myCBSEguide
- CBSE Previous Year Question...
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Geography
Table of Contents

myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Geography question papers and marking scheme for past 10 years are very useful to prepare for annual examinations. Geography ten year papers are available for free download in myCBSEguide app and website in PDF format. CBSE last year papers for Class 11 Geography and Last Year Question Paper & Solutions of 11 Geography are made available by CBSE every year just after the exams are over. CBSE marking scheme and blue print is provided along with the previous year question paper. This helps students find answer the most frequently asked question, How to prepare for CBSE exams. CBSE question papers of Class 11 Geography for 2018, 2017 and previous year exams are provided by CBSE, New Delhi. The best way to prepare for exams is to understand the questions pattern and practice them as given in previous year question papers.
Download Geography Question Papers as PDF
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2017
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2016
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2015
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2014
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2013
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2012
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2011
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2010
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2009
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2008
- CBSE Class 11 Geography Question Paper-2007
Question papers of Class 11 Geography
MyCBSEguide provides CBSE Class 11 Question Paper of Geography for the year 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015 with solutions in PDF format for free download. The previous year question papers last 10 year for all – NCERT books and based on CBSE latest syllabus must be downloaded and practiced by students. Class 11 Geography old question papers follow the blue print of that year only. Student must check the latest syllabus and marking scheme before using these previous year question papers. These old 5 to 10 year question papers are the best source to understand question paper pattern and chapter wise weightage in Class 11 th Geography question paper.
CBSE Geography questions papers
- solved question papers for Class 11
- Previous Year Question Papers 2016 (Main) and Marking Scheme
- cbse question papers for Class 11 with answers 2018
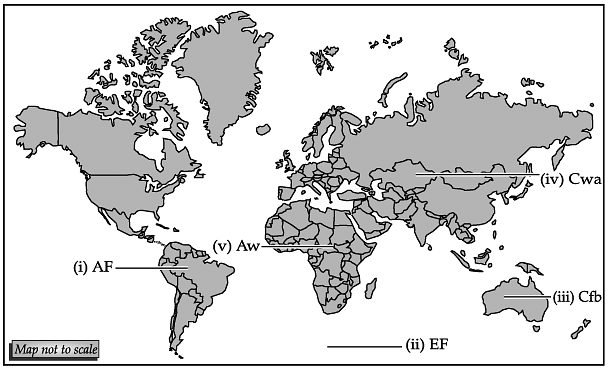
- cbse solved question papers for Class 11 free download
- Question Papers for 2016 Class XI
- CBSE Question Paper for Class 11 – Geography– 2018, 2017, 2016
- last 5 years question papers of cbse 11th Geography
- cbse previous year question papers Class 11 solved
- ncert question papers
- cbse old question papers Class 11 Geography
CBSE Question Papers for Class 11
CBSE question papers 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, 2006, 2005 and so on for all the subjects are available under this download link. Practicing real question paper certainly helps students to get confidence and improve performance in weak areas.
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Physics
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Chemistry
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Mathematics
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Biology
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Accountancy
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Business Studies
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Economics
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 History
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Political Science
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Physical Education
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Computer Science
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 English Core
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Hindi Elective
- CBSE Question Papers for Class 11 Other Subjects
To download CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Geography, Chemistry, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. MyCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Hindi Core
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Physical Education
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Political Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 History
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 English Core
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Computer Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Business Studies
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Economics
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Accountancy
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Biology
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Mathematics
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Chemistry
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 11 Physics
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Hindi Course-A
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 English Language and Literature
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 English Communicative
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Social Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Mathematics
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Hindi Course-A
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 English Language and Literature
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper - 3 | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q.1. The consequence of erosion is: (a) rockslide ( b ) sliding ( c ) deposition (d) landslide Ans: (c)
Q.2. The uppermost layer of the atmosphere above the ionosphere is known as the: (a) Exosphere (b) tropopause (c) mesopause (d) ionosphere Ans: (a)
Q.3. Mixed tides usually occur along the: (a) east coast of South America (b) west coast of South America (c) east coast of North America (d) west coast of North America Ans: (d)
Q.4. The atmosphere is indirectly heated by the earth’s: (a) radiation (b) insulation (c) convection (d) advection Ans: (a)
Q.5. Organisms of an ecosystem are linked together through: (a) food chain (b) ecology (c) biosphere (d) habitat Ans: (a)
Q.6. The Chenab is the largest tributary of the: (a) Beas (b) Brahmaputra (c) Indus (d) Jhelum Ans: (c)

Q.8. Pangaea began to split around: (a) 100 million years ago (b) 200 million years ago (c) 300 million years ago (d) 400 million years ago Ans: (b)
Q.9. Fill in the blanks : ____________comprises country/rural and town/urban planning. Ans: Regional planning
Q.10. The location where sinking of a plate occurs is called a: (a) Subduction Zone (b) Reduction Zone (c) Induction Zone (d) Deduction Zone Ans: (a)
Q.11. The temperature distribution is generally shown on the map with the help of: (a) heat budget (b) isotherms (c) mesotherms (d) radiotherms Ans: (b)
Q.12. India has an area of: (a) 1.28 million sq km (b) 3.28 million sq km (c) 4.28 million sq km (d) 5.28 million sq km Ans: (b)
Q.13. A river drains the water collected from a specific area, which is called its: (a) catchment area (b) attachment area (c) drainage area (d) watershed area Ans: (a)
Q.14. The gas that is transparent to the incoming solar radiation but opaque to the outgoing terrestrial radiation is known as : (a) Carbon dioxide (b) oxygen (c) nitrogen (d) helium Ans: (a)
Q.15. Which one of the following gases is transparent to incoming solar radiation and opaque to outgoing terrestrial radiation : (a) Oxygen (b) Nitrogen (c) Helium (d) Carbon dioxide Ans: (d)
Q.16. Read the Case Study given below and answer the questions that follow: Crust is the outermost solid part of the earth. It is brittle in nature. The thickness of the crust varies under the oceanic and continental areas. Oceanic crust is thinner as compared to the continental crust. The mean thickness of oceanic crust is 5 km whereas that of the continental is around 30 km. The continental crust is thicker in the areas of major mountain systems. It is as much as 70 km thick in the Himalayan region. The portion of the interior beyond the crust is called the mantle. The mantle extends from Moho’s discontinuity to a depth of 2,900 km. The upper portion of the mantle is called the no sphere. The word astheno means weak. It is considered to be extending upto 400 km. It is the main source of magma that finds its way to the surface during volcanic eruptions. The crust and the uppermost part of the mantle are called lithosphere. Its thickness ranges from 10-200 km. The lower mantle extends beyond the asthenosphere. It is in solid state. As indicated earlier, the earthquake wave velocities helped in understanding the existence of the core of the earth. The core mantle boundary is located at the depth of 2,900 km. The outer core is in liquid state while the inner core is in solid state. The core is made up of very heavy material mostly constituted by nickel and iron. It is sometimes referred to as the nife layer. Answer any three questions: (a) Which of the following layers of earth is brittle in nature? (i) Crust (ii) Mantle (iii) Core (iv) All of the above Ans: (i)
(b) Which of the following layers is referred to as Nife layer ? (i) Crust (ii) Mantle (iii) Core (iv) All of the above Ans: (iii)
(c) What is the correct sequence of the layers of the earth from innermost to outermost ? (i) Crust – mantle – core (ii) Core – mantle – crust (iii) Crust – core – mantle (iv) Mantle – core – crust Ans: (ii)
(d) The core mantle boundary is located at the depth of: (i) 2,300 km (ii) 2,700 km (iii) 2,600 km (iv) 2,900 km Ans: (iv)
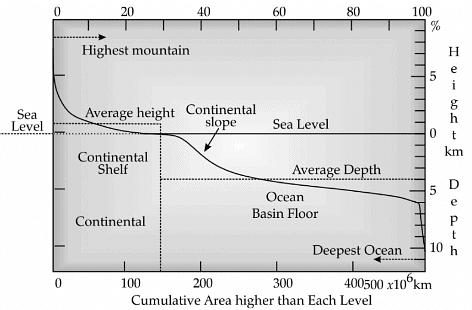
Answer any three questions: (a) According to the graph which of the following is in the correct sequence in terms of increasing height? (i) Continental Slope – Continental Shelf – Ocean Basin Floor (ii) Continental Shelf – Continental Slope –Ocean Basin Floor (iii) Continental Shelf– Ocean Basin Floor– Continental Slope (iv) Ocean Basin Floor – Continental Slope – Continental Shelf Ans: (iv)
(b) According to the graph what is the average depth of the ocean? (i) 11 km below the sea level (ii) 8 km below the sea level (iii) 4 km below the sea level (iv) 7 km below the sea level Ans: (iii)
(c) According to the graph what is the average height of the continent? (i) 8 km above the sea level (ii) 1 km above the sea level (iii) 4 km above the sea level (iv) 3 km above the sea level Ans: (ii)
(d) According to the graph the deepest point of the ocean is lies at: (i) 11 km below the sea level (ii) 8 km below the sea level (iii) 4 km below the sea level (iv) 7 km below the sea level Ans: (i)
Q.18. Geography is an integration of social sciences and physical sciences. Explain? Ans: (i) Geography is an integration of social sciences and physical sciences as the basic aim of both is to understand the reality of nature. All the social science disciplines, viz, sociology, political science, demography study different aspects of social reality. The branches of geography viz, social , political, economic and population and settlements are closely linked with these disciplines as each of them has spatial attributes. (ii) The core concern of political science is territory, people and sovereignty while political geography is also interested in the study of the state as a spatial unit as well as people and their political behaviour. (iii) History helps in knowing man-made activities over the period of time ,whereas Physics helps in calculating the effect of climate on man. The change in the climate further has an influence on the occupation of the people. (iv) Economics deals with the basic attributes of the economy such as production, distribution, exchange and consumption. Each of these attributes also has spatial aspects and here comes the role of economic geography. (v) Mathematics and arts also have contributed to the development of geography to measure area and dimensions of the earth. Hence, it can be rightly said that all the branches of social sciences have a close relationship with the physical sciences.
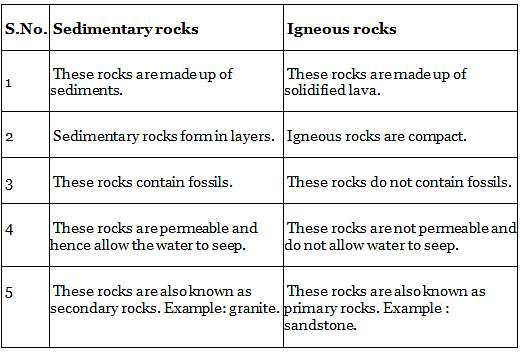
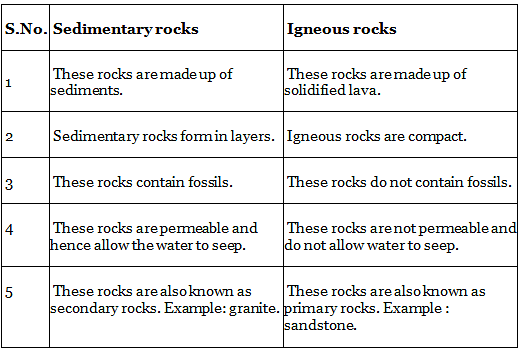
Q.19. Differentiate between sedimentary rocks and igneous rocks.
The size of India has endowed her with great physical diversity. Thus, you may appreciate the presence of lofty mountains in the north; large rivers such as Ganga, Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Krishna, Godavari and Kaveri; green forested hills in the North East and South India; and the vast sandy expanse of Marusthali. You may further appreciate that bounded by the Himalayas in the north, Hindukush and Sulaiman ranges in the northwest, Purvanchal hills in the North-East and by the large expanse of the Indian ocean in the south, it forms a great geographic entity known as the Indian subcontinent. It includes the countries — Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and India. The Himalayas, together with other ranges, have acted as a formidable physical barrier in the past. Except for a few mountain passes such as the Khyber, the Bolan, the Shipkila, the Nathula, the Bomdila, etc. it was difficult to cross it. It has contributed towards the evolving of a unique regional identity of the Indian subcontinent. The Peninsular part of India extends towards the Indian Ocean. This has provided the country with a coastline of 6,100 km in the mainland and 7,517 km in the entire geographical coast of the mainland plus the island groups Andaman and Nicobar located in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea. Thus India, as a country, is a physically diverse land providing occurrence of varied resources.
Q.20. What do you know about the oxygen cycle?
Differentiate between convectional rain and orographic rain? Ans: Oxygen is the main by-product of photosynthesis. It is involved in the oxidation of carbohydrates with the release of energy, carbon dioxide and water. The cycling of oxygen is a highly complex process. Oxygen occurs in a number of chemical forms and combinations. It combines with nitrogen to form nitrates and with many other minerals and elements to form various oxides such as the iron oxide, aluminium oxide and others. Much of oxygen is produced from the decomposition of water molecules by sunlight during photosynthesis and is released in the atmosphere through transpiration and respiration processes of plants.
Q.21. Explain the important features of the Brahmaputra River System?
On the basis of the size of the watershed, the drainage basins of India can be divided into how many groups. Ans: The Brahmaputra River System: (i) The Brahmaputra, one of the largest rivers of the world, has its origin in the Chemayungdung Glacier of the Kailash range near the Mansarovar lake. From here, it traverses eastward longitudinally for a distance of nearly 1,200 km in a dry and flat region of southern Tibet, where it is known as the Tsangpo, which means ‘the purifier.’ (ii) The Brahmaputra receives numerous tributaries in its 750 km long journey through the Assam valley. (iii) The Brahmaputra is well-known for floods, channel shifting and bank erosion. This is due to the fact that most of its tributaries are large, and bring large quantities of sediments owing to heavy rainfall in its catchment area.
On the basis of the size of the watershed, the drainage basins of India are grouped into three categories: (i) Major river basins with more than 20,000 sq. km of catchment area. It includes 14 drainage basins such as the Ganga, the Brahmaputra, the Krishna, the Tapi, the Narmada, the Mahi, the Pennar, the Sabarmati, the Barak, etc. (ii) Medium river basins with catchment area between 2,000-20,000 sq. km incorporating 44 river basins such as the Kalindi, the Periyar, the Meghna, etc. (iii) Minor river basins with catchment areas of less than 2,000 sq. km include a fairly good number of rivers flowing in the area of low rainfall.
Q.22. Discuss any five important minerals along with their characteristics. Ans: Some of the important minerals and their characteristics are: (i) Feldspar: Silicon and oxygen are common elements in all types of feldspar and sodium, potassium, calcium, aluminium, etc., are found in specific feldspar varieties. Half of the earth’s crust is composed of feldspar. It has light cream to salmon pink colour. It is used in ceramics and glass making. (ii) Quartz: It is one of the most important components of sand and granite. It consists of silica. It is a hard mineral virtually insoluble in water. It is white or colourless and used in radio and radar. It is one of the most important components of granite. (iii) Pyroxene: Pyroxene consists of calcium, aluminium, magnesium, iron and silica. Pyroxene forms 10 percent of the earth’s crust. It is commonly found in meteorites. It is in green or black colour. (iv) Amphibole: Aluminium, calcium, silica, iron, magnesium are the major elements of amphiboles. They form 7 per cent of the earth’s crust. It is in green or black colour and is used in the asbestos industry. Hornblende is another form of amphiboles. (v) Mica: It comprises potassium, aluminium, magnesium, iron, silica, etc., It forms 4 per cent of the earth’s crust. It is commonly found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. It is used in electrical instruments. (vi) Olivine: Magnesium, iron and silica are major elements of olivine. It is used in jewellery. It is usually a greenish crystal, often found in basaltic rocks. Besides these main minerals, other minerals like chlorite, calcite, magnetite, haematite, bauxite and barite are also present in some quantities in the rocks.
Q.23 Geography being a scientific discipline, what do you think how many categories of questions are geography concerned with? Explain. Ans: Geography as a scientific discipline is concerned with three sets of questions: (i) Some of the questions are related to the identification of the various patterns of natural and cultural features as found over the surface of the earth. These are the questions about ‘what’? (ii) The second kind of questions are related to the distribution of the natural and human/cultural features over the surface of the earth. These are the questions about ‘where’? (iii) The third kind of questions are related to the explanation or the causal relationships between features and the processes and phenomena. This aspect of geography is related to the question ‘why’.
Q.24. Why is geography considered as an important subject?
Explain different types of physical weathering. Ans: Geography is considered as an important subject because: (i) As we live on Earth, therefore, it is very important to understand the mechanism of our planet. It gives us a visual sense of the Earth’s surface. (ii) We are heavily dependent on the natural resources available on the Earth’s surface. In order to know how efficiently it can be used, it is important to study geography. (iii) Climate is a major deciding factor in the type of crops to be grown, human settlements, food to be eaten, shelter to be built, etc. To understand the interrelationship between the climate and human movements, it is important to study geography as a subject. (iv) It also helps us connect well and understand the changes that have taken place in the evolution of the Earth. It makes our understanding of the changes that have taken place throughout the geological time better. It also helps us know the land and people in a better sense.
Different types of physical weathering are: (i) Exfoliation: Exfoliation can occur due to expansion and contraction induced by temperature changes. Exfoliation domes and tors result due to unloading and thermal expansion respectively. Due to differential heating and resulting expansion and contraction of surface layers and their subsequent exfoliation from the surfaces results in smooth rounded surfaces in rocks. (ii) Frost: Frost is an active agent in cold climatic regions in high altitudes and the cracks are filled with water during the day time, this water is frozen at night when temperature falls below freezing point. (iii) Pressure: Many igneous and metamorphic rocks crystallise deep in the interior under the combined influence of high pressure and temperature. The salt near surface pores cause splitting of the grains within the rocks which eventually falls off, this results in granules disintegration.
Q.25. How did the Peninsular Drainage System evolve? Ans: Three major geological events in the distant past have shaped the present drainage systems of Peninsular India: (i) Subsidence of the western flank of the Peninsula leading to its submergence below the sea during the early tertiary period. Generally, it has disturbed the symmetrical plan of the river on either side of the original watershed. (ii) Upheaval of the Himalayas when the northern flank of the Peninsular block was subjected to subsidence and the consequent trough faulting. The Narmada and The Tapi flow in through faults and fill the original cracks with their detritus materials. Hence, there is a lack of alluvial and deltaic deposits in these rivers. (iii) Slight tilting of the Peninsular block from northwest to the southeastern direction gave orientation to the entire drainage system towards the Bay of Bengal during the same period.
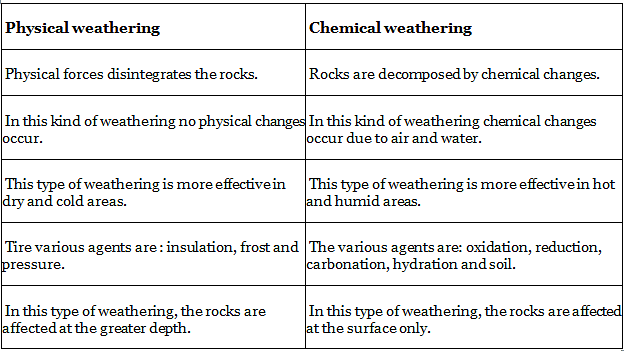
Q.26. Differentiate between physical weathering and chemical weathering. Ans:
Q.27. Write a note on the biospheres of India. Ans: A Biosphere Reserve is a unique and representative ecosystem of terrestrial and coastal areas which are internationally recognised within the framework of UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme. Ten Biosphere Reserves have been recognised by UNESCO on the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. Some of the important Biosphere reserves are as follows: (i) The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR): The first of the fourteen biosphere reserves of India, was established in September 1986. It embraces the sanctuary complex of Wayanad, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Mudumalai, the entire forested hill slopes of Nilambur, the Upper Nilgiri plateau, Silent Valley and the Siruvani hills. The total area of the biosphere reserve is around 5,520 sq. km. The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve possesses different habitat types, unspoilt areas of natural vegetation types with several dry scrubs, dry and moist deciduous, semi-evergreen and wet evergreen forests, evergreen sholas, grasslands and swamps. It includes the largest known population of two endangered animal species, namely the NilgiriTahr and the Lion-tailed macaque. The largest south Indian population of elephant, tiger, gaur, sambar and chital as well as a good number of endemic and endangered plants are also found in this reserve. The habitat of a number of tribal groups remarkable for their traditional modes of harmonious use of the environment are also found here. (ii) The Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve: It is situated in Uttaranchal includes parts of Chamoli, Almora, Pithoragarh and Bageshwar districts. The major forest types of the reserve are temperate. A few important species are silver weed and orchids like latifolia and rhododendron. The biosphere reserve has a rich fauna, for example the snow leopard, black bear, brown bear, musk deer, snowcock, golden eagle and black eagle. Major threats to the ecosystem are the collection of endangered plants for medicinal use, forest fires and poaching. (iii) Sunderbans Biosphere Reserve: It is located in the swampy delta of the river Ganga in West Bengal. It extends over a vast area of 9,630 sq. km and consists of mangrove forests, swamps and forested islands. Sunderbans is the home of nearly 200 Royal Bengal tigers. The tangled mass of roots of mangrove trees provide safe homes for a large number of species, from fish to shrimp. More than 170 bird species are known to inhabit these mangrove forests. (iv) Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve: The Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve covers an area of 105,000 hectares on the southeast coast of India. It is one of the world’s richest regions from a marine biodiversity perspective. The biosphere reserve comprises 21 islands with estuaries, beaches, forests of the nearshore environment, sea grasses, coral reefs, salt marshes and mangroves. Among the Gulf’’s 3,600 plant and animal species are the globally endangered sea cow (Dugong dugon) and six mangrove species, endemic to Peninsular India.
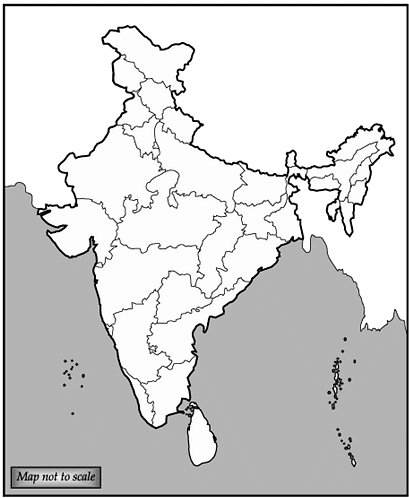
Q.29. Locate and label any five rivers with appropriate symbols on the given political outline map of India: (i) Kaveri (ii) Narmada (iii) Luni (iv) Tapi (v) Indus (vi) Brahmaputra (vii) Krishna
Top Courses for Humanities/Arts
Faqs on geography: cbse sample question paper - 3 - geography class 11 - humanities/arts, geography: cbse sample question paper - 3 | geography class 11 - humanities/arts, mock tests for examination, semester notes, video lectures, shortcuts and tricks, practice quizzes, sample paper, important questions, viva questions, previous year questions with solutions, study material, past year papers, objective type questions, extra questions.

Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper - 3 Free PDF Download
Importance of geography: cbse sample question paper - 3, geography: cbse sample question paper - 3 notes, geography: cbse sample question paper - 3 humanities/arts questions, study geography: cbse sample question paper - 3 on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
- Registration

- CBSE PAPERS
- CBSE eBOOKS
- HOME TUTORS
- LATEST JOBS
- CBSE SCHOOLS
- CLASSIFIED LISTINGS
- INDIAN EDUCATION
- EDUCATIONAL ARTICLES

EXPLORE CBSEGuess
Entrance exams, tutors zone.
- Practice Papers
CBSE Class XI Practice Papers
CBSE Class XI Geography Practice Papers for Examination
CBSE Class 11 Geography Solved Sample Papers 2023 Hindi Medium Mr. Pankaj
CBSE Class 11 Geography Hindi Medium Sample Papers for 2023 Examination.
CBSE Class 11 Geography Guess Papers 2023 Hindi Medium Mr. Sindhi
CBSE Class 11 Geography Guess Papers 2023 in Hindi Medium.
CBSE Class XI Geography Sample Papers for 2021 Exam in Hindi Medium Mr. Arun
CBSE Class XI Geography Sample ess Papers for 2021 Exam in Hindi Medium
CBSE Class 11 Geography Hindi Medium Guess Papers 2021 Mr. Arun
CBSE Class XI Geography Guess Papers in Hindi Medium
Class 11 CBSE Geography Sample Paper Miss Shubhi
CBSE Class XI Geography Sample Papers for 2020 Examination
CBSE Class XI Geography Guess Paper 2020 Miss Shubhi
CBSE Class XI Geography Guess Papers for 2020 Board Examination
Class XI Geography Guess Paper in Hindi medium Miss Anju
CBSE Class XI Geography Guess Papers Based on CBSE syllabus.
Class XI Geography Sample Question Paper Miss Shubhi
Class XI Geography Sample Paper Based on CBSE Syllabus for 2019 Class XI
Geography Guess Paper Mr. Suryaveer Singh
- Accountancy
- Biotechnology
- Business Studies
- Computer Science
- Informatics Practices
- Mathematics
- Physical Education
- Multimedia and Web Technology
- Political Science

ABOUT CBSEGuess
Cbse book store, stay connected, shop online, cbseguess loves you.

NCERT Solutions for Class 11th: Ch 1 India - Location
Ncert solutions for class 11th: ch 1 india - location indian physical environment , contact form.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 Geography As A Discipline
Class 11 geography chapter 1 geography as a discipline.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 Geography As A Discipline, (Geography) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions withinside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck withinside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students solve all of the questions and maintain their studies with out a doubt, we have provided step by step NCERT Solutions for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated solutions as a way to similarly assist the students and answering the questions right.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 Geography as a Discipline
Class 11 geography chapter 1 geography as a discipline.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1(i). Which one of the following scholars coined the term ‘Geography’? (a) Herodotus (b) Erathosthenese (c) Galileo (d) Aristotle. Answer: (b) Erathosthenese
Question 1(ii). Which one of the following features can be termed as ‘physical feature’? (a) Port (b) Road (c) Plain (d) Water park. Answer: (c) Plain
Question 1(iii). Make correct pairs from the following two columns and mark the correct option.
(a) 1B’2C,3A,4D (b) 1A,2D,3B,4C (c) 1D,2B,3C,4A (d) 1C,2A,3D,4B. Answer: (d) 1C.2A,3D,4B
Question 1(iv). Which one of the following questions is related to cause-effect relationship? (a) Why (b) Where (c) What (d) When. Answer: (a) Why
Question 1(v). Which one of the following disciplines attempts temporal synthesis? (a) Sociology (b) Geography (c) Anthropology (d) History. Answer: (a) History.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Question 2(i). What important cultural features do you observe while going to school? Are they similar or dissimilar? Should they be included in the study of geography or not? If yes, why? Answer: When we go to school we see shops, theatres, roads, temple, mosque, church, houses, government offices, etc on the way. These represent cultural features. All of these features are dissimilar. Yes, these must be included in the study of geography as they play an important role in understanding human geography. They are an inseparable part of social and cultural geography.
Question 2(ii). You have seen a tennis ball, a cricket ball, an orange and a pumpkin. Which one amongst these resembles the shape of the earth? Why have you chosen this particular item to describe the shape of the earth? Answer: We have seen tennis ball, a cricket ball, an orange and a pumpkin. Amongst them an orange resembles the shape of the earth the most because tennis ball and cricket ball are almost circles or spheres and pumpkin is comparatively longer. But earth is geoid type flatter towards poles which is like an orange.
Question 2(iii). Do you celebrate Van Mahotsava in your school? Why do we plant so many trees? How do the trees maintain ecological balance? Answer: Yes, we celebrate Van Mahotsava in our school. We plant many trees on this occasion because trees provide us oxygen, food, rubber, paper, medicinal herbs and uncountable life-giving things. Plants take in carbon dioxide and give oxygen and in this way they maintain ecological balance.
Question 2(iv). You have seen elephants, deer, earthworms, trees and grasses. Where do they live or grow? What is the name given to this sphere? Can you describe some of the important features of this sphere? Answer: We have seen elephants, deer, earthworms, trees and grasses. They live and grow on the biosphere. Important features of biosphere are as follows:
- The combined form of land sphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere where life is possible is called biosphere.
- Plants and animals are biotic elements of biosphere while soil, water, air, etc are abiotic elements.
- Both moving and non-moving living beings are seen on the biosphere. Moving living beings include animals, insects, birdsr aquatic animals, human beings, etc while non-moving beings include trees, plants, grass, etc.
Question 2(v). How much time do you take to reach your school from your house? Had the school been located across the road from your house, how much time would you have taken to reach school? What is the effect of the distance between your residence and the school on the time taken in commuting? Can you convert time into space and vice versa? Answer: It takes me around one hour to reach my school. Had my school been located across the road from my house, I could reach there within two minutes. Due to long distance between my residence and school a lot of time gets wasted in commuting. It affects my studies as lesser time is left for studies. Space can be converted into time as we say that so and place is at 45 minutes distance from here but time cannot be converted into space.
3. Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
Question 3(i). You observe every day in your surroundings that there is variation in natural as well as cultural phenomena. All the trees are not of the same variety. All the birds and animals you see, are different. All these different elements are found on the earth. Can you now argue that geography is the study of “areal differentiation”? Answer: We observe every day in our surroundings that there is variation in natural as well as cultural phenomena. All the trees are not of the same variety. All the birds and animals we see, are different. All these different elements are found on the earth. It is right to say that Geography is the study of “areal differentiation” but it will be absolutely wrong to say that geography is the study of only “areal differentiation.”
Geography as a discipline is related to space and takes note of spatial characteristics and attributes. It studies the patterns of distribution, location and concentration of phenomena over space and interprets them providing explanations for these patterns. It takes note of the associations and inter- relationships between the phenomena over space and interprets them providing explanations for these patterns. It also takes note of the associations and inter-relationships between the phenomena resulting from the dynamic interaction between human beings and their physical environment. Geography helps in understanding the reality in totality in its spatial perspective. Geography, thus, not only takes note of the differences in the phenomena from place to place but integrates them holistically which may be different at other places.
Question 3(ii). You have already studied geography, history, civics and economics as parts of social studies. Attempt an integration of these disciplines highlighting their interface. Answer: Geography is an integrated discipline. 1. Geography and History: The geographical factors have modified the course of history in different parts of the world. Every geographical phenomenon undergoes change through time and can be explained temporarily. The changes in landforms, climate, vegetation, economic activities, occupations and cultural developments have followed a definite historical course.
2.Geography and Civics: The core concern of political science is territory, people and sovereignty while political geography is also interested in the study of the state as a spatial unit as well as people and their political behaviour.
3. Geography and Economics: Economics deals with basic attributes of the economy such as production, distribution, exchange and consumption. Each of these attributes also has spatial aspects and here comes the role of economic geography to study the spatial aspects of production, distribution, exchange and consumption.
Project Work
Select forest as a natural resource. (i) Prepare a map of India showing the distribution of different types of forests. (ii) Write about the economic importance of forests for the country. (iii) Prepare a historical account of conservation of forests in India with focus on Chipko movements in Rajasthan and Uttaranchal. Answer: (ii) Forests are very important for the economy of a country.
- Forests provide shelter to wild animals.
- We get wood from forests.
- We get paper, grass, bamboo, medicinal herbs, rubber, tea, coffee, food items, fodder from animals, etc from trees.
- Trees play an important role in preventing soil erosion.
(iii) Attempt yourself.
B enefits of NCERT Solution for Class 11
NCERT Solution for Class 11 contains extremely important points, and for each chapter, each concept has been simplified to make it easier to remember and increase your chances of achieving excellent exam results. Exam Preparation References Here are some tips on how these solutions can help you prepare for the exam.
- This helps students solve many of the problems in each chapter and encourages them to make their concepts more meaningful.
- NCERT Solution for Class 11 encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam.
- These NCERT Solution For Class 11 are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
- Most of the questions in the exam are formulated in a similar way to NCERT textbooks. Therefore, students should review the solutions in each chapter in order to better understand the topic.
- It is free of cost.
Tips & Strategies for Class 11 Exam Preparation
- Plan your course and syllabus and make time for revision
- Please refer to the NCERT solution available on the cbsestudyguru website to clarify your concepts every time you prepare for the exam.
- Use the cbsestudyguru learning app to start learning to successfully pass the exam. Provide complete teaching materials, including resolved and unresolved tasks.
- It is important to clear all your doubts before the exam with your teachers or Alex (an Al study Bot).
- When you read or study a chapter, write down algorithm formulas, theorems, etc., and review them quickly before the exam.
- Practice an ample number of question papers to make your concepts stronger.
- Take rest and a proper meal. Don’t stress too much.
Why opt for cbsestudyguru NCERT Solution for Class 11 ?
- cbsestudyguru provide NCERT Solutions for all subjects at your fingertips.
- These solutions are designed by subject matter experts and provide solutions to every NCERT textbook questions.
- cbsestudyguru especially focuses on making learning interactive, effective and for all classes.
- We provide free NCERT Solutions for class 11 and all other classes.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

case study questions class 11 geography

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Competency based questions Class 11 Geography
DPS Guwahati (CBSE Affiliated School) has recently published Competency based questions for the students of class 11. Here in this page we have given class 11 science competency based questions provided by DPS Guwahati school.
(1) The study of physical geography is emerging as a discipline of evaluating and managing-
(a) Natural resources
(b) Natural calamities
(c) All of the above
(d) Population distribution
(2) Arrange the following geological eras correctly-
(i) Cainozoic
(ii) Mesozoic
(iii) Palaeozoic
(iv) Pre Cambrian
(3) The …………………………..is spotted with domal hills of granite rocks-
(a) Malwa plateau
(b) Meghalaya plateau
(c) Chotanagpur plateau
(d) Karnataka plateau
(4) The word astheno means-
(a) Fragile
(b) Irregular
(d) Viscous
(5) India was a large island situated off the Australian coast, in a vast ocean. The ……………… separated it from the Asian continent till about 225 million years ago.
(a) Tethys Sea
(b) Aral Sea
(c) Caspian Sea
(d) Black Sea
(6) Position of the Indian subcontinent (mostly Peninsular India) is traced with the help of the rocks analysed from the …………… area.
(c) Nainital
(7) The …………………..location of Peninsular India has provided links to its neighbouring regions through the sea and air routes.
(a) Continental
(b) Insular
(c) Maritime
(d) Strategic
(8) Bounded by the Himalayas in the north, ………………… in the northwest, Purvanchal hills in the north-east and by the large expanse of the Indian ocean in the south, India forms a great geographic entity known as the Indian subcontinent.
(a) Zaskar and Pir Panjal ranges
(b) Ladakh and Dhaoladhar ranges
(c) Siwalik and Kirtar ranges
(d) Hindukush and Sulaiman ranges
(9) India’s territorial limit further extends towards the sea upto …………… from the coast.
(a) 12 nautical miles
(b) 11 nautical miles
(c) 13 nautical miles
(d) 10 nautical miles
(10) The ………………………is the second largest river of Kerala.
(b) Periyar
(c) Chaliyar
(d) Bharathapuzha
(15) Consider and evaluate the following statements and choose the correct answer for them from the given options.
(1) Geography as an integrating discipline has interface with numerous natural and social sciences.
(2) All the sciences, whether natural or social, have one basic objective, of understanding the reality. Geography attempts to comprehend the associations of phenomena as related in sections of reality.
(a) Only statement 1 is correct
(b) Only statement 2 is correct
(c) Both statements are incorrect
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
(16) Consider and evaluate the following statements and choose the correct answer for them from the given options.
(1) Geography has strong interface with natural and social sciences. It follows its own methodology of study which makes it distinct from others.
(2) It has osmotic relationship with other disciplines.
(b) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
(c) Only statement 2 is correct
(d) Both statements are incorrect
(17) Consider and evaluate the following statements and choose the correct answer for them from the given options.
(1) In India, Himalayas have acted as great barriers and provided protection but the passes provided routes to the migrants and invaders from Central Asia. The sea coast has encouraged contact with people from East and Southeast Asia, Europe and Africa. Navigation technology helped European countries to colonise a number of countries of Asia and Africa, including India as they got accessibility through oceans.
(2) The anthropo-geographic factors have modified the course of history in different parts of the world.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
(18) There is a general understanding among the countries of the world to select the standard meridian in multiples of 7°30′ of longitude. That is why 82°30′ E has been selected as the ‘standard meridian’ of India. Indian Standard Time is ahead of Greenwich Mean Time by-
(a) 5 hours and 40 minutes
(b) 5 hours and 20 minutes
(c) 5 hours and 30 minutes
(d) 5 hours and 10 minutes
Source Based Questions
According to Wegener, all the continents formed a single continental mass and mega ocean surrounded the same. The super continent was named PANGAEA, which meant all earth. The mega-ocean was called PANTHALASSA, meaning all water. He argued that, around 200 million years ago, the super continent, Pangaea, began to split. Pangaea first broke into two large continental masses as Laurasia and Gondwanaland forming the northern and southern components respectively. Subsequently, Laurasia and Gondwanaland continued to break into various smaller continents that exist today. A variety of evidence was offered in support of the continental drift.
(19) When did Wegener put forth the continental drift theory?
A volcano is a place where gases, ashes and/or molten rock material – lava – escape to the ground. A volcano is called an active volcano if the materials mentioned are being released or have been released out in the recent past. The layer below the solid crust is mantle. It has higher density than that of the crust. The mantle contains a weaker zone called asthenosphere. It is from this that the molten rock materials find their way to the surface. The material in the upper mantle portion is called magma. Once it starts moving towards the crust or it reaches the surface, it is referred to as lava. The material that reaches the ground includes lava flows, pyroclastic debris, volcanic bombs, ash and dust and gases such as nitrogen compounds, sulphur compounds and minor amounts of chlorene, hydrogen and argon.
(20) Name the place which is famous for active volcanoes.
(a) Costa Rica
(b) Barren Island
(c) Hawaiian islands
The configuration of the surface of the earth is largely a product of the processes operating in the interior of the earth. Exogenic as well as endogenic processes are constantly shaping the landscape. A proper understanding of the physiographic character of a region remains incomplete if the effects of endogenic processes are ignored. Human life is largely influenced by the physiography of the region. Therefore, it is necessary that one gets acquainted with the forces that influence landscape development. To understand why the earth shakes or how a tsunami wave is generated, it is necessary that we know certain details of the interior of the earth. In the previous chapter, you have noted that the earth-forming materials have been distributed in the form of layers from the crust to the core. It is interesting to know how scientists have gathered information about these layers and what are the characteristics of each of these layers.
(21) Give one example each on exogenic and endogenic processes.
(a) Action of running water and earthquake
(b) Earthquake and volcanoes
(c) Earthquake and Tsunamis
(d) Action of running water and wind
With the help of technology, human beings moved from the stage of necessity to a stage of freedom. They have put their imprints everywhere and created new possibilities in collaboration with nature. Thus, we now find humanised nature and naturalised human beings and geography studies this interactive relationship. The space got organised with the help of the means of transportation and communication network. The links (routes) and nodes (settlements of all types and hierarchies) integrated the space and gradually, it got organised.
(22) Humanised nature refers to the school of-
(a) Environmental Determinism
(b) Neo-determinism
(c) Possibilism
(d) Stop and Go Determinism
Diagram Based Questions
(23) Name the portion marked ‘A’ in the given diagram.

(a) Barysphere
(b) Asthenosphere
(c) Centrosphere
(d) Barosphere
(24) Identify the type of volcano.

(a) Cinder Cone
(b) Shield Volcano
(c) Composite
(d) Caldera
(25) Identify the features marked ‘A’ and ‘B’ on the given diagram.

(a) Lapholith and Shield volcano
(b) Batholith and Cinder Cone
(c) Laccolith and Composite volcano
(d) Dome and Caldera
(26) Identify the sub-field marked as A on the given diagram.

(a) Anthropology
(b) Ethnology
(c) Behavioral geography
(d) Archaeology
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Manipur board class 6 social science chapter 15 the first empire, rs aggarwal class 8 test paper 4 solutions of cube and cube roots.

Duff and Dutt question bunch class 10 My Own True Family Page 207, 208
New learning composite mathematics class 5 s.k. gupta anubhuti gangal perimeter and area chapter 17a solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 Drainage System
- Last modified on: 3 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes

Table of Contents
Taking a close look at the CBSE Sample Papers and Marking Scheme, we have pointed out the important topics for CBSE case study questions in Class 11 Geography. This is crucial info for students because it gives them a heads-up on changes in the exam pattern. To understand this better, students can check out this article of Class 11 case study questions here. It’s like a guide to help them prepare smartly for the exams.
Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 11 Geography. All chapters are covered. Students are suggested to go through each and every question to score better marks in the exam.
Drainage System Case Study
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
Related Posts
Cbse class 11 geography case study questions, old chapter list.
Fundamentals of Physical Geography
- Chapter 1 Geography as a Discipline
- Chapter 2 The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
- Chapter 3 Interior of the Earth
- Chapter 4 Distribution of Oceans and Continents
- Chapter 5 Minerals and Rocks
- Chapter 6 Geomorphic Processes
- Chapter 7 Landforms and their Evolution
- Chapter 8 Composition and Structure of Atmosphere
- Chapter 9 Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature
- Chapter 10 Atmospheric Circulation and Weather Systems
- Chapter 11 Water in the Atmosphere
- Chapter 12 World Climate and Climate Change
- Chapter 13 Water (Oceans)
- Chapter 14 Movements of Ocean Water
- Chapter 15 Life on the Earth
- Chapter 16 Biodiversity and Conversation
Geography: India Physical Environment
- Chapter 1 India: Location
- Chapter 2 Structure and Physiography
- Chapter 3 Drainage System
- Chapter 4 Climate
- Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- Chapter 6 Soils
- Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
Practical Work in Geography
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Maps
- Chapter 2 Map Scale
- Chapter 3 Latitude, Longitude and Time
- Chapter 4 Map Projections
- Chapter 5 Topographical Maps
- Chapter 6 Introduction to Aerial Photographs
- Chapter 7 Introduction to Remote Sensing
- Chapter 8 Weather Instruments, Maps and Charts
Importance of Practicing Case Based and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Geography
Practicing case study and passage-based questions in Class 11 geography is pretty valuable. Here’s why:
- Real-world Application: Geography often deals with real-world situations. Case studies help you apply your theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, making your learning more meaningful.
- Analytical Skills: These questions require you to analyze information from passages and case studies, honing your analytical skills. This is crucial not just for exams but for understanding complex geographical issues in the world.
- Understanding Different Perspectives: Geography involves diverse perspectives on issues like climate change, urbanization, and resource management. Working on case studies helps you appreciate different viewpoints and develop a well-rounded understanding.
- Exam Preparation: Since these types of questions are common in exams, practicing them prepares you for what to expect. It ensures you’re comfortable tackling such questions during the actual test.
- Enhanced Research Skills: Case studies often require additional research to fully comprehend the context. This enhances your research skills, an important aspect of studying geography.
- Critical Thinking: Dealing with passages and case studies encourages critical thinking. You’re not just memorizing facts; you’re evaluating information and forming reasoned conclusions.
- Practical Application of Concepts: Geography isn’t just about memorizing facts and figures. Case studies allow you to practically apply the concepts you’ve learned in the classroom to real-world situations.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

GEOGRAPHY SOURCE-BASED QUESTIONS FOR CLASS IX

Written By Avinash Sharan
Class 9 | geography 9, 2 comment(s), 28th august 2022, geography source-based questions with answers from chapter 1.
Geography Source-based questions (SBQ) in Social Science is a new introduction in the question paper by CBSE. What is unique about Geography source-based questions ? While the topic is from the textbook, the questions may not be directly from the paragraph. How can a student perform well if the questions are from outside the textbook? Well, a student needs to apply the following three strategies to attempt Geography source-based questions (SBQ). They are:
Firstly, Read the chapter line by line.
Secondly, Develop an understanding of the topic.
Thirdly, Practice a lot to master s ource-based questions .
India-Size & Location – Chapter 1 For Practice

Geography source-based questions for class IX students
Q1. Geography Source-Based Questions From India – Size & Location
India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere. The mainland extends between latitudes 8°4’N and 37°6’N and longitudes 68°7’E and 97°25’E. The Tropic of Cancer (23° 30’N) divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea respectively. Find out the extent of these groups of islands from your atlas. The land mass of India has an area of 3.28 million square km. India’s total area accounts for about 2.4 percent of the total geographical area of the world. India is the seventh largest country in the world note that the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of the mainland is about 30°. Despite this fact, the east-west extent appears to be smaller than the north-south extent.
Read the paragraph carefully and answer the following questions:
i) What is the Latitudinal extent of India? 1.
a) 8°4’E and 37°6’W
b) 8°4’N and 37°6’S
c) 8°4’N and 37°6’N
d) 8°4’S and 37°6’S
Ans. c) 8°4’N and 37°6’N
ii) What is the Longitudinal extent of India? 1.
a) 68°7’E and 97°25’E
b) 68°7’W and 97°25’E
c) 68°7’E and 97°25’W
d) 68°7’N and 97°25’S
Ans. a) 68°7’E and 97°25’E
iii) Why the east-west extent of India appears to be smaller than the north-south extent? 2.
Ans. The distance between lines of latitude remains the same from the equator to the poles.
But, the distance between the lines of longitudes decreases as we move towards the poles.
India is slightly above the equator.
So, the lines of longitude come nearer and the East-West distance becomes less than the North-South distance.
8 Facts About Latitudes and Longitudes Which Is Not Explained In Schools
Q2. Topic: India’sLocation and Standard Time Meridian
India is bounded by the young fold mountains in the northwest, north, and northeast. South of about 22° north latitude, it begins to taper and extends towards the Indian Ocean, dividing it into two seas, the Arabian Sea on the west and the Bay of Bengal on its east. Note that the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of the mainland is about 30°. From Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh, there is a time lag of two hours. Hence, time along the Standard Meridian of India passing through Mirzapur (in Uttar Pradesh) is taken as the Indian standard time for the whole country. The latitudinal extent influences the duration of day and night, as one moves from south to north.
i) Name the young fold mountains that bound India from the northwest, north, and northeast. 1.
a) Aravalis
b) Himalayas
c) Karakoram
d) Purvanchal hills.
Ans. b) Himalayas
ii) If the time at the easternmost longitude of India is 11:30 P.M. What will be the time at the westernmost longitude of India? 1.
a) 1:30 A.M.
b) 1: 30 P.M.
c) 9:30 A.M.
d) 9:30 P.M.
Ans) d) 9:30 P.M.
How to calculate time using longitudes explained Step by step
iii) Which Longitude is considered the Indian Standard Time meridian for India and why? 2.
Ans) 82°30’E Longitude is considered the Indian Standard Time meridian for India.
This is because India’s Longitudinal extent is 68°7’E and 97°25’E.
It means almost 30 longitudes pass through India.
We know that there is a time difference of 4 minutes between two longitudes.
In such a case time at every place in India will be different and will create a lot of confusion.
Therefore, 82°30’E Longitude which passes through the center of India has been considered the Indian Standard Time meridian for India to avoid such confusion.
Q3. Topic: Source-Based Questions From India and The World
The Indian landmass has a central location between East and West Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian continent. The trans-Indian Ocean routes , which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia, provide a strategic central location for India. Note that the Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast. No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has and indeed, it is India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean, which justifies the naming of an Ocean after it.
i) What provides a strategic central location for India? 1.
Ans. The trans-Indian Ocean routes, which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia, provide a strategic central location for India.
ii) How did India get benefit from its long coastline? 1.
Ans. The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast. No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean.
III) Give two reasons which justify the naming of an Ocean after India. 2.
Ans. Two reasons which justify the naming of an Ocean after India are:
a) India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean
b) No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has.
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA – CLASS IX
4. Topic: India and the World
India’s contacts with the World have continued through ages but her relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contacts. The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travelers, while the oceans restricted such interaction for a long time. These routes have contributed to the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals, and the decimal system thus could reach many parts of the world. The spices, muslin, and other merchandise were taken from India to different countries. On the other hand, the influence of Greek sculpture, and the architectural styles of domes and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of our country.
i) Do you think the ocean routes helped India to establish close contact with the world during ancient times? 1.
Ans. No, it is the land routes and the passes across the mountains that helped India to establish close contact with the world during ancient times.
ii) What is India’s contribution to the world? 1.
Ans. India has contributed the ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals, and the decimal system along with spices and muslin to the world.
iii) What India has learned from other countries of the world? 2.
Ans. a) Greek sculpture, and
b) the architectural styles of domes and minarets.
5. Topic: Source-Based Questions From India’s Neighbours
India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia. India has 28 states and Eight Union Territories India shares its land boundaries with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north, and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east. Our southern neighbors across the sea consist of the two island countries, namely Sri Lanka and the Maldives . Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar , while the Maldives Islands are situated to the south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
i) Name a newly formed state and union territory of India? 1.
Ans. State – Telangana
Union Territory – Ladakh
ii) Sri Lanka and the Maldives lie in which sea/oceans? 1.
Ans. Both lie in the Indian Ocean.
iii) What is the old name of Myanmar? Which Indian states share borders with Myanmar? 2.
Ans. Burma is the old name of Myanmar.
Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram are the Indian states that share borders with Myanmar.
Conclusion: Source-Based Questions From India – Size & Location
Geography source-based questions are not very easy to answer. You need to practice a lot to answer Geography source-based questions. India – size & location is a small chapter but it has many concepts of Geography. Therefore, many types of source-based questions can be asked in this chapter. Solve all the above Geography source-based questions before going to the examination hall. I Hope, these Geography source-based questions will increase your understanding. Finally, It will also help you to easily attempt Geography source-based questions.
Now, would you like to attempt a challenging question?
What is the capital of Myanmar? Do write to me as soon as possible.
All the best.
You may like to read
Class IX Geography NTSE- Most expected questions
Project On Tsunami: 13 Pages You Must Include In Your Disaster Management Project
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

Disaster Management Project Page-Wise With Subheadings
Apr 20, 2024
How To Write a Disaster Management Project Page-wise? Most school students ask how to effectively write a disaster...

The Disaster Management Project 2024 On Nuclear War
Apr 17, 2024
Disaster Management Project 2024 On Nuclear War for class IX Disaster Management Project on Nuclear War is an...

Uncovering the Effects of Natural Disasters on Communities – A Disaster Management Project
Apr 14, 2024
Effects of Natural Disasters on Communities Natural disasters may be fatal as well as create economic, social, and...
Great Article Nice Information Enjoyed Reading It Thankyou for Sharing it
Thank you Kamaljeet. Keep visiting. Very soon we are going to upload more questions.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Case Study questions for Class 11 Geography are designed to test students' ability to apply knowledge to real-world scenarios. You will need to use your critical thinking and problem-solving skills to come up with the best solution. Class 11 Geography case study questions are meant to challenge you and help you hone your skills.
Importance of Practicing Case Based and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Geography. Practicing case study and passage-based questions in Class 11 geography is pretty valuable. Here's why: Real-world Application: Geography often deals with real-world situations. Case studies help you apply your theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios ...
3 months ago January 31, 2024 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 11 Geography Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters. ... 2024 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 11 Geography Chapter 9 Solar Radiation Heat Balance and Temperature.
Class 11 Geography Case Study Questions. The idea behind introducing the Case Study questions is to enhance competency-based learning among the students. Learners need to apply their problem-solving skills to get through these case-based questions. The senior secondary Geography syllabus aims to make the students understand the fundamental ...
Geography Class 11 Sample Paper Marking Scheme Question Paper Design 2023-24. Chapter Name. Periods. Weightage. Unit I Geography as a discipline. Chapter 1 Geography as a Discipline. 5. 3. Unit II The Earth.
Question papers of Class 11 Geography. MyCBSEguide provides CBSE Class 11 Question Paper of Geography for the year 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015 with solutions in PDF format for free download. The previous year question papers last 10 year for all - NCERT books and based on CBSE latest syllabus must be downloaded and practiced by students.
Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 NCERT Extra Questions Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions. Question 1. We study under physical geography: (a) Weather, soil, atmosphere, etc. (b) Agriculture (c) Population, Industry (d) Urban and rural settlement. Answer: (a) Weather, soil, atmosphere, etc. Question 2.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Geography: Fundamentals of Physical Geography. Chapter 1 Geography as a Discipline. Chapter 2 The Origin and Evolution of the Earth. Chapter 3 Interior of the Earth. Chapter 4 Distribution of Oceans and Continents. Chapter 5 Minerals and Rocks. Chapter 6 Geomorphic Processes. Chapter 7 Landforms and their Evolution.
Class 11 NCERT solutions answers all the questions given in the NCERT textbooks in a step-by-step process. Our Geography tutors have helped us put together this for our Class 11 Students. The solutions on Shaalaa will help you solve all the NCERT Class 11 Geography questions without any problems.
Q.18. Geography is an integration of social sciences and physical sciences. Explain? Ans: (i) Geography is an integration of social sciences and physical sciences as the basic aim of both is to understand the reality of nature.All the social science disciplines, viz, sociology, political science, demography study different aspects of social reality.
February 13, 2024. in 11th Class. Class 11 Geography Question Bank is hereby published. These are chapter-wise important questions for class 11 Geography in Hindi and English medium. You can solve these Geography questions after studying the class 11 Geography book thoroughly. Moreover this class 11 question bank helps you score full marks in ...
Informatics Practices. Mathematics. Physics. Physical Education. Multimedia and Web Technology. Political Science. CBSE Geography Class 11 Practice Papers for students appearing in CBSE Exams Conducted by CBSE. Class 11 CBSE Geography Practice Papers Free download for Teachers By CBSEGuess Experts.
Answer. A gulf is a large body of water that is almost encircled by land except for a small mouth that is opened out to the ocean. A strait is a naturally formed narrow strip of water between two continents, islands or two larger bodies of water. 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
NCERT Solution for Class 11 encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam. These NCERT Solution For Class 11 are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 3 | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download. Q.1. The consequence of erosion is: (a) rockslide ( b ) sliding ( c ) depo
Answer: The Class 11 Geography list of important questions are given on this page. Students who wish to learn the important questions can refer to the entire page and find the questions along with answers. Your preparation becomes easy by reading the entire questions available here. Question 2.
Here in this page we have given class 11 science competency based questions provided by DPS Guwahati school. Section- A. (1) The study of physical geography is emerging as a discipline of evaluating and managing-. (a) Natural resources. (b) Natural calamities. (c) All of the above.
Importance of Practicing Case Based and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Geography. Practicing case study and passage-based questions in Class 11 geography is pretty valuable. Here's why: Real-world Application: Geography often deals with real-world situations. Case studies help you apply your theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios ...
Here we are providing Class 11 Geography Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Atmospheric Circulation and Weather Systems. ... Air mass is important for climatological study. Air masses are related to atmospheric disturbances, cyclones, storms, and fronts. ... In each case, precipitation is likely to occur because warm air is rising ...
Answer: The endogenetic and exogenetic forces causing physical; stresses and chemical actions on earth materials and bringing about changes in the configuration of the earth's surface are known as geomorphic processes. Diastrophism and volcanism are endogenetic geomorphic processes. Question 2.
Q1. Geography Source-Based Questions From India - Size & Location. India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere. The mainland extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E. The Tropic of Cancer (23° 30'N) divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and ...