If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Unit 3: How do organisms reproduce?
About this unit.
In this unit, we explore why organisms reproduce, sexual and asexual reproduction, and learn in detail about sexual reproduction in flowers and human beings. The unit is aligned to the CBSE class 10 curriculum.
Introduction to reproduction
- Why reproduction (Intro) (Opens a modal)
- Reproduction, DNA, sexual & asexual (Opens a modal)
- Variation & it's importance (Opens a modal)
- Types of reproduction review (Opens a modal)
- Variation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Sexual and asexual reproduction Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Asexual reproduction and its types
- Fission (binary & multiple) with examples (Opens a modal)
- Budding, fragmentation, regeneration & spores (Opens a modal)
- Vegetative propagation (& advantages) (Opens a modal)
- Types of asexual reproduction Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Vegetative propagation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Introduction to sexual reproduction
- Why sexual reproduction (Faster variation) (Opens a modal)
- Germ cells, gametes & sexual reproduction (Opens a modal)
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
- Flower sexual parts (unisexual & bisexual) (Opens a modal)
- Flower: Parts of stamen, carpel (Opens a modal)
- Pollination (self & cross) (Opens a modal)
- Fertilisation, zygote, embryo, germination (Opens a modal)
- Parts of a flower Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Pollination and fertilisation in plants Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Human reproduction
- Puberty & physical changes (Opens a modal)
- Male reproductive system (humans) (Opens a modal)
- Female reproductive sys, menstruation & fertilisation (Opens a modal)
- Placenta | How do organisms reproduce (Opens a modal)
- Contraceptives (mechanical barriers, hormonal, surgical) (Opens a modal)
- Male reproductive system Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Female reproductive system Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- The reproductive system Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Reproductive health Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce includes all the intext and exercise questions. Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce NCERT questions and answers help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in Class 10 board exam. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 NCERT Questions and Answers
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce NCERT Questions and Answers are prepared by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Intext Questions
Intext Question (Page No. 128)
Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell. The DNA is the information site for making proteins and each specific type of protein leads to a specific type of body design. Thus, it is the DNA molecule that determines the body design of an individual. Therefore, it can be concluded that it is the DNA that gets transferred from parents to off-springs and makes them look similar.
Question 2: Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer: The reason why the variation is beneficial to the species than individuals is because sometimes the climatic changes have a drastic effect on the species, which makes their survival difficult. For examples, if the temperature of the water body increases, then there might be certain species of microorganisms which might die. This may result in disturbance in the environment. So, variation is beneficial to species and not for the individuals.
Intext Question (Page No. 133)
Question 1: How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Question 2: How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Answer: There are many advantages, if an organism reproduces through spores.
Advantages of spore formation:
- Large numbers of spores are produced in one sporangium.
- Spores are distributed easily by air to far-off places to avoid competition at one place.
- Spores are covered by thick walls to prevent dehydration under unfavourable conditions.
Question 3: Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer 3: Simple organisms such as Hydra and Planaria are capable of producing new individuals through the process of regeneration. The process of regeneration involves the formation of new organisms from its body parts. Simple organisms can utilize this method of reproduction as their entire body is made of similar kind of cells in which any part of their body can be formed by growth and development.
However, complex organisms have organ-system level of organization. All the organ systems of their body work together as an interconnected unit. They can regenerate their lost body parts such as skin, muscles, blood, etc. However, they cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration.
Question 4: Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Answer: Following are the advantages of practising vegetative propagation for growing some types of plants:
- Crops like orange, banana, pineapple do not have viable seeds, so vegetative propagation can be used.
- It is a rapid, cheap and easier method to grow crops.
- It can be used in places where seed germination fails.
- A good quality of variety can be preserved.
Question 5: Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) copying is an essential part of reproduction as it passes genetic information from parents to offspring. It determines the body design of an individual. The reproducing cells produce a copy of their DNA through some chemical reactions and result in two copies of DNA. The copying of DNA always takes place along with the creation of additional cellular structure. This process is then followed by division of a cell to form two cells.
Intext Question (Page No. 140)
Question 1: How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Answer: Pollination is defined as the process of transfer of pollens from anther to stigma. The process takes place with the help of pollinators like air, water and some insects.
Fertilization is defined as the fusion of male and female gametes. It takes place in the ovule and leads to the formation of zygote.
Question 2: What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer: The secretions from seminal vesicles and prostate glands lubricate the sperms and provide a fluid medium for easy transport of sperms. Their secretion also provides nutrient in the form of fructose, calcium, and some enzymes.
Question 3: What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Answer: Secondary sexual characteristics in girls:
- Increase in breast size and darkening of skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
- Appearance of hair in the genital area.
- Appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
- Increase in the size of uterus and ovary.
- Beginning of menstrual cycle.
- More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
Question 4: How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer: The embryo develops inside the mother’s body for about nine months. Inside the uterus, the outer tissue surrounding the embryo develops finger-like projections called villi. These villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood. They provide a large surface area for exchange of oxygen and nutrients. Also, there is a special tissue called placenta, which is embedded in the uterine wall. The embryo receives the oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood via the placenta. The waste materials produced by the embryo are also removed through the placenta.
Question 5: If a woman is using a copper−T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer: No, because usage of copper-T cannot stop the contact of body fluids. Hence, it cannot protect her from getting sexually transmitted diseases.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Exercise Questions
Question 1: Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in (a) amoeba (b) yeast (c) plasmodium (d) leishmania
Answer: (b) in yeast.
Question 2: Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings? (a) Ovary (b) Uterus (c) Vas deferens (d) Fallopian tube
Answer: (c) Vas deferens
Question 3: The anther contains (a) sepals (b) ovules (c) carpel (d) pollen grains
Answer: (d) pollen grains.
Question 4: What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer: Advantages of sexual reproduction:
- In sexual reproduction, more variations are produced. Thus, it ensures survival of species in a population.
- The new formed individual has characteristics of both the parents.
- Variations are more viable in sexual mode than in asexual one. This is because in asexual reproduction, DNA has to function inside the inherited cellular apparatus.
Question 5: What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
Answer: The testes are the male reproductive organs that are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
Functions of testes:
- Produce sperms
- Produce a hormone called testosterone, which brings about secondary sexual characters in boys.
Question 6: Why does menstruation occur?
Answer: Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilized, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
Question 7: Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Question 8: What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer: The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting of sperms and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females.
Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur.
Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as tubectomy.
Question 9: How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Question 10: How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Answer: Living organisms reproduce for the continuation of a particular species. It helps in providing stability to the population of species by producing a new individual that resembles the parents. This is the reason why cats give birth to only cats or dogs give birth to only dogs. Therefore, reproduction provides stability to populations of dogs or cats or any other species.
Question 11: What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer: Following are the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods:
- To control population
- To avoid unplanned pregnancy
- To avoid transfer of sexually transmitted diseases
Topics covered under Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – A Brief Discussion
Chapter Overview: Have you ever wondered why do organisms reproduce? Whatever the answer to this question but it is obvious that we see organisms because they reproduce. In this chapter, you will learn about the modes of reproduction used by unicellular such as fission, fragmentation, regeneration, budding, vegetative propagation and spore formation. All these modes are the asexual modes of of reproduction. Mutlicellular organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction over asexual mode. This chapter explains you the sexual mode of reproduction in plants and animals.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 8 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? Revision Notes - Free PDF Download
Chapter 10 in Science deals with the topic of 'How do organisms reproduce'. This chapter primarily discusses the reproductive system in living organisms and the types of reproductive systems, in particular. It shows the different methods of reproductive systems in plants and animals and distinguishes between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Reproduction Class 10 notes further elaborates on the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system. The chapter lays down the various intricacies associated with it and other related aspects. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science revision notes for All chapters:

Related Chapters
Access Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – How do Organisms Reproduce?
1. do organisms create exact copies of themselves .
The organisms are similar in their looks due to having similar body designs, which in turn indicates that the source for these designs must be similar. And hence reproduction is that process where these designs are created.
The nucleus of a cell contains the chromosomes, which carry the information for the inheritance of features from parents to the next generation. It is present in the form of DNA molecules.
The DNA present in the nucleus of a cell is the source of information for making proteins. If this information changes, then a different set of proteins will be synthesised which will eventually lead to altered body designs in the organisms.
Hence it can be noted that a basic event in reproduction involves the creation of a DNA copy.
This copying of DNA is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, after which the DNA copies separate with each of them having its own cellular apparatus. Thus, a cell divides to give rise to two cells.
Since this process of copying DNA is a biochemical process, it may not be reliable and it will lead to some variations each time.
If the created new DNA copy is not viable, then the cell will not survive. And the surviving cells will be similar but may not be identical to the original and will subtly differ from each other.
1.1 The Importance of Variation
The consistent DNA copying that happens during reproduction is essential to maintain the features of body design of an organism so that it can occupy its well-defined space or niche in the ecosystem.
Hence reproduction is very much linked with the stability of a population of a species.
The variations become important here as an organism may be suited for a specific niche and a drastic change in that due to unforeseen environmental conditions makes their survival difficult.
Hence in such situations when a few among the species have some variations, they stand a chance of survival in the new niche. And thus, these species adapt themselves to the new conditions and the species are maintained over a period of time.
It can be understood with an example. If a species of bacteria is living in the temperate waters and suddenly the temperatures rise due to global warming, then most of the bacteria in that water would not survive. But maybe a few variants among them who are able to resist the heat may survive and grow. In case the variations were not present, that entire species of bacteria would have become extinct.
Thus, the importance of variation lies in the survival of a species over time.
2. Modes of Reproduction
Reproduction can be defined as a process that involves the production of an offspring by a particular individual or individuals with the aim of propagating their species. Generally, reproduction happens during the reproductive phase of an organism. The mode of reproduction may vary in organisms. They can be broadly categorised as:
Asexual Mode of Reproduction:
The mode of reproduction by means of which a single individual creates a new generation of species is termed as asexual reproduction.
Generally unicellular organisms exhibit asexual mode of reproduction, though some of them exhibit sexual mode too.
Sexual Mode of Reproduction:
The mode of reproduction by means of which two individuals take art in the creation of a new generation of species is termed as sexual reproduction.
Types of Asexual Mode of Reproduction:
2.1.Fission:
In unicellular organisms the new individuals are created by the process of cell division or fission.
The nucleus of the cell divides into new individual cells under favourable conditions.
Fission can be of two types depending on the number of new individuals created.
Binary Fission: This division leads to the formation of two new individuals. These can be further divided based on their plane of division as:
Irregular binary fission: In this type of fission the plane of division of a cell is irregular, it can be in any plane. Example - Amoeba.
Transverse binary fission: In this type of fission the cells divide along a transverse plane. Example - Paramecium.
Longitudinal binary fission: In this type of fission the plane of cell division is longitudinal. Example - Euglena.
Multiple fission: This is the Division of a Single Cell into Many New Daughter Cells. Example - Plasmodium.
2.2.fragmentation: .
This is a process where an organism simply breaks up into smaller pieces when they are mature.
Each of the fragments or broken pieces grow into a new individual. There should be a cell that is capable of growing into a new individual in such organisms.
Example - Spirogyra.
2.3. Regeneration:
This is a process where some fully differentiated organisms can be cut or broken into pieces and each of their body parts have the ability to grow into a new individual.
Different cells in this mass of cut cells undergo a lot of changes in an organised manner to become different cells and tissues.
Example - Planaria, Hydra.
2.4. Budding:
This is a process where a protuberance like outgrowth which is called as bud grows by repeated cell division at a specific site and then they detach from the parent body to develop into a separate individual organism.
Example - Hydra.
2.5.Vegetative Propagation
This is the mode of reproduction by which plants reproduce asexually. In this mode, new plants are developed from a plant’s vegetative parts like stem, leaf, root. There are different methods of vegetative propagation that are carried out in plants which are as follows:
Stem Cutting: This involves cutting the stem into small pieces having internodes and axillary buds. These are then planted in the soil to propagate into new plants. This method is used in sugarcane, hibiscus, drumstick etc.
Layering: This is a method where the young stem of a plant is bent and buried in the soil to develop roots and thus a new plant. Once the new plant develops, the stem is detached from the parent plant. This is used in jasmine, bougainvillaea.
Grafting: This is a method wherein the stems of two different plants are cut and joined together to unite and start developing into a new plant. This is used in nutmeg, roses etc.
Leaf buds: This is a method in which the buds in the notches of leaves develop into new plants. This can be seen in bryophyllum.
Advantages of the Vegetative Propagation, Which are as Follows:
The plants that are grown by vegetative propagation bear flowers and fruits earlier as compared to the plants produced from seeds.
All plants that are produced this way are genetically similar to the parent plant and have all its characteristics.
2.6. Spore Formation:
Many multicellular organisms have specific reproductive parts.
They have tiny thread-like structures with a blob called sporangia.
These contain cells or spores which eventually develop into new individuals. The spores are very light and covered by a thick wall to protect them and when they come in contact with a moist surface they start to grow.
Example - Rhizopus.
3.Sexual Reproduction:
3.1. Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction?
The sexual mode of reproduction involves two organisms, a male and a female to create a new organism or offspring.
The sexual reproduction allows greater variations in a species as the two individuals involved in producing the offspring would have different patterns of variations. This process includes the combination of DNA of two different individuals and the resultant combination and variation would be unique.
Hence this ensures a mixing of the gene pool of the species within a population and it also ensures the survival of the species as this process generates more variations due to the genetic recombination.
The process of combining DNA of two different individuals during sexual reproduction will lead to an offspring with twice the amount of DNA than their previous generation.
The solution to this lies in the fact that there are certain specialised cells in such organisms called germ cells or gametes. These have half the number of chromosomes and, therefore half the amount of DNA in comparison to the other non-reproductive cells. The combination of these germ cells from two different individuals during the process of sexual reproduction restores the original number of chromosomes and DNA content in the new offspring.
The germ cells may be similar and not much different from each other in simple organisms. With the complexity of the organisms the germ cell also becomes specialised. One of the germ cells becomes large and stores food. This is known as the female gamete. The other germ cell which is small and motile is called the male gamete. These gametes lead to the differences in the bodies and reproductive systems of males and females.
3.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
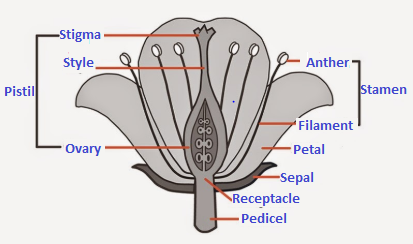
The process of sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of gametes to produce offspring. The reproductive parts in angiosperms (plants that flower and produce fruits and seeds) are located in the flower. The parts of a flower consist of sepals, petals, stamens and pistils.
The reproductive parts of the flower are stamen which contains the male gamete and the pistil containing the female gametes.
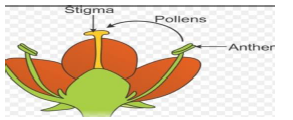
Stamen: This is the male reproductive part and is also known as the androecium. It consists of a filament and an anther that encloses the pollen grains. The pollen grains produce the male germ-cells or gametes.
Pistil: This is the female reproductive part of the flower and is also known as gynoecium. This is made of three parts, namely, stigma, style and ovary. The enlarged portion at the bottom of a pistil is the ovary that contains an ovule with an egg cell. The middle long part of the pistil is the style and the terminal sticky part is the stigma.
Based on the presence of the stamen or pistil, flowers can be classified as:
Unisexual: These are the flowers that contain either stamens or pistils. These are also called incomplete flowers. Example - papaya, mulberry, watermelon etc.
Bisexual: These are flowers that contains stamens as well as pistils. Example - Hibiscus, mustard, rose etc.
The process of sexual reproduction in plants starts with the fusion of the male and the female gametes, followed by the formation of a zygote that eventually develops into a new plant. The process is explained as follows:
Pollination:
The process of sexual reproduction in plants starts with the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of the pistil. This process is termed as pollination.
This is facilitated by pollinating agents like wind, birds, animals, water etc. which transfer the pollen grains.
There can be two types of pollination as follows:
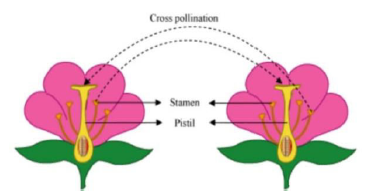
Self-Pollination: This involves the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. Example - wheat, peanut, etc.
Cross-Pollination: This type of pollination involves the transfer of the pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species. Example - apples, pumpkin etc.
Fertilization:
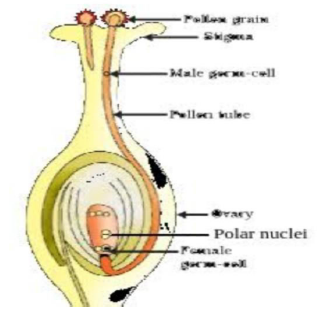
Through the process of pollination, the pollen is deposited in the style of the pistil. For the next process in reproduction, it needs to reach the female germ-cells which are present in the ovary.
To facilitate this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and reaches the ovule in the ovary of the pistil.
Here in the ovule the male germ-cell fuses with a female germ-cell to form a zygote. This process of fusion of the gametes is termed as fertilisation.
After the process of fertilization, the zygote thus formed, divides repeatedly to form an embryo inside the ovule. The ovule later develops into a seed.
And meanwhile the ovary grows and ripens into a fruit and the other parts of the flower, namely the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may be shed off.
The seed present inside the fruit encloses the future plant in its embryo.
Germination:
The seed that contains the new plant or embryo develops into a seedling when the conditions are suitable. This process is termed as germination. Certain conditions like nutrients, water and proper temperature are necessary for the process of germination.
The embryo gets its food from the reserve food material stored in the cotyledons. It also has a protective outer covering known as seed coat.
3.3. Reproduction in Human Beings.
The mode of reproduction in human beings is sexual mode. The reproductive phase of an individual is that phase of life when the individual is ready to reproduce an offspring. Changes are noticed at every phase of growth right from birth.
But there are some changes that begin in the teenage age that start to prepare us for the reproductive phase of life. This period of adolescence leads to sexual maturation. The body needs to create specialised germ-cells to take part in the sexual reproduction. The period of maturation of the reproductive tissues in the body is termed as puberty.
Numerous changes are noticed in both boys and girls during this period. The boys start to have hair growth on their face and body, voice change, active functioning of sweat and sebaceous glands, enlargement of penis etc. The changes in the girls include growth of pubic hair, enlargement of breasts, oily skin leading to pimples, onset of menstruation etc. Both of them undergo changes in their body appearance and they become more conscious of these bodily changes.
The process of fusion of germ-cells in sexual reproduction, the actual transfer of these germ-cells needs to be done. For the same special organs need to be present like penis in males and uterus in females for carrying the baby.
3.3.1. Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of organs that produce and transport the male germ-cell or gamete, male hormone testosterone and the organs which facilitate the discharge of male germ-cells into the female reproductive system for fertilization.
The male gamete is the sperm which is a tiny body containing the genetic material and they have a long tail for motility to help them reach the female germ-cell for fertilization.
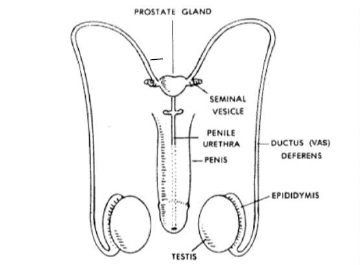
The system consists of some external organs like penis, scrotum, testes and internal organs like urethra, prostate and seminal vesicles.
Testes: Testes is the part that is responsible for the production of the male germ-cell or sperms and the male hormone testosterone. Testes are present in a structure known as scrotum, located outside the abdominal cavity. This is thus located because the formation of sperm requires a temperature that is lower than the normal body temperature. The hormone testosterone plays a role in regulating the formation of sperms and also the development of the secondary sexual characteristics that are seen in boys during puberty.
Vas Deferens: The sperms that are produced in the testes are stored in the epididymis. Vas deferens is a tube that transports these sperm to the urethra.
Urethra: This is a common passage for the sperm as well as urine. The same passage connects the urinary bladder and the vas deferens.
Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles: These glands are located along the vas deferens. They secrete a fluid, called semen that nourishes the sperm. This semen helps in the easier movement of sperms.
3.3.2. Female Reproductive System.
The female reproductive system includes the organs that produce the female germ-cells, provides site for fertilization of the gametes and development of the embryo into a new individual.
The female gametes are the eggs that are produced in the ovaries.
They also produce some hormones like estrogen and progesterone that are responsible for the onset of secondary sexual characteristics in girls at puberty.
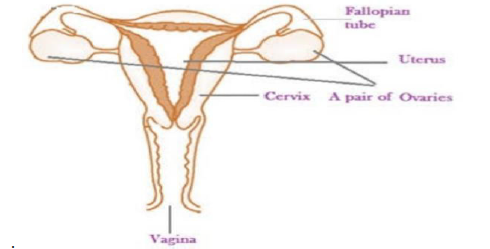
This system includes a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus and vagina that opens externally through the urethra.
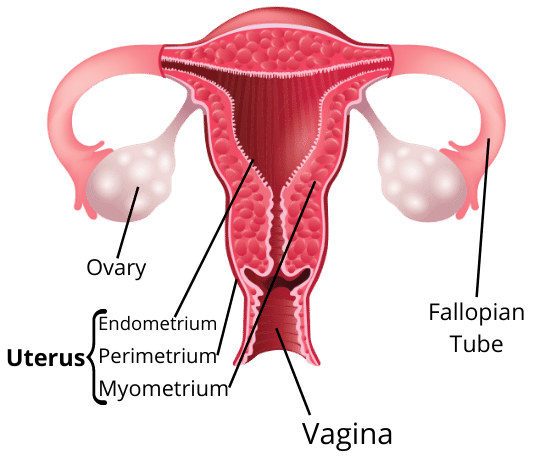
Ovaries: The ovaries are a pair of glands that are located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries protect the female gametes or eggs and make them suitable for fertilization. At birth the ovary of a girl contains thousands of eggs that are immature. After puberty, when the eggs mature, the ovaries release one egg every month. The ovaries also produce the hormones oestrogen and progesterone that are essential in bringing the secondary sexual changes in a girl at puberty.
Fallopian tube: This is also known as oviduct. This is a thin tube that connects the ovaries to the uterus. The eggs that are released by the ovary are transported through this tube.
Uterus: This is a bag-like muscular elastic structure into which the two oviducts open. The uterus is the site where the fertilized egg is implanted and it grows into a foetus. It is made of 3 tissues, outer perimetrium, middle layer of myometrium and the inner endometrium. This is also responsible for supporting the developing foetus during the entire gestation period.
Cervix: This is the site where the uterus opens into vagina. This facilitates a passage for the entry of the sperm into the uterus.
Fertilization and Development:
The process of fertilization of a male and female gamete or sperm and egg starts when the sperm enters the female reproductive system through the vaginal passage during a sexual intercourse. From the vaginal passage they move up through the uterus towards the fallopian tubes.
The eggs are present in the fallopian tube, meet the sperm and get fertilized.
The fertilized egg, which is known as the zygote, starts dividing repeatedly and travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus.
The ball of cells or embryo gets implanted in the endometrial lining of the uterus and continues to grow into a foetus. The embryo gets its nourishment from the mother through a special tissue called the placenta which acts as a connection between the mother and the developing embryo. It helps to transport glucose and oxygen to the embryo and remove the wastes generated by the embryo.
It takes about nine months for the complete development of the child inside the mother’s body. The child is born due to the rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles.
3.3.3. What Happens When the Egg is Not Fertilized?
An egg is released by the ovary every month in anticipation of it getting fertilised. In case the egg does not get fertilized, it can survive for only a day. Similar to the ovary releasing an egg every month, every month, the uterus too prepares itself to the fertilized egg by creating a thick and spongy lining in order to provide nourishment to the embryo.
When the fertilization does not occur, this lining too is not required and this lining and the egg is shed as blood and mucous through the vagina. This is called menstruation. This cycle occurs every month and lasts for about 2 - 8 days roughly.
3.3.4. Reproductive Health.
The process of sexual maturation is a gradual one which happens while the general body growth is ongoing. Some amount of sexual maturation does not prepare a young person to be sexually active or get married and bear children and bring them up.
Reproductive health deals with all these aspects concerned with healthy and safe sexual practices. It becomes difficult for the young people to make the correct choice given the various types of pressure they face from peers, family, society.
Lack of proper information and unhealthy sexual practices can lead them to contract some diseases from one partner to another and even to the offspring as a sexual act is an intimate physical contact between them. The diseases transmitted in this manner are termed as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), like bacterial infections such as gonorrhoea and syphilis, viral infections such as warts and HIV. These can lead to health complications and be fatal too if left untreated.
Reproductive health covers the area of safe sex to help young people. Pregnancy is a risk in a sexual act. As pregnancy is very demanding for the body and mind and has to be planned, unwanted pregnancies and abortions can be avoided by using some contraceptive methods.
The contraceptive methods can be by using physical barriers that block the entry of sperm into oviducts and not letting fertilization take place. Examples are condoms or coverings on the penis.
Contraceptive devices like Copper-T or intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) that are implanted in the uterus which does not allow the sperm to travel ahead.
The other contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body, preventing fertilization. These are mostly in the form of drugs which can be taken orally in a scheduled manner. Examples are pills like Mala D, I-pill etc.
Another method is the surgical one like vasectomy in males in which the vas deferens is blocked to prevent the transfer of sperm. In females, tubectomy is done which blocks the fallopian tube and thus prevents the egg from reaching the uterus. The surgical methods are more reliable and safer as compared to the other methods.
Though surgery is used to abort unwanted pregnancies, it has been widely misused by the people, especially for illegally aborting a female foetus.
There is a law in place to prevent this female foeticide (killing of a foetus), which states that prenatal sex determination is prohibited.
A proper ratio of males to females is essential to maintain a balance in the society and to have a healthy population too.
Chapter-wise CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Free PDFs
The links to Class 10 Science chapter-wise Revision Notes are given below.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Revision Notes
Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts Revision Note s
Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals Revision Note s
Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds Revision Note s
Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements Revision Notes
Chapter 6 Life Processes Revision Note s
Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination Revision Notes
Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? Revision Notes
Chapter 9 - Heredity and Evolution Revision Notes
Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notes
Chapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful World Revision Notes
Chapter 12 - Electricity Revision Notes
Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Revision Notes
Chapter 14 - Sources of Energy Revision Notes
Chapter 15 - Our Environment Revision Notes
Chapter 16 - Management of Natural Resources Revision Note s
How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 PDF Download
The chapter on reproduction of organisms will be introduced to the students for the first time. It becomes necessary that students gain a clear idea about the relevant concepts. While preparing, students may require short keynotes or revision notes. Further reference materials may be needed to make the understanding of concepts easier. Should a student feel the need for such materials, one can easily download the free PDF materials available over Vedantu's website.
Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce Notes
Several important aspects of the chapter are discussed in Class 10th Science Chapter 8 notes. Some of those are:
Importance of Variation in Species
Body design features from parent to offspring are preserved with the consistency present in DNA copying. However, it may so happen that changes in existing environmental conditions may need variation to occur in species. Without that, it could be that a particular species may go extinct. Hence, variation is also important for species for survival.
Types of Reproduction
There are two types of reproduction – (1) asexual mode of reproduction, and (2) sexual mode of reproduction.
In the asexual mode of reproduction, it is a single organism that creates the next generation of species. On the other hand, in sexual reproduction, two organisms are needed for creating the offspring.
It is important to note that reproduction in unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms is markedly different. More often than not, asexual reproduction takes place unicellular organisms. Such reproduction can happen through any of the following methods:
Fission – DNA is duplicated into two parts.
Fragmentation – Organisms when mature break up into smaller pieces.
Regeneration – Fully differentiated organisms are giving rise to individual organisms.
Budding – Detachment of bud for developing into a separate organism.
Vegetative Propagation – New plants created from vegetative parts of existing plants.
Spore Formation – Spores bursting out of sporangia develop into new individuals.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place with the joining of male pollen and female eggs. The male reproductive part is the stamen which produced pollen grains. The female reproductive part is the carpel, from which ovules generate from the ovary.
Reproduction in Human Beings
As mentioned in reproduction class 10 notes, the male reproductive system includes testis, vas deferens and the muscular organ, penis. The male gamete, sperms, are generated from testes. The movement of sperm happens through the vas deferens.
On the other hand, the female reproductive system consists of ovaries, oviducts, uterus and vagina opening out through the urethra. The female gametes, eggs, are developed within the ovaries. The movement of eggs happens through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube.
If you are seeking expert guidance on Class 10 reproduction notes or seek solutions to the doubts that you may have while preparing the chapter, reach out to us today! All you have to do is download the app, and get started.
What are the Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s Revision Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce
Provides quick, clear summaries of key concepts.
Simplifies complex topics for better understanding.
Efficient tool for last-minute exam prep.
Enhances retention of crucial information.
Supports effective exam preparation with key points and tips.
Saves time by consolidating information.
Prioritizes important topics and questions.
Offers practical examples for real-world connections.
Boosts student confidence for exams.
Related Study Materials for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
The links given below are for the various other study resources prepared by the subject experts at Vedantu on Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. These study materials are available for free download on Vedantu’s website and students can refer to them for their exam preparation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce?
NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? (Book Solutions)
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science: Previous Year Question Paper and Solutions Free Download (2007-2023)
For an enhanced comprehension of this subject, NCERT - Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce thoughtfully prepared by experienced educators at Vedantu is your invaluable companion. These notes break down the complexities of “How Do Organisms Reproduce” into easily digestible sections, helping you grasp new concepts and navigate through questions effortlessly quickly at the last minute as well. By immersing yourself in these notes, you not only prepare for your studies more efficiently but also develop a profound understanding of the subject matter.

FAQs on How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 8 (Free PDF Download)
1. What is Fission in Reproduction?
Ans: Fission, as discussed in How do organisms reproduce Class 10 notes, is the separation of a single body into two new bodies by duplication of the genetic material of the organism. In the process of fission, deoxyribonucleic acid undergoes division to form two parts. The second process is termed as cytokinesis. Binary fission is an example of asexual reproduction and organisms falling under Bacteria and Archaea exhibits this type of reproduction process.
2. What are the Benefits of Vegetative Propagation?
Ans: The most prominent advantages of vegetative propagation have been outlined in Class 10 Science Chapter 8 notes. One of the major benefits is that the new plants will retain the genetic material of a single parent. It means that if specific desirable traits have been identified in the parent plant, the same will be replicated in the offspring as well. However, for that to happen, growing conditions have to be kept the same.
Notes of Chapter 8 Science Class 10 also mentions that in the case of vegetative propagation, the immature seedling phase is bypassed. Such development helps in reaching the mature phase faster.
3. What is Meant by Spore Formation?
Ans: Spore formation has been explained lucidly in Class 10 Chapter 8 Science notes. It is a process of asexual reproduction exhibited by plants such as moss, ferns, fungi etc.
Spores are essentially reproductive bodies which are unicellular. Those are present in a sac-like structure known as sporangia. On attaining maturity, spores burst out from sporangia and transmitted to various places with the help of wind, air or water.
4. What is the Function of Pollination in Plant Reproduction?
Ans: Class 10 Reproduction notes discuss pollination as the procedure of transmitting pollen from the male part of a flower, anther, to the female part of a flower, stigma. However, it must be noted in this regard that such happens between a male part of one flower to the female part of another flower. With pollination, a seed is produced from fertilised flowers, leading to the formation of fruit.
5. Where can I find Class 10 Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce notes?
Ans: Vedantu offers students with revision notes of Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science. These notes are beneficial to students as it helps them to understand all the important topics and concepts in the chapter better. These notes are written by subject experts in a simple and easy language. Students will be able to score well in their exams with the help of these revision notes. Some of the topics discussed in these notes include importance of variation, modes of reproduction, fragmentation, regeneration, spore formation, and many more. Most of these terms and concepts are important for students to learn and understand.
6. What are the various topics covered in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science?
Ans: There are many important topics and concepts that are discussed in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science. Some of these topics include various modes of reproduction like asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, and reprodution in flowers. Students will even learn about the reproduction that involves cells, the process of DNA copy, and other additional cellular devices. Apart from this, students will learn about the DNA copying mechanisms as well. Other topics covered in Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce of Class 10 Science Science include the understanding of the body design and use of reproductive modes by different organisms.
7. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction?
Ans: Sexual reproduction refers to the mode of reproduction between two individuals. Sexual reproduction has many advantages. Some of these include:
The offspring produced by the parents have characteristics of both of them
Sexual reproduction ensures that there are more variations of the species. This ensures the survival of the species as well
The offspring has the tendency to adapt to the environmental changes that the offspring may face around them
It is known that sexual reproduction improves the health of all human beings
8. What do you mean by asexual reproduction?
Ans: Asexual reproduction refers to the mode of reproduction that involves a single individual creating new generation of species. Under this mode of reproduction, a single parent generates/produces a new offspring. These offspring are physically and genetically identical to their parents. There are many unicellular and multicellular organism that follow asexual reproduction. However, not all of them follow this mode of reproduction. Some of these unicellular organisms exhibit the sexual mode of reproduction as well. Asexual mode of reproduction can include parthenogenesis, budding, fission, and fragmentation.
9. How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Ans: Pollination refers to the process of transferring pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma. This process is done with the help of pollinators. Pollinators refer to the mode of transformation of pollen. These pollinators can include water, wind, and even a few insects. Whereas, fertilization refers to the process of a fusion between the male and female games. Fertilization takes place in the ovule. This further leads to the formation of zygote.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 10
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
How do Organisms Reproduce?
Ncert revision notes for chapter 8 how do organisms reproduce class 10 science.
→ Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth.
→ Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) which is the heredity material.
→ DNA replicates and forms new cells causing variation. So, these new cells will be similar but may not be identical to original cell.
→ Variations are useful for the survival of the individual and species over time as well as basis for evolution.
Asexual Reproduction
→ A single individual give rise to new individual.
→ Gametes are not formed.
→ New individual is identical to parent.
→ It is extremely useful as a means of rapid multiplication.
→ Adopted by lower organisms.
Sexual Reproduction
→ Two individuals i.e., one male and one female are needed to give rise to new individual.
→ Gametes are formed.
→ New individual is genetically similar but not identical to parents.
→ It is useful to generate more variations in species.
→ Adopted by higher organisms.
→ The parent cell divides into daughter cells.
• Binary fission : 2 cells are formed. Example: amoeba.
• Multiple fission : Many cells are formed. Example: Plasmodium.
Fragmentation
→ The organism breaks-up into smaller pieces upon maturation, each piece develops into new individual. Example: Spirogyra.
Regeneration
→ If organism is somehow cut or broken into many pieces, each piece grows into a complete organism. Example: Planaria, Hydra.
→ A bud is formed which develops into tiny individual. It detaches from parent body upon maturation and develops into new individual. Example: Hydra
Vegetative Propagation
→ In many plants, new plants develops from vegetative parts such as:
• By roots : Example: dahlias, sweet potato.
• By stem : Example: potato, ginger.
• By leaves : Example: bryophyllum (leaf notches bear buds which develop into plants).
Artificial methods in Vegetative Propagation
(i) Grafting : Example: Mango
(ii) Cutting : Example: Rose
(iii) Layering : Example: Jasmine
(iv) Tissue culture : New plants are grown by using growing tip of a plant.
→ These growing cells are kept in a culture medium leads to the formation of callus. Callus is then transferred to hormone medium which causes growth and differentiation. Example: ornamental plants, orchid.
• Benefits of tissue culture
→ We can grow plants like banana, rose, jasmine etc. that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
→ New plants are genetically similar to parents.
→ Helps in growing seedless fruits.
(v) Spore Formation : Spores are small bulb like structures which are covered by thick walls. Under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new organism. Example: Rhizopus
→ When reproduction takes place as a result of the fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction.
→ Fusion of gametes is called fertilization which results in variation.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
→ Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants.
→ A typical flower consists of four main whorls namely sepals, petals, stamen and pistil.
Types of Flowers
• Bisexual flower : Both male and female reproductive parts are present. Example: Hibiscus, mustard.
• Unisexual flower : Either male or female reproductive part is present. Example: Papaya, watermelon.
Structure of Flower
→ Pollen grains, produced in the anther, are transferred to the stigma of same flower ( self pollination ) or stigma of another flower ( cross pollination ) through agents like air, water or animals.
→ Pollen grains germinate and form pollen tubes which pass through style to reach upto the ovules present in ovary.
→ The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization. Zygote is produced inside the ovary.
→ Zygote divides to form embryo. Ovule develops thick coat and changes into seed gradually.
→ Ovary changes into fruit and other parts of flower fall off.
→ The seed germinates to form a plant under suitable conditions such as air, moisture etc.
→ Humans use sexual mode of reproduction.
→ Sexual maturation: The period of life when production of germ cells i.e. ova (female) and sperm (male) start in the body. This period of sexual maturation is called puberty.
Changes at Puberty
• Common in male and female
→ Thick hair growth in armpits and genital area.
→ Skin becomes oily, may result in pimples.
• In girls
→ Breast size begin to increase.
→ Girls begin to menstruate.
→ Thick hair growth on face.
→ Voice begin to crack.
These changes signals that sexual maturity is taking place.
→ A pair of testes are located inside scrotum which is present outside the abdominal cavity.
→ Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production of sperms.
→ Male germ cell i.e. sperms are formed here.
→ Testes release male sex hormone (testosterone).
Function of testes:
→ Regulate production of sperms.
→ Bring changes at puberty.
(ii) Vas deferens
→ It passes sperms from testes upto urethera.
(iii) Urethera
→ It is a common passage for both sperms and urine. Its outer covering is called penis.
(iv) Associated glands
→ Seminal vesicles and prostate gland add their secretion to the sperms. This fluid provide nourishment to sperms and make their transport easy.
→ Sperm along with secretion of glands form semen.
→ A pair of ovary is located in both sides of abdomen.
→ Female germ cells i.e. eggs are produced here.
→ At the time of birth of a girl, thousands of immature eggs are present in the ovary.
→ At the onset of puberty, some of these eggs start maturing.
→ One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
(ii) Oviduct or Fallopian tube
→ Receives the egg produced by the ovary and transfer it to the uterus.
→ Fertilisation i.e. fusion of gametes takes place here.
(iii) Uterus
→ It is a bag-like structure where development of the baby takes place.
→ Uterus opens into vagina through cervix.
• When egg is fertilised
→ The fertilized egg called zygote is planted in uterus and develops into an embryo.
→ The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. It provides a large surface area for the exchange of glucose, oxygen and waste material.
→ The time period from fertilization upto the birth of the baby is called gestation period. It is about 9 months.
• When egg is not fertilised
→ The uterus prepares itself every month to receive fertilized egg.
→ The lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy, required to support the embryo.
→ When fertilisation had not taken place, this lining is not needed any longer.
→ This lining breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucus.
→ This cycle takes around 28 days every month and called menstruation.
→ Reproductive health means a total well-being in all aspects of reproduction i.e. physical, emotional, social and behavioural.
• Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
→ Many diseases can be sexually transmitted such as:
(i) Bacterial: Gonorrhoea and syphilis
(ii) Viral: Warts and HIV-AIDS
→ Use of condom prevents these infections to some extent.
→ Contraception : It is the avoidance of pregnancy, can be achieved by preventing the fertilisation of ova.
• Methods of contraception
(i) Physical barrier
→ To prevent union of egg and sperm.
→ Use of condoms, cervical caps and diaphragm.
(ii) Chemical methods
→ Use of oral pills
→ These change hormonal balance of body so that eggs are not released.
→ May have side effects.
(iii) Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD)
→ Copper-T or loop is placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy.
(iv) Surgical methods
→ In males the vas deferens is blocked to prevent sperm transfer called vasectomy.
→ In females, the fallopian tube is blocked to prevent egg transfer called tubectomy.
→ The practice of killing a female child inside the womb is called female foeticide.
→ For a healthy society, a balanced sex ratio is needed that can be achieved by educating people to avoid malpractices like female foeticide and prenatal sex determination.
→ Prenatal sex determination is a legal offence in our country so as to maintain a balanced sex ratio.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Metals and Non-metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements
Related Questions
- NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 Science
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Study Notes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 1 Minute

Download free printable assignments and worksheets of class 10 Science. Free PDF Download- Best collection of notes, important questions , sample papers and NCERT Solution for CBSE Class 10 Science.
BIOLOGY: FOR CBSE CLASS 10 (Science Book 1) Kindle Edition
by MANJU KAUSHIK (Author) Format: Kindle Edition
Download our all new app for latest notes and useful assignments.
One App For All Your Needs.
Google Play Link: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.successrouternotes
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
1 thought on “ Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Study Notes ”
- Pingback: Science (CBSE Class 10) – Gurukul For JEE & NEET
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
How Do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science Notes And Questions
Please refer to How Do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 10 . You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Science How Do the Organisms Reproduce Notes and Questions
Multiple choice questions.
Question. ___________ is the portion on which grafting is done and it provides the roots? (a) Stock (b) Scion (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
Question . Which one of the options is incorrect? Vegetative propagation is practised because (a) Plants which produce non viable seeds can be grown. (b) It is a easier method than sowing seeds. (c) Such plants produce seeds and fruits much earlier than other methods (d) For obtaining better species of plants.
Question . What is the surgical method of contraception in female and male respectively? (a) Tubectomy and Vasectomy (b) Vasectomy and Copper-T (c) Tubectomy and Copper-T (d) None of these
Question . What is the puberty age in human males? (a) 8-10 (b) 10-12 (c) 12-14 (d) 14-16
Question . Which of these is not the function of the seminal vesicles present in human males? (a) To covert the sperms in a fluid medium. (b) To provide nutrition. (c) To make their transport easier. (d) To make them sticky.
Question . In which of the following plant bud in notches of leaves help in its propagation? (a) Radish (b) Bryophyllum (c) Bougainvillea (d) Jasmine
Question . The process of the transfer of pollen grains from the flower of one plant to the stigma of the flower of another plant of the same species is known as (a) Cross pollination (b) Fertilisation (c) Self pollination (d) None of the above
Question . Why are the testes located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum? (a) Because sperm formation requires more spaces. (b) Because sperm formation requires a lower temperature. (c) Because sperm formation requires a higher temperature. (d) None of the above.
Question . The two oviducts in a human female unite into an elastic bag like structure known as (a) Vagina (b) Uterus (c) Fallopian tube (d) Cervix
Question . Identify the organism

(a) Rhizobium (b) Rhizopus (c) Rhizoid (d) Mushroom
Question . The process where the unfertilised egg is released out of the body with the blood used to nourish the embryo is known as (a) Menstruation (b) Fertilisation (c) Germination (d) Pollination
Question . Unisexual flowers contain (a) Both stamen and carpel (b) Only stamen (c) Only carpel (d) Either stamen or carpel
Question . The process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells is known as? (a) Karyokinesis (b) Cytokinesis (c) Meiosis (d) Mitosis
Question . Choose the correct option
Question . Vegetative propagation in potato takes place through (a) Stem (b) Root (c) Leaves (d) Seed
Question .Which of these life processes of an organism helps in the growth of its population? (a)Nutrition (b) Respiration (c) Reproduction (d) Excretion
Question . Hydra reproduces————-by————— (a)sexually, budding (b)sexually, regeneration (c) asexually, budding (d)asexually, regeneration
Question .Which of these is a disadvantage of vegetative reproduction? (a)Offspring are genetically identical (b)It is rapid and economical method of reproduction (c)It produces seedless fruits (d)Disease of parent plant gets transferred to the offspring.
Question .When an organism breaks into a number of parts and each part develop into an individual, it is called: (a)Regeneration (b) Budding (c) Binary fission (d) Spore formation
Question . How many chromosomes are present in a ovum of human being? (a)29 (b)21 (c)22 (d)23
Question .The number of chromosomes in parents and offspring of a particular species remains constant due to— (a)doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation (b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation (c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation (d) halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
Question .In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are——– (a)stamen and anther (b)Filament and stigma (c) Anther and ovary (d) stamen and style
Question .In the list of organisms given below, those that does not reproduce by the asexual method are———— (a) Spirogyra (b) dog (c) yeast (d) amoeba
Question .Which of these is not a part of male reproductive system? (a)Scrotum (b) Oviduct (c) Vas-deferens (d) Prostrate gland
Question .The process of development of seedling from an embryo under suitable condition is called (a)Regeneration (b) Pollination (c) Germination (d) Dormancy
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion(A) is followed by a statement of reason(R). Mark the correct choice as: (a)Both assertion (A) and reason(R)are true and reason(R)is the correct explanation of assertion(A) (b)Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A) (c)Assertion (A) is true but reason(R) is false (d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R)is true
Question.Assertion (A): Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission Reason (A): Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction. Ans. Correct option (b)
Question.Assertion: Plants are vegetatively propagated even though they bear seeds Reason(R): Potatoes reproduces through tubers, apples by cutting etc Ans. Correct option (b)
Question.Assertion (A): In human male, testes are extra-abdominal which are present inside scrotum. Reason(R): Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production and storage of sperms. Ans. Correct option (a)
Question.Assertion (A): Surgical methods are most effective methods of contraception. Reason(R): Surgical method blocks gametes transport and hence prevent fertilization. Ans. Correct option (a)

Very Short Answer Questions
Question.Name the following: (a) The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy. Ans. Photosynthesis
(b) Organisms that can prepare their own food. Ans. Autotrophs
(c) The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Ans. Chloroplast
(d) Cells that surround a stomatal pore. Ans. Guard cells
(e) Organisms that cannot prepare their own food Ans. Heterotrophs
(f) An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in stomach that acts on proteins. Ans. Pepsin
Question. Name the correct substrates for the following enzymes. (a)Trypsin (b)Amylase (c)Pepsin (d)Lipase Ans. (a) Trypsin-Protein (b) Amylase-Starch (c) Pepsin-Protein (d) Lipase-Fats
Question. How do we know that two different individuals belong to the same species? Ans. Members of same species are capable of interbreeding the same species by the similarity in their body design and other physical features.
Question . Give the full form of DNA. Ans. Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid.
Question . When does copying of DNA occur? Ans. Copying of DNA occurs during cell division.
Question . Name two plants whose flowers are unisexual. Ans. Papaya, watermelon.
Question . What is fertilization? Ans. Fertilization is the process of fusion of the male and the female gametes.
Question . What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? Ans. DNA copying during reproduction is important for the transfer of parental characters to the offsprings.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is reproduction? Lists its two types. Ans. The production of new organism from the existing organism of the same species is called reproduction. Types of Reproduction (i)Asexual reproduction (ii) Sexual reproduction Asexual Reproduction-The production of new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells (gametes). Sexual Reproduction-The process of production of new organism from two parents by making use of sex cells (gametes)
Question. Name the method by which spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual? Ans. Under favourable conditions spirogyra reproduces by a process known as fragmentation. This is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Question. How does Planaria reproduce? Is this method sexual or asexual? Ans. Planaria reproduces by a process known as regeneration. It is a type of asexual reproduction.
Question. How does Plasmodium reproduce? Is this method sexual or asexual? Ans. Plasmodium reproduces by a process known as multiple fission. Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction.
Question.Define vegetative propagation. List its methods and advantages. Ans. In vegetative propagation new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants-stem, leaves or root without the help of any reproductive organ.
Natural methods of vegetative propagation
Artificial Method of Vegetative Propagation 1. Cutting 2. Layering 3. Grafting
Advantages of vegetative propagation (i)The new plant produced by artificial vegetative propagation will be exactly like parent plant. (ii)The fruit trees grown from cutting or grafting start to bear fruits much earlier. (iii)Many plants can be grown from just one parent plant. (iv)We can also get seedless plant by artificial propagation.
Question.Explain Binary Fission in Amoeba and Multiple fission in Plasmodium. Ans. In the process of fission, a unicellular organism splits to form two or more new organisms. It is of two types. (a)Binary fission: -In binary fission, the parent organism splits to form two new organisms. Examples-Amoeba, Paramecium, Leishmania etc (b)Multiple Fission: -In multiple fission the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at same time. Example-Plasmodium
Question.How will an organism benefit if it reproduces through spores? Ans. The reproduction by spores takes place in plants. Spores are covered by hard protective coat which enables them to survive in unfavorable conditions such as lack of food, water and extreme temperatures. When the conditions are favorable the spores can grow to produce new plants. Thus reproduction by spores’ benefits the plant because by surviving under adverse conditions, the spores make these plants live forever.
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction? Write the importance of such reproduction in nature. Ans. Basic requirement for sexual reproduction is formation of male and female gametes, fusion of gametes.
Importance Combination of DNA from two different individuals leads to increase in genetic variation in the organism. This leads to diversity in the population which helps in natural selection.
Question. List any four steps involved in sexual reproduction and write its two advantages. Ans. Steps of Sexual Reproduction * Formation of male and female gametes. * Transfer of male gamete to female gamete. * Fusion of gametes resulting in zygote formation. * Zygote grows into an embryo forming a new individual.
Advantages: * Increase genetic variation * Plays an important role in the origin of new species.
Question.Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings. Give three reasons in support of the statement. Ans. (i) For continuation of species (ii)It promotes diversity in characters (iii)Enhance the survival chances
Question. Draw a labeled diagram of a human male reproductive system. Ans.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Define pollination. Explain the different types of pollination. List two agents of pollination. How suitable pollination does leads to fertilization? Ans. Pollination: -Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the flower.
Types of pollination: (a) Self Pollination: Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma occurs in the same flower.
(b) Cross Pollination: Pollen is transferred from anther of one flower to stigma of another flower.
Agents of pollination : Wind, Water, Insects and Animals A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style, to reach the female germ cell in the ovary to cause fertilization.
Question. (a) Draw a neat diagram of female reproductive system of human being and label the following (i) Parts where eggs are formed (ii) Site of fertilization (iii) Place of implantation (iv) Place for entry of sperm (b)What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures. Ans (a)
(b)Contraception is the methods or ways to prevent fertilization and pregnancy in fertile females. Three major advantages of adopting contraceptive measures are as follows: (i)Help in family planning and population control. (ii)Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhea, HIV-AIDS etc. (iii)Prevention of unwanted pregnancies.
Question. (a) Write the function of following parts in human female reproduction system: (i)Ovary (ii) Oviduct (iii) Uterus (b)Describe in brief the structure and function of placenta. Ans (a) (i)Ovary: Release egg and female hormone estrogen (ii)Oviduct: Transportation of ovum from ovary to uterus and it is a site of fertilization. (iii)Uterus: Development of embryo (b)Placenta: It is a disc embedded in uterine wall which contains villi on the embryo side of the tissue and blood space on mother side. Function of placenta: (i) Provides nourishment to embryo from mother’s blood. (ii) Removal of waste embryo to mother’s blood.
Question.(a)Draw a well labeled diagram to show the process of fertilization in flowering plant. (b)Explain the process of double fertilization in angiosperm plant. Ans (a)
(b) Double Fertilization – It occurs when one male nucleus fuses with egg cell to form zygote and other male nucleus fuse with two polar nuclei.

We hope the above How Do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science
Related Posts

Introduction and Basics of Computers Class 11 Computer Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English The Hundred Dresses I Summary

User Defined Functions Class 12 Computer Notes and Questions

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. It also has a role of secretion of male sex hormone which brings changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Vas deferens unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra is a common passage for sperms and urine. The prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions so that sperms are now in a fluid.

(i) Name the sex hormone associated with males. (a) Testosterone (b) Progesterone (c) Oestrogen (d) None of these
Answer: (a) Testosterone
(ii) Which of the following statements is incorrect ? (a) Sperms are present in a fluid (b) Fluid provides nutrition to sperms (c) Fluid makes easier transportation of sperms (d) Fluid helps to bind the sperms together
(iii) Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because (a) sperms formation requires higher temperature than body temperature (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature (c) it is easier to transport sperms from the scrotum (d) None of these
Answer: (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature
(iv) Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) Sperms and urine has a common passage from urethra.
(b) Sperms have long tail that helps them to move forward. (c) Sperms contain genetic material. (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
Answer: (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
(v) What is the nature of semen? (a) slightly acidic (b) Neutral (c) Slightly basic (d) Strongly basic
Answer: (c) Slightly basic
Question 2:
Rohit collected some pond water which was dark green in color in a test tube. She took out green-colored mass from it and separated its filaments by using needles. She broke some filaments into small fragments and put them in a Petri dish containing clean water. She observed that after a few days the small fragments gave rise to complete filaments.
2.1) What do you think the mass of green filament was ? (a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament. (b) It was a colony of Volvox algae. (c) It was large brown algae. (d) It was a mass of fungal filaments
Answer:(a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament.
2.2) Organisms that reproduces in similar ways as Spirogyra is : (a) yeast (b) hydra (c) Planaria (d) Sea anemone
Answer: (d) Sea anemone
2.3) The small fragment gave rise to new filament. What does it indicate ? (a) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through budding. (b) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through spore formation. (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation. (d) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fission
Answer: (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation.
2.4) Which among the following organisms do not reproduce by fragmentation ? (a) Riccia (b) Selaginella (c) Aurelia (d) Marchantia
Answer: (c) Aurelia.
2.5) Select the correct statement from the following. (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (b) Both unicellular and multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (c) Fragmentation is sexual mode of reproduction. (d) Fragmentation is found only in algae
Answer: (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation
Question 3:
In humans, if the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day. Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg. Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization had taken place. Now, however, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
3.1) What is the sexual cycle in human female that takes place every 28 days and marked by bleeding ? (a) Sexual cycle (b) Reproductive cycle (c) Menstrual cycle (d) Blood cycle
Answer: (c) Menstrual cycle
3.2) If fertilisation takes place, it results in the formation of : (a) an embryo (b) a zygote (c) a foetus (d) a placenta
Answer: (b) a zygote
3.3) Why does vaginal bleeding occur in human females on attaining puberty ? (a) Unfertilised egg along with thick uterus lining come out of vagina in form of bleeding. (b) In human females, ovaries start releasing egg or ovum once every 28 days from the age of puberty. (c) If fertilisation does not occur then menstrual flow occurs at the end of cycle. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
3.4) In what conditions vaginal bleeding will not occur in a human female who has attained puberty ? (a) If the ovum is fertilised (b) If the ovum is not fertilised (c) If there is some hormonal imbalance in female (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
3.5) Mark one change from the following associated with sexual maturation in boys ? (a) loss of milk teeth (b) weight gain (c) increase in height (d) cracking of voice
Answer: (d) cracking of voice
Question 4: A newly married couple does not want have children for few years. They consulted a doctor who advised them barrier method and chemical method of birth control. Yet another couple who already have two children and are middle aged also consulted doctor for some permanent solution to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Doctor advised them surgical method of birth control.
Another category of contraceptives acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur. These drugs commonly need to be taken orally as pills. However, since they change hormonal balances, they can cause side-effects too. Other contraceptive devices such as the loop or the copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Again, they can cause side effects due to irritation of the uterus.
4.1) What are the barrier methods of birth control ? (a) Condoms (b) Oral pills (c) Surgery (d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) Condoms
4.2) How physical barrier prevent pregnancy ? (a) They kill the sperms. (b) They kill the ovum. (c) They prevent intercourse. (d) They prevent fertilisation
Answer: (d) They prevent fertilisation.
4.3) How chemical methods prevent pregnancy ? (a) Vaginal pills contain chemical called spermicides which kill the sperms. (b) Oral pills prevent ovulation so there will be no fertilisation. (c) Oral pills stop menstruation in females. (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
4.4) Select the correct statement regarding surgical method of birth control. (a) It involves termination of pregnancies in women particularly after eight weeks of conception. (b) Small portion of sperm duct or vas deferences in males is removed by surgical operation and both cut ends are ligated properly. (c) Small portion of oviducts in females is removed by surgical operation and cut ends are ligated. (d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: (d) Both (b) and (c)
4.5) Select the correct statement regarding birth control methods. (a) Barrier method of birth control also protects the couple from sexually transmitted diseases. (b) Some women experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because of change in hormonal balance in body. (c) Surgical method in males is called vasectomy and in females is called tubectomy. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

CBSE Class 10 Topper’s Answer Sheet PDF Download FREE – 2023

CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry MCQ Quiz
Download ntse foundation series for class 10th pdf, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Biotechnology
- Biochemistry
- Microbiology
- Cell Biology
- Cell Signaling
- Diversity in Life Form
- Molecular Biology
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus 2023-2024 Exam
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter-Wise Notes
Life Process
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 5 Life Processes
- Nutrition in Living Organism
- Autotrophic Nutrition - Definition, Types and Examples
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Nutrition In Human Beings - Carbohydrates, Vitamins, Proteins and Fats
- Respiration
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Means of Transportation In Plants
- Human Excretory System
- Excretion In Plants - Definition, Types, Transpiration, Examples
Control and Coordination
- NCERT Notes Class 10 Control and Coordination
- Human Nervous System - Structure, Function, and Types
- Reflex Action
- Brain Anatomy: Structure, Parts, and Function
- Protection of the Central Nervous System
- Coordination in Plants
- Movement Due to Growth in Plants
How does an Organism Reproduce?
How do organisms reproduce for class-10 cbse science notes.
- Asexual Reproduction - Definition, Characteristics, Types, Examples
- Human Reproductive System
- Male Reproductive System - Structure, Organs, Functions
Female Reproductive System
Heredity and evolution.
- Heredity and Evolution Notes Class 10 Notes
- How do the Traits and Characters get expressed?
- Sex Determination
- Evolution - Introduction, Causes, Need, Examples
- Acquired and Inherited Traits - Definition, Differences, Examples
- Speciation and Evolution
- Tracing Evolutionary Relationships
- Evolution Of Humans - History, Stages, Characteristics, FAQs
Our Environment
- Our Environment - Notes CBSE Class 10
- Components of Ecosystem - Biotic and Abiotic
- Food Chains and Food Webs
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Managing the Garbage we Produce
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 – Life Process
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter-13 Our Environment
CBSE Class 10 Chapter-7 How Organisms Reproduce: In the Organisms Reproduce chapter, we will learn the ability of organisms to produce offspring and carry out the next generation. Organisms reproduce in two ways asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Asexual is the mode of reproduction in which the production of the individual from a single parent takes place and sexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction in which the production of individuals from both parents.
Reproduction is the process in which the production of offspring takes place and is also a biological process in which organisms give rise to offspring.
The organism reproduces in two ways those are:
- Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction is the mode of reproduction in which the production of the individual from a single parent takes place. They are identically and genetically similar. In this process, the fusion of gametes does not take place. The gametes are not formed. it is extremely used as a means of rapid multiplications. Mostly it is present in lower animals and plants.
Asexual Reproduction can be further divided into:

It is defined as the splitting of unicellular organisms into two or more daughter cells. Many protozoa and bacteria simply divide into two halves during cells. In organisms such as amoeba the splitting of the parent cell into an equal half of the daughter cell, it can take place at any place.
- Binary fission: It is an asexual reproduction in which organisms duplicate their genetic material and divide into two parts (cytokinesis) and form new daughter cells.
- Multiple fission: It is an asexual reproduction in which organisms divide themselves into more than two daughter cells and the nucleus repeatedly divided and form a large no of nuclei.
Fragmentation
Fragmentation is the process through which an organism fragments into various parts.
This is not true for all multi-cellular organisms. They are unable to simply divide cells at a time. Because many multicellular organisms, as we have shown, are not just a collection of random cells, this is the case. Specialized cells are arranged into tissues, and tissues are arranged into organs, which must then be positioned in specific locations throughout the body.
Regeneration
The process through which plants and animals naturally replace or recover lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs, and even complete body parts to their original state.
Many fully differentiated creatures can produce new individuals from their constituent components. In other words, if the person is chopped or divided into many pieces, many of these bits will grow. into distinct people. Simple organisms like Hydra and Planaria, for instance, can be divided into countless pieces, and each one develops into a full organism.
Budding

A type of asexual reproduction wherein the generative anatomical point of the parent organism serves as the foundation for the development of the young individual. Some species allow buds to grow practically anywhere on the body. organisms like Hydra use regenerative cells in the process of reproduction budding. A Hydra bud forms as an outgrowth as a result of recurrent cell division at one particular point. When completely grown, these buds separate from the parent body and grow into new, independent individuals. They start as tiny individuals.
Vegetative Propagation

Vegetative propagation is the process of creating new plants from the older, non-reproductive portions of an existing plant, such as roots, shoots, and leaves. Many plants have elements including the root, stem, and leaves that, under the right circumstances, sprout new plants.
In many plants, new plants develop from develops from vegetative parts such as
- By roots- sweet potato
- By steam-potato
- By leaves -podophyllum
Tissue Culture
A method of biological research in which fragments of tissue from an animal or plant are transferred to an artificial environment in which they can continue to survive and function. Tissue or cells from a plant’s growing tip are removed in tissue culture to create new plants. After being placed in an artificial medium, the cells quickly divide to create a tiny cluster of cells or calluses. The callus is moved from another environment that contains hormones for differentiation and growth.
Spore Formation
It is possible to identify individual reproductive components in many basic multicellular organisms. The hyphae of the bread mold (Rhizopus) are the thread-like structures that formed on the bread. They do not serve as reproductive organs. The microscopic blob-on-a-stick formations, on the other hand, are engaged in reproduction. In the blobs, which are called sporangia, are cells, or spores, that may one day grow into fresh Rhizopus individuals. The spores are protected by strong walls that keep them from growing until they encounter another damp surface.
Also Read: Types of Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction is the mode of reproduction in which the production of individuals from both parents. In this process the fusion of gametes takes place. The gametes are formed. It involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete (haploids such as sperm or egg) fuse with another gamete and formed a zygote.
It is a natural reproduction method by which all multicellular organisms reproduce. DNA and cellular components must be copied to divide into two new cells from one. As we have learned, errors can occur throughout the DNA copying process, and these errors are what cause variances in creature populations. Variations cannot safeguard each creature, but in a population, they help guarantee the survival of the species. Therefore, it would make sense if organisms devised reproductive strategies that permitted an increasing amount of variety to be produced.
Although DNA-copying mechanisms are not 100% exact, they are accurate enough to make the process of variety formation fairly sluggish. Many of the resulting DNA copies would be inaccurate if the DNA copying mechanisms were to become less precise.
The importance of Variation
Variation can be defined as the variation in DNA sequences. It makes one organism different from the other organism. Variations in a species of an organism help to adapt to the environment, it also prevents the extinction of a species. Modes of reproduction are used by single organisms.
Also Read: Importance of Variation
Sexual Reproduction Plant
Flowers are reproductive parts of plants. A typical flower consists mainly of four parts– sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
Types of Flowers
- Bisexual flower -The flower that has both male and female reproductive organs is known as a bisexual flower because it has both stamens and carpels. The hibiscus, lily, mustard, rose, and sunflower is some examples of bisexual flowers.
- Unisexual flower -Unisexual flowers are those that only include stamens or carpels, the male or female reproductive organs. Cucumber, papaya, pumpkin, and bitter gourd are some examples of unisexual flowers.
Process of Sexual Reproduction in Plants

- The stigma is located at the end of the style and may be sticky. The ovary is located at the bottom, where it is enlarged. Ovules are found in the ovary, and each ovule contains an egg cell. male sperm cells.
- pollen grain unites with the female gamete inside the ovule to form. The zygote that results from the union of the germ cells, or fertilization, can develop into a new plant.
- Therefore, the pollen must be moved from the stamen to the stigma. Self- pollination is the term used to describe this pollen transfer when it takes place within the same flower. On the other hand, cross-pollination refers to the transfer of pollen from one flower to another. This pollen exchange from one.
- Zygote divides from the embryo. Ovule develops a thick coat and changes into seeds gradually.
- The ovary changes into fruit and other parts of the flower fall off.
- The seed germinates to form a plant under suitable conditions such as air, moisture, etc.
Also Read: Cross-Pollination and Self Pollination
Reproduction in Humans
Humans use a sexual mode of reproduction to reproduce. In humans, the male reproductive system includes the testes, which produce sperm, and the penis, which is used to deliver sperm to the female reproductive system during sexual intercourse. The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, which produce eggs, and the uterus, where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. Sexual maturation is the period of life when the production of germ cells i.e. ova (female)and sperm (male) starts in the body. This period of sexual maturation is called puberty .
Changes at Puberty
Following are the changes that occurred during puberty:
- Thick hair growth in armpits and genital area.
- Skin becomes oily, which may result in pimples.
- Breast size begins to increase.
- Girls begin to menstruate.
- Thick hair growth on the face.
- The voice begins to crack
Male Reproductive System

The male reproductive system consists of two portions one that produces germ cells and the other that delivers the germ cell to the site of fertilization. The human male reproductive systems consist of the following organs:-
- A pair of tests are located inside the scrotum which is present outside the abdominal cavity.
- The scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production of sperm.
- Male germ cells i.e., sperms are formed here.
- Testes release the male sex hormone (testosterone)
- Regular production of sperm.
- Bring changes at puberty.
- Vas Deferens: It passes sperm from tests up to the urethra.
- Seminal vesicles and prostate gland add their secretion to the sperms. This fluid provides nourishment to sperm and makes their transport easy.
- Sperm along with the secretion of glands from semen.

Female Reproductive System is the complex structure of organs which work together to produce offspring. Ovary,Fallopian tube, Uterus, Cervix and Vagina are included in the female reproductive system. The ovaries are the two small, almond-shaped glands located on either side of the pelvis, which produce and release eggs (ova) during the menstrual cycle. The fallopian tubes are thin, muscular tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus, and are the site where fertilization occurs if sperm are present.
The uterus, is a muscular organ where a fertilized egg implants and grows during pregnancy. The cervix is the narrow, lower end of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina. It produces mucus that helps sperm move through the reproductive tract. The vagina is the muscular tube that extends from the cervix to the external genitalia. It is the site where sperm are deposited during intercourse and serves as the birth canal during delivery.
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction i.e. physical emotional, social, and behavioral. As we’ve seen, sexual maturation occurs gradually over a period when the body’s basic growth is still occurring. Therefore, a certain level of sexual development does not imply that the body or the mind is prepared for having sex or for having and raising children. How can we tell if the body or the mind is prepared for such a weighty task? We are all facing a variety of stresses related to these challenges. Whether we want to or not, we may feel pressure from our friends to take part in a variety of activities.
FAQs on How Organisms Reproduce?
Q1: difference between binary fission and multiple fission.
In binary fission, the cell divides into two daughter cells whereas in multiple fission the dived daughter cell more cell two
Q2: Define reproduction.
Reproduction is the process in which the production of offspring takes place and is also a biological process in which organisms give rise to offspring.
Q3: Name two simple organisms having the ability to regenerate?
Hydra and Planaria are two organisms that have the ability to regenerate.
Q4: List four modes of asexual reproduction.
The four modes of asexual reproduction are : Binary fission Budding Regeneration Vegetative propagation.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Biology
- School Learning
- Otter.ai vs. Fireflies.ai: Which AI Transcribes Meetings More Accurately?
- Google Chrome Will Soon Let You Talk to Gemini In The Address Bar
- AI Interior Designer vs. Virtual Home Decorator: Which AI Can Transform Your Home Into a Pinterest Dream Faster?
- Top 10 Free Webclipper on Chrome Browser in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce
Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce Chapter 8 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
How do the Organisms Reproduce Assignments Class 10 Science
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. What are all organisms called which bear both the sex organs in the same individual. Give one example of such organism. Answer: Organisms which bear both male and female sex organs in the same individual are called bisexual. For example, Hibiscus.
Question. Name the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.| Answer: Reproduction is a life process that helps in multiplication of an organism and growth of its population.
Question. Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual. Answer: The method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favorable conditions is fragmentation. This is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Question. When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA? Answer: When a cell reproduces, DNA replication occurs which forms two similar copies of DNA.
Question. What happens when a mature Spirogyrafllament attains considerable length? Answer: When a mature Spirogyra flament attains considerable length it simply breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment then grows into a new Spirogyra.
QuestionName the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction. Answer: Calyx and corolla are parts of a flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Question. Name the largest cell present in human body. Answer: Ovum is the largest cell present in human body.
Question. What is DNA ? Answer: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a polymer made up of large number of nucleotide units. It carries genetic information from generation to generation.
Question. List two functions of ovary of human female reproductive system. Answer: Two functions of ovary of human female are: (i) production of female gametes i.e., ova (ii) secretion of female hormones i.e., estrogen and progesterone.
Question. What happens when a Planaria gets cut into two pieces? Answer: When Planaria is cut into two pieces then each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
Question. Name the method by which Hydra reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual ? Answer: Hydra generally reproduces through budding. It is an asexual method of reproduction.
Question. Define multiple fission. Give its one example. Answer: Multiple fission is an asexual mode of reproduction in which the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time. Multiple fission occurs in Plasmodium.
Question. List two unisexual flowers. Answer: Flowers of papaya and cucumber are unisexual.
Question. Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation. Answer: Bryophyllum propagates vegetatively by the buds produced at the margins of leaves.
Question. Name the causative agent of the disease ‘‘Kalaazar’’ and its mode of asexual reproduction. Answer: Causative agent of the disease Kala-azar is Leishmania. It reproduces asexually by binary fission.
Question. No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why? Answer: No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population because sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings by providing genetic variation.
Question. Identify and write the male reproductive parts from the list of di erent parts of a Flower given below: Stigma, Sepal, Anther, Petal, Ovule, Filament Answer: The male reproductive parts that are present in a flower from given list are: (i) anther and (ii) flament.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? Write two of its advantages. Answer: Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual reproduction in plants in which the parts other than seeds are used as propagules.
Question. Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration. Answer: Hydra and Planaria are two organisms that have the ability to regenerate.
Question. List four modes of asexual reproduction other than fission in the living organisms. Answer: The four modes of asexual reproduction other than ¬ssion in living organisms are : (i) budding (ii) spore formation (iii) regeneration and (iv) fragmentation.
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it (i) stigma and (ii) ovary. Answer: The labelled diagram of L.S. of flower is as follows:
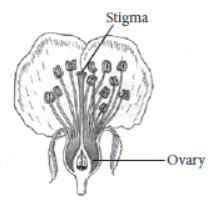
Question. What is AIDS? Which microbe is responsible for AIDS infection? State one mode of transmission of this disease. Explain in brief one measure for prevention of AIDS. Answer: AIDS is an infectious viral disease which weakens the immune system of human body and generally leads to death. It is caused by a retrovirus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). AIDS can be transmitted by having sexual contact with an infected person. Use of condoms which are physical barriers can reduce the risk of a sexual exposure to HIV.
Question. Draw longitudinal section of a bisexual flower and label the following parts on it. (a) Anther (b) Ovary (c) Stigma (d) Style Answer: L.S. of a bisexual flower is as follows:

Question. (i) Implantation (ii) Placenta (a) What is the average duration of human pregnancy? Answer: (a) The average duration of human pregnancy is 280 days or 40 weeks from first day of the woman’s last menstrual period, i.e., approximately 9 months.
Question. (i) that produces egg (ii) where fusion of egg and sperm takes place, and (iii) where zygote gets implanted. (a) Describe in brief what happens to the zygote after it gets implanted. Answer: (a) After implantation of zygote or embryo in the thick lining of the uterus, a disc-like special tissue develops between the uterus wall and the embryo, which is called as placenta. Placenta meets all the requirements for developing the fetus like nutrition, respiration, excretion, etc. When fetus (embryo) develops completely, the rhythmic contraction of uterus muscles gradually pushes the baby out of the mother’s baby through vagina a baby is born.
Question. (a) Name the part of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs. (b) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body. Answer: (a) In human female the fertilisation occurs in the oviducts or Fallopian tube. (b) The developing embryo gets nourishment from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. This is a disc like structure embedded in uterine wall. It contains villi that provides a large surface area to pass glucose and oxygen from mother to embryo. Placenta links the embryo to the mother through umbilical cord.
Question. What is placenta? Explain its function in humans. Answer: Placenta is an intimate connection between fetus and uterine wall of the mother to exchange the materials. It is a disc shaped structure embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on embryo’s side and blood spaces towards mother’s side. Blood spaces surround villi. Placenta performs the following functions : (i) All nutritive elements from maternal blood pass into the fetus through it. (ii) Placental helps in respiration i.e., supply of oxygen and removal of CO2 from fetus to maternal blood. (iii) Fetal excretory products diffiuse out into maternal blood through placenta and are excreted by mother. (iv) Placenta also secretes hormone.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Answer: Difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction is as follows :
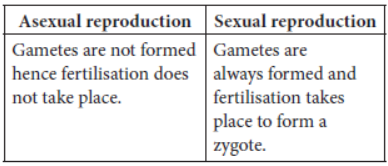
Species reproducing sexually have a better chance of survival as variation occurs only during the sexual reproduction. Variations are necessary for evolution and to increase chances of survival in changed environmental conditions.
Question. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction? What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? Answer: DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction as it results in passing of nearly same genetic information from parents to the offisprings. DNA replication also ensures that same number of chromosomes are passed from parents to offispring. Advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that sexual reproduction provides variations which is a major factor for evolution that helps in survival of species in changing environment.
Question. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower exhibiting germination of pollen on stigma and label (i) ovary, (ii) male germ-cell, (iii) female germ-cell and (iv) ovule on it. Answer: The diagram of the longitudinal section of flower is follows:

Question. Write names of those parts of a flower which serve the same function as the following do in the animals (i) testis (ii) sperm (iii) ovary (iv) egg. Answer: The parts of a flower which serve the same function as following do in the animals are (i) testis – anther of stamen (ii) sperm – pollen (iii) ovary – ovary of pistil (iv) egg – female germ cell present in ovule.
Question. List any two differences between pollination and fertilisation. Answer: Differences between pollination and fertilisation are as follows:
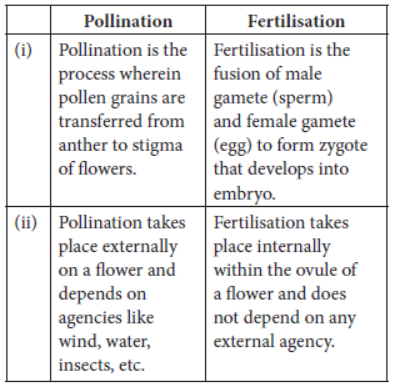
Question. Name one sexually transmitted disease each caused due to bacterial infection and viral infection. How can these be prevented? Answer: Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a sexually transmitted disease caused by HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus). These sexually transmitted disease can be prevented by following monogamy and by using male or female condoms during sexual act.
Question. (a) List two functions performed by testes in human beings. Answer: (a) The human male possesses two testes which are the primary reproductive organs lying outside the abdominal cavity. Testes are the sites where male gametes, i.e., sperms are produced. Testes also produce testosterone (male sex hormone).
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction. Write the importance of such reproductions in nature. Answer: The basic requirement for sexual reproduction is involvement of both sexes, i.e., male and female, to produce an offispring. It takes place by the combination of gametes which come from two different parents. The importance of sexual reproduction in nature are : • Fusion of male and female gametes coming from two different and sexually distinct individuals, exhibit diversity of characters in offisprings. • Meiosis during gametogenesis provides opportunities for new combination of genes, which leads to variation required for evolution and plays a prominent role in the origin of new species. Variations lead to the appearance of such characters, which fit to the changing environment, resulting in the survival of the species.
Question. What does HIV stands for? Is AIDS an infectious disease? List any four modes of spreading AIDS. Answer: HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease. It is transmitted sexually or through exposure to contaminated blood. Four modes of spreading AIDS are : (i) unprotected sex with an infected partner (ii) use of contaminated needle and syringes (iii) use of contaminated razors for shaving (iv) transfusion of infected blood or blood products.
Question. State the changes that take place in the uterus when : (a) Implantation of embryo has occurred. (b) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised. Answer: (a) Implantation is the close attachment of the blastocyst (young multicellular embryo) to the uterine wall. It is followed by a number of developmental changes in the thickened wall of uterus. An intimate connection between the fetal membrane and the uterine wall called placenta is formed. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. The placenta serves as the nutritive, respiratory and excretory organ of the fetus. (b) As the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself, every month to receive fertilised egg by making its lining thick and spongy to nourish the embryo if fertilisation had taken place. When the female gamete/egg is not fertilised, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place every month and is known as menstrual cycle.
Question. List any two steps involved in sexual reproduction and write its two advantage. Answer: The two main steps involved in sexual reproduction are: (i) formation of male and female gametes. (ii) fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete to form a new cell called zygote by the process of fertilisation. The two important advantages of sexual reproduction are: (i) It promotes diversity of characters in the offisprings through genetic variations. (ii) It plays an important role in continuous evolution of better organisms that may lead to the origin of new species.
Question. List three techniques that have been developed to prevent pregnancy. Which one of these techniques is not meant for males? How does the use of these techniques have a direct impact on the health and prosperity of a family? Answer: Methods developed to prevent pregnancy are: (i) barrier method, i.e., use of condoms, diaphragm, etc. (ii) chemical method, i.e., use of oral pills or vaginal pills. (iii) surgical method, i.e., vasectomy and tubectomy. Out of these methods, chemical method is not meant for males. Use of these techniques help to keep control over number of children in a family, which directly effects prosperity of a family. One of the most common reason for deterioration of women’s health is frequent conception and child bearing. Controlled chilbirth will directly affect women health and this will indirectly affect the prosperity of family and nation.
Question. (b) What is menstruation? Why does it occur? Answer: (b) Menstruation is the cyclic discharge of blood along with endometrial lining of the uterus and unfertilised egg in women. It last for 3-5 days. After the release of egg in the females, the uterine lining becomes thickened for the implantation of fertilised egg or zygote. In the absence of fertilisation, the egg along with endometrial lining is expelled out of the body in the form of menstruation.
Question. How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example. Answer: In organisms reproducing asexually, only single parent is involved in reproduction. Therefore, amount of DNA remains same from parent to offispring. For example in Amoeba, whole organism divides into two daughter individuals by binary fission. Therefore, amount of DNA remain constant. In organisms reproducing sexually. Reproduction take place with the help of formation of haploid gametes. Gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23 chromosomes. So, when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
Question. Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.
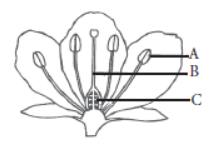
Answer: In the given figure part A is anther, part B is style and part C is ovule. Anther (A) is a part of male reproductive organ of flower called stamen. Large number of pollen grains are formed inside anther. Style (B) and ovule (C) are parts of female reproductive organ of flower called carpel / pistil. Style is a long conducting tube which gives the passage to pollen tube carrying male gametes so that it reaches ovary which contains one or more ovules. Ovules contain female gamete or egg. On fertilisation ovary converts into fruit and ovules give rise to seeds.
Question. What are sexually transmitted diseases? List two examples each of diseases caused due to (i) bacterial infection and (ii) viral infection. Which device or devices may be used to prevent the spread of such diseases? Answer: The diseases that are spread by sexual contact with an infected person are called sexually transmitted disease (STDs). (i) Bacterial infection causes Gonorrhoea, Syphilis. (ii) Viral infection causes AIDS, Genital herpes. STDs can be prevented by using male and female condoms.
Question. Suggest three contraceptive methods to control the size of human population which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country. State the basic principle involved in each. Answer: Three contraceptive methods which can help control human population are: (i) Condoms : It is a mechanical barrier which does not allow sperms and ovum to meet hence prevents fertilisation. Condoms are made of thin rubber/latex sheath used to cover the penis in the male and vagina/cervix in female just before coitus (intercourse) so that the ejaculated semen is not released in the female reproductive tract. (ii) Intrauterine devices (IUDs) : These are devices inserted by doctors or expert nurses in the uterus through vagina. These are presently available as non-medicated IUDs, copper releasing IUDs (CuT, etc.) and hormone releasing IUDs. They increase phagocytosis of sperms within uterus and suppress sperm motility and its fertilising capacity. They also make uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to sperms. (iii) Oral pills : Oral pills contain progesterone alone or a combination of progestogen and estrogen. They inhibit ovulation and make uterus unsuitable for implantation, hence prevent fertilisation.
Question. What are the functions of testis in the human male reproductive system? Why are these located outside the abdominal cavity? Who is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty? Answer: Testes, in human males, are the primary reproductive organs. They are the site of sperm formation. The testes also produce male sex hormone testosterone. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. The temperature of the testes in the scrotum is about 2–2.5°C lower than normal body temperature. This temperature is ideal for sperm formation and development. Hormone testosterone brings about the development of secondary sexual character during puberty in boys like growth of facial hair, deepening of voice, growth of scrotum and penis, accumulation of muscle mass, etc., and also regulates formation of sperms.
Question. What is meant by pollination? Name and differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants. Answer: The process of transfer of pollen grains from anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same species is known as pollination. The two modes of pollination are self pollination and cross pollination. Differences between self pollination and cross pollination are:
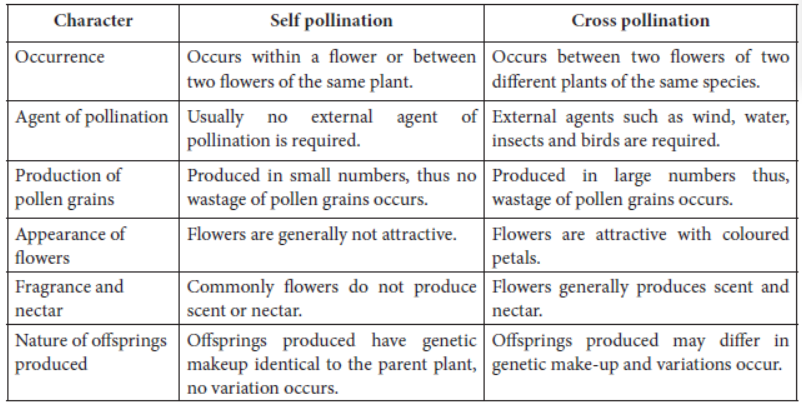
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly accurate, on the reproductionprocess? How does the amount of DNA remain constant through each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals? Answer: In the process of reproduction, if DNA copying is not perfectly accurate, variation occurs. These in turn may allow few individuals of a population to survive in an altered niche and becomes the basis of evolution and over time. Such variations are useful for the survival of species. The combination of DNA copies of two individuals (male and female) occurs during sexual reproduction. Reduction division (meiosis) during gamete formation halves the chromosome number in both male and female gametes. Since these two gametes fuse during fertilisation, the original number of chromosomes (as in the parent) is restored in the o spring. By this way the amount of DNA remains constant in each new generation.
Question. Reproduction is one of the most important characteristic of living beings. Give threereasons in support of the statement. Answer: Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings because : (i) it is essential for existence and continuity of a species. (ii) it helps to pass genetic information to next generation. (iii) it brings variations in next generation which is the basis for evolution.
Question. How does Plasmodium reproduce. Is this method sexual or asexual? Answer: Plasmodium reproduces through multiple fission method. In this method, the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time. is is an asexual method of reproduction.
Question. Write two differences between binary fission and multiple fission in a tabular form. Answer: Differences between binary fission and multiple fission are as follows:
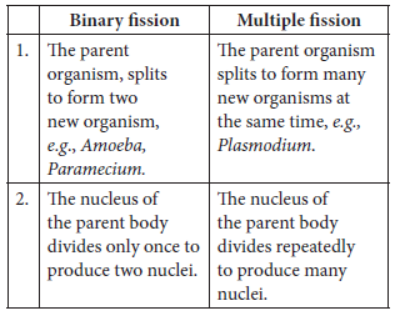
Question. List four advantages of vegetative propagation. Answer: The following are the advantages of vegetative propagation : (i) The characters of the parent plants are preserved hence a good variety produced can be propagated by vegetative means. (ii) The plants, which do not produce viable seeds or produce very few seeds, can be reproduced by this method, for example, banana, potato, grapes, sugarcane, rose, orange, etc. (iii) It is an easier, quicker and cheaper method of propagation. (iv) It is easier to get rid of pathogen from any part of plant by vegetative propagation.
Question. List four modes of asexual reproduction. Answer: The four modes of asexual reproduction are : (i) binary fission, (ii) budding (iii) regeneration and (iv) vegetative propagation.
Question. Draw labelled diagrams to illustrate budding in Hydra. Answer: The given diagram illustrates budding in Hydra:
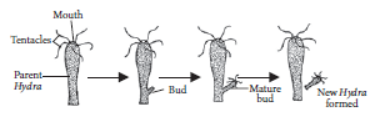
Question. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction? Answer: The process of reproduction results in the production of offsprings which are similar (but not identical) to parents. The exact blue print of body design is inherited in the o springs due to DNA replication (copying) in parent cell during reproduction. Thus, DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction.
Question. Explain the terms: (i) Implantation of zygote Answer: (i) Implantation of zygote refers to the process of attachment of the blastocyst on the inner wall of the uterus. It occurs on 7th day after fertilisation and is controlled by estrogen and progesterone hormones.
Question. Write the full form of DNA. Name the part of the cell where it is located. Explain its role in the process of reproduction of the cell. Answer: The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is located in the nucleus of a cell in the form of chromosomes. It contains information for the inheritance of characteristics from the parents to the next generation. Copying of DNA is an essential part of the process of reproduction because its makes possible the transmission of characteristics of the parents to its offsprings in the next generation. At the time of replication two copies of DNA are formed. DNA copying is accompanied by creation of additional cellular apparatus and then DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Thus, a cell divides to form two daughter cells.
Question. Describe the role of the following in human beings. (i) Seminal vesicles (ii) Prostate gland Answer: (i) Seminal vesicles are one pair of sac like structures near the base of bladder. Seminal fluid is a watery alkaline fluid that contains nutrients (fructose) which serve as a source of energy for the sperm. Each seminal vesicle releases its contents into the ejaculatory duct during ejaculation. (ii) Prostate gland is a single large gland that surrounds urethra. It secretes a slightly acidic, milky fluid that forms 25% of volume of semen. Secretion of prostate gland nourishes the sperms and helps in its mobility.
Question. With the help of diagrams show the different stages of binary fission in Amoeba. Answer: Different stages of binary fission in Amoeba are as follows:
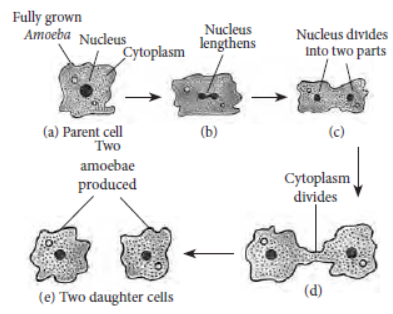
Question. What happens when (a) accidently, Planaria gets cut into manypieces (b) Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil (c) on maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts? Answer: (a) When Planaria accidently gets cut into many pieces then its each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. (b) When the Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil, the buds present in the notches along the leaf margin develop into new plants. This is known as vegetative propagation. (c) The sporangia of Rhizopus contain cells or spores that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals when it bursts on maturation.
Question. Describe reproduction by spores in Rhizopus. Answer: Fungus Rhizopus reproduces by spore formation. During the growth of Rhizopus, small rounded, bulb-like structures develop at the top of the erect hyphae. Such structures are called sporangia. Inside each sporangium, nucleus divides several times. Each nucleus gets surrounded by a little amount of cytoplasm to become spore. Large number of spores are formed inside each sporangium. After sometime sporangium bursts and spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions, they germinate into new individuals.
Question. (a) What is fragmentation in organisms? Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by this method. (b) What is regeneration in organism? Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram. Answer: (a) Fragmentation is the mode of reproduction in which parent body breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment develops into a new individual. It is a method of reproduction in many flamentous algae, mycelial fungi and thalloid bryophytes, e.g., Spirogyra. The given figure shows the process of fragmentation in Spirogyra.

(b) Regeneration may be defined as the ability of an organism to regenerates lost part of the body which have been removed as by injury or autotomy. Many fully differentiated organisms use this ability as a mode of reproduction and give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts. It is common in Hydra, Planaria, etc. The process of regeneration in Planaria is described in the figure given below.

Question. Describe the role of Fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system. Answer: Fallopian tubes are a pair of elongated, ciliated, muscular and tubular structures extending from close to ovaries to uterus. It is the site of fertilisation and helps in the conduction of ovum or zygote towards uterus by ciliary action and peristalsis.
Question. Define reproduction. How does it helps in providing stability to the population of species? Answer: The production of new organisms by the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction. It is linked to the stability of population of a species. DNA replication during reproduction ensures transfer of specific characters or body design features that is essential for an individual of a population to live and use that particular niche. Some variations present in a few individuals of population caused due to reproduction also help in their survival at changing niches.
Question. How do Plasmodium and Leishmania reproduce? Write one difference in their mode of reproduction. Answer: Plasmodium and Leishmania reproduce by the process of fission which is asexual mode of reproduction. Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission. About 1000 daughter cells are produced by the multiple fission of a Plasmodium. Leishmania reproduces by the process of binary fission. In Leishmania, the splitting of parent cell takes place in a definite plane (longitudinally) with respect to flagellum at its end to produce two daughter cells.
Question. What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction. Answer: Multiple fission refers to the process of asexual reproduction in which many individuals are formed from a single parent. This method of reproduction occurs in unfavourable conditions. The unicellular organism develops a protective covering called cyst, over the cell. The nucleus of the cell divides repeatedly producing many nuclei. Later on, each nucleus is surrounded by small amount of cytoplasm and many daughter cells are produced within the cyst. When conditions are favourable the cyst breaks and small offsprings are liberated. This type of reproduction is seen in some protozoans, e.g., malarial parasite (Plasmodium).
Question. What is the main difference between sperms and eggs of humans? Write the importance of this difference. Answer: The main difference between sperms and eggs of humans is that a sperm has X or Y chromosome whereas egg has X chromosome. This helps in determination of the sex of a person and maintaining the genetic continuity in the organisms.
Question. In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each. Answer: The main differences between fission and fragmentation are as follows:
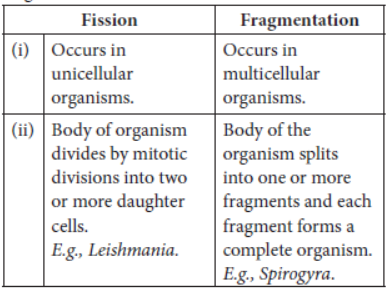
Question. Explain giving one example of each, the unisexual and the bisexual flowers. Answer: (i) Unisexual flowers : These flowers contain either stamens (male reproductive part) or carpel (female reproductive part). Example: Papaya, watermelon. (ii) Bisexual flower : The flower is said to be bisexual when both male and females parts i.e., stamens and carpels, are present on the same flower. Example : Hibiscus, mustard.
Question. What happens when (a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces (b) a mature Spirogyra flament attains considerable length (c) on maturation sporangia burst? Answer: (a) When Planaria is cut into two pieces then each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. (b) When a mature Spirogyra flament attains a considerable length it breaks into small pieces called fragments. These fragments grow into new individuals and this mode of reproduction is called fragmentation. (c) When a sporangium burst, large number of spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions they germinate into new individuals.
Question. State the role of placenta in the development of embryo. Answer: Placenta is a physiological connection between an embryo and uterine wall of the mother through which nutrients and other useful substances enter into fetus from mother’s blood and waste products like urea and carbon dioxide are expelled into mother’s blood from fetus.
Question. What is binary fission in organisms? With the help of suitable diagrams, describe the mode of reproduction in Amoeba. Answer: Binary fission is the division of adult parental body into two nearly equal daughter cells. It is the simplest and most common method of asexual reproduction found in protistan protozoans i.e. Amoeba, Paramecium, etc. Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts. When the Amoeba cell has reached its maximum size of growth, then first the nucleus of Amoeba lengthens and divides into two parts. After that the cytoplasm of Amoeba divides to form two smaller Amoeba (called daughter amoebae). Diagrammatic representation of binary fission in Amoeba is as follows :

Question. What is vegetative propagation? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing some types of plants. Select two plants from the following which are grown by this process : Banana, Wheat, Mustard, Jasmine, Gram Answer: Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of reproduction in plants. In this method, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves), without the help of any reproductive organs. Advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows: (i) Vegetative propagation is usually used for the propagation of those plants which produce either very few seeds or do not produce viable seeds. (ii) Seedless plants can be obtained by artificial vegetative propagation. (iii) Grafing is a propagation method which is very useful for fruit trees and flowering bushes. It enables to combine the most desirable characteristics of two plants. (iv) Plants like rose, sugarcane, cactus, etc., can be rapidly propagated through stem cuttings as this method produces new plants from just one plant quickly without waiting for flowers and seeds. Banana and jasmine are generally grown through vegetative propagation method.
Question. What is DNA copying? State its importance. Answer: DNA copying is the production of similar copies of DNA present in a cell using various chemical reactions. DNA copying is essential for reproduction through which the organisms pass on their body features to their offsprings. Moreover, minor alternations during the process of DNA copying result in the production of variations. Such variations are useful for the survival of species over time.
Question. List two advantages of vegetative reproduction practised in case of an orange plant. Answer: The two advantages of vegetative propagation practised in case of an orange plant are : (i) The new plants produced by vegetative propagation will be exactly like the parent plant. Therefore, any desirable features of the parent plant will be replicated in the new plants. (ii) The orange plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds, can also be propagated.
Question. Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria. How is this process different from reproduction? Answer: Planaria possesses great power of regeneration. If the body of Planaria somehow gets cut into a number of pieces, then each body piece can regenerate into a complete Planaria by growing all the missing parts. This is shown in following figure.

During the process of reproduction new organism is formed from the complete parent organism however, during fragmentation, a fragment of original parent body grows into new individual.
Question. List two advantages of practising vegetative propagation in plants. Select two plants raised by this method from the list given below : Banana, Gram, Pea, Rose, Tomato, Wheat Answer: Two advantages of the vegetative propagation of plants are : (i) Any desirable features of the parent plant can be replicated in the new plants. (ii) Flowers and fruits can be grown in a shorter time as compared to the plants grown from seeds. The two plants raised by this method are banana and rose.
Question. Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give one reason. Answer: When a cell reproduces, DNA replication occurs which results in formation of two similar copies of DNA. The process of copying the DNA have some variations each time. As a result, the DNA copies produced are similar to each other but may not identical sometimes.
Question. On cutting the body of an organism into many pieces, it was observed that many of these pieces developed as new individuals. Name the process and list two organisms in which this process may be observed. Draw a schematic diagram to illustrate the changes that are likely to be observed during the development of new individuals in any one of the organisms named. Answer: On cutting the body of an organism into many pieces, each of these pieces develop as new individuals. This process is known as regeneration. Hydra and Planaria are the organism in which this process may be observed. Following is the diagram show development of new individuals by regeneration of body parts of a parent Hydra.
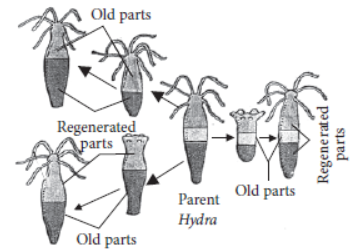
Question. With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the various steps of budding in Hydra. Answer: In multicellular organisms, such as Hydra, a small protuberance arises from one side of the body. The protuberance grows, and develops adult like structure. In Hydra it develops a hypostome and tentacles at its free end. It develops a basal disc at the point of attachment with the parent organism and finally gets detached to lead an independent life.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method. Answer: Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which the plant parts other than seeds are used as a propagule. Advantages of vegetative propagation : (i) Desirable character of the plant can be preserved through generation. (ii) Seedless plants can be grown through this method. Disadvantages of vegetative propagation : (i) Plants produced by this method posses less vigour and are more prone to diseases. (ii) Plants produced by this method show no genetic variation.
Question. List any two modes of asexual reproduction in animals. Under which mode of reproduction is vegetative propagation placed and why? List two advantages of vegetative propagation. Answer: The two modes of asexual reproduction in animals are : (i) fission (ii) fragmentation. Vegetative propagation is placed under asexual mode of reproduction because in this mode new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves), without the help of any reproductive organs.
Question. Name an organism which reproduces by spore formation. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow. Answer: Rhizopus reproduce by the method of spore formation. The three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow are moisture, suitable temperature and food (nutrition).
Question. (a) Name the following: (i) Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus. (ii) ‘Blobs’ that develop at the tips of the nonreproductive threads in Rhizopus. (b) Explain how these structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus. Answer: (a) (i)Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus are called hyphae. (ii) Blobs developing at the tip of hyphae are called sporangia which contain spores. (b) The structures called spores are present in sporangia which can develop into new Rhizopus individuals. These spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow.
Question. Why is ferilisation not possible without pollination? Answer: The process of pollination (in plants) ensures that male gametes bearing structure called pollen comes in contact with the female reproductive structure of the plant. Once the male and female gametes are in close vicinity, they fuse and fertilisation is accomplished. Hence, fertilisation cannot take place without pollination.
Question. List two preparations shown every month by the uterus in anticipation of pregnancy in humans. Answer: The two preparation shown every month by the uterus in anticipation of pregnancy in human are: (i) the wall of uterus becomes thick to receive the fertilised egg and (ii) the uterine wall is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
Question. State one genetically different feature between sperms and eggs of humans. What is its consequence? Answer: A sperm may have X or Y chromosomes whereas egg have X chromosomes. The consequence of this is that sperm decides the sex of the child because eggs contribute only X chromosome while sperms contribute either X or Y chromosomes to the offspring. Therefore, if a child inherits X chromosome from her father, will be a girl and the one that inherit Y chromosome will be a boy.
Question. “The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same”. Justify this statement. Answer: In sexual reproduction, two gametes, male and female, combines together to form a new cell ‘zygote’. The reproductive cells or gametes contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the non-reproductive cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosome and the human egg has also 23 chromosomes. So when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes in humans.
Question. Explain the term “regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra. Answer: The process of formation of entire organism from the body parts of a fully differentiated organism is called regeneration. It occurs by process of growth and development. Simple animal like Hydra shows regeneration. When a small piece of Hydra breaks of it grows into complete new Hydra. During regeneration, the cells of cut body part of the organism divide rapidly to make a mass of cells. The cells here move to their proper places within the mass where they have to form different types of tissues. In this way complete organism is regenerated.
Question. (a) What is spore formation? (b) Draw a diagram showing spore formation in Rhizopus. (c) List two advantages for organisms to reproduce themselves through spores. Answer: (a) Spore formation is the process of formation of microscopic reproductive structures called spores. These spores when detaches from the parent gives rise to a new individual. Reproduction by the formation of spores is a common method of asexual reproduction in some bacteria and most of the fungi. (b) Following figure shows the process of spore formation in Rhizopus.
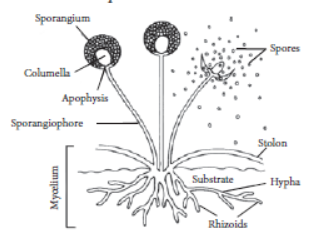
(c) Two advantages to spore producing organism are as follows: (i) Spores help organism to survive harsh environmental conditions as spores are covered by thick walls which protect them until they come in contact with moist surface and germinate. (ii) Spores are generally very small and light. Therefore, it ensures easy dispersal by wind, water and animal.
Question. List the parts of human male reproductive system which contribute fluid to the semen. State two advantages semen ofers to the sperms. Answer: The secretion of male accessory reproductive glands i.e., seminal vesicles, prostate gland and Cowper’s glands contribute fluid to the semen. The two advantages that semen offers to the sperms are : (i) it provides nutrition to the sperm and (ii) it also activates the sperms and make their transport easier into the vagina of female during sexual act.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located? Explain in brief the structure of its female reproductive parts. Answer: The reproductive organs of an angiosperm are stamen (male reproductive part) and carpel/pistil (female reproductive part). These are located in the flowers of an angiospermic plant. The given diagram shows the structure of female reproductive part of a flower.

A carpel is made of three parts : stigma, style and ovary. The top part of carpel is called stigma. Stigma is for receiving the pollen grains during pollination. Stigma is sticky so that pollen can stick to it. The middle part of carpel is called style. Style is a tube which connects stigma to the ovary. The swollen part at the bottom of a carpel is called ovary. The ovary contains ovules. Ovules contain the female gametes or female sex cells (egg) of the plant. There are usually many ovules in the ovary. Each ovule contains only one female gamete of the plant.
Question. (a) Mention the role of the following organs of human male reproductive system. (i) Testis (ii) Scrotum (iii) Vas deferens (iv) Prostate gland (b) What are the two roles of testosterone? Answer: (a) (i) Testis : The two testes in male are the sites where male gametes, i.e., sperms are formed. Testes also produce the male sex hormone called testosterone. (ii) Scrotum : The scrotum is a pouch of skin that lie outside abdominal cavity. The two testes lie in respective scrotal sacs. The scrotum acts as a thermoregulator and provides an optimal temperature for the formation of sperms. (iii) Vas deferens : This is a straight tube, about 40 cm long, which carries the sperms to the seminal vesicles, where mucus and a watery alkaline fluid containing fructose, mix with the sperms. (iv) Prostate gland : It is a single large gland that surrounds the urethra and produces a milky, slightly acidic secretion. Secretion of prostate gland nourishes and activates the sperm to swim. (b) Two roles of testosterone are : (i) It plays a key role in development of male secondary sex organs such as prostate, etc. (ii) It promotes the secondary sexual characteristics in males such as increased muscle and bone mass, growth of body hair, etc.
Question. List any four methods of contraception used by humans. How does their use have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of a family. Answer: The four methods of birth control which deliberately prevent fertilisation in humans are: (i) Barrier method- These are physical devices to prevent the entry of sperm in the female e.g., condoms. (ii) Chemical method – It involves the use of oral pills that check ovulation. These are mainly hormonal preparations and contain estrogen and progesterone. (iii) Intrauterine contraception device- These devices are implemented into uterus, e.g., copper – T, to prevent fertilisation. (iv) Surgical methods : These methods involves removal of a small portion of vas deferens in males or Fallopian tube in females to prevent fertilisation. Contraception prevents frequent pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases thus supports good health and prosperity of a family.
Question. Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts : (i) Female germ cell (ii) Male germ cell (iii) Ovary Answer: The flowers which contain only one sex organ, either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flowers. E.g., flowers of papaya and watermelon whereas the flowers which contain both the sex organs, stamens as well as carpel, are called bisexual flowers, e.g., flowers of Hibiscus and mustard. The given diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma.
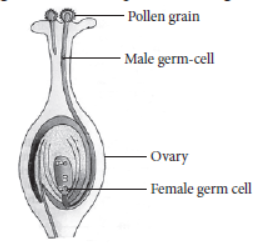
Question. List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction. Answer: Six specific characteristic of sexual reproduction are as follows: (i) Two different sexes, i.e., male and female are involved in this process. (ii) Sexual reproduction involves formation of special sex cells called gametes. (iii) Fusion of gametes or fertilisation takes place in the body of female (internal fertilisation) or outside (external fertilisation). (iv) Offisprings inherit traits from both parents (heredity) and also show some new traits of their own (variation), hence they are not clones of the parents. (v) Variations in sexually reproducing organisms arises on account of crossing over during meiotic division during gamete formation. (vi) It plays a prominent role in origin of new species as it leads to variations which accumulate over a period of time and get carried to successive generations.
Question. On the notice board of ultrasound clinics it is generally stated. “Here prenatal sex determination and disclosure of sex (boy or girl before birth) of fetus is not done. It is prohibited and punishable under law.” (a) List two advantages of imposing ban on prenatal sex determination. (b) What can students do to educate the society about the following? (i) The ill-effects of indiscriminate female feticide. (ii) Adopting small family norms Answer: (a) The two advantages of imposing ban on prenatal sex determination are (i) check on female feticide (ii) improving sex ratio in the country. (b) Students should educate the society as that (i) female feticide is reducing the number of girls drastically in some societies. For a healthy society, the male-female sex ratio must be maintained at almost the same level. Due to reckless female feticide, the male-female child sex ratio is declining at an alarming rate in some sections of our society. (ii) Children in a small family can be provided with all the resources from education, good amenities like food, clothing and healthy life style. As the family grows larger, the resources should be shared with increased number of member. Having fewer children also keeps the mother in good health.
Question. Name the two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower which contain the germ cells. State the location and function of its female reproductive part. Answer: The two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower which contain the germ cells are carpel (female reproductive part) and stamen (male reproductive part). Carpel is situated in the centre of the flower as a fask-shaped structure. A carpel is made up of three parts–stigma, style and ovary. The distal part of a carpel is called stigma. Stigma is responsible for receiving pollen during pollination. Style is an elongated tubular structure which connects stigma with ovary. The basal swollen part of carpel is ovary. Ovary bears several ovules. After fertilisation ovules form seeds and ovary forms the fruit.
Question. (a) List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction. (b)

(i) Name the part marked A in the diagram. (ii) How does A reaches part B? (iii) State the importance of the part C. (iv) What happens to the part marked D after fertilisation is over? Answer: (a) Variations arise in sexually reproducing organisms on account of the following : (i) Genetic variations occur of because DNA copying mechanism is not absolutely accurate. (ii) Creation of new combinations of genetic variations because variations from two individuals combine during fusion of gametes. (b) (i) A is pollen grain. (ii) Part B is stigma. It is the part of pistil (female reproductive organ) that receives pollen grains. Pollen grain reach stigma through various agencies like wind, water, insect, etc. (iii) Pollen tube (C) carries male gametes to the ovule present in ovary. Male gametes fuse with egg and secondary nucleus to give rise to zygote and endosperm. (iv) Female gamete (D) fuses with male gamete and converts to embryo after fertilisation.
Question. What is sexual reproduction? List its four significances. Answer: Sexual reproduction is the process of production of offispring by the fusion of male and female gametes. Here haploid gametes fuse to form diploid zygote which develop into a mature organism. Significances of sexual reproduction are as follows: (i) Sexual reproduction gives rise to genetic variations because of genetic recombination that takes place during fusion of gametes. (ii) Progenies arising through sexual reproduction sometimes show better combination of traits and get better adapted to their surroundings. (iii) Genetic recombination, interaction, etc. during sexual reproduction provide vigour and vitality to the offispring. (iv) Variations in genes play an important role in evolution.
Question. State in brief the changes that take place in a fertilised egg(zygote) till birth of the child in the human female reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilised? Answer: When the ovum (or egg) is fertilised in the oviduct, then a zygote is formed. The zygote divides rapidly by mitosis as it moves down slowly in the oviduct and forms a ball of cells. This hollow ball of cells, called an embryo sinks into the soft and thick lining of the uterus and gets embedded in it. The embedding of embryo in the thick lining of the uterus is called implantation. After implantation, a disc-like special tissue developsbetween the uterus wall (called uterine wall) and the embryo (or fetus), which is called placenta. The fetus is connected to placenta in mother’s body through umbilical cord. It is through the placenta that all the requirements of the developing fetus like nutrition, respiration and excretion, etc., are met from the mother’s body. The time period from the fertilisation upto the birth of the baby is called gestation. The average gestation period in humans (or the average during of human pregnancy) is about nine months. During the gestation period, the fetus grows to become a baby. Birth begins when the strong muscles in the walls of the uterus start to contract rhythmically. The rhythmic contraction of uterus muscles gradually pushes the baby out of the mother’s baby through vagina and a baby is born. If, a sperm is not available at the time of ovulation, then fertilisation of ovum (or egg) does not take place. Since the ovum (or egg) is not fertilised, so the thick and soft uterus lining having lot of blood capillaries in it is not required. The unfertilised ovum dies within a day and the uterus lining also breaks down. The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick and soft lining of the uterus alongwith its blood vessels is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
Question. Expand AIDS. List any four methods of prevention (control) of AIDS. Answer: AIDS is expanded as Acquired Immunode deficiency Syndrome. Four methods of prevention or control of AIDS are : (i) use of sterilised needles and syrings for injecting drugs or vaccine (ii) to avoid sex with multiple partners (iii) use of condoms during intercourse (iv) avoid use of contaminated razor in barber shop.
Question. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country. Answer: The general awareness regarding reproductive health in a society is significant as : (i) maintenance of personal hygiene among youngsters and proper knowledge of their reproductive parts helps them adjust with the physical changes and cope with emotional disturbance . (ii) reproductively healthy society must be free from the curse of child marriage which begets many complications at the level of individual and society both. (iii) proper care of expecting mothers, monitoring their health after child birth and care of new born help in building a healthy society. (iv) married couples aware of contraceptive methods lead a better married life as they are capable of avoiding unwanted pregnancies and have negligible chances of contracting sexually transmitted diseases. In past 50 years various areas related to reproductive health have been launched which have improved the reproductive health of our society in following ways : Two of them are : (i) reduced mortality rate of mother and infant (ii) birth control due to easily available contraceptive and reduced STDs cases.
Question. (a) Write the functions of each of the following parts in a human female reproductive system. (i) Ovary (ii) Uterus (iii) Fallopian tube (b) Write the structure and functions of placenta in a human female Answer: (a) (i) The ovaries in female are primary sex organs (or female gonads) which perform the dual function – production of female gametes (eggs or ova) and secretion of female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone). (ii) Uterus is a single, pear-shaped, highly muscular, hollow structure present in the pelvic cavity, lying between urinary bladder and rectum. If fertilisation takes place, the embryo gets implanted to the wall of uterus and grows there until birth. Development of foetus occurs inside uterus, hence it is also called womb. (iii) Oviducts or Fallopian tube are paired tubes originating near to the ovaries of their respective sides and extend upto uterus. The terminal part of Fallopian tube is funnel-shaped with fingerlike projections called fimbriae lying near ovary. Fimbriae pick up the ovum released from ovary and push it into Fallopian tube. Fertilisation also takes place in the oviduct.
Question. (a) Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.
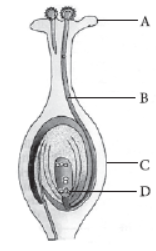
(b) What is pollination? Explain its signi- ficance. (c) Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develop after fertilisation into (i) seed, (ii) fruit. Answer: (a) In the given diagram A is stigma, B is pollen tube, C is ovary and D is female germ cell. (b) The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower is known as pollination. Pollination is important because it brings pollen grains to the female reproductive part (carpel) of the plant that leads to fertilisation. (c) Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg. After fertilisation, (i) ovule develops into seed (ii) ovary develops into fruit.
Question. Write two examples each of sexually transmitted diseases causes by (i) virus, (ii) bacteria. Explain how the transmission of such diseases be prevented? Answer: The infectious (communicable) diseases, which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person by sexual contact, are called sexually transmitted diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases caused by virus are : AIDS (Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome) and genital warts while caused by bacteria are gonorrhoea and syphilis. Preventive measures for the diseases are: (i) educating people in high risk groups. (ii) mutually faithful monogamous relationship. (iii) avoiding prostitution, multipartner sex and homosexuality. (iv) using condoms, etc.
Question. (a) Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label that part where (i) eggs develop (ii) fertilisation take place (iii) fertilised egg gets implanted (b) Describe, in brief, the changes that uterus undergoes (i) to receive the zygote (ii) if zygote is not formed. Answer: (a) The sectional view of human female reproductive system is as follows:

(i) Ovary is the part where eggs develop. (ii) Fallopian tube is the part where fertilisation takes place. (iii) Uterus is the part where fertilised egg gets implanted. (b) (i) When the ovum (or egg) is fertilised in the oviduct, then a zygote is formed. The uterus prepares itself every month to receive a zygote. The inner lining of uterus becomes thick and spongy with lot of blood capillaries in it. This would be required for nourishment and further development of embryo. (ii) If a sperm is not available at the time of ovulation, then fertilisation of ovum does not take place. Since the ovum (or egg) is not fertilised, so the thick and soft uterus lining having lot of blood capillaries in it is not required. The unfertilised ovum dies within a day and the uterus lining also breaks down. The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick and soft lining of the uterus alongwith its blood vessels in the form of vaginal bleeding is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
Question. List in tabular form the two differences between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Name and explain with the help of labelled diagram the process by which Hydra reproduces asexually. Answer: Differences between asexual and sexual forms of reproduction are following.

Hydra is simple multicellular animal. It reproduces asexually by the process of budding. In Hydra first a small outgrowth called ‘bud’ is formed on the side of its body by the repeated mitotic divisions of its cells. This bud then grows gradually to form a small Hydra by developing a mouth a tentacles. Finally, the tiny new Hydra detaches itself from the body of parent and lives as a separate organism. In this way, the parent Hydra produce a new Hydra. The following figure shows Hydra reproducing by the method of budding.
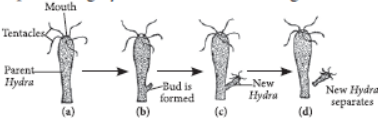
Question. (a) Explain why variations are observed in the offisprings of sexually reproducing organisms? Answer: (a) Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes coming from male and female parents. Variations occur due to (i) fusion of gametes which come from two different and sexually distinct individuals and (ii) meiosis which occurs during gametogenesis and create a new combination of genes. It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species and leads to variations required for evolution. Therefore, offisprings of sexually reproducing organisms show variation.
Question. (a) Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
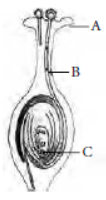
(b) Mention the role of gamete and zygote in sexually reproducing organisms. Answer: (a) A represents stigma. It receives the pollen grains from the anther of stamen. Stigma is sticky so that pollen can stick to it so that fertilisation can occur. B represents pollen tube. Pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells from the pollen grain at stigma to the ovules at the base of the carpel for the process of fertilisation. C represent female germ cell. Female germ cell fertilise with male germ cells to forms zygote which develops into an embryo within the ovule. Ovule converts into a seed that gives rise a new individual. (b) Role of Gamete : Gametes are the reproductive cells involved in sexual reproduction having half of the chromosome. Gametes carry variations generated during its formation (meiosis). A male gamete and a female gamete fuses to form zygote. Role of Zygote : The fusion of male gamete with female gamete forms a zygote during sexual reproduction. Zygote has normal number of chromosomes and new combinations of variation that express in new generation. The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form the embryo which has the potential to form a complete individual.
Question. (a) Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flower. (b) Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation. (c) How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals. Answer: (a) Unisexual flowers bear organs of only one sex, i.e., either stamen or pistil, e.g., papaya. Bisexual flowers contain both stamen and pistil, e.g., Hibiscus. (b) After fertilisation, the fertilised egg (or zygote) divides several times to from an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat around it and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary of flower develops and becomes a fruit (with seeds inside it). The other parts of flower like sepals, petals, stamens ,stigma and style dry up and fall of. Only the ovary is left behind. So, at the place on plant where we had a flower originally, we now have a fruit (which is the ovary of the flower containing seeds). A fruit protects the seeds. (c) The amount of DNA remain constant in each new generation because of formation of haploid gametes. Gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23 chromosomes. So, when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
Question. (a) Give an example of a bisexual flower. (b) Draw a longitudinal section of a pistil showing the germination of pollen grains. Label the following parts: (i) Stigma (ii) Male germ cell (iii) Female germ cell (iv) Ovary (v) Style (vi) Pollen tube Answer: (a) Hibiscus is an example of a bisexual flower. (b) Diagrammatic representation of pistil showing germination is as follows:

Question. Define the terms pollination and fertilisation. Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following: pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary. Answer: The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower is known as pollination. Fertilisation is the fusion of male gamete with the female gamete (or egg). Diagrammatic representation of pistil showing germination is as follows:

Related Posts

Assignments For Class 10 Chemistry

Assignments For Class 10 Mathematics Probability

Assignments Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations
- NCERT Exemplar
- Science Exemplar Class 10
- How Do Organisms Reproduce
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce
Ncert exemplar solutions class 10 science chapter 8 – free pdf download.
The NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce? is an important study resource for CBSE Class 10 students. This Exemplar can help them to clear their doubts and understand the concepts in an interactive way. NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science will cover important concepts that are more likely to be asked in examinations. Hence, students are advised to go through the NCERT Exemplar to ace their examinations.
These NCERT Class 10 Science Exemplar Solutions are prepared according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24. It has answers to 27 MCQs, 21 short answer questions 11 long answer questions which will help you to practise questions of varying difficulty on the reproduction of organisms. NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 provide an overview of the main concepts in the chapter and helps you to get well-versed in important topics from the chapter.
Download the PDF of the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – How Do Organisms Reproduce?

Access Answers to the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Multiple choice questions.
1. In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
(iii) yeast
(iv) Amoeba
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer is (b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Dog reproduce sexually, yeast reproduce by budding, Amoeba reproduce sexually and cultivated banana also reproduce asexually.
2. In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes (germ cells) are
(a) stamen and anther
(b) filament and stigma
(c) anther and ovary
(d) stamen and style
Answer is (c) anther and ovary
3. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) pollination, fertilisation, seedling, embryo
(b) seedling, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seedling
(d) embryo, seedling, pollination, fertilization
Answer is (c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seedling
Pollination leads to fertilization after which embryo is formed. Seedling comes out from embryo.
4. Offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because
(i) asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii) asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(iii) asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
(iv) asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer is (a) (i) and (ii)
Asexual reproduction involve single parent and there will be no exchange of gametes hence offspring looks similar to their parent.
5. Characters transmitted from parents to offspring are present in
(a) cytoplasm
(b) ribosome
(c) Golgi bodies
The answer is (d) genes
6. Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show
(a) only similarities with parents
(b) only variations with parents
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) neither similarities nor variations
Answer is (c) both similarities and variations with parents
7. A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Spirogyra and Yeast is that
(a) they reproduce asexually
(b) they are all unicellular
(c) they reproduce only sexually
(d) they are all multicellular
Answer is (a) they reproduce asexually
Amoeba reproduce by binary fission, Spirogyra reproduce by fragmentation, yeast reproduce by budding.
8. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
(b) division of a cell into two cells
(c) division of a cell into many cells
(d) formation of young cells from older cells.
Answer is (a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
Spirogyra reproduce by fragmentation. Spirogyra simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new individuals
9. The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called
(a) budding
(b) reduction division
(c) binary fission
(d) multiple fission
The answer is (d) multiple fission
Plasmodium divide into many daughter cells by binary multiple fission. In Multiple fission nucleus of the cell divides multiple times by mitosis then separates to create multiple daughter cells.
10. The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Answer is (a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
Gametes fuse to form a zygote during fertilization. After fertilization-embryo will be formed which will lead to seedling in plants.
11. The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant due to
(a) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
(b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
(c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
(d) halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
The answer is (b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
The halving of chromosome during gamete formation number of chromosome remain same as the somatic cell of an organism. Halving of gametes in a chromosomes is called the diploid number of chromosomes.
12. In Rhizopus, tubular thread-like structures bearing sporangia at their tips are called
(a) filaments
(c) rhizoids
The answer is (b) hyphae
Tiny blob-on-a-stick like structures involved in reproduction are called hyphae. The blobs are called sporangia, which contain cells, or spores, that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals.
13. Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from
(a) stem, roots and flowers
(b) stem, roots and leaves
(c) stem, flowers and fruits
(d) stem, leaves and flowers
The answer is (b) stem, roots and leaves
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction occurs in plants. In vegetative reproduction new plant is produced from vegetative parts of the plants such as roots, stem, leaf and buds. In vegetative reproduction plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its characteristics.
14. Factors responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are
(i) large number of spores
(ii) availability of moisture and nutrients in bread
(iii) presence of tubular branched hyphae
(iv) formation of round shaped sporangia
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
Answer is (c) (i) and (ii)
A large number of spores ensure a few spores survive even in adverse conditions. Availability of moisture and nutrients in the bread provides the necessary environment for the spore to grow into mould.
15. Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
(a) pollen grain and the upper surface of the stigma
(b) pollen grain on the upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
The answer is (d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Length of pollen tube ensures pollens reach the stigma to conduct pollination.
16. Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants
(iv) After fertilisation, they give rise to fruits
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer is (d) (ii) and (iv)
Flowers are not always bisexual hence statement i) is wrong. Only angiosperms produce flowers hence statement iii) is wrong.
17. Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross-pollination
(iv) Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer is (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Cross-pollination is necessary is unisexual flowers as they possess either stamen or pistil. Flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits because fruit is a mature ovary.
18. Which among the following statements are true for sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
(i) It requires two types of gametes
(ii) Fertilisation is a compulsory event
(iii) It always results in the formation of zygote
(iv) Offspring formed are clones
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer is (c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Off-springs produced from sexual reproduction cannot be clones hence statement iv) is wrong.
19. In Figure 8.1, the parts A, B and C are sequentially
(a) cotyledon, plumule and radicle
(b) plumule, radicle and cotyledon
(c) plumule, cotyledon and radicle
(d) radicle, cotyledon and plumule

Answer is (c) plumule, cotyledon and radicle
20. Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because
(a) sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
(b) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species
(c) genetic material comes from two parents of different species
(d) genetic material comes from many parents
The answer is (b) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species
In sexual reproduction zygote is formed by gametes produces by a male and a female. A male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote which fertilizes to produce new offspring. Because of the contribution of two parents, off-springs incur more variations.
21. Reproduction is essential for living organisms in order to
(a) keep the individual organism alive
(b) fulfil their energy requirement
(c) maintain growth
(d) continue the species generation after generation
The answer is (d) continue the species generation after generation
Reproduction is essential to the lineage of the species whereas other life processes are essential to keep the organism alive.
22. During adolescence, several changes occur in the human body. Mark one change associated with sexual maturation in boys
(a) loss of milk teeth
(b) increase in height
(c) cracking of voice
(d) weight gain
Answer is (c) cracking of voice
During adolescence Following changes occur in boys
- Growth of hairs in new parts of the body such as armpits, on the chest and between thighs near genital organ face, legs and on arms.
- Creaking of voice
- Skin becomes oily and pimples will start appearing
- Occasionally penis will erect especially while dreaming.
23. In human females, an event that reflects the onset of the reproductive phase is
(a) growth of body
(b) changes in hair pattern
(c) change in voice
(d) menstruation
The answer is (d) menstruation
- Growth of hairs in new parts of the body such as armpits, between thighs near genital organ thin hairs on face, legs and on arms.
- Start menstruation
- Breast size will increase
24. In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum, because it helps in the
(a) process of mating
(b) formation of sperm
(c) easy transfer of gametes
(d) all the above
The answer is (b) formation of sperm
Testes lying in the scrotum ensures the temperature of the testes remain lower than the body temperature. This helps in sperm production.
25. Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty?
(i) formation of germ cells
(ii) secretion of testosterone
(iii) development of placenta
(iv) secretion of estrogen
(c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (iv)
Answer is (c) (iii) and (iv)
Testis is a male reproductive organ but estrogen is produced in females. Placenta is formed in females during pregnancy.
26. The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for transport of sperms is
(a) testis → vasdeferens → urethra
(b) testis → ureter → urethra
(c) testis → urethra → ureter
(d) testis → vasdeferens → ureter
Answer is (a) testis → vasdeferens → urethra
Testis produces sperm which is transferred into epididymis through vasdeferns. From vasdeferens sperm is taken to urethra.
27. Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
(a) Syphillis
(b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV – AIDS
(d) Gonorrhoea
The answer is (b) Hepatitis
Hepatitis spread through contaminated water and food.
Short Answer Questions
28. In a bisexual flower in spite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
When stamens of a bisexual flower are removed. Cross-pollination can take place which results in fertilization and production of fruit.
29. Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organism? Give one reason.
Reproduction is the creation of a new individual. In unicellular organism cell division leads to the formation of new individuals. Hence cell division is a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms.
30. What is a clone? Why do offsprings formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity?
Clone are the aggregate of cell or organisms which are produced asexually. Asexual reproduction involve single parent and there will be no exchange of gametes hence offspring looks similar to their parent.
31. Explain how, offspring and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes?
Because of the halving of the chromosome during gamete formation number of chromosome remain same as somatic cell of an organism. Halving of gametes in a chromosomes is called a diploid number of chromosomes.
32. Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this.
Yeast requires energy for its growth and cell division. Water does not provide required energy whereas sugar provides energy hence yeast multiplies in sugar solution.
33. Why does bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread rather than on a dry slice of bread?
Spores of bread mould needs moisture to germinate and grow. Hence mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread.
34. Give two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
- Gametes are contributed by two individuals of the same species.
- Crossing over occur during meiosis.
35. Would a Planaria cut vertically into two halves regenerate into two individuals? Complete Figure 8.2 D and E by indicating the regenerated regions.
Yes Planaria cut vertically into two halves can regenerate into two individuals.

36. From the internet, gather information about the chromosome numbers of five animals and five plants. Correlate the number with the size of the organism and answer the following questions.
(a) Do larger organisms have more number of chromosomes/cells?
(b) Can organism with fewer chromosomes reproduce more easily than organisms with more number of chromosomes?
(c) More the number of chromosomes/cells greater is the DNA content. Justify.
- Size of the organism has nothing to do with chromosomes numbers
- Organism with fewer chromosomes need not reproduce easily compared to organisms with more number of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are made of DNA. Hence more number of chromosomes means more number of DNA.
37. In the tobacco plant, the male gametes have twenty-four chromosomes. What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete? What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote?
Number of chromosomes in both the gametes are equal hence a number of chromosomes in a female gamete of tobacco plant is 24. Combining both number of chromosomes in a zygote is 48.
38. Why cannot fertilisation take place in flowers if pollination does not occur?
Pollination is a process in which transfer of pollen grains from anthers to stigma takes place. If there is no pollination then there will be no fusion of gametes and fertilization do not take place.
39. Is the chromosome number of the zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Meiosis is a way of cell division in which a number of chromosomes get halved. After fertilization chromosomes become equal to that of somatic cells. After fertilization Mitosis takes place for the rest of the stages of life. Hence chromosomes remain constant.
40. Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization?
After fertilization zygote will be located in the ovary.
41. Reproduction is linked to stability of population of a species. Justify the statement.
Competition for food, predation is common in nature. If there is no reproduction species would have become extinct. Hence reproduction linked to population of the species.
42. How are general growth and sexual maturation different from each other?
General growth is all about growth of size. Sexual maturation is about achieving the ability to reproduce. General growth begins with the growth of an organism whereas sexual maturity is attained at a certain stage of life called adolescence.
43. Trace the path of sperm during ejaculation and mention the gland and their functions associated with the male reproductive system.
Sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for transport of sperms is testis → epididymis → vasdeferens → prostate→ urethra.
44. What changes are observed in the uterus if fertilisation does not occur?
Following changes occur in the uterus if fertilization does not occur
- Extra lining of Uterus degenerates
- Uterus lining fragments gets discharged through vagina
- Unfertilized egg gets discharged
- Menstruation takes place
45. What changes are observed in the uterus subsequent to implantation of the young embryo?
Following changes are observed in the uterus subsequent to implantation of the young embryo.
- Uterine lining thickens to support to developing embryo. (PLACENTA)
- Uterine lining is richly supplied with blood vessels so that nutrition and oxygen could be supplied to the developing foetus.
46. What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual act?
- Mechanical barriers prevents unwanted pregnancy
- Mechanical barriers prevent sexually transmitted diseases.
47. In the given Figure 8.3 label the parts and mention their functions
(a) Production of egg
(b) Site of fertilisation
(c) Site of implantation
(d) Entry of the sperms

- Vaginal passage

48. What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg?
The ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote is 1:2.
Sperm contains the genetic material from the father while the egg contains the genetic material from the mother. Sperm can either have X chromosome or Y chromosome but egg always have an X chromosome.
Long Answer Questions
49. Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction? With neat diagrams explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
In Budding, fragmentation and regeneration only a single parent is involved and there is no formation of gametes hence they are considered as asexual types of reproduction.
Regeneration of Planaria

Here the body of planaria cut into pieces and each piece has the ability to grow into a new organism. In the figure above the planaria body is cut into 3 pieces which regenerates into 3 individual cells.
50. Write two points of difference between asexual and sexual types of reproduction. Describe why variations are observed in the offspring formed by sexual reproduction.
In sexual reproduction, we can find more variations when compared to asexual mode of reproduction. Following are the reasons for that.
- Gene pool are contributed by two parents
- Crossing over that occur during meiosis results in more variation
- DNA replication also contributes to the variation
51. Distinguish between pollination and fertilisation. Mention the site and product of fertilisation in a flower. Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth and its entry into the ovule.
Ovary is the site of fertilization and pollination occurs externally

52. Distinguish between a gamete and zygote. Explain their roles in sexual reproduction.
53. Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gamete producing organs in the flower.
Ovary produces female gametes. Anthers produces male gametes.
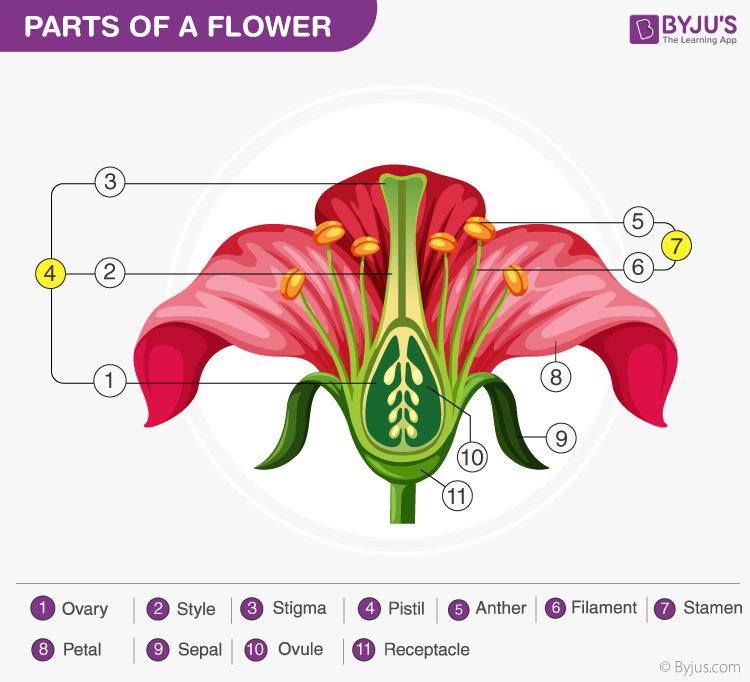
54. What is placenta? Mention its role during pregnancy?
Placenta is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and
oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of placenta. The developing embryo will also generate waste substances which can be removed by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta.
55. What are various ways to avoid pregnancy? Elaborate any one method.
Various ways to avoid pregnancy are given below
- Physical barrier
- Hormone Pills
- Surgical procedure
Barrier method: In the barrier methods of preventing pregnancy, the physical devices such as diaphragm (or cap) and condoms are used. Diaphragm (or Cap) is used by human females which is put over the cervix. Condoms are used by males.
56. How does fertilisation take place? Fertilisation occurs once in a month. Comment.
Once in a month, one egg is released from either of the ovaries. The egg gets transferred to the fallopian tube from the ovaries. Sperms swims towards the fallopian tube and only one sperm can penetrate the egg at a time. This process is called fertilization.
A menstrual cycle is composed of about 28 days. This means only one egg is available for fertilization in one menstrual cycle. Hence, it can be said that fertilization can occur only once in a month.
57. Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for the survival of an individual but for the stability of a species. Justify.
Competition for food, predation is common in nature. If there is no reproduction species would have become extinct. Hence reproduction linked to population if a species. New individuals carries the lineage of their parents. More number of organisms produces counterbalances the mortality that arises due to various factors. Like this reproduction helps in maintain stability of a species.
58. Describe sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them.
Disease that gets spread from person to person through sexual means are called sexually transmitted diseases. These include bacterial infections such as gonorrhoea and syphilis, and viral infections such as warts and HIV-AIDS.
Below are the ways to prevent sexually transmitted diseases
- Use of condoms or other physical barriers.
- Avoiding sexual contact with unknown partners.
- Avoid sharing towels or underclothing.
- Get a vaccination for hepatitis B.
Topics Covered in Exemplar Solutions for Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
How Do Organisms Reproduce? is an important and interesting chapter for CBSE Class 10 students . Students are recommended to study this chapter using the exemplar for a thorough understanding of the concepts included in the chapter.
- The Importance of Variation
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Vegetative Propagation
- Spore Formation
- Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction?
To ease your understanding of Biology topics, BYJU’S brings you video and animation lessons, infographics, tables, charts and notes . To get access to all study materials, visit BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8
What will i learn from chapter 8 of ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science, how do ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 8 help students to score well in the board exam, how can i answer the problems from ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 8 effortlessly, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Moved Permanently
The document has been permanently moved.

Search Form

How do organisms reproduce Worksheet-4
- This is the unicellular organism, which develops protective wall during unfavourable conditions and on getting favourable conditions splits to form many new organisms at the same time. Identify the organism.
A. Paramecium B. Amoeba
C. Plasmodium D. Leishmania
- Which of the following statements is/are not true about vegetative propagation in plants?
(i) It makes possible the propagation of some seedless fruit plants like banana, oranges, grapes etc.
(ii) It is the mean to produce genetically identical off-springs.
(iii) It brings more adaptability of plants to the changed environments.
(iv) It brings early flowering and fruiting in plants.
(v) It brings adequate dispersal of vegetative propagules and thus reduces overcrowding.
A. (ii) & (iv) B. (ii), (iv) & (v)
C. (i), (iii) & (iv) D. (iii) & (v).
- In the given flow chart what is the position of fruit?

A. X B. Y C. Z D. Both X & Y
- Which of the following pairs is incorrectly matched?
A. Rose – Cutting
B. Bougainvillea – Budding
C. Apple – Grafting
D. Grapevine – Layering
- Flowers that contain either stamens or carpels but not both are described as unisexual flowers and the plant species having male and female flowers on separate plants are called dioecious plants. Identify the odd one.
A. Papaya B. Mustard
C. Mulberry D. Watermelon
- Male gamete is the reproductive cell that fuses with female gamete to form zygote. Usually male gametes differ from female gametes as they are :
A. Small and contain stored food
B. Large and motile
C. Large and contain stored food
D. Small and motile
- Tissue culture is important for certain crops and few commercially important plants. Select the incorrect statement about the advantages of this technique.
A. It takes up relatively little space compared with growing plants in fields
B. It can be carried out independently of seasonal changes of climate
C. It is suitable for propagation of only seedless plants
D. It produces disease free plants
- The figure given below represents the longitudinal section of a flower. Which of the labelled parts are called as accessory whorls of flower?

A. P & Q B. Q & R C. R & S D. S & T
- Which of the following is the characteristic of wind pollinated flowers?
A. Pollen grains are light and dry whereas the stigma is long and sticky
B. Flowers are brightly coloured
C. Pollen grains are light, small and dusty whereas the stigma is hairy and feathery
D. Flowers are small with nectar and odour
- If the pollen grains are transferred from anther to the stigma of the different flower of another plant of same or different species, it is known as:
A. Allogamy
B. Autogamy
C. Cross pollination
D. Both Allogamy & Cross pollination
Answer Key:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fission is an asexual reproduction that is common in most unicellular organisms. When the fission results in two daughter cells, it is binary fission (e.g. paramecium). When fission results in many daughter cells, it is called multiple fission (e.g. Plasmodium). Planes of fission may be different for different organisms.
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,000 Mastery points! In this unit, we explore why organisms reproduce, sexual and asexual reproduction, and learn in detail about sexual reproduction in flowers and human beings. The unit is aligned to the CBSE class 10 curriculum.
Mint reproduces naturally by roots. Sugarcane, jasmine by stems and Biyophyllum by leaves. In biyophyllum buds are produced in the notches along the leaf margins and when they fall on the soil, they develop into new plants. Importance of Vegetative Propagation. Plants can bear flowers and fruits earlier.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 explains the various reproduction modes like. Sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction. Reproduction in flowering plants. It explains that reproduction involves the creation by the cell involved in the process of a DNA copy and additional cellular devices.
Class 10 Science How Do Organisms Reproduce Mind Map. Reproduction is a biological process in which an organism gives rise to young ones similar to themselves. Basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DN A copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell.
How do Organisms Reproduce? 129 Activity 8.2 8.2 MODES OF REPRODUCTION USED BY SINGLE ORGANISMS Activity 8.1 Dissolve about 10 gm of sugar in 100 mL of water. Take 20 mL of this solution in a test tube and add a pinch of yeast granules to it. Put a cotton plug on the mouth of the test tube and keep it in a warm place. After 1 or 2 hours, put a small drop of yeast culture from the test
This process takes place in unicellular organisms. It is of two types: Binary Fission - The organisms reproduce by binary fission only when adequate amounts of food and moisture is available. In this, the mother cell divides into two daughter cells, each containing a nucleus. Amoeba divides by binary fission. Multiple Fission - The ...
All these modes are the asexual modes of of reproduction. Mutlicellular organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction over asexual mode. This chapter explains you the sexual mode of reproduction in plants and animals. The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce includes all the intext and exercise questions.
Ans: Fission, as discussed in How do organisms reproduce Class 10 notes, is the separation of a single body into two new bodies by duplication of the genetic material of the organism. In the process of fission, deoxyribonucleic acid undergoes division to form two parts. The second process is termed as cytokinesis.
CBSE NCERT Revision Notes. 1. Introduction. Answer. → Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth. → Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) which is the heredity material. → DNA replicates and forms new cells causing variation.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Full chapter(Animation) | CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 | NCERTCHAPTERS:00:06 Importance of reproduction01:10 Asexual reproduc...
Download free printable assignments and worksheets of class 10 Science. Free PDF Download- Best collection of notes, important questions , sample papers and NCERT Solution for CBSE Class 10 Science. For more exclusive study material for science please click here Click here to book an appointment BIOLOGY: FOR CBSE CLASS 10 (Science Book 1) Kindle Edition … Continue reading Class 10 Science ...
1. Reproduction: The production of new organisms from the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction. 2. Types of reproduction: There are two types of reproduction- asexual and sexual: (i) Asexual reproduction: Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the ...
We provide step by step solutions for the questions given in Class 10 Science textbook as per CBSE Board guidelines from the latest NCERT book for Class 10 Science. The topics and sub-topics in Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce. 8.1 DO ORGANISMS CREATE EXACT COPIES OF THEMSELVES? 8.1.1 The Importance of Variation.
It is of two types. (a)Binary fission: -In binary fission, the parent organism splits to form two new organisms. Examples-Amoeba, Paramecium, Leishmania etc. (b)Multiple Fission: -In multiple fission the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at same time. Example-Plasmodium.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization.
CBSE Class 10 Chapter-7 How Organisms Reproduce: In the Organisms Reproduce chapter, we will learn the ability of organisms to produce offspring and carry out the next generation. Organisms reproduce in two ways asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Asexual is the mode of reproduction in which the production of the individual from a single parent takes place and sexual reproduction is ...
List any two steps involved in sexual reproduction and write its two advantage. Answer: The two main steps involved in sexual reproduction are: (i) formation of male and female gametes. (ii) fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete to form a new cell called zygote by the process of fertilisation.
These NCERT Class 10 Science Exemplar Solutions are prepared according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24. It has answers to 27 MCQs, 21 short answer questions 11 long answer questions which will help you to practise questions of varying difficulty on the reproduction of organisms. NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 provide an ...
D. Both Allogamy & Cross pollination. How do organisms reproduce Worksheet-4 Â This is the unicellular organism, which develops protective wall during unfavourable conditions and on getting favourable conditions splits to form many new organisms at the same time. Identify the organism. A.