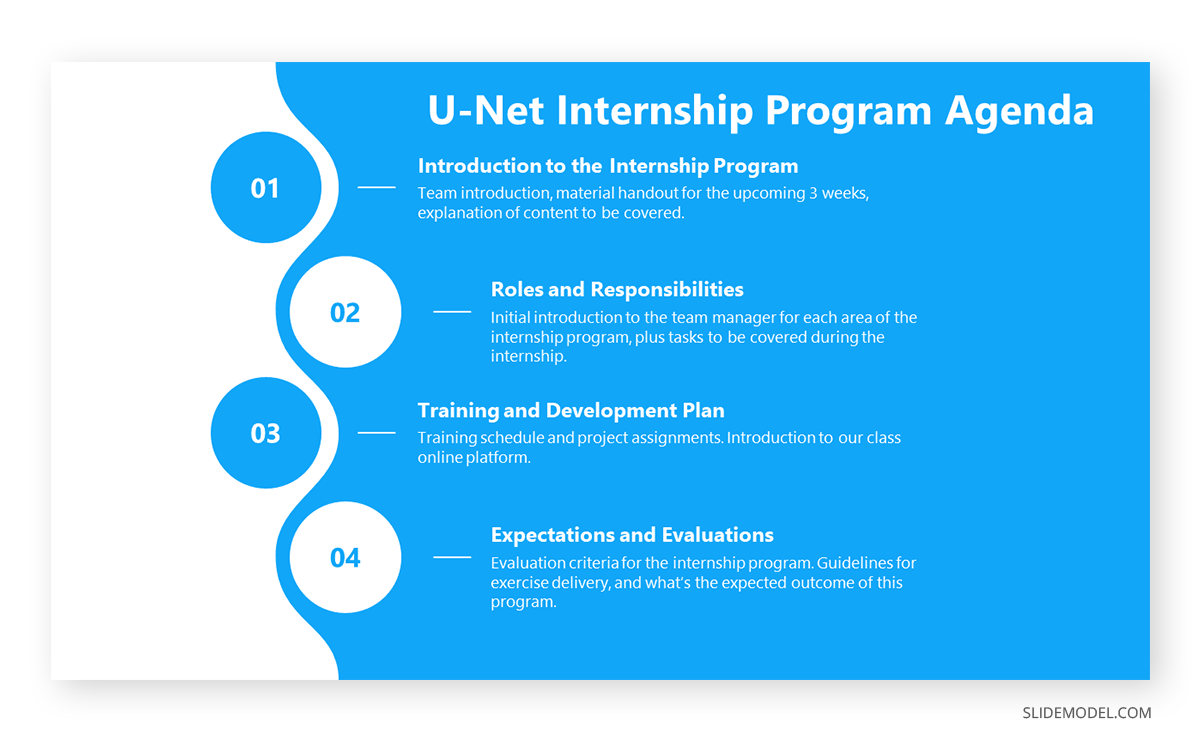
The body is the main part of the presentation and provides the content and information that the audience came to hear. It should feature the main points and details supporting your presentation’s objective. Depending on your topic, this could include data, arguments, case studies, examples, or demonstrations. Each main point should be clear and distinct, with evidence or examples substantiating it. The content should be tailored to your audience’s level of knowledge and interest.
Different presentations call for various structures. For example, a Product Presentation ’s structure should start by dividing the content into clear sections or headings. For instance, if presenting a new software tool, sections could include its features, benefits, and user feedback.

On the other hand, a Persuasive Presentation begins with stating the current situation or problem, followed by proposed solutions, evidence supporting those solutions, and the benefits of adopting your proposition.
Workshop or Training Presentations begin with an overview of what will be taught, followed by step-by-step instructions, examples, demonstrations, and summaries or quizzes after each major section.
One essential aspect is to plan the multimedia elements to include in your presentation, including audio, images, and video, depending on the presentation style you aim to deliver. Through our expertise, we want to share some tips on how to plan this kind of content:
- Using relevant content: Each image should be related to its accompanying content. Avoid using images just for decoration. If using videos, dedicate an entire slide to them rather than sticking them to a corner of your slide. Plan a powerful hook to connect your thoughts with these visual aids.
- Quality: Ensure all images are of high resolution and can be clearly viewed, even from a distance. Avoid pixelated or distorted images.
- Simplicity: Infographics and diagrams should be easy to understand. If presenting data, use simple charts or graphs instead of complex tables. Limit the amount of text on each slide to ensure clarity. This rule of simplicity also applies to written content and the structure of your speech. Use the Feynman Technique as a time-saver approach to simplify content to reach any knowledgeable audience.
- Consistency: A common cause of presentation failures is to distract the audience with an unprofessional look. Maintain a consistent style and color scheme for all images to give your presentation a polished and professional feel.
Along the path of creating these media elements, you can rethink your strategy for disclosing content. In general lines, you should present your points in a logical order, often from the most to least important or in a chronological sequence. This helps the audience follow along and build understanding step by step. Well-known practices like the storytelling technique follow this approach to maximize audience engagement.
Transition smoothly between points. Phrases like “moving on,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand” can guide your audience through your narrative. Break up long sections of spoken content with anecdotes, questions, or short videos. Such an approach adds variety and keeps the audience engaged.
A well-structured conclusion is the linchpin that holds your presentation together, reinforcing your main points and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. It is your final opportunity to communicate your message and encourage audience engagement. So, before you consider how to end a presentation , here are some powerful tips to ensure you conclude your presentation with impact.
End with a Strong Statement or Quote
This technique is commonly used in motivational presentations, where the speaker leaves the audience with a slide containing a quote related to the topic of the presentation, something that evokes inner reflection about the topic discussed.

Conclude your presentation with a strong, memorable statement or a powerful quote that ties back to your main message. This adds weight to your argument and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. If you aim to surprise your audience, silence can also be a strong statement if your presentation has to raise awareness about a problem.
Incorporate a Call-to-Action
Clearly communicate to your audience what you want them to do next. Whether it’s to adopt a new perspective, take specific action, or continue the conversation outside of the presentation, a clear call to action drives engagement and encourages your audience to act upon your message.
Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Pose thought-provoking questions that stimulate reflection and discussion. This opens the door for audience participation and engagement and allows you to interact with the audience in a Q&A session, or reach after your presentation concluded to network.

Additional Resources and Contact Info
Offer resources such as articles, websites, or books for those interested in exploring your topic further. This not only adds value to your presentation but also encourages the audience to engage with the content beyond the presentation itself.
Consider the way you leave a communication channel open with your audience. This can be in the format of a deliverable, writing down your contact data in the “Thank You” slide , or simply via speech to inform where they can know more about you and your work.
We already discussed the basic Introduction-Body-Conclusion framework for a presentation, but there are alternative approaches that can help you structure your talk.
Problem-Solution Framework
The Problem-Solution Framework is a compelling method to structure presentations, particularly when aiming to persuade or inform an audience about addressing specific challenges. The framework operates on a simple yet impactful premise: initially, highlight a problem or challenge that needs addressing and subsequently propose a viable solution or set of solutions.
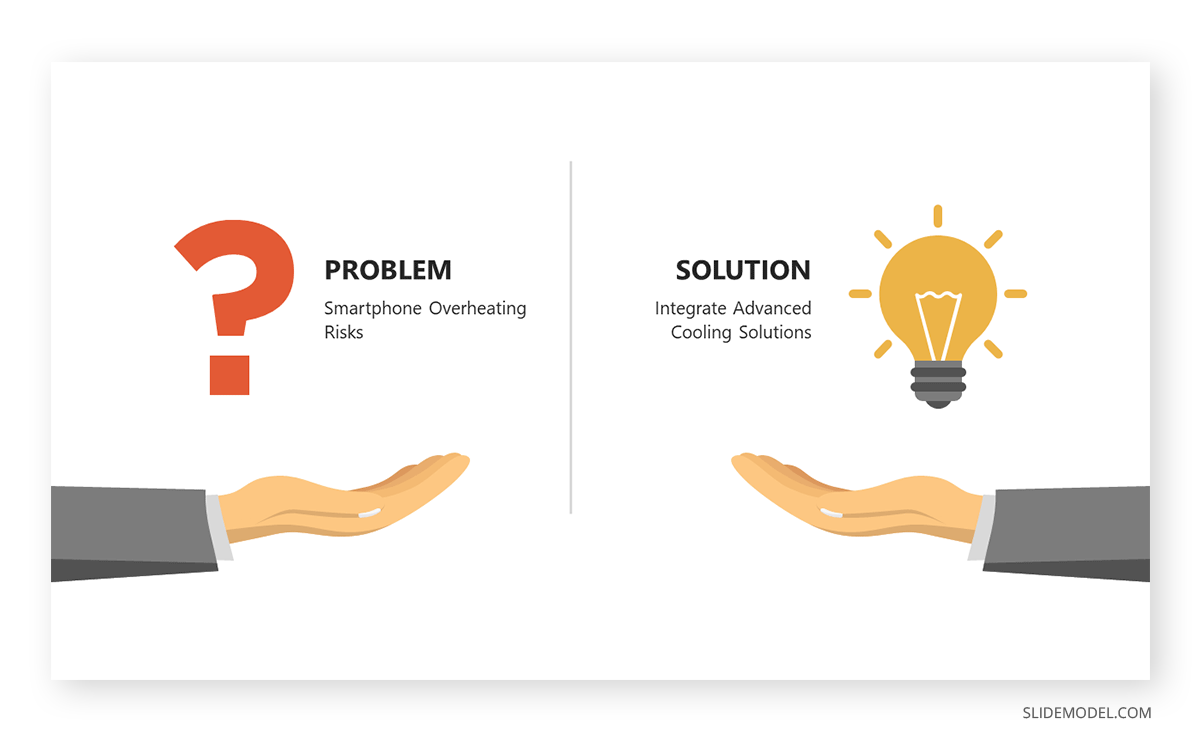
Starting with the problem establishes a context, engages the audience by highlighting pain points or challenges they may recognize, and creates a desire for resolution. It sets the stage for the solution to be perceived as necessary and valuable.
The solution phase offers that much-needed resolution. By presenting a clear, actionable solution or set of recommendations, the presenter provides a pathway to overcome the identified challenge. This structure is not only logical but also highly persuasive, as it appeals to the audience’s desire for resolution and improvement. In essence, the Problem-Solution Framework is both a guide for content organization and a psychological tool for persuasion.
Chronological Structure
The Chronological Structure is an intuitive and organized approach to presenting information based on a sequence of events or a progression in time. Whether recounting historical events, outlining the stages of a project, or narrating a personal story, this structure follows a clear beginning, middle, and end sequence. By presenting details in the order they occurred, the audience can easily follow the narrative, making connections between events and understanding causality.
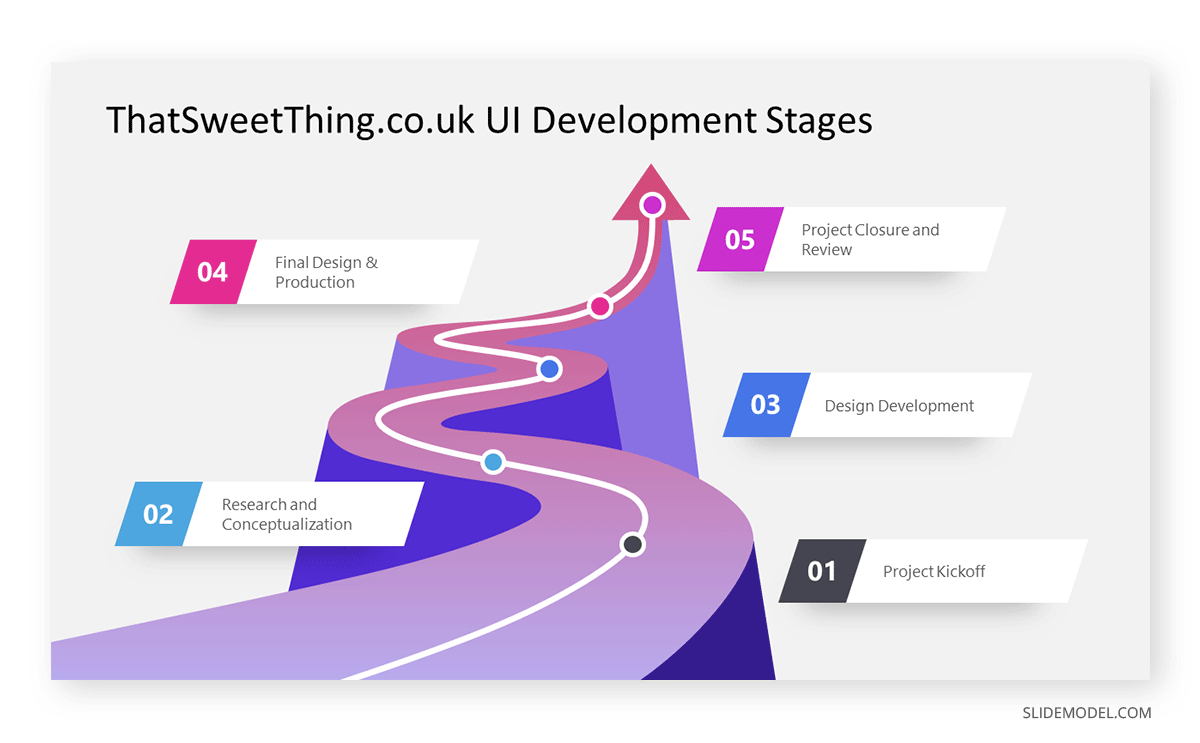
This structure is especially effective when the timeline of events is crucial to the narrative or when showcasing developments, evolutions, or growth over time. It provides clarity and eliminates confusion that might arise from a non-linear presentation. Moreover, by anchoring information on a timeline, the Chronological Structure aids memory retention, as the audience can mentally “map out” the journey of events. In sum, this method offers clarity and a compelling narrative arc, ensuring audience engagement from start to finish.
Comparative Structure
The Comparative Structure is a strategic approach to presentations that hinges on juxtaposing two or more elements, ideas, or solutions side by side. By examining similarities and differences, this method illuminates unique qualities, advantages, or drawbacks inherent in each element. Often employed in business scenarios like product comparisons, market analysis, or debates, the comparative structure helps audiences critically analyze options and make informed decisions.
Presenters utilizing this structure typically start by introducing the elements for comparison. They then delve into detailed analysis, often using criteria or metrics to maintain objective evaluations. Visual aids like Venn diagrams or comparison charts can enhance clarity and visual appeal.
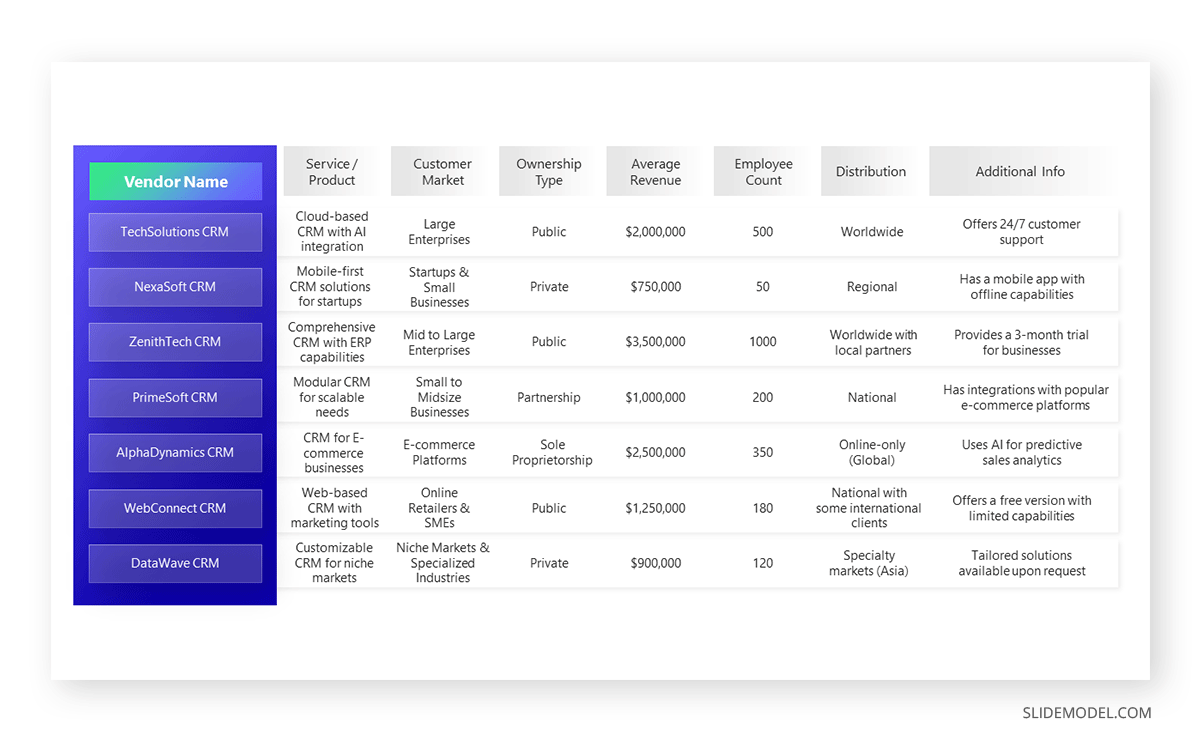
The strength of the Comparative Structure lies in its ability to foster critical thinking. By directly contrasting items, audiences are engaged, encouraged to weigh pros and cons, and ultimately arrive at a deeper understanding or more nuanced perspective on the subject matter.
Matrix Structure
The Matrix Structure offers an approach to organizing presentations by segmenting information into distinct categories or sections, akin to a grid or matrix. Instead of a linear flow, topics are grouped by themes, criteria, or any relevant classification, allowing for simultaneous exploration of multiple facets of a subject. Think of it as viewing a topic through various lenses concurrently.
For instance, in a business setting, a product might be examined in terms of design, functionality, market positioning, and customer feedback. Each of these constitutes a segment in the matrix.
Visually, the matrix can be represented using tables, grids, or quadrant charts, making the content easily digestible and engaging. A key advantage of this structure is its flexibility; presenters can delve deep into one segment or provide a broader overview of all areas, depending on the audience’s needs. Ultimately, the Matrix Structure ensures a comprehensive and multifaceted examination of a topic, providing depth and breadth in analysis.
Modular Structure
The final model we will study is the Modular Structure. It takes content and packs it into modules, which can be arranged at any other the presenter requires them to be. Each module addresses a specific topic or idea and is designed to be self-contained, ensuring clarity even if presented independently or in a different order. This adaptability makes the modular approach especially valuable in dynamic settings, such as workshops or conferences, where audience feedback or time constraints might necessitate adjustments on the fly.
For example, in a corporate training session, different modules could cover distinct skills or topics. Based on the attendees’ prior knowledge or the session’s time limit, the presenter can prioritize, omit, or rearrange modules without compromising the integrity of each segment.
By adopting the Modular Structure, presenters gain flexibility without sacrificing depth. This approach fosters a responsive presentation style, allowing speakers to tailor content in real-time, ensuring maximum relevance and engagement for their audience.
Even well-seasoned presenters can fall prey to these common mistakes in terms of presentation structure. Let’s learn how to prevent them.
Overloading with Information
It’s tempting to include every bit of knowledge you have on a topic. Still, information overload can quickly disengage an audience. Prioritize key points and leave out extraneous details. As famous architect, Mies van der Rohe famously coined, “Less is More.”
Weak Transitions
Jumping abruptly from one point to another can disrupt the flow and confuse listeners. Ensure smooth transitions between sections, signaling shifts in topics or ideas to keep the narrative cohesive.
Dull Design
While content is king, visual appeal matters. Relying solely on walls of text or bland slides can lose your audience’s interest. Incorporate engaging visuals, charts, and multimedia elements to enhance your message and retain attention.
Ignoring the Call to Action
Concluding your presentation without guiding the audience on the next steps or what’s expected of them can be a missed opportunity. Whether it’s seeking feedback, prompting a discussion, or encouraging an action, always have a clear call to action.
Good communication is all about making your point clear, especially in presentations. We’ve talked about how the right structure can keep your audience hooked. But there’s more to it. Think about your presentation. Is it telling your story the way you want? Is it reaching your audience? Take a step back and really look at how you’re laying it out. Don’t just go with the flow – choose your format wisely. Remember, every presentation tells a story, and how you set it up matters a lot.

Like this article? Please share
Design, Presentation Approaches Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Leave a Reply
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
By Krystle Wong , Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.


1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center

100+ Real Consulting Presentations from McKinsey, BCG, Bain, and More

By Paul Moss
We’ve gathered presentations from top consulting firms that you can use to inspire your own slide making.
For this post we’ve gathered 100+ real presentations from top consulting firms around the internet for you to review, analyze, and learn from. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and each provides a different look into how top quality consulting presentations get created and delivered to clients.
After finishing this article, make sure you check out our advanced courses to see how you can learn to build your own high-quality, consulting-style slides from scratch.
The Internet's Best Slides
Search through our curated library of REAL slides to find inspiration for your next presentation
- Reshaping NYCHA support functions (BCG)
- Loose dogs in Dallas: Strategic Recommendations to Improve Public Safety and Animal Welfare (BCG)
- Melbourne as a Global Cultural Destination (BCG)
- The Open Education Resources ecosystem (BCG)
- The True-Luxury Global Consumer Insight (7th Edition) (BCG)
- Evaluating NYC media sector development and setting the stage for future growth (BCG)
- The Electric Car Tipping Point (BCG)
- Projecting US Mail volumes to 2020 (BCG)
- Next Generation Manufacturing (2016) (BCG)
- Corporate Ventures in Sweden (2016) (BCG)
- Port of Los Angeles Clean Truck Program – March 2008 (BCG)
- USPS Future Business Model (McKinsey)
- Investment and Industrial Policy: A Perspective on the Future (McKinsey)
- Outperformers: High-growth emerging economies and the companies that propel them (McKinsey)
- Technology’s role in mineral criticality (World Materials Forum) (McKinsey)
- Challenges in Mining: Scarcity or Opportunity? (McKinsey)
- Modelling the potential of digitally-enabled processes, transparency and participation in the NHS (McKinsey)
- Addressing the Global Affordable Housing Challenge (2016) (McKinsey)
- Capturing the Full Electrical Efficiency Potential of the UK (2012) (McKinsey)
- Digital Luxury Experience (2017) (McKinsey)
- Digitally-Enabled Processes in the NHS (2014) (McKinsey)
- How Companies can Capture the Veteran Opportunity (2012) (McKinsey)
- Insurance Trends and Growth Opportunities for Poland (2015) (McKinsey)
- Laying the Foundations for a Financially Sound Industry (2013) (McKinsey)
- From Poverty to Empowerment (2014) (McKinsey)
- Consumer privacy in retail (Deloitte)
- TMT Outlook 2017: A new wave of advances offer opportunities and challenges (Deloitte)
- Deloitte SEA CFO Forum Southeast Asia Business Outlook (Deloitte)
- Deloitte Kenya Budget 2022/23 Webinar (Deloitte)
- The Shopping Centre Handbook 4.0 (Deloitte)
Bain & Co.
- 2011 China Luxury Market Study (Bain)
- Bain & UC Berkley Operational Excellence (2010) (Bain)
- Fintech New York: Partnerships, Platforms and Open Innovation (Accenture)
- Shaping the Sustainable Organization (Accenture)
- The Decade to Deliver: A Call to Business Action (Accenture)
- Fueling the Energy Future (Accenture)
- Cracking the Code on Consumer Fraud (Accenture)
- Right Cloud Mindset: Survey Results Hospitality (Accenture)
- Unleashing Competitiveness on the Cloud Continuum (Accenture)
- Whole Brain Leadership: New Rules of Engagement for the C-Suite (Accenture)
- Federal Technology Vision 2021: Full U.S. Federal Survey Findings (Accenture)
- Accenture Consumer Behavior Research: The value shake-up (Accenture)
- Tech Adoption and Strategy for Innovation & Growth (Accenture)
- Intelligent Operations for Future-Ready Businesses (Accenture)
- When, Where & How AI Will Boost Federal Workforce Productivity (Accenture)
- How fit is your allocation strategy? (EY)
- European Banking Barometer (2015) (EY)
- EY Price Point: global oil and gas market outlook, Q2 | April 2022 (EY)
- IBOR transition: Opportunities and challenges for the asset management industry (EY)
- Global Capital Confidence Barometer 21st edition (EY)
- Power transactions and trends Q2 2019 (EY)
- MAPS2018 Keynote address on EY report: Life Sciences 4.0 – Securing value through data-driven platforms (EY)
- EY Germany FinTech Landscape (EY)
PwC / Strategy&
- Project Management: Improving performance, reducing risk (PwC)
- World Economic Forum: The power of analytics for better and faster decisions by Dan DiFilippo (PwC)
- Apache Hadoop Summit 2016: The Future of Apache Hadoop an Enterprise Architecture View (PwC)
- Turning big data into big revenue (PwC)
- Medical Cost Trend: Behind the Numbers 2017 (PwC)
- PwC’s new Golden Age Index – how well are countries harnessing the power of older workers? (PwC)
- PwC’s Global Technology IPO Review — Q1 2015 (PwC)
- PwC Trends in the workforce (PwC)
- 18th Annual Global CEO Survey – Technology industry key findings (PwC)
- The FDA and industry: A recipe for collaborating in the New Health Economy (PwC)
- Making zero-emission trucking a reality (Strategy&)
- Sustainability strategies for Oil and Gas (Strategy&)
- Driving the sustainability agenda on C-level (Strategy&)
- The Diversity Imperative: 14th Annual Australian Chief Executive Study (Strategy&)
- Creating a Winning Recipe for a Meal Kits Program (LEK)
- The 4th Annual New Mobility Study 2019 (LEK)
- 2019 APAC Hospital Priority Study Overview (LEK)
- Rail industry cost and revenue sharing (2011) (LEK)
- 2019 Media and Entertainment Study (LEK)
- Navigating a digital-first home furnishings market (LEK)
- 5 Opportunities in the Nutritional Supplements Industry (LEK)
- Infrastructure Victoria – AZ/ZEV International Scan (LEK)
- The Rapidly Evolving Landscape of Meal Kits and E-commerce in Food & Beverage (LEK)
- Top 8 Insights From the 2018 Beauty, Health & Wellness Survey (LEK)
- 2018 Brand Owner Packaging Survey (LEK)
- 2016 Strategic Hospital Priorities Study (LEK)
- The Merchandising Evolution (and why NDC Matters) (LEK)
- Infrastructure beyond COVID-19 (LEK)
- China Exit or Co-Investment Opportunities for German PE Investors (LEK)
- Strategy Study 2014 ( AT Kearney)
- Australia: Taking Bigger Steps ( AT Kearney)
- Lifting the Barriers to Retail Innovation in ASEAN ( AT Kearney)
- The Future of Commercial Vehicle Powertrains (2012) ( AT Kearney)
- A.T. Kearney 2017 State of Logistics Report: Accelerating into Uncertainty ( AT Kearney)
- Pursuing Customer Inspired Growth ( AT Kearney)
- The Accelerating Growth of Frictionless Commerce ( AT Kearney)
- Consolidation of the US Banking Industry ( AT Kearney)
- Covid-19 and Effects on Turkey ( AT Kearney)
Booz Allen Hamilton, Alvarez & Marsal and others
- European Distressed Credit Watch List (Alvarez & Marsal)
- Corporate Headquarters Study 2018 (Roland Berger)
- The Lithium-Ion (EV) battery market and supply chain (Roland Berger)
- IP Theft (Booz Allen Hamilton)
- Booz Allen Hamilton and Market Connections: C4ISR Survey Report (Booz Allen Hamilton)
- Joining Forces: Interagency Collaboration and “Smart Power” (Booz Allen Hamilton)
- Booz Allen at a glance (Booz Allen Hamilton)
- Investor Presentation Deck (Booz Allen Hamilton)
- Responding to Covid-19 (2021) (Oliver Wyman)
- C ovid-19 Special Primer (2020) (Oliver Wyman)
- Building Up Immunity of the Financial Sector (Oliver Wyman)
- Customer Experience: The 14BN Risk Noted for Discussion (Oliver Wyman)

FREE Slide Design Course
Enroll in our free 5-day email course and learn how to design slides like a McKinsey consultant.
Complete hands-on exercises , review a realistic consulting case study , and get personalized feedback from your instructor!
Plus get a free copy of our Top 50 PowerPoint Shortcuts for Consultants cheat sheet.
Learn More ➔
Success! Please check your email.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe anytime.

Reshaping NYCHA support functions
Good: Realistic client presentation, clear slide structure, complete storyline
Not Good: Outdated, long and dense
Download this Presentation
Loose dogs in Dallas: Strategic Recommendations to Improve Public Safety and Animal Welfare
Good: Realistic client presentation, clear slide structure, insightful and clear charts
Not Good: Outdated, long and dense

Melbourne as a Global Cultural Destination
Good: Realistic client presentation, good structure, slides “guide” audience to insights
Not Good: Outdated design
The Open Education Resources ecosystem
Good: Clearly structured slides, good visuals, good illustrative charts
Not Good: Relatively short, slightly older, incomplete storyline

The True-Luxury Global Consumer Insight (7th Edition)
Good: Recent presentation, nice looking visuals, clear charts
Not Good: Not a client presentation, too much focus on design
Evaluating NYC media sector development and setting the stage for future growth
Good: Complete presentation (intro, exec. summary, etc.), good examples of subtitles
Not Good: Lacks clear recommendations

The Electric Car Tipping Point
Good: Clear and insightful charts, clutter-free slides, good titles
Not Good: Relatively short, not a client presentation
Projecting US Mail volumes to 2020
Good: Easy to understand, good insights and analysis, contrasts with McKinsey presentation on the same topic
Not Good: Old presentation

Next Generation Manufacturing (2016)
Good: Nice clean design, excellent visuals
Not Good: Not a client deliverable
Corporate Ventures in Sweden (2016)
Good: Strong overall flow, good visualization s
Not Good: Relatively short

Port of Los Angeles Clean Truck Program – March 2008
Good: Realistic slides and presentation, good structure
Not Good: Short
USPS Future Business Model
Good: Clear structure and analysis, insightful charts
Not Good: Outdated, lackluster design

Investment and Industrial Policy: A Perspective on the Future
Good: Variety of charts, good titles
Not Good: Over designed, not a client presentation

Outperformers: High-growth emerging economies and the companies that propel them
Good: Variety of charts, qualitative visuals, clear titles
Not Good: Poor use of color, minimal footnotes
Technology’s role in mineral criticality (World Materials Forum)
Good: Clear storyline, well-structured slides, good titles and subtitles
Not Good: Overuse of visuals, relatively short
Challenges in Mining: Scarcity or Opportunity?
Good: Complex explanations made simple, variety of visual types
Not Good: Inconsistent titles, some unprofessional visuals (clipart, etc.)
Modelling the potential of digitally-enabled processes, transparency and participation in the NHS
Good: Realistic client slides, data heavy
Not Good: Cluttered, incomplete storyline
Addressing the Global Affordable Housing Challenge (2016)
Good: Realistic slide structure, good charts, great slide titles
Not Good: Strange slide formatting, mediocre design
Capturing the Full Electrical Efficiency Potential of the UK (2012)
Good: Realistic client deliverable (full deck, dense slides, proper deck structure)

Digital Luxury Experience (2017)
Good: Variety of charts, good use of icons
Not Good: Short presentation, light on content, not a client deliverable

How Companies can Capture the Veteran Opportunity
Good: Examples of text-heavy slides, good action titles
Not Good: Minimal charts, unrealistic structure, repetitive slides
Insurance Trends and Growth Opportunities for Poland
Good: Well organized presentation, clear takeaways
Not Good: Old formatting, short presentation
Laying the Foundations for a Financially Sound Industry
Good: Multiple chart examples (waterfall, line, dot, column)
Not Good: Short presentation, “conference-style” presentation
From Poverty to Empowerment (2014)
Good: Good variety of data visualizations
Not Good: Unattractive formatting and style
Consumer privacy in retail
Good: Clear titles, good use of icons and color to show insights
Not Good: Short, not a client presentation
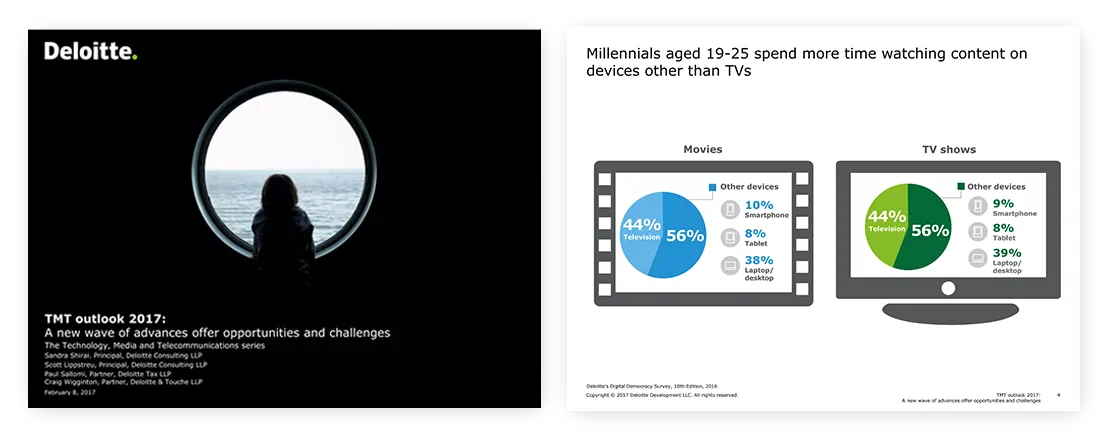
TMT Outlook 2017: A new wave of advances offer opportunities and challenges
Good: Survey insights highlighted well, good use of color, clear charts and visuals
Not Good: Not a client presentation, heavy focus on survey data
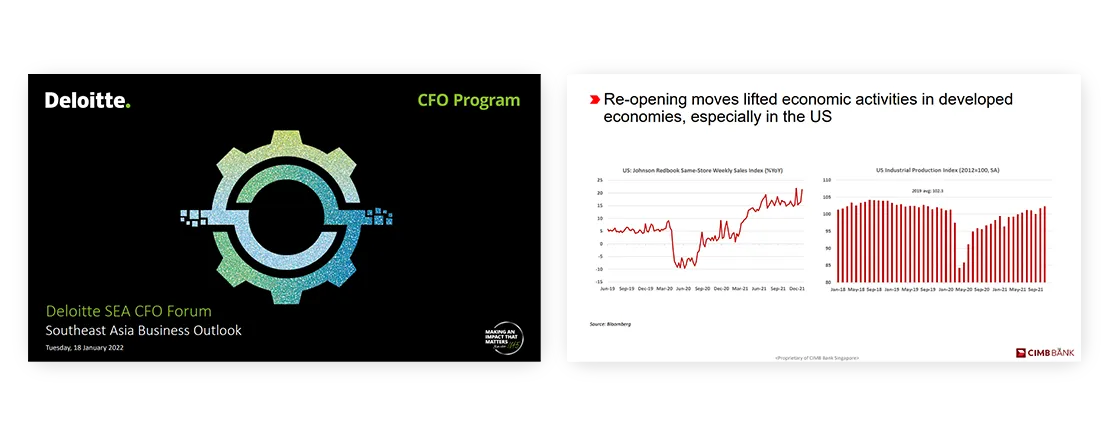
Deloitte SEA CFO Forum Southeast Asia Business Outlook
Good: Line chart examples
Not Good: Poor titles, strange use of black
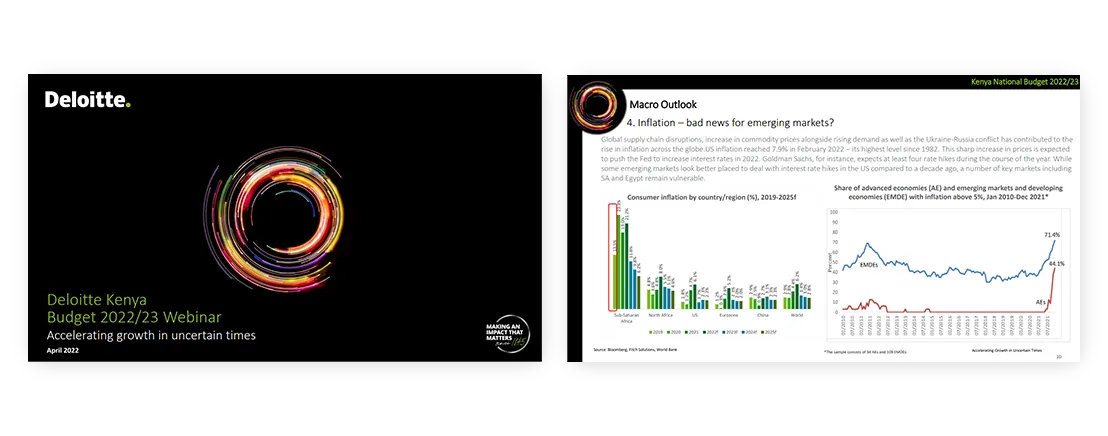
Deloitte Kenya Budget 2022/23 Webinar
Good: Consistent design, good colors
Not Good: Simple titles, meant for live presentation
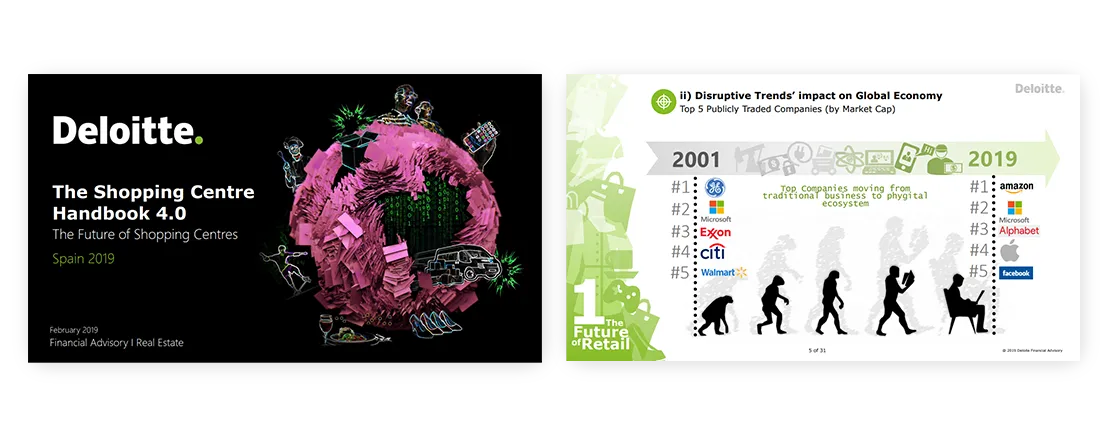
The Shopping Centre Handbook 4.0
Good: Some insights
Not Good: Too many graphics, strange design
2011 China Luxury Market Study
Good: Clear titles, good use of color to highlight insights
Not Good: Short presentation, marketing presentation
Bain & UC Berkley Operational Excellence (2010)
Good: Realistic presentation, lots of slides
Not Good: Outdated content, ugly design

Fintech New York: Partnerships, Platforms and Open Innovation
Good: Simple and clear slide design, good structure, insightful charts
Not Good: Short presentation, only a few “consulting style” slides
Shaping the Sustainable Organization
Good: Well structured slides, clear takeaways
Not Good: Rounded chart bars

The Decade to Deliver: A Call to Business Action
Good: Variety of charts, good design
Not Good: Not a client presentation

Fueling the Energy Future
Good: Illustrative charts and matrices
Not Good: Curved line charts

Cracking the Code on Consumer Fraud
Good: Mix of charts and numbers
Right Cloud Mindset: Survey Results Hospitality
Good: Nice slide titles and charts
Not Good: Text heavy sections

Unleashing Competitiveness on the Cloud Continuum
Good: Focus on takeaways, clear charts
Not Good: Ugly backgrounds, overuse of pictures
Whole Brain Leadership: New Rules of Engagement for the C-Suite
Good: Formatting, use of numbers
Not Good: Unnecessary graphics
Federal Technology Vision 2021: Full U.S. Federal Survey Findings
Good: Clear survey results, nice bar charts
Accenture Consumer Behavior Research: The value shake-up
Good: Color design, focus on insights
Not Good: Marketing focused
Tech Adoption and Strategy for Innovation & Growth
Good: Color contrast, text structure
Not Good: 3D charts
Intelligent Operations for Future-Ready Businesses
Good: Sankey chart, tables, presentation structure

When, Where & How AI Will Boost Federal Workforce Productivity
How fit is your allocation strategy?
Good: Some good charts, good use of color
Not Good: Light on content, short presentation, inconsistent slide structure
European Banking Barometer (2015)
Good: Nice titles and takeaways, good variety of charts
Not Good: Survey-focused presentation (i.e. not client deliverable)

EY Price Point: global oil and gas market outlook, Q2 | April 2022
Good: Insightful charts and tables
Not Good: Report style, text heavy
IBOR transition: Opportunities and challenges for the asset management industry
Good: Formatting
Not Good: Meant for live presentation
Global Capital Confidence Barometer 21st edition
Good: Formatting and structure, interesting charts
Power transactions and trends Q2 2019
Good: Insightful charts
Not Good: Meant as appendix or “leave behind”

MAPS2018 Keynote address on EY report: Life Sciences 4.0 – Securing value through data-driven platforms
Good: Realistic slides, clear titles, good formatting

EY Germany FinTech Landscape
Good: Formatting and structure, insightful charts
Not Good: Data heavy, appendix style slides

Project Management: Improving performance, reducing risk
Good: Variety of qualitative visuals, good use of icons, nice design
Not Good: B ad titles, light on content

World Economic Forum: The power of analytics for better and faster decisions by Dan DiFilippo
Good: Scatter plot examples

Apache Hadoop Summit 2016: The Future of Apache Hadoop an Enterprise Architecture View
Good: Qualtative visuals
Not Good: Short and marketing focused

Turning big data into big revenue
Good: Text heavy slide examples
Medical Cost Trend: Behind the Numbers 2017
PwC’s new Golden Age Index – how well are countries harnessing the power of older workers?
Good: Mix of charts and tables, clean formatting
Not Good: Inconsistent titles

PwC’s Global Technology IPO Review — Q1 2015
Good: Combination and column charts
Not Good: Report style presentation

18th Annual Global CEO Survey – Technology industry key findings
Good: Visualized data
Not Good: Incomplete titles
The FDA and industry: A recipe for collaborating in the New Health Economy
Good: Simple and clear titles
Not Good: Inconsistent structure

Making zero-emission trucking a reality
Good: Very realistic slides, overall great presentation
Not Good: Text heavy transition slides

Driving the sustainability agenda on C-level
Not Good: Short, some cluttered slides
The Diversity Imperative: 14th Annual Australian Chief Executive Study
Good: Chart heavy, realistic slides
Not Good: Short presentation

Creating a Winning Recipe for a Meal Kits Program
Good: Clear titles, good charts
Not Good: Dense, too many pictures/logos
The 4th Annual New Mobility Study 2019
Good: Variety of charts, good amount of content
Not Good: Lots of filler slides, inconsistent titles
2019 APAC Hospital Priority Study Overview
Good: Very good (and realistic) design, clear slide takeaways
Not Good: Very short presentation

Rail industry cost and revenue sharing (2011)
Good: Good introduction and executive summary, realistic client presentation
Not Good: Outdated, boring design
2019 Media and Entertainment Study
Good: Clear charts, good titles
Not Good: Very short, too much text

Navigating a digital-first home furnishings market
Good: Infographic style slides

5 Opportunities in the Nutritional Supplements Industry
Good: Great charts, good deck structure
Not Good: Not a client presentation, text heavy
Infrastructure Victoria – AZ/ZEV International Scan
Good: Realistic client presentation, wide variety of slides
Not Good: Very long
The Rapidly Evolving Landscape of Meal Kits and E-commerce in Food & Beverage
Good: Variety of basic charts, realistic design
Top 8 Insights From the 2018 Beauty, Health & Wellness Survey
Good: Good column chart examples
Not Good: Report style

2018 Brand Owner Packaging Survey
Good: Good visuals, multiple charts
2016 Strategic Hospital Priorities Study
Good: Multiple charts, good qualitative visuals
The Merchandising Evolution (and why NDC Matters)
Good: Good storyline, clear charts
Not Good: Weak titles, outdated style

Infrastructure beyond COVID-19
Good: Wide variety of slide types, realistic presentation
China Exit or Co-Investment Opportunities for German PE Investors
Good: Multiple data heavy slides, good charts
Not Good: Slightly old

Strategy Study 2014
Good: Variety of charts
Not Good: Reads like an infographic, poor choice of color

Australia: Taking Bigger Steps
Good: Illustrative chart, use of icons
Not Good: D istracting backgrounds and colors
Lifting the Barriers to Retail Innovation in ASEAN
Good: Simple to follow
Not Good: Minimal analysis, questionable stacked column chart
The Future of Commercial Vehicle Powertrains (2012)
Good: Realistic slides, excellent takeaways, good overall structure
Not Good: Older presentation, simplistic design

Pursuing Customer Inspired Growth
Good: Realistic client slides, multiple frameworks
Not Good: Short, outdated design

The Accelerating Growth of Frictionless Commerce
Good: Mix of charts, clear insights
Not Good: Distracting backgrounds, short presentation

Consolidation of the US Banking Industry
Good: A couple good titles
Not Good: Large text, minimal charts, distracting colors

Covid-19 and Effects on Turkey
Good: Consistent color, focus on insights
Not Good: Strange layout, marketing focused
Booz Allen Hamilton, Alvarez & Marsal and others
European Distressed Credit Watch List
Good: Simple charts
Not Good: Boring template, appendix heavy
Corporate Headquarters Study 2018
Good: Clear and simple slides, good variety of charts and visuals, not overly produced
Not Good: Not a typical client presentation, average slide titles
The Lithium-Ion (EV) battery market and supply chain
Good: Realistic titles and content-heavy slides
Not Good: Distracting background and colors
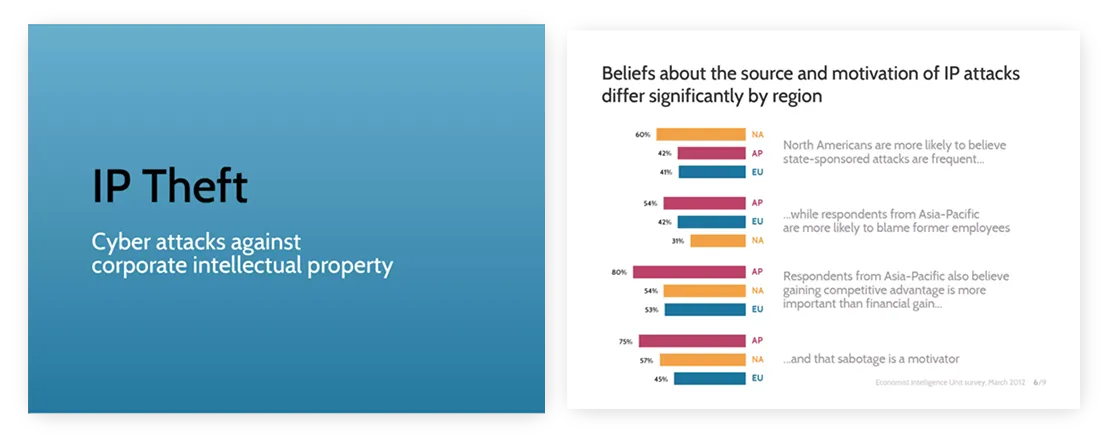
Good: Story flow, titles
Not Good: T itle page, overall design rs
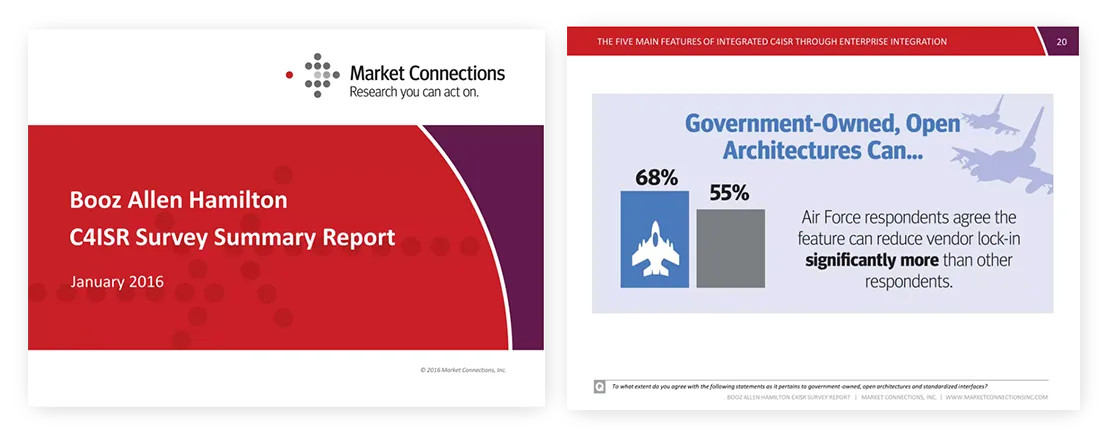
Booz Allen Hamilton and Market Connections: C4ISR Survey Report
Good: Simple bar charts
Not Good: Titles, design

Joining Forces: Interagency Collaboration and “Smart Power”
Good: Slide consistency
Not Good: Chart design, outdated

Booz Allen at a glance
Good: Easy-to-read charts
Not Good: Meant for live presentation, minimal content
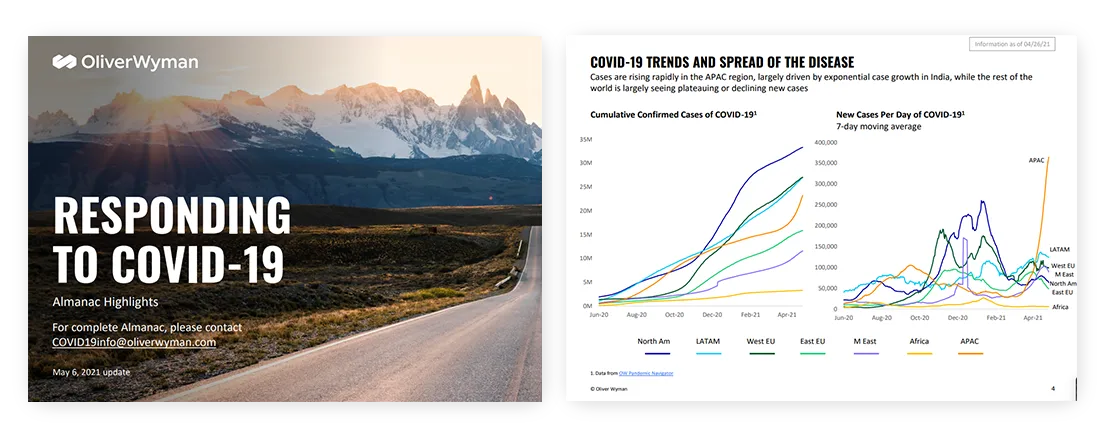
Responding to Covid-19 (2021)
Good: Excellent use of color, good overall design and visualizations
Not Good: “White Paper” style presentation (i.e. not client deliverable)
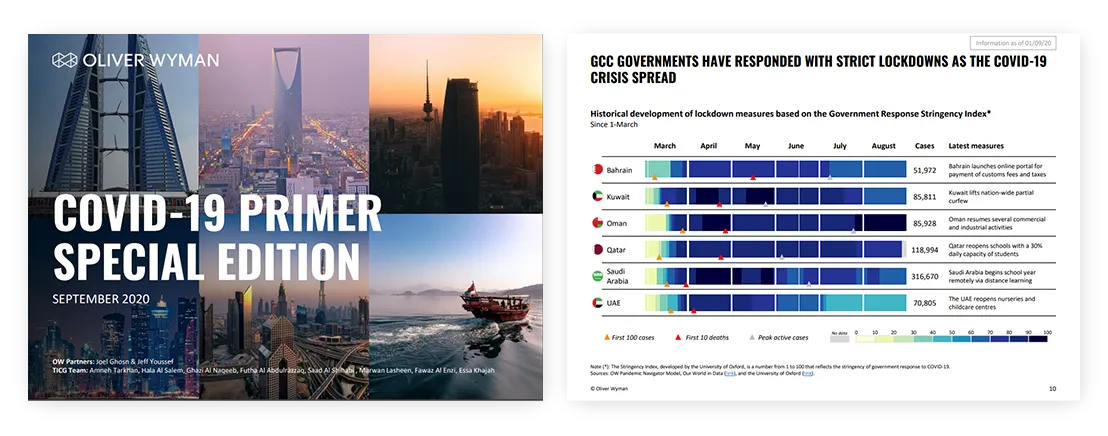
Covid-19 Special Primer (2020)
Good: Variety of data visualizations, nice color usage, clear takeaways
Building Up Immunity of the Financial Sector
Good: Clean design, interesting charts
Not Good: Some text heavy slides
Customer Experience: The 14BN Risk Noted for Discussion
Good: Simple design, good overall structure
Not Good: Inconsistent colors
- Print Friendly
The horror of the Key Bridge disappearing overnight
The bridge symbolized technological prowess and human connection. its collapse triggers darker emotions..

The video of the Francis Scott Key Bridge’s collapse now exists as a global icon, giving several billion people a seemingly intimate and shocking memory of a bridge they may never have seen or heard of until social media and journalism made it ubiquitous.
The video is fascinating, terrifying, mesmerizing, and it may confirm superstitions we often feel about things beyond our individual comprehension. How is it that airplanes stay up in the air, and tunnels don’t collapse under the weight of water and earth? Even the most agnostic brains will make quiet and reflexive supplication for protection before crossing a bridge as dramatic as the one that collapsed this week.
The loss of the bridge is first a human tragedy, for those injured or killed by its collapse. And then it is an economic shock, with a radiating toll that won’t be fully understood for years , and perhaps decades. But it’s also a powerful symbolic shock, given the metaphorical power of bridges as a form of connection, a symbol of our technical prowess, a point of civic pride and persistent desire to master and reshape the landscape.
On the day the Francis Scott Key Bridge opened in March 1977, the Baltimore Sun celebrated the views from the top of its giant steel-truss crossing: “In every direction from the harbor span lie dramatic vistas of the Port of Baltimore.” That included a marine terminal, the giant Bethlehem Steel plant and the Penn Central Canton rail yards. After delays and cost overruns, the new bridge was welcomed as yet more proof of the city’s ambition, its engineering prowess and its economic might.
The city hasn’t fared well in recent decades, and the newspaper’s breathless boosterism for new infrastructure sounds strangely dated. So, too, the name the bridge bears. We remember Francis Scott Key not only as the author of our national anthem’s lyrics, but also as an enslaver and staunch opponent of abolitionism. There is little enthusiasm for creating new memorials to him.
The Style section
But the Key Bridge was a marvel, and it remained a high point of any drive around the city of Baltimore until its collapse, early Tuesday morning, after being struck by a giant container ship. Since the middle of the last century, American infrastructure has been laid heavily and bluntly on the social and natural landscape. Interstate highways were plowed recklessly and cruelly through urban areas, too often dividing and polluting neighborhoods of the poor and people of color. Outside of cities, the standardized width, grades and slopes of the interstate highways seem designed to deny any connection to topography.
The Key Bridge, however, was a rare moment when your car seemed to soar, giving you a not-quite-bird’s-eye view of the peculiar geography and history of the East Coast. Any trip by train or highway along the heavily populated Mid-Atlantic seaboard involves myriad long bridges and tunnels to cross the bays, estuaries and wide rivers that stretch deep into the coastal plains. Baltimore is situated where it is because it provides safe harbor for ships. And many seemingly landlocked cities, like Richmond and Fredericksburg, lie near the last navigable point of major rivers that stretch fingers of trade and commerce into the country’s interior. Unlike the tunnels that carry Interstate 95 and I-895 across the harbor and Patapsco River, the Key Bridge offered an exhilarating experience of the landscape, and its connection to the early economy of colonial America.
A symbolic shock like Tuesday’s tends to lead the public toward darker emotions — horror, of course — but also fear, suspicion and even cynicism.
Like the photographs that emerge from wars or disaster, bombings, floods and earthquakes, the video of the bridge collapse doesn’t explain the things that feel most inexplicable. The more you watch it, the less it yields, until finally the mind flirts with some kind of metaphor or parable to make sense of it. Perhaps there is a fable of American decline or corruption or incompetence. It’s best not to amplify or extend the toxic theories that circulated in the immediate aftermath. But they are symptoms of the same phenomenon, a sudden, overwhelming craving for meaning, into which unscrupulous people will project their ugliest fancy.
In the video, the bridge faltered first on the left side of the frame, then in the center, and then its long truss snapped and the right span fell, all in a matter of a few seconds. The speed of its failure offers the first of the fables, that something must be desperately wrong with the design for it to collapse so quickly. But its rapid failure is directly related to the properties of a long, steel-truss bridge. Put simply: Each part of this bridge’s main span is helping the other parts do their work. Its elements are integrated into a whole, which allows less steel to bear more weight.
The engineering is fundamental to the bridge’s beauty. The main span of the Key Bridge, the one that flew high above the river allowing passage to ships beneath, sat on its four piers like a bird. Seen from a distance, it looked spidery and delicate. For centuries, advances in bridge technology have created a tension between efficiency — the ability to span greater distances with less structure — and an intuitive belief that bridges should be solid, heavy, formidable in their construction. When 18th-century London debated the design of a new Blackfriars bridge, Samuel Johnson argued vehemently for a heavier structure of semicircular arches, rather than what was built, a series of slightly more graceful semielliptical arches.
“The first excellence of a bridge built for commerce, over a large river, is strength,” he wrote in a 1759 public letter. He lost the argument, but his appeal to what seemed common sense — the old, round Roman arch was stronger and thus always preferable — still haunts our thinking about infrastructure, if we think of each project individually and unrelated to larger needs and systems.
But infrastructure isn’t just a collection of individual projects, but a larger collection of problems and responses. And to meet those demands efficiently, you build not the strongest bridge possible in every case, but the strongest necessary to meet a reasonable set of expectations and risks.
Sharp. Witty. Thoughtful. Sign up for the Style Memo newsletter.
The giant steel bridges the world began building in the 19th century embody the man-made sublime, delighting the eye and terrifying the mind with their ambition. Walt Whitman used to visit the great Eads Bridge in St. Louis to feast on the poetry of its design: “I have haunted the river every night lately, where I could look at the bridge by moonlight.” It was, he said, “a structure of perfection and beauty unsurpassable,” a sentiment more common when this technology was still new, and dazzling, and wasn’t routinely value-engineered out of the final design.
But when Benjamin Baker and John Fowler designed the equally beautiful Forth Bridge in Scotland, they had to demonstrate the engineering in a way that made its forces of tension and cantilevers intelligible to ordinary people. So, they had a picture taken of three men using chairs, broomsticks, weights and their arms to reproduce the logic of his design. In the middle, miraculously suspended in midair, sat Kaichi Watanabe, a Japanese engineer who was studying in the United Kingdom.
The image not only explained the bridge, but also made it human, extending its metaphorical power as a collective human project with collective benefits. It enacted in an almost comical way the basic trust we place in engineering that defies our individual comprehension.
There will be investigations and essential lessons learned from the tragedy earlier this week. People trying to bypass Baltimore will be inconvenienced, and people who live there will be unnecessarily burdened , but there will also be workarounds and adaptation. And slowly, the images, fables and analogies that govern our thinking about bridges will revert to where they have been for centuries: They are a means of connection, essential, often beautiful, sometimes terrifying, and never more so than when they are miraculous in their efficiency of design.
Baltimore bridge collapse
How it happened: Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge collapsed after being hit by a cargo ship . The container ship lost power shortly before hitting the bridge, Maryland Gov. Wes Moore (D) said. Video shows the bridge collapse in under 40 seconds.
Victims: Divers have recovered the bodies of two construction workers , officials said. They were fathers, husbands and hard workers . A mayday call from the ship prompted first responders to shut down traffic on the four-lane bridge, saving lives.
Economic impact: The collapse of the bridge severed ocean links to the Port of Baltimore, which provides about 20,000 jobs to the area . See how the collapse will disrupt the supply of cars, coal and other goods .
Rebuilding: The bridge, built in the 1970s , will probably take years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars to rebuild , experts said.
- The hero March 16, 2024 The hero March 16, 2024
- Your hair looks gorgeous. It cost ... what?! March 19, 2024 Your hair looks gorgeous. It cost ... what?! March 19, 2024
- On Fox News, Steve Doocy has become the unexpected voice of dissent March 22, 2024 On Fox News, Steve Doocy has become the unexpected voice of dissent March 22, 2024

- Other Sports

OSU Basketball: Steve Lutz Set to Bring Fast-Paced Style to Stillwater
The Cowboys have their new coach and a new style of play alongside him.
- Author: Ivan White
In this story:
Oklahoma State hired a new coach, and the product on the floor might look unrecognizable.
Throughout the past seven seasons, OSU has been a team focused primarily on defense. Under Mike Boynton, the team often tried to make games as ugly as possible and grind out low-scoring matchups.
Last season, OSU ranked 227th in pace, averaging 68 possessions per 40 minutes. Out of 362 teams, OSU’s style never stood out offensively and often led to sluggish performances on that side of the floor.
The Cowboys might have hired Steve Lutz because they wanted a significant shift in style. Although he has only been a head coach for three seasons, Lutz’s style has already garnered attention for his team’s fast offense.
In Boynton’s seven seasons, his team only cracked the top 100 in pace once. That came in 2021 when No. 1 pick Cade Cunningham helped the Cowboys to 41st in pace and the only NCAA Tournament appearance in that span.
Meanwhile, Lutz’s rank of 38 in his second season at Texas A&M Corpus Christi is the lowest-ranked pace he has had as a head coach. While with the Islanders, Lutz led one of the fastest teams in the country, but he took it to another level in his one season at Western Kentucky.
In 2024, the Hilltoppers ranked first in the nation in pace at 76 possessions per 40 minutes. Although the Hilltoppers were only 190th in offensive rating, that is still a significant step up from OSU’s placement at 247.
Lutz’s teams also typically get inside, with only 32.1% of Western Kentucky’s shots coming from 3-point range last season. With that style, offensive variance is somewhat limited and can contribute to a solid defensive team.
Last season, Western Kentucky ranked 36th in defensive rating. However, the team’s pace can overshadow its defensive ability, ranking 258th in points allowed per game.
Although Lutz might not be able to bring the same immediate success to OSU, a new style in Stillwater is bound for exciting results.
Want to join the discussion? Like AllPokes on Facebook and follow us on Twitter to stay up to date on all the latest Cowboys news. You can also meet the team behind the coverage.
Latest Cowboys News

OSU Basketball In Contact With NBA Prospect, Transfer Portal Forward

OSU Basketball: Walk-On Guard Naz Brown Enters Transfer Portal

OSU Basketball Center Listed As Top Transfer in College Basketball

Fox Sports’s Gottlieb Makes Pitch for Oklahoma State Coaching Job
Tracker: oklahoma state basketball transfer portal moves.
Research on the Influence Mechanism of Short Video Communication Effect of Furniture Brand: Based on ELM Model and Regression Analysis
- Shulan Yu Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
- Zehui Wu Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
The elaboration likelihood model (ELM) and regression analysis were used to investigate the impact of furniture brands’ communication strategies on consumer behavior through short video platforms. The work examined a set of representative short videos, analyzing how key features—such as content theme, duration (16-60 seconds), graphics, subtitles, background music, and title style—affected communication effectiveness. The ELM model uncovered the correlation between these video characteristics and the Communication Effect Index (DCI), with statistical significance confirmed by regression. Findings indicated that live broadcasts, graphical presentations, subtitles/topics, upbeat music, and exclamatory titles significantly enhanced communication efficiency. Limitations, including time-period sampling bias, sample size, and item duplication in the ELM application, were also considered. Based on these findings, the research offers optimization suggestions and future directions for furniture enterprises in leveraging short video marketing.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Are You a ‘Spring’ or a ‘Winter’? It Could Cost You $500 to Find Out.
Seasonal color analysis, a fad from the 1980s seeking to identify a person’s most flattering color palette, is drawing views and exasperation on TikTok.

By Callie Holtermann
A barefaced woman studies her reflection, trying on fabric bibs that could have been yanked from a production of “Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat.” In a video posted on TikTok last month, she is draped in lustrous silver, faint pink, a deep green that recalls a jalapeño pepper.
Standing behind her client as a hairdresser might, Tatum Schwerin oohs and aahs. “Stunning on you,” she says of one warm-toned tapestry. Another, with stripes of terra cotta and butter yellow, is “on the money.”
Ms. Schwerin, 44, calls herself the Color Analysis Queen on social media. She estimates that she conducts about 60 of these sessions a month at her home in Frisco, Texas, with the goal of identifying a palette that best suits a person’s skin, hair and eye colors.
Each 90-minute consultation costs $479. Ms. Schwerin said she was having trouble keeping up with demand.
Ms. Schwerin is among a wave of influencers turning seasonal color analysis, a classification system popular in the 1980s, into a viral phenomenon as well as a lucrative business. It posits that each person’s features can be sorted into a set of shades associated with winter, spring, summer or fall, and offers clothing and makeup recommendations to match.
@thecoloranalysisqueen Get started either virtually or in-person through the link in my bio! #thecoloranalysisqueen #coloranalysis #coloranalysistok #virtualcoloranalysis #styledbytatum #colorpalette #texasstylist #personalstylist #wardrobestylist #colorseasonanalysis ♬ original sound - The Color Analysis Queen
The system’s fans might once have attended a get-together “halfway between a Tupperware party and group therapy,” according to a New York Times article published in 1983. Now they congregate on Instagram and TikTok, where videos of Ms. Schwerin’s consultations regularly attract hundreds of thousands of views. Her biggest hit has been seen more than 30 million times.
A healthy slice of those viewers don’t see why anyone would pay nearly $500 to be told that they look pasty in blue.
“Watching these I feel the same as when someone shows me their baby sonogram,” a commenter wrote on one of Ms. Schwerin’s videos. “I DON’T SEE IT.”
Ms. Schwerin, a former stylist who took two online courses on color analysis, is undeterred. “I always like to say, ‘Have you tried on lipstick?’” she said. If so, “you surely can recognize that not all colors are equal on your skin.”
The idea of color seasons was popularized in part by Carole Jackson’s 1980 best seller “Color Me Beautiful.” Ms. Jackson offered four seasonal palettes that drew from the colors present in nature at that time of year: rich golds and browns for autumn, icy blues and whites for winter and so on.
Ms. Jackson, who ran a thriving business training color consultants, argued that a person’s season could be determined by the colors that made them look the perkiest. “See how Summer Mary looks drab in the yellow-tone camel and orange lipstick,” she wrote of a model in the book, “but comes to life in the pink shirt and pink makeup tones that are so complementary to her natural coloring.”
@sarah_novio Replying to @Toyia Am I a true winter or a dark winter? I honestly think I’m Dark Winter with my natural features but now that my hair is partially blue it made my skin more cool toned (appearing) #darkwintercolors #truewinterpalette #coloranalysis #coloranalysistok ♬ original sound - sarah_novio
Sarah Novio, 34, noticed color analysis taking over her social media feeds last year and began uploading her own videos about celebrities including Rihanna and Jameela Jamil. “Even though there was a lot of color analysis, I didn’t see a lot of people talking about people of color, or people with more melanin in their skin,” she said.
Ms. Novio uses Photoshop to test out swatches of different hues next to a person’s face. She tries to determine whether a person’s “undertones” are more yellow (warm) or more blue (cool), and if they look better to her in bright or muted colors, occasionally consulting the color wheel that she learned about in art school to make her recommendations.
Humans are sensitive to extremely fine differences in facial complexions, said Bevil Conway, a neuroscientist and artist who has studied how humans see color. It is true that our perceptions of those colors may shift based on how they contrast with the clothing or makeup around them.
Still, he was skeptical of the strict prescriptions offered by some color analysts. “People take a little grain of science and then it gets inflated to become a whole world,” Dr. Conway said. What is “flattering,” he added, is highly subjective: “Using it as a tool is fine. I think starting to make normative claims about beauty is where I would draw the line.”
Luckily for color analysis, subjectivity and disagreement tend to feed, not squash, a social media trend.
Some TikTok users post videos surrounding their faces with rainbow color wheel filters, asking commenters to determine their color season for them. (Professed experts tend to sneer at this approach.) Others have tried outsourcing color analysis to ChatGPT , which seems to identify almost everyone as an autumn.
Armchair color analysts argue in the comment sections of videos about celebrities like Jenna Ortega, Hailey Bieber and Beyoncé. The actress Zooey Deschanel posted a video last month “setting the record straight,” she wrote in the caption, that her much-debated color season was winter.
@missdarcei I got my personal color analysis done in Korea at @Colorwings in Seoul! #coloranalysis #korea #traveltiktok #beauty ♬ Aesthetic Music (Remastered 2022) - Bepo
Among the theory’s adherents, an in-person assessment remains the gold standard. Darcei Giles, a 32-year-old beauty content creator, flew 14 hours from Toronto to Seoul last year in part to get a color consultation there. She said her result — “bright spring” — had helped her shop more efficiently.
“It’s almost like finding out your zodiac sign for the first time and being like, Oh my god, that makes so much sense!” Ms. Giles said.
Ms. Novio thinks color analysis can make getting dressed less overwhelming, but she chalked up its popularity to a broader fascination with examining, rating and categorizing our appearances .
“People like to belong somewhere,” said Ms. Novio, who occasionally ignores her own “deep winter” classification to wear a favorite orange and brown striped sweater. “Being categorized in a season makes people feel that way.”
Callie Holtermann reports on style and pop culture for The Times. More about Callie Holtermann
Explore Our Style Coverage
The latest in fashion, trends, love and more..
Is Humanity Out of Fashion?: After a time of relative stability, fashion is in a period of uncertainty because of broader political and economic forces. Or is it simply a generational passing of the torch?
Boots, Backpack and a Ubiquitous App: Fourteen years and one Apple App of the Year award in, AllTrails has become something rare : a tool that works for both experts and newbies.
Alan Cumming’s Outsider Cabaret: The 59-year-old actor, who revels in doing “weird things all the time,” brings his cabaret show about aging to New York.
Gisele Bündchen on Healthy Eating: The supermodel opens up about life in Miami and her new cookbook, “Nourish.”
Does the Peace Sign Stand a Chance?: For a younger generation, the once-powerful protest symbol packs about as much of a punch as a smiley face.
New York City’s Easter Parade: A recurring cast of milliners and costumed spectators trading nods with the more casual participants — who found creative ways to create their own grand impressions — was a particular delight to see.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are more than ten common different effective presentation styles: 1. Visual Presentation Style. The visual style is great for anyone who wants to use your presentation to complement the main points of your speech. This visual presentation technique is perfect for people who have many important talking points.
3. Instructor Style. What it is: This presentation style allows you to deliver complex messages using figures of speech, metaphors, and lots of content -- just like your teachers and professors of old. Your decks should be built in logical order to aid your presentation, and you should use high-impact visuals to support your ideas and keep the audience engaged.
Data scientist. This presentation style uses facts, data, analysis and statistics to explain and expand upon talking points. A data scientist style helps speakers prove a point and persuade their audience. If you're giving a presentation on a subject that needs more facts and data to support it, this style may be a good choice.
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Tip #1: Include less text and more visuals in your presentation design. According to David Paradi's annual presentation survey, the 3 things that annoy audiences most about presentations are: Speakers reading their slides. Slides that include full sentences of text. Text that is too small to read.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
Analytical Presentation Style-Great at Technical Presentations and Scientific Talks. Last week, I gave an overview of the four main presentation styles. This week, we will cover the strengths and weaknesses of the Analytical Presentation Style. This is the style of presenter that is more "indirect" and "logical".
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
Here are some examples to consider: 1. Visual. The visual style involves using picture or video representations, such as a slideshow, to support discussion points. Many speakers employ this style by using charts, graphs, tables and colourful images to maintain audience concentration.
Persuasive Presentations. …. Motivational Presentations. …. Decision-making Presentations. …. Progress Presentations. …. Whichever Presentation Type You Choose, Create it With Beautiful.ai. Robby. Robby. The techniques a business professional employs when giving a speech are known as presentation styles. The best presentation style to ...
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company's mission, market analysis, and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and ...
1 Identify your audience. The first step in audience analysis is to identify who your audience is. You need to know the basic demographic characteristics of your listeners, such as their age ...
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
SWOT PowerPoint Template. This free PowerPoint template offers you a really complete and detailed option to present your SWOT analysis. You'll find here 3 original designs to organize your presentation. You can use the "X" diagram to make the slide look more dynamic.
This style of top-down communication works really well in a variety of settings, including email, face-to-face communication, and of course, PowerPoint presentations — which is what I'm going to focus on here. BCG Example. The first example on our list is BCG. The slide is an excellent example of the Pyramid Principle because it is well ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Audience analysis can make your presentation more relevant, credible, and memorable. Add your perspective Help others by sharing more (125 characters min.) Cancel
Be the first to add your personal experience. 4. Adapt your presentation. Be the first to add your personal experience. 5. Get feedback. 6. Here's what else to consider. Presenting information ...
Good: Easy to understand, good insights and analysis, contrasts with McKinsey presentation on the same topic. Not Good: Old presentation. Download this Presentation. Next Generation Manufacturing (2016) ... Not Good: "White Paper" style presentation (i.e. not client deliverable) Download this Presentation. Covid-19 Special Primer (2020)
Here are descriptions of each of the four presentations styles (the Closer, the Data Scientist, the Director and the Storyteller). See which style you think resonates with you, and then take the ...
Finally, effective presentation style is facilitated by cultivating self-awareness, refining self-portrayal (Foulkes, 2015), and ultimately developing an authentic presentational presence ... In this analysis of the qualitative research findings presentation as genre, we have provided considerations based on our reading of genre theory and ...
March 27, 2024 at 6:06 p.m. EDT. Part of the structure of Baltimore's Francis Scott Key Bridge on Wednesday after the ship's crash. (Steve Helber/AP) 7 min. The video of the Francis Scott Key ...
Joe Biden, Barack Obama and Bill Clinton. Sometimes when a president needs a hand, only another president - or another two - will do. President Joe Biden's bid for a second term and ...
Last season, OSU ranked 227th in pace, averaging 68 possessions per 40 minutes. Out of 362 teams, OSU's style never stood out offensively and often led to sluggish performances on that side of ...
The elaboration likelihood model (ELM) and regression analysis were used to investigate the impact of furniture brands' communication strategies on consumer behavior through short video platforms. The work examined a set of representative short videos, analyzing how key features—such as content theme, duration (16-60 seconds), graphics, subtitles, background music, and title style ...
Apr. 04, 2024 10:01 AM ET Dollarama Inc. (DLMAF) Stock, DOL:CA Stock. SA Transcripts. 145.59K Follower s. The following slide deck was published by Dollarama Inc. in conjunction with their 2024 Q4 ...
Ms. Schwerin is among a wave of influencers turning seasonal color analysis, a classification system popular in the 1980s, into a viral phenomenon as well as a lucrative business. It posits that ...