

Literature Review & Research Skills Guide: Use Google Scholar
- Introduction
- What is a Literature Review?
- Your research topic
- Topic Analysis
- Developing a Search Strategy
- Preliminary Reading
- Use Primo Search
- Use Google Scholar
- Use Journal Databases
- Sage Research Methods
- Managing your literature review
- Evaluation & Critical Appraisal
- Referencing
Using Google Scholar
Google Scholar allows you to locate resources such as articles, theses and books.
Unlike Primo Search, which is set to search the Library's holdings only, Google Scholar searches beyond Charles Sturt University Library and will include resources that are not available to you.
Set up Library Links to access the Library's online resources using these instructions .
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is a search engine for scholarly information. It makes available information records that its 'robots' find or that an author, university repository, or journal publisher have chosen to list. It is useful because it searches across many resources and returns many resource types, including journal articles and book chapters, though it is important to note that results are not always from academic-quality sources and it will return both results you do have access to via Charles Sturt Library, and those you do not.
The video to the right provides you with an overview of Google Scholar, including how to change the settings so that it shows you which search results are held in Charles Sturt Library's collection:
Citation Searching
You can see who has cited a resource from the results page in Google Scholar. Once you've located a source you like, you can view who has cited that resource by clicking on the 'Cited by x' link beneath the item record.

You will then see all of the resources that have cited the original item. Keep in mind that this does not include every resource that has ever cited the original item - it only includes those resources that are indexed in Google Scholar.

In the Google Scholar Search box at the top of the page, enter some keywords that you identified in your topic analysis
- Use the left hand menu to limit by date.
- Have you set your library links? Select the Find it at CSU links to access articles in our collection.
- You may notice that there is a mix of topics, including health, education etc. Add more keywords to your search to narrow it down.

Search Google Scholar
Using Google effectively
Citation searching
- << Previous: Use Primo Search
- Next: Use Journal Databases >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 11:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.csu.edu.au/education-research

Charles Sturt University is an Australian University, TEQSA Provider Identification: PRV12018. CRICOS Provider: 00005F.
How to Use Google Scholar for Research: A Complete Guide

To remain competitive, Research and Development (R&D) teams must utilize all of the resources available to them. Google Scholar can be a powerful asset for R&D professionals who are looking to quickly find relevant sources related to their project. With its sophisticated search engine capabilities, advanced filtering options, and alert notifications, using Google Scholar for research allows teams to easily locate reliable information in an efficient manner. Want to learn how to use google scholar for research? This blog post will cover how to use google scholar for research, how R&D professionals can exploit the potential of Google Scholar to uncover novel discoveries related to their projects, as well as remain apprised of advancements in their area.
Table of Contents
What is Google Scholar?
Overview of google scholar, searching with google scholar, finding relevant sources with google scholar, exploring related topics, evaluating sources found on google scholar, staying up to date with google scholar alerts, faqs in relation to how to use google scholar for research, how do i use google scholar for research, can you use google scholar for research papers, why is it important to use google scholar for research, are google scholar articles credible.
Google Scholar is a powerful research platform that enables users to quickly find, access, and evaluate scholarly information. It provides easy access to academic literature from all disciplines, including books, journal articles, conference papers, and more. Google Scholar offers researchers a wide range of tools for searching the web for the relevant content as well as ways to keep up with new developments in their field.
Google Scholar i s an online search engine designed specifically for finding scholarly literature on the internet. Google Scholar provides access to a vast array of scholarly literature from renowned universities and publishers around the world, simplifying the process of locating relevant material on any subject. In addition to its comprehensive indexing capabilities, Google Scholar also includes advanced search features such as citation tracking and alert notifications when new results are published in your chosen areas of interest.
The platform makes it a breeze for users to traverse multiple facets of a given topic by providing them with an array of different filters they can apply when conducting searches – these include things such as author name or publication date range; language; type (e.g., book chapter vs journal article); source material (e.g., open access only); etc Moreover, many results found through this platform come equipped with full-text PDFs available for download – so you don’t have to worry about pesky paywalls blocking your path while doing research.

Google Scholar is an invaluable resource for research and development teams, offering quick access to a wealth of scholarly information. Utilizing the proper search approaches, you can quickly locate precisely what you need by employing Google Scholar. Let’s look now at how to refine your results with advanced search techniques.
Key Takeaway: Google Scholar is a powerful research platform that gives researchers an array of tools to quickly locate, access and evaluate scholarly information. It provides users with advanced search features such as citation tracking and alert notifications, along with easy-to-apply filters for narrowing down results by author name or publication date range – making it the go-to tool for any researcher looking to cut through the noise.
Exploring with Google Scholar can be a useful approach to quickly locate applicable scholarly material. There are several different strategies that can be used to get the most out of this powerful tool.
Basic google scholar search strategies involve entering a few keywords or phrases into the search bar and then refining your results using filters, sorting options, and related topics. This method is ideal for those who require a rapid search of information without needing to expend an excessive amount of time researching exact terms, especially for those unfamiliar with searching databases such as Google Scholar. It’s also useful for those who don’t have a lot of experience in searching databases like Google Scholar.
Advanced search strategies allow users to take advantage of more sophisticated features such as Boolean operators , wildcards, and phrase searches. These tools make it easier to narrow down results by specifying exactly what you’re looking for or excluding irrelevant sources from your search results. Advanced searchers should also pay attention to synonyms when crafting their queries since these can help broaden the scope of their searches while still providing relevant results.
Finally, refining your results is key in order to ensure that you only see sources that are truly relevant and authoritative on the topic at hand. Filters such as date range, publication type, language, author name, etc., can help refine your query so that only high-quality sources appear in your list of results. Sorting options provide users with the ability to prioritize documents, enabling them to quickly locate relevant materials without needing to review a large number of irrelevant ones.
Utilizing Google Scholar can be advantageous for swiftly finding pertinent research materials, but it is essential to comprehend the search strategies and filters at hand in order to maximize your searches. By understanding how to identify keywords and phrases, explore related topics, and utilize sorting options and filters, you can ensure that you are finding all of the relevant sources for your research project.
Key Takeaway: Google Scholar is a great tool for quickly locating relevant research sources. Advanced searchers can make use of Boolean operators, wildcards and phrase searches to narrow down their results while basic search strategies such as entering keywords into the search bar work just fine too. Additionally, refining your results with filters and sorting options helps ensure that you only see high-quality sources related to your topic at hand.
Locating applicable materials via Google Scholar can be a challenging endeavor, particularly for those unfamiliar with the research process. To facilitate the research process, employing various strategies can expedite and refine the search for relevant sources through Google Scholar.
Making use of keywords and phrases is a powerful method for finding pertinent sources on Google Scholar. It is important to identify key terms related to your topic or research question so you can narrow down the results. Additionally, using quotation marks around multiple words will allow you to get more precise results as it searches for exact matches instead of individual words within a phrase.
Exploring related topics helps provide additional context when researching on Google Scholar. This includes looking at previous studies conducted on similar topics or areas of interest, which provides further insight into potential sources available from other researchers’ work in the field. Utilizing tools such as co-citation analysis also allows users to explore how different authors have been cited together over time by providing visualizations based on their connections and relationships with each other through citations.
Utilizing filters and sorting options such as language, date range, publication type, etc., enables users to refine their search even further so they only receive results that match their specific criteria. Sorting options like relevance ranking or date published also make it easier for them to find what they need without having to sift through hundreds of irrelevant documents manually. By utilizing these features effectively, researchers can save valuable time when searching for relevant sources in Google Scholar since all the information they need will already be organized accordingly right away, saving them an hour’s worth of manual labor.
By utilizing Google Scholar, research teams can quickly and easily find relevant sources for their projects. With the next heading, we will explore how to evaluate these sources for credibility and authority.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing the right keywords and phrases, exploring related topics, and utilizing filters are essential techniques for finding relevant sources quickly with Google Scholar. By taking advantage of the available features, you can swiftly and accurately pinpoint documents that meet your criteria.
To assess the reliability and authority of each source, consider factors such as the publication’s reputation, author credentials in the field, and when it was published. To do this, look for publications from reputable journals or authors with credentials in the field. Furthermore, consider when the source was issued – more modern pieces may be more pertinent and exact than older ones.
It is advantageous to be aware of the distinct kinds of publications that can appear in search results, such as scholarly articles, books, conference papers, and dissertations; each offering various degrees of precision and accuracy depending on their intent and target audience.
For example, a book chapter may provide an overview of a topic while a peer-reviewed journal article will contain more detailed information backed up by research evidence. Similarly, conference papers are typically shorter summaries of research projects whereas dissertations offer comprehensive coverage including methodology and analysis results. Understanding these differences helps you identify which sources are most suitable for your needs when conducting research using Google Scholar.
Evaluating sources found on Google Scholar is an important step to ensure the credibility and accuracy of research results. By setting up alerts with Google Scholar, you can stay informed about new research findings and manage your subscriptions accordingly.
Maximize your research efforts with Google Scholar. Assess credibility & authority, pay attention to the date of publication & understand different types of publications. #ResearchTips #GoogleScholar Click to Tweet
Google Scholar is an invaluable tool for staying up to date with the latest research in your field. With its alert feature, you can easily set up notifications so that you’re always on top of new developments. Setting up alerts and managing them effectively will help ensure that you never miss a beat when it comes to relevant information.
Begin your research by utilizing Google Scholar’s sophisticated search features such as keyword and phrase searches, sorting results according to relevance or date of publication, and excluding unrelated sources. Once you’ve identified the most pertinent topics related to your research interests, set up alerts for each one by clicking on the bell icon in the upper right corner of the page. This will allow Google Scholar to send notifications whenever new content is published about those specific topics.
When setting up alerts in Google Scholar, make sure that they are tailored specifically toward what matters most to you – this could include certain authors or journals whose work has particular relevance to your own research projects. You can also adjust how often these alerts are sent (daily or weekly) depending on how frequently new material is being published within those fields of study. Additionally, if there are any other sources outside of Google Scholar which may contain useful information (such as blogs), consider adding their RSS feeds into your alert system too so that all relevant updates appear in one place.
Finally, don’t forget to manage existing alerts regularly; this means keeping track of which ones are still relevant and deleting any no longer needed from time to time (this helps keep clutter down). Additionally, try experimenting with different combinations/filters within each alert until you find what works best for keeping yourself informed without getting overwhelmed with notifications.
Key Takeaway: Utilize Google Scholar to stay up-to-date on the latest research in your field – create tailored alerts for specific topics and authors, adjust frequency of notifications as needed, and manage existing alerts regularly. Stay ahead of the curve by gathering all pertinent news in one location.
Google Scholar is a great tool for conducting research. It provides access to millions of scholarly articles, books, and other sources from across the web. Google scholar works by entering keywords related to your topic into the search bar at the top of the page to quickly locate relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources from across the web. Then narrow down your results using filters such as date range or publication type.
Finally, skim through the abstracts and full texts to pinpoint useful information for your research project.
Yes, Google Scholar is a great resource for research papers. It offers access to an extensive range of scholarly literature from journals, books, and conference proceedings. The search engine provides a convenient way to locate the most recent research in any area by entering keywords or phrases.
Advanced capabilities, such as citation monitoring, can be utilized to track the latest citations of one’s own or others’ work.
Google Scholar is an invaluable tool for research, as it provides access to a vast range of scholarly literature from around the world. It allows researchers to quickly and easily search through millions of publications and journals in order to find relevant information.
Google Scholar also offers the ability to trace connections between different works, allowing researchers to stay abreast of recent developments in their field. With its user-friendly interface, Google Scholar makes researching easier than ever before.
Yes, Google Scholar articles are credible. They provide access to a wide range of academic literature from reliable sources such as peer-reviewed journals and conference proceedings. Expert scrutiny has been conducted to guarantee the accuracy and excellence of the articles before they are put up on Google Scholar. Additionally, each article includes information about its authorship and citation count which can help readers assess their credibility further.
Google Scholar provides a convenient way to uncover pertinent material, assess the quality of these sources with ease, and be informed about novel advancements in your area through notifications. Thus, R&D supervisors should know how to use google scholar for research. Also, R&D supervisors considering utilizing Google Scholar for investigation ought to recall that this apparatus should not supplant customary techniques, for example, peer survey or manual searching; rather it should supplement them.
With its powerful search capabilities and ability to keep researchers informed about their fields of interest, using Google Scholar for research can save time while providing more accurate results than ever before.
Unlock the power of research with Cypris . Our platform provides rapid time to insights, enabling R&D and innovation teams to quickly access data sources for their projects.
Similar insights you might enjoy

Gallium Nitride Innovation Pulse

Carbon Capture & Storage Innovation Pulse

Sodium-Ion Batteries Innovation Pulse
- Research Guides
Literature Review Tips in Education
- Google Scholar
- Literature Reviews
- Identifying Seminal/Core Sources
- Finding Scholarly Journal Articles
Limitations and Advantages of Google Scholar
- Assessing Research Impact/Metrics
- Staying Current
- Theses and Dissertations
Google Scholar can provide another source for locating scholarly articles for your literature review. To ensure a comprehensive literature search, always use Google Scholar along with other databases specific to your discipline.
Keep these pros and cons in mind when using Google Scholar:
Google offers these features:
- the ability to search using one simple search box
- the ability to cast a wide search across several different subject areas
- useful for locating "grey literature" (for example conference proceedings; dissertations; items in university repositories )
- an excellent tool for locating unique search topics
- an excellent tool for locating an article by title or a part of a citation
- a way to find related articles using the "Cited by" feature
Potential limitations of Google Scholar:
- Covers many different subject areas and will not be as comprehensive as a subject specific database
- Google does not specify criteria for inclusion of "scholarly" materials
- It is not easy to sort or filter results as easily as a database. Cannot narrow by peer-review, by discipline or by full-text content.
- Includes articles from questionable/predatory publishers
- Advanced search is not as sophisticated as in databases.
- It is not a fulltext database. Use the link through your library website. If fulltext is not available, request the article the your library's interlibrary loan/RACER service.
- << Previous: Finding Scholarly Journal Articles
- Next: Assessing Research Impact/Metrics >>
Stand on the shoulders of giants
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions, from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other web sites. Google Scholar helps you find relevant work across the world of scholarly research.

How are documents ranked?
Google Scholar aims to rank documents the way researchers do, weighing the full text of each document, where it was published, who it was written by, as well as how often and how recently it has been cited in other scholarly literature.
Features of Google Scholar
- Search all scholarly literature from one convenient place
- Explore related works, citations, authors, and publications
- Locate the complete document through your library or on the web
- Keep up with recent developments in any area of research
- Check who's citing your publications, create a public author profile

Disclaimer: Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
- Privacy & Terms
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Literature Review in Research (RRL Example)
What is an RRL in a research paper?
A relevant review of the literature (RRL) is an objective, concise, critical summary of published research literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article. In an RRL, you discuss knowledge and findings from existing literature relevant to your study topic. If there are conflicts or gaps in existing literature, you can also discuss these in your review, as well as how you will confront these missing elements or resolve these issues in your study.
To complete an RRL, you first need to collect relevant literature; this can include online and offline sources. Save all of your applicable resources as you will need to include them in your paper. When looking through these sources, take notes and identify concepts of each source to describe in the review of the literature.
A good RRL does NOT:
A literature review does not simply reference and list all of the material you have cited in your paper.
- Presenting material that is not directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with “A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y” and simply listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good RRL DOES:
- Present a brief typology that orders articles and books into groups to help readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions about a research topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your area of research
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous research indicates about a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the background of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
How long is a review of the literature for a research paper?
The length of a review of the literature depends on its purpose and target readership and can vary significantly in scope and depth. In a dissertation, thesis, or standalone review of literature, it is usually a full chapter of the text (at least 20 pages). Whereas, a standard research article or school assignment literature review section could only be a few paragraphs in the Introduction section .
Building Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to conceive of a literature review is to think about writing it as you would build a bookshelf. You don’t need to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, you can take the pieces that other researchers have cut out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your own “books”—that is, your own study methods, results, and conclusions.
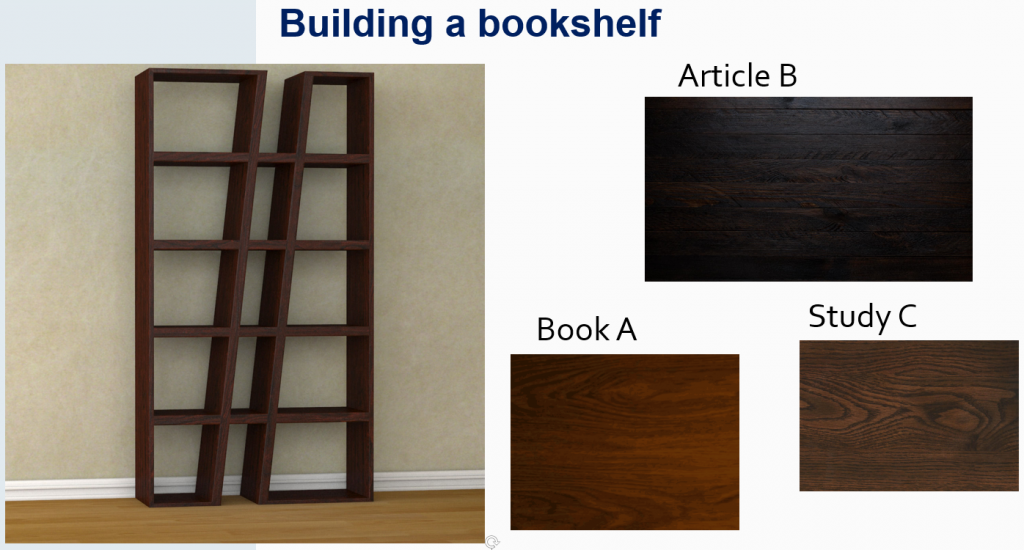
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review (RRL) are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the most important elements that a literature review provides.
Historical background for your research
Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a small way. Providing a historical background also demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make sure to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your work.
The current context of your research
Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, issues, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly being updated by new work, you can show where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
A discussion of relevant theories and concepts
Theories and concepts should provide the foundation for your research. For example, if you are researching the relationship between ecological environments and human populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connection to contextualize your study. If your study asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this direction.
Definitions of relevant terminology
In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. But if you present a term that is obscure or context-specific, you should define the meaning of the term in the Introduction section (if you are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature being reviewed.
Description of related relevant research
Include a description of related research that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work. You can use your literature review as evidence of what works, what doesn’t, and what is missing in the field.
Supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related research establishes your area of research as reputable and shows you are building upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews can differ in structure, length, amount, and breadth of content included. They can range from selective (a very narrow area of research or only a single work) to comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
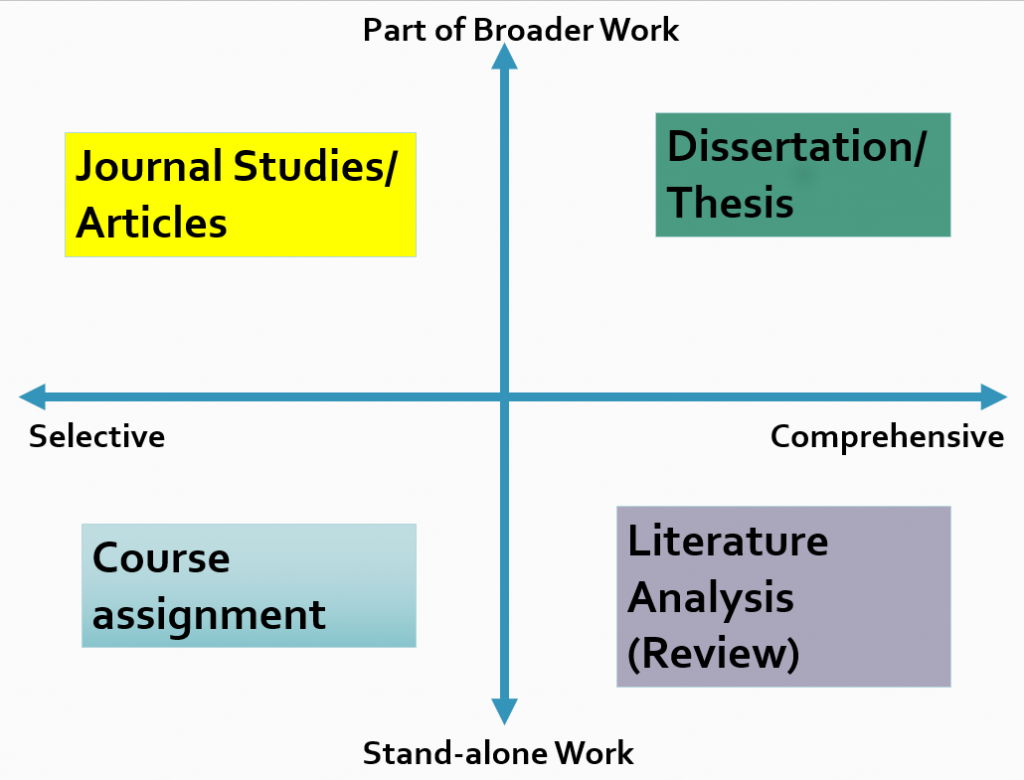
- A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work. It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the study; such a literature review is usually included in the Introduction section (but it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion section ).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand as a separate work—in this case, the entire article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Literature Reviews Found in Academic Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles (studies and surveys) and stand-alone literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study’s theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the structure of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest background information about a topic first and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale , finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often indistinguishable from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-alone literature review
The literature review published as a stand-alone article presents and analyzes as many of the important publications in an area of study as possible to provide background information and context for a current area of research or a study. Stand-alone reviews are an excellent resource for researchers when they are first searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a “review article” refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors’ own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms “Literature Review” or “Review of the Literature” in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

How to Write a Literature Review in 6 Steps
So how do authors turn a network of articles into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not usually a linear process—authors often go back and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their study. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the current work. This also means you will not be writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it before, during, and after your study is complete.
Here are some steps that will help you begin and follow through on your literature review.
Step 1: Choose a topic to write about—focus on and explore this topic.
Choose a topic that you are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers will find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient research conducted for a review. This will help you find the “sweet spot” for what to focus on.
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called “the literature.”
Step 3: Analyze the network of information that extends or responds to the major works in your area; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to identify intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the material that will be most useful to your review.
Step 4: Describe and summarize each article—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your study.
Determine 2-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; take notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to the topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given study, perhaps some of the main concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and then write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that introduce a study, these can be relatively short. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this information might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond to and/or confirm those sections in your own study. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or show a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are important to include in your literature review. In addition, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings will be valuable to review here.

Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5 but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the “golden thread” that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn’t have before reading your literature review. Make sure you know where to put the research question , hypothesis, or statement of the problem in your research paper so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions you want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your literature review will not only cover publications on your topics but will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps you will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your research and you can turn a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.
Literature Review (RRL) Examples
Because creating sample literature reviews would take too long and not properly capture the nuances and detailed information needed for a good review, we have included some links to different types of literature reviews below. You can find links to more literature reviews in these categories by visiting the TUS Library’s website . Sample literature reviews as part of an article, dissertation, or thesis:
- Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
- Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context (Martina Donnelly)
Sample stand-alone literature reviews
- Literature Review on Attitudes towards Disability (National Disability Authority)
- The Effects of Communication Styles on Marital Satisfaction (Hannah Yager)
Additional Literature Review Format Guidelines
In addition to the content guidelines above, authors also need to check which style guidelines to use ( APA , Chicago, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might have for how to structure such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals’ “Guide for Authors” pages. Additionally, use one of the four Wordvice citation generators below, choosing the citation style needed for your paper:
Wordvice Writing and Academic Editing Resources
Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure to receive professional proofreading services , including paper editing for your academic work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal.
See our academic resources for further advice on references in your paper , how to write an abstract , how to write a research paper title, how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter , and dozens of other research writing and publication topics.

Get started with research
- Choose and develop your topic
- Develop a search strategy
- Learn about peer review
- Search in Discovery
- Search in Google Scholar
Searching in Google Scholar
Search in google scholar @ rru - a video tutorial.
- Search in Library databases
- Keeping a search log
- Authority is constructed and contextual
- How to spot fake news
Google Scholar is the scholarly version of the search engine, and a good tool to search for scholarly literature in. In addition to scholarly literature, it also contains publicly available government documents, reports from NGOs and corporations, theses and dissertations from universities all over the world, and more.
Google Scholar is a great place to begin your research, because it searches for literature across every corner of the Internet, across disciplines, sources, and types of information, and will help you explore your topic in an even broader sense than Discovery might. It also uses a different algorithm than Discovery, so you will see different results on the first page- which is why it's a good idea to try the same search for both and see what comes up!
The downside of Google Scholar is that it does not have many filtering options, including a peer-reviewed filter. You'll have to investigate whether a source is actually credible. See our Evaluate Sources page in this guide for more.
RRU Library has made it possible for you to find scholarly material in our collection through Google. It is important to access Google Scholar from the RRU Library homepage to ensure you find our subscribed full text. Use the link for Google Scholar @ RRU from the “Find” box on the library homepage.
Watch the video below for a short tutorial and example of how to use Google Scholar.
Google Scholar @ RRU provides a way to broadly search for scholarly literature across many disciplines and sources, and find full-text articles to which the RRU Library subscribes.
Click to read the full video transcript
Google Scholar is a search tool that allows you to search for scholarly literature. Google Scholar is a good place to start your research or to find a specific journal article. Google Scholar will help you broadly explore your topic area because it searches across disciplines, sources, and types of information.
RRU Library has made it possible for you to find scholarly material in our collection through Google. It is important to access Google Scholar from the RRU Library homepage to ensure you find our subscribed full text. Use the link for Google Scholar @ RRU from the “Find” box on the library homepage at library.royalroads.ca. For example, a search for “disaster preparedness technology” will retrieve a number of articles that include a “Full text @ RRU” link. Click the “Full-text @ RRU” link next to the search result to authenticate with your RRU username and password.
To explore your topic further, try out the “Related articles” or “Cited by” features for each search result. The “Cited by” link will retrieve a list of articles that have referenced the article from your original search results. Click the quotation mark under the search result to view an APA-formatted citation for the article. Keep in mind that citations from Google Scholar should be treated as a first draft. Be sure to check all your citations and references for completeness and accuracy before submitting your work, and remember to make sure your citation follows the edition of APA that you have been instructed to use.
If you don’t see the “Full text @ RRU” link, let us know. The linking to our collection is not always accurate, so we may have the item you need even if Google says we don’t. Also, we can obtain articles that are not in our library collection through our interlibrary loan service. Request help from our staff via the Ask the Library link on our library homepage.
For more information, check out our Google Scholar resource guide .
- << Previous: Search in Discovery
- Next: Search in Library databases >>
- Last Updated: Jan 25, 2024 4:01 PM
- URL: https://libguides.royalroads.ca/getstartedwithresearch
Google Scholar
Using Google Scholar with your HarvardKey allows you to make the most of provided links, granting access to full text available through Harvard Library subscriptions.
Google Scholar can quickly surface highly cited peer-reviewed articles, abstracts, books, patents, scholarly web pages, and more.
Explore Google Scholar
Connect Google Scholar To Your Library Access
Connecting Google Scholar to your Harvard Library access is a good way to make sure you get access to articles that Harvard Library subscribes to.
Here's how:
- Go to Google Scholar and sign in to your Google account
- Look for the menu options
- Go into the settings and select "Library links"
- Type in Harvard and select: Harvard University - Try Harvard Library
- Deselect the box for WorldCat if shown
- Save your preferences
- Search your topic and look for the "Try Harvard Library" links to the right of the articles. This link should take you to Harvard's access to that item
Google Scholar Tips
- Like Google, Google Scholar allows searching of metadata terms, but unlike Google, it also indexes full text.
- Choose the default search or select “Advanced search” to search by title, author, journal, and date.
- For more advanced researchers, it is possible to specify phrases in quotation marks, enter Boolean queries, or search within fields.
- You may also create an account to set up your author profile or sign up for alerts.
- In settings, you may elect to limit your search by language and show citation import links.
- Results are returned in relevance-ranked order, generally favoring entries when search terms appear in document titles and prioritizing documents with larger citation counts.
Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France, Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
- Marco Pautasso

Published: July 18, 2013
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
- Reader Comments
Citation: Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol 9(7): e1003149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Editor: Philip E. Bourne, University of California San Diego, United States of America
Copyright: © 2013 Marco Pautasso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149.g001
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
- 1. Rapple C (2011) The role of the critical review article in alleviating information overload. Annual Reviews White Paper. Available: http://www.annualreviews.org/userimages/ContentEditor/1300384004941/Annual_Reviews_WhitePaper_Web_2011.pdf . Accessed May 2013.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 7. Budgen D, Brereton P (2006) Performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Proc 28th Int Conf Software Engineering, ACM New York, NY, USA, pp. 1051–1052. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500 .
- 16. Eco U (1977) Come si fa una tesi di laurea. Milan: Bompiani.
- 17. Hart C (1998) Doing a literature review: releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE.
- 21. Ridley D (2008) The literature review: a step-by-step guide for students. London: SAGE.
Advanced search
Saved to my library.


Start your free trial
Arrange a trial for your organisation and discover why FSTA is the leading database for reliable research on the sciences of food and health.
REQUEST A FREE TRIAL
- Research Skills Blog
Google Scholar: a review of literature examining its effectiveness as a search tool
By Dr Helena Korjonen on 08-Nov-2021 12:15:10

By Helena Korjonen, PhD Postdoctoral Researcher, Sustainable Food Practices, University of Luxembourg
Google Scholar (GS) is the top search engine used by those who are looking for scholarly content 1 . There are many reasons for this, not least that it feels familiar 2 , 3 . However, a review of the literature reveals that there are significant limitations to its effectiveness.
Lack of curation
The i nternet is full of ‘scholarly’ content, information, and data in various formats and of various quality. As John Naisbitt said , “We are drowning in information , but starv ed for knowledge”
When Google Scholar trawls the i nternet to seek out scholarly content, it does not assess it. It does not try to make sense of it for researchers in a logical indexed structure. And, unlike many trusted curated tools 4 , Google Scholar does not have transparent indexing guideline s that defin e what they collect, and why they collect it and make it available.
Recent research shows that Google Scholar is “unsuitable as a primary review for resources” 5 . Other research argues that Google Scholar has flaws and lacks technological features to enable systematic searching. As a result, it fails to adhere to several FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable) and cannot be classed as a professional searching tool 6 .
Google Scholar is not a curated controlled database. Content is harvested automatically.
Whilst there are some advantages to this, for example in the retrieval of grey literature 7 , there are also significant disadvantages.
Search results rankings
Research has shown that Google Scholar results can be dated. This presents an issue when most people don’t go beyond the first page of results when searching for papers.
The citation count of an article is a major factor in the Google Scholar results ranking 8 , 9 . This benefits publications from high Impact Factor sources, which are cited or linked to extensively around the Internet.
Unfortunately, new papers have what’s called a citation lag, and older papers are cited more often 10 . Newly published papers may be retrieved by GS, but they will be further down the results list and you may not see them.
P aper s can also be manipulated into a higher rank than it ‘deserves’ by placing words in titles or abstracts to increase recall or manipulate citing data 3 .
Should you need to include multi-lingual items in your search, there is a definite bias in Google Scholar towards English-language content. Documents published in languages other than English are relegated to positions that make them virtually invisible 8 .

Replicating your search
It is nearly impossible to replicate a search in GS, to retrieve the same references again. For this reason, it’s recommended to carefully document a search done in Google Scholar for full transparency 6 . That can be extremely time consuming.
References are often dropped unknowingly from GS 5 , 11 , 12 and you won’t even know the ones that might be missing 1 .
Using your results
In Google Scholar, once you have the results, it does not allow you to see beyond 1,000 records or to download more than 20 references to your bibliographic tool at a time. Most curated databases allow you to run your search, save it, download the results to your tool and revisit it.
How to search more effectively
IFIS has published a guide called Best Practice for Literature Searching . This provides guidance on where to search; how to formulate research questions and evaluate results. Click here to access the guide
(Image Credit: Kaitlyn Baker and Solen Feyissa at Unsplash )

- Gardner T, Inger S. How readers discover content: Trends in reader behaviour from 2005 to 2021. Renew Consultants. 2021; 17. Available from: https://renewconsultants.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/How-Readers-Discover-Content-2021.pdf
- Hemminger BM , Lu D , Vaughan KTL , Adams SJ . Information seeking behavior of academic scientists . Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology . 2007 ; 58(14): 2205 - 2225. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20686
- Georgas H . Google vs. the library: Student preferences and perceptions when doing research using Google and a federated search tool . portal: Libraries and the Academy . 2013 ; 13(2): 165 - 185.Available from: https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2013.0011
- Halevi G, Moed H, Bar-Ilan J. "Suitability of Google Scholar as a source of scientific information and as a source of data for scientific evaluation—Review of the literature. ." Journal of Informetrics. 2017; 11(3): 823-834. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.06.005
- Gusenbauer M, Haddaway NR. "Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta‐analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources." Research Synthesis Methods 2020; 11(2): 181-217. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1378
- Boeker M, Vach W, Motschall E. Google Scholar as replacement for systematic literature searches: Good relative recall and precision are not enough. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13(1):1-2. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-131
- Haddaway NR, Collins AM, Coughlin D, Kirk S. The role of Google Scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PloS One. 2015; 17;10(9): e0138237. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138237
- Beel J, Gipp B. Google Scholar's ranking algorithm: The impact of citation counts (an empirical study). Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science, RCIS 2009; 439–446. Available from: http://doi.org/10.1109/RCIS.2009.5089308
- Rovira C, Codina L, Guerrero-Solé F, Lopezosa C. Ranking by relevance and citation counts, a comparative study: Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, WoS and Scopus. Future Internet. 2019 Sep;11(9):202. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/fi11090202
- Khare R, Leaman R, Lu Z. Accessing biomedical literature in the current information landscape. Biomedical Literature Mining. 2014; 11-31. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0709-0_2
- Nicholas D, Boukacem‐Zeghmouri C, Rodríguez‐Bravo B, Xu J, Watkinson A, Abrizah A, Herman E, Świgoń M. Where and how early career researchers find scholarly information. Learned Publishing. 2017; 30(1): 19-29. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/leap.1087 .
- Jamali HR, Asadi S. Google and the scholar: The role of Google in scientists' information‐seeking behaviour. Online Information Review. 2010 Apr 20.. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/14684521011036990 .

- FSTA - Food Science & Technology Abstracts
- IFIS Collections
- Resources Hub
- Diversity Statement
- Sustainability Commitment
- Company news
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use for IFIS Collections
Ground Floor, 115 Wharfedale Road, Winnersh Triangle, Wokingham, Berkshire RG41 5RB
Get in touch with IFIS
© International Food Information Service (IFIS Publishing) operating as IFIS – All Rights Reserved | Charity Reg. No. 1068176 | Limited Company No. 3507902 | Designed by Blend

Research Basics: Find Articles Using Google Scholar
- Understanding the Assignment
- Choosing a Research Topic
- Refining a Research Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- Deciding What Types of Sources You Will Need
- Types of Sources
- Search Techniques
- Find Books & eBooks This link opens in a new window
- Choose a Database / Find Articles
- Find Articles Using the EBSCO Articles tab
- Find Journals
- Find Websites using Google
- Find Articles Using Google Scholar
- Find Government Documents This link opens in a new window
- Find Statistics This link opens in a new window
- Interlibrary Loan This link opens in a new window
- How to evaluate your sources This link opens in a new window
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources This link opens in a new window
- Popular vs. Scholary This link opens in a new window
- Wheel of Sources
- Incorporate Sources into Your Research Paper
- Paraphrasing
- Voice Markers
- Using Source Material to Develop/Support an Argument
- Reasons to Cite Your Sources
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Learning Checks
- Open Access Educational Resources
- Research Help
Ask a Librarian
Chat with a Librarian
Lisle: (630) 829-6057 Mesa: (480) 878-7514 Toll Free: (877) 575-6050 Email: [email protected]
Book a Research Consultation Library Hours

Connect Google Scholar to the BenU Library's Collection
1. starting in google scholar, choose settings..

2. Choose Library Links. Search “Benedictine” and check the boxes. Search "Worldcat" and check the box. Click Save.

You're done! Now when you search in Google Scholar, your results page will include BenU Library links along the right.

Search Google Scholar
Google Scholar promotes itself as a resource that provides one-stop shopping for scholarly literature. It searches across many disciplines and covers a wide variety of resources, including journal articles, theses, books, abstracts, and more. Although Google Scholar is aimed at the academic community, it uses a very broad definition of "scholarly literature."
It is important to realize that not everything in Google Scholar is peer reviewed.
Try a search:

Tutorial: Using Google Scholar
Remember to evaluate websites for reliability and accuracy before you use them in your research assignments.
- << Previous: Find Websites using Google
- Next: Find Government Documents >>
- Last Updated: Feb 2, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.ben.edu/research-basics
Kindlon Hall 5700 College Rd. Lisle, IL 60532 (630) 829-6050
Gillett Hall 225 E. Main St. Mesa, AZ 85201 (480) 878-7514
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
Advanced search
Saved to my library.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
In the Google Scholar Search box at the top of the page, enter some keywords that you identified in your topic analysis. Use the left hand menu to limit by date. Have you set your library links? Select the Find it at CSU links to access articles in our collection.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Google Scholar Library Links. To see links to BenU Library subscription content in your Google Scholar search results: Go to Google Scholar > Settings > Library Links. Search " Benedictine ". Check the boxes. Click Save and you're done! Google Scholar Library Links Tutorial. This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through the quick setup process.
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Key Takeaway: Google Scholar is a great tool for quickly locating relevant research sources. Advanced searchers can make use of Boolean operators, wildcards and phrase searches to narrow down their results while basic search strategies such as entering keywords into the search bar work just fine too. Additionally, refining your results with ...
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other ...
To ensure a comprehensive literature search, always use Google Scholar along with other databases specific to your discipline. Keep these pros and cons in mind when using Google Scholar: Google offers these features: the ability to search using one simple search box. the ability to cast a wide search across several different subject areas.
1. Identify relevant literature: The first and foremost step to conduct an RRL is to identify relevant literature. You can do this through various sources, online and offline. When going through the resources, make notes and identify key concepts of each resource to describe in the review.
In Google Scholar, when a research topic is searched, a list of publications is created. The default setting lists the most relevant publications first and can be changed to list the most recent publications first. For each article, a "Cited by" link is provided. Clicking on that link takes the reader to an article's "cited by" list.
Tips on how to write a review of related literature in research. Given that you will probably need to produce a number of these at some point, here are a few general tips on how to write an effective review of related literature 2. Define your topic, audience, and purpose: You will be spending a lot of time with this review, so choose a topic ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court ...
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study. This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called "the literature.".
Google Scholar is a great place to begin your research, because it searches for literature across every corner of the Internet, across disciplines, sources, and types of information, and will help you explore your topic in an even broader sense than Discovery might. It also uses a different algorithm than Discovery, so you will see different ...
Like Google, Google Scholar allows searching of metadata terms, but unlike Google, it also indexes full text. Choose the default search or select "Advanced search" to search by title, author, journal, and date. For more advanced researchers, it is possible to specify phrases in quotation marks, enter Boolean queries, or search within fields.
Google Scholar 5. Ketcham CM, Crawford JM (2007) The impact of review articles. Lab Invest 87: 1174-1185 . View Article Google Scholar 6. Boote DN, Beile P (2005) Scholars before researchers: on the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation.
Please show you're not a robot ...
Research has shown that Google Scholar results can be dated. This presents an issue when most people don't go beyond the first page of results when searching for papers. The citation count of an article is a major factor in the Google Scholar results ranking 8, 9. This benefits publications from high Impact Factor sources, which are cited or ...
It searches across many disciplines and covers a wide variety of resources, including journal articles, theses, books, abstracts, and more. Although Google Scholar is aimed at the academic community, it uses a very broad definition of "scholarly literature." It is important to realize that not everything in Google Scholar is peer reviewed.
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.