We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing

How to Write a White Paper [Tips & Templates]
By Chau Nguyen , Jun 28, 2023

So, you need to write a white paper.
And not just write it, you need to make it interesting too — especially if your goal is to establish thought leadership or generate leads.
Because here’s the thing: the average human attention span is less than that of a goldfish, so just plopping tons of data and text onto a page and calling it a day won’t work.
If your white paper lacks engagement, your readers may choose to leave. Even if they genuinely require the information, they may encounter difficulties due to excessive text. Moreover, retaining the painstakingly assembled information may become a challenge for them. Utilizing Venngage’s white paper maker can help overcome these obstacles.
In this article, I’ll break down how to write the best white paper for your business, design tips included. (Spoiler: visuals will help you get more engagement!) I’ll also include white paper templates you can edit and make your own.
Let’s get started!
Click to jump ahead:
How to structure a white paper, how to write your white paper, how to create a white paper outline, tips for designing an engaging white paper, faqs about white paper writing.
Most white papers follow a standard format that includes a:
Introduction
- Proposed solution
You may be wondering why there isn’t a problem statement section. After all, a white paper is supposed to dissect and provide solutions to a problem, yes?
Well, you can include the problem statement in the intro — intros explain what a white paper is about. This section is the perfect place to make a case for your white paper.
But of course, there’s no rigid format you should follow to a T. If it works better with your content, feel free to make your Problem Statement a separate section.
Now, let’s look at what you should write in each section with examples:
The title page is straightforward: it includes the title of your white paper and the name of the organization that produced it (or the author’s name).
This government white paper discusses the problem of illegal tobacco trade and proposes several approaches to address it:

Just so you know, some of our templates are free to use and some require a small monthly fee. Sign up is always free, as is access to Venngage’s online drag-and-drop editor.
You can also include a sub-headline under the title to further explain what it’s about:

The introduction should explain the purpose of the white paper and why the reader should care. It should be interesting (and informative) enough to hook the reader right away and keep them reading.
As mentioned, the introduction also contains your problem statement. In other words, it should provide an overview of the problem you’re trying to address. You don’t need to include too much information here, as that’s the role of the Background section.
Here’s an example:

The author introduces an overview of the problem — phishing scams — which is backed with visualized data that allows readers to grasp its impact at a glance:

Related : How to Visualize Data In Your White Papers
Here’s where you provide background information about the problem you’re discussing. This section tends to be research- and data-heavy.
Let’s revisit our “Approaches to Battling the Illegal Tobacco Trade” white paper. Here’s what the Background section looks like:
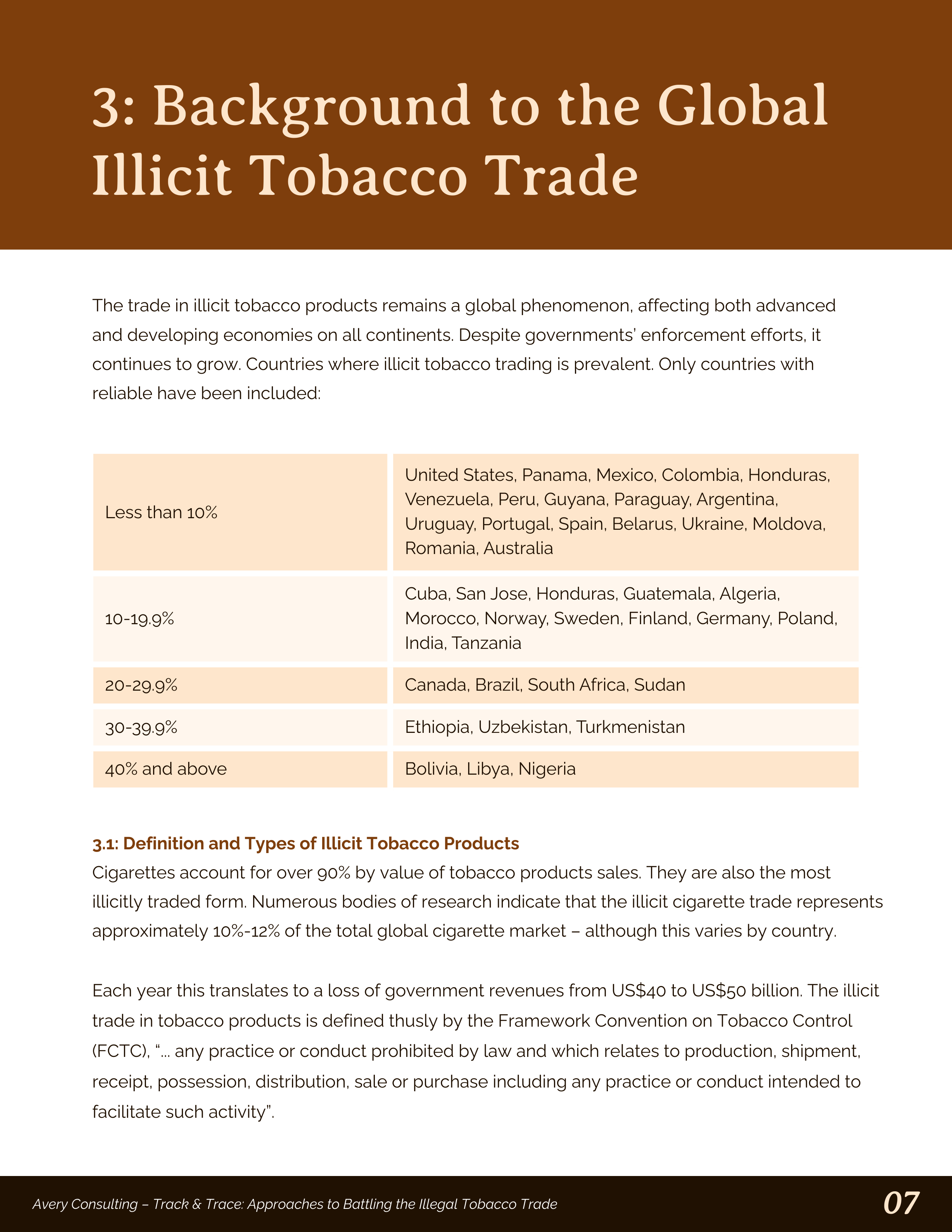
The author provides a table that lists the countries where illegal tobacco trading is present, from the least problematic (less than 10% of the industry) to the most (40% and above).
The author also includes some background information on illicit tobacco products, all backed by data:
“Cigarettes account for over 90% by value of tobacco product sales. They are also the most illicitly traded form. Numerous bodies of research indicate that the illicit cigarette trades represents approximately 10%–12% of the total cigarette market — although this varies by country.”
And why illegal tobacco trade is problematic:
“Each year this translates to a loss of government revenues from US$40 to US$50 billion.”
Now, onto the proposed solution.
This could be a product, a service or a course of action.
This government white paper addresses the sugar consumption crisis among children and proposes a policy to ban the sale of added-sugar products in schools:

Let’s look at another example. This technology white paper proposes a product as a solution: new technology that helps prevent falls in tilted chairs:

No matter what solution you propose, it should be well-supported with evidence. In the white paper above, the author presents elements that make their new technology the solution to fall prevention:

The conclusion should summarize the main points of the paper and provide recommendations for next steps:

You can also add a call to action here, like “contact the author for more information”. Or if you’re writing a white paper to gather more leads, you can add some information about your business too:

Note : white papers are academic in nature, so you should use reliable sources to back up your argument and include citations/references as needed.
Return to Table of Contents
Before making your white paper engaging, you first need to make it informative and credible. After all, it’s an important document to establish you as a thought leader in your industry.
Here are some guidelines to ensure the quality of your white paper:
Research your audience and topic well
Think about who will be reading your white paper. Are they actually experiencing the problem you’re trying to solve? Will your solution work for them? How much information will they need to be persuaded?
White papers are authoritative in nature, so people expect them to come with meaningful data from credible sources. Make sure you research your audience and your topic well to know how much data you need to make your case.
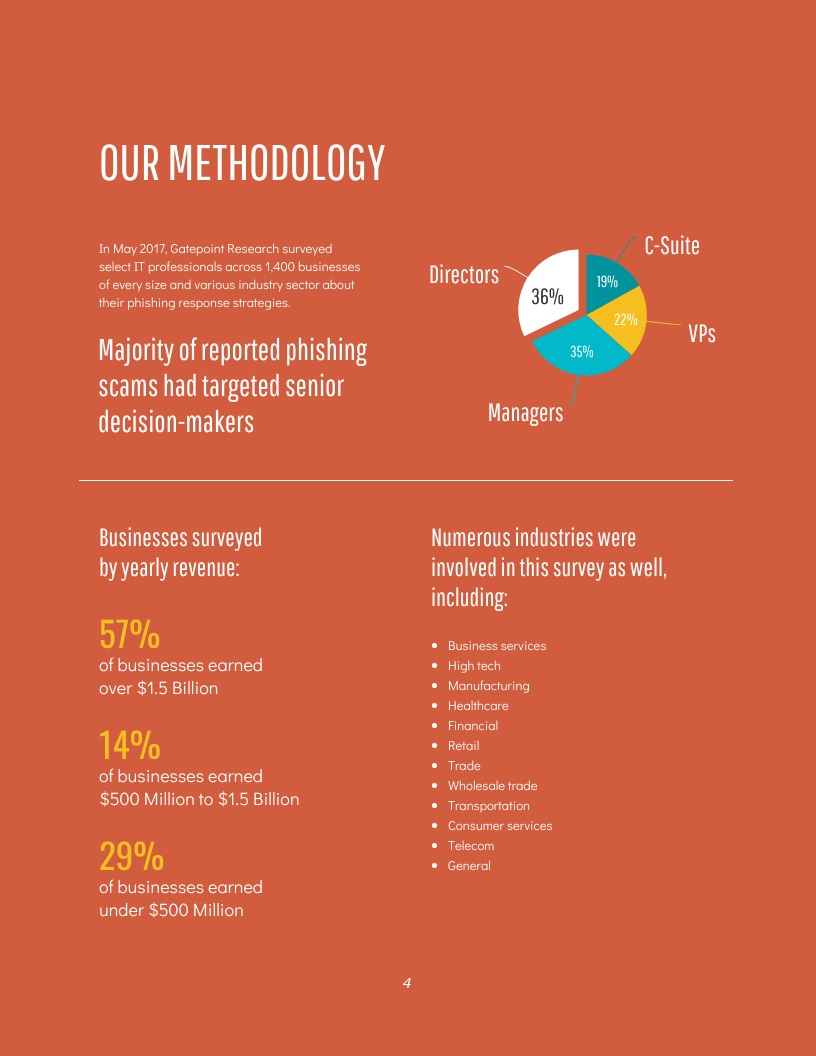
If your data comes from primary research, you can include your methodology as well for transparency and credibility:
Once you’ve nailed your research and solution, time to deliver all that information the best way you can. The language you use here must be the same as your audience’s: think of all the words and phrases they use often and try to incorporate them into your white paper writing.
You should also consider how people will read your paper — on desktop, on tablet or on mobile.
Mobile accounts for about 50% of global website traffic , reaching nearly 60% in Q2 2022.
Unless you have enough resources to create a responsive white paper ( like this one! ), you should make sure your document is legible on mobile. This means breaking up your paragraphs into smaller chunks of text and adding plenty of visuals so it’s easier on the eye:

I’ll touch on more tips to make your white paper engaging in the next section, so stay tuned!
Make sure people can scan your content
And to do that, you should break up your text with headings and subheadings. This helps keep your white paper organized and allows your reader to scan through the information easily.

You should also add a Table of Contents after the title page to help readers navigate your paper. Or in this case, the Table of Contents sits right on the first page:

Keep it succinct and to the point
There’s no standard length for this type of content, but a good rule of thumb is to write a white paper that’s around six pages. This should be enough space to do justice to your research and data, without overwhelming your readers.
Plus, it’s always good to be mindful of your audience’s time when creating any type of content.
As white papers provide expertise or a solution to a problem, your audience should be willing to devote a good amount of time and attention to your content… but don’t push your luck!
No matter how interested a reader is in a topic, they’ll drop off eventually if you ramble instead of getting to the point.
You can follow these ten useful pointers when creating your white paper outline:
- Define your purpose : Clearly identify the objective of your white paper. Determine what problem you’re addressing or what information you’re providing to your audience.
- Research and gather information : Conduct thorough research on the topic to gather relevant data, statistics, case studies, or expert opinions. This will help you support your key points and strengthen your arguments.
- Develop an introduction : Begin your white paper with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention and provides an overview of the topic. Clearly state the problem or opportunity you’re addressing and briefly outline your proposed solution.
- Organize main sections and subtopics : Identify the main sections that will structure your white paper. These sections should correspond to the key aspects or steps of your proposed solution. Break each section into subtopics that will be discussed in more detail.
- Provide supporting evidence : Within each section, present evidence, examples, and data to support your claims and validate your solution. Use clear and concise language to convey your points effectively.
- Include visuals and graphics : Visual elements such as charts, graphs, diagrams, or infographics can enhance the readability and understanding of your white paper. Incorporate relevant visuals where appropriate to illustrate complex concepts or data.
- Craft a conclusion : Summarize the main points discussed in the white paper and reiterate the proposed solution. Emphasize the benefits or value that readers can gain from implementing your recommendations.
- Add an executive summary : Write a concise executive summary at the beginning of your white paper, providing a brief overview of the entire document. This allows readers to quickly grasp the key points and decide if they want to read the full paper.
- Review and revise : After completing the initial draft, review and revise your white paper for clarity, coherence, and overall effectiveness. Ensure that the information flows logically, the language is concise and engaging, and there are no grammatical or spelling errors.
- Format and finalize : Format your white paper to make it visually appealing and reader-friendly. Use appropriate headings, subheadings, fonts, and spacing. Consider adding a table of contents for easy navigation. Finally, proofread your document one last time before publishing or sharing it.
Let’s say you’re looking for a white paper on sugar consumption in children. Would you read this:

Needless to say, applying visuals and data visualizations to your white paper makes a big difference. And you don’t need to be a professional designer to do so. Let’s look at some tips for creating an engaging white paper design:
1. Use a white paper template
If you don’t have the design skills to organize your draft into a well-designed document full of visuals, using a template is the way to go.
Venngage offers dozens of white paper templates you can edit for your business:

To get started, simply sign up for a free account , search for a white paper template and edit away.
To make it even easier for you, we’ve made a video walking you through editing a white paper template in Venngage. Check it out here:
2. Add data visualizations to your white papers
If you’ve got yourself some good data, don’t bury it under heaps of text.
While everyone on your team is busy creating boring Word documents, you can be the creative genius that uses charts and pictograms to craft a visually engaging white paper.
The type of charts you use will depend on the type of data you’re visualizing. We have a guide to picking what types of charts to use that can help you there.
You could use a line graph to show revenue growth over time . Or you could use pie charts to show parts of a whole, like in this policy white paper example:

Pro tip: with our online graph maker, you can create better charts and graphs than the standard Excel charts. A plain old bar graph won’t do much to inspire anyone, but a creative chart that tells a story can.
Pictograms are also a creative and effective way to visualize statistical data. Take a look at the white paper example below. Pictograms act as visual aids to showcase key statistics and changes in the IT sector:

Don’t be afraid to mix it up. They say variety is the spice of life — and this saying applies to white papers, too! This business white paper design, for example, combines both bar graphs and pie charts:

For more tips on visualizing data for your white paper, check out our post: How to Visualize Data In Your White Papers
3. Emphasize key points and takeaways with tables and text boxes
Visualizing information or data doesn’t mean just using graphs. When writing a white paper, you can also section off important pieces of information using tables and boxes.
In the white paper template below, the designers used a table to organize key points and takeaways from each main section:

Here’s another example of a white paper layout that uses a table to highlight some key statistics:

Breaking up lengths of text with boxes will help make your white paper easier to read, like in this example:

Which brings us to our next point…
4. Break up chunks of text with visuals
Visuals are perfect for illustrating ideas and emphasizing points.
Don’t be afraid to break up your text with visuals and create some breathing room in your white paper. You can even dedicate a whole page to pictures. Images give the eyes a rest and help reinforce information.
Take this white paper example — it dedicates a whole page to an evocative quote and photo:

Visual headers are also a great way to break up expanses of text while still having the visuals serve a purpose. You can create your own illustrations using icons — this can make for some fun and quirky headers, like in this workplace tech white paper:

5. Allow for plenty of white space on your pages
Speaking of giving your text some room to breathe, make sure you don’t crowd your pages with too much text or images.
Adding white space (or negative space) can help ensure your design isn’t too cluttered.
Check out how this example uses plenty of white space on nearly every page. The result? An organized and modern white paper design:

6. Use a consistent design that reflects your white paper topic
When you’re designing a multi-page document like a white paper or a report, your pages should have a cohesive look and feel.
(Note: by using a consistent design for your white paper, you’ll achieve unity — one of the 13 basic design principles .)
First, think of the themes reflected in your white paper. Is your white paper about social media engagement? Then using illustrations of birds (“tweeting”) or speech bubbles could work.
A white paper topic focused on establishing a sprint process could use race track visuals instead.
The hiring strategy white paper below uses greenery as the main design theme. Plants reflect the concept of growth associated with recruitment:

7. Incorporate your branding into your white paper design
To improve brand recognition, you need to have consistent branding across all marketing collateral. This not only helps your marketing efforts but also helps you maintain consistency in your internal and external comms.
Be sure to incorporate your logo , brand color palettes and fonts into your white paper design.
For business users, Venngage’s My Brand Kit makes it easy to save your logos, brand color palettes and brand fonts for later. Then, you can easily apply them to your designs with one click.
For example, you could change the colors of this white paper template…

…to this:

Try thinking of creative ways to incorporate your branding .
This white paper design, for instance, extends the use of its signature color beyond standard headers and icons. It actually applies a transparent color overlay to the images, adding a punch of color and reinforcing its brand palette in an unexpected way:

We have plenty more white paper design tips in our post on the top 20+ white paper examples you can use for your business. Check it out here: 20+ Page-Turning White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
What is a white paper?
A white paper is a well-researched, in-depth report that discusses a problem and proposes a solution to that problem. Here’s an example:

Typically backed up with lots of data and persuasive, factual evidence, quality white papers address complex concepts or problems, making them essential for any content marketing strategy.
For more information on the origin of white papers (including why they’re called “white papers” in the first place!), read our post: What is a White Paper? 15 White Paper Examples to Get Started .
What is the purpose of a white paper?
White papers often have original research to back them up, and take a strong stance on what needs to be done to solve a problem.
In other words, white papers advocate for the best solution to a particular problem, making them authoritative by nature. Which makes sense given that they’re often used by the government, like in this example:

But as more and more businesses use white papers, their purpose has changed a little.
They’re still an authoritative source of information, but rather than just to inform or educate, white papers can also influence an audience’s decision-making process.
This marketing white paper, for example, aims to persuade businesses to market themselves effectively in order to attract talent:

Companies can also use white papers to show that their product or service can best solve their customers’ problems. Of course, they still need to back their claims with research and evidence.

A cyber security company could use this white paper to showcase their expertise and offerings in order to drum up more business.
Make sure your white paper is not only informative but also engaging!
Remember how the average human attention span has dropped to below that of a goldfish?
Even when a reader is interested in the topic of your white paper and plans to devote a good chunk of their time reading it, they may still bounce if your content is too dense (read: walls of text).
So make sure you think of your audience when you write your white paper and follow our design tips to keep them engaged.
And remember, you can create a professional, well-designed white paper using one of Venngage’s white paper templates. It’s free to get started!
How to Write and Format a White Paper: The Definitive Guide

Table of Contents
What is a white paper, use and value, how to select a white paper topic:, white paper preparation, white paper format, final thoughts.
You’re ready to compile and share your company’s deep knowledge of your industry. A white paper seems like the perfect format. It’s a useful product to highlight your company’s expertise and a valuable tool in marketing.
But, how do you transform your knowledge into white paper content?
White papers are similar but distinct from business reports. In order to write a successful one, you need to understand the difference and include key elements. This article will help you decide if a white paper is right for you, and if yes, how to prepare and produce one.
To write a white paper, thoroughly research a topic and propose a comprehensive solution in a well-structured, factual, and persuasive document.
A white paper should include: 1. Title (accurate but enticing) 2. Abstract (including the Problem Statement) 3. Background (may be detailed and technical or broad and high-level, depending on audience) 4. Solution (the ‘ta-da’ moment of the white paper) 5. Conclusion (the summary of findings) 6. References (using correct industry format)
A white paper is an authoritative document intended to inform the reader on a particular topic fully. It combines expert knowledge and research into a document that argues for a specific solution or recommendation.
The white paper allows the reader to understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision.
White papers are data-centric, text-heavy business documents. Due to a large amount of data and research, white papers are deep reads and tend to have a formal tone.
Businesses write white papers both to record expertise and to market themselves to prospective customers.
White papers are generally written for an audience outside of the business. Therefore, they are a tool to attract readers to the company by offering top-quality, industry knowledge.
However, a white paper is not a sales pitch. It sells the company by highlighting the internal expertise and valuable recommendations, not by bidding for business.
Sales Pitch: 8 Ways ABC Marketing will save money on your social media budget
White paper: Social Media Advertising: Matching marketing needs and platforms

Write an actual white paper with individual instructor guidance.
Our Advanced Business Writing Course + Coaching includes written feedback and two live coaching sessions.
Choosing the right topic is essential to have your white paper read. There are three major factors:
1. Audience
As with any business writing, your audience is your first consideration. The white paper must be written with a target reader in mind. The audience may be long-time customers familiar with the industry or new prospective buyers who are entirely new to the field.
Reflect on the reader’s pain points or major questions. Within these topics, look for ones that have not been fully investigated or the available information is out-of-date.
2. Expertise
Your white paper should match and highlight your company’s expertise.
The entire document should provide a complete investigation, including external research and internal knowledge. The business’s own know-how informs the content that is included and how it is compiled.
3. Problem-based and solution-focused
White papers should identify and address a particular problem. The problem should be relevant and timely in your field. The document may focus on issues such as common dilemmas, new trends, changing techniques, and industry comparison.
The white paper must have a proposed solution or recommendation to answer the problem. This solution is based on thoroughly examining the problem and potential solutions.
The selected topic must be comprehensively researched. Pull information from online references, industry resources, and internal documents. White papers are data-focused, so they should be supported by significant research.
There’s no hard and fast rule on citations but you need to cite any information that is not public knowledge and that you didn’t know before beginning your research. However, understand that the reader’s confidence is likely to increase with an increasing number of cited references.
Of course, all resources must come from authoritative sites. In order to write a valuable document, all research materials must be from credible, reliable sources.
Read other white papers
Are there white papers covering your topic or area already? Read them to determine the knowledge gaps and the opportunities to build on existing content. This review will also ensure that your white paper is novel instead of redundant.
Use a mind-map
It can be overwhelming to keep track of the many sources, ideas, and content involved in preparing a white paper. A helpful organizational tool is the mind-map . A mind-map allows the writer to catalog and connect the many different pieces into one visual overview.
We suggest using the free tool MindMeister to organize your content. It’s simple to use and free.
FreeMind is another alternative but some organizations don't allow it to be used since it must be downloaded.
Don't forget visual elements
When designing a white paper, the written content is most important. However, taking the time to create an aesthetically pleasing design cannot be ignored. It should be remembered that the visuals used can greatly contribute to the overall impact of your white paper. By using visual elements such as images, animations, videos, charts, and graphs that reinforce and illustrate arguments, can greatly increase clarity for the reader while making key points stand out.
White papers generally follow a standard document format. The content order may seem similar to other business reports, but there is one major difference:
A white paper places the conclusion at the end.
Many business communications, such as technical reports or proposals, place the main conclusion at the beginning of the document. This order responds to the desires of the reader and their preference in receiving the information.
In a white paper, the content and research inform the reader and increase their understanding of the problem throughout the document. The final section provides the ‘ta-da!’ moment where the reader now receives the solution which is supported by the evidence in the document.
The reader’s journey and preferences in a white paper and business report differ. The major findings follow suit.
If you’re unsure of these distinctions or are looking to improve your business writing skills, consider enrolling in our online self-paced Technical Report Writing Course (see all of our courses here ).
And, no matter the journey, the document must be easy to understand and include informative headings for easy navigation.
Choose an accurate title
A good title is essential. It should clearly indicate what the reader will learn from the white paper. It should also be enticing.
Bland title example: White paper on Law 123.4 Referencing Environmental Impact Assessments.
Enticing title example: The Rules are Changing: White Paper on the Environmental Impact Assessment Legislation Proposals in 2018
The phrase ‘white paper’ does not necessarily need to be in the title at all. Some audiences are seeking that authoritative indicator. Other readers may be scared off from valuable content because of the term. As always, think of what your audience would prefer.
The abstract offers the reader a brief overview of the white paper’s main points. It allows the reader to ensure they have found a document relevant to their needs. After reading, the reader should be able to know if they are ‘in the right place.’
Problem statement
The problem statement specifies the issue the white paper will address. The problem needs to be defined and placed into a context to ensure it’s understood by the reader.
This section provides the background information required for the audience to grasp the problem and, ultimately, the solution. The content may be detailed and technical or broad and high-level. The content depends on the reader and the problem.
If original research is completed for the white paper, the methods should be communicated.
The ‘ta-da’ moment of the white paper.
Based on the preceding information, the solution is now presented. It is developed and argued for using the gathered evidence and the expertise of the author and their company.
This section summarizes the white paper’s major findings. Recommendations based on the solution are provided.
All sources used to develop the white paper must be collected and cited in this section. It adds validity to the document. It also gives the reader content for further research. Depending on your industry, follow MLA or APA citation formats.

Write any complex document and get personal feedback on your actual business writing.
Our Advanced Business Writing Course + Coaching includes written feedback and two live coaching sessions on any document.
Writing a good white paper is not a simple task. However, the investment of time and skill can produce a valuable document that shares your company’s knowledge, contributing to overall education and progress in your industry. And, a good white paper increases business opportunities. As you develop an informational document such as a white paper, it's helpful to strengthen your writing process with our Advanced Business Writing course.
Related Articles
How to improve your business english writing skills, how to write a request for proposal (rfp) response, 8 tools to help you create a proposal [free & paid], get notified of new articles.

- Business Writing Skills (54)
- Business Grammar (52)
- Technical Writing (32)
- Business Writing Resources (26)
- Business Email Writing (17)
- Business Writing Training (12)
- Business Proposals (10)
- Business Report Writing (7)
- Business Proofreading (4)
- Sales Writing (3)
- Executive Summary Writing (2)
- Customer Support Writing (1)
- Bailey Lang (1)
- Elisabeth O'Quinn (14)
- Grace Cuddy (6)
- Haley Larsen (4)
- Kara Latz (10)
- Katie Almeida Spencer (31)
- Malcolm Stiefel (1)
- Mary Cullen (134)
- Samantha Taylor (2)
- Terrance Collins (1)
- Tom DuPuis (10)
The 2024 Ultimate Guide: How to Write and Format a White Paper
The step by step guide to succeeding with white paper marketing.
.png)
- 1 What is a white paper?
- 2. White paper examples
- 3 How to write a white paper
- 4 Mistakes a white paper should avoid
- 5 White paper Format
- 6 Gating your white papers
- 7 White paper distribution
- 8 Handling your white paper leads
- 9 Choosing the right white paper template
- 10 Final thoughts
Introduction
White papers are a popular and powerful tool for content marketers. They can be used to position your company as a thought leader and authority on a subject by presenting useful and persuasive research findings and information about your products and services, White papers can also be used as a powerful asset to generate more leads when the information is valuable enough for readers to submit their personal details in order to access your findings. This ultimate guide will teach you everything you need to make white paper marketing a formidable addition to your content marketing strategy .

1. What is a white paper?
A white paper is an in-depth report or guide about a specific topic and the problems that surround it. It is meant to educate readers and help them to understand and solve an issue.
In the world of marketing, a white paper is a long-form piece of content , similar to an eBook . The difference between the two is that white papers tend to be more technical and in depth. The facts and opinions expressed in white papers are often backed by original research or statistics that the publisher has aggregated from reliable sources. They often include charts, graphs, tables, and other ways of visualizing data.
The term "white papers" originated in England as government-issued documents. One famous example is the Churchill White Paper , commissioned by Winston Churchill in 1922.
Today, the term is most commonly applied to “deep dive” style publications. Businesses — especially in the consulting, financial, or B2B sectors — use them to communicate their organization’s philosophy on a topic, make the case for the superiority of their product, or simply to present research findings related to their field.
White papers are no less editorial than other forms of content, but the depth of research lends them an authoritative tone. For this reason, they are good candidates for promoting thought leadership .
Who uses white papers?
In the past, white papers were most often produced by governmental agencies, NGOs, think tanks, consultancies, and financial institutions that needed to present the findings of their ongoing research in a succinct format.
With the widespread growth and adoption of content marketing (the creation and distribution of non-promotional content intended to generate interest in a business and its offerings), white papers have become more common in other industries as well. Any organization that engages in content marketing can benefit from producing white papers.
Their popularity across industries is due to their versatility. While all white papers have certain elements in common, a B2B startup will use them differently than a large consultancy, and both will use them differently from a governmental organization.
Types of white papers
There are numerous types of white papers a business might publish.
- One type is the backgrounder , in which the benefits of their product, service, or methodology are explained in depth.
- Another is a problem-solution approach, which walks the audience through the solution to a problem that is common in their industry.
Other types of white papers simply present a summary of useful statistics and information about the state of a particular field or industry. An example of this would be the Content Marketing Benchmarks Budgets and Trends from the Content Marketing Institute.
Whatever type you produce , the contents of your white paper should serve to showcase your expertise in a given area. Your audience is searching for an information document, and will look for an authoritative source — a business they perceive as having in-depth knowledge of a subject.
The contents of your white paper should serve to showcase your expertise in a given area.
The purpose of a white paper
White papers enable you to build trust with your audience. They show readers that you're reliable, experienced, and adept in a given domain. When potential customers search for an informational document to help them understand a problem or opportunity they're facing, and you provide them with a quality white paper that helps, they'll turn to you again in the future.
This perception of authority can also serve to boost sales in an organization. More than half the respondents to the Eccolo Media B2B Technology Content Survey reported having read a white paper before making a buying decision. Buyers prefer to purchase from vendors they trust and see as experts in their field.
Finally, white papers are extremely useful for lead generation . The Content Preferences Survey from DemandGen found that more than three-fourths of survey respondents were willing to exchange personal information for a white paper — more than for eBooks , case studies, analyst reports , podcasts, brochures , or infographics.
With all of these potential benefits, utilizing white papers in your content marketing strategy can produce great results.
More than three-fourths of survey respondents were willing to exchange personal information for a white paper.
2. White paper examples
When you think about white papers, you probably think of PDF articles with thousands of words. But times are changing and so is the way we produce and consume content.
Nowadays, every marketing collateral (including white papers) needs to be well written, well structured, and designed for every type of visitor.
Here are some great examples of white papers doing exactly that.
This unique one-pager presenting findings from the Developers at Work Survey demonstrates how a white paper should be done. The animated, interactive data charts show off just what's possible with our embed feature.
Open white paper example #1

Privacy and the GDPR - BDO
This well-produced special edition produced by BDO and creative agency Monte Media does an incredible job of turning a conventionally dull topic into a piece of content that's engaging and comes to life.
Open white paper example #2
This white paper is a step by step guide to succeeding with content marketing.
See more white paper examples
Start creating white papers with Foleon
3. How to write a white paper
Starting a white paper can be a daunting task. So much information and research are required that it’s easy to get lost in that portion of the work and let it become a roadblock to actually putting things on paper.
Even after the writing itself has begun, white papers are tricky to do well. Simply listing statistics without some form of narrative arc is a surefire way to keep your white paper from ever being read. Luckily, following a few simple guidelines can help keep a white paper engaging and make the process of finishing it much easier.
Pick the right topic
This might seem obvious, but without a topic that resonates with your audience, your white paper is not likely to be read. When choosing the right topic, you should consider three important criteria:
- It should be something you are qualified to write about.
- It should be something your audience is interested in.
- It should address a topic around which little content has been written already and thus fill a " content gap ."
Naturally, finding a topic that brings points 1 and 2 together is vital. White papers are meant to be authoritative pieces of content based upon the author's experience and expertise, so it's important to write about what you know . But you must match this to the interests of your readers if you're to produce something they'll be eager to engage with .
Don't be afraid to crowdsource information from within your organization. If the topic of a white paper is related to engineering, why not interview an engineer or have them look over what you’ve written? The same goes for other roles. Crowdsourcing knowledge means having the power of a true expert in many fields.
Finally, filling a "content gap" will help your white paper get noticed and gain traction. By addressing a topic no one else has written about definitely, your white paper will be more likely to rank highly on search engines and even be featured elsewhere on the web.
Pro tip: You can even ask your audience what they would like to see in your upcoming white paper. You'll get ideas, make your topic more relevant, and you'll generate buzz around your content even before it's finished. In fact, we used the same method for this guide!
Define your audience
Defining your audience goes hand in hand with choosing the right topic. But moving beyond your audience's interests, it’s important to think of the kinds of people who will be reading your white paper.
- Are they fellow professionals, well versed in your subject?
- Are they likely to be reading something they are relatively unfamiliar with?
Knowing this helps establish the voice you should use and whether industry-specific jargon is appropriate. It also narrows the scope of the research you should include. It’s always important to ensure all arguments are logically sound and well supported, but the stats and information presented should be relevant to the specific audience you're targeting.
Part of defining an audience in the age of Google centers around how people will find the white paper. This means thinking about which platforms specific personas use for research and what search terms they put in. Not only will this help a white paper get found by the right people, but it is useful when outlining the white paper later on.
Optimizing for keywords is important, but remember to write for people, not for search engines. Google is getting better all the time at understanding and matching search intent with relevant content . This has become particularly important with the advent of AI-powered language models which can produce long-form content at scale.
Wrap it in a great intro and outro
Ad with all good writing, your intro should serve to captivate your audience, pique their curiosity, and entice them to read further. It's good practice to provide a brief summary of what they'll find in the white paper and to emphasize exactly what benefit they'll get from reading it.
Your outro is equally important, especially if you're using your white paper to market your products or services. You should avoid any self-promotion in the body of your white paper, but you can certainly mention your relevant product offerings and how to obtain them — perhaps using a compelling call-to-action — at the end.
Pack it with value
White papers are not meant to be advertisements for your company, and you should avoid any overt promotion. Instead, you should provide plenty of useful information that will be valuable to readers even if they don't become customers. Emphasizing value is the key to a great white paper that will get shared and widely read.
Remember, white papers serve to showcase your expertise as a company or brand in a given field. Your readers should come away having learned something useful and with the impression that you're a reliable source of expert information. As pointed out earlier, generating this kind of reputation will lead to greater business success as buyers are more likely to purchase from companies they trust.
Emphasizing value is the key to a great white paper that will get shared and widely read.
Don’t be scared of multiple drafts
No first draft is ever a finished work. Elizabeth Bishop, the renowned and Pulitzer Prize-winning poet, wrote seventeen drafts of her poem “One Art” before it was completed. It’s now considered one of the best villanelles ever written .
While a white paper may not need seventeen drafts, there will undoubtedly be points missed and logical inconsistencies in the first version. Finishing a draft, stepping away, and coming back to it with a fresh mind is the best way to ensure quality. If there’s another good writer at your company, getting another set of eyes on it is even better.
Keep it interesting
White papers should be more detailed and thorough than blog posts or eBooks . This may cause them to be more dry and formal, but this doesn't mean they have to be boring.
A trap that white papers easily fall into is using statistics as a crutch and not maintaining interest throughout. Technical as it may be, you still want your white paper to be read. To make this happen, it’s useful to borrow techniques from fiction and creative nonfiction writers.
There are lots of resources for learning about a plot, but generally, it has five parts, as illustrated in Freytag’s pyramid:
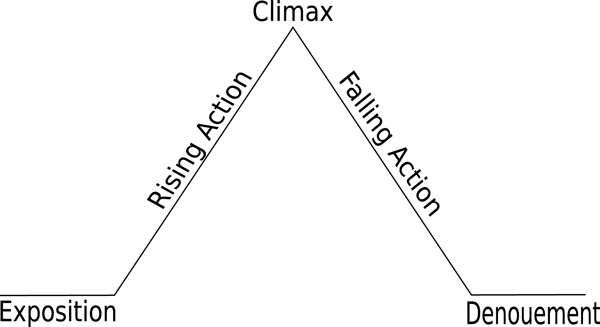
These won’t always correspond perfectly in a factual piece of writing like a white paper, but they can get you thinking about how to create and hold interest. Use those ideas to keep readers’ attention until the very end.
4. Mistakes a white paper should avoid
There are some pitfalls and common mistakes to avoid when writing a white paper. Each of these has the potential to make an otherwise stellar piece of content into a wasted effort. Here's a brief list of things to look out for.
Sounding like a sales pitch
When white papers are used as part of a marketing campaign where businesses showcase their product, a common mistake is to make them sound like a sales pitch . Don't let this happen; it will immediately turn your readers off. In a white paper, your audience is seeking unbiased, educational information that will help them, not try to persuade them. Save the sales pitches for other content, like product brochures .
Lack of adequate research
As previously mentioned, white papers should be well-researched documents. It’s true that conducting lengthy original research may be outside a marketing team’s budget, but merely including a few stats from the first page of a Google search simply won’t cut it.
Aggregating statistics and searching through scholarly work may take time, but the result will be worth it. For your white paper to achieve its intended effect, It’s important to establish your content as an authoritative source to which the audience would want to return.
Poor design
We'll go in-depth into design in the next section, but it's worth mentioning here. The written content of a white paper is what matters most, but neglecting design is a big mistake. Design makes your salient points stand out and helps the reader understand what they're reading. Using visuals (like images, animations , videos, charts, and graphs) that support your arguments is crucial.
Check out this white paper example built with Foleon!. Open the white paper
Not telling a story
White papers are informative and factual. We’ve driven that point home already. That doesn’t mean they should be boring. Backgrounders, problem-solution white papers, and research findings all have a story to tell, and the reader is far less likely to make it through the entire piece without some form of narrative to keep them engaged. Setting up a problem, elaborating on a solution, and including some type of success story is a proven formula for making any type of content more story-like.
Leaving it abstract
Because most white papers will involve sharing research findings, it can be easy to leave them in the realm of theory without explaining how to utilize those findings on a practical level. This is true more of backgrounders but can be the case with problem-solution white papers as well.
A good example is the abundant amount of content on employee engagement. Many B2B cases have covered the importance of employee engagement and the pitfalls of getting it wrong. Too little of this content goes further and gives concrete examples of what companies in specific verticals can do to alleviate the problem.
5. White paper format
Before addressing anything else, we first need to talk about the format you'll use.
A picture is no longer worth a thousand words. Today, its value is in the number of eyeballs it can keep glued to your content and the ratio of those viewers it convinces to click through to other sections of your website.
Your carefully crafted copy and painstakingly gathered statistics won’t earn those clicks on their own. The average human attention span is now less than that of a goldfish . And with 3.3 million Facebook posts, 448,800 tweets, and 149,513 emails sent every minute , competition for your readers' attention is intense, to say the least. Long form mediums like the white paper need serious sparkle just to compete.
How to format a white paper
You'll need more than just black text on a white background. Your design choices regarding things like color, typography, and the use of visuals will play a prominent role in the success of your white paper. Here are a few important principles to keep in mind for creating a quality white paper design.
Keeping mobile visitors in mind
More than 54% of internet traffic is now mobile , and web designers have adapted to this trend by creating what's known as responsive design . Before this, web pages simply scaled according to the size of a user's screen, retaining their layout. Naturally, this made most pages both unreadable and unnavigable on smaller devices.
Responsive design solved this by allowing elements on a page to rearrange, resize, or be completely hidden from view in response to the size of the screen. When a smaller screen is used, font-sizes increase, buttons become larger for touch screens, and the entire layout adjusts to make the page mobile-friendly.
But while this has become standard for web designers in a mobile-first world, producers of other digital content assets like white papers have generally not adapted . Surprisingly, most companies that offer white papers and eBooks on their websites still use PDF format .
The problem with PDFs is that they're unreadable on smaller screens . They're fixed-layout documents — they can't adjust or adapt to different screen sizes. Reading them on a mobile device requires excessive zooming and panning around, which is a terrible experience for users.
Mobile traffic is ever-increasing. If you decide to produce your white paper as a PDF , you risk excluding this vast segment of your audience. It's a design mistake that will cost you views and conversions.

See examples of responsive white papers
Emphasis and readability
Because in-depth white papers contain lots of text and visuals, as well as supplementary information like footnotes, figures, logos and copyright info, the danger is that your design becomes cluttered. Clutter accumulates before you realize it. You may choose a clean layout and color scheme, to begin with, but as you continue to add content, things can get crowded. Often, you must make tough choices about what not to include to strike the right balance between completeness and readability.
Good design makes bold choices and prioritizes important information. These choices and priorities affect layout, placement, color, font size, page order and more. Use these design elements to create emphasis on vital pieces of information. But be careful. Emphasizing too many pieces of information — or too few — will cause readers to struggle to discern what’s important.
Good design makes bold choices and prioritizes important information.
Have a look at what's trending
Bold fonts and color schemes are in. If you look at the hippest tech companies right now, you’ll see lots of pastels and color gradients. Of course, all that might change tomorrow. But still, a great way to get inspiration when you're just starting is to take a look at what design trends are currently popular.
U2's frontman, Bono, sings "every artist is a cannibal, every poet is a thief." And he's right. Good designers are always drawing inspiration from other designers. The best way to create a successful design is to spend a lot of time looking at what others are doing successfully. Use Evernote , or a bookmarking service to save white papers and other exceptional designs that you encounter for future reference.
Don’t know where to start looking? Dribbble and Behance are two networks where great designers share their latest work. They consistently have material that’s on the cutting edge of what’s trending.
Design for your audience
While trends may inspire you, it's more important to align your design with your audience and your subject matter.
- Will you be addressing suit-and-tie financial executives or blue-collar management at construction firms?
- Are you writing about changes to privacy regulations in the tech industry, or about the effects of farming on biodiversity?
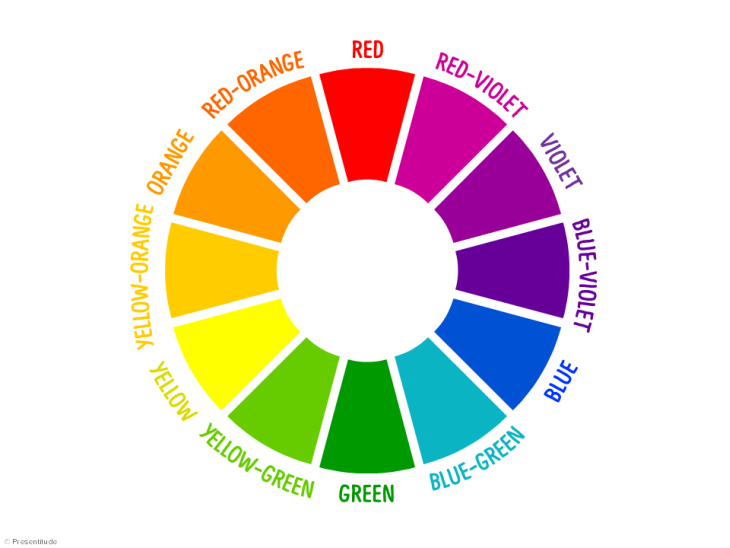
Your design should support and strengthen your topic. The colors and typography should be consistent with what you're writing about, the tone you've chosen, and the audience you've defined. Writing a white paper for a funeral parlor? Hot-pink headlines might be a bad choice. Taking color psychology into account can help you achieve the look and feel you're after.
Brush up on the basics
No prior knowledge of design? No problem.
If you don’t have a designer working with you in-house, you can still teach yourself the basics of design and check work against those principles. A big part of the battle is knowing the search terms that will get you the knowledge you need. Luckily, good primers on basic graphic design are abundant.
After doing a bit of reading, start creating. Don’t be afraid of making mistakes. If you create a white paper and don’t like the design, try to pinpoint what it is about the design that needs improvement. After the reading you’ve done, you’ll have the tools to critique your own work and the work of others. This is the best way to improve and create well designed white papers.
Choosing the right tools
At Foleon, we pride ourselves on providing a tool that makes creating responsive digital white papers easy, even for those with no prior graphic design experience.
Choosing a tool like this, which takes the guesswork out of design, will shorten the time it takes for you to produce great white papers. There is a vast ecosystem of tools out there, each of which is geared toward a different purpose and skillset. The right one will enable you as both a designer and a writer.
See how you can scale engaging content creation .
6. Gating your white papers
For most companies, lead generation and growing lists of contacts for the sales and marketing teams are important activities. Attracting visitors to your site and offering them something of value in exchange for their contact information is a proven method for filling the top of your funnel.
But for this type of inbound marketing to work, two things are needed: exceptional content that visitors are eager to acquire, and a method for gating (or walling off) that content behind a form.
Many brands skip the first part and move straight to the second. They quickly produce something mediocre and put it behind a form. This might work in the short term for generating lists, but keep in mind that users expect more from content they “pay” for. The quality of your gated content serves as an indicator of the quality of your brand will affect your ability to turn prospects into customers down the road.
So how do white papers fit into your b2b content marketing funnel ? They may act either as lead generation tools themselves or can be used to direct readers to other parts of a website that captures lead information.
What is gated content?
Walling expert content off behind a form designed to capture personal details is one of the most common techniques for generating leads. Gated content is any content that a reader cannot access until after they input some personal information, such as their name and email address. White papers and eBooks are two of the most common types of content used for this purpose.
Typically, a company will create a landing page that includes a description — and perhaps a preview — of what information readers can expect to find inside. The landing page will include a form for visitors to enter their personal information and thus gain access. After entering the required information, visitors are either presented with a download button or receive the gated content in their inbox.
There are plenty of variations on this formula, but the basic technique of providing “free” content and asking readers to “pay” by providing their personal information has been very important part of content marketing for a long time.
To gate or not to gate
While gating your best content is great for lead generation, there are some drawbacks as well. Walling off your white paper will mean it gets read by fewer people as not everyone is willing to give away their contact details.
An open-access white paper will be read by a wider audience. If it’s in-depth and authoritative, it may also do well organically and improve your search rankings. Gating it behind a form, however, will prevent search engines from indexing it.
It’s important to consider what the primary goal of your white paper is: disseminating information and gaining brand awareness or generating leads. If the latter is more important, then gating is a great option.
Semi-gating
Another variation on gated content — and one that’s growing in popularity — is semi-gating . This can give you the best of both worlds by allowing your white paper to reach a wider audience while still retaining the ability to generate leads.
Semi-gating gives readers a taste of your white paper without requiring them to give up any info. You can, for example, make the first few pages of your white paper open access, and then make visitors fill in a form to read more. This works well because digital content is so abundant and brands must offer more for free or risk visitors turning elsewhere.
Allow your white paper to reach a wider audience while still retaining the ability to generate leads.
Offering more content for free also builds trust and brand loyalty among your readers. Let them know your white papers are valuable and helpful, and they’ll be more interested in giving you their personal information. You’re also more likely to gain qualified leads if readers have a chance to sample your white paper before converting.
Of course, semi-gating doesn’t mean giving away your entire white paper. Typically, there’s at least one section of the white paper that is exclusive to those who go through the gating process. Semi-gating can help reach a wider audience, build trust and loyalty, increase lead quality, and still help you capture the contact information you need.
There’s a concept in marketing and design known as friction . Friction is anything that causes the sales process to slow down. It’s like a roadblock that makes it less likely prospects will convert, sign up, download, or purchase. It can be caused by a multitude of things including poor design, confusing navigation, subpar copy, too many form fields, and more.
Your ability to generate leads with a gated white paper will largely depend on how much friction is involved. Asking for more information than you really need is one common and unnecessary source of friction that can lead to losing potential readers.
The entire field of conversion rate optimization is geared toward removing friction — or making user interactions easier. CRO specialists make forms simpler, navigation more intuitive, and design CTAs that are more likely to be clicked. Optimizing your landing page for conversions is a vital part of any lead generation campaign.
But the reality is, asking for personal information will always be an obstacle for a large number of people. So the key here is to make the process easy and noninvasive as possible.
An excellent way to do this is by reducing the number of form fields to the bare minimum and using mid-gating to ensure your ask is timely and yields immediate value for the reader: "Fill out this form to get access to the rest of this white paper, we've saved the best for last!".
Create white papers and eBooks that integrate with your favorite CRM or marketing automation platform. Get started
7. White paper distribution
So, after following the tips in this guide, you create an engaging, informative white paper that inspires readers to take action and deepen their relationship with your company. You mid-gate (or semi-gate) it to capture readers’ information and gain valuable insight into the interests and demographics of your consumer base.
Now, you publish it on your website, sit back, and wait for your Pulitzer.
Only, the traffic never comes… Where did you go wrong? You didn't think about your white paper distribution strategy .
The importance of distribution
The internet isn’t the same as it once was. Thanks to the massive amount of content produced every day for and an ever-growing number of channels, it’s a lot harder to get noticed. Unless you’re Gabriel García Márquez back from the dead, simply writing something and posting it online doesn’t guarantee readership.
To get eyes on your white paper, you need to be smart not only about writing and design but distribution as well. Some content marketing thought leaders go so far as to claim that you should spend 20% of your time on content creation and 80% on promotion.
Distribution is all about identifying traction channels where your ideal customers consume content and making your white paper highly visible on those channels. Depending on the audience you defined in the beginning, some will be more relevant for you than others.
Social promotion
If you’re at all familiar with marketing, advertising, or online media, chances are you’re aware of how important social media is to visibility. People from all walks of life, and from all over the world, are on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Ensuring that you share your content regularly on these platforms will give you a solid base of promotion on which to build.
But it's not enough to simply write a post and tweet it into the void. Try to find communities like Facebook and LinkedIn groups where your target audience is likely to congregate. Search for relevant hashtags on Twitter and Instagram . Find subreddits relevant to your industry.
Once you’ve found your audience, it’s much easier to connect with them. If you contribute to these spaces regularly, you’ll have an easier time keeping their attention and distributing your white paper.
Influencers and earned media
Public relations isn’t what it once was; influencer marketing has taken its place as the way to get noticed by the masses.
These days, influencers — people with large, engaged followings on social media and newsletters — are better equipped to amplify your content than traditional journalists. They play a growing role in shaping public opinion and even in setting business trends . Shares from an influencer can even help you land spots in major publications the way press releases used to.
Social media is the best place to find influencers in your vertical. When you investigate the best communities in which to promote your white paper, look for the content that people are already referencing and sharing. Eventually, you’ll start to get a picture of who’s putting out content that’s getting widespread traction. These are the people whose voices can amplify your brand.
Start by interacting with them. Begin a conversation, comment on their pieces with regularity, and give them feedback on their work. There are great tools, like Voila Norbert and ContactOut , to help you quickly track down email addresses.
After building enough rapport, try offering to collaborate on future white papers or other types of content. This process can take some time because your goal here is to build a relationship.
Eventually, you can ask an influencer to share your white paper. You might even consider quoting them in the white paper itself — anything that gives them an incentive to share your work is helpful.
Pro tip: Try to find an expert in your white paper related subject and interview them. It will add value to your white paper and you'll increase the chance that the expert shares your content with his or her extensive network.
Email marketing
The jungle of online content may thicken daily, but there are a few places you can still get readers’ attention. Email distribution has stood the test of time in this regard. It provides greater ROI than social , and it shows no signs of weakening.
If the purpose of your white paper is lead generation, email marketing will not be applicable. But for boosting sales, building trust, and establishing your brand as a trustworthy source of information, it's important not to neglect your existing contact base.
Although email may not have the appealing viral possibilities associated with social media, it does have other advantages. Namely, anyone who subscribed to your email list chose to be there. This means you can expect a higher level of engagement from this audience than those who come in via other channels. Capitalize on their loyalty and engagement by encouraging contacts to share your white paper with their networks and thus multiply your distribution efforts.
This was discussed in the previous section, but it's worth mentioning again here: another big advantage of Foleon's gating features is that when your existing contacts share your white paper with their contacts, those people will be confronted with a login form that will allow you to capture their info and expand your email list further.
Going beyond the basics
The techniques discussed above are essential items in your white paper distribution toolbox. However, they’re not the only ones. The best way to distribute your white paper depends largely on your target audience and the industry to which your content speaks.
Take some time to critically evaluate and research how knowledge is shared in your industry. Every industry will be slightly different. Reaching people in these places is the best guarantee of effective distribution.
8. Handling your white paper leads
As we've discussed, white papers can serve a variety of objectives. They’re commonly used for thought leadership and to disseminate important research, relevant to a specific industry.
When it comes to content marketing, however, the most common use for white papers over the last several years has become lead generation. In chapter 6, we discussed how to bring readers to your white paper and capture their information.
Once you've properly gated your white paper and set up a solid distribution strategy, it's time to think about how you'll handle the leads that come in. If not properly tracked and nurtured, leads will quickly become cold and won't lead to increased sales for your company. So how do you follow up with leads and maximize the opportunity you’ve created with your white paper?
How to track your white paper leads
The buyer’s journey outlines the steps a person goes through, from becoming aware of a problem they have, to learning about different solutions to that problem, to eventually purchasing a product or service (hopefully yours) that solves their problem.
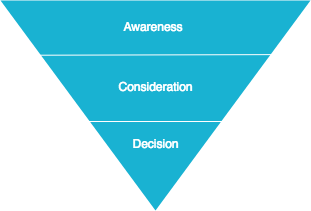
To maximize the chances your new leads become paying customers, you must take the abstract concept of a buyer’s journey and map it to your specific content ecosystem. The actions your prospects take on your website can be indicative of what stage of the journey they're in.
For example, you may see someone read a blog post on your site, then come back a day later to get your white paper, and then finally sign up for a free trial or an email list. After that, they might decide to make a purchase. As patterns begin to emerge around the journey your customers take, you'll learn what actions on your part can help them to advance.
There are many tools available to help you analyze this journey for yourself. Google Analytics is probably the most widely used. It lets you track and compile data regarding user behavior on your website. You can define goals and generate reports that will show you steps users tend to take before completing those goals.
Targeting stages of the buyer’s journey
As it becomes more clear what actions visitors take before purchasing, you'll better understand where to use your white paper in the buyer's journey.
The question you should seek to answer is, where does it provide the most value to your potential customers? Do you see greater success when accessing your gated white paper is a prospect's first interaction with your company? Or is it perhaps more effective to use it as an offer once visitors have returned a second (or third) time to your site?
You can see that white papers don't exist in isolation but act as a member of an ecosystem. The related blog posts, landing pages, emails, social messages, and follow up sequences must all be carefully orchestrated and properly timed.
This process takes practice. It takes trial and error, and you must be a keen observer of trends . However, that effort will pay off.
...white papers don't exist in isolation but act as a member of a content ecosystem.
Following up with your leads
Depending on where in the buyer's journey you use your white paper, the way you'll want to follow up with leads will be different.
- If, for example, your white paper targets the awareness stage and the leads you gather are relatively unfamiliar with your company, it might be smart to enroll them in an email sequence that highlights other pieces of content on your site such as blog posts that are relevant to the topic they showed interest in.
- If your white paper is for people in the consideration stage, and leads are already familiar with what you have to offer, you might consider following up by sending them special offers or exclusive deals — again, closely related to the topic of interest.
- If you're taking a highly targeted approach to distribution and using your white paper to generate hot leads that you think are already close to making a purchasing decision, the best way to follow up might be for a sales representative to reach out directly by phone.
This is what it means to nurture leads. By proactively keeping in touch with leads and offering them more relevant content, you maximize the likelihood of them becoming a customer.
9. Choosing the right white paper template
In 2021, Hubspot reported that 82% of marketers actively invest in content marketing. Thus, the need to create interactive content experiences that stand out amongst your competitors has never been more critical in your content marketing strategy as the volume of published white papers grows yearly.
For this reason, the visual representation of your white paper has become increasingly crucial for retaining your audience's interest. In addition to the value your white paper content provides your audience, the single most significant factor at your disposal to maintain content engagement is how your white paper is visually presented.
For whitepapers, the white paper template you opt for to present your content can significantly influence the success of your publication. The template is more than just a matter of aesthetics; it represents a strategic decision that affects user engagement, experience, and even how your brand is perceived.
Below are some factors you should carefully weigh when choosing your white paper template .
Target audience and content
The two biggest influences that will determine the selection of your white paper template are your target audience and the purpose of your content.
For example, if you create an annual report that provides Financial Services information or a research piece exploring trends in Software & IT salaries, you’ll want to use a template that easily represents data-rich elements such as tables and eye-catching statistics. In contrast, visually-oriented templates containing hi-res imagery or videos are better suited for online catalogs or digital magazines .
Think about your target audience's needs and how your template's layout can optimize your content's engagement.
Creative control with flexible features
You’ll get the most value out of your interactive white paper with a content creation platform that allows you to harness professionally designed white paper templates that are easy to use and fully customizable with a drag-and-drop interface. This will allow everyone in your team to create content quickly with no coding experience required.
Custom templates set your white paper up for success by providing a starting foundation to help guide the layout and structure of your content. Custom features allow you to design your white paper any way you like by quickly changing blocks, fonts, and colors according to your brand guidelines with the added ability to add or remove sections.
Mobile experience and device responsiveness
As of September 2023, over 55% of website traffic is from mobile devices. Therefore, it is essential that your white paper is responsive across all devices.
Most content creation platforms have integrated tools that automatically adapt your content to different screen sizes. However, to ensure the best possible user experience, you should always test your white paper on multiple devices as part of your content creation process before publishing.
Finally, website speed is one of the most significant factors influencing user experience and playing a pivotal role in organic rankings. According to section.io , 32.3% of visitors bounce from a webpage if it takes more than 7 seconds to load. Ensuring that your content creation platform and hosting services are optimized for website performance is critical in maximizing your readership when choosing your white paper template.
10. Final thoughts
Be prepared to write a lot more content.
By this point, you should have all the ingredients you need to make your white paper a rousing success. However, you’ll notice by now the reality that your white paper fits into a larger ecosystem of marketing actions and content.
In today’s business world, producing quality content is one of the best ways to get your target market's attention. But not everyone will be ready for the same piece of content at the same time.
From white papers to blog posts, to podcasts, the type of content that will drive conversions for your business is something you'll discover over time. What’s certain is that one type won't satisfy all your audience's needs. Because of that, you should be prepared to fill the rest of your buyer’s journey with other appropriate content.
This means lots of writing. There’s no way around that. It means coming up with content ideas, creating them, distributing them, and measuring their success — then rinsing and repeating. After this primer, you should be fully equipped for success writing not only white papers but whatever content you choose along your journey.
Foleon Guide
Marketing power plays.
Whether you're in content, comms, or demand gen, here are some novel tactics from Foleon’s Marketing team.

See your content in a Foleon Doc
Want to see your content in a Foleon Doc without lifting a finger? Here's your chance! Let us create a mock-up that's packed with media-rich features — just for you.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
White Paper: Purpose and Audience

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A white paper is a certain type of report that is distinctive in terms of purpose, audience, and organization. This resource will explain these issues and provide some other tips to enhance white paper content.
What is a White Paper?
Originally, the term white paper was used as shorthand to refer to an official government report, indicating that the document is authoritative and informative in nature. Writers typically use this genre when they argue a specific position or propose a solution to a problem, addressing the audience outside of their organization. Today, white papers have become popular marketing tools for corporations especially on the Internet since many potential customers search for information on the Web. Corporations use white papers to sell information or new products as solutions that would serve their customers' needs.
The Purpose of a White Paper
Typically, the purpose of a white paper is to advocate that a certain position is the best way to go or that a certain solution is best for a particular problem. When it is used for commercial purposes, it could influence the decision-making processes of current and prospective customers.
What Kind of Problems Do Readers Want to Solve?
The audience for a white paper can be the general public or multiple companies that seek solutions to their problems or needs. Typically, you will not know your audience personally, unlike when you write a recommendation report for your client. And yet, in order to persuade your audience, you need to focus on their needs. If you can address the problems that your readers want to solve, they will read your white paper for a solution. Otherwise, your white paper may not be read. It is important to emphasize your readers' interests rather than your interests, as shown in the example below:
How to Write a White Paper
#scribendiinc
Learn why white papers are a marketing must-have

A white paper is an in-depth, official, didactic document that discusses problems and how to solve them. Such papers are often used in political and business writing to instruct people and to help them make decisions. A well-written white paper can increase a company's market exposure immensely, so what are you waiting for?
What a white paper is and why it's useful
The term white paper is derived from white book , an official publication of a national government. Over time, white papers have come to refer to publications used by businesses for marketing purposes. For example, a company may publish a white paper in order to educate consumers about the benefits of a specified technology or product. The goal of a white paper is usually to describe the technology, product, or service in a way that people can easily understand. White paper documents are particularly valuable to potential customers because they provide unbiased information and analysis.
Get the word out there
White papers are distributed not only within a company, but also to other people in the same industry and to the general public. A well-written white paper serves an important educational function and uses plain language to explain complex issues in a straightforward manner.
Remember that white papers should be objective, provide adequate and appropriate detail, and be written in a clear, concise, and logical way. Overly promotional white papers have a tendency to end up in the trash bin.
Writing a white paper is not always an easy task; it often involves several contributors whose roles must be clearly defined at the outset of the project. Before attempting to write such a document, we recommend that you study your product. It is essential to explain how the product or service can be applied and why it is the best choice for customers. Furthermore, the intended audience must be properly identified, defined, and researched. There must also be agreement about the goals of the white paper and the strategies involved in writing it.
A white paper is valuable only if it contains information that the targeted audience needs and that might otherwise be difficult to find. Focusing on the needs of your audience is critical and directly affects how your white paper will be received. The more credible, unbiased, third-party information your white paper contains, the more useful it will be. You must also be able to back up any claims you make.

Tips for tackling a white paper
To help accomplish the goal of a white paper, which is to inform and persuade, consider the following:
- Provide a historical overview. It is often useful to discuss what lies behind the problem that your product or service purports to solve.
- Explain what potential customers should look for when seeking a solution to the problem. This provides you with the opportunity to promote your company.
- Provide examples. It is useful to describe situations where your solution would be especially valuable or to mention particular customers who have found success with your product or service.
The most effective white papers do not exceed 12 pages, although they should be substance heavy. Effective white papers contain a few well-organized figures and tables to help illustrate the points made, contain precise and creative subheadings, and make use of callouts and sidebars.
Format your white paper for success
Begin your white paper with an abstract informing the reader of what the document is all about. You may then discuss the problem and provide some background—but be brief! The next step is to discuss in general terms how the product or service works; only then can you explain how your product or service can solve a specific problem. This is where you will offer evidence that shows what the product or service can accomplish and why it is the best choice for the customer. Treat this portion as if you were conducting a business pitch . The last part is the conclusion, which is essentially a summary of the reasons why your product or service is the best option.
Polish your document before publishing it
Once you have written your white paper, review it for accuracy. If you have any doubts about how your white paper is organized or whether it achieves its intended purpose, send it along to our business editors for a professional opinion.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Business Plan

How to Write a Candidate Rejection Letter

How to Write a Press Release

Organizing Information for Business Writing
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Editing and Style
How to Write White Papers
Last Updated: December 26, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff . Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 749,370 times. Learn more...
A white paper is a one-to five-page document that describes a given problem and proposes a specific solution to the problem. It's commonly used in government and corporate settings. A typical white paper might list ways to meet a client's marketing needs, suggest the use of a certain product for a technical process, or identify ways to tackle municipal problems. To write a successful white paper, you must know your audience, state your problem clearly, and make a convincing and engaging argument of how to solve it. [1] X Research source
Engaging Your Audience

- For example, if your topic is community gardens, appeal to your readers as property owners and parents, as well as community decision-makers. They'll be interested in learning about the impact of gardening and local food on their property values, their children's health, and their children's education.

- If you're writing a white paper for an engineer, you should include lots of technical details and be lengthy in your descriptions.
- If you're writing for a government official, focus on policy-related implications.
- If you're writing for a corporate audience, focus on cost-effectiveness and growth potential.

- Closing the School-to-Prison Pipeline with Art
- Safer Cities through Community Gardens: A White Paper

- Student debt has grown exponentially over the past decade. Combined with the dismal job market new graduates face, their debt threatens to become the next economy-crashing bubble. Creditors and a number of economists have argued A, B, and C. However, these arguments do not address X, Y, and Z.

- After [interviewing experts, examining statistics, etc.], I became convinced that [two or three proposed solutions] do not adequately address the problem. This white paper will argue in favor of [your proposed solution] because it would [insert an objective reason here].
Discussing the Problem

- Examples of problems include "decreasing sales," "slow network speeds," or "management-employee conflicts."

- For example, a white paper on addressing climate change might discuss how hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) were once believed to be a safe replacement for chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which had produced a hole in the ozone layer. However, we now know that HFCs are actually dangerous greenhouse gases.

Arguing Your Solution

- If you're writing your paper within a corporate context, avoid mentioning your company's product at this point. Focus instead on what to expect in a solution.

Community Q&A
- Most white papers don't include footnotes or endnotes. However, it's always good practice to include a full bibliography at the end. Check with your employer as to the proper citation method (Chicago Manual, MLA, APA, etc.) to use. [10] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If this is your first white paper, check online for examples. Government and corporate websites, as well as academic databases, are full of white papers just waiting to be downloaded. You can access most of these resources for free. [11] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.uml.edu/whitepaper_style
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/professional_technical_writing/white_papers/index.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-white-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/professional_technical_writing/white_papers/organization_and_other_tips.html
- ↑ https://www-cdn.law.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/White-Papers-Guidelines.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/546/2/
About This Article

To write a white paper, start with an introduction summarizing a problem you’re dealing with, then how you propose to solve that problem. Detail possible solutions you have rejected and why you rejected them. Next, describe the problem you identified in greater depth and provide a historical overview of how it became a problem, then describe your solution in more detail. Use charts, graphs, and diagrams to back up your points and to make your paper easier to read. For advice on tailoring your paper to your audience, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Charice Smalls
Sep 7, 2020
Did this article help you?
Nancy Lyman
Apr 11, 2016
Cookie Schultz, PhD
Sep 3, 2016
Bader Alkhalili
May 31, 2016
May 31, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a White Paper?
Purpose of a white paper, how to write a white paper.
- White Paper FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Trading Strategies
What Is a White Paper? Types, Purpose, and How To Write One
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Investopedia / Michela Buttignol
A white paper is an informational document issued by a company or not-for-profit organization to promote or highlight the features of a solution, product, or service that it offers or plans to offer.
White papers are also used as a method of presenting government policies and legislation and gauging public opinion.
Key Takeaways
- A white paper promotes a certain product, service, or methodology to influence current and prospective customer or investor decisions.
- Three main types of white papers include backgrounders, numbered lists, and problem/solution white papers.
- A white paper provides persuasive and factual evidence that a particular offering is a superior product or method of solving a problem.
- White papers are commonly designed for business-to-business marketing purposes between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or between a wholesaler and a retailer.
White papers are sales and marketing documents used to entice or persuade potential customers to learn more about a particular product, service, technology, or methodology.
White papers are commonly designed for business-to-business (B2B) marketing purposes between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or between a wholesaler and a retailer. It can provide an in-depth report or guide about a specific product or topic and is meant to educate its readers.
The facts presented in white papers are often backed by research and statistics from reliable sources and can include charts, graphs, tables, and other ways of visualizing data. A white paper can communicate an organization’s philosophy or present research findings related to an industry.
Types of White Papers
A startup , large corporation, or government agency will use white papers differently. There are three main types of white papers, including backgrounders, numbered lists, and problem/solution white papers.
Backgrounders detail the technical features of a new product or service. Designed to simplify complicated technical information, they are used to:
•Support a technical evaluation
•Launch a product
•Promote a product or industry leader
Numbered lists highlight the key takeaways of a new product or service, and are often formatted with headings and bullet points such as the following familiar format:
•3 Questions to Ask
•5 Things You Need to Know
Problem/solution papers identify specific problems faced by potential customers and suggest a data-driven argument about how a featured product or service provides a solution to:
•Generate new sales
•Educate salespeople on product characteristics
•Build industry interest.
White papers differ from other marketing materials, such as brochures. Brochures and traditional marketing materials might be flashy and obvious, but a white paper is intended to provide persuasive and factual evidence that solves a problem or challenge.
White papers are commonly at least 2,500 words in length and written in an academic style.
A white paper should provide well-researched information that is not found with a simple internet search and have a compelling narrative to keep the reader's attention. The author of a white paper should:
• Research and fully define the topic.
• Create an accurate outline of information.
• Write an attention-grabbing introduction.
• Format the paper for easy reading.
• Revise and proofread.
What Is an Example of a White Paper?
All of these documents, publicly available on Microsoft’s website, focus on aspects of the company's suite of cloud services. In contrast with brochures, these white papers don’t have a clear sales pitch. Instead, they dive into relevant topics, such as cloud security, hybrid clouds, and the economic benefits of adopting cloud computing.
- An AI-First Infrastructure and Toolchain for Any Scale
- Moving your Mission Critical Mainframe Data to Azure
- Mesh and hub-and-spoke networks on Azure
- Backup and recovery overview for Azure users
- Backup and recovery overview for users new to Azure
How Have New Industries Used White Papers?
Cryptocurrencies have also been known to publish white papers during initial coin offerings (ICOs) and frequently issued white papers to entice users and "investors" to their projects.
Bitcoin famously launched a few months after the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto issued its famous white paper online in October 2008.
Why Is It Called a White Paper?
White Papers may have developed from the use of “Blue Papers” in 19th century Britain, where a Parliamentary report cover was blue. When a topic for the government was less serious, the blue cover was discarded and published with white covers. These reports were called White Papers. In the United States, the use of government white papers often means a background report or guidance on a specific issue.
A white paper is an informational document issued by a company, government agency, or not-for-profit organization to promote the features of a solution, product, or service that it offers or plans to offer. The facts presented in white papers are often backed by research and statistics from reliable sources and commonly written in one of three formats that include backgrounders, numbered lists, and problem/solution papers.
Copy Engineer. " The 3 Types of White Papers and When to Use Each One ."
Master Class. " How To Write a White Paper ."
Microsoft. " White Papers on the Cloud and Azure ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1246765443-418763aa3a7f4a059c29940b2d14779d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
How to Write a White Paper

Table of Contents
Originated in England in 1922, white papers today are one of the most popular types of content used across different industries, including business and marketing. Typically, they’re used to explore a particular subject matter related to a specific product or service and are highly targeted at generating sales leads.
Regardless of their popularity and wide usage, not every marketing content produced can be a white paper. That is why in this guide, we’ll discover what is white paper, its structure peculiarities, and its difference compared to the other content types like a college paper or a research paper, as well as provide some great ideas on making a unique article in a white paper format.
What Is a White Paper?
When you think about white papers, the first thing that comes to mind is PDF articles with thousands of words. However, society keeps evolving, and so does the content we consume today.
A white paper today is a document typically used by business professionals who want to share in-depth information concerning a specific topic. For instance, the white papers are used for sharing the marketing data, comparing different products/services/campaigns/etc., presenting the complex analysis or describing complex technology developed by a company or brand to the average consumer.
As a rule, the typical white paper is delivered in the form of a PDF document 2,000 to 2,500 words long. Because of the in-depth research, it might take weeks to research and analyze all the information to craft a salient and compelling argument. The white papers are pretty similar to academic papers since they are built in a structure of a factual, research-based document with the purpose of sharing specific facts or some technical information.
Talking about the purposes of white papers, there are different aspects of how they can be used:
- To generate more leads (for instance, the white papers can be offered in exchange for email addresses or other contact information).
- To build trust among the audience (for example, by tackling a certain problem/pain point, providing particular information on a certain topic).
- To boost sales (as an example, with the powerful data-driven content that impacts user decisions and behavior).
As you can see, white papers are really useful at present. But how can you create one?
Main to Know About the White Paper Structure
Now that you know the definition of a white paper, it’s time to figure out the main sections this type of content includes. Generally, all the white papers consist of the following sections.
A catching, original title that introduces a specific problem and is targeted at a certain audience category without mentioning the product name in it. Simply put, it should be more targeted on the potential benefits and not the feature-oriented ones.
Abstract/Executive Summary
Generally, this part will provide the direct, pithy statements of your research to engage the reader, as well as offer a clear, general summary of what your white paper is about. Regardless of the absence of details, it still must provide enough detail to satisfy readers and get them interested in the full version of your white paper.
Introduction
In this section, you should generally define the issue and provide some background words to explain why it is relevant – all this will benefit the credibility, as well as help you to find common ground with the target audience.
Problem Definition
This part should accurately identify the business problem without promoting the solutions you can offer. Make sure it’s written completely from the viewpoint of your potential customers and not the company that sells.
High-level Solution
Here, you’ll describe the list of relevant technologies available, including the ones offered by your business and competitors, for example. Try to support your arguments with specific tables, charts, or graphs to bolster your positions. This part should provide the key insights into the current state of affairs and where your solution will hit.
Solution Details
You’ll finally be able to describe your solution in detail with this part, explaining why your solution is out of competition. Strengthen your arguments with case studies or customer testimonials to show the performance of your solution and its results.
Business Benefits
Overall, that’s the most critical part of your white paper that can grab readers’ attention and provide the real statements on why your solution will work for them. As an example, that can be the ROI details, usability, speed of implementation, and many others – anything that can resolve or relieve the target customer’s pains.
This part emphasizes the benefits of a solution offered, as well as the risks it might lead without the use of a solution, by pointing out the most important things you want readers to remember.
Call to Action (CTA)
One of the most useful and powerful sections that are usually missed in many white papers. Simply put, it addresses your readers what they should do and how to do it: for instance, that can be an offer of a free trial version, free assessment, free gift certificate if you call today, etc.
Now that you know what makes the white paper different from the other formats of academic papers. Nevertheless, there are different types of white papers which organize the narrative in slightly divergent ways. That’s why our next paragraph will describe the main formats of white papers used today.
Choose the Appropriate White Paper Format
Regardless of their data-based nature, knowing the structure is not enough to learn how to write a white paper. Depending on what information you are to uncover in your academic paper, you’ll choose one of the following types of white papers:
Backgrounders
This type is used specifically to detail the technical characteristics or specifics of a new product/service. Typically, they’re designed to boost the readability of complicated and topic-specific information.
Problem-Solution Papers
That category is mainly targeted at the pain points of a certain problem or challenge that customer experiences in a related field. Here, the major goal of a white paper is to raise a data-based argument on how a product/service can resolve the problem, as well as its benefits compared to the other solutions available.
Numbered Lists
Under this type of white paper, authors can present the data as numbered lists, highlighting the key takeaways, strong sides, and benefits of a certain product/service. The main advantage of these white papers is turning the complicated topics into easy-readable and more digestible.
White Paper Topics & Structure: Best Practices
Once you’ve learned all the basics of how to write a white paper, it would also be great to get some useful insights on how to make a perfect academic work for nearly any purpose, no matter whether it’s a grading papers or the marketing content.
- Define the target topic and make research on it. Once the topic is finalized, give yourself enough time for in-depth research on it.
- Ensure the white paper explores large amounts of information, as it is a long-form document.
- Make an outline for the white paper, focusing on the target audience, specifics of your research, and the structure of your paper.
- Pay attention to the introduction of a white paper. Proofread the sentences, make a spell check and ensure it grabs your readers’ attention: focus on the most important and enticing details of your research, use exciting, active, and simple language to keep the audience focused and engaged.
- Keep in mind the focus of a white paper: to share factual, technical information. Avoid the business/brand marketing presentation voice in your content.
- Always check for plagiarism in your white papers before they’re submitted – to ensure the content is fully original and tackles a relevant problem.
- Keep your white paper in the format of a stand-alone document (typically, it is featured under an online PDF or a dedicated webpage that can be circulated independently)
All these tips seem to be clear and obvious. However, many writers today still overlook them while writing! Nevertheless, following these writing practices can significantly eliminate the delivery time and enhance the paper quality as well.
Get Your White Paper Delivered with Grademiners!
Related to the informational category of content, white papers have already become one of the most common types of document, the structure and writing specifics of which every student should know nowadays. It can deeply explore a specific topic, problem, or solution relevant to the business, which makes it one of the basic marketing tools to reach out to the general public.
Nevertheless, not everyone can create a perfect white paper right from the first attempt, especially with no inspiration or writing passion for this type of content. But you can always get professional writing assistance from the expert authors at Grademiners!
Our team has years of experience creating different types of academic papers for any industry, regardless of the educational level. So, no matter whether you’re a high-school student or a Ph. D., the service will find the best expert that ideally matches your requirements!

How Can I Make An A+ Editing Checklist For My Essay?

90 Topic Ideas For Research Paper On Feminism

9 Cause and Effect Topics for Your Essay and How to Answer Them
- Skip to Guides Search
- Skip to breadcrumb
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
- Skip to chat link
- Report accessibility issues and get help
- Go to Penn Libraries Home
- Go to Franklin catalog
Critical Writing Seminar: Craft Of Prose (Spring 2024): Researching the White Paper
- Getting started
- News and Opinion Sites
- Academic Sources
- Grey Literature
- Substantive News Sources
- What to Do When You Are Stuck
- Understanding a citation
- Examples of Quotation
- Examples of Paraphrase
- Chicago Manual of Style: Citing Images
- Researching the Op-Ed
- Researching Prospective Employers
- Resume Resources
- Cover Letter Resources
Research the White Paper
Researching the White Paper:
The process of researching and composing a white paper shares some similarities with the kind of research and writing one does for a high school or college research paper. What’s important for writers of white papers to grasp, however, is how much this genre differs from a research paper. First, the author of a white paper already recognizes that there is a problem to be solved, a decision to be made, and the job of the author is to provide readers with substantive information to help them make some kind of decision--which may include a decision to do more research because major gaps remain.
Thus, a white paper author would not “brainstorm” a topic. Instead, the white paper author would get busy figuring out how the problem is defined by those who are experiencing it as a problem. Typically that research begins in popular culture--social media, surveys, interviews, newspapers. Once the author has a handle on how the problem is being defined and experienced, its history and its impact, what people in the trenches believe might be the best or worst ways of addressing it, the author then will turn to academic scholarship as well as “grey” literature (more about that later). Unlike a school research paper, the author does not set out to argue for or against a particular position, and then devote the majority of effort to finding sources to support the selected position. Instead, the author sets out in good faith to do as much fact-finding as possible, and thus research is likely to present multiple, conflicting, and overlapping perspectives. When people research out of a genuine desire to understand and solve a problem, they listen to every source that may offer helpful information. They will thus have to do much more analysis, synthesis, and sorting of that information, which will often not fall neatly into a “pro” or “con” camp: Solution A may, for example, solve one part of the problem but exacerbate another part of the problem. Solution C may sound like what everyone wants, but what if it’s built on a set of data that have been criticized by another reliable source? And so it goes.
For example, if you are trying to write a white paper on the opioid crisis, you may focus on the value of providing free, sterilized needles--which do indeed reduce disease, and also provide an opportunity for the health care provider distributing them to offer addiction treatment to the user. However, the free needles are sometimes discarded on the ground, posing a danger to others; or they may be shared; or they may encourage more drug usage. All of those things can be true at once; a reader will want to know about all of these considerations in order to make an informed decision. That is the challenging job of the white paper author. The research you do for your white paper will require that you identify a specific problem, seek popular culture sources to help define the problem, its history, its significance and impact for people affected by it. You will then delve into academic and grey literature to learn about the way scholars and others with professional expertise answer these same questions. In this way, you will create creating a layered, complex portrait that provides readers with a substantive exploration useful for deliberating and decision-making. You will also likely need to find or create images, including tables, figures, illustrations or photographs, and you will document all of your sources.
Latin American Studies Librarian

Connect to a Librarian Live Chat or "Ask a Question"
- Librarians staff live chat from 9-5 Monday through Friday . You can also text to chat: 215-543-7674
- You can submit a question 24 hours a day and we aim to respond within 24 hours
- You can click the "Schedule Appointment" button above in librarian's profile box (to the left), to schedule a consultation with her in person or by video conference.
- You can also make an appointment with a Librarian by subject specialization .
- Connect by email with a subject librarian
Find more easy contacts at our Quick Start Guide
- Next: Getting started >>
- Last Updated: Jan 22, 2024 3:53 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.upenn.edu/c.php?g=1374611
How to Write a White Paper Properly
Writing a white paper is always a difficult job because you need to be creative, captivating, and precise. Therefore, this assignment requires a lot from the student, and your task is to be patient and diligent. So, if you want to find out how to write a white paper properly, you’ve probably come to the right place because we’re glad to help.
If you stay here, on our website, what will you get? We managed to collect the best hints, advice, and tips for writing a white paper. You will also discover something new (or not that new) about this paper’s meaning, purpose, structure, and formatting. Do you still hesitate if you know how to write a white paper properly and do it as fast as possible? Scroll down!
What is a White Paper and How to Deal with it?
Well, let’s talk about white paper meaning to be better aware of what to do when creating such a project.
Related essays:
- Symmetry in God’s Justice in Divine Comedy essay
- Migrant Culture in Contemporary Culture essay
- Does Death Scare? essay
- The Slum Residents Feeds off from Danger essay
The original white paper was meant to be used to get the important report to the ministers of government. In general, such documents are informative and authoritative. Typically, every single writer used the genre of a white paper to show the ability to argue a concrete position and/or come with a solution to the given issue.
Nowadays, it has changed a little. Now, the white paper definition takes a value of becoming the most popular tool of marketing among the others for various corporations. We can see it, especially on the Web, since there are a lot of potential clients and customers who got used to looking for information online, getting help from the Internet.
Marketing companies use white papers to merchandise new products as solutions that could serve the need of their clients. They can also simply give some new info for the loyal customers or the potential ones.
White Paper Structure: What are the Features?
One of the most important things while creating a white paper is following the paper’s structure. To help you in preparation of a great project, we are happy to present you the sections described below that must be followed while writing. Here we go:
- Title. Obviously, you want a catchy title which clearly tells about the issue you are going to solve, and that is also relevant for your target auditory.
- Abstract or General Summary. Maybe, you want to get your conclusion to the end and mention it here, but immediate grabbing of the reader’s attention is needed for a white paper. Nobody says that you have to put every single detail; simply show its summary and make the reader get to the end for the details. For now, provide him/her with the main info.
- White Paper Introduction. Describe the issue. Give your TA the background deliberation and discussion when building credibility. Try to find points of agreement with your readers and make them interested in the paper.
- Determination of the Problem (Issue). Stop selling until you define the issue. Smoothly write about a specific problem you are going to solve.
- Top-Ranking Solution. Mention and describe the technologies which are pertinent at the highest level including any other fellow methods (you’ll rebut them later). Try to maintain your personal arguments using various charts, some tables, and/or graphics. If you have to back your own words and personal position, you can quote experts in that industry. You must teach the TA on the modern level of technology.
- Solution Details. It’s time for describing your decision by including more details. You may start selling from now, but be careful and try avoiding too loud claims. Try soft approaching to the audience. Use an appropriated language for the TA of yours. It is the heart of your paper. It is possible to include some customer reviews and testimonials for supporting your personal arguments.
- Advantages of Solutions. If the previous step was your paper’s heart, this section could be called a paper’s soul. Grab the reader’s attention by providing the benefits of your suggestions. Discuss in details your own product or suggestion (whatever your topic is), tell that it is useful and that it was made according to all high standards. Show the readers that you understand their pressure points and that you can relieve them. Use testimonials to help people.
- White Paper Conclusion. It is a part of a quick summary that emphasizes your solution’s advantages and explains what can happen if the audience decides not to use the suggested product or service. A lot of readers can skip all the paper’s sections and view only this part. Imagine that the conclusion is unique and get it full of summarizing all the main points about your project and their solution.
- Call Your Readers to Action. There are a lot of papers that either lack this part or make it wrong. You need to tell the TA how they should act. The great idea is to finish the paper with the list of offers. It can be a free trial version or some gift/certificate for the reader if he/she calls today.
White Paper Format Peculiarities
The white paper format is usually similar to that of a common standard document. It can seem pretty comparable to the other reports in the business area, but for a white paper, there is one major rule that differs from the others’: white papers are formatted with the conclusions in the end. It’s different because many business companies are putting the main conclusions at the document’s beginning. In a business report and a white paper, the reader’s preferences differ. And no matter what they are looking for; the document must necessarily be easy to read and understand. It also must include informative headings. Why? For easy navigation.
White Paper Outline
Developing a white paper outline is a way for the writing process to start. The outline serves as a map to remind you about what you wanted to write about, what to mention and include. It has to ensure that information is put in the manner which is easy to follow. The described below tips provide good support for starting point:
- Don’t Skip the Part of an Outline. Obviously, it’ll take some time before the actual white paper writing. But it will save you from getting the wrong path of writing. Why? Everything’s simple. You get the plan, and you work by it.
- Make Your TA’s Needs the Target. Create a paper that’s focused on the needs of the TA, focus on their interests or/and weak points.
- Collaborate With Your Team When Creating the Outline. Make sure that every single person of your team is satisfied with the outline and is the part of its development. Let them work on the white paper too.
- Include Sections and its Subsections. It’s really important to break up your paper into different sections with subsections. This way, the writing becomes more readable and easier for the TA.
So, you have studied all of our tips and advice, and we hope our article will help you understand how to write a white paper properly, quickly, and qualitatively.
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![how to write an essay in white paper “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![how to write an essay in white paper “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![how to write an essay in white paper “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture

By Erik Hoel
Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated outputs drift across our feeds and our searches. The stakes go far beyond what’s on our screens. The entire culture is becoming affected by A.I.’s runoff, an insidious creep into our most important institutions.
Consider science. Right after the blockbuster release of GPT-4, the latest artificial intelligence model from OpenAI and one of the most advanced in existence, the language of scientific research began to mutate. Especially within the field of A.I. itself.

Adjectives associated with A.I.-generated text have increased in peer reviews of scientific papers about A.I.
Frequency of adjectives per one million words
Commendable

A study published this month examined scientists’ peer reviews — researchers’ official pronouncements on others’ work that form the bedrock of scientific progress — across a number of high-profile and prestigious scientific conferences studying A.I. At one such conference, those peer reviews used the word “meticulous” more than 34 times as often as reviews did the previous year. Use of “commendable” was around 10 times as frequent, and “intricate,” 11 times. Other major conferences showed similar patterns.
Such phrasings are, of course, some of the favorite buzzwords of modern large language models like ChatGPT. In other words, significant numbers of researchers at A.I. conferences were caught handing their peer review of others’ work over to A.I. — or, at minimum, writing them with lots of A.I. assistance. And the closer to the deadline the submitted reviews were received, the more A.I. usage was found in them.
If this makes you uncomfortable — especially given A.I.’s current unreliability — or if you think that maybe it shouldn’t be A.I.s reviewing science but the scientists themselves, those feelings highlight the paradox at the core of this technology: It’s unclear what the ethical line is between scam and regular usage. Some A.I.-generated scams are easy to identify, like the medical journal paper featuring a cartoon rat sporting enormous genitalia. Many others are more insidious, like the mislabeled and hallucinated regulatory pathway described in that same paper — a paper that was peer reviewed as well (perhaps, one might speculate, by another A.I.?).
What about when A.I. is used in one of its intended ways — to assist with writing? Recently, there was an uproar when it became obvious that simple searches of scientific databases returned phrases like “As an A.I. language model” in places where authors relying on A.I. had forgotten to cover their tracks. If the same authors had simply deleted those accidental watermarks, would their use of A.I. to write their papers have been fine?
What’s going on in science is a microcosm of a much bigger problem. Post on social media? Any viral post on X now almost certainly includes A.I.-generated replies, from summaries of the original post to reactions written in ChatGPT’s bland Wikipedia-voice, all to farm for follows. Instagram is filling up with A.I.-generated models, Spotify with A.I.-generated songs. Publish a book? Soon after, on Amazon there will often appear A.I.-generated “workbooks” for sale that supposedly accompany your book (which are incorrect in their content; I know because this happened to me). Top Google search results are now often A.I.-generated images or articles. Major media outlets like Sports Illustrated have been creating A.I.-generated articles attributed to equally fake author profiles. Marketers who sell search engine optimization methods openly brag about using A.I. to create thousands of spammed articles to steal traffic from competitors.
Then there is the growing use of generative A.I. to scale the creation of cheap synthetic videos for children on YouTube. Some example outputs are Lovecraftian horrors, like music videos about parrots in which the birds have eyes within eyes, beaks within beaks, morphing unfathomably while singing in an artificial voice, “The parrot in the tree says hello, hello!” The narratives make no sense, characters appear and disappear randomly, and basic facts like the names of shapes are wrong. After I identified a number of such suspicious channels on my newsletter, The Intrinsic Perspective, Wired found evidence of generative A.I. use in the production pipelines of some accounts with hundreds of thousands or even millions of subscribers.
As a neuroscientist, this worries me. Isn’t it possible that human culture contains within it cognitive micronutrients — things like cohesive sentences, narrations and character continuity — that developing brains need? Einstein supposedly said : “If you want your children to be intelligent, read them fairy tales. If you want them to be very intelligent, read them more fairy tales.” But what happens when a toddler is consuming mostly A.I.-generated dream-slop? We find ourselves in the midst of a vast developmental experiment.
There’s so much synthetic garbage on the internet now that A.I. companies and researchers are themselves worried, not about the health of the culture, but about what’s going to happen with their models. As A.I. capabilities ramped up in 2022, I wrote on the risk of culture’s becoming so inundated with A.I. creations that when future A.I.s are trained, the previous A.I. output will leak into the training set, leading to a future of copies of copies of copies, as content became ever more stereotyped and predictable. In 2023 researchers introduced a technical term for how this risk affected A.I. training: model collapse . In a way, we and these companies are in the same boat, paddling through the same sludge streaming into our cultural ocean.
With that unpleasant analogy in mind, it’s worth looking to what is arguably the clearest historical analogy for our current situation: the environmental movement and climate change. For just as companies and individuals were driven to pollute by the inexorable economics of it, so, too, is A.I.’s cultural pollution driven by a rational decision to fill the internet’s voracious appetite for content as cheaply as possible. While environmental problems are nowhere near solved, there has been undeniable progress that has kept our cities mostly free of smog and our lakes mostly free of sewage. How?
Before any specific policy solution was the acknowledgment that environmental pollution was a problem in need of outside legislation. Influential to this view was a perspective developed in 1968 by Garrett Hardin, a biologist and ecologist. Dr. Hardin emphasized that the problem of pollution was driven by people acting in their own interest, and that therefore “we are locked into a system of ‘fouling our own nest,’ so long as we behave only as independent, rational, free-enterprisers.” He summed up the problem as a “tragedy of the commons.” This framing was instrumental for the environmental movement, which would come to rely on government regulation to do what companies alone could or would not.
Once again we find ourselves enacting a tragedy of the commons: short-term economic self-interest encourages using cheap A.I. content to maximize clicks and views, which in turn pollutes our culture and even weakens our grasp on reality. And so far, major A.I. companies are refusing to pursue advanced ways to identify A.I.’s handiwork — which they could do by adding subtle statistical patterns hidden in word use or in the pixels of images.
A common justification for inaction is that human editors can always fiddle around with whatever patterns are used if they know enough. Yet many of the issues we’re experiencing are not caused by motivated and technically skilled malicious actors; they’re caused mostly by regular users’ not adhering to a line of ethical use so fine as to be nigh nonexistent. Most would be uninterested in advanced countermeasures to statistical patterns enforced into outputs that should, ideally, mark them as A.I.-generated.
That’s why the independent researchers were able to detect A.I. outputs in the peer review system with surprisingly high accuracy: They actually tried. Similarly, right now teachers across the nation have created home-brewed output-side detection methods , like adding hidden requests for patterns of word use to essay prompts that appear only when copied and pasted.
In particular, A.I. companies appear opposed to any patterns baked into their output that can improve A.I.-detection efforts to reasonable levels, perhaps because they fear that enforcing such patterns might interfere with the model’s performance by constraining its outputs too much — although there is no current evidence this is a risk. Despite public pledges to develop more advanced watermarking, it’s increasingly clear that the companies are dragging their feet because it goes against the A.I. industry’s bottom line to have detectable products.
To deal with this corporate refusal to act we need the equivalent of a Clean Air Act: a Clean Internet Act. Perhaps the simplest solution would be to legislatively force advanced watermarking intrinsic to generated outputs, like patterns not easily removable. Just as the 20th century required extensive interventions to protect the shared environment, the 21st century is going to require extensive interventions to protect a different, but equally critical, common resource, one we haven’t noticed up until now since it was never under threat: our shared human culture.
Erik Hoel is a neuroscientist, a novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Define your topic and research it. Before you start writing your white paper, you will need to define the specific topic you're writing about. Your particular topic may be a product or new business initiative. You'll substantiate your argument about why this topic is important with hard research.
Format and finalize: Format your white paper to make it visually appealing and reader-friendly. Use appropriate headings, subheadings, fonts, and spacing. Consider adding a table of contents for easy navigation. Finally, proofread your document one last time before publishing or sharing it.
If your instructor asks you to write a white paper, follow their instructions regarding length. Be prepared to write a minimum of five pages. Note that images should be used as supplements to the written word, not substitutes. In other words, one page of content is 300 words on average; if your assignment requires 10 pages, you should write ...
This article will help you decide if a white paper is right for you, and if yes, how to prepare and produce one. To write a white paper, thoroughly research a topic and propose a comprehensive solution in a well-structured, factual, and persuasive document. A white paper should include: 1. Title (accurate but enticing)
1. What is a white paper? A white paper is an in-depth report or guide about a specific topic and the problems that surround it. It is meant to educate readers and help them to understand and solve an issue. In the world of marketing, a white paper is a long-form piece of content, similar to an eBook.The difference between the two is that white papers tend to be more technical and in depth.
The Purpose of a White Paper. Typically, the purpose of a white paper is to advocate that a certain position is the best way to go or that a certain solution is best for a particular problem. When it is used for commercial purposes, it could influence the decision-making processes of current and prospective customers.
Add a text box and choose to write with AI. In the prompt window, explain the main topic of your white paper, what you're planning to cover and ask it to write an outline for you. If you're writing from scratch, use high-level headings for the critical sections of your content, and then branch out into subheadings.
Format your white paper for success. Begin your white paper with an abstract informing the reader of what the document is all about. You may then discuss the problem and provide some background—but be brief! The next step is to discuss in general terms how the product or service works; only then can you explain how your product or service can ...
8. Edit and proofread. Once you've completed your white paper, edit and proofread to ensure the utmost accuracy. You can either have a professional editor or writer go over your draft, or you can edit your document yourself. Be sure to edit for not only spelling and grammar but also for content.
If you're writing for a government official, focus on policy-related implications. If you're writing for a corporate audience, focus on cost-effectiveness and growth potential. 3. Choose a catchy title. Make it attention-grabbing but not over-the-top. Mention or allude to your problem.
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
Purpose - Readers use a white paper to learn, in detail, about a policy problem and its possible solutions. Leaders may use the white paper to inform their decision-making. For authors, the white paper is an opportunity to inform leaders and constituencies about a problem and to have an impact on how the problem is addressed through policy.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay. General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body. The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis.
White Paper: A white paper is an informational document, issued by a company or not-for-profit organization, to promote or highlight the features of a solution, product, or service. White papers ...
Ensure the white paper explores large amounts of information, as it is a long-form document. Make an outline for the white paper, focusing on the target audience, specifics of your research, and the structure of your paper. Pay attention to the introduction of a white paper.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
For example, if you are trying to write a white paper on the opioid crisis, you may focus on the value of providing free, sterilized needles--which do indeed reduce disease, and also provide an opportunity for the health care provider distributing them to offer addiction treatment to the user. However, the free needles are sometimes discarded ...
White Paper Introduction. Describe the issue. Give your TA the background deliberation and discussion when building credibility. Try to find points of agreement with your readers and make them interested in the paper. Determination of the Problem (Issue). Stop selling until you define the issue.
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Meanwhile, while fewer faculty members used AI, the percentage grew to 22% of faculty members in the fall of 2023, up from 9% in spring 2023. Teachers are turning to AI tools and platforms ...
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture. Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter. Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated ...