Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement?

- Share this story on facebook
- Share this story on twitter
- Share this story on reddit
- Share this story on linkedin
- Get this story's permalink
- Print this story
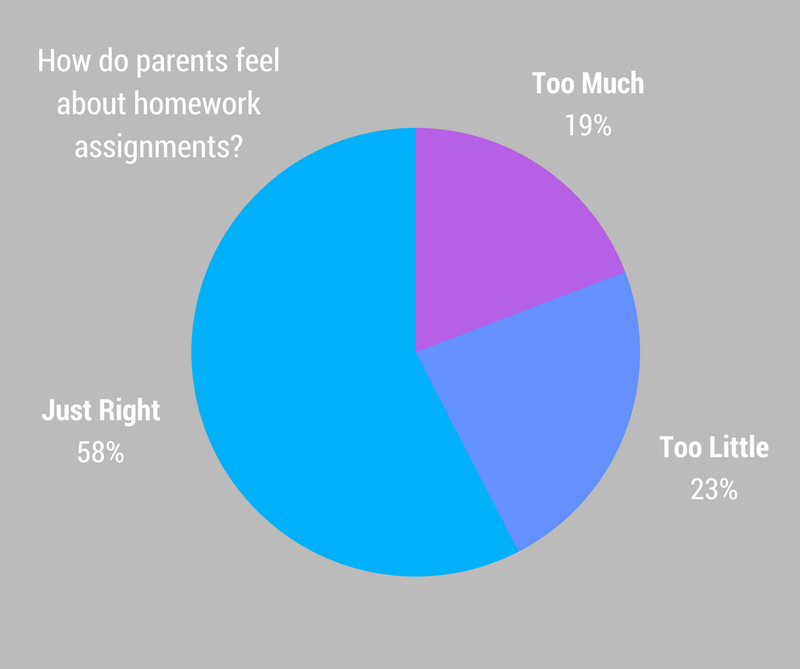
Educators should be thrilled by these numbers. Pleasing a majority of parents regarding homework and having equal numbers of dissenters shouting "too much!" and "too little!" is about as good as they can hope for.
But opinions cannot tell us whether homework works; only research can, which is why my colleagues and I have conducted a combined analysis of dozens of homework studies to examine whether homework is beneficial and what amount of homework is appropriate for our children.
The homework question is best answered by comparing students who are assigned homework with students assigned no homework but who are similar in other ways. The results of such studies suggest that homework can improve students' scores on the class tests that come at the end of a topic. Students assigned homework in 2nd grade did better on math, 3rd and 4th graders did better on English skills and vocabulary, 5th graders on social studies, 9th through 12th graders on American history, and 12th graders on Shakespeare.
Less authoritative are 12 studies that link the amount of homework to achievement, but control for lots of other factors that might influence this connection. These types of studies, often based on national samples of students, also find a positive link between time on homework and achievement.
Yet other studies simply correlate homework and achievement with no attempt to control for student differences. In 35 such studies, about 77 percent find the link between homework and achievement is positive. Most interesting, though, is these results suggest little or no relationship between homework and achievement for elementary school students.
Why might that be? Younger children have less developed study habits and are less able to tune out distractions at home. Studies also suggest that young students who are struggling in school take more time to complete homework assignments simply because these assignments are more difficult for them.
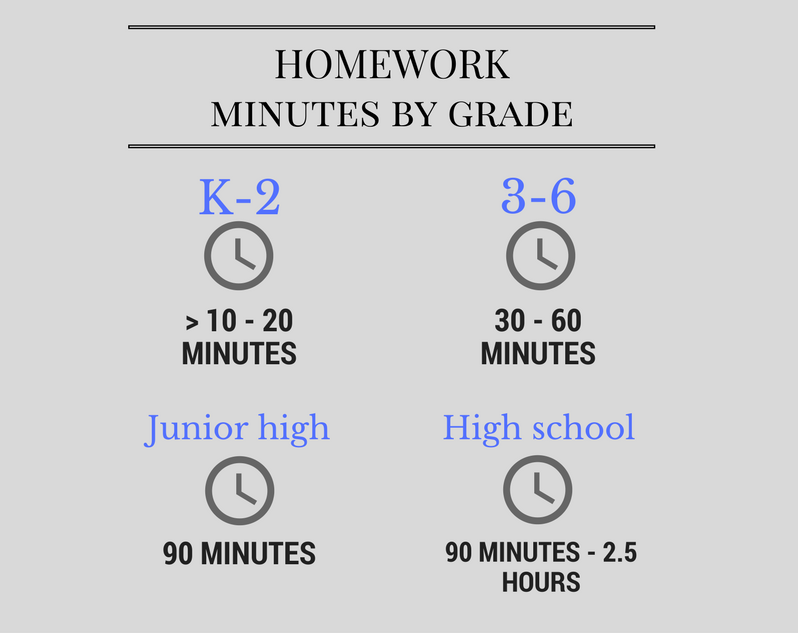
These recommendations are consistent with the conclusions reached by our analysis. Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until between 90 minutes and 2½ hours of homework a night, after which returns diminish.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what's going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Opponents of homework counter that it can also have negative effects. They argue it can lead to boredom with schoolwork, since all activities remain interesting only for so long. Homework can deny students access to leisure activities that also teach important life skills. Parents can get too involved in homework -- pressuring their child and confusing him by using different instructional techniques than the teacher.
My feeling is that homework policies should prescribe amounts of homework consistent with the research evidence, but which also give individual schools and teachers some flexibility to take into account the unique needs and circumstances of their students and families. In general, teachers should avoid either extreme.

Link to this page
Copy and paste the URL below to share this page.

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Strategizing resources leads to improved exam scores, according to Stanford scholars
A study from Stanford psychology scholars found that college students employing a strategic approach to the use of study resources improved their exam scores by an average of one-third of a letter grade.
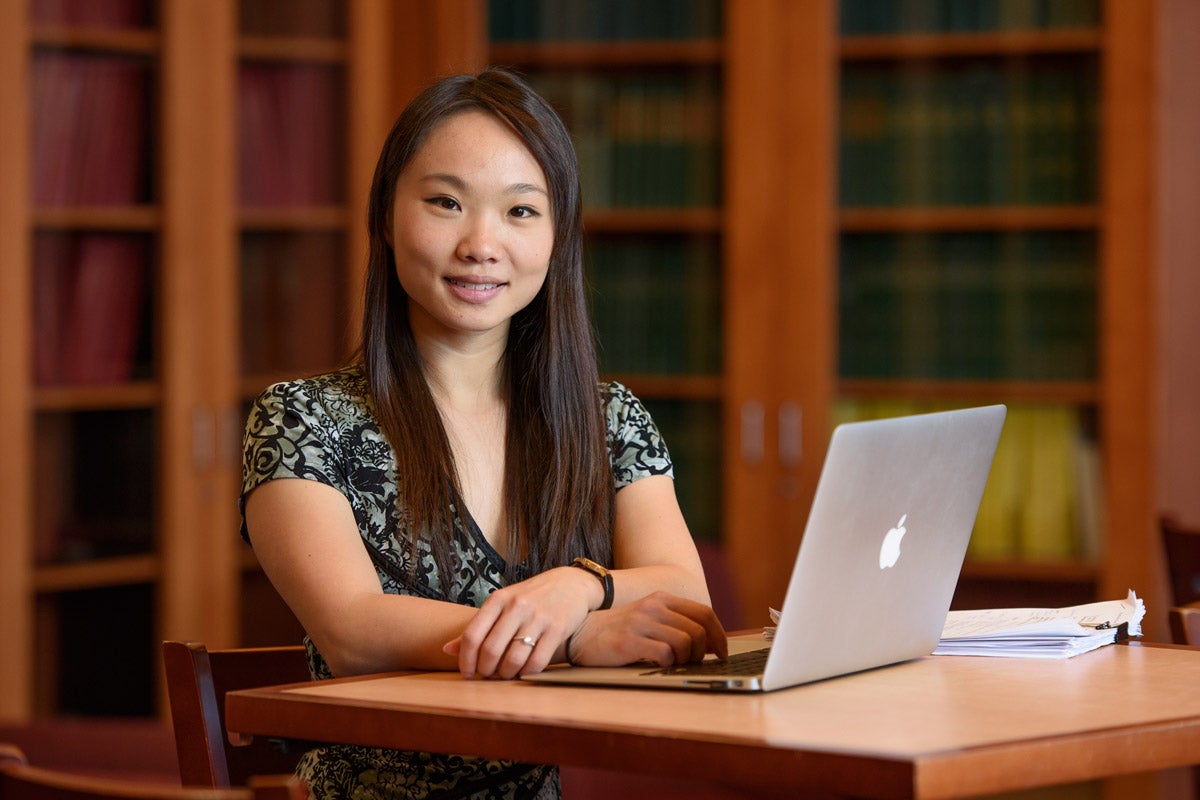

Patricia Chen is lead author on a paper that shows that a psychological intervention encouraging students to use available study resources in a strategic way made them more likely to perform better in class. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
Despite access to a trove of learning resources – including textbooks, online references and homework assignments – some students routinely fall short of their performance expectations.
The solution may not be to work harder, but more strategically. That’s the key takeaway from new research led by Stanford scholars, whose study published in Psychological Science found that applying a strategic approach to studying helped college students improve their exam scores by an average of one-third of a letter grade.
Inspiration to strategize
The study was inspired by meetings that lead author Patricia Chen, a postdoctoral research fellow in Stanford’s Department of Psychology , had with less-than-enthused students after they received their exam grades. Many of these students, she noticed, lamented their poor performances despite the great deal of effort that they had put into studying. The classic complaint seemed to be, “I studied really hard, and I’m just as smart as [another student]. I don’t understand why I didn’t do well.”
In response, Chen would ask these students, “Describe to me how you studied for the exam.” From the responses, Chen gleaned the insight that many students – intelligent and willing to work hard – fall short of performing to their potential because they don’t employ a strategic approach to their learning.
“Blind effort alone, without directing that effort in an effective manner, doesn’t always get you to where you want to go,” Chen said.
Power of self-reflection
The research team, which included Desmond Ong, a Stanford doctoral student in psychology, homed in on one important aspect of strategic learning – engaging in self-reflection to identify and use resources wisely. Prior research supports the general use of metacognition, or “thinking about one’s own thinking,” as a successful means to better learning and academic performance. But, before their studies, it remained to be seen whether specifically strategizing about one’s resource use would causally improve students’ academic performance.
The researchers developed a “Strategic Resource Use” intervention that blends educational and social psychological theories. The intervention, according to the study, “prompts students to think deliberately about how to approach their learning effectively with the resources available to them.”
The intervention was administered through brief online surveys sent to college students in an introductory statistics class about one week before their exams.
Students in the control group received a business-as-usual exam reminder. Students in the intervention group received the same exam reminder and a short Strategic Resource Use exercise: They were asked to think about what they expected to be on the upcoming exam and then strategize what kinds of resources they would use to study most effectively. Following this, the students were asked to explain why each resource they chose would be useful to their learning and then describe how they planned on using their chosen resources.
In two studies, students who strategized their resource use before studying outperformed comparable classmates in the control group by an average of one-third of a letter grade in the class. In the first study, students scored an average of 3.45 percentage points higher in the class, and in the second study, the average difference was 4.65 percentage points.
Why was the intervention so effective? The researchers found that the brief intervention exercise made students more self-reflective about how they approached their learning. In turn, this metacognition enabled students to use their resources more effectively, as their self-reports showed.
“It’s not merely about using a greater number of resources for studying. The important point here is using resources more effectively,” stressed Ong.
This strategic thinking also provided students with other psychological benefits, including feelings of empowerment regarding their education. Students who had taken the intervention perceived a greater control over their learning and expressed fewer negative feelings about their upcoming exams.
Chen emphasized it is important to consider the specific class environment before implementing the Strategic Resource Use intervention. The researchers note that the intervention has been tested – and found effective – in resource-rich environments, where students have access to textbooks, lecture notes, online resources, teaching assistants and other tools. But it is still unknown how well the intervention would work in resource-scarce environments. In resource-scarce environments, said Chen, it might be better for educators to focus on providing “a basic repertoire of resources” first.
A strategy for life
Chen proposes that the principle behind Strategic Resource Use can be applied beyond academics, including parenting, losing weight or learning a new skill at work.
“Actively self-reflecting on the approaches that you are taking fosters a strategic stance that is really important in life,” she said. “Strategic thinking distinguishes between people of comparable ability and effort. This can make the difference between people who achieve and people who have the potential to achieve, but don’t.”
Chen offered one more piece of advice: “Strategize how you want to effectively direct your efforts before you pour your energy into it.”
The study, “Strategic Resource Use for Learning: A Self-Administered Intervention That Guides Self-Reflection on Effective Resource Use Enhances Academic Performance,” was also co-authored by Omar Chavez, a graduate student at the University of Texas, and Brenda Gunderson, a senior lecturer at the University of Michigan.
Study: Homework Doesn’t Mean Better Grades, But Maybe Better Standardized Test Scores

Robert H. Tai, associate professor of science education at UVA's Curry School of Education
The time students spend on math and science homework doesn’t necessarily mean better grades, but it could lead to better performance on standardized tests, a new study finds.
“When Is Homework Worth The Time?” was recently published by lead investigator Adam Maltese, assistant professor of science education at Indiana University, and co-authors Robert H. Tai, associate professor of science education at the University of Virginia’s Curry School of Education , and Xitao Fan, dean of education at the University of Macau. Maltese is a Curry alumnus, and Fan is a former Curry faculty member.
The authors examined survey and transcript data of more than 18,000 10th-grade students to uncover explanations for academic performance. The data focused on individual classes, examining student outcomes through the transcripts from two nationwide samples collected in 1990 and 2002 by the National Center for Education Statistics.
Contrary to much published research, a regression analysis of time spent on homework and the final class grade found no substantive difference in grades between students who complete homework and those who do not. But the analysis found a positive association between student performance on standardized tests and the time they spent on homework.
“Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be,” Maltese said.
Tai said that homework assignments cannot replace good teaching.
“I believe that this finding is the end result of a chain of unfortunate educational decisions, beginning with the content coverage requirements that push too much information into too little time to learn it in the classroom,” Tai said. “The overflow typically results in more homework assignments. However, students spending more time on something that is not easy to understand or needs to be explained by a teacher does not help these students learn and, in fact, may confuse them.
“The results from this study imply that homework should be purposeful,” he added, “and that the purpose must be understood by both the teacher and the students.”
The authors suggest that factors such as class participation and attendance may mitigate the association of homework to stronger grade performance. They also indicate the types of homework assignments typically given may work better toward standardized test preparation than for retaining knowledge of class material.
Maltese said the genesis for the study was a concern about whether a traditional and ubiquitous educational practice, such as homework, is associated with students achieving at a higher level in math and science. Many media reports about education compare U.S. students unfavorably to high-achieving math and science students from across the world. The 2007 documentary film “Two Million Minutes” compared two Indiana students to students in India and China, taking particular note of how much more time the Indian and Chinese students spent on studying or completing homework.
“We’re not trying to say that all homework is bad,” Maltese said. “It’s expected that students are going to do homework. This is more of an argument that it should be quality over quantity. So in math, rather than doing the same types of problems over and over again, maybe it should involve having students analyze new types of problems or data. In science, maybe the students should write concept summaries instead of just reading a chapter and answering the questions at the end.”
This issue is particularly relevant given that the time spent on homework reported by most students translates into the equivalent of 100 to 180 50-minute class periods of extra learning time each year.
The authors conclude that given current policy initiatives to improve science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, education, more evaluation is needed about how to use homework time more effectively. They suggest more research be done on the form and function of homework assignments.
“In today’s current educational environment, with all the activities taking up children’s time both in school and out of school, the purpose of each homework assignment must be clear and targeted,” Tai said. “With homework, more is not better.”
Media Contact
Rebecca P. Arrington
Office of University Communications
[email protected] (434) 924-7189
Article Information
November 20, 2012
/content/study-homework-doesn-t-mean-better-grades-maybe-better-standardized-test-scores
Trending Today
Spending Too Much Time on Homework Linked to Lower Test Scores
A new study suggests the benefits to homework peak at an hour a day. After that, test scores decline.
Samantha Larson
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/e3/58/e3587081-d161-4c6e-b4f9-a94b3520c60d/homework.jpg)
Polls show that American public high school teachers assign their students an average of 3.5 hours of homework a day . According to a recent study from the University of Oviedo in Spain, that’s far too much.
While doing some homework does indeed lead to higher test performance, the researchers found the benefits to hitting the books peak at about an hour a day. In surveying the homework habits of 7,725 adolescents, this study suggests that for students who average more than 100 minutes a day on homework, test scores start to decline. The relationship between spending time on homework and scoring well on a test is not linear, but curved.
This study builds upon previous research that suggests spending too much time on homework leads to higher stress, health problems and even social alienation. Which, paradoxically, means the most studious of students are in fact engaging in behavior that is counterproductive to doing well in school.
Because the adolescents surveyed in the new study were only tested once, the researchers point out that their results only indicate the correlation between test scores and homework, not necessarily causation. Co-author Javier Suarez-Alvarez thinks the most important findings have less to do with the amount of homework than with how that homework is done.
From Education Week :
Students who did homework more frequently – i.e., every day – tended to do better on the test than those who did it less frequently, the researchers found. And even more important was how much help students received on their homework – those who did it on their own preformed better than those who had parental involvement. (The study controlled for factors such as gender and socioeconomic status.)
“Once individual effort and autonomous working is considered, the time spent [on homework] becomes irrelevant,” Suarez-Alvarez says. After they get their daily hour of homework in, maybe students should just throw the rest of it to the dog.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
Samantha Larson | | READ MORE
Samantha Larson is a freelance writer who particularly likes to cover science, the environment, and adventure. For more of her work, visit SamanthaLarson.com
- Our Mission
Research Trends: Why Homework Should Be Balanced
Research suggests that while homework can be an effective learning tool, assigning too much can lower student performance and interfere with other important activities.

Homework: effective learning tool or waste of time?
Since the average high school student spends almost seven hours each week doing homework, it’s surprising that there’s no clear answer. Homework is generally recognized as an effective way to reinforce what students learn in class, but claims that it may cause more harm than good, especially for younger students, are common.
Here’s what the research says:
- In general, homework has substantial benefits at the high school level, with decreased benefits for middle school students and few benefits for elementary students (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006).
- While assigning homework may have academic benefits, it can also cut into important personal and family time (Cooper et al., 2006).
- Assigning too much homework can result in poor performance (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015).
- A student’s ability to complete homework may depend on factors that are outside their control (Cooper et al., 2006; OECD, 2014; Eren & Henderson, 2011).
- The goal shouldn’t be to eliminate homework, but to make it authentic, meaningful, and engaging (Darling-Hammond & Ifill-Lynch, 2006).
Why Homework Should Be Balanced
Homework can boost learning, but doing too much can be detrimental. The National PTA and National Education Association support the “10-minute homework rule,” which recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night (10 minutes for first grade, 20 minutes for second grade, and so on, up to two hours for 12th grade) (Cooper, 2010). A recent study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90–100 minutes of homework per day, their math and science scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015). Giving students too much homework can lead to fatigue, stress, and a loss of interest in academics—something that we all want to avoid.
Homework Pros and Cons
Homework has many benefits, ranging from higher academic performance to improved study skills and stronger school-parent connections. However, it can also result in a loss of interest in academics, fatigue, and a loss of important personal and family time.
Grade Level Makes a Difference
Although the debate about homework generally falls in the “it works” vs. “it doesn’t work” camps, research shows that grade level makes a difference. High school students generally get the biggest benefits from homework, with middle school students getting about half the benefits, and elementary school students getting few benefits (Cooper et al., 2006). Since young students are still developing study habits like concentration and self-regulation, assigning a lot of homework isn’t all that helpful.
Parents Should Be Supportive, Not Intrusive
Well-designed homework not only strengthens student learning, it also provides ways to create connections between a student’s family and school. Homework offers parents insight into what their children are learning, provides opportunities to talk with children about their learning, and helps create conversations with school communities about ways to support student learning (Walker et al., 2004).
However, parent involvement can also hurt student learning. Patall, Cooper, and Robinson (2008) found that students did worse when their parents were perceived as intrusive or controlling. Motivation plays a key role in learning, and parents can cause unintentional harm by not giving their children enough space and autonomy to do their homework.
Homework Across the Globe
OECD , the developers of the international PISA test, published a 2014 report looking at homework around the world. They found that 15-year-olds worldwide spend an average of five hours per week doing homework (the U.S. average is about six hours). Surprisingly, countries like Finland and Singapore spend less time on homework (two to three hours per week) but still have high PISA rankings. These countries, the report explains, have support systems in place that allow students to rely less on homework to succeed. If a country like the U.S. were to decrease the amount of homework assigned to high school students, test scores would likely decrease unless additional supports were added.
Homework Is About Quality, Not Quantity
Whether you’re pro- or anti-homework, keep in mind that research gives a big-picture idea of what works and what doesn’t, and a capable teacher can make almost anything work. The question isn’t homework vs. no homework ; instead, we should be asking ourselves, “How can we transform homework so that it’s engaging and relevant and supports learning?”
Cooper, H. (1989). Synthesis of research on homework . Educational leadership, 47 (3), 85-91.
Cooper, H. (2010). Homework’s Diminishing Returns . The New York Times .
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003 . Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1-62.
Darling-Hammond, L., & Ifill-Lynch, O. (2006). If They'd Only Do Their Work! Educational Leadership, 63 (5), 8-13.
Eren, O., & Henderson, D. J. (2011). Are we wasting our children's time by giving them more homework? Economics of Education Review, 30 (5), 950-961.
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2015, March 16). Adolescents’ Homework Performance in Mathematics and Science: Personal Factors and Teaching Practices . Journal of Educational Psychology. Advance online publication.
OECD (2014). Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? PISA in Focus , No. 46, OECD Publishing, Paris.
Patall, E. A., Cooper, H., & Robinson, J. C. (2008). Parent involvement in homework: A research synthesis . Review of Educational Research, 78 (4), 1039-1101.
Van Voorhis, F. L. (2003). Interactive homework in middle school: Effects on family involvement and science achievement . The Journal of Educational Research, 96 (6), 323-338.
Walker, J. M., Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., Whetsel, D. R., & Green, C. L. (2004). Parental involvement in homework: A review of current research and its implications for teachers, after school program staff, and parent leaders . Cambridge, MA: Harvard Family Research Project.
- Your Stories
Evidence Based Living
Bridging the gap between research and real life
- In The Media
- The Learning Center
- Cornell Cooperative Extension
- Youth Development
- Health and Wellness
What we know about homework
I went looking for evidence and found lots of it: there are at least a half dozen systematic reviews about the importance and effectiveness of homework, and all of its nuances. The Center for Public Education and the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development both provide comprehensive essays that summarize the evidence on homework.
One 2007 analysis published by Duke University researchers in particular caught my attention . It included 50 separate studies on homework research that asked the specific question, “Does homework improve academic achievement?” This study followed an earlier meta-analysis of approximately 100 studies published by the same researchers in 1989. Both reviews conclude that homework does help to improve academic achievement, primarily in the middle and high school. For children in elementary school, the review concludes that while homework can help children develop good study habits, it does not help to improve students’ grades or standardized test scores.
Here are some other interesting take-home messages about homework:
- Students are more likely to complete and learn from homework assignments that have a purpose, for example, reviewing important concepts, improving students’ independence or providing opportunities to explore topics students are interested in.
- Homework assignments are most successful when they are easy enough for students to complete independently, but challenging enough to be interesting.
- Finding appropriate ways to involve parents with their children’s homework leads to improved academic performance.
- Homework provides more academic benefits for older students. For younger students, some homework can help them to establish study habits and routines, but too much homework detracts from family and play activities after school.
- There is strong evidence that homework improves learning for students with learning disabilities, most likely because these students benefit from additional time to practice new skills.
On a personal note, the evidence makes me wonder if my son receives a little too much homework for his age. In first grade, he receives a reading and a math assignment every day, and he often groans about completing them. I certainly plan to discuss the evidence about homework with his teacher at our first conference.
Homework word looks very easy, but for students they know more about it means. From a tutor point of view, Here are some other interesting take-home messages about homework like If a student will take homework help from experts, they will feel free to complete their own homework before deadline. They can feel stress free and can study well. Thanks
Speak Your Mind Cancel reply
A project at…, evidence-based blogs.
- Bandolier Evidence-Based Health Care
- British Psychological Society Research Digest
- Economics in Cooperative Extension
- EPB Exchange
- New Voices for Research
- Research Blogging
- Trust the Evidence
Subscribe by e-mail
Please, insert a valid email.
Thank you, your email will be added to the mailing list once you click on the link in the confirmation email.
Spam protection has stopped this request. Please contact site owner for help.
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Magazine Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
clock This article was published more than 11 years ago
Study: Homework linked to better standardized test scores

Researchers who looked at data from more than 18,000 10th-graders found there was little correlation between the time students spent doing homework and better grades in math and science courses. But, according to a study on the researc h, they did find a positive relationship between standardized test performance and the amount of time spent on homework.
The study , called ”When Is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association Between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” was conducted by Adam Maltese, assistant professor of science education at the Indiana University School of Education; Robert H. Tai, associate professor of science education at the Curry School of Education at the University of Virginia, and Xitao Fan, dean of education at the University of Macau.
According to a news release by Indiana University, the researchers looked at survey and transcript data from the students in an effort to explain their academic performance and concluded that despite earlier research to the contrary, homework time did not correlate to the final course grade that students received in math and science classes.
The value of homework has been the subject of various research studies over the years, yet there is still no conclusive evidence that it makes a big difference in helping students improve achievement. The most often-cited studies are those that conclude that there is virtually no evidence that it helps in elementary school but some evidence that it does improve academic performance in later grades. Yet this newest study looked at 10th graders and found no correlation.
The study did, however, find a positive association between time spent on homework and student scores on standardized tests. It doesn’t directly conclude that the homework actually affected the test scores, but the university release quotes Maltese as saying that “if students are spending more time on homework, they’re getting exposed to the types of questions and the procedures for answering questions that are not so different from standardized tests.”
That, of course, would depend on the kind of homework students receive. Maltese is further quoted as saying, “”We’re not trying to say that all homework is bad. It’s expected that students are going to do homework. This is more of an argument that it should be quality over quantity. So in math, rather than doing the same types of problems over and over again, maybe it should involve having students analyze new types of problems or data. In science, maybe the students should write concept summaries instead of just reading a chapter and answering the questions at the end.”
The co-authors also recommend that education policymakers better evaluate homework — the kinds of assignments that are most useful and the time required to make the work effective.
You may also be interested in this : 3 Healthy Guidelines for Homework

Is Homework Valuable or Not? Try Looking at Quality Instead

- Share article
Is there an end in sight to the “homework wars?”
Homework is one those never-ending debates in K-12 circles that re-emerges every few years, bringing with it a new collection of headlines. Usually they bemoan how much homework students have, or highlight districts and even states that have sought to cap or eliminate homework .
Now, a new analysis from the Center for American Progress suggests a more fruitful way of thinking about this problem. Maybe, it suggests, what we should be doing is looking at what students are routinely being asked to do in take-home assignments, how well that homework supports their learning goals (or doesn’t), and make changes from there.
The analysis of nearly 200 pieces of homework concludes that much of what students are asked to do aligns to the Common Core State Standards—a testament to how pervasive the standards are in the U.S. education system, even though many states have tweaked, renamed, or replaced them. However, most of the homework embodied basic, procedural components of the standards, rather than the more difficult skills—such as analyzing or extending their knowledge to new problems.
“We were surprised by the degree of alignment. And we were also surprised by the degree that the homework was rote, and how much some of this stuff felt like Sudoku,” said Ulrich Boser, a senior fellow at CAP. “It made the homework debate make a lot more sense about why parents are frustrated.”
It is also similar to the findings of groups like the Education Trust, which have found that classwork tends to be aligned to state standards, but not all that rigorous.
Collecting Homework Samples
The CAP analysis appears to be one of the first studies to look at homework rigor using a national survey lens. Many studies of homework are based on one school or one district’s assignments, which obviously limits their applicability. Attempts to synthesize all this research have led to some hard-to-parse conclusions. One of the most cited studies concludes there’s some connection for grades 6-12 between homework and test scores, but less so for elementary students, and less of an impact on actual grades.
Another problem is that students’ experiences with homework seem to vary so dramatically: A Brookings Institution report based on survey data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress concluded that, while on average students aren’t overburdened by homework, a subset of students do appear to get hours upon hours.
The CAP analysis, instead, was based on getting a sample of parents from across the country to send in examples of their children’s homework. The researchers used MTurk, a crowdsourcing service offered by Amazon.com to recruit parents. Of the 372 parents who responded, the researchers got a pile of 187 useable assignments. Next, John Smithson, an emeritus researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, had teams grade them on a taxonomy looking at both the content and the “cognitive demand,” or difficulty, of the work. The index fell on a 1 to 10 scale, with a score 4 to 6 range considered as “good” alignment.
The results? On average, math assignments fell within this range, while the ELA ones were slightly weaker, in the 3 to 5 range.
But the real eye-opening graphic is this one, which shows that by far the assignments were mostly low-level.

This makes some logical sense when you think about it. Just as with teaching and testing, it is much easier to write homework assignments prioritizing basic arithmetic drills and fill-in-the-blank vocabulary words than ones that get students to “prove” or “generalize” some tenet. (I suspect prepackaged curricula, too, probably lean more toward rote stuff than cognitively demanding exercises.)
Here’s another explanation: Many teachers believe homework should be for practicing known content, not learning something new. This is partially to help close the “homework gap” that surfaces because some students can access parent help or help via technology, while other students can’t. It’s possible that teachers are purposefully giving lower-level work to their students to take home for this reason.
To be sure, Boser said, it’s not that all lower-level work is intrinsically bad: Memorization does have a place in learning. But assignments like color-in-the-blank and word searches are probably just a waste of students’ time. “Homework assignments,” the study says, “should be thought-provoking.”
Study Limitations
The study does come with some significant limitations, so you must use caution in discussing its results. The surveyed population differs from the population at large, overrepresenting mothers over fathers and parents of K-5 students, and underrepresenting black parents. Also, the majority of the assignments the parents sent in came from the elementary grades.
The report makes suggestions on how districts can strategically improve the quality of their homework, rather than deciding to chuck it out altogether.
One is to is to audit homework assignments to make sure they’re actually useful at building some of the more difficult skills. Another is to extend the “curriculum revolution” of the last decade, which has focused more attention on the quality and alignment of textbooks and materials, to homework. A third is to use appropriate technology so students can access out-of-school supports for challenging homework.
A version of this news article first appeared in the Curriculum Matters blog.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Coco Gauff Is Playing for Herself Now
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
Does Studying Student Data Really Raise Test Scores?
- Posted February 20, 2020
- By Heather C. Hill

This article was originally published by Education Week .
Question: What activity is done by most teachers in the United States, but has almost no evidence of effectiveness in raising student test scores?
Answer: Analyzing student assessment data.
This practice arose from a simple logic: To improve student outcomes, teachers should study students’ prior test performance, learn what students struggle with, and then adjust the curriculum or offer students remediation where necessary. By addressing the weaknesses revealed by the test results, overall student achievement would improve.
Yet understanding students’ weaknesses is only useful if it changes practice. And, to date, evidence suggests that it does not change practice — or student outcomes. Focusing on the problem has likely distracted us from focusing on the solution.
With the birth of large-scale state assessments and widening data availability in the 1990s, school leaders and teachers could access information on student performance that was common across schools and classrooms. Many schools also instituted standardized “interim” assessments, claiming that this periodic, low-stakes testing could help teachers identify difficult content and struggling students before the state assessment, giving both teachers and students a chance to catch up. Over time, educational testing and data companies including the Achievement Network, NWEA, and McGraw-Hill’s Acuity began to sell interim assessments to schools and states, making such assessments (and their cousins, test-item banks that support formative assessment) a billion-dollar business.
Currently, a large number of teachers report they regularly get together to analyze student assessment results. In a 2016 survey by Harvard’s Center for Education Policy Research, 94 percent of a nationally representative sample of middle school math teachers reported that they analyzed student performance on tests in the prior year, and 15 percent said they spent over 40 hours that year engaged in this activity. Case-study research suggests that in many Title 1 schools, this activity is a cornerstone of teachers’ weekly or monthly collaborative time.
Understanding students’ weaknesses is only useful if it changes practice. And, to date, evidence suggests that it does not change practice — or student outcomes. Focusing on the problem has likely distracted us from focusing on the solution.
But here’s the rub: Rigorous empirical research doesn’t support this practice. In the past two decades, researchers have tested 10 different data-study programs in hundreds of schools for impacts on student outcomes in math, English/language arts, and sometimes science. Of 23 student outcomes examined by these studies, only three were statistically significant. Of these three, two were positive, and one negative. In the other 20 cases, analyses suggest no beneficial impacts on students. Thus, on average, the practice seems not to improve student performance.
One critical question, of course, is, why?
Observational studies suggest that teachers do, in fact, use interim assessments to pick out content that they need to return to. For instance, in a study published in 2009, Margaret E. Goertz and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania observed teachers planning to revisit math topics using a combination of whole-group and small-group instruction.
But Goertz and colleagues also observed that rather than dig into student misunderstandings, teachers often proposed non-mathematical reasons for students’ failure, then moved on. In other words, the teachers mostly didn’t seem to use student test-score data to deepen their understanding of how students learn, to think about what drives student misconceptions, or to modify instructional techniques.
My own recent experiences visiting schools imply this trend continues. Field notes from teacher data-team meetings suggest a heavy focus on “watch list” students — those predicted to barely pass or to fail the annual state reading assessment. Teachers reported on each student, celebrating learning gains or giving reasons for poor performance — a bad week at home, students’ failure to study, or poor test-taking skills. Occasionally, other teachers chimed in with advice about how to help a student over a reading trouble spot — for instance, helping students develop reading fluency by breaking down words or sorting words by long or short vowel sounds. But this focus on instruction proved fleeting, more about suggesting short-term tasks or activities than improving instruction as a whole.
The fact remains that having teachers themselves examine test-score data has yet to be proven productive, even after many trials of such programs.
Common goals for improving reading instruction, such as how to ask more complex questions or encourage students to use more evidence in their explanations, did not surface in these meetings. Rather, teachers focused on students’ progress or lack of it. That could result in extra attention for a watch-list student, to the individual student’s benefit, but it was unlikely to improve instruction or boost learning for the class as a whole.
In reviewing the research on teachers analyzing student data, I came across a small number of programs that included interim assessment as one part of a larger instructional package. While I excluded these studies from the formal review I undertook for this essay, they are notable nonetheless. One, by Janke M. Faber and colleagues in the Netherlands, focused on a program that not only contained computer-based interim assessments but also provided both instructionally focused feedback to teachers and students and personalized online student assignments. Another study, led by Jonathan A. Supovitz and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania, examined the Ongoing Assessment Project, a program that helps teachers create assessments and examine the results, then combines this practice with professional development focused on mathematics content and student thinking about that content. Both of these studies saw positive impacts, suggesting that the analysis of data can, when combined with strong supports for improved teaching, shift student outcomes. But the small number of programs that combine the study of data with wider instructional supports limits our ability to draw real conclusions.
In total, the research in this area suggests that district and school leaders should rethink their use of state and interim assessments as the focus of teacher collaboration. Administrators may still benefit from analyzing student assessment results to know where to strengthen the curriculum or to provide teacher professional learning. But the fact remains that having teachers themselves examine test-score data has yet to be proven productive, even after many trials of such programs.
For many schools, this news is disheartening. Retooling teacher collaborative time will be a major shift — and that’s assuming that schools can first identify more effective ways to help teachers improve their instruction. In our next column, we’ll cover possible replacement activities.
This essay is the second in an Education Week opinion series called Weighing the Research: What Works, What Doesn't , created by HGSE Professor of Education Heather C. Hill and Susanna Loeb , director of Brown University's Annenberg Institute for School Reform. The series aims to put the pieces of research together so that education decision-makers can evaluate which policies and practices to implement.

Usable Knowledge
Connecting education research to practice — with timely insights for educators, families, and communities
Related Articles

Strategies for Leveling the Educational Playing Field
New research on SAT/ACT test scores reveals stark inequalities in academic achievement based on wealth

How to Help Kids Become Skilled Citizens
Active citizenship requires a broad set of skills, new study finds

Extra Credit

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington
School of Education
School of education study: homework doesn’t improve course grades but could boost standardized test scores.
Thursday, November 15, 2012

School of Education resources and social media channels
- SOE Intranet
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Campbell Syst Rev
- v.17(4); 2021 Dec

PROTOCOL: The relationship between homework time and academic performance among K‐12 students: A systematic review
1 Evidence‐Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, and Evidence‐based Social Sciences Research Center, School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou China
Xiaoling Hu
2 School of Higher Education, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou China
Chunyan Liu
3 Evidence‐based Social Sciences Research Center, School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou China

Howard White
4 Campbell Collaboration, New Delhi India
Associated Data
This review will synthesize the results from publications focused on homework time and academic performance, and estimate the relationship between the two. Our objectives are: (1) To identify the extent of the relationship between homework time and students' academic performance; (2) To analyze the differences in the effectiveness of homework time across genders, grades, subject and regions; and (3) To identify the potential factors that affect homework time, such as academic subject, task difficulty, type of homework, mode of homework, parental involvement, and feedback on homework.
1. BACKGROUND
1.1. description of the condition.
Homework is defined as “any task assigned by schoolteachers intended for students to carry out during non‐school hours” (Cooper, 1989 ). This definition explicitly excludes (a) in‐school guided study; (b) home study courses delivered through the mail, television, audio or videocassette, or the internet; and (c) extracurricular activities such as sports and participation in clubs (Cooper et al., 2006 ). With the development of technology, web‐based homework has become more popular among teachers, with online platforms such as Blackboard, WebCT ( www.webct.com ), Homework Service ( https://hw.utexas.edu/bur/overview.html ), WebWorK, Study Island, and PowerSchool (Mendicino et al., 2009 ), as these allow students to do their homework online, and teachers to give feedback to students immediately (Callahan, 2016 ; Lucas, 2012 ; Mendicino et al., 2009 ). Therefore, in this systematic review, homework also includes online tasks performed outside the school.
The purpose of homework can be divided into instructional and noninstructional objectives (Lee & Pruitt, 1979 ). The most common instructional purpose of homework includes review, preview, and extension (Becker & Epstein, 1982 ; Lee & Pruitt, 1979 ; Mulhenbruck et al., 1999 ). The review assignments mainly offer the students an opportunity to practise newly acquired skills or review material learnt in class. The preview assignments introduce new skills or materials to help students prepare for unfamiliar knowledge before the class (Mulhenbruck et al., 1999 ), and the extension assignments involve the transfer of previously learned skills to new situations (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Lee & Pruitt, 1979 ). The noninstructional purpose of homework varies. It can be used to form better study habits, increase the students' sense of responsibility, enhance awareness of independent learning, and build communication between parents, children, and teachers (Becker & Epstein, 1982 ; González et al., 2001 ; Lee & Pruitt, 1979 ; Mulhenbruck et al., 1999 ; Van Voorhis, 2003 ). Homework can also be used to punish students (Epstein & Van Voorhis, 2001 ).
Homework is a common and widespread educational activity for many students across the world. As an achievement of the educational excellence movement, the level of homework was generalized, which was supported by the parents at the beginning. However, as homework increased more and more, parents and scholars realized the burden of homework on students. They complained that the students lost their childhood and called for less homework (Gill & Schlossman, 2003 ). Similarly, in the United Kingdom homework became common in the mid‐19th century, and was a matter of much debate in the 1880s as levels of homework increased in response to the introduction of payment by results for teachers and other factors (Hallam, 2004 ).
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) found that students feel the most pressured by the amount of homework (WHO, 2016 ). Meanwhile, parents continued to complain about excessive homework assigned to their children (Gill & Schlossman, 2003 , 2004 ; Jerrima et al., 2019 ; Xue & Zhang, 2019 ).
Homework is often argued to improve academic performance. However, the relationship between homework and academic performance has been debated for more than one hundred years (Cheema & Sheridan, 2015 ; Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Kitsantas et al., 2011 ; Kralovec & Buell, 2000 ; Trautwein, 2007 ). Although several meta‐analyses of the relationship between homework and performance have found a positive correlation between homework time and academic performance (Baş et al., 2017 ; Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Fan et al., 2017 ), it is difficult to establish causality. More academically inclined students, who get better grades regardless, may complete their homework more conscientiously. Conversely, students who are doing badly may study harder at home to catch up.
Still, it may also be the case that the effect is not linear. Some evidence has shown that academic performance increases with the increase in homework time, but begins to decline when homework time exceeds the optimal amount of time (Ackerman et al., 2011 ; Krzysztof et al., 2018 ; Reteig et al., 2019 ). Based on data from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) survey of 58,000 high school students in grades one and two, Keith ( 1982 ) found that for anyone with any level of ability, increasing the amount of homework will improve their performance. Homework plays a compensatory role; however, the amount of homework cannot be increased indefinitely, only moderately. If it exceeds a certain limit, it will lead to a decline in performance (Keith, 1982 ).
1.2. Description of the intervention
The intervention is the homework assigned by schoolteachers for nonschool hours, and completed independently by students without additional teaching, such as online tasks and activities in study club. The comparison condition is different time spent on the homework, and we plan to divide the comparisons into several groups, such as 0–15, 16–30, 31–45, 46–60, 61–90, 90–120 min, and more than 120 min. Any type of homework will be included, such as written, oral, or practical homework. We excluded homework allocated by other people such as parents or teachers from extracurricular schools, and in‐school guided study, home study courses, and extracurricular activities such as sports and participation in clubs were excluded. Homework related to psychotherapy was also outside our definition of homework.
1.3. Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework for this review is the theory of change that describes how homework may affect academic performance. Figure 1 below demonstrates the conceptual framework through which the interventions are hypothesized to lead to the intended outcomes.

Conceptual framework for intervention and outcomes of homework
As in Figure 1 , the law of readiness reveals that before commencing a certain learning activity, if the learners do well in the preparatory stages (including physiological and psychological) related to the corresponding learning activities, they can grasp the learning content more rapidly (Muhammad, 2015 ). Second, the law of exercise suggests that for a certain kind of connection formed by learners, the correct repetition of this action in practice will effectively enhance this connection. And, third, the law of effect indicates that all kinds of positive or negative feedback that learners get in the process of learning will strengthen or weaken the connection that learners have formed in their mind.
However, there are limits to our ability to stay focused, and when students spend too much time on homework, their cognitive load and mental fatigue increase, and they will feel tired and even lead to mental distress, such as anxiety, which may reduce rather than improve readiness.
Furthermore, if the purpose of homework is to achieve mastery or covering additional material, then when the content of homework has been fully understood by a student, doing more homework won't help. That is there are diminishing returns to the time spent on homework, which can reach zero.
Finally, if the students miss sleep because of long homework hours, they may be tired in school and so do worse in class or tests. Hence readiness is reduced, and the law of effect undermined as the student is not in a good condition to receive feedback or perform well.
In addition, a student's development should be multifaceted, while if they spent too much time on homework, they will lose time to take part in other activities which can contribute to their overall development.
1.4. Why it is important to do this review
Several systematic reviews have explored the effectiveness of homework in improving students' performance, but all the conclusions were based on the assumption of a linear correlation between homework time and performance, and none of them considered the impact of homework time on students' autonomous motivation. A summary of the evidence by Hallam ( 2004 ) makes no recommendation on the time spent on the homework. The UK Education Endowment Foundation's toolkit entry for homework for secondary school students notes quality is more important than quantity but gives no explicit recommendation on the amount of time that should be spent on homework.
Existing reviews leave the important practical question of homework time unanswered.
In 1989, Cooper conducted a review related to the relationship between homework and performance. The results showed that the average correlation for students in primary school, middle school, and high school between the amount of homework and performance was nearly r = 0; for students in middle school, it was r = .07; and for high school students, it was r = .25 (Cooper, 1989 ). In 2006, Cooper et al. ( 2006 ) conducted another systematic review to explore the effectiveness of homework to improve academic performance. The results showed that the correlation between homework time and performance for high school students was still 0.25, but for middle school students, it was nearly 0. However, they did not look explicitly at homework time.
All the above studies assumed that the correlation between homework and performance was linear, that is, that either more or less homework was better. Indeed, their reported effect size is the correlation coefficient, which is a measure of the linearity of a relationship. While homework can be a dull task that requires full mental effort, and there are limits to our ability to stay focused. Therefore, it is important for teachers, school managers, parents, and children themselves to establish the optimum duration of homework to improve its effectiveness.
1.5. The contribution of this review
Regardless of its aims of preparation, practice, extension or application, homework can be an effective means to improve student's academic achievement. Previous reviews indeed testify to the effectiveness of homework in relation to academic performance. More is not always better, and is restricted by students' ability to maintain their attention for a long time. The present systematic review plans to divide the participants into several groups according to the amount of time spent on homework, such as 0–15, 16–30, 31–45, 46–60, 61–90, 90–120 min, and more than 120 min to compare the test scores of different groups to identify the extent of the relationship between homework time and students' academic performance. We aim to investigate the role of homework in academic achievement, and to determine the optimum homework time by comparing the differences in outcomes between different groupings of homework time. This will be helpful for teachers and parents to better understand the role and utility of homework, and provide theoretical support for teachers to arrange homework.
2. OBJECTIVES
This review will synthesize the results from publications focused on homework time and academic performance, and estimate the relationship between the two. Our objectives are:
- 1. To identify the extent of the relationship between homework time and students' academic performance;
- 2. To analyze the differences in the effectiveness of homework time across genders, grades, subject and regions; and
- 3. To identify the potential factors that affect homework time, such as academic subject, task difficulty, type of homework, mode of homework, parental involvement, and feedback on homework.
3.1. Criteria for considering studies for this review
3.1.1. types of studies.
We will include treatment‐control group design or a comparison group design studies, to adequately address the effect of differing homework time on the academic performance of K‐12 students.
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that aim to explore the effect of homework time on academic performance by comparing the test score differences between different groups before and after the intervention will be included. In addition, non‐RCTs such as cohort studies (NRCTs), controlled before and after studies, and interrupted time series studies also will be included if they explicitly take homework as intervention, and report the time spent on homework and the mean and standard deviation of academic achievement.
Relevant correlational studies without mean and standard deviation of academic achievement will be excluded. Other study designs such as case studies, narrative reviews, and nonprimary studies such as editorials, book reviews, commentaries, and letters to the editor, will also be excluded. Qualitative evidence is also beyond the inclusion criteria in the present systematic review.
3.1.2. Types of participants
This review will include studies of K‐12 school students. We excluded children with disabilities, since the context and effects may be different for that population group. Students from special education schools are excluded. If the primary study includes mixed samples (e.g., special education and nonspecial education students), we will use the sub sample excluding special needs students if reported.
3.1.3. Types of interventions
In this review, we will explore the relationship between homework time and academic performance by comparing the academic scores with different amounts of time spent on homework. The eligible intervention studies must be clear that the intervention is homework assigned to students to complete during nonschool hours regularly by schoolteachers which aims to improve academic achievement. This does not mean that the intervention must consist of academic activities, but rather that the explicit expectation must be that the homework, regardless of the nature of the homework content, will result in improved academic performance. Furthermore, we will only include school‐based interventions, that is, homework allocated by other people such as parents or teachers from extracurricular schools, study clubs, and extracurricular activities such as sports and participation in clubs are excluded. Homework related to psychotherapy will also be excluded.
The comparison condition is different time spend on the homework, and we plan to divide the comparisons into several groups, such as 0–15, 16–30, 31–45, 46–60, 61–90, 90–120 min, and more than 120 min.
3.1.4. Types of outcome measures
The objective of the review is to explore the impact of homework on students' academic outcomes. We will extract the homework time and academic performance provided in the primary study. The homework time is the exact time or a time frame reported by students or parents. Academic performance will be measured by the teacher, exam results and/or by the research team using any valid standardized test and reported as test scores.
As valid standardized tests, we will consider norm‐referenced tests (e.g., Gates‐MacGinitie Reading Tests and Star Math), state‐wide tests (e.g., Iowa Test of Basic Skills), national tests (e.g., National Assessment of Educational Progress). If it is not clear from the description of outcome measures in the studies, we will use electronic sources to determine whether a test is standardized or not.
3.1.5. Primary outcomes
The primary outcome is academic performance (test score and standard deviation), and studies that have measured academic performance (and homework time) will be included.
3.1.6. Secondary outcomes
Academic motivation and quality of homework will be included as secondary outcomes.
3.2. Search methods for identification of studies
3.2.1. electronic searches.
The following databases will be searched from inception to present:
- Social Sciences Citation Index (Web of Science)
- ScienceDirect ( https://www.sciencedirect.com/ )
- Taylor & Francis Online Database ( https://www.tandfonline.com/ )
- The Campbell Library ( https://www.campbellcollaboration.org/better-evidence.html )
- ERCI (EBSCOhost)
- EBSCO ( http://search.ebscohost.com/ )
- JSTOR ( https://www.jstor.org/ )
- PsychArticles (ProQuest)
- PsychInfo (EBSCOhost)
- ProQuest Dissertations ( https://www.proquest.com/index )
- OCLC FirstSearch ( https://firstsearch.oclc.org/ )
Below, the search strategy for Web of Science is provided:
#1 TI = homework OR AB = homework
#2 TI = home‐work OR AB = home‐work
#3 #1 OR #2
#4 TS = K‐12 OR TS = preschool student* OR TS = pre‐school student* OR TS = Kindergarten
student* OR TS = middle school student* OR TS = high school student* OR TS = senior school
student* OR TS = primary school student* OR TS = pupil OR TS = schoolchild OR TS = junior
high school student* OR TS = school‐age
#5 TS = achievement OR TS = performance OR TS = grade OR TS = score OR TS = academic
achievement* OR TS = GPA OR TS = academic performance
#6 #3 AND #4 AND #5
3.2.2. Searching other resources
We will consult the following sources of gray literature, and search the websites of organizations devoted to the education research, to identify relevant unpublished studies and reports. The following gray literature resources will be searched with the keyword “homework”:
- What Works Clearinghouse ( https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/ )
- Education Endowment Foundation ( https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/ )
- European Educational Research Association ( http://www.eera-ecer.de/ )
- American Educational Research Association ( http://www.aera.net/ )
- Best Evidence Encyclopedia ( http://www.bestevidence.org/ )
- Open Grey ( http://www.opengrey.eu/ )
We will also search the Google Scholar with the keyword “homework,” and we will stop scan if there are 5 consecutive pages with no relevant studies.
The following international journals will be hand searched for relevant studies with the keyword “homework”:
- American Educational Research Journal
- Educational Psychologist
- Learning and Instruction
- Journal of Educational Research
- Journal of Educational Psychology
- Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness
- Journal of Experimental Education.
Additionally, the primary studies included in the previous systematic reviews on the relationship between homework and academic performance will be scanned, and the reference lists will also be searched. Furthermore, the studies of experts in the research of homework (such as Cooper Harris, Trautwein Ulric, and Xu jianzhong) will be searched systematically to check our search strategy, and they will be contacted to help identify other relevant studies if possible.
3.3. Data collection and analysis
3.3.1. selection of studies.
The selection of studies will be performed independently by the first two reviewers (Guo LP and Jieyun Li) in Rayyan ( https://rayyan.qcri.org/ ). All titles and abstracts of the records identified after retrieval will be screened, the potentially relevant references will be located with full‐text, and the primary studies that meet our criteria will be included for further analysis. Studies that meet the selection criteria and have the outcomes of interest measured, but do not report these outcome data, will be included and described in the results section of the review. Any discrepancies between the two reviewers will be resolved by consensus with another reviewer involved (Kehu Yang). The whole process of study screening will be based on the PRISMA guidelines (Moher et al., 2009 ).
3.3.2. Data extraction and management
Information extraction and coding will consist of two parts. The first is general information, including the information of primary study (publication, the year of publication, and the year of data collection), sample characteristics (e.g., sample size, gender, grade level, region, family economic status, parental education level), methodological characteristics (e.g., sampling method, measures of homework time, and the measure of academic performance), and the intervention characteristics (e.g., subject, mode of homework and the type of homework). The other is the effect size, including the homework time and the test score (The details are shown in Supporting Information Annex 1 ). This process will be conducted independently by two authors (Zheng Xu and Xing Xin), and disagreements between coders will be resolved by discussions with another author (Xiuxia Li).
- If a study contains multiple interventions (e.g., different homework modalities such as online vs. book‐based), the reviewers will only extract data that are eligible for this review.
- For academic performance, means, standard deviations (or information to estimate standard deviations), and the number of participants in each group will be extracted. If more than one measure is reported, we will extract all of them and analyze the measurement method as a moderator.
- For the homework time, we will extract the homework time interval reported in the primary studies and code the data as presented, either categorical or continuous. We will then create a continuous variable measure data set (using the mid‐point for data reported in categorical form) and at least two categorical data sets. The multiple categorical data sets will be used to test for sensitivity to the chosen thresholds, and then calculate the mean and standard deviations in each group. If the weekly homework time is reported instead of the daily homework time, we divide the total homework time by 5, and if the homework time is in hours, we convert it to minutes.
In case of controlled before and after studies, mean or median change from baseline scores will be extracted or computed by the reviewers if all necessary data are available. If change scores are not available or cannot be computed, post‐intervention values will be extracted by the reviewers.
3.3.3. Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
For RCTs, the Cochrane bias risk tool will be used to assess the quality of the method and potential defects (Higgins & Green, 2011 ). For nonrandomized studies (including cohort studies, controlled before and after studies, and interrupted time series studies), the risk of bias in nonrandomized studies of interventions (ROBINS‐I) will be used to check the quality of the individual study (Sterne et al., 2016 ). In addition, the grade will be used to rate the overall quality of the evidence included in this review, ranging from high, moderate, low, and very low, based on the assessment to study design, imprecision, inconsistency, indirectness, and publication bias (Atkins et al., 2004 ; Schünemann et al., 2013 ). The risk of bias assessment will be conducted by the two authors (Zheng Xu and Xing Xin), and any disaccord will be solved by discussion with another author (Xiuxia Li).
3.3.4. Dealing with missing data
If there are any missing data, we will contact the author at least twice to obtain more information if the correspondence address is available. If these data are unavailable, we will only analyze the available data, and the studies with missing data will be described in the Results section. Besides, the potential impact of missing data on comprehensive estimates will be considered in the Discussion section.
3.3.5. Assessment of heterogeneity
Forest plots will be inspected to visually investigate overlaps in the confidence intervals (CIs) of the results of the individual studies. The χ 2 test will be performed, and the Q statistics, I 2 and τ 2 index will be adopted to evaluate heterogeneity across studies. For Q statistics, a p value of .05 will be used as a threshold for statistical significance. The I 2 index refers to the truly observed variation ratio (Borenstein et al., 2009 ), and 25%, 50%, and 75% of the I 2 indicate low, medium, and high heterogeneity (Higgins & Thompson, 2002 ). And the parameter τ 2 is the between‐studies variance (the variance of the effect size parameters across the population of studies), that is, the variance of true effect sizes (across an infinite number of studies).
3.3.6. Assessment of reporting biases
Reporting bias, also called publication bias, refers to the potential of the studies with statistically significant findings to be accepted for publication, whilst those with statistically nonsignificant findings would hardly be accepted for publication. These studies would have a higher probability of being left in the “file drawer,” according to the so‐called “file drawer problem.” If 10 or more studies were identified, visual funnel plots and Egger's test of funnel plot symmetry were performed to evaluate potential publication bias (Rosenthal, 1979 ). If there is evidence of funnel plot asymmetry from a test, we will attempt to conduct the comparisons between the effect with that after trim and fill. The possible reasons for this (e.g., nonreporting biases, poor methodological quality leading to spuriously inflated effects in smaller studies, true heterogeneity, artefactual, and chance) will also be considered (Page et al., 2019 ).
3.3.7. Data synthesis
We will include all intervention studies that meet our inclusion criteria and extract the mean (M) and SD of test scores. We will take the standard mean difference (SMD) and CI as our effect size index. For subgroups, we plan to divide the outcomes into several groups by time spent on the homework, such as 0–15, 16–30, 31–45, 46–60, 61–90, 90–120 min, and more than 120 min, and then compare the difference of SMD between groups to explore the role of homework time on academic achievement.
If two or more studies are identified that have investigated the effect of homework time on academic performance with sufficiently available data, a random‐effects meta‐analysis will be performed to estimate the comprehensive effect due to the expected heterogeneity between groups using the Review Manager 5 software. The pooled estimates will be presented in forest plots. If quantitative synthesis is not suitable, narrative synthesis will be adopted.
3.3.8. Planned moderators
If statistically significant heterogeneity is detected, subgroup analyses with stratification analysis will be conducted to explore the source of heterogeneity based on the available data.
- Gender. Previous studies showed that girls more frequently reported managing their homework than boys (Mau & Lynn, 2000 ; Xu, 2007 ), and zero‐time homework students are most often male (Hagborg, 1991 ). Therefore, it is worth identifying the influence of gender on homework time and academic performance.
- Grade level. Existing reviews on homework suggest that the relationship between homework and performance is mediated by grade level (Baş et al., 2017 ; Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Fan et al., 2017 ). Thus, we include the grade level as a potential factor that moderates the linkage of homework time and academic performance.
- Region. Numerous studies indicated that there are regional differences in homework policies and practices (Chen & Stevenson, 1989 ; Tam & Chan, 2009 ; Zhu, 2015 ). The samples involved in the primary study on homework are from different regions (e.g., the United States and Asia); thus, we included the sampling region as a potential moderator in the present review.
- Publication year: Education systems are susceptible to influence of societal changes; thus, publication year is likely to be a moderator, as the homework time may change systematically over time (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Gill & Schlossman, 2004 ; Twenge et al., 2004 ). Thus, publication year may also potentially affect the effect sizes of homework time on performance.
- Mode of homework. With web‐learning popularized in education, online homework is being adopted by more teachers, and several researchers have argued about the effects of online homework compared to traditional homework (Callahan, 2016 ; Elias et al., 2017 ; Jonsdottir et al., 2017 ; Mendicino et al., 2009 ). In the present review, we will explore whether the relationship between homework time and academic performance is affected by the mode of homework.
- Type of homework. Teachers typically assign different kinds of homework according to their purpose. Such as reading story to parents, writing math exercises, and trying scientific experiments. In this review, we will divide the academic achievement into three groups: oral homework, paper homework and practical homework and explore whether the relationship between homework time and academic performance is different depending on the type of homework.
- The measure of academic performance: The methods used in previous homework studies included standardized tests and unstandardized assessments (Fan et al., 2017 ). Several studies suggested that the influence of homework on performance is larger with unstandardized assessments than with standardized tests (e.g., Cooper et al., 1998 ); therefore, there is a need to consider the measure of performance as a potential moderator.
- Subject. Several studies showed that time and effort input in homework varies depending on the subject (e.g., Trautwein, 2007 ; Trautwein & Lüdtke, 2009 ), and it is reasonable to suspect that homework may play a different role in different subjects (e.g., Cooper et al., 2006 ; Fan et al., 2017 ; Paschal et al., 1984 ).
3.3.9. Sensitivity analysis
In addition to the implicit sensitivity analysis in both the analysis of heterogeneity and subgroup analysis, the “One‐leave‐out” method is adopted for sensitivity analysis to check for outliers that potentially influence the overall results, and test the robustness of the meta‐analysis.
CONTRIBUTIONS OF AUTHORS
Liping Guo drafted the protocol, and all authors reviewed the draft and approved the final version.
DECLARATIONS OF INTEREST
All authors declare no potential interest.
INTERNAL SOURCES
This review is supported by funding of the Major Project of the National Social Science Fund of China: Research on the Theoretical System, International Experience, and Chinese Path of Evidence‐based Social Science.
Supporting information
Supplementary Information
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This review is supported by funding of the Major Project of the National Social Science Fund of China: Research on the Theoretical System, International Experience, and Chinese Path of Evidence‐based Social Science (No.: 19ZDA142).
Guo, L. , Li, J. , Xu, Z. , Hu, X. , Liu, C. , Xing, X. , Li, X. , White, H. , & Yang, K. (2021). PROTOCOL: The relationship between homework time and academic performance among K‐12 students: A systematic review . Campbell Systematic Reviews , 17 , e1199. 10.1002/cl2.1199 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ackerman, P. L. , Chamorro‐Premuzic, T. , & Furnham, A. (2011). Trait complexes and academic achievement: Old and new ways of examining personality in educational contexts . British Journal of Educational Psychology , 81 ( 1 ), 27–40. 10.1348/000709910X522564 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Atkins, D. , Eccles, M. , Flottorp, S. , Guyatt, G. H. , Henry, D. , Hill, S. , Liberati, A. , O'Connell, D. , Oxman, A. D. , Phillips, B. , Schünemann, H. , Edejer, T. T.‐T. , Vist, G. E. , Williams Jr, J. W. , & The GRADE Working Group . (2004). Systems for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations I: Critical appraisal of existing approaches The GRADE Working Group . BMC Health Services Research , 4 ( 1 ), 38. 10.1186/1472-6963-4-38 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baş, G. , Şentürk, C. , & Ciğerci, F. M. (2017). Homework and academic achievement: A meta‐analytic review of research . Issues in Educational Research , 27 ( 1 ), 30–50. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1130406 [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker, H. J. , & Epstein, J. L. (1982). Parent involvement: A survey of teacher practices . Elementary School Journal , 83 , 85–102. 10.2307/1001098 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borenstein, M. , Hedges, L. V. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta‐analysis . John Wiley & Sons. [ Google Scholar ]
- Callahan, J. T. (2016). Assessing online homework in first‐semester calculus . PRIMUS , 26 ( 6 ), 545–556. 10.1080/10511970.2015.1128501 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheema, J. R. , & Sheridan, K. (2015). Time spent on homework, mathematics anxiety and mathematics achievement: Evidence from a US sample . Issues in Educational Research , 25 , 246–259. http://www.iier.org.au/iier25/cheema.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen, C. , & Stevenson, H. W. (1989). Homework: A cross‐cultural examination . Child Development , 60 ( 3 ), 551–561. 10.2307/1130721 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, H. (1989). Homework . Longman. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, H. , Lindsay, J. J. , Nye, B. , & Greathouse, S. (1998). Relationships among attitudes about homework, the amount of homework assigned and completed, and student achievement . Journal of Educational Psychology , 90 ( 1 ), 70–83. 10.1037/0022-0663.90.1.70 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, H. , Robinson, J. C. , & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987−2003 . Review of educational research , 76 , 1–62. 10.3102/00346543076001001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elias, A. L. , Elliott, D. G. , & Elliott, J. A. W. (2017). Student perceptions and instructor experiences in implementing an online homework system in a large second‐year engineering course . Education for Chemical Engineers , 21 , 40–49. 10.1016/j.ece.2017.07.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Epstein, J. L. , & Van Voorhis, F. L. (2001). More than minutes: Teachers' roles in designing homework . Educational Psychologist , 36 , 181–193. 10.1207/S15326985EP3603_4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fan, H. , Xu, J. , He, J. , Cai, Z. , & Fan, X. (2017). Homework and students' achievement in math and science: A 30‐year meta‐analysis, 1986‐2015 . Educational Research Review , 20 ( 1 ), 35–54. 10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gill, B. P. , & Schlossman, S. L. (2003). Homework and the elusive voice of parents: Some historical perspectives . Teachers College Record , 105 ( 5 ), 846–871. 10.1111/1467-9620.00270 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gill, B. P. , & Schlossman, S. L. (2004). Villain or savior? The American Discourse on homework, 1850‐2003 . Theory Into Practice , 43 ( 3 ), 174–181. 10.1207/s15430421tip4303_2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- González, N. , Andrade, R. , Civil, M. , & Moll, L. (2001). Bridging funds of distributed knowledge: Creating zones of practice in mathematics . Journal of Education of Students Placed at Risk , 6 , 115–132. 10.1207/S15327671ESPR0601-2_7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hagborg, W. J. (1991). A study of homework time of a high school sample . Perceptual and Motor Skills , 73 ( 1 ), 103–106. 10.2466/pms.1991.73.1.103 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hallam, S. (2004). Homework: The evidence . University of London. [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins, J. P. T. , & Green, S. (Eds). (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011] . The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins, J. P. T. , & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis . Statistics in Medicine , 21 ( 11 ), 1539–1558. 10.1002/sim.1186 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jerrima, J. , Lopez‐Agudob, J. A. , & Marcenaro‐Gutierrez, O. D. (2019). The relationship between homework and the academic progress of children in Spain during compulsory elementary education: A twin fixed‐effects approach . British Educational Research Journal , 45 ( 5 ), 1021–1049. 10.1002/berj.3549 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jonsdottir, A. H. , Bjornsdottir, A. , & Stefansson, G. (2017). Difference in learning among students doing pen‐and‐paper homework compared to web‐based homework in an introductory statistics course . Journal of Statistics Education , 25 ( 1 ), 12–20. 10.1080/10691898.2017.1291289 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Keith, T. Z. (1982). Time spent on homework and high school grades: A large‐sample path analysis . Journal of Educational Psychology , 74 ( 2 ), 248–253. 10.1037/0022-0663.74.2.248 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitsantas, A. , Cheema, J. , & Ware, H. W. (2011). Mathematics achievement: The role of homework and self‐efficacy beliefs . Journal of Advanced Academics , 22 , 310–339. 10.1177/1932202x1102200206 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kralovec, E. , & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Krzysztof, K. , Duchowski, A. T. , Anna, N. , Cezary, B. , Izabela, K. , & Susana, M. C. (2018). Eye tracking cognitive load using pupil diameter and microsaccades with fixed gaze . PLOS One , 13 ( 9 ), 1–23. 10.1371/journal.pone.0203629 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee, J. F. , & Pruitt, K. W. (1979). Homework assignments: Classroom games or teaching tools? The Clearing House , 53 ( 1 ), 31–35. 10.2307/30185241 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lucas, A. R. (2012). Using webwork, a web‐based homework delivery and grading system, to help prepare students for active learning . Primus Problems Resources & Issues in Mathematics Undergraduate Studies , 22 ( 2 ), 97–107. 10.1080/10511970.2010.497834 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mau, W. C. , & Lynn, R. (2000). Gender differences in homework and test scores in mathematics, reading and science at tenth and twelfth grade . Psychology, Evolution & Gender , 2 ( 2 ), 119–125. 10.1080/14616660050200904 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mendicino, M. , Razzaq, L. , & Heffernan, N. T. (2009). A comparison of traditional homework to computer‐supported homework . Journal of Research on Technology in Education , 41 ( 3 ), 331–359. 10.1080/15391523.2009.10782534 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moher, D. , Liberati, A. , & Tetzlaff, J. , The PRISMA Group . (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta‐analyses: The PRISMA statement . PLOS Medicine , 6 ( 7 ), e1000097. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muhammad, H. I. (2015). Thorndike theory and it's application in learning . At‐Ta'lim: Journal Pendidikan , 1 ( 1 ), 37–47. https://ejournal.inzah.ac.id/index.php/attalim/article/view/166 [ Google Scholar ]
- Mulhenbruck, L. , Cooper, H. , Nye, B. , & Lindsay, J. J. (1999). Homework and achievement: Explaining the different strengths of relation at the elementary and secondary school levels . Social Psychology of Education , 3 , 295–317. 10.1023/A:1009680513901 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Page, M. J. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Sterne, J. A. C. (2019). Chapter 13: Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis. In Higgins J. P. T., Thomas J., Chandler J., Cumpston M., Li T., Page M. J., & Welch V. A. (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019) . Cochrane. https://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paschal, R. A. , Weinstein, T. , & WAlberg, H. J. W. (1984). The effects of homework on learning: A quantitative synthesis . The Journal of Educational Research , 78 ( 2 ), 97–104. 10.1080/00220671.1984.10885581 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reteig, L. C. , Brinka, R. L. , Prinssena, S. , Cohena, M. X. , & Slagter, H. A. (2019). Sustaining attention for a prolonged period of time increases temporal variability in cortical responses . Cortex , 117 , 16–32. 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.02.016 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal, R. (1979). The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results . Psychological Bulletin , 86 ( 3 ), 638–641. 10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schünemann, H. J. , Tugwell, P. , Reeves, B. C. , Akl, E. A. , Santesso, N. , Spencer, F. A. , Shea, B. , Wells, G. , & Helfand, M. (2013). Non‐randomized studies as a source of complementary, sequential or replacement evidence for randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews on the effects of interventions . Research Synthesis Methods , 4 ( 1 ), 49–62. 10.1002/jrsm.1078 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sterne, J. A. , Hernán, M. A. , Reeves, B. C. , Savović, J. , Berkman, N. D. , Viswanathan, M. , Henry, D. , Altman, D. G. , Ansari, M. T. , Boutron, I. , Carpenter, J. R. , Chan, A. W. , Churchill, R. , Deeks, J. J. , Hróbjartsson, A. , Kirkham, J. , Jüni, P. , Loke, Y. K. , Pigott, T. D. , … Higgins, J. P. (2016). ROBINS‐I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non‐randomized studies of interventions . BMJ , 355 , i4919. 10.1136/bmj.i4919 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tam, V. C. , & Chan, R. M. (2009). Parental involvement in primary children's homework in Hong Kong . School Community Journal , 19 ( 2 ), 81–100. http://www.adi.org/journal/fw09/TamChanFall2009.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein, U. (2007). The homework‐achievement relation reconsidered: Differentiating homework time, homework frequency, and homework effort . Learning and Instruction , 17 , 372–388. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.02.009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein, U. , & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Predicting homework motivation and homework effort in six school subjects: The role of person and family characteristics, classroom factors, and school track . Learning and Instruction , 19 ( 3 ), 243–258. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.05.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Twenge, J. M. , Zhang, L. , & Im, C. (2004). It's beyond my control: A cross‐temporal meta‐analysis of increasing externality in locus of control, 1960−2002 . Personality and Social Psychology Review , 8 ( 3 ), 308–319. 10.1207/s15327957pspr0803_5 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Voorhis, F. L. (2003). Interactive homework in middle school: Effects on family involvement and science achievement . Journal of Educational Research , 96 , 323–338. 10.1080/00220670309596616 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . (2016). Growing up unequal: Gender and socioeconomic differences in young people's health and well‐being . Health Behaviours in School‐Aged Children (HBSC) Study: International Report from the 2013/14 Survey (Health Policy for Children and Adolescents, No. 7).
- Xu, J. (2007). Middle‐school homework management: More than just gender and family involvement . Educational Psychology , 27 ( 2 ), 173–189. 10.1080/01443410601066669 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xue, H. P. , & Zhang, Y. (2019). Analysis of the academic burden level and difference of junior high school students in China: An Empirical Study Based on CEPS2015 data . Journal of Capital Normal University (Social Sciences Edition) , 1 ( 5 ), 147–166. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu, Y. (2015). Homework and mathematics learning: What can we learn from the TIMSS series studies in the last two decades? In Middleton J. A., Cai J., & Hwang S. (Eds.), Large‐scale studies in mathematics education (pp. 209–234). Springer International Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
Gray Matters: What role should homework play in learning?
Historical Background In the U.S., debates about the value of homework have been steady over the past century. In the beginning half of the 1900’s, homework was not nearly as common. Many school districts banned homework at the elementary and middle school levels in the belief that it only facilitated rote learning. That changed in the 1950’s when the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, creating the perception that the U.S. needed to increase the amount of students’ homework to be competitive in the space race. Over the next 50 years until the present, the popular view of homework switched every 15 years or so between support and condemnation. Today research has enhanced our understanding, but the debate continues.
Homework: What’s the Point? Numerous benefits are attributed to homework: better retention of factual knowledge, development of study habits, increased ability to manage time effectively, and heightened parental involvement. Evaluating exactly what of these benefits can be attributed to homework versus inherent differences in students or the quality of assignments presents obvious challenges. Further confounding research, homework often exacts costs in the form of increased stress and reduced sleep, which can negate potential benefits. Nonetheless, research to date provides guidance on homework’s role in achieving some of these goals.
Research Examples How much homework should be assigned? Although not unanimous, multiple studies on the relationship between homework time and academic achievement have shown that it is not a linear relationship: more homework does not equal more learning. One study of 7,451 13- year-old students administered a test of science and mathematics in addition to a survey of effort spent on homework, homework time, homework frequency, and the general circumstances around how homework was done. Results: student academic gains were associated with homework time up to 1 hour a day, after which increased homework time was associated with worse performance. This result varies with students’ ages.
How does the influence of homework change in different grades? While empirical studies have not yet explicitly compared the role of homework in different ages, a review of the literature reveals clear trends. A meta-analysis of 4,400 studies up until 2003 found that homework time had different effects depending on the grade of students. Results: up to two hours of homework showed the most benefit for high school students, up to an hour of homework showed some benefit for middle school students, and almost no benefit was found among elementary school students.
What homework factors contribute to academic performance? Studies that focus on the circumstances in which students complete homework have found that autonomy and effort are more important predictors of performance than homework time alone. One study of 483 eighth-graders from 20 classes analyzed students’ grades and standardized test scores in mathematics in relation to survey responses on homework effort. Students responded once in November and once in May of the academic year. Results: academic gains in grades and test scores were positively correlated to homework effort. However, other studies suggest that since effort and autonomy are highly correlated with students’ prior achievement, it’s difficult to say if this is a trait of the homework or of a certain kind of student.
How can homework best facilitate learning? Practices from the “ How can I improve longterm learning ” edition of Gray Matters 01 should be implemented in homework design to facilitate learning. For instance, using homework to continue practice on material and skills learned in previous weeks uses distributed practice to improve recall. Homework that offers adequate practice of important skills also helps reinforce skills in a variety of contexts. A survey of school leaders around homework best practices found similar results: homework can facilitate engagement when it is an authentic, engaging extension of the class. Results: homework should be designed intentionally, with reference to most effective forms of practice.
Does the effect of homework change when instruction occurs at home and exercises are done in class? In this case, the question is essentially if homework facilitates learning when it is done as a part class rather than at home. One model that represents this circumstance is the flipped classroom. Case studies done with ninth to twelfth-graders across a variety of subjects showed that achievement increased after implementing a model where students watched videos at home and practiced learning in class. In these schools the percentage of students passing standardized exams increased by up to 12%. Empirical studies comparing in-class work and at home work have repeated research design flaws, however, they generally indicate that in-class exercises have a positive effect for older students. Results: the research is inconclusive, but generally indicates that flipped classroom approaches have positive net benefits for high school students.
How frequently should homework be assigned? The research on frequency is not conclusive, however most studies suggest that classes that receive homework frequently tend to do better on tests of achievement. One such study administered standardized mathematics examinations to 2,939 grade 7 and 8 students across 20 classes. In addition to the exam, students answered questions on frequency of homework and the average amount of time spent on homework each evening. Results: Classes that had more frequent homework assignments had overall higher averages on the achievement tests.
Does homework change students’ attitudes towards school? Studies comparing the attitudes of students who received homework with those who did not receive homework generally found no significant results across a variety of grade levels. One study compared three different models for assigning arithmetic homework to 342 third-graders across twelve classrooms: teachers assigned no homework, assigned homework as usual, and were required to assign a constant amount of homework every night. Students answered questions measuring their attitudes towards school, teacher, arithmetic, spelling, reading, and homework. Results: no significant differences were found between the attitudes of the different groups.
Conclusion The quality of homework and the students who complete it vary significantly, however the general research trends suggest that assigning homework does have benefits at the middle and upper school levels. Frequency of assignment and students’ autonomy in finishing homework were also correlated with student achievement. These results provide guidelines on the appropriate quantity of homework, but how best to incorporate homework content into an overall progression of students’ learning remains for teachers to judge.
“Adolescents’ Homework Performance in Mathematics and Science: Personal Factors and Teaching Practices” by Rubén FernándezAlonso, Javier Suárez-Álvarez, and José Muñiz, Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015, 107(4), 1075.
“Ask the Cognitive Scientist Allocating Student Study Time” by Daniel T. Willingham, American Educator , 2002, 26(2), 37-39.
“Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003” by Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, Review of Educational Research , 2006, 76(1), 1-62.
“Does Homework Improve Learning?” by Alfie Kohn, AlfieKohn.org, 2006. “Effects of Arithmetic Homework upon the Attitudes of Third Grade Pupils Toward Certain School-related Structure” by Norbert Maertens, School Science and Mathematics , 1968, 68(7), 657-662.
“Flipped Learning Model Dramatically Improves Course Pass Rate for At-Risk Students, Clintondale high School, MI: A Case Study” by Pearson Education, May, 2013.
“Flipped Learning Model Increases Student Engagement and Performance, Byron High School, MN: A Case Study” by Pearson Education, June, 2013.
“Homework. Research on Teaching Monograph Series, Homework Versus In-class Supervised Study” by Harris Cooper, 1989, 77- 89.
“If They’d Only Do Their Work!” by Linda Darling-Hammond and Olivia Ifill-Lynch, Educational Leadership, 2008, 63(5), 8-13.
“Research Trends: Why Homework Should Be Balanced” by Youki Terada, Edutopia, 2015, July 31.
“Synthesis of Research on Homework” by Harris Cooper, Educational leadership, 1989, 47(3), 85-91.
“The Homework–Achievement Relation Reconsidered: Differentiating Homework Time, Homework Frequency, and Homework Effort” by Ulrich Trautwein, Learning and Instruction, 2007, 17(3), 372-388.
Gray Matters is dedicated to providing research-based answers to questions commonly raised by faculty and within the education community. Gray Matters is published by the Tiger Works Research & Development group at Avenues.
Find out more about Avenues’ admissions process and begin an online application for one of our global campuses.
About Avenues
Discover the people, places and values that make Avenues unique.
Find your future at Avenues: join the growing team that’s redefining K-12 education around the world.
Too Much Homework Can Lower Test Scores, Researchers Say

By: Natalie Wolchover Published: 03/30/2012 09:42 AM EDT on Lifes Little Mysteries
Piling on the homework doesn't help kids do better in school. In fact, it can lower their test scores.
That's the conclusion of a group of Australian researchers, who have taken the aggregate results of several recent studies investigating the relationship between time spent on homework and students' academic performance.
According to Richard Walker, an educational psychologist at Sydney University, data shows that in countries where more time is spent on homework, students score lower on a standardized test called the Program for International Student Assessment, or PISA. The same correlation is also seen when comparing homework time and test performance at schools within countries. Past studies have also demonstrated this basic trend.
Inundating children with hours of homework each night is detrimental, the research suggests, while an hour or two per week usually doesn't impact test scores one way or the other. However, homework only bolsters students' academic performance during their last three years of grade school. "There is little benefit for most students until senior high school (grades 10-12)," Walker told Life's Little Mysteries .
The research is detailed in his new book, "Reforming Homework: Practices, Learning and Policies" (Palgrave Macmillan, 2012).
The same basic finding holds true across the globe, including in the U.S., according to Gerald LeTendre of Pennsylvania State University. He and his colleagues have found that teachers typically give take-home assignments that are unhelpful busy work. Assigning homework "appeared to be a remedial strategy (a consequence of not covering topics in class, exercises for students struggling, a way to supplement poor quality educational settings), and not an advancement strategy (work designed to accelerate, improve or get students to excel)," LeTendre wrote in an email. [ Kids Believe Literally Everything They Read Online, Even Tree Octopuses ]
This type of remedial homework tends to produce marginally lower test scores compared with children who are not given the work. Even the helpful, advancing kind of assignments ought to be limited; Harris Cooper, a professor of education at Duke University, has recommended that students be given no more than 10 to 15 minutes of homework per night in second grade, with an increase of no more than 10 to 15 minutes in each successive year.
Most homework's neutral or negative impact on students' academic performance implies there are better ways for them to spend their after school hours than completing worksheets. So, what should they be doing? According to LeTendre, learning to play a musical instrument or participating in clubs and sports all seem beneficial , but there's no one answer that applies to everyone.
"These after-school activities have much more diffuse goals than single subject test scores," he wrote. "When I talk to parents … they want their kids to be well-rounded, creative, happy individuals — not just kids who ace the tests."
Follow Natalie Wolchover on Twitter @nattyover . Follow Life's Little Mysteries on Twitter @llmysteries , then join us on Facebook .
- Easy Answers to the Top 5 Science Questions Kids Ask
- Smart Answers for Crazy Hypothetical Questions
- Pointing Your Finger Makes You Credible to Kids
Copyright 2012 Lifes Little Mysteries, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Support HuffPost
Our 2024 coverage needs you, your loyalty means the world to us.
At HuffPost, we believe that everyone needs high-quality journalism, but we understand that not everyone can afford to pay for expensive news subscriptions. That is why we are committed to providing deeply reported, carefully fact-checked news that is freely accessible to everyone.
Whether you come to HuffPost for updates on the 2024 presidential race, hard-hitting investigations into critical issues facing our country today, or trending stories that make you laugh, we appreciate you. The truth is, news costs money to produce, and we are proud that we have never put our stories behind an expensive paywall.
Would you join us to help keep our stories free for all? Your contribution of as little as $2 will go a long way.
Can't afford to donate? Support HuffPost by creating a free account and log in while you read.
As Americans head to the polls in 2024, the very future of our country is at stake. At HuffPost, we believe that a free press is critical to creating well-informed voters. That's why our journalism is free for everyone, even though other newsrooms retreat behind expensive paywalls.
Our journalists will continue to cover the twists and turns during this historic presidential election. With your help, we'll bring you hard-hitting investigations, well-researched analysis and timely takes you can't find elsewhere. Reporting in this current political climate is a responsibility we do not take lightly, and we thank you for your support.
Contribute as little as $2 to keep our news free for all.
Dear HuffPost Reader
Thank you for your past contribution to HuffPost. We are sincerely grateful for readers like you who help us ensure that we can keep our journalism free for everyone.
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. Would you consider becoming a regular HuffPost contributor?
The stakes are high this year, and our 2024 coverage could use continued support. If circumstances have changed since you last contributed, we hope you’ll consider contributing to HuffPost once more.
Already contributed? Log in to hide these messages.
Before You Go
Popular in the community, from our partner, more in science.
globeteacher.com

How Does Homework Help You Prepare For Tests
A lot is taught at school and it is not always possible to sit and down and interact with each student individually to unearth where s/he is lagging behind. Schoolwork serves as a unit of measurement for a student’s grasp over a particular subject or topic. It allows the teacher to assess how well or how poorly as student is catching up with the daily proceedings of the class. Homework help college enables students as well to self-assess their strong and weak areas and resolve their problems accordingly.
Test performance
Homework tends to expand beyond the realms of what is taught at school. In doing so, it pushes the student to partake in research exercises as often s/he has to dig up extra materials in order to keep up with class lectures. As a result, especially for subjects that require you to refer to multiple sources of information, one can provide a better output in his/her answers in their respective tests than the average performer. It firms the student’s grip on a particular topic.
Homework help answers: developing habits
Benefits of homework are many and people will always be mentioning one or the other but in order to reap its harvests, one has to make it a habit to do their homework on a regular basis. Cross-checking of test questions and tasks that the teacher sets for the students throughout the year, on a particular subject, will reveal how if a student does his /her homework regularly, s/he are bound to find familiar questions in their tests.
Homework as a habit makes the student learn the subject in a smooth process and relaxes any form of tension that test-preparation at the eleventh hour might exert; one is able to retain a lot from the school curriculum through this habit.
To help improve oneself
In this busy world parents don’t have time for their children in order to sit with them and help them with their homework; not everyone can afford a paid tutor; for college students living away, far away from their homes, the few resorts they have, if a doubt is ever to arise, are their professors, books and the internet; while some are just too busy with other work (mostly non-academic) and several, too lazy. For these folks there are service providers who help them with their homework and related doubts in exchange of a certain sum of money.
These groups or organization or firms or however they call themselves, employ skilled professionals to solve your problems regarding your homework. They will do an essay for you, solve your trigonometry problems, write your term paper and so on. Their charges are not sky-high but there is no compromise with quality. If chosen wisely, students can avail themselves the best homework service .
Since these firms and organizations mostly work online, their services can be easily availed whenever and from wherever one feels like. Then again it is this online feature of these services that fraudsters tend to exploit to dupe one of his/her money. So it is necessary to choose wisely.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Harvard and Caltech Will Require Test Scores for Admission
The universities are the latest highly selective schools to end their policies that made submitting SAT or ACT scores optional.

By Anemona Hartocollis and Stephanie Saul
Harvard will reinstate standardized testing as a requirement of admission, the university announced Thursday, becoming the latest in a series of highly competitive universities to reverse their test-optional policies.
Students applying to enter Harvard in fall 2025 and beyond will be required to submit SAT or ACT scores, though the university said a few other test scores will be accepted in “exceptional cases,” including Advanced Placement or International Baccalaureate tests. The university had previously said it was going to keep its test-optional policy through the entering class of fall 2026.
Within hours of Harvard’s announcement, Caltech, a science and engineering institute, also said it was reinstating its testing requirements for students applying for admission in fall 2025.
The schools had been among nearly 2,000 colleges across the country that dropped test score requirements over the last few years, a trend that escalated during the pandemic when it was harder for students to get to test sites.
Dropping test score requirements was widely viewed as a tool to help diversify admissions, by encouraging poor and underrepresented students who had potential but did not score well on the tests to apply. But supporters of the tests have said without scores, it became harder to identify promising students who outperformed in their environments.
In explaining its decision to accelerate the return to testing, Harvard cited a study by Opportunity Insights , which found that test scores were a better predictor of academic success in college than high school grades and that they can help admissions officers identify highly talented students from low income groups who might otherwise had gone unnoticed.
“Standardized tests are a means for all students, regardless of their background and life experience, to provide information that is predictive of success in college and beyond,” Hopi Hoekstra, dean of the faculty of arts and sciences, said in a statement announcing the move.
“In short, more information, especially such strongly predictive information, is valuable for identifying talent from across the socioeconomic range,” she added.
Caltech, in Pasadena, Calif., said that reinstating testing requirements reaffirmed the school’s “commitment as a community of scientists and engineers to using all relevant data in its decision-making processes.”
Harvard and Caltech join a growing number of schools, notable for their selectivity, that have since reversed their policies, including Brown, Yale, Dartmouth, M.I.T., Georgetown, Purdue and the University of Texas at Austin.
For Harvard, the move comes at a time of transition, and perhaps a return to more conservative policies.
Last June, the Supreme Court struck down race-conscious college admissions in cases involving Harvard and the University of North Carolina, raising fears that with the demise of affirmative action, those schools would become less diverse.
And in January, Harvard’s first Black president, Claudine Gay, resigned under pressure from critics who said she had not acted strongly enough to combat antisemitism on campus after the Oct. 7 attack by Hamas on Israel, and under mounting accusations of plagiarism in her academic work, which she stood by.
The provost, Alan Garber, was named interim president, while the dean of the law school, John Manning, became interim provost, the university’s second-highest administrative position. Mr. Manning is considered a strong potential candidate to replace Dr. Gay. His background stands out for his conservative associations, having clerked for the former Supreme Court justice Antonin Scalia.
In the current climate on campus, a return to test scores could be seen as a return to tradition. It also may address concerns of many parents that the college admissions process, especially in elite institutions, is inscrutable and disconnected from merit.
Applications to Harvard were down by 5 percent this year, while those at many of its peer universities went up, suggesting that the recent turmoil may have dented its reputation. But it still received a staggering number of undergraduate applications — 54,008 — and admitted only 3.6 percent. Requiring test scores could make sorting through applications more manageable.
Critics of standardized tests have long raised concerns that the tests helped fuel inequality because some wealthier students raised their scores through high-priced tutoring. But recent studies have found that test scores help predict college grades, chances of graduation and post-college success, and that test scores are more reliable than high school grades, partly because of grade inflation in recent years .
But Robert Schaeffer, director of public education at FairTest, an organization that opposes standardized testing, said Thursday that the Opportunity Insights analysis had been criticized by other researchers. “Those scholars say that when you eliminate the role of wealth, test scores are not better than high school G.P.A.,” he said, adding that it is not clear whether that pattern is true among the admissions pool at super selective colleges such as Harvard.
Mr. Schaeffer said that at least 1,850 universities remain test optional, including Michigan, Vanderbilt, Wisconsin and Syracuse, which have recently extended their policies. “The vast majority of colleges will not require test scores.” An exception, he said, could be the University of North Carolina system, which is considering a plan to require tests, but only for those students with a G.P.A. below 2.8.
Acknowledging the concerns of critics, Harvard said that it would reassess the new policy regularly. The school said that test scores would be considered along with other information about an applicant’s experience, skills, talents, contributions to communities and references. They will also be looked at in the context of how other students are doing at the same high school.
“Admissions officers understand that not all students attend well-resourced schools, and those who come from modest economic backgrounds or first-generation college families may have had fewer opportunities to prepare for standardized tests,” William R. Fitzsimmons, Harvard’s dean of admissions and financial aid, said in a statement.
Harvard said that in the interest of selecting a diverse student body, it has enhanced financial aid and stepped up recruitment of underserved students by joining a consortium of 30 public and private universities that recruits students from rural communities.
An earlier version of this article misstated Robert Schaeffer’s position. He is the director of public education at FairTest, not the director.
How we handle corrections
Anemona Hartocollis is a national reporter for The Times, covering higher education. More about Anemona Hartocollis
Stephanie Saul reports on colleges and universities, with a recent focus on the dramatic changes in college admissions and the debate around diversity, equity and inclusion in higher education. More about Stephanie Saul

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until ...
Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night.
Despite access to a trove of learning resources - including textbooks, online references and homework assignments - some students routinely fall short of their performance expectations.
The time students spend on math and science homework doesn't necessarily mean better grades, but it could lead to better performance on standardized tests, a new study finds. "When Is Homework Worth The Time?" was recently published by lead investigator Adam Maltese, assistant professor of science education at Indiana University, and co ...
In surveying the homework habits of 7,725 adolescents, this study suggests that for students who average more than 100 minutes a day on homework, test scores start to decline. The relationship ...
There have been several theories on the areas of what help students achieve. One of ... statistics have shown that teachers are attempting to remedy low test scores by giving students more homework (O'Neill 2008). ... The reason most cited for giving homework to students is that the practice can improve students' retention and understanding ...
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Why Homework Should Be Balanced. Homework can boost learning, but doing too much can be detrimental. The National PTA and National Education Association support the "10-minute homework rule," which recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night (10 minutes for first grade, 20 minutes for second grade, and so on, up to two ...
Both reviews conclude that homework does help to improve academic achievement, primarily in the middle and high school. For children in elementary school, the review concludes that while homework can help children develop good study habits, it does not help to improve students' grades or standardized test scores.
Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987-2003. ... Does homework help? A review of research. Elementary School Journal 1960;60:212-224. ISI. ... Student and parental homework practices and the effect of English homework on student test scores. Dissertation Abstracts International 1992;53 10A 3490 (UMI No ...
Study: Homework linked to better standardized test scores. By Valerie Strauss. November 19, 2012 at 4:11 p.m. EST. Researchers who looked at data from more than 18,000 10th-graders found there was ...
Completing homework has been found to be associated with higher test scores and improved performance. ... Homework assignments can help consolidate knowledge, improve understanding, and develop ...
One of the most cited studies concludes there's some connection for grades 6-12 between homework and test scores, but less so for elementary students, and less of an impact on actual grades.
Homework assignments are influenced by more factors than any other instruc-tional strategy. Student differences may play a major role because homework allows students considerable discretion about whether, when, and how to complete assign-ments. Teachers may structure and monitor homework in a multitude of ways.
Cooper's analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school ...
In the past two decades, researchers have tested 10 different data-study programs in hundreds of schools for impacts on student outcomes in math, English/language arts, and sometimes science. Of 23 student outcomes examined by these studies, only three were statistically significant. Of these three, two were positive, and one negative.
School of Education study: Homework doesn't improve course grades but could boost standardized test scores. Thursday, November 15, 2012. A study led by an Indiana University School of Education faculty member finds little correlation between time spent on homework and better course grades for math and science students, but a positive relationship between homework time and performance on ...
The preview assignments introduce new skills or materials to help students prepare for unfamiliar knowledge before the class ... Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987−2003. Review of ... Gender differences in homework and test scores in mathematics, reading and science at tenth and twelfth grade ...
Critics have objected that even if homework doesn't increase grades or test scores, it has other benefits, like fostering good study habits and providing parents with a window into what kids are ...
Homework that offers adequate practice of important skills also helps reinforce skills in a variety of contexts. A survey of school leaders around homework best practices found similar results: homework can facilitate engagement when it is an authentic, engaging extension of the class. Results: homework should be designed intentionally, with ...
This type of remedial homework tends to produce marginally lower test scores compared with children who are not given the work. Even the helpful, advancing kind of assignments ought to be limited; Harris Cooper, a professor of education at Duke University, has recommended that students be given no more than 10 to 15 minutes of homework per night in second grade, with an increase of no more ...
Homework as a habit makes the student learn the subject in a smooth process and relaxes any form of tension that test-preparation at the eleventh hour might exert; one is able to retain a lot from the school curriculum through this habit. To help improve oneself. In this busy world parents don't have time for their children in order to sit ...
The preview assignments introduce new skills or materials to help students prepare for ... homework can be an effective means to improve student's academic achievement. ... characteristics (e.g., subject, mode of homework and the type of homework). The other is the effect size, including the homework time and the test score (The details ...
But recent studies have found that test scores help predict college grades, chances of graduation and post-college success, and that test scores are more reliable than high school grades, ...