
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding General Ledgers in Accounting
In the world of accounting, the general ledger holds a special place. It is the backbone of financial record-keeping, providing a comprehensive view of a company’s financial activities. Understanding how the general ledger works is crucial for anyone involved in accounting, from small business owners to seasoned professionals.
Understanding the General Ledger in Accounting
The general ledger is a fundamental component of accounting that plays a crucial role in tracking and managing a company’s financial transactions. It serves as a comprehensive record of all the financial activities and provides valuable insights into the financial health of the business.
Exploring the Importance of Ledger Accounts
At its core, the general ledger is a collection of ledger accounts, each representing a specific aspect of the company’s finances. These accounts can be compared to individual chapters in a financial storybook, where each chapter focuses on a particular asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
By categorizing financial transactions into these accounts, businesses can effectively monitor and analyze their financial performance. It allows them to make informed decisions, identify trends, and evaluate the impact of various financial activities on the overall financial position of the company.
Think of a ledger account as a bank statement for a specific aspect of a company’s finances. It records all incoming and outgoing money related to that aspect, providing a clear picture of the inflow and outflow of funds. This level of detail enables businesses to have a granular understanding of their financial activities and helps in identifying areas of improvement or concern.
Managing Finances with Sub-Ledgers
In some cases, the general ledger may become too large or complex to manage efficiently. That’s where sub-ledgers come into play. Sub-ledgers are like specialized branches of the general ledger, focusing on specific accounts or business functions.
For example, a business may have a separate sub-ledger for accounts receivable, accounts payable, and inventory. This division allows for easier tracking and analysis of specific financial activities. Sub-ledgers roll up into the general ledger, providing a consolidated view of the company’s overall financial picture.
By utilizing sub-ledgers, businesses can streamline their financial management processes and gain a deeper understanding of specific areas of their operations. It enables them to have a more detailed analysis of their accounts, identify any discrepancies, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Mastering the Art of Double-Entry Bookkeeping
Double-entry bookkeeping is the foundation of the general ledger. It ensures accuracy and integrity in financial recording by requiring each transaction to have an equal and opposite effect on different accounts.
This accounting method follows the principle that every debit must have a corresponding credit, maintaining the balance between assets, liabilities, and equity. For example, when a company sells a product, it records the sale as revenue in one account and the corresponding increase in a customer’s accounts receivable in another account.
By adhering to the principles of double-entry bookkeeping, businesses can maintain the accuracy of their financial records and ensure that their financial statements provide a true representation of their financial position. It also facilitates the identification of errors or discrepancies, making it easier to rectify them and maintain the integrity of the financial data.
In conclusion, the general ledger, with its ledger accounts, sub-ledgers, and double-entry bookkeeping, forms the backbone of accounting. It provides businesses with a comprehensive and detailed view of their financial activities, enabling them to make informed decisions, track their financial health, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
A Practical General Ledger Illustration
The general ledger is a fundamental tool in accounting that plays a crucial role in organizing and categorizing financial transactions. It serves as a comprehensive record of a company’s financial activities, providing a detailed account of all transactions.
Distinguishing Between General Ledger and General Journal
While the general ledger and general journal are both important accounting tools, they serve different purposes. The general journal is where transactions are first recorded, providing a chronological record of all financial activities. Each transaction is documented with details such as the date, description, and amounts involved. This chronological order allows for a clear and accurate representation of the sequence of events.
The general ledger, on the other hand, categorizes these transactions into specific accounts. It serves as a central repository for all the individual accounts, such as cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and various expense and revenue accounts. Each account in the general ledger contains a running balance that reflects the cumulative effect of all related transactions.
This categorization and organization of transactions in the general ledger enable businesses to track and analyze their financial data efficiently. It provides a clear overview of the company’s financial position and allows for accurate reporting and decision-making.
Comparing General Ledger and Trial Balance
One useful tool for verifying the accuracy of the general ledger is the trial balance. The trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, showing the debit and credit balances of each account. It ensures that the total debits equal the total credits, providing a check on the accuracy of the recorded transactions.
By comparing the total debits and credits, a business can quickly identify if there are any errors or imbalances in their accounting records. This reconciliation process ensures the integrity of the general ledger and the financial reports generated from it. It serves as a critical step in the overall accounting process, allowing businesses to identify and rectify any discrepancies before finalizing their financial statements.
Decoding General Ledger and Balance Sheet Differences
While the general ledger provides a detailed account of a company’s financial transactions, the balance sheet summarizes the financial position at a specific point in time. The balance sheet draws information from the general ledger to present a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
By analyzing the balance sheet, investors, lenders, and stakeholders can assess a company’s financial health and make informed decisions. It provides valuable insights into the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. The accuracy and reliability of the balance sheet heavily rely on the accuracy of the general ledger.
The general ledger acts as the backbone that supports the balance sheet, ensuring that the information presented is accurate and up-to-date. It provides the necessary details and supporting documentation for each account, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial position.
In conclusion, understanding the general ledger is essential for anyone involved in accounting. It is the key to accurate financial recording, analysis, and reporting. By exploring the importance of ledger accounts, managing finances with sub-ledgers, and mastering the art of double-entry bookkeeping, individuals can gain a solid foundation in accounting practices.
Moreover, by understanding the differences between the general ledger and general journal, comparing the general ledger with the trial balance, and decoding the relationship between the general ledger and the balance sheet, individuals can uncover the intricacies of financial reporting. This knowledge empowers businesses to maintain accurate financial records, make informed decisions, and present reliable financial statements.
So, dive into the world of general ledgers and unlock the power of accurate financial management. Discover the endless possibilities that come with a well-organized and meticulously maintained general ledger.
Related Posts

Motivational Quotes on Hard Work to Inspire Your Success

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Email Account for Your Needs

The Ultimate Guide to Responsive Website Templates in 2023
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- CA : 1001 Wilshire BlvdLos Angeles, CA 90017
- NY: 1178 Broadway, 3rd Floor #3067, New York, NY 10001
- +1 (888)-333-0992

- Accounting & Bookkeeping
- Ecommerce & Online Business
- How it Works
- Calculators
- General Ledger 101: Terms, Types, and Templates for Better Accounting
- Ledger Labs, Inc.
- Bookkeeping

- November 20, 2023
A general ledger is a company’s financial command center, where all the penny that comes in and goes out is recorded thoroughly. Frankly, from purchases to bill payments, people consider it more as the heartbeat of a business’ financial operations.
But what exactly is it? And why should you even care about it? The reasons are many. Read along to find out all the questions you’ve ever had about the GL.
What is a General Ledger and why is it important?
A General Ledger is a record of a company’s total financial accounts. However, the general ledger definition is much larger than just record keeping.
Why? Because there are multiple accounts recorded in a GL, and all of them are independently vital. The accounts usually recorded in the general ledger are:
- Liabilities
- Income or Revenue
These are the essential components that you need for efficient financial management.
There is just another thing you should know about. People often confuse between subledger vs general ledger. While they share the same last name, “ledger”, it doesn’t mean they have identical meanings. It’s quite the opposite, actually.
While a subledger is a comprehensive record of particular transaction types , a general ledger is a detailed overview of an organization’s financial standing and key performance.
Speaking of record keeping of transactions, we will take a slight detour here to look at GL codes.
What is a GL code?
A General Ledger or GL code is a unique alphanumeric string assigned to every financial entry in an organization’s ledger.
Consider this: Your business’ financial transactions are stored in a library. In this case, a GL code acts as the library call number.
That means it has a unique tag attached, which tells you where a specific book belongs and helps you find precisely what you are looking for. That “call number” is what a General Ledger Code is.
General ledger codes are typically used in accounting for classifying and recording every business transaction. These help enterprises record information about purchases, sales, and other transactions.
What else? GL codes show essential information, including debit or credit by location. An example would give you a clearer image. Let’s say there’s a number that reads “GL 531100”. In this case, 5 represents expense transactions, 53 would be operating supplies, 531 is federal supplies, and 5311 refers to office supplies.
Need further help with GL codes?
Talk to gary, our accounting whiz, what are the terms of a general ledger .
To understand a general ledger accounting, you need to understand these nine basic terms and their meanings.
So, here are the key nine terms of a general ledger:
- Accounts : The solo record for each type of asset, liability, revenue, equity and expense.
- Debits and Credits : This is a dual-entry system of accounting that describes an increase or decrease in accounts.
- Chart of Accounts (COA) : You can think of COA as an index to your financial books. This is an extensive list of all the services in the general ledger, usually organized by divisions and departments.
- Journal Entries : This is where you store individual records of every transaction. You’ll find all the vital information from the date to the accounts involved.
- Posting : This procedure helps transfer the details from a journal entry to the accounts of a general ledger.
- Trial Balance : This is where you list all the ledger accounts alongside respective debit or credit balances for verifying total debits equal to total credits.
- Fiscal Year : This is the calendar, a 12-month accounting period, that governments and businesses use for financial budgeting and reporting.
- Balance Sheet Accounts : These comprise assets (things the company owns), liabilities (things the company owes), and equity (owner’s share).
- Income Statement Accounts : This is where you record operational transactions, including revenue and expenses.
The above terms can be seen in general ledger example that we have added for you.
Notice how the general ledger encompasses all the data required for the 4 types of financial statements : income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement and statement of equity.
Exploring the different types of General Ledgers
The only way to maintain a comprehensive financial record system is through understanding what general ledger accounting actually is. Further, by understanding the types of General Ledgers we can decide which ones we need.
So, what types of GLs do you need to be aware of? Well, here they are:
1. Traditional General Ledger
This is more like the God of all ledgers because it has been part of accounting for decades now. This is where you keep an eye on transactions manually, entering debits and credits by hand or simple computer programs.
2. Accounts Payable Ledger
This is basically a subset of the general ledger and focuses on the penny your company owes to its suppliers. Know what is accounts payable here in detail.
3. Accounts Receivable Ledger
Converse of the accounts payable ledger, this is where you keep track of the money customers owe your company. This helps big time in predicting future revenue.
4. Tax Ledger
Just as the name suggests, it’s all about taxes. This can help you keep track of all tax-related transactions, ensuring compliance and accuracy.
5. Asset Ledger
From multiple office equipment to patents, the Asset Ledger is where you keep a record of all assets. The best part? This stores everything between depreciation, disposals, and asset management.
6. Expense Ledger
With an expense Ledger, you get a transparent picture of where exactly your money is going. That is because an expense ledger exclusively focuses on keeping a robust record of all the costs incurred by your business.
General Ledger Templates
By now, you would have known that a general ledger is a detailed record of all your financial transactions and account balances. Regarding financial management, a general ledger template can be your ultimate secret ingredient that solves most of your accounting problems.
But what makes an excellent general ledger template?
From customizable and specific to printable and reusable, a template can reduce a solid percentage of your tasks.
This is what general ledger entries should have:
- Account number (if applicable)
- Account name
- Beginning account balance
- Transaction type
- Customer, vendor and employee name in case applicable
- Debit and credit columns
- Description
Download your customizable General Ledger Template and instantly streamline accounting process!
What is a general ledger reconciliation process .
Now this is where we take you a step further into understanding the general ledger.
Simply put, just as much as knowing what a GL is, is essential, understanding what is general ledger reconciliation is equally important. Get ready because you are about to get a comprehensive rundown on GL reconciliation.
General Ledger Reconciliation is a process accountants use widely to verify the accuracy of account balances stored in a company’s general ledger. This is where you compare the ledger’s contents with the source documents, such as:
- Third-party Data
- Audit reports, bank statements, among other supporting papers
As you would have guessed, reconciliation aims to recognize and rectify discrepancies in the general ledger. Besides preventing errors and discrepancies, it can stop fraud and offer top-notch financial records for cash flow management and better decision-making.
If that’s not enough assurance, we don’t know what is! Truly speaking, nothing can beat the importance of a GL. Furthermore, let’s take a look at best practices of general ledger management that you should keep in mind.

5 Best Practices for General Ledger Management
As we said earlier, GL is the foundation of an organization’s financial reporting system. But, if you don’t know what effective GL management is, you’re one step away from making a big wrong decision. But don’t worry, we’re here for you.
We’ve curated a list of best practices you should definitely go through for managing a general ledger effectively:
1. Get a Clear Chart of Accounts
An organized chart of accounts offers a framework for classifying financial data and maintaining it properly. But remember to review and update it to ensure it aligns with the latest business operations. More clarity on chart of accounts and its types awaits here!
2. Perform Regular Journal Entries
Make it a habit to post journal entries to reflect all financial transactions regularly, including but not limited to revenue, expenses, and asset/liability adjustment.
3. Host Monthly Reconciliation
You must reconcile all General Ledger accounts with external sources, including bank statements, credit card statements, and customer or vendor invoices. The only reason why regular reconciliations are essential is because they help you rectify any discrepancy, avoiding errors that could accumulate with time.
4. Schedule Audits Periodically
This is where you should get an independent auditor to help you conduct periodic audits of the GL to verify whether all data is accurate.
5. Establish Data backup and Security measures
It is very important to have robust data backup and security processes to ensure all sensitive information is safe and not at all in jeopardy.
Reconciliation can done monthly, quarterly, or yearly. However, we usually recommend that you get it done monthly since it helps catch issues early.
Legal and Compliance Considerations in the U.S.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002 is a landmark legislation that substantially affected corporate governance and practices related to financial reporting in the U.S. It now has particular implications for general ledger maintenance, focusing more and more on accurate financial records.
This emphasis on accuracy ensures that a strong GL management system can:
- Indicate accurate transaction recording
- Establish internal controls ( SOX Section 404 ) for proper authorization, duty segregation, etc.
- Transparent document processes
- Address unusual transaction
Significance of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP acts as the framework to prepare financial statements that are primarily reliable and comparable across different organizations. Adhering to it ensures that the general ledger reflects the company’s financial standing properly, as per the accepted accounting principles.
Bottom Line
Summing up, we can say that a general ledger is basically a GPS. Just as a GPS guides you through unknown places, GL acts as the compass for your business. Simple, right?
From recording every financial transaction to identifying potential pitfalls, it has a solution you need to know. It is more like the backbone of your organization.
Why? Mainly because it gives you a roadmap that helps you make informed decisions. There’s good news if you’ve learned a thing or two reading this. It’s that we have more answers to some of the top questions!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a general ledger account?
A general ledger account, or GL account, is one of the basic elements of financial accounting. It indicates specific groups of financial activity, including assets, liabilities, and revenue/expenses.
2. What does a general ledger look like?
A general ledger almost resembles a T-shaped account with entries on debit and credit sides. While debits show an increase in assets or expenses, credits indicate a decrease in assets (or, often, a boost in liabilities or revenue).
3. What is general ledger reconciliation?
General ledger reconciliation is where you compare the balances of GL accounts with external sources, like bank statements, customer invoices, etc. This process is excellent for identifying errors or discrepancies between the general ledger and the external source.
4. What is the purpose of a general ledger?
The primary purposes of a GL include:
- Tracking financial transactions
- Preparing financial statements
- Maintaining full accuracy
- Ensuring regulatory compliance
- Helps analysis of financial data.
5. What is the general ledger in accounting? The general ledger, or GL, is the central bank of information for organizations. It is an accounting system that stores financial transactions, like revenue, assets, expenses, and liabilities. It is mainly used to create financial statements.
6. How to record employee retention credit in the general ledger?
The recording of Employment Retention Credit (ERC) is the GL is based on the Accounting method put in place. However, the general approach is when you create a separate GL account for the ERC. Besides, the credit is recorded as a reduction in payroll expenses. The corresponding debit entry is made to a tax receivable or deferred tax liability account.
Don't forget to share the knowledge
Get a free consultation, blog categories, related posts.
Our Services

Accounting & Bookkeeping Services
Accurate and timely accounting and bookkeeping to maximize ROI and spur growth.

- Controller Services
Build failproof processes that help you keep track of financials, compliances and more.

Virtual CFO Services
Make solid data-backed decisions, reduce costs and achieve consistent growth.

Tax Preparation and Tax Planning
The most thorough, efficient, and cost effective tax services you can get.

NetSuite Accounting
Connect with an expert team that will plan, implement, and deliver NetSuite migration, set up and operation.
Share the Knowledge
About author.
Instant Chat
Chat with our accountant instantly
Call our toll free number for more insights
Schedule a Meeting
Book no-frills meeting with our experienced accountants
Get immediate reply within a few hours from our accounting team
Subscribe to our newsletter
We publish fresh and power-packed insights every week on multiple platforms. Subscribe to our newsletter and get latest updates!

A tech savvy accounting and bookkeeping firm serving small and midsized businesses, we focus on building scalable accounting department for our clients.
Quick Links
- CFO Services
- Tax Compliance
- ERP Accounting
- Tax Optimization
- Strategic Finances
- Managing Business
Latest Posts
Appfolio property manager pricing 2024: is appfolio worth the investment, what is form 1120 everything you need to know, what is netsuite ap automation, appfolio property manager pricing, features & reviews, get your free balance sheet template.
Fill in the details and get your free template.

Unit 3: The Accounting Cycle
Posting to the general ledger, organizing journal entries.
We have covered a lot of new words and concepts in this chapter, this video gives you a preview of what happens next when we organize the journal entry information:
A journal entry is like a set of instructions. The carrying out of these instructions is known as posting . The video provides a clear description of where in the accounting cycle posting occurs. As stated earlier, posting is recording in the ledger accounts the information contained in the journal. The good news is you have already done the hard part — you have analyzed the transactions and created the journal entries. When you post, you will not change your journal entries . If you debit an account in a journal entry, you will debit the same account in posting. If you credit an account in a journal entry, you will credit the same account in posting. After transactions are journalized, they can be posted either to a T-account or a general ledger. Remember – a ledger is a listing of all transactions in a single account, allowing you to know the balance of each account. The ledger for an account is typically used in practice instead of a T-account but T-accounts are often used for demonstration because they are quicker and sometimes easier to understand. The general ledger is a compilation of the ledgers for each account for a business. Below is an example of what the T-Accounts would look like for a company.

In contrast to the two-sided T-account, the three-column ledger card format has columns for debit, credit, balance, and item description. The three-column form ledger card has the advantage of showing the balance of the account after each item has been posted. It is very important for you to understand the debit and credit rules for each account type or you may not calculate the balance correctly. Notice that we give an explanation for each item in the ledger accounts. Often accountants omit these explanations because each item can be traced back to the general journal for the explanation. The following are examples of Ledger cards for the some of the accounts from the same company shown in T-accounts above ( see how you get the same balance under either approach ).

Notice in these ledger examples that Cash is an asset and a debit increases an asset and a credit decreases an asset. Accounts Payable is a liability account and Design Services Revenue is a revenue account but both accounts increase with a credit and decrease with a debit.
Posting is always from the journal to the ledger accounts. Postings can be made (1) at the time the transaction is journalized; (2) at the end of the day, week, or month; or (3) as each journal page is filled. The choice is a matter of personal taste. When posting the general journal, the date used in the ledger accounts is the date the transaction was recorded in the journal, not the date the journal entry was posted to the ledger accounts.
The accounting equation serves as an error detection tool. If at any point the sum of debits for all accounts does not equal the corresponding sum of credits for all accounts, an error has occurred. It follows that the sum of debits and the sum of the credits must be equal in value. Double-entry bookkeeping is not a guarantee that no errors have been made—for example, the wrong ledger account may have been debited or credited, or the entries completely reversed.
If you would like to see what it looks like to move journal postings into a general ledger in Excel, watch this additional video .
- Posting to a Ledger. Authored by : ptionlinedivision. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QkgF1-6aOwQ . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- General Ledger, T Accounts and The Accounting Cycle (#17). Authored by : NotePirate. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ALJtfACHVY . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Snapsolve any problem by taking a picture. Try it in the Numerade app?
Glencoe Accounting: First Year Course
Mcgraw-hill, posting journal entries to general ledger accounts - all with video answers.

Chapter Questions
Use the step-by-step processes presented in this chapter for starting new ledger pages for the following accounts. Use the accounting stationery provided in your working papers. January 1 of the current year is the date.

David Serlo made the following cash investment in his business. Use the sixstep process to post the entry to the ledger accounts in your working papers.
Analyze the transaction that is described in Memorandum $47,$ and then record and post the required correcting entry in your working papers.

On July 7 Video Connection's accounting supervisor discovered that a July 3 transaction had been recorded incorrectly. The transaction, involving the purchase of advertising in the local newspaper with a $\$ 300$ check, was incorrectly journalized and posted to the Rent Expense account. In your working papers, record and post the correcting entry using Memorandum 13 as the source document.
The accounts used by Wilderness Rentals have been opened and are included in the working papers accompanying this textbook. The general journal transactions for March of the current year are also included. Instructions Post the transactions recorded on page 1 of the general journal to the accounts in the general ledger.
The ledger accounts for Hot Suds Car Wash are shown in your working papers Prepare a trial balance as of March 31 of the current year.
A partial chart of accounts for Kits $\&$ Pups Grooming follows. General Ledger 101 Cash in Bank 301 Abe Shultz, Capital 105 Accts. Rec. $-$ J. Alvarez 305 Abe Shultz, Withdrawals 120 Grooming Supplies 401 Boarding Revenue 130 Office Furniture 405 Grooming Revenue 140 Grooming Equipment 525 Salaries Expense 205 Accts. Pay.-Dogs \& Cats Inc. 1. In your working papers, open an account in the general ledger for each of these accounts. 2. Record the March transactions on page 1 of the general journal. 3. Post each journal entry to the appropriate ledger account. 4. Prove the ledger by preparing a trial balance.
The chart of accounts for Outback Guide Service follows. General Ledger 101 Cash in Bank 301 Juanita Ortega, Capital 115 Accts. Rec. -Podaski 302 Juanita Ortega, Withdrawals Systems Inc. 401 Guide Service Revenue 140 Computer Equipment 501 Advertising Expense 145 Hiking Equipment 150 Rafting Equipment 205 Accts. Pay. -Peak Equipment Inc. 207 Accts. Pay.-Premier Processors 1. In your working papers, open an account in the general ledger for each account in the chart of accounts. 2. Record the following transactions on page 1 of the general journal. 3. Post each journal entry to the appropriate accounts in the ledger. 4. Prove the ledger by preparing a trial balance.
An auditor reviewed the accounting records of Showbiz Video. The auditor wrote a list of transactions, outlined below, describing the errors discovered in the March records. The general journal for March and a portion of the general ledger are included in your working papers. 1. Record correcting entries on general journal page $22 .$ Use March 31 as the date and Memorandum 50 as the source document for all correcting entries. 2. Some errors will not require correcting entries but will require a general ledger correction. Make the appropriate general ledger corrections. 3. Post all correcting entries to the general ledger accounts.


General Ledger Q&A

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on March 26, 2023
Fact Checked
Why Trust Finance Strategists?
Test your learning about the general ledger by answering the 10 short questions given below. We suggest that you try to answer each question yourself before clicking on the "See answer" button.
If you find it difficult to answer any of these questions, read the article on the general ledger from the explanation section of this website.
1. What is a ledger? See answer
2. What is meant by posting? See answer
3. What is meant by balancing? See answer
4. What methods are used to prepare ledger accounts? See answer
5. What is meant by balance? See answer
6. What is difference between debit balance and credit balance? See answer
7. What is meant by zero balance? See answer
8. What abbreviations are used for debit and credit? See answer
9. A ledger account has two sides: a left side and a right side. In bookkeeping and accounting, what are these two sides called? See answer
10. What is meant by the term "posting reference" (PR) in relation to a ledger account? See answer
General Ledger Q&A FAQs
What is a general ledger.
A General Ledger (GL) is a Financial Statement that shows the various assets, liabilities, and equity of a company at a given point in time. The GL can be used to track overall performance, assess the financial position, and make business decisions.
How does the General Ledger work?
The GL receives input from all of a company's accounting transactions, including account entries, payments, and receipts. It then calculates balances for each account and produces Financial Statements.
What are the benefits of using a General Ledger?
The GL provides an overview of a company's overall financial health, making it an essential tool for business decision-making. Additionally, the GL can help businesses comply with financial regulations.
What are some common General Ledger functions?
Some common functions of a General Ledger include recording transactions, preparing Financial Statements, and reconciling accounts. Additionally, a GL can help manage budgeting and Cash Flow processes.
How do I get started using a General Ledger?
To get started using a General Ledger, you'll need to set up your account and create journal entries. You can then use this information to produce Financial Statements.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .

Related Topics
- Accounting Equation Q&A
- Adjusting Entries Q&A
- Cash Book Q&A
- Depreciation Q&A
- Dissolution of Partnership Q&A
- Distribution of Profit and Loss Q&A
- Formation and Organization Q&A
- General Journal Q&A
- Introduction to Accounting - Q&A
- Issuance of Shares and Debentures Q&A
- Material Costing Methods Q&A
- Non-Trading Concerns Q&A
- Retirement or Death of a Partner Q&A
- Special Journal Q&A
- Transaction Analysis Q&A
- Trial Balance Q&A
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
General Ledger
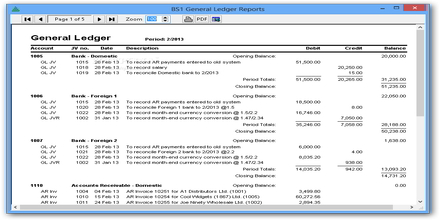
General Ledger is a company’s main accounting records. A general ledger is usually a complete record associated with financial transactions above the life of a business. The ledger holds account information that is usually prepare financial phrases, and includes is the reason for assets, liabilities, owner’s collateral, revenues and charges. A general ledger is usually used by firms that employ double-entry bookkeeping procedure – where every financial transaction is posted twice, as both a debit along with a credit, and in which each account provides two columns.

Operating Cash Flow Margin

Advantages of Fixed Audit Program

Days Sales Outstanding
Concept of Variance Analysis

Buildings could be Cooled without Using any Energy

Discussed on Personal Loans Pros and Cons
About Streptomycin

Teachers who Struggle with Stress are far less Satisfied with their Jobs
Perceived Organizational Support

Natural Allergy Treatment
Latest post.
Metamaterial Absorber
Regenerative Braking – an energy recovery mechanism

Researchers Investigate how we Experience Bitter Tastes

Researchers discovered the Oldest Undisputed evidence of Earth’s Magnetic Field

Negative Thermal Expansion (NTE)

Thermal Expansion
How to Assign Integrated Excel
The power of Microsoft Excel meets the power of McGraw Hill Connect in our Integrated Excel assignments. Excel opens seamlessly inside Connect with no additional software requirements. This short video will show you how easy it is to assign in your Connect course.
Attending a conference?
Checkout if mcgraw hill will be in attendance:.
General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation - Question 2 The requirements tab describes the purpose and input requirements for each ab. True or False True False
Gauth ai solution.
- Culture & Values
- Hiring Process
- Military & Veterans
- Careers FAQ
- Engineering
- Information Technology
- Power Plant Operator
- Professional
- Skilled / Craft
- Students / Early Careers
- View All Jobs
- Innovation / KSL
(Spring 2025) Student Intern - Accounting Govern. & Controls (Finance)
Date: May 15, 2024
Location: New Orleans, Louisiana, United States
Company: Entergy
Posting End Date:
Work Place Flexibility: Hybrid
Legal Entity: Entergy Services, Inc.-ESI (OLD)
*This will be a hybrid position.*
JOB SUMMARY/PURPOSE Supports the Accounting Department by participating in the day to day activities of the group. Assignments are made for specific tasks based on the needs of the department, including data analysis, general accounting or bookkeeping tasks, preparation of documents, spreadsheets, copies, etc. JOB DUTIES/RESPONSIBILITIES
- Supports the assigned Accounting Department with day to day tasks.
- Conducts data analysis.
- Prepares documents, spreadsheets, presentations, interoffice correspondence and copies.
- Conducts follow-ups in a detailed fashion.
- Handles multiple assignments and works within deadlines.
- Is proactive in forwarding work issues to the appropriate managers/supervisors. Works in a team.
MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS
Minimum education required of the position Pursuing undergrad or master's degree in accounting, finance or business related field.
GPA of 3.0 or higher required. Minimum experience required of the position Some work experience preferred. Minimum knowledge, skills and abilities required of the position General business and accounting knowledge. Self-starter with strong analytical and communication skills; Must be proficient in MS office tools - Word, Excel and PowerPoint; Excellent organizational skills; Strong and positive team attitude and interpersonal skills. Ability to prioritize work and to handle multiple tasks; Ability to understand scope and objective of each assignment. Additional job duties/responsibilities (Not in Description) :
Assistance in Accounting Departments including Miscellaneous Receivables, Affiliate Accounting, General Ledger and Reporting, Accounting Process and Controls.
Preferred knowledge, skills, and abilities :
General business and accounting knowledge. Self-starter with strong analytical and communication skills; Must be proficient in MS office tools - Word, Excel and PowerPoint; Excellent organizational skills; Strong and positive team attitude and interpersonal skills. Ability to prioritize work and to handle multiple tasks; Ability to understand scope and objective of each assignment.
* SQL knowledge is preferred.
Any certificates, licenses, etc. required for the position None
Primary Location: Louisiana-New Orleans Louisiana : New Orleans Job Function : Students / Early Careers FLSA Status : Nonexempt Relocation Option: No Relocation Offered Union description/code : NON BARGAINING UNIT Number of Openings : 1 Req ID: 114471 Travel Percentage :Up to 25%
An Equal Opportunity Employer, Minority/Female/Disability/Vets. Please click here to view the EEI page, or see statements below.
EEO Statement: The Entergy System of Companies provides equal employment opportunities (EEO) to all employees and applicants for employment without regard to race, color, religion, sex, gender, sexual orientation, gender identity or expression, national origin, age, disability, genetic information, marital status, amnesty, or status as a protected veteran in accordance with applicable federal, state and local laws. The Entergy System of Companies complies with applicable state and local laws governing non-discrimination in employment in every location in which the company has facilities. This policy applies to all terms and conditions of employment including, but not limited to, recruiting, hiring, placement, promotion, termination, layoff, recall, transfer, leaves of absence, compensation, and training. The Entergy System of Companies expressly prohibits any form of unlawful employee harassment based on race, color, religion, sex, gender, sexual orientation, gender identity or expression, national origin, age, genetic information, disability, or veteran status. Improper interference with the ability of the Entergy System of Company employees to perform their expected job duties is absolutely not tolerated.
Accessibility: Entergy provides reasonable accommodations for online applicants. Requests for a reasonable accommodation may be made orally or in writing by an applicant, employee, or third party on his or her behalf. If you are an individual with a disability and you are in need of an accommodation for the recruiting process please click here and provide your name, contact number, the accommodation requested and the requisition number that you are requesting the accommodation for. Employee Services will contact you regarding your request.
Additional Responsibilities: As a provider of essential services, Entergy expects its employees to be available to work additional hours, to work in alternate locations, and/or to perform additional duties in connection with storms, outages, emergencies, or other situations as deemed necessary by the company. Exempt employees may not be paid overtime associated with such duties.
Entergy Pay Transparency Policy Statement: The Entergy System of Companies (the Company) will not discharge or in any other manner discriminate against employees or applicants because they have inquired about, discussed, or disclosed their own pay or the pay of another employee or applicant. However, employees who have access to the compensation information of other employees or applicants as a part of their essential job functions cannot disclose the pay of other employees or applicants to individuals who do not otherwise have access to compensation information, unless the disclosure is (a) in response to a formal complaint or charge, (b) in furtherance of an investigation, proceeding, hearing, or action, including an investigation conducted by the employer, or (c) consistent with the Company’s legal duty to furnish information. 41 CFR 60-1.35(c). Equal Opportunity and Pay Transparency .
Pay Transparency Notice:
Pay Transparency Nondiscrimination Provision (dol.gov)
The non-confidential portions of the affirmative action program for individuals with disabilities and protected veterans shall be available for inspection upon request by any employee or applicant for employment. Please contact [email protected] to schedule a time to review the affirmative action plan during regular office hours.
WORKING CONDITIONS: As a provider of essential services, Entergy expects its employees to be available to work additional hours, to work in alternate locations, and/or to perform additional duties in connection with storms, outages, emergencies, or other situations as deemed necessary by the company. Exempt employees may not be paid overtime associated with such duties.
Please note: Authorization to work in the United States is a precondition to employment in this position. Entergy will not sponsor candidates for work visas for this position.
Job Segment: Accounting, Bookkeeping, Database, SQL, Data Analyst, Finance, Technology, Data
- Job Searches
- Job Categories
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Download the Entergy App
- Entergy.com
© 2018-2022 Entergy Corporation, All Rights Reserved. The Entergy name and logo are registered service marks of Entergy Corporation and may not be used without the express, written consent of Entergy Corporation.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Financial statements must be properly formatted, to include a description of all subtotals. In some general ledger questions, the financial statements need to be constructed by selecting the accounts and account elements that belong on the statement. The first four tabs will always be the same: Requirements, General Journal, General Ledger and ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like General Ledger questions contain multiple tabs., The requirements tab describes the purpose and input requirements for each tab., Journal entries are recorded on which tab? and more.
View Week 3 General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation.docx from ACC 290T at University of Phoenix. Week #3 General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation General Ledger Assignments - Student
Display the student instructions. Hide the student instructions. Print the instructions. Follow the steps below to complete the Introduction to General Ledger Online assignment. Each assignment will have an instruction page similar to this one, which will guide you through the steps required to complete a text problem using General Ledger Online.
The general ledger acts as the backbone that supports the balance sheet, ensuring that the information presented is accurate and up-to-date. It provides the necessary details and supporting documentation for each account, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the company's financial position. In conclusion, understanding the general ...
General Ledger 101: Terms, Types, and Templates for Better Accounting. A general ledger is a company's financial command center, where all the penny that comes in and goes out is recorded thoroughly. Frankly, from purchases to bill payments, people consider it more as the heartbeat of a business' financial operations.
View General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation - Question 8.pdf from ACC 290T at University of Phoenix. 12/10/2020 Assignment Print View Score: 0/0 Points 100 % Video
Posting is always from the journal to the ledger accounts. Postings can be made (1) at the time the transaction is journalized; (2) at the end of the day, week, or month; or (3) as each journal page is filled. The choice is a matter of personal taste. When posting the general journal, the date used in the ledger accounts is the date the ...
The general journal for March and a portion of the general ledger are included in your working papers. 1. Record correcting entries on general journal page $22 .$ Use March 31 as the date and Memorandum 50 as the source document for all correcting entries. 2. Some errors will not require correcting entries but will require a general ledger ...
Test your learning about the general ledger by answering the 10 short questions given below. We suggest that you try to answer each question yourself before clicking on the "See answer" button. If you find it difficult to answer any of these questions, read the article on the general ledger from the explanation section of this website.
For Individual Student Outline: Semester and year: Course and Section: Meeting Days/Times & Room: ... 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger 5 Adjustments and the Worksheet 6 Closing Entries and the Post-closing Trial Balance ... refer to the section Final Grade Evaluation for details on the required assignments, ...
GENERAL LEDGER PROBLEMS - General Ledger problems offer students the ability to record financial transactions in a series of statements using the same spreadsheet-based recording system that their end-of-chapter content is built on. By hyperlinking entries between statements, General Ledger problems allow students to see how transactions post from one statement to another while giving an ...
See Answer. Question: General Ledger questions contain multiple tabs. Journal entries are recorded on which tab? Show transcribed image text. There are 2 steps to solve this one.
View General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation - Question 12.pdf from ACC 290T at University of Phoenix. 12/10/2020 Assignment Print View Score: 0/0 Points 100 % Video
View Week 3 Practice Orientation General Ledger Questions Acct290 T.docx from ACCT 290T at Central Piedmont Community College. Week 3 Practice Orientation General Ledger Questions Acct290 T General ... Students also studied. Screen Shot 2022-07-01 at 3.07.15 PM.png. University of Phoenix. ACCOUNTING 290T. BIALEKS-ACCT105-M1.xlsx. Solutions ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like General Ledger questions contain multiple tabs., The requirements tab describes the purpose and input requirements for each tab., Journal entries are recorded on which tab? and more. ... End of Chapter Assignments - Student Orientation. 19 terms. paulaeuceda5. Preview. NRS 2020 ...
General Ledger is a company's main accounting records. A general ledger is usually a complete record associated with financial transactions above the life of a business. The ledger holds account information that is usually prepare financial phrases, and includes is the reason for assets, liabilities, owner's collateral, revenues and charges.
How to Assign Integrated Excel. The power of Microsoft Excel meets the power of McGraw Hill Connect in our Integrated Excel assignments. Excel opens seamlessly inside Connect with no additional software requirements. This short video will show you how easy it is to assign in your Connect course.
General Ledger Assignments - Student Orientation - Question 2 The requirements tab describes the purpose and input requirements for each ab. True or False True False
In the Default Account Assignment for General Ledger Accounts you define a specific setting for a G/L Account, a cost center assignment or a Free Cost Object assignment for example. But when viewing the journal entry of a business transaction (such as a Supplier or Customer Invoice), posting to the selected G/L Account, the defined setting is ...
In some general ledger questions, the financial statements will be generated automatically. True / False. True. In reviewing the General Ledger tab, you notice that the ending Cash balance is listed in parentheses. What does this indicate? -Cash has a normal ending balance. -Cash has an abnormal ending balance.
Ability to prioritize work and to handle multiple tasks; Ability to understand scope and objective of each assignment. Additional job duties/responsibilities (Not in Description) : Assistance in Accounting Departments including Miscellaneous Receivables, Affiliate Accounting, General Ledger and Reporting, Accounting Process and Controls.