- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

Education in India – A Detailed Analysis
Last updated on April 21, 2024 by ClearIAS Team
This article is a detailed analysis of the Education System of India.
The post covers various aspects of the problems faced by the Indian Education sector, the Constitutional provisions related to education, and the education policies adopted by modern India.
Also read: Learning Poverty
Table of Contents
History of Education in India
India has a rich tradition of imparting knowledge.
The ‘gurukul’ was a type of education system in ancient India with shishya (students) living with the guru in the same house. Nalanda has the oldest university system of education in the world. Students from across the world were attracted to Indian knowledge systems.
Many branches of the knowledge system had their origin in India. Education was considered a higher virtue in ancient India.
Add IAS, IPS, or IFS to Your Name!
Your Effort. Our Expertise.
Join ClearIAS
However, the renaissance and scientific thinking as happened in Europe didn’t happen in India at that time.
The British who took control of the Indian affairs by that time had different priorities. Education in British India initially lagged a lot.
However, later, the British established the modern education system still followed in India. They replaced age-old systems of education in the country with English ways .
Still, the education system in India needs a lot of reforms.
Also read: Examination System in India
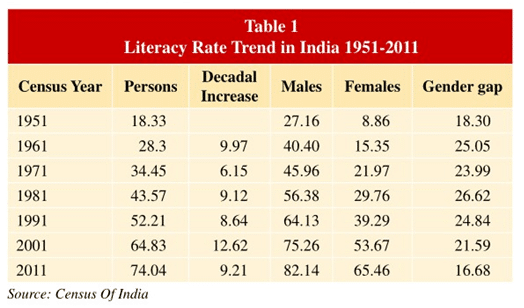
Current Status of Education in India: Data from Census 2011
UPSC Prelims Test Series 2024
Take All-India Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress!
- Literacy rate in India as per Census 2011: 74%.
- Literacy rate: Male: 82.1%; Female: 65.5%
- Kerala tops the rankings, followed by Delhi, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
- Bihar is the lowest among states, followed by Arunachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, etc., however, they are improving their position.
- Bihar has a literacy rate of 63.8%, and that of women is 53.3%.
- Literacy rates for both adults as well as youths have increased, still, the absolute number of illiterates in India is as much as India’s population was at the time of independence.
- The gender gap in terms of literacy began to narrow first in 1991 and the pace has accelerated, however still lags far behind the global female literacy rate of 7% (UNESCO 2015).
- There are large state variations in the gender gap.
- However, during 2001 – 2011, the male literacy rate increased by 6 percentage points but female literacy increased by nearly 12 percentage points. Achievement in female literacy in Bihar is noteworthy: from 33% in 2001 to 53% in 2011.
- Be that as it may, India is still lagging behind the world literacy rate of 86.3%(UNESCO 2015). A major group of states lies in the average rank i.e. just above the national level of 64.8 percent.
Indian Education System: The Present Pyramidal Structure
The Indian education system can broadly be considered as a pyramidal structure:
- Pre-primary level: 5-6 years of age.
- Primary (elementary) level: 6-14 years of age. Elementary-level education is guaranteed by our constitution under Article 21 A . For this level, the government has introduced Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) under the Right To Education(RTE) Act.
- Secondary level: Age group between 14-18. For this level, the government has extended SSA to secondary education in the form of the Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan .
- Higher education: generally of three levels: UG→ PG→ MPhil/PhD. To cater to the requirements of higher education, the government has introduced Rashtriya Uchhattar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA).
Read: Examination System in India
Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) related to Education
Goal 4 of SDG : Education for all – ensures equitable, inclusive, and quality education along with the promotion of lifelong learning opportunities for all by 2030.
Provisions in the Indian Constitution related to Education
- Under Article 45 in DPSP , it was mentioned that the government should provide free and compulsory education for all children up to the age of 14 years within 10 years from the commencement of the Constitution. As this was not achieved, Article 21A was introduced by the 86th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2002 , making elementary education a fundamental right rather than a directive principle. Article 45 was amended to provide for early childhood care and education to children below the age of six years.
- To implement Article 21A, the government legislated the RTE Act. Under this act, SSA – Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan – got a further impetus. SSA aims to provide Universalization of Elementary Education (UEE) in a time-bound manner.
- SSA has been operational since 2000-2001. Its roots go back to 1993-1994 when the District Primary Education Programme (DPEP) was launched. However, under the RTE Act, it got legal backing.
RTE Act 2009
- 86th Amendment Act 2002 introduced Article 21-A, which provides for free and compulsory education of all children in the age group of six to fourteen years as a Fundamental Right.
- The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act was enacted to implement this fundamental right.
Provisions of the RTE Act
- ‘Compulsory education’ means an obligation of the government to provide free elementary education and ensure compulsory admission, attendance, and completion of elementary education.
- Provision for a non-admitted child to be admitted to an age-appropriate class.
- Rational deployment of teachers, ensuring that there is no urban-rural imbalance in their postings.
- Prohibition of deployment of teachers for non-educational work, other than services like decennial census, elections, etc.
- It prohibits (a) physical punishment and mental harassment (b) screening procedures for admission of children (c) capitation fees (d) private tuition by teachers (e) running of schools without recognition.
- Development of curriculum in consonance with the values enshrined in the constitution, ensuring all-around development of the child, building a system of child-friendly and child-centered learning.
- To further inclusiveness, 25% reservation is provided for disadvantaged students in private schools.
Criticisms of the RTE Act
- Even though the RTE + SSA have increased access to schools, resulting in a high enrollment rate, dropout rates increased in tandem. However, there is inadequate attention given to this scenario.
- There is a fear of financial burden on the government for teacher recruitment and training.
- The grey area of teacher transfer is also not helping the cause.
- Since all state holidays are not relevant for all localities, such a calendar preparation by local authorities can increase attendance and can also encourage local panchayats to take ownership of schools.
- RTE students in private schools are paying extra fees as the schools claim that the government fund provided for the same is not adequate.
- Most private schools treat RTE as charity and demand that the onus of universalizing education should be on the government’s head rather than putting pressure on them.
- 70% of students are in government schools. So it must be fixed in priority, by providing infrastructure , teacher quality , and targeted learning for children from disadvantaged groups to provide an equitable education system.
- Under the RTE Act, till class 8, students should not be failed in exams. This is called the No detention policy. It had reduced dropout rates.
- There is growing criticism of the policy resulting in reducing the quality of elementary education. Hence the RTE Act was amended to scrap the policy.
- RTE Act prioritized schooling of children only from the age of 6, thus ignoring pre-school education. Kothari Commission had recommended the establishment of a center for the development of pre-primary education in each district.
- District Information System for Education (DISE) report states that 30% of primary and 15% of upper primary schools have higher PTRs.
- According to the Economic Survey 2018-19, the PTR at the national level for primary schools is 23 and 27 for secondary schools. Thus PTR appears to be satisfactory, as there are sufficient teachers. However, the main issue is a balanced deployment of teachers based on student strength.
- Even though the Student-Classroom ratio (SCR) improved in almost all of the States, there is disparity across the country.
Modern Education in India: The Evolution of the System through various policies
The British government had introduced modern education in India. From Macaulay’s minutes to Wood’s dispatch to several commissions like the Sadler Commission, 1904 Indian education policy, etc. built the foundation of the Indian education system during the colonial period.
Radhakrishnan committee
In 1948-49, the University Education Commission was constituted under Radhakrishnan . It molded the education system based on the needs of an independent India. The pre-Independent Indian education value system was catering to colonial masters. There was a need to replace Macaulayism with the Indian value system. ( Macaulayism is the policy of eliminating indigenous culture through the planned substitution of the alien culture of a colonizing power via the education system). Some of the values mentioned in the commission were:
- Wisdom and Knowledge
- Aims of the Social Order : the desired social order for which youths are being educated.
- Love for higher values in life
- Training for Leadership
The Independent Indian education system developed along the lines of this value framework. In the present times, where there are imminent threats of political ideologies hijacking the pedagogy of education and commercialization of education eroding value systems, it is appreciable to dust off the values promulgated by the commission. A recent controversial circular by the Central University of Kerala (CUK), directing that research topics for Ph.D. students must be by ‘national priorities’, and research in ‘irrelevant topics’ and ‘privilege areas’ must be discouraged, is a case in point.
Kothari commission
If the Radhakrishnan committee charted out the value system of the Indian education system, it was the Kothari Commission that provided the basic framework of the same. The commission provided for:
- Standardization of educational system on 10+2+3 pattern.
- Emphasized the need to make work experience and social/national service an integral part of education.
- Linking of colleges to several schools in the neighborhood.
- Equalization of opportunities to all and to achieve social and national integration .
- Neighborhood school system without social or religious segregation and a s chool complex system integrating primary and secondary levels of education.
- Establishment of Indian Education Service.
- On-the-job training of the teaching staff and efforts to raise the status of the teachers to attract talents into the profession.
- To raise expenditure on education from 2.9% of the GDP to 6% by 1985.
This committee report paved the way for the National Educational Policy 1968 which provided the base and roadmap for further development of the education system in India.
National Educational Policy 1968
- The policy provided for “radical restructuring” and equalization of educational opportunities to achieve national integration and greater cultural and economic development.
- Increase public expenditure on education to 6% of GDP.
- Provide for better training and qualification of teachers.
- Three-language formula : state governments should implement the study of a modern Indian language, preferably one of the southern languages, apart from Hindi and English in the Hindi-speaking states, and of Hindi along with the regional language and English in the non-Hindi-speaking states. Hindi was encouraged uniformly to promote a common language for all Indians.
National Educational Policy 1985
- The policy aimed at the removal of disparities and to equalize educational opportunities, especially for women, SC and ST.
- Launching of “Operation Blackboard” to improve primary schools nationwide.
- IGNOU, the Open University, was formed.
- Adoption of the “rural university” model , based on the philosophy of Mahatma Gandhi, to promote economic and social development at the grassroots level in rural India.
T.S.R.Subramanium committee report
- ECCE is inconsistent across states. So all government schools should have facilities for pre-primary education, which would facilitate pre-school education by the government instead of the private sector.
- The policy of no detention should be upheld only till class five and not till class eight.
- There is a steep rise in teacher shortage, absenteeism, and grievances.
- Need to constitute an Autonomous Teacher Recruitment Board.
- Four years integrated B.Ed. the course should be introduced.
- There is an inadequate integration of information technology (IT) and the education sector.
- The National Skills Qualification Framework should be scaled up.
- The choice of vocational courses should be in line with local opportunities and resources .
- Bringing formal certification for vocational education at par with conventional education certificates.
- All India Education Service.
- Existing separate laws governing individual regulators in higher education should be replaced by the said act.
- The role of existing regulatory bodies like UGC and AICTE should be revised.
- National Accreditation Board (NAB) subsuming the existing accreditation bodies.
Kasturirangan Report On School Education (Draft National Education Policy)
For restructuring the education system in India, the government is preparing to roll out a New Education Policy that will cater to Indian needs in the 4th Industrial Revolution by making use of its demographic dividend. Committee for Draft National Education Policy (chaired by Dr. K. Kasturirangan) submitted its report on May 31, 2019.
You can read about the National Education Policy 2020 in detail here .
School Education:
- Low accessibility.
- The curriculum doesn’t meet the developmental needs of children.
- Lack of qualified and trained teachers.
- Substandard pedagogy.
- Currently, most early childhood education is delivered through anganwadis and private preschools. However, there has been less focus on the educational aspects of early childhood.
- Guidelines for up to three-year-old children.
- Educational framework for three to eight-year-old children.
- This would be implemented by improving and expanding the Anganwadi system and co-locating anganwadis with primary schools.
- Expanding the ambit of the Act to all children between the ages of three to 18 years, thus including early childhood education and secondary school education.
- There should be no detention of children till class eight. Instead, schools must ensure that children are achieving age-appropriate learning levels.
- The current structure of school education is to be restructured based on the development needs of students.
- 10+2+3 structure to be replaced by 5-3-3-4 design comprising: (i) five years of foundational stage (three years of pre-primary school and classes one and two), (ii) three years of preparatory stage (classes three to five), (iii) three years of middle stage (classes six to eight), and (iv) four years of secondary stage (classes nine to 12).
- The current education system solely focuses on rote learning. The curriculum load should be reduced to its essential core content.
- Force students to concentrate only on a few subjects.
- Do not test learning in a formative manner.
- Cause stress among students.
- To track students’ progress throughout their school experience, State Census Examinations in classes three, five, and eight should be established.
- Restructure the board examinations to test only the core concept. These board examinations will be on a range of subjects. The students can choose their subjects and the semester when they want to take these board exams. The in-school final examinations may be replaced by these board examinations.
- Although establishing primary schools in every habitation has increased access to education, it has led to the development of very small schools making it operationally complex. Hence the multiple public schools should be brought together to form a school complex .
- A complex will consist of one secondary school (classes nine to twelve) and all the public schools in its neighborhood that offer education from pre-primary to class eight.
- These will also include anganwadis, vocational education facilities, and an adult education center.
- Each school complex will be a semi-autonomous unit providing integrated education across all stages from early childhood to secondary education.
- This will ensure that resources such as infrastructure and trained teachers can be efficiently shared across a school complex.
- A steep rise in a teacher shortage, lack of professionally qualified teachers, and deployment of teachers for non-educational purposes have plagued the system.
- Teachers should be deployed with a particular school complex for at least five to seven years.
- They will not be allowed to participate in any non-teaching activities during school hours.
- Existing B.Ed. the program will be replaced by a four-year integrated B.Ed. program that combines high-quality content, pedagogy, and practical training. An integrated continuous professional development will also be developed for all subjects.
- Separating the regulation of schools from aspects such as policymaking, school operations, and academic development.
- Independent State School Regulatory Authority for each state will prescribe basic uniform standards for public and private schools.
- The Department of Education of the State will formulate policy and conduct monitoring and supervision.
Higher Education
- According to the All India Survey on Higher Education , the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education in India has increased from 20.8% in 2011-12 to 25.8% in 2017-18. Lack of access is a major reason behind the low intake of higher education. The policy aims to increase GER to 50% by 2035.
- Multiple regulators with overlapping mandates reduce the autonomy of higher educational institutions and create an environment of dependency and centralized decision-making.
- The National Higher Education Regulatory Authority (NHERA) should replace the existing individual regulators in higher education. Thus the role of all professional councils such as AICTE would be limited to setting standards for professional practice. The role of the UGC will be limited to providing grants.
- Separate the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) from the UGC into an independent and autonomous body. It will function as the top-level accreditor and will issue licenses to different accreditation institutions. All existing higher education institutions should be accredited by 2030.
- Replacing the current system of establishing higher educational institutions by Parliament or state legislatures. Instead, institutions can be set up through a Higher Education Institution Charter from NHERA.
- Research universities focus equally on research and teaching.
- Universities focus primarily on teaching.
- Colleges focus only on teaching at undergraduate levels.
- All such institutions will gradually move towards full autonomy.
- Total investment in research and innovation in India has declined from 0.84% of GDP in 2008 to 0.69% in 2014. India also lags behind many nations in the number of researchers, patents, and publications.
- NRF will act as an autonomous body for funding, mentoring, and building the capacity for quality research.
- Undergraduate programs should be made interdisciplinary by redesigning their curriculum to include: a common core curriculum; and one/two area(s) of specialization.
- Introduce four-year undergraduate programs in Liberal Arts.
- By the next five years, five Indian Institutes of Liberal Arts must be set up as model multidisciplinary liberal arts institutions.
- Poor service conditions and heavy teaching loads, augmented by a lack of autonomy and no clear career progression system, have resulted in low faculty motivation.
- Introduction of a Continuous Professional Development program and permanent employment track system for faculty in all higher education institutions by 2030.
- The student-teacher ratio of not more than 30:1 must be ensured.
- All higher education institutions must have complete autonomy on curricular, pedagogical, and resource-related matters.
Read: Institutions of Eminence Scheme
Additional Key Focus Areas:
Additional key focus areas are (1) Technology in Education (2) Vocational Education (3) Adult Education and (4) the Promotion of Indian Languages.
Technology in Education
- Improving the classroom process of teaching, learning, and evaluation
- Aiding teacher training.
- Improving access to education.
- Improving the overall planning, administration, and management of the entire education system.
- Electrification of all educational institutions paves the way for technology induction.
- An autonomous body, the National Education Technology Forum, set up under the Mission, will facilitate decision-making on the use of technology.
- Single online digital repository to make available copyright-free educational resources in multiple languages.
Vocational Education
- Less than 5% of the workforce in the age group of 19-24 receives vocational education in India, in contrast to 52% in the USA, 75% in Germany and 96% in South Korea.
- Vocational courses : All school students must receive vocational education in at least one vocation in grades 9 to 12.
- Higher Education Institutions must offer vocational courses that are integrated into undergraduate education programs.
- The draft Policy targets to offer vocational education to up to 50% of the total enrolment in higher education institutions by 2025, up from the present level of enrolment of below 10%.
- National Committee for the Integration of Vocational Education for charting out plans for the above objectives.
Adult Education
As per Census 2011, India had a total of 26.5 crore adult non-literate (15 years and above).
- Establishing an autonomous Central Institute of Adult Education as a constituent unit of NCERT. It will develop a National Curriculum Framework for adult education.
- Adult Education Centers will be included within the school complexes.
- Relevant courses are made available at the National Institute of Open Schooling.
- National Adult Tutors Programme to build a cadre of adult education instructors and managers.
Education and Indian Languages
- The medium of instruction must be the mother tongue until grade 5, and preferably until grade 8.
- 3 language formula be continued and flexibility in the implementation of the formula should be provided. Implementation of the formula needs to be strengthened, particularly in Hindi-speaking states. Schools in Hindi-speaking areas should also teach Indian languages from other parts of India for national integration.
- To promote Indian languages, a National Institute for Pali, Persian, and Prakrit will be set up.
- The mandate of the Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology will be expanded to include all fields and disciplines to strengthen vocabulary in Indian languages.
Transforming Education
The policy talked about the synergistic functioning of India’s education system, to deliver equity and excellence at all levels, from vision to implementation, led by a new Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog.
Education Governance
Revitalize education governance by bringing in synergy and coordination among the different ministries, departments, and agencies.
- Constitute the National Education Commission or Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog, as an apex body for education headed by the Prime Minister. It would be responsible for developing, implementing, evaluating, and revising the vision of education and overseeing the implementation and functioning of bodies including the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), National Higher Education Regulatory Authority, and National Research Foundation.
- The Ministry of Human Resources and Development must be renamed the Ministry of Education to bring the focus back on education.
Financing Education
- The Draft Policy reaffirmed the commitment to spending 6% of GDP as a public investment in education.
- The draft Policy seeks to double the public investment in education from the current 10% of total public expenditure to 20% in the next 10 years. 5% will be utilized for higher education, 2% in school education, and 1.4% for early childhood care and education.
- There should be optimal and timely utilization of funds through the institutional development plans and by plugging loopholes in the disbursement of funds.
Criticism of the New Education Policy of India
- The New Education Policy lacks operational details.
- It is not clear from where the funding will be sourced.
- Enough importance is not given to innovation, startup culture or economic principles to be added to the curriculum.
- One-size-fits for all states can’t be a solution as each state in India is diverse in its educational needs. Controversy on NEET has shown this.
- With technological advancement and the democratization of knowledge, the policy should have focused more on how to teach rather than what to teach.
- Economic Survey 2017-18 mentioned the perils of the distinction between research institutions and universities in higher education. The policy recommendation of three distinct higher education institutions of research universities, teaching universities, and teaching colleges will further augment the gap between research and universities.
- The draft policy is silent on the Institutions of Eminence and agencies like the Higher Education Funding Agency.
- The role of Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog should be defined clearly. What would be its role vis-a-vis existing regulators? Also, there are criticisms from some quarters that RSA will open the door to the politicization of education.
- Earlier the 3-language formula proposed by the draft policy made Hindi compulsory in non-Hindi speaking states. However, after the furor, the proposal was removed.
- Even though the policy talks about bringing “unrepresented groups” into school and focusing on educationally lagging “ special education zones” , it doesn’t comprehensively address the inequalities prevalent in the system. It misses methods to bridge the gaps between rich and poor children.
- The policy proposes to remove the provision mandating that primary schools be within stipulated distance from students’ homes and common minimum infrastructure and facility standards that should be met by all schools. If a common minimum standard is not specified, it will create an environment where quality in some schools will fall further thus augmenting the inequalities between schools across the country.
India’s education history is rich with ambitious policies failing at the altar of inadequate implementation of the same. In the absence of a handholding mechanism for states to embark on the path-breaking reforms mentioned in the policy and that too in a short time, will be too much to ask.
Funding requirements and governance architecture pose major challenges in the implementation of the policy. Political commitment is required to increase funding. RTE Act expansion to include preschool should keep in mind the present infrastructure inadequacies and teacher vacancies.
Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog may face administrative problems and turf battles. Also, it will raise questions on the role of new bodies like the National Medical Council.
The recent controversy on 3 language formula shows the sensitivity of language education in India and care should be taken to appreciate the emotional overtures while implementing the same.
Politically acceptability, social desirability, technological feasibility, financial viability, administratively doability, and judicially tenability are 6 pillars that will impact the implementation of the policy.
Be that as it may, the new education policy aims to address the challenges of (i) access, (ii) equity, (iii) quality, (iv) affordability, and (v) accountability faced by the current education system. It aims to revitalize and equip the education system to meet the challenges of the 21st century and 4th industrial revolution rather than catering to 19th and 20th century needs of industrialization. Also, India is on the cusp of a demographic dividend, rather than entered into this phase. So the education system catering to these needs is not a luxury that we hope for but rather a dire need at this moment in Indian history.
The Problems associated with the Education System in India
HRD ministry: Over 1.4 million schools and 50,000 higher educational institutions are operating in India. Out of 907 universities, there are 399 state universities, 126 deemed-to-be universities, 48 central and 334 private universities.
- Even after more than a hundred years of “ Gokhale’s Bill”1911, where universal primary education was originally mooted, India is yet to achieve this goal.
- China had achieved it in the 1970s. As per Census 2011, over 26% of India’s population is still illiterate, compared to 4% in China. About 50% of India’s population has only primary education or less, compared to 38% in China. The 13% of the population with tertiary education at the upper end in India is comparable with China.
- Progress has been made in respect of female participation up to secondary level and GER for girls has exceeded that of boys.
- But the girl’s enrollment rate is lower than that of boys at the higher education level.
- A gap is visible across social categories in terms of enrollment rate at the higher education level.
- According to NSSO’s 71st round (2014), drop-out rates are very high for boys at the secondary school level. Reasons for the same are economic activities, lack of interest in education, and financial constraints.
- The transition rate from secondary school to senior secondary and further to higher education is very low.
Despite these highly ambitious education policies and elaborate deliberations on the same, the outcomes are rather shaky. Major criticisms and shortcomings of these policies and their implementations are:
- Half the population is crowded at the bottom, either illiterate or with only primary education. Meanwhile, a disproportionately large segment is at the upper end with tertiary education.
- The 2015 Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) reflects this deteriorating quality. The report opines that deficits in foundational reading and arithmetic skills are cumulative, which leaves students grossly handicapped for further education .
- India had fared poorly in the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) test in 2008, and 09.
- Education policies in India are focused on inputs rather than on learning outcomes.
- Teacher shortages.
- Local politics.
- Corruption in teacher appointment.
- Defects in teacher training.
- Socio-cultural factors like caste division, and cynical attitude towards the teaching profession.
- There is no accountability, as there is a guaranteed lifetime job independent of performance.
- From 1952-2012 , education expenditure as a percentage of total government expenditure increased from 7.92 to 11.7, and as a percentage of GDP increased from 0.64 to 3.31. But it has still not reached 6% of GDP, as was recommended by the Kothari Commission way back in 1964.
- Expenditure by the government on elementary education is more than tertiary level, but expenditure per student is more in tertiary. So there is a need to increase expenditure in all segments.
- All India survey on higher education has shown that in West Bengal Muslim students in universities are very low. Lack of education at the primary and secondary levels is said to be the main reason.
- Even though Article 15(4),(5) provides reservations for SC, ST, and OBC in higher education institutions , the Economic Survey 2018-19 points out their inadequate representation in these institutions.
- The suicide of Rohit Vemula, a Ph.D. scholar at the University of Hyderabad, in 2016 had brought forward the discrimination still existing in these institutions.
- Also, the representation of teachers at these levels is skewed against the backward class in spite of reservations. Article 16(4) provides for reservations of backward class in jobs.
- At the school level, poor children are primarily concentrated in government schools. The poor quality of government schools thus disproportionately affects these children and creates a vicious cycle of illiteracy.
- At the higher education level, the situation is more critical. One reason for the introduction of the National Medical Commission Bill is to curb the exorbitant fees charged by medical colleges.
- Youths coming out of the higher education system in India are not employable, as they lack relevant industry-level skills.
- India’s long-standing neglect of primary and secondary education has limited access to quality basic education. No skill development program can succeed without an underlying foundation of basic education.
- National Policy on Skill Development and Entrepreneurship 2015 (PMKVY) has shown disappointing results.
- Budget 2019-20 stated that the government enables about 10 million youth to take up industry-relevant skill training through the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY). The Budget has also increased focus on ‘new-age skills’ like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data, 3D Printing, Virtual Reality, and Robotic.
- Currently, B Tech courses in AI are offered mostly in premier institutions only.
- The budget 2019-20 proposed the National Sports Education Board for the development of sportspersons under the Khelo India program (2017).
Now we will look at each rung of the education ladder in India.
Early childhood education
- Early childhood education (ECE) is needed for cognitive development in the early stage.
- Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS) has a component for providing ECE through Anganwadis . But lack of effective regulation in this sector is eroding the quality of ECE.
- There is a National Early Childhood Care and Education Policy 2013 . However, the policy has not been properly implemented.
- There are multiple service providers but there is no clarity in the types of services provided.
- The sprawling of an unregulated private channel, both organized and unorganized, which is also spreading to rural areas, has led to inequitable access, uneven quality, and commercialization of ECE.
- Both Anganwadis and private schools focus on reading, writing, and arithmetic rather than cognitive and conceptual development.
- There is a decline in the quality and training of teachers.
- S.R. Subramanian’s committee report has brought focus to the quality deterioration in this sector.
Primary level
- There is an increasing trend of parents choosing private schools for the primary level. However, there is variable quality in private schools. Also, fees vary from school to school and are on the higher side.
- Eschew rigid curricula and make them more cognitive and flexible. There should be a broader cognitive approach than rote learning.
- There is a need for activity-based learning. Teachers should teach at the right level, rather than teaching for the average learner.
- The government has launched Padhe Bharat Bade Bharat – targeting early reading and writing. The twin-track approach of comprehension and math is the main focus.
- There is a supply-side problem . The government is pumping funds through government schools thus increasing the number of schools and thus enrollment. However, quality and inclusiveness have dropped and dropout rates increased. These lead to poor learning outcomes.
School Complex
- RTE and SSA have resulted in over-access but low-quality primary-level education. Now the aim should be to integrate these into school complexes, as mentioned by the Kasturirangan committee report, thus rationalizing the number of schools in an area.
- The ‘Adarsh’ integrated school system of Rajasthan is an example of a school complex system . Here one school provides classes from l to XII under one principal. There is one such school in every gram panchayat.
- This is an efficient way to solve teacher shortages and also to address the shortages of secondary schools. It can also address the problem of resource scarcity by integrating and rationalizing resources.
- Inclusive learning can be furthered through school.
- Also, these complexes can act as a pivot around which new reforms in education can be implemented.
Secondary level
ASER Rural 2017: In 2017, ASER changed the age group of the survey from primary level to secondary level. The report mentions the following:
- Enrollment is low in this age group. There is a high digital divide at this level. Low quality also persists at this level. There is a high amount of absenteeism as well.
- There is a need to expand RTE to cover the 14-18 age groups.
- To realize the demographic dividend, skill education for these groups is necessary.
Economic Survey 2018-19 points out that Indian demography is changing and it requires more quality secondary education system rather than merely an increasing number of primary-level schools.
Private fees
- The vagueness in the judgment regarding ‘reasonable surplus’ and ‘commercialization’ of education has watered down the outcome of the judgment.
- There are state laws for capping fees. However, implementation problems and litigation make them ineffective.
- CAG report mentioned misreporting and mismanagement by private schools. So laws should address this problem through stricter inspection, penalties, etc.
Higher education
There is an increasing number of higher education institutions but their quality is questionable, effectively making ‘islands of excellence amidst the sea of mediocrity. Increased accessibility to a low-quality higher education system has made democratization of mediocrity.
Raghuram Rajan, the ex-RBI governor, argued that India needs idea factories and universities by leveraging India’s inherent strengths like tolerance, diversity, etc. He said that there is a need for strong accreditation agencies and continuing education.
Problems of the higher education system in India
- There is a dual problem of both quality and quantity. The gross enrollment ratio (GER) in higher education is only 24.5.
- Even though education policy had an elitist bias in favor of higher education, the state of the same is much worse than the state of school education. Unlike school education, there is no national survey of the learning levels of college students.
- The desired levels of research and internationalization of Indian campuses remain weak points.
- Also, there is a low philanthropic investment in this sector. This creates an exclusive dependency on government funding by universities. This, in turn, reduces the autonomy and vision of these universities.
- Privatization of higher education has not been led by philanthropy but the commercial interest that does not have a symbiotic relationship with the vision of universities.
- These have led to inadequate human capacity, shoddy infrastructure, and weak institutions. Recommendations of the Narayana Murthy committee, on the role of the corporate sector in higher education, have not been implemented and thus channeling of CSR funds to higher education remains inadequate.
- Banks and financial institutions are not giving adequate attention to this area. Giving PSL status to these institutions can be considered.
- Indian higher education system is of a linear model with very little focus on specialization.
- UGC and AICTE act more as controllers of education than facilitators.
- Due to the mushrooming of colleges at a higher rate since the 1980s , there is a regulatory sprawl in higher education.
- Poor governance , with mindless over-regulation , is widespread in this sector. Educational institutions responded to this with claims of academic and institutional autonomy for themselves, which was mostly a smokescreen for a culture of sloth in these institutions.
- There is a concentration of powers, as these regulatory institutions control all aspects like accreditation, curriculum setting, professional standard-setting, funding, etc.
- Compartmentalization and fragmentation of the knowledge system.
- Disconnect with society.
- Overemphasis on entrance tests.
- Absence of innovation in learning methods.
- Corrosion of autonomy of universities.
- For long basic disciplines across the physical and social sciences and humanities were ignored.
- However, the Economic Survey 2017-18 mentioned that there is an increase in Ph.D. enrolment in India in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) due to efforts by the government to increase the number and quantum of fellowships. However, there are still fewer researchers in India in comparison to other countries.
- Budget 2019-20 proposes ‘Study in India’ with a focus on bringing foreign students to higher educational institutions in India to make India a “hub of higher education.”
- Higher education institutions are used as rewards for loyalists and channels of graft by political parties in power.
- Indian higher education system is plagued by unregulated and shoddy coaching institutions. The coaching industry makes around Rs. 24000 crores a year in India. Proper regulation of the same is required.
Research and development (R&D)
Economic Survey 2017-18 stated: “To transform from net consumer to net producer of knowledge, India should invest in educating its youth in science and mathematics, reform the way R&D is conducted, engage the private sector and the Indian diaspora, and take a more mission-driven approach in areas such as dark matter, genomics, energy storage, agriculture, and mathematics and cyber-physical systems”.
- Although Gross Expenditure on R&D (GERD) is consistently increasing, as a fraction of GDP it has been stagnant between 0.6-0.7 percent of GDP over the past two decades.
- The universities play a relatively small role in the research activities in India. There is a disconnection between research institutes and universities. This results in the compartmentalization of research activities and teaching into two separate silos.
- The separation of research from teaching leads to a situation where universities have students but need additional faculty support, while research institutes have qualified faculty but are starved of young students.
- India was, at one point, spending more on R&D as a percentage of GDP than countries like China – but currently, India under-spends on R&D.
- Doubling of R&D spending is necessary and much of the increase should come from the private sector and universities.
The need of the hour
- It is imperative to improve math and cognitive skills at the school level to make a difference at a higher level.
- There is a need to expand R&D in India and to go beyond paper presentations and patents to a broader contribution of providing value for society.
- There is also a need to encourage Investigator-led Research for funding science research. Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) 2008, a statutory body of DST, is a step in the right direction.
- 50:50 partnerships with SERB for industry-relevant research under the Ucchatar Avishkar Yojana (UAY) is the right way to go forward.
- It would strengthen state universities and provide knowledge in areas specific to a state.
- National Research Foundation, to fund, coordinate, and promote research at the college level, is proposed by the Kasturirangan report. It is reiterated in Budget 2019-20 : NRF will ensure the overall research ecosystem in the country is strengthened with a focus on areas relevant to national priorities without duplication of effort and expenditure. The funds available with all Ministries will be integrated into NRF.
- Link national labs to universities and create new knowledge ecosystems. Together they can link up with the commercial sectors and help develop industrial clusters.
- National Mission on Dark Matter
- National Mission on Genomics
- National Mission on Energy Storage Systems
- National Mission on Mathematics
- National Mission on Cyber-Physical Systems
- National Mission on Agriculture
- Ramanujan Fellowship Scheme.
- Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research ( INSPIRE ) Faculty Scheme.
- Ramalingaswami Re-entry Fellowship.
- Visiting Advanced Joint Research Faculty Scheme ( VAJRA ).
- Improve the culture of research thus ‘ ease of doing research’. There is a need for less hierarchical governance systems that encourage risk-taking and curiosity in the pursuit of excellence.
- Greater public engagement of the science and research establishment is needed. A greater effort at science communication is needed.
Government initiatives on higher education
The government is trying to revitalize the Indian higher education system and for this many initiatives have been launched. Let’s discuss the importance of them.
National Testing Agency (NTA) 2017
- NTA was set up for conducting entrance exams in higher educational institutions. It is based on the recommendations of the Ashok Mishra committee on IIT entrance 2015.
- It will conduct JEE, NEET, National Eligibility Test (NET), Common Management Admission Test (CMAT), and Graduate Pharmacy Aptitude Test (GPAT).
- It will provide diversity and plurality in higher education. It will also ensure independence and transparency in conducting the exams.
- However, it should be ensured that the computer-based test should not lead to further exploitation of rural students.
- NEET stands for National Eligibility cum Entrance Test . It is for admissions in medical courses by replacing a plethora of medical entrance tests with one national-level test.
- Supreme Court had said that NEET should be the sole basis for admission to medical courses.
- There is a controversy about whether urban and CBSE students will dominate NEET. The government should pay heed to this criticism.
- In Tamil Nadu doctors serving in rural areas get weightage in PG admission. NEET will effectively dislodge this system.
- This controversy brought forward the conflict between the fair and transparent system of admission to curb the commercialization of medical education and the socioeconomic goals of the state, which in the case of Tamil Nadu includes ensuring enough doctors for rural areas.
- Controversy on NEET has brought the following question to the limelight: should uniformity be thrust upon a country with such vast disparity and diversity? The political leadership should iron out the differences and produce a suitable admission policy. This task should not be left to the judiciary.
- Be that as it may, states can’t remain insulated from the need to upgrade their education standard.
RUSA: Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan 2013
- About 94 % of students in higher education study in 369 State universities, whereas less than 6% of students study in 150 Centrally-funded institutions.
- 11th 5-year plan (2007-12) opined that the center’s bias towards premier central institutions had skewed funding for these institutions mainly and thus neglected state-level institutions.
- State investment in higher education was declining. UGC’s system of direct release of funds to State institutions bypassing State governments also leads to a sense of alienation for the states.
- RUSA tried to correct this bias. The scheme aims at financing state institutions concerning their governance and performance.
- RUSA has shown the result in increasing the performance of state institutions and changing the way regulators function for the good. State Higher Education Council(SHEC) made medium-long-term state perspective plans.
- Cabinet in 2018 decided to continue the scheme. A renewed focus by the center on RUSA will be a success only if it is impartially administered and states are willing to heed the advice of SHEC.
HECI: Higher Education Commission of India bill
- On the recommendation of the Yashpal Committee 2010 for renovation and rejuvenation of higher education, the National Commission on Higher Education and Research bill was introduced but was not passed.
- HECI was proposed to act as an overarching regulator of higher education by replacing UGC, which will maintain academic standards, approve new educational institutions, etc. but with no funding powers.
- Draft Higher Education Commission of India (Repeal of University Grants Commission Act) Bill, 2018 was introduced in 2018. Budget 2019-20 proposed to bring a bill on HECI this year.
- The draft bill had separated funding and placed it under MHRD. This was criticized for the fear of increasing political control and reducing the autonomy of universities.
IoE: Institutions of Eminence 2017
- Around 2005, the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and the QS World University Rankings started, and in 2009 the Academic Ranking of World Universities started. From India, only the Indian Institute of Science was included in the top 500 every year. This prompted the government to introduce NIRF and IoE.
- Under IoE, UGC was tasked to select 10 government universities and 10 private ones as IoE. These would be given autonomy in operations.
- Selected government institutions would be provided with ₹1,000 crore over five years.
- The IoE tag is expected to help them achieve the world’s top 500 higher education institutions in a decade and later into the top 100.
- Institutes among the top 50 in the National Institute Ranking Framework rankings or in the top 500 in international ratings were eligible.
- The model for the sector remains dependent on state patronage.
- Entry into the global education race could now become an overriding concern when many systemic issues are plaguing the sector.
- Funding only for public institutions is discriminatory.
- Humanities institutions were neglected.
- Transparency in the selection process, and the public sharing of benchmarks and guidelines. The furor over the selection of Jio Institute, even before it functioned, had attracted many eyeballs and criticisms.
- Separate category to include sectoral institutions like IIM.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2015
NIRF is a methodology adopted by the MHRD to rank higher education institutions in India.
- NIRF is common for public and private institutions as well as state and central institutions. Comparison of state-level colleges with central and private colleges may lead to a vicious cycle of low funding, poor performance, and low ranks among state-level institutions because of the resource gap.
- So performance index values should be normalized concerning investments and resources that have gone into that institution. Also should consider making another ranking system for state-level institutions.
HEFA: Higher Education Financing Agency 2018
Introduced in Budget 2018-19, HEFA is a joint venture of MHRD and Canara Bank
- With an initial capital base of Rs 1,000 crores, it will act as a not-for-profit organization that will leverage funds from the market and supplement them with donations and CSR funds. These funds will be used to finance improvement in infrastructure in top institutions.
- It has been tasked with raising ₹1 lakh crore to finance infrastructure improvements in higher education by 2022.
Foreign Education Providers Bill 2013
- There is no account of programs delivered by foreign universities in India. Inadequate regulation has led to low-quality courses offered in this sector.
- The foreign Institution bill was not been able to pass in Parliament. However,
EQUIP report has mentioned the revival of this bill.
There are many other schemes and initiatives like SWAYAM, which offers open online courses from Class IX to post-graduation free of cost, GIAN and IMPRINT which are primarily focused on elite institutes like IITs and IISc.
APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Card
The Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) is a transformative initiative introduced in alignment with the National Education Policy (NEP) of 2020 and the National Credit and Qualifications Framework (NCrF).
It aims to provide a unified and accessible academic experience for students across India by assigning a unique and permanent 12-digit ID to every student, consolidating their academic achievements in one place.
Other Major Issues connected with the Education sector in India
The Indian education sector is also affected by other issues like the politicization of campuses, gender parity problems, poor-quality standards, etc.
Politicization of campuses
- JP movement had provided an impetus to the politicization of students.
- In Indian higher education institutions, university politics has become a launchpad for political ambitions.
- Though campus politics is vital for democracy, as it makes students better citizens, the negative side of the politicization of campuses has been visible across Indian campuses. Recent incidents at Kerala University are a case in point.
- One of the most important problems of student politics in India is that it acts as an appendage to political parties without having an independent identity or autonomy.
Gender Parity
- By parents → who send boys to private and girls to government schools. Economic Survey 2018-19: enrollment of girls is higher than that of boys in government schools but the pattern gets reversed in private schools. The gender gap in enrollment in private schools has consistently increased across age groups.
- By teachers → who reinforced the belief that boys are quick learners.
- Girls are eased out of school to work on home chores or get married.
- Economic Survey 2018-19 opines that BBBP has been a success and proposes to extend the cause of Gender equality by coining the slogan of BADLAV (Beti Aapki Dhan Lakshmi Aur Vijay-Lakshmi) to enhance the contribution of women in the workforce and the economy.
- For ranking states based on gender disparity, Digital Gender Atlas for Advancing Girl’s Education was launched by MHRD.
- In higher education, gender disparities still prevail in enrollment.
- Efforts by the Government through programs like Beti Padhao, and Beti Bachao, the GPI has improved substantially at the primary and secondary levels of enrolment.
Quality of education
Learning outcomes are not assessed in India as numerical outcomes. The 12th Five-Year Plan noted the need for measuring and improving learning outcomes.
- Children of illiterate parents can’t supplement school studies at home and also can’t afford expensive tuition, leading to a vicious cycle of illiteracy.
- From 2014 to 2018, there was a gradual improvement in both basic literacy and numeracy for Class III students but only a quarter of them are at grade level (ability to read and do basic operations like subtraction of Class II level).
- The report also shows that 1 out of 4 children leaving Class VIII are without basic reading skills (ability to read at least a Class II level).
Government initiatives
- Central Rules under the RTE Act were amended in February 2017 to include the defined class-wise and subject-wise learning outcomes.
- Nationwide sub-program of SSA to improve comprehensive early reading, writing, and early mathematics programs for children in Classes I and II.
Teacher Training
- Teachers play the most critical role in a student’s achievement.
- The need is for better incentives for teachers, investments in teacher capacity through stronger training programs, and addressing the problems in the teaching-learning process.
- However, teachers in India, especially in government schools, are considered a cog in the way to efficient governance. There is an inadequate focus on their motivation and skill updation.
- NCERT study shows that there is no systematic incorporation of teacher feedback into designing pieces of training. Also, there is no mechanism to check whether this training is translated into classroom performance.
- These results in de-professionalizing the teaching profession and curb a teacher’s “internal responsibility” — the sense of duty to the job.
- World Development Report on Education (2018) opined that both teaching skills and motivation matter. Individually targeted continued training is important. In line with this, MHRD and the National Council for Teacher Education launched the National Teacher Platform, or Diksha in 2017 . It is a one-stop solution to address teacher competency gaps.
- However, the current training through Diksha follows a one-size-fits-all approach. Even though the platform is designed to democratize both access to and creation of content by teachers, its real benefits are in the ability to provide continuous professional development which complements existing physical training.
- This technology-enabled platform allows training to become a continuous activity rather than an annual event and also creates a feedback loop ensuring the effectiveness of the material.
- Diksha has the potential to re-engineer in-service teacher training in India. It is important to create good content and also to ensure technology consumption by teachers, the role of headmasters in promoting teachers’ professional development, etc.
As India participates in the PISA in 2021, it is to be made sure that we recognize the importance of teachers and their role in education outcomes.
Private Schools vs Public Schools: The Big Debate in Education
At least 30% of students between the 6-14 age groups are in the private sector.
- There is an increasing perception that the quality of teaching in private schools is better than that of public schools. Thus there is a clamour for increasing the number of private schools and simultaneously limiting public spending on government schools.
- However, the claim on the quality of private schools is debatable as there is a wide disparity of the same among these schools.
Research paper by Geeta Gandhi Kingdon, professor of education and international development at the Institute of Education, London, offers insights into private-public school education in India:
- The paper points out that between 2010-11 and 2015-16, the average enrolment in government schools declined from 122 to 108 students per school, while in private schools it rose from 202 to 208.
- Nevertheless, according to the District Information System for Education (DISE), 65% of all school-going children, 113 million, get their education from government schools.
- The study points out that the migration to private schools is due to the belief among parents that these schools offer better value for money in terms of quality.
- IndiaSpend, in 2016, reported that despite the Rs 1.16 lakh crore spent on SSA, the quality of learning declined between 2009 and 2014. It also points out that less than one in five elementary school teachers in India are trained. Also, the contractual teachers, who are high in number in government schools, are likely to be less motivated and accountable.
- Preference for private school tutoring is there.
- The quality of schools varies between states. In 2016, in Kerala, the proportion of children enrolled in primary government schools increased from 40.6% in 2014 to 49.9% according to ASER 2016.
- States with better-functioning government schools have more expensive private schools as there is no market for the ‘low-fee’ budget private schools. Around 80% of private schools in India are ‘low’ fee schools.
- ASER 2016 has shown small improvements in learning outcomes in government schools.
- Between 2010-11 and 2015-16, the number of private schools grew by 35% – to 0.30 million. On the other hand, the number of government schools grew only by 1%, to 1.04 million. The migration out of government schools has left many of these economically unviable.
- Government teachers in India earn four times that of China but don’t perform as well. Up to 80% of India’s public expenditure on education is spent on teachers. There is a need to link teacher salaries to their accountability.
- However, the salary of private teachers is very low compared to their government counterparts. This is due to the “bureaucratically-set high ‘minimum wage’, which is being influenced by strong unions of government school teachers.
- Another reason for the low salary of private school teachers is that the private education sector offers salaries based on market factors of demand and supply. Since 10.5% of graduates are unemployed in India, there is a high supply of teachers.
- Rather than merely increasing the budget outlay for education, the need is to revise the Education policy for better accountability and monitoring mechanisms.
- Gandhi argued that a Public-private partnership (PPP) model may be the solution, with public sector funding and private resources for education, since reforming the present system may not be politically feasible.
Rather than debating about private versus public schools, the focus should be to enable the private sector to set up more schools under the scrutiny of regulatory authorities. There is no point in driving off the private initiative in schooling given the limited resources of the states. Private investment should be encouraged but made accountable for quality and conduct.
The above discussion showed the challenges of the Indian education system. A workforce that India wants to create in this digital age requires reforms in education at all levels. UNESCO’s Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2016 opined that India is expected to achieve universal primary education in 2050. India is 50 years late in achieving its global education commitments. If the nation wants fundamental changes in the education system, it has to meet the 2030 SDG targets on education. There is an urgent requirement for greater evolution in education in India.
Education Quality Upgradation and Inclusion Programme (EQUIP): How to transform Education in India?
EQUIP is a five-year vision plan on education, released by MHRD, by the Prime Minister’s decision to create a five-year vision plan for each Ministry.
The EQUIP project is crafted by ten expert groups led by experts within and outside the government:
- Group 1: Strategies for expanding access
- Group 2: Towards global best teaching/learning process
- Group 3: Promoting Excellence
- Group 4: Governance reforms
- Group 5: Assessment, Accreditation, and Ranking Systems
- Group 6: Promotion of research and innovation
- Group 7: Employability and Entrepreneurship
- Group 8: Using Technology for Better Reach
- Group 9: Internationalisation
- Group 10: Financing Higher Education
The groups have suggested initiatives to transform the education system completely. The goals set by the groups are:
- Double GER in higher education and resolve the geographically and socially skewed access to higher education institutions.
- Upgrade the quality of education to global standards.
- Position at least 50 Indian institutions among the top 1000 global universities.
- Introduce governance reforms in higher education for well-administered campuses.
- Accreditation of all institutions as an assurance of quality.
- Promote Research and Innovation ecosystems for positioning India in the top three countries in the world in matters of knowledge creation.
- Double the employability of the students passing out of higher education.
- Harness education technology for expanding the reach and improving pedagogy.
- Promote India as a global study destination.
- Achieve a quantum increase in investment in higher education.
We can see that each of the above goals has been known to us for a long time. The problem is its implementation. The political class and all other stakeholders should come together to achieve these goals. The plethora of government initiatives on higher education is a sure sign of the importance given by the political class in the reform of the education system of India. Let’s hope that a new dawn of Indian education is around the corner which will bring back the glory of ancient times when India was the centre of knowledge production.
As the Economic Survey 2016-17 points out, lack of health, malnourishment, etc. affects the cognitive ability of children. This will, in turn, have a detrimental effect on their future educational prospects. This leads to a vicious cycle of inter-generational illiteracy, poor health, and ultimately poverty. So education and health are complementary to each other and reforms in one sector should invariably be preceded and followed by reforms in other sectors. Human development as a whole can be considered as a wholesome development and we must appreciate the interlinkages of each section of human capital formation, be it health, education, digital literacy, skills, etc.
Also read: PM-USHA
In the larger domain of human capital , education, and skill development have a big role.
Census 2011 data on literacy gives us a quick perspective on the current status of education. However, education is not just about literacy.
RTE act acts as a cornerstone for Indian education. Nevertheless, it is the various education policies, charted out since Independence, which led to the historical evolution of the education system in India.
The results of these policies can be said to be mixed. There is still a lot of room for improvement.
There are various government initiatives targeting each level of the education system in India. The higher Education System is given a greater focus these days.
The latest update in the education sector is the Kasturirangan report or draft new education policy . It captures the need of the hour for reforming education.
The modern Indian education system is crying for a revamp. The draft New Education Policy (NEP) is the right moment to take stock of its history, achievements, and misgivings to chart out a futuristic education plan for 21st-century India.
Article by Sethu Krishnan M, curated by ClearIAS Team

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2025 (Online)
₹95000 ₹59000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2026 (Online)
₹115000 ₹69000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2027 (Online)
₹125000 ₹79000

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
November 27, 2019 at 10:33 pm
Wow what the largest matter of education is?. Very nice thank u sir
November 28, 2019 at 12:09 pm
Nice article but it is too long we need around 400 words which explains education in india,challenges,way forward only It is very hard to remember and segrate from given imp because all points look like imp please try to make it around 400 words only
November 28, 2019 at 2:00 pm
@MKM – The aim was to cover almost everything about Education in India as a comprehensive post. The post covers: (a) History of Education in India (b) Current Status of Education in India: Data from Census 2011 (c) RTE Act (d) Various Educational Policies in the past (e) The New National Educational Policy (NEP) (f) The Problems associated with the Education System in India (g) Education Quality Upgradation and Inclusion Programme (EQUIP): How to transform Education in India?
Though ClearIAS prefers short and crisp articles, for important areas like Education, we felt a detailed write-up would be useful.
Thank you for your feedback. We will continue to create concise articles as well.
November 28, 2019 at 12:35 pm
Good Source thank you Team.
November 28, 2019 at 1:56 pm
November 28, 2019 at 2:41 pm
November 29, 2019 at 7:45 am
This is a very nice and comprehensive information on education.
November 29, 2019 at 2:21 pm
Such a nice article sir thank you..
December 16, 2019 at 5:31 pm
March 30, 2020 at 12:48 pm
Sir,a small corrrection regarding literacy rate ranking, Kerala (93%)tops its followed by Lakshadweep(92 %), Mizoram (91 %) , Tripura (87.7 %) and Goa (87.4 %) as 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th places repectively according to 2011 census.
June 16, 2020 at 12:20 am
Excellent Work
August 31, 2020 at 1:14 pm
Thank you vry much team.🤗 You provide excellent data ,analysis,facts,etc…evrything at one doc.
November 16, 2020 at 10:47 pm
Absolutely amazing stuff. Can’t believe.. Thanks from the bottom of my heart ❤️❤️
May 27, 2021 at 12:38 pm
Great article about Education very informative thanks for sharing
May 31, 2021 at 11:55 pm
Well and easy to understand…thank u for the team
September 12, 2021 at 10:37 am
Very good and such a broad information thank u 💖.. Lots of love
December 16, 2021 at 11:10 am
Need to update with current data eg how much percentage of school/ children get access of online education in pandemic Era COVID challanges others family support etc thank
January 28, 2022 at 10:32 am
Thank you so much for your birthday support
February 27, 2022 at 5:33 pm
good information
June 10, 2022 at 3:00 pm
Nice article very informative…traditional classroom study should be changed into a smart classroom online
July 14, 2022 at 8:55 pm
December 18, 2022 at 1:05 am
Absolute coverage article, Kindly keep it up for your determined spectators.
May 28, 2023 at 9:10 pm
desserstation on education/slums/miagration par hindi me pdf mil sakta hai
January 23, 2024 at 8:06 pm
The analysis provides a comprehensive overview of India’s education system, highlighting its pyramid structure and alignment with Sustainable Development Goals. Constitutional provisions like Article 21A and the RTE Act aim for universal education. However, the RTE Act faces criticism. To enhance educational outcomes, addressing these concerns and ensuring effective implementation are imperative. Schools in Pataudi Gurgaon focus on quality, inclusivity, and overcoming criticisms can lead Indian education to new heights. Thank You Samriddhi Sharma
February 7, 2024 at 7:44 pm
It’s crucial to delve into the challenges confronting the Indian education sector and understand the constitutional framework and policies guiding it. Exploring these aspects sheds light on the complexities and opportunities within the system. However, it’s equally important to consider how these discussions translate into action at the grassroots level, especially in local communities like Rajajinagar, Bangalore. How are schools in rajajinagar bangaloreaddressing these systemic issues and implementing reforms to ensure quality education for all students? This intersection of policy discourse and on-the-ground realities is where meaningful change happens.
March 8, 2024 at 6:22 am
Is there any data on how many states provide free education to girls till grade X and how many provide it till grade XII?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025
Are you struggling to finish the upsc cse syllabus without proper guidance, take clearias mock exams: analyse your progress.
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- AP EAPCET Hall Ticket
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET UG Admit Card 2024 (Out) Live
- CUET 2024 Admit Card
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Education System In India Essay
Indian education reformers want to narrow the disparity in student achievement between rural and urban areas. India's educators work hard to overcome their country's challenges in providing quality education to all its citizens. Here are some sample essays on the education system in India.
100 Words Essay On Education System In India
India's education system is ideal for providing its students with a solid academic foundation. It emphasises lifelong learning and encourages its students to pursue higher education. It also develops the students' language skills by allowing them to study in both English and Indian languages. Such courses encourage ideal attitudes toward their nation and its people- creating a positive atmosphere for learning and growth.

India surrounds its students with Indian history, culture, religion, and literature throughout their schooling years. It promotes patriotism through encouraging students to study Indian history and culture. This can help them develop a sense of cultural pride that can inspire them to support the development of their home country.
200 Words Essay On Education System In India
Education is the most important aspect of any society. It is the foundation on which a society is built and the tool that allows its citizens to make the most of their lives. It allows the country to educate its people and earn revenue from their talents. However, there are always 2 sides to a coin, along with benefits there are also some issues.
Issues In The Indian Education System
The Indian education system is in a state of flux. A number of issues have cropped up in recent years, and there seems to be no clear solution in sight.
One of the biggest problems is the disparity between urban and rural students. The quality of education that students in rural areas receive is quite poor, and they often don't have access to the same resources as their urban counterparts. This leads to a huge achievement gap between students from different backgrounds.
There are also concerns about the level of education that students are receiving. Many experts believe that the curriculum is outdated and does not prepare students for the modern world. In addition, there is a lot of emphasis on rote learning, which does not allow students to think creatively or critically.
500 Words Essay On Education System In India
The education system in India is plagued with a number of issues that have a direct impact on the students. Addressing these issues will require systemic changes that ensure all students can access adequate resources.
Challenges of Accessibility and Quality
Let's take a closer look at two of the biggest challenges facing India's education system: accessibility and quality.
Accessibility is a huge issue in India. Due to poverty and the lack of infrastructure, many rural areas and poor urban neighbourhoods don't have adequate schools or teachers. As a result, many children are denied the right to an education.
And even when children have access to education, it's often of poor quality. Many schools are overcrowded and underfunded, which means that students don't have access to good teachers or up-to-date textbooks and other learning materials.
Impact of Gender Inequality
One issue impacting the students is gender inequality. Boys and girls are not given an equal opportunity to receive an education. This needs to change if India wants to become a developed nation. Girls need to be given the same opportunities as boys so that they can contribute to the growth of the country. There are many solutions that have been proposed to address this issue, but more needs to be done to implement them successfully.
Struggles of India’s Rural Areas
For many parts of the country, especially rural areas, the issues in India’s education system run even deeper. Much of the Indian population is still living without access to educational resources and other basic needs. To make matters worse, a large number of these people belong to marginalised communities, like those living in poverty or facing discrimination based on factors like gender or caste.
In rural areas, most schools are underfunded and lack basic facilities. These schools face varying levels of neglect when it comes to providing adequate teacher support as well as basic needs such as toilets, clean drinking water, and well-maintained buildings. As a result, attendance rates at primary schools are often very low and many drop out before completing schooling altogether.
Solutions for Improved Education
The Indian government has taken various steps to ensure that a quality education is accessible for all. In 2020, the government launched a new initiative called ‘National Education Policy’ (NEP) which promises to set up a new educational system in India with increased access, improved quality, and greater equity. This initiative will focus on strengthening school education by providing more resources and more qualified teachers, and introducing vocational training programs as an alternative to traditional education.
NEP also sets out some objectives for higher education that aim to make learning more interesting and accessible. These include setting up new autonomous colleges for research purposes, and improving the availability of faculty in universities. NEP also aims to bridge the digital divide by making information communication technology (ICT) an integral part of teaching and learning.
Furthermore, NEP plans to focus on addressing gender inequalities in the Indian education system by introducing measures such as affirmative action policies, gender sensitization training, flexible learning options and financial assistance schemes specifically for women. These strategies go a long way towards improving India’s educational system and ensuring better outcomes for students across the country.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Education System in India – A Comprehensive Analysis
From Current Affairs Notes for UPSC » Editorials & In-depths » This topic
The Indian education system, for a long time, is faced with the problem of inaccessibility and low-quality education that make Indians unemployable. Due to this, India is not able to use the potential of its human capital. Education is one of the vital tools that help a nation to develop. The government needs to address this issue through proactive involvement for the betterment of all Indian citizens.

This topic of “Education System in India – A Comprehensive Analysis” is important from the perspective of the UPSC IAS Examination , which falls under General Studies Portion.
How did it all begin?
- In ancient times, India followed the Gurukula system of education.
- This system involved the teacher teaching student many subjects like Sanskrit, Holy Scriptures, mathematics metaphysics, etc., in his home.
- The student stays in the teacher’s house as long as he wished or until the guru felt he had taught everything he could teach.
- All learning in Gurukula was closely linked to nature and life and not confined to memorizing information like it is today.
- The modern school system was brought to India, including the English language, originally by Lord Thomas Babington Macaulay in the 1830s.
- The curriculum was confined to the “modern” subjects such as science and mathematics, and subjects like metaphysics and philosophy were considered unnecessary.
- Teaching was limited to classrooms and the link with nature was broken, as also the close relationship between the teacher and students.
- Uttar Pradesh Board of High School and Intermediate Education was the first Board to be established in India in the year 1921.
- Later, other boards were established in several states.
- This kind of education system underwent reforms following independence from the British Empire.

Express Learning Programme (ELP)
- Optional Notes
- Study Hacks
- Prelims Sureshots (Repeated Topic Compilations)
- Current Affairs (Newsbits, Editorials & In-depths)
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- Post-Independence Indian History
- World History
- Art & Culture
- Geography (World & Indian)
- Indian Society & Social Justice
- Indian Polity
- International Relations
- Indian Economy
- Environment
- Agriculture
- Internal Security
- Disasters & its Management
- General Science – Biology
- General Studies (GS) 4 – Ethics
- Syllabus-wise learning
- Political Science
- Anthropology
- Public Administration
SIGN UP NOW
What is the structure of India’s schooling system since independence?
The Indian education system consists of the following levels of education:
- Pre-primary level : 5-6 years of age
- Primary (elementary) level : 6-14 years of age. It is guaranteed by the Indian Constitution under Article 21A . The elementary education is universalised by Sarva Shikha Abhiyan .
- Secondary level : 14-18 years of age. The government had extended SSA to secondary education through Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan .
- Higher Education in India generally has 3 levels: UG, PG and MPhil/Ph.D . The Centrally Sponsored Scheme, Rashtriya Uchhattar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) provides for the strategic funding to higher education institutions throughout the country.
Prelims Sureshots – Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims
A Compilation of the Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims, including Schemes, Freedom Fighters, Judgments, Acts, National Parks, Government Agencies, Space Missions, and more. Get a guaranteed 120+ marks!
What are the provisions of the Indian Constitution on education?
- Article 45 in Directive Principles of State Policy stated that the government should provide free and compulsory education to all until the age of 14 within 10 years from the commencement of the Constitution. Since it was not realized, Article 21A was introduced by the 86 th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2002 . It made elementary education a fundamental right rather than a directive principle.
- Article 45 was amended to provide for early childhood care and education to children below the age of 6 years.
Right to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 :
- In order to implement Article 21A , the parliament had passed the Right to Education Act .
- This Act provided necessary legal backing for the implementation of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).
- SSA is the government programme that provides for the Universalization of Elementary Education in a time-bound manner. It has been operational since 2000-01 .
Provisions:
- Free and compulsory education to all Indian children between 6 to 14 age groups. “Compulsory” here means the government must provide free elementary education and ensure compulsory admission, attendance and completion of elementary education to all Indian children.
- The non-admitted child must be admitted to an age-appropriate class.
- As per the Act, the government schools must provide free education to all children and they are managed by School Management Committees (SMCs).
- The private schools are to admit at least 25% of the children in their schools without a fee.
- This Act mandates a 25% reservation for the disadvantaged sections of the society that includes the SC and STs, Socially Backward Class and differently-abled.
- The standards like Pupil-Teacher Ratios (PTRs), buildings and infrastructure, schools’ working days, teacher’s working hours, qualifications and training of the teachers are defined under this Act.
- The deployment of teachers is rationalised so that there is no urban-rural imbalance.
- It prohibits the deployment of teachers for non-educational works, other than services like decennial census, elections, and disaster reliefs.
- It prohibits physical punishment and mental harassment, screen procedures for students’ admission, capitation fee, private tuition by teachers and running of non-recognized schools.
- This Act also states that the financial and other responsibilities should be shared between the Centre and state governments.
- It aims to make child free of fear, trauma and anxiety through a system of child-friendly and child-centred learning.
- The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (Amendment) Act, 2019 removed the clause for “No Detention Policy”.
- Though the RTE and SSA have increased accessibility to school that had resulted in a high enrolment rate, drop-out rates have increased. Little has been done to address this issue.
- Adequate importance is not given to PTR.
- There is a provision in this Act that allows the local authorities to decide on aspects related to the academic calendar. However, this has not been implemented.
- Since all state holidays are not relevant to all localities, decisions on the academic calendar should be in the hands of the local authorities so that there is an increase in attendance and the local governments can take ownership of the school.
- There is a difference between urban-rural and rich-poor in education. The RTE students in private schools are forced to pay extra fees because they claim that the government fund is inadequate.
- Most of the private schools treat RTE as a charity. They feel that the responsibility of universalization of education should be on the government’s hands and not them.
- The 2019 Amended Act scraps non-detention policy to allow detention for students of class V and VIII if they fail to pass in examinations.
- The provision of “non-detention policy” under the previous Act stated that the students till class 8 must not be failed in the exams. This was done to reduce the drop-out rate.
- The amendment was in response to the reducing quality of elementary education.
- This RTE Act gives more importance to the education of children from the age of 6. The Kothari Commission had recommended the establishment of centres for the development of pre-primary education in all districts.
- The RTE Act recommends a PTR of 30:1 for primary classes and 35:1 for upper primary classes. The District Information System for Education (DISE) report found that 30% of primary and 15% of the upper primary schools have higher PTRs.
- Despite the improvement in the Student-Classroom ratio (SCR), India still faces inequality in this context.
How did the modern education system evolve to the present state?
- As previously mentioned, the British colonial government introduced India’s modern education system.
- From Macaulay minute to Wood’s dispatch to several commissions like Sadler commission, 1904 Indian education policy etc., has built the foundation for the Indian education system during the colonial period.
Radhakrishnan Committee:
- In 1948-49, the University Education Commission was set up under Radhakrishnan.
- It shaped the education system of independent India based on the needs and aspirations of the newly-formed independent nation.
- It projected out the value system of the Indian Education System.
- Previously, the education system was only favouring the aspirations of the British government.
- For example, Macaulayism focused on eliminating indigenous culture through the planned substitution of British culture through education.
- Independent India’s education system is based on the following values as recommended by the commission:
- Wisdom and knowledge
- Aims of the social order
- Love for higher values of life
- Training for leadership
Kothari Commission :
- It gave the basic framework of the Indian education system.
- It recommended the following:
- Standardisation of the education system on a 10+2+3 pattern.
- Pointed out the need to make work experience and social and national service an integral part of education.
- Linking of colleges with several schools in the neighbourhood.
- Equal opportunities need to be provided for all to achieve national and social integration.
- Increase in the expenditure on education from 2.9% of the GDP to 6% by 1985.
- The banning Neighbourhood school system from separating students based on social or religious differences.
- A school complex system integrating primary and secondary levels of education.
- The Establishment of the Indian Education Service.
- The report by this committee paved the way for National Education Policy , 1968 which became the basis for further development of the Indian education system.
National Education Policy, 1968:
- It provided for the “radical restructuring” and equalization of educational opportunities to achieve national integration and greater cultural and economic development.
- It also increased the government’s expenditure on education to 6% of the GDP.
- It provided for the better qualification and training of the teachers.
- The three-language formula: The first language should be the mother tongue/regional language. The second language for the Hindi-speaking states should be modern Indian language. If it is non-Hindi speaking states it should be either Hindi or English. As for the third language, it can be either English or modern Indian language for the Hindi-speaking states and non-Hindi Speaking states. Hindi was encouraged in all states to promote a common language for all Indians.
National Educational Policy, 1985:
- Its objective is to remove differences and to provide equal educational opportunities especially to the marginalised sections of the society.
- It launched “Operation Blackboard” to improve primary schools across the nation.
- IGNOU was set up.
- The “Rural university” model was adopted based on the Gandhian philosophy. This was done to promote economic and social development at the grassroots level in rural India.
T.S.R.Subramanian Committee report:
- It was entrusted with the task of preparing a new education policy for India.
- It submitted a report to the government in May 2016.
- It had suggested numerous measures the government must take to improve education in India.
- Some of the key recommendations are:
- Education for children between 4 to 5 age groups must be declared a fundamental right. Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) is uneven across the states. So all the government schools should have facilities for pre-primary education so that too much reliance is not in private schools.
- This committee recommended that the “no-detention policy” should be upheld only till class V and not till class VIII.
- As there is an increase in the teacher shortage, absenteeism and grievances, there is a need for the establishment of an Autonomous Teacher Recruitment Board and 4 years integrated B.Ed. course.
- There is insufficient integration of Information and Communication Technology and the education sector.
- This committee recommended the enhancement of the National Skills Qualification Framework.
- The vocational training courses must be on par with the local opportunities and resources and the formal certification must be equivalent to the conventional education certificates.
- All India Education Service must be established.
- National Accreditation Board (NAB) must subsume the existing accreditation bodies.
What is the current state of India’s school education?
The following are the key findings of the latest Annual Status of Education Report, 2023:
- Youth Enrollment in Education : 86% of youth in the 14-18 age group are within the formal education system (school or college). At age 14, the percentage of youth not enrolled is 5%, increasing to 30% by age 18 .
- Educational Attainment Levels : 54% of youth in the 14-18 age group are enrolled in Std X or below, 25% in Std XI or XII, and 6% in undergraduate or other degree courses. 14% are not currently enrolled in any form of formal education .
- Gender Disparity in Enrollment : The enrollment gap between males and females in formal education widens with age. At age 18, 32% of females are not enrolled compared to 28% of males .
- Mathematical Ability : More than half of the youth struggle with division problems, with only 43% able to solve them correctly .
- Reading Skills : 53% of all 14-year-olds can read English sentences, increasing to about 60% for 18-year-olds. Of those who can read English sentences, 79% can explain their meaning .
- Applied Literacy and Numeracy Skills : A significant proportion of youth, even those who have completed eight years of schooling, lack foundational skills in reading and math .
- Financial Literacy : 76% of youth could not count money correctly, and 56% could correctly add weights in kilograms .
- Employment Among Youth : 42% of youth in the 14-18 age group are working, regardless of whether they are enrolled in formal education. Of these, 79% work in agriculture, primarily on their family’s farm .
- Digital Skills and Access : Mobile phone usage is widespread among youth (73% had used a mobile phone within the last week). However, significant gender differences exist, with higher male usage compared to females. Only 28% had used the Internet, and 26% had used computers in the last week .
- Geographical Awareness : 14% of youth could not identify a map of India, 36% couldn’t name the country’s capital, and 21% could not identify their state .
- Career Aspirations : Medicine is the most preferred career (18.1%), followed by engineering (11.6%). The majority of boys wish to join the Army or police, while teaching is the most common preference among females. Only 1.2% of rural youth aspire to work in the agriculture sector .
What are the problems faced by India’s education system?
Very few have higher education:
- Even after more than 100 years of the implementation of Gokhale Bill, 1911, universal primary education is still not achieved.
- According to the 2011 Census, about 26% of the Indian population is still illiterate.
- Currently, half of the population is either illiterate or with only primary education.
- According to Educational Statistics at a Glance (ESAG) 2018, the measures to provide primary education has produced results across social and gender categories in Gross Enrolment Rate (GER).
- There is an improvement in the female participation up to the secondary level and the GER for girls is more than the boys.
- However, the girl’s gross enrolment rate is less than boys at the higher education level.
- According to the National Sample Survey Office 71 st round, 2014, the drop-out rates are high for boys at the secondary level because of the economic activities, lack of interests and financial constraints.
- Also, the transition rate from secondary school to higher education is very low.
Limited outcomes from education policies :
The reasons for this are as follows:
- Higher priority is given to tertiary education when it comes to government spending. Though the government expenditure on elementary education is more than tertiary education, the expenditure per student is more in tertiary. Thus, the quality of elementary education is brought under question.
- The quality of education is poor. 2018 Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) pointed out the deficiency in the foundational reading and arithmetic skills. The students are not improving in their higher studies since they are not thorough in the basics.
- These policies are focused more on implementation rather than outcomes.
Problems with teachers:
- Limited availability of teachers
- Corruption in teacher appointment
- Limitations of teacher training
- Socio-cultural factors like a cynical attitude towards the teaching profession.
- There is no accountability for the government teachers as they are guaranteed lifetime job security despite the performance.
The Economic Divide:
- There is a stark difference between the rich and the poor at all levels of education.
- The poor children are mostly concentrated in the government schools where the education quality and facility is poor.
- In contrast, private schools, where the rich children are concentrated, provide a quality education leading to better results.
- This difference is because there is an unreasonable hike in the private school fee, making them unaffordable for the poor.
- The SC had once addressed this issue by stating that private schools have the power to increase the school fee. It had stated that a reasonable surplus can be generated by schools for the expansion of the institution. It had also pointed out the need for a balance of autonomy of institutions and measures to prevent commercialisation of education are necessary.
- The vagueness of this judgement has dampened its outcome.
- Though there are state laws that cap private school fees, the implementation and litigation problems have made them ineffective.
- The CAG report had also mentioned the cases of misreporting and mismanagement of the private schools. There is a need for stricter laws, inspections and penalties to address this issue.
Unemployable workforce:
- The educated youth in India are not employable since they lack the necessary industry-level skills.
- The Indian education system does not give priority to the basic foundation.
- Skill development programs cannot succeed without a basic foundation.
- The government measures to address the unemployment crisis like PMKVY has shown poor results because of this reason.
Issues with Research and Development :
- Though there is a steady increase in the Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD), as a fraction of the total GDP, it has remained stagnant between 0.6-0.7percent of the GDP for the past 2 decades.
- The universities play a relatively small role in research in India as there is a disconnection between research institutions and universities.
- The separation of research from teaching has resulted in a situation wherein the universities have students but lack additional faculty support, while the research institutes have qualified faculty but no young students to undertake research work.
- India currently spends very little on R&D purposes.
- Incentives must be provided for private companies and universities to increase their R&D activities.
Low-quality infrastructures and education in government schools :
- The RTE and SSA have increased the accessibility to government schools.
- However, the quality of education and infrastructure in these schools is dismal.
- There is a need for the rationalisation in the number of government schools in a particular area so that quality is given more focus instead of the quantity.
- Integrated school complexes like Rajasthan’s Adarsh, wherein one school provides classes from I to XII under one principal, is a need of the hour.
New Education Policy 2023 (NEP 2023)
- Aims to overhaul India’s education system to be more holistic, accessible, affordable, and relevant for the 21st century .
- Achieve 100% youth and adult literacy by 2030.
- Focus on imparting critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Increase Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) in higher education to 50% by 2025.
- Emphasize multidisciplinary and flexible learning, and employability through vocational exposure .
- Focus on equitable quality education for children aged 3-18 years.
- Emphasis on creativity, critical thinking, communication skills, and vocational skills.
- Introduction of innovative institutions like digital universities.
- Replacement of the 10+2 structure with a 5+3+3+4 system.
- Multilingual approach with a three-language formula up to Grade 12.
- Curriculum to integrate fundamental concepts, skills, and multidisciplinary education.
- Higher education to offer flexibility, integration with vocational education, and academic credit portability .
- Use of mother tongue/regional language as medium of instruction from Grades 1-5 .
- Integration of hands-on vocational education from Grade 6 onwards .
- Focus on joyful, engaging, and stress-free learning.
- Emphasis on experiential learning .
- Introduction of a 5+3+3+4 system aligned with cognitive growth stages.
- Reduction in curriculum load to prevent rote learning.
- Flexibility in undergraduate programs with entry/exit options.
- Board exams to assess core capacities instead of memorized facts .
- Overhaul of regulatory architecture.
- Restructuring of professional councils like AICTE and NCTE.
- Evolution of HEIs into large multidisciplinary colleges by 2040 .
- Hybrid learning combining online and offline instruction.
- Establishment of digital universities.
- Use of SWAYAM platform for online courses and virtual labs.
- Implementation of an academic bank for credit storage and transfer .
- Introduction of skills labs in schools from Grade 6.
- Opportunities for internships/apprenticeships .
- Targets for achieving quality education by 2040, including 50% GER by 2025.
- Development of a teacher vacancies database and virtual labs.
- Setting up the Higher Education Commission .
What can be the way forward?
- Embracing Holistic and Inclusive Education : The New Education Policy (NEP) 2023 sets a transformative path for India’s education system. It advocates for a holistic educational framework that nurtures critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving abilities, aligning with the needs of the 21st century. Emphasis should be placed on implementing this holistic approach at all educational levels to foster a generation of innovative, adaptable, and intellectually equipped individuals.
- Achieving Comprehensive Literacy : In line with NEP 2023’s ambitious goal to achieve 100% youth and adult literacy by 2030, concerted efforts are required at both governmental and grassroots levels. This includes enhancing accessibility to quality education across rural and urban divides and ensuring inclusive education for marginalized communities.
- Restructuring Curriculum and Pedagogy : The NEP 2023 introduces a progressive 5+3+3+4 curricular structure, which better aligns with the cognitive development stages of learners. This restructured approach necessitates a comprehensive revamp of the existing pedagogical practices, focusing on reducing rote learning and encouraging experiential and inquiry-based learning methods.
- Digital and Vocational Integration : In response to the rapidly evolving digital landscape, NEP 2023’s emphasis on digital empowerment and vocational education from an early age is a step forward. The integration of digital tools and vocational training in the curriculum can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, thus enhancing employability and adaptability in a dynamic job market.
- Addressing Environmental Education : As underscored by the UNESCO 2023 State of the Education Report for India, integrating environmental education into the curriculum is vital. Educating the young generation about climate change and sustainability practices is imperative for fostering environmental stewardship and addressing the global challenges of climate change.
- Fostering Research and Innovation : Strengthening research and innovation in educational institutions is crucial. Encouraging a research-oriented approach in higher education, coupled with adequate funding and support for innovative projects, can place India at the forefront of global educational and technological advancements.
- Collaborative Efforts for Implementation : Successful implementation of NEP 2023 requires collaborative efforts from various stakeholders including educators, policymakers, industry experts, and communities. Regular monitoring, feedback mechanisms, and adaptive strategies should be employed to ensure the policy’s objectives are met effectively and efficiently.
Revamping India’s education system can enable us to solve all of the current problems faced by India. This includes poverty, unemployment, intolerance, etc. The government must take steps to mend the existing lacunae in India’s education system so as to improve the lives of all Indians.
Test Yourself
Critically analyse how India’s education system can be revamped to address the current demands. (250 words).
- Academic Bank of Credit: will provide multiple entry and exit options for students in Higher education;
- 1st Year Engineering Programmes in Regional Languages
- Guidelines for Internationalization of Higher Education.
- Vidya Pravesh, a three month play based school preparation module for Grade 1 students
- Indian Sign Language as a Subject at secondary level
- NISHTHA 2.0, an integrated programme of teacher training designed by NCERT
- SAFAL (Structured Assessment For Analyzing Learning Levels), a competency based assessment framework for Grades 3, 5 and 8 in CBSE schools
- A website dedicated to Artificial Intelligence.
- DIKSHA is the nation’s digital infrastructure for providing high-quality e-content for school education in states and UTs, as well as QR-coded Energized Textbooks for all grade levels (one nation, one digital platform).
- Each class from 1 to 12 has one designated Swayam Prabha TV channel (one class, one channel).
- Shiksha Vani – makes extensive use of radio, community radio, and CBSE podcasts. Special e-content for the visually and hearing impaired developed on the Digitally Accessible Information System (DAISY) and in sign language on the NIOS website/YouTube.
- PM eVIDYA – unifies all initiatives related to digital education to enable multi-mode access to education.
- UNESCO 2023 State of the Education Report for India : This report emphasizes the role of education in addressing climate change, integrating environmental education into the curriculum, and promoting sustainable development . The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) aligns with the NEP 2020 in addressing climate change through school education. The report offers recommendations for enhancing the education sector’s role in combating climate change .
GET MONTHLY COMPILATIONS
Related Posts

UGC Directive on University Courses

Foreign university branch campuses in India – Prospects and challenges...

Role of Government Schools in Post-pandemic Learning Recovery
Nice Blog Great work. Thank you so much.
Nice Blog Great work.
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.

Compititive exams CTET, State TET, KVS, DSSSB, CUCET
Essay on The Indian Education System: Challenges and Opportunities 1000, 500, 300, 200 words
- Essay on The Indian Education System: Challenges and Opportunities

Introduction
Essay on The Indian Education System: The Indian education system is one of the oldest in the world, with a rich history dating back to ancient times. It has undergone numerous transformations over the centuries, but it continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of India. This essay explores the strengths and weaknesses of the Indian education system, its historical evolution, current challenges and potential opportunities for improvement.
Essay on The Indian Education System: A Journey of Challenges and Opportunities 500 words
Essay on the indian education system: challenges and opportunities 300 words, essay on education system in india 200 words, essay on education system in india 150 words, historical evolution.
The roots of the Indian education system can be traced back to the Gurukul system, where students lived with their gurus (teachers) and received holistic education encompassing not only academic subjects but also ethics, values and life skills. This system emphasized experiential learning and individualized instruction.
During British colonial rule, the education system underwent significant changes with a focus on producing a workforce to serve the colonial administration. This period saw the establishment of institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), which have since become renowned globally.
Strengths of the Indian Education System
- Diversity : India’s education system is vast and diverse, offering a wide range of subjects and courses, catering to the varied interests and talents of its students.
- Quality Institutions : India boasts several prestigious institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), and top-tier universities that have produced exceptional graduates who excel on the global stage.
- Strong Emphasis on STEM : The system places significant importance on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) education, contributing to India’s reputation as a hub for IT and engineering professionals.
- Global Diaspora : The Indian education system has produced a vast pool of skilled professionals who have excelled internationally, making India a significant contributor to the global workforce.
Challenges Faced
- Quality Disparities : While India has prestigious institutions, a majority of schools and colleges, especially in rural areas, lack basic infrastructure and quality teachers. This results in a stark rural-urban divide in education.
- Rote Learning : The system’s emphasis on rote memorization rather than critical thinking and problem-solving often stifles creativity and innovation among students.
- Pressure and Stress : A highly competitive environment and parental expectations can place immense pressure and stress on students, leading to mental health issues.
- Outdated Curriculum : The curriculum often lags behind in terms of relevance to real-world skills, emerging technologies and global trends.
- Inequality : Socio-economic disparities result in unequal access to quality education, perpetuating inequality.
Opportunities for Improvement
- Holistic Education : Incorporating holistic education that includes life skills, ethics and vocational training can prepare students for the complexities of the modern world.
- Teacher Training : Investing in teacher training and providing incentives for educators can improve the quality of instruction across the board.
- Flexible Curriculum : Regularly updating and adapting the curriculum to include relevant and contemporary subjects can better prepare students for the future job market.
- Digital Education : Leveraging technology for online and distance learning can bridge the urban-rural education gap and make education more accessible.
- Mental Health Support : Introducing mental health support services within educational institutions can help students cope with the pressures of academic life.
The Indian education system is at a crossroads, with both strengths and weaknesses. While it has produced brilliant minds and professionals, it also faces challenges related to quality, access and relevance. To truly harness its potential, India must address these issues and embrace reforms that prioritize holistic education, teacher development and adaptability to the changing global landscape. Only then can the Indian education system prepare its youth to excel not only in the domestic arena but also on the global stage.
Essay on The Indian Education System: An In-depth Analysis 600 words

Introduction :
The Indian education system has a rich and diverse history dating back thousands of years. With its roots in ancient Gurukul systems, it has evolved significantly over time to meet the changing needs of society. This essay delves into the Indian education system, its structure, challenges, and prospects.
Historical Background:
The origins of the Indian education system can be traced back to ancient times when education was imparted in Gurukuls, informal centers of learning under the guidance of a guru (teacher). This system emphasized holistic education, including subjects like mathematics, science, philosophy and ethics. However, the British colonial era (from the 18th to the 20th century) brought significant changes to India’s education system, introducing a more standardized, Westernized approach.
Structure of the Indian Education System:
- Pre-primary and Primary Education: The foundation of education in India starts with pre-primary and primary education, typically from ages 3 to 14. This stage is crucial for building a strong educational base.
- Secondary Education: After completing primary education, students move on to secondary education, which spans from grades 9 to 12. Here, they follow the curriculum set by respective state boards or national boards like the CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education).
- Higher Education: After completing secondary education, students have the option to pursue various streams, including science, arts, commerce and vocational courses. India has a vast higher education system comprising universities, colleges, and institutes offering undergraduate, postgraduate and doctoral programs.
- Technical and Professional Education: India boasts prestigious institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) that offer specialized technical and management education.
Challenges in the Indian Education System:
- Quality Disparities: There is a significant gap in the quality of education between urban and rural areas. Urban schools tend to have better infrastructure and teaching facilities, while rural schools often lack essential resources.
- Rote Learning: The system is often criticized for promoting rote learning over critical thinking and practical skills. This limits students’ creativity and problem-solving abilities.
- Overemphasis on Exams: The Indian education system is notorious for its heavy reliance on high-stakes exams, which can lead to immense stress and a narrow focus on exam-oriented education.
- Lack of Vocational Education: While there has been progress in recent years, vocational education remains underdeveloped in India. This limits opportunities for skill development and employment.
- Gender Disparities: Gender inequality still exists, with fewer girls having access to education, especially in rural areas.
Prospects for Reform:
- RTE Act: The Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009 is a significant step towards universalizing education by ensuring free and compulsory education for all children aged 6 to 14.
- Emphasis on Skill Development: There is a growing recognition of the importance of skill-based education to prepare students for the job market. Initiatives like Skill India aim to address this need.
- Digitalization: The use of technology in education, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, has gained momentum, making education more accessible and interactive.
- International Collaboration: Collaboration with foreign universities and institutions is on the rise, leading to the establishment of international campuses in India, which can enhance the quality of education.
Conclusion:
The Indian education system has a rich history but faces numerous challenges. However, ongoing reforms and initiatives offer hope for a brighter future. A shift towards a more holistic, skill-based and inclusive approach can help prepare the youth of India for the complex challenges of the 21st century and beyond, ensuring that education remains a tool for personal and national development.
Essay on strategies to promote a cleaner, greener and bluer future
Essay on restraint is the formula of solution 500, 250 words PDF
Essay on Child labour: 1000, 400, 300, 150 words
Essay on Global science for global wellbeing
Essay on Digitalization in daily life 1000 words

The Indian education system is a complex and multifaceted structure that has evolved over centuries. It is a critical component of the nation’s growth and development, playing a pivotal role in shaping the lives and aspirations of millions of young Indians. This short essay explores the Indian education system, highlighting its strengths, challenges and potential for transformation.
Historical Roots
The roots of the Indian education system can be traced back to ancient times, with institutions like Nalanda and Takshashila renowned for their pursuit of knowledge. The traditional Gurukul system, where students lived with teachers, was a hallmark of early Indian education. However, over time, the education system underwent significant changes, especially during British colonial rule, leading to the present structure.
- Diversity and Inclusivity : One of the system’s strengths is its inclusivity, catering to a diverse population with various languages, cultures and backgrounds. India offers a wide range of educational boards and mediums, allowing students to choose a system that suits them best.
- Strong Foundation in Science and Technology: The country has produced numerous skilled professionals who have excelled in fields such as engineering, medicine and information technology. Indian institutes like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) are globally recognized for their excellence.
- Competitive Examinations: India’s rigorous competitive examination system prepares students for challenges in various fields. Exams like the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) and the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) exam are examples of such assessments.
- Inequality : The education system grapples with stark inequalities, both in access and quality. Disparities in infrastructure, teacher quality and educational resources persist, creating a divide between urban and rural areas.
- Rote Learning : The emphasis on rote learning, where students memorize information without understanding its practical application, has been criticized for stifling creativity and critical thinking.
- Pressure and Stress: The intense competition for limited seats in prestigious institutions places immense pressure on students, often resulting in stress and mental health issues.
- Outdated Curriculum: The curriculum often lacks relevance to real-world challenges, leading to a gap between classroom education and practical skills needed for employment.
Opportunities for Reform
- Curriculum Overhaul : Updating the curriculum to incorporate practical skills, vocational training and a broader understanding of subjects can make education more relevant and engaging.
- Digitalization : Leveraging technology for education delivery can help bridge the urban-rural divide and improve access to quality education.
- Teacher Training: Investing in teacher training and professional development can enhance the quality of instruction and foster a more interactive learning environment.
- Emphasis on Holistic Development : Encouraging extracurricular activities, sports and arts alongside academics can promote holistic development and reduce the stress on students.
The Indian education system has come a long way, reflecting both its strengths and challenges. While it has produced outstanding professionals, it also faces the task of addressing inequalities and adapting to the changing needs of a globalized world. Through reforms, inclusivity and a focus on holistic development, India can continue to harness the potential of its vast youth population and build a brighter future for generations to come.
The Indian education system is a vast and intricate structure that has evolved over centuries. It comprises various stages, from primary to higher education, and plays a pivotal role in shaping the country’s future. However, it faces both challenges and opportunities in its quest for excellence.
One of the most significant challenges facing the Indian education system is accessibility. While strides have been made to increase enrolment, especially at the primary level, there is still a wide gap in access to quality education, particularly in rural areas. Infrastructure deficits, inadequate teacher training, and socio-economic disparities are obstacles that hinder many children from receiving a good education.
Another pressing issue is the rote-learning culture prevalent in the system. Traditional assessment methods often prioritize memorization over critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This can stifle creativity and hinder students from developing a deeper understanding of subjects.
However, there are opportunities for improvement. The digital revolution has the potential to bridge educational gaps. Online learning platforms and educational apps can provide access to quality resources, even in remote areas. Additionally, the National Education Policy 2020 aims to transform the system by focusing on holistic learning, vocational skills, and flexibility in curriculum choices.
Moreover, India’s diverse population is a unique asset. It fosters a rich cultural exchange and can be leveraged to create a more inclusive and globalized education system that prepares students for a competitive world.
In conclusion, the Indian education system faces challenges related to accessibility and outdated teaching methods. However, it also possesses significant opportunities for improvement through digital integration, policy reforms, and embracing diversity. Addressing these challenges while capitalizing on these opportunities is essential for shaping a brighter future for India’s students.
The education system in India is a complex and diverse landscape that reflects the country’s vast cultural and socioeconomic diversity. While it has made significant progress over the years, it still faces numerous challenges.
One of the key strengths of the Indian education system is its emphasis on academic excellence. India is home to some prestigious institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), which are renowned globally. Additionally, the country has a rich tradition of producing skilled professionals in fields such as medicine, engineering, and IT.
However, there are significant issues that need to be addressed. The system often places excessive pressure on students to excel in rote memorization rather than promoting critical thinking and creativity. The quality of education varies widely between urban and rural areas, with rural regions often lacking access to quality schools and teachers. Furthermore, socio-economic disparities persist, limiting educational opportunities for many.
In recent years, there has been a push for educational reform, with initiatives aimed at improving infrastructure, curriculum and teacher training. Additionally, the promotion of digital learning and vocational education is gaining momentum.
In conclusion, while the Indian education system has notable strengths, it also faces substantial challenges related to quality, accessibility and equity. Continued efforts to reform and modernize the system are essential to ensure that all children in India have access to a high-quality education.
The education system in India is a complex and multifaceted structure that plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s future. While it has made significant progress in recent years, challenges persist.
India’s education system consists of several stages, starting with primary education, followed by secondary and higher education. The government has implemented various schemes to promote enrollment and quality in primary schools, but issues like infrastructure gaps and teacher shortages persist, particularly in rural areas.
Secondary education faces issues of standardized curricula and a heavy emphasis on rote learning, which can hinder critical thinking and creativity. The higher education system, on the other hand, boasts prestigious institutions like the IITs and IIMs, but access and quality vary greatly across the country.
To address these challenges, India must focus on improving infrastructure, teacher training and curriculum development. Additionally, promoting a more holistic and skill-oriented approach to education can better prepare students for the demands of the modern world. Overall, the evolution of India’s education system is critical for the nation’s socio-economic development and global competitiveness.
Quick links:
Essay on Organic Farming Nurturing a Sustainable Future 100 to 800 words
Meaning of Local Self-government class 6 MCQs
Essay on Sustainable Development Goals free PDF
Important Time management for study effectively
Digital education in India free PDF
Social sharing ⬇️
Related Posts
Essay on jallianwala bagh massacre 13 april 1919, essay on vaisakhi festival celebration, essay on rabindranath tagore free pdf, essay on world earth day | essay on save earth, essay on internet free pdf | paragraph on internet, importance of literacy essay 1800 words free pdf, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Education Essay

Essay on Education
Nelson Mandela rightly said, “Education is the most important weapon to change the world.” Education plays an important role in the development of an individual and making him a knowledgeable citizen. It is the education that makes an individual self-reliant, helps to suppress the social evils and contribute towards the development of the society and nation as a whole.
Education helps in unravelling the mystery of nature. It enables us to understand and improve the working of our society. It creates conditions for a better life. Education brings out the capabilities to fight injustice happening in society. Every individual has the right to education.
Introduction
Education is a significant tool that provides knowledge, skill, technique, information and enables people to know their rights and duties towards their family, society and the nation. You can expand your vision and outlook to see the world around us. It changes our perception of life. Education builds up the ability to explore new things to enhance your creativity. Your creativity is a tool to develop the nation.
Importance of Education
People still don't realise what role education and being educated plays in our lives and society. So, before making people aware of education and working for their access, it is very important to understand the need and importance of education. Education includes traditional learning methods that include theories and modern methods that include practical implementation of the subjects.
In schools, education is categorised into four stages, and each stage is important for each student:
Primary
Secondary
Senior secondary
Education can be classified into Various Forms:
Formal education: teaches us the academic part of any course or class, skills, or theory.
Non Formal education: We learn from our community, culture, nation-based programs, and the society that we live in
Informal education: We learn from our life lessons, experiences, other people, their experiences, nature, surroundings, etc.
Education empowers everyone. It is an important aspect that shapes the modern and industrialised world. People need education to be able to cope up with the advancements in this competitive world. Following are some areas where education is needed:
Removing Poverty: Education helps in eradicating poverty from our society. An educated person can secure a good job and take care of all the basic needs and requirements of his family.
Safety and Security against Crime: A well-educated person cannot be easily duped or become a victim of any crime. They can develop the ability to stand against injustice.
Increases Productivity: Educated people are more productive. With the help of knowledge and skills, they can explore new ideas.
Confidence: A good education doesn’t mean to go to schools and colleges only. Education helps to become self-dependent and build great confidence within them so that they are able to accomplish difficult tasks.
Improved Standard of Life: On getting an education, quality of life gets improved. Education helps you to secure good jobs by which you can fulfil your dreams of buying a house or car or other luxury things.
Women Empowerment: Education helps in empowering women. Women can voice out themselves in the society against the injustice done to them. They can be self-reliant and need not be dependent on anyone. Women empowerment will bring a lot of development in society as well as in the nation.
Upliftment of the Economically Weaker Section: Education is the most significant ingredient to change the world. Illiterate people suffer the hardships of discrimination, untouchability and injustice prevailing in the society. With the advancement of education, the weaker section can improve their quality of life.
Communication: Communication is related to education. Good education helps to communicate better with others. It also improves our skills such as speech, body language, etc.
Development of a nation: The countries that focus on educating their citizens and have a higher education level are considered more developed nations in every aspect of their lives.
Individual growth: An educated individual always stands out in a crowd of uneducated people. They will be able to make better life decisions because with education comes knowledge. When an individual knows something, they will be able to understand things in a better manner.
Independent: Education acts as a catalyst for a human being to be independent. If an individual is educated enough, they can manage their own life without being dependent on anybody.
Success: Education helps in framing our mindset in a positive direction, and with this mindset, people can make their lives better. With education comes a degree, and with a degree comes a lot of opportunities. You just have to make a better choice for yourself, and everything will fall in place.
Talking particularly about India, education is a constitutional right of every citizen irrespective of caste, creed, race, religion, gender, etc. That’s the status given to education in India because educated people are always treated well and are well respected everywhere in the world.
Role of Education in Society
Education is the social institution through which the society provides its members with knowledge, facts, job skills and values. One of the most important roles of education is that it improves personal lives and helps society to run smoothly. As mentioned above, poverty can be eradicated and every individual can contribute towards the development of the country.
Education Creates a Better Society: An educated person is more likely to develop better moral and ethical values as compared to an uneducated person. Education brings equal opportunity for everyone and educated people will be able to create a better society.
Education is the Backbone of Society: Education is an integral part of human society. Lack of education gives birth to numerous social problems like poor health, conflicts, and poor living standards. Education helps people overcome all problems by finding better solutions.
Education Encourages Innovation and Creativity: Education leads to innovation. Innovation and creativity can only occur when skilled people know how to advance with different technologies. Educated people always can solve problems with the help of better techniques.
Education Creates a Better Human Being: Education is the most powerful weapon by which the entire perspective of the world can be changed. Through education, a person can develop good moral values. It helps us to become a better person in life.
Understanding the Responsibilities: As a social being, it becomes the responsibility of every individual to give something back to society and make it a better place for our next generation. An educated person is aware of his personal and social responsibilities.
Education helps in shaping the values of an individual. It helps individuals develop their moral values, humbleness, sympathy and empathy towards society, etc.
Students or any individual learn to express their viewpoints by reading, writing, learning. And these qualities or skills are taught with the help of education and nothing else.
Steps Taken to promote Education:
After discussing the importance of education, awareness is the next big step. People, especially those living in remote areas, should be aware and should have access to a better education system. The government has taken several steps for this purpose. It has started various initiatives to make education accessible to all and improve the quality of education for the betterment of every student.
Some of the Prominent Steps:
The formation of the Right to Education Act, 2009 made education a fundamental right for every child belonging to 6-14 years.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
Adult education and national development scheme
Beti bachao, beti padhao
Midday meal scheme and many more.
Various other initiatives that the government has taken are Udaan, Saksham, Pragati, etc., to make education accessible to every part of the county.
Conclusion:
Education is the pathway for a nation’s progress. Education is the backbone of society. The government should take all measures to provide education to every individual of the country. This will bring equality among people and when people improvise their way of living, they become more responsible towards society.
The literacy rate of more developed nations is also high, and the literacy of every nation depends upon its education system. The government undoubtedly has made laws and formulated schemes, but implementing those schemes is a major task.
The government, along with co-operation with the citizens, should make the society and nation a better place to live in. The growth of every nation depends upon the kind of population it has. A well-educated population will make a well-developed nation.

FAQs on Education Essay
1) Why is education important?
Education is important for the development of an individual. It is the most powerful weapon by which a person can contribute towards the development of the society and nation as a whole.
2) How is education a pathway to success?
Education provides job opportunities and also helps to expand your vision and change your outlook to see the world around us.
3) How can education help the economically backward people?
Uneducated or illiterate people do not have the ability to overcome hardships like discrimination, untouchability, and injustice. When these people get basic education, then they can become self-reliant and stand for their rights. With the advancement of education, they can improve their standard of living and poverty can be eradicated from the face of the Earth.
4) How are women empowered through education?
Education helps in empowering women. Women can voice out themselves in the society against the injustice done to them. They can be self-dependent. Women empowerment will bring a lot of development in society as well as in the nation.
5) What are the roles that education plays?
Education is vital in shaping the world and society. An educated society forms an educated nation. It is essential in creating a positive mindset and positive skills in an individual.
Teacher Education in India: An Overview
- First Online: 26 September 2023
Cite this chapter

- Jasim Ahmad 3
109 Accesses
Recently, India is encountering quick and sudden changes in teacher education. The one-year B.Ed. Program was converted into a two-year Program in 2015, and it was implemented abruptly and without much planning in the same year. While the stakeholders of teacher education are still busy in reflecting and debating the pros and cons of 2-year B.Ed. programme, NEP 2020 has declared that from 2030 the Integrated Teacher Education Programme (ITEP) i.e the 4-Year Integrated B.Ed. Programme will be the lone teacher education programme in the country for preparing secondary education teachers. It appears that teacher education is in the midst of a significant transformation. Teacher educators, pupil-teachers, and all other stakeholders are unsure what will happen and, if implemented, how it will be carried out in B.Ed. colleges and universities’ departments of teacher education. The vision and mission of teacher education, which directs and decides the fate of school education, must be crystal clear. This chapter attempts to revisit the development of teacher education in India, analyses current challenges, the prevailing curriculum framework, eligibility criteria for teacher educators, and forecasts some possible solutions to the issues and challenges confronting teacher education in the country.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ahmad, J. (2018a). Changing contours of teacher education in India: Issues, concerns and probable way-outs. University News , Association of Indian Universities, 56 (36), 3–11. ISSN-0566-2257.
Google Scholar
Ahmad, J. (2018b). Teacher education in India: A critical analysis, voices of teacher and teacher educator. NCERT, MHRD, GOI, VII (I), 24–36. ISSN 2455-1376.
Government of India Resolution of 1904 (1985) quoted in Kuldip Kaur (ed.), Education in India (1781–1985)-policies, planning and implementations . Centre for Research in Rural and Industrial Development (p. 301).
MHRD. (1998). National Policy on Education 1986 as modified in 1992, GOI.
National Archives of India, Selection from Educational Records, (i) 1960, Vol. I, Educational Reports (1859–71), (ii) 1965, Part 1: Development of Educational Service, 1781–1839.
National Archives of India, Selection from Educational Records. (1913). Educational Policy Resolution (pp. 301–302).
National Archives of India, Selection from Educational Records. (1815). Moira, Minute (p. 50).
National Archives of India, Selection from Educational Records. (1826). Sir Thomas Munro’s proposal, point 5, March 10 (p. 74).
National Archives of India, Selection from Educational Records. (1854). Wood’s despatch (p. 49).
NCERT. (1988). National curriculum for teacher education: A framework . Department of Teacher Education, NCERT.
NCTE. (1998). Curriculum framework for quality teacher education . National Council for Teacher Education.
NCTE. (1998). Policy perspectives in teacher education: Critique & documentation . National Council for Teacher Education.
NCTE. (2009). National curriculum framework for teacher education-towards preparing professional and humane teacher . National Council for Teacher Education, Wing-II, Hans Bhavan, Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg.
Nurullah, S., & Naik, J. P. (1964). A students’ history of education in India, 1800–1965 . Macmillan.
Rao, D. B. (1998). Teacher education in India . Discovery.
Sharma, N. K. (1976). Linguistics and educational aspiration under a colonial system: A study of Sanskrit education during British rule in India . Concept Publishing Company.
Siddiqui, M. A., Sharma, A. K., & Arora, G. L. (2009). Teacher education-reflection towards policy formulation . National Council for Teacher Education.
Singh, L. C. (2015), NCTE regulation 2014-A few reflections on their impact and prospects. University News, 53 (40).
Singh, L. C., & Neha (2016). Two-year B.Ed. Curriculum framework of national council for teacher education: Some persisting confusions. University News, 54 (14).
The Indian Education Commission, 1882 (1964). quoted in Nurullah and Naik. In Students’ handbook of education (p. 231).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Teacher Training & Non-formal Education (IASE), Faculty of Education, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, 110025, India
Jasim Ahmad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jasim Ahmad .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Teacher Training and Non-formal Education (IASE), Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India
Department of Educational Studies, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India
Aejaz Masih
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Ahmad, J. (2023). Teacher Education in India: An Overview. In: Ahmad, J., Masih, A. (eds) Teaching and Teacher Education in India. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-4985-4_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-4985-4_1
Published : 26 September 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-4984-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-4985-4
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Essay on Importance of Education
Importance of Education Essay
Education is one of the key components for an individual’s success. It has the ability to shape one’s life in the right direction. Education is a process of imparting or acquiring knowledge, and developing the powers of reasoning and judgement. It prepares growing children intellectually for a life with more mature understanding and sensitivity to issues surrounding them. It improves not only the personal life of the people but also their community. Thus, one cannot neglect the significance of Education in life and society. Here, we have provided an essay on the Importance of Education. Students can use this essay to prepare for their English exam or as a speech to participate in the school competition.
Importance of Education
The importance of education in life is immense. It facilitates quality learning for people throughout their life. It inculcates knowledge, belief, skill, values and moral habits. It improves the way of living and raises the social and economic status of individuals. Education makes life better and more peaceful. It transforms the personality of individuals and makes them feel confident.
Well said by Nelson Mandela, “Education is the most powerful weapon to change the world”. To elaborate, it is the foundation of the society which brings economic wealth, social prosperity and political stability. It gives power to people to put their views and showcase their real potential. It strengthens democracy by providing citizens with the tools to participate in the governance process. It acts as an integrative force to foster social cohesion and national identity.
In India, education is a constitutional right of every citizen. So, people of any age group, religion, caste, creed and region are free to receive education. An educated person is respected everywhere and well-treated in society. As a kid, every child dreams of being a doctor, lawyer, engineer, actor, sportsperson, etc. These dreams can come true through education. So, investment in education gives the best return. Well-educated people have more opportunities to get a better job which makes them feel satisfied.
In schools, education is divided into different levels, i.e., preschool, primary, secondary and senior secondary. School education comprises traditional learning which provides students with theoretical knowledge. However, now various efforts are being made to establish inbuilt application-based learning by adding numerous experiments, practicals and extracurricular activities to the school curriculum. Students learn to read, write and represent their viewpoints in front of others. Also, in this era of digital Education, anyone can easily access information online at their fingertips. They can learn new skills and enhance their knowledge.
Steps Taken By Government To Promote Education
Education is evidently an important aspect that no government can ignore in order to ensure the equitable development of a nation. Unfortunately, some children still do not have access to education. The Government has thereby taken initiatives to improve education quality and made it accessible to everyone, especially the poor people.
The Government passed the Right to Education Act 2009 (RTE Act 2009) on 4 August 2009. This Act came into effect on 1 April 2010, following which education has become the fundamental right of every child in India. It provides free and compulsory elementary education to children of the age group of 6-14 years in a neighbourhood school within 1 km, up to Class 8 in India. On similar lines, there are other schemes launched by the government, such as Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan , Mid-Day Meal , Adult Education and Skill Development Scheme, National Means cum Merit Scholarship Scheme, National Program for Education of Girls at Elementary Education, Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya, Scheme for Infrastructure Development in Minority Institutions, Beti Bachao , Beti Padhao, etc.
For our country’s growth, we require a well-educated population equipped with the relevant knowledge, attitude and skills. This can be achieved by spreading awareness about the importance of Education in rural areas. There is a famous saying that “If we feed one person, we will eliminate his hunger for only one time. But, if we educate a person, we will change his entire life”. Henceforth he will become capable of earning a livelihood by himself.
This essay on the Importance of Education must have helped students to improve their writing section for the English exam. They can also practice essays on other topics by visiting the CBSE Essay page. Keep learning and stay tuned with BYJU’S for the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams. Also, download the BYJU’S App for interactive study videos.
Frequently Asked Questions on Education Essay
How can the literacy rate in india be increased.
People in rural areas must be informed about the importance of providing education to their children. Also, with the COVID-19 situation, the government should take steps by providing laptops/phones for children to follow online classes.
Are girl children still denied their right to get educated?
Although awareness has now improved, there are still many villages in India where girl children are not provided with proper education or allowed to enrol themselves in schools. This mentality has to change for the betterment of the society.
Teaching subjects/academics alone is enough, or should students be introduced to other forms of educational activities too?
Extracurricular activities, moral value education, etc., are also as important as regular academic teachings.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

- High contrast
- Our history
- Children in India
- Our partners
- Where we work
- Frequently asked questions
- Press centre
Search UNICEF
- Quality education
Grade-appropriate education for all boys and girls.

- Available in:
Poor quality education is leading to poor learning outcomes in India, ultimately pushing children out of the education system and leaving them vulnerable to child labour, abuse and violence. Many classrooms continue to be characterized by teacher-centred rote learning, corporal punishment and discrimination.
Learning assessments show that many of those children who are in school are not learning the basics of literacy and numeracy or the additional knowledge and skills necessary for their all-round development as specified under the Right to Education Act.
Much remains to be done to ensure a child-friendly learning environment where all children benefit from gender-sensitive and inclusive classrooms, as well as the availability of improved water, sanitation and hygiene, and mid-day meal practices.
Every girl and boy in India has the fundamental right to quality education, an education one that helps them to acquire basic literacy and numeracy, enjoy learning without fear and feel valued and included irrespective of where they come from.
For the first time in 10 years, reading and arithmetic scores have improved in public funded schools at early grades (ASER 2016). In seven states (Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Telangana and Uttarakhand) reading level increased by 7 per cent at grade 3 level since 2014. This indicates that increase in learning is possible but takes time. Nevertheless, ASER 2018 showed that in grade 5 after more than four years of schooling, only half of all children could read a grade 2 level text fluently. The National Achievement Survey 2017 which was conducted for grades 3, 5 and 8 gave a similar picture with only 45.2 per cent of students achieving the targeted performance levels across all subjects and classes at the national level. States such as Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh with large populations of children from scheduled castes (SC), scheduled tribes (ST) and minority communities have the lowest scores. In the NAS 2017 girls scored slightly higher or as the same level as boys.
While governments both national and state have invested in large scale learning assessments, the challenge is in the use of assessment data for improving the delivery of education rather than letting it remain a simple data collection exercise.
Successful performance in school is supported by a wide range of abilities, attitudes and socio-emotional competencies, beyond traditional literacy and numeracy skills - life skills significantly contribute to learning and are an aspect of quality education. While there is an understanding around the importance of life skills , there is a possible lack of alignment between traditional curricula and a life-skills learning agenda and a lack of understanding of how these can be developed across the education continuum. The NEP brings this focus stressing the importance of leaning by doing.
Since March 2020, schools in India have been closed and learning has shifted to remote home-based learning for those who can access it. School closures will impact learning across the education system. Gains in enrolment, school completion, and learning must not get eroded due to the combination of schools being closed and socio-economic hardships related to Covid-19. According to the World Bank, five months of school closures due to COVID-19 will result in an immediate loss of 0.6 years of schooling adjusted for quality, bringing the effective learning that a student can achieve down from 7.9 years to 7.3 years. During this period of school closure, efforts have been made by governments to ensure continuity of learning for children while they have been home. Digital tools including internet based high tech tools like apps and online learning classes, social media platforms, television and radio were used extensively. India is now looking at delivering education programmes differently and speedily to employ solutions, that accelerate impact and achieve scale across interventions targeted at children and adolescents.
COVID-19 presents urgency as well as an incredible opportunity to act and transform the education system through technology using it as an important tool of capacity building, inclusiveness and quality learning, without replacing the essential role of teachers/facilitators. While technology is not a silver bullet to solve the problem of inequities in access and learning, it has huge potential for changing how teaching and learning is delivered in India, if employed in a systemic and inclusive way, empowering teachers, frontline workers, children and adolescents and increasing access to and quality of learning.
Currently around one-third of the 2.6 million secondary schools in India have ICT labs and a functional computer. Universal access to technology in homes is yet a dream in tribal belts, interior locations, rural areas, and amongst children with disabilities. Children with poor or no access to technology face most challenges in continuing to learn. There is disproportional access to the internet across state, further extending into the rural-urban schism, where 13 per cent people of over five years of age in rural areas can use the internet against 37 per cent in urban areas. Additionally, the digital dichotomy extends to the access to hardware and devices where the poorest students and marginalised communities, including girls, do not have access to smartphones, and even if they do, internet connectivity remains poor.
The main area of UNICEF engagement and support is elementary education especially early grades and the transition to secondary education. As schools remain closed and children learn remotely, UNICEF will engage with state government for expanding access to remote learning options. UNICEF will support the expanded use of technology and the use of online systems to improve governance in education, enhance capacity of teachers, teacher support systems, other education functionaries and participation of children for enhanced learning and skills development. But at the same time recognizing that quality learning requires quality teachers and teaching.
Implementation of the National Education Policy 2020 being a priority UNICEF will provide technical support at national and state level in the key areas related to curriculum revision, learning assessment and reporting, foundational learning, life skills and career guidance.
Explore more

UNICEF India appoints Kareena Kapoor Khan as National Ambassador #ForEveryChild

Meet the new UNICEF India Youth advocates
Gaurnashi, Nahid, Vinisha, Kartik sign up as new advocates for rights of children

Unleash Your Potential
I hope my story inspires young girls to think differently and who are determined to make a positive impact on our planet.

The Fun(Doo) Way to Upskill Yourself for the Future
An interactive chat-bot is changing lives of youth across India – in a manner that’s educative, easy and fun

Essay on Higher Education in India

In India, higher education is an important aspect in anyone’s life it gives students to learn more about anything and to pursue in that field. However, there are some challenges that Higher Education in Indi is facing and it need to be discussed. Since, India has one of the oldest education systems and is considered to be the pioneer in higher education in the world as it had Nalanda University.
Short and Long Essay on Status of Higher Education in India in English
Here is a long essay mentioned which tells about Higher education system in India including good, bad and what needs to focused to improve and other aspects.
10 Lines Essay on Higher Education in India (100-120 Words)
1) Higher education is considered the last stage of academic learning.
2) Higher studies are done after the successful completion of secondary education.
3) Colleges and universities are responsible for providing higher education.
4) India possesses a low level of about 23.6% higher education.
5) Many universities in India are unable to fulfill the criteria set by UGC.
6) Central, State, deemed, and private universities are the four higher education sectors in India.
7) Associate, bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral are the four higher education degrees in India.
8) India stands 59 th among 64 countries in terms of the education system.
9) Political interference, unavailability of facilities, lack of faculties, etc are the barriers to higher education in India.
10) India’s higher education condition can be improved by setting up good private institutions or through a partnership with foreign countries.
Long Essay on Higher Education in India – 1500 Words
Introduction
Higher Education for any student in the world are as important as basic important. It not only gives student to learn more about any specialization, but also makes understand student the practicality of that subject. Higher education in India means a degree learning and understanding more about a particular subject. Higher education in India includes Bachelors, Masters, Diploma and Doctorate program in a particular discipline.
Various institutes offer higher education in India and they are called Colleges and Universities. A record of 2015 mentions there are 760 universities and 38,498 colleges in India. These colleges provide education in various fields and works on practical development of students.
National Education Policy and Higher Education
To increase the GER to half continuously by 2035, NEP 2020 wants to make it continuous for half a century. It’s estimated that 3.5 crore or significantly more spots can be allocated to higher education organizations to make this agreement a reality.
A multi-disciplinary curriculum can be combined with courses in professional fields. One or both of the UG projects may last 3 or 4 years. There will be a variety of leave alternate options, and appropriate “certificates” will be issued to the understudies during their residency. The first year of study will conclude with a certificate, the second year with a preliminary confirmation, the third year with a Bachelor’s degree and the last year ending with a degree that demonstrates research insight at the end of the fourth year. A credit bank for academic development will be set up to track credits students acquire over the length of their academic journey.
Different classes of colleges will appear in accordance with the vision and mission of instructional organizations, such as educating serious colleges, research-centered colleges, and universities that grant degrees autonomously. Organizations will be granted independence in 15 years as the school association methodology is gradually eliminated.
Higher Education versus Skill Acquisition
Generally we don’t consider on skill acquisition in India. We are totally focused on theoretical part of education. This has been an issue. This issue causes a lot of students to be inferior while telling about their SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats).
Skill acquisition means to accomplish any specialty. It can be in studies or in any field. But, when we put the skills in front of higher education, things seem to be little bit different. People are busy with their curriculum so that they cannot find what their skills are. This disturbs them while choosing a job or figuring out their career field.
Studies that require skill development are not generally conducted by institutes. Finding and incorporating skills can provide chances of discovering yourself in your field. Even, in engineering people need to focus on presentation and speaking but they are not part of their curriculum. This leads to people doing jobs in a call centre and it discourages many students to stop themselves from growing.
Apart from all these, Indian education system is quite different especially in North India. The roots of this starts from class 10 th , parents decide student’s future and tells them what to do. If they score well in class 10 th then they are asked to either go with science. If their marks are average then they are asked to go for commerce and below average students are supposed to go with humanities stream. Sometimes these streams feel like a caste system in India. Parents never give time to understand what students want to do, what is their hobby and what do they want to pursue.
During the time of placements or job interview, people do not know what a SWOT analysis is. SWOT denotes Strength Weaknesses Opportunities and Threats. It allows any person to identify their negative and positive parts and work on it so that they can deliver their work. Many institutions don’t do that ultimately leads to drastic failure of students.
Skill acquisition and know strengths are important part of life. In the higher education field we should not study only getting a degree or to get a job but we should look completely over the skills so that we can utilize our strengths into what it suits us.
Higher Education Issues and Challenges in India
In India, Higher Education faces some challenges and issues that need to be seen by government. When compared with other agricultural nations, India has a very low level of advanced education, which is just 26.3%. In India, many schools and colleges do not meet the basic requirements set by the UGC, which renders them unable to position themselves from among top colleges around the globe.
- Enrollment and Faculties
More than 670 colleges exist in India today, no less than 38,000 universities, 817000 instructors and educators, and more than 28000000 understudies registered. School, college, student, and instructor numbers keep developing every year. The courses available to understudies are diverse. The number of students applying for master’s programs across the country exceeds 140,000,000. More than 20490000 understudies are enrolled in post-graduate programs. The year 2014 was selected for both research and confirmation to cover around 1370000 understudies.
- Quality Education
Attempting to expand new universities requires swindling money from understudies and their families. Long-term problems with quality training have been caused by deficiencies in staff and the inability of the state educational framework to draw in and retain good educators. Despite the abundance of job opportunities in advanced education, a large number of NET/PhD competitors are unemployed. Due to market opportunities and pioneering enthusiasm, numerous establishments are utilizing the carelessness of the administrative climate to offer ‘degrees’ not verified by Indian specialists, and a lot of foundations are obtaining funds by creating fake NGOs. Understudies from rural and semi-urban foundations regularly enroll in these organizations and universities.
However, in India, numerous colleges and schools have not met the UGC’s low standards. Consequently, we are not in position to place among the top universities in the world. Furthermore, reduced administrative financial assistance negatively impacts small and rural educational institutions. Thus, only a small number of first-class students can attend advanced education, reducing general access.
Higher Education as an agent of change
Higher education’s mission is to address large challenges and lead exploration in areas that are in need throughout the world, thereby supporting social values like welfare and social commitment. It is possible to be surprised to discover you are naturally talented in a certain area of math, to have a particular preference for moving, or to find a particular creator you enjoy more than others. Their time should be managed well, they should step up, and they should stay on top of things. It is these skills that can be applied to everyday concerns, from maintaining one’s living space to being a strong person to dominating at one’s job.
Today’s marketplace requires business people to have administration skills, progressive theoretical aptitudes, and development-improved learning abilities. Not just a couple of high school and college graduates are required. By doing this, it will enable schools to make the changes in curricular content, instructional methods, and task plans needed to ensure an undeniably strong link between what students in their institutions are learning and what graduates are reasonably expected to do. As a result, all understudies will have a better educational experience and prepare to function as managers with their multicultural smoothness.
Ideally, the new hire will possess the relevant experience, knowledge, and affiliations; this will allow him/her to stay on the cutting edge of the industry and interface such cutting edge practices to the development of the association. Aware of complex authoritative construction and implementing that information with discernment abilities and higher-request thinking, the hiring manager additionally expects that the new hire will develop a strong, encompassing, and flexible grasp of the organization.
Importance of Higher Education
Institutions today provide their students with various programs that prepare them to enter different economic areas, assist them with remaining in the work market for long, and keep pace with the changes in the worldwide economy and changes in technological advancements. Innovation and development are driven by advanced education. The majority of enormous universities suggest that students not settle on a space of focus until after their first year, or maybe even their sophomore year. While you might not be sure which employment you are interested in pursuing, you should remain mindful that academic environments are probably the best grounds to examine your options and settle on your choice.
Having the ability to distinguish and deal with issues in an appropriate way is beneficial for both personal and professional activities. This course teaches you basic reasoning skills no matter what you’re learning, from how to approach a scholarly thesis to how to operate a motor.
Higher Education in India needs to be emphasized in a good way. The matter is that it should not be limited to only getting a degree and getting a job. Institutes providing higher education should ensure that focusing on practical and skill based knowledge are quite important in the field. If this can be achieved then we won’t be having corporate slaves, rather than we would be having great leaders and productive candidates who would be delivering their best in their respective fields.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. GB Pant University is the biggest university in India.
Ans. Jawaharlal Nehru University was the first to receive A++ NAAC.
Ans. UGC stands for University Grants Commission.
Ans. Nalanda is considered to be the first University in the world.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.
Subscribe Now! Get features like

- Latest News
- Entertainment
- Real Estate
- RR vs PBKS Live Score
- Lok Sabha Election 2024
- Election Schedule 2024
- My First Vote
- IPL 2024 Schedule
- RR vs PBKS Live
- IPL Points Table
- IPL Purple Cap
- IPL Orange Cap
- The Interview
- Web Stories
- Virat Kohli
- Mumbai News
- Bengaluru News
- Daily Digest

CUET UG 2024 begins today, all papers of 1st day postponed in Delhi
Cuet ug 2024: on the first day, candidates will appear for chemistry, biology, english and general test papers..
The National Testing Agency (NTA) will start the third edition of the Common University Entrance Test (CUET UG 2024) today, May 15. On the first day of the entrance examination, university aspirants will appear for Chemistry, Biology, English and General Test papers. A day ahead of the exam, the NTA informed that these four papers have been postponed in Delhi due to “unavoidable reasons” and will be held on May 29. Revised admit cards will be issued to affected candidates, it said.

“Please note that the examination scheduled on 15 May 2024 wilI be held as per earlier communicated schedule in all other cities across the Country (including Gurugram, Ghaziabad, Faridabad, and Noida) and abroad. Further examinations scheduled on other dates (16n May, 17n May & 18h May 2024) at all centers including those in Delhi will be held as scheduled,” NTA said in the notification.
The rest of the candidates who will write the above-mentioned papers on the first day must reach their respective venues as per the reporting time and address mentioned on their admit cards.
Items allowed inside exam hall:
- Admit card along with self-declaration (undertaking)
- A simple transparent ball point pen
- Additional photograph (same as uploaded on the application form) to be pasted on the attendance sheet.
- Any one of the valid, original photo IDs– school identity card/ PAN card/ Driving License/ Voter ID/Passport/Aadhaar Card (with photograph)/E-Aadhaar with photograph/ Ration Card with photograph/Class 12 board admit card with photograph/ bank passbook with photograph.
- PwBD certificate, if applicable
- Personal transparent water bottle
- Sugar tablets/fruits (like banana/apple/orange) in case the candidate is diabetic
Candidates are advised not to carry any banned items as there may not be arrangement for safe keeping of the same.
For more details regarding the CUET UG 2024, candidates can contact 011 - 40759000 /011 -69227700 or e-mail at [email protected].
The candidates are also advised to be in touch with the NTA website(s) nta.ac.in and exams.nta.ac.in/CUET-UG/ for updates.

Join Hindustan Times
Create free account and unlock exciting features like.

- Terms of use
- Privacy policy
- Weather Today
- HT Newsletters
- Subscription
- Print Ad Rates
- Code of Ethics
- IPL Live Score
- T20 World Cup Schedule
- IPL 2024 Auctions
- T20 World Cup 2024
- Cricket Teams
- Cricket Players
- ICC Rankings
- Cricket Schedule
- T20 World Cup Points Table
- Other Cities
- Income Tax Calculator
- Budget 2024
- Petrol Prices
- Diesel Prices
- Silver Rate
- Relationships
- Art and Culture
- Taylor Swift: A Primer
- Telugu Cinema
- Tamil Cinema
- Board Exams
- Exam Results
- Competitive Exams
- BBA Colleges
- Engineering Colleges
- Medical Colleges
- BCA Colleges
- Medical Exams
- Engineering Exams
- Horoscope 2024
- Festive Calendar 2024
- Compatibility Calculator
- The Economist Articles
- Lok Sabha States
- Lok Sabha Parties
- Lok Sabha Candidates
- Explainer Video
- On The Record
- Vikram Chandra Daily Wrap
- EPL 2023-24
- ISL 2023-24
- Asian Games 2023
- Public Health
- Economic Policy
- International Affairs
- Climate Change
- Gender Equality
- future tech
- Daily Sudoku
- Daily Crossword
- Daily Word Jumble
- HT Friday Finance
- Explore Hindustan Times
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Subscription - Terms of Use
Essay on India For Students and Children
500+ words essay on india.
India is a great country where people speak different languages but the national language is Hindi. India is full of different castes, creeds, religion, and cultures but they live together. That’s the reasons India is famous for the common saying of “ unity in diversity “. India is the seventh-largest country in the whole world.
Geography and Culture
India has the second-largest population in the world. India is also knowns as Bharat, Hindustan and sometimes Aryavart. It is surrounded by oceans from three sides which are Bay Of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and Indian oceans in the south. Tiger is the national animal of India. Peacock is the national bird of India. Mango is the national fruit of India. “ Jana Gana Mana ” is the national anthem of India . “Vande Mataram” is the national song of India. Hockey is the national sport of India. People of different religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism , Jainism, Sikhism, Islam, Christianity and Judaism lives together from ancient times. India is also rich in monuments, tombs, churches, historical buildings, temples, museums, scenic beauty, wildlife sanctuaries , places of architecture and many more. The great leaders and freedom fighters are from India.
F lag of India
The indian flag has tricolors.
The first color that is uppermost color in the flag which is the saffron color, stands for purity. The second color i.e. the middle color in the flag is the white color and it stands for peace. The third color that is the lowest color in the flag is the green color and it stands for fertility. The white color has an Ashoka Chakra of blue color on it. Ashoka Chakra contains twenty-four spokes which are equally divided. India has 29 states and 7 union territories.

Follow this link to get a Physical and state-wise Map of India
My Favorite States from India are as follows –
Rajasthan itself has a glorious history. It is famous for many brave kings, their deeds, and their art and architecture. It has a sandy track that’s why the nuclear test was held here. Rajasthan is full of desert, mountain range, lakes, dense forest, attractive oases, and temples, etc. Rajasthan is also known as “Land Of Sacrifice”. In Rajasthan, you can see heritage things of all the kings who ruled over there and for that, you can visit Udaipur, Jodhpur, Jaisalmer, Chittaurgarh, etc.
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh is bigger than a foreign (Italy) country and smaller than Oman. It also has tourists attractions for its places. In Madhya Pradesh, you can see temples, lakes, fort, art and architecture, rivers, jungles, and many things. You can visit in Indore, Jabalpur, Ujjain, Bhopal, Gwalior and many cities. Khajuraho, Sanchi Stupa, Pachmarhi, Kanha national park, Mandu, etc. are the places must visit.
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir are known as heaven on earth . We can also call Jammu and Kashmir as Tourists Paradise. There are many places to visit Jammu and Kashmir because they have an undisturbed landscape, motorable road, beauty, lying on the banks of river Jhelum, harmony, romance, sceneries, temples and many more.
In Jammu and Kashmir, u can enjoy boating, skiing, skating, mountaineering, horse riding, fishing, snowfall, etc. In Jammu and Kashmir, you can see a variety of places such as Srinagar, Vaishnav Devi, Gulmarg, Amarnath, Patnitop, Pahalgam, Sonamarg, Lamayuru, Nubra Valley, Hemis, Sanasar, Anantnag, Kargil, Dachigam National Park, Pulwama, Khilanmarg, Dras, Baltal, Bhaderwah, Pangong Lake, Magnetic Hill, Tso Moriri, Khardung La, Aru Valley, Suru Basin,Chadar Trek, Zanskar Valley, Alchi Monastery, Darcha Padum Trek, Kishtwar National Park, Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary, Nyoma, Dha Hanu, Uleytokpo, Yusmarg, Tarsar Marsar Trek and many more.
It is known as the ‘God’s Own Country’, Kerala is a state in India, situated in the southwest region, it is bordered by a number of beaches; covered by hills of Western Ghats and filled with backwaters, it is a tourist destination attracting people by its natural beauty. The most important destinations which you can see in Kerela are the museum, sanctuary, temples, backwaters, and beaches. Munnar, Kovalam, Kumarakom, and Alappad.
India is a great country having different cultures, castes, creed, religions but still, they live together. India is known for its heritage, spices, and of course, for people who live here. That’s the reasons India is famous for the common saying of “unity in diversity”. India is also well known as the land of spirituality , philosophy, science, and technology.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Tips to answer multiple-choice, short-answer, and essay-type questions in exams
E xams are a stressful affair and they require smart strategies and techniques to excel. While in-depth learning is crucial, different types of questions demand specific strategies and approaches for solving.
Exams may appear in several formats including multiple choice questions, short answers and essays, each requiring different techniques of answering.
Below is a comprehensive guide to solving exams with different types of question patterns:
TIPS TO ANSWER MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
- The first and foremost thing to do is to read the questions properly. Often, students miss out on important details due to a lack of focus. Paying attention to each and every piece of information and reading with attention is crucial.
- After reading the question, try to predict the answer without referring to the given options. This increases your chances of selecting the correct answer through educated guessing.
- Using the process of elimination can do wonders. In this method, you eliminate the options you believe are incorrect. This narrows down your choices and aids in identifying the correct response.
- Paying attention to words such as 'always,' 'never,' 'sometimes,' 'most,' 'only,' 'many,' 'but,' and 'often' can help us better understand the sentence. These words tend to alter the meaning of the sentence and hence should be paid attention to and read properly.
- Â Understanding concepts thoroughly enables you to grasp the context of questions accurately and answer them correctly.
TIPS TO ANSWER SHORT QUESTIONS
- Read the question properly and comprehend it well. Understand whether you need to give a definition, provide examples, write a brief summary or offer comparisons.
- Write the answer to the point, avoiding unnecessary explanations and using keywords. This increases your chances of scoring higher.
- Use simple language and avoid complex terms, as they can confuse the examiner. The simpler your answer, the higher your score.
- Write your answers in a logical and organised manner. Structure your answers with separate paragraphs, bullet points, flowcharts, tables, etc., as this makes it easier for the examiner to read and understand your answer.
- During the preparatory phase, use colourful pens, flashcards, charts, and drawings to learn concepts well. This method helps in recollecting the answers during exams.
- Indulge in self-testing methods by practicing sample question papers, demo tests, and solving previous year question papers to understand the probable questions and the exam pattern.
- Having a time management strategy in place is important. Allocate time for different types of questions and try to solve them within the given time frame.
TIPS TO WRITE ESSAYS
- Understand the topic well and follow the instructions.
- Brainstorm ideas on the topic and plan the points you intend to include.
- Begin with an informative yet concise introduction, followed by a detailed body and a conclusion that summarizes your essay.
- Ensure the essay is well-structured and divided into a minimum of 3-4 paragraphs.
- Use quotations and examples to support the information you have written.
- Adhere to the specified time and word limits.
- Ensure your essay is written in simple and clear language.
- Always remember to proofread the essay to eliminate grammatical and spelling errors.
- Make reading a regular practice to enhance language proficiency and facilitate a smoother flow of thoughts.
By implementing such strategic approaches, you can efficiently answer your questions. It is important to study diligently and practice with sample papers.
During the exam, take the time to read the question paper properly during the allocated reading time and manage your time effectively.
- Article by Nischal Narayanam, mathematical child prodigy, winner of the National Child Award (Gold Medal), youngest double Guinness World Record holder in memory power, first Indian to win the World Memory Championship title, youngest CA, and Founder and Mentor at Nischals
Watch Live TV in English
Watch Live TV in Hindi


30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Chess in 500 Words in English for School Students

- Updated on
- May 14, 2024

Essay on Chess: Chess is known as the ‘Royal Game’ as it was popular among the nobility in ancient and medieval times. Some find chess interesting, some not, but this two-man game can teach you the art of winning and losing in life. Originating in ancient India, this timeless game has journeyed through epochs, shaping civilisations and captivating minds worldwide. Let’s discuss more through an essay on chess.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 Origins of Chess: Chaturanga and Its Legacy
- 1.2 From India to Persia and Beyond
- 1.3 Medieval Europe: Adoption and Adaptation
- 1.4 Standardization and Globalization: The Rise of FIDE
- 1.5 Indian Chess: A Renaissance and Future Prospects
- 1.6 Conclusion
Essay on Chess in 500 Words
Chess is a game of strategy and intellect. It has a rich history that spans centuries and continents. From its humble beginnings in ancient India to its modern-day status as a global phenomenon, the evolution of chess reflects the cultural exchanges and innovations of civilisations throughout history.
Quick Read: Essay on the Role of Youth in Nation-Building
Origins of Chess: Chaturanga and Its Legacy
The origins of chess trace back to the ancient Indian game of Chaturanga, which flourished around the 6th century. Chaturanga, meaning “four divisions,” was a precursor to modern chess, featuring distinct military divisions represented by pieces on a 64-square board. While the exact origins remain shrouded in mystery, evidence suggests that Chaturanga played a pivotal role in the development of chess, with its strategic gameplay and unique piece movements laying the foundation for the game we know today.
From India to Persia and Beyond
The expansion of chess beyond India began in the 7th century when Indian rulers shared the game with the Sasanian Empire in Persia. Renamed Shatranj or Chaturang in Persia, chess underwent adaptations, including the introduction of new pieces like the firzan (counsellor). The game’s journey along the Silk Road facilitated its spread to East Asia, where it evolved into variants such as Chinese chess. The cultural exchanges along these trade routes influenced regional variations, enriching the diversity of chess gameplay.
Medieval Europe: Adoption and Adaptation
The introduction of chess to medieval Europe occurred through the Arab Empire, which patronised the game despite prohibitions on gambling. As chess spread across Northern Africa and Europe, it underwent further adaptations to suit local customs and preferences. While basic chess sets were prevalent during this period, the game gained popularity among European nobility, paving the way for elaborately crafted boards and pieces.
Standardization and Globalization: The Rise of FIDE
By the 19th century, efforts to standardize chess led to the development of the Staunton design, endorsed by Howard Staunton, a prominent chess player of the era. This standardisation facilitated organized competitions and tournaments, laying the groundwork for the establishment of FIDE (Fédération Internationale des Échecs) in 1924. FIDE’s formation marked a significant milestone in the globalization of chess, creating a unified framework for international competition and governance.
Indian Chess: A Renaissance and Future Prospects
Despite its ancient origins, India’s contributions to chess were revitalized in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, with players like Vishwanathan Anand emerging as world champions. This resurgence reflects India’s enduring connection to the game and its ongoing efforts to produce world-class talent. The rise of young prodigies like Gokesh symbolises India’s continued prominence in the world of chess, reaffirming its legacy as the birthplace of this timeless game.
Quick Read: Essay on Voting Rights in India: 500 Words in English for Students
Chess’s evolution from its origins in ancient India to its global prominence today exemplifies the enduring appeal of strategic gameplay and intellectual challenge. As the game continues to adapt and thrive in diverse cultural contexts, it remains a testament to the human capacity for creativity, ingenuity, and competitive spirit. Whether played on a digital platform or across a traditional board, chess transcends boundaries, uniting players across time and space in the pursuit of victory and mastery.
Ans: As we navigate the chessboard of life, let’s remember the valuable lessons we can learn from this timeless game. Whether we play for fun or aspire to become chess champions, the strategic world of chess is an exceptional realm that rewards dedication, patience, and the thrill of a well-executed strategy.
Ans: Playing chess can improve our mental and problem-solving skills. It is a game of strategy, where we can learn how to make plans and achieve our life goals. Chess is an educational tool and can help students enhance their focus. Moreover, chess can teach the art of winning and losing.
Ans: The game of chess was born in India during the Gupta dynasty in the 6th century. Today, more than 1500 years later, it is played in 172 countries.
Popular Essay Topics
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Aayushi Vardhan
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Education News
TS ECET 2024 Answer Key Out! Download Now, Raise Objections by May 12th
Visual Stories


COMMENTS
Higher Education. According to the All India Survey on Higher Education, the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education in India has increased from 20.8% in 2011-12 to 25.8% in 2017-18. Lack of access is a major reason behind the low intake of higher education. The policy aims to increase GER to 50% by 2035.
The Indian education system is quite an old education system that still exists. It has produced so many genius minds that are making India proud all over the world. In this Essay on Indian Education System will discuss about Pros and Cons of it.
Essay on Indian Education. Education plays an important role in the development of an individual and makes him a knowledgeable citizen. It is the Education that makes an individual self-reliant, helps to suppress social evils, and contributes towards the development of the society and nation as a whole. Education helps in unraveling the mystery ...
100 Words Essay On Education System In India. India's education system is ideal for providing its students with a solid academic foundation. It emphasises lifelong learning and encourages its students to pursue higher education. It also develops the students' language skills by allowing them to study in both English and Indian languages.
The RTE Act recommends a PTR of 30:1 for primary classes and 35:1 for upper primary classes. The District Information System for Education (DISE) report found that 30% of primary and 15% of the upper primary schools have higher PTRs. Despite the improvement in the Student-Classroom ratio (SCR), India still faces inequality in this context.
Essay on Education system in India 150 words. The education system in India is a complex and multifaceted structure that plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation's future. While it has made significant progress in recent years, challenges persist. India's education system consists of several stages, starting with primary education ...
Essay on Education System in India in 100 words. The education system in India comprises four levels: pre-primary, primary, secondary and senior secondary system; all these levels are well-structured and developed to systemically introduce students to the subject matter, develop their language and cognitive skills and prepare them for higher ...
Essay on Indian Education System. Indian Education System Essay is mainly divided into four stages. Lower primary. Upper primary. High school and. Higher secondary. The age group of lower primary school is 6 years to 10 years, for upper primary, it is 11 and 12 years. Children start their high school usually at the age of 13 ends at 15 or 16.
Education is like a key that opens doors to a world of knowledge, opportunities, and growth. In India, a vast and diverse country, the education system plays a crucial role in shaping the future of millions of students. In this essay, I will argue that the Indian education system has its strengths and challenges, and it is continually evolving ...
Education in India is primarily managed by the state-run public education system, which falls under the command of the government at three levels: central, state and local.Under various articles of the Indian Constitution and the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009, free and compulsory education is provided as a fundamental right to children aged 6 to 14.
ABSTRACT. India's performance in education presents a conundrum that is not easily explained. While it has expanded access to most parts of the country, and established world class institutions of higher education, it still has among the highest number of out of school children and a very poor record of school learning levels.
Education plays an important role in the development of an individual and making him a knowledgeable citizen. It is the education that makes an individual self-reliant, helps to suppress the social evils and contribute towards the development of the society and nation as a whole. Education helps in unravelling the mystery of nature.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, India's poor educational records have been exacerbated, with schools being closed since March 2020. As can be seen from Figures 2 and 2A, schools in India have been closed for the largest number of weeks. The map also reveals that schools in India have been closed for 69 weeks - the longest duration that ...
500+ Words Essay on Education. Education is an important tool which is very useful in everybody's life. Education is what differentiates us from other living beings on earth. It makes man the smartest creature on earth. It empowers humans and gets them ready to face challenges of life efficiently. With that being said, education still remains ...
Abstract. Recently, India is encountering quick and sudden changes in teacher education. The one-year B.Ed. Program was converted into a two-year Program in 2015, and it was implemented abruptly and without much planning in the same year. While the stakeholders of teacher education are still busy in reflecting and debating the pros and cons of ...
The importance of education in life is immense. It facilitates quality learning for people throughout their life. It inculcates knowledge, belief, skill, values and moral habits. It improves the way of living and raises the social and economic status of individuals. Education makes life better and more peaceful.
UNICEF works with the government and partners to address issues around the gender gap in primary and secondary education. It also seeks to ensure that, all children complete primary schooling, with girls and boys having equal access to quality education. We provide gender responsive technical support to enable out-of-school girls and boys to ...
Disadvantages of Digital Education in India. • Less face-to-face communication with fellow students and teachers. • Lack of discipline, motivation and self-confidence among students. • Increased screen time resulting in poor eyesight and less physical activity. • Unavailability of technically trained teachers to teach the students.
500 Words Essay on Women Education in India. Our India is a developing country. Moreover, it is one of the largest democracies. Since the day of Independence, our country has remarkable development in all the fields. And this was all possible because of the increase in education for all the genders. The gender equality took the country to new ...
UNICEF/UN0271971/Hajra. Available in: English. हिंदी. Poor quality education is leading to poor learning outcomes in India, ultimately pushing children out of the education system and leaving them vulnerable to child labour, abuse and violence. Many classrooms continue to be characterized by teacher-centred rote learning, corporal ...
This essay explores this relationship based on several research articles and opines that in the case of Indian education system, it is important to have policies in place that will help eliminate ...
Short and Long Essay on Status of Higher Education in India in English. Here is a long essay mentioned which tells about Higher education system in India including good, bad and what needs to focused to improve and other aspects. 10 Lines Essay on Higher Education in India (100-120 Words) 1) Higher education is considered the last stage of ...
@article{Mitra2024IndiasET, title={India's emerging trends and meanings in healthy human-nature relationships: Indian outdoor education practitioner perspectives}, author={Soumya Mitra and Vinathe Sharma-Brymer and Denise Mitten and Janet Ady}, journal={Journal of Adventure Education and Outdoor Learning}, year={2024}, url={https://api ...
A day ahead of the exam, the NTA informed that these four papers have been postponed in Delhi due to "unavoidable reasons" and will be held on May 29. Revised admit cards will be issued to ...
500+ Words Essay on India. India is a great country where people speak different languages but the national language is Hindi. India is full of different castes, creeds, religion, and cultures but they live together. That's the reasons India is famous for the common saying of " unity in diversity ". India is the seventh-largest country in ...
Story by India Today Education Desk ... Ensure the essay is well-structured and divided into a minimum of 3-4 paragraphs. Use quotations and examples to support the information you have written.
As a first step towards improving astronomy education in schools, we at the OAE (Office of Astronomy for Education) India Center are conducting a baseline survey to understand the status of astronomy education in India. The survey instrument consists of 16 questions that can be categorised into five sections, addressing astronomy in the curriculum, general astronomy knowledge, cultural ...
Essay on Chess in 500 Words. Chess is a game of strategy and intellect. It has a rich history that spans centuries and continents. From its humble beginnings in ancient India to its modern-day status as a global phenomenon, the evolution of chess reflects the cultural exchanges and innovations of civilisations throughout history.
TS ECET 2024 answer key and question papers are out! Download them from ecet.tsche.ac.in to check your answers and estimate your score. Use the answer key by May 12th to submit objections if you ...