Charles Darwin

(1809-1882)

Who Was Charles Darwin?
Charles Robert Darwin was a British naturalist and biologist known for his theory of evolution and his understanding of the process of natural selection. In 1831, he embarked on a five-year voyage around the world on the HMS Beagle , during which time his studies of various plants and an led him to formulate his theories. In 1859, he published his landmark book, On the Origin of Species .
Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, in the tiny merchant town of Shrewsbury, England. A child of wealth and privilege who loved to explore nature, Darwin was the second youngest of six kids.
Darwin came from a long line of scientists: His father, Dr. R.W. Darwin, was a medical doctor, and his grandfather, Dr. Erasmus Darwin, was a renowned botanist. Darwin’s mother, Susanna, died when he was only eight years old.
His father hoped he would follow in his footsteps and become a medical doctor, but the sight of blood made Darwin queasy. His father suggested he study to become a parson instead, but Darwin was far more inclined to study natural history.
While Darwin was at Christ's College, botany professor John Stevens Henslow became his mentor. After Darwin graduated Christ's College with a bachelor of arts degree in 1831, Henslow recommended him for a naturalist’s position aboard the HMS Beagle .
The ship, commanded by Captain Robert FitzRoy, was to take a five-year survey trip around the world. The voyage would prove the opportunity of a lifetime for the budding young naturalist.
On December 27, 1831, the HMS Beagle launched its voyage around the world with Darwin aboard. Over the course of the trip, Darwin collected a variety of natural specimens, including birds, plants and fossils.
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S CHARLES DARWIN FACT CARD

Darwin in the Galapagos
Through hands-on research and experimentation, he had the unique opportunity to closely observe principles of botany, geology and zoology. The Pacific Islands and Galapagos Archipelago were of particular interest to Darwin, as was South America.
Upon his return to England in 1836, Darwin began to write up his findings in the Journal of Researches , published as part of Captain FitzRoy's larger narrative and later edited into the Zoology of the Voyage of the Beagle .
The trip had a monumental effect on Darwin’s view of natural history. He began to develop a revolutionary theory about the origin of living beings that ran contrary to the popular view of other naturalists at the time.
Theory of Evolution
Darwin’s theory of evolution declared that species survived through a process called "natural selection," where those that successfully adapted or evolved to meet the changing requirements of their natural habitat thrived and reproduced, while those species that failed to evolve and reproduce died off.
Through his observations and studies of birds, plants and fossils, Darwin noticed similarities among species all over the globe, along with variations based on specific locations, leading him to believe that the species we know today had gradually evolved from common ancestors.
Darwin’s theory of evolution and the process of natural selection later became known simply as “Darwinism.”
At the time, other naturalists believed that all species either came into being at the start of the world or were created over the course of natural history. In either case, they believed species remained much the same throughout time.
'Origin of Species'
In 1858, after years of scientific investigation, Darwin publicly introduced his revolutionary theory of evolution in a letter read at a meeting of the Linnean Society . On November 24, 1859, he published a detailed explanation of his theory in his best-known work, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection.
In the next century, DNA studies provided scientific evidence for Darwin’s theory of evolution. However, controversy surrounding its conflict with Creationism — the religious view that all of nature was born of God — is still found among some people today.
Social Darwinism
Social Darwinism is a collection of ideas that emerged in the late 1800s that adopted Darwin’s theory of evolution to explain social and economic issues.
Darwin himself rarely commented on any connections between his theories and human society. But while attempting to explain his ideas to the public, Darwin borrowed widely understood concepts, such as “survival of the fittest” from sociologist Herbert Spencer.
Over time, as the Industrial Revolution and laissez faire capitalism swept across the world, social Darwinism has been used as a justification for imperialism, labor abuses, poverty, racism, eugenics and social inequality.
Following a lifetime of devout research, Charles Darwin died at his family home, Down House, in London, on April 19, 1882. He was buried at Westminster Abbey .
More than a century later, Yale ornithologist Richard Brum sought to revive Darwin's lesser-known theory on sexual selection in The Evolution of Beauty .
While Darwin's original attempts to cite female aesthetic mating choices as a driving force of evolution was criticized, Brum delivered an effective argument via his expertise in birds, earning selection to The New York Times ' list of 10 best books of 2017.
QUICK FACTS
- Name: Charles Darwin
- Birth Year: 1809
- Birth date: February 12, 1809
- Birth City: Shrewsbury
- Birth Country: England
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection. His views and “social Darwinism” remain controversial.
- Science and Medicine
- Astrological Sign: Aquarius
- University of Edinburgh
- Interesting Facts
- Although Charles Darwin originally went to college to be a physician, he changed career paths when he realized that he couldn't stomach the sight of blood.
- Charles Darwin had a mountain named after him, Mount Darwin, in Tierra del Fuego for his 25th birthday. The monumental gift was given by Captain FitzRoy.
- Death Year: 1882
- Death date: April 19, 1882
- Death City: Downe
- Death Country: England
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Charles Darwin Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/scientists/charles-darwin
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E; Television Networks
- Last Updated: March 29, 2021
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- A man who dares to waste one hour of time has not discovered the value of life.
- [How great the] difference between savage and civilized man is—it is greater than between a wild and [a] domesticated animal.
- If all men were dead, then monkeys make men. Men make angels.
- I am a complete millionaire in odd and curious little facts.
- Multiply, vary, let the strongest live and the weakest die.
- For the shield may be as important for victory, as the sword or spear.
- I see no good reason why the views given in this volume should shock the religious feelings of anyone."[In 'Origin of the Species']
- A grain in the balance may determine which individuals shall live and which shall die—which variety or species shall increase in number, and which shall decrease, or finally become extinct.
- If it could be demonstrated that any complex organ existed, which could not possibly have been formed by numerous, successive, slight modifications, my theory would absolutely break down. But I can find out no such case.
- The extinction of species and of whole groups of species, which has played so conspicuous a part in the history of the organic world, almost inevitably follows from the principle of natural selection.
- There is grandeur in this view of life...from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved.
Famous British People

Mick Jagger

Agatha Christie

Alexander McQueen

The Real Royal Scheme Depicted in ‘Mary & George’

William Shakespeare

Anya Taylor-Joy

Kate Middleton, Princess of Wales

Kensington Palace Shares an Update on Kate

Amy Winehouse

Prince William

Where in the World Is Kate Middleton?
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Charles darwin.
Charles Darwin and his observations while aboard the HMS Beagle , changed the understanding of evolution on Earth.
Biology, Earth Science, Geography, Physical Geography
Historic photograph of Charles Darwin in profile.
Photograph by Chronical/Alamy Stock Photo

Charles Darwin was born in 1809 in Shrewsbury, England. His father, a doctor, had high hopes that his son would earn a medical degree at Edinburgh University in Scotland, where he enrolled at the age of sixteen. It turned out that Darwin was more interested in natural history than medicine—it was said that the sight of blood made him sick to his stomach. While he continued his studies in theology at Cambridge, it was his focus on natural history that became his passion.
In 1831, Darwin embarked on a voyage aboard a ship of the British Royal Navy, the HMS Beagle, employed as a naturalist . The main purpose of the trip was to survey the coastline of South America and chart its harbors to make better maps of the region. The work that Darwin did was just an added bonus.
Darwin spent much of the trip on land collecting samples of plants, animals, rocks, and fossils . He explored regions in Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and remote islands such as the Galápagos. He packed all of his specimens into crates and sent them back to England aboard other vessels.
Upon his return to England in 1836, Darwin’s work continued. Studies of his samples and notes from the trip led to groundbreaking scientific discoveries. Fossils he collected were shared with paleontologists and geologists, leading to advances in the understanding of the processes that shape the Earth’s surface. Darwin’s analysis of the plants and animals he gathered led him to question how species form and change over time. This work convinced him of the insight that he is most famous for— natural selection . The theory of natural selection says that individuals of a species are more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their genes to the next generation when they inherit traits from their parents that are best suited for that specific environment. In this way, such traits become more widespread in the species and can lead eventually to the development of a new species .
In 1859, Darwin published his thoughts about evolution and natural selection in On the Origin of Species . It was as popular as it was controversial. The book convinced many people that species change over time—a lot of time—suggesting that the planet was much older than what was commonly believed at the time: six thousand years.
Charles Darwin died in 1882 at the age of seventy-three. He is buried in Westminster Abbey in London, England.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Charles Darwin: Biography, Theories, Contributions
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
Duncan1890 / Getty Images
Biography of Charles Darwin
- Best Known For
Natural Selection and Evolution
- Controversies
- Research on Emotions
- Views on Women
- Contributions
Charles Darwin was a renowned British naturalist and biologist best known for his theory of evolution through natural selection. His theory that all life evolved from a common ancestor is now a cornerstone of modern science, making Darwin one of the most influential individuals in history. It is difficult to overstate the monumental influence his work has had on our scientific understanding of the world.
This article discusses Charles Darwin's life and work, including his famous theory of natural selection as well as some of his lesser-known research on human emotion.
Charles Darwin was born in Shrewsbury, England, on February 12, 1809. His father was a wealthy doctor, and his grandfather on his mother's side was the noted potter Josiah Wedgwood. After his mother’s death when he was eight, Darwin began attending boarding school with his older brother.
Darwin originally began his studies at the University of Edinburgh Medical School, but later developed an interest in ministry and botany, eventually receiving his degree from Cambridge in 1831.
His famed voyage to the Galapagos Islands led to the observations that served as the basis for Darwin's groundbreaking theory of natural selection.
In 1839, Darwin married his cousin Emma Wedgwood. They had 10 children together, with seven surviving to adulthood. In 1859, he published his observations and ideas in his book "On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection."
Darwin's ideas were heavily debated in his own time and continue to spark controversy today. In contrast to this, Darwin himself lived a secluded life at his home in England, where he continued to work as a highly regarded scientist.
Darwin died on April 19, 1882, and is buried at Westminster Abbey in London, England.
Darwin's Illness
For much of his adult life, Darwin had an undiagnosed chronic illness that limited his activities. Symptoms included physical complaints such as stomach pain and dizziness, as well as signs of panic attacks such as shortness of breath and heart palpitations.
One theory suggests that he may have had panic disorder with agoraphobia . This diagnosis would also explain his secluded lifestyle, difficulty with public speaking, and struggles when meeting with colleagues.
Other proposed diagnoses include mercury poisoning, allergies, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. However, many researchers now believe that he had an adult-onset mitochondrial disorder.
What Was Charles Darwin Most Famous For?
Charles Darwin is most famous for his theory of evolution through the process of natural selection. Since introducing his ideas in “On the Origin of the Species,” his work has revolutionized the scientific understanding of how species evolve over time. This helped lay the foundation for modern biological sciences .
His Studies on the Galapagos Islands
During a voyage on a ship called the HMS Beagle, Darwin traveled to the Galapagos Islands, a journey that had a profound influence on his thinking and ideas. During this trip, he noticed interesting variations in the different species of finches that lived on the islands.
The beaks of these birds appeared to vary depending on the native food sources where the birds lived. Darwin hypothesized that the variations he observed resulted from natural selection that favored birds with beaks suited to the local food sources.
There are 14 species of finches found on the Galapagos Islands, which are now collectively referred to as "Darwin's finches."
In “On the Origin of the Species,” Darwin suggested that all species on Earth, including humans, evolved from common ancestors. The diversity found in all species, he explained, results from changes that occur gradually over very long periods of time, a process he referred to as “descent with modification.” This happens through natural selection, where certain traits that benefit an organism's survival are more likely to be passed down.
Because these organisms are more likely to survive and reproduce, those beneficial traits are more likely to be handed down. This leads to the adaptation and evolution of species.
Charles Darwin's concept of evolution through natural selection suggested that species change slowly over time as a response to their environment. This theory changed our scientific understanding of the diversity of life on Earth and laid the groundwork for the development of modern biology.
How Does Natural Selection Work?
According to Darwin, the individuals within a population possess variations, some of which are better suited to the environment in which they live. As a result, those with these adaptations are more likely to survive, reproduce, and thus pass these advantageous characteristics down to their offspring.
Over time, this process gradually leads the adaptive traits to become more prominent and can eventually lead to the emergence of new species.
The Five Principles of Natural Selection
The five principles of natural selection described by Charles Darwin can be remembered using the acronym VISTA, standing for variation, inheritance, selection, time, and adaptation.
- Variation : In all populations of any species, there are individual variations in different traits. The species' members can vary in appearance, size, abilities, immunity, and numerous other characteristics. Many of these variations result from genetic inheritance but can also occur due to random mutations.
- Inheritance : The various traits organisms possess can be inherited through genetic inheritance. In other words, when members of a species reproduce, their offspring are more likely to also possess those same traits.
- Selection : Environmental resources are limited, so organisms with advantageous characteristics that make it easier for them to survive are more likely to thrive in their environment and reproduce. This increased chance of reproduction means that their children are more likely to have the same traits that helped their ancestors survive.
- Time : As time passes, each generation continues to produce more offspring with advantageous characteristics. With the passage of time, the beneficial traits continue to accumulate, resulting in significant changes in the characteristics of the entire population.
- Adaptation : Such traits eventually become more common in the population, making the entire species better suited to survive in their environment.
What Does ‘Survival of the Fittest’ Mean?
An important part of natural selection is the idea of ‘survival of the fittest.’ The phrase was first introduced in 1854 by Herbert Spencer in his book "The Principles of Biology."
The idea suggests that when it comes to each organism's struggle to survive and reproduce, those with traits that make them the best suited to their environment are the most likely to survive and pass down their genes to the next generation.
In this context, "fitness" refers to an organism's ability to survive in its environment and reproduce. It is the traits that help the individual survive that are considered most advantageous.
Fitness does not refer to physical strength. Instead, it means the individual has traits that make them better suited for life in a specific environment. For example, an organism with coloring that camouflages it from predators would be considered a better fit, from an evolutionary perspective, than coloring that makes it more susceptible to becoming prey.
Fitness can refer to a wide variety of characteristics. This might include physical attributes such as camouflage, speed, strength, or agility. It might also refer to behavioral adaptations that confer a greater chance of survival. Migration, hibernation, and courtship behaviors are a few examples of behavioral adaptations influenced by evolution.
Controversies Surrounding Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Darwin's theory was considered shocking and controversial after its introduction. While the theory is accepted by nearly all scientists today, Darwin's ideas are still disputed or rejected by some people.
Darwin and his work have remained controversial in the more than 140 years since his death. One survey found that a third of U.S. adults reject the idea that humans evolved through natural selection, views that correspond with rates of religious belief.
One critic during Darwin's time was the English comparative anatomist and paleontologist Richard Owen. While Owen agreed that evolution occurred, he was a vocal critic of Darwin's idea of natural selection. Instead, he proposed the existence of predetermined "archetypes" that guide the evolutionary changes that species experience.
During Darwin's time, some critics suggested that the lack of transitional fossils (demonstrating the gradual progression of a species over time) was evidence that Darwin’s evolutionary theory was wrong. In the subsequent years, however, many of these so-called "missing links" have been added to the fossil record, providing paleontological support for these evolutionary transitions.
Other critics focus on their belief that all life results from divine creation. However, it is important to note that Darwin's theory of evolution does not focus on how life originated. Instead, Darwin's theory of natural selection explains how life evolved over time and how this explains the diversity of life on Earth.
While there have been debates and criticisms from various sources, it is important to note that Darwin was highly regarded in his own time. Support from the scientific community continued to build over the years, and more evidence supporting Darwin's theory accumulated from various fields.
Charles Darwin’s Research on Human Emotions
While Darwin is best known for his theory of evolution, he also studied and wrote about a wide range of topics, from plants to sea life. Beyond his work as a naturalist, he also conducted one lesser-known experiment on the study of human emotions , making him one of the earliest experimental psychology researchers.
In archival research looking at Darwin's letters and other writings, researchers found references to a small experiment that Darwin had conducted at home. Darwin had corresponded with the French physician Guillaume Duchenne de Boulogne, who had used electrical impulses to stimulate facial muscles into specific expressions, which were then recorded on photographic plates. Using this method, Duchenne suggested that the human face is capable of expressing at least 60 distinct emotions.
Darwin disagreed. Using Duchenne's plates, Darwin devised his own experiment, a single-blind study in which he randomized the order of the plates and then presented them to over 20 participants (i.e., Darwin's guests). He then asked his guests to identify the emotions represented in the photographic slides.
In studying Darwin's notes, researchers discovered that the participants agreed when it came to the basic emotions , such as happiness , surprise, and fear. For more ambiguous photographs, responses were much more mixed.
In Darwin's view, only those emotions that were readily identifiable and agreed upon by observers represented universal emotions.
Darwin's observations and conclusions in this and other studies he conducted helped inform his 1872 book "The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals." In this book, Darwin emphasized the importance of emotional expression in both humans and animals, suggesting that:
- Some emotional expressions are universal
- Some emotions have a biological, evolutionary basis
- These universal expressions evolved through natural selection because they aid in survival, reproduction, and communication
- Humans and animals display similar emotions, suggesting they have a common evolutionary origin
Darwin's work offered insights into the importance of emotions, their evolutionary roots, and their universality across cultures and species . His observations also helped lay the groundwork for future research on the psychology of human emotions.
However, Darwin's ideas about emotion were eclipsed by his more famous theory of natural selection. It wasn't until the 1960s that psychologist Paul Ekman returned to Darwin's findings and, using methods similar to those originally pioneered by Darwin, found additional evidence for the existence of basic, universal human emotions.
Try the emotion experiment yourself!
The Darwin Correspondence Project allows viewers to see the original photographic plates Duchenne and Darwin used this in their experiments. You can also give your own response and see how your interpretation compares to those of Darwin's guests.
What Were Charles Darwin’s Views on Women?
While Darwin revolutionized the field of science, his views on women were far from progressive. His attitudes reflected the prevailing sexist, misogynistic ideas of his time. In his published writings, he echoed the societal and cultural beliefs that women were inferior to men, viewing them as less intelligent.
In his book "The Descent of Man," Darwin wrote, "Woman seems to differ from man in her mental disposition, chiefly in her greater tenderness and less selfishness."
Darwin suggested that the purported superiority of men stemmed from sexual selection, a mode of natural selection in which men compete for mates, leading to the evolution of characteristics that improve their reproductive fitness, including intelligence, physical strength, and competitiveness.
He believed that women's roles were primarily as domestic caretakers and nurturers, which, in his view, did not require strong intellectual capabilities.
There is evidence that Darwin's ideas changed somewhat over time, often influenced by the women in his life, including his wife, daughters, and women intellectuals. While he could not be regarded as a feminist thinker, research on his private correspondence suggests that his views on women were more complex than what appears in his published writing.
Who Did Charles Darwin Influence?
In addition to his profound influence on the biological sciences, Darwin inspired a number of other scientists and researchers in their own work.
Some of these thinkers included:
- Alfred Russel Wallace : A contemporary of Darwin, Wallace was an English naturalist and explorer who independently introduced the idea of evolution through natural selection. His own ideas were published in 1858 along with some of Darwin's earlier writings, prompting Darwin to publish "On the Origin of the Species" the next year.
- William James : The founder of the functionalist school of thought in psychology was heavily influenced by the work of Charles Darwin. This school of thought suggests that the functions of the mind exist because they serve a purpose in survival and adaptation. This idea has its roots in Darwin's theory of natural selection. James was also heavily influenced by Darwin's writings on the topic of emotions. According to the James-Lange theory of emotions , emotions stems from the physiological reactions people experience in response to environmental stimuli.
- Ronald A. Fisher : A British mathematician and biologist, Fisher is considered a founder of modern statistical science. He also played an important role in what is known as modern synthesis, which involved integrating Darwin's natural selection with Mendelian genetics in order to explain how genetic variations within a group can be affected by natural selection.
How Does Charles Darwin’s Work Affect Modern Science Today?
It is difficult to overstate the enormous impact of Darwin's work on modern science. Some of the ways that science continues to be impacted by Darwin's theory of evolution include:
- Evolutionary sciences : The theory of evolution plays an essential role in biology as well as other fields that explain how life has adapted and changed over time, including genetics and evolutionary psychology .
- Medicine : Researchers continue to use their understanding of evolutionary science to study how diseases originate, spread, and mutate.
- Scientific education : While Darwin's ideas remain controversial for some, his work has helped advance scientific literacy and understanding among the general public.
Barloon TJ, Noyes R Jr. Charles Darwin and panic disorder . JAMA . 1997;277(2):138-141. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540260052035
Hayman J, Finsterer J. Charles Darwin's mitochondrial disorder: Possible neuroendocrine involvement . Cureus . 2021;13(12):e20689. doi:10.7759/cureus.20689
Cohen JI. Exploring the nature of science through courage and purpose: a case study of Charles Darwin's way of knowing . Springerplus . 2016;5(1):1532. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-3053-0
Palmer DH, Kronforst MR. Divergence and gene flow among Darwin's finches: A genome-wide view of adaptive radiation driven by interspecies allele sharing . Bioessays . 2015;37(9):968-974. doi:10.1002/bies.201500047
National Academy of Sciences (US). Evidence Supporting Biological Evolution . Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences: Second Edition. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1999.
American Museum of Natural History. How does natural selection work ?
Offer J. From ‘natural selection’ to ‘survival of the fittest’: On the significance of Spencer’s refashioning of Darwin in the 1860s . Journal of Classical Sociology . 2014;14(2):156-177. doi:10.1177/1468795X13491646
Lampe DJ, Kantorski B, Pollock JA. Charles Darwin Synthetic Interview: A 19th century scientist speaks in the 21st century . J STEM Outreach . 2018;1(1):10.15695/jstem/v1i1.1. doi:10.15695/jstem/v1i1.1
Johnson CN. Charles Darwin, Richard Owen, and natural selection: A question of priority . J Hist Biol . 2019;52(1):45-85. doi:10.1007/s10739-018-9514-2
Snyder PJ, Kaufman R, Harrison J, Maruff P. Charles Darwin's emotional expression "experiment" and his contribution to modern neuropharmacology . J Hist Neurosci . 2010;19(2):158-170. doi:10.1080/09647040903506679
Reynolds EH, Broussolle E. Allbutt of Leeds and Duchenne de Boulogne: Newly discovered insights on Duchenne by a British neuropsychiatrist . Rev Neurol (Paris) . 2018;174(5):308-312. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2017.07.012
Ludwig RJ, Welch MG. Darwin's other dilemmas and the theoretical roots of emotional connection . Front Psychol . 2019;10:683. Published 2019 Apr 12. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00683
Wolf K. Measuring facial expression of emotion . Dialogues Clin Neurosci . 2015;17(4):457-462. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.4/kwolf
Darwin, C. R. 1871. The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex . London: John Murray. Volume 1. 1st edition.
Davis AC, Arnocky S. Darwin versus Wallace: Esthetic evolution and preferential mate choice . Front Psychol . 2022;13:862385. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.862385)
University of Cambridge. Darwin's women .
National History Museum. Who was Alfred Russel Wallace ?
Reddy RP, Korde SP, Kanungo S, et al. Neural correlates of emotion: Acquisition versus innate view point . Indian J Psychol Med . 2014;36(4):385-391. doi:10.4103/0253-7176.140720
Bradley B. Natural selection according to Darwin: cause or effect ? Hist Philos Life Sci . 2022;44(2):13. doi:10.1007/s40656-022-00485-z
National Academy of Sciences (US); Avise JC, Ayala FJ, editors. 13, Darwin and the Scientific Method . In the Light of Evolution: Volume III: Two Centuries of Darwin . Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2009.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Biography Online

Charles Darwin Biography

Charles Darwin was born on 12 February 1809 in Shrewsbury, Shropshire. He was born into a wealthy and influential family. His grandfathers included – China manufacturer Josiah Wedgwood, and Erasmus Darwin, one of the leading intellectuals of 18th century England.
Darwin planned to study medicine at Edinburgh University, but later, at the instigation of his father, changed to studying Divinity at Christ’s College, Cambridge University. Darwin was not a great student, preferring to spend time in outdoor pursuits; he spent a lot of time examining natural science and beetle collecting. After gaining a passionate interest in natural science, Darwin was offered a place on the HMS Beagle to act as a natural scientist on a voyage to the coast of South America.
At the time, religion was a powerful force in society, and most people took the Bible as the infallible, literal word of God. This included the belief that God created the world in seven days, and the world was only a few thousand years old. However, on the voyage, Darwin increasingly began to see evidence of life being much older. In particular Lyell’s ‘Principles of Geology’ suggested that fossils were evidence of animals living hundreds of thousands of years ago.
On the voyage, Darwin made copious notes about specimens he found on his voyages. In particular, at the Galapagos Islands 500 miles west of South America, Darwin was struck by how the Finch was different on each individual island. He noticed that the Finch had somehow adapted to the various aspects of the particular island.
Over the next 20 years, Darwin worked on the dilemma of how species evolve and can end up being quite different on different islands. Influenced by the work of Thomas Malthus, Darwin came up with a theory of natural selection and gradual evolution over time.
“In the struggle for survival, the fittest win out at the expense of their rivals because they succeed in adapting themselves best to their environment.”
– Charles Darwin
Darwin continued to refine his theory, and would intensively breed plants to work on his theories. However, realising how controversial his ideas were, Darwin delayed publishing them. It was not until learning that another naturalist, Alfred Russel Wallace had developed similar ideas, that Darwin was galvanised into publishing his own book.
In 1859, the ground-breaking ‘ On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection ‘ was published. It immediately gained widespread interest and attention, leading to intense debate about the contention that man – by implication was descended from animals like the ape.
“Owing to this struggle for life, any variation, however slight and from whatever cause proceeding, if it be in any degree profitable to an individual of any species, in its infinitely complex relationship to other organic beings and to external nature, will tend to the preservation of that individual, and will generally be inherited by its offspring.”
– Charles Darwin, Origin of Species (1859)
However, by the time he died on 19 April 1882, his ideas had increasingly become accepted – at least by the scientific and non-religious society. He was given a state burial at Westminster Abbey.
Darwin’s Religious Beliefs
Darwin was brought up in the Church of England, and at one point was being trained to be an Anglican priest. Like many of his generation, he took the Bible as the literal word of God and often quoted it as a source of moral authority. However, after his epic voyage to South America, he became doubtful of the Bible as a source of history; he also felt no reason why all religions couldn’t be true.
From 1849, he stopped going to church, though he never considered himself to be an atheist. He felt that ‘agnostic’ suited his beliefs more closely. He wrote in his autobiography that he eventually gave up Christianity as he disagreed with the conclusion that all non-believers spend eternity in hell.
“I can indeed hardly see how anyone ought to wish Christianity to be true; for if so the plain language of the text seems to show that the men who do not believe, and this would include my Father, Brother and almost all my best friends, will be everlastingly punished.”
He was politically liberal, being an opponent of slavery. He experienced the brutality of how people treated their slaves in a Spanish colony.
“I have watched how steadily the general feeling, as shown at elections, has been rising against Slavery. What a proud thing for England if she is the first European nation which utterly abolishes it!”
Letter to J. S. Henslow (March 1834)
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan. “ Biography of Charles Darwin ”, Oxford, UK. www.biographyonline.net – 4th Sept. 2012. Updated 21st February 2018.
The Origin of Species: Charles Darwin

The Origin of Species: Charles Darwin at Amazon
About Charles Darwin

Who was Charles Darwin? at Amazon
Facts about Charles Darwin
- He was the grandson of Josiah Wedgwood the famous furniture manufacturer.
- He studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh but found lectures dull.
- He learned taxidermy from John Edmonstone, a freed black slave.
- Darwin became an enthusiastic Beetle collector – which was a craze at the time.
- His father sent him to Christ’s College, Cambridge with the intention of training him as an Anglican parson. He later gave up Christianity.
- His five-year voyage on HMS Beagle established him as an eminent geologist and popular writer. His observations would be used to develop his theory of evolution.
- He sometimes questioned his own scientific discoveries. ‘I feel most deeply that this whole question of creation is too profound for human intellect.’
- In modified form, Darwin’s theory of evolution is now seen as the unifying theory of the life sciences.
- On the new Galápagos Islands Darwin saw many samples of animals which showed relations to animals in other parts of the world, e.g. Mockingbirds in Chile.
- During the Beagle expedition, Darwin shipped home a total of 1,529 species preserved in spirit and 3,907 labelled dried specimens.
- Darwin and Wallace’s theories on evolution were both presented on the same day in 1858 to the Linnean Society of London.
- Darwin took 22 years from the end of the voyage to publish his findings – he was worried about the reaction of people. It is said the thought of Wallace publishing first, galvanised him into action
- The full title of Origin of Species is On the Origin of Species by means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life .
- Darwin did not coin the phrase ‘survival of the fittest’. It was added to the fifth edition of Origin of Species. The phrase came from economist Herbert Spencer.
- Darwin has appeared on more UK stamps than anyone outside the Royal Family.
- Seven months after the publication of ‘Origin of Species’ the famous 1860 Oxford evolution debate occurred between Thomas Henry Huxley and Bishop Samuel Wilberforce. The debate is considered to be a great moment in natural history – and a key moment in the acceptance of evolution.
Related pages

- Quotes by Charles Darwin
Very Nice Introduction of Charles Darwin.
- March 08, 2018 5:29 AM
- By Pogiako69
Charles Darwin is the best guy ever
- October 17, 2017 3:14 PM
- Biography of Charles Darwin, Originator of the Theory of Evolution
- Evolution Scientists
- History Of Life On Earth
- Human Evolution
- Natural Selection
- The Evidence For Evolution
- Habitat Profiles
- Marine Life
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/McNamara-headshot-history1800s-5b7422c046e0fb00504dcf97.jpg)
Charles Darwin (February 12, 1809–April 19, 1882) was a naturalist who originated the theory of evolution through the process of natural selection. Darwin holds a unique place in history as the foremost proponent of this theory. While he lived a relatively quiet and studious life, his writings were controversial in their day and still routinely spark controversy.
As an educated young man, he embarked on an astounding voyage of discovery aboard a Royal Navy ship. Strange animals and plants he saw in remote places inspired his deep thinking about how life might have developed. And when he published his masterpiece, " On the Origin of Species ," he profoundly shook up the scientific world. Darwin's influence on modern science is impossible to overstate.
Fast Facts: Charles Darwin
- Known For : Originating the theory of evolution through natural selection
- Born : February 12, 1809 in Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England
- Parents : Robert Waring Darwin and Susannah Wedgwood
- Died : April 19, 1882 in Downe, Kent, England
- Education : Edinburgh University, Scotland, Cambridge University, England
- Published Works : On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection
- Awards and Honors : Royal Medal, Wallaston Medal, Copley Medal (all for outstanding achievements in the sciences)
- Spouse : Emma Wedgwood
- Children : William Erasmus Darwin, Anne Elizabeth Darwin, Mary Eleanor Darwin, Henrietta Emma Darwin, George Howard Darwin, Elizabeth Darwin, Francis Darwin, Leonard Darwin, Horace Darwin, Charles Waring Darwin
- Notable Quote : “In the struggle for survival, the fittest win out at the expense of their rivals because they succeed in adapting themselves best to their environment.”
Charles Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, in Shrewsbury, England. His father was a medical doctor, and his mother was the daughter of the famous potter Josiah Wedgwood. Darwin’s mother died when he was 8, and he was essentially raised by his older sisters. He was not a brilliant student as a child, but he went on to study at the University of Edinburgh Medical School in Scotland , at first intending to become a doctor.
Darwin took a strong dislike to medical education and eventually studied at Cambridge . He planned to become an Anglican minister before becoming intensely interested in botany. He received a degree in 1831.
Voyage of the Beagle
On the recommendation of a college professor, Darwin was accepted to travel on the second voyage of the H.M.S. Beagle . The ship was embarking on a scientific expedition to South America and islands of the South Pacific, leaving in late December 1831. The Beagle returned to England nearly five years later, in October 1836.
Darwin's position on the ship was peculiar. A former captain of the vessel had become despondent during a long scientific voyage because, it was assumed, he had no intelligent person to converse with while at sea. The British Admiralty thought sending an intelligent young gentleman along on a voyage would serve a combined purpose: he could study and make records of discoveries while also providing intelligent companionship for the captain. Darwin was chosen to go aboard.
Darwin spent more than 500 days at sea and about 1,200 days on land during the trip. He studied plants, animals, fossils, and geological formations and wrote his observations in a series of notebooks. During long periods at sea, he organized his notes.
In the Galapagos
The Beagle spent about five weeks in the Galapagos Islands . During that time, Darwin made a series of observations that had a significant impact on his new theories about natural selection. He was particularly intrigued by his discovery of major differences between species on different islands. He wrote:
The distribution of tenants of this archipelago would not be nearly so wonderful if, for instance, one island has a mocking-thrush and a second island some other quite distinct species... But it is the circumstance that several of the islands possess their own species of tortoise, mocking-thrush, finches, and numerous plants, these species having the same general habits, occupying analogous situations, and obviously filling the same place in the natural economy of this archipelago, that strikes me with wonder.
Darwin visited four of the Galapagos Islands, including Chatham Island (now San Cristobal), Charles (now Floreana), Albemarle, and James (now Santiago). He spent much of his time sketching, collecting specimens, and observing animals and their behavior. His discoveries would change the scientific world and rock the foundations of Western religion.
Early Writings and Influences
Darwin married his cousin Emma Wedgwood in 1839, and they eventually had ten children, seven of whom survived to adulthood. Illness prompted him to move from London to the country in 1842. His scientific studies continued, and he spent years studying various lifeforms to better understand their evolutionary processes.
Three years after returning to England, Darwin published the "Journal of Researches," an account of his observations during the expedition aboard the Beagle. The book was an entertaining account of Darwin's scientific travels and was popular enough to be published in successive editions.
Darwin also edited five volumes titled "Zoology of the Voyage of the Beagle," which contained contributions by other scientists. Darwin himself wrote sections dealing with the distribution of animal species and geological notes on fossils he had seen.
Development of Darwin's Thinking
The voyage on the Beagle was, of course, a highly significant event in Darwin’s life, but his observations on the expedition were hardly the only influence on the development of his theory of natural selection. He was also greatly influenced by what he was reading.
In 1838 Darwin read an "Essay on the Principle of Population," which the British philosopher Thomas Malthus had written 40 years earlier. The ideas of Malthus helped Darwin refine his own notion of “survival of the fittest.”
Malthus had been writing about overpopulation and discussed how some members of society were able to survive difficult living conditions. After reading Malthus, Darwin kept collecting scientific samples and data, eventually spending 20 years refining his own thoughts on natural selection.
Publication of His Masterpiece
Darwin’s reputation as a naturalist and geologist had grown throughout the 1840s and 1850s, yet he had not revealed his ideas about natural selection widely. Friends urged him to publish them in the late 1850s; it was the publication of an essay by Alfred Russell Wallace expressing similar thoughts that encouraged Darwin to write a book setting out his own ideas.
In July 1858, Darwin and Wallace appeared together at the Linnean Society of London. And in November 1859, Darwin published the book that secured his place in history: "On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection." He later published another volume, "The Descent of Man," which went even further into his then-controversial ideas about how humans, specifically, had evolved.
Later Life and Death
"On the Origin of Species" was published in several editions, with Darwin periodically editing and updating material in the book. And while society debated Darwin's work, he lived a quiet life in the English countryside, content to conduct botanical experiments. He was highly respected, regarded as a grand old man of science. He died on April 19, 1882, and was honored by being buried at Westminster Abbey in London .
Charles Darwin was not the first person to propose that plants and animals adapt to circumstances and evolve over eons of time. But Darwin's book put forth his hypothesis in an accessible format and led to controversy. Darwin's theories had an almost immediate impact on religion, science, and society at large.
- “ Charles Darwin: Gentleman Naturalist .” Darwin Online.
- Desmond, Adrian J. “ Charles Darwin .” Encyclopedia Britannica , 8 Feb. 2019.
- Liu, Joseph, and Joseph Liu. “ Darwin and His Theory of Evolution .” Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project, 19 Mar. 2014.
- Charles Darwin's Finches
- Charles Darwin and His Voyage Aboard H.M.S. Beagle
- Evidence Darwin Had for Evolution
- Interesting Facts About Charles Darwin
- 8 People Who Influenced and Inspired Charles Darwin
- Charles Darwin WebQuest
- The Legacy of Darwin's "On the Origin of Species"
- Biography of Charles Lyell
- What Is Evolution?
- 5 Misconceptions About Natural Selection and Evolution
- 6 Things Charles Darwin Did Not Know
- An Overview of the Galapagos Islands
- What Is Darwinism?
- Survival of the Fittest vs. Natural Selection
- Modern Evolutionary Synthesis
Accept cookies?
We use cook ies to give you the best online experience and to show personalised content and marketing. We use them to improve our website and content as well as to tailor our digital advertising on third-party platforms. You can change your preferences at any time.
Popular search terms:
- British wildlife
- Wildlife Photographer of the Year
- Explore the Museum
Anthropocene
British Wildlife
- Collections
Human evolution
What on Earth?

Unveiling a statue of Charles Darwin at the Museum, 1885.
During Beta testing articles may only be saved for seven days.
Create a list of articles to read later. You will be able to access your list from any article in Discover.
You don't have any saved articles.
Charles Darwin: History’s most famous biologist
Charles Robert Darwin (1809-1882) transformed the way we understand the natural world with ideas that, in his day, were nothing short of revolutionary.
He and his fellow pioneers in the field of biology gave us insight into the fantastic diversity of life on Earth and its origins, including our own as a species.

Photograph of Charles Robert Darwin taken at his home, Down House, in 1881.
Charles Darwin is celebrated as one of the greatest British scientists who ever lived, but in his time his radical theories brought him into conflict with members of the Church of England.
Young Charles Darwin
Born in 1809 in Shrewsbury, Shropshire, Darwin was fascinated by the natural world from a young age. Growing up he was an avid reader of nature books and devoted his spare time to exploring the fields and woodlands around his home, collecting plants and insects.
In 1825 Darwin enrolled in medical school at the University of Edinburgh, where he witnessed surgery on a child. Surgeries at the time would have been carried out without the use of anaesthetic or antiseptics, and fatalities were common.
Watching this procedure left Darwin so traumatised that he gave up his studies without completing the course.
During his time in Edinburgh, Darwin also paid for lessons in taxidermy from John Edmonstone , a former enslaved man from Guyana. The skills Edmonstone taught Darwin became crucial just a few years further into his career.
After his time in Scotland, Darwin went to Cambridge University to study theology.
The voyage of HMS Beagle
In no rush to take holy orders, in 1831 Darwin accepted an offer to embark on a five-year voyage aboard HMS Beagle.

Drawing of H.M.S. Beagle from A Naturalist’s Voyage Round the World by Charles Darwin.
He was recommended by one of his Cambridge professors for the role as naturalist and companion to the ship’s captain, Robert FitzRoy.
The journey would change both his life and the trajectory of Western scientific thinking.
Darwin explored remote regions and marvelled at a world so different from the one he knew. He encountered birds with bright blue feet, sharks with T-shaped heads and giant tortoises.
On his travels Darwin collected plants, animals and fossils, and took copious field notes. These collections and records provided the evidence he needed to develop his remarkable theory.

The shells in this specimen drawer were collected by Charles Darwin during the voyage of the HMS Beagle.
Darwin returned to England in 1836. A highly methodical scholar, constantly collecting and observing, he spent many years comparing and analysing specimens before finally declaring that evolution occurs by a process of natural selection.
What is the theory of natural selection?
To this day the theory of evolution by natural selection is accepted by the scientific community as the best evidence-based explanation for the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
The theory proposes that the ‘fittest’ individual organisms - those with the characteristics best suited to their environment - are more likely to survive and reproduce. They pass on these desirable characteristics to their offspring.
Gradually these features may become more common in a population, so species change over time. If the changes are great enough, they could produce a new species altogether.
On his travels Darwin had collected finches from many of the Galápagos Islands - off the coast of Ecuador - which helped him to formulate his idea.
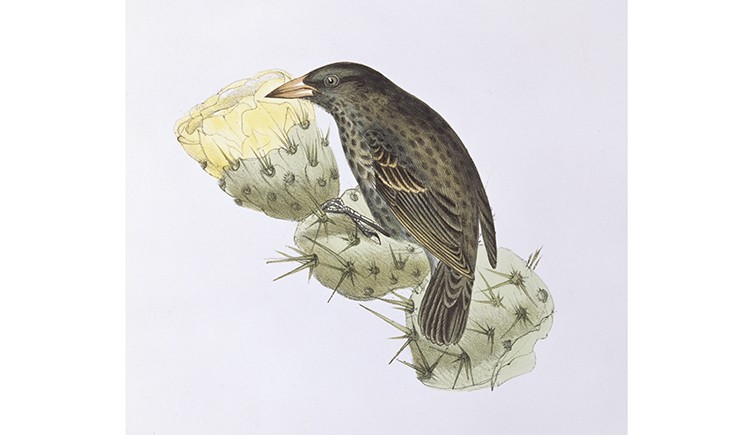

Cactus finch Geospiza scandens from Charles Darwin’s Zoology of the Voyage of the H.M.S. Beagle.
Some of these finches had stout beaks for eating seeds, others were insect specialists. But Darwin realised that they were all descendants of a single ancestor. As they dispersed to different islands, the birds had adapted to eat the various foods available. Natural selection had produced 13 different species of finch.

Darwin’s pigeons
From his travels on HMS Beagle, Darwin suspected that the environment might naturally manipulate species, causing them to change over time - but he couldn’t find a means to explore this effectively in the wild.
Experimenting with artificial selection in pigeons gave him a way to study how far a species could change.
By artificially selecting features - crossing birds with particular characteristics to generate different offspring - he gathered valuable evidence for evolution by natural selection.
To illustrate his theory, Darwin bred the birds to have exaggerated features.

Original line drawing of an English Pouter pigeon from the book Variation in Animals and Plants under Domestication by Charles Darwin.
The similarity between artificial selection and natural selection is at the heart of his explanation of evolution in his revolutionary book On the Origin of Species.
After completing his experiments, he gave all 120 of his pigeon specimens to the Museum. They are currently part of our bird collections kept at Tring , Hertfordshire.
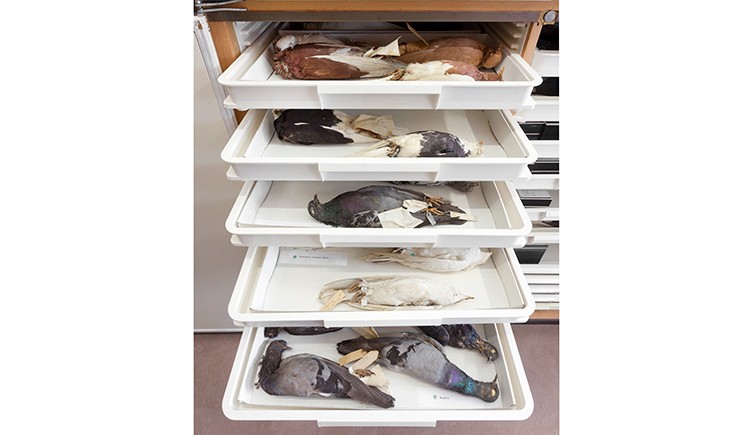

Fancy breeds of rock dove Columbia livia donated to our collections by Charles Darwin in 1867.
A shared discovery
Darwin knew his radical ideas would be met with stiff opposition. Even after 20 years of research, he worried about how his theory of evolution would be received as it challenged widely held religious beliefs of the time.
He delayed publishing on the topic for a great number of years while he assembled a mountain of evidence. When he learned that the young naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace had developed similar ideas, Darwin volunteered to send Wallace's ideas to a journal for immediate publication.

Letter sent to Charles Darwin by Alfred Russel Wallace.
On advice from friends, the two scientists organised a joint announcement. Their theory of evolution by natural selection was presented at the Linnean Society in London.
Both had studied the natural world extensively and made a number of observations that were critical to the development of the theory.
The following year, Darwin published the contentious but now-celebrated book, ‘On the Origin of Species’.
On the Origin of Species
Published in 1859, On the Origin of Species provoked outrage from some members of the Church of England as it implicitly contradicted the belief in divine creation.
Despite accusations of blasphemy, the book quickly became a bestseller.

Foreign language first editions of some works by Charles Darwin.
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex - which Darwin published in 1871 - fuelled even greater debate as it suggested that humans descended from apes.
The Bishop of Oxford famously asked Thomas Huxley, one of Darwin’s most enthusiastic supporters, whether it was through his grandfather or grandmother that he claimed descent from a monkey.
Despite the attacks, Darwin’s conviction in the scientific explanation that best fit the available evidence remained unshaken.
He was keen for his ideas to reach as many people as possible and for his books to be read in many different languages. Part of his success has been attributed to his conversational and approachable writing style.
On the Origin of Species was so influential that within a year it had been published in German. In Darwin's lifetime, his book was translated into German, Danish, Dutch, French, Hungarian, Italian, Polish, Russian, Serbian, Spanish and Swedish.
Our Library has 478 editions of On the Origin of Species in 38 languages and in Braille.

Japanese translation of On the Origin of Species, Shu No Kigen, published in 1914 as a five-volume, pocket-sized edition.
Darwin and the tree of life
Charles Darwin used the concept of a tree of life in the context of the theory of evolution to illustrate that all species on Earth are related and evolved from a common ancestor.

Darwin’s first sketch of the tree of life, found in one of his notebooks from 1837. Image reproduced with kind permission of the Syndics of Cambridge University Library .
The tips of the branches show the species that are still alive today. The tree also shows those that are now extinct. Darwin explained:
‘From the first growth of the tree, many a limb and branch has decayed and dropped off; and these fallen branches of various sizes may represent those whole orders, families, and genera which have now no living representatives, and which are known to us only in a fossil state.’
Orders, families and genera are all groups that can be used to classify organisms.
The lines on the tree show evolutionary relationships between species. For example, a recent version of the tree of life would show a line between some types of dinosaurs and the earliest birds, as scientists reason that birds evolved from a particular lineage of dinosaurs.
This means that species that are closely related are found close together stemming from the same branch.
For example, humans, chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans are all great apes, so they all belong to the same branch of the tree of life.
Darwin’s legacy
Although Darwin’s theory of evolution has been modified over time, it remains fundamental to the study of the natural world. Darwin changed not only the way we see all organisms, but also the way we see ourselves.
- Museum history
- Charles Darwin

Explore the Darwin collection
The Museum Library contains the worlds largest collection of works by and about Charles Darwin.

Explore the collections
From giant fossil mammals to mysterious moths, uncover the colourful stories behind some of our most fascinating specimens.
Related posts

In high spirits: meet Charles Darwin's octopus
Brimming with enthusiasm for the natural world, even Charles Darwin didn't always get it right.
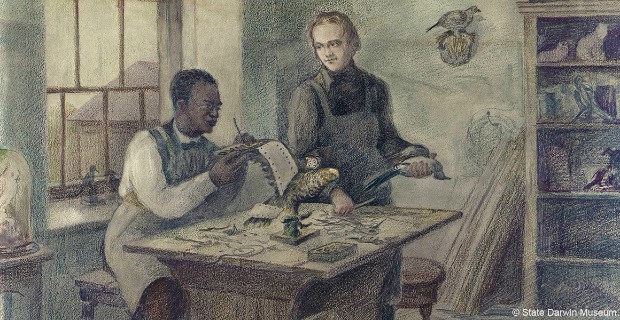
John Edmonstone: the man who taught Darwin taxidermy
John Edmonstone was a former enslaved man who taught the young Charles Darwin the skill of taxidermy.

What is natural selection?
Natural selection is one of the core processes of evolution - but how does it work and will it ever end?

Who was Alfred Russel Wallace?
An intrepid explorer and brilliant naturalist, Alfred Russel Wallace co-published the theory of evolution by natural selection with Charles Darwin.
Don't miss a thing
Receive email updates about our news, science, exhibitions, events, products, services and fundraising activities. We may occasionally include third-party content from our corporate partners and other museums. We will not share your personal details with these third parties. You must be over the age of 13. Privacy notice .
Follow us on social media
Charles Darwin
By kristen richard | dec 16, 2019.

SCIENTISTS (1809–1882); SHREWSBURY
When Charles Darwin's book, On the Origin of Species , came out in 1859, it completely changed the way people view life itself. For some, it was enlightening; for others, it was blasphemous. And now, more than 160 years later, his theory of evolution through natural selection is still a hotly debated subject. Read on for facts, quotes, and more on Charles Darwin.
1. Charles Darwin was a scientist and naturalist who was pretty bad at math.

Charles Darwin, born in Shrewsbury, England in 1809, was a biologist and naturalist best known for his theory of evolution through natural selection, which is the idea that organisms change over time through heritable traits that better allow them to adapt to environmental challenges. Those that don't, die off, which is why it has subsequently been dubbed "survival of the fittest."
Unfortunately, Darwin's connection to the world of science didn't lend itself to a love of math. After struggling with the subject in college, Darwin was forced to hire a tutor in 1828. But when he continued to lag behind, he fired the tutor after just a few weeks. To Darwin, algebra was a "repugnant" subject, but as he got older, he regretted his impatience with math.
2. Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution through Natural Selection (or Darwinism) came about at the same time as Alfred Russel Wallace's.

Charles Darwin began studying what would become known as natural selection in the 1830s , but, concerned about the public reaction, he sat on his new theory for decades. By the mid-1850s, British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace had begun independently working on his own ideas of natural selection and knew Darwin had been involved in similar research. Wallace even sent Darwin a paper he had written on the subject to peer review it, and the two later collaborated on a new paper on the subject in 1858.
Then, in 1859, Darwin finally went public with his theory with On The Origin of Species . No longer shackled to the niche scientific community, Darwin's book presented these world-shaking ideas to the masses, forever linking the scientist to this famed theory. Wallace, on the other hand, often goes overlooked.
3. Charles Darwin's Voyage on the H.M.S. Beagle led to many of his breakthroughs.
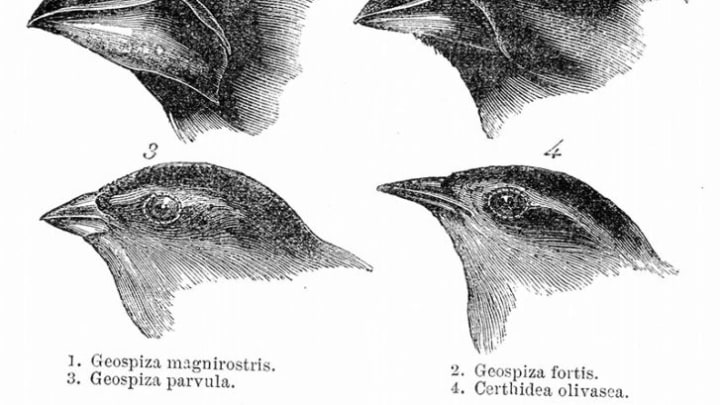
On December 27, 1831, Darwin set sail aboard the H.M.S. Beagle on a five-year voyage to the Pacific Islands, the Galápagos Islands, and South America. It was on this journey that a 22-year-old Darwin would visit several continents, ship more than 1500 species back home to study, and fill notebook after notebook with his discoveries. While on the Galápagos , finches were particularly vital to Darwin as he was forming his theory of natural selection. He observed the variations in the shape of their beaks ( some had longer, pointier beaks, while others were short and stout) from island to island, further confirming that the unique challenges in each environment led finches with specific traits to become dominant.
4. Charles Darwin’s Book On The Origin of Species took 25 years to write.

Darwin devoted his life to science and had a few published works, but On The Origin of Species is his most well-known book. It illustrates his theory of evolution and process of natural selection and was published on November 24, 1859. But a work of such significance isn't easy: On the Origin of Species took Charles Darwin 25 years to write.
5. Charles Darwin had 10 Children with his first cousin.

Charles Darwin married his first cousin, Emma Wedgwood, on January 29, 1839. The two shared the same grandfather, Josiah Wedgwood. Together, the couple had 10 children:
- Elizabeth Darwin: 1847–1929
- George Darwin: 1845–1912
- Henrietta Darwin: 1843–1927
- Mary Darwin: 1842
- Anne Darwin: 1841–1851
- William Darwin: 1839–1949
- Francis Darwin: 1848–1925
- Leonard Darwin: 1850–1943
- Horace Darwin: 1851–1928
- Charles Darwin: 1856–1858
Charles Darwin was a botanist and experimented with breeding plants in his greenhouse. He found that cross-fertilization produced much healthier plants than self-fertilization, and it’s said he worried whether his children would have health issues due to their parents being so closely related.
Two of his other children didn’t make it into adulthood. And three that did survive and marry were never able to have any children of their own.
6. Charles Darwin was a foodie before that was a thing.

While studying at Cambridge, Darwin became a member of the Glutton Club . This was basically a group of friends who would meet up once a week to eat "birds and beasts, which were before unknown to human palate." This led to a wide variety of peculiar meals, such as iguanas, armadillos, and plenty of rodents. The club apparently disbanded after a particularly hideous taste of a brown owl, which Darwin said was "indescribable."
Books written by Charles Darwin.
Other than On the Origin of Species , Charles Darwin's other books include:
- The Effects of Cross and Self Fertilization in the Vegetable Kingdom
- The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals
- The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex
- The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species
- The Formation of Vegetable Mould, Through the Action of Worms
- The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication
- On the Various Contrivances by Which British and Foreign Orchids Are Fertilised by Insects.
Famous quotes from Charles Darwin.
- “A man who dares to waste one hour of time has not discovered the value of life.”
- “If I had my life to live over again , I would have made a rule to read some poetry and listen to some music at least once every week.”
- "Man selects only for his own good ; Nature only for that of the being which she tends."
- “Ignorance more frequently begets confidence than does knowledge: it is those who know little, not those who know much, who so positively assert that this or that problem will never be solved by science.”

Darwin's writings are consequently of interest to an extremely large number and wide variety of readers. This site contains the largest collection of his writings ever created with thousands of new discoveries available nowhere else and thousands of publications by other writers about Darwin and his influence. See his complete Publications and Manuscripts .
Darwin Online is the only source in the world for the complete works of Charles Darwin- see his Publications and Papers & Manuscripts .
• Darwin: A biographical sketch
• timeline, • darwin's life in pictures, • the complete library of charles darwin, • the complete photographs of darwin, • darwin and religion, • beagle voyage materials, • recollections of darwin, • darwin's funeral, • obituaries of darwin, • reviews of darwin's works.
Darwin's personal 'Journal'. Introduction Text & image The most useful reference work ever published for almost anything relating to Darwin with thousands of new discoveries is: Paul van Helvert & John van Wyhe, Darwin: A Companion (2021). See in Darwin Online : Freeman, Charles Darwin: A companion . 2d ed. Text
For more detailed accounts of Darwin's life on this site see:
The autobiography of Charles Darwin . Text The life and letters of Charles Darwin (1887). Vol. 1 Text Vol. 2 Text Vol. 3 Text More letters of Charles Darwin (1903). Vol. 1. Text Vol. 2. Text * Very many other biographies of Darwin are available in the supplementary works . John van Wyhe
File last up 12 February, 2024 e -->e -->
Local Histories
Tim's History of British Towns, Cities and So Much More
A Brief Biography of Charles Darwin
By Tim Lambert
His Early Life
Charles Darwin was one of the great scientists of the 19th century. He was born on 12 February 1809 at the Mount House, Shrewsbury. His father was a doctor. His mother died when he was 8 years old. Charles had one brother and four sisters. Up to the age of 8 Charles was taught by an older sister. He then began school. From his earliest years, Charles Darwin was interested in natural history. However, he was a poor scholar.
He went to Edinburgh University to study medicine but left after 2 years. His father decided he should be a clergyman so Charles Darwin then went to Cambridge University.
Charles Darwin left Cambridge University in 1831. The same year he signed up to sail, without pay, as a naturalist on a ship called the Beagle. Its captain was Robert Fitzroy and it sailed on 27 December 1831.
In February 1832 the Beagle reached Brazil. They stayed in Brazil until July 1832 then sailed to Montevideo. Darwin spent three years in different parts of South America collecting specimens. Then in September 1835, the Beagle sailed to the Galapagos Islands.
Charles Darwin was surprised to learn the local people could tell by looking at a tortoise which island it came from. Darwin also studied finches. Each island had a different species of finch. Later Darwin concluded that all were descended from a single species of finch. On each island, the finches diverged and became slightly different.
In December 1835 Charles Darwin visited New Zealand and Tahiti. In January 1836 he reached Australia. The beagle then sailed to Mauritius and South Africa before sailing north into the Atlantic.
Finally, the Beagle arrived at Falmouth on 2 October 1836 and two days later Darwin arrived in Shrewsbury.
Charles Darwin then wrote several books about his voyage. The first was Journal of Researches , an account of his voyage. He also wrote Coral Reefs , published in 1842, Volcanic Islands (1844), and Geographical Observations on South America (1846). Darwin gained a reputation as a brilliant geologist.
Meanwhile, Darwin was influenced by a geologist called Charles Lyell. In 1830 he published a book called Principles of Geology . In it, Lyell proposed a theory called uniformitarianism. He showed that rocks and the landscape were formed over vast periods by very slow processes. However, Lyell did not believe that one species of animal could change into another.
Charles Darwin disagreed. By 1836 he believed that species of animals could change. In July 1837 Darwin began to write notes about his theory. He called his notes The Transmutation of Species .
In October 1838 Darwin thought of how one species could change into another. He noticed that individual members of a species vary. Furthermore, all animals are competing with each other to survive. If the environment changed in some way, say if a new, faster predator appeared then any herbivores that could run slightly faster than other members of its species would be more likely to survive and reproduce. Any herbivores that ran slightly slower than most would be more likely to be eaten. Slowly a new, faster herbivore would evolve. This was later called the survival of the fittest.
Meanwhile, on 11 November 1838, Charles Darwin proposed to his cousin Emma Wedgwood. They married on 29 January 1839. As well as getting married Darwin became more famous as a scientist. On 24 January 1839, he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society. Darwin’s first son was born on 27 December 1839. Altogether he had 10 children.
For years Charles Darwin studied nature looking for evidence to support his theory. For much of that time, he suffered from ill health.
Then in 1858 Charles Darwin received a letter from Alfred Russel Wallace. It turned out that Wallace had independently devised a theory of evolution by natural selection.
Therefore Wallace’s work and Darwin’s theory were presented to a scientific society called the Linnaean Society on 1 July 1858. The two men’s work was also published in the society’s journal.
Darwin was now galvanized into publishing his theory. And so his monumental work The Origin of Species was published on 24 November 1859. It proved to be a bestseller. However, Darwin’s book was criticized by some people.
In 1860 T. H. Huxley (a supporter of Darwin) had a public debate with Darwin’s opponent Bishop Wilberforce (known as ‘Soapy Sam’). The bishop was defeated and gradually the theory of evolution was accepted.
Charles Darwin published 10 more books after 1859. Six were about botany, one was about earthworms. Only three were about evolution. One of these was The variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication (1868). He also published The Descent of Man in 1871. In it, he explained his ideas about the evolution of man. In 1872 Darwin published The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals .

Darwin’s last book was on earthworms and was published in October 1881 shortly before he died. Charles Darwin died of a heart attack on 19 April 1882. He was 73.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

- DIGITAL MAGAZINE
MOST POPULAR
Charles Darwin and the Mystery of Life!
Find out about charles darwin and his theory of evolution..
In 1831, a young naturalist called Charles Darwin boarded a ship called the HMS Beagle and set out on a fantastic five-year voyage around the world to study and collect animal, plant and rock samples.
Darwin was amazed at the variety of species he saw on his adventure. The Beagle visited the Galápagos Islands (a group of 19 islands and more than 100 islets and rocks in the Pacific Ocean, about 1,000km off the coast of Ecuador in South America) and while he was there Darwin collected specimens and made notes that would eventually change the way people thought about the world…
Creature Clues?
Darwin noticed that although the different islands had similar creatures and plants, many seemed to have adapted to suit their local environments. Finches (a type of bird), for example, had different beaks on each island, suited to eating the particular seeds or insects found there! He also noted remarkable differences between the mockingbirds found on San Cristobal, Floreana and two other islands. When he returned to England he devoted his time trying to figure out why they varied from place to place.
The mystery solved
In 1858, Darwin revealed his ‘ theory of evolution by natural selection ’, to explain how animals adapted to their environment to survive. And the following year, he published On The Origin Of Species – a book that would change the world forever! Darwin explained how species can ‘ evolve ’ (change or develop) over time through a process called ‘ Natural Selection ’. This shocked everyone because, until then, it was widely believed that all the animals on the planet had been made at the same time by one creator. Some people still believe that today. But Darwin scientifically proved all the species on Earth had evolved from earlier species – and that includes us!
Want to meet some of the incredible creatures that Darwin encountered on his voyage? Then join us as NG KiDS heads to the Galápagos Islands !
Camouflaged marine iguanas: ©tim herbert. all other images: getty images uk, leave a comment.
Your comment will be checked and approved shortly.
WELL DONE, YOUR COMMENT HAS BEEN ADDED!
Goooooooooooooooooooooooood
very helpful thank you!
this is very helpful
Wow!! I love learning science! This is one of the best I've read!! I like science especially if it's biology or zoology.
Very Helpful
I love learning!!! This is sooo coolllll!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!1
thank you!!!!!
This is great for your brain
WOW This site gives me a lot of information and facts
Darwin has proved nothing. If animals evolved why arent they doing that today ? Theres plenty more evidence to prove a Creator than evolution. Ours is the only planet in the universe that can sustain life. The miracle of the human body itself is enough to prove something so complex cant just come out of nothing. Did a watch put itself together? We are trillions of times more complex than that. So is the world and everything in it. Darwin was a fraud.
The info helped at school
dfirojgfokfkgjf
j bhb nhn nn =
sick info helped me with my school work
If I could go back in time Charles darwin would be one of the people I would meet thanks
this really helped with my homework thanks
CUSTOMIZE YOUR AVATAR
More like general science.
15 Facts About The Human Body!

Female wildlife rangers!
10 facts about Albert Einstein
Human digestive system

Sign up to our newsletter
Get uplifting news, exclusive offers, inspiring stories and activities to help you and your family explore and learn delivered straight to your inbox.
You will receive our UK newsletter. Change region
WHERE DO YOU LIVE?
COUNTRY * Australia Ireland New Zealand United Kingdom Other
By entering your email address you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy and will receive emails from us about news, offers, activities and partner offers.
You're all signed up! Back to subscription site
Type whatever you want to search
More Results

You’re leaving natgeokids.com to visit another website!
Ask a parent or guardian to check it out first and remember to stay safe online.

You're leaving our kids' pages to visit a page for grown-ups!
Be sure to check if your parent or guardian is okay with this first.

Charles Darwin Biography

Charles Darwin was the preeminent naturalist of the nineteenth century. His theories on evolution by natural selection created the basis for all modern studies on evolution. He was born Charles Robert Darwin on February 12, 1809, in Shrewsbury, Shropshire England. Charles Darwin was the second son of Susannah Wedgwood and Robert Waring Darwin. The couple also had three sisters older than Charles. Robert Darwin was a doctor and Susannah the daughter of Josiah Wedgwood, an early Unitarian and pottery industrialist. Robert Darwin's father, Charles' grandfather, Erasmus Darwin, was a doctor and poet who authored Zoonomia; or the Laws of Organic Life, in 1794. When Charles Darwin was eight his mother died and his three older sisters became his primary caregivers. He displayed a keen interest in medicine, science, and psychology and was inspired by his father's observation of medicine in everyday life. He did not enjoy his very traditional schooling however, where he was taught the Classics and discouraged from studying science and chemistry. Because of his interest in chemistry and sciences Darwin was ridiculed in school by students and the headmaster and given the nickname of "Gas." His distinguished father, possibly falsely convinced his son was not committed to his studies by accounts of the headmaster, enrolled Darwin at Edinburgh University to study medicine in 1825. At the time Edinburgh offered the most forward-thinking education in science of any university in Britain. Among his studies were extensive chemistry lessons and studies of natural science. Perhaps most impactful to Darwin's education at Edinburgh were the freethinking lecturers the university attracted. They were often banned from speaking at traditional universities like Oxford and Cambridge. While those universities refused to separate themselves from science grounded in Anglicanism, these dissenters challenged the religious stronghold over science in areas like anatomy and mental processes of both humans and animals. Charles was encouraged to understand primitive creatures like invertebrates which inspired him to contemplate the origin of all species. Darwin's father observed that though his son was studying medicine, he could not stomach surgery and was uninterested in human anatomy. Fearing that his son would become aimless without being able to dedicate himself to medicine, in 1828 he transferred Darwin to Christ's College in Cambridge. This education was in stark contrast to Edinburgh and Darwin was treated as a young Anglican gentleman. He engaged in common social activities like drinking and shooting. He studied botany under Reverend John Stevens Henslow and went on his first expedition to Wales with Reverend Adam Sedgwick in 1831. Inspired by accounts of expeditions in South America, Darwin found a place for himself as a naturalist on board the HMS Beagle. The ship was commanded by Robert Fitzroy, a young aristocrat who did not want to sail by himself but planned to do a coastal land survey of Patagonia and also return three "savages" from Tierra del Fuego to their homeland. Darwin brought his books, weapons, and a newly acquired skill set for preservation of animal carcasses. The journey was long and arduous, but Darwin as a self-financed naturalist was able to leave the ship for long periods of time to attend to his other interests. He was fascinated by the vastness of the ocean and its creatures and observed the geologic features of the coast line. Darwin's time onboard and off was very solitary and he was disgusted by the slavery and genocide by battle he observed during his time in South America. He often left heavily populated areas to explore the Rio de Janeiro rainforests and their insect inhabitants. Another labor of love Darwin pursued during this expedition was a large-scale excavation of multiple different extinct mammal bones, which began his contemplation of why these animals did in fact go extinct. His observations on geological features led to his assumption that the land had risen above the sea in many areas and prompted thought the vast time span the earth and its creatures had witnessed. When Fitzroy and Darwin returned he had completed a 770 page diary detailing his notes and sketches, but had more questions about evolution that he had left with. The diary had been published and led to a grant obtained from the Treasury that allowed him to enlist experts on zoology for a series of collaborative papers from 1838-1843 that described his animal specimens, published as Zoology of the Voyage of the H.M.S. Beagle. Darwin became well known and sought to reckon his religious beliefs with what he had observed from both animal and human societal norms like slavery. Darwin was influenced by Thomas Malmuth's Essay on the Principle of Population. The economic paper from 1838 led to a series of poor laws that sought to reduce overpopulation. Darwin applied some of these principles for humanity to what he had observed in the wild and created his own mechanism called "natural selection." He created a 35 page sketch of his theory but did not immediately try to publish it, partially because he had seen from his wife, Emma Wedgwood, a kind of horror when he had tried to convey his theories on evolution. Darwin moved himself and his family to the village of Downe which felt very isolated from society. He continued his study and published works on coral reefs, botany, insects and geology, but largely tried to stay out of the public eye and did not confess his theory of evolution to many, fearing it to be akin to confessing a sin. Considering the persecution of Atheists by Anglican laws, this was not a far-fetched fear, though Darwin still maintained a belief in God as the almighty creator. Darwin solidified his role as a prominent resource on biological principles after a groundbreaking study on barnacles that revealed hermaphroditic traits and further sparked his interest in the difference between female and male form. As time and society progressed the stage was set for more acceptance of Darwin's theories and Darwin lost much belief in God after his daughter's death. Series of further studies on artificial breeding and production were rounding out his theory and providing a strategy on how to present it. He felt greater haste to complete a publication when confronted with Alfred Russel Wallace's letter and sketches that seemed to indicate similar theories to his own. Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859 with tremendous personal anxiety as to how it would be received. The reception was not as disastrous as he anticipated and Cambridge folk were beginning to accept scientific realities while dissenters greatly embraced his theories. Three reviews of his studies were published and in 1864, supported by Alfred Huxley, Darwin received the Copley Medal from the Royal Society. The 1860s found Darwin in ever-declining health and his wife Emma caring for him and their remaining children. He published six editions of On the Origin of Species during this time period and attempted to defend and move around criticisms by tying in his knowledge of botany and bees to prove natural selection. As natural selection became widely accepted, Darwin plowed forward into an analysis of morality and traits of the human race entitled The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex in 1871. His work on facial expression, The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals, from 1872, sought to disprove the Divine belief in facial structure. By the end of his life, Darwin was hailed for his scientific contributions and shielded from intense criticism by friends like Huxley. By the 1880s he was in very poor heath and he died on April 19th, 1882. His burial in the town of Downe was perceived as too low-brow, and with Huxley's persuasion Darwin's body was buried at Westminster Abbey.

- What Is ID?
Charles Darwin: A Short Biography
Charles Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, the very day that, half-way across the world in a log shack in Kentucky, Nancy Lincoln would give birth to Abraham, a boy with a likewise hidden destiny. Charles was preceded by Marianne, Caroline, Susan, and his best boyhood friend and only brother, Erasmus, and then Emily came along afterward.
Familial Influences
Charles was the son of Robert Darwin, a prosperous physician and industrial financier. Robert was the son of the famous physician-poet-evolutionist Erasmus Darwin . Today we remember Charles and forget Erasmus, but for nearly the first three decades of Charles’ life, he was Erasmus Darwin’s grandson — the grandson of England’s most famous evolutionist (or transmutationist, as it was then called).
That’s an important point to make about his life. Charles Darwin didn’t discover evolution. Evolution was old hat as a theory, and had been circulating in radical circles in England and France for at least a half-century before he was born. Charles imbibed the theory from his grandfather and father. Although Erasmus died before his grandson was born, Charles carefully studied his grandfather’s evolutionary treatise, the Zoonomia , sometime in the mid-1820s, long before he stepped on the HMS Beagle . Robert Darwin affirmed transmutationism as well, although he kept his opinions to himself.
So, when Charles Darwin was hurried off to medical school at Edinburgh in 1825, he was already well-versed in evolutionary theory. When he got there, he soon realized that he wasn’t cut out for medicine (as he discovered, there’s nothing like witnessing surgery without anesthetic on a small boy to sharpen one’s sense of vocation to medicine, or lack thereof). Rather than spend time on his studies, he began working under the transmutationist, Robert Grant , and generally had a good time, riding, shooting, eating, and acting the young gentleman.
It soon became clear to his father, that Charles was failing at the family vocation of medicine. It was decided that, as a last resort, he might cut it as an Anglican parson with a country parish. Few demands, a fair living, and lots of time for shooting, running dogs, hunting, and amateur natural history. Darwin shuffled off to Cambridge in January of 1828 to get an undergraduate degree in preparation for more advanced study to become a man of the cloth.
We should not overrate Darwin’s piety here. The Darwins were long-standing liberal Whigs. Erasmus was, if anything, the thinnest of theists, and Robert was most likely an atheist. The Anglican Creed and the Bible were considered relics of superstitious ages they dearly hoped would be left far behind as the Enlightenment marched forward. That Robert would send his son to become an Anglican parson tells us more about the state of the Anglican Church at the time than it does about Charles’ piety. That Charles could, in his Autobiography , insist that at the time he accepted the Creed and the literal truth of the Bible reveals him as less than forthright.
Voyage on The Beagle
At Cambridge Charles met two very important Anglican priests who were also top scientists, John Henslow and Adam Sedgwick . Under their kind tutelage, Charles was probably as close to a theist as he ever would become, although the effect of their guidance and passion for science was to confirm Charles’ vocation as a naturalist rather than a country parson. It was, in fact, Henslow that arranged for Darwin to join Captain Robert FitzRoy on the HMS Beagle after his graduation from Cambridge in 1831. After long delays, the Beagle launched from England’s shores on December 27, 1831 to sail around the world collecting and measuring for the enhancement of Britain’s place as a growing world mercantile power.
Right away Darwin got seasick. He was sick nearly the whole time he was at sea during the Beagle’s five-year voyage. But violent nausea wouldn’t end when he finally stepped off ship in October of 1836. The voyage of the Beagle marked the beginning of Darwin’s life-long struggle against his head and stomach. Whatever the cause of his perpetual bouts of retching later on — a strange “bug” picked up on his odyssey, frail nerves, his addiction to taking snuff, a diet rich in sweets, a hereditary malady — he spent nearly his entire life as if he’d never gotten off the Beagle , suffering long periods of debilitating nausea and vomiting, accompanied by headaches, interrupted only occasionally by bouts of good health.
Darwin spent the two decades after the Beagle cementing his place in England’s scientific society. He lived a kind of intellectual double life, gaining public respectability by his non-evolutionary scientific work, even while he was working away, right from the very beginning, at his theory of evolution in private. As his private notebooks make clear, from 1838 on Darwin was bent on making a purely materialistic, reductionist account of evolution, one that completely eliminated the need for divine intervention and oversight.
Marriage and Family
By this time, he had largely lost any faint traces of theism that he may have gained at Cambridge, and had fallen back into the Darwin hereditary religious skepticism bordering on atheism. After he proposed to his cousin Emma Wedgwood , he was honest enough to tell her of his unbelief. She was heartbroken, but married him anyway at the beginning of 1839. They would have a long and happy marriage despite their deepest mismatch about God, and would bring ten new Darwins into the world, only seven of which would live beyond childhood.
Substantiating the Theory of Evolution
Although as an heir to the Darwin fortune, Charles didn’t have to work, he threw himself into developing his scientific career and his theory with such zeal that he was always teetering on ruining his already fragile health. He wanted his theory to be perfect, perfectly argued and perfectly backed up by endless facts. He was also afraid of the backlash against him if he published so radical a theory, which the public already associated with atheism.
Who knows how long he would have worked on his theory without publishing if he hadn’t received a surprise in June of 1858: a clear and concise account of evolution by natural selection that couldn’t have been a more accurate synopsis of Darwin’s own. It was written by Alfred Russel Wallace . He’d been scooped! Darwin was crestfallen.
The truth was that evolution had been in the air for some time, and many others had been working along the same lines as Darwin. Wallace was just one of them. The two issued a joint paper, read at Linnean Society on the first of July, 1858. Wallace was still overseas. Darwin was not there either. His youngest boy, Charles junior, had died at the end of June, the last of the Darwin children and the third child to die before adulthood. The dark side of the survival of the fittest.
Darwin began working feverishly on a full statement of his theory, but ended up writing what he considered a mere synopsis, The Origin of Species , publishing it in November of 1859. It shocked the public, not because evolution was new, but because Darwin was an already well-known and respected scientist whose work had been heralded among the conservative British scientific society. He was a turncoat, not a revolutionary.
Promoting the Theory
Immediately upon publishing, he threw himself into an enormous international effort to have his theory affirmed, pulling every string available. Four men were particularly influential as his helpmates in this endeavor: Charles Lyell , Asa Gray , Thomas Huxley , and Joseph Hooker . Along with his co-discover, Alfred Wallace, they strove to make Darwinism respectable.
Ironically, three of these men — Lyell, Gray, and Wallace — affirmed evolution but thought that natural selection alone was radically insufficient to account for man’s moral and intellectual nature. Evolution needed God. Their “defection” so peeved Darwin that he wrote another book, The Descent of Man (1871), in which he made his case that our moral, intellectual, and “spiritual” aspects are all derived from natural and sexual selection. Evolution did not need God, thank you.
The cost for reducing our moral nature to an effect of natural selection was high. It meant that “morality” is merely the name we give for any particular existing society’s habits and social structures. Whatever these are — polygamy, monogamy, cannibalism, infanticide, gentlemanly behavior, courage, compassion toward all or just toward members of one’s tribe — they must have contributed to the survival of that society via natural selection. Furthermore, if natural selection is the root of all morality, and fitness is the criterion for evolutionary success, then, as Darwin rightly concluded, society should not allow the unfit to breed. Interesting thought from a perpetually sick man, whose own ten children inherited his physical weaknesses.
Death and Resting Place
Darwin spent the rest of his life working on more specialized monographs that supported his theory and answering his critics with successive editions of the Origin of Species . On April 19, 1882 death, the great creative force of evolution, finally came to call on Charles Darwin. Hooker, Huxley, and Wallace were among the pallbearers to his final resting place in Westminster Abbey next to Sir John Herschel, the famed astronomer who rejected Darwinism, near the eminent Charles Lyell who would only accept a modified form of it, and close to Sir Isaac Newton whom it would have horrified.
Resources for Further Information
- A Timeline of the Life of Charles Darwin
- The Complete Works of Charles Darwin Online
- Darwin Correspondence Project
- Darwin: The Life of a Tormented Evolutionist by Adrian Desmond and James Moore
- Charles Darwin: The Power of Place by Janet Browne
- Darwin Myth: The Life and Lies of Charles Darwin by Benjamin Wiker

COMMENTS
Charles Darwin (born February 12, 1809, Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England—died April 19, 1882, Downe, Kent) was an English naturalist whose scientific theory of evolution by natural selection became the foundation of modern evolutionary studies. An affable country gentleman, Darwin at first shocked religious Victorian society by suggesting that ...
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection. His views, and "social Darwinism," remain controversial.
Charles Darwin was born in 1809 in Shrewsbury, England. His father, a doctor, had high hopes that his son would earn a medical degree at Edinburgh University in Scotland, where he enrolled at the age of sixteen. It turned out that Darwin was more interested in natural history than medicine—it was said that the sight of blood made him sick to ...
Charles Robert Darwin FRS FRGS FLS FZS JP (/ ˈ d ɑːr w ɪ n / DAR-win; 12 February 1809 - 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology.His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science.
Biography of Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin was born in Shrewsbury, England, on February 12, 1809. His father was a wealthy doctor, and his grandfather on his mother's side was the noted potter Josiah Wedgwood. After his mother's death when he was eight, Darwin began attending boarding school with his older brother.
Biography. Charles Robert Darwin was born in Shropshire, England, on February 12, 1809. He came from a relatively illustrious and well-to-do background: his father, Robert Darwin (1766-1848), was a wealthy and successful surgeon, and his uncle Josiah Wedgwood (1730-1795) was the son of the founder of the pottery and china works that still ...
Charles Darwin Biography Charles Darwin (1809 - 1882) was an English Natural scientist who laid down a framework for the theory of evolution - showing how Man evolved from lower life forms. At the time, his research and publication led to bitter controversy, but his theory of evolution and natural selection later became accepted within the ...
Updated on July 29, 2021. Charles Darwin (February 12, 1809-April 19, 1882) was a naturalist who originated the theory of evolution through the process of natural selection. Darwin holds a unique place in history as the foremost proponent of this theory. While he lived a relatively quiet and studious life, his writings were controversial in ...
Charles Darwin: History's most famous biologist. Charles Robert Darwin (1809-1882) transformed the way we understand the natural world with ideas that, in his day, were nothing short of revolutionary. He and his fellow pioneers in the field of biology gave us insight into the fantastic diversity of life on Earth and its origins, including our ...
Lived 1809 - 1882. Charles Darwin is often cited as the greatest biologist in history. His most famous work, On the Origin of Species, explains the theory of evolution by natural selection, providing numerous supporting examples. Darwin believed that all of life on earth had descended from a common ancestor, whose offspring could vary slightly
1. Charles Darwin was a scientist and naturalist who was pretty bad at math. A portrait of scientist Charles Darwin from the 1880s. / iStock Via Getty Images Plus. Charles Darwin, born in ...
Biography. Perhaps no one has influenced our knowledge of the natural world as much as English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809-1882). His theory of evolution by natural selection, now the unifying theory of the life sciences, explained where all of the astonishingly diverse kinds of living things came from and how they became exquisitely adapted to their particular environments.
Charles Darwin was one of the great scientists of the 19th century. He was born on 12 February 1809 at the Mount House, Shrewsbury. His father was a doctor. His mother died when he was 8 years old. Charles had one brother and four sisters. Up to the age of 8 Charles was taught by an older sister. He then began school.
Find out about Charles Darwin and his theory of evolution. In 1831, a young naturalist called Charles Darwin boarded a ship called the HMS Beagle and set out on a fantastic five-year voyage around the world to study and collect animal, plant and rock samples. Darwin was amazed at the variety of species he saw on his adventure.
Charles Darwin Biography. Charles Darwin was the preeminent naturalist of the nineteenth century. His theories on evolution by natural selection created the basis for all modern studies on evolution. He was born Charles Robert Darwin on February 12, 1809, in Shrewsbury, Shropshire England. Charles Darwin was the second son of Susannah Wedgwood ...
Charles Darwin Biography. Learn how Charles Darwin became one of the most influential scientists of all time with this short biographical video. Darwin's tale is a fascinating one, involving a unique expedition on the HMS Beagle to the Galapagos Islands. Darwin studied the variations found in related species and slowly formed unique theories ...
Charles Darwin was an English scientist who studied nature. He is known for his theory of evolution by natural selection. According to this theory, all living things are struggling to survive. The living things that have the most helpful traits for their environment tend to survive. These living things then pass along their helpful traits to ...
You know the name, but who exactly was Charles Darwin? Join us on a whistle-stop tour of Darwin's life and legacy, from his epic voyage across the globe to t...
Benjamin Wiker. History. Charles Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, the very day that, half-way across the world in a log shack in Kentucky, Nancy Lincoln would give birth to Abraham, a boy with a likewise hidden destiny. Charles was preceded by Marianne, Caroline, Susan, and his best boyhood friend and only brother, Erasmus, and then Emily ...
This biography video will answer the following questions; What theory is Charles Darwin famous for? What did Charles Darwin discover? What is Charles Darwin'...
Charles Darwin: towards a bio-religious and colonial genealogy of evolutionary being. ... and thirdly, the value of the differences between the so-called races of man'. See Charles Darwin, The Descent of Man and Selection in Relation to Sex, Cambridge: Cambridge University ... Darwin: A Very Short Introduction, London: Oxford Paperbacks, 2003 ...