Taking supplier collaboration to the next level
Companies with advanced procurement functions know that there are limits to the value they can generate by focusing purely on the price of the products and services they buy. These organizations understand that when buyers and suppliers are willing and able to cooperate, they can often find ways to unlock significant new sources of value that benefit them both.
Buyers and suppliers can work together to develop innovative new products, for example, boosting revenues and profits for both parties. They can take an integrated approach to supply-chain optimization, redesigning their processes together to reduce waste and redundant effort, or jointly purchasing raw materials. Or they can collaborate in forecasting, planning, and capacity management—thereby improving service levels, mitigating risks, and strengthening the combined supply chain.
Earlier work has shown that supplier collaboration really does move the needle for companies that do it well. In one McKinsey survey of more than 100 large organizations in multiple sectors, companies that regularly collaborated with suppliers demonstrated higher growth, lower operating costs, and greater profitability than their industry peers (Exhibit 1).
Despite the value at stake, however, the benefits of supplier collaboration have proved difficult to access. While many companies can point to individual examples of successful collaborations with suppliers, executives often tell us that they have struggled to integrate the approach into their overall procurement and supply-chain strategies.

Barriers to collaboration
Several factors make supplier collaboration challenging. Projects may require significant time and management effort before they generate value, leading companies to prioritize simpler, faster initiatives, even if they are worth less. Collaboration requires a change in mind-sets among buyers and suppliers, who may be used to more transactional or even adversarial relationships. And most collaborative efforts need intensive, cross-functional involvement from both sides, a marked change to the normal working methods at many companies. This change from a cost-based to a value-based way of thinking requires a paradigm shift that is often difficult to come by.
The actual value generated by collaborating can also be difficult to quantify, especially when companies are also pursuing more conventional procurement and supply-chain improvement strategies with the same suppliers, or when they are simultaneously updating product designs and production processes. And even when companies have the will to pursue greater levels of supplier collaboration, leaders often admit that they don’t have the skill, lacking the structures they need to design great supplier-collaboration programs, and being short of staff with the capabilities to run them. After all, what great supplier collaboration necessitates is much more than the mere application of a process or framework—it requires the buy-in and long-term commitment of leaders and decision makers.
A shared perspective
To understand more about the factors that hamper or enable supplier-collaboration programs, we partnered with Michigan State University (MSU) to develop a new way of looking at companies’ use of supplier collaboration. The Supplier Collaboration Index (SCI) is a survey- and interview-based benchmarking tool that assesses supplier-collaboration programs over five major dimensions (Exhibit 2).
During 2019, researchers from McKinsey and MSU rolled out the Index in a pilot project involving a dozen leading consumer-goods companies in North America, along with ten to 15 of each company’s strategic suppliers. We collected more than 300 written responses from more than 130 organizations, and conducted in-depth interviews with around 60 buyer and supplier executives. The work provides some important insights on the state of supplier collaboration today, revealing the elements of collaboration that companies and suppliers believe are working well, and the areas that present the greatest challenges.
The results of our consumer-industry benchmark are summarized in Exhibit 3, with average buyer and supplier perceptions of their own collaboration programs rated from one (low) to ten (high) in each of the five dimensions.
Overall, the research reveals close alignment between buyers and suppliers on the relative strength of most dimensions. It also shows a clear drop in perceptions of strength as the discussion moves from theory (strategic alignment) to execution (value creation and sharing, organizational governance).
The in-depth interviews conducted with senior buyer and supplier personnel as part of the SCI data-collection process provide further insights into the challenges companies face in each of the five dimensions, while also revealing some examples of best practices that lower-performing companies can emulate.
Would you like to learn more about our Operations Practice ?
Achieving strategic alignment.
Benchmark participants understood who their strategic suppliers are, although they do not all use formal segmentation approaches to categorize their supply bases. Likewise, suppliers understood their strategic importance to their customers. Buyers and suppliers agreed that there was good alignment on the pursuit of sources of value beyond cost—but also agreed that their efforts to capture these value sources were not always successful.
The first step for an organization is to define what it wants to achieve from its collaboration efforts, and what it needs to do to realize those goals. Internal alignment and commitment by senior managers to ensure appropriate resources are available is also critical. For example, in a quest to develop more sustainable detergents, Unilever partnered with Novozyme—a major supplier of enzymes— to jointly develop new enzyme solutions. The collaboration leveraged each party’s strengths, merging Unilever’s understanding of which types of stains and materials were most relevant with Novozyme’s reagent-optimization capabilities. The partnership resulted in two enzyme innovations that improved product performance, increased market penetration, and allowed the company to target premium-branded competitors. Moreover, the new formulation performed well at lower temperatures, helping customers save energy and reduce CO2 emissions.
Joint business planning
Joint business planning is a collaborative planning process in which the company and its supplier align on short- and long-term business objectives, agree on mutual targets, and jointly develop plans to achieve set objectives (exhibit). It brings a formal approach to collaboration with suppliers and helps to engage stakeholders from different functions in the collaboration effort.
Joint business planning works best when companies have a clear understanding of the strategic suppliers with which they want to engage, and where they have strong core supplier management capabilities in place. The approach can be applied at several levels. At its simplest, joint planning can involve aligning on metrics and value sharing agreements. At its most advanced it can include joint investment to create new sources of value.
Other organizations participating in SCI have introduced formal methods to promote greater strategic alignment, such as by introducing a joint business-planning approach. The buyer and supplier align on short- and long-term business objectives, set out mutual targets, and jointly develop plans to achieve objectives. Areas of opportunity for collaboration include growth, innovation, productivity, quality, and margins (see sidebar, “Joint business planning”).
Communication and trust
Buyers and sellers both describe high levels of trust in relationships that they consider strategic. In most cases, that trust has been built up over time, based on longstanding business relationships. Companies involved in collaborations tend to appreciate each other’s capabilities, understand each other’s businesses, and believe that their partners will stick to the commitments they make.
Companies are less convinced, however, that their partners will be ready to put the interests of the collaboration above the interests of their own organization. Many interview participants noted that greater transparency over sensitive areas such as costs was key to attaining the highest level of collaboration, but said that this goal was often difficult to achieve.
Building trust takes time and effort. Often this means starting small, with simple collaboration efforts that deliver results quickly, building momentum. This way, companies can demonstrate a serious approach to collaboration and their willingness to share gains fairly. More importantly, companies should base their relationships on transparency and information sharing as a foundation, with the expectation that greater trust will follow.
Cosmetics company L’Oréal follows this approach to encourage collaborative innovation. Through open dialogs concerning company goals and long-term commitment, L’Oréal has been able to establish an effective codevelopment process. The company’s annual “Cherry Pack” exhibition, for example, offers suppliers a preview of the consumer trends that the company will be working on, and asks them to develop packaging solutions in harmony with these trends. During the exhibition, L’Oréal creates a trust-based forum for suppliers to present the ideas and products in development—including ideas that have yet to be patented. The forum thus gives suppliers access to practical short- and long-term ideas and projects that ultimately accelerate packaging innovation.
Cross-functional engagement
To generate value from changes in manufacturing methods, quality-assurance regimes, or supply-chain processes, representatives from the respective functions on both sides of the partnership will need to work together. Yet this type of cross-functional engagement is something most benchmark participants find extremely difficult. Executives reported that while traditional relationships—such as those between buyers and supplier sales teams, or suppliers and buyer R&D functions—were strong, wider cross-functional engagement was patchy and poorly managed at best.
Improving cross-functional engagement is a leadership issue. Organizations with the most successful collaboration programs use a formal approach to manage cross-functional teams, with clearly defined roles and responsibilities on both sides of the partnership, backed by changes to internal incentive systems to promote full participation in collaboration projects.
Some companies, such as P&G, have taken a step further in creating cross-functional teams solely focused on joint innovation with suppliers. By creating a practice of “open innovation,” P&G aimed to coordinate its efforts and leverage the skills and interests of people throughout the company to assess the competitive landscape, identify types of innovation that can help develop disruptive ideas, and identify appropriate external partners. For innovation to work, P&G has stressed the need to integrate cross-functional teams that, in turn, integrate business strategy with operations—which requires a broad network of interactions.

Unlocking enterprise efficiencies through zero-based design
Value creation and sharing.
The pursuit of shared value is the reason buyers and suppliers take part in collaboration projects, so unsurprisingly procurement executives consider it the most important dimension of their collaboration efforts. Yet few participants in our study track the impact of collaboration on sources of value beyond cost reductions. Where companies have tracked the impact of collaboration projects on revenues, margins, or other metrics, they have done so only for a handful of high-profile projects.
For buyers, additional volume remains the most common way that the extra value created by collaboration projects is shared. Some partnerships had made use of other types of value sharing, such as performance-based incentives for suppliers. Where these approaches were employed, both buyers and suppliers were happy with the results. That suggests significant opportunity for companies to expand their use of such approaches, provided they can reach agreement on cost baselines and incentive structures.
Cleansheet cost modeling
Many of the potential sources of value targeted by supplier-collaboration efforts depend upon a mutual understanding of the true costs of a product or service. Achieving that sort of transparency can, however, be difficult in buyer-supplier relationships. Suppliers may be reluctant to reveal too much about their own manufacturing processes and costs, fearing that this information will be used against them in negotiations, and buyers may not want to let suppliers know just how critical they are.
Cleansheet cost-modeling approaches have risen to prominence in recent years as a tool to allow an open, fact-based cost discussion between buyers and suppliers. A cleansheet calculates the cost of each step during the creation of a product, component, or service, using a database of information on the materials, labor, factory space, equipment, time, and energy required to complete each step—and the implications for the desired product volumes on the utilization of those resources.
Cleansheet cost transparency helps collaboration partners generate ideas for design and process improvements. The approach can also underpin value-sharing agreements, allowing organizations to establish clear cost baselines and measure improvements against them.
Cost transparency is a critical enabler here. Some companies have found cleansheet cost modeling to be a very effective way to conduct fact-based discussions on costs and improvement opportunities with their collaboration partners (see sidebar, “Cleansheet cost modeling”).
ASML, a lithography-equipment manufacturer for the semiconductor industry, operates a value-sharing mechanism for its suppliers. The company allows suppliers to maintain healthy margins (as a volatility buffer), provides financing for the infrastructure needed to make its products, and offers staggered purchase guarantees. In this way, ASML incentivizes and rewards its strategic suppliers for prioritizing its business, gains access to cutting-edge technology, and reduces costs and improves stability in an industry with short lifecycles affected by substantial swings in demand.
Throughout its long history of collaboration with suppliers, P&G has used a wide range of commercial models to partner with suppliers across the entire R&D chain. Its value-sharing models range from shared fund pools for codevelopment of products to licensing agreements for commercialization. The flexibility to employ different mechanisms has allowed P&G to tap into supplier innovation without the need to overinvest in the development of deep partnerships with every potential collaborator.
Organization and governance
Like cross-functional engagement, the organization and governance of supplier-collaboration programs suffers from a lack of formal structures and processes. Interviewees admitted that their companies, both buyers and suppliers, were relatively lax in tracking and valuing their supplier-collaboration efforts. Few organizations had done anything to align the incentives of project participants within their own organizations, and most relied on informal mechanisms to share feedback or review progress with partners.
Introducing a clearer governance structure for the overall supplier-collaboration program and for individual projects has the potential to significantly improve outcomes in most organizations. Two-way scorecards, for example, allow buyers and suppliers to let each other know if they are effectively supporting the goals of the program. Governance of collaboration projects should be cross-functional, with appropriate incentives introduced throughout the organization to encourage full participation and ensure both parties pursue long-term win-win opportunities, not just short-term savings.
Supplier advisory boards
A supplier advisory board (or council) serves as a neutral and collaborative forum for the exchange of ideas between the host company and a group of strategic suppliers. Such boards are widely used by companies with mature procurement organizations, and they do so for a variety of reasons. A board may advise on key industry trends, risks, and potentially disruptive threats in the supplier ecosystem. Or they may provide a place for companies to explore the potential impact of business decisions on sourcing strategy. Some boards act as a hub for projects to improve operational processes between the company and its suppliers. Others are assembled to support special projects, such as joint innovation programs or sustainability initiatives.
An advisory board is usually chaired by an executive business sponsor and sourcing lead. Buyer-side members include representatives of multiple functions, such as marketing, legal, and R&D. On the supplier side, companies usually nominate a lead strategic supplier, along with around a dozen supplier board members chosen from the strategic supplier base. Those suppliers are selected after evaluation against a matrix of criteria determined by the objectives of the board.
Several leading organizations have created supplier advisory boards to provide high-level support and guidance for their supplier-management and supplier-collaboration programs. These boards act as a forum for the supplier base to advise on key issues and collaborate with the organization to further its business agenda. Companies use their supplier advisory boards to help manage risks and disruptive threats to the supplier ecosystem, and such boards also serve as a neutral space for the exchange of ideas between the host company and a group of strategic suppliers (see sidebar, “Supplier advisory boards”).
Toyota has been a prominent example of supplier collaboration, whose success can be explained in part by the use of clearly defined targets and supplier-performance metrics. These are built into contracts that hold suppliers accountable for continued improvements in quality, cost, and delivery performance. The company governs supplier relationships using a steering committee, staffed with relevant senior stakeholders from both organizations, to define the scope and objectives of the collaboration, review progress, and take action to remove roadblocks and resolve issues as they arise.
The Supplier Collaboration Index has already revealed several major opportunities for companies seeking to expand and improve their supplier-collaboration efforts. Some of those opportunities are quite straightforward, such as more proactive management of cross-functional teams involved in collaboration projects, or the introduction of formal governance systems to manage those projects. Others, such as greater cost transparency between buyers and suppliers, or the use of performance-based supplier-incentive mechanisms, may require more time and effort to achieve.
Excelling at supplier collaboration requires a more active and engaged working relationship with suppliers. It also calls for a change in mindset, encouraging both buyers and suppliers to commit to the long-term pursuit of value from their collaborative relationships. We end with eight steps that any organization can take to put its collaboration efforts on the right track.
- Start by identifying those suppliers that offer unique joint opportunities to create and retain significant value.
- Align strategically with these partners to define joint objectives and develop a compelling business case for both parties.
- Adopt a methodical and structured approach to define the scope, pace and targets for joint projects, including a clear methodology on how to measure value creation.
- Define simple, clear value-sharing mechanisms, and align incentives of the cross-functional team accordingly.
- Invest in allocating the appropriate resources and building the required infrastructure to support the program.
- Create a governance model focused on performance, implementation tracking, and hardwiring supplier collaboration into core operational processes.
- Foster a culture founded in proactive communication, transparency, consistency, and knowledge sharing, to strengthen long-term partnerships.
- Invest in building world-class organizational capabilities to ensure sustainability over time.
For any organization seeking to improve the performance of its procurement practices, supplier collaboration can no longer be considered a nice-to-have. As companies reach the limits of conventional purchasing practices, further progress will require a new approach based on close relationships, cross-functional engagement, and the shared pursuit of new value.
Agustin Gutierrez is a partner in McKinsey’s Mexico City office; Ashish Kothari is a partner in the Denver office, Carolina Mazuera is a consultant in the Miami office, and Tobias Schoenherr is the Hoagland-Metzler Endowed Professor of Purchasing and Supply Management at Michigan State University.
The authors wish to thank Juby Cherian, Pat Mitchell, and Valeria Saborio for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

COVID-19: Implications for business

Reopening safely: Sample practices from essential businesses
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
SupplyChainManagement →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.

Relational Supply Contracts pp 103–108 Cite as
Case Study: Supplier Relationship Management at Volkswagen Group
- Michaela Isabel Höhn 2
- First Online: 01 January 2009
1868 Accesses
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems ((LNE,volume 629))
On the occasion of the VW Group Supplier Awards in 2005, Mr. Garcia Sanz, Member of the Board of Management of Volkswagen AG responsible for procurement, honored the award winning suppliers, saying: “Partnership is a key element of our long-term strategy. In these turbulent times, the Volkswagen Group Award recognizes successful cooperation” (BNET 2005). This declaration made us curious, how Volkswagen Group manages supplier relationships. The case study at hand stems from interviews with experts in procurement at Volkswagen Group, Wolfsburg, Germany, in August 2008. Given our model approach, we were particularly interested in the management of buyer-supplier relationships, the contracts employed and the handling of quality issues. In the following, we will document Volkswagen Group’s current approach to Supplier Relationship Management including the different models for supplier management.
Volkswagen AG is a growing global corporation with eight car brands, ca. €105 billion sales revenue, over 5.7 million vehicles produced per year, ca. 325,000 employees, and 42 production facilities located in Europe, Asia, Africa, and America (Garcia Sanz 2007). Based in Wolfsburg, Germany, Volkswagen Group is Europe’s largest and one of the world’s leading car manufacturers: As regards sales volume, Volkswagen Group is the fourth largest automaker worldwide (2006). The purchase quota is around 60–70%.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
WHU-Otto Beisheim School of Management, Burgplatƶ 2, 56179, Vallendar, Germany
Dr. Michaela Isabel Höhn
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Michaela Isabel Höhn .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Höhn, M.I. (2010). Case Study: Supplier Relationship Management at Volkswagen Group. In: Relational Supply Contracts. Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems, vol 629. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02791-8_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02791-8_7
Published : 19 August 2009
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-642-02792-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-642-02791-8
eBook Packages : Business and Economics Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How a Global CPG Leader Optimized $500M of Direct Materials Spend and Exceeded Savings Goal With GEP
Case studies.
Read our case studies to see how our clients, including hundreds of Fortune 500 and Global 2000 enterprises, leveraged our supply chain and procurement technology solutions and strategies to overcome significant challenges.
These stories offer an in-depth view of our client engagements and explain exactly how we secured excellent outcomes.

Consumer Packaged Goods
How a global fast-food chain saved $22m on a key raw material category with gep.
Leading Telecom Company Saves $25 Million Through eAuctions by Partnering With GEP

Global Fast-Food Chain Develops Supply Risk Mitigation Strategy With GEP

Real Estate Leader Centralizes Procurement, Saves 20% on Addressable Spend

Leading Retailer Achieves 40% Reduction in Cost of Goods Sold and 16% Improvement in Gross Margins

UK Chemicals Giant Achieves 55% More Savings Than Targeted With GEP's Expertise

How a Global CPG Leader Optimized $500M of Direct Materials Spend and Exceeded Savings Goal by Partnering With GEP

Industrial Manufacturing
How a u.s.-based manufacturer mitigated supply risks in china operations by partnering with gep.

How a Fortune 500 CPG Company Saved 20% on Key Raw Material Category by Partnering With GEP
Key insights.
Procurement and supply chain leaders worldwide look to GEP for process, technology and industry expertise, and we are happy to share our learnings from years of complex problem solving. The GEP Knowledge Bank encompasses proprietary research, issue-orientated white papers and webinars, case studies, and playbooks and primers.
- Category Management (168)
- Supply Chain (286)
- Source to Pay (461)
- Finance (4)
- Procure to Pay (96)
- Procurement Strategy (379)
- Sourcing (209)
- Spend Management (122)
- Procurement Technology (305)
- Procurement Transformation (178)
- Supplier Management (106)
Send us your question(s)
Request for a business proposal
Share your thoughts, comments and suggestions
Schedule a live demo of our software
Explore our latest thought leadership, ideas, and insights on the issues that are shaping the future of business and society.
- Reshape our future with Generative AI
- Leading sustainability
- The future of technology
- Marketing for customer experience
- Our research library
- Expert perspectives
Choose a partner with intimate knowledge of your industry and first-hand experience of defining its future.
- Aerospace and defense
- Banking and capital markets
- Consumer products
- Energy and utilities
- Hospitality and travel
- Life sciences
- Manufacturing
- Media and entertainment
- Public sector
Discover our portfolio – constantly evolving to keep pace with the ever-changing needs of our clients.
- Customer first
- Cybersecurity
- Data and artificial intelligence
- Enterprise management
- Intelligent industry
- Sustainability
Become part of a diverse collective of free-thinkers, entrepreneurs and experts – and help us to make a difference.
- Why join Capgemini
- Life at Capgemini
- Meet our people
- Back Career paths
- Students and graduates
- Experienced professionals
- Our professions
- Careers at Capgemini Engineering
- Careers at Capgemini Invent
- Back Join us
- Recruitment process
- Interview tips
See our latest news, and stories from across the business, and explore our archives.
- Press releases
- Analyst recognition
- Client stories
- Inside stories
- Social media
We are a global leader in partnering with companies to transform and manage their business by harnessing the power of technology.
- Back Who we are
- The way we work
- Our innovation ecosystem
- Values and Ethics
- Nobel International Partner
- Back Management and governance
- Board of Directors
- Executive committee
- Responsible business
- Environment, Social & Governance
- Back Corporate Social Responsibility
- CSR partnerships
- Digital inclusion
- Diversity and inclusion
- Environmental sustainability
- Social Response Unit
- Back Passion for sport
- The America’s Cup
- Peugeot Sport
- World Rugby
- Technology partners
- Asia Pacific
- Europe & Middle East
Our number one ranked think-tank
Explore our brands
Explore our technology partners
Explore careers with our brands
Generative AI
Management team, building a successful supplier network – a real-world case study.

Digital purchasing and invoice networks are essential to any successful digital procurement program. They provide visibility to suppliers and customers, improve performance management and risk process efficiency, reduce source-to-pay cycle times, and improve working capital.
However, for digital purchasing and invoice networks to be successful, they need to continue to grow. While much of this growth should be organic, there needs to a continued focus on driving adoption. Organizations often approach the implementation of digital platforms and supplier portals such as Ariba, Coupa, and Tungsten with a “build it and they will come” approach – only to fail to see the value in the investments they have made after 2–3 years.
This blog tells the story of how Capgemini successfully implemented Taulia for a Consumer Products client, onboarding its people efficiently to ensure it operated effectively. It’s worth noting that the success of this story is due to the collaborative efforts of Capgemini and the clients’s accounts payables and procurement teams.
Cleaning up master data
The onboarding team comprised of people who already knew and understood the client’s and Capgemini’s processes, as well as members of the vendor’s technical team.
Capgemini managed the client’s accounts payable and part of the procurement processes, working closely with the vendors and client to ensure they had the necessary knowledge to successfully implement the supplier network. The team worked together to develop the solution – with the Capgemini team providing inputs on any relevant business processes.
One of the fundamental factors of this project was updating all vendor data. The Capgemini team conducted a clean up of the vendor’s master data processes to ensure all data was clear and active.
Change management requires careful planning
Change management implementation was divided into phases. First, the teams identified critical, non-critical, essential, and monopoly suppliers, preparing lists for each phase of the onboarding program.
Next, the Capgemini team took responsibility for communication, looping in experts to answer potential questions regarding supplier networks, and preparing standard documents and letter drafts. Providing reliable knowledge and communication was vital not only for the client, but also to convince vendors of the benefits implementation could bring. In Taulia’s case, for example, vendors are offered an early payment discount that motivates suppliers to adopt the platform.
Following the initial communication, vendors were given a transitional period to enrol and adopt Taulia. This was followed by a push to ensure vendors leveraged the platform effectively. For Taulia, one of the early challenges was reducing manual invoice uploading efforts for vendors. To resolve this, the teams worked to improve integration, while also reducing duplicate invoices caused by change or resubmission of certain invoices. While these were often caught by system controls, Capgemini implemented further improvements to identify issues at the point of submission and provide immediate feedback.
Once these challenges were addressed, the teams continued monitoring the process and adding new suppliers when appropriate. Currently, 80% of vendors leverage Taulia and 60% of transactions are processed with zero human interference – although some invoices need to be manually posted due to price or quantity discrepancy.
Five factors to build a successful supplier network
Establishing a supplier network is a long-term process. In the Taulia case above, the initial program took around two years to complete. Success was ensured through strong collaboration and partnership with the client and supplier from day one. Capgemini also leveraged a methodology that was customized to the client’s individual circumstances to successfully drive adoption.
Based on our experience of building digital invoicing and purchasing networks for multiple clients, there are five key factors that dictate program success:
- Leverage a clear network adoption strategy, including updating and communicating your supplier policies, and enforcing them consistently
- Design processes around the specific business requirements and challenges
- Clean vendor data with up-to-date contact details – categorized by supplier importance and transaction volume
- Implement a strong change management approach to address any potential resistance both internally and from your suppliers
- Adopt strong category management and finance governance that adapts to changing business requirements.
Onboarding your suppliers to digital purchasing and invoice networks alone won’t deliver the savings you expect. To be successful, supplier networks need to continue to grow, with continued focus on driving adoption and change management among your people and vendors.
To learn how Capgemini’s Digital Procurement Services offer can maximize your digital investment to drive compliance and control across your procurement function, contact: [email protected]
Read Capgemini Invent’s Digital Procurement Research 2020–2021 , which contains some of the best practice learning’s from numerous projects and a comprehensive market overview of more than 30 procurement solution providers around the world.
Padmashri SR i s responsible for driving frictionless service delivery and the establishment of industry best practices to realize benefits in terms of service excellence, better process controls, reduced cost of operations, enhanced revenues, and improved client satisfaction.
We are sorry, the form submission failed. Please try again.
Brought to you by:

Walmart: Supply Chain Management
By: P. Fraser Johnson, Ken Mark
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Walmart. Set in 2019, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to…
- Length: 16 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jul 8, 2019
- Discipline: Operations Management
- Product #: W19317-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Walmart. Set in 2019, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to compare Walmart's source of competitiveness with those of other retailers-both online including Amazon.com and traditional brick-and-mortar retailers, such as Target-to develop insights into the management of a large, complex, global supply chain network. As competition between Walmart and its online and offline competitors heated up, a key challenge for the company's president and chief executive officer was deciding what changes made to Walmart's expanding supply chain would best support its strategic objectives. What supply chain capabilities would Walmart need as its business model continued to evolve?
Learning Objectives
This case can be used in an undergraduate or MBA course in supply chain management, operations management, business strategy, international business, logistics, purchasing, or marketing. It can provide an introduction to supply chain management using a company with which most students are familiar. In doing so, it allows students to learn how Walmart has built up its supply chain capabilities over the past five decades, and how the company leveraged these capabilities to become the world's largest retailer. Combining the Walmart case with the "Amazon.com: Supply Chain Management" case (W18451) in back-to-back classes provides a powerful illustration of the differences between two leading companies and demonstrates the importance of alignment of supply chain competencies with organizational strategy. After completion of this case, students will be able to: Assess Walmart's supply chain and identify its key competitive advantages. Quantify Walmart's ability to generate value from its supply chain. Identify potential opportunities and challenges for Walmart to improve its supply chain. Analyze the effects of the opportunities and challenges facing Walmart on its growth and evolution.
Jul 8, 2019 (Revised: Sep 9, 2019)
Discipline:
Operations Management
Geographies:
United States
Industries:
Retail trade
Ivey Publishing
W19317-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Building Insights Into Supply Chains: A Case Study

Image: iStock.com/metamorworks
For time-sensitive or temperature-controlled cargo, most shippers will agree that high-quality, real-time tracking information is crucial. Though that technology can be expensive, the investment is easy to justify when it could mean the difference between an on-time delivery and spoiled cargo. But for general cargo — which does not have strict timeline requirements — it can be harder for shippers to justify that cost. Individualized tracking information simply isn’t as critical for those standard loads. And if shippers do decide to invest in tracking devices for general cargo, rarely is the technology advanced enough to make a sizable difference to their bottom line.
Some leaders in the shipping space argue that this view is shortsighted — and could cost companies far more than they realize. Without the data that tracking technology could provide, they believe, many shippers lose out on important insights into their general cargo — data that could significantly improve travel timelines and ultimately justify that initial cost.
Two of these leaders are Maersk, a provider of transportation and logistics services, and Tive, a global leader in supply chain and logistics visibility technology. Both organizations felt that the potential value of tracking insights into general cargo was too important to overlook. So when Erez Agmoni, global head of innovation at Maersk, and Krenar Komoni, founder and CEO of Tive, crossed paths at a supply chain event at MIT a few years back, it was no surprise that they found a common purpose.
Both Agmoni and Komoni knew that tracking technology was too costly to be used across every type of cargo. “Unless it’s valuable, perishable cargo,” says Agmoni, “nobody will want to just go and track every single container, every single shipment — especially considering a few years ago, when it was really expensive.” Agmoni and Komoni knew they needed to develop a more affordable solution that could provide data that was actually relevant to all types of general cargo shipments.
The Proof of Concept
In the years following the MIT event, Agmoni and Komoni explored alternatives that could offer the value they sought at a price point shippers would accept. The first step in their experiment was to design a proof of concept. The team at Maersk took on the task, beginning with outreach. “We went to customers, we brought them in, we started some discussions,” says Agmoni. “We looked into what could help them improve their supply chains.” Over the course of their research, customers commonly expressed frustration with transit times: They were unreliable, inaccurate, and did little to help them plan around the situation at hand. That’s when Agmoni had an idea. Instead of tracking each individual shipment — which, as customers were saying, wasn’t providing the information they actually needed — they could also track aggregated data.
The Maersk Innovation Center designed a proof of concept for a means of keeping tabs on thousands of shipments without having to view each one individually. In other words, they would track aggregated data from thousands of shipments, starting with a route from Los Angeles to Memphis. Tive, meanwhile, started building the hardware and the backend technology. Once the product was ready, Tive ensured that all of the trackers were properly installed at the warehouse in Los Angeles, and that each of them was linked to the appropriate shipment and order.
From there, Tive’s data science and data analytics teams, with input from Maersk, went to work analyzing the data from the trackers — looking at which algorithms they wanted to run on the dataset to figure out what insights they could gain. “Working together, we were able to find some really interesting things,” says Komoni. In the end, the higher-level view yielded surprising insights.
The Results
On the drive from Los Angeles to Memphis, there are two main routes from which truckers can choose: a southern route, which runs near the U.S.–Mexico border, and a northern route, which is a slightly more direct line from point A to point B. On all navigation systems, the northern route is estimated to be two hours faster than its counterpart. But when Maersk and Tive started looking at the aggregated data, they learned something that they couldn’t have known from individualized tracking information.
“When we started to look at the aggregated data,” says Agmoni, “we found out that the northern route is taking six days, plus or minus two — so four to eight days.” Though Google Maps will estimate the drive to be 32 hours, it’s expected that drivers will need to stop and rest along the way, stretching the trip out into several days. But when they looked at the presumably slower, southern route, the average driver was completing the trip in four to six days. Not only was this faster, but the driving estimate was more precise.
To understand why this was, they had to go back to the data. Using a collection of tools and graphs that they’d custom built for this purpose, Tive began to calculate the idle times along each route. “What we said is, ‘why don’t we figure out where the trucks are stopping for the longest time?’” says Komoni. “And then we mapped that out, and we saw these big red spots on areas where they’re stopping on the southern route and also where they’re stopping on the northern route.
”It quickly became clear from the data that drivers on the northern route were stopping much more frequently than on the southern route. “We couldn’t know why they’d do that,” says Agmoni, “so we had to call some of them. And we learned a very interesting thing.”
After speaking with some of the drivers, they learned that rest stops on the northern route are small and, more often than not, completely full. “It’s a very busy route,” says Agmoni. “They don’t trust that there will be space at the rest stop when they’ve reached the maximum hours of driving. So they start looking two or three stops beforehand. If there is one, they stop; if not, they’ll go to the next on the route.” On the southern route, however, the stops are more reliable. Drivers can trust that when they need to make a stop, there will be space for them to do so — allowing them to maximize the number of hours that they can drive, and shortening the total transit time altogether.“
That really helped us to change the way we route things. You can’t find this information if you follow one shipment at a time; you really need the aggregated data,” says Agmoni.
“It's great insight,” Komoni adds, “because now you finally have value that you can sell. You can justify the cost on all types of general cargo — and not just on time-sensitive, temperature-sensitive, high-value shipments.”
Maersk and Tive’s proof of concept was a clear success, allowing them to move forward in the development of their product.
The Solution
Using what they learned, Maersk has since developed a new product called Ocean + Transload, a solution for cargo transportation that improves transit time variability, reduces carbon emissions, and helps minimize detention and demurrage charges.
“It’s a replacement for the inland port solutions that carriers sell,” says Agmoni. Typically with intermodal travel, carriers see a lot of fluctuation in transit times. “The intermodal connection of international containers is not to the level of our customer expectation,” he says.
With Ocean + Transload, they can take containers and translate them into trailers by putting them back on the rail or on the road. “And of course we are adding visibility trackers to all those shipments at no extra cost — to provide our customers with a solution that first, gives them a much more precise time, and second, sends alerts way in advance when the shipment is about to arrive.” Armed with this increased visibility into their shipments, customers no longer need to follow up to receive updates on the status of their shipment. Updates come to them directly.
According to Komoni, the uniformity of the data made possible by the collaboration was a central component to the solution’s success. “I think that uniformity is the real value that allows Maersk to do aggregated analytics and understand insights for their customers. There is tremendous value in uniformity,” he says.
What started as a shared frustration at the lack of tracking information on general cargo shipments resulted in not only a successful collaboration between two companies — it also provided a much-needed advancement in tracking technology and shipping analytics that will help companies make smarter and more cost-efficient decisions across the supply chain.
RELATED CONTENT
RELATED VIDEOS
Five Critical Challenges Facing Pharma Supply Chains
Subscribe to our daily newsletter.
Timely, incisive articles delivered directly to your inbox.

Popular Stories

How Businesses Can Cut Supply Chain Costs Without Jeopardizing Long-Term Growth

Fashion Brands Make Earth Day Commitment to Preserve Endangered Forests

Podcast | Thinking Beyond Cost: New Executive Priorities for Supply Chains

Why Planning Isn’t Enough to Achieve True Operational Excellence

U.K. Brexit Import Checks Delayed, Causing Confusion
Digital edition.

2024 Supply Chain Management Resource Guide: There's Only One Way Off a Burning Platform
Case studies, recycled tagging fasteners: small changes make a big impact.

Enhancing High-Value Electronics Shipment Security with Tive's Real-Time Tracking

Moving Robots Site-to-Site
Jll finds perfect warehouse location, leading to $15m grant for startup, robots speed fulfillment to help apparel company scale for growth.
- History of the SCRC
- SCRC Events
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Industry Engagement
- Current Partners
- Partner Successes
- Practicum Experience
- Client Project Showcase
- Student Engagement
- Undergraduate Opportunities
- Graduate Research Assistantship
- Graduate Opportunities
- Student Profiles
- Alumni Profiles
- Thought Leaders
- Executive Advisors
- SCM Resources
- SCRC Director’s Blog
- SCM Article Library
- Coronavirus and Supply Chain Management
- Ethical Apparel Index
- Poole Thought Leadership
Case Studies: Developing Collaborative Supplier Partnerships
Case studies.
Dell Computers Eric Scott Limited Volkswagen Brazil
h2. Dell Computers ( 27 )
Early on Dell Computers recognized the benefits of collaborative supply chain relationships and adopted the practice while developing its “Dell Direct Model” in 1995. This innovative model of efficiency included something the computer industry had never experienced: a high velocity, low cost distribution system with direct customer relationships and build–to–order manufacturing. By instituting collaborative supplier relationships, Dell Computers was able to achieve significant cost savings and maintain a competitive advantage over competitors for several years.
To accomplish this, Dell first pared down its supplier companies from 204 to 47. Then, in order to operate on a just–in–time ( JIT ) inventory basis, these suppliers warehoused their components only 15 minutes from the Dell factory. This JIT inventory system decreased inventory costs and led to a 6% profit advantage in components which was passed along to consumers, while reducing inventory from 30 to 13 days- well ahead of the industry average at the time of 75 to 100 days. Other advantages of Dell’s JIT system included easier customization of computers to customers’ exact specifications, lessened likelihood of obsolete raw materials, ability to adjust production levels to meet demand, and a finished product ready for shipment just 36 hours after an order was placed.
After a computer was assembled, it was sent to one of Dell’s many contracted shippers. In yet another move to decrease inventory, lower costs, and increase efficiency, Dell had these shippers house the monitors for their computer systems. By email, Dell would notify the appropriate shipper that a system was ready and at the same time the shipper would schedule the monitor for concurrent delivery to the customer. This resulted in a savings of $30 in freight costs per monitor, resulting in another way that Dell could pass on savings to consumers.
Integrated supplier and distributor networks were instrumental in the success of Dell Computers. By using a JIT inventory system, Dell’s inventory turnover time was reduced by 57% and production space expanded due to the decreased storage area needed for inventory. Without these relationships, Dell would not have been able to support a 50+% growth rate for 3 consecutive years that lead to $12 billion in annual sales by 1997.
h2. Eric Scott Limited ( 28 )
As a small leather-goods manufacturer, Eric Scott Limited believes in improving supply chain operations through collaboration with suppliers and customers. By switching from a home-grown IT system to Made2Manage Systems’ VIP enterprise portal solution in 1999, Eric Scott Limited has been able to enhance communications with its partners both up- and down stream. Implementation of the system required overcoming suppliers’ issues before the advantages could be reaped.
One major concern of Eric Scott Limited was the protection of their customers’ data and information. To ensure customer privacy, the two companies worked out a sort of “hybrid hosting” where the collaboration servers are hosted by Made2Manage and the customer data is kept behind Scott’s firewall. This managed gateway approach allows for a relatively high degree of collaboration between the two businesses.
An advantage of the Made2Manage system was the ability it offered Scott to communicate through electric data interchange ( EDI ) with customers and suppliers. Orders come in by EDI where the Made2Manage system schedules them for manufacture and shipment and then sends notification to the customer. Also, this real time data is available on the portal where customers can access the site at any time to check on the status of their orders and pay their invoices on line.
Another benefit of the VIP software is that the system portal provides a collaborative forum for the suppliers. This allows suppliers to check on inventory status with the company and have pre-set reorder points for shipments. The portal also permits customers to exchange virtual design documents and store them, thereby reducing prototypes and the entire timeline from the product’s conception to its delivery.
Collaborative relationships managed through Made2Manage Systems’ software and technology allowed a small company like Eric Scott Limited to add big value in dealings with both suppliers and customers. As Scott expanded into new markets, VIP enterprise portal solutions offered them opportunities to provide additional services around product distribution. From managed gateways and forums for reordering and design development to EDI capabilities that schedule manufacture and shipment of orders, send customer notifications, provide 24 – hour online order checking and invoice payment options, Eric Scott Limited’s adoption of partnership collaboration techniques and use of technology have ensured benefits for all involved.
h2. Volkswagen Brazil ( 29 )
In 1997, Volkswagen (VW) implemented the modular consortium concept of supply chain management at its new assembly complex in their Brazilian plant. In order to for this concept to be successful, VW first had to drastically reduce its number of suppliers from 400 to only 8. Then, these 8 suppliers were invited to locate their bases of operations at the VW Brazil plant where they were provided with their own offices and staffs. In addition, VW asked them to each invest an additional $50 million in their respective modules. For agreeing to this investment and sharing of risk, the partners were guaranteed long-term contracts from 5 to 15 years.
At the facility, seven modules are sequentially integrated with each partner occupying a section of the plant and taking full responsibility for the quality control and mounting of complete assemblies. VW approves the final vehicle and the partners only receive payment on this completely finished product, and not on the individual parts as is the normal industry custom. By basically outsourcing the assembly operation, VW not only reduces its assembly labor costs, but is able to focus on logistics, engineering, quality assurance, and customer service.
This type of partnership has presented unique challenges for VW and the supplier partners to overcome. A plan of daily meetings, constant communication of all the partners, and the integration of 52 information systems providing immediate data access is used to coordinate their many activities. In order to prevent conflicts between the different staffs, wages and benefits are the same and all employees wear identical uniforms featuring a VW logo and their firm’s logo. Finally, a master craftsperson that takes personal responsibility for the vehicles performs final tests and conduct a pre-delivery functional audit to ensure quality standards and maintain conformity within the production process.
Although implementing the modular consortium has produced many challenges, the benefits are noteworthy. By introducing the modular concept, VW’s overall costs are down 15 – 25% and flexibility has increased due to the small number of suppliers. Also, individual customization of orders is made quicker through increased communication and easier decision making. Most importantly, gain sharing rewards of reductions in product defects and order fulfillment times, and improvements in on-time delivery and product performance have been seen throughout the plant. The success of this venture was made possible through planning, communication, and hard work to ensure quality standards – now VW and its supplier partners are reaping rewards through increased revenues.
- Supplier Partnerships
Import Page Template

- Our Strategy
- Sally Guyer
- Tim Cummins
- Julian Davis
- Julia Duryee
- Katheryn Lacey
- Nikki Mackay
- Our Governance
- Association Objectives
- Latest Research
- Commissioned & Partnered Research
- Capability Maturity Analysis & Benchmark
- Contract Design & Simplification
- Competency Management Program
- Contract Terms Analysis & Benchmark
- Contracting Health Check
- Contracting Standards
- Contracting Principles
- SaaS Contracting Guide
- Contract Design Pattern Library
- Software Comparison Tool
- Tips and Checklists
- Content Hub
- News from WorldCC
- Commitment Matters
- Stronger Together
- Contracting Excellence Journal
- Women and Negotiation
- Fundamentals of Commercial & Contract Management
- Commercial & Contract Management Certification
- Supplier Relationship Management Certification
- Modern Procurement Programs
- Statement of Work
- Managing Contracts Virtually
- Negotiation Master Classes
- Commercial Awareness Program
- Contract Management MOOC
- Business Ethics
- Relational Contracting
- Contract Design Workshops
- Agility Workshops
- Post Award Excellence
- Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
- Apprenticeships
- Why Choose Commerce and Contracting
- Career development
- Secure a job
- Americas 2024
- Virtual Events
- Member Meetings
- The Negotiation Room
- Innovation and Excellence Awards
- Leaders of the Future
- Innovators of the Future
- Events Calendar
- Student Connect
- Service Provider and Vendor
- Enterprise and Corporate
- Academic Symposium
- Inspiring Women
Case study: optimising partnerships with supplier relationship management
In the ever-evolving procurement and supplier engagement landscape, North West London Procurement Services (NWLPS) has emerged as a frontrunner, pioneering a comprehensive Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) framework. This strategic initiative, meticulously aligned with the organisation's 2022 - 2025 “Stronger Together” strategy, aimed to strengthen partnerships, maximise value, and stimulate innovation with key suppliers. This case study explores the in-depth design, execution, and impact of NWLPS's SRM framework, outlining the key components and phases that propelled its success.
Why Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)?
In the past, NWLPS viewed suppliers through a narrow procurement lens, focusing solely on the transactional outcome of contracts, not on building long-term relationships with their suppliers. However, NWLPS recognised that strategic suppliers are increasingly crucial in enabling service user satisfaction and care delivery. It became clear that these partnerships needed to evolve beyond mere procurement into deeper, outcome-driven relationships capable of unlocking shared goals, driving innovation, and mitigating ecosystem risks.
Without effective SRM capabilities, exchanges were happening in isolation, with no comprehensive view of strategic supplier performance, continuity planning, or the ability to accelerate key growth initiatives. Formalising an SRM approach addresses these gaps by establishing a structured process for nurturing supplier relationships in alignment with the overall business strategy.
Project Objectives
At the heart of NWLPS SRM framework lies a set of well-defined objectives that aim to transform supplier relationships into strategic partnerships that drive business growth and operational excellence. This approach to SRM extends beyond transactional engagements to enable NWLPS to maximise the value derived from supplier relationships.
- Strengthening partnerships: Fostering mutually beneficial collaborations to maximise value.
- Enhancing innovation: Pursuing strategic collaboration with suppliers to develop cutting-edge solutions.
- Optimising cost efficiency: Leveraging economies of scale and streamlining processes to reduce expenditures.
- Improving operational efficiency: Fostering transparent communication to eliminate inefficiencies.
The A natomy of NWLPS's SRM Framework
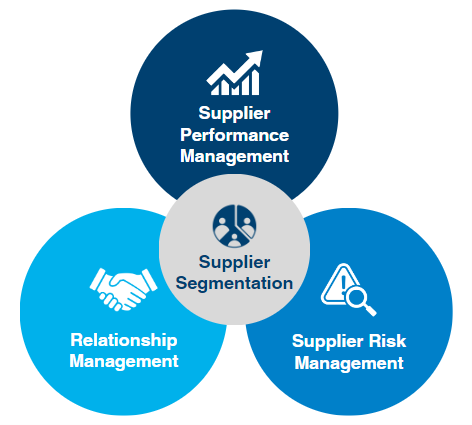
- Supplier Segmentation: Effective segmentation facilitates decision-making and prioritisation of resources for improved scalability and flexibility.
- Relationship Management: Cultivating mutually beneficial partnerships through proactive engagement, collaboration and active communication.
- Supplier Performance Management: Monitor and develop their suppliers to ensure good service at the optimum total cost of ownership.
- Supplier Risk Management: Implement processes to monitor, evaluate, and mitigate supplier risks.
SRM Skills Academy
61% of Chief Procurement Officers highlight "Increasing level of supplier collaboration" as their top priority for 2023, (Deloitte, 2023).
A crucial pillar of the SRM framework is developing the skills and mindset across NWLPS to manage strategic supplier relationships effectively. To enable this, a dedicated SRM Academy has been designed to focus on strengthening SRM within the Category Divisions.
World Commerce & Contracting (WorldCC) SRM Certification
The development of a skilled team to steward long-term supplier partnerships is key to extracting and expanding the value delivered through the SRM approach. NWLPS opted to enrol staff on the WorldCC SRM Certification programs; the only industry-recognised accredited programs to provide a comprehensive, relevant, and flexible learning experience. The Certifications enabled NWLPS staff to build competencies to:
- Structure and lead collaborative supplier engagements
- Employ value-based supplier segmentation
- Set clear performance expectations
- Govern for risk and continuity Identify and execute innovation opportunities
- Demonstrate critical problem-solving and conflict resolution
- Understand data analytics to inform SRM
- Utilise digital tools and AI enablement Consider sustainable procurement best practices Improve contract and performance optimization
Lee Jackson, Managing Director – North West London Procurement Services commented, “The WorldCC SRM Certification ensures consistency in our supplier practices and provides our team with more knowledge to effectively manage supplier relationships. It serves as a tool for enhancing our procurement outcomes which in turn helps our patients at the NHS and local communities.”
Achievements to date
Since embarking on its SRM journey, NWLPS has achieved significant milestones, laying a solid foundation for strong, value-driven supplier relationships, from within its Manage & Enable division, led by Lynda Hopkins, Procurement Excellence Director. From identifying key strategic partners to establishing robust performance metrics and fostering innovation, the NWLPS team has made consistent progress in transforming its supplier ecosystem.
To download the case study in full please visit: https://www.worldcc.com/Portals/IACCM/Files/Case Study - NHS NWLPS.pdf
- Excellence Journal
More resources
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
Marketing and growth leaders
Cybersecurity and privacy leaders
Risk leaders
EY Center for Board Matters
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
Supply chain and operations
EY Partner Ecosystem
Explore Services
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
MBA and advanced-degree students
Student and entry level programs
Contract workers
EY-Parthenon careers
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
Energy and resources
How data analytics can strengthen supply chain performance
13-Jul-2023 Ben Williams
How Takeda harnessed the power of the metaverse for positive human impact
26-Jun-2023 Edwina Fitzmaurice
Banking and Capital Markets
How cutting back infused higher quality in transaction monitoring
11-Jul-2023 Ron V. Giammarco
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
EY is now carbon negative
19-Sep-2022 Carmine Di Sibio
Our commitment to audit quality
13-Nov-2023 Julie A. Boland
No results have been found
Recent Searches

BEPS 2.0: as policies evolve, engagement is key
It remains to be seen whether the US will align its tax law with the OECD/G20’s global BEPS 2.0 rules. MNEs will feel the impact in 2024. Learn more.

How GenAI strategy can transform innovation
Companies considering or investing in a transformative GenAI strategy should tie generative artificial intelligence use cases to revenue, cost and expense. Learn more

Top five private equity trends for 2024
Read about the five key trends private equity firms will emphasize in 2024 as they create value
Select your location
close expand_more

How supply chain helps an electronics manufacturer connect customers
A global electronics company diversifies its manufacturing locations to increase its supply chain resilience.
- 1. Better question
- 2. Better answer
- 3. Better working world
How EY can help
The better the question
How can a supply chain deliver electronic devices on demand?
A US-based electronics manufacturer reduces supply chain risk to keep its customers tuned to all the right channels.
Explore our Offerings
Supply Chain & Operations Consulting Services
Discover how EY's supply chain team can help your business redefine its end-to-end supply chain and operations to support your enterprise objectives.
The electronics industry is facing steep supply chain challenges, reaching all the way back to the raw materials that make up those tiny components keeping people connected in real time.
A leading electronics supplier that provides mobile devices to consumers and public entities was experiencing shortfalls due to overreliance on materials and manufacturing in Asia. A perfect storm of factors, including the COVID-19 global pandemic and widespread geopolitical instability, has weakened the global supply chain, and cross-border labor is no longer guaranteed.
Transportation delays, both in the air and on the water, are extending production lead times. Country-specific tax and trade regulations are also threatening shipping timelines and slowing product delivery dates for customers.
“Corporate leaders at this electronic device company recognized that supply chain resilience has become an urgent business imperative for their organization,” said Jim Morton, Executive Director for the Ernst & Young LLP Business Consulting supply chain practice. “With most of their customer base in the US, they recognized that they needed to diversify their sourcing and production options as effectively as possible, which meant varying manufacturing locations to complement their global portfolio.”
Leaders engaged an integrated EY team experienced in supply chain modeling and optimization , tax and trade. The team developed a comprehensive plan that would diversify manufacturing and alleviate the organization’s long-term supply chain risk.
EY teams’ extensive tax experience, deep understanding of global incentives and locations, and keen geopolitical business perspective showed the client how it can continue to help consumers access critical mobile devices and carve a sustainable new path forward for its business.
Diversified manufacturing locations reduce supply chain risk
An integrated digital model evaluates multiple operation sites to yield informed decisions.
Geostrategic Business Group
Our Geostrategic Business Group (GBG) can help your business translate geopolitical insights into business strategy to manage political risk. Find out how.
With its deepest manufacturing roots in Asia, the mobile device provider needed to diversify its production footprint. Supply chain disruptions, longer ocean transport times, region-specific trade restrictions and frequent unexpected delays were pushing leaders to consider adding manufacturing sites closer to the US – the location of their corporate headquarters and most of their customer base.
Research from EY teams shows that 64% of companies have re-shored some elements to improve sustainability. In addition, 42% of companies said that ensuring sustainable and diverse sourcing was a priority. With data such as these in mind, the company turned to an EY cross-practice team for a strategy to augment core operations in more accessible and stable locations, reducing its overall supply chain risk while maintaining existing operations in Asia and elsewhere. Faced with a daunting and costly business decision, leaders needed assurance they could diversify their manufacturing and still procure the right materials, maintain quality standards, and deliver reliable products to meet urgent user needs.
The EY team assessed and designed a more diverse supply chain network with the company’s global business in mind.
Supply chain optimization was done based on a computerized model to assess the global supply chain, mapping raw materials to flow of goods, to distribution centers and finally to customer locations. The model evaluated current networks against future state options, assessing millions of site variables rapidly to provide leadership with the informed perspective they needed. The EY digital model brought an integrated view of the tax considerations inherent in ramping up manufacturing in new sites and countries, including customs duties, direct and indirect tax implications and country-specific regulations. The EY Geostrategic Business Group provided clarity around government labor, trade policies and local laws to further optimize recommendations, blending speed and cost to enable on-demand inventory.
"With recent supply chain disruption, trade wars and geopolitical uncertainty, this global electronics leader needed an integrated supply chain model so they could successfully diversify their manufacturing portfolio, avoid production delays, and address country-specific issues,” said Morton. “The EY supply chain optimization model helped them make more informed decisions and select their new manufacturing site in North America.”
End-to-end supply chain analysis was conducted by tracking the company’s highest-priority devices. Validated data inputs were primed and transitioned from a flow-constrained model to a demand-driven model. The analysis evaluated economic value added with the future state footprint, insourcing vs. outsourcing manufacturing operations, tax considerations, skilled labor availability, geopolitical factors, ESG and carbon footprint impact, and the reduction of supply chain complexity.
A supply chain scorecard was created by the EY team to help leaders evaluate manufacturing sites more critically, assessing six key supply chain factors:

Using the information gathered by the EY scorecard and digital assessment tools, the electronics company was able to ultimately select a new near shore location as its next manufacturing site. With this new location identified, EY teams will now work with the client to build out a roadmap to ramp up operations – including manufacturing providers, tax implications, geopolitical and regulatory guidance.
The better the world works
Supply chain optimization keeps customers connected around the world
The forward-thinking EY supply chain model diversifies production and minimizes risk.
For a leading electronics provider that serves millions of customers around the world, keeping the organization’s supply chain operating smoothly is of paramount importance. Comprehensive EY supply chain modeling and optimization for this organization was designed with a future state supply chain in mind, so that the organization could vary its manufacturing portfolio, maintain current production quotas, mitigate risk and reduce excess product inventory by 27%.
The EY digital supply chain optimization model helped the electronics leader assess site locations across countries, geopolitical factors, trade implications, trade risk and tax regulations. The manufacturing site scorecard helped the company narrow down possible manufacturing sites and identify specific locations within countries that will help the organization further reduce their carbon emissions by 15%. The supply chain solution will also increase the organization’s efficiency by reducing the length of haul from production site to customer by 50%, and by lowering labor costs.
“Our integrated supply chain model, which included extensive tax experience and deep geopolitical business perspective across locations, provided this electronics powerhouse a solution that would help them diversify and de-risk their supply chain, allowing important communication devices to continue to be readily available worldwide,” said Morton.
As the company works to ramp up its newest manufacturing location in North America, EY teams will be on board to help it conduct continued geopolitical and tax analysis, develop end-to-end supply chain analysis, establish timing, and evaluate distribution footprint expansion.
- 50% reduction in the average length of haul from production to consumer
- 27% reduction of excess product inventory in the pipeline
- 15% reduction in future carbon emissions impact from transport
- Lower duty costs on products imported from the near shore location
- Potential cost savings gained from business incentives provided by the near shore location
EY OpsChain Contract Management Solution
Discover how EY's OpsChain Contract Management Solution can help your TMT business boost speed, visibility and trust along your digital value chain. Learn more.
Related topics

Glenn Steinberg
Helping companies transform, create value and optimize business performance. Thirsty for knowledge. Ski enthusiast. Husband and father of two Michigan Wolverines.

Greg Cudahy
Years of experience in global operations transformation, price and revenue optimization, sourcing, integrated planning, supply chain synchronization and collaborative applications.
Explore our case study library
EY Consulting case studies are a window into how we work alongside our clients to deliver strategic, sustainable growth.

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Legal and privacy
- Accessibility
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

Photo: Pixabay/geralt
7 mini case studies: successful supply chain cost-reduction and management
Rob O'Byrne
Group Managing Director - Logistics Bureau
If you were to tell me that your company had never looked at its supply chain costs and sought to deliver reductions, I would be mightily surprised. On the other hand, if you told me your company hasn’t been able to sustain any progress in supply chain cost reduction, I wouldn’t be surprised at all.
Most companies begin with the best intentions to achieve successful and sustainable supply chain cost management, but somehow seem to lose momentum, only to see costs increase again in short order.
The following seven mini case studies explore a few high-profile companies that have managed to sustain their supply chain cost-reduction efforts and keep expenses under control. The challenges faced by these organisations and the steps they took, may provide some inspiration for successful long-term cost management within your organisation.
1. Deere & Company
Deere & Company (brand name John Deere) is famed for the manufacture and supply of machinery used in agriculture, construction, and forestry, as well as diesel engines and lawn care equipment. In 2014, Deere & Company was listed 80th in the Fortune 500 America’s ranking and was 307th in the 2013 Fortune Global 500 ranking.
Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenges: Deere and Company has a diverse product range, which includes a mix of heavy machinery for the consumer market, and industrial equipment, which is made to order. Retail activity is extremely seasonal, with the majority of sales occurring between March and July.
The company was replenishing dealers’ inventory weekly, using direct shipment and cross-docking operations from source warehouses located near Deere & Company’s manufacturing facilities. This operation was proving too costly and too slow, so the company launched an initiative to achieve a 10% supply chain cost reduction within four years.
The Path to Cost Reduction: The company undertook a supply chain network-redesign program, resulting in the commissioning of intermediate “merge centers” and optimization of cross-dock terminal locations.
Deere & Company also began consolidating shipments and using break-bulk terminals during the seasonal peak. The company also increased its use of third-party logistics providers and effectively created a network that could be optimized tactically at any given point in time.
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: Deere & Company’s supply chain cost-management achievements included an inventory decrease of $1 billion, a significant reduction in customer delivery lead times (from ten days to five or less) and annual transportation cost savings of around 5%.
One of the world’s largest manufacturers of computer chips, Intel needs little introduction. However, the company needed to reduce supply chain expenditure significantly after bringing its low-cost “Atom” chip to market. Supply chain costs of around $5.50 per chip were bearable for units selling for $100, but the price of the new chip was a fraction of that, at about $20.
The Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenge: Somehow, Intel had to reduce the supply chain costs for the Atom chip, but had only one area of leverage—inventory.
The chip had to work, so Intel could make no service trade-offs. With each Atom product being a single component, there was also no way to reduce duty payments. Intel had already whittled packaging down to a minimum, and with a high value-to-weight ratio, the chips’ distribution costs could not be pared down any further.
The only option was to try to reduce levels of inventory, which, up to that point, had been kept very high to support a nine-week order cycle. The only way Intel could find to make supply chain cost reductions was to bring this cycle time down and therefore reduce inventory.
The Path to Cost Reduction: Intel decided to try what was considered an unlikely supply chain strategy for the semiconductor industry: make to order . The company began with a pilot operation using a manufacturer in Malaysia. Through a process of iteration, they gradually sought out and eliminated supply chain inefficiencies to reduce order cycle time incrementally. Further improvement initiatives included:
- Cutting the chip assembly test window from a five-day schedule, to a bi-weekly, 2-day-long process
- Introducing a formal S&OP planning process
- Moving to a vendor-managed inventory model wherever it was possible to do so
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: Through its incremental approach to cycle time improvement, Intel eventually drove the order cycle time for the Atom chip down from nine weeks to just two. As a result, the company achieved a supply chain cost reduction of more than $4 per unit for the $20 Atom chip—a far more palatable rate than the original figure of $5.50.
3. Starbucks
Like Intel, Starbucks is pretty much a household name, but like many of the most successful worldwide brands, the coffee-shop giant has been through its periods of supply chain pain. In fact, during 2007 and 2008, Starbucks leadership began to have severe doubts about the company’s ability to supply its 16,700 outlets. As in most commercial sectors at that time, sales were falling. At the same time, though, supply chain costs rose by more than $75 million.
Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenges: When the supply chain executive team began investigating the rising costs and supply chain performance issues, they found that service was indeed falling short of expectations. Findings included the following problems
- Fewer than 50% of outlet deliveries were arriving on time
- Several poor outsourcing decisions had led to excessive 3PL expenses
- The supply chain had, (like those of many global organisations) evolved, rather than grown by design, and had hence become unnecessarily complex
The Path to Cost Reduction: Starbucks’ leadership had three main objectives in mind to achieve improved performance and supply chain cost reduction. These were to:
- Reorganize the supply chain
- Reduce cost to serve
- Lay the groundwork for future capability in the supply chain
To meet these objectives, Starbucks divided all its supply chain functions into three main groups, known as “plan” “make” and “deliver”. It also opened a new production facility, bringing the total number of U.S. plants to four.
Next, the company set about terminating partnerships with all but its most effective 3PLs . It then began managing the remaining partners via a weekly scorecard system, aligned with renewed service level agreements.
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: By the time Starbucks had completed its transformation program, it had saved more than $500 million over the course of 2009 and 2010, of which a large proportion came out of the supply chain, according to Peter Gibbons, then Executive Vice President of Global Supply Chain Operations.
Like Deere & Company, AGCO is a leading global force in the manufacture and supply of agricultural machinery. The company grew substantially over the course of two decades, achieving a considerable portion of that growth by way of acquisitions.
As commonly happens when enterprises grow in this way, AGCO experienced increasing degrees of supply chain complexity, along with associated increases in cost, but for many years, did little to address the issue directly, primarily due to the decentralized and fragmented nature of its global network.
In 2012, AGCO’s leaders recognised that this state of affairs could not continue and decided to establish a long-term program of strategic optimisation.
Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenges: With five separate brands under its umbrella, AGCO’s product portfolio is vast. At the point when optimisation planning began, sourcing and inbound logistics were managed by teams in various countries, each with different levels of SCM maturity, and using different tools and systems.
As a result of the decentralised environment, in which inbound logistics and transport management were separate operational fields, there was insufficient transparency in the supply chain. The enterprise as a whole was not taking advantage of synergies and economies of scale (and the benefits of the same). These issues existed against a backdrop of a volatile, seasonal market.
The Path to Cost Reduction: Following a SCOR supply chain benchmarking exercise, AGCO decided to approach its cost reduction and efficiency goals by blending new technology—in the form of a globally integrated transport management system (TMS)—with a commitment to form a partnership with a suitably capable 3PL provider.
As North and South American divisions of the company were already working with a recently implemented TMS, leaders decided to introduce the blended approach in Europe, with commitments to replicate the model, if successful, in its other operating regions.
With the technology and partnership in place, a logistics control tower was developed, which integrates and coordinates all daily inbound supply activities within Europe, from the negotiation of carrier freight rates, through inbound shipment scheduling and transport plan optimisation to self-billing for carrier payment.
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: Within a year and a half of their European logistics solution’s go-live, AGCO achieved freight cost reductions of some 18%, and has continued to save between three and five percent on freight expenditure, year-on-year, ever since. Having since rolled the new operating model out in China and North America, the company has reduced inbound logistics costs by 28%, increased network performance by 25% and cut inventory levels by a quarter.
Headquartered in Westport Connecticut, Terex Corporation may not be such a well-known name, but if your company has ever rented an aerial working platform (a scissor-lift or similar), there is a good chance it was manufactured by Terex and dispatched to the rental company from its transfer center in North Bend, Washington.
The North Bend facility is always full of lifting equipment. The company makes most pieces to order and customizes them to meet customers’ unique preferences. Terex maintained a manual system for yard management at the transfer centre, which generated excessive costs for what should have been a relatively simple process of locating customers’ units to prepare them for delivery.
The Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenge: A wallboard and sticker system was a low-tech solution for identifying equipment items in the yard at Terex. While inexpensive in itself, the solution cost around six minutes every time an employee had to locate a unit in the yard. It also required a considerable number of hours to be spent each month taking physical inventories and updating the company’s ERP platform.
The Path to Cost Reduction: Terex decided to replace the outdated manual yard management process with a new, digital solution using RFID tracking. Terex decided to replace the outdated manual yard management process with a new, digital solution using RFID tracking. Decision-makers chose a yard management software (YMS) product, and then had the transfer centre surveyed before initiating a pilot project covering a small portion of the yard.
After a successful pilot, the company approved the solution for full-scale implementation, replacing stickers, yard maps, and wallboard with electronic tracking and digital inventory management. As of December 2017, Terex was planning to integrate the yard management solution with its ERP platform to enable even greater functionality.
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: While the YMS cannot reconcile inventory automatically with the Terex ERP application, it does at least provide a daily inventory count via its business intelligence module. That alone has saved the labour costs previously incurred in carrying out manual counts.
More importantly, though, the RFID-based unit identification and location processes have saved the company around 70 weeks per year in labour costs, by cutting the process-time down from six minutes, to a mere 30 seconds per unit.
Avaya is a global force in business collaboration and communications technology, and not so many years ago, was operating what, by its own executives’ admission, was a worst-in-class supply chain. That situation arose as the result of multiple corporate acquisitions over a short space of time. The company was suffering from a range of supply chain maladies, including a long cash-to-cash cycle, an imbalance in supplier terms and conditions, excess inventory, and supply chain processes that were inefficient and wholly manual.
The Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenge: After Avaya purchased Nortel Enterprise Solutions in 2009, the freshly merged company found itself but loosely in control of an unstable and ineffective supply chain operation. Aside from having too many disparate and redundant processes, the company had multiple IT solutions, none of which provided a holistic view of the supply chain or supported focused analysis.
The Path to Cost Reduction: Avaya’s senior management team realized that its technology solutions, which varied from being inadequate to inappropriate, were causing many of its problems. The various acquisitions and mergers had transformed Avaya into a different kind of enterprise, and what it needed, rather than a replacement for all the discrete systems, was one solution to tie them all together.
To that end, the company put its trust in cloud technology, which was relatively immature at the time, and migrated all processes onto one platform, which was designed to automate non-value-added activities and integrate those critical to proactive supply chain management, namely:
- Point of sale analysis
- Procurement analysis
- Supplier communication
- Supply and demand planning
- Inventory planning
- Inbound and outbound logistics planning
Of course, the technology was merely an enabler, and to transform its supply chain operation, Avaya embarked on a long-term, phased program to standardize processes, initiate a culture change, invest in top talent, and implement a system of rigorous benchmarking and KPI tracking .
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: Avaya’s program of transformation took place over a period of three to four years, between 2010 and 2014. The path to cost reduction was a long one, but ultimately successful.
By making a conscious effort to lead the enterprise into a new way of thinking, change business culture, and unify technology under a single platform, Avaya has improved inventory turns by more than 200%, reduced cash tied-up in stock by 94%, and cut its overall supply chain expenditure in half.
This dramatic turnaround also required the company to switch from a preoccupation with improving what it was doing, to a process of questioning what it was doing and why.
7. Sunsweet Growers
This final mini-case study in our collection, highlights how sometimes, excess supply chain costs are not about warehousing and transportation, but can be attributable to inefficiencies in manufacturing or production and—often at the root of it all—forecasting and planning.
Sunsweet Growers is the world’s biggest producer of dried fruits and a little over a decade ago, found that while it was managing distribution operations well, high production costs were inflating end-to-end supply chain expenditure.
The Supply Chain Cost Reduction Challenge: When the leadership at Sunsweet looked into the company’s production cost issues, recognition soon dawned that the distribution network was at least partly behind the problems. As a result, the company looked at how it could redesign the network to take out some of the production costs.
Later, it became apparent that although a redesign would yield some benefits, one of the most significant issues was in the approach to demand forecasting. Sunsweet was using a manual forecasting approach, with spreadsheets being the only technology involved.
The inefficiencies of this approach proved not only to hamper effective forecasting and production planning, but the knock-effect was an excess of warehouses in the network—so forecasting proved to be both a driver of production cost, and a key to improving the distribution network.
The Path to Cost Reduction: As in a number of the studies we’ve explored here, technology played a large part in solving Sunsweet’s problems. After evaluating some 30 different software solutions, the company finally settled on a supply chain planning suite, and planned its improvement program to make use of each of the solution’s modules in sequence, allowing ROI to be realized in phases as each module was implemented and leveraged.
At the same time, Sunsweet implemented a sales and operations planning program (S&OP) that once established, enabled plant resource requirements to be anticipated months—rather than weeks—in advance. As the overall improvement plan passed through its five phases, positive results accumulated and as hoped, software ROI reached 100% even before the company completed its full implementation.
Supply Chain Cost Management Results: Of course, the objective of Sunsweet’s improvement program was not merely to achieve a 100% return on investment in its supply chain planning platform. The aim was to reduce production costs, and although the company hasn’t published hard figures to quantify the total financial gain, it has claimed the following wins:
- A 15 to 20% increase in forecasting accuracy
- A reduction in overtime from 25% to 8% in production facilities
- A 30% reduction in finished-goods spoilage
- Number of warehouses in the United States cut from 28 to just eight
- A transportation cost-per-unit that remained static for two years despite increased utilization of costly refrigerated transport and rising fuel costs
From the achievements documented above, and highlighted in several industry publications and articles, you don’t need to be too much of a mathematician to deduce that cost savings would have been considerable.
Making Supply Chain Cost Reductions Stick
Of course, the above case studies are merely summaries of the changes these high-profile brands made to their supply chains. What can be seen from these brief accounts, though, is that for an enterprise to make significant and sustainable cost improvements, substantial change must take place.
- Deere & Company had to overhaul its network completely.
- Intel had to shift an entire supply chain to a new and previously unheard of strategy in its sector.
- Starbucks had to shake up its third-party relationships and increase production capacity.
- AGCO had to invest in technology and collaborative partnerships with external service providers.
- Terex had to implement costly (but effective) RFID tracking capabilities.
- Sunsweet Growers needed a best-of-breed software solution, and an S&OP program to improve forecasting and planning.
- Avaya needed to change company culture, implement cloud technology, rethink processes completely, and invest in the best supply chain talent it could find.
At the same time, none of the changes took place overnight. Each of the companies tackled issues in phases, effectively learning more as they went along.
You Won’t Find Savings in the Comfort Zone
When it comes to making supply chain cost reductions that stick, you should explore every avenue. However, at the root of high costs, there will usually be one major factor requiring innovation, whether it’s the network, inventory strategy, the working relationships with supply chain partners, or some other element of your operation.
Seldom do companies make decent savings by whittling away piecemeal at what seem, on the face of it, to be the most pressing issues of the day (such as direct transportation costs or supplier pricing).
If you want to see sustainable cost reductions, your company will need to view the big picture from a new angle or two, and be prepared to step outside of the comfort zone to which it will have become accustomed.
Rob O’Byrne is a supply chain consultant, coach and author with 40+ years experience in Supply Chain management. He is the expert making the blog called Logistics Bureau .
- # case studies
- # management
- # Supply Chain Management
- # T&L
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Supplier Relationship Management: A Case Study in the Context of Health Care

2009, Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
Related Papers
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
Tobias Mettler
Structural changes and increasing market dynamics in the health care sector intensify the hospitals' needs for cost-savings and process optimization. The adoption of new information and communication technology (ICT) is thereby seen as opportunity to improve not only efficiency and effectiveness but also the quality of health services. As costs for drugs continuously increase, especially hospital pharmacies will be in
Journal of theoretical and applied electronic …
María Verónica Alderete
International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics
Journal of theoretical and applied electronic commerce research
ABSTRACT The design of business models is of decisive importance and as such it has been a major research theme in service and particularly electronic markets. Today, different definitions of the term and ideas of core constructs of business models exist. In this paper we present a unified vocabulary for business models that builds upon the elementary perception of three existing, yet very dissimilar ontologies for modeling the essence of a business. The resulting unified business model vocabulary not only condenses existing knowledge, but also tries to concatenate and (thematically) group the identified constructs into domain, enterprise, and value concepts. The resulting vocabulary helps business model designers in shaping the basic notions of their businesses.
Shubhashis Kumar Shil
Auctioning multi-dimensional items is a key challenge, which requires rigorous tools. This study proposes a multi-round, first-score, semi-sealed multi-attribute reverse auction system. A fundamental concern in multi-attribute auctions is acquiring a useful description of the buyers’ individuated requirements: hard constraints and qualitative preferences. To consider real requirements, we express dependencies among attributes. Indeed, our system enables buyers eliciting conditional constraints as well as conditional preferences. However, determining the winner with diverse criteria may be very time consuming. Therefore, it is more useful for our auction to process quantitative data. A challenge here is to satisfy buyers with more facilities, and at the same time keep the auctions efficient. To meet this challenge, our system maps the qualitative preferences into a multi-criteria decision rule. It also completely automates the winner determination since it is a very difficult task for buyers to estimate quantitatively the attribute weights and define attributes value functions. Our procurement auction looks for the outcome that satisfies all the constraints and best matches the preferences. We demonstrate the feasibility and measure the time performance of the proposed system through a 10-attribute auction. Finally, we assess the user acceptance of our requirements specification and winner selection tool.
Raafat Saadé , Raul Valverde
The paper examines the effect of E-Supply Chain Management Systems in the North American electronics manufacturing services industry. A causal and descriptive research study was conducted based on a survey applied to thirty six individuals in electronic manufacturing services firms in order to determine the impact of e-supply chain management on their key supply chain operations. Results of the research revealed that e-supply chain management had a positive effect in the electronic manufacturing services industry as these showed that the profits of the firm increased and internal communications were improved due to the implementation of e-supply chain management. The research also showed that e-supply chain management systems have many technical issues such as problems with process automation and transmission of supply chain data, e-procurement effectiveness, integration with existing systems and the monitoring of inventory systems and purchasing process. Several recommendations are made to overcome these challenges including employee training and re-engineering of business processes for better system integration.
carlos cares
Yulissa Anguis Fuster * Industria y Negocios *
Dr. Hatice CALIPINAR
E-procurement is a deriving benefit attained from technological enhancements rather than using traditional a paper based method in procurement operations. The main objectives of this study are observing the usage ratio of technological equipment in operations which are closely related with e-procurement activities and potential methods for improving the general performance in hospitals. A case study strategy is taken as a research strategy for attaining information from the investigated hospitals and data collection methods of semi structured interviews and nonparticipant observations are used. From the perspective of e-procurement, more technological tools can be used for activities in pharmacies, and drug flow from doctor to patient can be improved. Application of the proposed advice given to pharmacies operating in hospitals can ensure significant time and money savings without too much time or financial investment. Presenting the situation of e-procurement adoption for pharmacie...
ENTERPRISE INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Kyung Jin Cha
Nowadays, information technology (IT) outsourcing companies face enduring demands to reduce cost while increasing productivity. This pressure leads many IT outsourcing companies to rely on outsourcing arrangements with IT personnel suppliers. In order to maximise efficiency, outsourcing companies have focused on fostering high-performing suppliers through improved collaboration and mutual relations. However, it is very difficult to advance to a long-term partnership using the existing outsourcing process because of insufficient collaboration between IT outsourcing companies and their suppliers. Based on collaboration perspective of supply chain management (SCM), this study identifies the critical success factors for collaborative strategic partnerships and presents an evaluation framework for assessing and managing suppliers. We have developed an organisational process model for Supplier relationship management (SRM)-based collaboration which includes some of the key constructs from the previous studies and interviews with the IT outsourcing industry people. In this study, we will identify four types of strategic suppliers and suggest approaches for improving collaborative relationship between an IT outsourcing company and its partner companies. In addition, to validate the feasibility of the proposed model, we applied it to a well-known Korean IT outsourcing company ‘A’.
RELATED PAPERS
Dawn Gregg , Steven Walczak
Iris Junglas
Alejandro Valencia-Arias , Luis German Ruiz Herrera
Virpi Tuunainen
Mariela Rico , Maria Laura Taverna
Andreja Pucihar
Ian Macinnes
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Design Science Research in Information Systems and Technology - DESRIST '09
pamela marendi
Sergio Godoy
Lakshman Krishnamurthi
Nicolás M . Somma , Sergio -etcheverry , Claudia Labarca
Fredrick Muema
Celia Fabiola Vásquez García
Tanja Kaurin
Silvana Dakduk
Josefin Lassinantti
Paolo Spagnoletti , Andrea Resca , Stefano Za
Martin Otundo Richard
Syed Saburul Alam
Avinash Shukla
E+M Ekonomie a Management
Julita Markiewicz-Patkowska
Piers Campbell
Gianluigi Viscusi
Efthymios Constantinides
Luigi Mittone
Ahmad Samed Al-Adwan
Samuel Fosso Wamba
Arnold Kamis
riyanti isaskar
Nikolaos Matsatsinis
Prof A. Selvarasu
Efthymios Constantinides , María del Carmen Alarcón del Amo
Yao-hua Tan
Delfina Soares
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Apple Case Study
Advertisement
Supported by
Dubai’s Extraordinary Flooding: Here’s What to Know
Images of a saturated desert metropolis startled the world, prompting talk of cloud seeding, climate change and designing cities for intensified weather.
- Share full article

By Raymond Zhong
Scenes of flood-ravaged neighborhoods in one of the planet’s driest regions have stunned the world this week. Heavy rains in the United Arab Emirates and Oman submerged cars, clogged highways and killed at least 21 people. Flights out of Dubai’s airport, a major global hub, were severely disrupted.
The downpours weren’t a freak event — forecasters anticipated the storms several days out and issued warnings. But they were certainly unusual. Here’s what to know.
Heavy rain there is rare, but not unheard-of.
On average, the Arabian Peninsula receives a scant few inches of rain a year, although scientists have found that a sizable chunk of that precipitation falls in infrequent but severe bursts, not as periodic showers.
U.A.E. officials said the 24-hour rain total on Tuesday was the country’s largest since records there began in 1949 . But parts of the nation had experienced an earlier round of thunderstorms just last month.
Oman, with its coastline on the Arabian Sea, is also vulnerable to tropical cyclones. Past storms there have brought torrential rain, powerful winds and mudslides, causing extensive damage.
Global warming is projected to intensify downpours.
Stronger storms are a key consequence of human-caused global warming. As the atmosphere gets hotter, it can hold more moisture, which can eventually make its way down to the earth as rain or snow.
But that doesn’t mean rainfall patterns are changing in precisely the same way across every corner of the globe.
In their latest assessment of climate research , scientists convened by the United Nations found there wasn’t enough data to have firm conclusions about rainfall trends in the Arabian Peninsula and how climate change was affecting them. The researchers said, however, that if global warming were to be allowed to continue worsening in the coming decades, extreme downpours in the region would quite likely become more intense and more frequent.
The role of cloud seeding isn’t clear.
The U.A.E. has for decades worked to increase rainfall and boost water supplies by seeding clouds. Essentially, this involves shooting particles into clouds to encourage the moisture to gather into larger, heavier droplets, ones that are more likely to fall as rain or snow.
Cloud seeding and other rain-enhancement methods have been tried across the world, including in Australia, China, India, Israel, South Africa and the United States. Studies have found that these operations can, at best, affect precipitation modestly — enough to turn a downpour into a bigger downpour, but probably not a drizzle into a deluge.
Still, experts said pinning down how much seeding might have contributed to this week’s storms would require detailed study.
“In general, it is quite a challenge to assess the impact of seeding,” said Luca Delle Monache, a climate scientist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in La Jolla, Calif. Dr. Delle Monache has been leading efforts to use artificial intelligence to improve the U.A.E.’s rain-enhancement program.
An official with the U.A.E.’s National Center of Meteorology, Omar Al Yazeedi, told news outlets this week that the agency didn’t conduct any seeding during the latest storms. His statements didn’t make clear, however, whether that was also true in the hours or days before.
Mr. Al Yazeedi didn’t respond to emailed questions from The New York Times on Thursday, and Adel Kamal, a spokesman for the center, didn’t immediately have further comment.
Cities in dry places just aren’t designed for floods.
Wherever it happens, flooding isn’t just a matter of how much rain comes down. It’s also about what happens to all that water once it’s on the ground — most critically, in the places people live.
Cities in arid regions often aren’t designed to drain very effectively. In these areas, paved surfaces block rain from seeping into the earth below, forcing it into drainage systems that can easily become overwhelmed.
One recent study of Sharjah , the capital of the third-largest emirate in the U.A.E., found that the city’s rapid growth over the past half century had made it vulnerable to flooding at far lower levels of rain than before.
Omnia Al Desoukie contributed reporting.
Raymond Zhong reports on climate and environmental issues for The Times. More about Raymond Zhong

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Identify your sourcing objectives and criteria. 2. Conduct market research and analysis. 3. Negotiate and finalize contracts and agreements. 4. Implement and manage the supplier relationship. 5.
During 2019, researchers from McKinsey and MSU rolled out the Index in a pilot project involving a dozen leading consumer-goods companies in North America, along with ten to 15 of each company's strategic suppliers. We collected more than 300 written responses from more than 130 organizations, and conducted in-depth interviews with around 60 ...
Read HICX's supplier management case studies & learn how businesses have digitally transformed with our supplier management solutions & industry-leading expertise. Mondelez International selected HICX to provide a complete supplier information management and on-boarding solution as the foundations of its Supplier Central service.
104 7 Case Study: Supplier Relationship Management at Volkswagen Group As part of an integrated supply chain management, called "Value Net Management" at Volkswagen Group, the firm integratessuppliers more and more in the purchasing process and tries to combine its own innovation strength with suppliers to gain best results on the market.
New research on supply chains from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including supply chain management, digital supply chains, and improving global supply chains. ... In a recent case study, Willy Shih examines factors that go into deciding where companies should locate production centers. Open for comment; 0 Comments. 04 Dec 2019 ...
They cover different aspects of supply chain management and feature a broad range of companies and situations. SCM case study examples would include an SCM selection project for a manufacturer, or an SCM implementation for a distributor or logistics provider. SCM case studies also feature TEC's own case studies, showing how we've helped ...
It represents one of the largest snack companies in the world with global net revenues of $26.5 billion and net earnings of $3.5 billion in 2020. With a strong supplier diversity program, Mondelēz International is committed to serving a high quality, innovative supplier base that reflects its own diversity in the products it offers. As part of ...
New research on supply chain management from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including what brands can do to monitor their suppliers' factory conditions, how Japan's earthquake and tsunami and caused havoc on retailers and car manufacturers, and the push to improve labor standards in global supply chains.
The case study at hand stems from interviews with experts in procurement at Volkswagen Group, Wolfsburg, Germany, in August 2008. Given our model approach, we were particularly interested in the management of buyer-supplier relationships, the contracts employed and the handling of quality issues. In the following, we will document Volkswagen ...
Procurement and supply chain leaders worldwide look to GEP for process, technology and industry expertise, and we are happy to share our learnings from years of complex problem solving. The GEP Knowledge Bank encompasses proprietary research, issue-orientated white papers and webinars, case studies, and playbooks and primers. Supply Chain and ...
Building a successful supplier network - a real-world case study. Capgemini. 2021-08-05. Digital purchasing and invoice networks are essential to any successful digital procurement program. They provide visibility to suppliers and customers, improve performance management and risk process efficiency, reduce source-to-pay cycle times, and ...
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) plays an important role in the reduction of costs and the optimization of performance in industrial enterprises. Despite enormous investments in innovation, the health care sector has not experienced fundamental ...
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Walmart. Set in 2019, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to compare Walmart's source of competitiveness with those of other retailers-both online including Amazon.com and traditional brick-and-mortar retailers, such as Target-to develop insights into the ...
96% of invoices and over $200M of spend is processed through Coupa. Digitized supplier management. "Time to value was immediate. If someone asked me about Coupa for BSM, I'd say it's a no-brainer." When Ionis took its subsidiary public, it presented challenges as Ionis began onboarding twice as many suppliers.
For time-sensitive or temperature-controlled cargo, most shippers will agree that high-quality, real-time tracking information is crucial. Though that technology can be expensive, the investment is easy to justify when it could mean the difference between an on-time delivery and spoiled cargo. But ...
translates and amends the current findings for the health care context, and presents a case study illustrating the impact of the implementation of SRM principles in a leading Swiss hospital. Key words: Business Networking, E-Business, E-Collaboration, E-Procurement, Health Care, Supplier Relationship Management, Supply Management
Case Studies. h2. Dell Computers ( 27) Early on Dell Computers recognized the benefits of collaborative supply chain relationships and adopted the practice while developing its "Dell Direct Model" in 1995. This innovative model of efficiency included something the computer industry had never experienced: a high velocity, low cost ...
Integrating SRM practices into routine supplier management. Proactively identifying and addressing supply chain risks. ... aimed to strengthen partnerships, maximise value, and stimulate innovation with key suppliers. This case study explores the in-depth design, execution, and impact of NWLPS's SRM framework, outlining the key components and ...
Supply chain optimization was done based on a computerized model to assess the global supply chain, mapping raw materials to flow of goods, to distribution centers and finally to customer locations. The model evaluated current networks against future state options, assessing millions of site variables rapidly to provide leadership with the ...
The following seven mini case studies explore a few high-profile companies that have managed to sustain their supply chain cost-reduction efforts and keep expenses under control. The challenges faced by these organisations and the steps they took, may provide some inspiration for successful long-term cost management within your organisation. 1.
Supplier relationship management (SRM) as defined by (Akam p and Müller, 2013) is the. practice of planning, implementing, de veloping and monitoring company r elationship with the current and ...
The paper examines the effect of E-Supply Chain Management Systems in the North American electronics manufacturing services industry. A causal and descriptive research study was conducted based on a survey applied to thirty six individuals in electronic manufacturing services firms in order to determine the impact of e-supply chain management on their key supply chain operations.
The current state of the art in the field is reviewed, the current findings for the health care context are translated and amends, and a case study illustrating the impact of the implementation of SRM principles in a leading Swiss hospital is presented. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) plays an important role in the reduction of costs and the optimization of performance in industrial ...
Management document from American InterContinental University, 3 pages, In the aftermath of the case study, Apple has made strides in addressing the labor issues within its supply chain. The company has taken steps to enhance transparency by publishing supplier responsibility reports and conducting assessments of suppliers. C
One recent study of Sharjah, the capital of the third-largest emirate in the U.A.E., found that the city's rapid growth over the past half century had made it vulnerable to flooding at far lower ...