Essay on Greenhouse Effect for Students and Children
500 words essay on greenhouse effect.
The past month, July of 2019, has been the hottest month in the records of human history. This means on a global scale, the average climate and temperatures are now seen a steady rise year-on-year. The culprits of this climate change phenomenon are mainly pollution , overpopulation and general disregard for the environment by the human race. However, we can specifically point to two phenomenons that contribute to the rising temperatures – global warming and the greenhouse effect. Let us see more about them in this essay on the greenhouse effect.
The earth’s surface is surrounded by an envelope of the air we call the atmosphere. Gasses in this atmosphere trap the infrared radiation of the sun which generates heat on the surface of the earth. In an ideal scenario, this effect causes the temperature on the earth to be around 15c. And without such a phenomenon life could not sustain on earth.
However, due to rapid industrialization and rising pollution, the emission of greenhouse gases has increased multifold over the last few centuries. This, in turn, causes more radiation to be trapped in the earth’s atmosphere. And as a consequence, the temperature on the surface of the planet steadily rises. This is what we refer to when we talk about the man-made greenhouse effect.


Causes of Greenhouse Effect
As we saw earlier in this essay on the greenhouse effect, the phenomenon itself is naturally occurring and an important one to sustain life on our planet. However, there is an anthropogenic part of this effect. This is caused due to the activities of man.
The most prominent among this is the burning of fossil fuels . Our industries, vehicles, factories, etc are overly reliant on fossil fuels for their energy and power. This has caused an immense increase in emissions of harmful greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfides, etc. This has multiplied the greenhouse effect and we have seen a steady rise in surface temperatures.
Other harmful activities such as deforestation, excessive urbanization, harmful agricultural practices, etc. have also led to the release of excess carbon dioxide and made the greenhouse effect more prominent. Another harmful element that causes harm to the environment is CFC (chlorofluorocarbon).
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Some Effects of Greenhouse Effect
Even after overwhelming proof, there are still people who deny the existence of climate change and its devastating pitfalls. However, there are so many effects and pieces of evidence of climate change it is now undeniable. The surface temperature of the planet has risen by 1c since the 19th century. This change is largely due to the increased emissions of carbon dioxide. The most harm has been seen in the past 35 years in particular.
The oceans and the seas have absorbed a lot of this increased heat. The surfaces of these oceans have seen a rise in temperatures of 0.4c. The ice sheets and glaciers are also rapidly shrinking. The rate at which the ice caps melt in Antartica has tripled in the last decade itself. These alarming statistics and facts are proof of the major disaster we face in the form of climate change.
600 Words Essay on Greenhouse Effect
A Greenhouse , as the term suggests, is a structure made of glass which is designed to trap heat inside. Thus, even on cold chilling winter days, there is warmth inside it. Similarly, Earth also traps energy from the Sun and prevents it from escaping back. The greenhouse gases or the molecules present in the atmosphere of the Earth trap the heat of the Sun. This is what we know as the Greenhouse effect.

Greenhouse Gases
These gases or molecules are naturally present in the atmosphere of the Earth. However, they are also released due to human activities. These gases play a vital role in trapping the heat of the Sun and thereby gradually warming the temperature of Earth. The Earth is habitable for humans due to the equilibrium of the energy it receives and the energy that it reflects back to space.
Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect
The trapping and emission of radiation by the greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere is known as the Greenhouse effect. Without this process, Earth will either be very cold or very hot, which will make life impossible on Earth.
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon. Due to wrong human activities such as clearing forests, burning fossil fuels, releasing industrial gas in the atmosphere, etc., the emission of greenhouse gases is increasing.
Thus, this has, in turn, resulted in global warming . We can see the effects due to these like extreme droughts, floods, hurricanes, landslides, rise in sea levels, etc. Global warming is adversely affecting our biodiversity, ecosystem and the life of the people. Also, the Himalayan glaciers are melting due to this.
There are broadly two causes of the greenhouse effect:
I. Natural Causes
- Some components that are present on the Earth naturally produce greenhouse gases. For example, carbon dioxide is present in the oceans, decaying of plants due to forest fires and the manure of some animals produces methane , and nitrogen oxide is present in water and soil.
- Water Vapour raises the temperature by absorbing energy when there is a rise in the humidity.
- Humans and animals breathe oxygen and release carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
II. Man-made Causes
- Burning of fossil fuels such as oil and coal emits carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which causes an excessive greenhouse effect. Also, while digging a coal mine or an oil well, methane is released from the Earth, which pollutes it.
- Trees with the help of the process of photosynthesis absorb the carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Due to deforestation the carbon dioxide level is continuously increasing. This is also a major cause of the increase in the greenhouse effect.
- In order to get maximum yield, the farmers use artificial nitrogen in their fields. This releases nitrogen oxide in the atmosphere.
- Industries release harmful gases in the atmosphere like methane, carbon dioxide , and fluorine gas. These also enhance global warming.
All the countries of the world are facing the ill effects of global warming. The Government and non-governmental organizations need to take appropriate and concrete measures to control the emission of toxic greenhouse gases. They need to promote the greater use of renewable energy and forestation. Also, it is the duty of every individual to protect the environment and not use such means that harm the atmosphere. It is the need of the hour to protect our environment else that day is not far away when life on Earth will also become difficult.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Understanding Global Change
Discover why the climate and environment changes, your place in the Earth system, and paths to a resilient future.
Greenhouse effect

Life as we know it would be impossible if not for the greenhouse effect, the process through which heat is absorbed and re-radiated in that atmosphere. The intensity of a planet’s greenhouse effect is determined by the relative abundance of greenhouse gases in its atmosphere. Without greenhouse gases, most of Earth’s heat would be lost to outer space, and our planet would quickly turn into a giant ball of ice. Increase the amount of greenhouse gases to the levels found on the planet Venus, and the Earth would be as hot as a pizza oven! Fortunately, the strength of Earth’s greenhouse effect keeps our planet within a temperature range that supports life
On this page
What is the greenhouse effect, earth system models about the greenhouse effect, how human activities influence the greenhouse effect, explore the earth system, investigate, links to learn more.
For the classroom:
- Teaching Resources

Global Change Infographic
The greenhouse effect occurs in the atmosphere, and is an essential part of How the Earth System Works. Click the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change Infographic . Locate the greenhouse effect icon and identify other topics that cause changes to, or are affected by, the greenhouse effect.
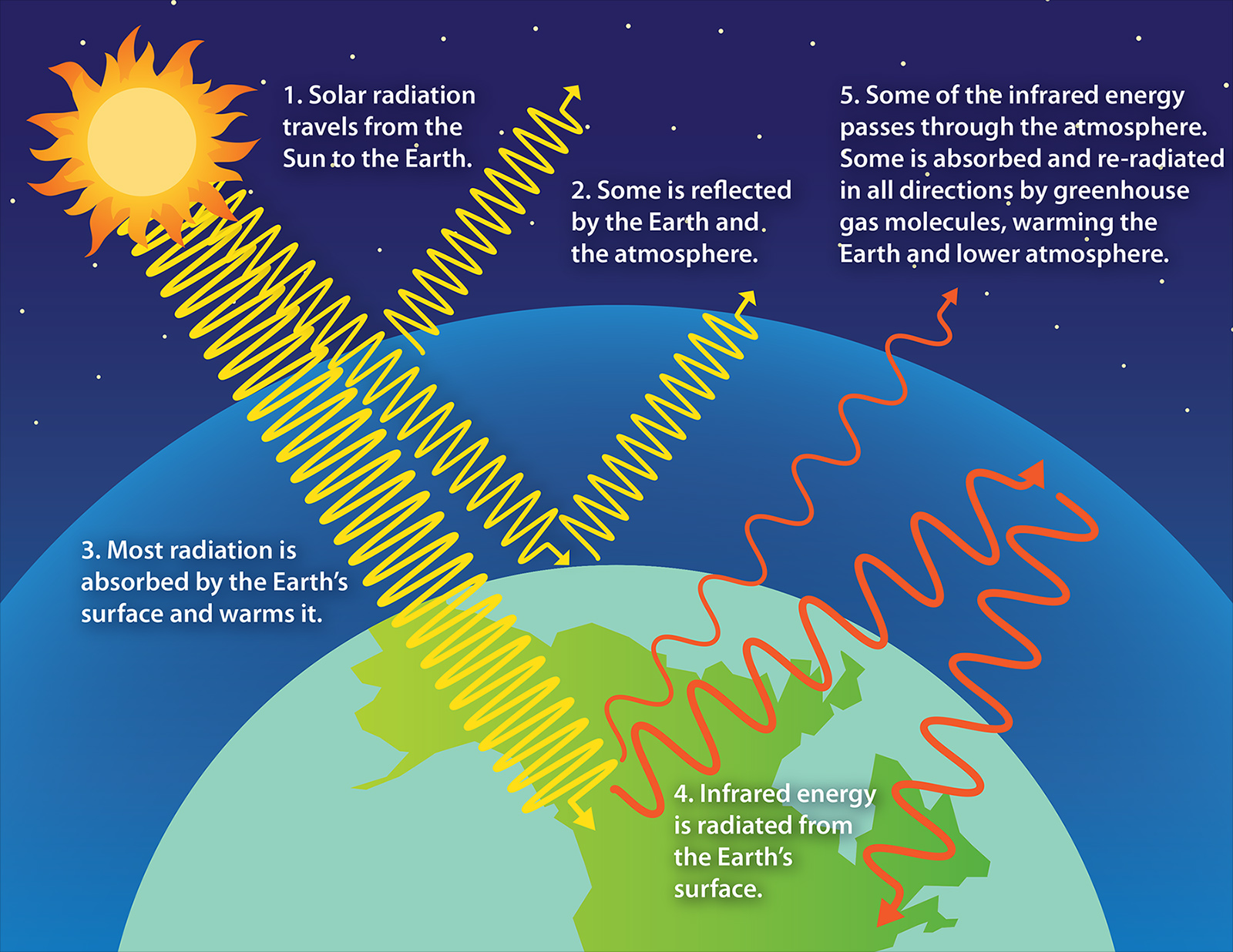
Adapted from the Environmental Protection Agency greenhouse effect file
Greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and water vapor significantly affect the amount of energy in the Earth system, even though they make up a tiny percentage of Earth’s atmosphere. Solar radiation that passes through the atmosphere and reaches Earth’s surface is either reflected or absorbed . Reflected sunlight doesn’t add any heat to the Earth system because this energy bounces back into space.
However, absorbed sunlight increases the temperature of Earth’s surface, and the warmed surface re-radiates as long-wave radiation (also known as infrared radiation). Infrared radiation is invisible to the eye, but we feel it as heat.
If there were not any greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, all that heat would pass directly back into space. With greenhouse gases present, however, most of the long-wave radiation coming from Earth’s surface is absorbed and then re-radiated in all directions many times before passing back into space. Heat that is re-radiated downward, toward the Earth, is absorbed by the surface and re-radiated again.
Clouds also influence the greenhouse effect. A thick, low cloud cover can enhance the reflectivity of the atmosphere, reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth’s surface, but clouds high in the atmosphere can intensify the greenhouse effect by re-radiating heat from the Earth’s surface.
Altogether, this cycle of absorption and re-radiation by greenhouse gases impedes the loss of heat from our atmosphere to space, creating the greenhouse effect. Increases in the amount of greenhouses gases will mean that more heat is trapped, increasing the amount of energy in the Earth system (Earth’s energy budget), and raising Earth’s temperature. This increase in Earth’s average temperature is also known as global warming.
This Earth system model is one way to represent the essential processes and interactions related to the greenhouse effect. Hover over the icons for brief explanations; click on the icons to learn more about each topic. Download the Earth system models on this page. There are a few ways that the relationships among these topics can be represented and explained using the Understanding Global Change icons ( download examples ).
The greenhouse effect, which influences Earth’s average temperature, affects many of the processes that shape global climate and ecosystems. This model shows some of the other parts of the Earth system that the greenhouse effect influences, including the water cycle and water temperature .
Humans directly affect the greenhouse effect through activities that result in greenhouse gas emissions. The Earth system model below includes some of the ways that human activities increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Releasing greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, and increases Earth’s average air temperatures (also known as global warming). Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the greenhouse effect.
Click the scene icons and bolded terms on this page to learn more about these process and phenomena.
Learn more in these real-world examples, and challenge yourself to construct a model that explains the Earth system relationships.
- Ancient fossils and modern climate change
- How Global Warming Works
- NASA: Global Climate Change: A Blanket Around the Earth
- UCAR Center for Science Education: The Greenhouse Effect
- IPCC: What is the Greenhouse Effect?
- Indicators of Change (NCA.2014)
- Human influence on the greenhouse effect
- The Carbon Cycle and Earth’s Climate

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

21.1: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47008

- Melissa Ha and Rachel Schleiger
- Yuba College & Butte College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Earth’s Temperature is a Balancing Act
Earth’s temperature depends on the balance between energy entering and leaving the planet. When incoming energy from the sun is absorbed, Earth warms. When the sun’s energy is reflected back into space, Earth avoids warming. When energy is released from Earth into space, the planet cools. Many factors, both natural and human, can cause changes in Earth’s energy balance, including:
- Changes in the greenhouse effect, which affects the amount of heat retained by Earth’s atmosphere;
- Variations in the sun’s energy reaching Earth;
- Changes in the reflectivity of Earth’s atmosphere and surface.
Scientists have pieced together a picture of Earth’s climate, dating back hundreds of thousands of years, by analyzing a number of indirect measures of climate such as ice cores, tree rings, glacier size, pollen counts, and ocean sediments. Scientists have also studied changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun and the activity of the sun itself.
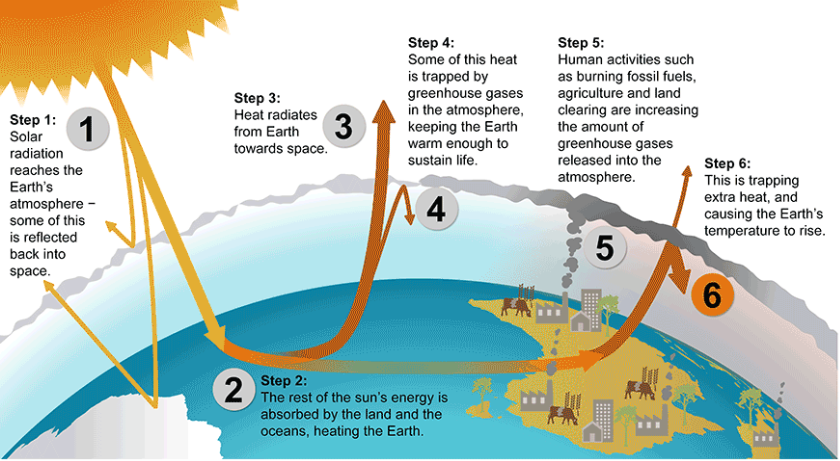
The historical record shows that the climate varies naturally over a wide range of time scales. In general, climate changes prior to the Industrial Revolution in the 1700s can be explained by natural causes, such as changes in solar energy, volcanic eruptions, and natural changes in greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations. Recent changes in climate , however, cannot be explained by natural causes alone. Research indicates that natural causes are very unlikely to explain most observed warming, especially warming since the mid-20th century. Rather, human activities, especially our combustion of fossil fuels, explains the current warming (figure \(\PageIndex{a}\)). The scientific consensus is clear: through alterations of the carbon cycle, humans are changing the global climate by increasing the effects of something known as the greenhouse effect.
The Greenhouse Effect Causes the Atmosphere to Retain Heat
Gardeners that live in moderate or cool environments use greenhouses because they trap heat and create an environment that is warmer than outside temperatures. This is great for plants that like heat, or are sensitive to cold temperatures, such as tomato and pepper plants. Greenhouses contain glass or plastic that allow visible light from the sun to pass. This light, which is a form of energy, is absorbed by plants, soil, and surfaces and heats them. Some of that heat energy is then radiated outwards in the form of infrared radiation, a different form of energy. Unlike with visible light, the glass of the greenhouse blocks the infrared radiation, thereby trapping the heat energy, causing the temperature within the greenhouse to increase.
The same phenomenon happens inside a car on a sunny day. Have you ever noticed how much hotter a car can get compared to the outside temperature? Light energy from the sun passes through the windows and is absorbed by the surfaces in the car such as seats and the dashboard. Those warm surfaces then radiate infrared radiation, which cannot pass through the glass. This trapped infrared energy causes the air temperatures in the car to increase. This process is commonly known as the greenhouse effect .
The video below made for kids, but provides a clear and simple introduction to the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect also happens with the entire Earth. Of course, our planet is not surrounded by glass windows. Instead, the Earth is wrapped with an atmosphere that contains greenhouse gases (GHGs). Much like the glass in a greenhouse, GHGs allow incoming visible light energy from the sun to pass, but they block infrared radiation that is radiated from the Earth towards space (figure \(\PageIndex{b}\)). In this way, they help trap heat energy that subsequently raises air temperature. Being a greenhouse gas is a physical property of certain types of gases; because of their molecular structure they absorb wavelengths of infrared radiation, but are transparent to visible light. Some notable greenhouse gases are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and methane (CH 4 ). GHGs act like a blanket, making Earth significantly warmer than it would otherwise be. Scientists estimate that average temperature on Earth would be -18º C without naturally-occurring GHGs.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the recent and ongoing rise in global average temperature near Earth’s surface. It is caused mostly by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is causing climate patterns to change. However, global warming itself represents only one aspect of climate change.
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to any significant change in the measures of climate lasting for an extended period of time. In other words, climate change includes major changes in temperature, precipitation, or wind patterns, among other effects, that occur over several decades or longer.
The Main Greenhouse Gasses
The most important GHGs directly emitted by humans include CO 2 and methane. Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is the primary greenhouse gas that is contributing to recent global climate change. CO 2 is a natural component of the carbon cycle, involved in such activities as photosynthesis, respiration, volcanic eruptions, and ocean-atmosphere exchange. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and changes in land use, release very large amounts of CO 2 to the atmosphere, causing its concentration in the atmosphere to rise.
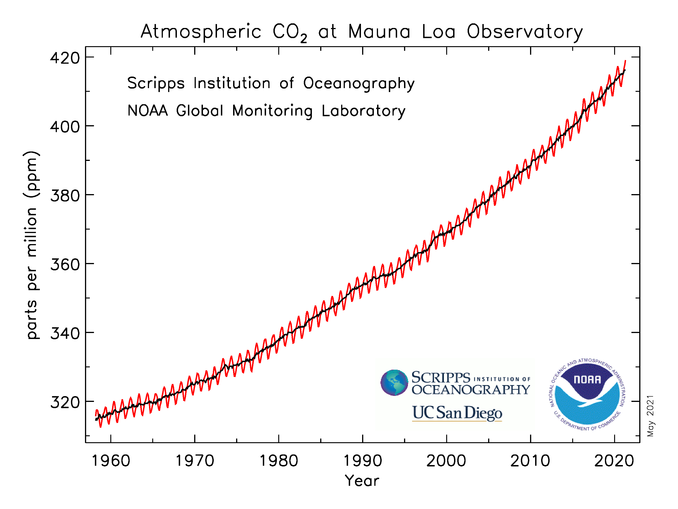
Atmospheric CO 2 concentrations have increased by 45% since pre-industrial times, from approximately 280 parts per million (ppm) in the 18th century to 409.8 ppm in 2019 (figure \(\PageIndex{c}\)). The current CO 2 level is higher than it has been in at least 800,000 years, based on evidence from ice cores that preserve ancient atmospheric gases (figure \(\PageIndex{d-f}\)). Human activities currently release over 30 billion tons of CO 2 into the atmosphere every year. While some volcanic eruptions released large quantities of CO 2 in the distant past, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) reports that human activities now emit more than 135 times as much CO 2 as volcanoes each year. This human-caused build-up of CO 2 in the atmosphere is like a tub filling with water, where more water flows from the faucet than the drain can take away.
Other Greenhouse Gasses
Although this concentration is far less than that of CO 2 , methane (CH 4 ) is 28 times as potent a greenhouse gas. Methane is produced when bacteria break down organic matter under anaerobic conditions and can be released due to natural or anthropogenic processes. Anaerobic conditions can happen when organic matter is trapped underwater (such as in rice paddies) or in the intestines of herbivores. Anthropogenic causes now account for 60% of total methane release. Examples include agriculture, fossil fuel extraction and transport, mining, landfill use, and burning of forests. Specifically, raising cattle releases methane due to fermentation in their rumens produces methane that is expelled from their GI tract. Methane is more abundant in Earth’s atmosphere now than at any time in at least the past 650,000 years, and CH 4 concentrations increased sharply during most of the 20th century. They are now more than two and-a-half times pre-industrial levels (1.9 ppm), but the rate of increase has slowed considerably in recent decades.
Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas and also the most important in terms of its contribution to the natural greenhouse effect, despite having a short atmospheric lifetime. Some human activities can influence local water vapor levels. However, on a global scale, the concentration of water vapor is controlled by temperature, which influences overall rates of evaporation and precipitation. Therefore, the global concentration of water vapor is not substantially affected by direct human emissions.
Ground-level ozone (O 3 ), which also has a short atmospheric lifetime, is a potent greenhouse gas. Chemical reactions create ozone from emissions of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds from automobiles, power plants, and other industrial and commercial sources in the presence of sunlight (as discussed in section 10.1). In addition to trapping heat, ozone is a pollutant that can cause respiratory health problems and damage crops and ecosystems.
Changes in the Sun’s Energy Affect how Much Energy Reaches Earth
Climate can be influenced by natural changes that affect how much solar energy reaches Earth. These changes include changes within the sun and changes in Earth’s orbit. Changes occurring in the sun itself can affect the intensity of the sunlight that reaches Earth’s surface. The intensity of the sunlight can cause either warming (during periods of stronger solar intensity) or cooling (during periods of weaker solar intensity). The sun follows a natural 11-year cycle of small ups and downs in intensity, but the effect on Earth’s climate is small. Changes in the shape of Earth’s orbit as well as the tilt and position of Earth’s axis can also affect the amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface.
Changes in the sun’s intensity have influenced Earth’s climate in the past. For example, the so-called “ Little Ice Age ” between the 17th and 19th centuries may have been partially caused by a low solar activity phase from 1645 to 1715, which coincided with cooler temperatures. The Little Ice Age refers to a slight cooling of North America, Europe, and probably other areas around the globe. Changes in Earth’s orbit have had a big impact on climate over tens of thousands of years. These changes appear to be the primary cause of past cycles of ice ages, in which Earth has experienced long periods of cold temperatures (ice ages), as well as shorter interglacial periods (periods between ice ages) of relatively warmer temperatures.
Changes in solar energy continue to affect climate. However, solar activity has been relatively constant, aside from the 11-year cycle, since the mid-20th century and therefore does not explain the recent warming of Earth. Similarly, changes in the shape of Earth’s orbit as well as the tilt and position of Earth’s axis affect temperature on relatively long timescales (tens of thousands of years), and therefore cannot explain the recent warming.
Changes in Reflectivity Affect How Much Energy Enters Earth’s System
When sunlight energy reaches Earth it can be reflected or absorbed. The amount that is reflected or absorbed depends on Earth’s surface and atmosphere. Light-colored objects and surfaces, like snow and clouds, tend to reflect most sunlight, while darker objects and surfaces, like the ocean and forests, tend to absorb more sunlight. The term albedo refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected from an object or surface, often expressed as a percentage. Earth as a whole has an albedo of about 30%, meaning that 70% of the sunlight that reaches the planet is absorbed. Sunlight that is absorbed warms Earth’s land, water, and atmosphere.
Albedo is also affected by aerosols. Aerosols are small particles or liquid droplets in the atmosphere that can absorb or reflect sunlight. Unlike greenhouse gases (GHGs), the climate effects of aerosols vary depending on what they are made of and where they are emitted. Those aerosols that reflect sunlight, such as particles from volcanic eruptions or sulfur emissions from burning coal, have a cooling effect. Those that absorb sunlight, such as black carbon (a part of soot), have a warming effect.
Natural changes in albedo, like the melting of sea ice or increases in cloud cover, have contributed to climate change in the past, often acting as feedbacks to other processes. Volcanoes have played a noticeable role in climate. Volcanic particles that reach the upper atmosphere can reflect enough sunlight back to space to cool the surface of the planet by a few tenths of a degree for several years. Volcanic particles from a single eruption do not produce long-term change because they remain in the atmosphere for a much shorter time than GHGs.
Human changes in land use and land cover have changed Earth’s albedo. Processes such as deforestation, reforestation, desertification, and urbanization often contribute to changes in climate in the places they occur. These effects may be significant regionally, but are smaller when averaged over the entire globe.
Scientific Consensus: Global Climate Change is Real
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was created in 1988 by the United Nations Environment Programme and the World Meteorological Organization. It is charged with the task of evaluating and synthesizing the scientific evidence surrounding global climate change. The IPCC uses this information to evaluate current impacts and future risks, in addition to providing policymakers with assessments. These assessments are released about once every every six years. The most recent report, the 5th Assessment, was released in 2013. Hundreds of leading scientists from around the world are chosen to author these reports. Over the history of the IPCC, these scientists have reviewed thousands of peer-reviewed, publicly available studies. The scientific consensus is clear: global climate change is real and humans are very likely the cause for this change.
Additionally, the major scientific agencies of the United States, including the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), also agree that climate change is occurring and that humans are driving it. In 2010, the US National Research Council concluded that “Climate change is occurring, is very likely caused by human activities, and poses significant risks for a broad range of human and natural systems”. Many independent scientific organizations have released similar statements, both in the United States and abroad. This doesn’t necessarily mean that every scientist sees eye to eye on each component of the climate change problem, but broad agreement exists that climate change is happening and is primarily caused by excess greenhouse gases from human activities. Critics of climate change, driven by ideology instead of evidence, try to suggest to the public that there is no scientific consensus on global climate change. Such an assertion is patently false.
Current Status of Global Climate Change and Future Changes
Greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere will continue to increase unless the billions of tons of anthropogenic emissions each year decrease substantially. Increased concentrations are expected to do the following:
- Increase Earth’s average temperature (figure \(\PageIndex{g}\)),
- Influence the patterns and amounts of precipitation,
- Reduce ice and snow cover, as well as permafrost,
- Raise sea level (figure \(\PageIndex{h}\)),
- Increase the acidity of the oceans.
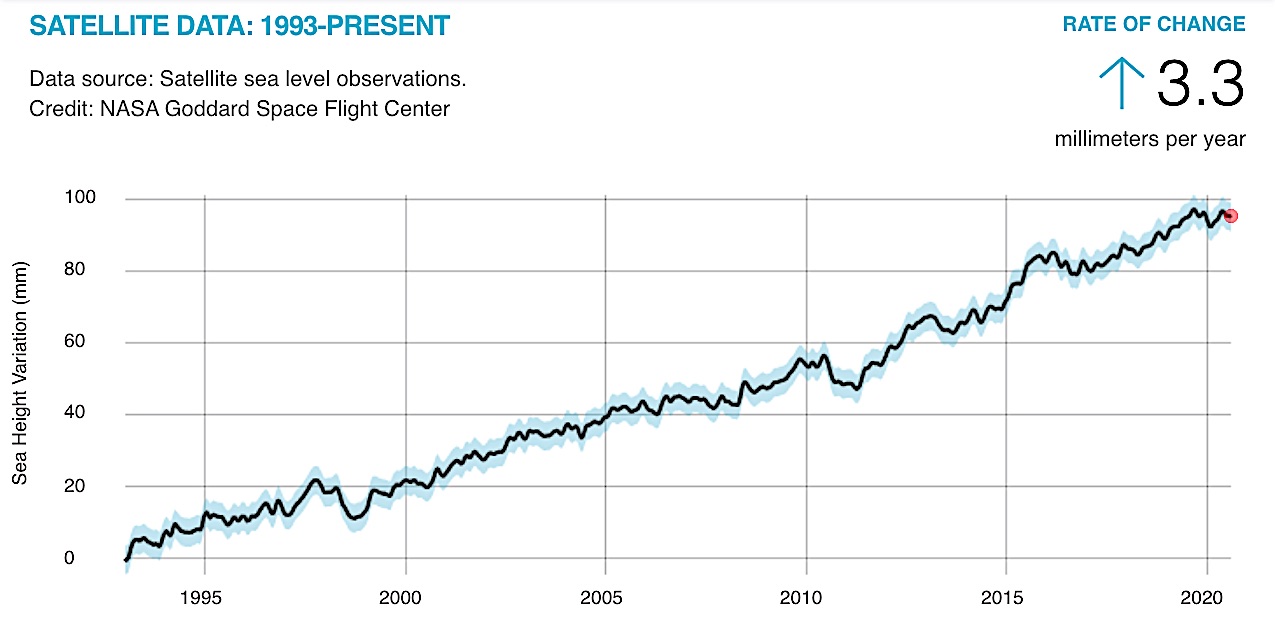
Figure \(\PageIndex{h}\): Sea height variation (mm) over time. Sea height has increased about 3.3 millimeters per year on average since 1993. Data is from satellite sea level observations by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Image by NASA (public domain).
These changes will impact our food supply, water resources, infrastructure, ecosystems, and even our own health. The magnitude and rate of future climate change will primarily depend on the following factors:
- The rate at which levels of greenhouse gas concentrations in our atmosphere continue to increase,
- How strongly features of the climate (e.g., temperature, precipitation, and sea level) respond to the expected increase in greenhouse gas concentrations,
- Natural influences on climate (e.g., from volcanic activity and changes in the sun’s intensity) and natural processes within the climate system (e.g., changes in ocean circulation patterns).
Past and Present-day GHG Emissions Will Affect Climate Far into the Future
Many greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for long periods of time. As a result, even if emissions stopped increasing, atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations would continue to remain elevated for hundreds of years. Moreover, if we stabilized concentrations and the composition of today’s atmosphere remained steady (which would require a dramatic reduction in current greenhouse gas emissions), surface air temperatures would continue to warm. This is because the oceans, which store heat, take many decades to fully respond to higher greenhouse gas concentrations. The ocean’s response to higher greenhouse gas concentrations and higher temperatures will continue to impact climate over the next several decades to hundreds of years.
Future Temperature Changes
Climate models project the following key temperature-related changes:
- Average global temperatures are expected to increase by 2°F to 11.5°F by 2100, depending on the level of future greenhouse gas emissions, and the outcomes from various climate models.
- By 2100, global average temperature is expected to warm at least twice as much as it has during the last 100 years.
- Ground-level air temperatures are expected to continue to warm more rapidly over land than oceans.
- Some parts of the world are projected to see larger temperature increases than the global average.
Future Precipitation and Storm Events
Patterns of precipitation and storm events, including both rain and snowfall are likely to change. However, some of these changes are less certain than the changes associated with temperature. Projections show that future precipitation and storm changes will vary by season and region. Some regions may have less precipitation, some may have more precipitation, and some may have little or no change. The amount of rain falling in heavy precipitation events is likely to increase in most regions, while storm tracks are projected to shift towards the poles. Climate models project the following precipitation and storm changes:
- Global average annual precipitation through the end of the century is expected to increase, although changes in the amount and intensity of precipitation will vary by region.
- The intensity of precipitation events will likely increase on average. This will be particularly pronounced in tropical and high-latitude regions, which are also expected to experience overall increases in precipitation.
- The strength of the winds associated with tropical storms is likely to increase. The amount of precipitation falling in tropical storms is also likely to increase.
- Annual average precipitation is projected to increase in some areas and decrease in others.
Future Ice, Snowpack, and Permafrost
Arctic sea ice is already declining drastically. The area of snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased since 1970. Permafrost temperature has increased over the last century, making it more susceptible to thawing. Over the next century, it is expected that sea ice will continue to decline, glaciers will continue to shrink, snow cover will continue to decrease, and permafrost will continue to thaw.
For every 2°F of warming, models project about a 15% decrease in the extent of annually averaged sea ice and a 25% decrease in September Arctic sea ice. The coastal sections of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets are expected to continue to melt or slide into the ocean. If the rate of this ice melting increases in the 21st century, the ice sheets could add significantly to global sea level rise. Glaciers are expected to continue to decrease in size. The rate of melting is expected to continue to increase, which will contribute to sea level rise.
Future Sea Level Change
Warming temperatures contribute to sea level rise by expanding ocean water, melting mountain glaciers and ice caps, and causing portions of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to melt or flow into the ocean. Since 1870, global sea level has risen by about 8 inches. Estimates of future sea level rise vary for different regions, but global sea level for the next century is expected to rise at a greater rate than during the past 50 years. The contribution of thermal expansion, ice caps, and small glaciers to sea level rise is relatively well-studied, but the impacts of climate change on ice sheets are less understood and represent an active area of research. Thus, it is more difficult to predict how much changes in ice sheets will contribute to sea level rise. Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets could contribute an additional 1 foot of sea level rise, depending on how the ice sheets respond.
Regional and local factors will influence future relative sea level rise for specific coastlines around the world (figure \(\PageIndex{i}\)). For example, relative sea level rise depends on land elevation changes that occur as a result of subsidence (sinking) or uplift (rising), in addition to things such as local currents, winds, salinity, water temperatures, and proximity to thinning ice sheets. Assuming that these historical geological forces continue, a 2-foot rise in global sea level by 2100 would result in the following relative sea level rise:
- 2.3 feet at New York City
- 2.9 feet at Hampton Roads, Virginia
- 3.5 feet at Galveston, Texas
- 1 foot at Neah Bay in Washington state

Future Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters decreasing in pH. Oceans become more acidic as carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions in the atmosphere dissolve in the ocean. This change is measured on the pH scale, with lower values being more acidic. The pH level of the oceans has decreased by approximately 0.1 pH units since pre-industrial times, which is equivalent to a 25% increase in acidity. The pH level of the oceans is projected to decrease even more by the end of the century as CO 2 concentrations are expected to increase for the foreseeable future. Ocean acidification adversely affects many marine species, including plankton, mollusks, shellfish, and corals. As ocean acidification increases, the availability of calcium carbonate will decline. Calcium carbonate is a key building block for the shells and skeletons of many marine organisms. If atmospheric CO 2 concentrations double, coral calcification rates are projected to decline by more than 30%. If CO 2 concentrations continue to rise at their current rate, corals could become rare on tropical and subtropical reefs by 2050.
Mismatched Interactions
Climate change also affects phenology, the study of the effects of climatic conditions on the timing of periodic lifecycle events, such as flowering in plants or migration in birds. Researchers have shown that 385 plant species in Great Britain are flowering 4.5 days sooner than was recorded earlier during the previous 40 years. In addition, insect-pollinated species were more likely to flower earlier than wind-pollinated species. The impact of changes in flowering date would be mitigated if the insect pollinators emerged earlier. This mismatched timing of plants and pollinators could result in injurious ecosystem effects because, for continued survival, insect-pollinated plants must flower when their pollinators are present.
Likewise, migratory birds rely on daylength cues, which are not influenced by climate change. Their insect food sources, however, emerge earlier in the year in response to warmer temperatures. As a result, climate change decreases food availability for migratory bird species.
Spread of Disease
This rise in global temperatures will increase the range of disease-carrying insects and the viruses and pathogenic parasites they harbor. Thus, diseases will spread to new regions of the globe. This spread has already been documented with dengue fever, a disease the affects hundreds of millions per year, according to the World Health Organization. Colder temperatures typically limit the distribution of certain species, such as the mosquitoes that transmit malaria, because freezing temperatures destroy their eggs.
Not only will the range of some disease-causing insects expand, the increasing temperatures will also accelerate their lifecycles, which allows them to breed and multiply quicker, and perhaps evolve pesticide resistance faster. In addition to dengue fever, other diseases are expected to spread to new portions of the world as the global climate warms. These include malaria, yellow fever, West Nile virus, zika virus, and chikungunya.
Climate change does not only increase the spread of diseases in humans. Rising temperatures are associated with greater amphibian mortality due to chytridiomycosis (see Invasive Species ). Similarly, warmer temperatures have exacerbated bark beetle infestations of coniferous trees, such as pine an spruce.
Climate Change Affects Everyone
Our lives are connected to the climate . Human societies have adapted to the relatively stable climate we have enjoyed since the last ice age which ended several thousand years ago. A warming climate will bring changes that can affect our water supplies, agriculture, power and transportation systems, the natural environment, and even our own health and safety.
Carbon dioxide can stay in the atmosphere for nearly a century, on average, so Earth will continue to warm in the coming decades. The warmer it gets, the greater the risk for more severe changes to the climate and Earth’s system. Although it’s difficult to predict the exact impacts of climate change, what’s clear is that the climate we are accustomed to is no longer a reliable guide for what to expect in the future.
We can reduce the risks we will face from climate change . By making choices that reduce greenhouse gas pollution, and preparing for the changes that are already underway, we can reduce risks from climate change. Our decisions today will shape the world our children and grandchildren will live in.
You can take steps at home, on the road, and in your office to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the risks associated with climate change. Many of these steps can save you money. Some, such as walking or biking to work, can even improve your health! You can also get involved on a local or state level to support energy efficiency, clean energy programs, or other climate programs.
Suggested Supplementary Reading
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2013. 5th Assessment: Summary for Policymakers .
NASA. 2018. Global Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet . This website by NASA provides a multi-media smorgasbord of engaging content. Learn about climate change using data collected by NASA satellites and more.
Attributions
Modified by Melissa Ha from the following sources:
- Climate and the Effects of Global Climate Change from General Biology by OpenStax (licensed under CC-BY )
- Climate Change from Environmental Biology by Matthew R. Fisher (licensed under CC-BY )
- Carbon Cycle from Biology by John W. Kimball (licensed under CC-BY )

What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
Watch this video to learn about the greenhouse effect! Click here to download this video (1920x1080, 105 MB, video/mp4). Click here to download this video about the greenhouse effect in Spanish (1920x1080, 154 MB, video/mp4).
How does the greenhouse effect work?
As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers.
A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight shines into the greenhouse and warms the plants and air inside. At nighttime, it's colder outside, but the greenhouse stays pretty warm inside. That's because the glass walls of the greenhouse trap the Sun's heat.

A greenhouse captures heat from the Sun during the day. Its glass walls trap the Sun's heat, which keeps plants inside the greenhouse warm — even on cold nights. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide , trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases .
During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 58 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius), on average.

Earth's atmosphere traps some of the Sun's heat, preventing it from escaping back into space at night. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
How are humans impacting the greenhouse effect?
Human activities are changing Earth's natural greenhouse effect. Burning fossil fuels like coal and oil puts more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
NASA has observed increases in the amount of carbon dioxide and some other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. Too much of these greenhouse gases can cause Earth's atmosphere to trap more and more heat. This causes Earth to warm up.
What reduces the greenhouse effect on Earth?
Just like a glass greenhouse, Earth's greenhouse is also full of plants! Plants can help to balance the greenhouse effect on Earth. All plants — from giant trees to tiny phytoplankton in the ocean — take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen.
The ocean also absorbs a lot of excess carbon dioxide in the air. Unfortunately, the increased carbon dioxide in the ocean changes the water, making it more acidic. This is called ocean acidification .
More acidic water can be harmful to many ocean creatures, such as certain shellfish and coral. Warming oceans — from too many greenhouse gases in the atmosphere — can also be harmful to these organisms. Warmer waters are a main cause of coral bleaching .

This photograph shows a bleached brain coral. A main cause of coral bleaching is warming oceans. Ocean acidification also stresses coral reef communities. Credit: NOAA


Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
How Do We Reduce Greenhouse Gases?
To stop climate change , we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasing. For the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase. There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing: we can stop adding them to the air, and we can increase the Earth’s ability to pull them out of the air.
This is called climate mitigation . There is not one single way to mitigate climate change. Instead, we will have to piece together many different solutions to stop the climate from warming. Below are descriptions of the main methods that we can use.
Many of these solutions are already being implemented in places around the world. Some can be tackled by individuals, such as using less energy, riding a bike instead of driving, driving an electric car, and switching to renewable energy. Other actions to mitigate climate change involve communities, regions, or nations working together to make changes, such as switching power plants from burning coal or gas to renewable energy and growing public transit.
Use less electricity.
Taking steps to use less electricity, especially when it comes from burning coal or gas, can take a big bite out of greenhouse gas emissions. Worldwide, electricity use is responsible for a quarter of all emissions.
Some steps that you can take to use less electricity are simple and save money, like replacing incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs that use less electricity, adding insulation to your home, and setting the thermostat lower in the winter and higher in the summer, especially when no one is home. There are also new technologies that help keep buildings energy efficient, such as glass that reflects heat, low-flow water fixtures, smart thermostats, and new air conditioning technology with refrigerants that don’t cause warming. In urban and suburban environments, green or cool roofs can limit the amount of heat that gets into buildings during hot days and help decrease the urban heat island effect .

Green roof on the Walter Reed Community Center in Arlington, VA, US Credit: Arlington County on Flickr/CC BY-SA 2.0
Generate electricity without emissions.
Renewable energy sources include solar energy, geothermal energy, wind turbines, ocean wave and tidal energy, waste and biomass energy, and hydropower. Because they do not burn fossil fuels, these renewable energy sources do not release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as they generate electricity. Nuclear energy also creates no greenhouse gas emissions, so it can be thought of as a solution to climate change. However, it does generate radioactive waste that needs long-term, secure storage.
Today, the amount of electricity that comes from renewable energy is growing. A few countries, such as Iceland and Costa Rica, now get nearly all of their electricity from renewable energy. In many other countries, the percentage of electricity from renewable sources is currently small (5 - 10%) but growing.

Wind turbines can be on land or in the ocean, where high winds are common. Credit: Nicholas Doherty on Unsplash
Shrink the footprint of food.
Today, about a fifth of global carbon emissions come from raising farm animals for meat. For example, as cattle digest food they burp, releasing methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, and their manure releases the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide. And forests, which take carbon dioxide out of the air, are often cut down so that cattle have space to graze.
Eating a diet that is mostly or entirely plant-based (such as vegetables, bread, rice, and beans) lowers emissions. According to the Drawdown Project , if half the population worldwide adopts a plant-rich diet by 2050, 65 gigatons of carbon dioxide would be kept out of the atmosphere over about 30 years. (For a sense of scale, 65 gigatons of carbon dioxide is nearly two-years-worth of recent emissions from fossil fuels and industry.) Reducing food waste can make an even larger impact, saving about 90 gigatons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere over 30 years.

Eating a plant-rich diet lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Credit: Victoria Shes on Unsplash
Travel without making greenhouse gases.
Most of the ways we have to get from place to place currently rely on fossil fuels: gasoline for vehicles and jet fuel for planes. Burning fossil fuels for transportation adds up to 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. We can reduce emissions by shifting to alternative technologies that either don’t need gasoline (like bicycles and electric cars) or don’t need as much (like hybrid cars). Using public transportation, carpooling, biking, and walking leads to fewer vehicles on the road and less greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Cities and towns can make it easier for people to lower greenhouse gas emissions by adding bus routes, bike paths, and sidewalks.

Electric bicycles can be a way to get around without burning gasoline. Credit: Karlis Dambrans/CC BY 2.0
Reduce household waste.
Waste we put in landfills releases greenhouse gases. Almost half the gas released by landfill waste is methane, which is an especially potent greenhouse gas. Landfills are, in fact, the third largest source of methane emissions in the U.S., behind natural gas/petroleum use and animals raised for food production (and their manure). In the U.S., each member of a household produces an average of 2 kg (4.4 lbs) of trash per day. That's 726 kg (1660 lbs) of trash per person per year! Conscious choices, including avoiding unnecessary purchases, buying secondhand, eliminating reliance on single-use containers, switching to reusable bags, bottles, and beverage cups, reducing paper subscriptions and mail in favor of digital options, recycling, and composting, can all help reduce household waste.
Reduce emissions from industry.
Manufacturing, mining for raw materials, and dealing with the waste all take energy. Most of the products that we buy — everything from phones and TVs to clothing and shoes — are created in factories, which produce up to about 20% of the greenhouse gases emitted worldwide.
There are ways to decrease emissions from manufacturing. Using materials that aren’t made from fossil fuels and don’t release greenhouse gases is a good start. For example, cement releases carbon dioxide as it hardens, but there are alternative products that don’t create greenhouse gases. Similarly, bioplastics made from plants are an alternative to plastics that come from fossil fuels. Companies can also use renewable energy sources to power factories and ship the products that they create in fuel-saving cargo ships.
Take carbon dioxide out of the air.
Along with reducing the amount of carbon dioxide that we add to the air, we can also take action to increase the amount of carbon dioxide we take out of the air. The places where carbon dioxide is pulled out of the air are called carbon sinks. For example, planting trees, bamboo, and other plants increases the number of carbon sinks. Conserving forests, grasslands, peatlands, and wetlands, where carbon is held in plants and soils, protects existing carbon sinks. Farming methods such as planting cover crops and crop rotation keep soils healthy so that they are effective carbon sinks. There are also carbon dioxide removal technologies, which may be able to pull large amounts of greenhouse gases out of the atmosphere.

As the trees and other plants in a forest use sunlight to create the food they need, they are also pulling carbon dioxide out of the air. Credit: B NW on Unsplash
© 2020 UCAR
- Solving Climate Change
- Why Earth Is Warming
- The Greenhouse Effect
- What's Your Carbon Footprint?
- Classroom Activity: Mitigation or Adaptation?
- Classroom Activity: Solving the Carbon Dioxide Problem
- Stabilization Wedges (Activity and Resources)
- Biology Article
- Greenhouse Effect Gases
Greenhouse Effect
Table of Contents
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Greenhouse gases, causes of greenhouse effect, effects of greenhouse effect, runaway greenhouse effect, greenhouse effect definition.
“Greenhouse effect is the process by which radiations from the sun are absorbed by the greenhouse gases and not reflected back into space. This insulates the surface of the earth and prevents it from freezing.”
A greenhouse is a house made of glass that can be used to grow plants. The sun’s radiations warm the plants and the air inside the greenhouse. The heat trapped inside can’t escape out and warms the greenhouse which is essential for the growth of the plants. Same is the case in the earth’s atmosphere.
During the day the sun heats up the earth’s atmosphere. At night, when the earth cools down the heat is radiated back into the atmosphere. During this process, the heat is absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere. This is what makes the surface of the earth warmer, that makes the survival of living beings on earth possible.
However, due to the increased levels of greenhouse gases, the temperature of the earth has increased considerably. This has led to several drastic effects.
Let us have a look at the greenhouse gases and understand the causes and consequences of greenhouse effects with the help of a diagram.
Also Read: Global Warming
“Greenhouse gases are the gases that absorb the infrared radiations and create a greenhouse effect. For eg., carbondioxide and chlorofluorocarbons.” Greenhouse Effect Diagram

The Diagram shows Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide are the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect
The major contributors to the greenhouse gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc. The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases never let the radiations escape from the earth and increase the surface temperature of the earth. This then leads to global warming.
Also Read: Our Environment
The major causes of the greenhouse effect are:
Burning of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are an important part of our lives. They are widely used in transportation and to produce electricity. Burning of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide. With the increase in population, the utilization of fossil fuels has increased. This has led to an increase in the release of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Deforestation
Plants and trees take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Due to the cutting of trees, there is a considerable increase in the greenhouse gases which increases the earth’s temperature.
Nitrous oxide used in fertilizers is one of the contributors to the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
Industrial Waste and Landfills
The industries and factories produce harmful gases which are released in the atmosphere.
Landfills also release carbon dioxide and methane that adds to the greenhouse gases.

The main effects of increased greenhouse gases are:
Global Warming
It is the phenomenon of a gradual increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere. The main cause for this environmental issue is the increased volumes of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane released by the burning of fossil fuels, emissions from the vehicles, industries and other human activities.

Depletion of Ozone Layer
Ozone Layer protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. It is found in the upper regions of the stratosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer results in the entry of the harmful UV rays to the earth’s surface that might lead to skin cancer and can also change the climate drastically.
The major cause of this phenomenon is the accumulation of natural greenhouse gases including chlorofluorocarbons, carbon dioxide, methane, etc.
Smog and Air Pollution
Smog is formed by the combination of smoke and fog. It can be caused both by natural means and man-made activities.
In general, smog is generally formed by the accumulation of more greenhouse gases including nitrogen and sulfur oxides. The major contributors to the formation of smog are automobile and industrial emissions, agricultural fires, natural forest fires and the reaction of these chemicals among themselves.
Acidification of Water Bodies
Increase in the total amount of greenhouse gases in the air has turned most of the world’s water bodies acidic. The greenhouse gases mix with the rainwater and fall as acid rain. This leads to the acidification of water bodies.
Also, the rainwater carries the contaminants along with it and falls into the river, streams and lakes thereby causing their acidification.
This phenomenon occurs when the planet absorbs more radiation than it can radiate back. Thus, the heat lost from the earth’s surface is less and the temperature of the planet keeps rising. Scientists believe that this phenomenon took place on the surface of Venus billions of years ago.
This phenomenon is believed to have occurred in the following manner:
- A runaway greenhouse effect arises when the temperature of a planet rises to a level of the boiling point of water. As a result, all the water from the oceans converts into water vapour, which traps more heat coming from the sun and further increases the planet’s temperature. This eventually accelerates the greenhouse effect. This is also called the “positive feedback loop”.
- There is another scenario giving way to the runaway greenhouse effect. Suppose the temperature rise due to the above causes reaches such a high level that the chemical reactions begin to occur. These chemical reactions drive carbon dioxide from the rocks into the atmosphere. This would heat the surface of the planet which would further accelerate the transfer of carbon dioxide from the rocks to the atmosphere, giving rise to the runaway greenhouse effect.
In simple words, increasing the greenhouse effect gives rise to a runaway greenhouse effect which would increase the temperature of the earth to such an extent that no life will exist in the near future.
Also Read: Environmental Issues
To learn more about what is the greenhouse effect, its definition, causes and effects, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download the BYJU’S app for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is global warming.
The gradual increase in temperature due to the greenhouse effect caused by pollutants, CFCs and carbon dioxide is called global warming. This phenomenon has disturbed the climatic pattern of the earth.
List gases which are responsible for the greenhouse effect.
The major greenhouse gases are: 1) Carbon dioxide 2) Methane 3) Water 4) Nitrous oxide 5) Ozone 6) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
What is the greenhouse effect?
What are the major causes of the greenhouse effect.
Burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, farming and livestock production all contribute to the greenhouse effect. Industries and factories also play a major role in the release of greenhouse gases.
What would have happened if the greenhouse gases were totally missing in the earth’s atmosphere?

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
thank you for this information this is so good
Thank you for such an informative topic
thanks for lot’s of information
Thanks for a lot information😊
Thanks again for your help
It is so much helpfull for him. thanks for this information
Thanks a lot for this information, it helped to improve my understanding.
Thank you so much. This has improved my understanding
Thank you for this information it is so interesting 👌👌
The information given by Byju’s are too useful
The term is deeply explained which is very helpful in understanding it really helps me so thank you Byju’s.
Thanks a lot for the information, it helped a lot
Thanks a lot. Very informative
Thank you sir for this beautiful explanation of topics
Thank u so much Byjus for the explanation of this topic
thankyou so much this information was very helpful
thi is so helpfull for study
Nice information
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

The Greenhouse Effect and our Planet
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gases.
Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Geography, Human Geography
Loading ...

Greenhouse gases include gases such as carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gases. These greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface. Then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere . The gases act like the glass walls of a greenhouse. In other words, they are warming.
The greenhouse effect happens when these gases gather in Earth's atmosphere. According to scientists, without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature of Earth would drop from 57 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius) to as low as negative 0.4 degrees F (minus 18 degrees C).
Do We Blame the Industrial Revolution ? Some greenhouse gases come from natural sources. For example, evaporation adds water vapor to the atmosphere. Animals and plants release carbon dioxide when they breathe. Methane is released naturally from decomposition, when soils and living things break down. Volcanoes —both on land and under the ocean —release greenhouse gases.
The Industrial Revolution happened in the late 1700s and early 1800s, when factories began producing more. Since then, people have been releasing larger quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 2004. Emissions of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), rose about 80 percent during that time.
The amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere far exceeds Earth's natural amount seen over the last 650,000 years.
Most of the CO 2 that people put into the atmosphere comes from burning fossil fuels . Cars, trucks, t rains and planes all burn fossil fuels. Many electric power plants do, as well. Another way humans release CO 2 into the atmosphere is by cutting down forests , because trees contain large amounts of carbon.
Human Activity + Greenhouse Gases = A Warming Earth People add methane to the atmosphere through livestock farming, landfills and fossil fuel production such as coal mining and natural gas processing. Nitrous oxide comes from agriculture and fossil fuel burning.
Fluorinated gases include chlorofluoro carbons (CFCs), hydro chlorofluoro carbons (HCFCs), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). They are produced during the manufacturing of refrigeration and cooling products. Some come through aerosol cans , such as some hairsprays or spray paint.
As greenhouse gases increase, so does the temperature of Earth. The rise in Earth's average temperature contributed to by human activity is known as global warming .
The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change Even slight increases in average global temperatures can have huge effects.
Perhaps the biggest effect is that glaciers and ice caps melt faster than usual. The meltwater d rains into the oceans , causing sea levels to rise.
Glaciers and ice caps cover about 10 percent of the world's land. They hold between 70 and 75 percent of the world's freshwater . If all of this ice melted, sea levels would rise about 70 meters (230 feet).
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change says that the global sea level rose about 1.8 millimeters (0.07 inch) per year from 1961 to 1993. It rose about 3.1 millimeters (1/8 inch) per year since 1993.
This seems like only a tiny bit, but rising sea levels can cause flooding in cities along the coasts . This could force millions of people in low-lying areas out of their homes, such as in Bangladesh, the U.S. state of Florida, and the Netherlands.
Millions more people in countries such as Peru and India depend on water from melted glaciers . They use it for drinking, watering crops and hydroelectric power . Rapid loss of these glaciers would greatly hurt those countries.
Predictable Rain is Important to Many Greenhouse gas emissions also affect changes in precipitation , such as rain and snow .
In the 20th century, precipitation increased in eastern parts of North and South America, Northern Europe, and northern and Central Asia. However, it has decreased in parts of Africa, the Mediterranean, and southern Asia.
As climates change, so do the habitats for living things. Animals that are adapted to a certain climates might become threatened. Many humans depend on predictable rain patterns to grow specific crops . If the climate of an area changes, the people who live there may no longer be able to grow the crops they depend on for survival.
Scientists aren't the only Ones Who Can Help
- Drive less. Use public transportation , carpool, walk, or ride a bike.
- Fly less. Airplanes produce huge amounts of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduce, reuse, and recycle .
- Plant a tree. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, keeping it out of the atmosphere.
- Use less electricity .
- Eat less meat. Cows are one of the biggest methane producers.
- Support alternative energy sources that don’t burn fossil fuels.
Artificial Gas
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the only greenhouse gases not created by nature. They are created through refrigeration and aerosol cans.
CFCs, used mostly as refrigerants, are chemicals that were developed in the late 19th century and came into wide use in the mid-20th century.
Other greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, are emitted by human activity, at an unnatural and unsustainable level, but the molecules do occur naturally in Earth's atmosphere.
Audio & Video
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Examples >
- Essay Topics
Essays on Greenhouse Effect
75 samples on this topic
The variety of written assignments you might get while studying Greenhouse Effect is stunning. If some are too confusing, an expertly crafted sample Greenhouse Effect piece on a related topic might lead you out of a deadlock. This is when you will definitely praise WowEssays.com ever-widening collection of Greenhouse Effect essay samples meant to ignite your writing creativity.
Our directory of free college paper samples showcases the most vivid instances of high-quality writing on Greenhouse Effect and related topics. Not only can they help you develop an interesting and fresh topic, but also exhibit the effective use of the best Greenhouse Effect writing practices and content organization techniques. Also, keep in mind that you can use them as a source of authoritative sources and factual or statistical information processed by real masters of their craft with solid academic experience in the Greenhouse Effect field.
Alternatively, you can take advantage of practical write my essay assistance, when our experts provide a unique example essay on Greenhouse Effect tailored to your individual requirements!
Global Warming: Cause And Mitigation Essay Template For Faster Writing
Proper essay example about global warming.
Global warming describes the gradual increase in Earth’s and its oceans’ temperature that changes the Earth’s climate. It shows that the Earth’s temperature increases due to the effect of greenhouses gases such as extensive emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) due to different factors. It is observed that human activity is the important cause of global warning that influenced the physical mechanism of climate change.
Effect of greenhouse gases in changing the Earth's temperature
Proper Essay Example About Greenhouse Gas Experiment
Free the green movement essay sample.
Introduction
Free Health Video Summaries Essay Example
Expertly crafted report on rdf production from msw and landfill, development in oil and gas retail industries {type) to use as a writing model.
Influence of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) 2
Free Climate Change And Marine Animals Research Paper: Top-Quality Sample To Follow
Inspiring essay about global climate change, good environmental pollution and human health research paper example, geography assignment on geography questions, good essay about united nations headquarters.
New York, NY 10017
Nameteacherclassdate Essay
Stakeholders on each side of the issue essays example.
Business Final Essay
Good Example Of Research Proposal On Solar And Nuclear Energy
The search or an alternative source of energy is needed due to the increasing populations of the world, higher demand in electricity and the depletion of the resources of the Earth. The whole scope of the available solutions was available through the study of journals, scientific magazines, online articles and periodicals, and books on the topic of applying alternative sources of energy so as to find the best possible solution In view of the global warming problem, this issue has been extensively studied by many scientists. I will utilize their vision on some available alternatives.
This is needed in order to determine which solution will best mitigate and facilitate the solution to the problem.
Example Of Should The World Keeping Using Nuclear Power Essay
DD Month YYYY
Sample Essay On Climate Change Response
The concerns about climate change among the public members and the scientific community are increasing. The members of the public and the scientific community are in the urge to understand the potential causes and impacts of climate change. The trends in the climate and temperatures around the world indicate that global warming is taking place (Botkin & Keller, 1995, p. 45). Provide one piece of data scientists offer to show that the climate is changing globally and give the expected impacts of climate change in my area.
How scientists learn about past global temperatures and climate
The Climate Change Act Of 2008: Development And Implementation {type) To Use As A Writing Model
Example of carbon dioxide (co2) emissions report.
Purpose The goal of this investigation was to ascertain whether there would be an increase or a decrease in global CO2 emission over the next 40 years and provide possible reasons for the same.
Is Global Warming a Hoax Research Paper
Global warming is probably one of the most publicized environmental problems. Everywhere you can find activists of the fight for reducing the impact of humanity on the planet's climate. If in fact humanity leads to a marked increase in global sea level, producing carbon dioxide, which is often considered to be the cause of global warming, of course, something must be done about it.
Example Of Is Climate Change Man-Made Argumentative Essay
The major role of communicator research paper sample, list of figures academic report example.
Figure 1 Schematic representation of hot water solar system in a building 11 Figure 2 Twenty Years Solar Energy Consumption in different regions 12
Benefits of Solar Energy
Free Research Paper About Proof That Manmade Global Warming Does Exist
Greenhouse effect research papers example, good atmosphere and climate change project based assessment essay example, greenhouse effect essay sample.
- What causes climate change? Define the Greenhouse Effect
Free Essay About Global Warming
Good example of essay on ecotourism, the savior of our environment: steps towards alleviating the impact, good example of research proposal on causes and effects of global warming, argument research paper examples.
Is global climate caused by human activities?
Good Academic Essay About Global Warming
Carbon dioxide reduction (or abatement) essay sample, how the sun produces heat and light essays example.
What is sunlight?
Example Of Size, Location And Composition Research Paper
Venus: Location, Size, Composition and Features
(Author’s Full Name) (Institution Name)
Venus is the second planet from the sun in our solar system. Its orbital day lasts for approximately 225 Earth days, and it does not have a moon or any other similar satellite orbiting around it. It is the brightest and the most easily recognizable astral body from the Earth, after the Moon. Named after the Roman Goddess of love and fertility and often linked with femininity in popular culture and mythology, this paper examines the physical description, unique features and the significance in the solar system of the planet Venus.
Good Example Of Research Paper On Any Topic (Writer's Choice)
YourFirstNameYourLastName
Any Topic (Writer's Choice) Essays Examples
YourFirstName YourLastName
Responsibility For Our Environment Essay
Free solar system astronomy: global warming is not the suns fault essay example, what causes global warming research paper sample, example of essay on sustainability: the impact of recyclable.
MATERIALS ON THE TEXTILE INDUSTRY
Good Example Of Essay On Wind Energy
Good essay on global warming, sample essay on global warming and its causes.
XX December 2013
Example Of Main Contributing Factors of Global Warming Essay
Good example of term paper on global warming, is it hoax or real, global warming argumentative essay samples, argumentative essay on global warming.
What is Global Warming
What is global warming, and how is it affecting the Earth and its inhabitants? Global warming is sometimes referred to as the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the absorption of energy radiated from the Earth's surface by carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere, causing the atmosphere to become warmer. The greenhouse effect is what is causing the temperature on the Earth to rise, and creating many problems that will begin to occur in the coming decades.
Effects of Global Warming
Good Example Of Effects Of Pollution Research Paper
Environmental studies case study examples.
Theory of Global Warming and Climate Change
Greenhouse Gases and their Sources
The Myth Of Global Cooling Argumentative Essay Examples
<Student’s name> <Professor’s name>
Global Warming Pollutants and Ways to Curb Them Essay Sample
Environmental issues in russia article review examples, example of essay on the greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases and global warming research paper examples.
The Human Factor
Engineering Research Paper Examples
Free research paper on hybrid cars, research paper on hybrid cars, environmental issues essay.
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Essay on Greenhouse Effect: Causes, Problems, Effects and Prevention
The process by which radiation from a planet’s atmosphere warms its surface to a temperature which exceeds the normal temperature of the planet is called greenhouse effect. If a planet’s atmosphere contains greenhouse gases, the atmosphere will radiate the energy in various directions. Some part of this radiation will be towards the surface, making it warm. The downward component of the radiation, which is the strength of the greenhouse effect will depend on the atmosphere’s temperature and amount of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere.
The earth’s atmosphere is warmed by absorbing infrared thermal radiation from the sun. The greenhouse gases which are present in the atmosphere radiate energy, some of which is directed to the surface and lower atmosphere. The mechanism which produces this difference between the actual surface temperature and effective temperature is due to the temperature, knows as greenhouse effect.
The natural greenhouse effect of the earth is critical to support life. Human activities such as burning the fossil fuels and clearing the forests have made an intense impact on natural greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
History of Greenhouse Effect
The term greenhouse effect was first used by atmospheric scientists in early 1800s. The existence of greenhouse effect was brought up by Joseph Fourier in 1824. In 1896, the effect was fully qualified by Svante Arrhenius, who made the first quantitative prediction of global warming because of a hypothetical doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide. At the time, it was used to describe the naturally occurring functions of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere, and did not have any negative subtexts. It was not until the mid 1950s that greenhouse effect was teamed with concern for climate change.
Greenhouse gases that cause Greenhouse Effect
The major gases which contribute to the greenhouse effect on earth are as follows:-
- Water vapor 36-70%
- Carbon dioxide 9-26%
- Methane 4-9%
The below mentioned activities release gases which prove to be harmful for the planet. Following are the six major greenhouses which play a lead role in the greenhouse effect and global warming:-
1. Carbon dioxide (CO2)
It is a naturally occurring gas, produced by living organisms and fermentation. Carbon dioxide which is emitted from fuel burning is responsible for approx 87% of global warming, and has alarmingly increased by 27% since the industrial revolution.
2. Methane (CH4)
Methane is a naturally occurring inflammable gas which is produced by decomposition of organic matters and geological coal formations. The landfills hole the major credit to release methane, which adds up into the atmosphere and leads the global warming.
3. Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Nitrogen oxides are naturally occurring from microbial action present in the soil. It is also produced by burning of fuels. Due to the increased use of nitrogen based fertilizers and catalytic converters in automobiles, the production of nitrogen oxides has raised, thus disturbing the ecosystem balance.
4. Hydrofluorocarbon gases (HFCs)
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), coolant, cleaning and propellant gases were blacklisted internationally due to its harmful effect on the ozone layer. HFCs also play a crucial part in global warming, and are 4,000 to 10,000 times more harmful than carbon dioxide.
5. Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6)
Very low atmospheric concentration can make it a good test gas for gas concentration monitors. SF6 is a man-made gas used in water leakage detection for cable cooling systems and insulating materials for high voltage equipment.
6. Perfluorocrbons (PFCs)
PFCs are man-made replacement gases for CFCs, but they also result as a by-product of aluminum smelting. They are also used as a purging agent for semi conductor manufacturing. They cause severe damage to the atmosphere too.

What does increased greenhouse gases indicate?
The increase in greenhouse gases directly increases the heat on the planet’s surface and lower atmosphere. It has a dangerous effect as it can reduce or even create holes in the ozone layer. Due to this, harmful rays such as ultra violet rays can seep in though the thin areas and cause damage on earth.
What are the causes of greenhouse effect?
1. burning the fossil fuels.
Fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil are an integral part of our lives, the elements which play a vital role in daily routines. The most important use of fossil fuels occurs in producing electricity and transportation. On burning the fossil fuels, the carbon dioxide stored inside them is released, which combines with oxygen in the air, resulting in production of carbon dioxide. As the population is increasing, the numbers of vehicles have made a high leap too. Due to this, the pollution has increased in the atmosphere. As these vehicles run, carbon dioxide is released, which is one of the main gases responsible for increase in greenhouse effect.
Electricity related emissions are high because we are still dependant on coal for generating electricity, which releases a huge amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Since it is the primary source of generating electricity, the loss of fossil fuels is massive, due to which the global warming has increased.
2. Deforestation
A major section of the land on our earth is covered by the forests. They are very important for a sustainable life on earth, as plants give out oxygen and inhale the carbon dioxide. Thus, the ecosystem is balanced due to the presence of trees. Sadly, large scale development of the urban landscapes has resulted in depletion of green cover of the earth. Forests are now being burnt down or chopped off to build concrete buildings instead. On burning the wood, the stored carbon is converted back to carbon dioxide, which adds up into the atmosphere, increasing the pollution.
3. Industrial waste and landfills
Various industries which are involved in cement production, fertilizers, extraction of oil, coal mining activities etc produce harmful greenhouse gases. Also, landfills filled with garbage produce carbon dioxide and methane, which play a major role in the greenhouse effect.
4. Population rise
Increase in population over the decades has led to high demand for food, clothing and shelter. Machines used in our daily lives such as air conditioners also exhale harmful gases, which contribute to the greenhouse effect. Also, more number of people means more usage of fossil fuels, which has made the situations much worse.
What are the harmful effects of greenhouse effect?
The adverse effects of greenhouse effect are alarming. They are already being experienced on the earth now, and can go much adverse changes in the near future. The major harmful effects of greenhouse effect are listed below:
- The sea levels will rise. There is more than 5,773,000 cubic miles of water present in form of ice caps, glaciers and permanent snow. According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, if all of the glaciers met, the sea level would rise by 230 feet! This will not happen all at once, but the levels will rise certainly, submerging the low-lying areas.
- The balance of the global ecosystem will be affected. The fresh water stored in the ice caps will desalinate the ocean as they melt. The desalination in the gulf current will play a negative impact on the ocean currents, which regulate temperatures. It will be difficult to draw a pattern of warming and cooling in some areas.
- Warmer water and stronger hurricanes will be more frequent than now. Due to the rise in oceans’ temperature, the probability of frequent and stronger hurricanes may also become a threat.
- Weather patterns will continue to change. Most of the regions that are currently subjected to droughts will face much challenging conditions. The wet region will get wetter too. Mountain glaciers and snow caps will further shrink which will jeopardize many water supply systems. These negative changes have already begun to show their impact in some parts of the world.
- Ecosystems will be stressed due the impact of greenhouse effect and global warming. Flora and fauna will be massively affected. The animals which cannot adapt to the climatic changes will extinct over the time, thus misbalancing the ecosystem balance. A variety of pests and tropical diseases are expected to sprout in the warmer regions. Valuable species especially in the arctic will be the worst affected.
Evidence to the changes in earth’s climate: Global Warming
The effects of greenhouse effect and global warming have already started showing up in some parts of the world. Situations are predicted to get much worse. Some of the observations recorded by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) are as follows: -
- Eleven out of twelve warmest years since 1850 occurred between 1996 and 2006. Average global temperatures have risen by approximately 0.74C between 1906 and 2005. This rise in temperature is widespread throughout the world, but higher at the northern latitudes.
- Sea levels have increased during the same period. Since 1961, the average rate has been 1.8 mm per year, but has now further increased to 3.1 mm per year since 1993.
- Some of the climate changes agencies from the United States have reported that the oceans all over the world are getting warmer at a rate much higher than predicted. The warming has occurred approximately 50% faster over that last century, than it was calculated previously.
A number of human activities contribute to the greenhouse effect, which has brought us to the alarming situations today. If continued without taking precautions to save the earth, the situations are going to be worse. Some of the human activities which produce greenhouse gases are as follows: -
- Fuel combustion
- Vehicle transport and automobiles
- Energy industries
- Use of oil and natural gas
- Metal production manufacturing industries and construction
- Fugitive emissions from fuels
- Mineral products
- Chemical industries
- Production of halocarbons
- Solvent and other product use
- Consumption of halocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride
- Production of halocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride
- Enteric fermentation
- Rice cultivation
- Agricultural soils
- Prescribes burning of savannas
- Solid waste disposal on land
- Wastewater handling
- Waste incineration
- Field burning of agricultural residues
What preventive should be taken against greenhouse effect?
It would not be late today if we take an initiative to make the earth a reliable place to live in. to reduce the harmful effects of greenhouse gases on the earth and atmosphere, change must be brought in our daily routine and lifestyles. Here are some of the best suggestive steps to keep in mind to reduce greenhouse gas emissions:-
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Following the three Rs in your daily life can make a difference too. Buying products with minimal packaging will help in reducing waste. Through recycling half of your household waste, 2,400 pounds of carbon dioxide can be saved from adding up in the atmosphere.
- By adding insulation to the walls, installing caulking or weather stripping around doors and windows.
- Lower the heat while sleeping and keep the temperature moderate all the time.
- Installing a programmable thermostat can save a large amount of carbon dioxide from being released. By setting it just 2 degrees lower during winter and higher in summer can save approx. 2,000 pounds of carbon dioxide each year.
- Replace the light bulbs with Compact Fluorescent Lights It is better to use compact fluorescent light (CFL) than the usual light bulbs. By replacing just one 60-watt incandescent light bulb with a CFL, over $30 will be saved over the life of the bulb. Also, the CFL gives off 70 percent less heat than the light bulbs and lasts 10 times longer than them too.
- Drive less and drive smart Walking and biking are a great form of exercise. Not only they will keep you fit, but also make your contribution towards saving the planet, since less driving means lesser emissions. Every gallon of gas saved will keep 20 pounds of carbon dioxide away from the atmosphere.
- Use less hot water Set your water heater at 120 degrees and wrap it in an insulating blanket if it is 15 years old. Also, use low flow showerheads to save hot water and approx 350 pounds of carbon dioxide every year.
- Buy energy efficient products Home appliances now come in a wide range of energy efficient models, and compact fluorescent bulbs are designed to use much lesser amount of energy than the regular light bulbs.
- Plant a tree Trees are the best solution to fight against the greenhouse effect and global warming. Not only they inhale carbon dioxide and release oxygen for us, plantation will also help in restoring the disturbed ecological balance.
- Use the ‘off’ switch Save electricity and reduce global warming by using power only when you need it. Make a habit to switch off lights, television, computer and other electronic devices when they are not in use. Turn off the water tap when you do not need the water. These simple steps will help you in reducing the energy usage and burning of fossil fuels. Less energy usage means less dependence on fossil fuels, which on burning contribute to the harmful greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse effect Essay Conclusion
Greenhouse effect and global warming are the biggest threat to human race and the biggest environmental challenge of 21st century that we need to tackle. It is important for all citizens to become fully aware of the causes and harmful consequences of greenhouse effect and global warming. The main culprits of greenhouse effect and global warming is the growing emission of harmful gases such as Methane, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide resulting from emissions of industrial activities, incomplete combustion of petrol and diesel from vehicles as well as growing emissions of CFCs from air conditioners. It is important for individuals to choose greener alternatives such as cycling, hybrid clean fuels and for industries and governments to choose environmental friendly production methods and energy sources. Immediate action on this greenhouse effect and global warming is necessary to tackle this environmental problem.
Want to read more sample Essays from essay writers at Assignmenthelp.net ? We have sample essays on 1000s of important essay topics and essay writing prompts. Our online writers can train students to write high quality school and college essays based on evidence, facts, examples and data findings to support claims. Learn about how to develop a style of reasoning in your essay to develop new writing ideas, connect claims and evidence.
Get help of online essay writers to learn about stylistic or persuasive elements, how to make word choice for essay or how to use appeals to emotion which can add power to the ideas expressed in your essay.
Looking for online essay writing help and essay editors for college essays, school essays, admission essay or your term paper? Assignmenthelp.net’s online essay writers are available 24x7 online to help students with writing essays, editing essay, proofreading, referencing and citation help as well as checking for grammar and spellings. Order Essay writing help now!

- MassiveMark Playground
- Transliteration Playground
- Professional Practice Test
- Assignmenthelp Services
- Custom Writing help
- Free Assignment Samples
- Free Homework Help Samples
- Terms of Use
- Refund Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
600 Words Essay on Greenhouse Effect. A Greenhouse, as the term suggests, is a structure made of glass which is designed to trap heat inside. Thus, even on cold chilling winter days, there is warmth inside it. Similarly, Earth also traps energy from the Sun and prevents it from escaping back. The greenhouse gases or the molecules present in the ...
greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.. The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear. French mathematician Joseph Fourier is sometimes given ...
greenhouse effect. phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape. greenhouse gas. gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases.. Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from ...
The greenhouse effect occurs in the atmosphere, and is an essential part of How the Earth System Works. Click the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change Infographic. Locate the greenhouse effect icon and identify other topics that cause changes to, or are affected by, the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect also happens with the entire Earth. Of course, our planet is not surrounded by glass windows. Instead, the Earth is wrapped with an atmosphere that contains greenhouse gases (GHGs).Much like the glass in a greenhouse, GHGs allow incoming visible light energy from the sun to pass, but they block infrared radiation that is radiated from the Earth towards space (figure ...
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? The Short Answer: The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to live.
The greenhouse effect is the process through which heat is trapped near Earth's surface by substances known as 'greenhouse gases.'. Imagine these gases as a cozy blanket enveloping our planet, helping to maintain a warmer temperature than it would have otherwise. Greenhouse gases consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide ...
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...
The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life. Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent it from escaping into space. About half of the sun's radiation that ...
Welcome to our database, which has extensive coverage in numerous essay samples. Tips on Writing a Great Greenhouse Effect Essay. The problem of greenhouse gases is acute for the global society, not only in the United States of America. First, you can write about the concept of the greenhouse effect and talk about how the mounting carbon ...
Definition. The greenhouse effect on Earth is defined as: "The infrared radiative effect of all infrared absorbing constituents in the atmosphere.Greenhouse gases (GHGs), clouds, and some aerosols absorb terrestrial radiation emitted by the Earth's surface and elsewhere in the atmosphere.": 2232 The enhanced greenhouse effect describes the fact that by increasing the concentration of GHGs in ...
Greenhouse Effect). They are very efficient in trapping heat into the atmosphere; therefore, it results in the greenhouse effect. The solar energy is absorbed by the earth's surface and then reflected back to the atmosphere as heat. Then as the heat goes out to space, greenhouse gases absorb a part of the heat.
To stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasing.For the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase. There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing: we can stop adding them to the air ...
Essay About Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Our earth contains a specific climate system, continuous increase of the common temperature of the Earth's climate system resulting in warming.
greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. (To a lesser extent, surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap ...
On the one hand, we have the greenhouse effect to thank for the presence of life on earth; without it, our planet would be cold and unlivable. But beginning in the mid- to late-19th century, human ...
A greenhouse is a house made of glass that can be used to grow plants. The sun's radiations warm the plants and the air inside the greenhouse. The heat trapped inside can't escape out and warms the greenhouse which is essential for the growth of the plants. Same is the case in the earth's atmosphere. During the day the sun heats up the ...
greenhouse effect. noun. phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape. greenhouse gas. noun. gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere.
The earth is heating from the greenhouse effect. Without the o-zone. layer there blocking the heat from leaving the atmosphere, earth would become. very cold and lifeless. If not for the greenhouse effect, the earth would be. 33 degrees C colder than it is now. Other proof that the greenhouse effect.
Essays on Greenhouse Effect. 75 samples on this topic . The variety of written assignments you might get while studying Greenhouse Effect is stunning. If some are too confusing, an expertly crafted sample Greenhouse Effect piece on a related topic might lead you out of a deadlock. This is when you will definitely praise WowEssays.com ever ...
Greenhouse effect Essay Conclusion. Greenhouse effect and global warming are the biggest threat to human race and the biggest environmental challenge of 21st century that we need to tackle. It is important for all citizens to become fully aware of the causes and harmful consequences of greenhouse effect and global warming.
The Greenhouse Effect is the roll that the atmosphere plays in insulating and warming the earth's surface. The atmosphere is the part of the earth that is covered by a thin blanket of gasses. Nitrogen and oxygen are the main gasses in our atmosphere. We would not be able to survive without oxygen.
For example, in the discussion about greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect, a readout strategy could involve how a student interprets the interaction between gases and radiation. If a student consistently applies an only one type of radiation readout strategy, it means they might perceive all interactions between greenhouse gases and ...