- Skip to main content
- Skip to main navigation
- Canadian History Hall
The Great Depression

Following the New York stock market crash in October 1929, Canada sank into 10 long years of economic and social despair.
The New York stock market collapsed in the fall of 1929, as stocks lost 39 per cent of their value, or 10 times the U.S. government’s annual budget. The crash unleashed a wave of disaster that would affect the whole world for the next 10 years.
Canada was among the most profoundly affected countries. Goods no longer sold; businesses laid off workers in alarming numbers; family revenues sank; and government aid was insufficient. In the winter of 1933, Canada’s unemployment rate reached around 20 per cent. In spite of it all, people looked for signs of hope, often in the form of political miracles.
“The children complain of hunger and cold. It is impossible for me to adequately provide the things they ask [for]; it is heartbreaking.” Letter from Arsène Gaudet to Prime Minister R. B. Bennett, February 9, 1934
During the Depression, jobs and money were so scarce and needs so great that families had no option but to adapt. New outfits were made from older pieces of clothing. Furniture was built from scrap lumber. Here, a woman in Elginburg, Ontario, made a quilt by stitching together Quaker Oats flour sacks. The result: an attractive “beggar’s quilt” featuring hand-dyed squares.


Reacting to the Crisis
For many, the bleak situation led to desperation. Was there any way out: a light at the end of the tunnel? Solutions seemed to lie in activism and labour unions, and in various proposals for Canadian political reform.

The On to Ottawa Trek
During the spring of 1935, unemployed British Columbia workers from remote federal government relief camps converged on Vancouver to protest against the camps’ poor conditions. For two months, they were mobilized by the Workers’ Unity League, a communist-inspired union. The league sent 1,000 strikers to Ottawa by train to protest what they saw as the injustices of capitalism. But the On to Ottawa Trek was halted at Regina, when the government forbade the trains to continue. On July 1, local police and the Royal Canadian Mounted Police violently crushed a demonstration. The trek ended in defeat and resentment.

Political Solutions?
The dire economic and social circumstances that Canadians were facing led to repeated calls for political reform. The traditional parties — Liberal and Conservative — recognized the need for change. From the extreme Left to the extreme Right, Canadians sought ways of putting an end to the nightmare of the Great Depression.
A Renewed Conservatism
Holding power in Ottawa and led by Prime Minister R. B. Bennett, the Conservative Party changed direction in 1935. It proposed a New Deal, similar to the one in the United States, which expanded the role of the state in the economy.
Social Catholicism
Condemning the abuses of both capitalism and communism, Catholics around the world sought a third way, encouraged by Pope Pius XI and his 1931 letter Quadragesimo Anno . Social Catholicism was active in French Canada, particularly in the École sociale populaire and political parties like the Action libérale nationale.

Convention of the Action libérale nationale in Sorel, Quebec Photographer unknown, July 22 or 23, 1938 CMH, Photographic Archives, IMG2015-0380-0001-Dm
Democratic Socialism
In 1933, intellectuals, activists and farmers adopted the Regina Manifesto. It was the basis of a new party: the Co‑operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF). Its first leader, James Shaver Woodsworth, preached the Social Gospel: improvement of the human condition through Christian principles. The CCF would later become the New Democratic Party.
During the Depression, communist ideology gained popular support, particularly from union members. But the Communist Party of Canada had little success at election time, despite the efforts of Tim Buck, its charismatic leader from 1929 to 1962.

Canadian Labour History, 1850–1999
Photo at top of page: Montréal soup kitchen Photographer unknown, 1931 Library and Archives Canada, a168131
Search The Canadian Encyclopedia
Enter your search term
Why sign up?
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
- MLA 8TH EDITION
- Encyclopedia, The Canadian. "Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary)". The Canadian Encyclopedia , 09 July 2021, Historica Canada . www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary. Accessed 16 May 2024.
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , 09 July 2021, Historica Canada . www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary. Accessed 16 May 2024." href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- APA 6TH EDITION
- Encyclopedia, T. (2021). Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary). In The Canadian Encyclopedia . Retrieved from https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary
- The Canadian Encyclopedia . Retrieved from https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary" href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- CHICAGO 17TH EDITION
- Encyclopedia, The Canadian. "Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary)." The Canadian Encyclopedia . Historica Canada. Article published July 09, 2021; Last Edited July 09, 2021.
- The Canadian Encyclopedia . Historica Canada. Article published July 09, 2021; Last Edited July 09, 2021." href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- TURABIAN 8TH EDITION
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , s.v. "Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary)," by The Canadian Encyclopedia, Accessed May 16, 2024, https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , s.v. "Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary)," by The Canadian Encyclopedia, Accessed May 16, 2024, https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/great-depression-in-canada-plain-language-summary" href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
Thank you for your submission
Our team will be reviewing your submission and get back to you with any further questions.
Thanks for contributing to The Canadian Encyclopedia.
Great Depression in Canada (Plain-Language Summary)
Article by The Canadian Encyclopedia
Updated by Fred Glover
Published Online July 9, 2021
Last Edited July 9, 2021
The Great Depression took place in Canada and around the world in the 1930s. The term “Depression” is used to describe an economic decline that lasts for a long time. During the worst period of the Depression about 30 percent of Canadians were unemployed. This made life very difficult because Canada had few social programs at the time. This changed because of the Depression. In the 1930s the government created social programs to help those in need. It also became more involved in the economy.
(This article is a plain-language summary of the Great Depression in Canada. If you are interested in reading about this topic in more depth, please see our full-length entry, Great Depression in Canada .)

Causes of the Great Depression
The event that started the Great Depression was the stock market crashes that occurred in the fall of 1929. Within weeks many important companies lost much of their value. The stock market crashed because companies produced too many goods and the prices of the goods went down. There was little demand and too much supply. Soon after the crash many businesses went bankrupt, and tens of thousands of Canadians lost their jobs. This made the economy worse. People did not have money to spend. So, more businesses went bankrupt. When more businesses went bankrupt, more people lost their jobs. It was a vicious cycle.
The problem was especially bad in the western provinces. The western economy depended on exports and international trade, which collapsed. The prairies had also suffered from years of drought. This caused huge crop failures.
Government Responses

The federal government was not very involved in the economy at the start of the Depression. Many economists and politicians believed in an idea called laissez-faire (or leave it alone ) economics. They thought that the economy would work best if the government left it alone. According to this idea, only capitalists should guide the economy. In the 1930s many people began to question this idea. The unemployment rate was very high. Poor people were getting poorer. And the economy was not improving.
Canada had two prime ministers during the Depression. William Lyon Mackenzie King was prime minister from 1926 to 1930 and from 1935 to 1948. R.B. Bennett was the prime minister from 1930 to 1935. At first, neither of them wanted the federal government to get involved. They thought that churches and local and provincial governments should provide social services . Without federal help, many local governments went bankrupt. So did the Prairie provinces.
Some politicians were very different from Bennett and King. They wanted the government to get involved. One of the most important of these politicians was J.S. Woodsworth . He was the leader of the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation . This was Canada’s first socialist party.
In time, many other Canadians started to believe that the federal government should intervene. They thought that if it didn’t, the economy wouldn’t recover. Prime Minister Bennett then changed his mind. In 1932, the federal government created work camps for single, unemployed men. But conditions at these camps were bad. Some of the men went on strike or rioted .
Bennett’s government also created the Bank of Canada . It was responsible for the money supply. He also created the Canadian Wheat Board . The board made sure the prices of wheat was good for the farmers. Bennett also planned to introduce a minimum wage and unemployment insurance . But he lost the election to Mackenzie King in 1935.
After becoming prime minister, King set up the National Employment Commission. It recommended that King spend money on creating jobs. He was reluctant to do so. The Second World War , however, made him change his mind. The Canadian state became highly involved in the economy because of the war. In 1940, his government created an employment insurance program. Later, it created a family allowance program. By the end of the war, the federal government was much more involved in the economy.
- Great Depression
Associated Collections
Responsible government, recommended, the great depression in canada, the great crash of 1929 in canada, welfare state, social and welfare services.

Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF)
Economy and labour.
- Essay Samples Essays
The Great Depression in Canada Essay
The term ‘depression’ in economics lacks a formal definition. It is often referred to a period of crisis in finance and commerce. In this context, an economic crisis is defined as a period that is characterized with declining prices and output by more than 10 percent. The rate of unemployment also seems to increase during the period of economic depression. Based on these notions, in an old joke it has been stated that “a recession is when your neighbor loses his or her job; a depression is when you lose your job”.
Struggling with your HW?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease. Just fill in your HW requirements and you can count on us!
- Customer data protection
- 100% Plagiarism Free
One of the examples of a depression is often regarded to be the great depression witnessed by Canada. The period of depression was recorded to instigate during the summer of 1929 and extended till the spring of 1933. For the Canadian citizens, the depression period of the 1930s is still considered to be the most devastating decade of the century. The major cause for this was the crash in the stock market, which is often considered to be the consequence of the wheat crop crash in Canada. With due consideration to the notion of a depression and its emergence in the Canadian economy, the main objective of this paper will be to understand the major causes of the economic turmoil and also to describe the aftermath of the depression. A brief description of the total scenario of Canada in the historical context of the great depression will be presented in this paper.
Historical Background
The great depression of Canada existed during the 1930s as an era of economic poverty. The reasons for this depression in Canada can be related with various economic factors such as economic dependency, poverty, and unemployment among others. The period of depression initially was recorded in the year 1929, when United States discontinued purchasing goods from the Canadian market. This resulted in lockouts in many of the Canadian industries and thus contributed to the financial crisis. A huge number of Canadians became jobless and homeless lacking the basic amenities required to lead a healthy life. Even after getting a job, the Canadians were often paid at extremely low rates, which were not enough to fulfill their basic needs. The remaining unemployed Canadians used to move across the country in search of jobs and thus increased the liabilities of the government through inbound migration trends.
Used our essay samples for inspiration ?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
In Canada, the financial crisis was first observed in 1928 after the wheat crop crash had emerged resulting in the crash of the Wall Street Stock Market that later took the form of the great depression. One of the major causes of the depression in Canada was the over-production and over-expansion in the industrial sectors. During the 1920s, almost every industry in Canada was expanding and many new industries came into existence. As a result of this, the factory owners generally used to pile up huge stocks of goods. Consequently, after the crash of the stock market, these owners panicked and in order to slow down the production they laid off a huge number of workers. This resulted in a huge unemployment problem within the economy, which fuelled up a financial crisis in Canada. Therefore, the sale also went down causing an economic misbalance.
Furthermore, the Canadian economy remained entirely dependent upon a few primary products such as wheat, minerals and fish. Accordingly, the economy could not bear the loss from financial crisis as the demand for these goods went down after the unemployment problem. The economy of Canada was also related closely with the economy of the United States. Hence, with the emergence of a crisis within the American economy, the economic conditions of Canada also deterioted by a considerable extent. All through the 1920s, credit purchase became more and more favored in Canada. The added interest payments with the principle amount made many families go under huge debts4.
Another very popular trend in the Canadian market at that time was the credit buying of stocks. Due to this reason, the Canadians increasingly considered “buying on margin”, which means a person needed to invest only 10% of the total price of the stock which he wanted to purchase while the rest was loaned by the brokers at a very high rate of interest. The Canadians expected the stock prices to go up when they could sell the stocks at a higher price. However, the stock prices went dramatically down resulting in the stock owners’ panic which forced them to sell their stocks as soon as they could further inhibit the stock prices. These were the major problems which later resulted in the great depression4.
In Canada, the decline in the economy began during the summer of 1929 and continued with this declining trend till the spring of 1933. During the initial phase of the great depression, the stock prices witnessed inflation, which was almost near to the breaking point. Ultimately, people began to realize that no return could be expected from stock buying. As a result everyone started to sell their shares in large quantities and as soon as possible. The chief economic personalities of that time tried to uphold the stock market by investing as much as they could; however, it seemed to have no positive outcomes and the stock market collapsed within a short span of time. Unemployment was also a major factor for the great depression to take place in Canada. As a result of the over production or over supply, the factories panicked and laid off a huge number of workers which lead to unemployment. When the rate of unemployment increased in the economy, there was a decline in the demand, which caused the great depression in Canada to grow deeper2.
Another major factor for the great depression was the severe drought and other economic difficulties, which ruined the Canadian economy. Because of the fact that wheat was grown in huge amounts in Canada and was also imported from other countries, the supply of wheat substantially increased to surpass the actual demand and thus the Canadian farmers were left with huge quantities of wheat in stock. The Canadian farmers also witnessed a dreadful drought over an array of summer seasons in a row.. The ongoing challenges witnessed by the European economies also contributed in the severity of the great depression in Canada due to extensive trade linkages. However, the most important factor was the weakness of Great Britain after the Second World War to satisfy the needs and demands of the natives effectively. This weakness of Great Britain deepened the effect of the great depression in Canada because of the reason that Britain and US were among the major trading partners of Canada2.
Only a few countries witnessed such the full effects of the great depression of 1930s and Canada was among them. It has been estimated that between the year 1929 and 1933, the gross national expenditure of Canada was reduced by 42% and in the later years, about 30% of the labor force of Canada was unemployed. Reports further stated that after the great depression, at least 1 out of every 5 Canadians became dependent upon the relief for survival given by the government.
Moreover, Canada derived almost 33% of its gross national income from the export trades. The western provinces of Canada were observed to be almost completely dependent upon the export business and were among the major sufferers of the great depression of Canada. In Saskatchewan, the wheat crop crash resulted in the lowest price of wheat ever recorded in history. As a result of this, the total provincial income of Canada was oppressed by 90% within two years. This made almost 66% of the total rural population dependent on the government relief6.
Whereas, the other western provinces could have been considered to be technically bankrupt from 1932 and onwards. However, the effect of the great depression was not the same among the people. It was distributed unequally between different classes. Although the wage rates in Canada declined throughout the 1930s, the price of commodities dropped even faster. As a result, the farmers and the small businessmen were forced to bear the adverse effects of the economic hardship.
From the above discussion, it can be concluded that the main reason for the depression to take place in the Canadian economy was the crash of the stock market along with the wheat crop crash. Moreover, the over expansion of the Canadian industrial sectors also played an important role in deepening the effect of the great depression. The factory owners in order to bear the loss from the piled up stocks, laid off a huge number of employees giving rise to unemployment in the economy. This resulted in the financial crisis of the economy and compelled the commodity prices to go down steeply. Besides, the undiversified nature of the Canadian business sectors can also be considered as a cause for the great depression. Therefore, it is advisable that an economy should try to diversify and be flexible as much as possible rather than depending upon only a few business sectors with the intention to avoid depression. It can be inferred in this context that the consequences of depression should be studied continuously within an economy with due consideration to identify the occurrence of such an event in the initial stage and thus to take necessary resolutions accordingly.
Works Cited
Ascension Collegiate, 2006. “The Great Depression Comes to Canada”. “Causes of the Great Depression”. http://www.ascension.k12.nf.ca/curriculum/social/canhistory_1201/new_page_8.htm
Horn, Michiel. The Great Depression of the 1930s in Canada. Ottawa: The Canadian Historical Association, 1984.
Haines, Michael R. & Steckel, Richard Hall. A Population History of North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
Knoop, Todd A. Recessions and Depressions: Understanding Business Cycles. California: ABC-CLIO. LLC, 2009.
Peterson, Lois, No Date. “The Great Depression in Canada”. “The Great Depression was a period of economic hardship during the 1930s”. http://loispeterson.webs.com/Pages/The%20Great%20Depression%20handout.pdf
The Globe, 2009. “The Great Depression in Canada”. “Worst Is Over Now, Future Is Glorious, Bennett Confident. Greatest Prosperity Ever Known Lies Ahead, Says Premier”. http://www.themontrealreview.com/great_depression.php
Yes Net, No Date. “Great Depression of Canada”. “The Cause of the Depression”. http://www.yesnet.yk.ca/schools/projects/canadianhistory/depression/depression.html
Related Essays
Find Free Essays
We provide you with original essay samples, perfect formatting and styling
Request must contain at least 2 characters
Popular Topics
Samples by Essay Type
Cite this page
About our services
Level High School
This sample is NOT ORIGINAL. Get 100% unique essay written under your req
- Only $11 per page
- Free revisions included
Studyfy uses cookies to deliver the best experience possible. Read more.
Studyfy uses secured cookies. Read more.


The Great Depression
October 24, 1929, marked the beginning of a four-day stock market crash in the United States that had global ramifications.

October 24, 1929, marked the beginning of a four-day stock market crash in the United States that had global ramifications. Canada, with its resource-based economy, suffered immensely. The pain was amplified by a drought that plagued Western Canada during the dirty thirties. The depression ended in 1939 with the advent of the Second World War, which kick-started the world’s economies.
Number of shares sold on October 29, 1929, by panicked New York Stock Exchange investors. Today known as “Black Tuesday,” the final day of the stock market crash wiped out billions of dollars of share value.
Canada’s national unemployment rate in 1933.
Year that relief camp workers in Western Canada launched the On-to-Ottawa Trek to protest poor working conditions. The trek ended in Regina with a police crackdown that left one officer dead and injured hundreds of protesters.
Amount in cents paid per day to men working in federal unemployment relief camps , which operated from 1932 to 1936.
Approximate number of prairie homesteaders who, due to drought, abandoned their farms during the dirty thirties and relocated to other provinces.
Sign up for any of our newsletters and be eligible to win one of many book prizes available.
At Canada’s History, we highlight our nation’s past by telling stories that illuminate the people, places, and events that unite us as Canadians, while understanding that diverse past experiences can shape multiple perceptions of our history.
Canada’s History is a registered charity. Generous contributions from readers like you help us explore and celebrate Canada’s diverse stories and make them accessible to all through our free online content.
Please donate to Canada’s History today. Thank you!
This article originally appeared in the October-November 2019 issue of Canada’s History .
Themes associated with this article
- Business & Industry
- Media & Communications
- National Politics
- Social Justice
Advertisement
You might also like...
Dust and Depression
Prairie families in the 1930s watch their farms — and hopes — blow away while they wait for rain.

Dreams in the Dust: The Story of Tom Sukanen
As an ocean-going vessel took shape on a Saskatchewan farm during the Great Depression, it was clear that its builder was either a genius or a madman.
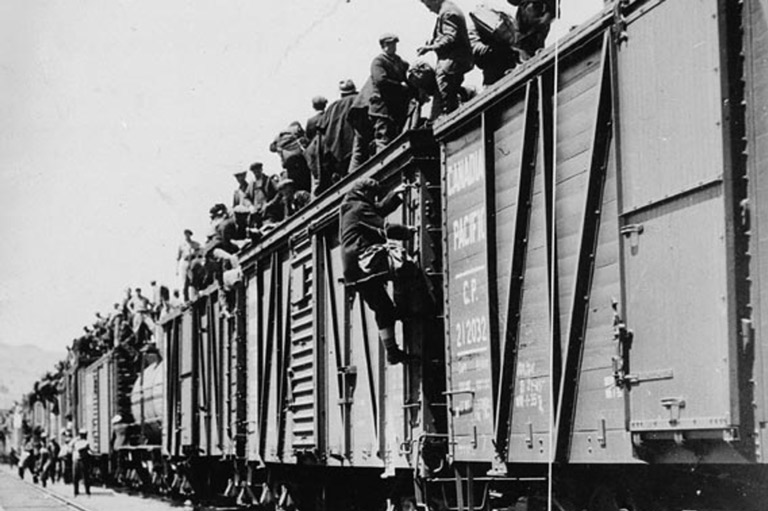

The Regina Riot
During the Great Depression, more than a thousand single unemployed men rode the rails in an organized protest that ended in a bloody clash.
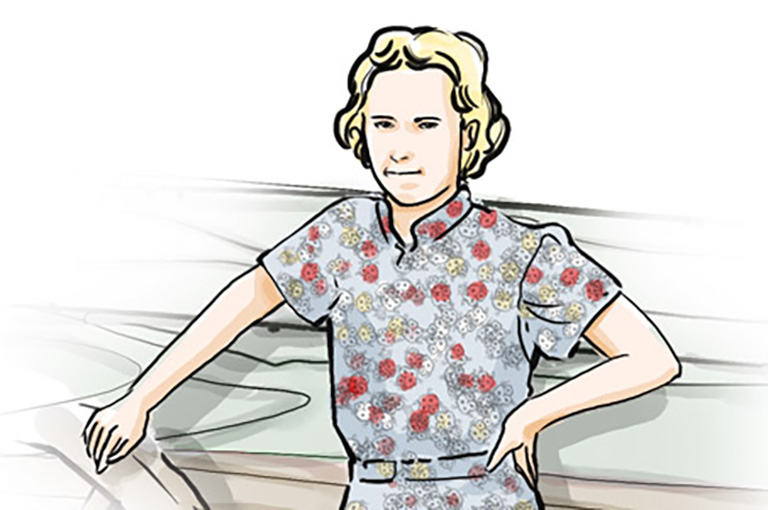

Flour Sack Dress
With a few threads and an eye for detail, the unappealing pantry bag became a Depression-era fashion item for working-class women in rural Canada.

The Bank That Went Bust
In the 1920s, Ottawa took control of the business of banking. It was forced to. A great bank had collapsed and many Canadians were ruined.
Related to Business & Industry

Montreal Chronicles: Come Aboard!
Joanne Burgess, professor at the University of Quebec in Montreal, highlights key moments in the history of Montreal’s port.

Guarding the Gold
On the eve of the Second World War, England worried for its wealth. War was costly. But the gold to pay the price of victory lay vulnerable in London. The solution — ship England’s treasure overseas, to Canada. And so began Operation Fish.

The World's Oldest Multinational
Challenges and change have always been part of Hudson’s Bay Company’s three-and-a-half-century history.

The Golden Age of the General Store
Life before malls.
Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada Essay
The great depression in Canada began in 1929 due to the conditions prevailing in the United States. Being neighbors and so closely interrelated both of the countries enjoyed considerable partnerships in the various areas of cooperation. Canadian economy went into tatters and the commodity most affected by the depression was wheat. Wheat is the primary export of Canada was hugely affected and in turn, affected the whole economy of the country. Due to the depression in the United States, the people across the border were not able to buy the wheat produced and cultivated in Canada and as a result, the exports declined.
The investment opportunities swindled to their lowest ebb and the unemployment rose to more than 25 %. Anyhow these conditions were not the result of a single factor but the outcome of a plethora of issues ranging from World War 1 to the conscription, British intervention, and conditions in the US are to be blamed as well. World War 1 started around 1914 and Britain waged it against the axis. Being an ally to Britain Canada had to send in troops to wage the war. This put huge strains on the economy and when the war that was supposed to take not more than 3 months was taking more than three years 1 , heads began to rise and people started questioning the conceptuality behind involving the troops to fight somebody else’s war.
By August Britain had declared war on Germany and as part of the conglomerate, Canada was constrained to join. At first, Canadians fought under British command but later Canadian started taking stock of the situation and managed to employ their own strategies through their commanders. Before long it was realized that in order to win the war some policies need to be reconsidered. Such as the policies regarding recruitment and planning. This involved the enforcement of the “Military Service Act” in 1917. This was the basis of Conscription in Canada.
There was fierce opposition to the act from all quarters mostly from French Canadians like Wilfred Bourassa and the rest. Prime Minister Robert Borden was in a quandary about the repercussions until his government collapsed. But Robert managed to unify his party under a partnership with Liberal Opposition and this served him a fruitful purpose. Conscription meant that people were to be drafted out to fight the war. It was due to the shortage of troops that this step had to be taken. English Canadians were in favor of the act but the Quebec Canadians however were not.
The Military Service Act was enforced in 1918, which caused more than 500,000 men to be liable for military duty 2 . There were however many exemptions and loopholes in the act which exempted almost everybody who would have participated in the war effort. There were widespread riots in Quebec and a lot of people were killed. It was sometime after that the exemptions were lifted and people had to join in, however, only around twenty-five thousand people actually joined the war effort. World War 1 ended in around a year and thus only a handful of Canadians were actually involved in the war effort because of the act. This nevertheless resulted in separations among the Government and in the year 1920, Borden retired and his heir was defeated in the next election. This ultimately ended the crises and steps were taken by the new Government to improve the economy which ultimately resulted in the end of the great depression.
- Berton, Pierre (1990). Pg no 542-543 – The great depression, 1929-1939.
- History of the Canadian Peoples, 1867-Present, Alvin Finkel & Margaret Conrad, 1998, Published by Pelham Books.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, September 20). Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada. https://ivypanda.com/essays/great-depression-of-canada-and-conscription-during-world-war-i-in-canada/
"Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada." IvyPanda , 20 Sept. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/great-depression-of-canada-and-conscription-during-world-war-i-in-canada/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada'. 20 September.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada." September 20, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/great-depression-of-canada-and-conscription-during-world-war-i-in-canada/.
1. IvyPanda . "Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada." September 20, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/great-depression-of-canada-and-conscription-during-world-war-i-in-canada/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada." September 20, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/great-depression-of-canada-and-conscription-during-world-war-i-in-canada/.
- The Fall River Axe Murders
- Pros and Cons of Eighteen Year Olds Serving in the Armed Forces
- The History of the Australian Church: Charles Strong’s Religious Activity and Aspirations
- Toronto Athenaeum Club: Labor Center
- Canada Role in the Cold War
- The Canadian Depression Causes
- Money in the "Sheriff of Cape Breton" Case Study
- Potlatch Ban and Eurocentrism in Canada
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services Editing Proofreading Rewriting
- Extra Tools Essay Topic Generator Thesis Generator Citation Generator GPA Calculator Study Guides Donate Paper
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us About Us Testimonials FAQ
- Studentshare
- The Great Depression in Canada
The Great Depression in Canada - Essay Example

- Subject: History
- Type: Essay
- Level: Ph.D.
- Pages: 6 (1500 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: waelchilane
Extract of sample "The Great Depression in Canada"
- Cited: 0 times
- Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF The Great Depression in Canada
Economyc depression, depression: definition, symptoms, researchers and treatment, metropolitan growth in canada 1991-2001, consequences of dirty thirties in canada, unemployment in canada during interwar period, psychology research designs, association between diabetes and depression, the association between sleep disorder and depression.

- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Great Depression of the early 1930s was a worldwide social and economic shock. Few countries were affected as severely as Canada. Millions of Canadians were left unemployed, hungry and often homeless.The decade became known as the Dirty Thirties due to a crippling drought in the Prairies, as well as Canada's dependence on raw material and farm exports.
Introduction. The Great Depression in Canada lasted from 1929 to 1939. Like many fledgling industrial nations at that time which included its neighbor the United States and Great Britain, this was a period marked by both financial and social problems. Unemployment attained a high of 27% when the depression was at its hardest in 1933.
The Great Depression began in the United States as an ordinary recession in the summer of 1929. The downturn became markedly worse, however, in late 1929 and continued until early 1933. ... Canada and many smaller European countries started to revive at about the same time as the United States, early in 1933. On the other hand, France, which ...
The Great Depression. Following the New York stock market crash in October 1929, Canada sank into 10 long years of economic and social despair. The New York stock market collapsed in the fall of 1929, as stocks lost 39 per cent of their value, or 10 times the U.S. government's annual budget. The crash unleashed a wave of disaster that would ...
The Great Depression took place in Canada and around the world in the 1930s. The term "Depression" is used to describe an economic decline that lasts for a long time. During the worst period of the Depression about 30 percent of Canadians were unemployed. This made life very difficult because Canada had few social programs at the time.
A Montreal soup kitchen in 1931. The worldwide Great Depression of the early 1930s was a social and economic shock that left millions of Canadians unemployed, hungry and often homeless. Few countries were affected as severely as Canada during what became known as the "Dirty Thirties", due to Canada's heavy dependence on raw material and farm exports, combined with a crippling Prairies drought ...
The Great Depression in Canada Essay. The term 'depression' in economics lacks a formal definition. It is often referred to a period of crisis in finance and commerce. In this context, an economic crisis is defined as a period that is characterized with declining prices and output by more than 10 percent. The rate of unemployment also seems ...
October 24, 1929, marked the beginning of a four-day stock market crash in the United States that had global ramifications. Canada, with its resource-based economy, suffered immensely. The pain was amplified by a drought that plagued Western Canada during the dirty thirties. The depression ended in 1939 with the advent of the Second World War ...
CANADA, GREAT DEPRESSION INLike most of the industrialized world in the 1920s, Canada enjoyed an uneven prosperity during the latter years of that decade. Internal economic growth was based on speculation (in real estate and on the stock market) and a great wave of consumer spending on houses, automobiles, and household appliances, all financed on credit and promoted by a newly-developed ...
The unemployment rate increased from 4.2% in 1929 to about 27% in 1933 in Canada, as the aftermath of the market crash unfolded itself. The crisis affected everyone at each level of the society. Wages were cut down, production dropped by 45% and the food was scarcely available. In 1931, nearly a third of the population in Montreal depended on ...
The Great Depression was a terrible point in Canadian history, and for most of the world. It was a point in time where thousands of people lost their jobs, and even lost their homes because of the depressed economy. Business was booming in the early 1920s, but when companies tried to expand, and therefore issued stocks, the economy was thrown off.
"The Great Depression: Canada's Century." July 1999. Web. Haubrich, Joseph. "Nonmonetary Effects of Financial Crisis: Lessons from the Great Depression in Canada." Journal of Monetary Economics 25 (1990): 223-252. Print. Horn, Michiel. The Great Depression of the 1930s in Canada, Ottawa: Canadian Historical Association, 1984. Print.
The Great Depression was an economic downturn in America that lasted from 1929 until about 1939, making it the longest lasting depression ever experienced by the industrialized world. The stock market crash caused a chain reaction that involved problems such as unemployment, deflation, an increase in debt, and general poverty for lower class ...
Great Depression Canada Essay. The Great Depression hit the U.S. and Canada with a force that sent their governments scrambling to try to pull their respective countries back together. In many ways the Great Depression was the great divider of the people and the government. Both countries faced protests, mass unemployment, and wrecked economies.
1313 Words6 Pages. The great depression in Canada started in 1929 and ended in 1939. This essay is going to talk about how the great depression had affected Canada economically, socially as well as politically. The Great Depression had affected Canada significantly as there was a drop in the economy, the economic drop had also affect the ...
Pg no 542-543 - The great depression, 1929-1939. History of the Canadian Peoples, 1867-Present, Alvin Finkel & Margaret Conrad, 1998, Published by Pelham Books. This essay, "Great Depression of Canada and Conscription During World War I in Canada" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database.
This paper ''The Great Depression in Canada'' tells that the term 'depression' in economics lacks a formal definition. It is often referred to a period of ... (The Great Depression in Canada Essay Example | Topics and Well Written Essays - 1500 Words) The Great Depression in Canada Essay Example ...
Intro: Following the crash of the US market on October 29, 1929. Unemployment rates peaked in 1933 (500,000) which was twice of what it was in 1921. 1 in 5 people were unemployed. The great depression was devastating for Canada due to it dependency on farming natural resources. For example, Saskatchewan experienced record low prices in record ...
The Development of Canada through the Great Depression October 29, 1929, "Black Tuesday", was the beginning of the end to the roaring twenties. After a decade of unlimited growth and prosperity, the drastic crash in the stock market on Black Tuesday would set a continuous downward trend that would last more than six years.
The Great Depression was a time of great economic crisis during the 1930s. It began in the United States, but quickly spread throughout much of the world over time. During this period, much of society were out of work, hungry, and homeless. In the heart of the city, people would stand in long lines at soup kitchens to get a bite to eat.
The Development of Canada through the Great Depression October 29, 1929, "Black Tuesday", was the beginning of the end to the roaring twenties. After a decade of unlimited growth and prosperity, the drastic crash in the stock market on Black Tuesday would set a continuous downward trend that would last more than six years.
Often referred to as the 'Dirty Thirties', was the Great Depression in Canada. Starting October 29, 1929, the New York stock markets decreased value caused many citizens in Canada to lose their jobs, homes, and other belongings. Over five years, the national spending in Canada fell 42 percent and 30 percent of eligible working Canadians ...
The Great Depression In Canada Essays. Causes of the Great Depression of the 1930s. Introduction The stock market in the United States crashed in 1929, and stock market prices dropped dramatically, an event known as the Great Crash/Wallstreet Crash. This enormous stock market fall was the catalyst for the Great Depression, a severe global ...